Effect of L-Arginine or L-Lysine on the Quality of Duck Meat Patties during Freeze-thaw Cycles
-
摘要: 本文研究L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸对反复冻融鸭肉饼品质的影响,旨在为L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸作为冷冻保护剂在肉制品中的应用提供理论依据。在鸭肉饼加工工艺中,于腌制环节添加L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸,并将制作好的鸭肉饼进行反复冻融循环,从质构、蒸煮损失、色差、pH、挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)、硫代巴比妥酸反应物(TBARS)、低场核磁共振、微观结构指标来评价鸭肉饼的品质。结果表明,随着冻融循环次数的增加,空白组鸭肉饼的硬度、弹性、粘聚性、咀嚼性、a*值、pH和P21显著降低(P<0.05),蒸煮损失、TVB-N值和TBARS值显著升高(P<0.05)。在5次冻融循环后,L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸对鸭肉饼品质的劣变有显著的抑制作用(P<0.05),而且L-精氨酸组鸭肉饼的蒸煮损失分别比空白组和三聚磷酸盐(Sodium tripolyphosphate,STP)组低13.23%和6.93%(P<0.05)。此外,在5次冻融循环后,L-精氨酸组的TVB-N值和TBARS值分别比空白组低41.92%和63.47%(P<0.05),均为四组中最低。这表明L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸处理能在冻融循环过程中有效抑制鸭肉饼腐败变质、脂肪氧化,改善保水性,使鸭肉饼保持良好的品质特性,且L-精氨酸效果更好。Abstract: In this study, the effects of L-arginine or L-lysine on the quality of duck meat patties during repeated freeze-thaw cycles were studied to provide a theoretical basis for the application of L-arginine or L-lysine as cryoprotectant in meat products. L-arginine or L-lysine was added in the marinating process of duck meat patties, and the prepared duck meat patties was treated with freeze-thaw cycles. The texture, cooking loss, color, pH, total volatile base nitrogen (TVB-N), thiobarbituric reactive substances (TBARS), low-field nuclear magnetic resonance, and microstructure were measured to evaluate the quality of duck meat patties. The results showed that with the increase of freeze-thaw cycles, the hardness, springiness, cohesiveness, chewiness, a* value, pH and P21 of duck meat patties in the blank group decreased significantly (P<0.05), while the cooking loss, TVB-N value and TBARS value increased significantly (P<0.05). After five freeze-thaw cycles, L-arginine or L-lysine significantly inhibited the deterioration of duck meat patties quality (P<0.05), and the cooking loss of duck meat patties in L-arginine group was 13.23% and 6.93% higher than those in blank group and sodium tripolyphosphate (STP) group, respectively (P<0.05). In addition, after five freeze-thaw cycles, the TVB-N value and TBARS value of L-arginine group were 41.92% and 63.47% lower than those of blank group (P<0.05), respectively, which were the lowest among the four groups. Therefore, the L-arginine or L-lysine treatment could effectively inhibit spoilage, the oxidation of fat, improve water retention, and maintain good quality characteristics of duck meat patties.
-
Keywords:
- freeze-thaw cycles /
- L-arginine /
- L-lysine /
- duck meat patties /
- quality
-
鸭肉因其高蛋白、脂肪含量适中、低胆固醇和特殊风味而成为中国最受欢迎的肉类产品之一[1]。冷冻是广泛应用于肉类产品的长期储存的基本技术,可以抑制微生物的生长并延缓氧化,从而延长产品的货架期[2]。冷冻肉是肉类产品在国内外各区域之间流通和进出口贸易的主要形态。据估计,全球冷冻食品市场将持续增长,预计到2027年将达到4408亿美元[3]。在冷冻过程中,形成的冰晶可能会对细胞的完整性产生很大影响,使冷冻食品产生不良的感官品质和营养损失,从而导致食品品质下降[4]。在解冻过程中,冷冻食品内部冰晶体转化为液态水,但这部分的水分是不可能完全被重新吸收的,从而导致汁液流失、酶促或非酶促等不良生化反应[5]。然而,在实际的生产、贮藏、运输、零售、消费和其他环节中,由于冷链技术和冷链系统的不健全导致环境温度波动,造成冷冻肉制品经历反复冻融过程是不可避免的。冻融循环期间冰晶和重结晶会对肌肉细胞和肌肉纤维造成不可逆的损伤,导致肉制品脂肪氧化、蛋白质氧化变性、汁液流失、颜色变暗、嫩度下降等营养价值和感官品质劣化[6]。随着人们生活水平的显著提高,食品品质和营养价值已成为消费者最关心的问题[7]。因此,提高冷冻肉的品质和营养价值已成为肉品加工领域的热点问题。
冷冻保护剂是一系列用于保护冷冻储存期间的肉制品的品质和营养价值的食品添加剂[8],可以减少冰晶形成对肌肉组织的损伤,抑制脂质氧化和延缓蛋白质变性。冷冻保护剂表面的一些官能团,可以与蛋白质分子相互作用或结合,从而增强蛋白质的水合作用,防止结合水的流失,进一步稳定蛋白质结构[9]。目前,许多研究人员已经成功开发出来多种不同类型的冷冻保护剂,例如糖、碳水化合物衍生物、蛋白质、蛋白水解物和多聚磷酸盐等[10]。然而,这些冷冻保护剂都存在各种各样的不足,例如糖有天然的甜味、蛋白质水解物经济成本高等问题。因此,开发安全、绿色、经济、高效的新型冷冻保护剂,并研究其对肉制品品质的影响,具有非常重要的理论和实际价值。
