Composite Edible Film Containing Microcapsules Composed of Shrimp-derived Bioactive Peptide Preparation and Preservation Potential
-
摘要: 针对南美白对虾易腐败和黑变问题,以羟丙甲基纤维素( HPMC)、虾活性肽微胶囊为成膜原料,研发具有保鲜功能的复合可食膜。采用单因素实验,以膜的机械性能、水蒸气透过率等为指标,考察羟丙甲基纤维素添加量、甘油添加量及虾活性肽微胶囊添加量对复合可食膜的成膜效果及膜性能的影响,并进一步研究虾活性肽微胶囊添加量对复合可食膜的红外光谱和自由基清除能力的影响,优化复合可食膜制备工艺;开展覆膜包装贮藏实验,以感官评分、pH、挥发性盐基氮含量、菌落总数等为指标,探究复合可食膜对南美白对虾的保鲜作用。结果表明,经单因素实验优化,复合可食膜的最佳膜材添加量为:羟丙甲基纤维素12%、甘油0.4%、微胶囊3%,此条件下,膜的综合性能佳。由膜抗氧化性能测定实验可得,当微胶囊添加量为3%及以上时,膜的抗氧化性能较好。傅里叶红外光谱显示,微胶囊添加量为3%~4%时,微胶囊与膜组分的交联作用较强。贮藏实验证实,复合可食膜可抑制虾体腐败,改善虾体感官,减缓机体pH上升、挥发性盐基氮激增和菌落总数增加等腐败现象,其贮藏期较无保护组可延长3~4 d,且总体保鲜效果优于HPMC空白膜甚至保鲜(PE)膜,展现出对南美白对虾的良好保鲜作用。Abstract: Shrimp body had to face with spoilage and melanosis when it come to food preservation. In this study, a kind of composite edible film (CEF) composed of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC) and shrimp-derived bioactive peptide microcapsule (SBPM), was developed to preserve the body of Penaeus vannamei. First of all, single-factor experiments were conducted by monitoring the mechanical performance and the water vapor permeability (WVP) of CEF, in order to investigate the influence of the dosages of HPMC, glycerol and SBPM, upon the formulation properties and mechanical strength of the film. The FTIR and free radical scavenging capacity of CEF were also determined when the SBPM addition changed and then, the optimum preparation process of CEF was ascertained based on the results mentioned above. In addition, the preservation-effect of CEF on fresh Penaeus vannamei was evaluated by inspecting some important items such as the sensory evaluation, pH, total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and aerobic bacterial count of shrimp flesh. The results of the single-factor experiments indicated the optimum amounts of HPMC, glycerol and SBPM were 12%, 0.4% and 3%, respectively, and the comprehensive performance of CEF was satisfied under this optimum condition. The antioxidant ability of CEF was excellent when the dosage of SBPM was not less than 3% and, the interaction between SBPM and other membrane fractions was powerful when the addition amount of SBPM came to be 3%~4%, which was indicated by the FTIR results. More importantly, the spoilage