Effects of Different Drying Methods on Physicochemical Properties and Antibiotic Content of Auricularia auricularia
-
摘要: 本文系统探究了自然晾晒、热风干燥和真空微波干燥三种处理方式对黑木耳的干燥效率,并评价了不同处理对黑木耳的理化特性影响以及喹诺酮类抗生素(恩诺沙星、环丙沙星)的降解效果。结果表明,以自然晾晒的黑木耳为参照,黑木耳在80 ℃热风干燥条件下所需的干燥时间大幅缩短为150 min,在2.4 kW真空微波干燥条件下继续缩短为15 min;热风干燥和真空微波干燥处理对黑木耳中粗蛋白、粗脂肪、粗纤维、灰分含量无显著影响(P>0.05),经干燥处理后总糖含量分别下降了1.34%和2.28%,且理化指标仍满足国标要求。此外,自然干燥过程中恩诺沙星、环丙沙星的降解率分别为16.32%和14.22%;80 ℃热风干燥条件下两种抗生素降解率分别为35.37%和32.39%,2.4 kW真空微波干燥处理下两种抗生素降解率分别为36.11%和33.19%,表明两种处理方式对抗生素降解没有显著差异(P>0.05)。因此,真空微波干燥处理时间短、效率高,对黑木耳理化指标影响较小且具有良好抗生素残留降解效果,为食用菌干燥及质量安全控制提供了新思路。Abstract: In this paper, the drying efficiency of natural drying, hot air and vacuum microwave on Auricularia auricula were systematically investigated, and the changes of physicochemical properties of Auricularia auricula and the degradation effect of quinolones (enrofloxacin, ciprofloxacin) were also evaluated. The results showed that the drying time of Auricularia auricula was greatly shortened to 150 min with the hot air drying (80 ℃) and 15 min with vacuum microwave (2.4 kW) compared with the natural drying. With the treatments of hot air drying and vacuum microwave drying, there was no significant effect on the content of crude protein, fat, fiber and ash in Auricularia auricula, and the total sugar content decreased by 1.34% and 2.28%, respectively. The physicochemical indexes still met the National Standard requirements. In addition, the degradation rates of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin during natural drying were 16.32% and 14.22%, while that of hot air drying were 35.37% and 32.39%, and vacuum microwave drying were 36.11% and 33.19%, respectively. The results indicated that there was no significant difference in antibiotic degradation between the two treatments. Therefore, vacuum microwave drying exhibits the advantages of less treatment time and effect on the physicochemical indexes, higher drying efficiency and better antibiotic degradation effect, which provides a new idea for the drying and quality control of edible fungi.
-
Keywords:
- Auricularia auricula /
- hot air drying /
- vacuum microwave drying /
- antibiotics /
- degradation
-
黑木耳(Auricularia auricula)风味独特、营养丰富,含有维生素、铁、磷、钙等多种营养物质,是世界上四种最重要的栽培食用菌之一[1]。我国作为世界第一的木耳生产大国,2021年全国黑木耳产量已超过710万吨且其产业规模仍在不断扩大。目前,黑木耳的加工以其干制品为主,种植户对木耳的干燥方式仍主要是自然晾晒。作为干制过程中最传统的方式,主要缺点是干燥速率低和受环境影响较大。热风干燥技术以其操作简易、物料处理量大和成本低等优点,在木耳干燥过程中的使用和探索也更加广泛[2],但物料加热时由外向内进行热传导,传热和传质方向相反,相比自然干燥速率较高但干燥能力仍有待提高[3]。此外,微波处理以其干燥速率快、热效率高等特点,在农产品加工行业具有较好的应用前景[4−5],也为工业化加工中黑木耳的干燥处理提供了可能。鉴于不同干燥方式的机制差异较大,其对应的干燥效率及对干制品的理化特性影响也较大,探究不同处理方式对黑木耳理化特性影响是非常重要的。