L-精氨酸(L-arginine,L-Arg)和L-赖氨酸(L-lysine,L-Lys)都是天然、安全、市售、经济的食品添加剂。同时,有许多科学家研究发现L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸能够改善肉制品的质地、保水、嫩度、颜色等品质特性[11−14]。目前,还没有关于L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸作为冷冻保护剂,减少冻融循环期间肉制品品质劣变的研究。因此,本文通过测定质构(TPA)、蒸煮损失、色差、pH、挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)、硫代巴比妥酸反应物(TBARS)、低场核磁共振(LF-NMR)和微观结构来研究L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸对反复冻融鸭肉饼品质的影响,以期为今后研究肉类及肉制品的冻融循环保护作用提供理论指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜鸭(每只鸭净重大约为2.5 kg) 宁波北仑区春晓菜市场;新鲜猪肥膘、食用盐、香辛料、调味品 浙江省宁波市物美超市;L-精氨酸、L-赖氨酸 河北华阳生物科技有限公司;三聚磷酸盐(Sodium tripolyphosphate,STP) 徐州海成食品添加剂有限公司;MgO、H3BO3、HCl、甲基红指示剂、溴甲酚绿指示剂、三氯乙酸、乙二胺四乙酸二钠、硫代巴比妥酸、PBS缓冲液、戊二醛、乙醇、叔丁醇 均为分析纯,麦克林公司。
BSA224S电子分析天平 北京赛多利斯仪器系统有限公司;XHF-DY高速分散器 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;H180R高速冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;SG-4059C数显恒温水浴锅 上海硕光电子科技有限公司;FE20pH 计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海);SWG-2300色差计 上海硕光电子科技有限公司;P9紫外分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;K9840凯氏定氮仪 济南哈农仪器有限公司;50FG/A冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;TA-XT2i质构分析仪 英国 Stable Micro System公司;MesoMR23-060H-II 核磁共振分析仪 苏州纽迈分析仪器股份有限公司;Sigma300扫描电镜 德国蔡司公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 鸭肉饼制作
屠宰新鲜鸭后,将鸭胴体于4 ℃保温箱中保存,2 h之内送至实验室。在实验室内将新鲜鸭胴体进行分割处理,取鸭胸肉,去皮,剔除筋膜以及可见脂肪,切割成2 cm×2 cm×2 cm大小的块状样品,将切割好的鸭肉样品随机分为四组,用绞肉机绞碎,在这个过程中加入相同的调味品和香辛料(调味品和香辛料按照以下比例:葱姜蒜粉0.1%、五香粉0.3%、糖1%、味精0.16%、食盐1.5%、花椒粉0.04%、β-环糊精0.1%、红曲0.2%、料酒1%),分别加入三种不同冷冻保护剂(0.5%(w/v)L-精氨酸溶液、0.5%(w/v)L-赖氨酸溶液、0.4%(w/v)STP),以不加冷冻保护剂的组为空白组(Control),使鸭肉肉糜的质量变为原来的110%,并放置在4 ℃冰箱中腌制2 h,之后放入绞肉机中快速绞拌2 min,形成肉糜,然后加入提前绞碎的猪背膘(鸭肉:猪背膘的比例为8:2),再用绞肉机快速绞拌混匀1 min,在绞肉机绞拌过程中加入冰水(12%)。最后用肉饼模具压成肉饼,将所有样品用真空包装袋中真空包装贮藏于−18 ℃的冰箱中,冷冻贮藏5 d后,在4 ℃下自然解冻24 h,此时完成一次冻融循环。按照上述方法依次完成3次和5次冻融循环。将0、3和5次冻融循环的每种处理组的样品随机抽取进行分析。
1.2.2 质构(TPA)的测试
根据Wang等[15]的方法,略有改动,使用质构分析仪对鸭肉饼的TPA进行测定。鸭肉饼在已经预热的烤箱(250 ℃)中双面烤制10 min,然后将鸭肉饼于室温下冷却到室温。冷却后,将鸭肉饼从中间切成长为25 mm,宽为25 mm,高度为10±0.5 mm的长方体。测定参数设置为:P/50探头,测前速度为5.0 mm/s,测试速度为1.0 mm/s,测后速度为5.0 mm/s,下压应变40%,循环两次,两次压缩中停顿时间为5.0 s,触发力5.0 g。测定结果以硬度、弹性、咀嚼性、凝聚性表示。
1.2.3 蒸煮损失的测定
根据Cheng等[16]的方法,略微修改,测定鸭肉饼的蒸煮损失。取鸭肉饼样品(5±0.5 g)置于离心管中,在80 ℃水浴环境中加热至内部中心温度达到70 ℃后取出,将样品冷却至室温,然后用滤纸擦干样品渗出的水分后称重。蒸煮损失的计算公式如下:
1.2.4 色差的测定
参考Fu等[17]的方法,并略作修改。测定鸭肉饼上不同位置的六个点的色差,取平均值。色差仪使用前先在白色和黑色标准板上校准,设置D65光源,角度10°,再对鸭肉饼进行测定,分别记录L*,a*,b*值。
1.2.5 pH的测定
按照国标GB/T 5009.237-2016《食品pH值的测定》的方法[18],测定鸭肉饼的pH。
1.2.6 挥发性盐基氮(Total volatile base nitrogen,TVB-N)的测定
按国标GB/T 5009.228-2016《食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》中的自动凯氏定氮仪法[19],测定鸭肉饼的TVB-N值。
1.2.7 硫代巴比妥酸反应物(Thiobarbituric reactive substances,TBARS)的测定
按国标GB/T 5009.181-2016《食品中丙二醛的测定》中的分光光度法[20],测定鸭肉饼的TBARS值。
1.2.8 低场核磁共振(Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance,LF-NMR)的测定
根据Pan等[21]的方法,使用MesoMR23-060H-II 核磁共振分析仪利用Carr-Purcell-MeiboomGill(CPMG)脉冲序列测定鸭肉饼的横向弛豫时间(T2)。将鸭肉饼(5 g)样品放入核磁管中,然后用核磁共振分析仪进行测定。CPMG的参数设置为:质子共振频率为23 MHz,半回波时间τ值为150 µs,NECH值为8000。对原始数据进行归一化处理后,采用CONTIN软件分析弛豫时间,并输出3个弛豫时间(T2b、T21、T22)及其所占面积分数(P2b、P21、P22)。
1.2.9 微观结构
根据Sriket等[22]的方法,并略作修改,利用扫描电镜(Scanning Electron Microscopy,SEM)观察鸭肉饼的微观结构。将肉饼切成5 mm×5 mm×5 mm的立方体,用2.5%的戊二醛固定2 h,然后用0.1 mol/L PBS缓冲液(pH6.25)清洗1 h,再进行不同梯度的乙醇脱水(50%、70%、90%、100%),每次处理15 min,最后用叔丁醇置换3次,每次处理15 min,于−80 ℃预冻12 h,在冷冻干燥48 h后取出。喷金150 s,用SEM观察鸭肉饼的微观结构。5.0 kV加速电压下500倍放大观察样品的微观结构。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均设置三个平行,所有数据均用平均数±标准差表示。采用SPSS 26.0统计软件进行单因素方差分析,Duncan多重比较进行差异显著性分析。显著性水平设为P<0.05。数据结果用GraphPad Prism 9 和OriginPro 2021b绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼TPA的影响
