Analysis of Phenolic Composition Changes and Antioxidant Activity of Mulberry before and after Fermentation
-
摘要: 目的:旨在分析桑葚饮料发酵前后酚类物质的组成变化和抗氧化功能差异。方法:利用毕赤酵母菌(Pichia kudriavzevii)和融合魏斯氏乳酸菌(Weissella confusa)通过二次发酵桑葚制备桑葚饮料,比较桑葚发酵前后酚类物质对DPPH、OH、ABTS+自由基的清除能力及还原力,并通过非靶向代谢组学技术对不同组别样品差异代谢物进行鉴定,进而探究发酵前后酚类物质组成变化与抗氧化性能之间的相关性。结果:发酵后桑葚酚类物质(1 mg/mL)对DPPH自由基清除率由发酵前的45.97%±2.23%提高到59.01%±3.59%(P<0.05);对OH自由基清除率由发酵前的68.68%±1.23%提高到78.55%±0.57%(P<0.05);发酵后的桑葚饮料中酚类物质的还原力显著提高(P<0.05);发酵前后的酚类化合物对ABTS+自由基清除能力无显著差异(P>0.05)。从发酵前后桑葚酚类物质中共筛选出46种差异代谢物,包括3种花色苷类、10种酚酸类、18种类黄酮及15种其它酚类物质,其中发酵后上调和下调的代谢物分别为26种和20种,共涉及4个相关代谢通路,包括植物次生代谢产物的生物合成、苯丙烷类生物合成、类黄酮生物合成和花色苷生物合成。58.70%的酚类物质与DPPH和OH自由基清除率呈正相关。结论:桑葚经发酵后酚类物质组成变化及含量的增加使得抗氧化能力得到明显上调。Abstract: Objective: To analyze the changes in phenolic composition and antioxidant function of mulberry beverage before and after fermentation. Methods: Mulberry beverage was prepared by a secondary fermentation method using Pichia kudriavzevii and Weissella confusa. The scavenge rate and reducing power of phenolic substances on DPPH, OH, ABTS+ free radicals before and after mulberry fermentation were compared. The differential metabolites in different samples were identified using non targeted metabolomics techniques. Then the correlation between changes in phenolic composition before and after fermentation and antioxidant performance was further explored. Results: The free radical scavenging rates of mulberry phenolic substances (1 mg/mL) on DPPH increased from 45.97%±2.23% before fermentation to 59.01%±3.59% after fermentation (P<0.05), while the scavenging rates on OH increased from 68.68%±1.23% to 78.55%±0.57% after fermentation (P<0.05). The reducing power of phenolic substances in fermented mulberry beverages was significantly increased (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the ability of phenolic compounds to scavenge ABTS+ radicals before and after fermentation (P>0.05). A total of 46 differential metabolites were screened from mulberry phenolic substances before and after fermentation, including 3 anthocyanins, 10 phenolic acids, 18 flavonoids, and 15 other phenolic substances, of which 26 metabolites were up-regulated and another 20 metabolites were down-regulated, involving a total of 4 related metabolic pathways, including the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in plants, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, flavonoid biosynthesis, and anthocyanin biosynthesis. 58.70% of phenolic substances were positively correlated with DPPH and OH radical clearance rates. Conclusion: Both the changes in phenolic composition and increased content of mulberry after fermentation result in a significant upregulation of antioxidant capacity.
-
Keywords:
- mulberry /
- fermentation /
- polyphenols /
- antioxidant activity /
- non-targeted metabolomics
-
桑葚是一种营养价值极高的药食同源植物,被称为“民间圣果”[1],具有抗氧化[2]、抗肿瘤、降血糖和降血脂等功效[3],是21世纪的最佳保健果品之一[4]。这些功能源于桑葚中的各种功能成分,如酚类化合物、多糖、有机酸、维生素等[5]。作为其中主要的活性物质之一,酚类能够参与植物生长发育、基因表达和信号传导,同时在一定程度上影响植物源食品的感官品质[6]。此外,酚类物质还具有抗氧化、抑菌、抗炎、降血糖等多种活性[7]。桑葚能抑制自由基对人体的损伤,并促进人体产生抗氧化应激反应[8]。而在桑葚抗氧化性能中酚类物质起决定性作用,主要包括酚酸、类黄酮、花色苷等[6,8]。
目前,对酚类物质的提取多集中于通过有机溶剂浸提和超声波辅助法,再考察温度、pH和光照对其稳定性的影响[9−10],而对于结构和组成鉴定较少,高效液相色谱与质谱联用法(LC-MS)可快速分析酚类物质组成[11],有助于深入研究其特征成分与抗氧化活性之间的关联[12]。
桑葚发酵是微生物代谢的过程,酵母菌将糖转化为醇类、酯类以及其它代谢物,乳酸菌将产生酸类和酶,这些代谢物对桑葚饮料的感官品质有很大的影响[13−14],同时还能提高功能活性。孙白虎[13]研究乳酸菌发酵桑葚汁的抗氧化能力时发现,发酵能提高酚类物质的含量,并提高抗氧化能力。在过去的几十年里,转录组学、蛋白质组学和代谢组学技术已经被应用许多研究领域中[15]。利用代谢组学技术为差异代谢物的代谢途径和目标活性物质的研究提供了新的思路[16]。本研究旨在探究桑葚发酵前后酚类的抗氧化性能,利用非靶向代谢组学分析找到桑葚发酵前后酚类的差异代谢物,探究其组成变化及涉及的主要代谢通路,进而探索通过发酵技术对桑葚酚类代谢途径中代谢物的影响,为桑葚产品开发提供新的思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
