Exploring the Mechanism of Action of Resveratrol in the Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation
-
摘要: 目的:采用网络药理学和分子对接技术识别分析白藜芦醇抗非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)的潜在靶点和作用机制,并结合临床数据以及分子生物学实验进行初步验证。方法:通过Swiss Target Prediction数据库和Target net数据库筛选白藜芦醇靶点,通过数据库Genecards、OMIM、TTD收集NSCLC靶点,利用Venny 2.1.0平台获得药物和疾病靶点的交集;应用Cytoscape 3.7.2软件与String数据库生成靶标蛋白互作网络(PPI),并进行拓扑分析;利用Metascape数据库对交集靶标进行基因本体(GO)功能富集与京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)通路富集分析,得到交集靶标的基因图谱;利用Autodock Vina 软件对排名前三位的核心靶基因与白藜芦醇进行分子对接验证;通过癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)数据库获得临床病例样本,分析相关靶基因在NSCLC患者(n=1017)和健康人群(n=627)的表达情况;细胞水平采用Western Blot检测不同浓度(30、50 μmol/L)白藜芦醇对人肺腺癌A549细胞SRC、EGFR及PI3K/AKT信号通路蛋白表达的影响。结果:筛选得到的潜在靶点共有40个,经过拓扑分析得到关键靶点8个,其中EGFR、SRC、ESR1等靶点与NSCLC密切相关;白藜芦醇抗NSCLC主要涉及肿瘤蛋白多糖、雌激素信号通路、PI3K/AKT等多条信号通路;分子对接显示,白藜芦醇与关键靶点具有稳定的结合能力;临床样本结果显示,靶基因EGFR、SRC、ESR1、HSP90AA1以及MMP9的表达在NSCLC中上调;TNF、CDC42以及RELA的表达在NSCLC中下调;细胞实验结果表明,白藜芦醇药物干预以剂量依赖的方式抑制了人肺腺癌A549细胞中SRC、EGFR、p-PI3K和p-AKT的蛋白表达。结论:揭示了白藜芦醇在治疗NSCLC的过程中涉及多个作用靶点及多条信号通路,明确了白藜芦醇可通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路发挥其抗癌效应。
-
关键词:
- 白藜芦醇 /
- 非小细胞肺癌 /
- 网络药理学 /
- 癌症基因组图谱 /
- PI3K/AKT信号通路
Abstract: Objective: To explore the potential therapeutic targets and mechanisms of resveratrol in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), a comprehensive study was conducted incorporating network pharmacology, molecular docking methods, and experimental validation. Methods: The targets of resveratrol were searched on Swiss Target Prediction database and Target net database. NSCLC targets were gathered from Genecards, OMIM, TTD databases. The intersection of drug targets and disease targets was obtained using Venny 2.1.0 platform. Next, Cytoscape 3.7.2 software was applied along with the String database to generate target protein interaction networks (PPI) and perform topological analysis. GO functional enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of intersecting targets were conducted using the Metascape database, resulting in gene maps of the intersecting targets. Molecular docking studies were performed for the top three ranked core targets and resveratrol using Autodock Vina software. Clinical case samples