TPA通过模拟人类口腔中的咀嚼过程,对肉制品的硬度、弹性、咀嚼性等质地质量进行评价[23]。表1显示冻融循环对鸭肉饼质构的影响。随着冻融循环次数增加,空白组的硬度、弹性和咀嚼性都显著降低(P<0.05)。然而,与新鲜样品相比,在5次冻融循环时,空白组的粘聚性显著降低(P<0.05),但3次和5次冻融循环之间变化不显著。多次冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼的硬度和咀嚼性下降,可能是因为随着冻融循环次数的增加,样品中冰晶尺寸变大,导致样品的微观结构发生不可逆的机械损伤所造成的[15]。同时,有研究表明水分流失和蛋白质变性也是造成反复冻融循环下肉制品的TPA特性降低的重要因素[16]。
表 1 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼TPA的影响Table 1. Effects of different treatment on the TPA of duck meat patties during freeze-thaw cycles冻融循环(次) 组别 硬度(N) 弹性 粘聚性 咀嚼性(N) 0 Control 2182.02±73.63Aab 0.63±0.01Aa 0.59±0.02Aab 798.69±97.2Aa L-Arg 2097.18±75.83Ab 0.64±0.02Aa 0.61±0.02Aa 794.35±83.02Aa L-Lys 1920.60±86.63Ac 0.61±0.02Aa 0.55±0.02Ab 635.37±21.27Ab STP 2339.21±113.14Aa 0.62±0.01Aa 0.62±0.01Aa 903.00±29.85Aa 3 Control 1250.18±64.3Bc 0.58±0.02Bb 0.54±0.04ABa 406.18±40.16Bb L-Arg 1691.5±52.85Ba 0.61±0.01ABa 0.60±0.04Aa 620.77±104.76Ba L-Lys 1481.34±132.9Bb 0.60±0.01Aab 0.55±0.03Aa 476.58±68.43Bb STP 1719.78±121.19Ba 0.60±0.01Bab 0.58±0.02Ba 621.45±32.64Ba 5 Control 787.67±105.42Cc 0.47±0.02Cc 0.53±0.02Bb 241.74±41.47Cd L-Arg 1457.73±90.55Ca 0.59±0.01Ba 0.57±0.02Aa 495.84±19.87Ba L-Lys 1167.61±73.52Cb 0.55±0.02Bb 0.53±0.01Ab 323.18±20.26Cc STP 1241.81±114.41Cb 0.56±0.01Cab 0.57±0.01Ba 424.51±54.47Cb 注:不同大写字母表示不同冻融循环次数的同一处理组样品之间存在显著差异(P<0.05);不同小写字母表示相同冻融循环次数的不同处理组的样品之间存在显著差异(P<0.05);表2同。 如表1所示,在5次冻融循环后,L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸组与空白组的质构参数差异显著(P<0.05)。经过5次冻融循环后,添加L-精氨酸的鸭肉饼的硬度(1457.73 N)、弹性(0.59)、粘聚性(0.57)和咀嚼性(495.84 N)均显著高于空白组(硬度787.67 N、弹性0.47、粘聚性0.53和咀嚼性241.74 N)(P<0.05),为四组最高。上述结果表明,L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸能够有效抑制鸭肉饼在冻融循环过程中品质的劣变,且L-精氨酸效果更好。这可能是由于L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸可以抑制鸭肉饼的氧化变性[24−25],从而维持鸭肉饼的质构特性。
2.2 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼蒸煮损失的影响
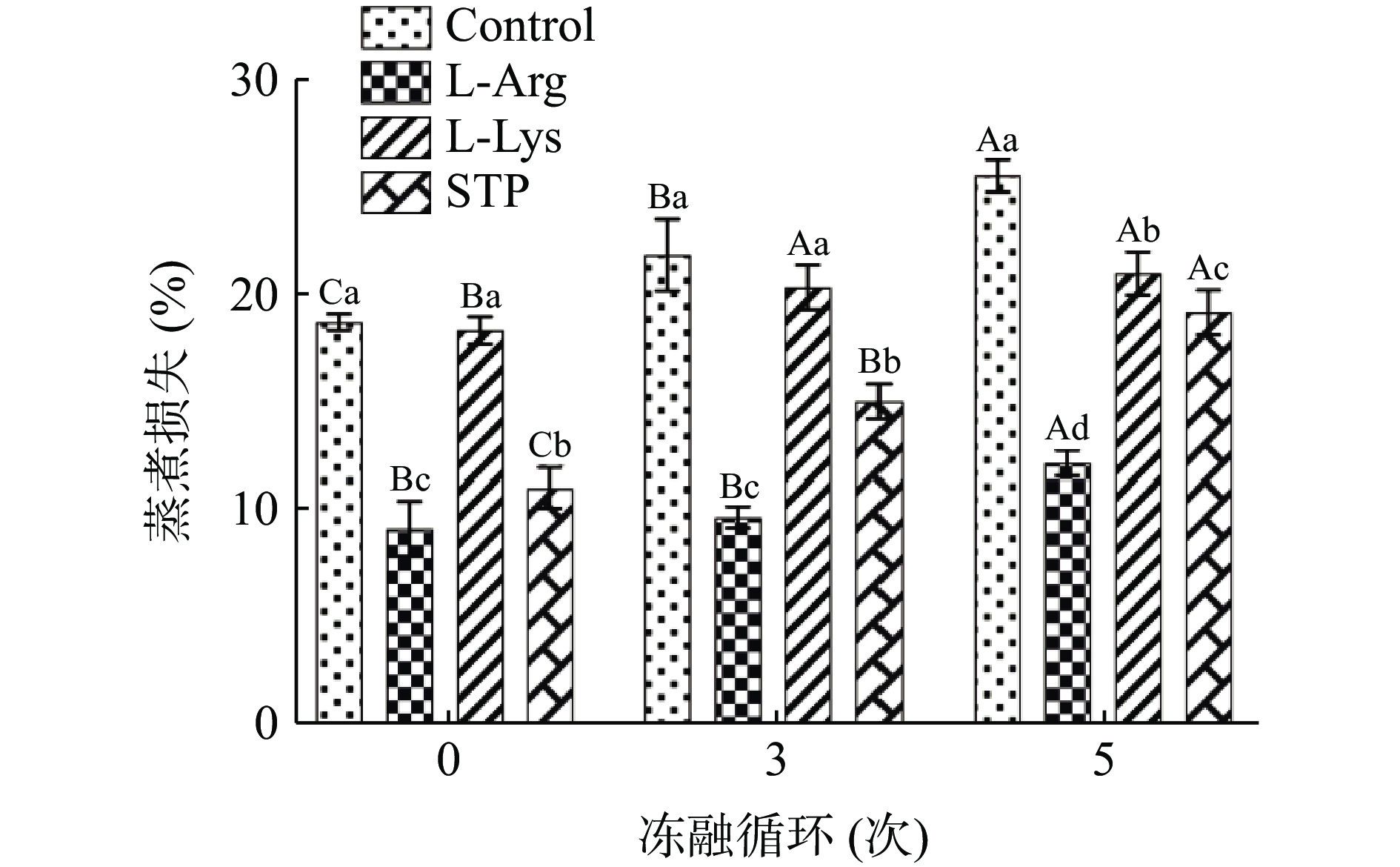
蒸煮损失是评价肉制品保水能力的重要指标[26]。冻融循环对鸭肉饼蒸煮损失的影响如图1所示。对未处理的鸭肉饼而言,冻融循环次数越多,蒸煮损失越高(P<0.05)。未冻融时,空白组蒸煮损失为18.62%,5次冻融循环后的空白组蒸煮损失为25.36%(P<0.05)。蒸煮损失的变化和样品的持水能力密切相关,并且蒸煮损失的增加会对肉制品的重量、外观和感官特性造成不利的影响[23]。在反复冻融循环情况下,冰晶反复形成和融化会对肌肉组织造成机械损伤,并导致其持水能力减弱[27]。Fan等[28]也发现了类似的结果,即鱼丸随着冻融循环次数的增多,蒸煮损失也随之逐渐增大(P<0.05)。
从图1可以看出,添加L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸可以降低鸭肉饼在冻融循环中蒸煮损失,在一定程度上保持鸭肉饼的持水能力。尤其是在5次冻融循环后,L-精氨酸组的蒸煮损失(12.3%)是四组里面最低。这可能是因为L-精氨酸可以诱导肌原纤维蛋白(Myofibrillar protein,MP)的pH进一步偏离等电点,从而在肌丝之间提供足够的空间来保持水分,并提供额外的MP位点来结合水[29],从而使鸭肉饼保持良好的持水能力。
2.3 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼色差和pH的影响
颜色在冷冻肉制品的外观和可接受性中起着重要的作用。反复冻融循环对不同处理的鸭肉饼L*、a*、b*的影响如表2所示。空白组L*值从42.01(0次冻融循环)上升到49.14(5次冻融循环)。反复的冷冻和解冻过程导致鸭肉饼表面有大量的自由水,导致肉饼的光反射强度增加,这是鸭肉饼的L*值升高的原因[30]。在多次冻融循环过程中,空白组a*值显著下降(P<0.05)。a*值的降低可能与冻融过程中肌红蛋白(Myoglobin,Mb)的降解和渗出有关;另一方面,脂质氧化产物也可能降低Mb的稳定性,促进Mb的氧化,导致a*值下降[2],样品TBARS值(图3)结果也能说明这一点。随着冻融循环周期的增加,b*值的变化趋势与a*值相反。Mancini等[31]研究表明,b*是因为OMb-Fe2+/Mb-Fe2+的氧化。在3次和5次冻融循环时,L-精氨酸组和L-赖氨酸组的a*值显著高于空白组,b*值显著低于空白组(P<0.05),并且在5次冻融循环时,L-精氨酸组的a*值是四组处理中最高的,b*值是最低的。这一结果说明添加L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸都可以减少鸭肉饼的色泽和可接受性在冻融循环过程中的恶化,其中L-精氨酸的效果最好。Ning等[32]研究结果表明,L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸可以将样品中含有的三价铁还原成二价铁,高铁肌红蛋白还原为肌红蛋白,这可能是L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸处理的样品b*值较低和a*值较高的原因。