桑葚 黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市甘南县甘南林场提供的龙桑一号(Morus abla L.cv. Longsang 1);从桑葚酵素体系中分离得到酵母菌与乳酸菌 黑龙江大学生物工程专业实验室提供,经生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司鉴定为毕赤酵母菌(Pichia kudriavzevii,保藏号CGMCC 22027)和融合魏斯氏乳酸菌(Weissella confusa,保藏号CGMCC 22028);氯化钾、乙酸钠、抗坏血酸、无水乙醇 分析纯,中国天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;大孔树脂AB-8 非极性,中国天津市光复科技发展有限公司;乙腈 色谱纯,美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;甲酸、甲酸铵 色谱纯,中国江苏默克生命科学有限公司。
SB-5200DT超声清洗仪 中国宁波新艺超声设备有限公司;Vanquish超高效液相系统 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;Q Exactive Focus质谱检测器 配有电喷雾离子源(ESI)及Proteowizard数据处理系统,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;Biofuge 22R高速冷冻离心机 美国Beckman公司;HB-10旋转蒸发仪 德国IKA。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 桑葚发酵饮料制备
桑葚饮料按照本课题组前期优化方案制备[17],桑葚(Morus abla L.cv. Longsang 1)解冻洗净,在100 mL纯净水中添加30 g桑葚和10 g糖配制成桑葚饮料,榨汁混合后进行灭菌(80 ℃ 15 min)。将活化后的毕赤酵母菌(Pichia kudriavzevii)以8%接种量接种到桑葚饮料中,在30 ℃下发酵29 h后,再将融合魏斯式乳酸菌(Weissella confusa)以4%接种量接种继续发酵29.5 h,以未接菌的桑葚饮料为对照,发酵结束后过滤、巴氏灭菌,将其在4 ℃下保藏。设定发酵前桑葚饮料对照组(UF),发酵后桑葚饮料组(PW)进行以下分析。
1.2.2 酚类物质提取纯化
将50 g桑葚饮料置于烧杯中,按1:6的料液比加入80%的乙醇溶液,40 ℃超声40 min,6000 r/min离心15 min,将上清液在45 ℃旋转蒸发后冷冻干燥,得到酚类粗提物。再利用AB-8大孔树脂纯化,设置粗提物的上样浓度为1 mg/mL、洗脱液为pH3的60%乙醇,洗脱流速为1 mL/min,收集洗脱液经45 ℃旋转蒸发后冷冻干燥,参照Wang等[18]的方法,测得最后多酚含量为634.14±12.92 mg/g,用作后续实验。
1.2.3 酚类抗氧化能力测定
设置酚类和VC溶液浓度分别是0.01、0.2、0.4、0.8、1 mg/mL,参考GBT 39100-2020对DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力进行测定,参考文献进行酚类OH自由基清除能力[19]、总还原能力测定[20]。
1.2.4 酚类物质组成分析
1.2.4.1 高效液相色谱与质谱联用样品前处理
参照刘莹[21]的方法,取适量酚类物质于2 mL 离心管中;加入400 µL甲醇溶液(−20 ℃保存),涡旋混合1 min;13400×g 4 ℃离心10 min,取全部上清液,转移至新的2 mL离心管中,浓缩干燥;准确加入150 µL 80%甲醇水配制的2-氯-L-苯丙氨酸(0.0004%)溶液(4 ℃保存)复溶样品,取上清液用0.22 μm膜过滤,滤液转入到检测瓶中,待用。
1.2.4.2 高效液相色谱与质谱联用分析条件
参照刘莹[21]的方法,色谱条件:采用ACQUITY UPLC® HSS T3(2.1 mm×150 mm,1.8 µm)色谱柱,柱温为40 ℃,进样量2 μL,流速为0.25 mL/min。正离子模式:流动相为0.1%甲酸乙腈(C)和0.1%甲酸水(D),梯度洗脱程序为:0~1 min,2% C;1~9 min,2%~50% C;9~12 min,50%~98% C;12~13.5 min,98% C;13.5~14 min,98%~2% C;14~20 min,2% C。负离子模式:流动相为乙腈(A)和5 mol/L甲酸铵水(B),梯度洗脱程序为:0~1 min,2% A;1~9 min,2%~50% A;9~12 min,50%~98% A;12~13.5 min,98% A;13.5~14 min,98%~2% A;14~17 min,2% A。质谱条件:利用电喷雾离子源(ESI),在正负离子模式下分别采集数据。正负离子喷雾电压分别为3.50和−2.50 kV,鞘气流速30 arb,辅助气流速10 arb。毛细管温度325 ℃,以分辨率70000进行一级全扫描,一级离子扫描范围m/z 81~1000,并采用HCD进行二级裂解,碰撞电压为30%,二级分辨率为17500,采集信号前3离子进行碎裂,同时采用动态排除去除无必要的MS/MS信息。将分子离子进行碎裂,检测获得的分子离子碎片信息进行定性分析。
1.3 数据处理
利用Origin 2018版软件进行方差分析,P<0.05表示差异显著。LC-MS数据通过Proteowizard软件包(v3.0.8789)中MS Convert工具将原始质谱下机文件转换为mzXML文件格式,采用R XCMS软件包对数据进行处理。通过Simca软件将所得代谢物峰面积数据进行PCA分析,将二级质谱数据结合BioDeepDB、mzCloud在线数据库比对酚类物质的质核比和保留时间进行鉴定分析。将酚类差异代谢物结合KEGG数据库进行相关代谢通路分析。通过微生信平台将酚类差异物质的峰面积及四种抗氧化指标进行相关性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 酚类物质抗氧化能力分析
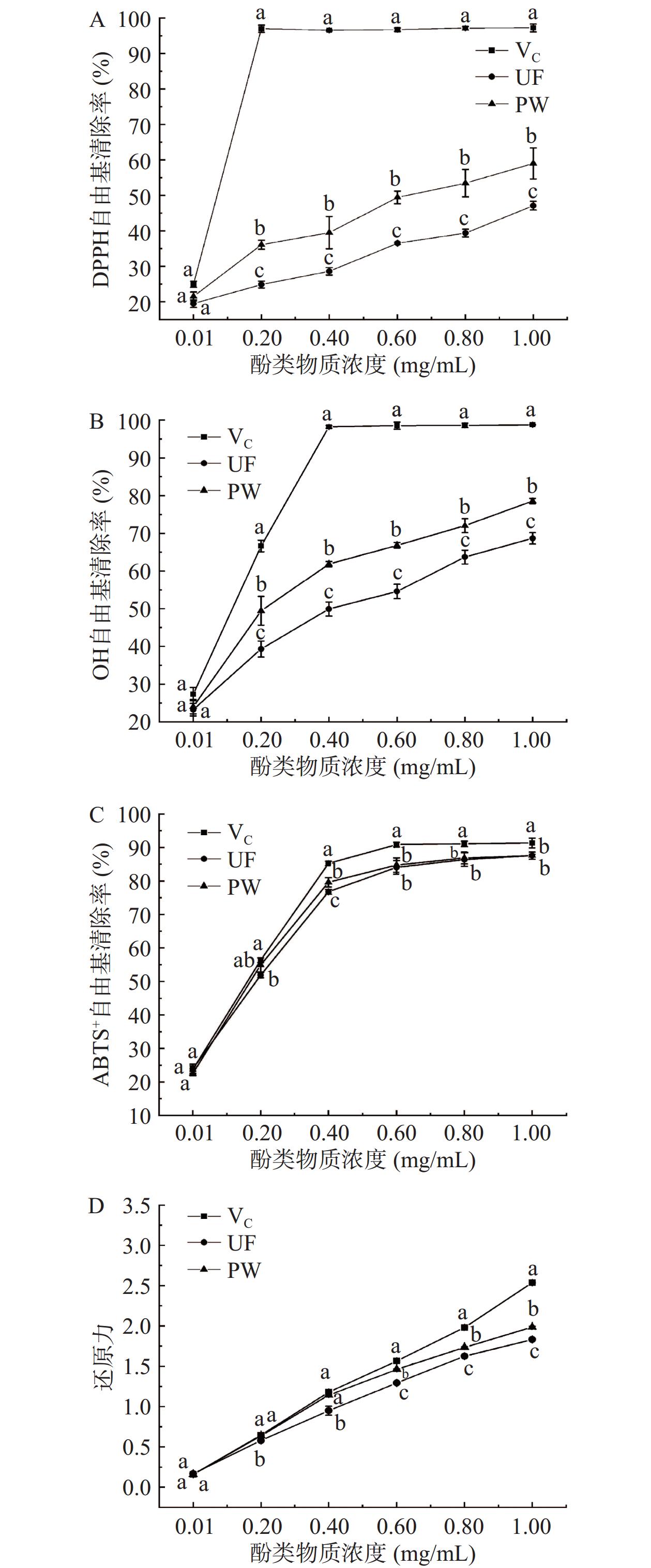
在发酵过程中,由于微生物水解作用会影响桑葚发酵饮料的抗氧化活性,因此利用多种方法同时评价其抗氧化能力(图1)。
自由基是指含有未配对电子的游离分子和离子,其在生物体内参与氧化还原反应,对机体产生氧化损伤[22]。在酚类物质的抗氧化能力研究中,大多数都体现出对自由基的清除能力和总还原力[23−24]。其中清除自由基的能力是由于缺乏自由基电子,使自由基与酚羟基反应,形成更稳定的自由基半醌结构,从而减少自由基的氧化[25]。本研究中发酵前后酚类物质均对DPPH、OH、ABTS+自由基存在一定清除作用,且抗氧化能力均随浓度的增大呈上升趋势。当酚类物质浓度为1 mg/mL时,UF的DPPH自由基清除率为45.97%±2.23%,PW的清除率为59.01%±3.59%;OH自由基清除率UF为68.68%±1.23%,PW为78.55%±0.57%,ABTS+自由基清除率UF为87.55%±0.87%,PW为87.56%±0.33%,VC为91.31%±1.19%。发酵后较发酵前饮料的酚类物质对DPPH自由基和OH自由基清除率显著增高(P<0.05),ABTS+自由基清除率与VC相似。总还原能力中发酵后酚类物质抗氧化能力与VC更接近。范金波等[26]研究发现,蓝莓与黑加仑中1 mg/mL多酚物质对DPPH自由基清除率低于10%,而桑葚中1 mg/mL多酚物质对OH自由基清除率低于20%,该结果低于本实验中同一浓度下酚类物质的抗氧化性能指标,表明该实验中提取的酚类物质抗氧化活性更强。
2.2 主成分分析(PCA)
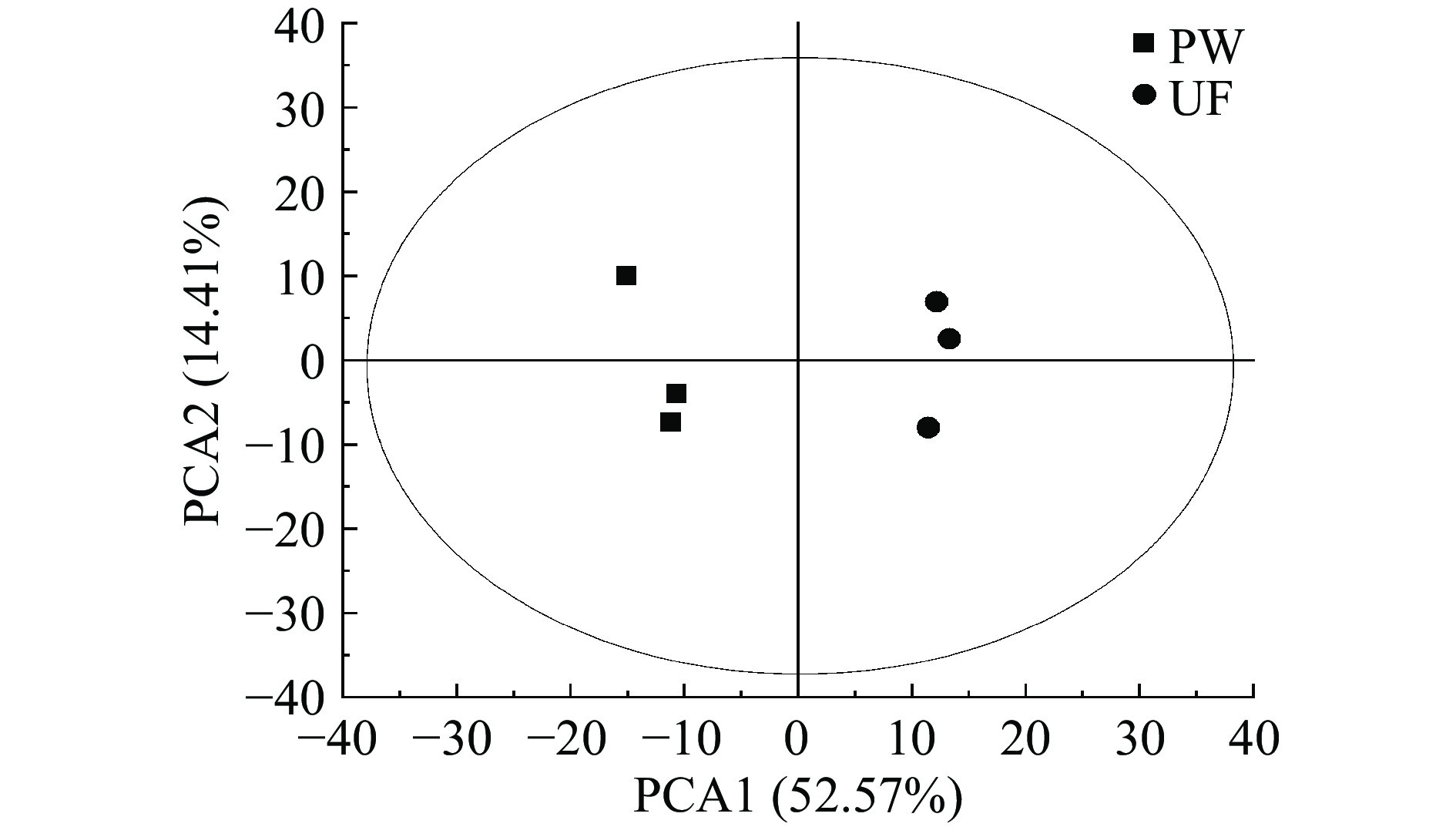
为了将不同组别在代谢物积累上的差异辨别出来,采用主成分分析方法(PCA)对样品进行分类,便于掌握发酵桑葚前后酚类物质代谢物的整体情况。以样品在第一主成分(PC1)和第二主成分(PC2)形成的平面上投影得分值为空间坐标,可以直接地反映样品间的相似性。
由图2可知,发酵前后的酚类物质平行样比较集中,证明组内差异较小,具有良好的稳定性和重复性。而PW与UF间得到了明显的分离。PC1和PC2总贡献率为66.98%。该模型的交叉验证主要参考R2X等参数,R2X是模型的可解释度,R2X=0.671,大于0.5证明模型较好。结果表明,不同组别间的代谢物差异较大,可以有效分离,该结果能用来研究发酵前后桑葚酚类的代谢物差异。
2.3 发酵前后桑葚酚类差异代谢物筛选及分析
P值作为判定发酵前后酚类物质差异代谢物的重要指标,将t检验的P<0.05的代谢物作为筛选标准,得到酚类差异代谢物鉴定分析结果如表1所示。本实验比较发酵前后桑葚酚类物质,共鉴定出46种差异代谢物,包括3种花色苷类、10种酚酸类、18种黄酮类、15种其它酚类物质,其中26种上调,20种下调。
表 1 差异代谢物定性分析结果Table 1. Qualitative analysis of differential metabolites种类 序号 中文名称 质核比 保留