were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database to analyze the expression of relevant targets in NSCLC patients (n=1017) and healthy controls (n=627). The effects of different concentrations (30 and 50 μmol/L) of resveratrol on the protein expression of SRC, EGFR and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells were examined using Western Blot at the cellular level. Results: Total of 40 potential targets were screened out, followed by obtaining 8 key targets after topological analysis. These keys targets, including EGFR, SRC, and ESR1 were closely associated with NSCLC. The treatment of NSCLC with resveratrol primarily involved multiple signaling pathways, such as tumor proteoglycans, estrogen signaling and PI3K/AKT. Molecular docking results demonstrated that resveratrol had a good binding ability with the target protein. Clinical sample results revealed that the expression of EGFR, SRC, ESR1, HSP90AA1, and MMP9 was upregulated, while the expression of TNF, CDC42, and RELA was downregulated in NSCLC patients. Cellular experiments indicated that resveratrol could inhibit the protein expression of SRC, EGFR, p-PI3K, and p-AKT in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Conclusion: This study demonstrates that resveratrol involves multiple targets and signaling pathways in the treatment of NSCLC, and clarifies that resveratrol could exert its anti-cancer effects by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. -
肺癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,发病率和死亡率高于结肠癌、乳腺癌和前列腺癌,在所有恶性肿瘤中排名第一[1−2]。依照组织病理学特征,可分为小细胞肺癌(Small cell lung cancer,SCLC)与非小细胞肺癌(Non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)。NSCLC为肺癌发病率最高的分型之一,占所有肺癌病例的80%~85%[3]。根据组织学类型,NSCLC主要分为鳞状细胞癌、腺癌、大细胞癌,每种类型的癌细胞通过不同的方式生长和扩散[4]。可用于肺癌的治疗包括手术、放疗、化疗、免疫调节治疗和分子靶向治疗[1]。以化疗为基础的方案仍然是治疗的首选选择。然而,化疗对晚期NSCLC患者仍然不够有效,5年生存率仅为15%,中位生存期为10~12个月[5]。因此,需要进一步探索NSCLC发生发展的机制,为NSCLC治疗寻找新的靶点。
白藜芦醇是一种天然的多酚类植物抗毒素,它广泛存在于葡萄皮,葡萄酒,浆果,坚果等物质中[6]。相关研究证实,白藜芦醇具备诸多生理和药理活性,如抗氧化、抗炎、保护心脏和抗癌属性[7]。白藜芦醇的抗癌特性已在几种不同类型的癌症中得到证实,包括乳腺癌、结肠癌、子宫内膜癌等[6−8]。Wang等[9]发现在NSCLC原位大鼠模型中,白藜芦醇通过抑制STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF通路抑制肿瘤进展。另一项研究报道了白藜芦醇通过调控p53、Bax、Bcl-2和caspase-3的表达来抑制人肺腺癌A549细胞的增殖并诱导凋亡[10]。这些研究为检测白藜芦醇与NSCLC之间的关系提供了线索,但白藜芦醇对肺癌发挥抑制作用的潜在靶点和分子机制仍未完全清楚。
