Sulfated Modification and Bioactivity Analysis of Polysaccharide from Porphyra
-
摘要: 以紫菜为原料,采用微波辅助酶法制备紫菜多糖,浓硫酸法合成硫酸化紫菜多糖,通过单因素及正交试验对紫菜多糖硫酸化修饰工艺条件进行优化,利用傅里叶红外光谱仪鉴定修饰结果,并比较浓硫酸法与氯磺酸-吡啶法对硫酸化多糖抗氧化与降血糖活性的影响。结果表明:浓硫酸法进行硫酸化的最佳条件为料液比1:80 g/mL,紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比10:9 g/g,反应时间33 min,最高取代度为2.94;红外光谱指征修饰后的紫菜多糖在801、1123 cm−1处有硫酸基团的特征吸收峰,硫酸基团的可能取代位置为C-6;硫酸化后的紫菜多糖对DPPH、O2−和OH自由基的清除作用及α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用均显著高于硫酸化前(P<0.05);浓硫酸法修饰紫菜多糖的抗氧化活性及降血糖活性均显著高于氯磺酸-吡啶法(P<0.05),说明浓硫酸法更适用于紫菜多糖的硫酸化修饰。研究结果为开展食源性紫菜多糖的进一步利用提供了参考。Abstract: The polysaccharides were obtained by microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction from Porphyra, and then modified by sulphate method. Single factor and orthogonal experiments were used to optimize the sulfated modification process of polysaccharides, which were identified by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity changes of the polysaccharides modified by sulphate and chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method were also studied. Results showed that the optimal technology parameters were the ratio of solid to liquid 1:80 g/mL, the mass ratio of Porphyra polysaccharide to ammonium sulfate 10:9 g/g, reaction time 33 min, and the maximum degree of substitution was 2.94. FT-IR showed that the characteristic absorption peaks of sulfate radical group appeared near 801 and 1123 cm−1, and the possible substitution position of sulfate radical group was C-6. The sulfate modification could significantly improve the scavenging ability of DPPH, O2− and OH free radicals and the inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase activity of the polysaccharides (P<0.05). The antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity of the polysaccharides modified by sulphate method were both higher than that by chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method (P<0.05), indicating that sulphate method was applicable to modify the Porphyra polysaccharide. This study provides a theoretical basis for the further development of polysaccharides from Porphyra as a functional food.