of shrimp body could be controlled by covering the body with CEF and, the sensory of seafood might be maintained by this film, as evidenced by the inhibitory effects of CEF on the raising of body pH, the jump of TVB-N and the increase of aerobic bacterial count in shrimp fresh. The quality guarantee period of fresh body in CEF group could be prolonged by 3~4 days as compared with that in unprotected group, while the overall freshness-keeping ablility of CEF was superior to that of HPMC film even PE film, indicating the potent protective effect of CEF on the fresh of Penaeus vannamei.
-
南美白对虾(Penaeus vannamei)是中国主要的对虾养殖品种,具有壳薄体肥、肉质鲜甜、营养丰富等优点。然而南美白对虾在运输、贮存和销售过程中,可能因黑变病、自身蛋白质内源性化学反应、酶促反应、脂肪分解等效应导致虾体组织液化,发生腐败变质,产生消费者不可接受的感官变化,甚至失去食用价值。如何控制虾体的腐败速率、延长贮藏期,成为当前的热点问题[1−2]。
对虾保鲜技术主要有物理保鲜(如低温贮藏)、化学保鲜(如保鲜剂、臭氧保鲜)及生物保鲜(如壳聚糖及各类活性提取物)[3],优缺点各异,可一定程度延长对虾的贮藏期。近年来,可食膜以覆膜和涂膜的形式应用于肉类及水产品保鲜,并通过加入抗菌剂、抗氧化剂、天然活性成分如蛋白[4]、精油[5]等,进一步抑制微生物生长、防止蛋白质变质、延缓脂质氧化及异味形成、减少水分损失,提高食品质量,达到保鲜效果,已成为食品包装领域的研究热点[6−9]。多糖、脂质、蛋白来源广泛、可降解,均可作为可食膜的膜材,但是单一膜材往往难以满足食品加工和开发的需要。蛋白基可食膜往往存在膜的机械强度差,易断裂、脆损、不透明等缺陷[10];多糖基可食膜的机械性能、透明性较好,但阻湿性和阻油性不佳[11]。结合单一膜材的技术特点,制备复合可食膜(composite edible film,CEF),可改善单一膜材的技术缺陷。以蛋白-多糖基复合膜为例,蛋白发挥增稠和凝胶作用,可提高成膜溶液的稳定性[12],而多糖(如羟丙甲基纤维素,hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose,HPMC)具有优良的控释、缓释能力、成膜性以及稳定性,二者组成的复合膜具有适度的水分屏障性能、优良的阻氧性能以及较好的抗拉强度[13]。因此,蛋白/多糖复合膜可作为可食膜的基质,应用于食品保鲜。
南美白对虾蛋白肽具有多种生物活性功能,已受到广泛关注[14−16]。笔者在前期研究发现,虾活性肽具有较好的抗氧化活性和免疫活性,且对HepG2、BEL-7402等细胞株无明显毒性,安全性好[17]。其他研究表明,在可食膜中添加南美白对虾副产物蛋白质浓缩物可提高膜的光阻性能、拉伸强度、抗氧化和抗菌性能[18]。再者,利用微胶囊技术制备虾活性肽微胶囊(shrimp-derived bioactive peptide microcapsule,SBPM),能进一步减少氧化、化学物质等对虾活性肽的影响,更好保护虾活性肽的活性成分,有效提高虾活性肽的稳定性。因此,虾活性肽微胶囊有望作为可食膜组分应用于对虾保鲜,而基于多糖和虾活性肽微胶囊的多糖/蛋白复合膜更令人期待。
目前,内含虾活性肽微胶囊的HPMC复合膜对南美白对虾进行保鲜处理鲜有报道。本研究以SBPM和HPMC制备CEF,探究CEF对南美白对虾的保鲜效果,评估CEF对南美白对虾贮藏期的延长作用,为CEF应用于对虾保鲜提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
虾活性肽微胶囊(SBPM) 参考文献[17]制备;南美白对虾(活虾) 厦门市新华都(厦大店);羟丙甲基纤维素(HPMC) 安徽山河药用辅料股份有限公司;丙三醇 西陇化工股份有限公司;二苯基苦味酰基苯肼(2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH) 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;SDA培养皿 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;其余试剂 均为市售分析纯。