时间(s)P值 峰面积(mAU·min) 变化趋势 发酵前 发酵后 花
色
苷1 矢车菊素3-O-(6-O-丙二酰基-β-D-葡萄糖苷) 535.11 523.8 0.0038** 7930053.9 18027413.7 ↑ 2 矢车菊素3-葡萄糖苷 449.11 469.2 0.0018** 56075864.9 18612678.5 ↓ 3 矢车菊素3-(6-咖啡酰基)葡萄糖苷 611.16 352.5 0.0001** 6422528.6 18155704.5 ↑ 酚
酸1 3,4-二羟基苯乙酸 167.04 94.1 0.0001** 993500.7 133945.3 ↓ 2 香草扁桃酸 198.19 619.7 0.0128* 4009956.1 7479375.0 ↑ 3 反式阿魏酸 193.05 338.3 0.0009** 18285684.9 46320238.3 ↑ 4 芥子酸 207.07 382.7 0.0470* 97829002.5 120284458.1 ↑ 5 羟基苯基乳酸 182.05 144.8 0.0041** 742694.9 460844.5 ↓ 6 没食子酸 169.01 84.4 0.0001** 40291778.2 1476319.7 ↓ 7 5-羟基吲哚乙酸 190.05 297.4 0.0385* 21562887.0 34204296.6 ↑ 8 3-脱氢莽草酸 171.03 79.9 0.0003** 2941927.3 393490.7 ↓ 9 3,4-二羟基氢化肉桂酸 181.05 376.5 0.0014** 6992926.3 19471374.3 ↑ 10 3-羟基苯甲酸 138.03 118.1 0.0091** 1494778.2 950463.8 ↓ 类
黄
酮1 槲皮素4',7-二葡糖苷 607.13 291.5 0.0265* 377377.0 32925.2 ↓ 2 扁蓄苷 434.08 268.7 0.0466* 398195.2 260119.5 ↓ 3 芹菜素4'-O-葡萄糖 433.13 570.7 0.0010** 21441.5 782002.2 ↑ 4 槲皮素3-阿拉伯糖苷 433.08 323.8 0.0036** 1551899.3 574427.4 ↓ 5 甘草苷 417.12 97.4 0.0068** 6587036.3 21715.7 ↓ 6 橙皮素 303.09 518.1 0.0067** 12066316.0 15235765.0 ↑ 7 圣草酚 287.06 558.1 0.0024** 1861810.3 3545255.3 ↑ 8 樱花亭 285.08 777.9 0.0001** 582132.0 2749706.0 ↑ 9 5,7-二甲氧基黄酮 281.08 756.1 0.0001** 266555.1 5480145.7 ↑ 10 木犀草碱 271.06 657.8 0.0008** 1406236.7 3855778.0 ↑ 11 (2S)-甘草苷元 271.06 657.8 0.0001** 98419.7 443456.5 ↑ 12 杨梅素 301.03 599.1 0.0017** 13408274.7 905696.5 ↓ 13 麦芽酚 125.02 89.6 0.0001** 1296137.2 70320241.2 ↑ 14 木犀草素7-葡萄糖 448.10 367.4 0.0250* 21923326.1 30530199.6 ↑ 15 刺芒柄花素 267.20 784.2 0.0352* 21939142.2 1353502.9 ↓ 16 生物素A 283.17 849.6 0.0481* 1135990.6 14194629.8 ↑ 17 芹菜素 269.05 642.7 0.0001** 17184700.5 549561.4 ↓ 18 5,7-白杨素 253.05 735.2 0.0007** 1204465.3 2391814.4 ↑ 其
它1 N-阿魏酰基-1,4-丁二胺 265.15 380.0 0.0001** 17410922.0 287392.8 ↓ 2 芥子醇 209.08 697.7 0.0051** 22323439.0 40979686.0 ↑ 3 4-羟基苯乙烯 119.05 307.4 0.0001** 5369199.0 27089465.0 ↑ 4 4-羟基苯乙醛 136.06 348.1 0.0001** 10017509.0 3149718.0 ↓ 5 3-羟基苯甲醛 123.04 470.9 0.0081** 9526250.0 11071953.0 ↑ 6 3,4-二羟基苯基乙醛 152.06 268.7 0.0026** 92090296.0 1496601.0 ↓ 7 芥子碱 293.16 739.5 0.0001** 10366329.0 116000000.0 ↑ 8 血清素 159.09 362.6 0.0001** 2898634.0 1151910.0 ↓ 9 2,6-二甲氧基苯酚 155.07 655.6 0.0001** 5844268.0 14428558.0 ↑ 10 1-萘酚 145.06 486.6 0.0003** 4583512.0 9913822.0 ↑ 11 (-)-香芹酚 153.13 473.5 0.0193* 8745552.0 10540312.0 ↑ 12 辣椒素 286.18 765.2 0.0001** 42662.9 1518102.0 ↑ 13 (Z)-白藜芦醇 227.08 88.6 0.0011** 11281908.0 4383068.0 ↓ 14 间甲酚 107.05 160.6 0.0002** 693982.2 401547.9 ↓ 15 4-甲基儿茶酚 123.05 98.5 0.0012** 2071516.0 1159673.0 ↓ 注:变化趋势中,“↑”是经发酵后上调物质,“↓”是经发酵后下调物质;*差异显著(P<0.05),**差异极显著(P<0.01),表2同。 发酵后较发酵前上调花色苷2种、酚酸5种、类黄酮11种、其它酚类8种;下调花色苷1种、酚酸5种、类黄酮7种、其它酚类7种。由上述对比可知,桑葚发酵后上调花色苷、类黄酮及其它酚类物质个数较下调多,进而证实发酵过程中丰富了酚类物质,提高生物活性能力。将发酵前与发酵后酚类物质中上调和下调的峰面积分别相加,可得发酵后总花色苷减少,类黄酮、酚酸及其它酚类物质增加。发酵后显著上调的包括:矢车菊素3-(6-O-丙二酰基-β-D-葡萄糖苷)、矢车菊素3-(6-咖啡酰基)、香草扁桃酸、反式阿魏酸、芹菜素4'-O-葡萄糖、圣草酚、芥子醇、3-羟基苯甲醛和1-萘酚等;下调的包括:3-羟基苯甲酸、槲皮素4',7-二葡糖苷和杨梅素等酚类物质。Kwaw等[27]通过植物乳杆菌、嗜酸乳杆菌和副干酪乳杆菌发酵桑葚,采用LC-MS鉴定其中酚类物质,共有3种花色苷、5种类黄酮和11种酚酸物质,该结果较本实验鉴定酚类物质数量较少,说明本实验所用桑葚中酚类物质更丰富。
2.4 酚类差异代谢物的代谢通路分析
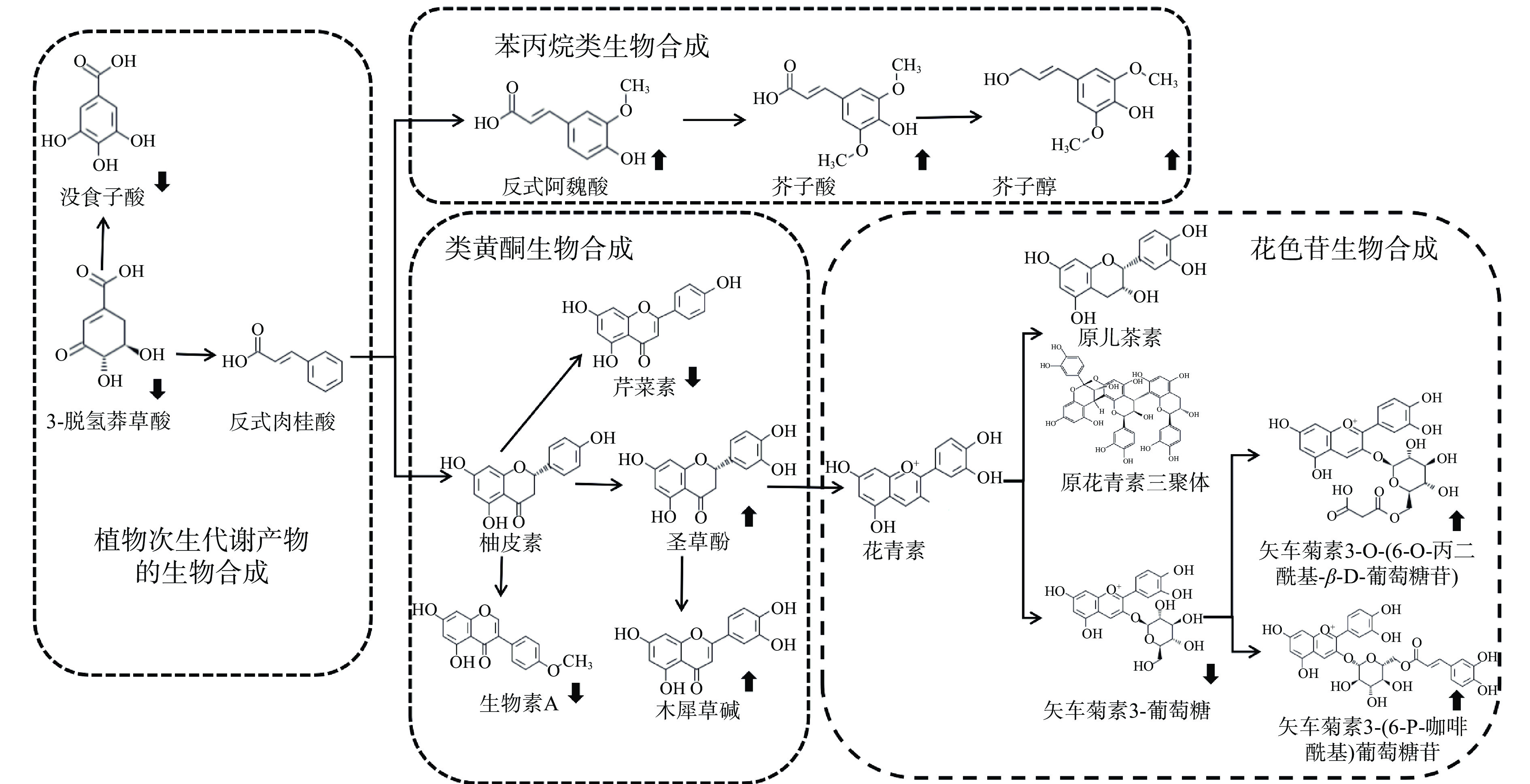
代谢通路分析是阐明不同样品之间代谢变化机制的重要工具。基于KEGG数据库,分析了酚类物质所参与的代谢途径。在整个发酵中共鉴定了4个相关代谢通路,分别是植物次生代谢产物的生物合成、苯丙烷类生物合成、类黄酮生物合成、花色苷生物合成。以植物中酚类相关代谢途径为指导,参考有关文献并结合上述代谢物及代谢通路,绘制桑葚饮料中酚类物质代谢途径如图3[28−32]。结果表明,经发酵后的桑葚饮料通过植物次生代谢产物的生物合成途径下调了没食子酸的表达量,生成反式肉桂酸,经苯丙烷类生物合成途径上调反式阿魏酸、芥子酸和芥子醇的表达量,以提高酚酸类物质的含量。同时经过类黄酮生物合成途径上调圣草酚和木犀草碱等类黄酮类物质,进一步通过花色苷合成途径上调矢车菊素的衍生物。
2.5 酚类差异代谢物与抗氧化能力相关性分析
桑葚的抗氧化能力被认为与其具有抗氧化功能的活性物质有关,如花色苷、酚酸、类黄酮等多酚类物质。因此,将发酵前后桑葚酚类差异代谢物含量与抗氧化能力之间进行相关性分析(表2)。结果表明,其中与DPPH和OH自由基清除率呈正相关的均有27种,占总酚类物质的58.70%;与ABTS+自由基清除率呈正相关的共有11种,占总酚类物质的23.91%,与还原力呈正相关的有20种,占总酚类物质的43.48%。因此推断58.70%、58.70%、23.91%和43.48%的酚类物质依次对DPPH、OH、ABTS+自由基清除能力及还原力具有贡献作用。其中芥子碱与DPPH自由基清除能力相关系数最高;矢车菊素3-O-(6-O-丙二酰基-β-D-葡萄糖苷)与OH自由基清除能力正相关系数最高;N-阿魏酰基-1,4-丁二胺与还原力相关系数最高;生物素A对ABTS+自由基清除能力正相关系数最高。将所得数据进行统计学分析,发现发酵后酚类物质对DPPH自由基、OH自由基、还原力与发酵前具有差异极显著分别有12个、38个和37个,而对ABTS+的作用中发酵前后酚类物质均差异不显著(P>0.05),这表明发酵前后酚类物质的组成变化将会影响不同的抗氧化能力指标。通过比较四大类酚类物质中与四种抗氧化指标呈正相关的个数占该大类中总个数的百分比,结果可得四种酚类物质对抗氧化活性贡献率的大小顺序是花色苷>类黄酮>其它>酚酸。