-
Keywords:
- Porphyra /
- polysaccharide /
- sulfated /
- antioxidant activity /
- hypoglycemic activity
-
紫菜(Porphyra)是我国重要的药食同源红藻,紫菜中含有多糖、蛋白质、维生素等多种活性物质[1]。其中,紫菜多糖的结构与琼胶类似,占紫菜干质量的20%~40%,含量丰富且易提取[2],在抗氧化、降血糖等生物活性方面发挥着重要作用[3−5]。
天然多糖生物活性相对较弱,常采用化学修饰的方法改善其生物活性,其中,硫酸化修饰是多糖化学修饰中常用的修饰方法之一[6−7]。硫酸化修饰主要通过在多糖的糖基上引入硫酸基团,使多糖结构发生改变进而增加多糖的生物活性[8−9]。浓硫酸法[10]和氯磺酸-吡啶法[11]是多糖硫酸化修饰的主要方法。氯磺酸-吡啶法进行硫酸化修饰,具有取代度高、产物回收率高的优点,但腐蚀性极强,对人体危害巨大[12−13];而浓硫酸法则具有产物杂质少,且易分离的优势[14]。现有研究指征不同硫酸化修饰方法对多糖生物活性的影响不一,如:浓硫酸法进行硫酸化修饰能显著提高老鸦瓣多糖对DPPH自由基的清除能力,但对羟自由基的清除能力的影响较弱[15];氯磺酸-吡啶法进行硫酸化修饰显著增强了鸡腿菇多糖对羟自由基的清除能力,但对超氧阴离子自由基的清除作用较弱[16]。尚不明确与氯磺酸-吡啶法相比,浓硫酸法修饰紫菜多糖是否更适用于生物活性的提高。
以广西北部湾紫菜为研究对象,采用浓硫酸法对紫菜多糖进行硫酸化修饰,通过单因素和正交试验获取最佳酯化条件,初步鉴定修饰前后的多糖结构,比较不同硫酸化修饰方法(氯磺酸-吡啶法和浓硫酸法)对紫菜多糖抗氧化活性和降血糖活性的影响,以期明确紫菜多糖的硫酸化修饰方法,进一步提高其原有生物活性,为紫菜多糖的进一步开发与利用提供参考依据和数据支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
紫菜 采自广西北部湾海域(20°54'10″~21°40'30″ N,109°05'20″~109°11'35″ E),经大连海洋大学邢坤副教授鉴定为红藻门紫菜属;阿卡波糖(99%)、4-硝基苯-α-D-葡萄糖苷(98%)、α-葡萄糖苷酶(10 U/mg) Sigma公司;中性蛋白酶(50 U/mg) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;其余试剂均为国产分析纯。
DFT-200高速万能粉碎机 温岭市林大机械有限公司;AL104高密度电子天平 梅特力-托利多仪器公司;LGJ-50C冷冻干燥机 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;DH-9077A电热恒温干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;TDL-5000bR台式离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;KW-1000DC水浴锅 州蒙特仪器制造公司;UV-2600紫外分光光度计 株式会社岛津制作所;DF-101S恒温加热磁力搅拌器 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;MultiskanGO全波长扫描酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;Nicolet6700傅里叶红外光谱仪 上海莱睿科学仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 紫菜多糖的提取
参照冯学珍等[17]的方法,略作修改。取新鲜采集的紫菜反复清洗,自然风干后粉碎、过筛于干燥器中备用。准确称取粉末5.00 g,95%无水乙醇浸泡过夜,冷冻干燥,加适量蒸馏水调节溶液pH至7.0,600 W微波辅助提取90 s,离心,浓缩,醇沉,静置过夜,沉淀干燥得紫菜粗多糖。将紫菜粗多糖与中性蛋白酶按1:0.5于50 ℃水浴反应2 h,后沸水灭活5 min,重复多次,直至测定280 nm处无吸收峰,说明蛋白质已除。将酶解液离心,减压浓缩,干燥得紫菜多糖(Porphyra polysaccharide,PP)。
1.2.2 浓硫酸法制备硫酸化紫菜多糖的工艺优化
1.2.2.1 浓硫酸法
称取0.10 g紫菜多糖与浓硫酸按照一定料液比混合后置于带有干燥管和搅拌装置的三颈烧瓶中,加入2.5 mL正丁醇,通过温和搅拌的方法,冰浴冷却至0 ℃,加入一定量的硫酸铵,反应一定时间。反应结束后调节溶液pH至7.0,透析,离心,上清液减压浓缩,冷冻干燥即得硫酸化紫菜多糖(Sulfated Porphyra polysaccharide,SPP)。
