Residue Analysis and Exposure Assessment of Methylsiloxane Oligomers in Fried Chicken and French Fries
-
摘要: 快餐中的油炸食品深受广大消费者喜爱,但随着对挥发性甲基硅氧烷的安全性的日益关注,消泡剂聚二甲基硅氧烷 (Polydimethylsiloxanes,PDMS)中甲基硅氧烷的低聚物单体在油炸食品中的残留亟需研究。本研究采用QuEChERS-气相色谱-串联质谱(GC-MS/MS)建立了炸鸡和油炸薯条中甲基硅氧烷低聚物的高效灵敏的检测方法。利用该法对从快餐店购买的33种炸鸡和30种炸薯条进行了分析并采用点评估方法进行了初步的暴露评估。结果检出八甲基环四硅氧烷(Octamethyl cyclotetrasiloxane,D4)~六甲基二硅氧烷 (Hexamethyldisiloxane,D18)和十甲基四硅氧烷(Decamethyl tetrasiloxane,L4)~三十甲基十四硅氧烷(Triaconta methyltetradecasiloxane,L14),并且甲基硅氧烷低聚物在炸鸡中的总含量中位数(514.61 ng·g−1)高于炸薯条(83.4 ng·g−1)。炸鸡和炸薯条中甲基硅氧烷(分子量<1000)的每日估计最高摄入量(Estimated daily intake,EDI)分别为164.94 ng·kg−1·d−1和13.09 ng·kg−1·d−1,低于PDMS的每日允许摄入量(Acceptable daily intake,ADI)0.8 mg·kg−1·d−1。一些小分子的甲基硅氧烷低聚物如D4~十六甲基环六硅氧烷(Dodecamethyl cyclohexasiloxane,D6)等在长期低剂量摄入以及富集作用下,对人体的潜在危害还需进一步的关注。本研究为炸食快餐中甲基硅氧烷低聚物残留的安全性评价以及后续的深入研究提供了科学依据。Abstract: The fried food in fast food is deeply loved by consumers. However, with the increasing concern about the safety of volatile methylsiloxanes, the residue of oligomer monomer of methylsiloxanes from defoamer PDMS in fried food needs to be studied urgently. In this study, an efficient and sensitive method for the determination of methylsiloxane oligomers in fried chicken and French fries was established using QuEChERS-gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). A total of 33 fried chickens and 30 French fries purchased from fast food restaurants were analyzed and a preliminary exposure assessment using a point assessment method was carried out. The results showed that octamethyl cyclotetrasiloxane (D4)~hexamethyldisiloxane (D18) and decamethyl tetrasiloxane (L4)~triaconta methyltetradecasiloxane (L14) were detected, and the median total content of methylsiloxane oligomers in fried chicken (514.61 ng·g−1) was higher than that in French fries (83.4 ng·g−1). The estimated daily intake (EDI) of methylsiloxanes (molecular weight <1000) in fried chicken and French fries was 164.94 ng·kg−1·d−1 and 13.09 ng·kg−1·d−1, respectively, which was lower than the PDMS acceptable daily intake (ADI) (0.8 mg·kg−1·d−1). However, the potential hazards of some volatile methylsiloxanes such as D4~dodecamethyl cyclohexasiloxane (D6) need to be further investigated after long-term low dose intake and enrichment. This study provides a scientific basis for the safety evaluation and subsequent in-depth study of methylsiloxanes residues in fried food fast food.
-
Keywords:
- fried food /
- methylsiloxanes /
- detection /
- exposure assessment
-
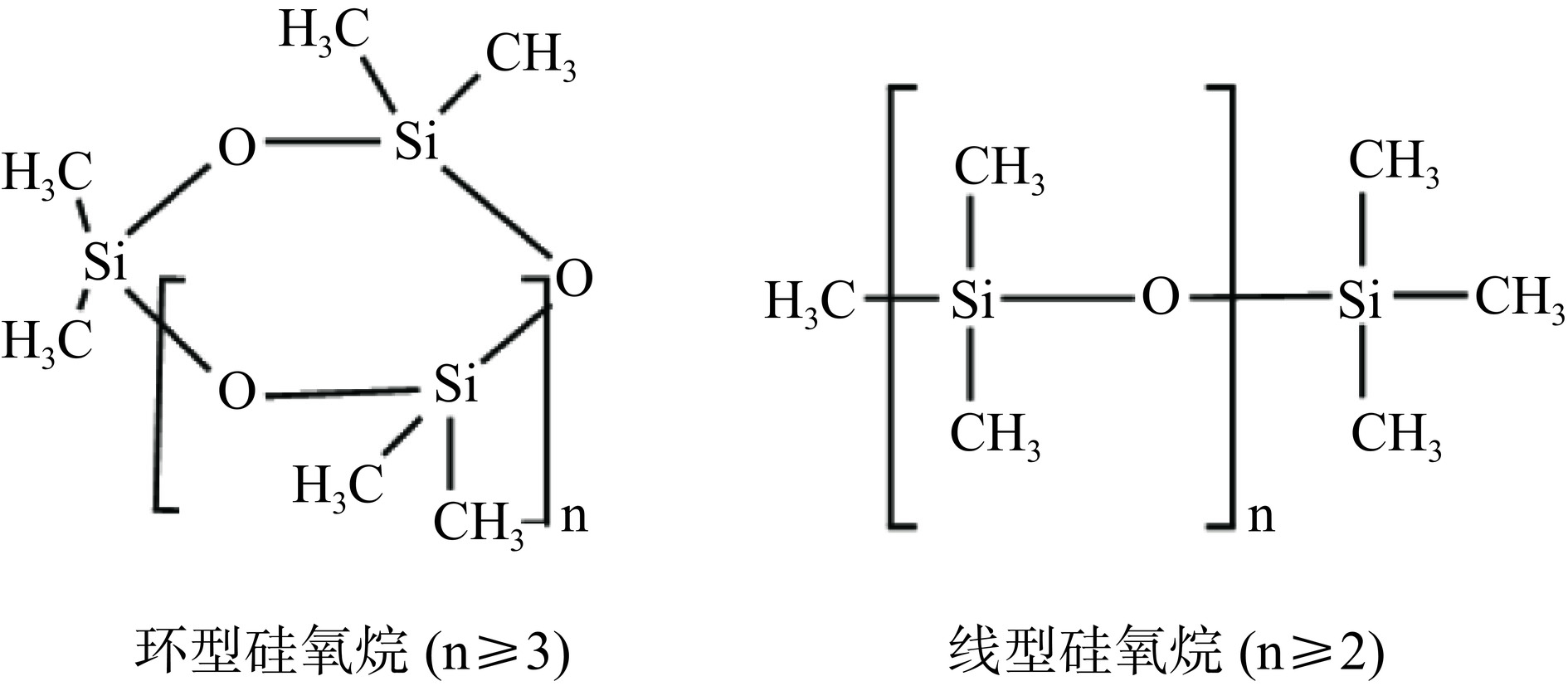
甲基硅氧烷依据主链结构可分为线型甲基硅氧烷(Linear methylsiloxane,LMS)和环型甲基硅氧烷(Cyclic methylsiloxane,CMS)两大类,通常分别用Ln和Dn表示(n为硅原子数),其结构通式见图1[1−2]。挥发性甲基硅氧烷(Volatile methylsiloxanes,VMS)为一些小分子易挥发的甲基硅氧烷,如六甲基环三硅氧烷(Hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane,D3)~D6,L4~L6。近代毒理学研究表明,一些VMS对水生生物及哺乳动物的多种生理过程有直接或间接的毒性作用[3−5],且具有生物体富集性[6−9]和雌激素效应[10],在食品中的安全性也已引起关注[11]。
