Determination of 16 Kinds of Organochlorine and Pyrethroid Pesticide Residues in Nuts by Gas Chromatography
-
摘要: 建立气相色谱法(gas chromatography,GC)检测坚果中16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留的分析方法。样品通过丙酮:正己烷(3:7,V:V)提取,0.2 mL浓硫酸磺化净化,有机氯和拟除虫菊酯经DB-17MS色谱柱(30 m×0.32 mm,0.25 μm)分离,气相色谱-电子捕获检测器(gas chromatography-electron capture detector,GC-ECD)定量检测。有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药在0.01~0.20 μg/mL浓度范围内与对应的峰面积呈现良好的线性关系,决定系数(r2)均在0.996以上,方法检出限为0.1~0.4 μg/kg;分别对不同基质(开心果、澳洲坚果、腰果、碧根果、核桃、巴旦木)样品进行低(10 μg/kg)、中(40 μg/kg)、高(100 μg/kg)3个浓度加标提取率实验,提取率范围为81.6%~119.5%,相对标准偏差(relative standard deviation,RSDs)为1.03%~5.36%。本方法分析简单、准确度高、重复性好,适用于坚果中16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留的测定。Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to establish an analytical method for the determination of 16 organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide residues in nuts by gas chromatography (GC). The samples were extracted by acetone:hexane (3:7, V:V), purified by 0.2 mL concentrated sulfuric acid sulfonation, and the organochlorines and pyrethroids were separated by a DB-17MS column (30 m×0.32 mm, 0.25 μm), and quantified by gas chromatography-electron capture detector (GC-ECD). The results showed that the organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides showed good linearity in the concentration range of 0.01~0.20 μg/mL and the corresponding peak areas. The determination coefficients (r2) were above 0.996, and the limits of detection were 0.1~0.4 μg/kg. In this study, the spiked recovery experiments were also performed on samples of different matrices (pistachios, macadamia nuts, cashew nuts, pistachios, walnuts, and padanuts) at low (10 μg/kg), medium (40 μg/kg), and high (100 μg/kg) concentrations, respectively. The extraction rates ranged from 81.6% to 119.5% with the relative standard deviations (RSDs) of 1.03%~5.36%. The method is simple, accurate, reproducible and suitable for the determination of 16 organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide residues in nuts.
-
Keywords:
- nuts /
- organochlorine /
- pyrethroid /
- concentrated sulfuric acid sulfonation /
- gas chromatography
-
坚果中含有不饱和脂肪酸、蛋白质、矿物质、维生素、纤维素、以及帮助催化脂肪的其他微量元素,具有保护心脏、美肌,抗氧化、改善视力、补脑等特殊的功能[1−2]。美国食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)在2007年向全球提出将坚果食品列为B级健康食品[3−4]。坚果果树生长过程中容易受到病虫害的侵害,喷洒农药是果树的病虫害防治重要手段之一。以六六六、滴滴涕、五氯硝基苯为代表的有机氯杀虫剂为坚果禁用农药,但因具备杀虫种类多,高效、低毒、经济效益好等特点,容易在坚果果树的病虫害防治过程中被果农误用;菊酯类农药可以高效杀灭鳞翅目幼虫,可喷洒防治蝽象类害虫。喷洒到果树上的农药需要一定周期降解,果农对喷洒农药的时间掌握不准或违规使用,容易造成果实中农药残留出现超标的现象的发生,加之随着人们生活水平的提高,坚果的质量安全问题越来越受到人们的重视[5−6],我国GB 2763-2014《食品安全国家标准 食品中农药最大残留限量》标准中对各类坚果农药残留限量作出了明确规定。
目前,关于有机氯及拟除虫菊酯农药多残留检测方法主要有气相色谱(gas chromatography,GC)、高效液相色谱-质谱法(high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrography,HPLC-MS)[7−11]、气相色谱-质谱法(gas chromatography-mass spectrography,GC-MS)等[12−13],前处理方法有凝胶渗透[14]、固相萃取[15−17]、QuECHERS[16−18]等方法。GC-MS和HPLC-MS相对GC来说,设备价格、后期维护成本较高、对人员的基本操作专业技能有比较高的要求,其次,因电子捕获检测器(electron capture detector,GC-ECD)对电负性强的化合物有响应,可以用来测定有机氯和拟除虫菊酯类农药,所以本研究选择GC-ECD进行有机氯、拟除虫菊酯检测[19]。前处理方面采用浓硫酸磺化样本提取液能够达到有效净化杂质目的,避免污染进样口、石英毛细管柱。采用硫酸磺化处理相对于固相萃取和QuECHERS进行前处理[20],避免了农药残留在浓缩、换相过程中的损失,提升检测效率、节约检测成本。
因此,本研究以坚果为实验对象,丙酮:正己烷(V:V=3:7)为提取溶剂,运用磺化法进行样本净化,GC-ECD检测有机氯和拟除虫菊酯。以期为检测人员准确测定坚果中有机氯和拟除虫菊酯类农药残留量提供技术参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
乙腈、正己烷 色谱纯,天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;丙酮、无水硫酸钠 、硫酸 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;标准溶液:α-六六六、β-六六六、γ-六六六、δ-六六六、p,p’-滴滴滴(p,p’-DDD)、p,p’-滴滴伊(p,p’-DDE)、p,p’-滴滴涕(p,p’-DDT)、o,p’-滴滴涕(o,p’-DDT)、α-硫丹、β-硫丹、甲氰菊酯、氯氟氰菊酯、氯菊酯、氰戊菊酯、溴氰菊酯、五氯硝基苯 100 μg/mL,坛墨质检科技股份有限公司;开心果、澳洲坚果、紫皮腰果、碧根果、核桃、巴旦木 各500 g,三只松鼠股份有限公司。
GC-7890B气相色谱仪 配备ECD检测器及Agilent OpenLAB CDS工作站、DB-17MS、DB-1701石英毛细管色谱柱 30 m×0.32 mm,0.25 μm,美国安捷伦公司;AUW220D电子分析天平 (精度0.01 mg) 日本岛津公司;N1-28全自动氮吹浓缩仪 上海屹尧仪器科技发展有限公司;XK80-A涡旋混合器 江苏新康医疗器械有限公司;T25均质器 德国IKA公司;Milli-Q Direct 8超纯水机 美国默克公司;TDZ5-WS低速离心机、TG16-WS高速离心机 湖南湘仪离心机仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药混合标准溶液的配制
分别移取100 μg/mL的α-六六六、β-六六六、γ-六六六、δ-六六六、p,p’-DDD、p,p’-DDE、p,p’-DDT、o,p’-DDT、五氯硝基苯、硫丹(α-硫丹、β-硫丹)、甲氰菊酯、氯氟氰菊酯、氯菊酯、氯菊酯、氰戊菊酯、氰戊菊酯、溴氰菊酯标准储备液100 μL于10 mL容量瓶中,用正己烷定容至刻度,配制成浓度为1.0 μg/mL的有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药混合标准溶液,将混合标准溶液用正己烷稀释成质量浓度为0.01、0.02、0.05、0.10、0.20 μg/mL的系列标准溶液。