1.2.2.2 单因素实验方法
准确量取2.5 mL正丁醇,在料液比1:80 g/mL、紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比10:6 g/g、反应时间25 min条件下,研究料液比(1:70、1:80、1:90、1:100、1:110 g/mL)、紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比(10:4、10:6、10:8、10:10、10:12 g/g)、反应时间(15、20、25、30、35 min)对硫酸化紫菜多糖取代度的影响。
1.2.2.3 正交试验设计
在单因素实验设计的条件下,选取料液比(A)、紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比(B)和反应时间(C)作为正交试验因素,每个因素选择3个水平,以SPP取代度为指标,采用L9(34)正交试验进行工艺优化。具体的正交试验设计因素及水平见表1。
表 1 硫酸化紫菜多糖的正交试验设计因素及水平Table 1. Levels and factors of orthogonal experiments of SPP水平 A 料液比
(g/mL)B 紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比
(g/g)C 反应时间
(min)1 1:75 10:9 27 2 1:80 10:10 30 3 1:85 10:11 33 1.2.3 氯磺酸-吡啶法制备硫酸化紫菜多糖
参照CHEN等[18]的方法,略作修改。准确称取0.1 g紫菜多糖悬浮于10.0 mL的N,N-二甲基甲酰胺中,搅拌20 min后,加入装有酯化试剂(V氯磺酸:V吡啶=1:3)的三颈瓶中,75 ℃水浴条件下反应1.5 h。反应完成后,加入适量冰水,以2.5 mol/L的NaOH调节溶液pH至中性。加入三倍体积的无水乙醇于4 ℃冰箱中过夜,离心、透析、浓缩、冷冻干燥即得硫酸化紫菜多糖(SPP1)。
1.2.4 取代度测定
1.2.4.1 硫酸根含量测定
标准曲线的绘制采用氯化钡-明胶法[19]。称取干燥至恒重的硫酸钾粉末217.50 mg,以1.0 mol/L的盐酸定容至50.0 mL容量瓶,得硫酸根标准溶液。准确吸取不同体积的硫酸钾标准溶液(0.08、0.16、0.24、0.32、0.40 mL),加入1.0 mol/L的盐酸补足至0.4 mL,加入7.6 mL 3%三氯乙酸和2.0 mL 0.2%的氯化钡-明胶溶液,充分摇匀,静置15 min后,在360 nm处测定吸光度A1,以2.0 mL 0.5%的明胶溶液代替氯化钡-明胶溶液,重复上述操作,在360 nm处测定吸光度A2。以硫酸根的浓度为横坐标,A1-A2为纵坐标绘制标准曲线。
1.2.4.2 取代度的测定
取硫酸化紫菜多糖2.00 mg,溶于1.0 mol/L盐酸中,充分振摇,待完全溶解后置沸水浴中反应1 h,吸取0.2 mL反应液进行样品分析,按照1.2.4.1测定吸光值,根据标准曲线计算硫酸根的百分含量后按式(1)计算取代度DS(Degree of substitution,DS):
DS=1.62S32−1.02S (1) 式中:DS为样品取代度,S为硫酸根的百分含量(%)。
1.2.5 红外光谱分析
分别称取2.00 g硫酸化修饰前后的紫菜多糖样品,溴化钾压片,在4000~500 cm−1的波数范围内经傅里叶变换红外光谱仪测定。
1.2.6 生物活性分析
1.2.6.1 抗氧化活性分析
分别配制不同质量浓度修饰前后的紫菜多糖溶液,以相同质量浓度的维生素C作为阳性对照,参考冯书珍等[20]的方法,测定其对DPPH、O2−和OH自由基的清除能力并计算IC50值。紫菜多糖对DPPH、O2−和OH自由基的清除率按式(2)计算。
清除率(%)=(1−A样品−A对照A空白)×100 (2) 式中:A样品是样品组的吸光度值,A对照是对照组的吸光度值,A空白是空白组的吸光度值。
1.2.6.2 降血糖活性分析
以阿卡波糖为阳性对照,参考冯学珍等[21]的方法,测定不同质量浓度下硫酸化前后的紫菜多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用并计算IC50值。紫菜多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率按式(3)计算。
抑制率(%)=(1−A药物反应−A药物对照A空白反应−A空白对照)×100 (3) 式中:A药物反应是药物反应组的吸光度值,A药物对照是药物对照组的吸光度值,A空白反应是空白反应组的吸光度值,A空白对照是空白对照组的吸光度值。
1.3 数据处理