电子螺旋测微器 上海宪南实业有限公司;Sartorius BSA224S电子分析天平 赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;RCT digital S025磁力器搅拌器 艾卡仪器设备有限公司;Zealway S225P超声波清洗机 致微(厦门)仪器有限公司;DHG-9035A电热鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;SMS-TA.XT PlusC质构仪 北京微讯超技仪器技术有限公司;UV-1780紫外可见分光光度计 岛津仪器(苏州)有限公司;Tensor 27&Tensor 37红外光谱仪 布鲁克光谱仪器公司;SHP-080Y生化培养箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 CEF的制备
称取一定量的HPMC粉末,加水搅拌溶胀20 min后形成HPMC溶液,制得成膜基液。将甘油、SBPM分别添加到基液中,搅拌混匀后进行超声脱泡(超声功率100 W,处理时间15 min)。最后将膜液倒入20 cm×10 cm自制有机玻璃成膜器中,水平流延1 min后,放入烘箱中50 ℃干燥30 min,揭膜即得CEF。
1.2.2 CEF性能的测定方法
1.2.2.1 机械性能的测定
将膜裁剪成宽度20 mm,长度45 mm的长条试样,选取膜的四周及中心点,利用螺旋测微器测定膜的厚度。在间隔30 mm,拉伸速率1 mm/s的条件下,利用质构仪进行拉伸试验[19]。拉伸强度(tensile strength,TS)和断裂伸长率(elongation at break,EB)分别按公式(1)和(2)计算。
TS=FS (1) 式中:F为膜断裂时最大拉力(N);S为膜横截面积(mm2)。
EB(%)=L1−L0L0×100 (2) 式中:L0为拉伸前膜的长度(mm);L1为拉伸后膜的长度(mm)。
1.2.2.2 水蒸气透过率的测定
取直径15 mm、容量10 mL的圆口玻璃瓶,准确移取6 mL超纯水置于瓶中。将膜裁剪成20 mm×20 mm置于瓶口,并用封口膜封口,使膜与瓶口完全贴合。然后将玻璃瓶置于装有变色硅胶的恒温干燥器中(RH:0%),每隔12 h称重一次,持续36 h[20]。膜的水蒸气透过率(water vapor permeability,WVP)按公式(3)计算:
WVP=Δm⋅dA⋅t⋅ΔP (3) 式中:Δm为t重量变化量(g);d为膜的厚度(mm);A为玻璃瓶口面积(m2);t为间隔时间(s);ΔP水蒸气压差(Pa)。
1.2.2.3 透光率和不透明度的测定
膜裁剪成适宜大小,并紧贴于比色皿一侧。以空白比色皿校正基线,对贴膜比色皿进行全波扫描(200~800 nm),并于600 nm波长条件下测定不同膜样品的透光率[21],按公式(4)计算膜的不透明度值。
T=−lgT600d (4) 式中:T600为600 nm波长下的光透过率;d为膜的厚度(mm)。
1.2.2.4 CEF的傅里叶红外光谱表征
采用傅里叶变换衰减全反射法(ATR-FTIR),通过红外光谱仪对CEF进行扫描分析,扫描波数范围400~4000 cm−1,仪器分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描次数32次。
1.2.2.5 CEF抗氧化性能的测定
将膜裁剪成20 mm×20 mm大小,加水搅拌溶解,即得膜浸泡液。加入DPPH甲醇溶液混合,室温避光反应30 min,在517 nm测定混合液的吸光度[22]。DPPH自由基清除率按公式(5)计算:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=A1−A2A1×100 (5) 式中:A1:甲醇溶液的吸光度(Abs);A2:混合液的吸光度(Abs)。
1.2.3 CEF的配方筛选
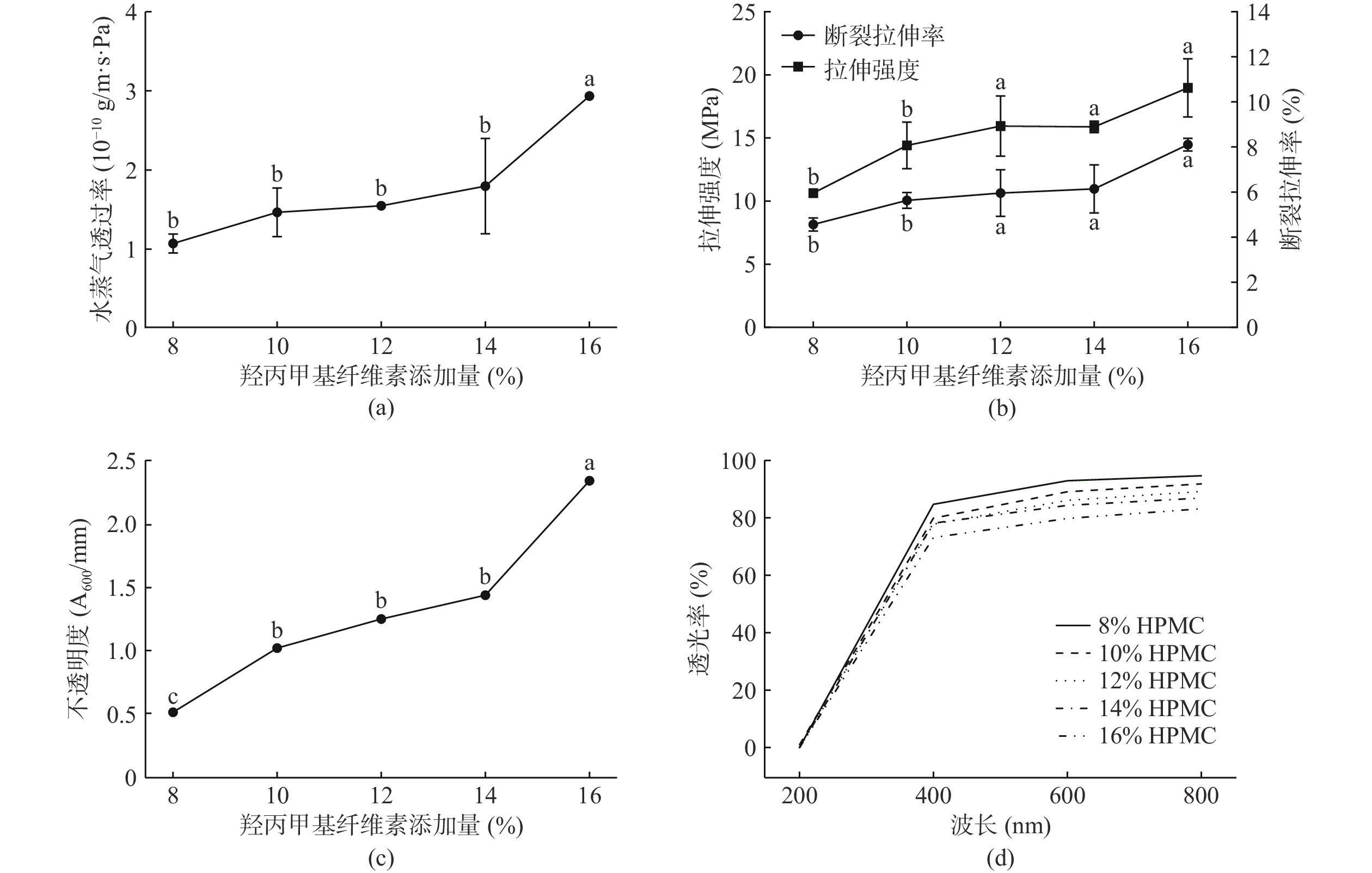
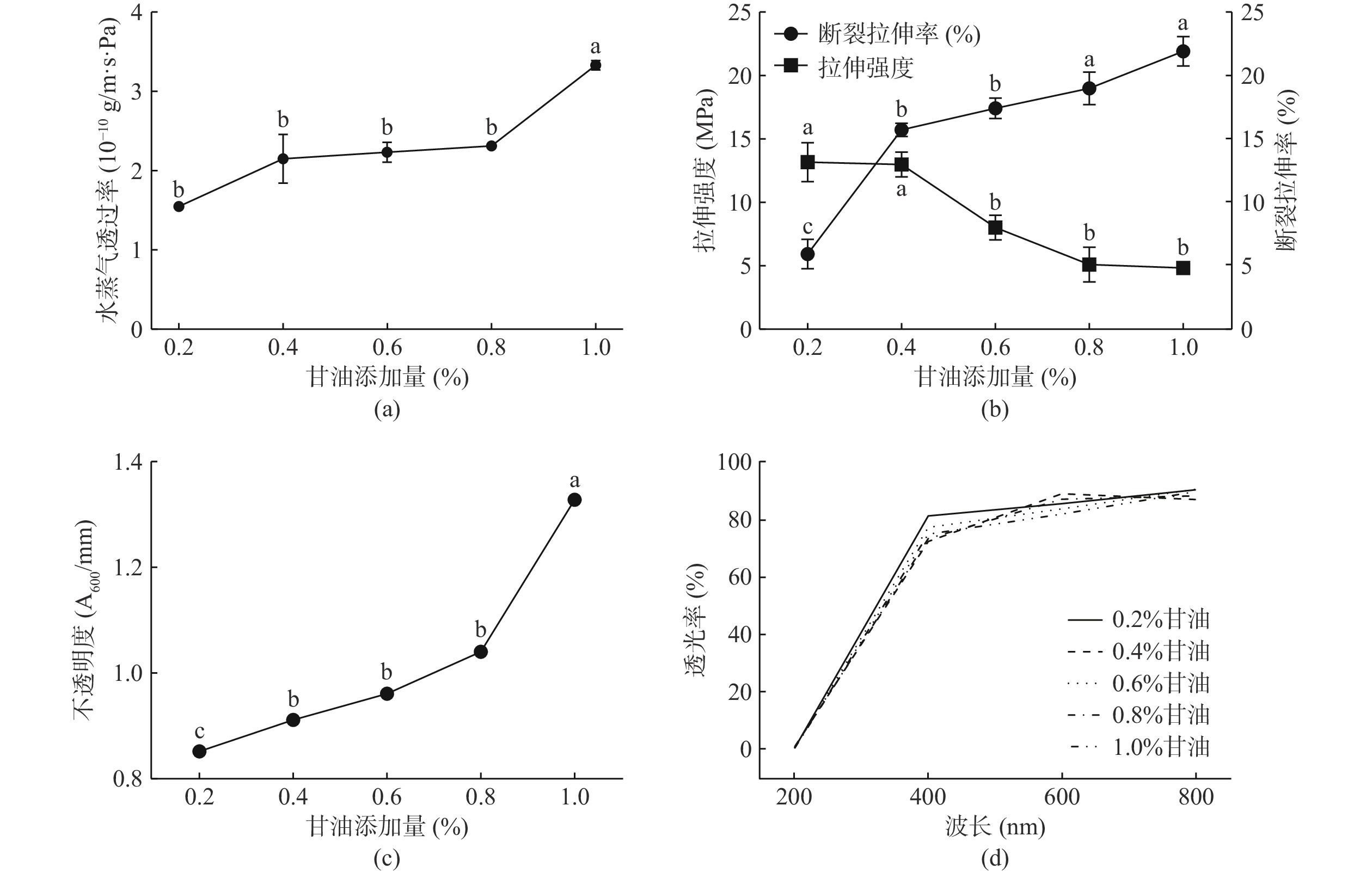
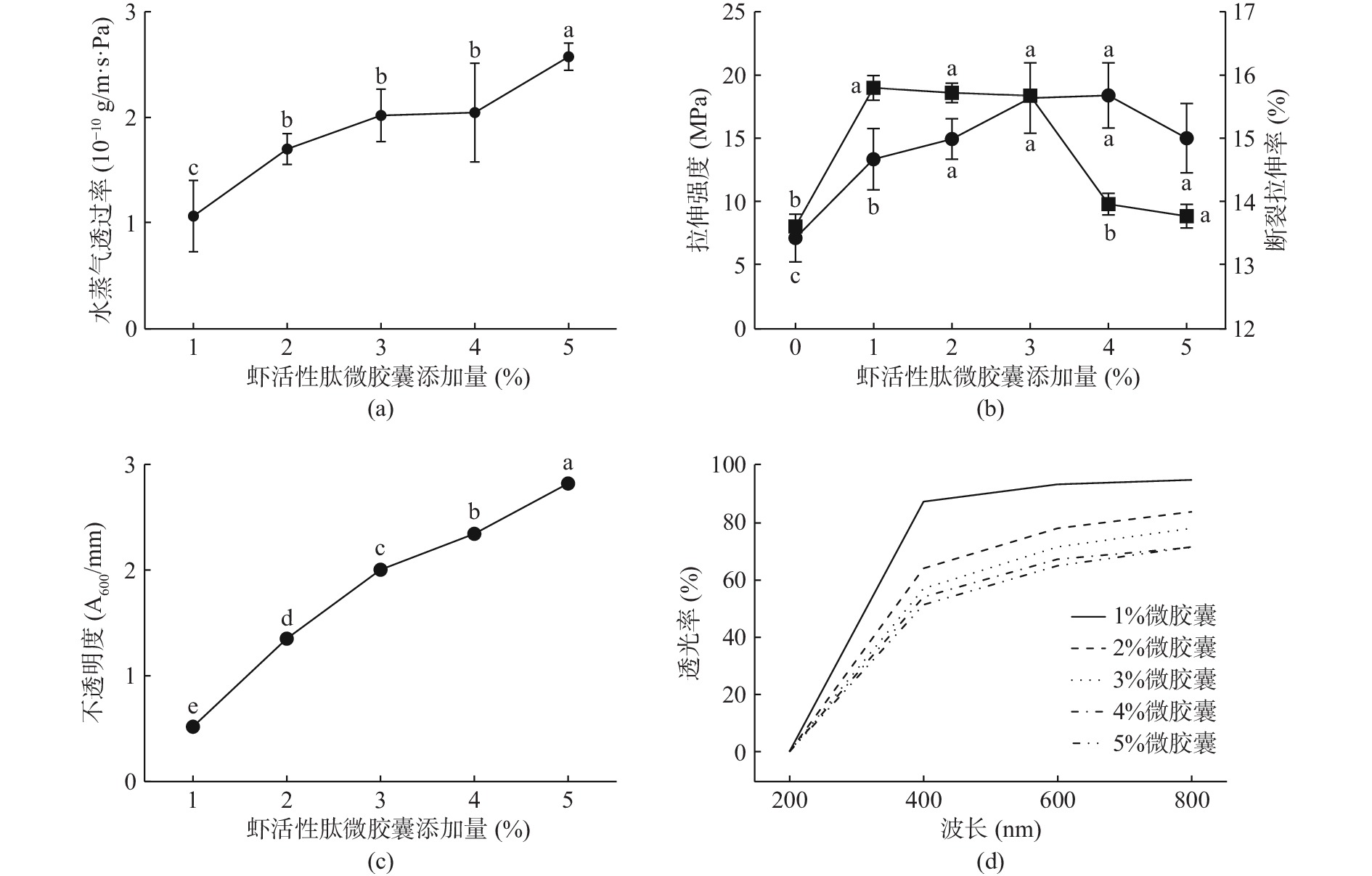
以膜的水蒸气透过率(Water vapor permeability,WVP)、拉伸强度、断裂伸长率、不透明度、透光率等为考察指标,进行单因素实验,考察各因素对CEF的成膜效果及膜性能的影响,优化CEF制备工艺[19]:固定甘油添加量0.4%,SBPM添加量2%,改变HPMC添加量(8%、10%、12%、14%、16%);固定HPMC添加量12%,SBPM添加量2%,改变甘油添加量(0.2%、0.4%、0.6%、0.8%、1.0%);固定HPMC添加量12%,甘油添加量0.4%,改变SBPM添加量(1%、2%、3%、4%、5%)。
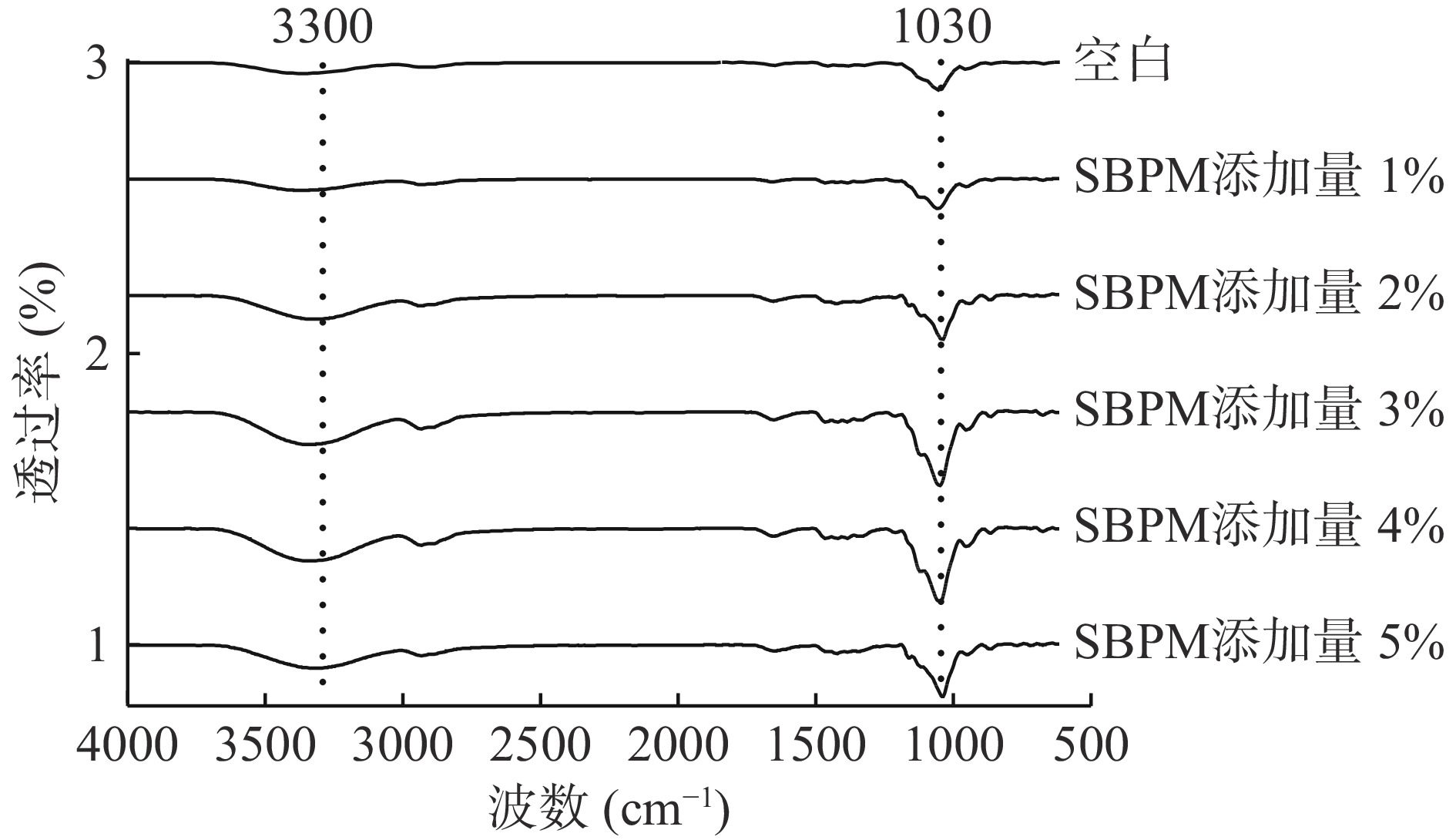
此外,进一步研究SBPM添加量(1%、2%、3%、4%、5%)对CEF的红外光谱和DPPH自由基清除能力的影响,以便确定复合可食膜的最优配方。
1.2.4 CEF对虾体的保鲜作用研究
1.2.4.1 样品的处理
市售南美白对虾剔除死虾、残虾后,剩余活体用水反复冲洗两次,加入碎冰使其猝死。CEF的试验分组及样品处理如下:将预处理的虾随机分为4组,包括无膜组、HPMC空白膜组、保鲜膜(PE膜)组和CEF组;每组含4只活体,分装于干净托盘并覆膜包装后,置于4 ℃冷藏。