表 2 酚类差异代谢物与抗氧化能力之间相关因子Table 2. Correlation factors between phenolic differential metabolites and antioxidant capacity种类 序号 中文名 DPPH OH ABTS+ 还原力 花色苷 1 矢车菊素 3-O-(6-O-丙二酰基-β-D-葡萄糖苷) 0.90878* 0.98624** 0.00001 −0.99582** 2 矢车菊素 3-葡萄糖苷 −0.90878* −0.98143** 0.00001 0.99582** 3 矢车菊素 3-(6-咖啡基)葡萄糖苷 0.88743* 0.97954** −0.02921 −0.99147** 酚酸 1 3,4-二羟基苯乙酸 −0.90632* −0.99061** −0.19335 0.97187** 2 香草扁桃酸 0.83988* 0.93449** −0.19204 −0.91938** 3 反式阿魏酸 0.91663* 0.95247** −0.15324 −0.97348** 4 芥子酸 0.50862 0.77957 −0.29947 −0.77030 5 羟基苯基乳酸 −0.98012** −0.96073** −0.20443 0.97259** 6 没食子酸 −0.92135** −0.99480** −0.14385 0.98984** 7 5-羟基吲哚乙酸 0.66997 0.80957 −0.50138 −0.82340* 8 3-脱氢莽草酸 −0.92173** −0.99406** −0.11694 0.99476** 9 3,4-二羟基氢化肉桂酸 0.84295* 0.94802** −0.09223 −0.97074** 10 3-羟基苯甲酸 −0.96483** −0.91825** −0.35504 0.94081** 类黄酮 1 槲皮素4’,7-二葡糖苷 −0.96390** −0.89187* −0.34072 0.92982** 2 扁蓄苷 −0.91754** −0.85857* −0.09250 0.85637* 3 芹菜素4'-O-葡萄糖 0.78482 0.92352** 0.08970 −0.93557** 4 槲皮素3-阿拉伯糖苷 −0.92116** −0.95360** −0.34962 0.94891** 5 甘草苷 −0.88882* −0.97715** 0.06209 0.98670** 6 橙皮素 0.43285 0.71030 −0.18543 −0.71260 7 圣草酚 0.89155* 0.92484** −0.20599 −0.95853** 8 樱花亭 0.87325* 0.98143** −0.04497 −0.98384** 9 5,7-二甲氧基黄酮 0.81166* 0.96205** 0.01947 −0.96434** 10 木犀草碱 0.81626* 0.94189** −0.03201 −0.96177** 11 (2S)-甘草苷元 0.90868* 0.96683** −0.02001 −0.98842** 12 杨梅素 −0.87578* −0.98172** −0.22992 0.96519** 13 麦芽酚 0.81059 0.96500** 0.00517 −0.96418** 14 木犀草素7-葡萄糖 0.77696 0.83057* −0.44205 −0.85729* 15 刺芒柄花素 −0.91603* −0.82383* 0.09212 0.87574* 16 生物素A 0.84997* 0.96222** 0.12845 −0.97175** 17 芹菜素 −0.94136** −0.99043** −0.08836 0.99811** 18 5,7-白杨素 0.87541* 0.95412** −0.15034 −0.97315 其它 1 N-阿魏酰基-1,4-丁二胺 −0.91754** −0.98572** −0.04432 0.99835** 2 芥子醇 0.75689 0.91517* −0.21056 −0.92652** 3 4-羟基苯乙烯 0.87469* 0.97525** −0.00622 −0.98720** 4 4-羟基苯乙醛 −0.88429* −0.96770** 0.03707 0.98736** 5 3-羟基苯甲醛 0.73048 0.88531* −0.14505 −0.89043* 6 3,4-二羟基苯基乙醛 −0.90284* −0.98926** −0.01395 0.99363** 7 芥子碱 0.91170* 0.98352** −0.04437 −0.99341** 8 血清素 −0.91977** −0.99623** −0.10116 0.99049** 9 2,6-二甲氧基苯酚 0.89086* 0.96871** −0.01544 −0.99039** 10 1-萘酚 0.82636* 0.94691** 0.04114 −0.96459** 11 (-)-香芹酚 0.73305 0.80200 −0.23375 −0.86512* 12 辣椒素 0.87559* 0.98073** −0.01014 −0.98913** 13 (Z)-白藜芦醇 −0.95771** −0.98305** −0.06978 0.99550** 14 间甲酚 −0.93294** −0.98421** −0.15504 0.99517** 15 4-甲基儿茶酚 −0.91586* −0.97257** −0.08699 0.97122** 将酚类差异物质和抗氧化能力之间相关性与上述发酵前后酚类物质含量变化进行结合分析,结果表明经发酵后的上调的酚类物质与DPPH和OH自由基清除能力之间呈正相关,与还原力呈负相关,且与ABTS+自由基清除能力相关性不明显。
3. 讨论与结论
已有研究发现,在玫瑰果酒发酵期间,酚类化合物,特别是黄酮苷、异黄酮类、黄酮醇和花色苷等是鉴定出最丰富的差异代谢物,这些物质对果酒的品质起主要作用[33]。本研究以发酵前后桑葚酚类物质为研究对象,选择了与酚类相关的次生代谢物进行代谢组学分析,结果表明,从中共筛选出酚类差异代谢物共有46种,包括花色苷、类黄酮、酚酸类及其它酚类物质。
短时间的发酵会使酚类物质增加,这是因为高浓度的糖促进了酚类在发酵液中的溶解,以及酵母发酵过程产生的有机酸与酚类反应,产生酚酸类化合物,这些酚酸在不断地聚合,并在氧化反应过程中与花色苷及酒石酸结合,进而生成对羟基类肉桂酸和酚类[33]。本实验中酚类物质经过发酵后含量增加,证实了上述结果。
有研究表明蜂蜜中含有15种常见酚类,包括没食子酸、白杨素和绿原酸等,具有较好的DPPH自由基清除能力[34]。邵郅胜等[20]研究欧李叶片不同生长阶段中酚类含量与抗氧化性时发现,酚类主要包括总酚、总黄酮、原花青素、花色苷等,且酚类物质含量与抗氧化活性之间存在协同关系,抗氧化活性随多酚含量增加而提高。本研究结果表明发酵后酚类物质含量增加,且抗氧化性能增加,这与上述研究结果一致。
酚类的生物合成是植物次生代谢中的重要分支,虽然不同物种中酚类的种类和含量不同,但基本合成途径相似且已基本清楚[35]。已有研究表明,基于非靶向代谢组学技术比较发酵前后果蔬酚类的组成变化,发现乳酸菌发酵影响了酚类物质的组成[36]。本研究结合KEGG数据库和代谢组学结果,证明发酵前后酚类组成变化存在差异,而这种差异源于发酵菌种对于桑葚饮料的介导作用,进而提高抗氧化能力。因本实验通过LC-MS技术进行酚类提取物测定,因此在二级质谱数据中还含有氨基酸及有机酸。结合微生物代谢途径可知,经发酵后总氨基酸与有机酸的含量下降,这是因为氨基酸一部分为菌株提供氮源,另一部分代谢成有机酸,而有机酸可以经过三羧酸循环等代谢途径彻底被氧化生成CO2和H2O,同时为发酵过程中的菌株提供能量。该结果将为通过发酵技术提高桑葚饮料酚类物质的抗氧化能力提供理论支持。而本实验中选用的两株菌均是来自于桑葚酵素体系中筛选得到的,下一步将研究桑葚饮料发酵后酚类物质在体内抗氧化功能的变化及机制。
综上,发酵前后桑葚酚类差异代谢物共有4大类46种,包括3种花色苷类、10种酚酸类、18种类黄酮及15种其它酚类。发酵后花色苷类含量下降,而酚酸、类黄酮和其它酚类含量均有所提高。酚类主要涉及4个代谢途径,包括植物次生代谢产物的生物合成、苯丙烷类生物合成、类黄酮生物合成和花色苷生物合成。发酵前后桑葚酚类均对DPPH、OH、ABTS+自由基有显著清除能力,同时有一定的还原力,且PW的4种抗氧化能力指标均高于UF。酚类差异代谢物中芥子碱、矢车菊素3-O-(6-O-丙二酰基-β-D-葡萄糖苷)、生物素A和N-阿魏酰基-1,4-丁二胺依次与DPPH、OH、ABTS+的自由基清除能力和还原力的正相关系数最大。