同时,近年来自然环境不同基质及食品中都检测到人类和兽用抗生素的残留。喹诺酮类抗生素作为常见兽药成分,随着使用量增大不断地排放到自然环境中。残留的抗生素通过动物源性食品或其他途径迁移最终进入人体,在人体内不断积累,对人体的健康构成严重危害。如首次进入个体后导致敏感个体致敏,肌体再次接触后产生的过敏反应及变态反应[6],损伤器官[7],急性中毒[8]等。现阶段,对于抗生素控制的探究主要集中于水源中多种抗生素污染问题处理[9]和食品中抗生素污染控制[10−11]等,食用菌中抗生素的限量标准及检测方法研究较少;而木耳干燥阶段的研究,主要集中于不同干燥方式其对品质的影响[12],对干燥过程黑木耳中抗生素残留变化研究较少,基于黑木耳干制过程的抗生素控制研究未见报道。因此,本研究基于自然晾晒、热风干燥和真空微波干燥三种不同处理方式,系统解析不同干燥工艺参数对应的黑木耳干燥时间,评价不同干燥处理对黑木耳的理化特性是否有显著影响,并探究三种处理方式对黑木耳中抗生素的降解效果。通过比较对黑木耳的干燥时间、对抗生素的降解效果及对理化指标的影响,选择更加高效的木耳干燥处理方法,为黑木耳干燥及食用菌加工过程中抗生素等质量安全因子的控制提供技术支持和数据支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黑木耳(柞水木耳) 采收自陕西省商洛市柞水县下梁镇西川村;甲醇、甲酸、乙腈 色谱纯,四川西陇科学有限公司;乙二胺四乙酸二钠、柠檬酸、磷酸二氢钠、无水硫酸钠、氯化钠 分析纯,广州光华科技股份有限公司;二乙胺-N-丙基硅烷(PSA) 烟台青云仪器设备有限公司;恩诺沙星(纯度≥98%)、环丙沙星(纯度≥98%) 阿拉丁试剂有限公司。
HC-3018R型高速冷冻离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;LC-20A型高效液相色谱仪、UV-1700型紫外可见分光光度计 日本岛津公司;FW-400AD高速万能粉碎机 天津鑫博得仪器有限公司;VYS-4ZH1/2V真空微波干燥机 南京澳润微波科技有限公司;DHG-9146A热风干燥机 上海精宏实验设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 不同干燥处理过程中木耳水分含量变化
黑木耳热风干燥操作规程[13]中对热风干燥的温度范围控制在了40~58 ℃,结合刘清斌等[14]方法,本实验研究40~80 ℃条件热风干燥对木耳干燥过程中的水分含量变化影响;参考任爱清等[5]、梁昌祥等[15]方法结合实际试验设备探究0.8~2.4 kW条件下的木耳含水率变化情况。
1.2.1.1 自然干燥
将鲜木耳单层放置在室温下(25 ℃)自然干燥,干燥期间每12 h取样测定含水率并记录水分含量变化,待木耳中含水率低于12%后停止干燥。
1.2.1.2 热风干燥
将鲜木耳单层放置在热风干燥机中并分别设置干燥温度为40、50、60、70、80 ℃,每10 min取样测定含水率,记录木耳中水分含量变化,待木耳含水率低于12%后停止干燥。
1.2.1.3 真空微波干燥
将鲜木耳均匀置于真空微波设备专用托盘内,设置真空度为86 kPa、干燥温度为50℃,分别设置干燥功率为0.8、1.2、1.6、2.0、2.4 kW,每5 min取样测定含水率,待木耳含水率低于12%后停止干燥。
1.2.1.4 木耳中含水率的计算
湿含量一般以物料中的水分与绝干物料的质量比表示,本实验在恒定干燥条件下进行,通过测定复水黑木耳在一定时间后湿含量(即M湿重−M干重),来表示干燥时间与相对含水率X的关系曲线[16]。准确称量鲜木耳质量并记录为M湿重,干燥过程中每次取样后记录木耳的质量记为M干重,计算获得木耳干燥处理过程中相对含水率并绘制干燥曲线。干燥过程中每组处理最少做三个平行试验。
(1) 式中:M湿重表示含水鲜木耳质量,g;M干重表示干燥不同时间后的质量,g。
1.2.2 不同干燥处理对木耳基础理化特性的影响
参照国标检测方法要求,对不同条件处理后木耳中总糖(GB/T 15672-2009 食用菌中总糖含量测定)[17]、粗蛋白(GB 5009.5-2016 食品中蛋白质的测定)[18]、粗脂肪(GB 5009.6-2016 食品中脂肪的测定)[19]、粗纤维(GB/T 5009.10-2003 植物类食品中粗纤维的测定)[20]、灰分(GB 5009.4-2016 食品中灰分的测定)[21]等基础理化指标进行评价,分析干燥条件对其品质的影响。
1.2.3 不同干燥处理对木耳中抗生素降解影响评价
1.2.3.1 样品制备
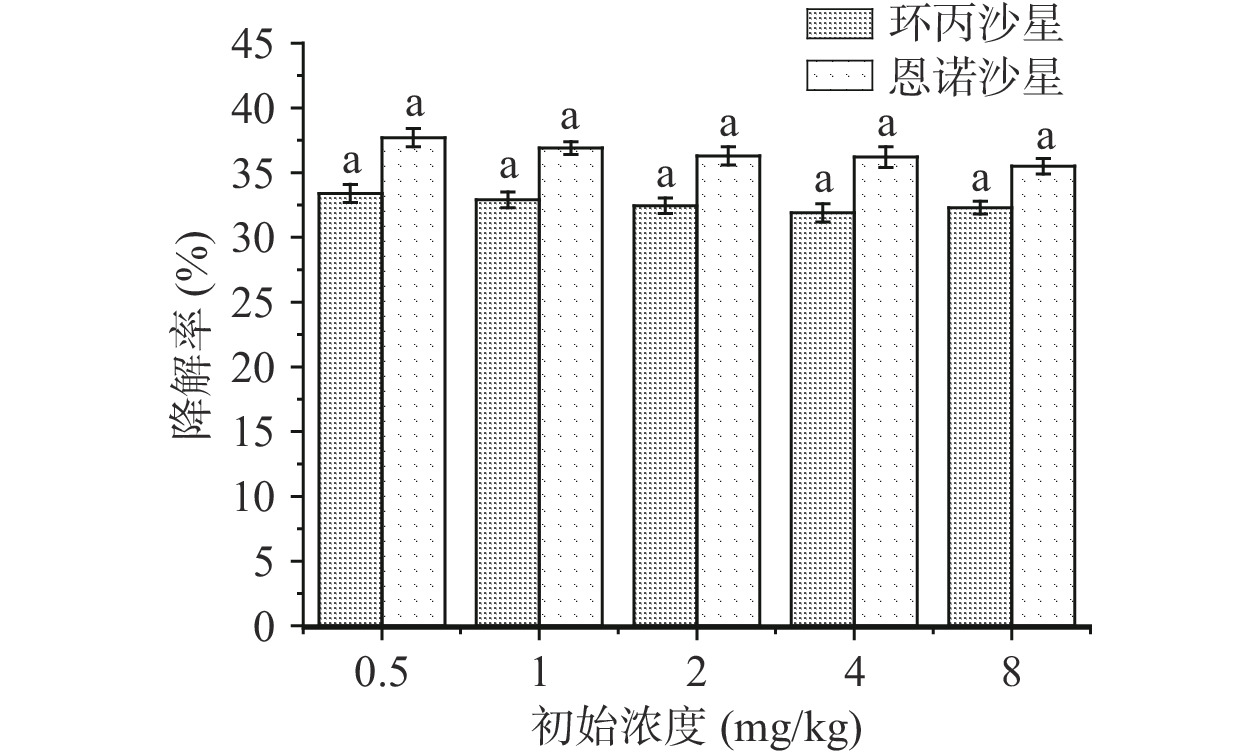
为探究不同干燥处理对黑木耳中抗生素降解效果影响,参照GB/T 6192-2019中黑木耳[22]的理化指标要求,以木耳中抗生素含量0.05 mg/kg为参照,将其最低浓度确定为0.5 mg/kg并设置不同梯度。具体样品制备过程为:将干制的黑木耳分别浸泡在抗生素浓度为1、2、4、8、16 mg/kg的加标溶液中(室温25 ℃),调整浸泡时间并取样检测黑木耳中抗生素含量,使黑木耳中抗生素含量为0.5、1、2、4、8 mg/kg。
1.2.3.2 自然干燥过程中抗生素含量变化
将含有0.5、1、2、4、8 mg/kg抗生素的木耳样品单层放置在室温下(25 ℃)自然干燥72 h,待木耳满足GB/T 6192-2019中干制黑木耳水分含量要求,即含水率低于12%时停止干燥,评价抗生素初始浓度对两种抗生素降解效果的影响。
1.2.3.3 热风干燥过程中抗生素含量变化
探究热风干燥处理在不同温度条件下,对干燥过程中木耳抗生素的降解效果影响。将含有0.5、1、2、4、8 mg/kg抗生素的木耳样品单层放置在热风干燥机中,60 ℃条件下连续处理220 min,待木耳中含水率低于12%时停止干燥,测定抗生素含量。同时,将含有0.5 mg/kg抗生素的木耳单层放置在热风干燥机中并设置干燥温度分别为40、50、60、70、80 ℃,待木耳含水率低于12%后停止干燥。干燥过程中,前3 h间隔30 min取样,3 h后间隔1 h取样,测定抗生素含量变化。评价热风干燥过程中抗生素初始浓度和干燥温度对抗生素含量变化影响。
1.2.3.4 真空微波干燥过程中抗生素含量变化
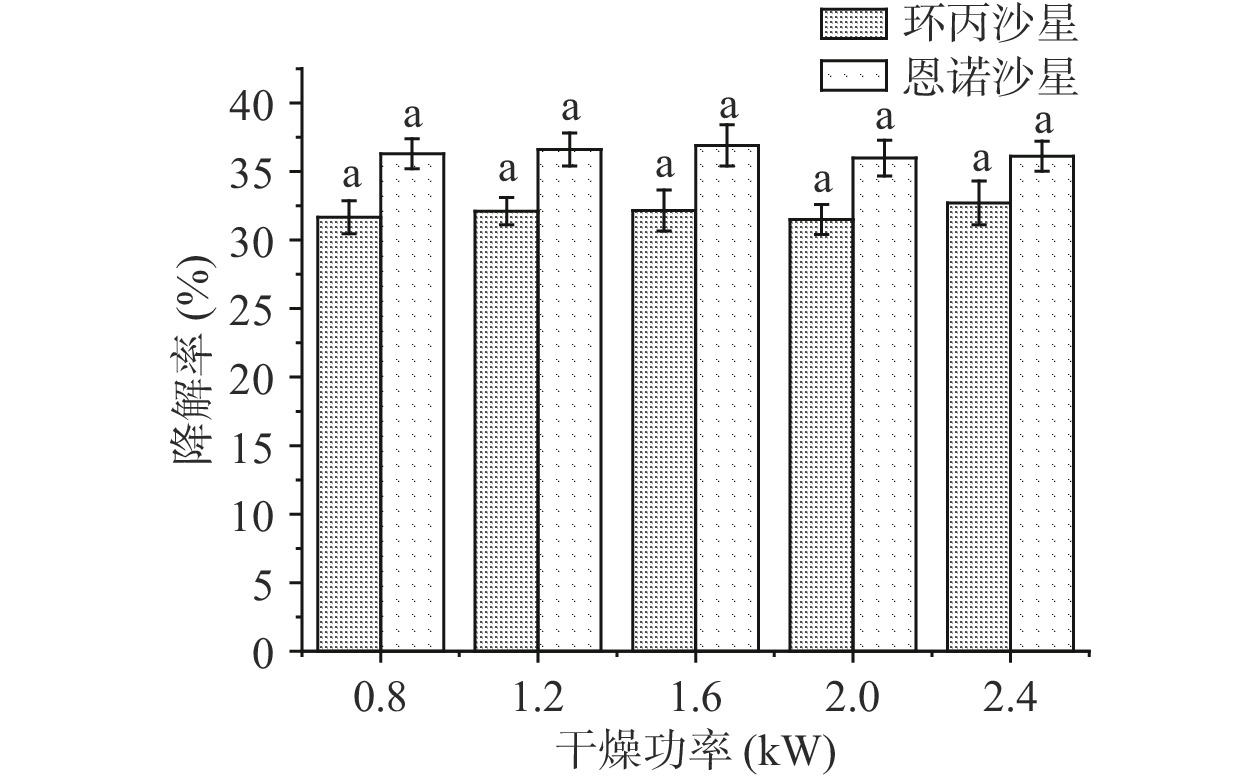
