Optimization of the Fermentation Process of Mulberry Juice by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Changes in Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity during Fermentation
-
摘要: 以桑葚为原材料,采用植物乳杆菌、长双歧杆菌对桑葚汁进行单菌株和混合菌株发酵,利用单因素实验和响应面试验探究发酵桑葚汁的最佳发酵工艺,并测定分析桑葚汁在发酵过程中的功能性成分(总黄酮、总花青素、总酚)和抗氧化活性(ABTS+自由基清除率、DPPH自由基清除率、羟自由基清除率、总抗氧化能力)等。结果表明,发酵桑葚汁最佳发酵工艺为菌种添加量0.06%,初始pH6.1,发酵温度37 ℃,低聚果糖添加量0.09%。乳酸菌发酵提高了发酵桑葚汁的功能性成分和抗氧化活性;单菌株和混合菌株相比,混合菌株发酵可显著提高(P<0.05)桑葚汁功能性化合物含量,且未发酵桑葚汁和混合菌株发酵48 h后含量分别为总黄酮4.18~6.36 mg/mL,总花青素0.67~1.95 mg/mL,总酚12.62~18.65 mg/mL;混合菌株发酵48 h桑葚汁的抗氧化活性得到明显提升,ABTS+自由基清除率61.81%~88.17%,DPPH自由基清除率52.78%~81.64%,羟自由基清除率37.38%~86.07%,总抗氧化能力17.85~29.49 mmol/L。植物乳杆菌、长双歧杆菌混合菌株发酵具有更好的感官特性。研究可为桑葚精深加工提供理论参考。Abstract: Using mulberry as raw material, single and mixed strains of Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum were used to ferment mulberry juice, and single-factor and response surface tests were used to investigate the optimal fermentation process of fermented mulberry juice, and to determine and analyze the functional components (total flavonoids, total anthocyanins, total phenols) and antioxidant activities (ABTS+ free radical scavenging rate, DPPH free radical scavenging rate, hydroxyl radical scavenging rate, total antioxidant capacity), etc. The results showed that the optimal fermentation process for fermented mulberry juice was 0.06% strain addition, initial pH6.1, fermentation temperature 37 ℃, and 0.09% oligofructose addition. The fermentation of lactic acid bacteria improved the functional components and antioxidant activity of fermented mulberry juice. Compared with single strain and mixed strain, the fermentation of mixed strain significantly increased (P<0.05) the content of functional compounds in mulberry juice, and the contents of unfermented mulberry juice and mixed strain after 48 h fermentation were 4.18~6.36 mg/mL of total flavonoids, 0.67~1.95 mg/mL of total anthocyanins, 12.62~18.65 mg/mL of total phenols. And 48 h fermentation of the mixed strains significantly improved the antioxidant activity of mulberry juice, with ABTS+ free radical scavenging rate 61.81%~88.17%, DPPH free radical scavenging rate 52.78%~81.64%, hydroxyl radical scavenging rate 37.38%~86.07%, total antioxidant capacity 17.85~29.49 mmol/L. The fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum and Bifidobacterium longum mixed strains had better organoleptic properties. The study can provide a theoretical reference for the deep processing of mulberry.
-
Keywords:
- mulberry /
- lactic acid bacteria /
- fermentation process /
- functionality /
- antioxidant activity
-
桑葚(Fructus mori),又名桑葚子、桑果等,为桑科植物桑树的果实[1]。桑葚中含有丰富的活性蛋白、维生素、氨基酸、胡萝卜素和矿物质等营养成分[2−3],营养价值非常高,享有“民间圣果”的美誉。桑葚还具有延缓衰老、保护血管、保护视力、提高免疫力、促进消化和预防便秘的功效[4−6]。但桑葚采收期短,不易贮藏,每年有大量的桑葚腐烂在田地,因此将桑葚加工为果酒和饮料等产品可有效解决桑葚采收期的困难,同时能提高桑葚的商业价值,满足人们对桑葚的需求。尹俊涛等[7]以蔓越莓与桑葚为原料研究蔓越莓桑葚复合饮料工艺;孙百虎[8]通过不同乳酸菌发酵桑葚汁,其活菌数均超过11 lg(CFU/mL),且乳酸菌发酵能有效提高总酚和总黄酮含量。
乳酸菌(lactic acid bacteria,LAB),是能将碳水化合物发酵产生大量乳酸的一类无芽孢、革兰氏染色阳性细菌的统称[9];乳酸菌能改善动物机体的肠道菌群结构,维持肠道菌群平衡[10−11];乳酸菌发酵产生的各种消化酶可以将大分子物质分解为小肽、葡萄糖等更易被消化吸收的小分子颗粒状物质,有助于机体的吸收,提高机体的免疫功能[12−14];乳酸菌发酵可提高产品的营养价值,改善产品风味[15−17]。长双歧杆菌具有调节人体肠道,改善健康的功效作用,可适用于乳酸菌食品的加工过程。植物乳杆菌广泛应用于水果、蔬菜、牛羊乳和酒类等各类食品,用来制作各类乳酸菌加工制品。虽然关于乳酸菌发酵桑葚汁的相关研究较多,但对单菌株和混合菌株发酵桑葚汁工艺优化及单菌株和混合菌株发酵之间的功能性成分和抗氧化活性的区别研究较少。因此本研究采用植物乳杆菌、长双歧杆菌对桑葚汁进行单菌株和混合菌株发酵实验,利用单因素和响应面试验优化桑葚汁发酵工艺,并测定单菌株和混合菌株发酵桑葚汁的pH、可溶性固形物、乳酸菌活菌数、总糖、总酸、功能性成分和抗氧化活性,对比分析不同乳酸菌发酵桑葚汁的区别,研究可为桑葚的深加工利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