聚二甲基硅氧烷(Polydimethylsiloxane,PDMS)常用在炸油中,它具有抗氧化性、稳定性、减少脂肪的热劣化作用,并可作用消泡剂。据《中国食品添加剂使用卫生标准》(GB2760-2014)[12]规定,PDMS最大允许添加量为0.1~0.3 g·kg−1。PDMS的暂行每日允许摄入量(Acceptable daily intake,ADI)为0~0.8 mg·kg−1·d−1[13] 。PDMS在食品中被检出的研究已有报道。如研究人员用原子吸收光谱法[14−15]、电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer,IPC-OES)[16−17]分析了食用油及炸油样品中PDMS;吴惠勤等[18]采用裂解气相色谱-质谱法(Pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,PGC-MS)对不同品牌炸鸡翅中PDMS的裂解产物进行了定性和定量分析,结果表明食用油及炸制食品中PDMS均有检出。我国也已出台《动植物油脂中聚二甲基硅氧烷的测定》[19],其测试方法为,试样中的聚二甲基硅氧烷经航空煤油提取,采用IPC-OES外标法测定试样提取液中的总硅含量。
快餐中的油炸食品深受广大消费者喜爱,但随着全球对甲基硅氧烷(尤其是VMS)安全性的日益关注,PDMS作为炸油中常用的消泡剂,在高温使用后,其小分子的低聚物单体如D4、D5、D6(分子量<1000),在生物进程中具有毒性作用,具有潜在的致癌风险[20],其在油炸食品中的分析研究及暴露风险也亟需审视,而已有的国家标准(测总硅含量)并不能满足低聚物单体的研究需要,且炸制快餐中甲基硅氧烷低聚物单体残留的相关研究欠缺。因此,本研究建立并利用QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS方法对市售33种炸鸡和30种炸薯条中甲基硅氧烷低聚物单体残留进行了检测分析和初步的暴露评估,以期为快餐店油炸食品中甲基硅氧烷的安全风险研究提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
样品采集 在北京市60家快餐店购买了30种炸薯条和33种炸鸡制品(包括11种鸡块、10种鸡排、4种鸡腿、3种鸡翅、3种鸡米花和2种鸡条);标准品:八甲基环四硅氧烷(D4,>98.0%)、十甲基四硅氧烷(L4,>97.0%)、十甲基环五硅氧烷(D5,>99.0%)、四(三甲硅烷氧基)硅(M4Q,97%)、十二甲基五硅氧烷(L5,97%)、十二甲基环六硅氧烷(D6,>98.0%) 日本梯希爱公司;聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS) 西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司;正己烷、乙腈、乙酸乙酯 色谱级,赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;PSA(粒径50 μm,孔径60 Å)、C18(粒径50 μm,孔径60 Å) 北京迪科马科技有限公司;氯化钠、无水硫酸镁 分析纯,北京化工厂;高纯氦气、高纯氮气 北京氧利来科技发展有限公司。
7890B-7000C气相色谱串联质谱仪、HP-5MS 色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm) 美国Agilent 公司;KQ 5200E超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;SC-3610低速离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;ME104E电子分析天平 瑞士梅特勒-托利多公司;移液枪(2.5 μL,25 μL,100 μL,1000 μL,5 mL) 德国Eppendorf公司;有机系滤膜(0.22 μm) 天津市科亿隆实验设备有限公司;ME104E电子分析天平 瑞士梅特勒-托利多公司;S2-A81绞肉机 九阳股份有限公司;2 mL样品小瓶 上海安谱公司;一次性无菌注射器(2 mL) 上海治宇医疗器械有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 混合标准液的配制
甲基硅氧烷标准工作液的配制:将VMS混标母液(D4~D6、L4、L5)10 μg/mL以及PDMS混标母液10 μg/mL逐级稀释,配制浓度为一系列浓度为0.5、1、10、50、100、200、500 ng/mL的混标溶液,内标为M4Q(终浓度为100 ng/mL),置于4 ℃冰箱中储存。
1.2.2 QuEChERS样品前处理方法
准确称取均质后的样品3.000 g(±0.001 g)于50 mL具塞离心管中,加入5 mL正己烷,剧烈涡旋10 s后,在30 ℃ 超声5 min,静置至室温。取上清液2 mL,加入200 mg MgSO4、炸鸡样品处理加入20 mg PSA(炸薯条样品处理加入10 mg PSA)、30 mg C18,剧烈涡旋1 min,4500 r/min下离心3 min,取1 mL上清液过0.22 μm有机滤膜至GC样品小瓶,待GC-MS/MS检测。
1.2.3 GC-MS/MS条件
GC条件[20]:HP-5MS色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm);载气为高纯氦气,流速1.5 mL/min;进样口温度280 ℃;升温程序为初始温度50 ℃,先以25 ℃/min升到180 ℃,再以10 ℃/min升至300 ℃(保持10 min),自动进样,进样量1 μL。MS条件:离子源温度250 ℃;四级杆温度150 ℃;电子轰击离子源(EI源);电子能量70 eV;采用多重反应监测(MRM)模式采集数据,15种硅氧烷的保留时间、离子对及碰撞电压见表1。
表 1 15种甲基硅氧烷的保留时间、离子对及碰撞电压Table 1. Retention time, ion pairs and collision voltage of 15 methylsiloxanes序号 物质 分子式 分子量 保留时间
