Mitigative Effect of Grape Skin Extract on Arsenic-induced Small Intestinal Toxicity in a Mouse Model
-
摘要: 目的:探究砷摄入对小肠的毒性及葡萄果皮提取物(grape skin extract,GSE)的干预效应。方法:模拟人类饮水砷暴露,小鼠饮用浓度10 mg/L的砷溶液56 d,建立小鼠砷中毒模型,并用不同浓度GSE隔天灌胃干预(150 mg/kg bw和300 mg/kg bw);取小鼠小肠组织,显微镜观察组织形态结构;试剂盒法检测还原型谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)和H2O2含量,及总超氧化物歧化酶(total superoxide dismutase,T-SOD)活性;qRT-PCR检测紧密连接基因和炎症通路IL-6/JAK2/STAT-3基因表达水平。结果:砷染毒后,小鼠小肠绒毛变短、排列紊乱,黏膜固有层及黏膜下层大量炎细胞浸润;小肠组织的GSH含量和T-SOD活性分别降低17.1%和25.2%,MDA和H2O2含量分别增加68.8%和54.3%(P<0.05);细胞紧密连接基因ZO-1、ZO-2、occludin、claudin-1和claudin-7显著下调表达(P<0.05);炎症通路IL-6/JAK2/STAT-3基因转录水平显著增高(P<0.05)。GSE高浓度干预组(300 mg/kg bw),小肠黏膜损伤减轻,肠绒毛趋于正常,炎症浸润减轻;与砷染毒组比较,GSH含量增加17.9%、T-SOD活性升高14.3%、MDA和H2O2含量分别减少33.8%和25.4%(P<0.05);紧密连接基因显著上调表达(P<0.05);炎症通路IL-6/JAK2/STAT-3基因转录显著降低(P<0.05)。GSE低浓度干预(150 mg/kg bw)对砷毒性有一定的缓解作用,但差异不显著,无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:GSE通过抑制砷暴露诱导的小肠组织氧化应激、炎症反应及功能基因转录下调,缓解砷的小肠毒性,对机体具有保护作用。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the arsenic-induced small intestinal toxicity and the protective effect of grape skin extract (GSE) against arsenic toxicity. Methods: The small intestinal toxicity was induced by 10 mg/L arsenic via drinking water for 56 days, and was intervened with GSE (150 mg/kg bw and 300 mg/kg bw) by gavage every other day in mice. Small intestine tissue samples of mice were collected and observed by microscope. Glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA) and H2O2 contents, as well as total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) were determined by using commercial kits. qRT-PCR was used to detect expression levels of the tight junction genes and the inflammatory pathway IL-6/JAK2/STAT-3 genes. Results: The results showed that 56 days exposure to 10 mg/L arsenic via drinking water resulted in shortened and disordered intestinal villi, with large numbers of inflammatory cells infiltrating the mucosa propria and submucosa. GSH content and T-SOD activity decreased by 17.1% and 25.2%, while MDA and H2O2 contents increased by 68.8% and 54.3%, respectively (P<0.05) in the small intestinal tissue of arsenic-treated mice. The mRNA levels of IL-6, JAK2 and STAT-3 were upregulated in the small intestinal tissue of mice exposed to arsenic (P<0.05). Meanwhilethe mRNA levels of the ZO-1, ZO-2, occludin, claudin1 and claudin7 genes, which encode the key components of tight junction (TJ) complexes, were downregulated (P<0.05). However, the application of GSE (300 mg/kg bw) significantly alleviated