1.2.4.2 感官评定
参照GB/T 16291.1-2012《感官分析 选拔、培训与管理评价员一般导则 第1部分:优选评价员》[23],筛选具有敏感的生理感觉能力和良好的评价心理的食品专业感官评定人员5名按表1,对虾的气味、色泽、形态等五方面进行感官评分,以评分总和的均值作为试验最终结果。总和均值在9~10分为消费者完全接受,7~8分为消费者可以接受,5~6分为消费者勉强接受,0~4为消费者不可接受[24]。
表 1 感官评分标准Table 1. Criteria for sensory evaluation项目 评价要求 分值 气味 虾鲜味浓,无异味 2 虾鲜味稍淡,无异味 1.5 轻微的腥臭味 1 强烈的氨味和腥臭味 0 色泽 虾体的颜色正常,表壳有光泽 2 虾头稍发黑、虾体有零星墨绿色斑点 1.5 虾体黑变严重,发黄发白,光泽暗 1 虾体完全变黑,色泽发暗,无光泽 0 形态 头胸甲与体节间连接紧密 2 头胸甲与体节间连接较紧密 1.5 头胸甲与体节间松动 1 头胸甲与体节分离,虾体残缺 0 组织 虾肉组织紧密有弹性 2 虾肉组织稍微变软,弹性降低 1.5 虾肉组织软化,弹性差 1 虾肉组织呈海绵状,无弹性 0 漂烫液 鲜香味浓,无异味,漂烫液澄清,无漂浮物 2 鲜香味较浓,略带虾腥味,漂烫液较澄清,少许漂浮物 1.5 鲜味淡,虾腥味重,漂烫液较为浑浊,杂质较多 1 无鲜味,虾腥臭味重,漂烫液浑浊,杂质多 0 1.2.4.3 pH测定
参照GB 5009.237-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定》[5],测定虾肉的pH。
1.2.4.4 挥发性盐基氮含量的测定
参照GB 5009.228-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》[25],按微量扩散法测定。
1.2.4.5 细菌总数的测定
参照GB 4789.2-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验菌落总数测定》[26],按平板计数法测定菌落总数。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2016和GraphPad Prism 8.0软件进行数据分析处理及绘图,结果用平均值±标准差(mean±SD)表示,显著性分析中不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 膜组分对CEF性能的影响
2.1.1 HPMC添加量对CEF性能的影响
图1(a)表明,CEF的WVP随HPMC添加量增加呈上升趋势,这与HPMC为亲水聚合物有关。HPMC用量增加,亲水基团增多,亲水性凸显,从而破坏膜的网络结构,降低致密性,导致WVP逐渐变大。HPMC添加量递增时,膜的TS、EB均有所上升(图1(b)),部分原因在于HPMC分子中的羟基与活性肽链上的氨基通过氢键相互作用,增强了分子之间的粘附力,提高膜的韧性,进而提升膜的机械性能[27]。图1(c)、图1(d)显示,提高HPMC添加量还可能加重膜不透明度、降低膜透光率,导致膜的光学性能下降。当HPMC添加量为12%时,膜液流动性、成膜效果好,膜的WVP较低、机械性能佳,且光学性能较好。
2.1.2 甘油对CEF性能的影响
从图2(a)可知,增大甘油添加量,可提升膜的亲水性基团数目,提高水蒸气在膜表面的吸附溶解和扩散能力[28],导致膜的WVP上升。此外,甘油保水性强,对膜的水分起到稳定作用,并可降低高分子间的结合力[19]。因此,甘油添加量的增加可引起膜的TS下降, EB上升(见图2(b))。图2(c)、图2(d)则表明,增大甘油添加量还会引起膜T值上升、T600下降,这可能与增加甘油浓度会造成膜液浓度上升、最终导致膜液颜色加深有关。当甘油添加量为0.4%时,膜柔韧性较好,膜完整性好,易于脱膜,而且膜的WVP较低,机械性能佳,光学性能较好。因此,优选甘油添加量为0.4%。
2.1.3 SBPM对CEF性能的影响
肽为亲水物质,提高SBPM添加量,容易引起膜的吸湿性增强、黏性变大,造成WVP上升(图3(a)),进而降低膜的机械性能(图3(b))。相对于空白HPMC膜,SBPM添加量为1%~3%时可显著增强膜的机械性能(图3(b))。此外,由于所制SBPM为淡黄色,提高其添加量还会出现膜不透明度升高、透光率降低等不良后果(图3(c)、图3(d))。SBPM添加量为3%时,膜的WVP较低,机械性能和光学性能较好。
2.1.4 CEF的红外光谱特征
1030 cm−1附近的红外吸收峰源于膜C-O-C的反对称伸缩振动[29]。由图4可知,随着SBPM添加量增加,该峰逐渐变窄,强度变大。3300 cm−1附近的吸收峰反映-OH的伸缩振动,表明SBPM与膜组分的羟基发生交联;此峰的强度随SBPM比例的增加而增大,说明交联程度增加。当SBPM添加量在3%~4%时,C-O-C伸缩振动峰蓝移至1045 cm−1值,-OH的伸缩振动强度达到最大值,说明此时SBPM与膜组分的交联作用较强,这与2.1.3同样SBPM添加量下,膜的机械性能和光学性能较好保持一致。