(min)离子对及碰撞电压(eV) 离子对1 离子对2 1 八甲基环四硅氧烷D4 C8H24O4Si4 296.62 2.935 281>73 (25) 281>265 (15) 2 十甲基四硅氧烷L4 C10H30O3Si4 310.69 3.369 207>191 (20) 207>73 (40) 3 十甲基环五硅氧烷D5 C10H30O5Si5 370.77 3.895 355>267 (10) 267>251 (20) 4 十二甲基五硅氧烷L5 C12H36O4Si5 384.84 4.416 281>73 (25) 147>73 (20) 5 十二甲基环六硅氧烷D6 C12H36O6Si6 444.92 4.900 341>73 (20) 341>91 (15) 6 十四甲基六硅氧烷L6 C14H42O5Si6 458.99 5.348 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 7 十六甲基七硅氧烷L7 C16H48O6Si7 533.15 6.285 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 8 十八甲基八硅氧烷L8 C18H54O7Si8 607.30 7.346 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 9 二十甲基壬硅氧烷L9 C20H60O8Si9 681.46 8.523 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 10 二十二甲基十硅氧烷L10 C22H66O9Si10 755.61 9.764 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 11 二十四甲基十一硅氧烷L11 C24H72O10Si11 829.76 11.006 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 12 二十六甲基十二硅氧烷L12 C26H78O11Si12 903.92 12.210 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 13 二十八甲基十三硅氧烷L13 C28H84O12Si13 978.08 13.359 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 14 三十甲基十四硅氧烷L14 C30H90O13Si14 1052.23 14.444 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 15 十二甲基五硅氧烷M4Q (I.S) C12H36O4Si5 384.8393 4.103 281>73 (25) 147>73 (20) 1.2.4 炸鸡、炸薯条中甲基硅氧烷的膳食暴露评估
参考文献[21−22],采用点评估方法对炸鸡中甲基硅氧烷进行暴露量的初步评估。
EDI=C炸鸡或薯条×W炸鸡或薯条×BIOBW 式中:EDI:估计日摄入量(Estimated daily intake,EDI)(ng∙kg−1∙day−1);C炸鸡或薯条:炸鸡或薯条中VMS及PDMS的浓度(ng∙g−1);W炸鸡或薯条:每天炸鸡或薯条的摄入量(g∙day -1)[23],20~60周岁男子平均每日摄入量为5 g∙day−1;20~60周岁女子平均每日摄入量为4 g∙day−1;BIO:生物利用率,此处为1[24];BW:体重(kg)[25],20~60周岁男子,平均体重70 kg;20~60周岁女子,平均体重55 kg。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均重复3次,结果用平均值±标准差表示。本实验运用Microsoft Excel 2016进行数据处理,采用Origin 8.0绘图软件绘制图形。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 QuEChERS方法的条件优化
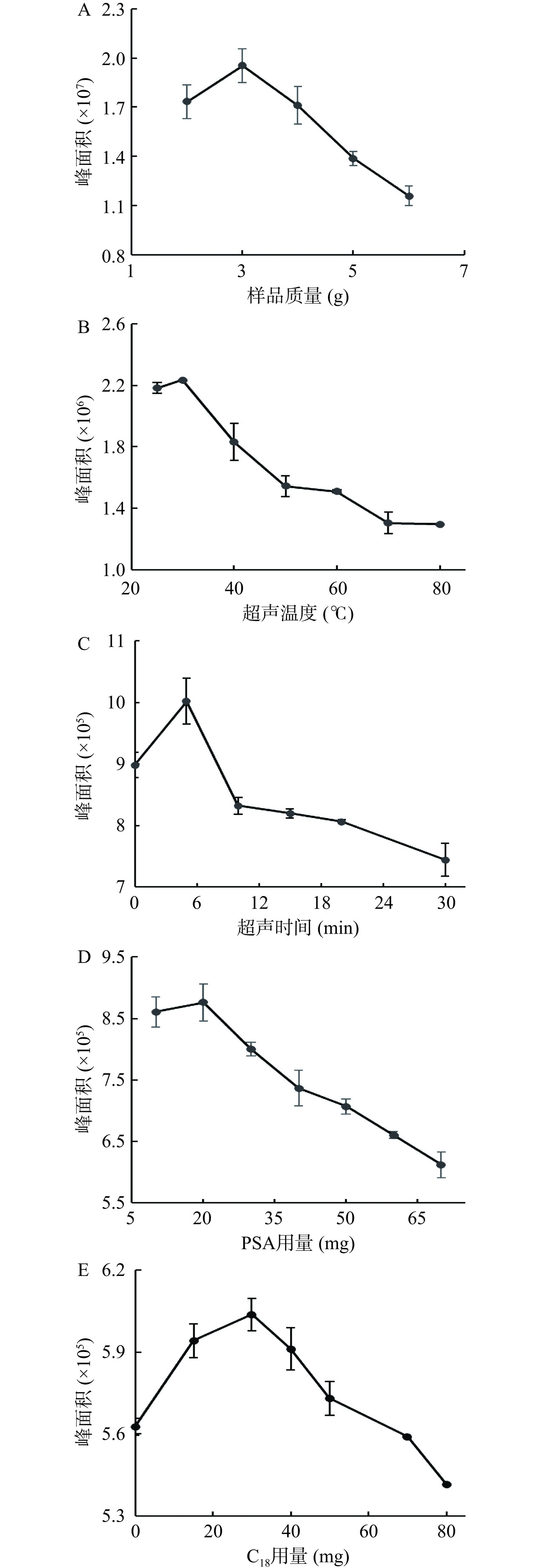
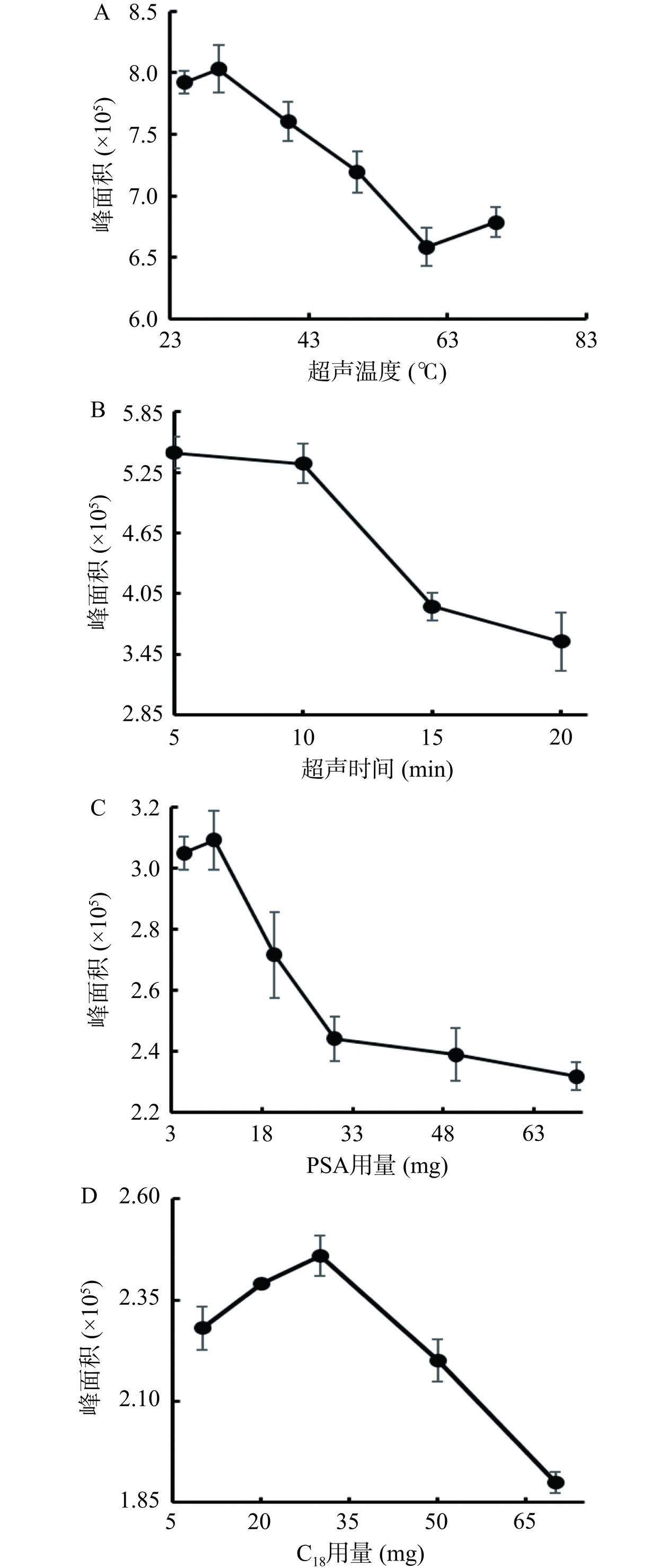
甲基硅氧烷为亲脂性化合物,在正己烷和二氯甲烷等有机溶剂中均有较好的溶解能力,并能与水相形成明显的分层。使用正己烷进行液液萃取和离心后,有机相在溶液上层,易于分液操作,因此最终选择正己烷作为萃取溶剂。采用单因素实验,在炸鸡和炸薯条样品的QuEChERS前处理方法中分别考察了样品量、超声时间、超声温度、PSA用量和C18用量对甲基硅氧烷总峰面积大小的影响(图2和图3)。
由于两种样品均为油炸食品,且炸鸡中油脂含量高于薯条,因此直接考察炸鸡的样品量。如图2A所示,炸鸡样品量在2~3 g内,甲基硅氧烷总峰面积升高,在超过3 g后,峰面积逐渐下降,推测随着料液比的增加,正己烷中硅氧烷的浓度趋于饱和,导致正己烷溶液的萃取能力下降。图2B、图3A显示,无论是炸鸡还是炸薯条样品,当超声温度低于30 ℃时,峰面积随着超声温度升高而增高,当温度大于30 ℃时,随着超声温度的升高,正己烷的萃取能力下降。由图2C、图3B可知,无论是炸鸡还是炸薯条样品,5 min后随着超声时间的延长,硅氧烷峰面积降低。这可能是由于在超声萃取前期,样品内外存在着较大的浓度差,硅氧烷迅速从样品中溶出,而硅氧烷挥发性强且在正己烷中溶解性好,在较低温度或短时间内就能达到较高的提取效果,但随着温度或时间延长,超声波产生热量和空化效应加大了对硅氧烷的挥发及结构破坏,从而导致提取率下降。
在炸鸡样品中,PSA在10~20 mg范围内,硅氧烷峰面积有所增加;但当PSA用量大于20 mg时,随着PSA用量的增加,总硅氧烷的峰面积逐渐下降,这可能是由于PSA可通过极性相互作用和弱阴离子相互作用优先吸附色素、脂肪酸类干扰物,但随着PSA量的增加可能吸附一部分甲基硅氧烷(图2D)。与炸鸡不同,薯条成分主要为淀粉类物质,且油脂成分含量较少,所以PAS的用量在10 mg时最佳(图3C),少于炸鸡样品中PSA的用量。由图2E和图3D可知,无论是炸鸡还是炸薯条样品,随着C18用量的增加,总甲基硅氧烷的峰面积先增大后减小,在30 mg出现拐点。C18可通过非极性相互作用保留弱极性的脂肪酸类、烯烃类、维生素E、甾类、色素及油脂等大分子基质干扰物,从而将吸附在基质中的目标物质释放,但随着C18用量的不断增加,C18开始吸附非极性的小分子硅氧烷,从而使得总甲基硅氧烷的峰面积降低。
最终,炸鸡和炸薯条样品的QuEChERS方法的最优条件为:样品量3 g,超声温度30 ℃,超声时间5 min,PSA 炸鸡20 mg、炸薯条10 mg,C18用量30 mg。
2.2 甲基硅氧烷的定量方法及评价
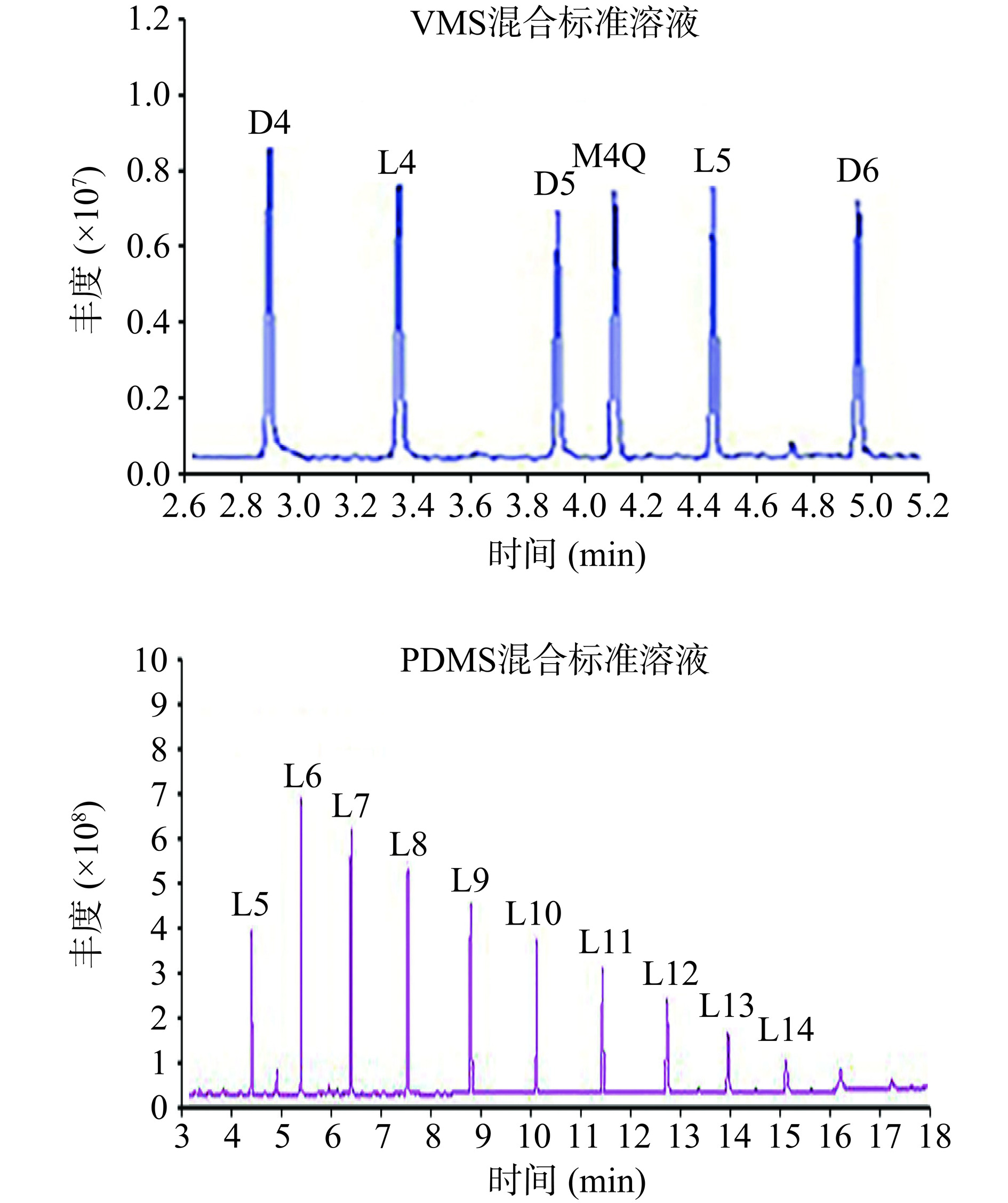
在全扫描模式下,确定甲基硅氧烷的保留时间,并得到各物质的一级质谱图,再根据一级质谱图选择相对强度较大且具有特征性的离子作为母离子[26],分别对目标物的离子对、碰撞能量(5~50 eV)、扫描时间、驻留时间等一系列参数进行了优化。采用标准品对照进行定性,VMS混标和PDMS混标的色谱图见图4。其中D4~D6、L4、L5用VMS混标(内标M4Q)进行定量。但由于无法获得L6~L14的单一标准品,而仅能购得PDMS混标,因此,参考已有文献[27−28],先利用归一化法确定PDMS混标中的LMSs(L5~L14)的百分含量(%)(表2),然后同样采用内标(M4Q)标准曲线法对L6~L14进行定量。