1.2.2 样品前处理
称取2.0 g(精确到0.01 g)粉末状坚果(去壳研磨成粉状过80目筛)样品置于50 mL塑料离心管中,分别加入2.0 mL水、1.0 g无水硫酸钠,振荡混匀后加入丙酮:正己烷(3:7,V:V)试剂10 mL,置振荡器上剧烈振荡5 min,1342×g离心3 min,取全部上清液,将上清液置于氮吹仪中,40 ℃水浴氮吹至近干,将浓缩溶液用正己烷定容至1.0 mL,定容液中加入0.2 mL硫酸除去脂质等杂质,弃去硫酸,有机相用2 mL 2%硫酸钠溶液清洗,以2683×g离心3 min,有机相过0.45 μm有机系滤膜上机供GC-ECD测定。
1.2.3 条件优化
1.2.3.1 提取溶剂的选择
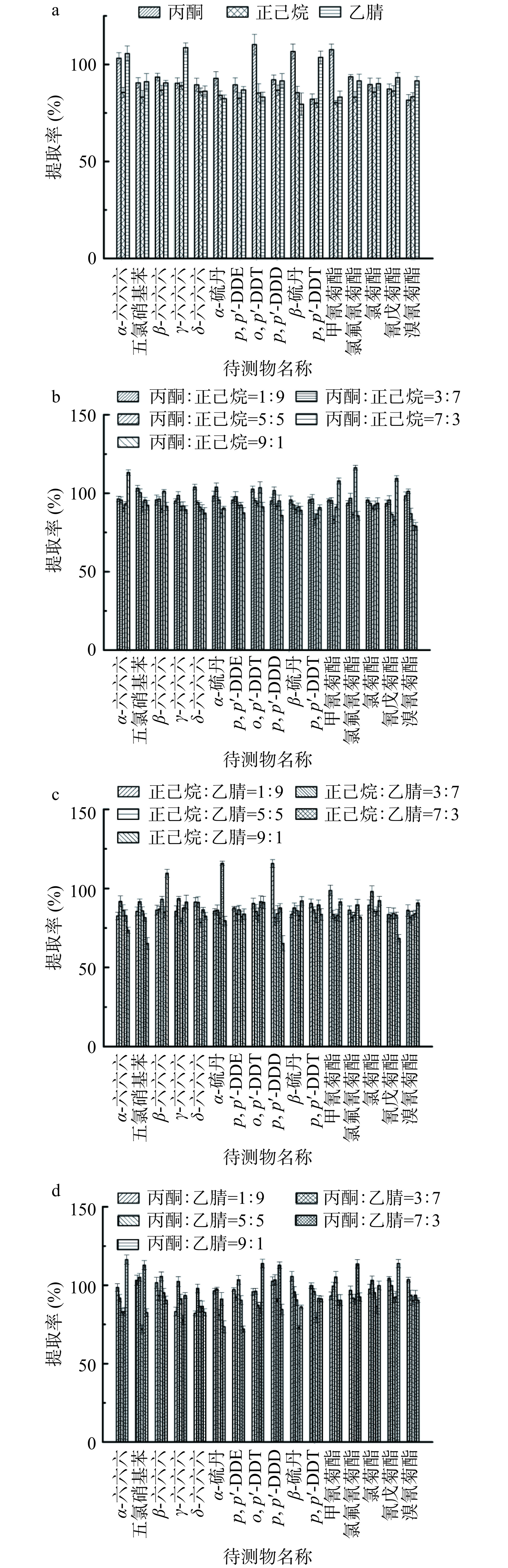
选择乙腈、丙酮、正己烷、乙腈:丙酮(1:9、3:7、5:5、7:3、9:1 V:V)、乙腈:正己烷(1:9、3:7、5:5、7:3、9:1 V:V)、丙酮:正己烷(1:9、3:7、5:5、7:3、9:1 V:V)不同比例提取溶剂,考察对有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药的提取率的影响。
1.2.3.2 提取次数的选择
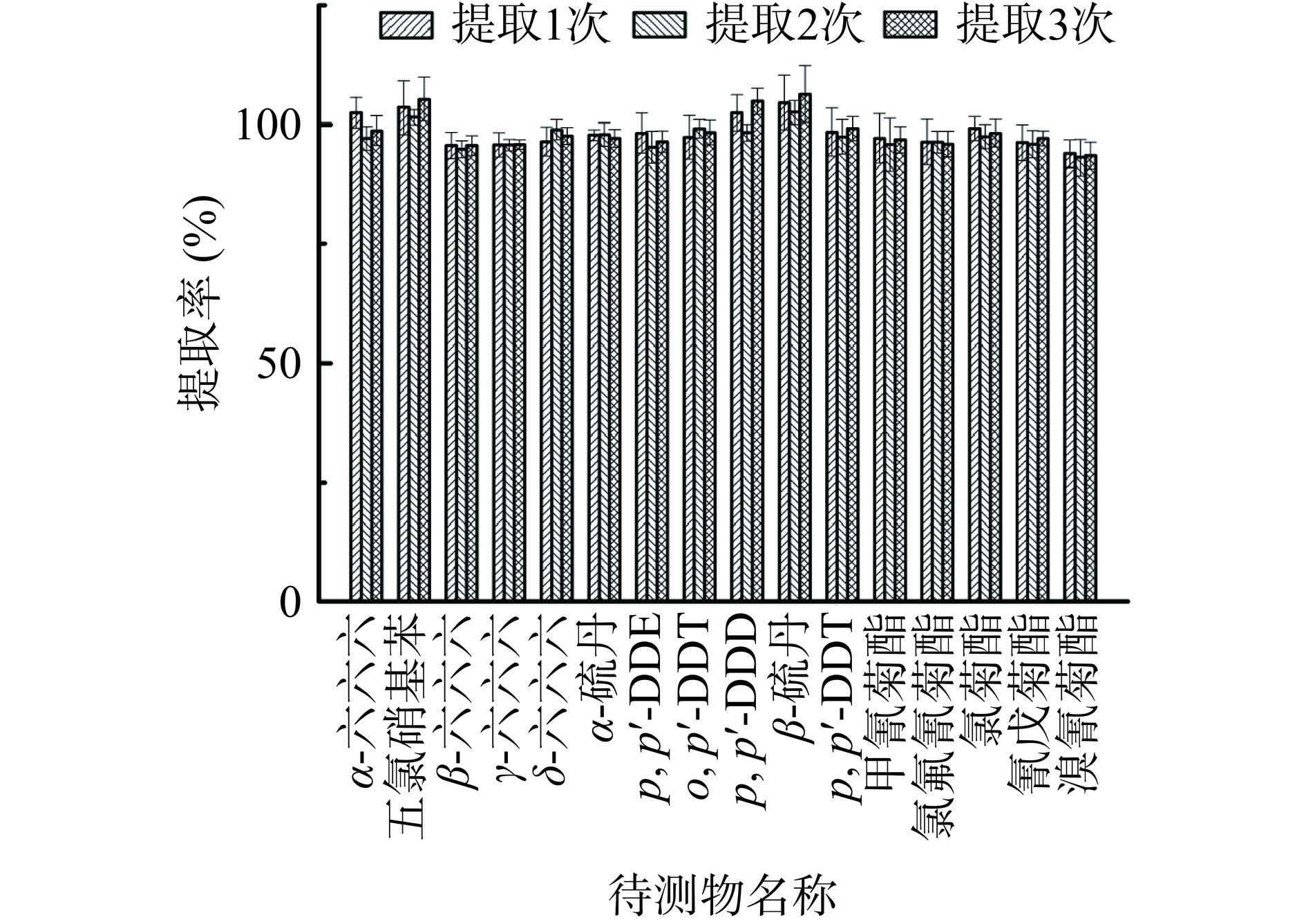
为了实现对坚果样品中农残的充分提取,使用相同提取试剂对坚果样品中农残的提取次数分别为1、2、3次,考察对检测结果的影响。
1.2.3.3 氮吹温度的选择
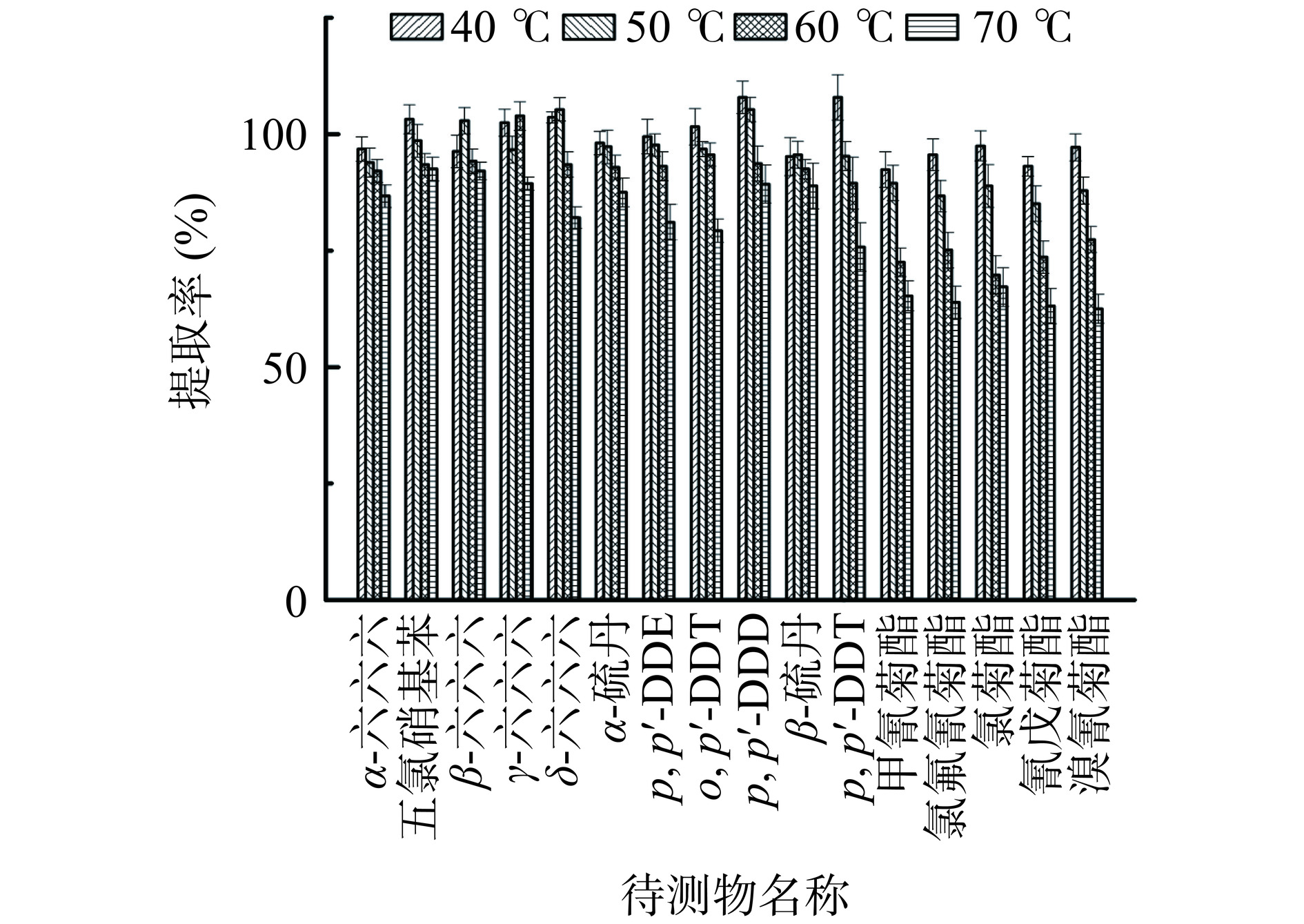
为了考察氮吹温度对检测结果的影响,分别使用40、50、60、70 ℃对坚果样品进行氮吹。
1.2.3.4 定容试剂的选择
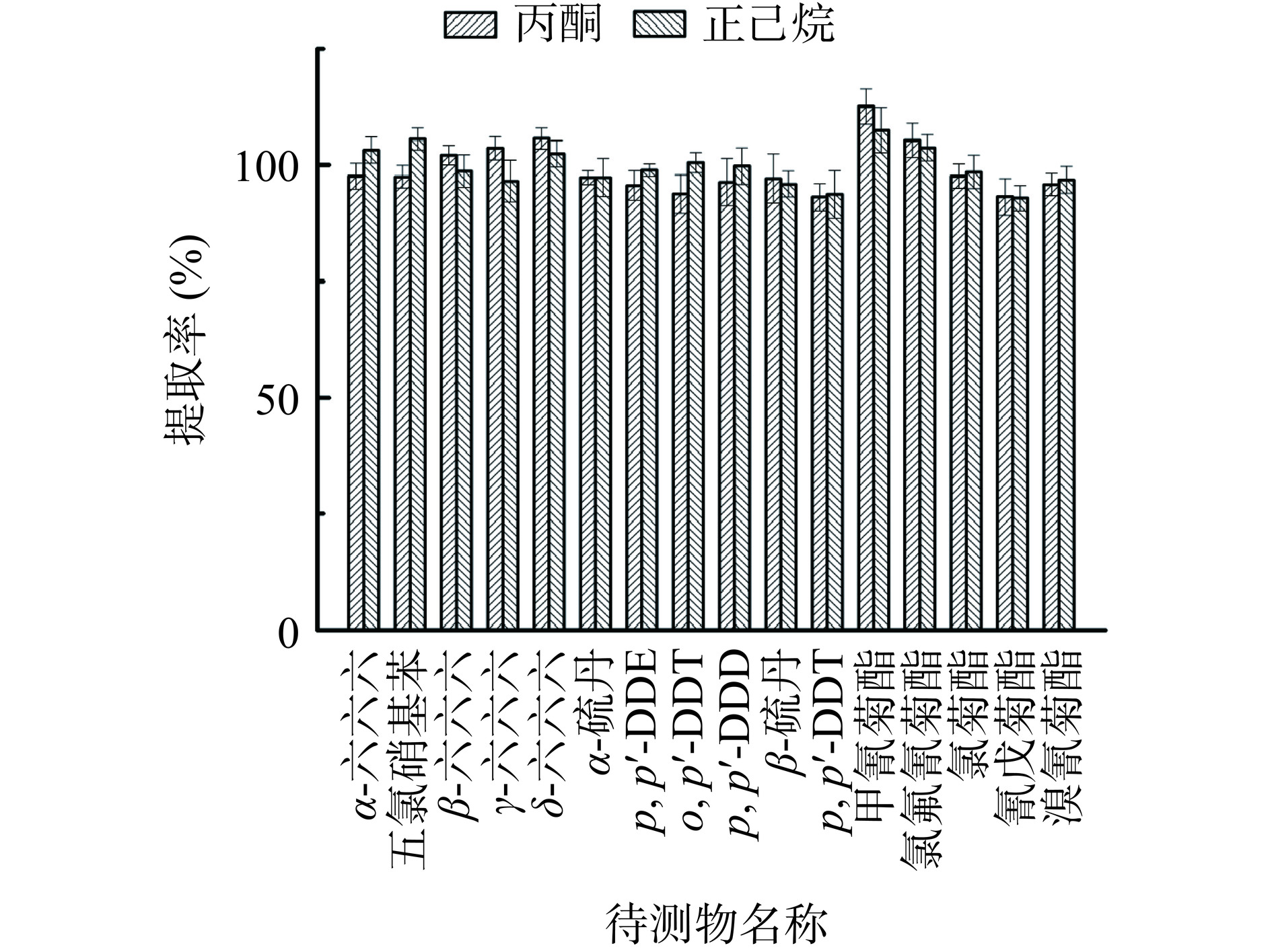
本文用丙酮:正己烷(3:7 V:V)提取,为了考察定容试剂对提取率的影响,分别用丙酮、正己烷对坚果样品进行最终定容。
1.2.3.5 磺化试剂体积的选择
考虑到定容后会有杂质产生,污染进样口、检测器等,研究使用0.5、1.0、2.0 mL浓硫酸对样本进行磺化净化。
1.2.4 色谱条件
检测器:ECD;进样器温度:250 ℃;检测器温度:300 ℃;进样量:1.0 μL;不分流进样;载气:N2(纯度≥99.999%);流速:1 mL/min。升温程序为初始温度设置为100 ℃,保留1 min,以15 ℃/min升温至160 ℃,保留1.5 min,再以5 ℃/min升温至280 ℃,保留10 min。
1.2.5 提取率的计算
W(%)=C样×V样C标×V标×100 式中:W表示有机氯和拟除虫菊酯提取率,%;C样表示样品中有机氯和拟除虫菊酯的质量浓度,mg/mL;V样表示样品最终定容体积,mL;C标表示添加标品中有机氯和拟除虫菊酯的质量浓度,mg/mL;V标表示添加标品体积,mL。
1.3 数据处理
本实验数据经Origin Pro 9.0绘图软件分析处理作出相应色谱图,采用WPS 2022软件处理提取率、相对标准偏差等相关实验数据。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 样品前处理条件的优化
2.1.1 提取溶剂的选择
农药残留分析中,根据农药极性、样本性质的不同选择不同极性的提取剂,常用的提取剂有乙腈、甲醇、丙酮、二氯甲烷、正己烷、石油醚。分别用乙腈、丙酮、正己烷,乙腈:丙酮(1:9、3:7、5:5、7:3、9:1 V:V)、乙腈:正己烷(1:9、3:7、5:5、7:3、9:1 V:V)、丙酮:正己烷(1:9、3:7、5:5、7:3、9:1 V:V)不同比例进行提取,考虑到使用正己烷提取样品时,提取率低,不能有效提取坚果组织中的残留农药;使用丙酮提取坚果样本时,提取油脂较多,不利于样本的下一步净化;乙腈能够有效提取多种农药残留,但价格相对较贵,且浓缩时间长,为了克服单一提取溶剂提取样本的不足,且正己烷:乙腈、丙酮:乙腈组合试剂提取率没有丙酮:正己烷组合试剂好,提取率为65.2%~115.7%,72.1%~116.3%,而丙酮:正己烷混合提取剂在后续的氮吹、净化效果,提取率方面均有较好的表现且通过数据得知用丙酮:正己烷(3:7,V:V)为提取试剂时,16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留量提取率为93.5%~103.5%,相对标准偏差(relative standard deviation,RSDs)值为1.11%~3.62%。提取溶剂是确保样品中各类农药残留提取效率、准确度的关键因素[21−23],本文最终选择丙酮:正己烷(3:7,V:V)为提取试剂,具体结果如图1。
2.1.2 提取次数的选择
采用丙酮:正己烷(V:V=3:7)对坚果样品提取1、2、3次,考察提取次数对检测结果的影响。结果显示,提取1次的提取率为93.9%~104.6%,RSDs为1.11%~5.71%;提取2次的提取率为93.1%~102.6%,RSDs为1.21%~5.51%;提取3次的提取率为93.5%~106.4%,RSDs为1.0%~5.9%。具体结果见图2。提取次数的选择是16种农药残留的提取效率的关键控制点[24],但随着提取次数的增加,提取液里面的杂质也显著上升,为后续除杂过程增加难度,且从成本,效率上考虑,试剂、人员花费时间较多,结合综合情况考虑将样品提取次数确定为1次。
2.1.3 氮吹温度的选择
本实验分别考察40、50、60、70 ℃氮吹温度对检测结果的影响,结果显示不同氮吹温度对坚果中有机氯、拟除虫菊酯的农药残留影响较大,40、50 ℃氮吹温度对有机氯影响不大,提取率为92.2%~107.9%,RSDs为1.22%~4.91%,但随着温度的升高提取率有着明显的降低,拟除虫菊酯类农药残留在40 ℃氮吹温度下提取率均在92.4%~97.5%之间,RSDs为1.11%~5.22%,在50、60、70 ℃氮吹温度提取率随着温度的升高越来越低,50 ℃提取率为85.1%~89.5%,60 ℃提取率为69.8%~77.4%,70 ℃提取率只有62.5%~67.4%,在较高温度氮吹下所检测物质可能发生分解,影响检测结果的准确性。不同氮吹温度的选择是16种农药残留的提取效率的关键控制点[25],控制提取温度在40 ℃左右时,提取效果明显提升,但超过该温度后,提取效果相差较大[26]。所以研究选择40 ℃氮吹温度。具体实验结果见图3。
2.1.4 定容试剂的选择
研究分别考察丙酮、正己烷作为样品上机定容试剂对检测结果的影响。用丙酮定容提取率为93.1%~112.6%,RSDs为1.50%~5.31%;用正己烷定容提取率为92.9%~107.5%,RSDs为1.30%~5.14%,结果显示两者作为定容试剂,结果无差异。定容试剂的选择是16种农药残留复溶提取的关键控制点[27−28],同时也影响实验色谱柱的使用寿命,常用的定容剂有丙酮、乙酸乙酯、正己烷、石油醚等。但是丙酮极性相对较大,对色谱柱损伤较大,对坚果中其他杂质也有很好的溶解效果,且与浓硫酸发生反应。所以研究选用正己烷作为定容试剂。具体结果见图4。
2.1.5 磺化试剂体积的选择
研究使用0.2、0.5、1.0 mL浓硫酸对样本进行磺化处理,经不同体积浓硫酸磺化后,样本色谱峰无明显差异,杂质均能有效去除,提取率均能达到80%以上。磺化试剂体积的选择是16种农药残留净化技术的关键控制点[29−30],添加体积较多的浓硫酸时,16种农药残留的提取率没有明显提升,而过多的浓硫酸对色谱柱和仪器有较大的伤害,SN/T 0145-2010《进出口植物产品中六六六、滴滴涕残留量测定方法 磺化法》需要2~3次磺化,六六六和滴滴涕提取率范围在77.8%~104.0%,而本实验选用0.2 mL的浓硫酸作为磺化试剂体积一次磺化,且提取率在83.2%~101.1%。单样品检测时间短,提高了16种农药残留检测效率。具体结果见图5。
2.2 方法学验证
2.2.1 线性关系与检出限
本研究采用在空白基质坚果样品中添加经逐级稀释的混合标准工作液进行加标实验,以各农药的质量浓度(X,μg/mL)为横坐标,峰面积(Y)为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线。考察16种有机氯、有机磷、拟除虫菊酯类的农药残留。在相应线性范围内,各农药分离效果较好,结果见图6,且线性关系良好,决定系数(r2)均在0.996以上。结果按照3倍信噪比(S/N=3)计算方法检出限满足检测的要求。计算得出本方法中的各物质检出限在0.1~0.4 μg/kg之间,结果见图6和表1。结果表明基于GC检测坚果中的16种农药残留具有较高的灵敏度,检出限较低,具有较强的可行性。
表 1 16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类的农药残留的线性方程、决定系数和检出限、定量限(n=6)Table 1. Linear equations, determination coefficients, detection limits and quantitation limits of 16 kinds of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide residues (n=6)化合物名称 保留时间(min) 线性方程 决定系数r2 检出限(μg/kg) 定量限(μg/kg) α-六六六 10.774 Y=333615X−1480 0.9993 0.1 0.3 五氯硝基苯 11.779 Y=207302X−493 0.9997 0.1 0.3 β-六六六 12.276 Y=297296X−1230 0.9994 0.1 0.3 γ-六六六 13.447 Y=90130X−320 0.9997 0.1 0.3 δ-六六六 14.449 Y=166200X−1019 0.9990 0.1 0.3 α-硫丹 17.920 Y=224809X−743 0.9995 0.3 0.9 p,p’-DDE 19.010 Y=144948X−704 0.9989 0.1 0.3 o,p’-DDT 20.877 Y=84504X−356 0.9990 0.2 0.6 p,p’-DDD 21.288 Y=71379X−289 0.9993 0.1 0.3 β-硫丹 21.405 Y=126033X−583 0.9992 0.3 0.9 p,p’-DDT 22.219 Y=66390X−388 0.9980 0.2 0.6 甲氰菊酯 24.117 Y=89925X−633 0.9995 0.2 0.6 氯氟氰菊酯 25.031 Y=223303X−2031 0.9997 0.2 0.6 氯菊酯 27.503/27.801 Y=30616X−652 0.9961 0.4 1.2 氰戊菊酯 31.368/31.883 Y=75284X−758 0.9985 0.4 1.2 溴氰菊酯 33.808 Y=56534X−309 0.9992 0.2 0.6 2.2.2 加标提取率及精密度