2.1.5 CEF的抗氧化活性
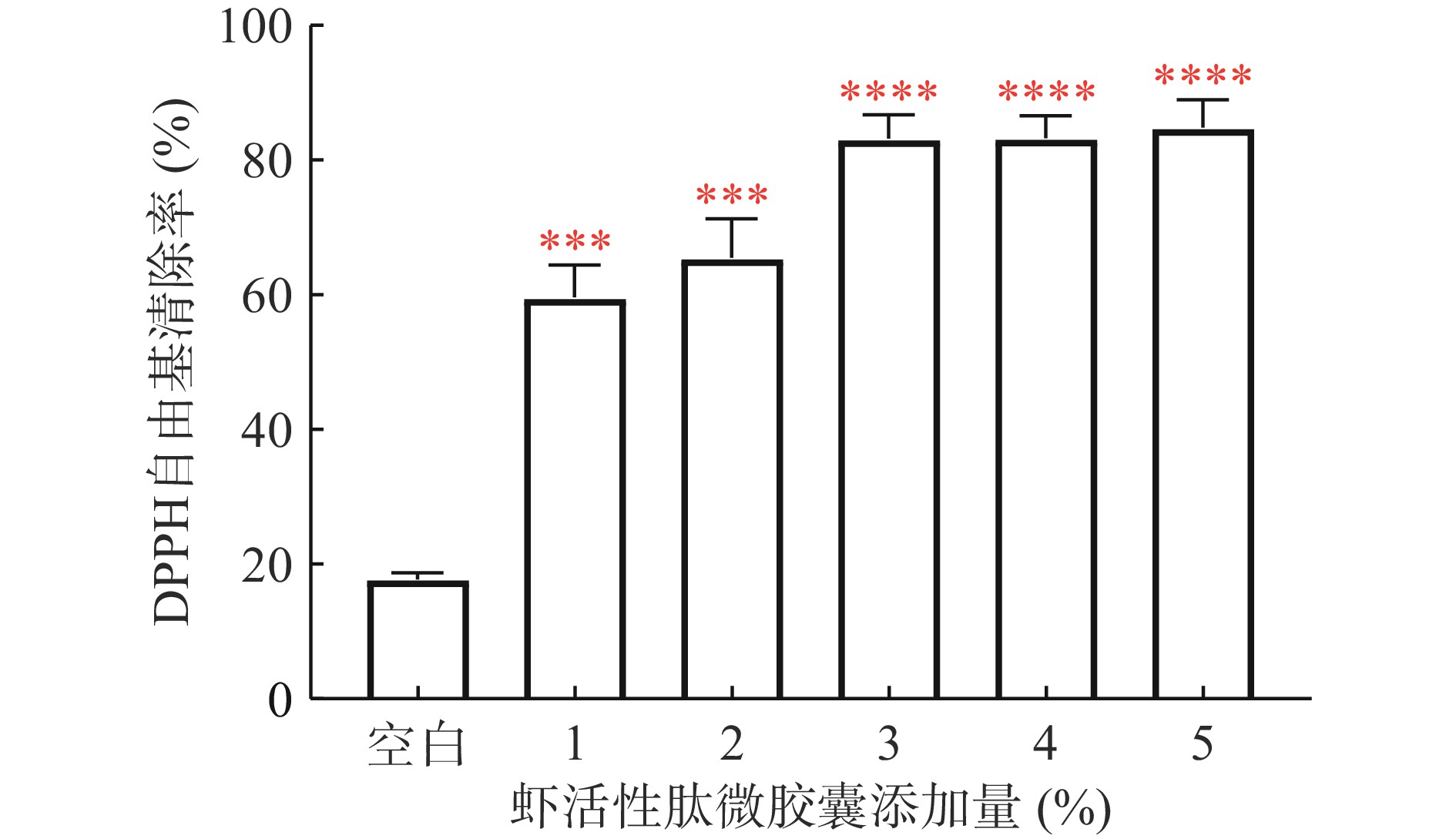
可食膜的抗氧化能力是膜保鲜效果的关键因素。提高膜的抗氧化能力有利于延缓食品的腐败。如图5所示,HPMC空白膜对DPPH自由基的清除率较低(<20%),抗氧化性能较弱。添加SBPM的可食膜的DPPH自由基清除能力均显著高于空白膜组(P<0.05),且该能力随着SBPM添加量的提升逐渐增强,印证了虾活性肽的抗氧化能力。SBPM添加量为3%及以上时,膜的抗氧化性能不再显著增加。
综上,SBPM添加量为3%时,SBPM与膜组分HPMC交联效果较好,形成致密的网状结构,此时膜的WVP较低,机械性能和光学性能较好,抗氧化能力达到最大值。因此,优选SBPM添加量为3%,用于保鲜作用研究。
2.2 CEF对虾体的保鲜作用
2.2.1 感官评价
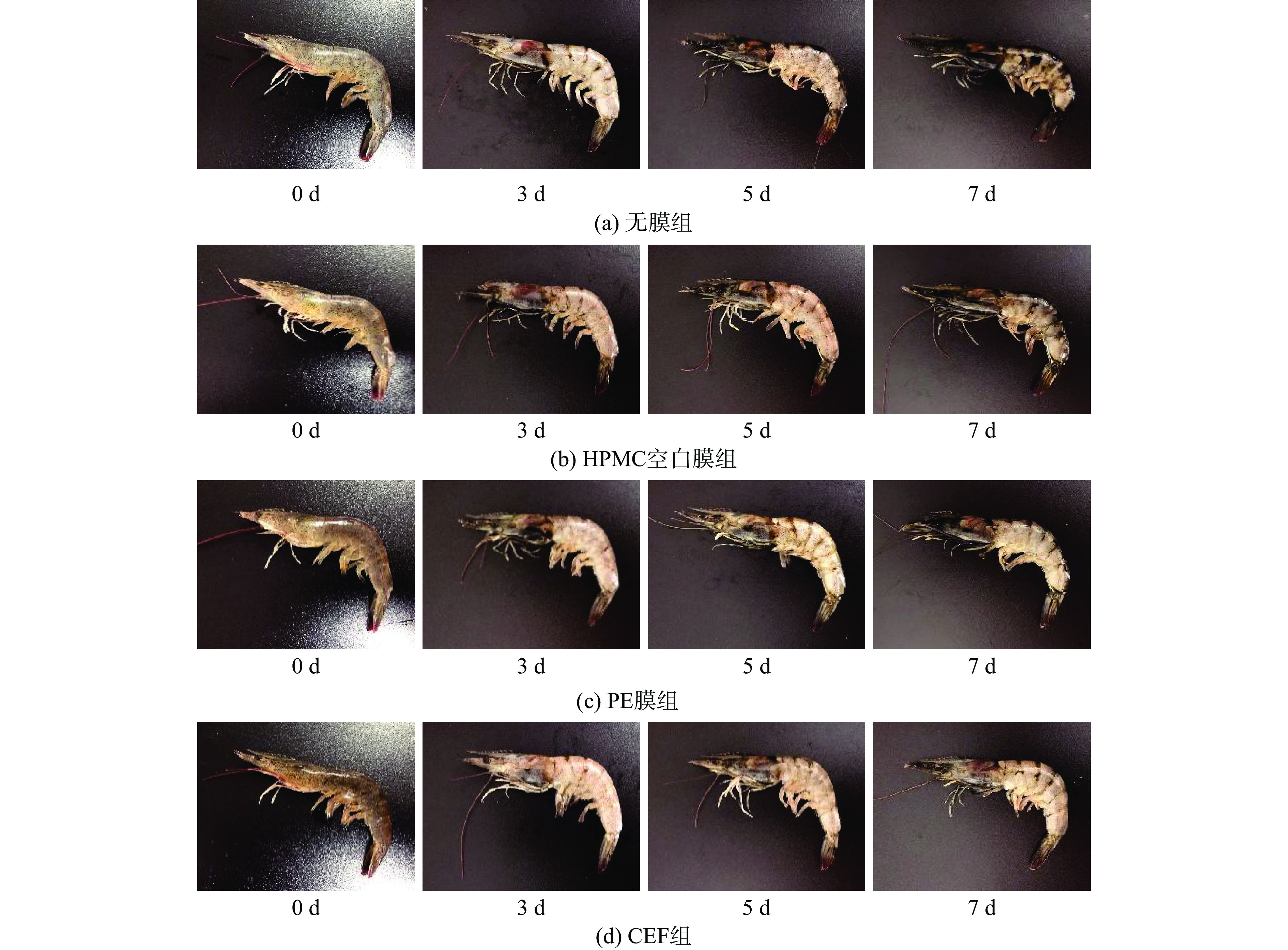
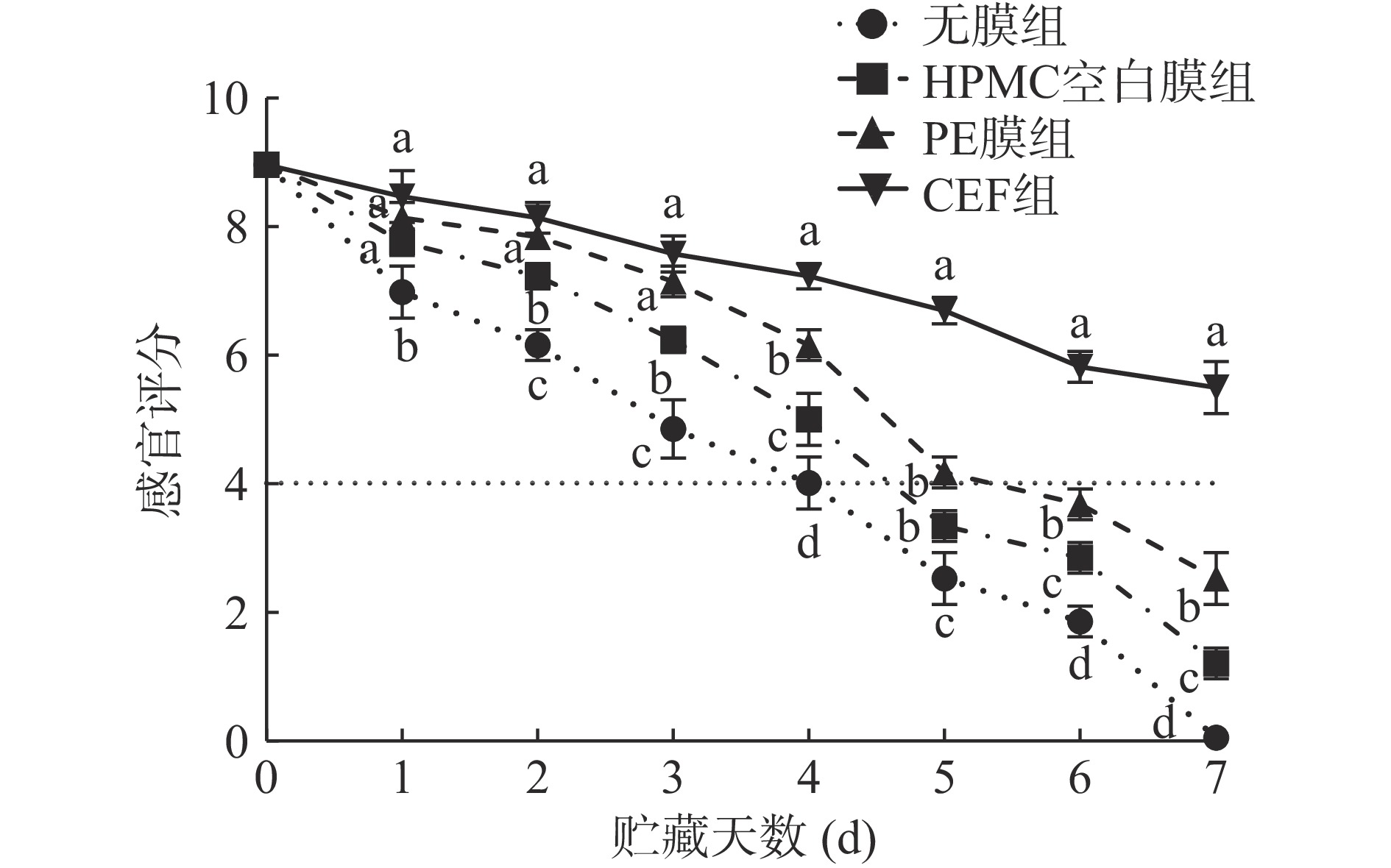
在贮藏期间,可通过虾体的气味、色泽、形态等指标评价对虾鲜度。由图6、图7可知,随着贮藏时间延长,各组感官评分均呈下降趋势。在贮藏第3 d时,各组的虾头均出现一定的黑变现象。无膜组感官评分下降最快,并于第4 d低于限值(4分以下表明虾已不被消费者接受)[30]。HPMC空白膜机械强度较低、耐水性较差,易出现覆膜表面破损,导致后期虾头黑变严重、虾体光泽度变暗等,第5 d起消费者已不能接受该组虾的整体感官。得益于较好的机械性能及气体阻隔性,PE组在贮藏前期保鲜效果较好,但后期覆膜表面出现大量水蒸气凝结,一定程度上加快了虾头、肢节处的黑变速度,于第5 d逼近限值。CEF组在气味评分项中相较于对照组的优势明显,无明显腐败腥味,光泽度略微变暗,漂烫水较为澄清;在贮藏中后期,肢节处出现发黑,虾头不可避免产生黑变。
2.2.2 虾体pH
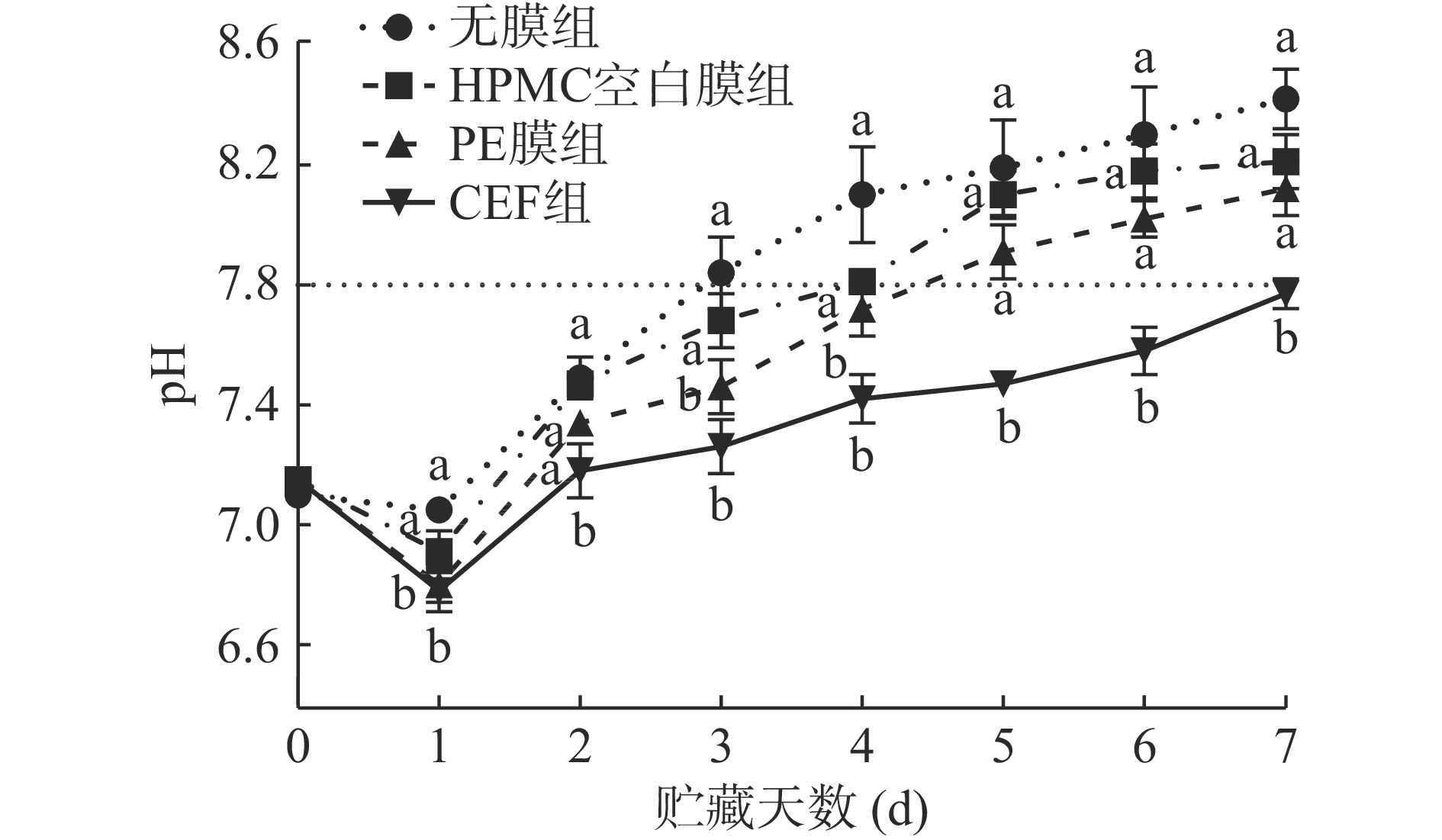
虾体的pH≤7.7表示品质优良[31],pH7.8为判断对虾鲜度及消费者可接受的质量范畴的重要拐点[32]。如图8所示,在贮藏前期(1 d左右)由于对虾糖原降解产生酸性物质,引起各组对虾pH下降。而后受微生物的影响,对虾中的蛋白质、氨基酸及含氮物质分解为氨、三甲胺、吲哚、组胺等碱性物质,导致虾体pH上升[33]。在贮藏第3 d,无膜组的pH超过限值(7.8)。HPMC空白膜机械强度低,在贮藏中易出现覆膜破损,受外界环境影响pH上升较快。PE膜组的阻隔性好,pH上升趋势较慢,表明其腐败进程较慢,于第5 d超过限值。CEF组在贮藏过程(7 d)中pH均未超过限值。可见CEF能在一定程度上减少微生物对虾的影响,保持虾的品质及可接受性。
2.2.3 对虾挥发性盐基氮含量
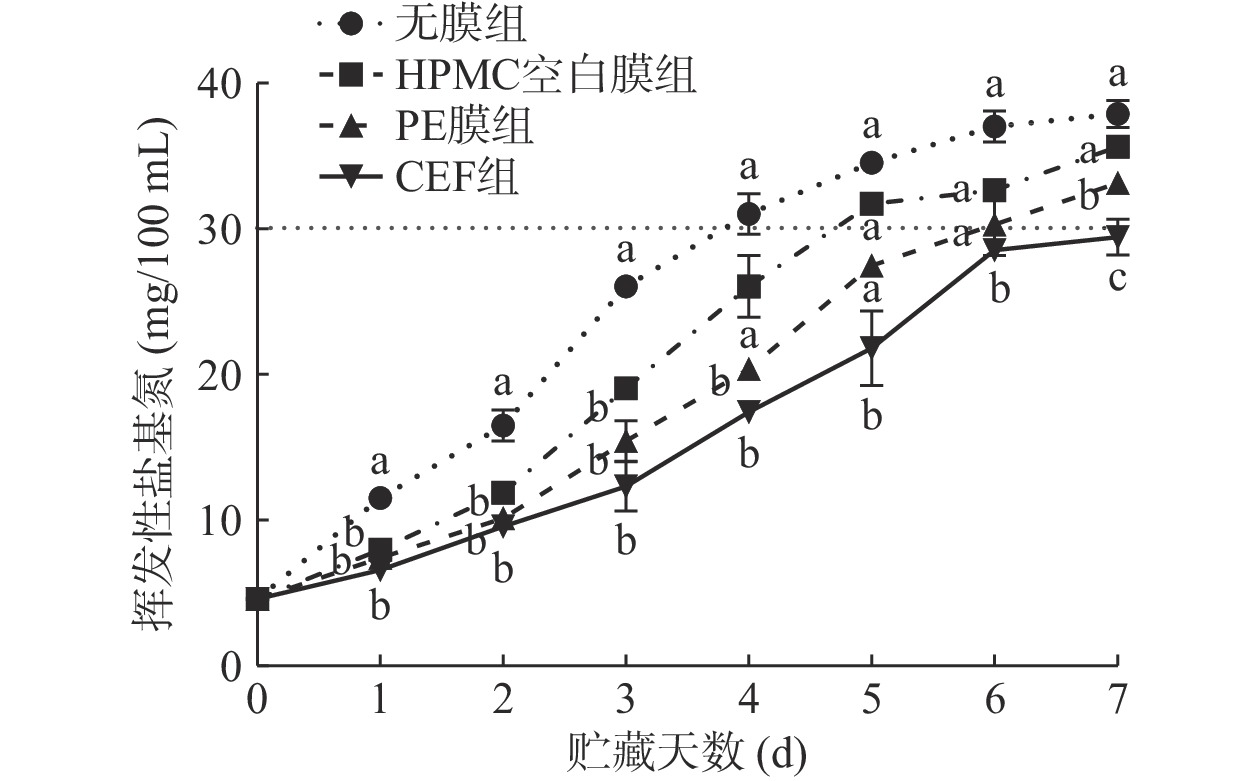
挥发性盐基氮含量是反映水产品腐败变质的重要指标。海水鱼虾的挥发性盐基氮含量应≤30 mg/100 g[34]。如图9所示,随着贮藏时间的延长,挥发性盐基氮含量随之上升,其中无膜组、HPMC空白膜组上升速度较快,分别于第4、5 d超过限值(30 mg/100 g),而PE膜组得益于PE膜良好的致密性、阻氧性,保鲜效果良好,但贮藏后期水蒸气在膜内表面聚集,加速了虾体腐败,于第6 d超过限值。在贮藏期间(7 d),复合可食膜组的挥发性盐基氮含量均未超过限值,其保质期较无膜组延长了3 d,较HPMC空白膜组延长了2 d,表明采用CEF覆膜可有效延缓对虾的腐败,降低虾体的挥发性氨、三甲胺等低级胺类化合物的生成速率。这与CEF良好的阻氧性与阻湿性密切相关。
2.2.4 对虾菌落总数
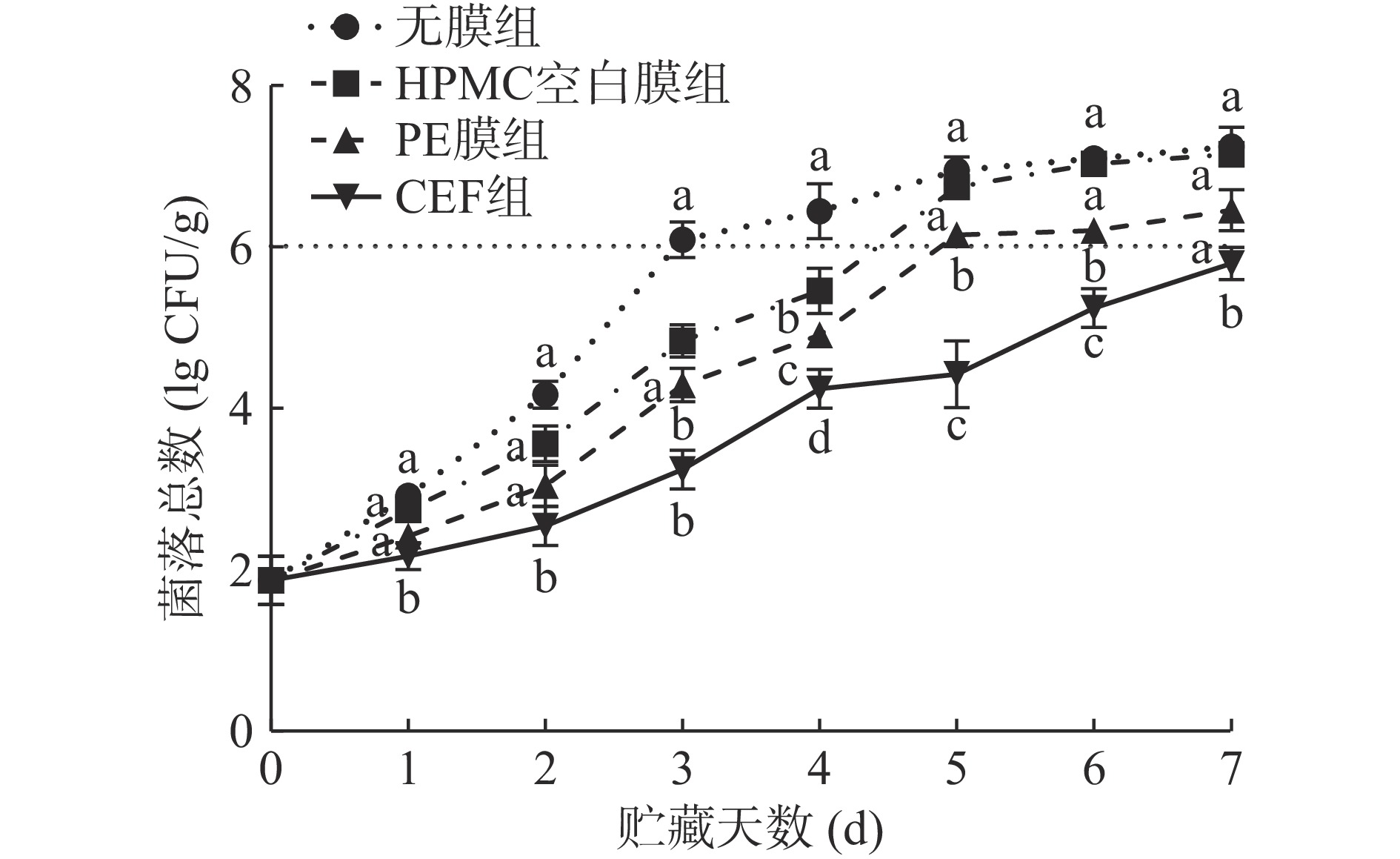
虾类的一级鲜度、二级鲜度及腐败终点所对应的菌落总数分别为≤5.0、5.0~5.7及6.0 lg(CFU/g)[35]。如图10所示,在无保鲜措施的情况下,无膜组受微生物污染严重,第4 d超过限值6.0 lg(CFU/g)。HPMC空白膜组,由于膜的气体阻隔性和耐水性差、覆膜易破损,贮藏后期受微生物污染严重。PE膜的气体阻隔性好,有效隔绝了氧气及微生物的污染,但后期膜表面有大量水蒸气聚集,加快了微生物的生长繁殖。CEF组在贮藏期间(7 d)的菌落总数均低于其他组且未超过限值。这是因为CEF的机械性能较好、WVP低、气体阻隔性较好,可降低外界微生物对虾体的影响。此外,CEF具有较好的抗氧化性能,也可在一定程度上减缓虾体腐败。
3. 讨论与结论
本研究利用HPMC良好的成膜性、稳定性及控释性,结合SBPM的抗氧化活性,通过HPMC与SBPM的共混、交联制备CEF,并对膜性能进行优化,较优的膜材添加量为:HPMC添加量12%,甘油添加量0.4%,SBPM添加量3%。以此配方研制的CEF的机械、光学等性能较佳,抗氧化作用显著。