桑葚 采摘自新疆阿克苏;长双歧杆菌(Bifidobacterium longum 18,BL)、植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum 56,LP) 西安米先尔生物科技有限公司;碳酸钠、柠檬酸、果胶酶(酶活30000 U/g) 均为食品级,购自江苏佰叶生物科技有限公司;低聚果糖(食品级)、葡萄糖(食品级)、盐酸、三氯乙酸、三氯化铁、亚硝酸钠、过硫酸钾、水杨酸、铁氰化钾 均为分析纯,购自天津运盛化学品有限公司;MRS培养基 购自天津市盛奥化学试剂有限公司;DPPH、ABTS、芦丁、没食子酸 购自成都市科龙化工试剂厂;无水乙酸钠、氢氧化钠、硫酸亚铁、30%过氧化氢、硝酸铝、硫酸铜 分析纯,购自武汉荆隆化工有限公司;磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠 均为分析纯,购自福晨化学试剂厂;酚酞、3,5二硝基水杨酸(DNS)、碘、碘化钾 购自天津市盛放化学试剂;福林酚 分析纯,购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;总抗氧化试剂盒 购自北京索宝莱科技有限公司。
HWS-24恒温水浴锅 上海精密仪器仪表有限公司;BM04高精度数显糖度计 惠州市优普森仪器有限公司;pHS-3C型pH计 上海蚁霖科学仪器有限公司;FA1004型电子天平 上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司;L18-Y912C九阳破壁机 九阳泰盛有限公司;330-5B型恒温培养箱 玖蓝科学仪器;XFS-280CB型高压灭菌锅 尚城仪器经营部;SW-CJ-2FD型超净工作台 鸿运实验仪器;UV759紫外可见分光光度仪 上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司;DNM-9602G酶标分析仪 北京普朗新技术有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 桑葚汁发酵工艺流程
桑葚挑选→榨汁过滤→果胶酶浸提→调配发酵液→高温杀菌→接种乳酸菌发酵→发酵桑葚汁成品
1.2.2 桑葚汁发酵工艺操作要点
桑葚挑选:挑选无虫害、无霉病的桑葚,用蒸馏水将桑葚表面的污垢进行清洗,清洗完成后沥干表面水分。
榨汁过滤:将沥干水分的桑葚进行榨汁,随后用8层无菌纱布进行过滤,得到桑葚汁。
果胶酶浸提:称取0.03%果胶酶(30000 U/g)加入过滤得到的桑葚汁中,随后放入45 ℃恒温水浴锅中酶解2 h。
调配发酵液:向发酵液中添加低聚果糖,随后使用碳酸钠调节酶解后发酵液的初始pH,使用数显糖度计测定发酵液的可溶性固形物为16.43°Brix。
高温杀菌:将调配好的发酵液放入水浴锅中进行高温杀菌(95 ℃灭菌30 min),灭菌完成后自然冷却至室温。
接种乳酸菌发酵:向冷却好的发酵液中加入活化菌株(10 mL葡萄糖水溶液活化20 min,活化后的菌种浓度为6.0 lg(CFU/mL),将活化好的菌株按一定比例接种至发酵液中,随后放入恒温培养箱中进行厌氧发酵48 h,发酵完成后得到成品。
1.2.3 桑葚汁发酵工艺单因素实验
1.2.3.1 菌种类型对感官评分和活菌数的影响
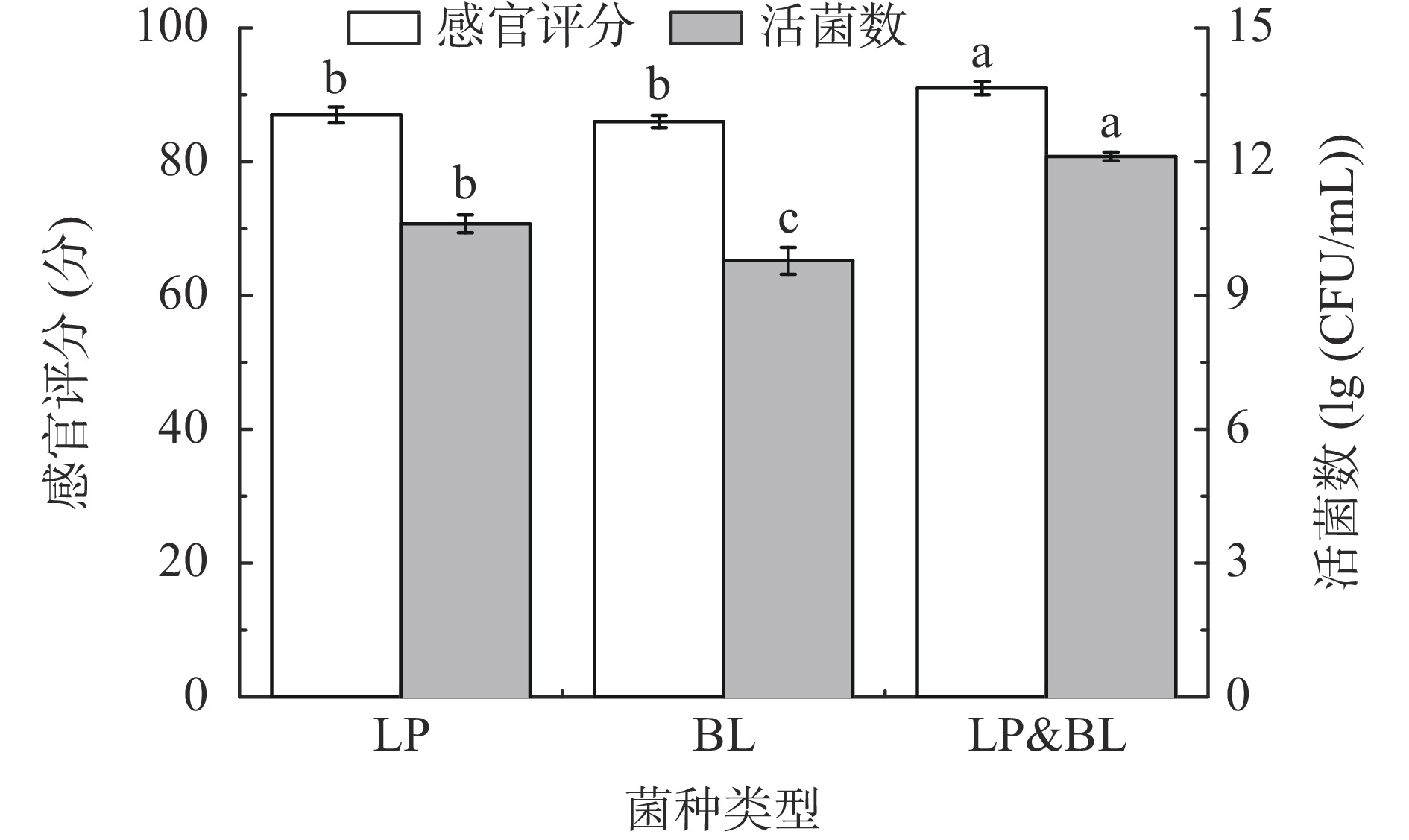
设置菌种类型为LP、BL、LP&BL(1:1),按照1.2.1中的工艺流程进行样品处理,固定初始pH为6.0,低聚果糖添加量0.09%,菌种添加量0.06%,发酵温度37 ℃,以发酵后的感官评分和活菌数为评价指标,确定最佳发酵菌种类型。
1.2.3.2 初始pH对感官评分和活菌数的影响
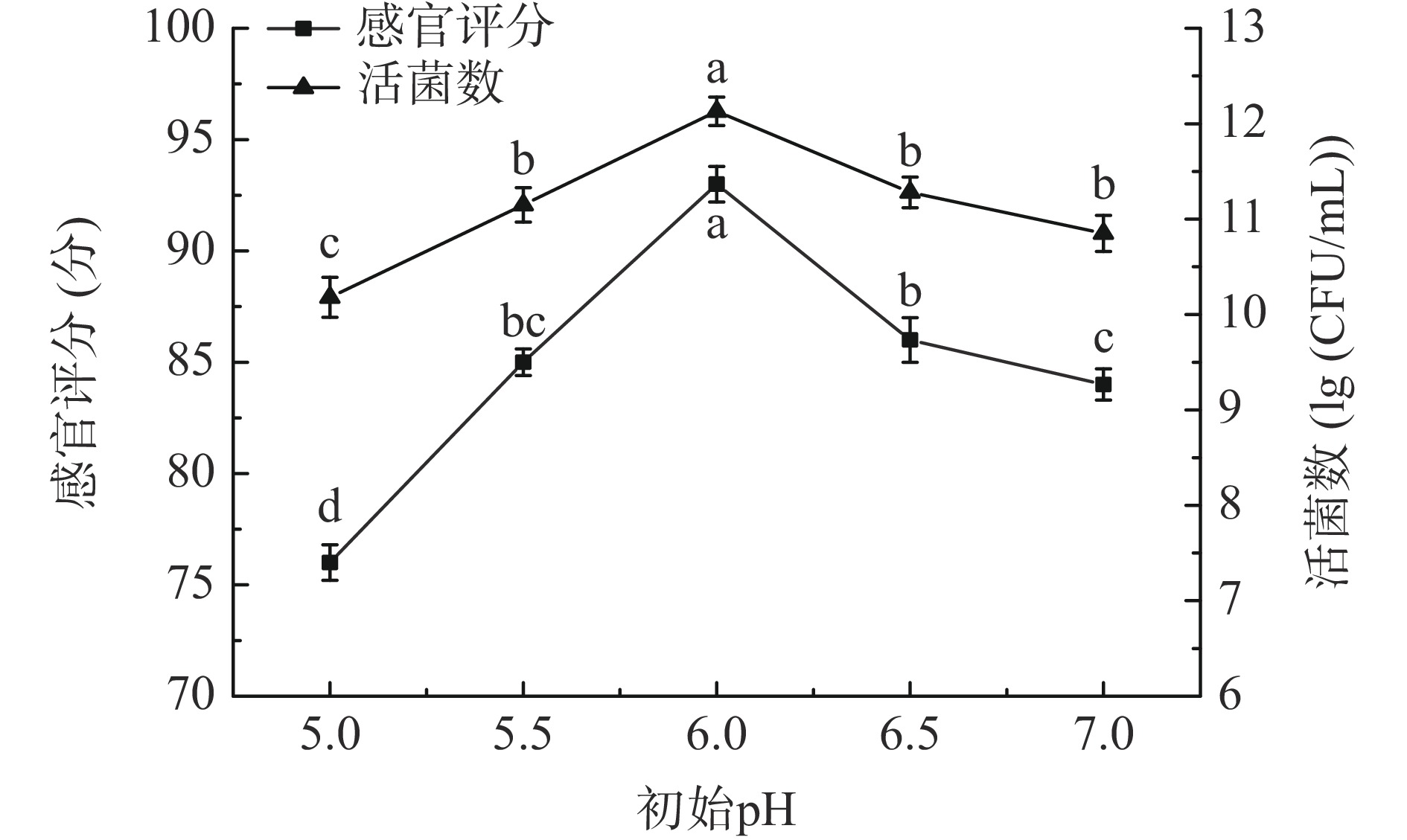
设置初始pH为5.0、5.5、6.0、6.5、7.0,按照1.2.1中的工艺流程进行样品处理,固定菌种类型为LP&BL(1:1),低聚果糖添加量0.09%,菌种添加量0.06%,发酵温度37 ℃,以发酵后的感官评分和活菌数为评价指标,确定最佳初始pH。
1.2.3.3 低聚果糖添加量对感官评分和活菌数的影响
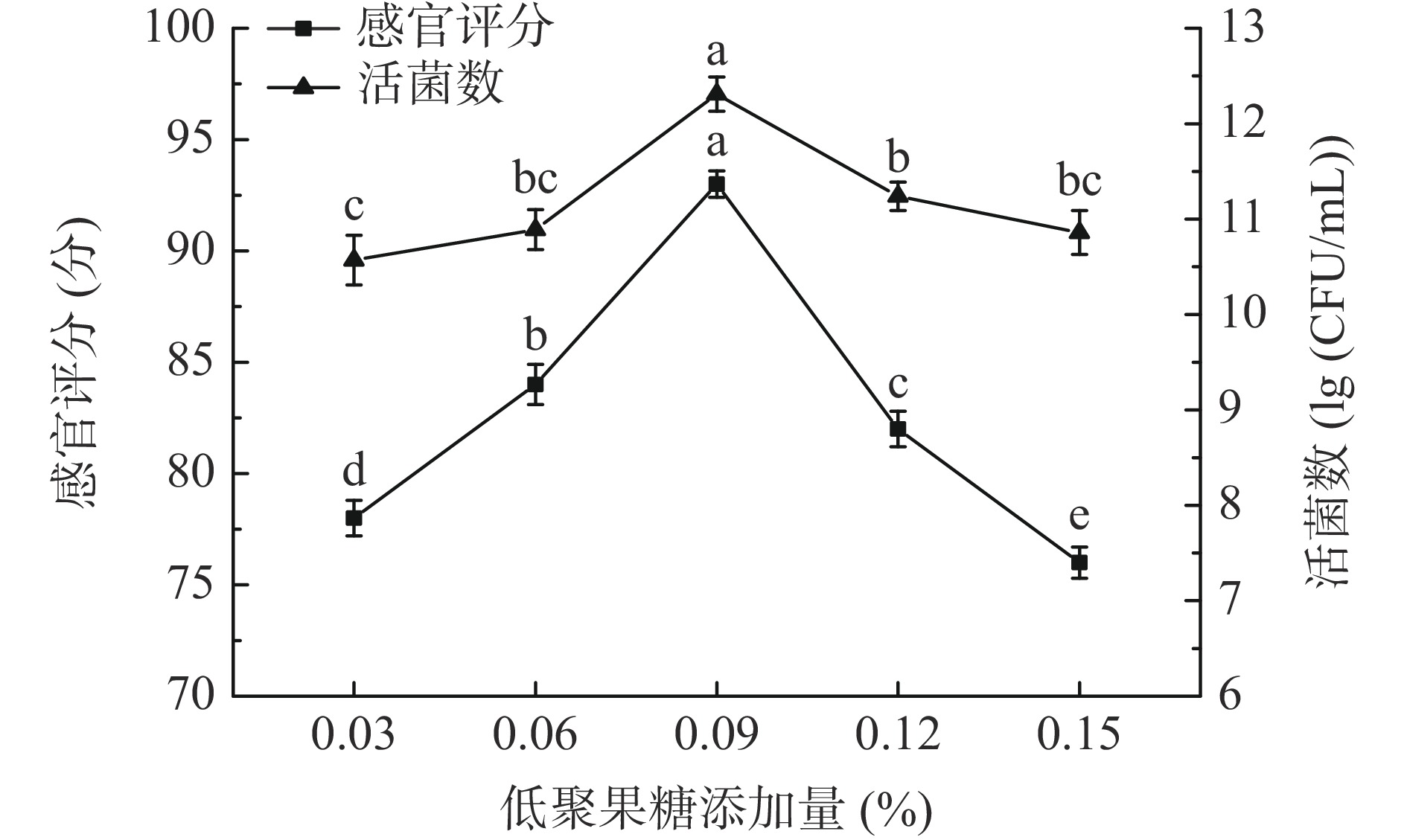
设置低聚果糖添加量为0.03%、0.06%、0.09%、0.12%、0.15%,按照1.2.1中的工艺流程进行样品处理,固定菌种类型为LP&BL(1:1),初始pH为6.0,菌种添加量0.06%,发酵温度37 ℃,以发酵后的感官评分和活菌数为评价指标,确定最佳低聚果糖添加量。
1.2.3.4 菌种添加量对感官评分和活菌数的影响
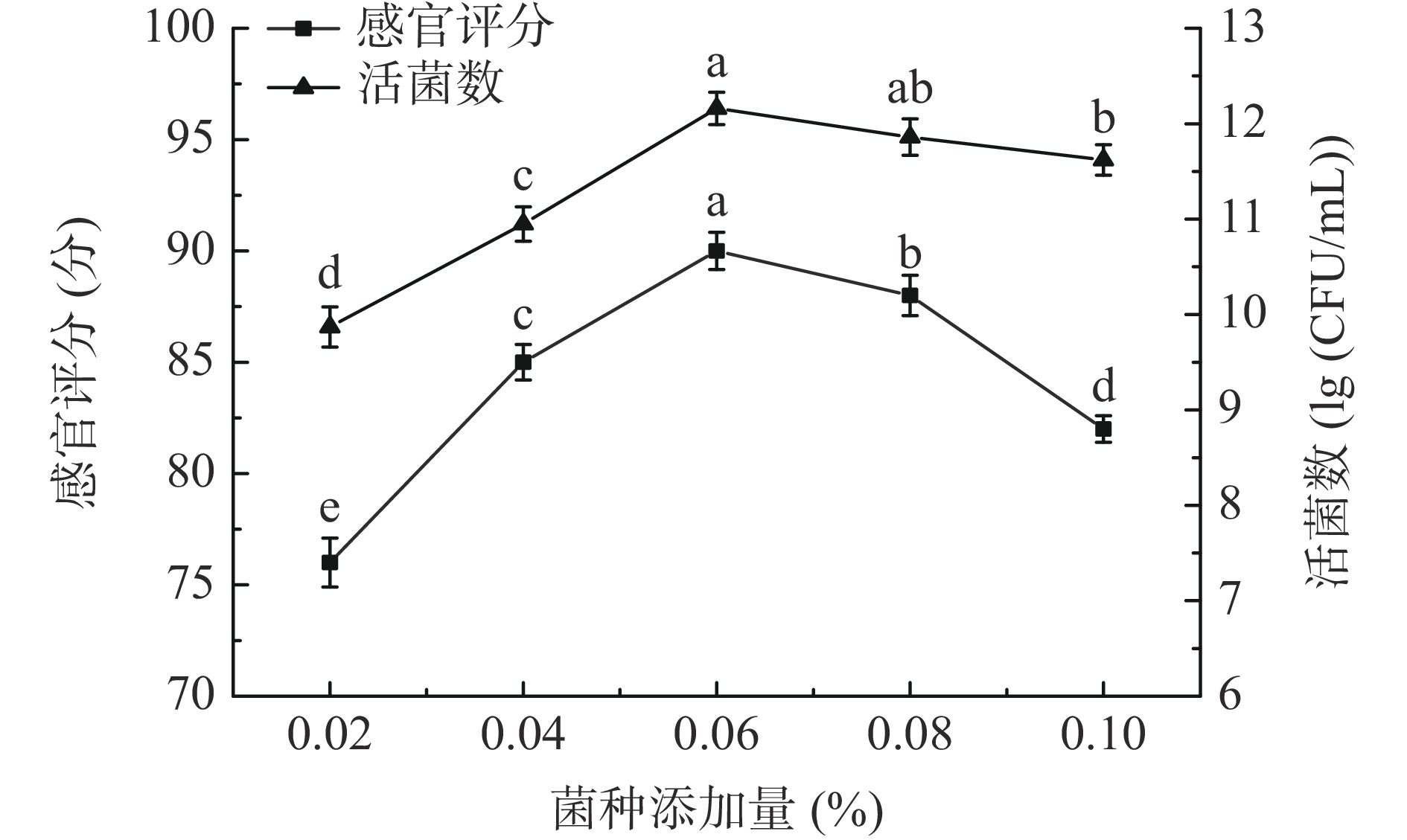
设置菌种添加量为0.02%、0.04%、0.06%、0.08%、0.10%,按照1.2.1中的工艺流程进行样品处理,固定菌种类型为LP&BL(1:1),初始pH为6.0,低聚果糖添加量0.09%,发酵温度37 ℃,以发酵后的感官评分和活菌数为评价指标,确定最佳菌种添加量。
1.2.3.5 发酵温度对感官评分和活菌数的影响
设置发酵温度为33、35、37、39、41 ℃,按照1.2.1中的工艺流程进行样品处理,固定菌种类型为LP&BL(1:1),初始pH为6.0,低聚果糖添加量0.09%,菌种添加量0.06%,以发酵后的感官评分和活菌数为评价指标, 确定最佳发酵温度。
1.2.4 桑葚汁发酵工艺响应面试验
以单因素实验结果为基础,选择菌种添加量、初始pH、发酵温度和低聚果糖添加量为影响因素,以感官评分和活菌数为响应值进行响应面试验,响应面试验因素与水平见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平Table 1. Response surface test factors and levels因素 水平 −1 0 1 A菌种添加量(%) 0.04 0.06 0.08 B初始pH 5.5 6.0 6.5 C发酵温度(℃) 35 37 39 D低聚果糖添加量(%) 0.06 0.09 0.12 1.2.5 感官评价
参照盛洁等[18]方法稍作修改,制定发酵桑葚汁的感官评价标准;感官评价选取15名身体健康且经过感官评价培训的人员,按照感官评分表对发酵桑葚汁进行感官评定,最终评价结果取平均值,感官评分表见表2。
表 2 发酵桑葚汁感官评分表Table 2. Sensory score table of fermented mulberry juice评分项目 评分标准 分值(分) 色泽
(20分)能呈现桑葚汁的深红色,色泽均匀 15~20 较能呈现桑葚汁的深红色,色泽较均匀 6~14 不能呈现桑葚汁的深红色,色泽不均匀,有杂色 <6 口感
(40分)口感协调,酸甜适中 30~40 口感较协调,但稍酸或稍甜 20~29 口感略协调,但过酸或过甜 10~19 口感不协调 <10 气味
(20分)气味协调,桑葚气味浓郁,无杂味 15~20 气味适中,桑葚气味较淡,稍有杂味 8~14 气味不协调,有杂味 <8 形态
(20分)组织形态均匀,无沉淀 15~20 组织形态较均匀,略有沉淀 7~14 组织形态不均匀,有沉淀 <7 1.2.6 理化指标检测方法
采用pH计测定pH;可溶性固形物采用数显糖度计进行测定;乳酸菌活菌数测定参照GB 4789.35-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 乳酸菌检验》[19],总糖测定采用3,5二硝基水杨酸法[20];总酸测定参照GB 123456-2021《食品安全国家标准 食品中总酸的测定》[21]。
1.2.7 功能性成分检测方法
1.2.7.1 总酚含量测定
参照Kwaw等[22]方法稍作修改;取 2 mL成品样品,加入13 mL蒸馏水、1.5 mL福林酚,室温避光放置5 min,加入3 mL 12%碳酸钠溶液,蒸馏水定容25 mL。室温避光放置90 min,于765 nm波长测定吸光度,使用没食子酸为标准品制作标准曲线y=0.1125x+0.046,R²=0.9958,总酚含量以没食子酸含量计。
1.2.7.2 总黄酮含量测定
参照Gao等[23]方法稍作修改;取2 mL成品样品加入0.6 mL 5%亚硝酸钠溶液,放置6 min;加入0.6 mL 10%硝酸铝溶液,放置6 min;再加8 mL 4%氢氧化钠溶液;用蒸馏水定容至15 mL,充分摇晃3 min。于508 nm波长测定吸光度,使用芦丁为标准品制作标准曲线y=0.0539x+0.0158,R²=0.9979,总黄酮含量以芦丁含量计。
1.2.7.3 总花青素含量测定
采用pH示差法;取10 mL成品样品,用氯化钾-盐酸缓冲液(pH1.0)和乙酸钠-盐酸缓冲液(pH4.5)定容至20 mL;避光放置90 min,于525 nm和700 nm波长测定吸光度。
