Isolation, Identification, Screening and Fermentation Process Optimization of Bacillus Producing High Antimicrobial Lipopeptide
-
摘要: 为了筛选出高产抗菌脂肽的芽孢杆菌并确定其最佳发酵工艺条件,研究从传统发酵豆酱中分离和鉴定产抗菌脂肽芽孢杆菌菌株,通过正交试验研究了发酵接种量、发酵填液量、发酵时间、发酵温度等发酵条件对芽孢杆菌脂肽产量的影响。结果表明,从9份东北传统发酵豆酱中分离筛选得到27株芽孢杆菌,经16S rDNA鉴定,其中6株芽孢杆菌具有合成脂肽的基因sfp、fenB和ituA。通过单位菌体脂肽产量和抑菌效果测定发现,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20和解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46表现优异,单位菌体脂肽产量达106和72 mg,且对革兰氏阳性和阴性指示菌均有较强的抑菌效果。正交试验发现贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20最佳发酵工艺为:接种量3%,发酵填液量20%,发酵时间36 h,发酵温度32 ℃;枯草芽孢杆菌SN-46最佳发酵工艺为:接种量2%,发酵填液量40%,发酵时间24 h,发酵温度32 ℃。在此条件下发酵的两株芽孢杆菌单位菌体脂肽产量优化前为106.11和76.23 mg/g,优化后分别提高了21.85%和23.84%。研究结果有效地增加了芽孢杆菌抗菌脂肽的产量。Abstract: In order to screen out Bacillus sp. with high production of antimicrobial lipopeptide and determine its optimal fermentation conditions, the study isolated and identified antimicrobial lipopeptide-producing Bacillus sp. strains from traditional fermented soybean paste, and adopted orthogonal test to investigate how lipopeptide production by Bacillus sp was affected by fermentation conditions, such as fermentation inoculum amount, fermentation filling volume, fermentation time and fermentation temperature. The results showed that 27 strains of Bacillus sp. were isolated and screened out from 9 portions traditional fermented soybean paste of the Northeast, among which 6 strains were identified by 16S rDNA as having the genes sfp, fenB and ituA for synthesizing lipopeptide. According to the determination of lipopeptide yield and inhibition effect, Bacillus subtilis SN-20 and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SN-46 showed excellent performance with the yield of 106 and 72 mg of lipopeptide per unit, and strong inhibition effect on both gram-positive and negative indicator bacteria. The optimal fermentation process of Bacillus subtilis SN-20 was found to be 3% inoculum, 20% fermentation filler, 36 h fermentation time and 32 ℃. The optimal fermentation process of Bacillus subtilis SN-46 was 2% inoculum, 40% fermentation filler, 24 h fermentation time and 32 ℃. Under these conditions, the unit biomass yields of lipopeptides for the two strains of Bacillus before optimization were 106.11 and 76.23 mg/g, respectively. After optimization, they increased by 21.85% and 23.84%, respectively. The study results effectively increased the production of antimicrobial lipopeptides from Bacillus.
-
芽孢杆菌是一类广泛存在于自然环境中的微生物,因其在生物制药、食品工业、农业以及环保等诸多领域的实际应用,引起了科研领域的深入探索和研究[1−2]。其中,由芽孢杆菌非核糖体产生的脂肽类次级代谢物展现了极大的研究价值[3−4]。这类物质凭借其独特的化学结构、生物活性及巨大的应用潜力,赢得了人们广泛关注。
脂肽具有低毒性、容易降解、理化性质稳定和作用机制多样等特点,能与大多数微生物的细胞膜相互作用,因此脂肽对腐败菌能表现出高效、广谱的抑菌作用,目前已在食品行业中得到一定应用[5]。在一些食品加工过程中,添加合适的脂肽可以提高食品加工性能,降低热处理强度,提升食品风味和营养价值。例如,在面包中添加芽孢杆菌脂肽,能够对面包的比容和弹性起到增强作用,并且能延缓面包老化[6]。在奶制品和肉制品中添加芽孢杆菌脂肽,对肠炎沙门氏菌产生良好灭活效果[7]。然而由于目前脂肽产量低,生产成本较高,无法实现大规模产业化生产,致使脂肽的发展处在瓶颈时期,严重制约了脂肽的实际应用[8−9]。因此,尽快挖掘筛选高产脂肽的优良菌株,优化发酵工艺,降低脂肽的生产成本,具有重要意义[10−11]。