探究真空微波干燥处理在不同微波功率条件下,对干燥至恒重的木耳中抗生素降解效果影响。将含有0.5、1、2、4、8 mg/kg抗生素的木耳样品单层均匀置于微波专用托盘内,设置真空度86 kPa、干燥温度上限为50 ℃、干燥功率1.6 kW对样品连续处理45 min,待木耳中含水率低于12%时停止干燥,测定抗生素含量。同时,将含有0.5 mg/kg抗生素的木耳进行真空微波干燥处理,设置功率分别为0.8、1.2、1.6、2.0、2.4 kW,待木耳含水率低于12%后停止干燥。干燥过程中,每5 min取样测定抗生素含量变化。评价真空微波干燥处理过程中抗生素初始浓度和功率对抗生素含量变化影响。
1.2.3.5 木耳中抗生素含量检测
参照张科明等[23]检测多种兽药残留的前处理方法并做修改。
样品处理:取木耳样品约100 g,用粉碎机粉碎、混匀后装入洁净的密封袋,密闭并标明编号,于干燥处保存。
提取:称取1 g样品置于100 mL塑料离心管中,加入8 ml Na2EDTA-Mcllvaine缓冲液,涡旋振荡1 min,再加入17 mL 5%甲酸乙腈,涡旋振荡1 min,然后加入2 g 氯化钠、3 g 无水硫酸钠,迅速摇匀,涡旋振荡1 min,以5000 r/min离心 5 min,取出上清液待净化。
净化:称取0.15 g PSA(乙二胺-N-丙基硅烷),并加入0.5 g无水硫酸钠置于10 mL离心管中,向其中加入上述离心管中的上清液5 mL后充分混合,以5000 r/min离心5 min,吸取上清液1 mL过0.22 μm有机相滤膜,装瓶,于−20 ℃保存,供高效液相色谱测定。
色谱条件:色谱柱:C18柱4.6×150 mm;流速:0.8 mL/min;柱温:30 ℃;进样量:20 μL;流动相A为乙腈,流动相B为0.7%(v/v)磷酸水溶液,等度洗脱(A相20%:B相80%),检测器:荧光检测器。
1.3 数据处理
每个试验均做3次平行,使用Origin 2018软件作图,采用SPSS 18软件对数据进行显著性检验(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同干燥处理过程中木耳水分含量变化
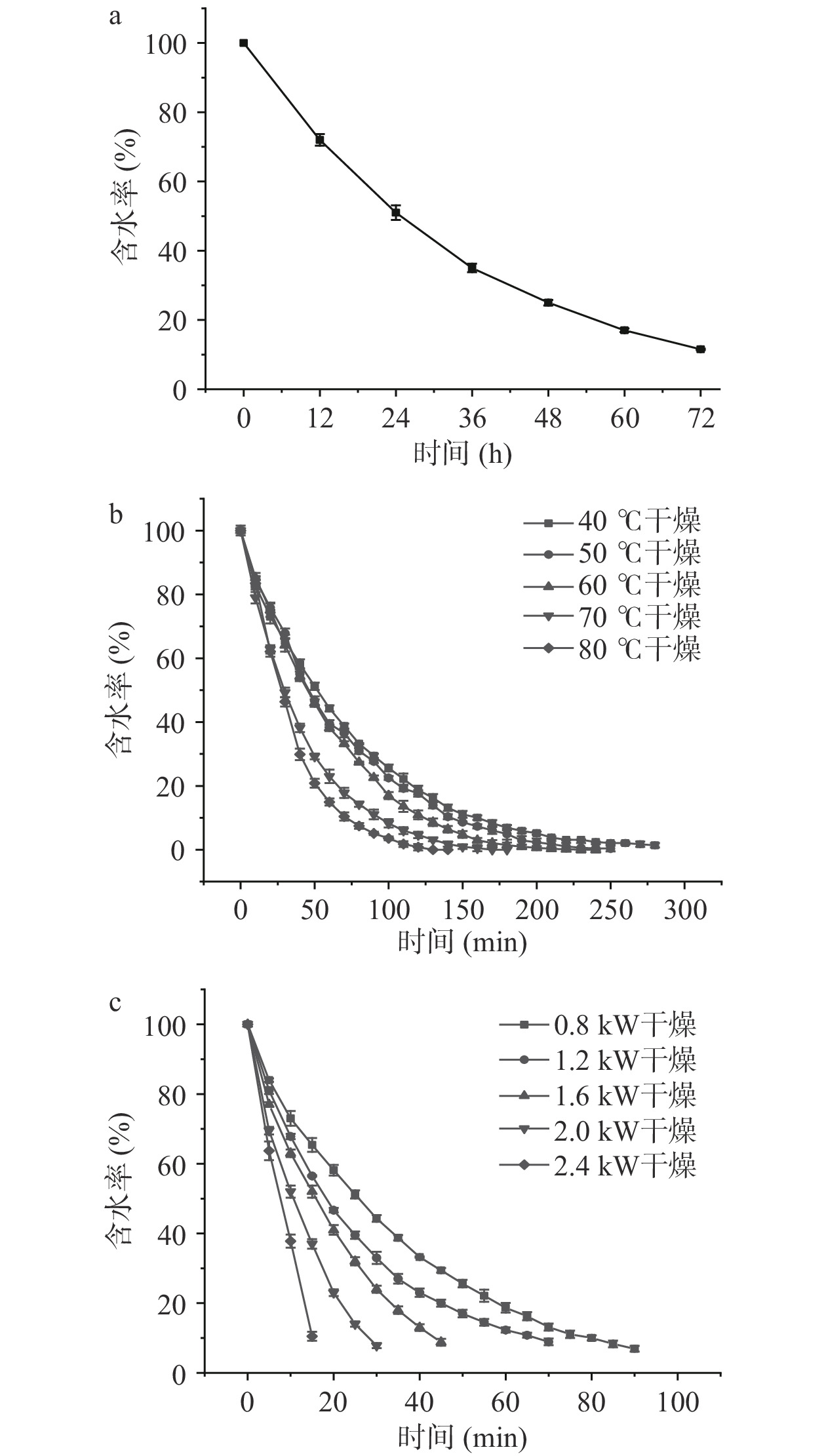
自然干燥、热风干燥、真空微波干燥三种不同干燥方式对鲜木耳干燥至水分含量12%以下所需的时间如表1所示,其干燥过程中的水分含量变化曲线如图1所示。表1中所示自然干燥将木耳水分含量降至12%以下所需的干燥时间为72 h,这个时间在热风干燥则缩短至150 min,且随温度上升所需时间进一步缩短,在80 ℃热风干燥条件下仅需150 min;真空微波干燥由于真空环境,过高的温度使物料无法通过空气散热而破坏营养物质,故控制真空度86 kPa及温度上限为50 ℃,干燥木耳所需的时间随干燥功率的上升而呈下降趋势,在2.4 kW真空微波干燥条件下仅需15 min即可将木耳水分含量降至12%以下。如图1a所示,木耳在自然干燥下水分含量的变化曲线没有明显的加速干燥阶段,而这个现象在图1b和图1c中,体现则较为明显,尤其随干燥温度上升或干燥的功率上升,木耳的加速干燥阶段则越明显的体现。不同干燥方式的干燥效率有明显区别,热风干燥相对于自然干燥干燥速率有明显增加,真空微波干燥则在这一程度上出现更明显的增加。Morales[8]的研究采用真空微波干燥技术干燥新鲜脐橙皮,与传统的热风干燥相比,VMD的干燥时间缩短了90.7%~94.7%,也证明了真空微波干燥的干燥效率。
表 1 不同干燥处理木耳所需时间Table 1. Time required for drying Auricularia auricula by different drying methods干燥方式 将木耳降至12%水分含量以下
所需的干燥时间自然干燥 25 ℃自然晾晒 72 h 热风干燥 40 ℃热风干燥 280 min 50 ℃热风干燥 250 min 60 ℃热风干燥 220 min 70 ℃热风干燥 180 min 80 ℃热风干燥 150 min 真空微波干燥 0.8 kW真空微波干燥 90 min 1.2 kW真空微波干燥 70 min 1.6 kW真空微波干燥 45 min 2.0 kW真空微波干燥 30 min 2.4 kW真空微波干燥 15 min 2.2 不同干燥处理对木耳理化指标的影响
确定了不同种干燥方式干燥木耳所需的干燥时间后,评价不同种干燥方式对木耳中的营养理化指标是否有较大影响,参照GB/T 6192-2019黑木耳中的基本理化指标对总糖、粗蛋白、粗脂肪、粗纤维、灰分含量进行测定,结果如表2所示。其中总糖含量在80 ℃热风干燥和2.4 kW真空微波干燥时分别下降1.34%和2.28%,但仍高于国家标准要求的总糖含量≥22%,这与梁晓君等[24]的研究结果相同,经过热风干燥和真空微波干燥后的玉木耳粉总糖含量均有不同程度下降且有显著性变化(P<0.05)。其余理化指标如粗蛋白、粗脂肪、粗纤维、灰分等在自然干燥、热风干燥、真空微波干燥等不同干燥条件下均无显著性变化(P>0.05),且均符合GB/T 6192-2019中黑木耳的理化指标要求。梁晓君等在对玉木耳的粗纤维、粗脂肪、粗蛋白时得出粗蛋白与粗脂肪没有显著性变化(P>0.05),而对粗脂肪含量有显著性影响(P<0.05),本试验中粗脂肪含量则无显著性变化(P>0.05)。Bondaruk等[25]的研究也表明50、70 ℃的热风干燥与6~24 kPa的真空微波干燥使马铃薯的总糖含量降低约1%~16%。故不同干燥方式对木耳的品质影响变化不大,其中总糖含量有较小影响,则可通过不同干燥方式对木耳的干燥时间及后续讨论对木耳种抗生素的降解情况评价其干燥效果。