A=pH1(A525−A700)−pH4.5(A525−A700) 总花色苷含量(mg/mL)=A×MWε×I×DF×1000 式中:MW为矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷分子量449.2;ε为矢车菊素-3-葡萄糖苷摩尔消光系数26900;I为比色皿光程1 cm;DF为稀释因子10。
1.2.8 抗氧化指标检测方法
1.2.8.1 DPPH自由基清除率、ABTS+自由基清除率和总抗氧化能力测定
参照Chen等[24]方法;DPPH自由基清除率和ABTS+自由基清除率按下式计算:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=1−(A1−A2A3)×100 式中:A1为样品吸光值,A2为对照组吸光值,A3为空白组吸光值。
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=(A1−A2A1)×100 式中:A1为空白组吸光值,A2为样品吸光值。
总抗氧化能力中以硫酸亚铁为标准品制作标准曲线y=0.0995x+0.1209,R²=0.9936,总抗氧化能力以硫酸亚铁含量表示。
1.2.8.2 ·OH清除率测定
参照李佩佩等[25]方法;·OH清除率按下式计算:
⋅OH清除率(%)=1−(A1−A2A3)×100 式中:A1为样品吸光值,A2为对照组吸光值,A3为空白组吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验平行测定3次,对得到的数据采用Design-ExpertV8.0.6和SPSS 25.0分析处理实验数据,origin8.0作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果与分析
2.1.1 菌种对桑葚汁感官评分和活菌数的影响
由图1可知,不同乳酸菌发酵的感官评分和活菌数各不相同,植物乳杆菌发酵的活菌数比长双歧杆菌高,呈显著性差异(P<0.05),可能是植物乳杆菌适应生长能力较强,在桑葚汁发酵液中的生长代谢较好;在菌种发酵方式方面,植物乳杆菌和长双歧杆菌均匀混合配比发酵桑葚汁的感官评分和活菌数最高,可能是由于混合菌种发酵时不同种类菌种发酵特性的协同作用,丰富了产品的口感,同时提高活菌数。综合考虑感官评分和活菌数的变化,选择植物乳杆菌和长双歧杆菌均匀混合配比进行发酵。
2.1.2 初始pH对桑葚汁感官评分和活菌数的影响
不同初始pH对发酵产品的感官评分和活菌数均有影响;由图2可知,感官评分和活菌数随pH的升高呈先增大后降低的变化趋势,当桑葚汁初始pH为6.0时其感官评分和活菌数最高。感官评分的变化可能是在初始pH较小时发酵液环境适宜乳酸菌的繁殖,乳酸菌发酵可增加发酵液中的有机酸类和低浓度乙醛等芳香物质,且乳酸菌发酵可使发酵液中的物质更细腻[26],提升产品口感;初始pH为6.0时达到乳酸菌发酵最适生长环境,感官评分最高。随着初始pH升高,碳酸钠加入量过多使得产品风味变差,感官评分降低。活菌数变化趋势可能是由于乳酸菌的生长繁殖条件所影响,在初始pH较低的环境下会增加乳酸菌的发酵延滞期,乳酸菌的生长繁殖会减缓[27];初始pH升高会使发酵液中的离子平衡发生移动,降低发酵液中的有效营养成分,限制了乳酸菌的生长繁殖。综合考虑感官评分和活菌数的变化,故选择初始pH为5.5、6.0和6.5进行响应面试验。
2.1.3 低聚果糖添加量对桑葚汁感官评分和活菌数的影响
低聚果糖由植物的果糖短链组成,是一种水溶性膳食纤维,同时也被作为益生元应用于益生菌生长研究中[28]。由图3可知,随着低聚果糖添加量的增大,感官评分和活菌数均呈现先升高后下降的趋势。在低聚果糖添加量为0.09%时,感官评分最高为93分,活菌数达到最大值为12.31 lg(CFU/mL),这可能是由于低聚果糖具有促进益生菌生长的功能[29−30];当添加适量低聚果糖时,可有效促进桑葚汁中乳酸菌的生长繁殖,低聚果糖添加量过多时,加快了乳酸菌的生长速度,其代谢产物乳酸等酸类化合物产量增大,影响了发酵液中乳酸菌的活菌数量,同时使产品口感受到影响。综合考虑,故选择低聚果糖添加量0.06%、0.09%、0.12%进行响应面试验。
2.1.4 菌种添加量对桑葚汁感官评分和活菌数的影响
由图4可知,菌种添加量在0.02%~0.06%范围内感官评分和活菌数均呈上升趋势,且上升幅度较大,当菌种添加量为0.06%时,感官评分和活菌数达到最大,分别为90分和12.16 lg(CFU/mL);菌种添加量大于0.06%时,感官评分和活菌数均下降,感官评分下降幅度较大。可能是由于菌种添加量过高时,发酵液内的营养成分无法满足过量乳酸菌的生长代谢需求,影响乳酸菌的生长繁殖,近而降低活菌数量[31];同时过量乳酸菌在发酵时会产生大量酸类化合物,使桑葚汁感官评分降低。综合考虑选择菌种添加量0.04%、0.06%和0.08%进行响应面试验。
2.1.5 发酵温度对桑葚汁感官评分和活菌数的影响
由图5可知,活菌数随着发酵温度上升呈先增大后减小的趋势,发酵温度在37 ℃时活菌数达到最大;这可能是由于乳酸菌的最适生长温度所致,当温度过高时会使乳酸菌失去活性,影响乳酸菌的活菌数[32]。发酵温度为37 ℃时感官评分最大为90分,发酵温度高于37 ℃感官评分降低,可能是由于温度过高影响了桑葚汁中香味成分,破坏桑葚汁中的呈味物质,同时乳酸菌发酵也对感官评分有所影响。综合考虑感官评分和活菌数的变化,选择发酵温度35、37和39 ℃进行响应面试验。
2.2 响应面试验结果与分析
2.2.1 试验设计方案与结果
根据单因素实验结果,选取菌种添加量(0.04%、0.06%、0.08%)、初始pH(5.5、6.0、 6.5)、发酵温度(35、37和39 ℃)和低聚果糖添加量(0.06%、0.09%、0.12%)为影响因素,以感官评分和活菌数为响应值进行响应面试验,试验设计方案与结果见表3。
表 3 响应面试验设计方案与结果Table 3. Response surface experimental design and results实验号 A菌种
添加量B初始
pHC发酵
温度D低聚果糖
添加量Y感官
评分(分)M活菌数(lg
(CFU/mL))1 −1 0 −1 0 78.2 10.3 2 1 0 0 1 85.7 11.2 3 0 0 1 1 89.8 11.8 4 0 0 0 0 91.3 12.2 5 −1 0 1 0 83.5 11.3 6 0 0 0 0 90.1 12.3 7 0 1 1 0 89.6 11.6 8 1 0 1 0 88.3 11.5 9 0 1 −1 0 81.5 11.1 10 1 0 −1 0 81.1 10.8 11 −1 0 0 −1 80.5 10.5 12 0 0 0 0 90.3 12.2 13 0 0 −1 1 81.2 11.2 14 0 −1 0 1 82.5 11.3 15 0 1 0 1 87.3 11.7 16 1 −1 0 0 78.5 11.2 17 0 −1 0 −1 75.9 10.8 18 0 −1 1 0 76.6 11.1 19 0 1 0 −1 84.8 11.3 20 0 0 0 0 91.7 12.4 21 −1 1 0 0 83.8 10.9 22 0 0 1 −1 78.6 11.3 23 −1 0 0 1 83.8 10.9 24 1 0 0 −1 83.5 11.4 25 0 −1 −1 0 73.8 10.7 26 0 0 −1 −1 76.9 10.8 27 −1 −1 0 0 75.3 10.1 28 1 1 0 0 89.6 11.2 29 0 0 0 0 90.5 12.2 2.2.2 回归模型与方差分析
利用响应面处理软件进行数据整理拟合,得到桑葚汁发酵工艺感官评分(Y)和活菌数(M)的多元二次回归方程:
Y=90.78+1.80A+4.50B+2.81C+2.51D+0.65AB+0.48AC−0.27AD+1.32BC−1.02 BD+1.72CD−3.51A2−5.09B2−5.10C2−3.67D2
M=12.26+0.27A+0.22B+0.31C+0.17D−0.20AB−0.075AC−0.15AD+0.025BC−0.025BD+0.025CD−0.80A2−0.59B2−0.53C2-0.44D2