网络药理学是以系统生物学理论为基础,针对特定分子靶标进行药物分子模拟及设计的新兴学科,通过对靶点网络的综合分析,发掘药物作用的潜在信号通路,明确药物疗效的作用机理[11]。分子对接技术是利用计算机高精度对接模拟,基于分子模型模拟配体-靶标相互结合[12]。本研究应用网络药理学方法和分子对接技术进行靶标预测,分析白藜芦醇抑制NSCLC的可能作用机制,运用临床病例验证及细胞实验进一步评估,提高结果的可靠性。为后续研究及临床应用提供一定参考价值。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
人肺腺癌A549细胞 上海细胞库;白藜芦醇(分子质量228.24 g/mol,纯度>99.99%)、脱脂牛奶粉末 MCE公司;青-链霉素溶液、0.25%胰酶细胞消化液、聚偏二氟乙烯膜(PVDF) 上海碧云天公司;胎牛血清(FBS)、DMEM细胞培养基 美国赛默飞公司;PBS缓冲液、PMSF蛋白酶抑制剂、蛋白酶抑制剂、磷酸酶抑制剂 生工生物工程公司;预染蛋白Marker、BCA蛋白定量试剂盒、RIPA裂解液、5×上样缓冲液(5×loading Buffer)、TBST缓冲液、聚丙烯酰胺凝胶快速配置试剂盒(SDS-PAGE)、ECL化学发光液 武汉博士德公司;Anti-GAPDH抗体、Anti-SRC抗体、Anti-EGFR抗体、Anti-p-PI3K抗体、Anti-p-AKT抗体、HRP标记羊抗兔IgG 武汉ABclonal公司。
CKX41倒置显微镜 日本Olympus公司;Midi 40细胞培养箱 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra Cell垂直电泳仪、rans-Blot SD半干电转膜仪、ChemiDoc™ Imaging System WB全自动化学发光成像仪 上海伯乐公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 白藜芦醇靶点的筛选
通过数据库PubChem(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)得到化合物白藜芦醇化学结构,并保存对应Canonical SMILES号。此外,通过结合Swiss Target Prediction(swisstargetprediction.ch)和Target net数据库(targetnet.scbdd.com)得到白藜芦醇的潜在作用靶点。
1.2.2 NSCLC的靶点筛选
通过数据库Genecards(https://www.genecards.org)和数据库OMIM(https://www.omim.org)以及数据库TTD(db.idrblab.net),对NSCLC潜在靶点进行筛选。
1.2.3 药物-疾病-靶点网络分析
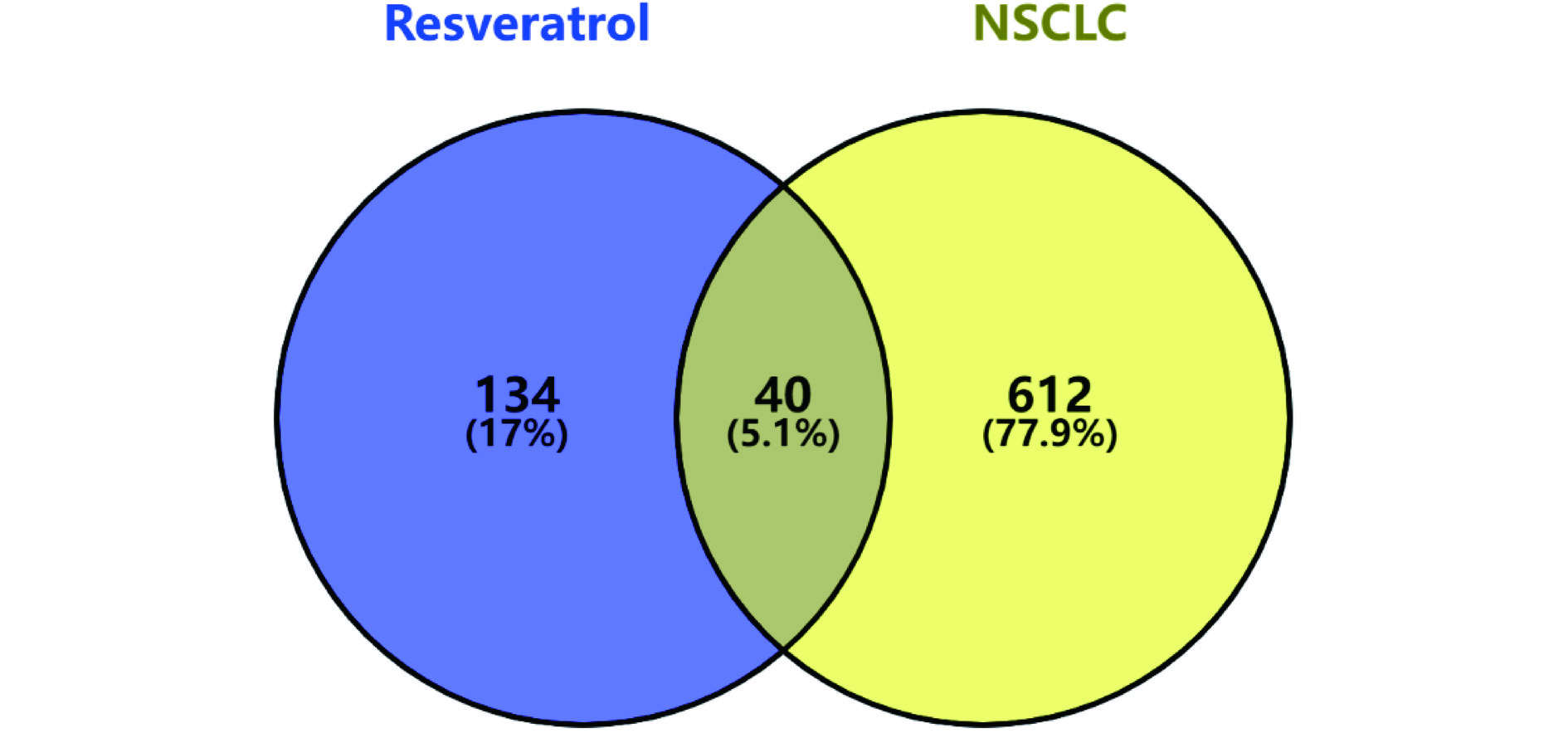
将数据库预测的白藜芦醇的靶点和NSCLC的靶点上传到Venny 2.1.0平台(bioinfogpcnb.csic.es/tools/venny),获取药物的靶点和疾病的靶点交集,绘制白藜芦醇与NSCLC的交集靶点Venny图。
1.2.4 PPI网络构建与分析
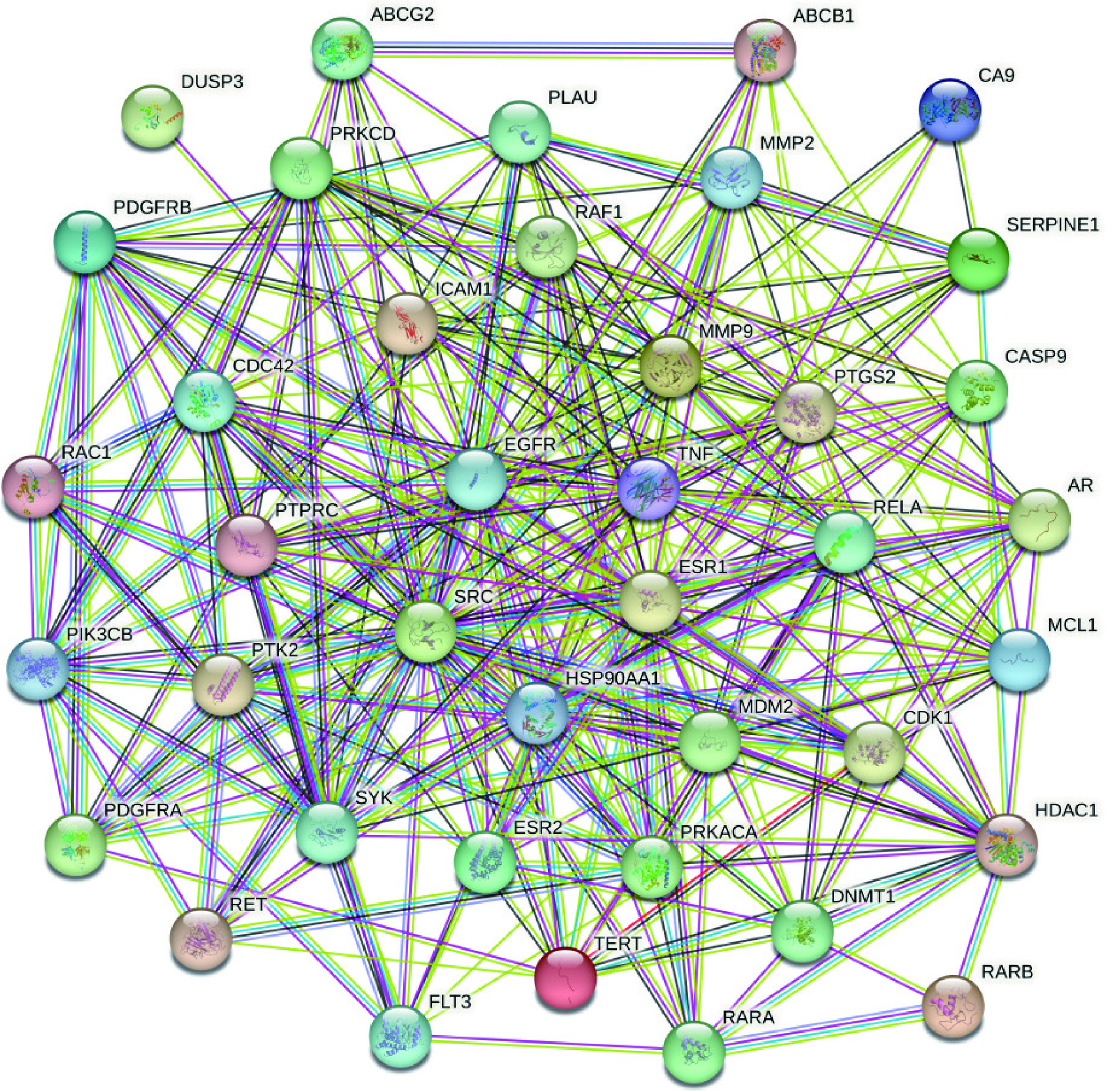
将筛选出的白藜芦醇与NSCLC共有靶点,导入STRING数据库(https://string-db.org),种属定义为“Homo sapiens”进行分析,构建药物靶蛋白和疾病靶蛋白PPI网络,其最低阈值取中等 “medium confidence”得到靶蛋白相互作用的核心网络关系。导入Cytoscape 3.7.2软件包,进一步绘制药物靶蛋白和疾病靶蛋白相互作用网络图。对网络的拓扑参数进行软件分析和计算,得到各个靶点的度值(degree)和介数(betweenness centrality,BC)等,直观显示排名前十名的靶标蛋白[11]。
1.2.5 GO和KEGG富集分析
为了解释药物靶点对基因功能的影响,将以上选取的白藜芦醇和NSCLC共有靶点引入Metascape数据库(https://metascape.org)中,与R语言结合,获得对应的GO和KEGG通路富集结果。
1.2.6 分子对接
选取白藜芦醇和NSCLC互作蛋白PPI网络中度值排名前三位的关键靶点,实现了白藜芦醇与靶蛋白的分子对接,通过进一步在PubChem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)检索获取白藜芦醇的3D结构式。在PDB数据库(https://www.rcsb.org)将关键靶点PDB格式进行下载,EGFR、SRC、ESR1等靶蛋白PDB编号分别为6z4b、1o4k以及2r6y。用Pymol软件处理去水和配体,保存[6]。利用Autodock Vina和Pymol软件将3个关键靶点与白藜芦醇进行分子对接。
1.2.7 癌症基因组图谱分析临床数据
从癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)数据库获得NSCLC病人(样本数为1017例)和健康人群(样本数为627例)的临床信息,使用R软件v4.0.3对筛选出的八个核心靶基因进行统计分析,两组样本显著性通过Wilcox检验,P<0.05被认为具有统计学意义。
1.2.8 细胞培养及干预
将A549细胞悬液接种于培养皿,置于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养。实验分为空白对照组和白藜芦醇药物干预组。待细胞处于对数生长期时进行给药处理,空白对照组不做药物处理,药物干预组分别使用浓度为30、50 μmol/L的白藜芦醇干预。
1.2.9 Western Blot检测蛋白表达
收集各组细胞加入增强型RIPA裂解液冰上孵育45 min,将裂解液在12000 g,4 ℃下离心10 min提取蛋白。蛋白浓度使用BCA蛋白定量试剂盒检测。将总蛋白与上样缓冲液混合,进行SDS-PAGE电泳,凝胶常规处理后,将蛋白转移到PVDF膜,5%脱脂牛奶封闭1 h,加入合适浓度的GAPDH(内参),SRC、EGFR、p-PI3K、p-AKT一抗4 ℃孵育过夜,与抗兔辣根过氧化物酶偶联抗体在室温下孵育1 h,孵育后常规洗膜处理,ECL化学发光显影,使用Bio-Rad 凝胶成像系统观察蛋白表达。Image J软件对目的条带进行统计分析,蛋白相对表达水平=目的条带灰度值/GAPDH条带灰度值。
1.3 数据处理
数据处理使用GraphPad Prism 8统计软件分析,数据检测至少重复3次,以均数±标准差(¯x±SD)表示。组间比较采用方差分析,方差齐性时,用one-way ANOVA检验,两两比较则用LSD-t检验;方差不齐时,采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验。P<0.05表示有统计学差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 白藜芦醇药物靶点及非小细胞肺癌疾病靶点的获取
从PubChem中检索化合物白藜芦醇的Canonical SMILES号,通过Swiss Target Prediction 数据库和Target net数据库检索获取到预测靶点一共174个。应用Genecards、OMIM、TTD这三个数据库进行疾病靶点的筛选,得到652个NSCLC相关靶点。
2.2 PPI网络分析及关键靶点筛选
预测得到的白藜芦醇靶点与NSCLC相关靶点交集共40个,如图1所示。将40个靶点上传至STRING数据库,得到靶点之间的PPI网络,不同颜色的边代表不同类型,边的粗细代表关联分值大小,节点即为靶点,如图2所示。将度值从大到小排序,前五位的有EGFR、SRC、ESR1、HSP90AA1、TNF;介数越大的靶点在药物作用过程中越关键,其排名前5位的靶点分别为ESR1、MMP9、CDC42、TNF、RELA ,如表1所示。整合度值和介数前5位的靶点,去除重复,得到以下基因 EGFR、SRC、ESR1、HSP90AA1、TNF、MMP9、CDC42、 RELA为主要关键靶点。预测其可能为白藜芦醇作用的关键靶标。
表 1 白藜芦醇治疗非小细胞肺癌疾病前10个关键靶点Table 1. Top 10 key targets of resveratrol for non-small cell lung cancer disease排名 靶点 度值 介数 1 EGFR 36 0.00124992 2 SRC 35 0.000946 3 ESR1 32 0.155644281 4 HSP90AA1 28 0.004130466 5 TNF 27 0.045638836 6 MDM2 22 0.018748213 7 MMP9 22 0.092457286 8 PTGS2 21 0.015035819 9 RELA 20 0.036363867 10 CDC42 19 0.076126149 2.3 GO与KEGG富集分析
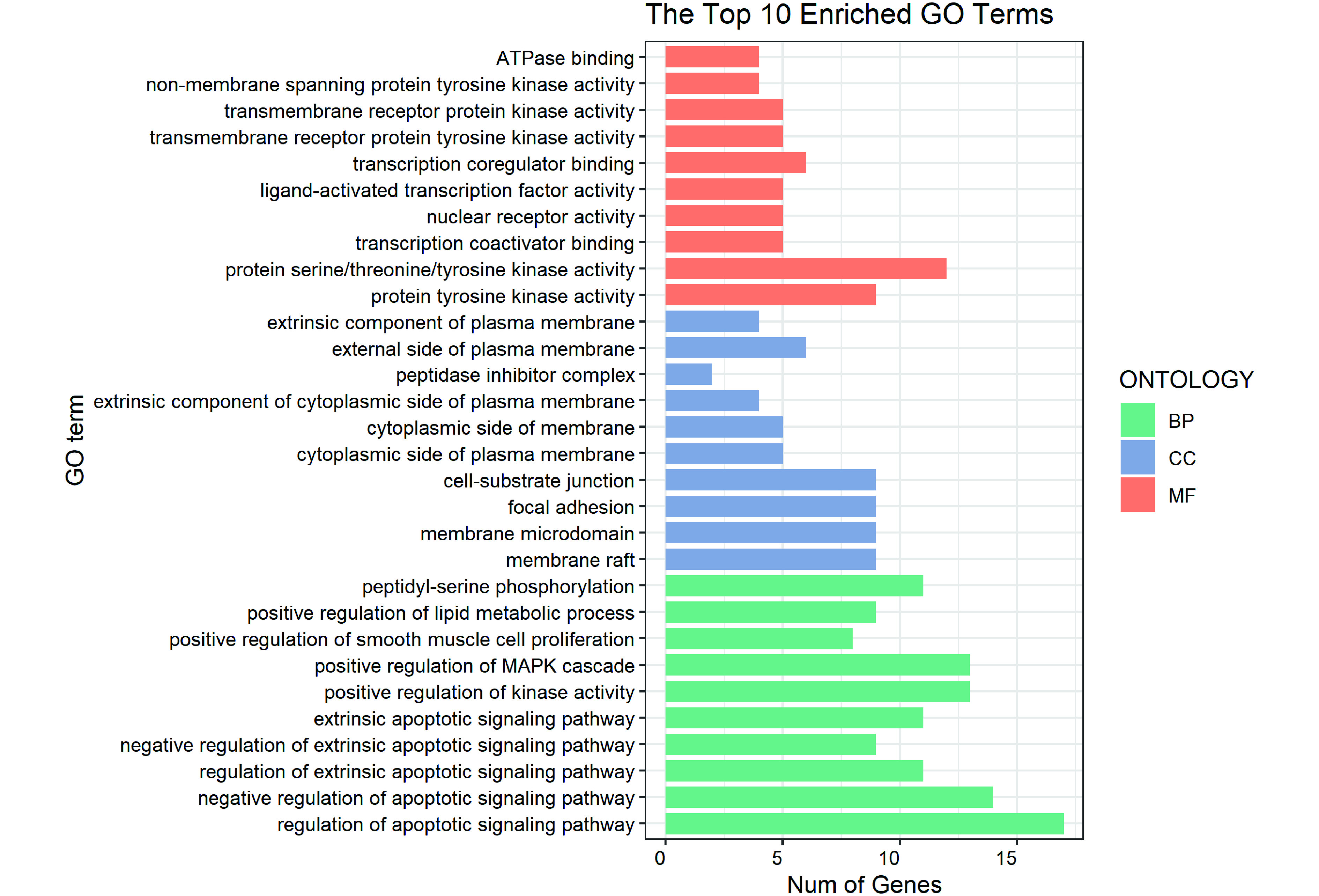
将筛选出的40个靶标基因于Metascape数据库做GO功能分析和KEGG通路富集分析。GO富集分析包括三种,分别是生物过程(biological process,BP)、分子功能(molecular function,MF)以及细胞组分(cellular component,CC)。利用R语言可视化处理排序在前10位具有显著性差异的基因富集结果,如图3所示。BP研究结果表明交集基因集中于调控细胞凋亡信号通路(regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway)、细胞凋亡信号通路负调节(negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway)、激酶活性正调节(positive regulation of kinase activity)等生物过程。CC的富集结果显示交集基因主要分布在薄膜筏(membrane raft)、膜微域(membrane microdomain)、局部粘连(focal adhesion)等细胞部位。MF富集结果表明交集基因参与调控蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性(protein tyrosine kinase activity)、蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸/酪氨酸激酶活性(protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity)、转录辅助因子结合(transcription coactivator binding)等分子功能发挥治疗非小细胞肺癌的作用。