采用Microsoft Excel 2021、SPSS(SPSS 22.0 Windows,SPSS Inc,Chicago,USA)、Origin 2022、正交设计助手II(V 3.1)和Graphpad Prism 9对数据进行统计分析与作图。硫酸化前后的紫菜多糖的抗氧化活性和降血糖活性进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA,置信水平95%),多重比较用S-N-K法,结果以¯x+σ/√n的形式表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
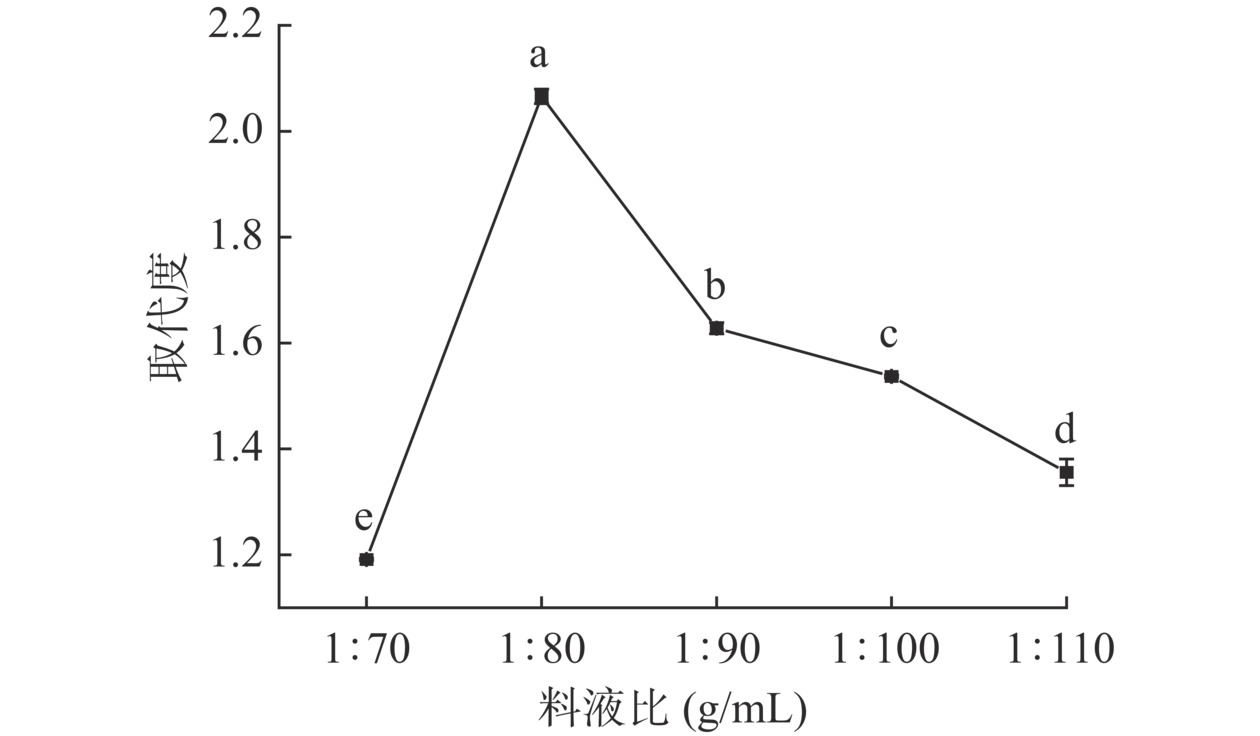
2.1.1 料液比对取代度的影响
随着料液比的增大,SPP的取代度呈现先升高后降低的趋势(图1)。在料液比为1:80 g/mL时,取代度达到最大值2.07±0.01,当料液比大于1:80 g/mL后,取代度呈现逐渐显著下降的趋势(P<0.05),分析原因可能是由于过高的浓硫酸含量会破坏多糖结构[22],导致取代度降低。因此,将料液比确定在1:75~1:85 g/mL范围内最合适。
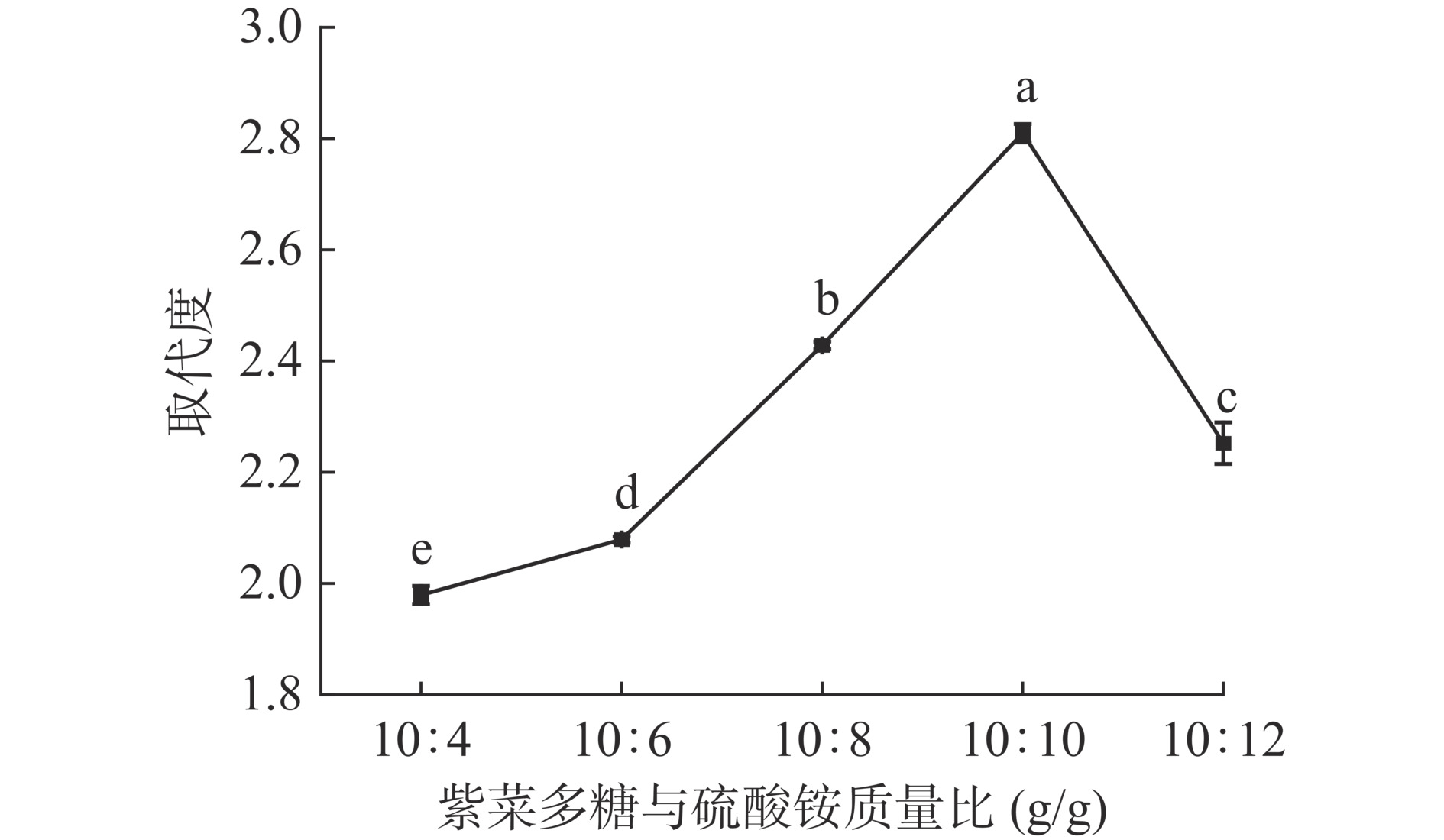
2.1.2 紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比对取代度的影响
随着紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比的增加,其取代度呈现先显著增大后显著减小趋势(P<0.05,图2),在10:10 g/g时达到最大,为2.81±0.02,说明此时硫酸化反应完全,取代度最高;当紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比大于10:10 g/g时,多糖溶液中硫酸铵含量过高,酸性太强,容易造成多糖降解,且易造成板结现象,硫酸化反应不充分,导致取代度降低[23]。因此,紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比选择10:8~10:12 g/g范围内最合适。
2.1.3 反应时间对取代度的影响
由图3可知,在15~30 min内,SPP的取代度随反应时间的延长逐渐增大,在反应时间为30 min时,SPP的取代度最高,为2.850±0.001,当反应时间大于30 min时(35 min),取代度显著下降(P<0.05)。推测原因可能是在30 min内,利于酯化剂的扩散,进而促进酯化剂与多糖分子结合,取代度升高;随着时间进一步增加,反应体系中硫酸浓度过高,导致糖苷键断裂,取代度降低[24]。因此,反应时间确定为25~35 min合适。
2.2 紫菜多糖硫酸化最佳工艺条件的确定
2.2.1 正交试验结果
影响硫酸化紫菜多糖取代度的因素依次为A>C>B,即料液比>反应时间>紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比(表2)。方差分析结果(表3)表明,料液比显著影响硫酸化紫菜多糖的取代度(P<0.05),反应时间、紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比对取代度无显著影响(P>0.05)。硫酸化修饰紫菜多糖SPP的最优条件组合为A2C3B1,结合单因素实验结果,最终确定SPP的最佳工艺为:料液比1:80 g/mL、反应时间为33 min、紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比为10:9 g/g,最高取代度为2.94,高于杨燕敏等[25]对红枣多糖硫酸化修饰的研究。
表 2 硫酸化紫菜多糖的正交试验结果Table 2. Orthogonal experimental results of SPP试验号 因素 取代度 A 料液比 B 紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比 C 反应时间 1 1 1 1 1.04 2 1 2 3 1.38 3 1 3 2 2.29 4 2 2 2 2.85 5 2 3 1 1.68 6 2 1 3 2.94 7 3 2 1 2.10 8 3 3 3 1.16 9 3 1 2 1.42 k1j 1.57 2.49 1.56 k2j 1.80 2.11 1.71 k3j 1.61 2.19 1.83 R 0.93 0.4 0.58 因素排序 A>C>B 最佳组合 A2C3B1 表 3 方差分析结果Table 3. Variance analysis results因素 偏差平方和 自由度 F比 显著性 A 5.13 2 11.29 0.001 B 0.79 2 1.74 0.201 C 1.54 2 3.39 0.054 误差 4.55 20 总计 12.02 26 2.2.2 验证实验