表 2 不同干燥方式对木耳理化指标影响Table 2. Effects of different drying methods on physicochemical indexes of Auricularia auricula干燥条件 总糖(%) 粗蛋白(%) 粗脂肪(%) 粗纤维(%) 灰分(%) 自然干燥 39.89±0.11a 12.18±0.17a 0.54±0.03a 4.60±0.15a 4.20±0.08a 热风干燥40 ℃ 39.05±0.20b 12.09±0.13a 0.49±0.02a 4.60±0.10a 4.13±0.07a 热风干燥50 ℃ 38.96±0.13b 12.32±0.11a 0.50±0.03a 4.50±0.15a 4.20±0.08a 热风干燥60 ℃ 38.34±0.25c 12.05±0.05a 0.46±0.03a 4.60±0.15a 4.15±0.11a 热风干燥70 ℃ 38.80±0.15b 12.22±0.08a 0.49±0.02a 4.60±0.15a 4.21±0.13a 热风干燥80 ℃ 38.55±0.11c 12.16±0.08a 0.48±0.03a 4.50±0.10a 4.21±0.13a 真空微波干燥0.8 kW 38.20±0.26c 12.18±0.10a 0.50±0.03a 4.50±0.10a 4.20±0.13a 真空微波干燥1.2 kW 38.11±0.25c 12.22±0.07a 0.49±0.03a 4.60±0.10a 4.20±0.08a 真空微波干燥1.6 kW 38.00±0.16c 12.15±0.09a 0.50±0.03a 4.50±0.10a 4.13±0.05a 真空微波干燥2.0 kW 37.59±0.11d 12.29±0.08a 0.48±0.02a 4.60±0.10a 4.13±0.05a 真空微波干燥2.4 kW 37.61±0.16d 12.16±0.11a 0.50±0.03a 4.60±0.15a 4.20±0.10a 注:同列右肩不同的小写字母表示具有显著差异(P<0.05)。 2.3 不同干燥处理对木耳中抗生素降解影响评价
2.3.1 自然干燥处理的抗生素含量变化
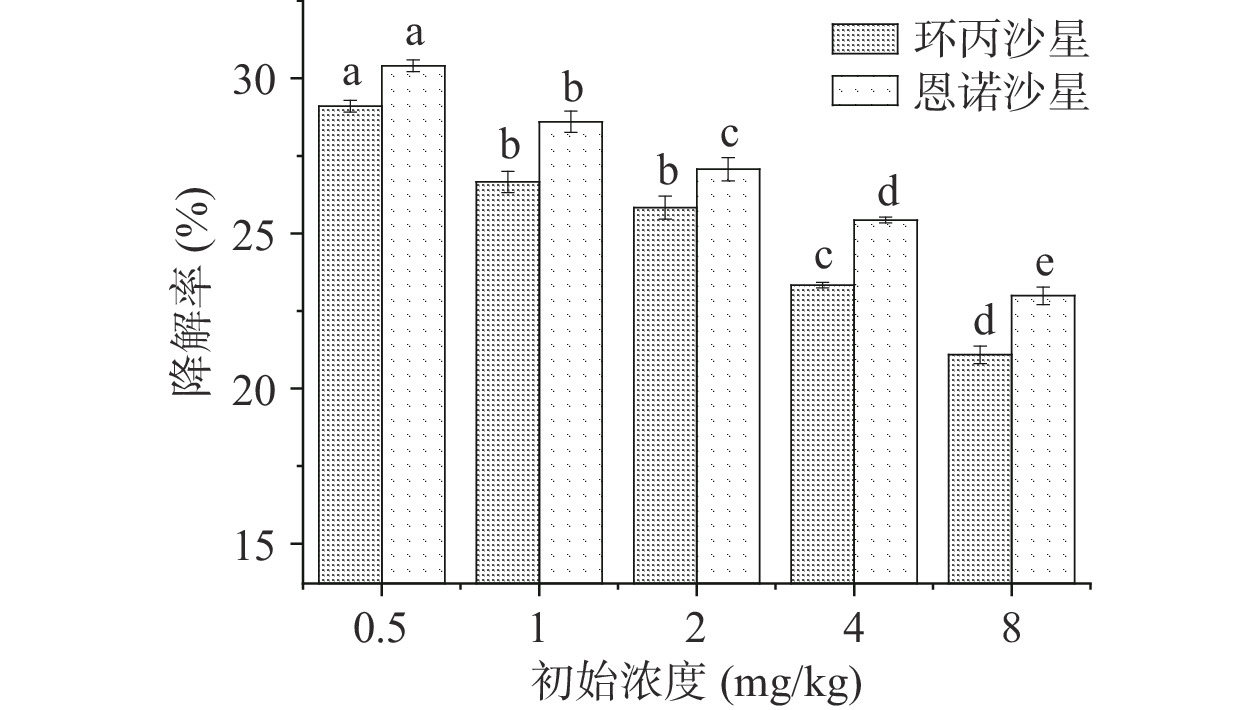
自然干燥过程中抗生素初始浓度对木耳中抗生素降解的影响如图2所示。恩诺沙星与环丙沙星两种抗生素在自然干燥过程中的降解效果受抗生素初始浓度的影响,降解率随木耳中抗生素初始浓度含量的降低从9.67%升高至16.32%,在抗生素浓度为0.5 mg/kg时恩诺沙星与环丙沙星的降解率分别为16.32%和14.22%。说明木耳中低浓度的抗生素在干燥过程中更易被降解,且在不同抗生素浓度情况下,恩诺沙星的降解效果均高于环丙沙星。在自然晾晒干燥的过程中,抗生素的降解应该伴随着光降解作用,目前采用较多的化学降解方法仍然为光催化氧化法[26−27],光催化法原理是利用光催化剂产生光生电子和光生空穴,通过自由基与目标污染物共同作用下发生氧化反应,将抗生素分解成小分子的无机物质,从而消除对环境的污染。王浩楠等[28]认为抗生素在阳光照射下没有光敏剂的催化也会发生光降解,只是有各种光敏催化剂的参与会使光催化降解效果大幅提升。结合郭洪光等[29]、刘杨等[30]的试验结果得出,恩诺沙星与环丙沙星的四个主要降解路径,通过一系列的脱氟、光裂解、取代、加成及脱氨基反应,最终导致目标物开环裂解,氧化反应主要集中在喹诺酮类抗生素核心的C-F键、羧酸基团及哌嗪基团上。
2.3.2 热风干燥过程中抗生素含量变化
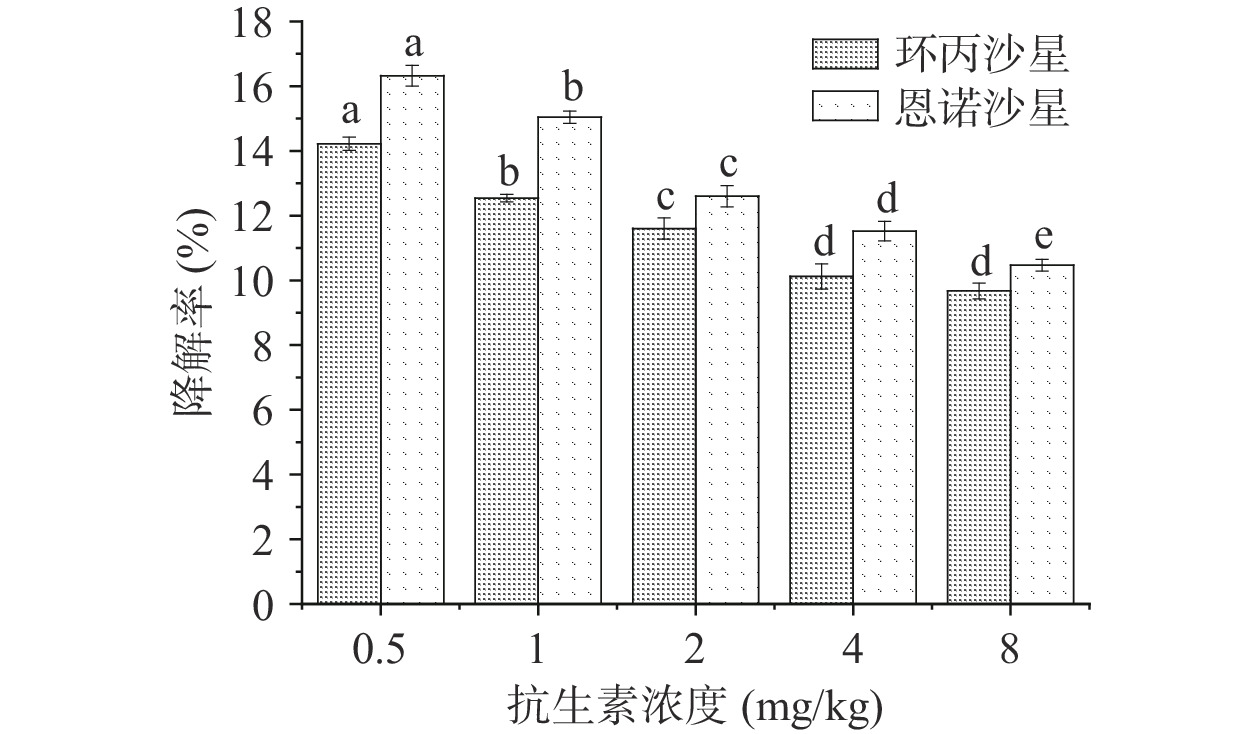
热风干燥下抗生素初始浓度对热风干燥降解木耳中抗生素的影响结果如图3所示。图中热风干燥下抗生素的降解效果仍随木耳中抗生素初始浓度的升高而降低。故恩诺沙星、环丙沙星两种抗生素浓度在0.5~8 mg/kg范围内时,抗生素初始浓度为0.5 mg/kg的黑木耳在热风干燥后抗生素降解率最高,两种抗生素的降解率分别可达30.4%、29.1%,而在抗生素初始浓度为8 mg/kg时的两种抗生素降解效果则分别只有22.99%和21.09%,但相较于自然晾晒干燥方式对木耳中的抗生素降解效果均有明显提高。
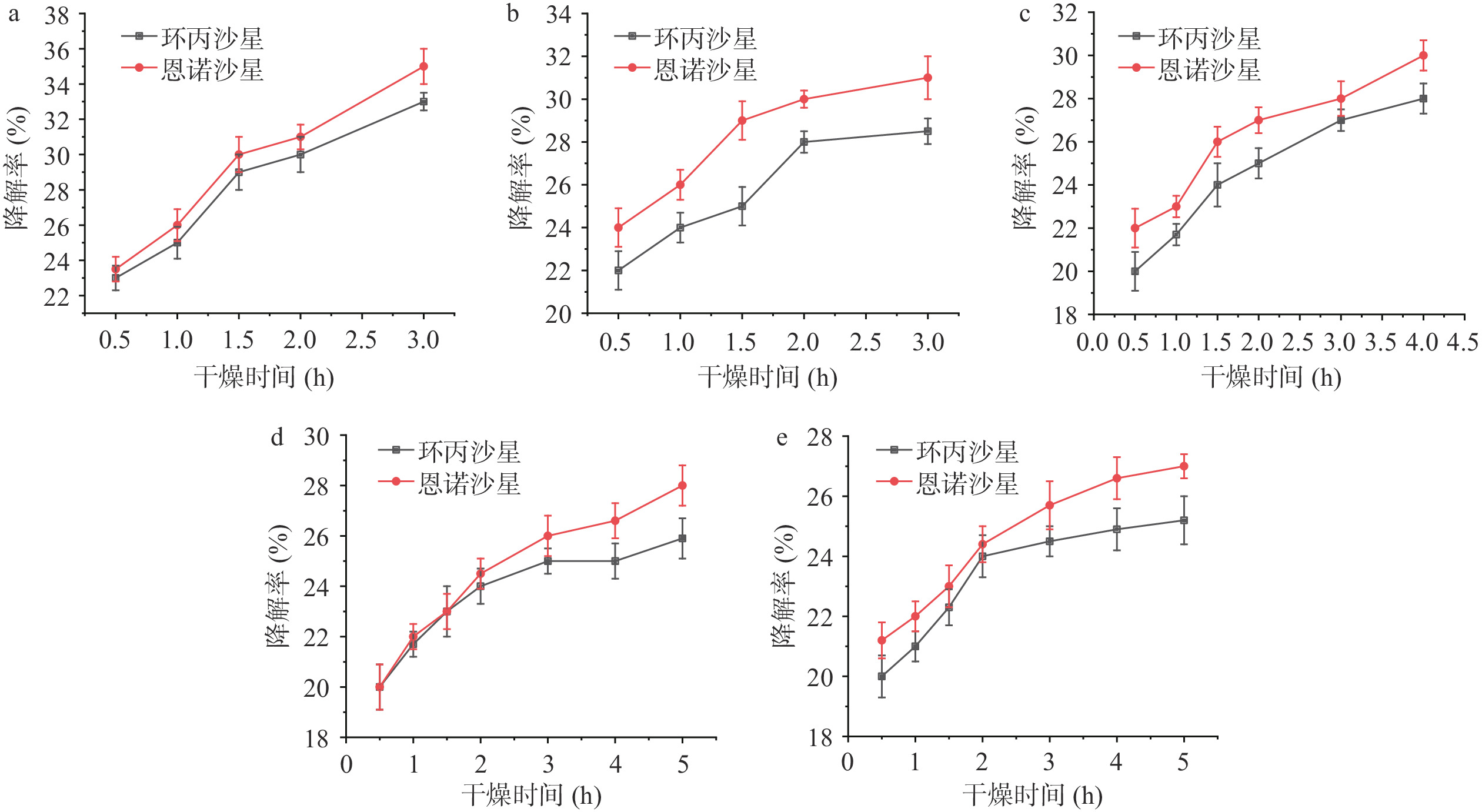
40~80 ℃热风干燥降解木耳中抗生素残留的变化情况及其干燥过程中的水分含量变化情况如图4所示。图4a在80 ℃热风干燥下,恩诺沙星、环丙沙星两种抗生素在木耳干燥至水分含量12%以下的降解效果最好,分别为35.37%和33.19%;图4b~图4e表示40~70 ℃的热风干燥对木耳中抗生素残留的降解情况变化,其中40 ℃的热风干燥对抗生素降解率最低,50~70 ℃的热风干燥将木耳水分含量降低至12%以下时,降解效果在25%~32%之间且抗生素的降解率会随温度升高而升高。在不同温度的干燥试验中,温度降低也有利于木耳的干燥。在80 ℃时将木耳的水分含量降至12%以下仅需150 min,而在40 ℃下的热风干燥则需280 min,对木耳的干燥效率有较大影响。刘博等[31]研究了热处理对去除鸡粪中氟喹诺酮类抗生素的效果,结果表明在处理时间40 min,温度达190 ℃时,鸡粪中喹诺酮类抗生素去除率可达64.5%~85.1%;温度升高至220 ℃时,4种诺酮类抗生素去除率均高于94.1%,也证明热效应对抗生素的降解作用。张健等[32]也研究了喹诺酮类抗生素的热降解过程,以及热分解反应动力学方程的构建。结果表明,热风干燥在40~80℃时,温度越高对抗生素的降解效果相对越好,且恩诺沙星的降解效果均好于环丙沙星,这可能与抗生素的热分解效应有关。
2.3.3 真空微波干燥处理的抗生素含量变化
真空微波干燥过程中抗生素初始浓度对木耳中抗生素降解的影响如图5所示。恩诺沙星与环丙沙星两种抗生素在真空微波干燥过程中的降解效果同样受抗生素初始浓度的影响,在抗生素浓度为0.5 mg/kg时恩诺沙星与环丙沙星的降解率分别为36.72%和33.22%。恩诺沙星的降解效果均高于环丙沙星,且初始浓度对真空微波干燥降解木耳中抗生素的规律变化与热风干燥、自然干燥都相同,木耳中抗生素的降解率均会随抗生素初始浓度含量的降低而升高,进一步说明当抗生素含量较低时,对抗生素的降解效果相对更好。不同干燥功率下真空微波干燥降解抗生素的情况如图6所示,不同干燥功率下木耳中抗生素残留的降解率没有显著性变化(P<0.05),试验中真空度均设置为86 kPa。为保证木耳干燥过程中物料品质不被明显破坏,试验中温度上限设置均为50 ℃,则热效应在不同功率的微波干燥下对抗生素的降解效果可能相同,使其对木耳中抗生素残留的降解率没有显著性变化(P>0.05)。但随干燥功率升高,电磁波产生的高频电磁场让物料内部分子从原来的随机分布状态转向依照电场的性排列取向,在高频电磁场作用下造成分子的运动和相互摩擦从而产生能量使得介质温度不断提高,从而使物质干燥速率显著增加。这与唐小闲等[33]对小黄姜真空微波干燥研究的结论相同,微波功率越大,干燥速率越快,干基含水率达到平衡时所需干燥时间越短。在干燥功率为0.8 kW时所需干燥时间为100 min,当干燥功率升高至2.4 kW时,干燥速率最快,可直接将干燥时间缩短为15 min,且对木耳的基础营养指标影响较小,故真空微波干燥显然可以作为干燥阶段的最快速干燥方式,但在干燥过程中对抗生素的降解效果方面,其与热风干燥差别却不大。