表 2 PDMS混合标准中L5~L14的百分含量Table 2. Percentage of L5~L14 in the PDMS mixture standard名称 L5 L6 L7 L8 L9 L10 L11 L12 L13 L14 百分含量(%) 11.63 23.46 20.26 15.31 11.12 7.47 4.73 2.89 1.96 1.17 对QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS法检测炸鸡、炸薯条中甲基硅氧烷进行仪器性能及方法学评价,如表3所示。以目标物与内标M4Q的峰面积之比为纵坐标,以相应的目标物与内标M4Q的质量浓度之比为横坐标,绘制各目标物的内标标准工作曲线。以不低于3倍信噪比(S/N≥3)确定目标物检出限(LOD),以S/N≥10确定定量下限(LOQ),结果如表3 所示。D4~L14的线性范围为0.64~1405.95 ng/mL,决定系数(R2)不低于0. 9918。D4~L14的检出限为0.17~0.54 ng/mL,定量限为0.57~1.78 ng/mL,日内精密度小于6.0%,表明仪器检测甲基硅氧烷的灵敏度及稳定性良好,所建方法能够满足定量要求。分别对炸鸡、炸薯条中14种甲基硅氧烷进行加标回收率检测及RSD 计算,3个加标水平,每个水平平行3次,按1.2进行处理并测定。14种甲基硅氧烷在炸鸡中的加标回收率为75.02%~109.86%,RSD值均小于15%(除L6为20.8%);在炸薯条中的方法回收率为75.28%~102.31%(L12~L14除外),RSD值均小于15%。该检测方法具有良好的准确度和精密度。
表 3 炸鸡和炸薯条中VMS及PDMS检测方法评价Table 3. Evaluation of detection method for VMS and PDMS in fried chicken and French fries物质 标准曲线 线性范围
(ng∙mL−1)R2 LOD
(ng∙mL−1)LOQ
(ng∙mL−1)日内精密度
(%)平均回收率(%)及精密度(%) 炸鸡1 炸薯条2 D4 y=0.6134x+0.1764 1.05~523.75 0.9963 0.44 1.46 1.09 87.13 (4.1) 93.17 (7.7) L4 y=1.8182x−0.0457 1.01~504.75 0.9998 0.17 0.57 0.22 99.68 (9.8) 89.63 (2.3) D5 y=0.7778x+0.335 1.03~516.0 0.9988 0.29 0.98 3.43 109.86 (8.7) 83.47 (3.4) L5 y=1.291x−0.1187 1.01~503.5 0.9995 0.48 1.59 0.62 89.11 (11.6) 93.67 (6.1) D6 y=0.6767x+0.7063 1.02~509.75 0.9918 0.35 1.17 5.88 92.52 (7.2) 102.31 (2.1) L6 y=0.8243x−0.0708 1.76~1405.95 0.9986 0.36 1.21 0.58 90.97 (20.8) 79.64 (14.3) L7 y=1.0237x−0.0711 1.55~1241.24 0.9977 0.33 1.11 0.38 93.98 (13.2) 79.80 (12.6) L8 y=0.8772x−0.0213 1.31~1048.71 0.9974 0.54 1.78 0.22 95.99 (13.5) 78.70 (13.3) L9 y=0.9212x−0.0041 1.12~1116.48 0.9976 0.48 1.61 0.32 94.34 (5.0) 93.47 (4.3) L10 y=0.9739x+0.0299 0.88~876.74 0.9990 0.50 1.65 0.40 97.75 (8.9) 81.38 (5.4) L11 y=0.9728x+0.0855 0.64~640.62 0.9959 0.42 1.41 0.23 93.11 (10.4) 75.28 (4.2) L12 y=1.1824x+0.1481 1.65~412.15 0.9933 0.42 1.40 0.71 81.42 (7.4) 63.63 (4.3) L13 y=1.4477x+0.1708 0.87~217.86 0.9976 0.26 0.88 0.77 75.02 (10.3) 62.09 (4.2) L14 y=1.7506x+0.1616 0.93~93.47 0.9968 0.22 0.74 1.28 76.06 (14.7) 60.13(16.5) 注:1. 炸鸡中回收率三个加标水平:40、70、100 ng/g;2. 炸薯条中回收率三个加标水平:20、50、100 ng/g。 2.3 样品中甲基硅氧烷的检出结果
炸鸡样品中VMS(D4~D6、L4和L5)的检出率为6%(D4)~100%(L4),L6~L14的检出率为27%(L7)~79%(L10)。14种甲基硅氧烷的平均含量在5.68(D4)~262.90(D6)ng∙g−1之间。炸鸡中 D6含量最高,平均值为262.9 ng∙g−1。炸薯条中14种甲基硅氧烷检出率为3%(L8)~100%(L4~L7),L8~L14几乎无检出,L4~L7检出率均为100%,D6、D5检出率>80%,平均含量在0.02(L10)~23.57(D6)ng∙g−1之间。14种甲基硅氧烷中的D6在炸薯条中含量最高,平均值为23.57 ng∙g−1。炸鸡、炸薯条中14种甲基硅氧烷检出率及含量检测结果如图5所示。
此外,还在炸鸡(薯条)中检出CMS(D7~D18),由于缺乏相应的标准品,无法准确定量,采用D6(M4Q做内标)的标准曲线对D7~D18进行了半定量分析[27]。炸鸡中CMS(D7~D18)的检出率为96.97%(D7)~100%(D11);∑CMS(D7~D18)的平均含量为438.63 ng∙g−1,最大含量为1047.59 ng∙g−1。炸薯条中CMS(D7~D18)的检出率为47%(D15)~100%(D7);∑CMS(D7~D18)的平均含量为238.07 ng∙g−1,最大含量为1570.49 ng∙g−1。炸制食品中检出聚二甲基硅氧烷早已有报道,如吴慧勤等[18]利用裂解气相色谱-质谱(PGC-MS)分析了不同品牌炸鸡翅, 结果发现炸鸡翅样品均含有聚二甲基硅氧烷,含量在 23~42 mg∙kg−1之间,高于本研究的检测结果。这说明,炸制食品中的聚二甲基硅氧烷的检出可能具有普遍性,但导致其含量差异的原因还需进一步研究。
使用Levene 法的F检验,对∑CMS(MW<1000)和∑LMS(MW<1000)在33种炸鸡和30种薯条这两类样品中的含量的差异性进行分析。在置信度为95%水平下,得出:P∑CMS(MW<1000)=0.006、P∑LMS(MW<1000)=0.000,P值均<0.05,表明在炸鸡和薯条中的∑LMS和∑CMS差异显著;且炸鸡中∑LMS和∑CMS含量均高于薯条,可能的原因是,根据相似相溶原理,较高脂肪含量的炸鸡更易吸附脂溶性的甲基硅氧烷[11]。