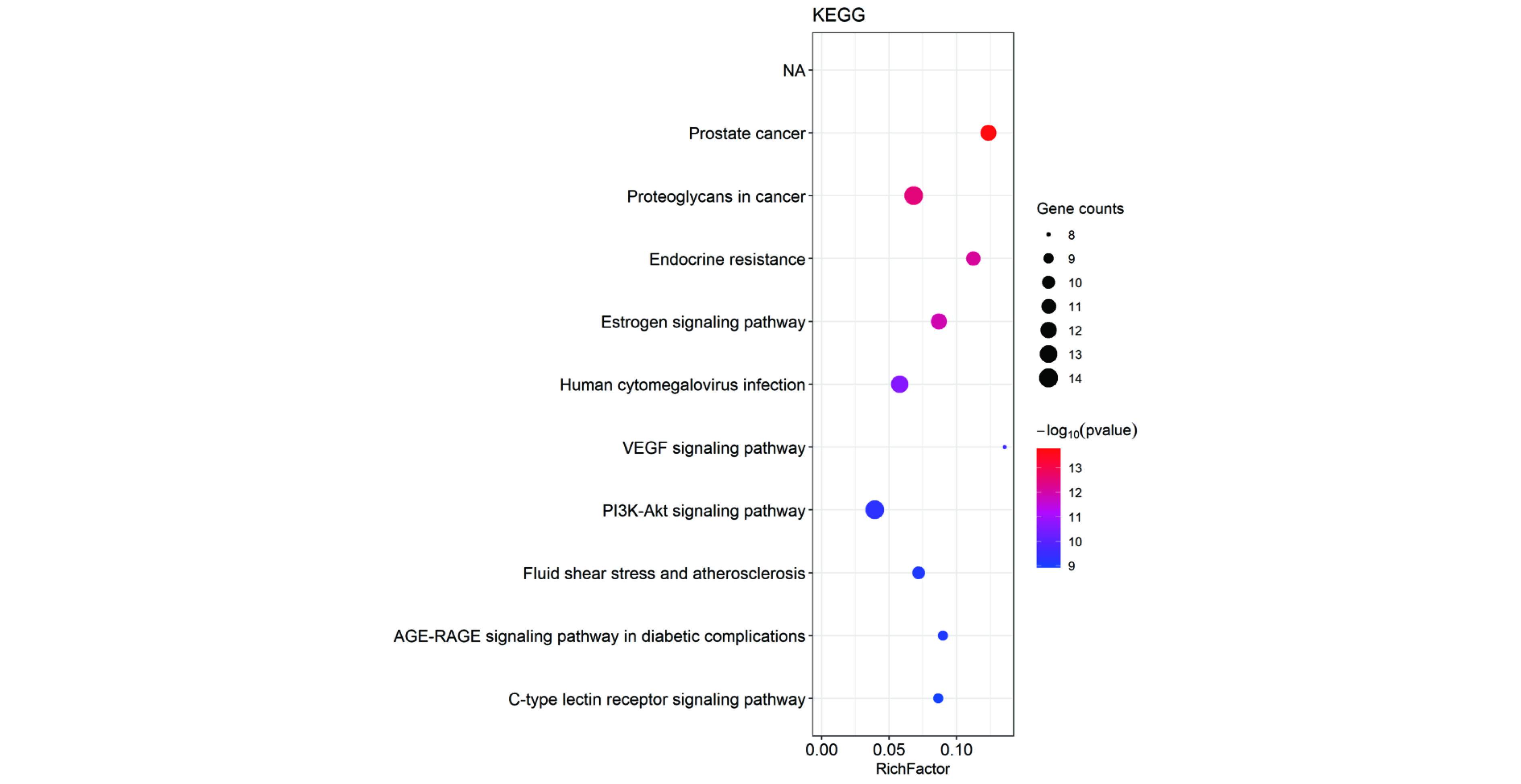
在Metascape数据库进行KEGG通路富集分析共获得131条KEGG条目,取前10个主要通路进行数据处理后,得到KEGG通路分析气泡图,纵坐标代表靶标基因主要参与的信号通路,如图4所示。结果显示,白藜芦醇治疗NSCLC的相关信号通路有肿瘤蛋白多糖通路(proteoglycans in cancer)、内分泌抵抗通路(endocrine resistance)、雌激素信号通路(estrogen signaling pathway)、人巨细胞病毒感染通路(human cytomegalovirus infection)、PI3K-AKT(PI3K-Akt signaling pathway)等多条信号通路。
2.4 分子对接分析
为了进一步评估白藜芦醇与关键靶标之间的结合能力,提高靶标网络的准确性,利用Autodock Vina对排名前三位核心靶点和白藜芦醇做分子对接分析,对接过程中设置参数,调整X-Y-Z坐标和网格大小,找到灵活对接的最佳对接条件,并记录受体和配体的对接位置。分子对接结果的分析是指结合能,结合能小于0,说明受体分子与配体分子能自发结合且产生相互作用,结合能越小,说明化合物所需的自由能越少,对接能力越强,对接后分子的稳定性越高[6,11]。对接结果表明,白藜芦醇和三个核心靶蛋白结合自由能均在-5 kcal/mol以下,表明结合高度稳定,具有对接意义,如表2所示。最后,使用Pymol软件可视化分析和观察白藜芦醇和靶标的对接结果,结果显示白藜芦醇通过可见的氢键相互作用与其蛋白质靶标结合,靶点的疏水口袋也被白藜芦醇药物所占据,如图5所示。
表 2 对接参数及相应计算结果Table 2. Docking parameters and corresponding calculation results靶点 结合能(kcal/mol) 氢键相互作用 疏水作用 EGFR −5.3 THR909,GLN982 LYS806,PHE910,ILE938,ILE981 SRC −5.4 ARG34,GLU37,THR38,THR39,LYS62 HIS60 ESR1 −8.0 GLU353,ARG394,PHE425,HIS524 LEU387,LEU391,PHE404,ILE424,LEU428 2.5 核心靶基因在NSCLC中的表达水平
为探究核心靶基因的表达水平与NSCLS发生发展的关系,利用癌症基因组图谱(TCGA)数据库获得基因表达数据以及NSCLC患者(n=1017)和正常健康人群(n=627)临床数据集,通过筛选、提取并分析靶基因在TCGA数据库中 NSCLC患者及健康对照人群中的表达数据 ,结果表明与健康人群相比,核心靶基因EGFR、SRC、ESR1、HSP90AA1以及MMP9的表达在NSCLC病人中显著上调,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);而TNF、CDC42以及RELA的表达相比于健康人群,在NSCLS病人中显著下调,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),如图6所示。这些发现表明通过网络药理学筛选预测的靶基因与NSCLC的发生发展密切相关。
2.6 白藜芦醇对A549细胞蛋白表达的影响
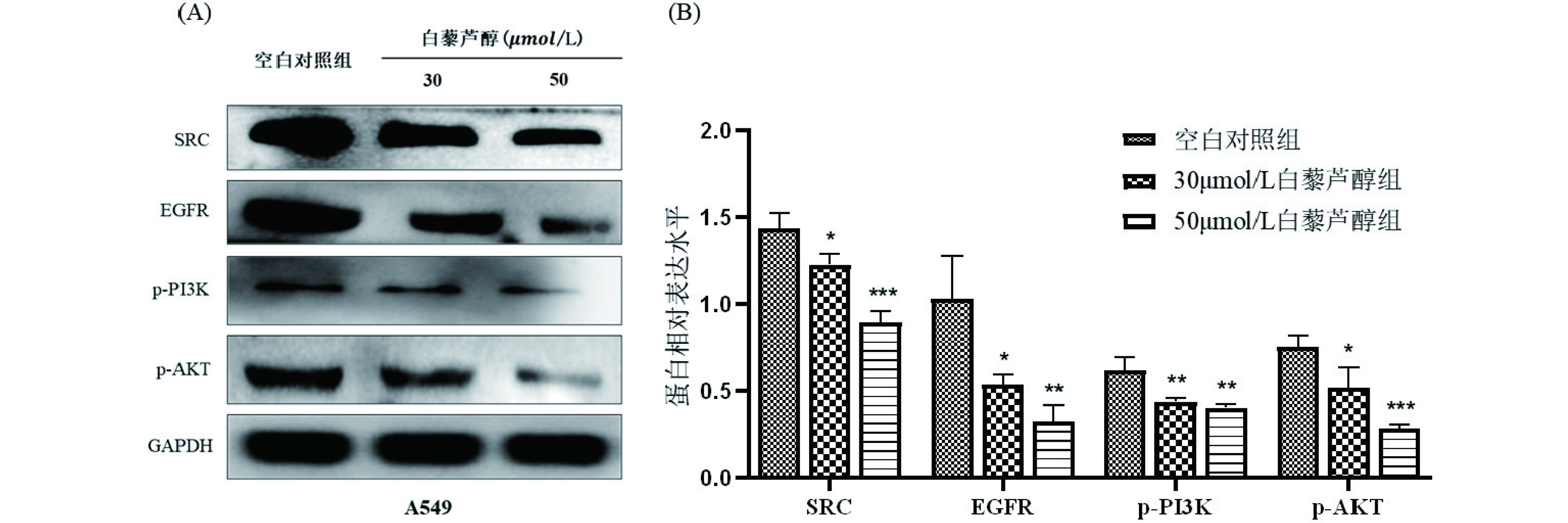
根据网络药理学和临床样本分析的数据,进一步探究白藜芦醇对相关靶基因及信号通路的影响。根据上述结果,在八个核心靶基因中选择排名前两位的EGFR和SRC进行初步验证,TCGA临床样本结果提示EGFR和SRC在NSCLC中具有高表达或高活性的特点,如图6所示。且有研究表明SRC可通过与激活的EGFR起协同作用,参与激活其下游信号通路,从而影响肿瘤细胞的增殖[13−14]。根据KEGG富集分析,PI3K-AKT通路具有较强的生物学意义,为进一步分子生物学实验验证提供了方向。因此,使用不同浓度(30、50 μmol/L)的白藜芦醇处理人肺腺癌A549细胞,利用Western Blot实验进行初步探究白藜芦醇对靶蛋白EGFR和SRC及其下游PI3K/AKT信号通路蛋白的影响,如图7所示。WesternBlot结果显示,与空白对照组相比,白藜芦醇药物干预抑制了A549细胞中SRC、EGFR、p-PI3K和p-AKT的活性并以剂量依赖的方式降低了蛋白的表达,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),如图8所示。
3. 讨论与结论