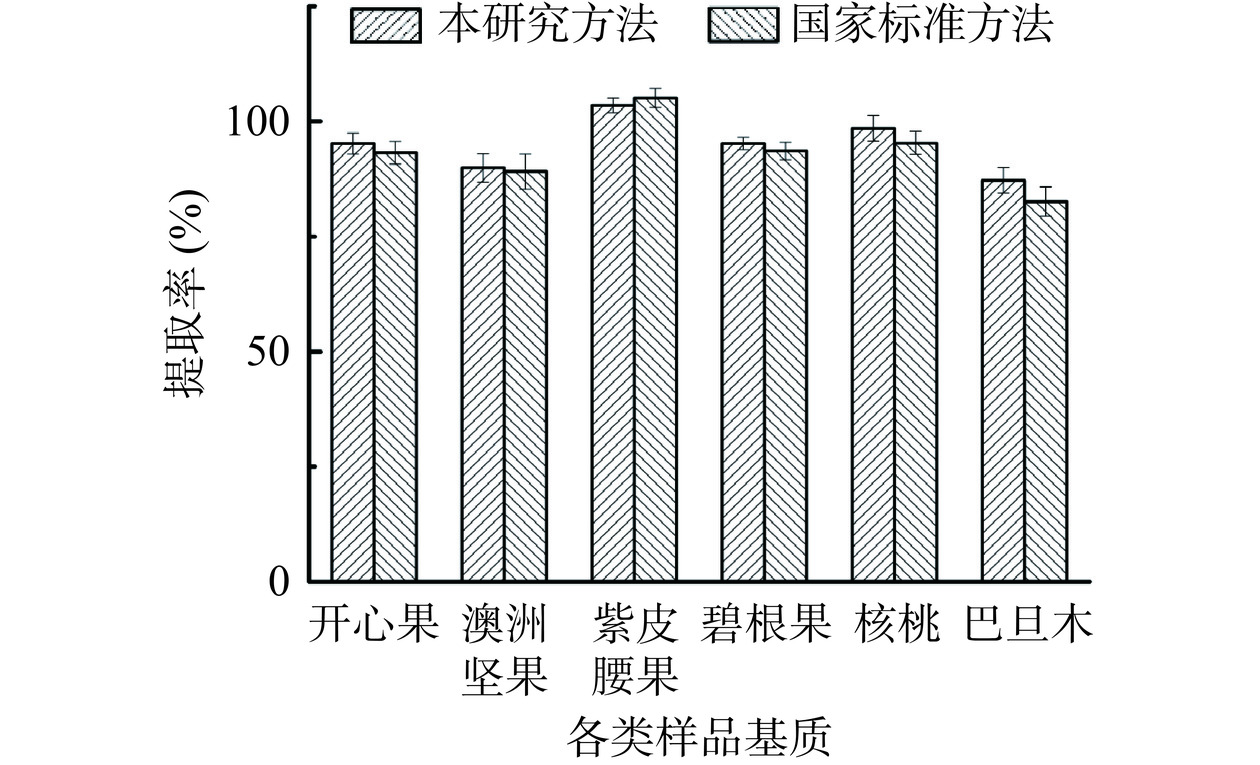
为了考察方法的准确性,分别于开心果、澳洲坚果、紫皮腰果、碧根果、核桃、巴旦木基质的空白样品中加入不同浓度水平的混合标准溶液,分别制备得到为10、40、100 μg/kg不同质量浓度的3个加标样品,每个加标浓度分别制备6个平行样品,计算其平均提取率及精密度。检测结果显示样品检测提取率为81.6%~119.5%,RSDs为1.03%~5.36%,满足GB/T 27404-2008《实验室质量控制规范 食品理化检测》附录F.1和F.3相关要求,采用本研究方法与GB/T 5009.19-2008《食品中有机氯农药多组分残留量的测定》、GB/T 5009.110-2003《植物性食品中氯氰菊酯、氰戊菊酯和溴氰菊酯残留量的测定》、SN/T 0145-2010《进出口植物产品中六六六、滴滴涕残留量测定方法 磺化法》、NY/T 761-2008《蔬菜和水果中有机磷、有机氯、拟除虫菊酯和氨基甲酸酯类农药多残留的测定》方法进行对比实验,本研究方法检测开心果、澳洲坚果、紫皮腰果、碧根果、核桃和巴旦木平均提取率为87.2%~103.5%,国家标准方法的提取率范围为82.6%~105.1%,结果优于国家标准方法。表明本方法的准确度和精密度较好,能够用于坚果中16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留量的测定。具体数据见表2、图7。
表 2 不同基质的加标提取率和精密度(n=6)Table 2. Spiked extraction rates and RSDs of spiked standard in different matrices (n=6)样品基质 化合物名称 10 μg/kg 40 μg/kg 100 μg/kg 样品基质 化合物名称 10 μg/kg 40 μg/kg 100 μg/kg 提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)开心果 α-六六六 91.6 3.55 95.3 4.13 103.2 2.61 碧根果 α-六六六 95.8 3.52 98.9 2.59 98.6 2.56 五氯硝基苯 87.2 3.83 101.2 2.15 98.2 2.19 五氯硝基苯 99.5 2.59 96.7 2.31 98.5 1.92 β-六六六 93.5 2.89 93.8 3.16 95.3 2.16 β-六六六 96.1 3.60 95.3 3.56 96.1 2.81 γ-六六六 96.1 3.15 97.8 4.19 98.5 2.09 γ-六六六 92.5 4.59 94.5 3.81 95.4 1.82 δ-六六六 87.6 4.36 105.3 4.35 96.3 2.13 δ-六六六 96.7 5.29 96.1 3.61 97.1 1.88 α-硫丹 92.3 2.95 95.6 3.68 96.5 2.91 α-硫丹 97.8 2.53 95.9 4.29 98.2 1.92 p,p’-DDE 95.6 3.36 98.6 3.87 98.5 2.46 p,p’-DDE 91.5 3.58 92.5 4.39 95.8 2.65 o,p’-DDT 97.8 3.45 95.8 3.67 97.6 2.19 o,p’-DDT 96.5 5.31 96.8 3.12 97.2 2.16 p,p’-DDD 88.9 4.59 99.2 3.66 98.9 2.95 p,p’-DDD 95.3 2.59 95.6 3.09 97.4 2.19 β-硫丹 93.6 2.33 102.5 4.19 95.6 2.96 β-硫丹 96.2 3.76 96.4 4.15 97.8 1.95 p,p’-DDT 85.9 4.56 95.3 3.64 96.1 2.34 p,p’-DDT 95.6 3.68 95.7 4.36 97.7 1.03 甲氰菊酯 102.9 3.15 105.3 3.52 96.3 2.09 甲氰菊酯 105.6 2.69 95.6 3.59 98.1 1.09 氯氟氰菊酯 105.3 4.78 103.6 5.27 95.8 1.95 氯氟氰菊酯 109.5 2.97 96.8 4.09 102.1 2.34 氯菊酯 110.9 3.81 102.7 3.81 102.6 2.46 氯菊酯 113.5 3.68 102.6 2.95 96.5 2.15 氰戊菊酯 108.2 3.25 98.5 3.67 98.7 2.05 氰戊菊酯 109.5 3.65 96.8 3.69 97.5 2.35 溴氰菊酯 105.7 3.94 96.7 3.91 103.6 3.05 溴氰菊酯 108.6 3.94 95.2 3.57 98.6 2.19 澳洲坚果 α-六六六 91.5 4.79 95.6 3.65 98.6 2.67 核桃 α-六六六 96.5 3.65 98.6 3.46 98.9 2.34 五氯硝基苯 98.3 3.25 98.1 3.91 98.7 2.15 五氯硝基苯 101.5 3.19 98.7 3.59 98.7 2.15 β-六六六 95.5 3.68 95.2 4.59 96.5 2.05 β-六六六 95.6 3.97 95.7 3.19 96.3 2.33 γ-六六六 89.6 3.59 96.8 4.57 95.3 1.92 γ-六六六 97.8 2.56 96.3 2.95 98.4 2.16 δ-六六六 89.8 4.65 98.2 4.53 98.6 1.98 δ-六六六 96.9 5.13 97.8 2.09 98.5 1.09 α-硫丹 101.5 4.19 96.5 3.59 97.8 2.31 α-硫丹 96.5 5.24 96.8 4.13 97.8 1.58 p,p’-DDE 91.6 4.52 93.4 3.61 95.6 2.37 p,p’-DDE 101.3 4.67 98.3 4.19 98.5 2.13 o,p’-DDT 92.3 3.59 94.2 3.67 95.7 2.55 o,p’-DDT 105.8 4.91 98.5 3.57 98.8 1.67 p,p’-DDD 93.5 2.98 96.2 4.16 96.8 2.61 p,p’-DDD 106.5 4.29 97.6 3.56 98.6 1.38 β-硫丹 93.5 3.57 97.1 4.38 98.2 2.39 β-硫丹 98.5 4.77 98.5 4.01 98.5 2.06 p,p’-DDT 81.6 3.64 92.5 4.51 95.6 2.75 p,p’-DDT 112.6 3.75 102.5 3.06 98.5 2.04 甲氰菊酯 103.6 2.95 95.6 3.67 98.4 3.12 甲氰菊酯 116.5 3.58 95.3 3.19 97.6 1.96 氯氟氰菊酯 119.5 4.36 105.3 3.46 102.5 3.09 氯氟氰菊酯 107.6 4.39 106.8 3.71 103.5 1.51 氯菊酯 102.6 4.12 97.8 3.95 103.6 2.46 氯菊酯 109.3 4.95 103.5 3.86 97.9 2.16 氰戊菊酯 105.3 4.36 103.6 4.16 105.2 2.98 氰戊菊酯 109.5 4.13 106.5 4.65 96.8 2.03 溴氰菊酯 106.7 3.57 102.5 3.69 104.1 2.65 溴氰菊酯 112.3 3.95 103.6 3.67 103.5 1.66 腰果 α-六六六 91.5 2.35 102.6 4.61 101.9 2.13 巴旦木 α-六六六 93.2 3.69 95.6 4.98 98.6 1.43 五氯硝基苯 99.8 5.01 98.5 4.39 103.6 2.36 五氯硝基苯 98.6 4.59 99.3 5.36 99.9 1.46 β-六六六 95.3 3.49 101.6 4.68 98.5 2.59 β-六六六 94.3 4.16 93.5 4.17 95.6 1.39 γ-六六六 94.2 3.89 99.5 3.91 98.7 2.65 γ-六六六 95.8 3.58 95.3 3.57 98.2 1.28 δ-六六六 93.6 2.95 95.8 3.56 96.3 1.95 δ-六六六 96.5 4.28 97.8 3.49 97.6 2.61 α-硫丹 103.5 2.35 96.1 3.64 96.8 1.61 α-硫丹 95.2 5.29 97.6 3.57 98.5 1.59 p,p’-DDE 98.1 2.95 97.2 3.98 98.9 1.12 p,p’-DDE 98.1 3.46 97.6 4.31 97.6 2.39 o,p’-DDT 95.4 3.97 96.8 3.19 97.8 2.36 o,p’-DDT 91.6 3.65 97.9 4.19 98.9 2.15 p,p’-DDD 91.3 4.56 98.2 4.12 98.6 2.61 p,p’-DDD 93.6 3.29 95.6 3.61 99.2 2.03 β-硫丹 96.7 4.69 95.6 4.35 97.8 2.21 β-硫丹 96.5 3.37 97.1 2.56 98.6 1.61 p,p’-DDT 108.8 5.01 98.1 3.65 98.5 2.44 p,p’-DDT 93.7 5.11 95.2 3.94 96.3 1.68 甲氰菊酯 109.5 3.59 102.6 3.68 102.1 2.79 甲氰菊酯 112.5 2.97 103.2 4.19 96.7 1.92 氯氟氰菊酯 117.2 3.68 97.6 4.62 102.3 2.71 氯氟氰菊酯 109.3 3.65 108.5 4.16 98.6 1.87 氯菊酯 109.5 3.59 98.2 4.55 98.5 2.75 氯菊酯 108.5 3.48 105.3 3.81 102.1 2.05 氰戊菊酯 112.3 3.99 92.5 3.69 103.2 2.71 氰戊菊酯 116.5 3.57 103.2 3.86 103.2 2.65 溴氰菊酯 98.6 2.36 95.3 3.91 104.2 2.76 溴氰菊酯 112.5 3.69 103.6 3.64 98.6 1.68 2.2.3 准确度