the damage and inflammatory infiltration in small intestine. Compare to the As group, GSH content and T-SOD activity increased by 17.9% and 14.3%. MDA and H2O2 contents decreased by 33.8% and 25.4% (P<0.05). Arsenic-mediated gene expression in the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway was down-regulated (P<0.05). Moreover, the arsenic-induced down-regulation of TJ genes were markedly relieved in the As+GSE (300 mg/kg bw) group (P<0.05). The As+GSE (150 mg/kg bw) group had a certain alleviating effect on arsenic toxicity, but the difference had no statistical significance (P>0.05). Conclusion: The application of GSE provides significant protection against arsenic-induced small intestinal toxicity by attenuating the oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, and inhibiting the down-regulation of some functional genes.
-
砷(Arsenic,As)是自然环境中广泛存在的类金属元素,可通过消化道、呼吸道、皮肤黏膜等进入体内,饮水摄入是人群暴露的主要途径[1]。世界上许多地区的地下水砷含量超出世界卫生组织(WHO)规定的饮用水限值标准(≤10 µg/L)[2−3]。据不完全统计,全球约有2亿人饮用水砷含量超标[4],我国高砷地下水暴露人群达1960万[5]。流行病学调查显示,砷暴露会增加呼吸系统、消化系统、心血管系统及内分泌代谢系统等疾病发生,与皮肤癌、肺癌、肝癌、膀胱癌、肾癌等多种癌症的发生有关[6]。
小肠是机体消化吸收的重要器官,也具有黏膜免疫功能。紧密连接(TJ)是肠黏膜上皮细胞间相互连接的主要形式,是胃肠道选择性屏障的基础。有多种蛋白质参与TJ的形成,包括密封蛋白(claudin)、闭合蛋白(occludin)、外周蛋白(ZO)等,这些蛋白质表达异常会导致TJ结构或分布异常,破坏粘膜屏障[7]。经口摄入的砷可直接作用于胃肠道黏膜产生毒性作用,并通过胃肠道吸收进入血液,随血液循环分布到其他脏器组织,引起肝脏[8]、肾脏[9]、睾丸[10]等多系统器官组织的结构损伤、炎症应答,出现全身毒性。但关于哺乳动物砷暴露致小肠毒性的研究较少。体外实验表明,砷暴露会引起肠上皮细胞氧化应激、炎症反应及TJ蛋白的重排[11−12];禽类动物砷暴露后,肠道会发生氧化应激和炎症反应[13−14] 。
植物天然活性成分可调节机体抗氧化能力、减轻不良刺激引发的氧化应激和炎症应答[15]。葡萄果皮提取物(grape skin extract,GSE)富含原花青素和花青素等多酚类化合物,具有抗氧化、清除自由基、抗炎等生物学活性[16],对吸烟、镉暴露诱发的啮齿类动物肺部炎症、器官退化、遗传损伤等具有明显的抑制作用[17−18]。研究表明,葡萄皮及葡萄籽提取物可以减轻砷对大鼠心脏的氧化损伤,缓解砷的心脏毒性[19];GSE可以缓解小鼠睾丸组织的氧化损伤,减轻砷的雄性生殖毒性[20]。GSE主要活性成分原花青素可通过抑制肠道PI3K/AKT信号途径发挥抗炎和肠粘膜功能结构保护作用[21],白藜芦醇可以逆转三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠结肠炎所致的菌群失调,抑制炎性Th1/Th17细胞,对结肠炎症和临床症状有明显的减轻作用[22]。本地出产的成熟玫瑰香葡萄果实,此品种葡萄品质优良,种植广泛,果皮颜色较深,色素含量高,体外实验证实其果皮提取物能强效抗氧化、阻断亚硝胺合成[23],但GSE是否拮抗砷的小肠毒性未见报道。
本研究以小肠为研究对象,通过建立饮水砷暴露小鼠模型和GSE干预实验,检测砷暴露及GSE干预对小肠的组织结构、氧化应激、炎症应答的影响,探讨GSE对砷致小鼠小肠毒性的缓解作用,以及为高砷地区居民提供日常可食用的天然产物缓解砷毒性,达到保护机体健康的目的。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
亚砷酸钠 德国默克公司;超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)、过氧化氢(H2O2)、丙二醛(MDA)检测试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;Trizol 天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;反转录试剂盒及qPCR试剂盒 Takara Bio(大连)有限公司;砷检测标准品 国标检测认证有限公司(北京);芦丁、没食子酸、福林酚 上海阿拉丁生化科技有限公司;浓硝酸 中国上海华药化学试剂有限公司;戊巴比妥钠 上海倍卓生物科技有限公司;4周龄SPF级雄性小鼠(体重15±2 g) 军事医学科学院,动物合格证号:SCXK(军)2021-0007;全价小鼠饲料 北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司。