称取1.00 g紫菜多糖,在最佳硫酸化工艺条件下(料液比1:80 g/mL、反应时间33 min、紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比10:9 g/g)进行实验,计算硫酸化紫菜多糖的取代度。结果表明,硫酸化紫菜多糖的平均取代度为2.94,与正交试验结果一致。
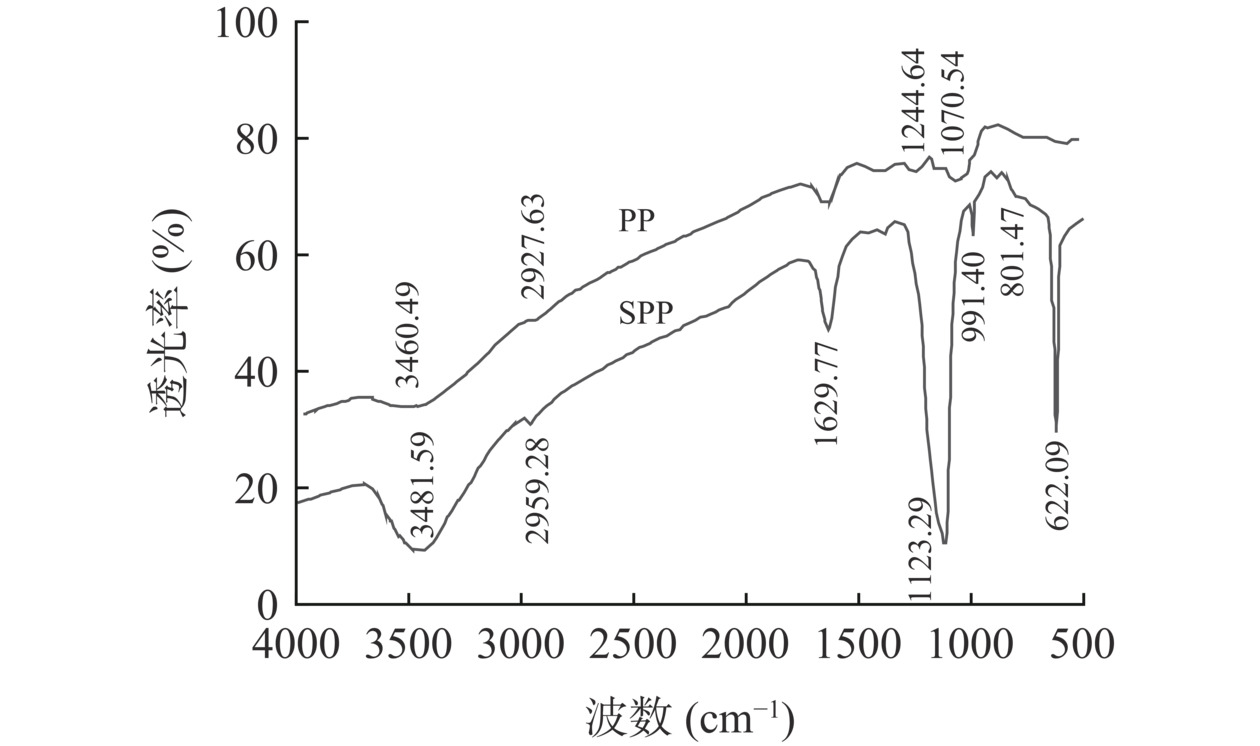
2.3 红外光谱分析
如图4所示,SPP和PP均在3500~3300、3000~2800、2000~1500、1400~700 cm−1范围内显示出多糖的特征吸收峰[26−28]。与PP相比,SPP在1100~1250和800~850 cm−1范围内出现吸收峰,均提示存在硫酸基团[29−30],即在1123.29 cm−1出现的吸收峰,对应S=O的不对称伸缩振动;在801.47 cm−1出现的吸收峰,可能与半乳糖C-6上C-O-S的对称伸缩振动有关,说明硫酸基团在C-6上发生了较大的取代[31]。结果表明采用浓硫酸法对紫菜多糖进行硫酸化修饰是成功的。紫菜多糖经硫酸化修饰后其主体结构基本未被破坏,但由于受硫酸基团的影响,多糖的透光率也发生变化,其它特征吸收峰相比原始位置发生了偏移[32]。
2.4 硫酸化修饰前后的生物活性分析
2.4.1 抗氧化活性分析
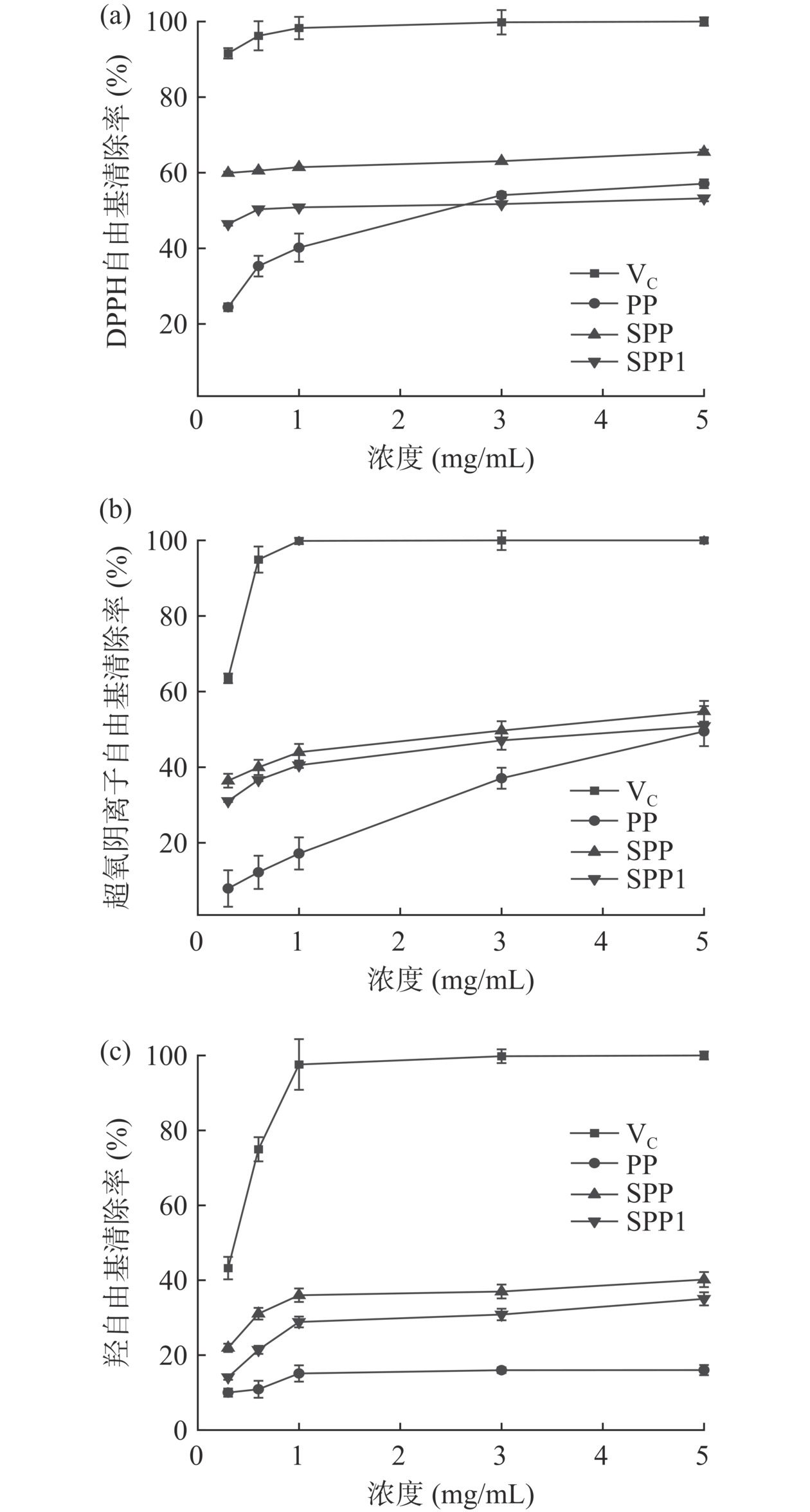
SPP、SPP1和PP对DPPH、超氧阴离子、羟自由基的清除作用均随着浓度的增大而增大(图5)。与XU等[33]的研究不同,在0~5 mg/mL浓度范围内,SPP、SPP1对DPPH、超氧阴离子、羟自由基三种自由基清除率的IC50均显著低于PP(P<0.05,表4),说明硫酸化修饰后的紫菜多糖抗氧化活性显著高于修饰前,这可能是由于硫酸基团的加入对自由基的清除能力存在促进作用,进而增强紫菜多糖的抗氧化活性[32]。浓硫酸法修饰后的紫菜多糖,其对三种自由基的清除率均显著高于氯磺酸-吡啶法(P<0.05),说明浓硫酸法更适用于促进紫菜多糖的抗氧化活性。
表 4 硫酸化修饰前后紫菜多糖生物活性的半抑制浓度(IC50)Table 4. IC50 of Porphyra polysaccharide before and after sulfate modification多糖 IC50(mg/mL) DPPH自由基 超氧阴离子自由基 羟自由基 α-葡萄糖苷酶 SPP 0.004±0.003c 2.69±0.33c 19.44±0.89c 13.56±0.35c SPP1 0.95±0.63b 4.32±0.53b 23.89±0.50b 16.24±1.47b PP 2.40±0.40a 5.23±0.29a 26.59±0.98a 26.18±4.66a 注:同列不同小写字母表示不同紫菜多糖IC50间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 2.4.2 降血糖活性分析
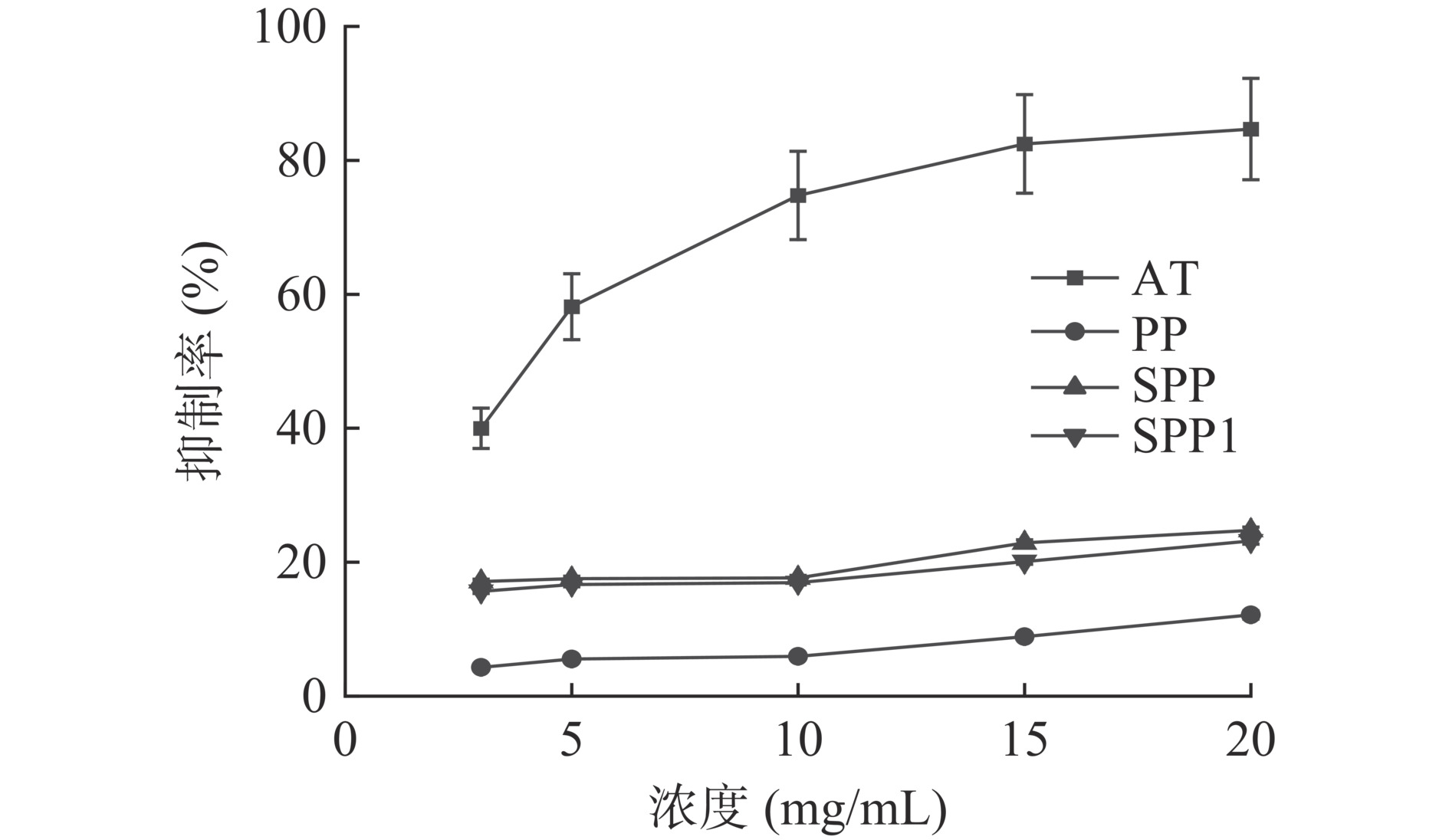
SPP、SPP1和PP均对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有一定的抑制作用,且随着浓度的增加,抑制作用逐渐增强(图6)。当浓度达到20 mg/mL时,SPP、SPP1和PP对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率最高,分别为24.27%、23.17%、11.89%;在0~20 mg/mL浓度范围内,SPP、SPP1对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制作用的IC50值显著低于PP(P<0.05,表4),分别为13.56±0.35、16.24±1.47、26.18±4.66 mg/mL,说明硫酸化修饰可以显著增强紫菜多糖的降血糖活性,与XIAO等[34]的研究一致,这可能是由于硫酸基团的加入,增强了多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用,导致葡萄糖从活性位点的扩散变慢,延缓了葡萄糖的吸收速度[35−36]。其中,SPP1的降血糖活性的IC50显著高于SPP(P<0.05),说明与氯磺酸-吡啶法相比,浓硫酸法修饰能显著提高紫菜多糖的降血糖活性。
3. 结论
采用浓硫酸法对广西北部湾紫菜多糖进行硫酸化修饰,影响取代度的关键因素为:料液比>反应时间>紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比。确定最佳工艺优化条件为:料液比1:80 g/mL,反应时间33 min,紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比10:9 g/g,最高取代度为2.94。红外光谱表明,紫菜多糖经硫酸化修饰后出现硫酸基团特征吸收峰,其硫酸基团的可能取代位置为C-6。