本研究的准确度采用GB/T 27404-2008附录F.5中提出的“重复分析标准物质(实物标样)或水平测试品,测定含量(经提取率校正后)平均值与真值的偏差”的方法进行评定。由于寻找16种农残质控样较为困难,所以实验采样空白样品加标的方式,约定理论加标量为真值。实验制备20 μg/kg加标样品,进行6次平行检测,同时检测样品的提取率,计算平均值,经提取率校正后得到测定值,测定值与约定真值的偏差范围在−6.5%~+9.0%,满足GB/T 27404-2008附录F.5中规定的测定真值在0.010~10.000 mg/kg范围内,偏差范围为−20%~+10%的要求,说明本方法检测结果准确、可信,具体结果见表3。
表 3 检测结果与约定真值的偏差(n=6)Table 3. Detection deviations of measured values and the conventional true value (n=6)样品基质 化合物名称 20 μg/kg 样品基质 化合物名称 20 μg/kg 检测结果 偏差(%) 检测结果 偏差(%) 开心果 α−六六六 19.8 −1.0 碧根果 α−六六六 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 20.2 1.0 五氯硝基苯 20.1 0.5 β−六六六 20.3 1.5 β−六六六 20.1 0.5 γ−六六六 19.9 −0.5 γ−六六六 21.5 7.5 δ−六六六 19.6 −2.0 δ−六六六 19.8 −1.0 α−硫丹 20.2 1.0 α−硫丹 19.9 −0.5 p,p’-DDE 19.9 −0.5 p,p’-DDE 19.6 −2.0 o,p’-DDT 19.6 −2.0 o,p’-DDT 19.5 −2.5 p,p’-DDD 19.7 −1.5 p,p’-DDD 19.7 −1.5 β−硫丹 20.5 2.5 β−硫丹 20.3 1.5 p,p’-DDT 19.2 −4.0 p,p’-DDT 20.5 2.5 甲氰菊酯 19.3 −3.5 甲氰菊酯 19.8 −1.0 氯氟氰菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氯氟氰菊酯 21.6 8.0 氯菊酯 20.9 4.5 氯菊酯 20.6 3.0 氰戊菊酯 20.5 2.5 氰戊菊酯 19.1 −4.5 溴氰菊酯 20.8 4.0 溴氰菊酯 21.1 5.5 澳洲坚果 α−六六六 19.6 −2.0 核桃 α−六六六 19.7 −1.5 五氯硝基苯 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 20.3 1.5 β−六六六 19.7 −1.5 β−六六六 20.2 1.0 γ−六六六 20.2 1.0 γ−六六六 20.5 2.5 δ−六六六 20.1 0.5 δ−六六六 19.8 −1.0 α−硫丹 19.5 −2.5 α−硫丹 19.2 −4.0 p,p’-DDE 19.8 −1.0 p,p’-DDE 19.5 −2.5 o,p’-DDT 19.1 −4.5 o,p’-DDT 19.3 −3.5 p,p’-DDD 19.6 −2.0 p,p’-DDD 19.5 −2.5 β−硫丹 20.8 4.0 β−硫丹 19.2 −4.0 p,p’-DDT 20.9 4.5 p,p’-DDT 19.8 −1.0 甲氰菊酯 21.1 5.5 甲氰菊酯 19.6 −2.0 氯氟氰菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氯氟氰菊酯 19.3 −3.5 氯菊酯 19.6 −2.0 氯菊酯 21.1 5.5 氰戊菊酯 16.9 −5.5 氰戊菊酯 20.8 4.0 溴氰菊酯 19.2 −4.0 溴氰菊酯 20.6 3.0 腰果 α−六六六 19.3 −3.5 巴旦木 α−六六六 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 19.8 −1.0 β−六六六 19.9 −0.5 β−六六六 19.6 −2.0 γ−六六六 21.3 6.5 γ−六六六 20.2 1.0 δ−六六六 19.5 −2.5 δ−六六六 20.3 1.5 α−硫丹 20.3 1.5 α−硫丹 19.5 −2.5 p,p’-DDE 20.6 3.0 p,p’-DDE 19.6 −2.0 o,p’-DDT 19.5 −2.5 o,p’-DDT 19.7 −1.5 p,p’-DDD 19.8 −1.0 p,p’-DDD 19.8 −1.0 β−硫丹 19.4 −3.0 β−硫丹 19.8 −1.0 p,p’-DDT 19.6 −2.0 p,p’-DDT 19.7 −1.5 甲氰菊酯 16.7 −6.5 甲氰菊酯 19.1 −4.5 氯氟氰菊酯 21.6 8.0 氯氟氰菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氯菊酯 21.3 6.5 氯菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氰戊菊酯 21.8 9.0 氰戊菊酯 19.3 −3.5 溴氰菊酯 21.5 7.5 溴氰菊酯 19.2 −4.0 2.3 实际样品的测定
从市面上购买开心果、澳洲坚果、紫皮腰果、碧根果、核桃、巴旦木各5份样品采用本研究方法进行检测,均未检出上述16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留,检测结果均符合GB 2763-2014要求。
3. 结论
本研究基于浓硫酸磺化净化技术,建立了一种气相色谱法测定坚果中16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留量的分析方法。通过对样品提取条件的优化,采用丙酮:正己烷(3:7,V:V)提取坚果中16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留,对6种坚果样品提取1次,用40 ℃氮吹温度,最终用正己烷定容,0.2 mL浓硫酸磺化净化,探索出适用于16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留检测方法。有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类农药残留在35 min内达到完全分离,本研究方法16种物质的检测限在0.1~0.4 μg/kg之间,决定系数(r2)均大于0.996,提取率为81.6%~119.5%,RSDs为1.03%~5.36%。本研究方法前处理简单高效、提取率、精密度良好,可作为坚果企业实验室农药残留检测筛查参考方法,能够满足科学研究、监管监测要求,具有较高的实际应用价值。
-
表 1 16种有机氯、拟除虫菊酯类的农药残留的线性方程、决定系数和检出限、定量限(n=6)
Table 1 Linear equations, determination coefficients, detection limits and quantitation limits of 16 kinds of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide residues (n=6)
化合物名称 保留时间(min) 线性方程 决定系数r2 检出限(μg/kg) 定量限(μg/kg) α-六六六 10.774 Y=333615X−1480 0.9993 0.1 0.3 五氯硝基苯 11.779 Y=207302X−493 0.9997 0.1 0.3 β-六六六 12.276 Y=297296X−1230 0.9994 0.1 0.3 γ-六六六 13.447 Y=90130X−320 0.9997 0.1 0.3 δ-六六六 14.449 Y=166200X−1019 0.9990 0.1 0.3 α-硫丹 17.920 Y=224809X−743 0.9995 0.3 0.9 p,p’-DDE 19.010 Y=144948X−704 0.9989 0.1 0.3 o,p’-DDT 20.877 Y=84504X−356 0.9990 0.2 0.6 p,p’-DDD 21.288 Y=71379X−289 0.9993 0.1 0.3 β-硫丹 21.405 Y=126033X−583 0.9992 0.3 0.9 p,p’-DDT 22.219 Y=66390X−388 0.9980 0.2 0.6 甲氰菊酯 24.117 Y=89925X−633 0.9995 0.2 0.6 氯氟氰菊酯 25.031 Y=223303X−2031 0.9997 0.2 0.6 氯菊酯 27.503/27.801 Y=30616X−652 0.9961 0.4 1.2 氰戊菊酯 31.368/31.883 Y=75284X−758 0.9985 0.4 1.2 溴氰菊酯 33.808 Y=56534X−309 0.9992 0.2 0.6 表 2 不同基质的加标提取率和精密度(n=6)