CX43型显微镜 日本奥林巴斯公司;HC-2518R型高速冷冻离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;TP350型 PCR仪 TaKaRa公司;Synergy H1型多功能酶标仪 美国BioTek公司;CFX ConnectTM Optics Module型RT-PCR仪 美国Bio-Rad公司;Multiwave PRO微波消解仪 奥地利安东帕公司;电感耦合等离子体质谱仪NexION350x 美国珀金埃尔默公司 。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 GSE制备与酚类化合物含量测定
玫瑰香GSE在实验前新鲜制备,采用本实验室前期建立的方法提取[24]。剥取果皮,60 °C烘至恒重,粉碎过40目筛,以1 g细粉加浓度40%的乙醇20 mL的比例混匀,超声波辅助浸提,离心取上清,于40 °C、100 r/min的旋转蒸发仪上浓缩,真空干燥成粉末状,储于4 °C备用。
GSE中的总酚含量采用福林-酚法测定[25],总黄酮含量用Al(NO3)3-NaNO2-NaOH比色法测定[26],总花色苷含量用pH示差法测定[27],原花青素含量用正丁醇/盐酸法测定[28]。总酚、总黄酮、总花色苷和原花青素含量分别表示为没食子酸当量/g干提取物、芦丁当量/g干提取物、花青素-3-葡萄糖苷当量/g干提取物和mg/g干提取物(n=3)。
1.2.2 动物分组与处理
小鼠实验严格遵守山西大学动物伦理委员会提供的指导方案执行,遵守实验动物相关国家标准(GB/T 39760-2021 《实验动物 安乐死指南》)。模拟居民饮水砷暴露,实验动物采用自由饮用亚砷酸钠水溶液的方式摄入砷。4周龄SPF级雄性C57BL/6小鼠,随机分为4组(n=6):空白对照组、As组、As+GSE1组,As+GSE2组。各组动物自由饮水与摄食,喂食山西医科大学提供的专用全价饲料,饲养温度23±1 °C,湿度55%±10%,光照12 h/d。对照组小鼠饮用蒸馏水,As组及As+GSE组小鼠饮用水砷浓度为10 mg/L。参照前期研究结果[20],As+GSE1和As+GSE2干预组小鼠分别以GSE 150 mg/kg bw或300 mg/kg bw的剂量隔天灌胃,同期,对照组及As组小鼠以相同体积的蒸馏水灌胃。实验周期为56 d。
1.2.3 动物解剖与取材
用1%的戊巴比妥钠麻醉小鼠,迅速打开腹腔摘取空肠,预冷生理盐水漂洗。取长度0.5 cm的空肠组织固定于4%的中性甲醛中,用于组织病理学分析;其余空肠组织经液氮速冻后-80 ℃保存。
1.2.4 切片的制备与观察
取甲醛固定的空肠组织,梯度酒精脱水、二甲苯透明、石蜡包埋,切成4~5 µm厚的切片。苏木素-伊红(H&E)染色,光学显微镜观察。
1.2.5 氧化应激指标检测
取冻存组织100~150 mg,加入9倍体积的生理盐水匀浆,3500 r/min低温离心15 min,取上清液用于检测。MDA、H2O2和GSH含量,及T-SOD活性按南京建成生物工程研究所试剂盒操作说明测定。蛋白含量测定采用考马斯亮蓝法[29],牛血清白蛋白做标准曲线。以蛋白含量(mg/g)为横坐标x,吸光度为纵坐标y,绘标准曲线,得回归方程y=0.9463x+0.0297。
1.2.6 紧密连接蛋白及IL-6/JAK2/STAT3信号通路基因的检测
为研究砷暴露是否影响小肠紧密连接蛋白相关基因及炎症通路IL-6/JAK2/STAT3基因表达,以及GSE的干预作用,采用RT-PCR法检测小肠组织紧密连接中ZO-1、ZO-2、occludin、claudin-1、claudin-7及炎症通路IL-6、JAK2、STAT3基因的相对表达量。Trizol法提取空肠组织总RNA,按照TaKaRa反转录试剂盒操作说明合成cDNA,用TaKaRa荧光定量PCR试剂盒检测靶基因(表1)相对表达量。CFX Connect TM荧光定量PCR仪进行基因扩增:采用两步法,步骤一:95 ℃ 30 sec;步骤二:95 ℃ 5 sec,60 ℃ 30 sec,40个循环。以β-actin为内参,采用2−∆∆Ct法计算靶基因的相对表达量。
表 1 RT-qPCR引物序列Table 1. Primer sequences used for real-time quantitative PCR基因 正向引物(5'→3') 反向引物(5'→3') ZO-1 TGGGAACAGCACACAGTGAC GCTGGCCCTCCTTTTAACAC ZO-2 CCATGGGCGCGGACTATCTGA CTGTGGCGGGGAGGTTTGACTTG occludin ACCCGAAGAAAGATGGATCG CATAGTCAGATGGGGGTGGA claudin-1 TTCTGGGAGGTGTCCTACTT AGGTGTTGGCTTGGGATAAG claudin-7 GGGAGATGACAAAGCGAAGA CTGATGACCAATCCAGGAACA IL-6 TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC JAK2 ACAATGAAATGGAGGC ACAGGCGTAATACCACAAGC STAT3 TTGAAGACGTACCCTGTGCC GAGGCCATGAGCTCCTTGTT 1.2.7 组织总砷含量测定