-
表 1 差异代谢物定性分析结果
Table 1 Qualitative analysis of differential metabolites
种类 序号 中文名称 质核比 保留
时间(s)P值 峰面积(mAU·min) 变化趋势 发酵前 发酵后 花
色
苷1 矢车菊素3-O-(6-O-丙二酰基-β-D-葡萄糖苷) 535.11 523.8 0.0038** 7930053.9 18027413.7 ↑ 2 矢车菊素3-葡萄糖苷 449.11 469.2 0.0018** 56075864.9 18612678.5 ↓ 3 矢车菊素3-(6-咖啡酰基)葡萄糖苷 611.16 352.5 0.0001** 6422528.6 18155704.5 ↑ 酚
酸1 3,4-二羟基苯乙酸 167.04 94.1 0.0001** 993500.7 133945.3 ↓ 2 香草扁桃酸 198.19 619.7 0.0128* 4009956.1 7479375.0 ↑ 3 反式阿魏酸 193.05 338.3 0.0009** 18285684.9 46320238.3 ↑ 4 芥子酸 207.07 382.7 0.0470* 97829002.5 120284458.1 ↑ 5 羟基苯基乳酸 182.05 144.8 0.0041** 742694.9 460844.5 ↓ 6 没食子酸 169.01 84.4 0.0001** 40291778.2 1476319.7 ↓ 7 5-羟基吲哚乙酸 190.05 297.4 0.0385* 21562887.0 34204296.6 ↑ 8 3-脱氢莽草酸 171.03 79.9 0.0003** 2941927.3 393490.7 ↓ 9 3,4-二羟基氢化肉桂酸 181.05 376.5 0.0014** 6992926.3 19471374.3 ↑ 10 3-羟基苯甲酸 138.03 118.1 0.0091** 1494778.2 950463.8 ↓ 类
黄
酮1 槲皮素4',7-二葡糖苷 607.13 291.5 0.0265* 377377.0 32925.2 ↓ 2 扁蓄苷 434.08 268.7 0.0466* 398195.2 260119.5 ↓ 3 芹菜素4'-O-葡萄糖 433.13 570.7 0.0010** 21441.5 782002.2 ↑ 4 槲皮素3-阿拉伯糖苷 433.08 323.8 0.0036** 1551899.3 574427.4 ↓ 5 甘草苷 417.12 97.4 0.0068** 6587036.3 21715.7 ↓ 6 橙皮素 303.09 518.1 0.0067** 12066316.0 15235765.0 ↑ 7 圣草酚 287.06 558.1 0.0024** 1861810.3 3545255.3 ↑ 8 樱花亭 285.08 777.9 0.0001** 582132.0 2749706.0 ↑ 9 5,7-二甲氧基黄酮 281.08 756.1 0.0001** 266555.1 5480145.7 ↑ 10 木犀草碱 271.06 657.8 0.0008** 1406236.7 3855778.0 ↑ 11 (2S)-甘草苷元 271.06 657.8 0.0001** 98419.7 443456.5 ↑ 12 杨梅素 301.03 599.1 0.0017** 13408274.7 905696.5 ↓ 13 麦芽酚 125.02 89.6 0.0001** 1296137.2 70320241.2 ↑ 14 木犀草素7-葡萄糖 448.10 367.4 0.0250* 21923326.1 30530199.6 ↑ 15 刺芒柄花素 267.20 784.2 0.0352* 21939142.2 1353502.9 ↓ 16 生物素A 283.17 849.6 0.0481* 1135990.6 14194629.8 ↑ 17 芹菜素 269.05 642.7 0.0001** 17184700.5 549561.4 ↓ 18 5,7-白杨素 253.05 735.2 0.0007** 1204465.3 2391814.4 ↑ 其
它1 N-阿魏酰基-1,4-丁二胺 265.15 380.0 0.0001** 17410922.0 287392.8 ↓ 2 芥子醇 209.08 697.7 0.0051** 22323439.0 40979686.0 ↑ 3 4-羟基苯乙烯 119.05 307.4 0.0001** 5369199.0 27089465.0 ↑ 4 4-羟基苯乙醛 136.06 348.1 0.0001** 10017509.0 3149718.0 ↓ 5 3-羟基苯甲醛 123.04 470.9 0.0081** 9526250.0 11071953.0 ↑ 6 3,4-二羟基苯基乙醛 152.06 268.7 0.0026** 92090296.0 1496601.0 ↓ 7 芥子碱 293.16 739.5 0.0001** 10366329.0 116000000.0 ↑ 8 血清素 159.09 362.6 0.0001** 2898634.0 1151910.0 ↓ 9 2,6-二甲氧基苯酚 155.07 655.6 0.0001** 5844268.0 14428558.0 ↑ 10 1-萘酚 145.06 486.6 0.0003** 4583512.0 9913822.0 ↑ 11 (-)-香芹酚 153.13 473.5 0.0193* 8745552.0 10540312.0 ↑ 12 辣椒素 286.18 765.2 0.0001** 42662.9 1518102.0 ↑ 13 (Z)-白藜芦醇 227.08 88.6 0.0011** 11281908.0 4383068.0 ↓ 14 间甲酚 107.05 160.6 0.0002** 693982.2 401547.9 ↓ 15 4-甲基儿茶酚 123.05 98.5 0.0012** 2071516.0 1159673.0 ↓ 注:变化趋势中,“↑”是经发酵后上调物质,“↓”是经发酵后下调物质;*差异显著(P<0.05),**差异极显著(P<0.01),表2同。 表 2 酚类差异代谢物与抗氧化能力之间相关因子
Table 2 Correlation factors between phenolic differential metabolites and antioxidant capacity
种类 序号 中文名 DPPH OH ABTS+ 还原力 花色苷 1 矢车菊素 3-O-(6-O-丙二酰基-β-D-葡萄糖苷) 0.90878* 0.98624** 0.00001 −0.99582** 2 矢车菊素 3-葡萄糖苷 −0.90878* −0.98143** 0.00001 0.99582** 3 矢车菊素 3-(6-咖啡基)葡萄糖苷 0.88743* 0.97954** −0.02921 −0.99147** 酚酸 1 3,4-二羟基苯乙酸 −0.90632* −0.99061** −0.19335 0.97187** 2 香草扁桃酸 0.83988* 0.93449** −0.19204 −0.91938** 3 反式阿魏酸 0.91663* 0.95247** −0.15324 −0.97348** 4 芥子酸 0.50862 0.77957 −0.29947 −0.77030 5 羟基苯基乳酸 −0.98012** −0.96073** −0.20443 0.97259** 6 没食子酸 −0.92135** −0.99480** −0.14385 0.98984** 7 5-羟基吲哚乙酸 0.66997 0.80957 −0.50138 −0.82340* 8 3-脱氢莽草酸 −0.92173** −0.99406** −0.11694 0.99476** 9 3,4-二羟基氢化肉桂酸 0.84295* 0.94802** −0.09223 −0.97074** 10 3-羟基苯甲酸 −0.96483** −0.91825** −0.35504 0.94081** 类黄酮 1 槲皮素4’,7-二葡糖苷 −0.96390** −0.89187* −0.34072 0.92982** 2 扁蓄苷 −0.91754** −0.85857* −0.09250 0.85637* 3 芹菜素4'-O-葡萄糖 0.78482 0.92352** 0.08970 −0.93557** 4 槲皮素3-阿拉伯糖苷 −0.92116** −0.95360** −0.34962 0.94891** 5 甘草苷 −0.88882* −0.97715** 0.06209 0.98670** 6 橙皮素 0.43285 0.71030 −0.18543 −0.71260 7 圣草酚 0.89155* 0.92484** −0.20599 −0.95853** 8 樱花亭 0.87325* 0.98143** −0.04497 −0.98384** 9 5,7-二甲氧基黄酮 0.81166* 0.96205** 0.01947 −0.96434** 10 木犀草碱 0.81626* 0.94189** −0.03201 −0.96177** 11 (2S)-甘草苷元 0.90868* 0.96683** −0.02001 −0.98842** 12 杨梅素 −0.87578* −0.98172** −0.22992 0.96519** 13 麦芽酚 0.81059 0.96500** 0.00517 −0.96418** 14 木犀草素7-葡萄糖 0.77696 0.83057* −0.44205 −0.85729* 15 刺芒柄花素 −0.91603* −0.82383* 0.09212 0.87574* 16 生物素A 0.84997* 0.96222** 0.12845 −0.97175** 17 芹菜素 −0.94136** −0.99043** −0.08836 0.99811** 18 5,7-白杨素 0.87541* 0.95412** −0.15034 −0.97315 其它 1 N-阿魏酰基-1,4-丁二胺 −0.91754** −0.98572** −0.04432 0.99835** 2 芥子醇 0.75689 0.91517* −0.21056 −0.92652** 3 4-羟基苯乙烯 0.87469* 0.97525** −0.00622 −0.98720** 4 4-羟基苯乙醛 −0.88429* −0.96770** 0.03707 0.98736** 5 3-羟基苯甲醛 0.73048 0.88531* −0.14505 −0.89043* 6 3,4-二羟基苯基乙醛 −0.90284* −0.98926** −0.01395 0.99363** 7 芥子碱 0.91170* 0.98352** −0.04437 −0.99341** 8 血清素 −0.91977** −0.99623** −0.10116 0.99049** 9 2,6-二甲氧基苯酚 0.89086* 0.96871** −0.01544 −0.99039** 10 1-萘酚 0.82636* 0.94691** 0.04114 −0.96459** 11 (-)-香芹酚 0.73305 0.80200 −0.23375 −0.86512* 12 辣椒素 0.87559* 0.98073** −0.01014 −0.98913** 13 (Z)-白藜芦醇 −0.95771** −0.98305** −0.06978 0.99550** 14 间甲酚 −0.93294** −0.98421** −0.15504 0.99517** 15 4-甲基儿茶酚 −0.91586* −0.97257** −0.08699 0.97122** -
[1] 王艺霖. 桑葚干红酿造工艺及功能性成分的变化研究[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2017. [WANG Y L. Research on the brewing technology of mulberry dry red wine and the changes of functional components[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017. WANG Y L. Research on the brewing technology of mulberry dry red wine and the changes of functional components[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.
[2] LEE J S, KIM Y R, SONG I G, et al. Cyanidin-3-glucoside isolated from mulberry fruit protects pancreatic β-cells against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis[J]. Internationan Journal of Molecular Medicine,2015,35(2):405−412. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.2013
[3] REN X X, SUN Y, GUO Q F, et al. Ameliorating effect of the total flavonoids of Morus nigra L. on prediabetic mice based on regulation of inflammation and insulin sensitization[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(39):12484−12501. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c04970
[4] 杨婉媛, 陈晓维, 罗文珊, 等. 桑葚的功效成分及加工利用研究进展[J]. 中国果菜,2022,42(12):48−53,84. [YANG W Y, CHEN X W, LUO W S, et al. Research progress of functional components and processing and utilization of mulberry[J]. China Fruit & Vegetable,2022,42(12):48−53,84. YANG W Y, CHEN X W, LUO W S, et al . Research progress of functional components and processing and utilization of mulberry[J]. China Fruit & Vegetable,2022 ,42 (12 ):48 −53,84 .[5] D’URSO G, MES J J, MONTORO P, et al. Identification of bioactive phytochemicals in mulberries[J]. Metabolites,2020,10(1):7.
[6] 董盼豪. 桑葚酚类物质研究及全组分果汁研发[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2021. [DONG P H. Study on phenolic compounds of mulberry fruit and whole-component juice development[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2021. DONG P H. Study on phenolic compounds of mulberry fruit and whole-component juice development[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2021.
[7] RAHMAN M M, RAHAMAN M S, ISLAM M R, et al. Role of phenolic compounds in human disease:Current knowledge and future prospects[J]. Molecules,2022,27(1):233.
[8] JIANG D Q, GUO Y, XU D H, et al. Antioxidant and anti-fatigue effects of anthocyanins of mulberry juice purification (MJP) and mulberry marc purification (MMP) from different varieties mulberry fruit in China[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2013,59:1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.05.023
