Influence of Different Improvers on Germination Brown Rice-Wheat Flour Dough Properties and Steamed Bread Quality
-
摘要: 研究了不同浓度的改良剂羟丙基甲基纤维素(hydroxypropyl methylcellulose,HPMC)、黄原胶(xanthan gum,XG)和葡萄糖氧化酶(Glucose oxidase,GOX)对发芽糙米-小麦面粉(1:1)面团性质和馒头品质的影响。以不添加改良剂为对照,分析不同面团的热机械性能和吹泡特性,并以色泽、质构、比容、高径比和感官得分为指标,评价不同馒头的整体品质。结果表明,HPMC的添加显著(P<0.05)降低了面团的形成时间、稳定性、C2和CS。然而,XG和GOX的添加增加了面团的形成时间、稳定性和C2。不同改良剂的添加可能增强了蛋白质与蛋白质或淀粉分子之间的相互作用,从而加强面团的面筋网络。此外,改良剂的添加显著(P<0.05)提高了馒头弹性和感官评分。因此,适当添加HPMC和XG可以改善发芽糙米-小麦面粉馒头品质。本研究为改善馒头品质和促进GBRF在面制品体系中的应用提供了理论参考。Abstract: Different levels of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), xanthan gum (XG) and Glucose oxidase (GOX) were applied to germination brown rice-wheat flour (1:1) to evaluate the effects of improvers on the dough properties and Chinese steamed bread (CSB) quality. With no improver as control, thermo-mechanical and alveograph properties of different dough were analyzed, and the overall quality of different steamed bread was evaluated by color, texture, specific volume, height/diameter ratio and sensory score. The results showed that the addition of HPMC significantly (P<0.05) decreased the dough development time, stability, C2 and CS. However, the addition of XG and GOX increased the dough development time, stability and C2. The addition of different improvers might enhance the interaction between protein and protein or starch molecules, thus strengthening the gluten network of the dough. In addition, the addition of improve significantly (P<0.05) improved the springiness and sensory score of CSB. Therefore, proper addition of HPMC and XG could improve the quality of germination brown rice-wheat flour steamed bread. This study provides a theoretical reference for improving the quality of steamed bread and promoting the application of GBRF in Flour products systems.