3. 结论
本文系统探究了自然晾晒、热风干燥和真空微波干燥三种处理方式对黑木耳的干燥效率,对黑木耳的理化特性影响以及喹诺酮类抗生素(恩诺沙星、环丙沙星)的降解效果。黑木耳干制过程中,80 ℃热风处理需要150 min,2.4 kW真空微波干燥需要15 min,大幅缩短了木耳干燥所需时间。以自然晾晒的黑木耳为参照,热风干燥及真空微波干燥对木耳的总糖含量略有影响,对其他的基础理化指标无显著影响(P>0.05),理化指标仍满足国标要求。此外,自然干燥过程中恩诺沙星、环丙沙星的降解率分别为16.32%和14.22%;80 ℃热风干燥和2.4 kW真空微波干燥时恩诺沙星的降解率分别为35.37%和36.11%,环丙沙星的降解率分别为33.19%和32.39%,这两种处理方式对抗生素降解没有显著差异,相对自然干燥有显著提高。因此,真空微波干燥处理时间短、效率高,对黑木耳理化指标影响较小且具有良好抗生素残留降解效果,为食用菌干燥及质量安全控制提供了新思路。在具体木耳大批量干制过程中,考虑到控制生产成本问题,可在提高木耳干燥效率的基础上,合理选择木耳干燥方式。木耳生产加工中需要控制的污染因素很多,本文重点讨论了干燥方式对木耳中的抗生素降解效果,后续研究可对木耳中多种主要因素如农药残留、重金属等同时评价。
-
表 1 不同干燥处理木耳所需时间
Table 1 Time required for drying Auricularia auricula by different drying methods
干燥方式 将木耳降至12%水分含量以下
所需的干燥时间自然干燥 25 ℃自然晾晒 72 h 热风干燥 40 ℃热风干燥 280 min 50 ℃热风干燥 250 min 60 ℃热风干燥 220 min 70 ℃热风干燥 180 min 80 ℃热风干燥 150 min 真空微波干燥 0.8 kW真空微波干燥 90 min 1.2 kW真空微波干燥 70 min 1.6 kW真空微波干燥 45 min 2.0 kW真空微波干燥 30 min 2.4 kW真空微波干燥 15 min 表 2 不同干燥方式对木耳理化指标影响
Table 2 Effects of different drying methods on physicochemical indexes of Auricularia auricula
干燥条件 总糖(%) 粗蛋白(%) 粗脂肪(%) 粗纤维(%) 灰分(%) 自然干燥 39.89±0.11a 12.18±0.17a 0.54±0.03a 4.60±0.15a 4.20±0.08a 热风干燥40 ℃ 39.05±0.20b 12.09±0.13a 0.49±0.02a 4.60±0.10a 4.13±0.07a 热风干燥50 ℃ 38.96±0.13b 12.32±0.11a 0.50±0.03a 4.50±0.15a 4.20±0.08a 热风干燥60 ℃ 38.34±0.25c 12.05±0.05a 0.46±0.03a 4.60±0.15a 4.15±0.11a 热风干燥70 ℃ 38.80±0.15b 12.22±0.08a 0.49±0.02a 4.60±0.15a 4.21±0.13a 热风干燥80 ℃ 38.55±0.11c 12.16±0.08a 0.48±0.03a 4.50±0.10a 4.21±0.13a 真空微波干燥0.8 kW 38.20±0.26c 12.18±0.10a 0.50±0.03a 4.50±0.10a 4.20±0.13a 真空微波干燥1.2 kW 38.11±0.25c 12.22±0.07a 0.49±0.03a 4.60±0.10a 4.20±0.08a 真空微波干燥1.6 kW 38.00±0.16c 12.15±0.09a 0.50±0.03a 4.50±0.10a 4.13±0.05a 真空微波干燥2.0 kW 37.59±0.11d 12.29±0.08a 0.48±0.02a 4.60±0.10a 4.13±0.05a 真空微波干燥2.4 kW 37.61±0.16d 12.16±0.11a 0.50±0.03a 4.60±0.15a 4.20±0.10a 注:同列右肩不同的小写字母表示具有显著差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] YAO H W, LIU Y, MA Z F, et al. Analysis of nutritional quality of black fungus cultivated with corn stalks[J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2019(9590251).
[2] 陈思羽, 白冰, 刘春山, 等. 木耳旋转式热风干燥装置研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2017,45(4):202−204. [CHEN S Y, BAI B, LIU C S, et al. Study on rotary hot air drying device of fungus[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2017,45(4):202−204.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.04.063 CHEN S Y, BAI B, LIU C S, et al. Study on rotary hot air drying device of fungus[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(4): 202−204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.04.063