取冻存的空肠组织样品约50 mg,加入0.75 mL浓硝酸在Multiwave PRO微波系统(Anton Par GmbH)中消化,加超纯水定容至10 mL。程序条件:功率爬坡700 W,10 min;保持功率700 W,6 min;功率爬坡1400 W,10 min;保持功率1400 W,30 min;冷却至70 °C;内部温度限值240 ℃;红外温度限值190 °C[30]。使用NexION 350x电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(IC-PMS)检测总砷含量。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS 21软件对数据进行统计分析,结果以均值±标准误表示。通过单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),LSD和Dunnett's T3做多重比较,检验各组之间的差异显著性。图中不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(P<0.05),相同字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 GSE酚类物质含量
玫瑰香葡萄GSE中主要酚类物质含量检测结果见表2,文献报道这些酚类物质在不同品种的葡萄皮中含量差异较大[31−33],深色葡萄果皮中这几类主要成分含量较高,浅色果皮提取物中含量较低。本结果中总酚、总黄酮、总花色苷和原花青素含量较高,这与玫瑰香葡萄果皮颜色较深有关。
表 2 GSE中总酚、总黄酮、总花色苷及原花青素含量Table 2. Contents of total phenolics, total flavonoid, total anthocyanin, and proanthocyanidin in GSE成分 浓度(mg/g) 总酚 60.60±2.34 总黄酮 60.95±5.17 总花色苷 4.45±0.22 原花青素 22.22±1.52 2.2 小鼠一般情况、体重变化、砷摄入量及小肠组织总砷含量
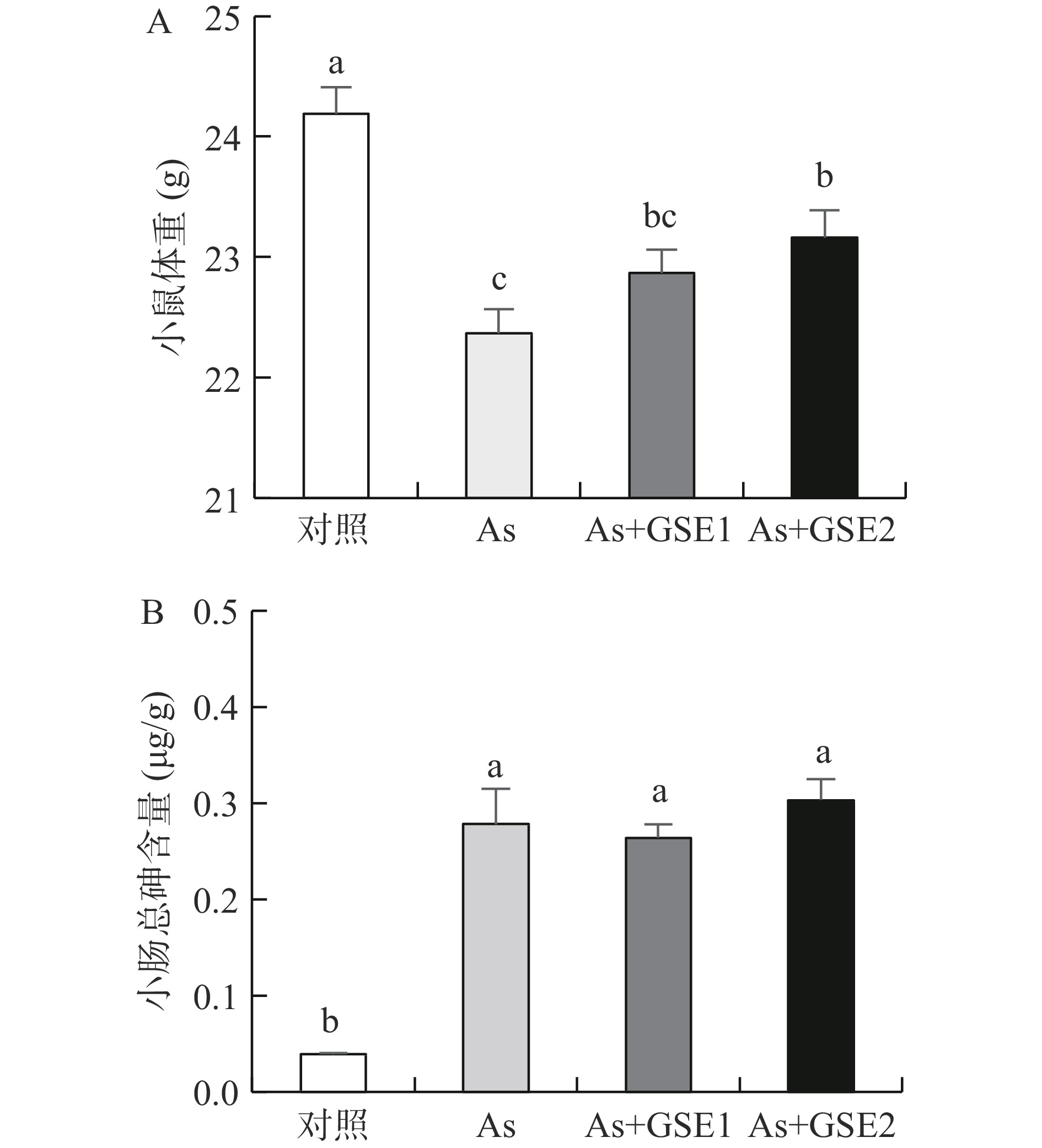
实验期间小鼠外观、饮食和活动正常,未出现死亡。已有研究证实,饮水摄入砷可对小鼠全身多系统脏器如心脏、肺脏、肝脏、肾脏和雄性生殖系统等产生毒性作用[8],本研究选择了相同的砷暴露浓度和暴露时间,并且测得主要脏器砷含量均显著增高(结果未展示),小鼠砷中毒模型建成。饮用含砷水56 d后,与空白对照组相比,As组小鼠体重显著降低(P<0.05);与As组比较,As+GSE2组体重显著上升(P<0.05),As+GSE1组体重略有升高,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(图1)。根据饮水量和体重计算砷摄入量,As组为1.76±0.18 mg/kg/day,As+GSE1和As+GSE2组分别为1.81±0.23 mg/kg/day和1.83±0.09 mg/kg/day。As组与As+GSE组小鼠的砷摄入量无明显差异(P>0.05)。砷含量测定结果(图1)表明,As组与As+GSE组小肠组织总砷含量显著高于对照组(P<0.05),分别是对照组的7.13、6.70、7.77倍;但As+GSE1和As+GSE2小肠组织总砷含量与As组无显著差异(P>0.05)。结果表明:经口摄入砷会导致小肠组织总砷含量明显升高,有较多的砷富集在小肠;GSE干预对小鼠砷摄入量及小肠组织总砷含量无明显影响,GSE不能通过减少小肠组织的总砷含量来实现保护作用。
2.3 砷对小肠组织结构的影响及GSE的干预效应
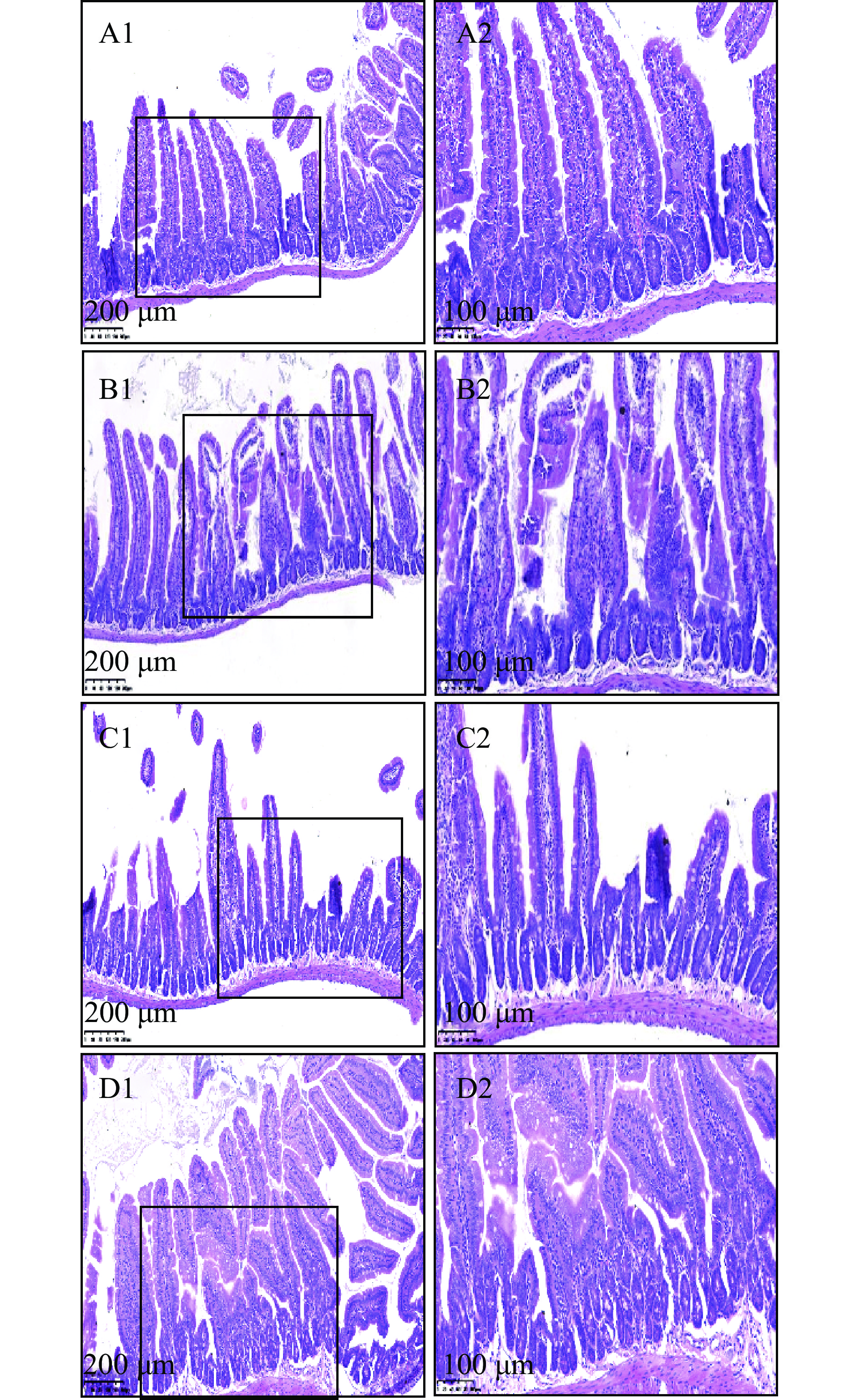
组织切片观察发现(图2),空白对照组小鼠小肠黏膜结构完整,肠绒毛排列紧密整齐,长度一致;As组小肠绒毛萎缩变短、排列紊乱,肠隐窝较少,黏膜固有层及黏膜下层大量炎细胞浸润(图2B);As+GSE2组小鼠小肠黏膜结构完整,绒毛排列整齐一致,肠隐窝较As组增多,未见明显炎细胞浸润;As+GSE1组小肠形态结构有所改善,但可见黏膜结构损伤及炎细胞浸润。结果表明,饮水砷暴露造成了小鼠小肠组织结构损伤,引起炎症反应;一定浓度的GSE干预能抑制砷引发的小肠黏膜损伤,降低组织炎症反应,高浓度GSE的干预效果好于低浓度组。
2.4 砷对小肠组织的氧化损伤及GSE的干预效应
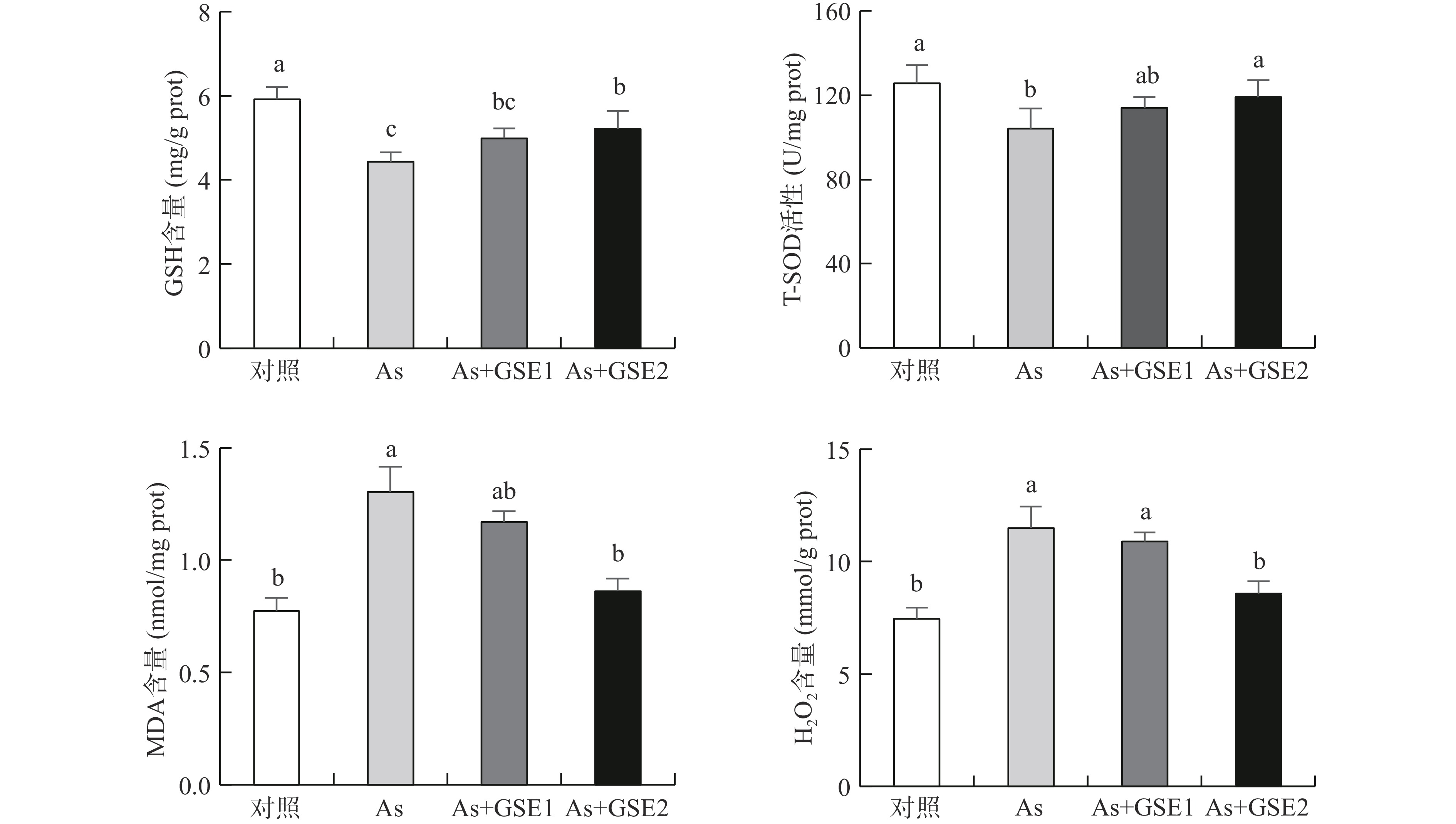
饮用含砷水56 d后,与空白对照组相比,As组小鼠小肠组织的GSH含量减少25.2%、T-SOD活性降低17.1%、H2O2含量增加54.3%、MDA含量增加68.8%,各指标与对照组差异显著(P<0.05)(图3);与As组相比,As+GSE2干预组GSH含量增加17.9%、T-SOD活性升高14.3%、H2O2含量减少25.4%、MDA含量减少33.8%,均与As组差异显著(P<0.05);As+GSE1组GSH含量和T-SOD活性略升高,MDA和H2O2含量略降低,但差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结果表明:饮水砷摄入可使小肠组织氧化应激,高水平活性氧引发组织氧化损伤;一定浓度的GSE可提高小肠组织抗氧化能力,避免组织氧化损伤。
2.5 砷对小肠组织紧密连接(TJ)相关基因转录的影响及GSE的干预效应
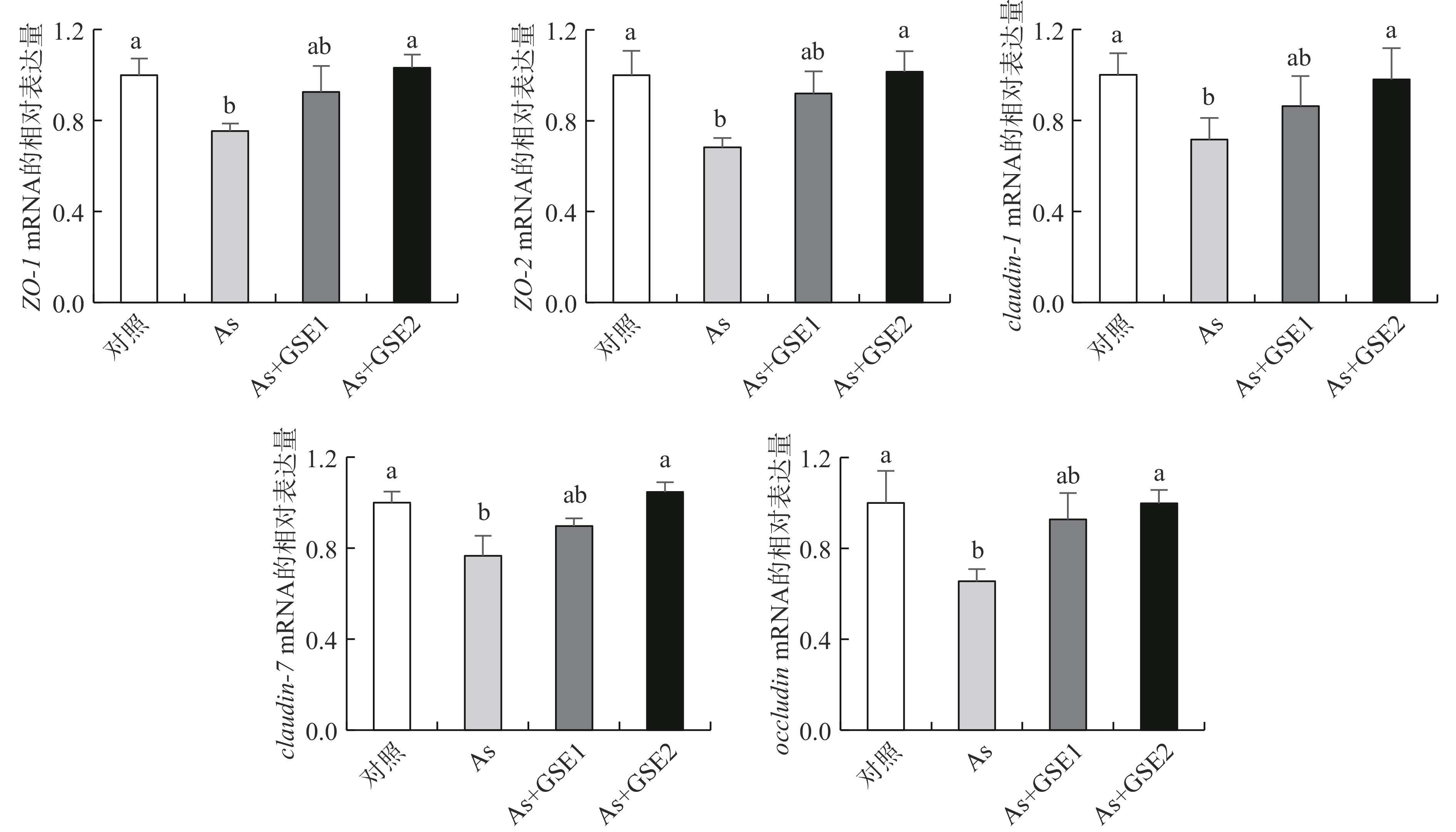
基因转录检测发现,As组小鼠小肠TJ基因ZO-1、ZO-2、occludin、claudin-1和claudin-7的mRNA水平显著低于空白对照组(P<0.05);As+GSE2组中这些基因mRNA水平显著高于As组(P<0.05),恢复至对照组水平;As+GSE1组这些基因mRNA水平有所升高,但与As组差异不显著(P>0.05)(图4)。结果表明,饮水砷摄入能抑制小鼠小肠组织TJ基因的表达,从而减少TJ相关蛋白的合成,影响TJ正常结构;一定浓度的GSE干预可以减轻砷对TJ基因表达的抑制,促使TJ相关蛋白的合成,从而维持肠黏膜屏障功能。
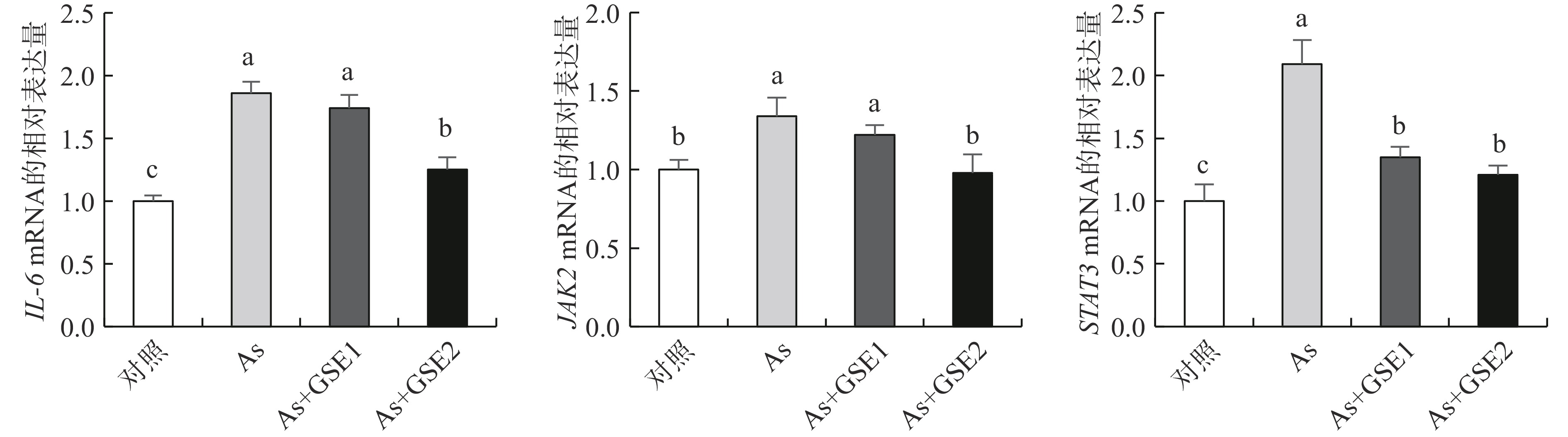