-
馒头(Chinese steamed bread,CSB)是以小麦面粉(wheat flour,WF)为主要原料制作的发酵食品,作为中国北方居民的膳食主食,几乎占小麦消费量的40%[1]。如今考虑到健康饮食、营养安全等各方面原因,使用混合面粉生产高品质CSB是一种新的趋势。研究表明,在面包中添加发芽糙米粉(germinated brown rice flour,GBRF)可以显著提高营养价值[2]。因此,在CSB中添加GBRF可能增强产品的营养价值和感官属性。
稻谷经脱壳过程分离为稻壳和糙米(brown rice,BR),BR可进一步分离成淀粉性胚乳(约92%)、胚(约2%)、麸皮(约6%)[3]。糙米的碾磨精制过程中胚部和麸皮被去除,只保留了营养素单一的淀粉性胚乳,称为精米,也叫白米(white rice,WR)。麸皮和胚中含有许多营养素和生物活性成分,包括γ-氨基丁酸、膳食纤维、γ-谷维素、维生素和矿物质等,因此含有麸皮和胚部的BR比WR具有更高的营养价值[4]。但由于糙米中植酸盐、糠蜡等物质以及麸皮的存在,导致糙米制品存在吸水率低,不易煮熟、口感粗糙、风味不佳等问题。通过发芽可有效改善熟化糙米的蒸煮品质、口感、质地、风味等属性,从而提高食用质量[5]。此外有关研究报道,在BR的萌发过程中,由于吸收水分的增加以及一些生化反应的发生,导致质地软化、聚合物降解,并促进GABA、可溶性膳食纤维、γ-谷维素和抗氧化剂如维生素E、酚类化合物等植物化学物质的合成和积累[6]。但根据籽粒类型或不同的浸泡、发芽条件,关键营养物质含量的增加或减少往往会有不同的结果。
在中水分面制食品(如面包、馒头等)中使用各种改良剂(乳化剂、亲水胶体和酶等),可提高小麦面粉(Wheat flour,WF)面团的可加工性,起到改善产品感官品质的作用。Liu等[7]向全麦馒头中添加戊聚糖酶和葡萄糖氧化酶(Glucose oxidase,GOX)显著提高了面筋网络的连续性、延伸性和致密性,从而增强面团品质。使用羟丙基甲基纤维素(hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, HPMC)可改善面糊和黑糯米面团的流变特性[8]。Li等[9]发现,果胶、瓜尔胶和黄原胶(xanthan gum,XG)可以改善面包质量,增加面团体积稳定性和气体保留。因此,本研究以GBRF和WF为研究对象,评估不同改良剂HPMC、XG和GOX对GBRF-WF面团热机械性能、吹泡特性、破损淀粉值以及GBRF-WF馒头品质的影响,以期为改善馒头品质和促进GBRF在面制品体系中的应用提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
小麦面粉 哈尔滨金沙河集团;糙米 黑龙江黑土庄园有机农业发展有限公司;活性干酵母 安琪酵母有限公司;HPMC 上海阿拉丁生化科技有限公司;GOX 河南万邦实业有限公司;XG 河南中兴化工有限公司;谷朊粉 安徽安特食品有限公司;其他化学试剂均为分析纯级,上海蓝季生物有限公司。
THZ-98A恒温振荡器、BPG-9070A精密鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;WK-500B新诺多功能粉碎机 上海新诺仪器设备有限公司;Mixolab2混合试验仪、Alveograph吹泡仪、SDmatic破损淀粉仪 法国肖邦仪器公司;TA-XT Plus质构仪 北京盈盛恒泰科技有限责任公司;CM-700d色差仪 日本柯尼卡美能达公司;HE83水分测定仪 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;YDX-120两用蒸饭柜 北京广利鸿盛厨房设备有限公司;16/13豪华食品醒箱 澳大利亚联合厨房用具有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 GBRF的制备