硫酸化修饰后的紫菜多糖,其对DPPH、超氧阴离子、羟自由基的清除作用及α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用,均显著高于硫酸化前(P<0.05),说明应用硫酸化修饰提高紫菜多糖生物活性是可行的。同时,浓硫酸法对紫菜多糖抗氧化活性、降血糖活性的促进作用显著高于氯磺酸-吡啶法(P<0.05),约高1.59%~12.28%,说明应用硫酸化修饰促进紫菜多糖生物活性时,可优先考虑浓硫酸法。
本文基于前期研究结果,侧重解析了硫酸化修饰对广西北部湾紫菜多糖原有生物活性如抗氧化活性、降血糖活性的促进作用,浓硫酸法是否同样适用于显著增加食源性海藻多糖新的生物活性,如抗凝血活性、降血脂活性等,值得进一步研究。
-
表 1 硫酸化紫菜多糖的正交试验设计因素及水平
Table 1 Levels and factors of orthogonal experiments of SPP
水平 A 料液比
(g/mL)B 紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比
(g/g)C 反应时间
(min)1 1:75 10:9 27 2 1:80 10:10 30 3 1:85 10:11 33 表 2 硫酸化紫菜多糖的正交试验结果
Table 2 Orthogonal experimental results of SPP
试验号 因素 取代度 A 料液比 B 紫菜多糖与硫酸铵质量比 C 反应时间 1 1 1 1 1.04 2 1 2 3 1.38 3 1 3 2 2.29 4 2 2 2 2.85 5 2 3 1 1.68 6 2 1 3 2.94 7 3 2 1 2.10 8 3 3 3 1.16 9 3 1 2 1.42 k1j 1.57 2.49 1.56 k2j 1.80 2.11 1.71 k3j 1.61 2.19 1.83 R 0.93 0.4 0.58 因素排序 A>C>B 最佳组合 A2C3B1 表 3 方差分析结果
Table 3 Variance analysis results
因素 偏差平方和 自由度 F比 显著性 A 5.13 2 11.29 0.001 B 0.79 2 1.74 0.201 C 1.54 2 3.39 0.054 误差 4.55 20 总计 12.02 26 表 4 硫酸化修饰前后紫菜多糖生物活性的半抑制浓度(IC50)
Table 4 IC50 of Porphyra polysaccharide before and after sulfate modification
多糖 IC50(mg/mL) DPPH自由基 超氧阴离子自由基 羟自由基 α-葡萄糖苷酶 SPP 0.004±0.003c 2.69±0.33c 19.44±0.89c 13.56±0.35c SPP1 0.95±0.63b 4.32±0.53b 23.89±0.50b 16.24±1.47b PP 2.40±0.40a 5.23±0.29a 26.59±0.98a 26.18±4.66a 注:同列不同小写字母表示不同紫菜多糖IC50间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] HE D, WU S Y, YAN L P, et al. Antitumor bioactivity of porphyran extracted from Pyropia yezoensis Chonsoo2 on human cancer cell lines[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(15):6722−6730. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9954
[2] 赵保力, 张英锋, 李长江, 等. 紫菜多糖的提取及化学成分[J]. 化学教学,2010,275(3):52−54,65. [ZHAO B L, ZHANG Y F, LI C J, et al. Extraction and chemical composition of polysaccharides from Porphyra[J]. Education of Chemistry,2010,275(3):52−54,65.] ZHAO B L, ZHANG Y F, LI C J, et al. Extraction and chemical composition of polysaccharides from Porphyra[J]. Education of Chemistry, 2010, 275(3): 52−54,65.