对拟合的模型进行方差分析,结果见表4,感官评分(Y)和活菌数(M)的模型为差异极显著(P<0.01),失拟项结果显示不显著(P>0.05),且感官评分(Y)和活菌数(M)模型的相关系数分别为R2(Y)=96.52%、R2(M)=97.07%,校正系数分别为R2Adj(Y)=93.04%、R2Adj(M)=94.13%,综上可知感官评分(Y)和活菌数(M)的模型拟合度较好,模型可用于桑葚汁发酵工艺的结果预测。
表 4 回归模型方差分析Table 4. Variance analysis of regression models方差来源 平方和(Y/M) 自由度 均方(Y/M) F值(Y/M) P值(Y/M) 显著性(Y/M) 模型 808.21/9.53 14/14 57.73/0.68 27.75/33.1 <0.0001/<0.0001 **/** A 38.88/0.91 1/1 38.88/0.91 18.69/44.14 0.0007/<0.0001 **/** B 243/0.56 1/1 243/0.56 116.8/27.4 <0.0001/0.0001 **/** C 94.64/1.14 1/1 94.64/1.14 45.49/55.49 <0.0001/0.0001 **/** D 75.5/0.33 1/1 75.5/0.33 36.29/16.21 <0.0001/0.0012 **/** AB 1.69/0.16 1/1 1.69/0.16 0.81/7.78 0.3827/0.0145 /* AC 0.9/0.022 1/1 0.9/0.022 0.43/1.09 0.5208/0.3132 / AD 0.3/0.09 1/1 0.3/0.09 0.15/4.38 0.7087/0.0551 / BC 7.02/2.50E-03 1/1 7.02/2.50E-03 3.38/0.12 0.0875/0.7325 / BD 4.2/2.50E-03 1/1 4.2/2.50E-03 2.02/0.12 0.1771/0.7325 / CD 11.9/2.50E-03 1/1 11.9/2.50E-03 5.72/0.12 0.0314/0.7325 */ A2 79.95/4.16 1/1 79.95/4.16 38.43/202.34 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** B2 167.78/2.25 1/1 167.78/2.25 80.64/109.21 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** C2 168.6/1.79 1/1 168.6/1.79 81.04/87.24 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** D2 87.52/1.25 1/1 87.52/1.25 42.07/60.62 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** 残差 29.13/0.29 14/14 2.08/0.021 失拟 27.24/0.26 10/10 2.72/0.026 5.77/3.2 0.0529/0.1369 / 纯误差 1.89/0.032 4/4 0.47/8.00E-03 总和 837.34/9.81 28/28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01),*表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 由表4可知,感官评分(Y)模型中一次项A、B、C、D和二次项A2、B2、C2、D2对感官评分结果呈差异极显著(P<0.01),交互项CD呈差异显著(P<0.05),其余为不显著(P>0.05);活菌数(M)模型中一次项A、B、C、D和二次项A2、B2、C2、D2对活菌数结果呈差异极显著(P<0.01),交互项AB呈差异显著(P<0.05),其余为不显著(P>0.05);同时F值能反映出响应面因素对响应值的影响大小,响应面因素对感官评分(Y)的影响顺序为初始pH>发酵温度>低聚果糖添加量>菌种添加量,对活菌数(M)的影响顺序为发酵温度>菌种添加量>初始pH>低聚果糖添加量。
2.2.3 响应面因素交互作用
响应面三维立体图是由响应面因素与响应值构成,可通过响应面三维立体图的曲面弯曲坡度反映两个响应面因素之间的交互作用强弱,曲面弯曲坡度越大,交互作用越强,对响应值的影响越大;同时响应面三维立体图中的等高线图反映出两个响应面因素间的交互作用显著性,等高线图越接近椭圆的说明两个响应面因素间的交互作用越明显,呈显著性差异[33−34]。
由图6可知,感官评分(Y)和活菌数(M)与四个响应面因素间形成的响应面图曲面弯曲坡度均较大,且坡面较陡,说明四个响应面一次项和二次项因素对感官评分(Y)和活菌数(M)的影响均为差异极显著;发酵温度(C)和低聚果糖(D)形成的响应面图坡度较小,说明二者交互作用对感官评分(Y)的影响为差异显著;同时菌种添加量(A)和初始pH(B)的交互作用对活菌数(M)的影响为差异显著。
2.2.4 模型验证实验
通过响应面软件模拟分析得到响应面因素对感官评分影响的发酵桑葚汁工艺参数为菌种添加量0.066%,初始pH6.24,发酵温度37.48 ℃,低聚果糖0.101%,此时感官评分最高为93.175分。响应面因素对活菌数影响的发酵桑葚汁工艺参数为菌种添加量0.062%,初始pH6.083,发酵温度37.41℃,低聚果糖0.094%,此时活菌数最高为12.354 lg (CFU/mL)。发酵桑葚汁工艺以活菌数为第一评价指标,感官评分为第二评价指标,在活菌数最高的条件下,感官评分为92.885分,与感官评分最优条件下的差别较小。故综合考虑发酵桑葚汁工艺参数为菌种添加量0.062%,初始pH6.083,发酵温度37.41℃,低聚果糖0.094%,便于实际生产操作,根据实际情况将工艺参数微调为菌种添加量0.06%,初始pH6.1,发酵温度37℃,低聚果糖0.09%,对此工艺参数进行实际验证实验,得到感官评分为93分,活菌数为12.32 lg(CFU/mL),与模型拟合预测值基本一致,说明此模型较切合实际情况。
2.3 乳酸菌对发酵桑葚汁理化指标的影响
由表5可知,在乳酸菌发酵过程中,随着发酵的深入,BL、LP和LP&BL的TSS均呈现逐渐降低的趋势,降低幅度较小;且在LP&BL发酵中,TS由未发酵时的68.49 mg/mL降低为发酵48 h的57.44 mg/mL,呈现显著性(P<0.05)降低,这可以归因于乳酸菌菌株利用其进行生长代谢和生物转化为乳酸;TS含量变化可以被认为是发酵过程中消耗糖类化合物和产生有机酸之间的平衡作用[35]。同理,发酵桑葚汁pH呈下降趋势,TA呈上升趋势;TA含量变化表明乳酸菌菌株在发酵过程中产生了酸性化合物。与单菌株发酵相比,混合菌株随着发酵时间的延长TA含量显著升高(P<0.05)。混合菌株发酵能显著提高发酵桑葚汁的总酸含量,降低总糖含量,促进乳酸菌的生长繁殖。
表 5 桑葚汁发酵过程中理化指标变化Table 5. Changes of physical and chemical indexes during fermentation of mulberry juiceCON BL-24 h LP-24 h LP&BL-24 h BL-48 h LP-48 h LP&BL-48 h pH 6.04±0.10a 5.07±0.06b 5.16±0.07b 5.10±0.15b 4.11±0.08c 4.12±0.07c 4.01±0.05c TSS (°Brix ) 16.43±0.02a 15.45±0.04c 15.63±0.05b 15.53±0.05c 15.32±0.06de 15.36±0.03d 15.24±0.01e TS (mg/mL) 68.49±1.16a 55.76±0.43d 61.99±0.78b 58.56±0.79c 57.81±0.98c 58.67±1.05c 57.44±0.67cd TA (g/L) 2.99±0.19e 3.64±0.12d 3.58±0.06d 4.38±0.21c 4.79±0.03b 4.59±0.04bc 5.07±0.05a 注:TSS代表可溶性固形物,TS代表总糖,TA代表总酸, 不同小写字母表示同一指标各数据之间呈显著差异(P<0.05)。 2.4 乳酸菌对发酵桑葚汁功能性成分影响