BR的萌芽参考Xu等[10]的方法并改进。BR用蒸馏水清洗三次,并在0.5%次氯酸钠溶液中消毒15 min后用足够的蒸馏水清洗。在30 ℃下将BR浸泡在2 mmol/L氯化钙水溶液中12 h后,排空浸泡液置于培养皿中,并用纱布覆盖,在30 ℃和85%相对湿度的恒温振荡器中黑暗条件下发芽24 h。发芽后,发芽糙米(germinated brown rice,GBR)在45 ℃的鼓风干燥箱中干燥7 h后,使用多功能粉碎机将GBR研磨成粉,并用80目筛网进行筛分备用。
1.2.2 GBRF-WF馒头的制备
GBRF-WF馒头的制备参考Wu的方法并改进[11]。参考文献[7−9]改良剂的添加量略微改动,将添加HPMC(1%、2%、3%、4%)、XG(0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%)和GOX(0.01%、0.02%、0.03%、0.04%)的GBRF-WF混合粉(1:1)100 g与60%、35 ℃的温水;10%的谷朊粉;1.5%的活性干酵母(以混合粉质量计)混合并揉合至表面光滑均匀,无生粉夹杂。以不含改良剂的GBRF-WF面团为对照组,将每个面团分为三个50±0.5 g的样品,在38 ℃和80%相对湿度的条件下,于食品醒箱中分别发酵90 min和20 min。最后将面团在蒸饭柜中蒸20 min,冷却60 min后进行测试。
1.2.3 热机械性能测定
使用混合试验仪分别测量了恒温混合期和加热和冷却期的GBRF-WF面团热机械性能。Mixolab2设置为遵循Chopin+程序,试验初始温度为30 ℃,保温时间为8 min,然后以4 ℃/min的速度将温度升至90 ℃。保温时间为8 min后,温度以−4 ℃/min的速度将温度降至50 ℃,搅拌速度恒为80 r/min,总实验时间为45 min。
1.2.4 吹泡特性试验
参考GB/T 14614.4-2005的方法使用吹泡仪进行吹泡特性试验[12]。吹泡特性参数由计算机软件程序自动记录,P:面团韧性,表示抵抗变形的能力;L:面团延展性或面筋气体保持能力;P/L:表示韧性和延展性之间的平衡;W:面团烘焙强度或气泡膨胀至破裂所需能量。
1.2.5 破损淀粉值(SD)测定
使用破损淀粉仪测定破损淀粉值,将120 mL蒸馏水、3.0 g硼酸粉末、3.0 g碘化钾粉末和一滴硫代硫酸钠溶液加入反应容器中。准确称量1 g GBRF-WF面粉,用勺子放入破损淀粉仪中,仪器循环6~7 min后,记录样品的破损淀粉含量[13]。
1.2.6 比容和高径比测定
对冷却后的GBRF-WF馒头样品进行称重,用油菜籽置换法测定其体积,并计算比容[14]。用游标卡尺测量馒头的直径和高度,并计算高径比以确定形状。
1.2.7 色泽测定
使用色度计的反射率法测定馒头的表面颜色,工作条件为:C/2光源,测定光斑直径为10 mm,以标准陶瓷白板为标准样。色泽指标为L*(0:黑色,100:白色)、a*(−a*:绿色,+a*:红色)、b*(−b*:蓝色,+b*:黄色)[15]。
1.2.8 质地分析
使用质构仪进行质地剖面分析(TPA)。参数设置为试验前速度为1 mm/s、测试速度1 mm/s、试验后速度为2 mm/s、触发力5 g、保持时间5 s、压缩率40%,数据采集速率200 pps,记录样品硬度,弹性,咀嚼性,内聚性[16]。
1.2.9 感官评价
参考Zhu等[17]的方法对GBRF-WF馒头进行感官评价。随机对馒头样品进行编号,评分标准按照GB/T21118-2007。挑选食品专业年龄在23岁至26岁之间的15名(男生7人,女生8人)学生,以GBRF-WF馒头为样本进行适当培训后组建一个感官评价小组。饭后2 h后进行感官评价,评分标准如表1。