表 2 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼色差和pH的影响Table 2. Effects of different treatment on the color and pH of duck meat patties during freeze-thaw cycles冻融循环(次) 组别 颜色 pH L* a* b* 0 Control 42.01±1.06Cab 18.70±0.16Aa 21.16±0.91Ba 5.94±0.01Ad L-Arg 40.47±1.40Bb 17.19±0.96Abc 20.91±1.24Ab 6.52±0.01Aa L-Lys 43.36±0.93Ba 17.78±0.31Aab 21.16±0.16Ba 5.96±0.02Ac STP 40.83±0.73Cb 17.69±0.53Aab 21.23±0.52Ba 6.26±0.01Ab 3 Control 45.25±0.83Ba 14.59±0.43Bb 22.89±0.95Ba 5.91±0.00Bd L-Arg 42.54±0.41Ab 16.46±0.62ABa 21.28±0.92Ab 6.47±0.01Ba L-Lys 45.39±1.23Aa 15.53±0.82Bab 21.64±0.25Bab 5.94±0.00Bc STP 43.08±1.59Bb 14.80±0.44Bb 22.50±0.35Bab 6.22±0.02Bb 5 Control 49.14±0.93Aa 12.61±0.72Cc 24.83±1.02Aa 5.88±0.01Cd L-Arg 44.03±0.78Ac 15.30±0.75Ba 22.69±0.94Ab 6.42±0.02Ca L-Lys 46.46±0.68Ab 14.22±0.69Cab 23.14±0.42Ab 5.91±0.01Cc STP 47.13±0.80Ab 13.31±0.76Cbc 23.29±0.78Aab 6.09±0.01Cb pH是食品稳定性的重要参数之一,与导致食品变质的微生物和化学反应有关[33]。如表2所示,随着冻融循环次数的增加,空白组鸭肉饼样品的pH显著降低(P<0.05)。pH降低的原因是冻融循环过程中由于蛋白质变性和细胞的机械损伤造成肌肉组织水分流失,导致溶质浓度增加和氢离子的释放[34−35]。在5次冻融循环后,L-精氨酸组的pH显著高于空白组和STP组(P<0.05),是四组里面最高的,比空白组高0.54,比STP组高0.33。这表明鸭肉饼经过L-精氨酸处理后其pH偏离MP等电点的程度高于空白组和STP组,从而增强了肌原纤维内粗细丝之间的静电斥力,导致肌原纤维的溶胀,而截留更多的水分子[36]。同时,负电荷的增加还会加强蛋白质分子与水分子的相互作用,从而保持冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼的保水能力[37]。
2.4 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼TVB-N的影响
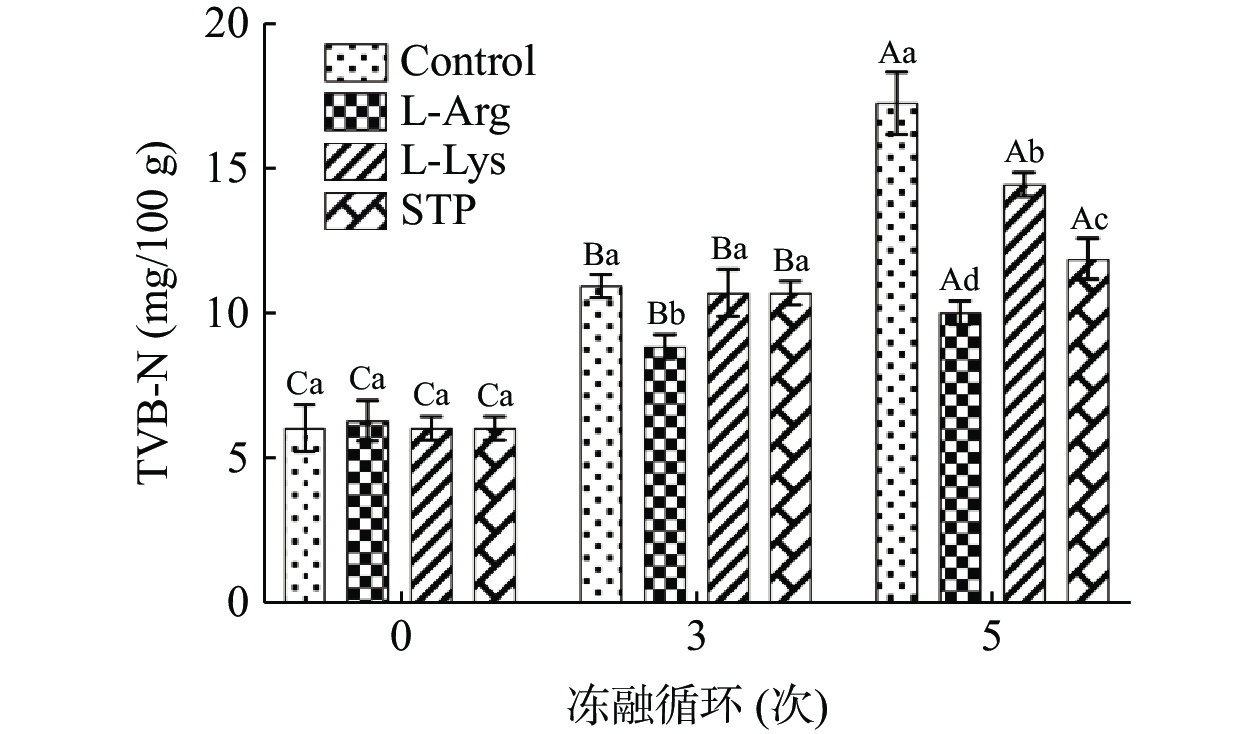
TVB-N由氨、胺等碱性含氮物质组成,是评估肉制品新鲜度的主要指标[38]。不同处理条件下在冻融循环中鸭肉饼的TVB-N值如图2所示。在未冻融循环时,所有组样品的TVB-N值基本一致,差异不显著,表明所有组的鸭肉饼都处于良好的食用品质。随着冻融循环次数的增加,空白组的鸭肉饼样品的TVB-N值逐渐显著增加(P<0.05)。特别是当5次冻融循环时,空白组的TVB-N值急剧增加,为17.27 mg/100 g,已经超过国家标准(TVB-N值≤15 mg/100 g)[39],样品发生严重的变质。TVB-N值的增加是由于蛋白质和非蛋白氮化合物的降解导致的。随着冻融循环次数的增加,样品中内源酶和腐败菌的活性显著增强,大量的氨基酸被降解,脱氨基作用增强,产生大量的5'-腺嘌呤核苷酸(AMP)和氨氮[40],导致TVB-N值增加。
如图2所示,在5次冻融循环时,L-精氨酸组样品的TVB-N值为10.03 mg/100 g,未超过国家标准[39],分别比空白组、L-赖氨酸组和STP组样品低7.24、4.44和1.87 mg/100 g(P<0.05)。这表明添加L-精氨酸可减少冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼的TVB-N形成,保持鸭肉饼的新鲜度。生物胺是由氨基酸的脱羧作用形成的,氨基酸脱羧酶能加速脱羧作用,而酸性环境有利于这一过程[41]。所以,由表2可知,L-精氨酸可以提高鸭肉饼pH,从而具有抑制微生物代谢和蛋白质分解的作用[29],减少TVB-N值的增加。
2.5 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼TBARS的影响
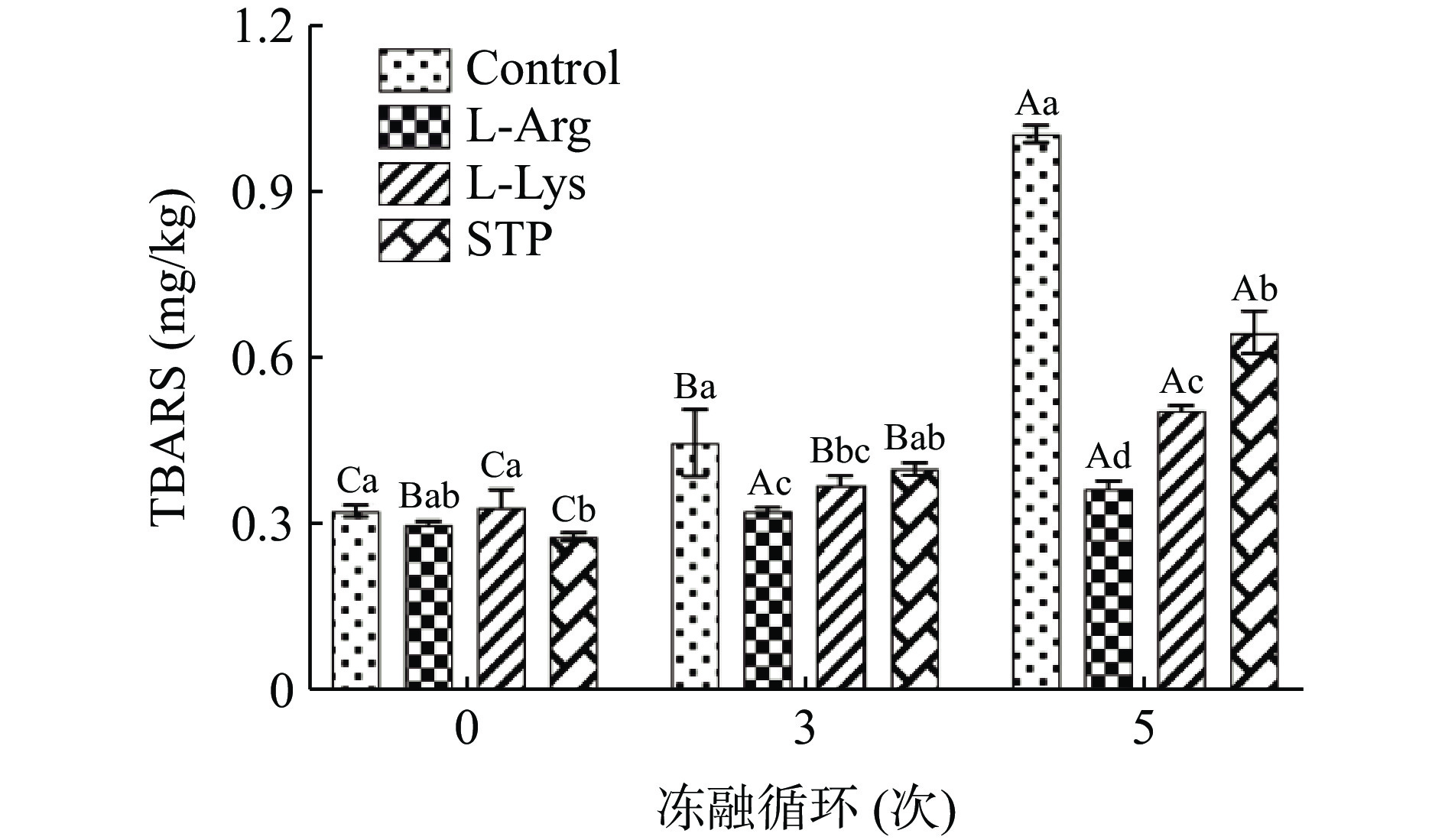
鸭肉饼在多次冻融过程中可能会引起脂质氧化,而肉制品的脂质氧化会影响其风味、颜色、质地和营养价值[42]。因此,可以通过测定TBARS值来评价冻融循环中的鸭肉饼样品的脂质氧化情况,结果如图3所示。从0次到5次冻融循环,空白组TBARS值从0.33 mg/kg显著增加至1.00 mg/kg(P<0.05)。Qi等[43]也发现了类似的结果,在多次冻融循环过程中羊肉样品的TBARS值显著升高。这是因为多次冻融循环形成的冰晶会损伤肌肉细胞,导致促氧化剂(如氧化酶、血红素铁等)的释放,从而加速脂质氧化[44]。根据图3所示,添加L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸可以抑制鸭肉饼在多次冻融循环中的脂质氧化,且抑制效果显著优于添加STP。尤其是在5次冻融循环后,L-精氨酸组的TBARS值(0.37 mg/kg)显著低于空白组(1.00 mg/kg)和STP组(0.65 mg/kg)(P<0.05),为四组最低。这可能是由于L-精氨酸具有清除自由基和螯合金属阳离子的能力[45],从而抑制鸭肉饼在冻融循环过程中的脂质氧化,保持鸭肉饼的品质。Xu等[46]也发现,添加L-精氨酸和L-赖氨酸也可以抑制乳化肠的脂肪氧化。
2.6 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼水分分布的影响
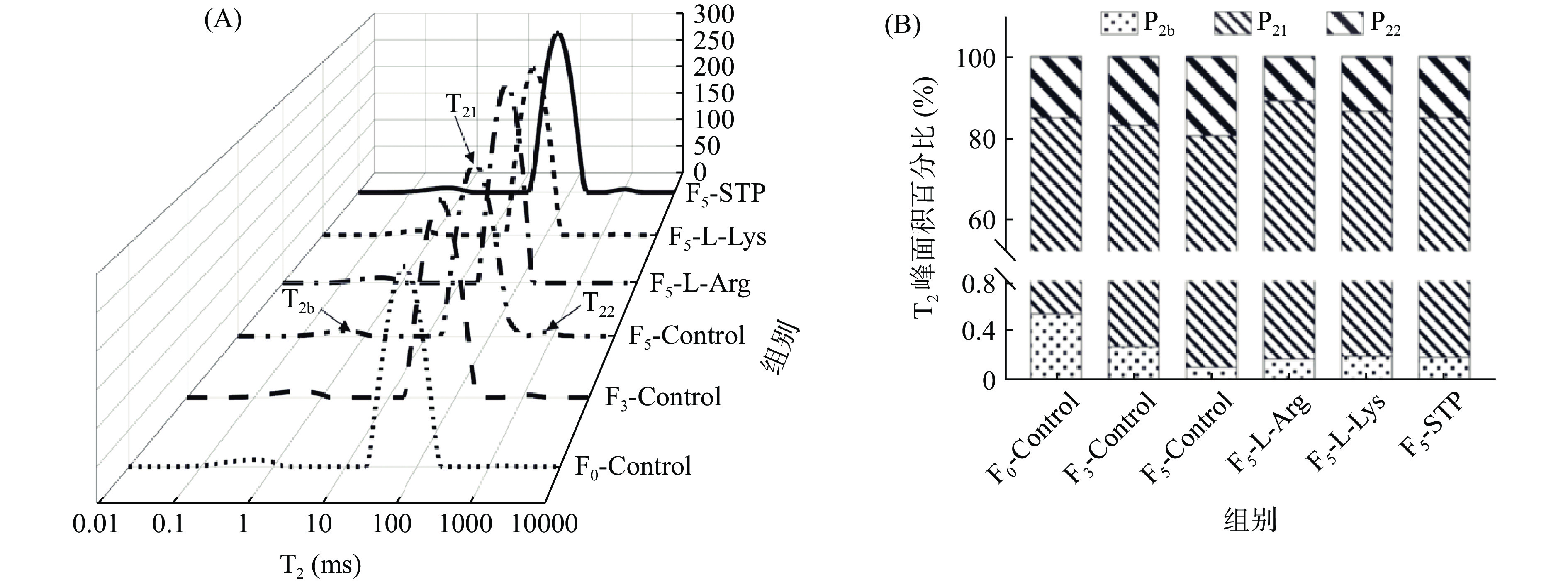
LF-NMR是表征肉中水的流动性和分布的重要检测方法[47]。T2弛豫时间可以表示出肌肉组织中三种不同状态的水:T2b(1~10 ms)代表与大分子紧密结合的结合水,T21(10~100 ms)被认为是肌原纤维蛋白网络中的不易流动水,T22(100~1000 ms)代表存在于肌原纤维外的自由水[48]。反复冻融鸭肉饼T2弛豫时间及P2相应峰面积占总面积的百分比变化如图4 A和B所示。根据图4A所示,空白组鸭肉饼随着冻融循环次数的增加T2弛豫时间逐渐右移,说明肌肉组织毛细血管在冻融循环过程中受到损伤。不同T2弛豫时间的相应峰面积占总面积的百分比代表每个积分中质子的相对含量,用P2表示(图4B)。随着冻融循环次数的增加,空白组鸭肉饼样品的P2b和P21都显著降低,P22显著升高(P<0.05)。在冻融循环过程中,肌纤维组织的破坏主要与重结晶、冰晶体积增大、分布不均有关。损伤的肌纤维很难从细胞外空间重新吸收融化的水,导致部分不易流动水转化为自由水[2]。Lan等[49]也观察到类似的结果,即随着冻融循环次数的增加,虾的P21显著降低(P<0.05),这说明在冻融循环过程中虾中的不易流动水向自由水转化占主导地位。