为了降低脂肽的生产成本,突破脂肽的发展瓶颈,本文从传统豆酱中分离筛选出高产脂肽的优良芽孢杆菌菌株,在单因素实验结果的基础上利用正交试验对其产脂肽发酵工艺进行优化,以期提高脂肽产量,旨在为脂肽的进一步研究和开发奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)SNSA-11、单增李斯特氏菌(Listeria Monocytogenes)SNLM-8、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)SNEC-16、沙门氏菌(Salmonella)SNS-9、铜绿假单胞菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)SNPA-1等指示菌 沈阳农业大学食品学院菌种库提供;无水乙醇 上海迈瑞尔化学技术有限公司;氯化钠、结晶紫、胰蛋白胨、甲醇、异丙醇、酵母浸粉 上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;甘油 河南醇盛化工产品有限公司;从丹东、锦州和沈阳等地采集到9份传统发酵豆酱样品。
YXQ-LS-70A型高压蒸汽灭菌锅 邢台钜都科技有限公司;YT-PCR仪 山东云唐智能科技有限责任公司;JP-K300型凝胶成像仪 上海嘉鹏科技有限公司;XIANDE2000A型7旋转蒸发仪 上海贤德实验仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 培养基的配制
配制LB培养基:在1000 mL去离子水中溶解10 g胰蛋白胨、5 g酵母浸粉和10 g氯化钠,对于液体培养基,直接进行121 ℃、20 min高温灭菌;固体培养基在上述步骤的基础上添加20 g的琼脂,充分搅拌直到完全溶解后灭菌。
1.2.2 豆酱中芽孢杆菌的初筛
取1 g豆酱放入装有9 mL生理盐水的试管中,混合后85 ℃水浴加热25 min进行梯度稀释。稀释后涂布于LB固体培养基,37 ℃培养24 h,挑取单菌落备份,同时进行革兰氏染色,将蓝色、细长且呈杆状的菌体保留[12−13]。
1.2.3 芽孢杆菌16S rDNA基因和脂肽合成基因测定
将初筛中的菌体活化,提取菌株DNA,选择细菌通用引物进行菌株基因测序。查阅文献,获得3对脂肽合成基因PCR引物序列如表1所示,进行PCR扩增[14−15]。细菌通用引物扩增程序为94 ℃ 5 min,94 ℃ 30 s,58 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 1 min,30个循环,72 ℃ 10 min。脂肽合成基因引物扩增程序为:94 ℃ 3 min,94 ℃ 15 s,55 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 30 s,30个循环,72 ℃ 10 min。
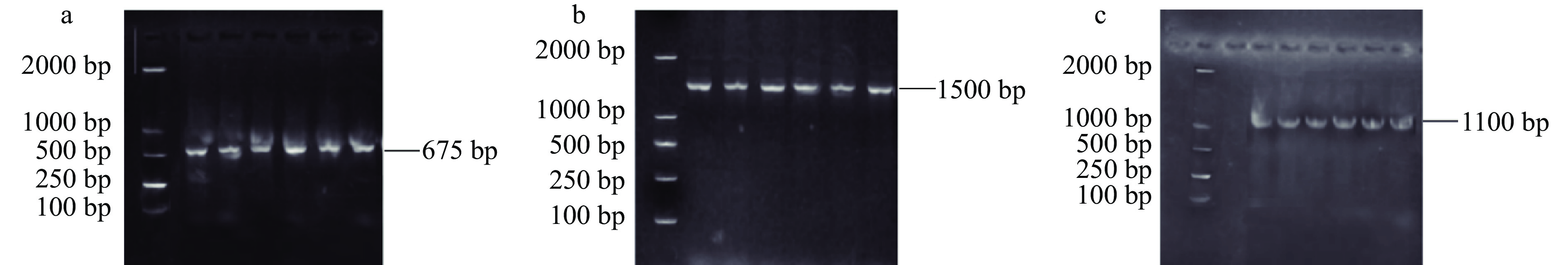
表 1 引物设计Table 1. Primer design名称 靶基因 引物名称 引物序列(5'→3') 扩增长
度(bp)细菌鉴定 细菌通用
引物27 F AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG 1500 1492 R CTACGGCTACCTTGTTACGA Surfactin sfp Sfp-F ATGAAGATTTACGGAATTTA 675 Sfp-R TTATAAAAGCTCTTCGTACG Fengycin fenB fenB-F CTATAGTTTGTTGACGGCTC 1500 fenB-R CAGCACTGGTTCTTGTCGCA Iturin ituA ituA-F ATGTATACCAGTCAATTCC 1100 ituA-R GATCCGAAGCTGACAATAG 1.2.4 系统发育树的构建
将16S rDNA扩增产物送至上海派森诺生物医药科技有限公司进行测序,结果经NCBI数据库对比,采用MEGA 7.0.软件进行聚类分析,构建系统发育树[16]。
1.2.5 脂肽粗提物的制备
将筛选得到的产脂肽芽孢杆菌按照2%接种量接种于液体LB培养基,并于200 r/min摇床中37 ℃培养24 h,8500 r/min离心15 min后收集芽孢杆菌上清液滤液,残留菌体称重后记录。调节上清滤液pH至2.0,4 ℃冰箱中过夜,再次10000 r/min离心10 min后收集沉淀,甲醇萃取后调节pH至7.0,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤得到脂肽粗提液。将脂肽粗提液旋转蒸发,所得产物即为脂肽粗提物,称重后记录[17−18]。
1.2.6 脂肽抑菌谱测定
将指示菌制成活菌数为106 CFU/mL的菌悬液。采用滤纸片法测定芽孢杆菌脂肽样品抑菌特性,在滤纸片上分别滴加20 μL微孔滤膜过滤后的脂肽粗提物,培养记录抑菌圈大小[19−21]。
1.2.7 脂肽发酵工艺优化试验
1.2.7.1 菌株发酵接种量对菌株产脂肽的影响
选择发酵填液量为40%,发酵时间为24 h,发酵温度为37 ℃,分别改变SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌的接种量为1%、2%、3%、4%和5%,200 r/min摇床中培养,发酵后计算单位菌体脂肽产量。
1.2.7.2 菌株发酵填液量对菌株产脂肽的影响
选择发酵接种量为2%,发酵时间为24 h,发酵温度为37 ℃,分别改变SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌的发酵填液量为20%、40%、60%、80%和100%的培养基中,200 r/min摇床中培养,发酵后计算单位菌体脂肽产量。
1.2.7.3 菌株发酵时间对菌株产脂肽的影响
选择发酵接种量为2%,发酵填液量为40%,发酵温度为37 ℃,分别改变SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌的发酵时间为12、24、36、48、和60 h,200 r/min摇床中培养,发酵后计算单位菌体脂肽产量[22]。
1.2.7.4 发酵温度对菌株产脂肽的影响
选择接种量为3%,发酵填液量为40%,发酵时间为24 h,分别改变SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌的培养温度为27、32、37和42、47 ℃,200 r/min摇床中培养,发酵后计算单位菌体脂肽产量。
1.2.8 脂肽发酵工艺正交试验优化
根据单因素分析结果,采用L9(34)正交试验表,正交因素水平表如表2所示,对发酵接种量、发酵填液量、菌液发酵时间和发酵温度进行3水平正交试验,以确定最佳发酵工艺[23]。