表 1 GBRF-WF馒头感官评价表Table 1. Sensory evaluation table of GBRF-WF Chinese steamed bread项目 分值(分) 评分标准 色泽 15 颜色明亮均匀(10.1~15分),颜色暗淡不均匀(5.1~10分),
颜色灰暗不均匀(0~5分)外观 20 表面光滑、馒头立体圆润(16.1~20分),体积微缩、表面褶皱、
形状不饱满(10.1~16分),体积萎缩严重、表面褶皱程度大(0~10分)内部结构 10 纵切面气孔均匀且密集(7.1~10分),气孔大小适中,较不密集(4.1~7分),气孔少且大小不均匀(0~4分) 口味 15 有发酵香味、微甜、浓郁的发芽糙米香气(10.1~15分),甜味下降、发芽糙米香气较淡
(5.1~10分),无香气和甜味(0~5分)适口性 20 面质柔软适口(16.1~20分),面质柔软度轻微下降(10.1~16分),
面质稍硬、口感粗糙(0~10分)弹性 20 面体回弹速度快、能复原(16.1~20分),回弹性和复原度减弱(10.1~16分),
回弹弱、复原度差(0~10分)1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复三次,实验结果均以平均值±标准偏差表示。采用SPSS软件进行数据统计、单因素方差分析(ANOVA)和Tukey HSD显著性差异检验,P<0.05具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
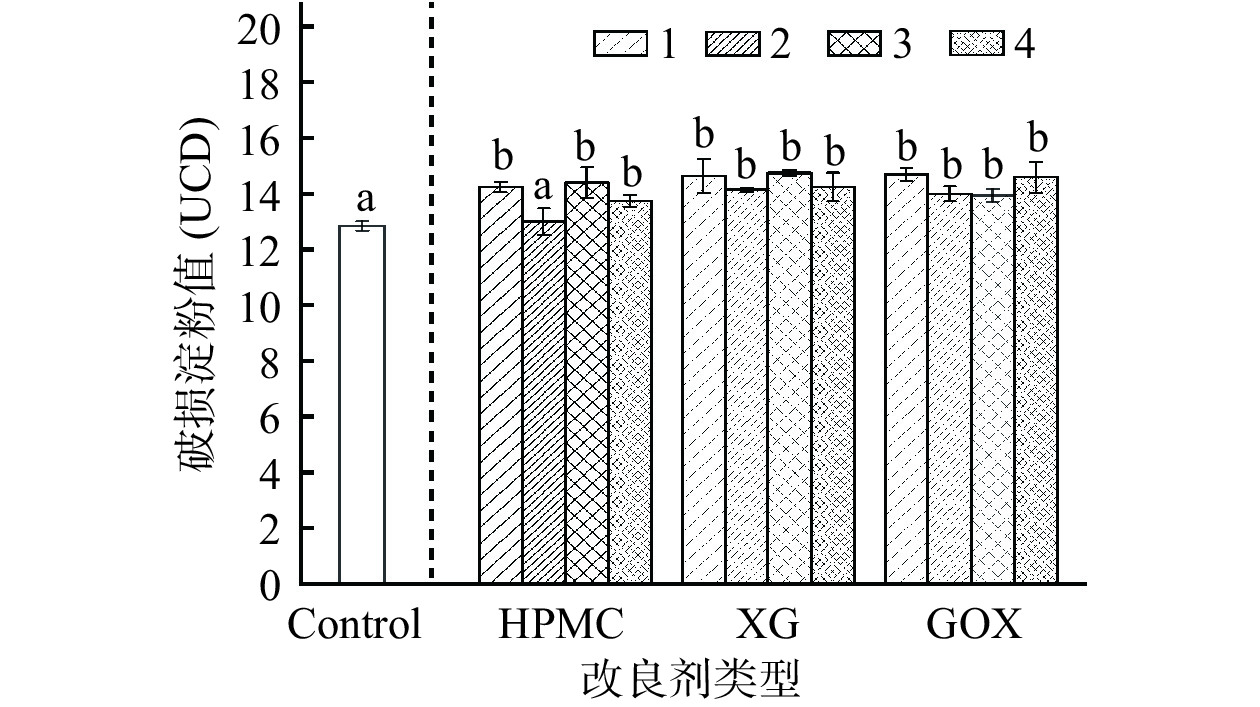
2.1 改良剂对混合粉破损淀粉含量的影响
与对照组(12.85)相比(图1),除添加2% HPMC的样品外,其他实验样品的DS值均显著(P<0.05)增加,添加0.3% XG的样品DS值含量最高(14.75)。相关研究表明,较高破损淀粉含量的精制面粉制得的馒头具有较高的比容、相对较低的硬度、较高的胶粘性和耐嚼性,这可能是由于较高破损淀粉含量使馒头醒发性增加,使馒头获得较高品质[18]。但也有报道,破损淀粉含量会导致面团吸水率增加、搅拌稳定性能降低,无法支撑馒头的体积[19]。因此,结合热机械性能和吹泡特性实验结果,添加0.3% XG适当增加了GBRF-WF混合粉的破损淀粉值,有利于改善制得馒头品质。
2.2 改良剂对GBRF-WF面团热机械性能的影响
2.2.1 恒温混合期
添加改良剂的GBRF-WF面团吸水率、形成时间和稳定时间如表2所示。与对照组相比,添加HPMC、XG和0.01% GOX后,GBRF-WF面团吸水率增加,而添加0.02%、0.03%和0.04% GOX对吸水率无显著影响,HPMC和XG均为亲水胶体,可能与亲水胶体结构中的羟基通过氢键导致更多的水相互作用有关[20]。不同的改良剂对形成时间(development time,DT)值的影响不同,原因可能是这些聚合物的分子结构影响了水合过程的动力[21]。添加4.0% HPMC显著(P<0.05)降低了GBRW面团的DT值(从5.29 min降低到2.49 min),而添加0.2%、0.3%、0.4%的XG和0.03%、0.04%的GOX显著(P<0.05)提高了面团的DT值,表明添加HPMC可缩短面团的水合时间。稳定时间(stability time,ST)代表面团强度,较软的面团ST值较短[22]。与对照组相比,添加HPMC明显降低了面团的ST值,添加0.4% XG的样品显著(P<0.05)提升了面团的ST值,表明XG可减缓面团的形成,从而提升面团强度、增加面团稳定时间。