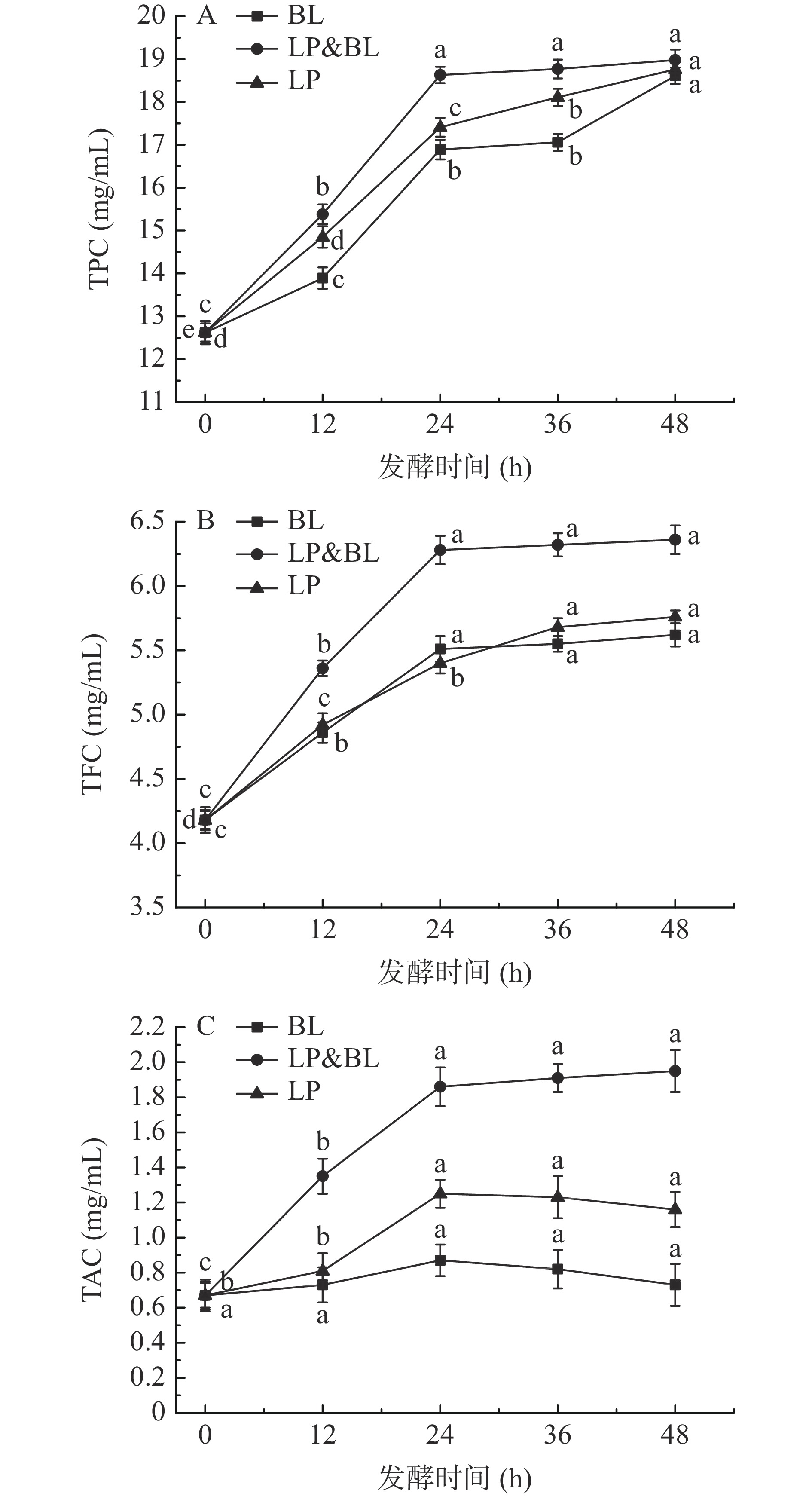
由图7可知,总酚(TPC)、总黄酮(TFC)和总花青素(TAC)的含量在发酵各阶段间均有不同的变化趋势,发酵桑葚汁与未发酵桑葚汁相比,乳酸菌发酵能有效提高发酵桑葚汁的功能性化合物含量;这可能是因为在发酵过程中乳酸菌会产生一些特定的水解酶,而这些特定的水解酶将发酵液中复杂的酚类化合物去糖基化,使其分解成分子量较小、结构组成较简单的酚酸化合物[36],这与Gan等[37]研究结果一致,其利用乳酸菌发酵豆奶,发现乳酸菌发酵可有效提高总酚含量。发酵桑葚汁间的化合物浓度差异可能是由于不同乳酸菌自身的生理特性以及在发酵时所分泌的产物不同所致。
TPC含量如图7(A),在单菌株发酵方式中,随着发酵时间的延长,TPC含量呈逐渐增大的变化趋势;其中发酵48 h的TPC含量最高;同时在发酵后24 h中混合菌株发酵TPC含量趋于平稳(P>0.05);产生这种趋势变化可能是发酵过程中乳酸菌生长代谢所引起的,乳酸菌代谢过程中产生的物质将复杂的酚类化合物分解为结构简单的化合物,分子量变小[38],提高了TPC含量;随着发酵时间的延长,乳酸菌生长降低pH,致使乳酸菌生长繁殖受到限制,代谢产物分泌受阻,生长速度减缓;TPC含量趋于稳定。
TFC含量如图7(B), TFC含量变化中单菌株发酵与混合菌株发酵相比,混合菌株发酵方式的TFC含量较高,这可能是由乳酸菌发酵产生的酶类物质将复杂的多酚分解为小分子的黄酮醇物质[39]。在发酵前24 h中,TFC含量升高趋势较大,呈显著差异(P<0.05);发酵时间36 h至48 h中,TFC含量变化趋于稳定(P>0.05),可能是由于发酵初期发酵液环境适宜乳酸菌生长繁殖,其生长速度较快,代谢产物较多,对多酚物质分解为黄酮醇物质加快,发酵后期随着乳酸菌含量增多,发酵液pH降低,致使乳酸菌生长速度减缓。
TAC含量变化如图7(C),发酵前24 h中植物乳杆菌发酵和混合菌株发酵的TAC含量呈显著上升趋势(P<0.05),发酵24 h至48 h中长双歧杆菌和植物乳杆菌的单菌株TAC含量呈下降趋势,混合菌株发酵的TAC含量趋于稳定(P>0.05),在发酵开始至发酵结束中混合菌株发酵的TAC含量高于长双歧杆菌和植物乳杆菌的单菌株发酵;混合菌株发酵的TAC含量由未发酵时0.67 mg/mL增加为发酵48 h后的1.95 mg/mL;这可能是由于发酵初期乳酸菌生长繁殖使得花青素中结合态转变为游离态,增加了其含量;发酵后期单菌株发酵的花青素含量下降可能是由于花青素不太稳定的原因所致,发酵后期混合菌株发酵的花青素含量趋于稳定(P>0.05)可能是由于乳酸菌菌株间的协同作用,混合菌株发酵更深层次影响TAC的含量。混合菌株发酵能提高TAC含量可能与TAC易受外界环境条件(光照、温度和发酵类型等)的影响有关[40]。
综上所述,植物乳杆菌和长双歧杆菌均匀混合配比的混合菌株发酵可有效提高发酵桑葚汁中的TPC、TFC和TAC含量。
2.5 乳酸菌对发酵桑葚汁抗氧化活性影响
由表6可知,与未发酵样品相比,发酵样品拥有较高的抗氧化活性,呈显著性差异(P<0.05),说明乳酸发酵对抗氧化活性的提高具有积极的影响,乳酸菌在发酵时可以增加发酵液中的总酚等化合物的含量,同时增加具有给质子特性化合物的可用性,这些化合物有效地提高了DPPH自由基清除率和ABTS+自由基清除率抗氧化反应中阳离子还原率[41],从而提高抗氧化活性;混合菌株发酵桑葚汁的抗氧化活性要优于单菌株发酵。混合菌株发酵48 h时的抗氧化活性显著(P<0.05)高于单菌株发酵。
表 6 桑葚汁发酵过程中抗氧化活性变化Table 6. Changes in antioxidant activity during fermentation of mulberry juice指标 CON BL-24 h LP-24 h LP&BL-24 h BL-48 h LP-48 h LP&BL-48 h DPPH自由基清除率(%) 52.78±0.67f 58.13±0.36e 64.46±0.17d 73.34±1.20b 67.17±0.82c 68.36±1.14c 81.64±0.59a ABTS+自由基清除率(%) 61.81±0.56f 72.68±0.41e 76.20±1.34d 82.50±0.57c 77.37±0.85d 83.81±0.71b 88.17±0.57a T-AOC (mmol/L) 17.85±0.70d 18.54±0.94d 18.81±0.37d 21.42±1.09c 22.23±0.65bc 23.29±0.79b 29.49±0.71a ·OH清除率(%) 37.38±1.21g 45.19±1.04f 59.74±0.80d 74.48±0.65b 57.40±1.21e 65.20±0.94c 86.07±0.89a 注:T-AOC代表总抗氧化能力,不同小写字母表示同一指标各数据之间呈显著差异(P<0.05)。 3. 结论
本研究以植物乳杆菌和长双歧杆菌为发酵菌株,分别进行单菌株发酵和混合菌株发酵,优化桑葚汁发酵工艺及探讨桑葚汁发酵时的功能品质。研究结果表明,在优化发酵工艺方面,混合菌株发酵桑葚汁的感官评分和活菌数最高,在此基础上利用响应面试验得到最佳发酵工艺参数为菌种添加量0.06%,初始pH6.1,发酵温度37 ℃,低聚果糖添加量0.09%,此时感官评分最高为93 分,活菌数为12.32 lg (CFU/mL);在发酵桑葚汁的功能品质方面,混合菌株发酵可以提高乳酸菌活菌数量、功能性化合物含量和抗氧化活性。在桑葚汁发酵过程中,混合菌株发酵具有较好的生物活性和化合物特性,总黄酮含量由4.18 mg/mL增加为6.36 mg/mL,总花青素由0.67 mg/mL增加为1.95 mg/mL,总酚含量由12.62 mg/mL增加为18.65 mg/mL;同时ABTS+自由基清除率、DPPH自由基清除率、羟自由基清除率和总抗氧化能力均得到有效提高。因此,植物乳杆菌和长双歧杆菌混合发酵可有效提高发酵桑葚汁的感官体验和功能特性,可为桑葚深加工提供一种新的高附加值产品。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平
Table 1 Response surface test factors and levels
因素 水平 −1 0 1 A菌种添加量(%) 0.04 0.06 0.08 B初始pH 5.5 6.0 6.5 C发酵温度(℃) 35 37 39 D低聚果糖添加量(%) 0.06 0.09 0.12 表 2 发酵桑葚汁感官评分表
Table 2 Sensory score table of fermented mulberry juice
评分项目 评分标准 分值(分) 色泽
(20分)能呈现桑葚汁的深红色,色泽均匀 15~20 较能呈现桑葚汁的深红色,色泽较均匀 6~14 不能呈现桑葚汁的深红色,色泽不均匀,有杂色 <6 口感
(40分)口感协调,酸甜适中 30~40 口感较协调,但稍酸或稍甜 20~29 口感略协调,但过酸或过甜 10~19 口感不协调 <10 气味
(20分)气味协调,桑葚气味浓郁,无杂味 15~20 气味适中,桑葚气味较淡,稍有杂味 8~14 气味不协调,有杂味 <8 形态
(20分)组织形态均匀,无沉淀 15~20 组织形态较均匀,略有沉淀 7~14 组织形态不均匀,有沉淀 <7 表 3 响应面试验设计方案与结果
Table 3 Response surface experimental design and results
实验号 A菌种
添加量B初始
pHC发酵
温度D低聚果糖
添加量Y感官
评分(分)M活菌数(lg
(CFU/mL))1 −1 0 −1 0 78.2 10.3 2 1 0 0 1 85.7 11.2 3 0 0 1 1 89.8 11.8 4 0 0 0 0 91.3 12.2 5 −1 0 1 0 83.5 11.3 6 0 0 0 0 90.1 12.3 7 0 1 1 0 89.6 11.6 8 1 0 1 0 88.3 11.5 9 0 1 −1 0 81.5 11.1 10 1 0 −1 0 81.1 10.8 11 −1 0 0 −1 80.5 10.5 12 0 0 0 0 90.3 12.2 13 0 0 −1 1 81.2 11.2 14 0 −1 0 1 82.5 11.3 15 0 1 0 1 87.3 11.7 16 1 −1 0 0 78.5 11.2 17 0 −1 0 −1 75.9 10.8 18 0 −1 1 0 76.6 11.1 19 0 1 0 −1 84.8 11.3 20 0 0 0 0 91.7 12.4 21 −1 1 0 0 83.8 10.9 22 0 0 1 −1 78.6 11.3 23 −1 0 0 1 83.8 10.9 24 1 0 0 −1 83.5 11.4 25 0 −1 −1 0 73.8 10.7 26 0 0 −1 −1 76.9 10.8 27 −1 −1 0 0 75.3 10.1 28 1 1 0 0 89.6 11.2 29 0 0 0 0 90.5 12.2 表 4 回归模型方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of regression models