本研究共筛选出40个白藜芦醇治疗NSCLC的作用靶点,并以可视化和交互的模式呈现。通过构建交集靶点的PPI蛋白互作网络和拓扑学分析,最终获得八个关键靶基因,分别为EGFR、SRC、ESR1、HSP90AA1、TNF、MMP9、CDC42、 RELA。EGFR属于酪氨酸激酶受体家族,在上皮源性恶性肿瘤中经常过度活跃[15]。靶向EGFR的受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂已用于NSCLC的临床治疗[16]。但仍有TKIs治疗耐药的出现[17]。因此白藜芦醇有可能为其联合NSCLC的靶向治疗协同抗肿瘤活性带来新契机。SRC参与许多细胞信号转导的调控,对肿瘤的生长、转移以及血管生成有着至关重要的作用[18]。在NSCLC中具有高表达或高活性的特点[19]。研究表明,SRC可通过与激活的EGFR起协同作用,参与激活下游信号通路影响肿瘤细胞增殖[13],也可通过调节G1/S转化影响细胞周期[20]。ESR1是雌激素受体的一种亚型[21],研究表明ESR1通过与靶基因启动子中的雌激素应答元件和AP-1增强子元件结合,促进基因转录[22]。此外,ESR1信号传导也可能与影响T细胞浸润的肿瘤微环境因素相关[23]。HSP90α是热休克蛋白家族成员[24],被认为在肺癌的侵袭和迁移调节中起关键作用[25]。TNF及其受体在NSCLC中广泛表达[26],研究表明TNF可以促进细胞死亡或肿瘤生长[27]。MMP9是一种基质金属蛋白酶[28],研究发现MMP9的表达水平在NSCLC中显著上调,通过PI3K信号转导级联抑制EGFR信号可显著调节NSCLC的MMP9的表达[29]。CDC42已被确定在许多人类癌症中表达异常,包括NSCLC[30]。此外,也有研究报道肿瘤区域RELA表达与炎症浸润强度相关[31]。
GO功能富集分析白藜芦醇治疗NSCLC的相关靶基因,提示白藜芦醇抗癌作用与细胞凋亡有密切关系。已有研究证实了白藜芦醇通过促进细胞凋亡在NSCLC中的抗肿瘤作用[9],这与本研究预测结果一致。KEGG通路富集分析表明白藜芦醇在治疗NSCLC的过程中主要涉及肿瘤蛋白多糖、雌激素、PI3K-AKT等多条信号通路。研究发现雌激素途径在NSCLC发展中的作用是多方面的,一方面,雌激素可易位到细胞核调节基因的转录[32];另一方面雌激素可以激活SRC导致下游信号传导的激活,包括RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK和PI3K/AKT途径[33−34]。PI3K/AKT通路调节细胞生长和增殖,在癌症中经常由于突变、扩增、缺失、甲基化和翻译后修饰而失调[35]。在NSCLC中,PI3K/AKT信号通路与肿瘤发生进展密切相关[36]。以上富集分析显示了白藜芦醇的潜在靶点分布于多个生物过程及信号通路,这些有效成分协同起到防治NSCLC的作用,为后续研究提供了思路。
利用TCGA数据库初步分析临床样本中靶基因的表达与NSCLC发生发展的关系。结果提示核心靶基因EGFR、SRC、ESR1、HSP90AA1以及MMP9的表达在NSCLC中显著上调,TNF、CDC42以及RELA的表达在NSCLS中显著下调(P<0.05)。进一步在细胞水平上探讨白藜芦醇抗NSCLC的潜在作用机制,由于SRC的激活参与了癌症的进展且与EGFR之间存在相互作用,影响着许多下游蛋白,抑制SRC可能会中断EGFR的下游信号通路。通过Western Blot实验,结果提示白藜芦醇抑制了A549细胞中SRC、EGFR、p-PI3K、p-AKT的活性和蛋白表达,这可能导致癌细胞侵袭和迁移能力的下降。揭示了白藜芦醇发挥其抗癌效应可能是通过抑制NSCLC中SRC相关信号通路,包括PI3K/AKT信号通路。
综上所述,本研究基于网络药理学与实验验证就白藜芦醇治疗NSCLC的抗癌效应进行了初步探讨,为后续白藜芦醇的基础研究和临床应用提供理论依据和参考价值。
-
表 1 白藜芦醇治疗非小细胞肺癌疾病前10个关键靶点
Table 1 Top 10 key targets of resveratrol for non-small cell lung cancer disease
排名 靶点 度值 介数 1 EGFR 36 0.00124992 2 SRC 35 0.000946 3 ESR1 32 0.155644281 4 HSP90AA1 28 0.004130466 5 TNF 27 0.045638836 6 MDM2 22 0.018748213 7 MMP9 22 0.092457286 8 PTGS2 21 0.015035819 9 RELA 20 0.036363867 10 CDC42 19 0.076126149 表 2 对接参数及相应计算结果
Table 2 Docking parameters and corresponding calculation results
靶点 结合能(kcal/mol) 氢键相互作用 疏水作用 EGFR −5.3 THR909,GLN982 LYS806,PHE910,ILE938,ILE981 SRC −5.4 ARG34,GLU37,THR38,THR39,LYS62 HIS60 ESR1 −8.0 GLU353,ARG394,PHE425,HIS524 LEU387,LEU391,PHE404,ILE424,LEU428 -