在对虾保鲜实验中,采用CEF对南美白对虾进行覆膜保鲜,结果表明对实验组南美白对虾贮藏期较对照组延长了3~4 d。笔者在另一实验中以浸涂的方式探究复合可食膜涂膜液对虾的保鲜作用,发现在复合涂膜液配比为HPMC 15 g/L、SBPM 15 g/L、4 ℃冷藏条件下,南美白对虾的保鲜期可达7 d,相比对照组延长了3~4 d[17],与本文报道的CEF(覆膜)的保鲜效果相接近(贮藏时间较对照组延长2~4 d)。由此可见,虾活性肽可应用于对虾保鲜,且效果良好,可从多个层次加以阐释。首先,有关研究表明蛋白质水解物和生物肽因其具有抗氧化活性,通过抑制氧化酶的作用,减缓食品酸败、腐败的进程[36],而本文所制备虾活性肽已被证实具有较好的抗氧化活性[17],具备食品保鲜的相应性能。其次,有学者发现南美白对虾或其副产物中具有抗菌肽或有抗菌活性的蛋白-脂质浓缩物[18,37],根据同一物种中相似组成物或具有相似的生物活性的规律[38],暗示南美白对虾活性肽除抗氧化活性外,可能具有一定抗菌性能,这从涂膜保鲜实验结果可得到相应的印证。再者,虾活性肽经微胶囊化后再加入到羟丙甲基纤维素包衣中,无论是采用覆膜或涂膜方式,其活性受微胶囊和包衣的双重保护趋于更稳定,因此保鲜效果更佳。
本实验研制的CEF能以覆膜或涂膜的方式应用于南美白对虾保鲜,为虾的运输保藏提供更多的技术选择。后续研究可着眼于提高CEF的综合性能,特别是膜的机械性能,并开展中试放大、规模化生产等技术研究,进一步提升CEF对虾体理化指标和感官品质的保护作用。
-
表 1 感官评分标准
Table 1 Criteria for sensory evaluation
项目 评价要求 分值 气味 虾鲜味浓,无异味 2 虾鲜味稍淡,无异味 1.5 轻微的腥臭味 1 强烈的氨味和腥臭味 0 色泽 虾体的颜色正常,表壳有光泽 2 虾头稍发黑、虾体有零星墨绿色斑点 1.5 虾体黑变严重,发黄发白,光泽暗 1 虾体完全变黑,色泽发暗,无光泽 0 形态 头胸甲与体节间连接紧密 2 头胸甲与体节间连接较紧密 1.5 头胸甲与体节间松动 1 头胸甲与体节分离,虾体残缺 0 组织 虾肉组织紧密有弹性 2 虾肉组织稍微变软,弹性降低 1.5 虾肉组织软化,弹性差 1 虾肉组织呈海绵状,无弹性 0 漂烫液 鲜香味浓,无异味,漂烫液澄清,无漂浮物 2 鲜香味较浓,略带虾腥味,漂烫液较澄清,少许漂浮物 1.5 鲜味淡,虾腥味重,漂烫液较为浑浊,杂质较多 1 无鲜味,虾腥臭味重,漂烫液浑浊,杂质多 0 -
[1] 邓文静, 姜迎迎, 钱磊, 等. 复合生物保鲜剂对南美白对虾保鲜效果的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(5):84−91. [DENG W J, JIANG Y Y, QIAN L, et al. Effect of a compound biological preservative on Penaeus vannamel[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(5):84−91.] DENG W J, JIANG Y Y, QIAN L, et al . Effect of a compound biological preservative on Penaeus vannamel[J]. Food Research and Development,2022 ,43 (5 ):84 −91 .[2] 林瑞环. 虾类酚氧化酶生化性质对比分析与黑变机制初步研究[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2021. [LIN R H. Comparative analysis on the characteristic of phenol oxidase in different shrimps and preliminary study on the melanosis mechanism[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2021.] LIN R H. Comparative analysis on the characteristic of phenol oxidase in different shrimps and preliminary study on the melanosis mechanism[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2021.
[3] 张溪, 蓝蔚青, 刘嘉莉, 等. 南美白对虾防黑变保鲜技术研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(15):294−300. [ZHANG X, LAN W Q, LIU J L, et al. Preservation technology for inhibiting melanosis in Litopenaeus vannamei:A review[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(15):294−300.] ZHANG X, LAN W Q, LIU J L, et al . Preservation technology for inhibiting melanosis in Litopenaeus vannamei: A review[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019 ,45 (15 ):294 −300 .[4] ARANCIBIA M Y, BALLERO M L-C, GóMEZ-GUILLéN M, et al. Chitosan coatings enriched with active shrimp waste for shrimp preservation[J]. Food Control,2015,54:259−266. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.02.004