如图4B所示,在F5时,空白组、L-精氨酸组、L-赖氨酸组、STP组样品的P21分别为80.55%、89.06%、86.44%、84.89%,P22分别是19.34%、10.76%、13.35%、14.92%,差异显著(P<0.05)。以上结果说明在冻融循环都为5次的时候在鸭肉饼中添加L-精氨酸可以减少水分的流失,效果比L-赖氨酸和STP好。这可能是由于L-精氨酸可以降低冻融循环过程中蛋白质氧化变性的程度,限制水的流动,减少水分流失[46]。另一方面可能是因为L-精氨酸可以使样品的pH偏离MP的等电点,增加静电效应,最终导致水迁移率降低[13]。
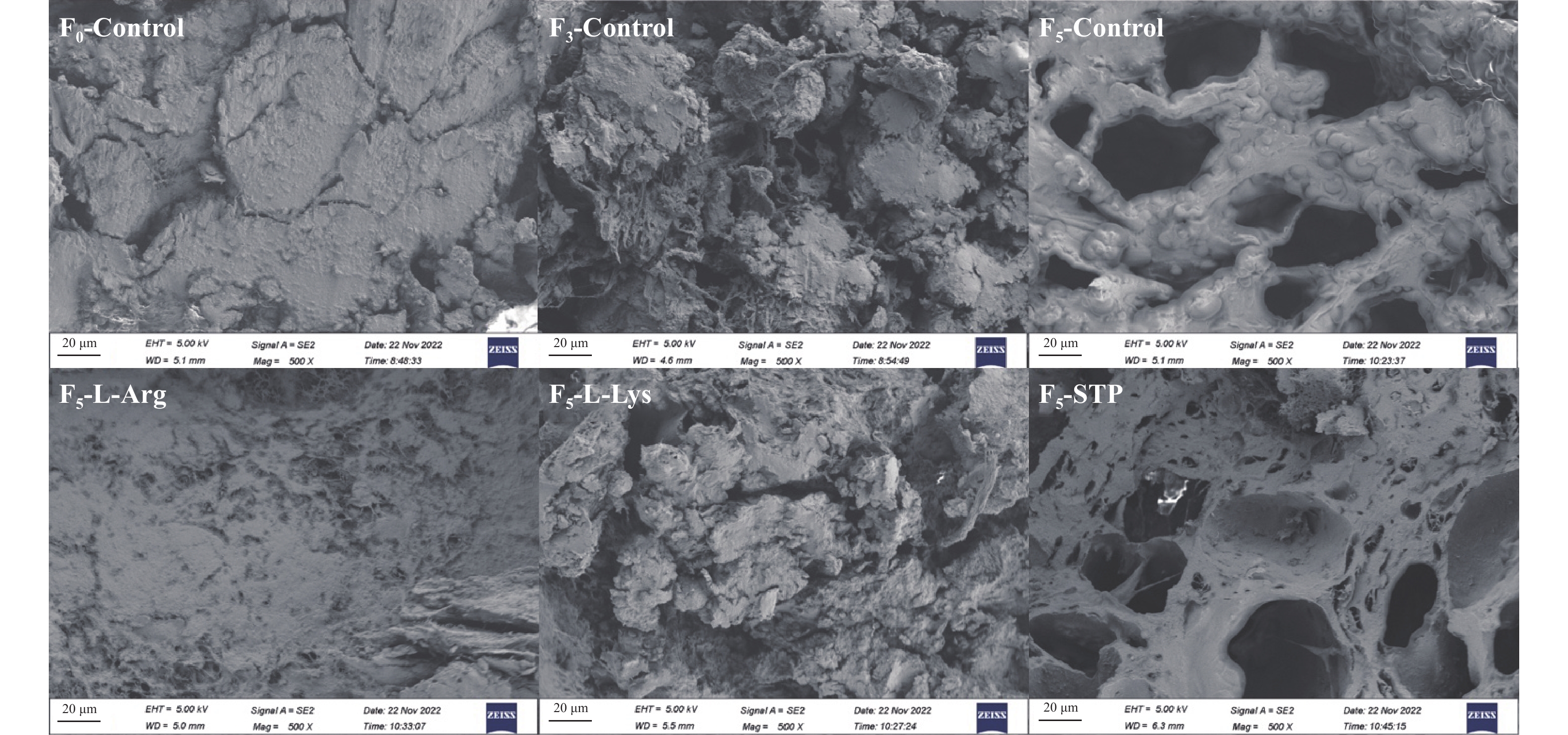
2.7 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼微观结构的影响
肌肉微观结构的变化可以直观地反映肌原纤维的机械损伤程度[16]。经过0、3和5次冻融循环后鸭肉饼的微观结构如图5所示。结果表明,冻融循环前肌纤维无明显孔洞,肌纤维结构相对连续致密。然而,随着冻融循环次数的增加,空白组肌肉组织结构变得不连续、疏松,气孔不规则。这可能是因为在多次冻融循环中肌肉细胞内外反复形成大量冰晶,从而破坏完整的肌肉组织结构[15],导致解冻后出现更大的孔洞。解冻后,未被肌原纤维重新吸收的水分变为自由水。因此,微观结构的变化证明多次冻融循环后不易流动水的减少[50],这一结果与LF-NMR的结果一致。
在F5下,L-精氨酸组的物理损伤程度较空白组低,组织结构较好。结果表明,L-精氨酸可以通过限制冰晶的生长,抑制由冻融循环引起的肌肉组织的破坏。Zhang等[13]研究发现添加L-精氨酸可以减少鸡肉肌肉纤维间的间隙,降低样品的蒸煮损失。因此,L-精氨酸可以维持冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼的微观结构的稳定,从而使鸭肉饼保持良好的品质。
3. 结论
本研究表明L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸处理能够抑制冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼品质的劣变。TPA、蒸煮损失、色差和pH的结果表明,L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸处理能够使鸭肉饼在冻融循环过程中保持良好的质地、保水能力、色泽等品质特性。此外,从TVB-N和TBARS的结果表明,L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸可以抑制鸭肉饼在冻融循环过程中的腐败变质和脂肪氧化。LF-NMR和SEM的结果表明,L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸处理可以阻止冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼水分的迁移,抑制大冰晶的形成,从而保护肌肉组织的微观结构。因此,L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸作为冷冻保护剂应用于冻肉产品,保护产品质量,延长产品货架期是可行的,为今后研究控制和减缓冻肉的品质的劣变提供非常重要的理论依据和实际价值。然而,L-精氨酸或L-赖氨酸对冻肉产品风味的影响还需进一步探讨。
-
表 1 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼TPA的影响
Table 1 Effects of different treatment on the TPA of duck meat patties during freeze-thaw cycles
冻融循环(次) 组别 硬度(N) 弹性 粘聚性 咀嚼性(N) 0 Control 2182.02±73.63Aab 0.63±0.01Aa 0.59±0.02Aab 798.69±97.2Aa L-Arg 2097.18±75.83Ab 0.64±0.02Aa 0.61±0.02Aa 794.35±83.02Aa L-Lys 1920.60±86.63Ac 0.61±0.02Aa 0.55±0.02Ab 635.37±21.27Ab STP 2339.21±113.14Aa 0.62±0.01Aa 0.62±0.01Aa 903.00±29.85Aa 3 Control 1250.18±64.3Bc 0.58±0.02Bb 0.54±0.04ABa 406.18±40.16Bb L-Arg 1691.5±52.85Ba 0.61±0.01ABa 0.60±0.04Aa 620.77±104.76Ba L-Lys 1481.34±132.9Bb 0.60±0.01Aab 0.55±0.03Aa 476.58±68.43Bb STP 1719.78±121.19Ba 0.60±0.01Bab 0.58±0.02Ba 621.45±32.64Ba 5 Control 787.67±105.42Cc 0.47±0.02Cc 0.53±0.02Bb 241.74±41.47Cd L-Arg 1457.73±90.55Ca 0.59±0.01Ba 0.57±0.02Aa 495.84±19.87Ba L-Lys 1167.61±73.52Cb 0.55±0.02Bb 0.53±0.01Ab 323.18±20.26Cc STP 1241.81±114.41Cb 0.56±0.01Cab 0.57±0.01Ba 424.51±54.47Cb 注:不同大写字母表示不同冻融循环次数的同一处理组样品之间存在显著差异(P<0.05);不同小写字母表示相同冻融循环次数的不同处理组的样品之间存在显著差异(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 不同处理条件对冻融循环过程中鸭肉饼色差和pH的影响
Table 2 Effects of different treatment on the color and pH of duck meat patties during freeze-thaw cycles
冻融循环(次) 组别 颜色 pH L* a* b* 0 Control 42.01±1.06Cab 18.70±0.16Aa 21.16±0.91Ba 5.94±0.01Ad L-Arg 40.47±1.40Bb 17.19±0.96Abc 20.91±1.24Ab 6.52±0.01Aa L-Lys 43.36±0.93Ba 17.78±0.31Aab 21.16±0.16Ba 5.96±0.02Ac STP 40.83±0.73Cb 17.69±0.53Aab 21.23±0.52Ba 6.26±0.01Ab 3 Control 45.25±0.83Ba 14.59±0.43Bb 22.89±0.95Ba 5.91±0.00Bd L-Arg 42.54±0.41Ab 16.46±0.62ABa 21.28±0.92Ab 6.47±0.01Ba L-Lys 45.39±1.23Aa 15.53±0.82Bab 21.64±0.25Bab 5.94±0.00Bc STP 43.08±1.59Bb 14.80±0.44Bb 22.50±0.35Bab 6.22±0.02Bb 5 Control 49.14±0.93Aa 12.61±0.72Cc 24.83±1.02Aa 5.88±0.01Cd L-Arg 44.03±0.78Ac 15.30±0.75Ba 22.69±0.94Ab 6.42±0.02Ca L-Lys 46.46±0.68Ab 14.22±0.69Cab 23.14±0.42Ab 5.91±0.01Cc STP 47.13±0.80Ab 13.31±0.76Cbc 23.29±0.78Aab 6.09±0.01Cb -