2.6 砷对炎症通路IL-6/JAK2/STAT3相关基因转录的影响及GSE的干预效应
与对照组相比,As组小鼠小肠组织中炎症相关基因IL-6、JAK2和STAT3的mRNA水平明显增高(P<0.05);与As组比较,As+GSE2组中IL-6、JAK2和STAT3基因转录水平显著降低(P<0.05),As+GSE1组STAT3的mRNA水平明显降低(P<0.05),IL-6和JAK2基因转录下降不显著(P>0.05)(图5)。不同处理组中炎症通路IL-6/JAK2/STAT3的激活状态不同,与小肠组织切片中的炎性细胞浸润现象一致。结果表明,饮水砷暴露可使小鼠小肠组织中炎症通路IL-6/JAK2/STAT3激活,炎细胞浸润,而一定浓度的GSE干预可以抑制小肠炎症通路的激活,抑制炎性细胞浸润。
3. 讨论与结论
小肠肠腔表面的绒毛是其发挥消化吸收功能的主要结构,其损伤会影响肠道消化吸收及黏膜免疫功能[10]。本研究砷暴露组小鼠小肠绒毛萎缩、排列紊乱,炎症细胞浸润,这些改变会影响小肠的正常功能,减弱肠道消化和吸收功能,这可能是导致砷组小鼠体重下降的一个重要原因。GSE 300 mg/kg bw干预可明显改善小肠组织形态结构,使绒毛长度和排列恢复正常,炎细胞浸润减轻,从而改善小肠功能,使小鼠体重增加。
进入体内的砷在进行生物转化的过程中会导致超氧阴离子、羟自由基等活性氧自由基的大量产生,增加H2O2等的累积,使组织细胞内活性氧(ROS)水平升高[34],出现氧化胁迫。细胞内有多种抗氧化酶和非酶抗氧化分子GSH、VE、VC等组成的抗氧化系统,可协同消除细胞内的活性氧自由基,维持氧化还原平衡。GSH中的巯基(–SH)能螯合胞内砷离子,加速无机砷在体内的甲基化过程,促进砷的代谢与排泄[35],砷摄入会加速GSH的消耗,降低GSH水平。SOD是细胞主要的抗氧化酶,其基因转录和酶活性可诱导性升高,但是持续的高水平ROS可破坏酶的蛋白质结构,导致酶活性下降。本研究中砷组小鼠小肠组织SOD活性和GSH含量降低,H2O2和MDA浓度提高,说明长期饮水砷摄入破坏了小肠组织的氧化还原平衡,引起脂质过氧化,氧化损伤是造成小肠损伤的重要原因。GSE 富含酚类生物活性分子,可增加受试动物的抗氧化活性来减轻砷对大鼠心脏和小鼠雄性生殖的氧化损伤[19−20]及吸烟对小鼠肺部的氧化损伤[17]。玫瑰香GSE灌胃干预能提高小鼠小肠组织的SOD活性和GSH含量,降低H2O2和MDA浓度,说明GSE对砷摄入引发的小肠损伤有显著抑制作用,可能是GSE中的多酚类生物活性成分能够通过供氢、淬灭单线态氧、螯合及还原等作用清除自由基[36],提高了组织的抗氧化能力,对组织器官的结构和功能产生保护作用。GSE干预组高水平GSH在细胞清除活性氧、降低氧化胁迫,促进氧化还原平衡方面发挥了作用,但是并未减少小肠组织砷含量,可能是由于进入体内的砷主要通过尿排泄,随着砷暴露逐渐富集在小肠组织中的砷因为化学形态的转变而难以排泄,致使本文采用的GSE干预对降低小肠砷含量作用不大,具体机制有待进一步的研究。
组织细胞的氧化胁迫会引发蛋白质氧化损伤,砷摄入诱发的组织氧化胁迫可使肠黏膜细胞多种功能蛋白质氧化损伤,如紧密连接蛋白受损、蛋白复合体破坏[37],而同期小肠组织中TJ基因 ZO-1、ZO-2、occludin、claudin-1和claudin-7的转录抑制将导致紧密连接蛋白的合成不足,影响细胞间的有序连接,使肠壁结构完整性受到影响。文献报道,葡萄籽原花青素可增加大鼠肠道ZO-1及occludin基因及蛋白的表达,通过调节大鼠肠道通透性和抑制氧化应激来降低断奶后腹泻的发生率[38]。本研究中,GSE能显著抑制饮水砷摄入引起的小肠氧化应激反应,降低蛋白质氧化损伤,减少紧密连接蛋白等的损伤;与此同时,GSE干预还可解除砷对紧密连接蛋白基因转录的抑制,提高基因转录水平,促使紧密连接蛋白的合成增加,从而补充紧密连接复合体中受损的蛋白分子,修复蛋白复合体,维持小肠上皮细胞间紧密连接的稳定性。
研究表明,饮水砷暴露能够激活ROS敏感的核转录因子NF-κB与STAT-3等炎症信号通路,介导炎症反应,诱发肾脏组织损伤[9]。IL-6作为炎症因子,可激活JAK2/STAT3通路,启动相关基因表达,调控炎症免疫,产生一系列生理病理反应,参与肠道炎症疾病的发生发展[39]。本研究结果显示,砷染毒后小鼠小肠组织中编码 IL-6/JAK2/STAT3信号通路组分的基因表达上调,与砷摄入诱发的小肠组织炎症同时发生,说明小肠炎症反应与IL-6/JAK2/STAT3炎症通路的激活有关,IL-6/JAK2/STAT3参与介导砷摄入引发的肠道炎症。GSE干预抑制了小鼠IL-6/JAK2/STAT3炎症途径基因的转录和炎细胞浸润,也在一定程度上说明砷摄入激活该炎症途径与小肠炎症反应有关,玫瑰香GSE对炎症基因转录的抑制在保护小肠组织形态中具有作用。此外,研究发现从植物中提取的酚类物质混合物比单一成分具有更强的抗炎作用[40],其中的酚类物质可能存在协同作用。本研究首次证实了GSE对砷染毒小鼠小肠IL-6/JAK2/STAT3炎症信号通路的抑制作用,提供了更为全面的GSE减轻砷暴露诱发的小肠炎症反应的分子机制,证实了GSE对小肠损伤的保护作用。GSE作为天然植物多酚混合物,可能具有比单一成分更好的抗氧化抗炎功效,在砷毒性防治方面具有很好的应用前景。
总之,饮水砷摄入可增加小鼠空肠组织H2O2水平,引起氧化损伤和组织结构病理性改变,激活IL-6/JAK2/STAT3炎症通路,抑制紧密连接基因ZO-1、ZO-2、occludin、claudin-1和claudin-7的转录,从而影响小肠的消化吸收功能和黏膜免疫。富含植物多酚的玫瑰香GSE作为抗炎、抗氧化的天然物质,对砷引起的小鼠小肠损伤具有多方面的保护作用。本研究结果为GSE作为一种抗氧化、抗炎和肠黏膜保护剂在拮抗砷中毒方面的应用提供了理论支持。
-