Table 2 Spiked extraction rates and RSDs of spiked standard in different matrices (n=6)
样品基质 化合物名称 10 μg/kg 40 μg/kg 100 μg/kg 样品基质 化合物名称 10 μg/kg 40 μg/kg 100 μg/kg 提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)提取率
(%)RSDs
(%)开心果 α-六六六 91.6 3.55 95.3 4.13 103.2 2.61 碧根果 α-六六六 95.8 3.52 98.9 2.59 98.6 2.56 五氯硝基苯 87.2 3.83 101.2 2.15 98.2 2.19 五氯硝基苯 99.5 2.59 96.7 2.31 98.5 1.92 β-六六六 93.5 2.89 93.8 3.16 95.3 2.16 β-六六六 96.1 3.60 95.3 3.56 96.1 2.81 γ-六六六 96.1 3.15 97.8 4.19 98.5 2.09 γ-六六六 92.5 4.59 94.5 3.81 95.4 1.82 δ-六六六 87.6 4.36 105.3 4.35 96.3 2.13 δ-六六六 96.7 5.29 96.1 3.61 97.1 1.88 α-硫丹 92.3 2.95 95.6 3.68 96.5 2.91 α-硫丹 97.8 2.53 95.9 4.29 98.2 1.92 p,p’-DDE 95.6 3.36 98.6 3.87 98.5 2.46 p,p’-DDE 91.5 3.58 92.5 4.39 95.8 2.65 o,p’-DDT 97.8 3.45 95.8 3.67 97.6 2.19 o,p’-DDT 96.5 5.31 96.8 3.12 97.2 2.16 p,p’-DDD 88.9 4.59 99.2 3.66 98.9 2.95 p,p’-DDD 95.3 2.59 95.6 3.09 97.4 2.19 β-硫丹 93.6 2.33 102.5 4.19 95.6 2.96 β-硫丹 96.2 3.76 96.4 4.15 97.8 1.95 p,p’-DDT 85.9 4.56 95.3 3.64 96.1 2.34 p,p’-DDT 95.6 3.68 95.7 4.36 97.7 1.03 甲氰菊酯 102.9 3.15 105.3 3.52 96.3 2.09 甲氰菊酯 105.6 2.69 95.6 3.59 98.1 1.09 氯氟氰菊酯 105.3 4.78 103.6 5.27 95.8 1.95 氯氟氰菊酯 109.5 2.97 96.8 4.09 102.1 2.34 氯菊酯 110.9 3.81 102.7 3.81 102.6 2.46 氯菊酯 113.5 3.68 102.6 2.95 96.5 2.15 氰戊菊酯 108.2 3.25 98.5 3.67 98.7 2.05 氰戊菊酯 109.5 3.65 96.8 3.69 97.5 2.35 溴氰菊酯 105.7 3.94 96.7 3.91 103.6 3.05 溴氰菊酯 108.6 3.94 95.2 3.57 98.6 2.19 澳洲坚果 α-六六六 91.5 4.79 95.6 3.65 98.6 2.67 核桃 α-六六六 96.5 3.65 98.6 3.46 98.9 2.34 五氯硝基苯 98.3 3.25 98.1 3.91 98.7 2.15 五氯硝基苯 101.5 3.19 98.7 3.59 98.7 2.15 β-六六六 95.5 3.68 95.2 4.59 96.5 2.05 β-六六六 95.6 3.97 95.7 3.19 96.3 2.33 γ-六六六 89.6 3.59 96.8 4.57 95.3 1.92 γ-六六六 97.8 2.56 96.3 2.95 98.4 2.16 δ-六六六 89.8 4.65 98.2 4.53 98.6 1.98 δ-六六六 96.9 5.13 97.8 2.09 98.5 1.09 α-硫丹 101.5 4.19 96.5 3.59 97.8 2.31 α-硫丹 96.5 5.24 96.8 4.13 97.8 1.58 p,p’-DDE 91.6 4.52 93.4 3.61 95.6 2.37 p,p’-DDE 101.3 4.67 98.3 4.19 98.5 2.13 o,p’-DDT 92.3 3.59 94.2 3.67 95.7 2.55 o,p’-DDT 105.8 4.91 98.5 3.57 98.8 1.67 p,p’-DDD 93.5 2.98 96.2 4.16 96.8 2.61 p,p’-DDD 106.5 4.29 97.6 3.56 98.6 1.38 β-硫丹 93.5 3.57 97.1 4.38 98.2 2.39 β-硫丹 98.5 4.77 98.5 4.01 98.5 2.06 p,p’-DDT 81.6 3.64 92.5 4.51 95.6 2.75 p,p’-DDT 112.6 3.75 102.5 3.06 98.5 2.04 甲氰菊酯 103.6 2.95 95.6 3.67 98.4 3.12 甲氰菊酯 116.5 3.58 95.3 3.19 97.6 1.96 氯氟氰菊酯 119.5 4.36 105.3 3.46 102.5 3.09 氯氟氰菊酯 107.6 4.39 106.8 3.71 103.5 1.51 氯菊酯 102.6 4.12 97.8 3.95 103.6 2.46 氯菊酯 109.3 4.95 103.5 3.86 97.9 2.16 氰戊菊酯 105.3 4.36 103.6 4.16 105.2 2.98 氰戊菊酯 109.5 4.13 106.5 4.65 96.8 2.03 溴氰菊酯 106.7 3.57 102.5 3.69 104.1 2.65 溴氰菊酯 112.3 3.95 103.6 3.67 103.5 1.66 腰果 α-六六六 91.5 2.35 102.6 4.61 101.9 2.13 巴旦木 α-六六六 93.2 3.69 95.6 4.98 98.6 1.43 五氯硝基苯 99.8 5.01 98.5 4.39 103.6 2.36 五氯硝基苯 98.6 4.59 99.3 5.36 99.9 1.46 β-六六六 95.3 3.49 101.6 4.68 98.5 2.59 β-六六六 94.3 4.16 93.5 4.17 95.6 1.39 γ-六六六 94.2 3.89 99.5 3.91 98.7 2.65 γ-六六六 95.8 3.58 95.3 3.57 98.2 1.28 δ-六六六 93.6 2.95 95.8 3.56 96.3 1.95 δ-六六六 96.5 4.28 97.8 3.49 97.6 2.61 α-硫丹 103.5 2.35 96.1 3.64 96.8 1.61 α-硫丹 95.2 5.29 97.6 3.57 98.5 1.59 p,p’-DDE 98.1 2.95 97.2 3.98 98.9 1.12 p,p’-DDE 98.1 3.46 97.6 4.31 97.6 2.39 o,p’-DDT 95.4 3.97 96.8 3.19 97.8 2.36 o,p’-DDT 91.6 3.65 97.9 4.19 98.9 2.15 p,p’-DDD 91.3 4.56 98.2 4.12 98.6 2.61 p,p’-DDD 93.6 3.29 95.6 3.61 99.2 2.03 β-硫丹 96.7 4.69 95.6 4.35 97.8 2.21 β-硫丹 96.5 3.37 97.1 2.56 98.6 1.61 p,p’-DDT 108.8 5.01 98.1 3.65 98.5 2.44 p,p’-DDT 93.7 5.11 95.2 3.94 96.3 1.68 甲氰菊酯 109.5 3.59 102.6 3.68 102.1 2.79 甲氰菊酯 112.5 2.97 103.2 4.19 96.7 1.92 氯氟氰菊酯 117.2 3.68 97.6 4.62 102.3 2.71 氯氟氰菊酯 109.3 3.65 108.5 4.16 98.6 1.87 氯菊酯 109.5 3.59 98.2 4.55 98.5 2.75 氯菊酯 108.5 3.48 105.3 3.81 102.1 2.05 氰戊菊酯 112.3 3.99 92.5 3.69 103.2 2.71 氰戊菊酯 116.5 3.57 103.2 3.86 103.2 2.65 溴氰菊酯 98.6 2.36 95.3 3.91 104.2 2.76 溴氰菊酯 112.5 3.69 103.6 3.64 98.6 1.68 表 3 检测结果与约定真值的偏差(n=6)
Table 3 Detection deviations of measured values and the conventional true value (n=6)