[1] NIE P, HU W, ZHANG T, et al. Synergistic induction of erlotinib-mediated apoptosis by resveratrol in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells by down-regulating survivin and up-regulating PUMA[J]. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry,2015,35(6):2255−2271. doi: 10.1159/000374030
[2] ZHAO Q S, HU L L, WANG Z D, et al. Resveratrol-loaded folic acid-grafted dextran stearate submicron particles exhibits enhanced antitumor efficacy in non-small cell lung cancers[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications,2017,72:185−191.
[3] CHIOU W C, HUANG C, LIN Z J, et al. α-Viniferin and ε-viniferin inhibited TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion in lung cancer cells through downregulation of vimentin expression[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(11):2294. doi: 10.3390/nu14112294
[4] MA L, LI W, WANG R, et al. Resveratrol enhanced anticancer effects of cisplatin on non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and cell apoptosis[J]. International Journal of Oncology,2015,47(4):1460−1468. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3124
[5] HU S, LI X, XU R, et al. The synergistic effect of resveratrol in combination with cisplatin on apoptosis via modulating autophagy in A549 cells[J]. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica (Shanghai),2016,48(6):528−535. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmw026
[6] ZHONG Z, GUO X, ZHENG Y. Network pharmacology-based and molecular docking analysis of resveratrol's pharmacological effects on type I endometrial cancer[J]. Anti-cancer Agents In Medicinal Chemistry,2022,22(10):1933−1944. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666211015140455
[7] GAO P, REN G. Identification of potential target genes of non-small cell lung cancer in response to resveratrol treatment by bioinformatics analysis[J]. Aging (Albany NY),2021,13(19):23245−23261. doi: 10.18632/aging.203616
[8] YUAN L, ZHOU M, HUANG D, et al. Resveratrol inhibits the invasion and metastasis of colon cancer through reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the AKT/GSK-3β/Snail signaling pathway[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports,2019,20(3):2783−2795.