方差来源 平方和(Y/M) 自由度 均方(Y/M) F值(Y/M) P值(Y/M) 显著性(Y/M) 模型 808.21/9.53 14/14 57.73/0.68 27.75/33.1 <0.0001/<0.0001 **/** A 38.88/0.91 1/1 38.88/0.91 18.69/44.14 0.0007/<0.0001 **/** B 243/0.56 1/1 243/0.56 116.8/27.4 <0.0001/0.0001 **/** C 94.64/1.14 1/1 94.64/1.14 45.49/55.49 <0.0001/0.0001 **/** D 75.5/0.33 1/1 75.5/0.33 36.29/16.21 <0.0001/0.0012 **/** AB 1.69/0.16 1/1 1.69/0.16 0.81/7.78 0.3827/0.0145 /* AC 0.9/0.022 1/1 0.9/0.022 0.43/1.09 0.5208/0.3132 / AD 0.3/0.09 1/1 0.3/0.09 0.15/4.38 0.7087/0.0551 / BC 7.02/2.50E-03 1/1 7.02/2.50E-03 3.38/0.12 0.0875/0.7325 / BD 4.2/2.50E-03 1/1 4.2/2.50E-03 2.02/0.12 0.1771/0.7325 / CD 11.9/2.50E-03 1/1 11.9/2.50E-03 5.72/0.12 0.0314/0.7325 */ A2 79.95/4.16 1/1 79.95/4.16 38.43/202.34 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** B2 167.78/2.25 1/1 167.78/2.25 80.64/109.21 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** C2 168.6/1.79 1/1 168.6/1.79 81.04/87.24 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** D2 87.52/1.25 1/1 87.52/1.25 42.07/60.62 <0.0001<0.0001 **/** 残差 29.13/0.29 14/14 2.08/0.021 失拟 27.24/0.26 10/10 2.72/0.026 5.77/3.2 0.0529/0.1369 / 纯误差 1.89/0.032 4/4 0.47/8.00E-03 总和 837.34/9.81 28/28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01),*表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 5 桑葚汁发酵过程中理化指标变化
Table 5 Changes of physical and chemical indexes during fermentation of mulberry juice
CON BL-24 h LP-24 h LP&BL-24 h BL-48 h LP-48 h LP&BL-48 h pH 6.04±0.10a 5.07±0.06b 5.16±0.07b 5.10±0.15b 4.11±0.08c 4.12±0.07c 4.01±0.05c TSS (°Brix ) 16.43±0.02a 15.45±0.04c 15.63±0.05b 15.53±0.05c 15.32±0.06de 15.36±0.03d 15.24±0.01e TS (mg/mL) 68.49±1.16a 55.76±0.43d 61.99±0.78b 58.56±0.79c 57.81±0.98c 58.67±1.05c 57.44±0.67cd TA (g/L) 2.99±0.19e 3.64±0.12d 3.58±0.06d 4.38±0.21c 4.79±0.03b 4.59±0.04bc 5.07±0.05a 注:TSS代表可溶性固形物,TS代表总糖,TA代表总酸, 不同小写字母表示同一指标各数据之间呈显著差异(P<0.05)。 表 6 桑葚汁发酵过程中抗氧化活性变化
Table 6 Changes in antioxidant activity during fermentation of mulberry juice
指标 CON BL-24 h LP-24 h LP&BL-24 h BL-48 h LP-48 h LP&BL-48 h DPPH自由基清除率(%) 52.78±0.67f 58.13±0.36e 64.46±0.17d 73.34±1.20b 67.17±0.82c 68.36±1.14c 81.64±0.59a ABTS+自由基清除率(%) 61.81±0.56f 72.68±0.41e 76.20±1.34d 82.50±0.57c 77.37±0.85d 83.81±0.71b 88.17±0.57a T-AOC (mmol/L) 17.85±0.70d 18.54±0.94d 18.81±0.37d 21.42±1.09c 22.23±0.65bc 23.29±0.79b 29.49±0.71a ·OH清除率(%) 37.38±1.21g 45.19±1.04f 59.74±0.80d 74.48±0.65b 57.40±1.21e 65.20±0.94c 86.07±0.89a 注:T-AOC代表总抗氧化能力,不同小写字母表示同一指标各数据之间呈显著差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 乔健, 李国鹏, 杜丽清, 等. 桑葚果实不同发育期品质测定及其相关性分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(17):24−29. [QIAO Jian, LI Guopeng, DU Liqing, et al. Quality determination and correlation analysis of mulberry fruit at different stages of development[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(17):24−29. QIAO Jian, LI Guopeng, DU Liqing, et al. Quality determination and correlation analysis of mulberry fruit at different stages of development[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(17): 24−29.