[5] 郑玉玺, 严秀玲, 何宇轩, 等. 壳聚糖-荔枝木质精油可食膜延长刀额新对虾的货架期[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(8):152−159. [ZHENG Y X, YAN X L, HE Y X, et al. Shelf life extension of metapenaeus ensis by chitosan-litchi wood essential oil edible films[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(8):152−159.] ZHENG Y X, YAN X L, HE Y X, et al . Shelf life extension of metapenaeus ensis by chitosan-litchi wood essential oil edible films[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021 ,37 (8 ):152 −159 .[6] 马东辉. 含乳酸菌可食膜的制备及对鲜切哈密瓜保鲜效果的研究[D]. 雅安:四川农业大学, 2020. [MA D H. Study on preparation of edible films containing lactic acid bacteria and application on fresh-keeping of fresh-cut cantaloupe[D]. Yaan:Sichuan Agricultural University, 2020.] MA D H. Study on preparation of edible films containing lactic acid bacteria and application on fresh-keeping of fresh-cut cantaloupe[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2020.
[7] 曾少甫, 胡长鹰, 匡衡峰, 等. 肉桂醛在壳聚糖复合活性包装膜中的释放及在鲜猪肉冷藏中的应用[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(9):182−189. [ZENG S H, HU C Y, KUANG H F, et al. Release of cinnamaldehyde from active chitosan composite packaging films and its application in quality preservation of fresh pork[J]. Food Science,2018,39(9):182−189.] ZENG S H, HU C Y, KUANG H F, et al . Release of cinnamaldehyde from active chitosan composite packaging films and its application in quality preservation of fresh pork[J]. Food Science,2018 ,39 (9 ):182 −189 .[8] LIU W J, XIE J, LI L, et al. Properties of phenolic acid-chitosan composite films and preservative effect on Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2021, 1239(1):130531.
[9] LIU Y, ZHU Y L, YANG Y, et al. Quality improvement of shrimp ( Litopenaeus vannamei) during refrigerated storage by application of Maillard peptides/water-soluble chitosan coating[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2022,10(9):2980−2988.