[1] HOU W F, LIN Y L, ZHANG Y J, et al. Effects of kojic acid on changes in the microstructure and myofibrillar protein of duck meat during superchilled storage[J]. Journal of Food Science,2023,88(3):977−987. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16448
[2] PAN N, DONG C H, DU X, et al. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the quality of quick-frozen pork patty with different fat content by consumer assessment and instrument-based detection[J]. Meat Science,2021,172:108313. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108313
[3] ZHAO Y H, POWELL-PALM M J, WANG J J, et al. Analysis of global energy savings in the frozen food industry made possible by transitioning from conventional isobaric freezing to isochoric freezing[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2021,151:111621. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111621
[4] BOUCHENDHOMME T, SORET M, GRARD T, et al. Differentiating between fresh and frozen-thawed fish fillets by muscle fibre permeability measurement[J]. Food Control,2023,147:109567. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109567
[5] 周纷. 大黄鱼加工副产物的白鲢鱼糜凝胶品质特性的研究[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2020. [ZHOU F. Study on gel quality characteristics of silver carp surimi from processing by-products of large yellow croaker[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2020.] ZHOU F. Study on gel quality characteristics of silver carp surimi from processing by-products of large yellow croaker[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2020.
[6] BAI X, SHI S, KONG B H, et al. Analysis of the influencing mechanism of the freeze–thawing cycles on in vitro chicken meat digestion based on protein structural changes[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,399:134020. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134020
[7] CURTAIN F, GRAFENAUER S. Plant-based meat substitutes in the flexitarian age:An audit of products on supermarket shelves[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(11):2603. doi: 10.3390/nu11112603
[8] WALAYAT N, XIONG H G, XIONG Z Y, et al. Role of cryoprotectants in surimi and factors affecting surimi gel properties:A review[J]. Food Reviews International,2022,38(6):1103−1122. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2020.1768403
[9] U P, GEORGE S. Influence of cryoprotectant levels on storage stability of surimi from Nemipterus japonicus and quality of surimi-based products[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2014,51(5):982−987. doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0590-y
[10] LIU Z L, YANG W G, WEI H M, et al. The mechanisms and applications of cryoprotectants in aquatic products:An overview[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,408:135202. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135202
[11] DOS SANTOS A L A A, LORENZO J M, GONÇALVES C A A, et al. Impact of lysine and liquid smoke as flavor enhancers on the quality of low-fat Bologna-type sausages with 50% replacement of NaCl by KCl[J]. Meat Science,2017,123:50−56. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2016.09.001
[12] GUO X X, TAO S, PAN J F, et al. Effects of L-Lysine on the physiochemical properties and sensory characteristics of salt-reduced reconstructed ham[J]. Meat Science,2020,166:108133. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108133