表 2 正交因素水平表Table 2. Orthogonal factor level table水平 因素 A培养发酵
接种量(%)B发酵
填液量(%)C发酵
时间(h)D发酵
温度(℃)1 1 20 24 32 2 2 40 36 37 3 3 60 48 42 1.3 数据处理
每组试验均三次重复试验,实验数据采用SPSS 25.0软件进行处理;采用Origin软件进行作图,显著性水平为P<0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 豆酱中芽孢杆菌的分离纯化
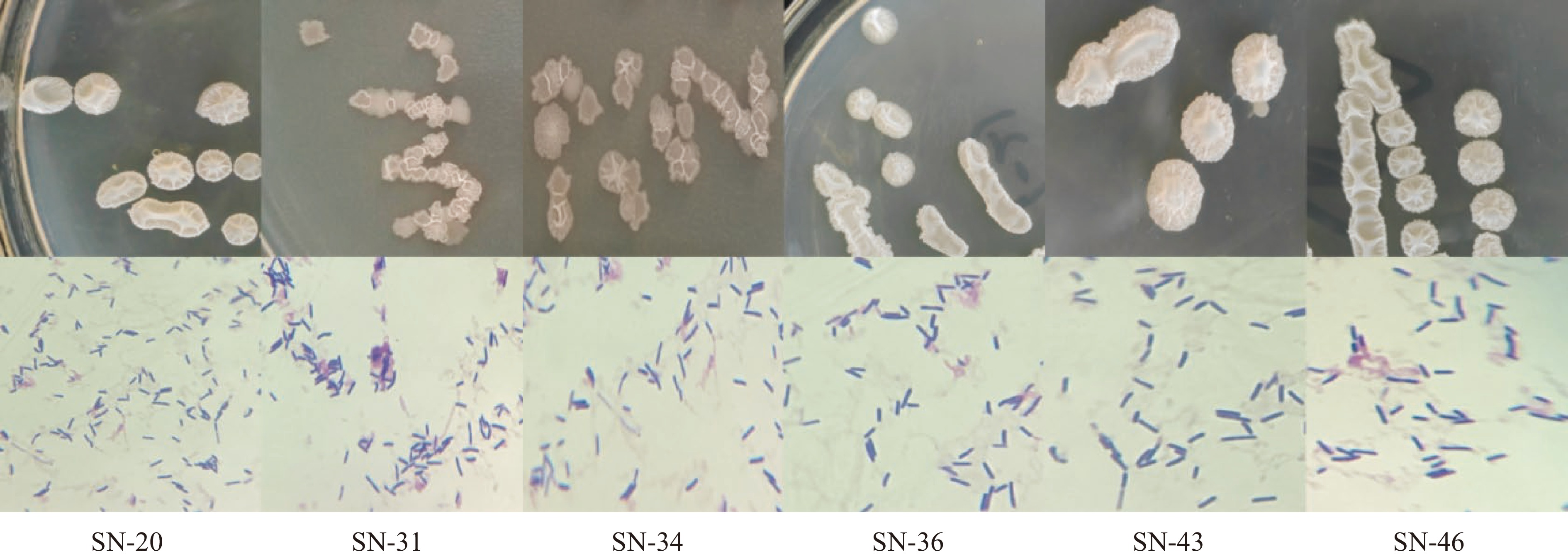
通过对菌体的革兰氏染色和菌落的形态学观察,初步推测在9份传统发酵豆酱样品中筛选出32株疑似为芽抱杆菌的菌株,部分菌落和菌体形态学观察结果如图1所示。由菌落图可以看出,疑似芽孢杆菌的菌落呈圆形、白色向上凸起,表面光滑、不透明、整齐;由镜检图可以看出,疑似芽孢杆菌的菌株经革兰氏染色后呈现紫色短棒状或杆状,单独或成链状排列,部分菌体能够产生芽孢,芽孢位于菌体中间近圆形,根据所观察形态特征,推测所筛选菌中含有芽孢杆菌。
2.2 豆酱中芽孢杆菌的16S rDNA序列分析
以细菌通用引物扩增后,选择扩增产物在1500 bp处产生清晰明亮条带的菌株,将扩增产物测序结果在NCBI上进行同源性比对分析,对比结果如表3所示。通过分子生物学技术对32株细菌的DNA提取,进行16S rDNA扩增片段检测及基因序列同源性分析,发现芽孢杆菌不同种同源性均大于99%,最终鉴定出27株芽孢杆菌。经同源性比对分析,27株菌分别为解淀粉芽孢杆菌8株、枯草芽孢杆菌9株、贝莱斯芽孢杆菌7株、高地芽孢杆菌1株、地衣芽孢杆菌2株,菌株同源性均>99%,部分菌株同源性达到100%。
表 3 芽孢杆菌菌株名称及测序后同源性对比结果Table 3. Bacillus strain name and homology comparison results after sequencing序号 菌株名称 发酵豆酱产地 鉴定名称 同源性 1 SN-2 辽宁锦州 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.96% 2 SN-4 辽宁沈阳 地衣芽孢杆菌 99.97% 3 SN-5 辽宁丹东 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 4 SN-6 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 5 SN-9 辽宁锦州 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.93% 6 SN-11 辽宁沈阳 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.97% 7 SN-12 辽宁沈阳 地衣芽孢杆菌 99.93% 8 SN-15 辽宁锦州 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 9 SN-17 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.87% 10 SN-18 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 11 SN-20 辽宁沈阳 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 12 SN-21 辽宁丹东 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 99.97% 13 SN-22 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.95% 14 SN-23 辽宁丹东 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.99% 15 SN-25 辽宁沈阳 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 16 SN-27 辽宁锦州 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 17 SN-31 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.95% 18 SN-34 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 19 SN-35 辽宁沈阳 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.93% 20 SN-36 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.86% 21 SN-38 辽宁丹东 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 22 SN-40 辽宁锦州 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 23 SN-41 辽宁沈阳 高地芽孢杆菌 99.62% 24 SN-43 辽宁丹东 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 25 SN-46 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 26 SN-47 辽宁丹东 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 99.93% 27 SN-48 辽宁锦州 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 99.93% 2.3 芽孢杆菌菌株脂肽相关合成基因PCR扩增
目前,分子生物技术广泛被应用于微生物种属鉴定研究中,特别是以16S rDNA序列分析作为微生物系统分类的主要依据,其选取具有高度的保守性而且长度适中,通过PCR扩增和序列分析,挖掘判断菌株是否含有目的基因,最终对细菌的遗传信息、基因差异、发育进化和分类进行研究。夏京津等[24]和宋本超等[25]也采用类似方法,选择ituA基因(1100 bp)、fenB基因(1500 bp)和sfp基因(675 bp)的保守序列作为靶基因对筛选得到的芽孢杆菌芽孢杆菌菌株脂肽相关合成基因进行PCR扩增,结果如图2所示。菌株SN-20、SN-31、SN-34、SN-36、SN-43和SN-46号菌株的扩增产物分别在675 bp(图2a)、1500 bp(图2b)和1000 bp(图2c)处有清楚明亮条带,表明27株芽孢杆菌中有6株菌株含有芽孢杆菌脂肽类物质Surfactin、Iturin和Fengycin合成基因片段,即此6株菌具有合成脂肽的能力。