表 1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used for real-time quantitative PCR
基因 正向引物(5'→3') 反向引物(5'→3') ZO-1 TGGGAACAGCACACAGTGAC GCTGGCCCTCCTTTTAACAC ZO-2 CCATGGGCGCGGACTATCTGA CTGTGGCGGGGAGGTTTGACTTG occludin ACCCGAAGAAAGATGGATCG CATAGTCAGATGGGGGTGGA claudin-1 TTCTGGGAGGTGTCCTACTT AGGTGTTGGCTTGGGATAAG claudin-7 GGGAGATGACAAAGCGAAGA CTGATGACCAATCCAGGAACA IL-6 TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC JAK2 ACAATGAAATGGAGGC ACAGGCGTAATACCACAAGC STAT3 TTGAAGACGTACCCTGTGCC GAGGCCATGAGCTCCTTGTT 表 2 GSE中总酚、总黄酮、总花色苷及原花青素含量
Table 2 Contents of total phenolics, total flavonoid, total anthocyanin, and proanthocyanidin in GSE
成分 浓度(mg/g) 总酚 60.60±2.34 总黄酮 60.95±5.17 总花色苷 4.45±0.22 原花青素 22.22±1.52 -
[1] SMITH A H, LOPIPERO P A, BATES M N, et al. Arsenic epidemiology and drinking water standards[J]. Science,2002,296:2145−2146. doi: 10.1126/science.1072896
[2] World Health Organization. Arsenic in drinking water[S]. Geneva:World Health Organization, 2001. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/facesheetsfs210/en/print.html.
[3] MUNOZ A, CHERVONA Y, HALL M, et al. Sex-specific patterns and deregulation of endocrine pathways in the gene expression profiles of Bangladeshi adults exposed to arsenic contaminated drinking water[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology,2015,284:330−338. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.02.025
[4] CHAKRABORTI D, RAHMAN M M, DAS B, et al. Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in India[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2017,25:1165−1181. doi: 10.1007/s10040-017-1556-6
[5] RODRÍGUEZ-LADO L, SUN G, BERG M, et al. Groundwater arsenic contamination throughout China[J]. Science,2013,341(6148):866−868. doi: 10.1126/science.1237484
[6] LIU F F, WANG J P, ZHENG Y J, et al. Biomarkers for the evaluation of population health status 16 years after the intervention of arsenic-contaminated groundwater in Xinjiang, China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013,262:1159−1166. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.058
[7] GONZÁLEZ-MARISCAL L, TAPIA R, CHAMORRO D. Crosstalk of tight junction components with signaling pathways[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,2008,1778:729−756. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.08.018