[2] 魏雪琴, 陈美钰, 游赵微, 等. 响应面法优化桑葚酵素食用凝胶的制备工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(19):247−254. [WEI Xueqin, CHEN Meiyu, YOU Zhaowei, et al. Optimization of preparation process of gel for vegetarian fermentation of mulberry fermentation by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(19):247−254. WEI Xueqin, CHEN Meiyu, YOU Zhaowei, et al . Optimization of preparation process of gel for vegetarian fermentation of mulberry fermentation by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (19 ):247 −254 .[3] CHEN X B, SOHOULI M H, NATEGHI M, et al. Impact of mulberry consumption on cardiometabolic risk factors:A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials[J]. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics,2022,47(12):1982−1993. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13822
[4] GAO T Q, CHEN J L, XU F, et al. Mixed mulberry fruit and mulberry leaf fermented alcoholic beverages:Assessment of chemical Composition, antioxidant capacity in vitro and sensory evaluation[J]. Foods,2022,11(19):3125. doi: 10.3390/foods11193125
[5] 夏川林, 殷浩, 王香君, 等. 桑葚功能性成分研究现状与综合利用[J]. 四川蚕业,2021,49(3):42−45. [XIA Chuanlin, YIN Hao, WANG Xiangjun, et al. Research status and comprehensive utilization of functional components of mulberry[J]. Sichuan Sericulture,2021,49(3):42−45. XIA Chuanlin, YIN Hao, WANG Xiangjun, et al . Research status and comprehensive utilization of functional components of mulberry[J]. Sichuan Sericulture,2021 ,49 (3 ):42 −45 .[6] ZHANG S R, XING X, CHU Q, et al. Impact of co-culture of Lactobacillus plantarum and Oenococcus oeni at different ratios on malolactic fermentation, volatile and sensory characteristics of mulberry wine[J]. LWT,2022,169:113995. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113995
[7] 尹俊涛, 刘艳怀, 雷勇, 等. 蔓越莓桑葚复合饮料工艺优化及配方研究[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(7):48−52. [YIN Juntao, LIU Yanhuai, LEI Yong, et al. Process optimization and formulation study of cranberry mulberry compound beverage[J]. Food Industry,2022,43(7):48−52. YIN Juntao, LIU Yanhuai, LEI Yong, et al . Process optimization and formulation study of cranberry mulberry compound beverage[J]. Food Industry,2022 ,43 (7 ):48 −52 .[8] 孙百虎. 不同乳酸菌对发酵桑葚汁酚类物质含量及抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(1):92−97. [SUN Baihu. Effects of different lactic acid bacteria on phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of fermented mulberry juice[J]. China Brewing,2022,41(1):92−97. SUN Baihu . Effects of different lactic acid bacteria on phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of fermented mulberry juice[J]. China Brewing,2022 ,41 (1 ):92 −97 .[9] QU L Y, JIN C Y, GAO Q S, et al. Effects of selenium-enriched Lactobacillus fermented corn stalks on cattle rumen fermentation[J]. Computer Informatization and Mechanical System,2022,5(4):74−80.
[10] LIU J, XIE H P, GAO Y, et al. Soybean protein isolate treated with transglutaminase (TGase) enhances the heat tolerance of selected lactic acid bacteria strains to spray drying[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,404(PB):134676.
[11] 吕蕾, 杨晓萍, 王阿利, 等. 酱油渣中具有抑菌活性的乳酸菌的筛选及其抑菌特性[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(18):137−144. [LÜ Lei, YANG Xiaoping, WANG Ali, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria with bacteriostatic activity in soy sauce residue and their bacteriostatic properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(18):137−144. LÜ Lei, YANG Xiaoping, WANG Ali, et al . Screening of lactic acid bacteria with bacteriostatic activity in soy sauce residue and their bacteriostatic properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (18 ):137 −144 .[12] SARA R S, MARIA R I, MARIA R P, et al. Lactic acid bacteria as biocontrol agents to reduce Staphylococcus aureus growth, enterotoxin production and virulence gene expression[J]. LWT, 2022, 170:114025.