[3] WU Y T, HUO Y F, XU L, et al. Purification, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Porphyra haitanensis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,165(2):2116−2125.
[4] ZENG A, YANG R, YU S, et al. A novel hypoglycemic agent:polysaccharides from laver (Porphyra spp.)[J]. Food Funct,2020,11(10):9048−9056. doi: 10.1039/D0FO01195A
[5] LI Y T, HUO Y F, WANG F, et al. Improved antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of enzymatically degraded Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2020,44(5):e13189.
[6] HU H B, LI H M, HAN M G, et al. Chemical modification and antioxidant activity of the polysaccharide from Acanthopanax leucorrhizus[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2019,487:107890−107890.
[7] 苏靖程, 张传单, 范方宇. 无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维硫酸酯化改性及性质分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(3):255−261. [SU J C, ZHANG C D, FAN F Y. Sulfation modification and properties analysis of soluble dietary fiber from Rosa sterilis pomace[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(3):255−261.] doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022070092 SU J C, ZHANG C D, FAN F Y. Sulfation modification and properties analysis of soluble dietary fiber from Rosa sterilis pomace[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(3): 255−261. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022070092
[8] ZHAO Y P, WANG H G, TIAN N N, et al. Sulfate modification and evaluation of in vitro Anti-HIV activity of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides[J]. Chemistry Select,2022,7(37):e00695.
[9] LI Z W, DU Z M, WANG Y W, et al. Chemical modification, characterization, and activity changes of land plant polysaccharides:A review[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(19):4161.
[10] 巩晓佩. 硫酸化修饰红枣多糖的结构表征及生物活性的研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学, 2021. [GONG X P. Study on the structure characterization and biological activity of sulfated modified jujube polysaccharide[D]. Shihezi:Shihezi University, 2021.] GONG X P. Study on the structure characterization and biological activity of sulfated modified jujube polysaccharide[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2021.
[11] 谭西, 周欣, 陈华国. 多糖结构修饰研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(4):341−349, 356. [TAN X, ZHOU X, CHEN H G. Research progress on structural, modification of polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(4):341−349, 356.] doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.04.057 TAN X, ZHOU X, CHEN H G. Research progress on structural, modification of polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(4): 341−349, 356. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.04.057
[12] 伍磊. 硫酸酯化裂褶多糖的制备、结构表征及其体外活性研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2021. [WU L. Study on the preparation, structure characterization and in vitro bioactivities of sulfated schizophyllan[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2021.] WU L. Study on the preparation, structure characterization and in vitro bioactivities of sulfated schizophyllan[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021.
[13] 刘波, 袁利鹏, 熊波, 等. 多糖的硫酸酯化及其对结构和功能活性的影响研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(22):372−375. [LIU B, YUAN L P, XIONG B, et al. Research advance in polysaccharides sulfated and its effect on the structure and function activity of polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(22):372−375.] doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.22.068 LIU B, YUAN L P, XIONG B, et al. Research advance in polysaccharides sulfated and its effect on the structure and function activity of polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2015, 36(22): 372−375. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.22.068
[14] 徐瑶. 超声波辅助苹果膳食纤维硫酸酯化改性[D]. 西安:陕西科技大学, 2015. [XU Y. The Ultrasound-assisted sulfated modification of dietary fiber from apple[D]. Xian:Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2015.] XU Y. The Ultrasound-assisted sulfated modification of dietary fiber from apple[D]. Xian: Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2015.
[15] CAO Y Y, JI Y H, LIAO A M, et al. Effects of sulfated, phosphorylated and carboxymethylated modifications on the antioxidant activities in-vitro of polysaccharides sequentially extracted from Amana edulis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,146:887−896. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.211
[16] 李国荣, 刘娜女, 张静, 等. 鸡腿菇多糖硫酸酯化条件的优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(11):127−133. [LI G R, LIU N N, ZHANG J, et al. Optimization on the sulfated modification of polysaccharides from Coprinus comatus and evaluation of antioxidant activity[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Nat Sci Ed), 2010, 38(11):127−133.] LI G R, LIU N N, ZHANG J, et al. Optimization on the sulfated modification of polysaccharides from Coprinus comatus and evaluation of antioxidant activity[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Nat Sci Ed), 2010, 38(11): 127−133.
[17] 冯学珍, 伍善广, 孔靖, 等. 超声辅助提取石莼多糖工艺优化及其清除DPPH·自由基活性研究[J]. 中药材,2013,36(11):1870−1872. [FENG X Z, WU S G, KONG J, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharide from Ulva lactuca and its scavenging DPPH· free radical activity[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2013,36(11):1870−1872.] doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2013.11.030 FENG X Z, WU S G, KONG J, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharide from Ulva lactuca and its scavenging DPPH· free radical activity[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2013, 36(11): 1870−1872. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2013.11.030
[18] CHEN F, HUANG G L, YANG Z Y, et al. Antioxidant activity of Momordica charantia polysaccharide and its derivatives[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,138:673−680. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.129
[19] 姚秋萍, 何可群, 黎璐, 等. 鱼腥草多糖硫酸酯化修饰及清除自由基活性[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(8):36−39. [YAO Q P, HE K Q, LI L. Sulfated modification and scavenging effect on free radicals of Houttuynia cordata polysaccharides[J]. The Food Industry,2019,40(8):36−39.] YAO Q P, HE K Q, LI L. Sulfated modification and scavenging effect on free radicals of Houttuynia cordata polysaccharides[J]. The Food Industry, 2019, 40(8): 36−39.