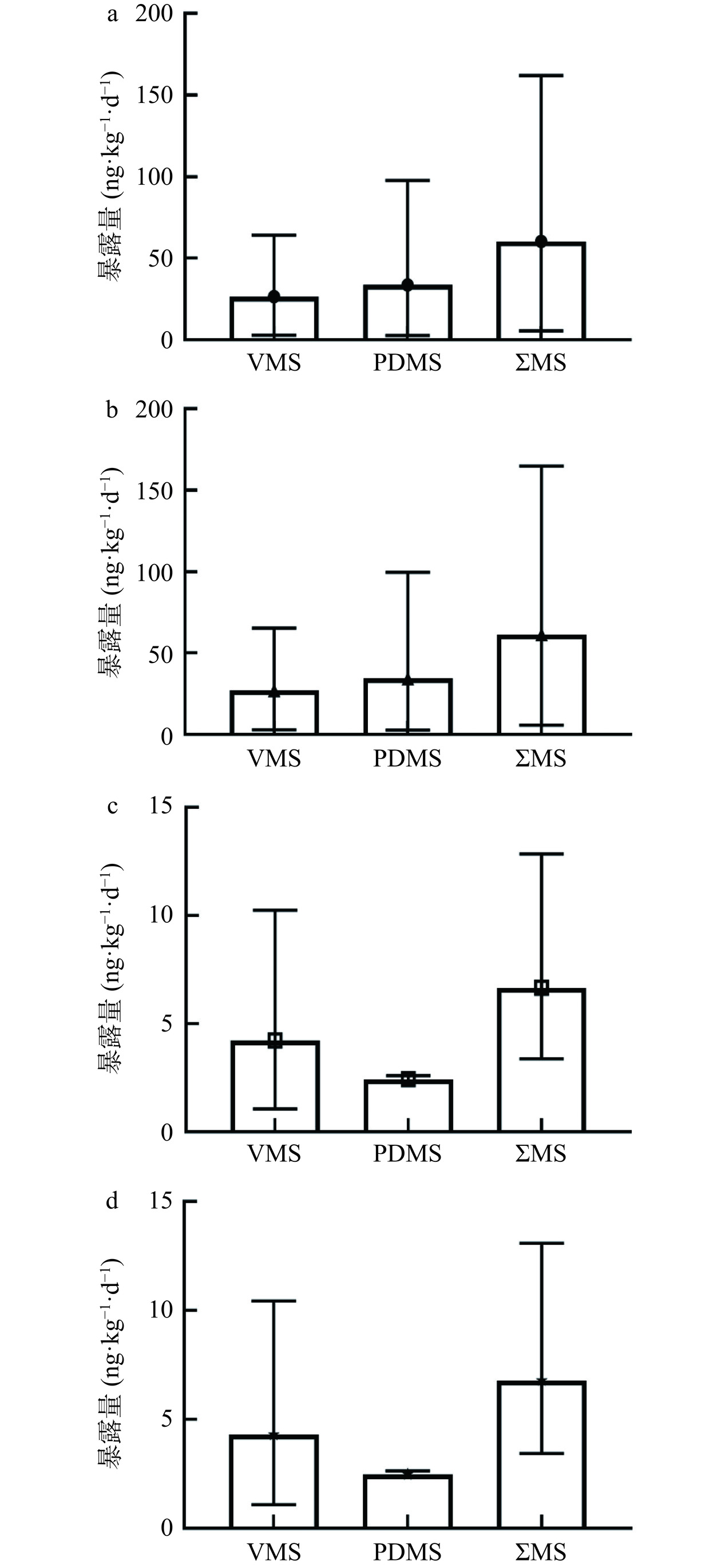
2.4 炸鸡、炸薯条中甲基硅氧烷暴露评估
根据1.2.4所述公式,计算得到炸鸡、炸薯条中14种甲基硅氧烷的初步的估计每日摄入量(Estimated daily intake,EDI),结果如图6所示。炸鸡中男性与女性ΣVMS(D4~D6、L4和L5)总体暴露量为2.88~65.38 ng·kg−1·d−1。炸鸡中男性与女性ΣMS(L4~L14,D4~D6)的总体暴露量为5.62~164.94 ng·kg−1·d−1。薯条中每日摄入量未见报道,因此采用炸鸡的数据进行暴露评估。炸薯条中∑MS(L4~L14,D4~D6)的最高暴露量为13.09 ng·kg−1·d−1。整体来看,炸鸡中甲基硅氧烷暴露量均高于炸薯条。炸鸡中男性与女性∑MS(L4~L14,D4~D6)的总体暴露量(中位数)为36.76 和37.43 ng·kg−1·d−1,高于炸薯条中男性与女性∑MS(L4~L14,D4~D6)的总体暴露量(中位数)5.96 和 6.07 ng·kg−1·d−1。女性对炸鸡与炸薯条中∑MS(L4~L14,D4~D6)的暴露量与男性基本相当。
目前对于食用油脂、水果、鸡翅等食品中PDMS的检出已有报道,此外,我国也已出台国标GB 5009.254-2016《动植物油脂中聚二甲基硅氧烷的测定》,是以测定试样提取液中的总硅进行定量。动物学实验表明,高聚合度的PDMS基本不被消化道吸收,对人体影响不大,只有低分子量(如分子量<1000)的甲基硅氧烷可能会被消化道吸收[29]。但目前,对于更易于被人体吸收的小分子(分子量<1000)的甲基硅氧烷低聚物的检测和暴露评估还较缺乏。炸鸡(薯条)中的甲基硅氧烷残留可能来源于消泡剂PDMS中的甲基硅氧烷的低聚物。已有研究显示,在高温下,高聚合的PDMS可降解成甲基硅氧烷的低聚物[30]。
如果仅考虑易于被人体吸收的分子量小于1000的甲基硅氧烷,并忽略D7~D18半定量的检测误差,则炸鸡中ΣMS(L4~L14,D4~D18)(MW<1000)暴露量为10.31~241.13 ng·kg−1·d−1,炸薯条中ΣMS(L4~L14,D4~D18)(MW<1000)暴露量为4.77~127.31 ng·kg−1·d−1。炸鸡中的ΣMS(L4~L14,D4~D18)暴露量高于薯条。女性对炸鸡中∑MS(L4~L14,D4~D18)的平均暴露量(93.34 ng·kg−1·d−1)与男性对炸鸡中∑MS(L4~L14,D4~D18)(91.67 ng·kg−1·d−1)的平均暴露量较接近。炸鸡和炸薯条中∑MS的暴露量均低于PDMS暂行ADI标准0.8 mg·kg−1·d−1[13]。由于缺乏标准品,油炸食品中甲基硅氧烷低聚物残留的研究受到限制,但小分子甲基硅氧烷的残留所导致的安全性应引起关注,尤其是已经在环境领域被普遍关注的VMS。
3. 结论
PDMS常用做炸油中的消泡剂,在炸制食品的过程中,其中的甲基硅氧烷的低聚物可能残留至炸食中。本文建立了用QuEChERS-GC-MS/MS检测炸鸡、炸薯条中甲基硅氧烷低聚物残留的新方法,方法灵敏可靠。通过对市场上33种炸鸡和30种炸薯条样品的检测发现,检出D4~D18,L4~L14,L4在炸鸡样品中100%检出,L4~L7在薯条样品100%检出。炸鸡中ΣMS(L4~L14,D4~D6)男性与女性的总体暴露量为5.62~164.94 ng·kg−1·d−1,炸薯条中∑MS(L4~L14,D4~D6)男性与女性的总体暴露量0.25~13.09 ng·kg−1·d−1。根据PDMS的ADI建议量,在仅考虑通过炸鸡、炸薯条摄入而造成的甲基硅氧烷(总量)的暴露风险处于可接受范围,但对小分子(分子量<1000)甲基硅氧烷低聚物的长期低剂量摄入是否存在累积或潜在毒性还需深入研究。
-
表 1 15种甲基硅氧烷的保留时间、离子对及碰撞电压
Table 1 Retention time, ion pairs and collision voltage of 15 methylsiloxanes
序号 物质 分子式 分子量 保留时间
(min)离子对及碰撞电压(eV) 离子对1 离子对2 1 八甲基环四硅氧烷D4 C8H24O4Si4 296.62 2.935 281>73 (25) 281>265 (15) 2 十甲基四硅氧烷L4 C10H30O3Si4 310.69 3.369 207>191 (20) 207>73 (40) 3 十甲基环五硅氧烷D5 C10H30O5Si5 370.77 3.895 355>267 (10) 267>251 (20) 4 十二甲基五硅氧烷L5 C12H36O4Si5 384.84 4.416 281>73 (25) 147>73 (20) 5 十二甲基环六硅氧烷D6 C12H36O6Si6 444.92 4.900 341>73 (20) 341>91 (15) 6 十四甲基六硅氧烷L6 C14H42O5Si6 458.99 5.348 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 7 十六甲基七硅氧烷L7 C16H48O6Si7 533.15 6.285 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 8 十八甲基八硅氧烷L8 C18H54O7Si8 607.30 7.346 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 9 二十甲基壬硅氧烷L9 C20H60O8Si9 681.46 8.523 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 10 二十二甲基十硅氧烷L10 C22H66O9Si10 755.61 9.764 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 11 二十四甲基十一硅氧烷L11 C24H72O10Si11 829.76 11.006 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 12 二十六甲基十二硅氧烷L12 C26H78O11Si12 903.92 12.210 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 13 二十八甲基十三硅氧烷L13 C28H84O12Si13 978.08 13.359 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 14 三十甲基十四硅氧烷L14 C30H90O13Si14 1052.23 14.444 221>73 (20) 147>73 (20) 15 十二甲基五硅氧烷M4Q (I.S) C12H36O4Si5 384.8393 4.103 281>73 (25) 147>73 (20) 表 2 PDMS混合标准中L5~L14的百分含量