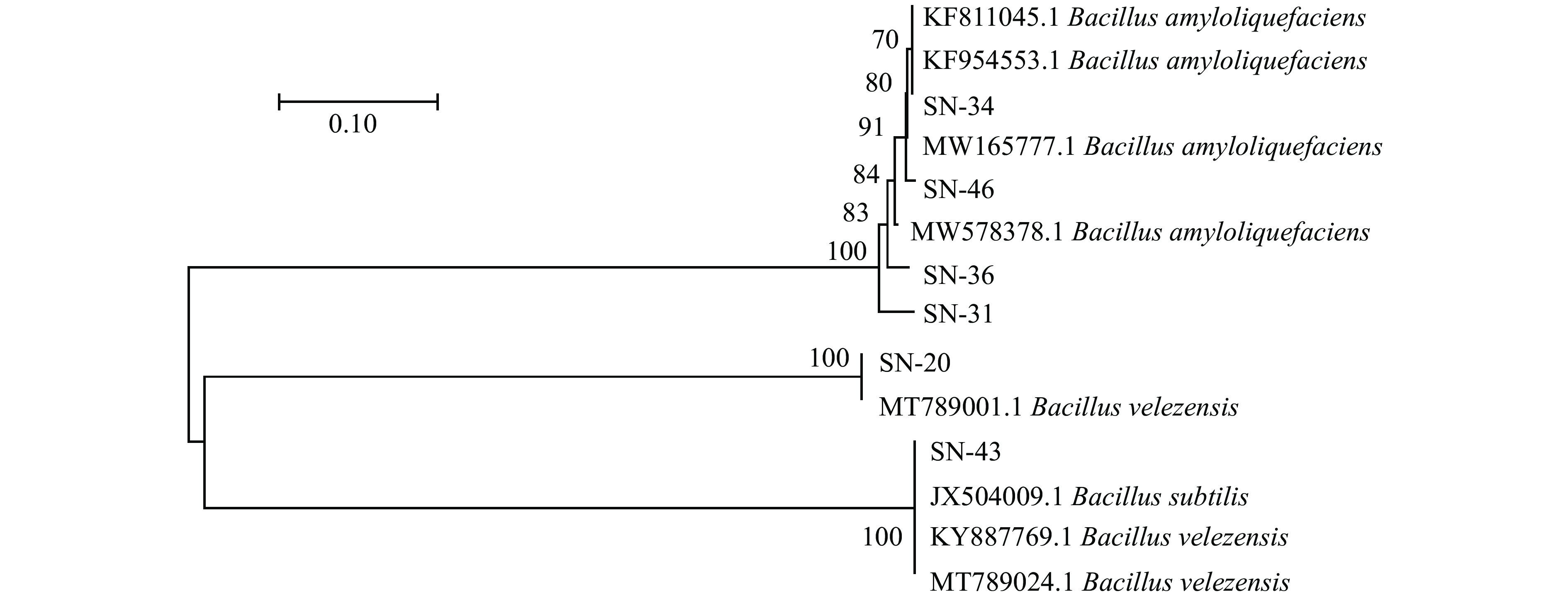
将6株芽孢杆菌16S rDNA测序结果在NCBI与GenBank中公布的芽孢杆菌基因序列进行同源性对比,获得相似率最高的基因序列后,进行系统发育树的构建,结果如图3所示。通过构建系统发育树,可以证明6株菌株为芽孢杆菌属。其中SN-20号菌株与贝莱斯芽孢杆菌同源性较高。SN-31、SN-34、SN-36和SN-46号菌株解淀粉芽孢杆菌具有更高的同源性。SN-43号菌株与枯草芽孢杆菌处在同一分支,同源性高达100.00%。
2.4 芽孢杆菌产脂肽性能测定
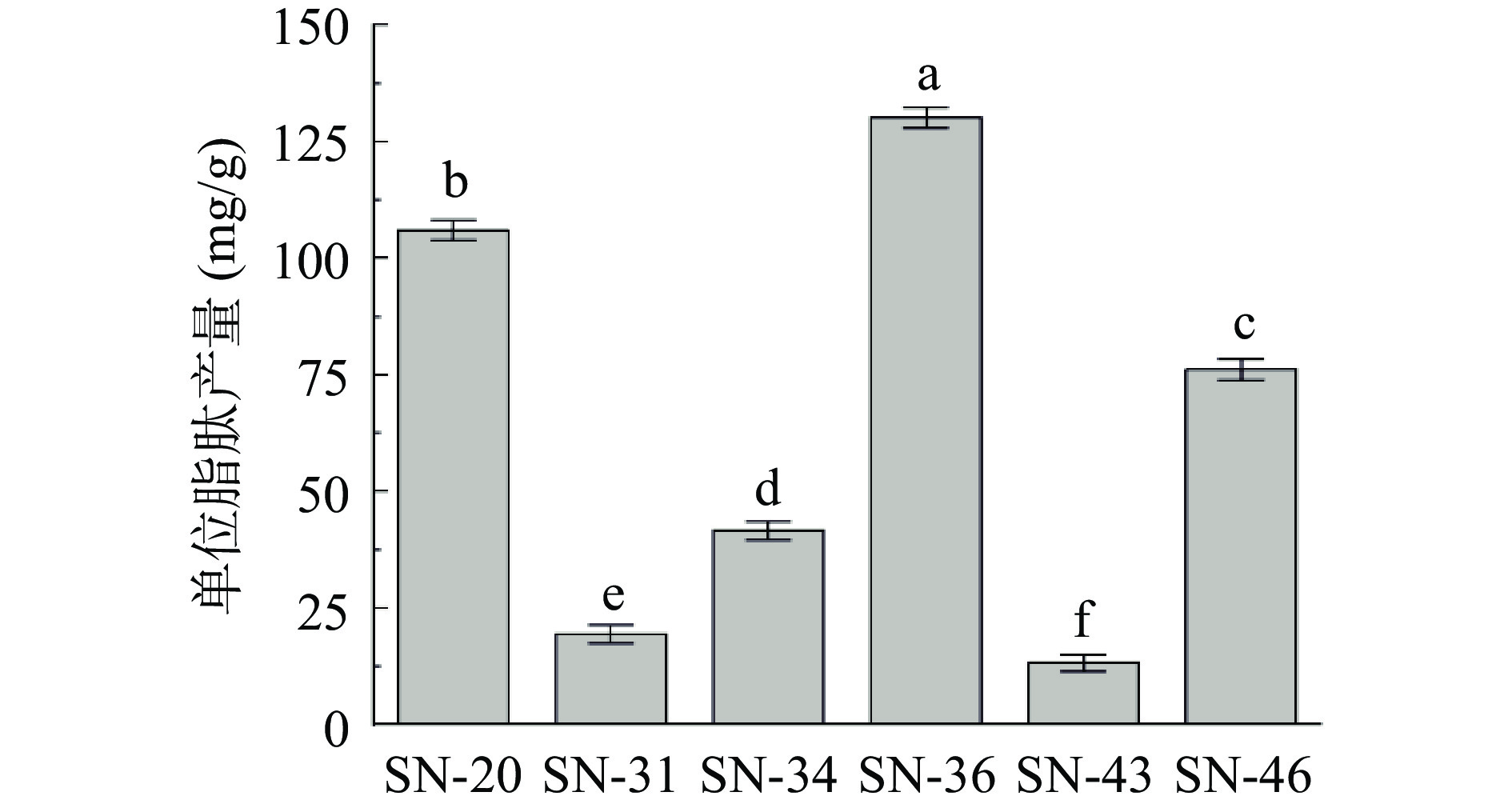
6株芽孢杆菌粗脂肽产量如图4所示,在相同的发酵情况下,菌株SN-20、SN-36和SN-46的单位脂肽产量明显优于菌株SN-31、SN-34和SN-43,分别达到106.11、130.17和76.23 mg/g,而另外3株菌单位脂肽产量均在42 mg/g以下,表明菌株SN-20、SN-36和SN-46具有作为高产脂肽菌株的开发潜力。
2.5 芽孢杆菌脂肽抑菌能力测定
使用滤纸片法,以金黄色葡萄球菌、单增李斯特氏菌、大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌和铜绿假单胞菌为供试指示菌测量脂肽抑菌活性,结果如表4所示。6种芽孢杆菌对革兰氏阳性菌中的金黄色葡萄球菌和单增李斯特菌的最大抑菌圈均超过10 mm,而对革兰氏阴性菌中的大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌和铜绿假单胞菌存在无抑制的情况,研究结果与Das等[26]研究一致,表明脂肽对革兰氏阳性菌的抑制效果优于对革兰氏阴性菌。此外,SN-20和SN-46种菌株对5种指示菌均有抑制作用,而其他菌株对指示菌存在无抑制的情况,表明SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌相对另外4株菌株更具有优秀的抑菌能力。
表 4 脂肽对指示菌的抑菌效果Table 4. Antibacterial effect of lipopeptide on indicator bacteria金黄色
葡萄球菌单增李斯
特氏菌大肠杆菌 沙门氏菌 铜绿假
单胞菌SN-20 +++ +++ ++ + ++ SN-31 ++ ++ + + − SN-34 ++ + − + + SN-36 ++ ++ + − − SN-43 ++ + + − − SN-46 +++ ++ + ++ ++ 注:“+++”抑菌直径大于10 mm,“++”抑菌直径5~10 mm,“+”抑菌直径小于5 mm,“−”无抑菌圈。 2.6 芽孢杆菌脂肽发酵工艺优化试验
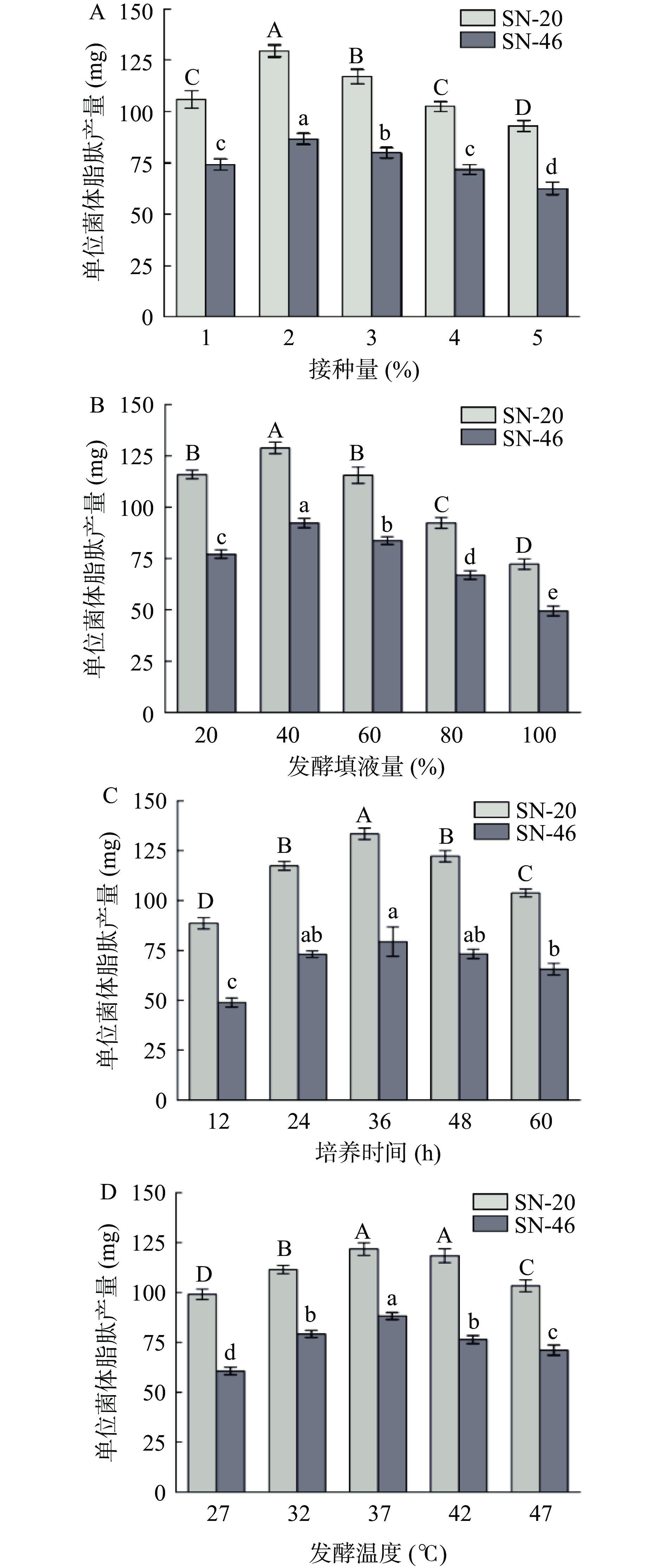
通过脂肽提取量与菌体发酵情况和抑菌试验结果,发现贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20和解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46号菌单位菌体产脂肽量多且具有广谱抑菌特性,因此选取贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20和枯草芽孢杆菌SN-46作为进行脂肽发酵优化试验菌株。对2株芽孢杆菌进行发酵接种量、填液量、发酵时间和发酵温度单因素试验,结果如图5所示。
在微生物发酵过程中,接种量即为初始添加到生物反应器中的菌体量,直接影响微生物的生长和代谢产物的生成,进而影响脂肽的产量。不同发酵接种量对单位菌体脂肽产量如图5A所示,结果显示SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌随着接种量的增加单位菌体产量先增大,在接种量为2%时产量达到最大,之后随着接种量的增加而降低,研究结果与孙彦婷等[27]一致,推测原因是过量的接种量会造成培养溶液营养不足,菌体数量达到饱和,导致脂肽产量降低。
培养基填液量是影响产物生产和微生物生长关键参数之一,不同的发酵填液量对芽孢杆菌单位菌体脂肽产量的结果如图5B所示,结果显示SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌单位菌体脂肽产量随填液量的增加呈现先增加后减少的趋势,在填液量为40%时单位菌体产量最大。推测由于芽孢杆菌为好氧或兼性厌氧,随着填液量的增加,锥形瓶在恒温摇床发酵过程中搅拌困难,导致氧气和养分分布不均,从而影响微生物生长和脂肽产量[28]。
发酵时间的长短会影响微生物生长阶段,进而影响产物的合成和积累。不同的发酵时间对芽孢杆菌单位菌体脂肽产量的影响结果如图5C所示,与纪明山等[29]研究结果相似,随着发酵时间的增加,SN-20和SN-46号芽孢杆菌脂肽产量迅速增加,在36 h产量达到最大,36 h之后产量逐渐减少。推测原因是通过芽孢杆菌非核糖体合成酶系合成的脂肽在菌体生长稳定期产生,在发酵后期,由于养分枯竭和废物积累,芽孢杆菌的生长和脂肽的生产开始减缓[30]。
发酵温度是决定菌种生长和产物形成的关键参数之一,发酵温度的选择对于脂肽的产量尤为关键。不同的发酵温度对芽孢杆菌单位菌体脂肽产量的结果如图5D所示,结果表明2株芽孢杆菌在37 ℃时脂肽产量最大,之后随着温度继续增加对脂肽产量的影响不大,推测原因是芽孢杆菌具有耐热特性,温度的增加不会对芽孢杆菌生长有明显影响,这与Ye等[31]研究一致。
2.7 芽孢杆菌脂肽正交优化试验
芽孢杆菌是一种兼性厌氧的细菌微生物,其在无氧和有氧环境下可生长并产生不同的代谢产物[32]。在菌株发酵过程中,菌株接种量、培养环境中氧气的含量、菌株培养发酵时间和发酵温度等因素均对菌体的生长和代谢产物的生成产生影响[33]。为探究芽孢杆菌最佳发酵工艺组合,本研究与Ju等[34]研究方法一致,通过单因素实验和正交试验,用较少的试验次数找到各因素之间关系,准确且快速的判断出芽孢杆菌脂肽类化合物提取条件的最佳组合[35],优化结果如表5和表6所示。