样品基质 化合物名称 20 μg/kg 样品基质 化合物名称 20 μg/kg 检测结果 偏差(%) 检测结果 偏差(%) 开心果 α−六六六 19.8 −1.0 碧根果 α−六六六 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 20.2 1.0 五氯硝基苯 20.1 0.5 β−六六六 20.3 1.5 β−六六六 20.1 0.5 γ−六六六 19.9 −0.5 γ−六六六 21.5 7.5 δ−六六六 19.6 −2.0 δ−六六六 19.8 −1.0 α−硫丹 20.2 1.0 α−硫丹 19.9 −0.5 p,p’-DDE 19.9 −0.5 p,p’-DDE 19.6 −2.0 o,p’-DDT 19.6 −2.0 o,p’-DDT 19.5 −2.5 p,p’-DDD 19.7 −1.5 p,p’-DDD 19.7 −1.5 β−硫丹 20.5 2.5 β−硫丹 20.3 1.5 p,p’-DDT 19.2 −4.0 p,p’-DDT 20.5 2.5 甲氰菊酯 19.3 −3.5 甲氰菊酯 19.8 −1.0 氯氟氰菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氯氟氰菊酯 21.6 8.0 氯菊酯 20.9 4.5 氯菊酯 20.6 3.0 氰戊菊酯 20.5 2.5 氰戊菊酯 19.1 −4.5 溴氰菊酯 20.8 4.0 溴氰菊酯 21.1 5.5 澳洲坚果 α−六六六 19.6 −2.0 核桃 α−六六六 19.7 −1.5 五氯硝基苯 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 20.3 1.5 β−六六六 19.7 −1.5 β−六六六 20.2 1.0 γ−六六六 20.2 1.0 γ−六六六 20.5 2.5 δ−六六六 20.1 0.5 δ−六六六 19.8 −1.0 α−硫丹 19.5 −2.5 α−硫丹 19.2 −4.0 p,p’-DDE 19.8 −1.0 p,p’-DDE 19.5 −2.5 o,p’-DDT 19.1 −4.5 o,p’-DDT 19.3 −3.5 p,p’-DDD 19.6 −2.0 p,p’-DDD 19.5 −2.5 β−硫丹 20.8 4.0 β−硫丹 19.2 −4.0 p,p’-DDT 20.9 4.5 p,p’-DDT 19.8 −1.0 甲氰菊酯 21.1 5.5 甲氰菊酯 19.6 −2.0 氯氟氰菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氯氟氰菊酯 19.3 −3.5 氯菊酯 19.6 −2.0 氯菊酯 21.1 5.5 氰戊菊酯 16.9 −5.5 氰戊菊酯 20.8 4.0 溴氰菊酯 19.2 −4.0 溴氰菊酯 20.6 3.0 腰果 α−六六六 19.3 −3.5 巴旦木 α−六六六 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 19.8 −1.0 五氯硝基苯 19.8 −1.0 β−六六六 19.9 −0.5 β−六六六 19.6 −2.0 γ−六六六 21.3 6.5 γ−六六六 20.2 1.0 δ−六六六 19.5 −2.5 δ−六六六 20.3 1.5 α−硫丹 20.3 1.5 α−硫丹 19.5 −2.5 p,p’-DDE 20.6 3.0 p,p’-DDE 19.6 −2.0 o,p’-DDT 19.5 −2.5 o,p’-DDT 19.7 −1.5 p,p’-DDD 19.8 −1.0 p,p’-DDD 19.8 −1.0 β−硫丹 19.4 −3.0 β−硫丹 19.8 −1.0 p,p’-DDT 19.6 −2.0 p,p’-DDT 19.7 −1.5 甲氰菊酯 16.7 −6.5 甲氰菊酯 19.1 −4.5 氯氟氰菊酯 21.6 8.0 氯氟氰菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氯菊酯 21.3 6.5 氯菊酯 19.5 −2.5 氰戊菊酯 21.8 9.0 氰戊菊酯 19.3 −3.5 溴氰菊酯 21.5 7.5 溴氰菊酯 19.2 −4.0 -
[1] REN E F, NIU D B, LIU G D. Study on the analysis of nutrient components of macadamia nut and the comprehensive utilization of its processing byproducts[J]. Food Res Dey,2020,41(6):194−199.
[2] 摆小琴, 张娅俐, 洪晶, 等. 坚果品质检测方法研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(22):8737−8744. [BAI X Q, ZHANG Y L, HONG J, et al. Research progress on the quality detection methods for nuts[J]. J Food Saf Qual,2021,12(22):8737−8744.] doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.22.014 BAI X Q, ZHANG Y L, HONG J, et al. Research progress on the quality detection methods for nuts[J]. J Food Saf Qual, 2021, 12(22): 8737−8744. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.22.014
[3] SINA N, METIDI S, MORTEZA N, et al. Association of total nut, tree nut, peanlt, and peanut butter consumption with cancer incidence and mortality. A comprehensive systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Adv Nutr,2021,12(3):793−808. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa152
[4] 韩世鹤, 高媛, 蔡雪静, 等. 美国食品药品监督管理局农药残留监控计划分析及借鉴[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(12):4709−4713. [HAN S H, GAO Y, CAI X J, et al. Analysis and reference of food and drug administration’s pesticide residue monitoring plan[J]. J Food Saf Qual,2021,12(12):4709−4713.] doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.12.001 HAN S H, GAO Y, CAI X J, et al. Analysis and reference of food and drug administration’s pesticide residue monitoring plan[J]. J Food Saf Qual, 2021, 12(12): 4709−4713. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.12.001
[5] 林颖菲, 黄巨璧, 黄敏堂, 等. 澳洲坚果主要病虫害防治和果园管理[J]. 植物医生,2021,34(6):66−70. [LIN Y F, HUANG J B, HUANG M T, et al. Study on control of main pests of macadamia nut and management of orchards of this fruit[J]. Plant Doct,2021,34(6):66−70.] doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.zwys.2021.06.013 LIN Y F, HUANG J B, HUANG M T, et al. Study on control of main pests of macadamia nut and management of orchards of this fruit[J]. Plant Doct, 2021, 34(6): 66−70. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.zwys.2021.06.013
[6] 仕影, 陈景三, 于稳欠, 等. 农药对人体健康及生态环境的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2022,50(6):53−59. [SHI Y, CHEN J S, YU W Q, et al. Effects of pesticides on human health and ecological environment[J]. J Anhui Agric Sci,2022,50(6):53−59.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2022.06.012 SHI Y, CHEN J S, YU W Q, et al. Effects of pesticides on human health and ecological environment[J]. J Anhui Agric Sci, 2022, 50(6): 53−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2022.06.012