[9] YANG J F, OU X Q, ZHANG X X, et al. Effect of different solvents on the measurement of phenolics and the antioxidant activity of mulberry ( Morus atropurpurea Roxb.) with accelerated solvent extraction[J]. Journal of Food Science,2017,82(1-3):605−612.
[10] LI F H, YAN H M, LI W Z, et al. A comparative study of the effects of ultrafiltration membranes and storage on phytochemical and color properties of mulberry juice[J]. Journal of Food Science,2019,84(12):3565−3572. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14935
[11] 朱雯绮. 茶叶籽油内源性酚类化合物鉴定及抗氧化相互作用研究[D]. 江苏:扬州大学, 2021. [ZHU W Q. Identification and antioxidant interaction of endogenous phenolic compounds in tea seed oil[D]. Jiangsu:Yangzhou University. ZHU W Q. Identification and antioxidant interaction of endogenous phenolic compounds in tea seed oil[D]. Jiangsu: Yangzhou University.
[12] 姚佳, 白泽慧, 李驰, 等. 马铃薯中的酚类物质及其生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(7):160−166. [YAO J, BAI Z H, LI C, et al. Research progress on phenols and their biological activities in potatoes[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(7):160−166. YAO J, BAI Z H, LI C, et al . Research progress on phenols and their biological activities in potatoes[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022 ,47 (7 ):160 −166 .[13] 孙百虎. 不同乳酸菌对发酵桑葚汁酚类物质含量及抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(1):92−97. [SUN B H. Effects of different lactic acid bacteria on phenolic contents and antioxidant capacity of fermented mulberry juice[J]. China Brewing,2022,41(1):92−97. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.01.016 SUN B H . Effects of different lactic acid bacteria on phenolic contents and antioxidant capacity of fermented mulberry juice[J]. China Brewing,2022 ,41 (1 ):92 −97 . doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.01.016[14] 时蒙蒙, 周鹤, 依力扎提·热依木江, 等. 果汁与果浆发酵工艺和酵母品种对桑葚酒酚类和有机酸的影响[J]. 新疆农业大学学报,2022,45(1):31−37. [SHI M M, ZHOU H, ELIZATI R, et al. Effects of juice and pulp fermentation process and yeast varieties on phenolic and organic acids in mulberry wine[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University,2022,45(1):31−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8614.2022.01.005 SHI M M, ZHOU H, ELIZATI R, et al . Effects of juice and pulp fermentation process and yeast varieties on phenolic and organic acids in mulberry wine[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University,2022 ,45 (1 ):31 −37 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8614.2022.01.005[15] GARCÍA C J, GIL M I, TOMAS-BARBERAN F A. LC-MS untargeted metabolomics reveals early biomarkers to predict browning of fresh-cut lettuce[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2018,146:9−17. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.07.011
[16] 王伟华, 韩占江. 新疆慕萨莱思酒天然活性成分的代谢组学研究进展—以原花青素为例[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2013,4(6):1810−1814. [WANG W H, HAN Z J. Research progress on metabonomics method of natural active ingredients in Musalais wine in Xinjiang—taking procyanidins for example[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2013,4(6):1810−1814. WANG W H, HAN Z J . Research progress on metabonomics method of natural active ingredients in Musalais wine in Xinjiang—taking procyanidins for example[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2013 ,4 (6 ):1810 −1814 .[17] 韩晓云, 刘莹, 闫福超, 等. 一种适于寒地桑葚发酵饮料混合菌株及其应用:中国, 113416674B[P]. 2022-11-15. [HAN X Y, LIU Y, YAN F C, et al. A mixed strain suitable for cold mulberry fermented beverages and its application, China, 113416674B[P]. 2022-11-15. HAN X Y, LIU Y, YAN F C, et al. A mixed strain suitable for cold mulberry fermented beverages and its application, China, 113416674B[P]. 2022-11-15.