[10] 郑顺姬, 曹向禹, 隋智慧. 角蛋白膜的制备及应用研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料,2021,49(4):251−256. [ZHENG S J, CAO X Y, S Z H. Research progress of preparation and application of keratin film[J]. New Chemical Materials,2021,49(4):251−256.] ZHENG S J, CAO X Y, S Z H . Research progress of preparation and application of keratin film[J]. New Chemical Materials,2021 ,49 (4 ):251 −256 .[11] 曹侃, 王天杰. 可食膜在食品中的应用进展[J]. 武汉轻工大学学报,2019,38(1):22−26,66. [CAO K, WANG T J. Progress in the application of edible membrane in food[J]. Journal of Wuhan Polytechnic University,2019,38(1):22−26,66.] CAO K, WANG T J . Progress in the application of edible membrane in food[J]. Journal of Wuhan Polytechnic University,2019 ,38 (1 ):22 −26,66 .[12] 任佳欣, 遇世友, 许锡凯, 等. 可食性蛋白膜在食品包装中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(9):320−326. [REN J X, YU S Y, XU X K, et al. Application research progress of edible protein film in food packaging[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(9):320−326.] REN J X, YU S Y, XU X K, et al . Application research progress of edible protein film in food packaging[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020 ,41 (9 ):320 −326 .[13] 李昱杰. 多糖基可食性复合膜在食品保鲜中的应用[J]. 现代食品,2022,28(5):24−27. [LI Y J. Application of polysaccharide-based edible composite film in food preservation[J]. Modern Food,2022,28(5):24−27.] LI Y J . Application of polysaccharide-based edible composite film in food preservation[J]. Modern Food,2022 ,28 (5 ):24 −27 .[14] 王晋, 张风, 周爱梅, 等. 虾头、虾壳抗氧化肽的分离纯化及其对秀丽隐杆线虫的抗氧化作用[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(3):56−63. [WANG J, ZHANG F, ZHOU A M, et al. Purifcation of antioxidant peptides derived from enzymatic hvdrolysates of shrimp heads and shells and their antioxidant protection in caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Food Science,2019,40(3):56−63.] WANG J, ZHANG F, ZHOU A M, et al . Purifcation of antioxidant peptides derived from enzymatic hvdrolysates of shrimp heads and shells and their antioxidant protection in caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Food Science,2019 ,40 (3 ):56 −63 .[15] 孙洁, 李燕, 施文正, 等. 虾类生物活性肽的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(4):261−268. [SUN J, LIN Y, SHI W Z, et al. Research progress of shrimp bioactive peptides in shrimps[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(4):261−268.] SUN J, LIN Y, SHI W Z, et al . Research progress of shrimp bioactive peptides in shrimps[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021 ,47 (4 ):261 −268 .[16] JIANG W W, REN K Y, YANG Z Y, et al. Purification, identification and molecular docking of immunomodulatory peptides from the heads of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Foods,2022,11(20):3309. doi: 10.3390/foods11203309
[17] 吴泽龙. 虾加工副产物中活性肽提取工艺及功效研究[D]. 福州:福建农林大学, 2022. [WU Z L. Study on extraction technology and efficacy of bioactive peptides from shrimp processing by-products[D]. Fuzhou:Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University, 2022.] WU Z L. Study on extraction technology and efficacy of bioactive peptides from shrimp processing by-products[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agricultural and Forestry University, 2022.
[18] MIRARI Y. ARANCIBIA, AILÉN A, et al. Development of active films of chitosan isolated by mild extraction with added protein concentrate from shrimp waste[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,43:91−99. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.05.006
[19] 翁武银, 刘光明, 苏文金, 等. 鱼皮明胶蛋白膜的制备及其热稳定性[J]. 水产学报,2011,35(12):1890−1896. [WENG W Y, LIU G M, SU W J, et al. Preparation and thermal stability of gelatin edible films from shark skins[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2011,35(12):1890−1896.] WENG W Y, LIU G M, SU W J, et al . Preparation and thermal stability of gelatin edible films from shark skins[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2011 ,35 (12 ):1890 −1896 .[20] WU J L, GE S Y, LIU H, et al. Properties and antimicrobial activity of silver carp ( Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) skin gelatin-chitosan films incorporated with oregano essential oil for fish preservation[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life,2014,2(1):7−16. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2014.04.004
[21] 陶忠. 淡水鱼糜蛋白可食膜的性质改良及其应用研究[D]. 厦门:集美大学, 2013. [TAO Z. Improvement and application study of fresh-water fish surimi edible films[D]. Xiamen:Jimei University, 2013.] TAO Z. Improvement and application study of fresh-water fish surimi edible films[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2013.
[22] 王丽岩. 壳聚糖基活性包装膜的性能及其在食品贮藏中应用的研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2013. [WANG L Y. Studies on performance of chitosan based activity packaging films and applications in food storage[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2013.] WANG L Y. Studies on performance of chitosan based activity packaging films and applications in food storage[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2013.
[23] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 中华人民共和国国家标准 GB/T 16291.1-2012 感官分析选拔、培训与管理评价员一般导则 第 1 部分:优选评价员[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2012. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the people's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration Committee. National standards of the people's Republic of China. GB/T 16291.1-2012 Sensory analysis-general guidance for the selection, training and monitoring of assessors-part 1:Selected assessors[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2012.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the people's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration Committee. National standards of the people's Republic of China. GB/T 16291.1-2012 Sensory analysis-general guidance for the selection, training and monitoring of assessors-part 1: Selected assessors[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2012.
[24] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.237-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.237-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of food pH [S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.237-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of food pH [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[25] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.228-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.228-2016 National standard for food safety. Determination of volatile salt nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.228-2016 National standard for food safety. Determination of volatile salt nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[26] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 4789.2-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 4789.2-2016 National Standard for food safety. Food microbiological test. Determination of total bacterial colony[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 4789.2-2016 National Standard for food safety. Food microbiological test. Determination of total bacterial colony[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[27] 孙丽娜, 姜淑娟, 郭莲东, 等. TG酶和羟丙基甲基纤维素改善乳清蛋白可食膜性能[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(10):236−239,250. [SUN L N, JIANG S J, GUO L D, et al. TGase and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose improved properties of whey protein edible film[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(10):236−239,250.] SUN L N, JIANG S J, GUO L D, et al . TGase and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose improved properties of whey protein edible film[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018 ,39 (10 ):236 −239,250 .[28] 段林娟, 卢立新. 甘油含量对MC/WG可食性复合膜性能的影响[J]. 包装工程,2011,32(1):43−45. [DUAN L J, LU L X. Effect of glycerol content on the properties of MC/WG edible composite film[J]. Packaging Engineering,2011,32(1):43−45.] DUAN L J, LU L X . Effect of glycerol content on the properties of MC/WG edible composite film[J]. Packaging Engineering,2011 ,32 (1 ):43 −45 .[29] 李东坡, 武志杰, 梁成华, 陈利军, 张玉兰, 聂彦霞. 红外光谱分析醋酸酯淀粉包膜尿素膜降解特征[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(6):1519−1525. [LI D B, WU Z J, LIANG C H et al, Analysis of the character of film decomposition of starch acetate (SA) coated urea by infrared spectrum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(6):1519−1525.] LI D B, WU Z J, LIANG C H et al, Analysis of the character of film decomposition of starch acetate (SA) coated urea by infrared spectrum[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(6): 1519−1525.
[30] 方佳琪, 韩情, 马阳瑜, 等. 一种多金属氧酸盐对多酚氧化酶的抑制活性评价及在南美白对虾保鲜上的应用[J]. 食品与机械, 2023, 39(3):114−121. [FANG J Q, HAN Q, MA Y Y, et al, Evaluation of inhibitory activity of a polyoxometallate on polyphenol oxidase andits application in the preservation of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Food & Machinery, 2023, 39(3):114−121.] FANG J Q, HAN Q, MA Y Y, et al, Evaluation of inhibitory activity of a polyoxometallate on polyphenol oxidase andits application in the preservation of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Food & Machinery, 2023, 39(3): 114−121.
[31] MARSHALL D L, WIESE-LEHIGH P L. Comparison of impedance, microbial, sensory, and pH methods to determine shrimp quality[J]. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology,1997,6(2):17−31. doi: 10.1300/J030v06n02_03
[32] S. I. SHAMSHAD, KHER-UN-NISA, M. RIAZ, et al. Shelf life of shrimp (Penaeus merguiensis) stored at different temperatures[J]. Journal of Food Science, 1990, 55(5):1201-1205.
[33] 朱兰兰, 殷邦忠, 周德庆, 等. 流通过程对南美白对虾贮藏保鲜的影响[J]. 农产品加工(学刊),2011(3):7−10. [ZHU L L, YIN B Z, ZHOU D Q, et al. Effects of transportation on fresh-keeping of Litopenaeus Vannamei[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products,2011(3):7−10.] ZHU L L, YIN B Z, ZHOU D Q, et al . Effects of transportation on fresh-keeping of Litopenaeus Vannamei[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products,2011 (3 ):7 −10 .[34] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 2733-2015, 食品安全国家标准 鲜、冻动物性水产品[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2015. [National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 2733-2015, National Food Safety Standard for Fresh and Frozen Animal Fish[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2015.] National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 2733-2015, National Food Safety Standard for Fresh and Frozen Animal Fish[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2015.
[35] AI-DAGAL M M, BAZARAA W A. Extension of shelf life of whole and peeled shrimp with organic acid salts and bifidobacteria[J]. Journal of Food Protection, 1999, 62(1):51−56.
[36] TKACZEWSKA J. Peptides and protein hydrolysates as food preservatives and bioactive components of edible films and coatings-A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2020, 106: 298−311.
[37] ALEMÁN A , GONZÁLEZ F , ARANCIBIA M, et al. Comparative study between film and coating packaging based on shrimp concentrate obtained from marine industrial waste for fish sausage preservation[J]. Food Control, 2016, 70:70325−70332.
[38] HU J, LI S H, LV Q, et al. Characterization of the dual functions of LvCrustinVII from Litopenaeusvannamei as antimicrobial peptide and opsonin[J]. Marine Drugs,2022,20(3):157. doi: 10.3390/md20030157





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