[13] HE Z S, ZHANG H, WANG T, et al. Effects of five different lactic acid bacteria on bioactive components and volatile compounds of oat[J]. Foods,2022,11(20):3230. doi: 10.3390/foods11203230
[14] 冯丹丹, 胡萍, 许浩翔, 等. 乳酸菌发酵刺梨汁体外降血糖、降血脂活性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(8):212−219. [FENG Dandan, HU Ping, XU Haoxiang, et al. Study on hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering activity of lactic acid bacteria fermented prickly pear juice in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(8):212−219. FENG Dandan, HU Ping, XU Haoxiang, et al . Study on hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering activity of lactic acid bacteria fermented prickly pear juice in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022 ,48 (8 ):212 −219 .[15] 梁红敏, 郭亚芸, 史红梅. 不同乳酸菌发酵葡萄酵素过程中代谢产物及其抗氧化特性分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(24):170−176. [LIANG Hongmin, GUO Yayun, SHI Hongmei. Analysis of metabolites and antioxidant characteristics of grape enzymes fermented by different lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(24):170−176. LIANG Hongmin, GUO Yayun, SHI Hongmei . Analysis of metabolites and antioxidant characteristics of grape enzymes fermented by different lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Research and Development,2021 ,42 (24 ):170 −176 .[16] FERNANDA B T, BORGHI V L, SOARES J N, et al. Fruit bioactive compounds:Effect on lactic acid bacteria and on intestinal microbiota[J]. Food Research International,2022,161:111809. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111809
[17] 扈莹红, 陈晓慧, 常学东, 等. 酒曲中乳酸菌的筛选及其在板栗糯米饮料发酵中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(5):138−146. [HU Yinghong, CHEN Xiaohui, CHANG Xuedong, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria in koji and its application in fermentation of chestnut glutinous rice beverage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(5):138−146. HU Yinghong, CHEN Xiaohui, CHANG Xuedong, et al . Screening of lactic acid bacteria in koji and its application in fermentation of chestnut glutinous rice beverage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (5 ):138 −146 .[18] 盛洁, 田欢, 刘原野, 等. 响应面法优化红枣益生菌发酵饮料工艺[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(2):203−208. [SHENG Jie, TIAN Huan, LIU Yuanye, et al. Optimization of probiotic fermented beverage process of red jujube by response surface method[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(2):203−208. SHENG Jie, TIAN Huan, LIU Yuanye, et al . Optimization of probiotic fermented beverage process of red jujube by response surface method[J]. China Brewing,2021 ,40 (2 ):203 −208 .[19] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 4789.35-2016食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 乳酸菌检验[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016:1−8. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 4789.35-2016 National food safety standard-Food microbiology test-Lactic acid bacteria test[S] Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016:1−8. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 4789.35-2016 National food safety standard-Food microbiology test-Lactic acid bacteria test[S] Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016: 1−8.
[20] 刘彩华, 曾嘉童, 包竹君, 等. 3,5-二硝基水杨酸比色法测定芒果的可溶性糖含量[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(9):2892−2900. [LIU Caihua, ZENG Jiatong, BAO Zhujun, et al. Determination of soluble sugar content of mango by 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetric method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Detection,2022,13(9):2892−2900. LIU Caihua, ZENG Jiatong, BAO Zhujun, et al . Determination of soluble sugar content of mango by 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid colorimetric method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Detection,2022 ,13 (9 ):2892 −2900 .[21] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 12456-2021食品安全国家标准 食品中总酸的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2008:1−6. [National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 12456-2021 National food safety standard-Determination of total acid in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2008:1−6. National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 12456-2021 National food safety standard-Determination of total acid in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008: 1−6.
[22] KWAW E, MA Y K, TCHABO W, et al. Effect of lactobacillus strains on phenolic profile, color attributes and antioxidant activities of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,250:148−154. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.009
[23] GAO H, WEN J J, HU J L, et al. Momordica charantia juice with Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation:Chemical composition, antioxidant properties and aroma profile[J]. Food Bioscience,2019,29:62−72. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2019.03.007
[24] CHEN Y, PAN H L, HAO S X, et al. Evaluation of phenolic composition and antioxidant properties of different varieties of Chinese citrus[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,364:130413. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130413
[25] 李佩佩, 颉向红, 王聪, 等. 不同发酵方式下枸杞饮料主要成分及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(24):90−97. [LI Peipei, JIE Xianghong, WANG Cong, et al. Main components and antioxidant activity of goji berry beverages under different fermentation methods[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2019,45(24):90−97. LI Peipei, JIE Xianghong, WANG Cong, et al . Main components and antioxidant activity of goji berry beverages under different fermentation methods[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2019 ,45 (24 ):90 −97 .[26] 沈燕飞. 乳酸菌发酵苹果原浆过程中的基本组分与抗氧化活性变化[D]. 杭州:浙江工业大学, 2019:10−13. [SHEN Y F. The basic components and antioxidant activity of lactic acid bacteria fermented apple slurry process[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University of Technology, 2019:10−13. SHEN Y F. The basic components and antioxidant activity of lactic acid bacteria fermented apple slurry process[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2019: 10−13.
[27] CAI W C, TANG F X, ZHAO X X, et al. Different lactic acid bacteria strains affecting the flavor profile of fermented jujube juice[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2019,43(2):14095.
[28] NIU Z H, ZOU M J, BEI T T, et al. Effect of fructooligosaccharides on the colonization of Lactobacillus rhamnosus AS 1.2466T in the gut of mice[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2023,12(2):607−613. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.063
[29] DOU Y Q, YU X, LUO Y L, et al. Effect of fructooligosaccharides supplementation on the gut microbiota in human:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(16):3298−3298. doi: 10.3390/nu14163298
[30] CUI S M, GUO W L, CHEN C L, et al. Metagenomic analysis of the effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and fructooligosaccharides (FOS) on the fecal microbiota structure in mice[J]. Foods,2022,11(9):1187−1187. doi: 10.3390/foods11091187
[31] CHEN C, LU Y Q, YU H Y, et al. Influence of 4 lactic acid bacteria on the flavor profile of fermented apple juice[J]. Food Bioscience,2019,27:30−36. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2018.11.006
[32] PENG W, MENG D, YUE T, et al. Effect of the apple cultivar on cloudy apple juice fermented by a mixture of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Lactobacillus fermentum[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,340:127922. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127922
[33] 赵欢, 贺晓龙, 王晓涧, 等. 基于响应面法优化北虫草蛋卷工艺及其品质分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(12):185−192 [ZHAO Huan, HE Xiaolong, WANG Xiaojian, et al. Optimization of cordyceps egg roll process and quality analysis based on response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(12):185−192. ZHAO Huan, HE Xiaolong, WANG Xiaojian, et al . Optimization of cordyceps egg roll process and quality analysis based on response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023 ,44 (12 ):185 −192 .[34] 罗蓉, 蔡旭, 薛宏坤, 等. 响应面法优化超声辅助低共熔溶剂提取山楂总黄酮工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(22):229−237. [LUO Rong, CAI Xu, XUE Hongkun, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted low eutectic solvent extraction process of hawthorn total flavonoids by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(22):229−237. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022010235 LUO Rong, CAI Xu, XUE Hongkun, et al . Optimization of ultrasound-assisted low eutectic solvent extraction process of hawthorn total flavonoids by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (22 ):229 −237 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022010235[35] BAI X, HAN M Z, YUE T L, et al. Control of post-acidification and shelf-life prediction of apple juice fermented by lactobacillus[J]. Food Control,2022,139:109076. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109076
[36] WU Y, LI S, TAO Y, et al. Fermentation of blueberry and blackberry juices using Lactobacillus plantarum, Streptococcus thermophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum:Growth of probiotics, metabolism of phenolics, antioxidant capacity in vitro and sensory evaluation[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,328:129083.
[37] GAN R Y, SHAH N P, WANG M F, et al. Lactobacillus plan tarum WCFS1 fermentation differentially affects antioxidant capacity and polyphenol content in mung bean ( Vigna radiata) and soya bean ( Glycine max) milks[J]. Journal of Food processing and Preservation,2016,41(1):e12944.
[38] WU C Y, LI T L, QI J, et al. Effects of lactic acid fermentation-based biotransformation on phenolic profiles, antioxidant capacity and flavor volatiles of apple juice[J]. LWT,2020,122:109064. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109064
[39] LIU Y Y, SHENG J, LI J J, et al. Influence of lactic acid bacteria on physicochemical indexes, sensory and flavor characteristics of fermented sea buckthorn juice[J]. Food Bioscience,2022,46:101519. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101519
[40] SHENG J, SHAN C H, LIU Y Y, et al. Comparative evaluation of the quality of red globe grape juice fermented by Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2022,57:2235−2248. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.15568
[41] EIDI F, POOR-REZA G F, OATADRAHIMI A, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus on serum uremic toxins (phenol and P-cresol) in hemodialysis patients:A double blind randomized clinical trial[J]. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN,2018,28:1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2018.09.003
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 李恩静,王丹,李赫婧,杨红莲. 基于微滴数字聚合酶链式反应法定量检测婴幼儿配方乳粉中乳杆菌. 食品科技. 2025(02): 334-342 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈佳,张琳琳,王晓茹,肖霄,张凯江,郭金颖,辛文,杨帛,孙伟. 基于微滴式数字PCR技术检测树莓制品的定量分析方法. 现代食品. 2024(07): 196-201 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 秦爱,王娟,邓方进,余秋地,周朝旭,李根容,肖昭竞. 数字聚合酶链式反应技术在食品安全核酸检测领域中的研究进展及标准化现状. 食品科学. 2024(18): 350-360 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李恩静,王丹,李龙,李赫婧,杨红莲. 基于微滴数字PCR技术检测致敏原芒果成分. 食品与机械. 2024(09): 50-55+115 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周志刚,杜东东,孟德龙,赵雅洁,李道君,栾银银,药园园,杨雅麟. 基因检测技术在饲料原料物种鉴定中的研究. 饲料工业. 2023(04): 1-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 闫邦奇,徐淼锋,王祥红,水克娟,林伟,张卫东,廖力. 名贵中药降香的实时荧光PCR检测方法研究. 中国口岸科学技术. 2023(02): 86-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陈佳琛,陈晨,张瑞,彭瑛琪,贺丽霞,狄慧. 实时荧光PCR法鉴别莜面中掺杂淀粉的植物源性. 食品安全导刊. 2023(11): 122-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