[3] 李定金, 段秋霞, 段振华, 等. 黑木耳功能性成分及其干燥技术研究进展[J]. 保鲜与加工,2020,20(6):233−237. [LI D J, DUAN Q X, DUAN Z H, et al. Research progress on functional components and drying technology of black fungus[J]. Preservation and Processing,2020,20(6):233−237.] LI D J, DUAN Q X, DUAN Z H, et al. Research progress on functional components and drying technology of black fungus[J]. Preservation and Processing, 2020, 20(6): 233−237.
[4] 刘冬梅, 花军. 木耳微波干燥特性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2014,42(18):5956−5957. [LIU D M, HUA J. Study on microwave drying characteristics of fungus[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2014,42(18):5956−5957.] LIU D M, HUA J. Study on microwave drying characteristics of fungus[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(18): 5956−5957.
[5] 任爱清, 邓珊, 林芳, 等. 不同干燥处理对黑木耳粉理化特性和微观结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(11):75−81. [REN A Q, DENG S, LIN F, et al. Effects of different drying treatments on physicochemical properties and microstructure of black fungus powder[J]. Food Science,2022,43(11):75−81.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210602-017 REN A Q, DENG S, LIN F, et al. Effects of different drying treatments on physicochemical properties and microstructure of black fungus powder[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(11): 75−81. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210602-017
[6] BACANLI M, BAŞARAN N. Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 2019, 125: 462-466.
[7] RENNIE T J W, SOUZA N D, DONNAN P T, et al. Risk of acute kidney injury following community prescription of antibiotics:Self-controlled case series[J]. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation,2019,34(11):1910−1916. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy187
[8] MORALES A M C. Nephrotoxicity of antimicrobials and antibiotics[J]. Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease,2020,27(1):31−37. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.08.001
[9] WANG Q, LIU B, CAO J, et al. The impacts of vacuum microwave drying on osmosis dehydration of tilapia fillets[J]. Journal of Food Process Engineering,2019,42(1):e12956. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.12956
[10] 段培宇, 陈寒玉, 张宝忠, 等. 动物源性食品中抗生素类污染物生物检测技术研究进展[J]. 环境化学,2022,41(2):581−590. [DUAN P Y, CHEN H Y, ZHANG B Z, et al. Research progress on biological detection technology of antibiotic pollutants in animal derived food[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2022,41(2):581−590.] DUAN P Y, CHEN H Y, ZHANG B Z, et al. Research progress on biological detection technology of antibiotic pollutants in animal derived food[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(2): 581−590.