表 5 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20菌株正交试验结果Table 5. Orthogonal experimental results of Bacillus velezensis SN-20实验号 A B C D 单位菌体产量(mg) 1 1 1 1 1 110.6 2 1 2 2 2 105.6 3 1 3 3 3 108.4 4 2 1 2 1 118.6 5 2 2 3 2 109.4 6 2 3 1 3 105.4 7 3 1 3 2 114.5 8 3 2 1 3 109.4 9 3 3 2 1 117.1 k1 108.2 114.57 108.47 115.43 k2 111.13 108.13 113.77 109.83 k3 113.67 110.3 110.77 107.73 R 5.47 6.44 5.3 7.7 SS 44.9 64.29 42.38 95.06 排序 D>B>A>C 表 6 解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46菌株正交试验结果Table 6. Orthogonal experimental results of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SN-46实验号 A B C D 单位菌体产量(mg) 1 1 1 1 1 82.4 2 1 2 2 2 84.2 3 1 3 3 3 77.9 4 2 1 2 1 78.5 5 2 2 3 2 82.8 6 2 3 1 3 85.4 7 3 1 3 2 75.2 8 3 2 1 3 82.5 9 3 3 2 1 85.6 k1 81.5 78.7 83.43 82.17 k2 82.23 83.17 82.77 80.73 k3 81.1 82.97 78.63 81.93 R 1.13 4.47 4.8 1.44 SS 1.98 38.2 40.57 3.55 排序 C>B>D>A 由于芽孢杆菌合成次级代谢产物是个复杂过程,致使不同的芽孢杆菌菌株的最佳发酵条件具有明显的差异。陈莉等[36]研究发现枯草芽孢杆菌K-6-9菌株最佳发酵工艺条件为发酵时间18 h,发酵温度37 ℃,接种量2%。张丽姣等[37]研究发现解淀粉芽孢杆菌PB6最佳发酵工艺条件为发酵时间96 h,发酵温度30 ℃,接种量4%。在本研究中,由表5和表6可知,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20发酵工艺影响因素大小为发酵温度>发酵填液量>发酵接种量>发酵时间,解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46为发酵时间>发酵填液量>发酵温度>发酵接种量,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20最佳发酵工艺为:接种量3%,发酵填液量20%,发酵时间36 h,发酵温度32 ℃。解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46最佳发酵工艺为:接种量2%,发酵填液量40%,发酵时间24 h和发酵温度为32 ℃。采用4种因素水平进行验证试验发现,SN-20和SN-46单位菌体脂肽产量为129.3 mg和94.4 mg。这些研究结果的差异是否是由于不同芽孢杆菌菌株的生理特性不同,或者是受到了菌株原产地区气候条件的影响,目前仍未完全明确。因此,对各种芽孢杆菌菌株的最佳发酵条件进行深入、细致的研究和探索仍是必要的。
3. 结论
本文从传统豆酱中筛选出27株芽孢杆菌,发现贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20、解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-31、解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-34、解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-36、枯草芽孢杆菌SN-43、解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46具有合成脂肽的相关基因,其中贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20和解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46号菌单位菌体产脂肽量多且具有广谱抑菌特性。通过正交试验得知贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20和解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46的最佳发酵工艺为菌株发酵接种量为3%和2%,菌株填液量为20%和40%,发酵时间为36 h和24 h,发酵温度均为32 ℃。以贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20和解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46为发酵菌株,采用其最佳发酵工艺条件后,单位菌体脂肽产量增加量达21.85%和23.84%,有效地提高了脂肽产量,有助于实现脂肽大规模生产。
-
表 1 引物设计
Table 1 Primer design
名称 靶基因 引物名称 引物序列(5'→3') 扩增长
度(bp)细菌鉴定 细菌通用
引物27 F AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG 1500 1492 R CTACGGCTACCTTGTTACGA Surfactin sfp Sfp-F ATGAAGATTTACGGAATTTA 675 Sfp-R TTATAAAAGCTCTTCGTACG Fengycin fenB fenB-F CTATAGTTTGTTGACGGCTC 1500 fenB-R CAGCACTGGTTCTTGTCGCA Iturin ituA ituA-F ATGTATACCAGTCAATTCC 1100 ituA-R GATCCGAAGCTGACAATAG 表 2 正交因素水平表
Table 2 Orthogonal factor level table
水平 因素 A培养发酵
接种量(%)B发酵
填液量(%)C发酵
时间(h)D发酵
温度(℃)1 1 20 24 32 2 2 40 36 37 3 3 60 48 42 表 3 芽孢杆菌菌株名称及测序后同源性对比结果
Table 3 Bacillus strain name and homology comparison results after sequencing