Table 2 Percentage of L5~L14 in the PDMS mixture standard
名称 L5 L6 L7 L8 L9 L10 L11 L12 L13 L14 百分含量(%) 11.63 23.46 20.26 15.31 11.12 7.47 4.73 2.89 1.96 1.17 表 3 炸鸡和炸薯条中VMS及PDMS检测方法评价
Table 3 Evaluation of detection method for VMS and PDMS in fried chicken and French fries
物质 标准曲线 线性范围
(ng∙mL−1)R2 LOD
(ng∙mL−1)LOQ
(ng∙mL−1)日内精密度
(%)平均回收率(%)及精密度(%) 炸鸡1 炸薯条2 D4 y=0.6134x+0.1764 1.05~523.75 0.9963 0.44 1.46 1.09 87.13 (4.1) 93.17 (7.7) L4 y=1.8182x−0.0457 1.01~504.75 0.9998 0.17 0.57 0.22 99.68 (9.8) 89.63 (2.3) D5 y=0.7778x+0.335 1.03~516.0 0.9988 0.29 0.98 3.43 109.86 (8.7) 83.47 (3.4) L5 y=1.291x−0.1187 1.01~503.5 0.9995 0.48 1.59 0.62 89.11 (11.6) 93.67 (6.1) D6 y=0.6767x+0.7063 1.02~509.75 0.9918 0.35 1.17 5.88 92.52 (7.2) 102.31 (2.1) L6 y=0.8243x−0.0708 1.76~1405.95 0.9986 0.36 1.21 0.58 90.97 (20.8) 79.64 (14.3) L7 y=1.0237x−0.0711 1.55~1241.24 0.9977 0.33 1.11 0.38 93.98 (13.2) 79.80 (12.6) L8 y=0.8772x−0.0213 1.31~1048.71 0.9974 0.54 1.78 0.22 95.99 (13.5) 78.70 (13.3) L9 y=0.9212x−0.0041 1.12~1116.48 0.9976 0.48 1.61 0.32 94.34 (5.0) 93.47 (4.3) L10 y=0.9739x+0.0299 0.88~876.74 0.9990 0.50 1.65 0.40 97.75 (8.9) 81.38 (5.4) L11 y=0.9728x+0.0855 0.64~640.62 0.9959 0.42 1.41 0.23 93.11 (10.4) 75.28 (4.2) L12 y=1.1824x+0.1481 1.65~412.15 0.9933 0.42 1.40 0.71 81.42 (7.4) 63.63 (4.3) L13 y=1.4477x+0.1708 0.87~217.86 0.9976 0.26 0.88 0.77 75.02 (10.3) 62.09 (4.2) L14 y=1.7506x+0.1616 0.93~93.47 0.9968 0.22 0.74 1.28 76.06 (14.7) 60.13(16.5) 注:1. 炸鸡中回收率三个加标水平:40、70、100 ng/g;2. 炸薯条中回收率三个加标水平:20、50、100 ng/g。 -
[1] HAMELINK J L. The handbook of environmental chemistry[M]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1992.
[2] HOBSON J F, ATKINSON R, CARTER W P L. Volatile methylsiloxane[M]. Berlin:Springer-Heidelberg, 1997.
[3] HE Y, SU S A, LYU Y, et al. Occurrence of methylsiloxanes in sediments from a subtropical river-lake system in eastern China and its implication for ecological risks[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,223:1−8.
[4] WOODBURN B K, SESTON M R, KIM J, et al. Benthic invertebrate exposure and chronic toxicity risk analysis for cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes:Comparison of hazard quotient and probabilistic risk assessment approaches[J]. Chemosphere,2018,192:337−347. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.140
[5] 孙宏雨, 李栋学, 徐琳, 等. 生物体内环形挥发性甲基硅氧烷的分布, 行为及效应研究进展[J]. 环境化学,2022,41(1):193−204. [SUN Hongyu, LI Dongxue, XU Lin, et al. Research progress on the distribution, behavior and effects of cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in organisms[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2022,41(1):193−204.] doi: 10.1002/etc.5258 SUN Hongyu, LI Dongxue, XU Lin, et al. Research progress on the distribution, behavior and effects of cyclic volatile methylsiloxanes in organisms[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(1): 193−204. doi: 10.1002/etc.5258