[8] 闫志鹏, 张君玲, 席银璘, 等. 饮水型砷暴露对小鼠多系统脏器的毒性作用[J]. 环境科学学报,2021,41(8):3394−3400. [YAN Z P, ZHANG J L, XI Y L, et al. Toxic effects of arsenic exposure via drinking water on multiple organs in mice[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021,41(8):3394−3400.] doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0569 YAN Z P, ZHANG J L, XI Y L, et al . Toxic effects of arsenic exposure via drinking water on multiple organs in mice[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021 ,41 (8 ):3394 −3400 . doi: 10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0569[9] JI P Y, LI Z Y, WANG H, et al. Arsenic and sulfur dioxide co-exposure induce renal injury via activation of the NF- kB and caspase signaling pathway[J]. Chemosphere,2019,224:280−288. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.111
[10] ZENG Q, YI H L, HUANG L Q, et al. Reduced testosterone and Ddx3y expression caused by long-term exposure to arsenic and its effect on spermatogenesis in mice[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,2018,63:84−91. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2018.08.012
[11] CALATAYUD M, GIMENO-ALCANIZ J V, VELEZ D, et al. Trivalent arsenic species induce changes in expression and levels of proinflammatory cytokines in intestinal epithelial cells[J]. Toxicology Letters,2014,224:40−46. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.09.016
[12] CHIOCCHETTI G M, VÉLEZ D, DEVESA V. Effect of subchronic exposure to inorganic arsenic on the structure and function of the intestinal epithelium[J]. Toxicology Letters,2018,206:80−88.
[13] WANG Y, ZHAO H J, LIU J J, et al. Copper and arsenic-induced oxidative stress and immune imbalance are associated with activation of heat shock proteins in chicken intestines[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2018,60:64−75. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.038
[14] ZHONG G L, WAN F, LAN J, et al. Arsenic exposure induces intestinal barrier damage and consequent activation of gut-liver axis leading to inflammation and pyroptosis of liver in ducks[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,788:14778.
[15] TSAO R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols[J]. Nutrients, 2010:1231-1246.
[16] MAGRONE T, MAGRONE M, RUSSO M A, et al. Recent advances on the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of red grape polyphenols: in vitro and in vivo studies[J]. Antioxidants,2019,9(1):35−35. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010035
[17] PIRES K M P, VALENÇA S S, RESENDE Â C, et al. Grape skin extract reduced pulmonary oxidative response in mice exposed to cigarette smoke[J]. Medical Science Monitor International Medical Journal of Experimental & Clinical Research,2011,17(8):187−195.