[7] 易幸. GB 2763-2021中茶叶农药残留限量和检测方法的探析[J]. 农药科学与管理,2022,43(5):8−15. [YI X. Analysis of pesticide maximum residue limit in tea and the detection methods in GB 2763-2021[J]. Pestic Sci Admin,2022,43(5):8−15.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5480.2022.05.003 YI X. Analysis of pesticide maximum residue limit in tea and the detection methods in GB 2763-2021[J]. Pestic Sci Admin, 2022, 43(5): 8−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5480.2022.05.003
[8] 殷晓燕, 吴翠玲. 蔬菜水果中多农残检测样品前处理方法与分析[J]. 食品安全导刊,2010(4):26−27. [YIN X Y, WU C L. Analysis on the pre-processing method of detection samples of pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits[J]. Chin Food Saf Mag,2010(4):26−27.] doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2010.04.001 YIN X Y, WU C L. Analysis on the pre-processing method of detection samples of pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits[J]. Chin Food Saf Mag, 2010(4): 26−27. doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2010.04.001
[9] 毕军, 任君, 赵云峰, 等. QuEChERS-冷冻诱导液液萃取/液相色谱-高分辨质谱法测定蔬菜水果中77种农药残留[J]. 分析测试学报,2021,40(9):1316−1327. [BI J, REN J, ZHAO Y F, et al. Determination of 77 pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry coupled with QuEChERS and cold induced liquid-liquid extraction[J]. J Instr Anal,2021,40(9):1316−1327.] doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.20123108 BI J, REN J, ZHAO Y F, et al. Determination of 77 pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits by liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry coupled with QuEChERS and cold induced liquid-liquid extraction[J]. J Instr Anal, 2021, 40(9): 1316−1327. doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.20123108
[10] SUN T, FAN Y W, FAN P Z, et al. Use of graphene coated with Zno nanocomposites for microextraction in packed syringe of carbamate pesticides from juice samples[J]. J Separat Sci,2019,42(12):2131−2139. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201900257
[11] 金雅慧, 秦丽, 俞卫甫. 基质效应对茭白中12种有机氯和拟除虫菊酯类农药残留检测的影响[J]. 林业科技情报,2022,54(2):6−9. [JIN Y H, QIN L, YU W F. Effect of matrix effect on the detection of residues of 12 organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides in Zizania latifolia[J]. Forest Sci Technol Inform,2022,54(2):6−9.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3303.2022.02.002 JIN Y H, QIN L, YU W F. Effect of matrix effect on the detection of residues of 12 organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides in Zizania latifolia[J]. Forest Sci Technol Inform, 2022, 54(2): 6−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3303.2022.02.002
[12] 许芮菡, 谢倩文, 李旭军, 等. 基于多壁碳纳米管改进QuEChERS法结合气相色谱-串联质谱检测茶叶中10种拟除虫菊酯类农药残留[J]. 色谱,2022,40(5):469−476. [XU R H, XIE Q W, LI X J, et al. Modified QuEChERS method based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes coupled with gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the detection of 10 pyrethroid pesticide residues in tea[J]. Chin J Chrom,2022,40(5):469−476.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.11015 XU R H, XIE Q W, LI X J, et al. Modified QuEChERS method based on multiwalled carbon nanotubes coupled with gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the detection of 10 pyrethroid pesticide residues in tea[J]. Chin J Chrom, 2022, 40(5): 469−476. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.11015
[13] 蒋康丽, 扈斌, 吴兴强, 等. 自动QuEChERS结合气相色谱-串联质谱法测定花生中297种农药残留[J]. 分析测试学报,2021,40(9):1257−1270. [JIANG K L, HU B, WU X Q, et al. Analysis of 297 pesticides residues in peanut by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with automatic QuEChERS[J]. J Instr Anal,2021,40(9):1257−1270.] doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.21010406 JIANG K L, HU B, WU X Q, et al. Analysis of 297 pesticides residues in peanut by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with automatic QuEChERS[J]. J Instr Anal, 2021, 40(9): 1257−1270. doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.21010406
[14] TEKLEWEINI G, ABABO W, ONYANGO J A, et al. Determination of occurrences distribution, health impacts of organochlorine pesticides in soils of central China[J]. Int J Environ Resh Pub Health,2019,16(1):1−18.