[20] 冯书珍, 谢广燕, 刘南英, 等. 两种海藻内生菌的分离及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2020,39(6):99−105. [FENG S Z, XIE G Y, LIU N Y, et al. Isolation and antioxidative activities of algal endophytes[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2020,39(6):99−105.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2020.06.014 FENG S Z, XIE G Y, LIU N Y, et al. Isolation and antioxidative activities of algal endophytes[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2020, 39(6): 99−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2020.06.014
[21] 冯学珍, 覃慧逢, 冯书珍. 网地藻多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶体外抑制作用的研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(3):35−40. [FENG X Z, QIN H F, FENG S Z. Study on inhibition kinetics of polysaccharide from Dictyota dichotoma on α-glucosidase[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(3):35−40.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.03.007 FENG X Z, QIN H F, FENG S Z. Study on inhibition kinetics of polysaccharide from Dictyota dichotoma on α-glucosidase[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(3): 35−40. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.03.007
[22] 高爽, 王鑫, 马永强, 等. 硫酸酯化甜玉米芯多糖的制备[J]. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,32(5):537−541. [GAO S, WANG X, MA Y Q, et al. Sulfated modification of polysaccharides from sweet corn cobs[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce (Natural Sciences Edition),2016,32(5):537−541.] GAO S, WANG X, MA Y Q, et al. Sulfated modification of polysaccharides from sweet corn cobs[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce (Natural Sciences Edition), 2016, 32(5): 537−541.
[23] 李思雨. 小球藻多糖提取纯化及其改性研究[D]. 南宁:广西民族大学, 2022. [LI S Y. Study on extraction, purification and modification of Chlorella polysaccharide[D]. Nanning:Guangxi Minzu University, 2022.] LI S Y. Study on extraction, purification and modification of Chlorella polysaccharide[D]. Nanning: Guangxi Minzu University, 2022.
[24] 马波, 鞠家宽. 硫酸酯化洋葱多糖的制备及其抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2019,30(6):73−78. [MA B, JU J K. Preparation and antioxidative activities of sulfated onion polysaccharides[J]. China Food Additives,2019,30(6):73−78.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2019.06.009 MA B, JU J K. Preparation and antioxidative activities of sulfated onion polysaccharides[J]. China Food Additives, 2019, 30(6): 73−78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2019.06.009
[25] 杨燕敏, 郑振佳, 李桂芹, 等. 改性红枣多糖的制备和结构表征[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(9):8−14. [YANG Y M, ZHEN Z J, LI G Q, et al. Preparation and structure characterization of modified Jujube polysaccharides[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(9):8−14.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.09.002 YANG Y M, ZHEN Z J, LI G Q, et al. Preparation and structure characterization of modified Jujube polysaccharides[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(9): 8−14. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.09.002
[26] BARTOLOMEU W S S, MIGUEL A C, ANA I. B, et al. Chemical characterization and antioxidant activity of sulfated polysaccharide from the red seaweed Gracilaria birdiae[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2012,27(2):287−292. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.10.005
[27] 陈红漫, 郭龙伟, 章少在, 等. 小分子苦瓜多糖MCPⅡa的纯化及结构分析[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(10):90−94. [CHEN H M, GUO L W, ZHANG S Z, et al. Purification and structural analysis of a polysaccharide from bitter gourd (Momordica charantia)[J]. Food Science,2015,36(10):90−94.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201510018 CHEN H M, GUO L W, ZHANG S Z, et al. Purification and structural analysis of a polysaccharide from bitter gourd (Momordica charantia)[J]. Food Science, 2015, 36(10): 90−94. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201510018
[28] 侯萍, 马军, 陈燕, 等. 几种海藻粗多糖的理化性质及结构特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报,2018,37(2):55−62. [HOU P, MA J, CHEN Y, et al. Analysis of physicochemical properties and structure characteristics of several crude algal polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography,2018,37(2):55−62.] HOU P, MA J, CHEN Y, et al. Analysis of physicochemical properties and structure characteristics of several crude algal polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(2): 55−62.
[29] 郭金英, 朱蓓茹, 任国艳, 等. 发菜胞外多糖硫酸化条件的优化及红外光谱分析[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(24):61−67. [GUO J Y, ZHU B R, REN G Y, et al. Optimization of sulfation conditions and infrared spectroscopy analysis of Nostoc flagelliforme exopolydsaccharide[J]. Food Science,2016,37(24):61−67.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201624009 GUO J Y, ZHU B R, REN G Y, et al. Optimization of sulfation conditions and infrared spectroscopy analysis of Nostoc flagelliforme exopolydsaccharide[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(24): 61−67. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201624009
[30] LIANG W, MAO X, PENG X, et al. Effects of sulfate group in red seaweed polysaccharides on anticoagulant activity and cytotoxicity[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,101:776−785. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.010
[31] HEN Z H, LIU Y X, WANG D, et al. Preparation, chemical structure and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of sulfated polysaccharide from Grifola frondosa[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2022,98:105289. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.105289
[32] 朱影, 屠洁, 赵静, 等. 硫酸酯化修饰对白背三七多糖抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2017,165(11):64−70. [ZHU Y, TU J, ZHAO J, et al. Effects of sulfating modification on antioxidative activities of polysaccharides from Gynura davaricata (L.)DC[J]. China Food Additives,2017,165(11):64−70.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2017.11.004 ZHU Y, TU J, ZHAO J, et al. Effects of sulfating modification on antioxidative activities of polysaccharides from Gynura davaricata (L.)DC[J]. China Food Additives, 2017, 165(11): 64−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2017.11.004
[33] XU Y Q, GAO Y K, LIU F, et al. Sulfated modification of the polysaccharides from blackcurrant and their antioxidant and α-amylase inhibitory activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,109:1344−1354. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.164
[34] XIAO H, FU X, CAO C, et al. Sulfated modification, characterization, antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharides from Sargassum pallidum[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:407−414. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.197
[35] ANUSREE M, KAJAL C. Pharmacological potential of sulfated polygalactopyranosyl-fucopyranan from the brown seaweed Sargassum wightii[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology,2018,30(3):1971−1988. doi: 10.1007/s10811-017-1385-y
[36] 靳文娟, 鲁晓翔. 硫酸化鸡油菌多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的影响[J]. 食品科技,2012,37(8):168−172. [JIN W J, LU X X. The effects of sulfating Cantharellus cibarius polysaccharide on α-glucosidase activity[J]. Food Science and Technology,2012,37(8):168−172.] doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2012.08.008 JIN W J, LU X X. The effects of sulfating Cantharellus cibarius polysaccharide on α-glucosidase activity[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2012, 37(8): 168−172. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2012.08.008





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