[11] GU H B, XIE W H, DU A, et al. Overview of electrocatalytic treatment of antibiotic pollutants in wastewater[J]. Catalysis Reviews, 2021:1−51.
[12] ZHANG Y K, SHI Q W, JIANG W, et al. Comparison of the chemical composition and antioxidant stress ability of polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula under different drying methods[J]. Food Function,2022,54(5):2938−2951.
[13] 黑木耳热风干燥操作规程[J]. 农业工程技术, 2015(17):45−46. [Hot air drying operation procedure of black fungus[J]. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 2015(17):45−46.] Hot air drying operation procedure of black fungus[J]. Agricultural Engineering Technology, 2015(17): 45−46.
[14] 刘清斌, 周宇. 复水黑木耳热风干燥特性的研究[J]. 食品科技,2008(11):87−90. [LIU Q B, ZHOU Y. Study on hot air drying characteristics of rehydration black fungus[J]. Food Science,2008(11):87−90.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2008.11.025 LIU Q B, ZHOU Y. Study on hot air drying characteristics of rehydration black fungus[J]. Food Science, 2008(11): 87−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2008.11.025
[15] 梁昌祥, 黄彩奕, 梁明华, 等. 真空微波干燥木耳技术研究[J]. 农产品加工,2022(1):32−36. [LIANG C X, HUANG C Y, LIANG M H, et al. Study on vacuum microwave drying technology of fungus[J]. Agricultural Product Processing,2022(1):32−36.] LIANG C X, HUANG C Y, LIANG M H, et al. Study on vacuum microwave drying technology of fungus[J]. Agricultural Product Processing, 2022(1): 32−36.
[16] 任爱清, 曹珍珍, 唐小闲, 等. 黑木耳真空微波干燥过程中水分迁移变化规律研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2022,35(11):99−103. [REN A Q, CAO Z Z, TANG X X, et al. Study on the change law of moisture migration during vacuum microwave drying of black fungus[J]. Grain and Oil,2022,35(11):99−103.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2022.11.021 REN A Q, CAO Z Z, TANG X X, et al. Study on the change law of moisture migration during vacuum microwave drying of black fungus[J]. Grain and Oil, 2022, 35(11): 99−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2022.11.021
[17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 15672-2009 食用菌中总糖含量测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2009:1−2. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 15672-2009 Determination of total sugar content in edible fungi[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2009:1−2.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 15672-2009 Determination of total sugar content in edible fungi[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009: 1−2.