[13] ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG D J, HUANG Y J, et al. Effects of basic amino acid on the tenderness, water binding capacity and texture of cooked marinated chicken breast[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,129:109524. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109524
[14] NING C, LI L X, FANG H M, et al. L-Lysine/L-arginine/L-cysteine synergistically improves the color of cured sausage with NaNO2 by hindering myoglobin oxidation and promoting nitrosylmyoglobin formation[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,284:219−226. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.116
[15] WANG B, LI F F, PAN N, et al. Effect of ice structuring protein on the quality of quick-frozen patties subjected to multiple freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Meat Science,2021,172:108335. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108335
[16] CHENG S S, WANG X H, LI R R, et al. Influence of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on quality characteristics of beef semimembranous muscle:With emphasis on water status and distribution by LF-NMR and MRI[J]. Meat Science,2019,147:44−52. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.08.020
[17] FU L, DU L H, SUN Y Y, et al. Effect of lentinan on lipid oxidation and quality change in goose meatballs during cold storage[J]. Foods,2022,11(7):1055. doi: 10.3390/foods11071055
[18] 中华人民共和国国家卫生部. GB 5009.237-2016, 食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 5009.237-2016 National standard for food safety. Determination of pH value of food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 5009.237-2016 National standard for food safety. Determination of pH value of food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[19] 中华人民共和国国家卫生部. GB 5009.228-2016, 食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 5009.228-2016 National Standard for Food Safety. Determination of volatile base nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 5009.228-2016 National Standard for Food Safety. Determination of volatile base nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[20] 中华人民共和国国家卫生部. GB 5009.181-2016, 食品安全国家标准 食品中丙二醛的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 5009.181-2016 National standard for food safety. Determination of malondialdehyde in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 5009.181-2016 National standard for food safety. Determination of malondialdehyde in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[21] PAN N, HU Y F, LI Y, et al. Changes in the thermal stability and structure of myofibrillar protein from quick-frozen pork patties with different fat addition under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Meat Science,2021,175:108420. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108420
[22] SRIKET P, BENJAKUL S, VISESSANGUAN W, et al. Comparative studies on the effect of the freeze–thawing process on the physicochemical properties and microstructures of black tiger shrimp ( Penaeus monodon) and white shrimp ( Penaeus vannamei) muscle[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,104(1):113−121. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.11.004
[23] LI J H, SHI J Y, HUANG X W, et al. Effects of pulsed electric field on freeze-thaw quality of Atlantic salmon[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2020,65:102454.