序号 菌株名称 发酵豆酱产地 鉴定名称 同源性 1 SN-2 辽宁锦州 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.96% 2 SN-4 辽宁沈阳 地衣芽孢杆菌 99.97% 3 SN-5 辽宁丹东 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 4 SN-6 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 5 SN-9 辽宁锦州 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.93% 6 SN-11 辽宁沈阳 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.97% 7 SN-12 辽宁沈阳 地衣芽孢杆菌 99.93% 8 SN-15 辽宁锦州 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 9 SN-17 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.87% 10 SN-18 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 11 SN-20 辽宁沈阳 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 12 SN-21 辽宁丹东 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 99.97% 13 SN-22 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.95% 14 SN-23 辽宁丹东 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.99% 15 SN-25 辽宁沈阳 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 16 SN-27 辽宁锦州 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 17 SN-31 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.95% 18 SN-34 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 19 SN-35 辽宁沈阳 枯草芽孢杆菌 99.93% 20 SN-36 辽宁锦州 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 99.86% 21 SN-38 辽宁丹东 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 100.00% 22 SN-40 辽宁锦州 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 23 SN-41 辽宁沈阳 高地芽孢杆菌 99.62% 24 SN-43 辽宁丹东 枯草芽孢杆菌 100.00% 25 SN-46 辽宁沈阳 解淀粉芽孢杆菌 100.00% 26 SN-47 辽宁丹东 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 99.93% 27 SN-48 辽宁锦州 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌 99.93% 表 4 脂肽对指示菌的抑菌效果
Table 4 Antibacterial effect of lipopeptide on indicator bacteria
金黄色
葡萄球菌单增李斯
特氏菌大肠杆菌 沙门氏菌 铜绿假
单胞菌SN-20 +++ +++ ++ + ++ SN-31 ++ ++ + + − SN-34 ++ + − + + SN-36 ++ ++ + − − SN-43 ++ + + − − SN-46 +++ ++ + ++ ++ 注:“+++”抑菌直径大于10 mm,“++”抑菌直径5~10 mm,“+”抑菌直径小于5 mm,“−”无抑菌圈。 表 5 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌SN-20菌株正交试验结果
Table 5 Orthogonal experimental results of Bacillus velezensis SN-20
实验号 A B C D 单位菌体产量(mg) 1 1 1 1 1 110.6 2 1 2 2 2 105.6 3 1 3 3 3 108.4 4 2 1 2 1 118.6 5 2 2 3 2 109.4 6 2 3 1 3 105.4 7 3 1 3 2 114.5 8 3 2 1 3 109.4 9 3 3 2 1 117.1 k1 108.2 114.57 108.47 115.43 k2 111.13 108.13 113.77 109.83 k3 113.67 110.3 110.77 107.73 R 5.47 6.44 5.3 7.7 SS 44.9 64.29 42.38 95.06 排序 D>B>A>C 表 6 解淀粉芽孢杆菌SN-46菌株正交试验结果
Table 6 Orthogonal experimental results of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SN-46
实验号 A B C D 单位菌体产量(mg) 1 1 1 1 1 82.4 2 1 2 2 2 84.2 3 1 3 3 3 77.9 4 2 1 2 1 78.5 5 2 2 3 2 82.8 6 2 3 1 3 85.4 7 3 1 3 2 75.2 8 3 2 1 3 82.5 9 3 3 2 1 85.6 k1 81.5 78.7 83.43 82.17 k2 82.23 83.17 82.77 80.73 k3 81.1 82.97 78.63 81.93 R 1.13 4.47 4.8 1.44 SS 1.98 38.2 40.57 3.55 排序 C>B>D>A -
[1] ZHANG B, XU L L, DING J L, et al. Natural antimicrobial lipopeptides secreted by Bacillus spp. and their application in food preservation, a critical review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,127:26−37.