[18] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 5009.5-2016 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016:1−3. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016:1−3.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016: 1−3.
[19] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 5009.6-2016 食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016:1−2. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016:1−2.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016: 1−2.
[20] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 5009.10-2003 植物类食品中粗纤维的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2003:68−69. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 5009.10-2003 Determination of crude fiber in plant food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2003:68−69.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 5009.10-2003 Determination of crude fiber in plant food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2003: 68−69.
[21] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 5009.4-2016 食品中灰分的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016:1−4. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB 5009.4-2016 Determination of ash in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016:1−4.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB 5009.4-2016 Determination of ash in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016: 1−4.
[22] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 6192-2019 黑木耳[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2019:1−4. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 6192-2019 Black fungus[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2019:1−4.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 6192-2019 Black fungus[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2019: 1−4.
[23] 张科明, 梁飞燕, 邓鸣, 等. QuEChERS结合液相色谱-串联质谱法快速测定猪肉中多类兽药残留[J]. 色谱,2016,34(9):860−867. [ZHANG K M, LIANG F Y, DENG M, et al. Rapid determination of multiple veterinary drug residues in pork by QuEChERS combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chromatogram,2016,34(9):860−867.] ZHANG K M, LIANG F Y, DENG M, et al. Rapid determination of multiple veterinary drug residues in pork by QuEChERS combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Chromatogram, 2016, 34(9): 860−867.
[24] 梁晓君, 廖才学, 黄振勇, 等. 不同干燥和粉碎方式对玉木耳粉粉体特性和营养成分的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(1):96−100,109. [LIANG X J, LIAO C X, HUANG Z Y, et al. Effects of different drying and crushing methods on powder characteristics and nutritional components of Auricularia auricula powder[J]. Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(1):96−100,109.] LIANG X J, LIAO C X, HUANG Z Y, et al. Effects of different drying and crushing methods on powder characteristics and nutritional components of Auricularia auricula powder[J]. Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(1): 96−100,109.
[25] BONDARUK J, MARKOWSKI M, BLASZCZAK W. Effect of drying conditions on the quality of vacuum-microwave dried potato cubes[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2007,81(2):306−312. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.10.028
[26] 常东浩, 葛菁萍. 生态环境中抗生素检测与降解方法的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报,2021,37(27):59−64. [CHANG D H, GE Q P. Research progress on detection and degradation methods of antibiotics in ecological environment[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2021,37(27):59−64.] CHANG D H, GE Q P. Research progress on detection and degradation methods of antibiotics in ecological environment[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 37(27): 59−64.
[27] 刘宏, 庞族族, 石林, 等. 光催化降解喹诺酮类抗生素的研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2023, 43(10):34−41. [LIU H, PANG Z Z, SHI L, et al. Research progress on photocatalytic degradation of quinolones antibiotics[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2023, 43(10):34−41.] LIU H, PANG Z Z, SHI L, et al. Research progress on photocatalytic degradation of quinolones antibiotics[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2023, 43(10): 34−41.
[28] 王浩楠, 李凤祥, 姜记威, 等. 光催化降解水体中磺胺类抗生素的研究进展[J]. 化工环保,2021,41(2):127−133. [WANG H N, LI F X, JIANG J W, et al. Research progress on photocatalytic degradation of sulfonamide antibiotics in water[J]. Chemical industry Environmental Protection,2021,41(2):127−133.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2021.02.001 WANG H N, LI F X, JIANG J W, et al. Research progress on photocatalytic degradation of sulfonamide antibiotics in water[J]. Chemical industry Environmental Protection, 2021, 41(2): 127−133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2021.02.001
[29] 郭洪光, 刘杨, 柯亭伶, 等. UV/PS工艺降解水中环丙沙星的产物及机理分析[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),2017,44(6):151−157. [GUO H G, LIU Y, KE T L, et al. Analysis of degradation products and mechanism of ciprofloxacin in water by UV/PS process[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Science Edition),2017,44(6):151−157.] GUO H G, LIU Y, KE T L, et al. Analysis of degradation products and mechanism of ciprofloxacin in water by UV/PS process[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 44(6): 151−157.
[30] 刘杨, 张永丽, 周鹏. 软铋矿铁酸铋活化过一硫酸盐降解环丙沙星机理及产物研究[J]. 工程科学与技术,2022,54(5):203−209. [LIU Y, ZHANG Y L, ZHOU P. Study on the mechanism and product of ciprofloxacin degradation by peroxymonosulfate activated by soft bismuth ferrite[J]. Engineering Science and Technology,2022,54(5):203−209.] LIU Y, ZHANG Y L, ZHOU P. Study on the mechanism and product of ciprofloxacin degradation by peroxymonosulfate activated by soft bismuth ferrite[J]. Engineering Science and Technology, 2022, 54(5): 203−209.
[31] 刘博, 薛南冬, 张石磊, 等. 热处理技术去除鸡粪中氟喹诺酮类抗生素及影响因素研究[J]. 环境工程,2015,33(2):84−87,68. [LIU B, XUE N D, ZHANG S L, et al. Study on the removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in chicken manure by heat treatment technology and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Engineering,2015,33(2):84−87,68.] LIU B, XUE N D, ZHANG S L, et al. Study on the removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in chicken manure by heat treatment technology and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2015, 33(2): 84−87,68.
[32] 张健, 陈栋华, 袁誉洪, 等. 喹诺酮类药物的热稳定性及其热分解非等温动力学研究[J]. 药学学报,2000(6):445−450. [ZHANG J, CHEN D H, YUAN Y H, et al. Study on thermal stability and non-isothermal kinetics of thermal decomposition of quinolones[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica,2000(6):445−450.] ZHANG J, CHEN D H, YUAN Y H, et al. Study on thermal stability and non-isothermal kinetics of thermal decomposition of quinolones[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2000(6): 445−450.
[33] 唐小闲, 刘艳, 咸兆坤, 等. 小黄姜真空微波干燥特性及其动力学研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(10):87−94. [TANG X X, LIU Y, XIAN Z K, et al. Study on vacuum microwave drying characteristics and kinetics of Xiaohuangjiang[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(10):87−94.] TANG X X, LIU Y, XIAN Z K, et al. Study on vacuum microwave drying characteristics and kinetics of Xiaohuangjiang[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(10): 87−94.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 石启龙,刘静,赵亚. 基于温度分布和水分状态分布的扇贝柱蛋白质加热变性数值模拟. 食品工业科技. 2025(05): 239-247 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李晓燕,丁奕涵,矫佳伟,巩雪,李立,王天娜. 农产品超声辅助热泵干燥技术的研究进展. 包装工程. 2024(09): 53-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘静,赵亚,石启龙. 果蔬和水产品新型干燥预处理技术研究进展及未来展望. 食品工业科技. 2022(10): 32-42 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 刘静,赵亚,石启龙. 渗透剂预处理对扇贝柱热泵干燥动力学及品质特性的影响. 食品科学技术学报. 2022(03): 145-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵亚,朱智壮,石启龙,刘静. 成膜预处理提高扇贝柱超声波辅助热泵干燥效率及品质. 农业工程学报. 2022(18): 274-283 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吴紫茼,金婧彧,马亚娟,王佳荣,王阳阳,刘亚琼,王颉. 海湾扇贝柱(Argopecten irradians)干制过程中蛋白质变化对品质特性的影响. 食品科技. 2021(10): 115-121 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