[9] WANG H, JIA R, LÜ T, et al. Resveratrol suppresses tumor progression via inhibiting STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF pathway in an orthotopic rat model of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. OncoTargets and Therapy,2020,13:7057−7063. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S259016
[10] WANG X, WANG D, ZHAO Y. Effect and mechanism of resveratrol on the apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549[J]. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics,2015,73(2):527−531. doi: 10.1007/s12013-015-0696-3
[11] LI X, WEI S, NIU S, et al. Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu decoction against sepsis[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine,2022,144:105389. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105389
[12] PINZI L, RASTELLI G. Molecular docking:Shifting paradigms in drug discovery[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(18):4331. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184331
[13] PAN Z, WANG K, WANG X, et al. Cholesterol promotes EGFR-TKIs resistance in NSCLC by inducing EGFR/Src/Erk/SP1 signaling-mediated ERRα re-expression[J]. Molecular Cancer,2022,21(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01547-3
[14] MIN W, HE C, ZHANG S, et al. c-Src increases the sensitivity to TKIs in the EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Frontiers in Oncology,2021,11:602900. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.602900
[15] CHEN Y, HOU L. HCRP-1 alleviates the malignant phenotype and angiogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via the downregulation of the EGFR/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Oncology Letters,2022,24(5):387. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13507
[16] SORIA J C, OHE Y, VANSTEENKISTE J, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. New England Journal of Medicine,2018,378(2):113−125. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1713137
[17] YE L, CHEN X, ZHOU F. EGFR-mutant NSCLC:Emerging novel drugs[J]. Current Opinion In Oncology,2021,33(1):87−94. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000701
[18] OKUZAKI D, YAMAUCHI T, MITANI F, et al. c-Src promotes tumor progression through downregulation of microRNA-129-1-3p[J]. Cancer Science,2020,111(2):418−428. doi: 10.1111/cas.14269
[19] HUANG W C, KUO K T, WANG C H, et al. Cisplatin resistant lung cancer cells promoted M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via the Src/CD155/MIF functional pathway[J]. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research,2019,38(1):180−197.
[20] WANG D, GAO J, ZHAO C, et al. Cyclin G2 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by binding to IGFBP3 and regulating the FAK-SRC-STAT signaling pathway[J]. Frontiers in Oncology,2020,10:560572. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.560572
[21] ATMACA A, AL-BATRAN S E, WIRTZ R M, et al. The validation of estrogen receptor 1 mRNA expression as a predictor of outcome in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer[J]. International Journal of Cancer,2014,134(10):2314−2321. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28571
[22] CHENG T D, DARKE A K, REDMAN M W, et al. Smoking, sex, and non-small cell lung cancer:Steroid hormone receptors in tumor tissue (S0424)[J]. Journal of the National Cancer Institute,2018,110(7):734−742. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx260
[23] OH M S, ANKER J F, CHAE Y K. High gene expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors is associated with decreased T cell infiltration in patients with NSCLC[J]. Cancer Treatment and Research Communications,2021,27:100317. doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2021.100317
[24] ZHONG B, SHEN J, ZHANG C, et al. Plasma heat shock protein 90 alpha:A valuable predictor of early chemotherapy effectiveness in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Medical Science Monitor,2021,27:e924778.
[25] DONG Z, YANG P, QIU X, et al. KCNQ1OT1 facilitates progression of non-small-cell lung carcinoma via modulating miRNA-27b-3p/HSP90AA1 axis[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2019,234(7):11304−11314. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27788
[26] LIU Y, GAO Y, LIN T. Expression of interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in non-small cell lung cancer and its relationship with the occurrence and prognosis of cancer pain[J]. Annals of Palliative Medicine,2021,10(12):12759−12766. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-3471
[27] GONG K, GUO G, BECKLEY N, et al. Tumor necrosis factor in lung cancer:Complex roles in biology and resistance to treatment[J]. Neoplasia,2021,23(2):189−196. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2020.12.006
[28] MONDAL S, ADHIKARI N, BANERJEE S, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in cancer:A minireview[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2020,194:112260. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112260
[29] LI J, WANG H, KE H, et al. MiR-129 regulates MMP9 to control metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Tumor Biology,2015,36(8):5785−5790. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3247-z
[30] LI Y, WANG Z, LI Y, et al. MicroRNA-29a functions as a potential tumor suppressor through directly targeting CDC42 in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncology Letters,2017,13(5):3896−3904. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5888
[31] GIOPANOU I, LILIS I, PAPALEONIDOPOULOS V, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of nuclear factor-κΒ expression patterns in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(7):e0132527. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132527
[32] TANG H, LIAO Y, CHEN G, et al. Estrogen upregulates the IGF-1 signaling pathway in lung cancer through estrogen receptor-β[J]. Molecular Oncology,2012,29(4):2640−2648.
[33] TIAN L, LI Y, LIU H L, et al. Exposure to PM2.5 enhances the PI3K/AKT signaling and malignancy of ERα expression-dependent non-small cell lung carcinoma[J]. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences,2021,34(4):319−323.
[34] CHAPPELL W H, STEELMAN L S, LONG J M, et al. Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR inhibitors:Rationale and importance to inhibiting these pathways in human health[J]. Oncotarget,2011,2(3):135−164. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.240
[35] TAN A C. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[J]. Thoracic Cancer,2020,11(3):511−518. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13328
[36] ZHANG H B, QIU X M, ZHANG Y C, et al. Circ_0017639 facilitates proliferative, migratory, and invasive potential of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Bioengineered,2022,13(1):1590−1601. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2020390





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