[2] VACA J, ORTIZ A, SANSINENEA E. Bacillus sp. bacteriocins:Natural weapons against bacterial enemies[J]. Current Medicinal Chemistry,2022,29(12):2093−2108. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210527093041
[3] ALI N, PANG Z J, WANG F H, et al. Lipopeptide Biosurfactants from Bacillus spp.:Types, production, biological activities, and applications in Food[J]. Journal of Food Quality,2022,2022:3930112.
[4] ZHAO H B, SHAO D Y, JIANG C M, et al. Biological activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2017,101(15):5951−5960. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8396-0
[5] JAYAKUMAR A, RADOOR S, NAIR I C, et al. Polyvinyl alcohol-nanocomposite films incorporated with clay nanoparticles and lipopeptides as active food wraps against food spoilage microbes[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life,2021,30:100727. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100727
[6] 张楠楠. 产脂肽枯草芽孢杆菌的发酵优化以及在面包中的应用[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2017. [ZHANG N N. Study on the production optimization of lipopepetide from Bacillus subtilis and application in Bread[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2017.] ZHANG N N. Study on the production optimization of lipopepetide from Bacillus subtilis and application in Bread[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[7] 陈亮, 秦素雅, 衡军影, 等. 微生物抗菌肽在食品工业中的应用研究进展[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(5):119−126. [CHEN L, QING S Y, HENG J Y, et al. Research and application advances of antimicrobial peptides in food industry[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2018,39(5):119−126.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2383.2018.05.021 CHEN L, QING S Y, HENG J Y, et al . Research and application advances of antimicrobial peptides in food industry[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2018 ,39 (5 ):119 −126 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2383.2018.05.021[8] JIMOH A A, LIN J. Enhancement of Paenibacillus sp. D9 Lipopeptide biosurfactant production through the optimization of medium composition and its application for biodegradation of hydrophobic pollutants[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2019,187(3):724−743. doi: 10.1007/s12010-018-2847-7
[9] HU F X, LIU Y Y, LI S. Rational strain improvement for surfactin production:Enhancing the yield and generating novel structures[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2019,18:42. doi: 10.1186/s12934-019-1089-x
[10] GEYS R, SOETAERT W, VAN BOGAERT I. Biotechnological opportunities in biosurfactant production[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology,2014,30:66−72. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2014.06.002
[11] ZANOTTO A W, VALERIO A, DE ANDRADE C J, et al. New sustainable alternatives to reduce the production costs for surfactin 50 years after the discovery[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2019,103(21-22):8647−8656. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10123-7
[12] 刘小翠, 安志鹏. 小米发酵液中高发酵性能芽孢杆菌的分离筛选与鉴定[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(9):21−25. [LIU X C, AN Z P. Isolation and identification of high fermentation performance Bacillus strain in fermentation broth of millet[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(9):21−25.] doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.09.005 LIU X C, AN Z P . Isolation and identification of high fermentation performance Bacillus strain in fermentation broth of millet[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019 ,44 (9 ):21 −25 . doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.09.005[13] CAO C X, LIU Y M, LI Y, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant potential of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus velezensis SN-1 from spontaneously fermented Da-Jiang[J]. Glycoconjugate Journal,2020,37(3):307−317. doi: 10.1007/s10719-020-09923-1
[14] 魏新燕, 黄媛媛, 黄亚丽, 等. 甲基营养型芽孢杆菌BH21对葡萄灰霉病菌的拮抗作用[J]. 中国农业科学,2018,51(5):883−892. [WEI X Y, HUANG Y Y, HUANG Y L, et al. Antagonism of Bacillus methylotrophicus strain BH21 to Botrytis cinerea[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2018,51(5):883−892.] doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.05.007 WEI X Y, HUANG Y Y, HUANG Y L, et al . Antagonism of Bacillus methylotrophicus strain BH21 to Botrytis cinerea[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2018 ,51 (5 ):883 −892 . doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.05.007[15] HU J H, DONG B Z, WANG D, et al. Genomic and metabolic features of Bacillus cereus, inhibiting the growth of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by synthesizing secondary metabolites[J]. Archives of Microbiology,2023,205(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-03351-5
[16] KIM P I, BAI H, BAI D, et al. Purification and characterization of a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus thuringiensis CMB26[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2004,97(5):942−949. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02356.x
[17] MA Y X, KONG Q, QIN C, et al. Identification of lipopeptides in Bacillus megaterium by two-step ultrafiltration and LC-ESI-MS/MS[J]. Amb Express,2016,6:79. doi: 10.1186/s13568-016-0252-6
[18] DIMKIC I, STANKOVIC S, NISAVIC M, et al. The profile and antimicrobial activity of Bacillus lipopeptide extracts of five potential biocontrol strains[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2017,8:925. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00925
[19] 刘宇帅, 张杰, 钟瑾, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌TF28抗菌脂肽芬芥素的分离鉴定及抑菌作用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志,2018,38(10):20−29. [LIU Y S, ZHANG J, ZHONG J, et al. Isolation and identification of antibacterial lipopeptides fengycin produced by Bacilus amyloliquefaciens TF28 and its anti-funga mechanism studies[J]. China Biotechnology,2018,38(10):20−29.] LIU Y S, ZHANG J, ZHONG J, et al . Isolation and identification of antibacterial lipopeptides fengycin produced by Bacilus amyloliquefaciens TF28 and its anti-funga mechanism studies[J]. China Biotechnology,2018 ,38 (10 ):20 −29 .[20] 黄华毅, 黄咏槐, 黄焕华, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌STO-12脂肽类物质抑菌活性及其特性分析[J]. 林业与环境科学,2018,34(4):8−14. [HUANG H Y, HUANG Y H, HUANG H H, et al. Antifungal activities and characterization of lipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis STO-12[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science,2018,34(4):8−14.] HUANG H Y, HUANG Y H, HUANG H H, et al . Antifungal activities and characterization of lipopeptides produced by Bacillus subtilis STO-12[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science,2018 ,34 (4 ):8 −14 .[21] 王皓楠, 靳鹏飞, 康迅, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌HAB-6抑菌物质及其相关基因的分析[J]. 江苏农业科学,2018,46(4):79−83. [WANG H N, JIN P F, KANG X, et al. Analysis of bacteriostatic substances and related genes of Bacillus amylolyticus HAB-6[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(4):79−83.] WANG H N, JIN P F, KANG X, et al . Analysis of bacteriostatic substances and related genes of Bacillus amylolyticus HAB-6[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2018 ,46 (4 ):79 −83 .[22] 韩玉竹, 邓钊, 张宝, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌H15产抗菌肽的发酵条件优化和提取方法比较研究[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(15):135−141. [HAN Y Z, DENG Z, ZHANG B, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions for production of antifungal peptides by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H15 and comparison of extraction methods for antifungal peptides[J]. Food Science,2015,36(15):135−141.