[18] GOLLUCKE A B, CLAUDIOA S R, YAMAMURAA H, et al. Grape skin extract mitigates tissue degeneration, genotoxicity, and oxidative status in multiple organs of rats exposed to cadmium[J]. European Journal of Cancer Prevention,2016,27:70−78.
[19] SFAXI I, CHARRADI K, LIMAM F, et al. Grape seed and skin extract protects against arsenic trioxide induced oxidative stress in rat heart[J]. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology,2016,94:168−176. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2015-0088
[20] 闫志鹏, 高俊宇, 王瑞廷, 等. 葡萄果皮提取物对砷致雄性小鼠生殖毒性的缓解作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(23):302−305,314. [YAN Z P, GAO J Y, WANG R T, et al. Mitigative effect of grape skin extracts on arsenic-induced reproductive toxicity in male mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(23):302−305,314.] YAN Z P, GAO J Y, WANG R T, et al . Mitigative effect of grape skin extracts on arsenic-induced reproductive toxicity in male mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020 ,41 (23 ):302 −305,314 .[21] 姜从桥, 朱平胜, 时依, 等. 原花青素B2对三硝基苯磺酸结肠炎模型小鼠肠炎及肠屏障的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2019,39(7):778−783. [JIANG C Q, ZHU P S, SHI Y, et al. Protective effect of procyanidin B2 on intestinal barrier and against enteritis in a mouse model of trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid-induced colitis[J]. Journal of South Medical University,2019,39(7):778−783.] JIANG C Q, ZHU P S, SHI Y, et al . Protective effect of procyanidin B2 on intestinal barrier and against enteritis in a mouse model of trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid-induced colitis[J]. Journal of South Medical University,2019 ,39 (7 ):778 −783 .[22] RASHEED A H, BUSBEE P B, MITZI N, et al. Resveratrol modulates the gut microbiota to prevent murine colitis development through induction of Tregs and suppression of Th17 cells[J]. Journal of Leukocyte Biology: An Official Publication of the Reticuloendothelial Society,2019(2):106.
[23] 范瑞霞, 仪慧兰. 葡萄果皮提取物清除自由基、亚硝酸盐及阻断亚硝胺合成的研究[J]. 营养学报,2017,39(6):583−587. [FAN R X, YI H L. Study on the effects of grape skin extracts on scavenging free radicals and nitrite and inhibiting nitrosamine synthesis[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2017,39(6):583−587.] FAN R X, YI H L . Study on the effects of grape skin extracts on scavenging free radicals and nitrite and inhibiting nitrosamine synthesis[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2017 ,39 (6 ):583 −587 .[24] 范瑞霞, 仪慧兰. 响应面法在葡萄果皮色素超声辅助提取工艺中的应用[J]. 山西大学学报(自然科学版),2015,38(4):721−725. [FAN R X, YI H L. Application of response surface methodology in ultrosound-asisted extraction of pigment from grape skin[J]. Journal of Shanxi University (Nature Science Edition),2015,38(4):721−725.] FAN R X, YI H L . Application of response surface methodology in ultrosound-asisted extraction of pigment from grape skin[J]. Journal of Shanxi University (Nature Science Edition),2015 ,38 (4 ):721 −725 .[25] SINGLETON V L, ORTHOFER R, LAMUELA-RAVENTÓS R M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent[J]. Methods in Enzymology,1999,299(1):152−178.
[26] LIU P H, WANG C N, YANG X, et al. Preliminary test of chemical components and content determination of total flavonoids in different parts of Gonocaryum lobbianum[J]. Medicinal Plant,2013,4:46−50.
[27] LEE J, DURST R W, WROLSTAD R E. Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method:collaborative study[J]. Journal of AOAC International,2005,88:1269−1278. doi: 10.1093/jaoac/88.5.1269
[28] PORTER L J, HRSTICH L N, CHAN B G. The conversion of procyanidins and prodelphinidins to cyanidin and delphinidin[J]. Phytochemistry,1986,25:223−230.
[29] BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,1976,72:248−254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
[30] 刘淑萍, 李荣斋, 张雨佳. 微波消解-原子荧光光谱法测量小麦粉中砷[J]. 中国食品工业,2021,1(1):46−50. [LIU S P, LI R Z, ZHANG Y J. Measurement of arsenic in wheat flour by microwave digestion atomic fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. China Food Industry,2021,1(1):46−50.] LIU S P, LI R Z, ZHANG Y J . Measurement of arsenic in wheat flour by microwave digestion atomic fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. China Food Industry,2021 ,1 (1 ):46 −50 .[31] HARSHA P S, GARDANA C, SIMONETTI P, et al. Characterization of phenolics, in vitro reducing capacity and anti-glycation activity of red grape skins recovered from winemaking by-products[J]. Bioresource Technology,2013,140:263−268. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.092
[32] GOLLUCKE A B, CLAUDIO S R, YAMAMURA H, et al. Grape skin extract mitigates tissue degeneration, genotoxicity, and oxidative status in multiple organs of rats exposed to cadmium[J]. European Journal of Cancer Prevention, 2018(1).
[33] JARIYAPAMORNKOON N, YIBCHOKANUN S, ADISAKWATTANA S. Inhibition of advanced glycation end products by red grape skin extract and its antioxidant activity[J]. BMC Complementary & Alternative Medicine,2013,13(1):171.
[34] JOMOVA K, JENISOVA Z, FESZTEROVA M, et al. Arsenic toxicity oxidative stress and human disease[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology,2011,31(2):95−107. doi: 10.1002/jat.1649
[35] FLORA S J. Arsenic-induced oxidative stress and its reversibility[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2011,51:257−281. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.008
[36] NASSIR-ASl M, HOSSEINZADEH H. Review of the pharmacological effects of Vitis vinifera (Grape) and its bioactive compounds[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2009,23(9):1197−1204. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2761
[37] LI X J, WANG W T, HOU Y, et al. Arsenic interferes with spermatogenesis involving Rictor/mTORC2-mediated blood-testis barrier disruption in mice[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environemtal Safety,2013,257:114914.
[38] SONG P X, ZHANG R J, WANG X X, et al. Dietary grape-seed procyanidins decreased postweaning diarrhea by modulating intestinal permeability and suppressing oxidative stress in rats[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry,2011,59:6227−6232. doi: 10.1021/jf200120y
[39] MUSSO A, DENTELLI P, CARLINO A, et al. Signal transducer and activators of transcription 3 signaling pathway:an essential mediator of inflammatory bowel disease and other forms of intestinal inflammation[J]. Inflammatory Bowel Disease,2005,11(2):91−98. doi: 10.1097/00054725-200502000-00001
[40] JOSKOVA M, SADLONOVA V, NOSALOVA G, et al. Polyphenols and their components in experimental allergic asthma[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology,2013,756(756):91.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