[6] 阿依古丽, 程家丽, 苏帅, 等. 甲基硅氧烷的污染现状及其环境风险[J]. 环境工程,2020,18:121−123. [AYIGULI, CHENG Jiali, SU Shuai, et al. Pollution status and environmental risks of methyl siloxane[J]. Modern Chemical Research,2020,18:121−123.] AYIGULI, CHENG Jiali, SU Shuai, et al. Pollution status and environmental risks of methyl siloxane[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2020, 18: 121−123.
[7] QUINN A L, DALU A, MEEKER L S, et al. Effects of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane (D4) on the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge and levels of various reproductive hormones in female Sprague-Dawley rats[J]. Reproductive Toxicology,2007,23(4):532−540. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.02.005
[8] 张松林, 吴丽华. 环甲基硅氧烷的环境分布、行为与效应研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报,2016(11):72−85. [ZHANG SONGLIN, WU LIHUA, et al. The research progress of environmental distribution, behavior and effects of cyclic methylsiloxanes[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2016(11):72−85.] ZHANG SONGLIN, WU LIHUA, et al. The research progress of environmental distribution, behavior and effects of cyclic methylsiloxanes[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2016(11): 72−85.
[9] 刘海秋. 甲基硅氧烷对水生生物富集效应的研究[D]. 大连:大连海事大学, 2017. [LIU Haiqiu. Bioaccumulation effect of methyl siloxanes in aquatic organisims[D]. Dalian:Dalian Maritime University, 2017.] LIU Haiqiu. Bioaccumulation effect of methyl siloxanes in aquatic organisims[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2017.
[10] FABIO B, ARMINDA A, VERA H. A review of bioaccumulation of volatile methylsiloxanes in aquatic ecosystems[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,824:1−19.
[11] 封棣, 张喜荣, 戚冬雷. 甲基硅氧烷对人体暴露途径的研究进展[J]. 环境化学,2018,37(5):1022−1036. [FENG Di, ZHANG Xirong, QI Donglei. Human exposure pathways of methylsiloxanes:A review of recent studies[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2018,37(5):1022−1036.] FENG Di, ZHANG Xirong, QI Donglei. Human exposure pathways of methylsiloxanes: A review of recent studies[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(5): 1022−1036.
[12] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准食品添加剂使用标准:GB2760-2014[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2015. [National Health and Family Planning Commission. National food safety standard-Food additive use standards:GB2760-2014[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2015.] National Health and Family Planning Commission. National food safety standard-Food additive use standards: GB2760-2014[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2015.
[13] CHOI C W, JEONGE J Y, PARK H S, et al. Evaluation of toxicological data on food additives and guideline for ADI establishment polydimethylsiloxane as emulsifier[J]. Journal of Food Hygiene and Safety,2009,24(4):352−356.