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201515025 HAN Y Z, DENG Z, ZHANG B, et al . Optimization of fermentation conditions for production of antifungal peptides by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H15 and comparison of extraction methods for antifungal peptides[J]. Food Science,2015 ,36 (15 ):135 −141 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201515025[23] 王晓, 龚彬婷, 昝青佳, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌B17养分需求、发酵条件与绿原酸含量关系的研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2021,40(Z4):3492−3499. [WANG X, GONG B T, ZAN Q J, et al. Study on the relationship between nutrient requirements, fermentation conditions and chlorogenic acid content of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B17[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2021,40(Z4):3492−3499.] doi: 10.13417/j.gab.040.003492 WANG X, GONG B T, ZAN Q J, et al . Study on the relationship between nutrient requirements, fermentation conditions and chlorogenic acid content of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B17[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2021 ,40 (Z4 ):3492 −3499 . doi: 10.13417/j.gab.040.003492[24] 夏京津, 陈建武, 宋怿, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌HE活性成分鉴定及抗菌特性分析[J]. 南方水产科学,2019,15(3):41−49. [XIA J J, CHEN J W, SONG Y, et al. Identification of antibacterial substances from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HE and analysis of antibacterial characteristics[J]. South China Fisheries Science,2019,15(3):41−49.] XIA J J, CHEN J W, SONG Y, et al . Identification of antibacterial substances from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HE and analysis of antibacterial characteristics[J]. South China Fisheries Science,2019 ,15 (3 ):41 −49 .[25] 宋本超, 赵冬梅, 杨志辉, 等. 马铃薯黑痣病菌拮抗菌的筛选鉴定及生防因子分析[J]. 生物技术通报,2019,35(8):9−16. [SONG B C, ZHAO D W, YANG Z H, et al. Screening and identification of an antagonistic bacterium against Rhizoctonia solani and analysis of biocontrol factor[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2019,35(8):9−16.] SONG B C, ZHAO D W, YANG Z H, et al . Screening and identification of an antagonistic bacterium against Rhizoctonia solani and analysis of biocontrol factor[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2019 ,35 (8 ):9 −16 .[26] DAS B, SARKAR C, DAS D, et al. Telavancin:A novel semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide agent to counter the challenge of resistant Gram-positive pathogens[J]. Therapeutic Advances in Infectious Disease,2017,4(2):49−73. doi: 10.1177/2049936117690501
[27] 孙彦婷, 康宇, 詹妍, 等. 鸡源凝结芽孢杆菌的分离鉴定及耐受性分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2022,49(11):4187−4196. [SUN Y T, KANG Y, ZHAN Y, et al. Isolation, identification and stress resistance analysis of Bacillus coagulans from chickens[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2022,49(11):4187−4196.] SUN Y T, KANG Y, ZHAN Y, et al . Isolation, identification and stress resistance analysis of Bacillus coagulans from chickens[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2022 ,49 (11 ):4187 −4196 .[28] 郑喆, 李柳, 赵笑, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌凝乳酶发酵生产条件及其酶学性质的研究[J]. 食品科技,2018,43(2):1−8. [ZHENG Z, LI L, ZHAO X, et al. The fermentation conditions for production of rennet by Bacillus subtilis and its enzymatic properties[J]. Food Science and Technology,2018,43(2):1−8.] doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2018.02.001 ZHENG Z, LI L, ZHAO X, et al . The fermentation conditions for production of rennet by Bacillus subtilis and its enzymatic properties[J]. Food Science and Technology,2018 ,43 (2 ):1 −8 . doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2018.02.001[29] 纪明山, 王毅婧. 地衣芽孢杆菌生防菌株SDYT-79发酵条件优化[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2011,42(2):164−169. [JI M S, WANG Y J. Optimizing fermentation condition for the antagonistic Bacillus licheniformis SDYT-79 strain[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2011,42(2):164−169.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2011.02.007 JI M S, WANG Y J . Optimizing fermentation condition for the antagonistic Bacillus licheniformis SDYT-79 strain[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2011 ,42 (2 ):164 −169 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2011.02.007[30] 张楠楠, 徐丹, 尹婷, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌产脂肽的发酵条件优化[J]. 安徽农业科学,2017,45(15):108−112. [ZHANG N N, XU D, YIN T, et al. Optimization on fermentation condition of surfactin by Bacillus subtilis ATCC 21332[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2017,45(15):108−112.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.15.034 ZHANG N N, XU D, YIN T, et al . Optimization on fermentation condition of surfactin by Bacillus subtilis ATCC 21332[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2017 ,45 (15 ):108 −112 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.15.034[31] YE M, SUN L H, YANG R, et al. The optimization of fermentation conditions for producing cellulase of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its application to goose feed[J]. Royal Society Open Science,2017,4(10):171012. doi: 10.1098/rsos.171012
[32] 罗楚平, 刘邮洲, 吴荷芳, 等. 脂肽类化合物bacillomycin L抗真菌活性及其对水稻病害的防治[J]. 中国生物防治学报,2011,27(1):76−81. [LUO C P, LIU Y Z, WU H F, et al. Antifungal activity and rice disease biocontrol performance of lipopeptide antibiotic bacillomycin L[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2011,27(1):76−81.] LUO C P, LIU Y Z, WU H F, et al . Antifungal activity and rice disease biocontrol performance of lipopeptide antibiotic bacillomycin L[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control,2011 ,27 (1 ):76 −81 .[33] SIVARANJANI V, LAWRANCE I, YASMIN K, et al. Batch experiments towards remediation of phenolic syntan using individual as well as co-culture of Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology,2019,35(9):137.
[34] JU S Y, CAO Z L, WONG C, et al. Isolation and optimal fermentation condition of the Bacillus subtilis Subsp. natto strain WTC016 for nattokinase production[J]. Fermentation-Basel,2019,5(4):92. doi: 10.3390/fermentation5040092
[35] 王军强, 王连国, 郭荣君, 等. 枯草芽胞杆菌B006产表面活性素的培养条件优化[J]. 生物技术通报,2017,33(4):214−221. [WANG J Q, WANG L G, GUO R J, et al. Optimization of culture conditions for the enhancement of surfactin production from Bacillus substilis B006[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2017,33(4):214−221.] doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2017.04.028 WANG J Q, WANG L G, GUO R J, et al . Optimization of culture conditions for the enhancement of surfactin production from Bacillus substilis B006[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2017 ,33 (4 ):214 −221 . doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2017.04.028[36] 陈莉, 汪立平, 赵勇, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌K-6-9发酵条件优化及放大[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(3):172−176. [CHEN L, WANG L P, ZHAO Y, et al. Optimization of cultural conditions and amplification of Bacillus Subtilis-K-6-9[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(3):172−176.] doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.03.054 CHEN L, WANG L P, ZHAO Y, et al . Optimization of cultural conditions and amplification of Bacillus Subtilis-K-6-9[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014 ,35 (3 ):172 −176 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.03.054[37] 张丽姣. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌胞外多糖发酵优化及功能研究[D]. 天津:天津科技大学, 2015. [ZHANG L J. Fermentation condition and functional study of exopolysaccharides from bacillus amyloliouefaciens[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2015.] ZHANG L J. Fermentation condition and functional study of exopolysaccharides from bacillus amyloliouefaciens[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2015.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