[24] WEN R X, HU Y Y, ZHANG L, et al. Effect of NaCl substitutes on lipid and protein oxidation and flavor development of Harbin dry sausage[J]. Meat Science,2019,156:33−43. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.05.011
[25] LIU S X, ZHANG Y W, ZHOU G H, et al. Lipolytic degradation, water and flavor properties of low sodium dry cured beef[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2019,22(1):1322−1339. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2019.1642354
[26] LI F F, WANG B, KONG B H, et al. Impact of ultrasound-assisted saline thawing on the technological properties of mirror carp ( Cyprinus carpio L.)[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemstry,2022,86:1350−4177.
[27] XIA X F, KONG B H, LIU Q, et al. Physicochemical change and protein oxidation in porcine longissimus dorsi as influenced by different freeze–thaw cycles[J]. Meat Science,2009,83(2):239−245. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2009.05.003
[28] FAN L X, RUAN D N, SHEN J D, et al. The role of water and oil migration in juiciness loss of stuffed fish ball with the fillings of pig fat/meat as affected by freeze-thaw cycles and cooking process[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,159:113244. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113244
[29] CHEN L, BAO P Q, WANG Y, et al. Improving quality attributes of refrigerated prepared pork chops by injecting L-arginine and L-lysine solution[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,153:112423. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112423
[30] ZHANG M C, XIA X F, LIU Q, et al. Changes in microstructure, quality and water distribution of porcine longissimus muscles subjected to ultrasound-assisted immersion freezing during frozen storage[J]. Meat Science,2019,151:24−32. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.01.002
[31] MANCINI R A, HUNT M C. Current research in meat color[J]. Meat Science,2005,71(1):100−121. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.03.003
[32] NING C, BAO P Q, ZHANG D J, et al. Reduction and coordination properties of L-Lysine/L-arginine/L-cysteine for the improvement of the color of cured sausage[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,312:126122. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.126122
[33] SUPAWONG S, PARK J W, THAWORNCHINSOMBUT S. Effect of rice bran hydrolysates on physicochemical and antioxidative characteristics of fried fish cakes during repeated freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Food Bioscience,2019,32:100471. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2019.100471
[34] LEYGONIE C, BRITZ T J, HOFFMAN L C. Impact of freezing and thawing on the quality of meat:Review[J]. Meat Science,2012,91(2):93−98. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.01.013
[35] LIU C, XIONG Y L, RENTFROW G K. Kiwifruit protease extract injection reduces toughness of pork loin muscle induced by freeze-thaw abuse[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2011,44(10):2026−2031. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.05.019
[36] ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG D J, HUANG Y J, et al. L-arginine and L-lysine degrade troponin-T, and L-arginine dissociates actomyosin:Their roles in improving the tenderness of chicken breast[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,318:126516. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126516
[37] BAO P Q, CHEN L, WANG Y, et al. Quality of frozen porcine Longissimus lumborum muscles injected with L-arginine and L-lysine solution[J]. Meat Science,2021,179:108530. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108530
[38] SUN Q X, CHEN Q, XIA X F, et al. Effects of ultrasound-assisted freezing at different power levels on the structure and thermal stability of common carp ( Cyprinus carpio) proteins[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2019,54:311−320. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2019.01.026
[39] 中华人民共和国国家卫生部. GB 2707-2016, 食品安全国家标准 鲜(冻)畜、禽产品[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 2707-2016 National Standard for Food Safety. Fresh (frozen) livestock and poultry products[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] Ministry of health of the people's Republic of China. GB 2707-2016 National Standard for Food Safety. Fresh (frozen) livestock and poultry products[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[40] SHAO Y, WANG L, CHEN C S, et al. Antioxidant capacity of fermented soybeans and their protective effect on protein oxidation in largemouth bass ( Micropterus salmoides) during repeated freezing-thawing (FT) treatments[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,91:213−221. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.01.048
[41] SANTOS M H S. Biogenic amines:Their importance in foods[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,1996,29(2−3):213−231. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(95)00032-1
[42] ALI S, ZHANG W G, RAJPUT N, et al. Effect of multiple freeze–thaw cycles on the quality of chicken breast meat[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,173:808−814. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.095
[43] QI J, LI C B, CHEN Y J, et al. Changes in meat quality of ovine longissimus dorsi muscle in response to repeated freeze and thaw[J]. Meat Science,2012,92(4):619−626. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.06.009
[44] QIAN J, YAN L F, YING K Q, et al. Plasma-activated water:A novel frozen meat thawing media for reducing microbial contamination on chicken and improving the characteristics of protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,375:131661. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131661
[45] ZHANG Y W, GUO X Y, PENG Z Q, et al. A review of recent progress in reducing NaCl content in meat and fish products using basic amino acids[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,119:215−226.
[46] XU P, ZHENG Y D, ZHU X X, et al. L-lysine and L-arginine inhibit the oxidation of lipids and proteins of emulsion sausage by chelating iron ion and scavenging radical[J]. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences,2018,31(6):905. doi: 10.5713/ajas.17.0617
[47] ZHANG M C, LI F F, DIAO X P, et al. Moisture migration, microstructure damage and protein structure changes in porcine longissimus muscle as influenced by multiple freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Meat Science,2017,133:10−18. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2017.05.019
[48] WU Z Y, MA W R, XIAN Z J, et al. The impact of quick-freezing methods on the quality, moisture distribution and microstructure of prepared ground pork during storage duration[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2021,78:105707. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105707
[49] LAN W Q, HU X Y, SUN X H, et al. Effect of the number of freeze-thaw cycles number on the quality of Pacific white shrimp ( Litopenaeus vannamei):An emphasis on moisture migration and microstructure by LF-NMR and SEM[J]. Aquaculture and Fisheries,2020,5(4):193−200. doi: 10.1016/j.aaf.2019.05.007
[50] ZHANG W D, GUAN W L, CAI L Y, et al. Effects of magnetic nanometer combined with radio frequency or microwave thawing on physicochemical properties of myofibrillary protein in sea bass[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,154:112585. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112585





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