[14] 林舒忆, 贾彦博, 陈美春, 等. 空气/氩气双通气-原子吸收石墨炉法测定食用油中的二甲基硅氧烷[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(24):9226−9229. [LIN Shuyi, JIA Yanbo, CHEN Meichun, et al. Determination of the content of polydimenthylsiloxane by graphite furance automic absorption spectrometry with air-oxygen double ventilation technology in edible oils[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2020,11(24):9226−9229.] LIN Shuyi, JIA Yanbo, CHEN Meichun, et al. Determination of the content of polydimenthylsiloxane by graphite furance automic absorption spectrometry with air-oxygen double ventilation technology in edible oils[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2020, 11(24): 9226−9229.
[15] 汪雨, 祖文川, 李冰宁, 等. 氧化亚氮-乙炔火焰-连续光源原子吸收光谱法测定植物油中的聚二甲基硅氧烷[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(2):198−200. [WANG Yu, ZU Wenchuan, LI Bingning, et al. Determination of polydimethylsiloxane in vegetable oils using continuum source atomic absorption spectrometer with nitrous oxide-acetylene flame[J]. Food Science,2015,36(2):198−200.] WANG Yu, ZU Wenchuan, LI Bingning, et al. Determination of polydimethylsiloxane in vegetable oils using continuum source atomic absorption spectrometer with nitrous oxide-acetylene flame[J]. Food Science, 2015, 36(2): 198−200.
[16] 乐粉鹏, 辛明亮, 吴瑛, 等. ICP-OES有机进样法测定食用油脂中聚二甲基硅氧烷的含量[J]. 食品科技,2013,11(38):303−306. [YUE Fenpeng, XIN Mingliang, WU Ying, et al. Determination of content of poiydimetjylsioxane in edible oils by organic direct injection ICP-OES[J]. Food Science and Technology,2013,11(38):303−306.] YUE Fenpeng, XIN Mingliang, WU Ying, et al. Determination of content of poiydimetjylsioxane in edible oils by organic direct injection ICP-OES[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2013, 11(38): 303−306.
[17] 高峰, 李小林, 冯骞, 等. 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定食品中聚二甲基硅氧烷的含量[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(8):182−185. [GAO Feng, LI Xiaolin, FENG Qian, et al. Determination of dimethylpolysiloxanes in foodstuffs by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2013,34(8):182−185.] GAO Feng, LI Xiaolin, FENG Qian, et al. Determination of dimethylpolysiloxanes in foodstuffs by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[J]. Food Science, 2013, 34(8): 182−185.
[18] 吴惠勤, 林晓珊, 朱志鑫等. 食品中聚二甲基硅氧烷检测方法研究[J]. 分析测试学报,2010,29(12):1143−1146. [WU Huiqin, LIN Xiaoshan, ZHU Zhixin, et al. Study on method for determination of polydimethylsiloxane in food[J]. Instrumental Analysis,2010,29(12):1143−1146.] WU Huiqin, LIN Xiaoshan, ZHU Zhixin, et al. Study on method for determination of polydimethylsiloxane in food[J]. Instrumental Analysis, 2010, 29(12): 1143−1146.
[19] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准动物油脂中聚二甲基硅氧烷的测定:GB5009.254-2016[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission. Determination of polydimethylsiloxane in animal fats and fats according to national food safety standard:GB5009.254-2016[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission. Determination of polydimethylsiloxane in animal fats and fats according to national food safety standard: GB5009.254-2016[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[20] 栗真真. 食品接触硅橡胶制品中非目标物的分析研究[D]. 北京:北京工商大学, 2016. [LI Zhenzhen. Research on non-target substances in food contact silicone rubber products[D]. Beijing:Beijing Technology and Business University, 2016.] LI Zhenzhen. Research on non-target substances in food contact silicone rubber products[D]. Beijing: Beijing Technology and Business University, 2016.
[21] 吴晓丽, 赵毕, 齐小娟, 等. 食品中化学污染物风险评估方法研究进展[J]. 预防医学,2020,32(7):682−685. [WU Xiaoli, ZHAO Bi, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Review on the risk assessment methods for chemical pollutants in food[J]. Prev Med,2020,32(7):682−685.] WU Xiaoli, ZHAO Bi, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Review on the risk assessment methods for chemical pollutants in food[J]. Prev Med, 2020, 32(7): 682−685.
[22] 刘文静, 潘葳. 福建产后花生黄曲霉毒素污染分布及膳食暴露评估[J]. 粮食与饲料工业,2016(11):28−31. [LIU Wenjing, PAN Wei. Peanut aflatoxins contamination and evaluation on dietary exposure in Fujian Province[J]. Cereal and Industry,2016(11):28−31.] LIU Wenjing, PAN Wei. Peanut aflatoxins contamination and evaluation on dietary exposure in Fujian Province[J]. Cereal and Industry, 2016(11): 28−31.
[23] KHAN I A, YIQUM C, ZONGSHUAI Z, et al. Occurrence of heterocyclic amines in commercial fast-food meat products available on the Chinese market and assessment of Human exposure to these compounds[J]. Journal of Food Science,2019,84(1):192−200. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14418
[24] FRANZEN A, VAN LANDINGHAM C, GREENE T, et al. A global human health risk assessment for decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (D5)[J]. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology,2016,74:25−43. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.10.023
[25] SANCH S J, LLORCA M, PIC Y, et al. Volatile dimethylsiloxanes in market seafood and freshwater fish from the Xúquer River, Spain[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2016,54:236−243.
[26] 葛丹阳, 刘桂华, 姜欢, 等. GC-MS/MS法测定食品接触用硅橡胶制品中6种环硅氧烷迁移量[J]. 分析测试学报, 2022, 41(10):1486−1493. [GE Danyang, LIU Guihua, JIANG Huan, et al. Determination of migration of six cyclosiloxanes in silicone rubber products for food contact by GC-MS/MS [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2019, 84(1):192−200.] GE Danyang, LIU Guihua, JIANG Huan, et al. Determination of migration of six cyclosiloxanes in silicone rubber products for food contact by GC-MS/MS [J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2019, 84(1): 192−200.
[27] FENG D, ZHANG X R, YUAN H, et al. Identification, migration, and childhood exposure of methylsiloxanes in silicone infant bottle nipples marketed in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,829:154449. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154449
[28] XU L, ZHI L Q, CAI Y Q. Methylsiloxanes in children silicone-containing products from China:Profiles, leaching, and children exposure[J]. Environmen International,2017,101:165−172.
[29] 任东升, 周志俊. 聚二甲基硅氧烷应用及安全性评估概况[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志,2011,23(2):181−185. [REN Dongsheng, ZHOU Zhijun. An overview on the application and safety assessment of polydimethylsiloxane[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene,2011,23(2):181−185.] doi: 10.13590/j.cjfh.2011.02.005 REN Dongsheng, ZHOU Zhijun. An overview on the application and safety assessment of polydimethylsiloxane[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2011, 23(2): 181−185. doi: 10.13590/j.cjfh.2011.02.005
[30] CAMINOA G, LOMAKINB S M, LAGEARD M. Thermal polydimethylsiloxane degradation. Part 2. The degradation mechanisms[J]. Polymer,2002,43(7):2011−2015. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00785-6
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李梦,席婉婷,胡竞月,岳芽,戢得蓉. 马铃薯全粉在粗粮发酵饼干中的应用. 农产品加工. 2023(10): 6-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 江冠宇,田晓菊,张惠玲. 不同干燥方法对欧李叶袋泡茶的影响. 食品工业. 2022(06): 116-121 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