[18] WANG Z J, LIN Y M, LI T T, et al. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant capacities of mulberry ( Morus atropurpurea Roxb.) juices from different cultivars[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2019,22(1):1340−1352. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2019.1646272
[19] 全国生化检测标准化技术委员会. GB/T 39100-2020 多肽抗氧化性测定 DPPH和ABTS法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2020. [National technical committee for standardization of biochemical testing. GB/T 39100-2020. Determination of antioxidant activity for polypeptides—DPPH and ABTS methods[S]. Beijing:Standaros Press of China, 2020. National technical committee for standardization of biochemical testing. GB/T 39100-2020. Determination of antioxidant activity for polypeptides—DPPH and ABTS methods[S]. Beijing: Standaros Press of China, 2020.
[20] 邵郅胜, 杨波, 朱成, 等. 不同生长阶段欧李叶片酚类物质含量及其抗氧化性[J]. 西北植物学报,2022,42(10):1720−1727. [SHAO Z S, YANG B, ZHU C, et al. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity in leaves of Cerasus humilis at different growth stages[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2022,42(10):1720−1727. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2022.10.1720 SHAO Z S, YANG B, ZHU C, et al . Phenolic content and antioxidant activity in leaves of Cerasus humilis at different growth stages[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica,2022 ,42 (10 ):1720 −1727 . doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2022.10.1720[21] 刘莹. 桑葚发酵菌种筛选及其发酵效果评价[D]. 哈尔滨:黑龙江大学, 2022. [LIU Y. Screening of mulberry fermentation strains and evaluation of their fermentation effects[D]. Harbin:Heilongjiang University, 2022. LIU Y. Screening of mulberry fermentation strains and evaluation of their fermentation effects[D]. Harbin: Heilongjiang University, 2022.
[22] 武乾英. 酸浆多酚抗炎活性的研究[D]. 太原:山西农业大学, 2017. [WU Q Y. Anti-inflammatory effect of polyphenols from Physalis alkekengi fruit[D]. Taiyuan:Shanxi Agricultural University, 2017. WU Q Y. Anti-inflammatory effect of polyphenols from Physalis alkekengi fruit[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2017.
[23] IMRAN M, KHAN H, SHAH M, et al. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of certain Morus species[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B,2010,11(12):973−980. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1000173
[24] OSZMIAŃSKI J, NOWICKA P, TELESZKO M, et al. Analysis of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in wild blackberry fruits[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2015,16(7):14540−14553.
[25] 王俏, 邹阳, 钟耕, 等. 多酚类单体物质抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2011,32(1):137−140,145. [WANG Q, ZOU Y, ZHONG G, et al. Study on the antioxidant activities of polyphenol monomer[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011,32(1):137−140,145. WANG Q, ZOU Y, ZHONG G, et al . Study on the antioxidant activities of polyphenol monomer[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011 ,32 (1 ):137 −140,145 .[26] 范金波, 蔡茜彤, 冯叙桥, 等. 桑葚、蓝莓、黑加仑中多酚类物质的抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2015,41(2):157−162. [FAN J B, CAI X T, FENG X Q, et al. Antioxidant activity of polyphenols in mulberry, blueberry, and blackcurrant[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2015,41(2):157−162. FAN J B, CAI X T, FENG X Q, et al . Antioxidant activity of polyphenols in mulberry, blueberry, and blackcurrant[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2015 ,41 (2 ):157 −162 .[27] KWAW E, MA Y K, TCHABO W, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus strains on phenolic profile, color attributes and antioxidant activities of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,250:148−154. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.009
[28] 刘飞, 郭美丽. 花色苷生物代谢途径中相关酶的研究进展[J]. 药学服务与研究,2011,11(1):34−38. [LIU F, GUO M L. Advances in research on enzymes related to the biometabolism pathway of anthocyanins[J]. Pharmaceutical Care and Research,2011,11(1):34−38. LIU F, GUO M L . Advances in research on enzymes related to the biometabolism pathway of anthocyanins[J]. Pharmaceutical Care and Research,2011 ,11 (1 ):34 −38 .[29] 李菊, 李玉梅, 苟亚妮, 等. 酚酸类物质代谢及其化感效应研究进展[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2019(8):175−182. [LI J, LI Y M, GOU Y N, et al. Research progress in phenolic acid metabolism and allelopathic effect[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2019(8):175−182. LI J, LI Y M, GOU Y N, et al . Research progress in phenolic acid metabolism and allelopathic effect[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2019 (8 ):175 −182 .[30] 尚军, 吴旺泽, 马永贵. 植物苯丙烷代谢途径[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2022,38(11):1467−1476. [SHANG J, WU W Z, MA Y G. Phenylpropanoid metabolism pathway in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2022,38(11):1467−1476. SHANG J, WU W Z, MA Y G . Phenylpropanoid metabolism pathway in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2022 ,38 (11 ):1467 −1476 .[31] 刘立新, 梁鸣早. 植物次生代谢作用及其产物概述[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,2009(5):82−86. [LIU L X, LIANG M Z. Overview of plant secondary metabolism and its products[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China,2009(5):82−86. LIU L X, LIANG M Z . Overview of plant secondary metabolism and its products[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China,2009 (5 ):82 −86 .[32] 单杨, 刘娟, 王振, 等. 生物合成柑橘类黄酮研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(11):1−13. [SHAN Y, LIU J, WANG Z, et al. Research progress on the biosynthesis of flavonoids in citrus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institude of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(11):1−13. SHAN Y, LIU J, WANG Z, et al . Research progress on the biosynthesis of flavonoids in citrus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institude of Food Science and Technology,2019 ,19 (11 ):1 −13 .[33] SETFORD P C, JEFFERY D W, GRBIN P R, et al. Factors affecting extraction and evolution of phenolic compounds during red wine maceration and the role of process modelling[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2017,69:106−117.
[34] 曾林晖, 熊增星, 周晓晴, 等. 蜂蜜中酚类物质的测定及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业,2023,44(3):287−292. [ZENG L H, XIONG Z X, ZHOU X Q, et al. Determination of phenolic compounds in honey and its antioxidant activities[J]. The Food Industry,2023,44(3):287−292. ZENG L H, XIONG Z X, ZHOU X Q, et al . Determination of phenolic compounds in honey and its antioxidant activities[J]. The Food Industry,2023 ,44 (3 ):287 −292 .[35] 华晓雨, 陶爽, 孙盛楠, 等. 植物次生代谢产物-酚类化合物的研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报,2017,33(12):22−29. [HUA X Y, TAO S, SUN S N, et al. Research progress on phenolic compounds of plant secondary metabolites[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2017,33(12):22−29. HUA X Y, TAO S, SUN S N, et al . Research progress on phenolic compounds of plant secondary metabolites[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2017 ,33 (12 ):22 −29 .[36] 唐富豪, 滕建文, 韦保耀, 等. 基于非靶向代谢组学评价传统发酵对客家酸芥菜酚类化合物组成的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(8):128−133. [TANG F H, TENG J W, WEI B Y, et al. Evaluation of the influence of traditional fermentation on the composition of phenolic compounds in Hakka pickled mustard greens based on non-targeted metabolomic[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(8):128−133. TANG F H, TENG J W, WEI B Y, et al . Evaluation of the influence of traditional fermentation on the composition of phenolic compounds in Hakka pickled mustard greens based on non-targeted metabolomic[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021 ,47 (8 ):128 −133 .





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