[15] HU B X, SUN D W, PU H B, et al. Rapid nondestructive detection of mixed pesticides residues on fruit surface using SERS combined with self-modeling mixture analysis method[J]. Talanta,2020,217:120998. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120998
[16] HU S P, ZHAO M, MAO Q Q, et al. Rapid one-step cleanup method to minimize matrix effects for residue analysis of alkaline pesticides in tea using liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chem,2019,299:125146. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125146
[17] 杨沈丽. 固相萃取-气相色谱质谱法测定水中4种拟除虫菊酯类农药[J]. 化学工程师,2021,35(12):27−29. [YANG S L. Determination of four pyrethroid pesticides in water by solid phase extraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Chem Eng,2021,35(12):27−29.] doi: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20211227 YANG S L. Determination of four pyrethroid pesticides in water by solid phase extraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Chem Eng, 2021, 35(12): 27−29. doi: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20211227
[18] 刘琳, 马腾飞, 贾孙悦, 等. 改良QuEChERS方法结合气相色谱测定红甜菜中20种农药残留[J]. 中国农学通报,2021,37(35):110−117. [LIU L, MA T F, JIA S Y, et al. Determination of 20 pesticide residues in red beet by modified QuEChERS method combined with gas chromatography[J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull,2021,37(35):110−117.] doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0684 LIU L, MA T F, JIA S Y, et al. Determination of 20 pesticide residues in red beet by modified QuEChERS method combined with gas chromatography[J]. Chin Agric Sci Bull, 2021, 37(35): 110−117. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0684
[19] 官金艳, 苏小路, 胡亦清, 等. QuEChERS-气相色谱法快速测定桃胶中16种有机磷农药残留[J]. 分析科学学报,2022,38(2):260−264. [GUAN J Y, SU X X, HU Y Q, et al. Determination of 16 organophosphorus pesticide residues in peach gum by QuEChERS-gas chromatography[J]. J Anal Sci,2022,38(2):260−264.] doi: 10.13526/j.issn.1006-6144.2022.02.022 GUAN J Y, SU X X, HU Y Q, et al. Determination of 16 organophosphorus pesticide residues in peach gum by QuEChERS-gas chromatography[J]. J Anal Sci, 2022, 38(2): 260−264. doi: 10.13526/j.issn.1006-6144.2022.02.022
[20] 曾霞, 于雅汇, 王鸟, 等. QuEChERS前处理技术在农药多残留检测中的研究进展[J]. 当代化工研究,2022(6):33−35. [ZENG X, YU Y H, WANG N, et al. Research progress of QuEChERS pretreatment technology in the detection of pesticide residues[J]. Mod Chem Res,2022(6):33−35.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2022.06.011 ZENG X, YU Y H, WANG N, et al. Research progress of QuEChERS pretreatment technology in the detection of pesticide residues[J]. Mod Chem Res, 2022(6): 33−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2022.06.011
[21] 邵林, 刘晓云, 李福敏, 等. 多壁碳纳米管结合气相色谱-电子捕获检测法同时测定茶叶中16种有机氯类农药残留[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(20):8136−8140. [SHAO L, LIU X Y, LI F M, et al. Simultaneous determination of 16 kinds of organochlorine pesticide residues in tea by multi walled carbon nanotubes combined with gas chromatograph-electron capture detection[J]. J Food Saf Qual,2021,12(20):8136−8140.] SHAO L, LIU X Y, LI F M, et al. Simultaneous determination of 16 kinds of organochlorine pesticide residues in tea by multi walled carbon nanotubes combined with gas chromatograph-electron capture detection[J]. J Food Saf Qual, 2021, 12(20): 8136−8140.
[22] 杨延峰, 袁晓丽. 气相色谱法测定茶叶中有机氯和拟虫菊酯类农药残留的基质效应[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(20):7482−7488. [YANG Y F, YUAN X L. Matrix effects of the determination of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide residues in tea by gas chromatography[J]. J Food Saf Qual,2020,11(20):7482−7488.] doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2020.20.053 YANG Y F, YUAN X L. Matrix effects of the determination of organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticide residues in tea by gas chromatography[J]. J Food Saf Qual, 2020, 11(20): 7482−7488. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2020.20.053
[23] LI S, YU P P, CENG Z, et al. Analysis of pesticide residues in commercially available Chenpi using a modified QuEChERS method and GC-MS/MS determination[J]. J Pharm Anal,2020,10(1):60−69. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2019.01.005
[24] LIU C, JI Y H, JIANG X, et al. The determination of pesticides in tea samples followed by magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube-based magnetic solid-phase extraction and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. New J Chem,2019,43(14):5395−5403. doi: 10.1039/C8NJ06536E
[25] 金美奇, 豆小文, 付延伟, 等. 山楂常见有机氯、有机磷及拟除虫菊酯农药残留的膳食暴露研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现化,2020,22(10):3702−3710. [JIN M Q, DOU X W, FU Y W, et al. Dietary exposure research of common organochlorine, organophosphorus and pyrethroid pesticides residues in hawthorn[J]. Mode Tradit Chin Medic Mater-Med World Sci Technol,2020,22(10):3702−3710.] JIN M Q, DOU X W, FU Y W, et al. Dietary exposure research of common organochlorine, organophosphorus and pyrethroid pesticides residues in hawthorn[J]. Mode Tradit Chin Medic Mater-Med World Sci Technol, 2020, 22(10): 3702−3710.
[26] LY T K, HO T D, BEHRA P, et al. Determination of 400 kinds of pesticide residues in green tea leaves by UPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS combined with QuEChERS extraction and mixed-mode SPE clean-up method[J]. Food Chem,2020,326:126928. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126928
[27] 石勤艳, 姚颖辉, 侯义德, 等. 气相色谱法测定保康茶叶中有机氯农药残留[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(1):158−164. [SHI Q Y, YAO Y H, HOU Y D, et al. Determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in Baokang tea samples by gas chromatography[J]. J Food Saf Qual,2020,11(1):158−164.] doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2020.01.028 SHI Q Y, YAO Y H, HOU Y D, et al. Determination of organochlorine pesticide residues in Baokang tea samples by gas chromatography[J]. J Food Saf Qual, 2020, 11(1): 158−164. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2020.01.028
[28] 孟庆顺, 孙丽, 卜媛媛. 气相色谱法测定大米中多种有机氯和拟除虫菊酯残留的方法优化[J]. 粮食与饲料工业,2021(6):61−63,67. [MENG Q S, SUN L, BU Y Y. Optimization of gas chromatography for determination of organochlorine and pyrethroid residues in rice[J]. Cere Feed Ind,2021(6):61−63,67.] doi: 10.7633/j.issn.1003-6202.2021.06.014 MENG Q S, SUN L, BU Y Y. Optimization of gas chromatography for determination of organochlorine and pyrethroid residues in rice[J]. Cere Feed Ind, 2021(6): 61−63,67. doi: 10.7633/j.issn.1003-6202.2021.06.014
[29] 周建征, 李林, 任晓曦. QuEchERS-气相色谱法测定玉米中有机磷农药残留[J]. 农产品加工,2022(11):73−75. [ZHOU J Z, LI L, REN X X. Determination of 4 pesticide residues in maize by improved QuEChERS method combined with GC[J]. Farm Prod Process,2022(11):73−75.] doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2022.06.019 ZHOU J Z, LI L, REN X X. Determination of 4 pesticide residues in maize by improved QuEChERS method combined with GC[J]. Farm Prod Process, 2022(11): 73−75. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2022.06.019
[30] 马韵婕. 常见农药残留检测技术的应用分析[J]. 食品安全导刊,2022(5):174−176. [MA Y J. Application analysis of common pesticide residue detection technology[J]. Chin Food Saf Mag,2022(5):174−176.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2022.5.spaqdk202205062 MA Y J. Application analysis of common pesticide residue detection technology[J]. Chin Food Saf Mag, 2022(5): 174−176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2022.5.spaqdk202205062
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 刘影,庞富,陈佳鸿,陈炯葵,蔡烁仪. 本草清咽润喉糖的配方优化及抗氧化研究. 农产品加工. 2024(21): 41-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张敏君,段雪伟,王燕,杨慧文,刘冰,向文静,由天辉. 构树根皮活性成分乙醇提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(11): 196-203 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王蕙雯. 豫西自然发酵柿子醋抗氧化性研究. 江苏调味副食品. 2023(03): 20-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 裴文清,吕泸楠,王靖宇,浦思琦,雷霜,王春丽. 木瓜皮多酚和黄酮提取工艺优化及酪氨酸酶与胰脂肪酶抑制活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(01): 188-195 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 周新崇,易灿,刘进兵. 微波辅助提取崀山脐橙皮总黄酮及生物活性研究. 邵阳学院学报(自然科学版). 2022(02): 87-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张清月,董姝慧,李胤豪,赵艳丽,史彬林,闫素梅. 诺丽果不同提取物抗氧化能力的比较研究. 中国粮油学报. 2022(05): 144-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 关随霞,王蕙雯,杨肖瑞,郭淑敏,张翅,张培杰,李道敏. 大青叶总黄酮提取工艺优化及抗氧化性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2022(09): 138-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈慧玲,刘芳,钟恒勤,王伟枫. 超声波辅助乙醇提取百香果皮黄酮的工艺优化及黄酮抗氧化性测定. 宁德师范学院学报(自然科学版). 2022(03): 280-287 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 任海云,韩瑞,张磊. 基于Box-Behnken响应面法优化党参抗氧化活性组分提取工艺. 中医药信息. 2022(12): 5-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 赵雨晴,王宝庆,徐汉,刘楠楠. 醉鱼草总黄酮的提取及抗氧化活性研究. 化学试剂. 2021(07): 979-985 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杨青青,龚吉军. 响应面法优化超声辅助葛根浸提工艺及浸提液抗氧化活性研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2021(13): 5409-5417 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