表 2 不同改良剂添加量对GBRF-WF面团混合测试参数的影响Table 2. Effect of different amounts of improver on mixing test parameters of GBRF-WF dough改良剂种类 添加量(%) 吸水率(%) 形成时间(min) 稳定时间(min) Control 0 62.52±0.02abc 5.29±0.24c 7.54±0.19d HPMC 1 67.81±0.02e 3.79±0.06b 5.82±0.14c 2 71.01±0.02f 2.72±0.01a 3.91±0.16b 3 74.60±0.03g 2.54±0.02a 3.15±0.13a 4 75.34±0.65h 2.49±0.17a 3.91±0.16b XG 0.1 62.79±1.04bcd 5.69±0.21c 7.58±0.28d 0.2 62.83±0.02bcd 7.47±0.95d 7.86±0.05d 0.3 63.13±0.23cd 8.20±0.05d 8.00±0.45de 0.4 63.23±0.40cd 8.20±1.25d 8.42±0.01e GOX 0.01 63.56±0.48d 5.55±0.22c 7.69±0.08d 0.02 61.96±0.03ab 5.74±0.11c 7.76±0.26d 0.03 61.90±0.35ab 7.72±0.17d 8.02±0.48de 0.04 61.72±0.03a 7.80±0.09d 7.96±0.08de 注:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),表3~表6同。 2.2.2 加热冷却期
Mixolab2曲线的第二阶段表明,GBRF-WF面团的淀粉糊化特性受到混合和加热的限制。C2、C3、C4和C5是研究改良剂对面团热机械性能影响的重要参数[19]。C2表示由于暴露于物理机械和热应力而导致的面团稠度损失,由表3可知,添加XG和GOX后,GBRF-WF面团的C2值无显著变化,但添加HPMC的样品C2显著降低(P<0.05)。添加不同的改良剂导致C3变化显著(P<0.05),随着HPMC添加量的增加,GBRF-WF面团糊化峰值C3降低,原因可能与蛋白质聚集体引起的淀粉颗粒溶胀能力降低以及β-葡聚糖的降解有关[23]。相反,C3值随着GOX和XG的添加而增加,尤其是0.4% XG最高。与对照组相比,添加3%和4% HPMC的面团C4显著(P<0.05)降低,但添加XG和GOX的面团的C4值差异不显著。C5是冷却时产生的最大扭矩,代表淀粉的回生特性,改良剂对C5值有不同的影响,2% HPMC和0.3% XG的添加,会使C5值降低,表明GBRF-WF面团的老化速率和硬度下降。但GOX的加入导致C5值增加,可能与淀粉和阿拉伯木聚糖(Arabinoxylan,AX)之间的相互作用有关。GOX通过氧化反应促进AX凝胶的生成。此外,AX的持水能力在氧化后发生变化,这影响了面团中淀粉的糊化和回生以及自由水的分布[24−25]。CS值随着HPMC含量的增加而显著(P<0.05)降低,而添加0.2%和0.4% XG的样品CS值相比对照组明显增加,0.1%、0.3% XG和GOX对GBRF-WF馒头CS值没有显著影响。
表 3 不同改良剂添加量对GBRF-WF面团加热冷却测试参数的影响Table 3. Effect of different amounts of improver on parameters of GBRF-WF dough during complete tests改良剂种类 添加量(%) C2(Nm) C3(Nm) C4(Nm) C5(Nm) CS(Nm) -α(Nm/min) β
(Nm/min)γ
(Nm/min)T0~T1 Control 0 0.28±0.01d 1.37±0.01cd 0.35±0.01bc 0.42
±0.01bcde1.03±0.01d 0.093
±0.001bc0.273
±0.013ab0.138
±0.004def56.1bc~74.6c HPMC 1 0.23±0.01c 1.31±0.01c 0.34±0.01bc 0.41±0.01bcd 0.90±0.01c 0.083
±0.001b0.293
±0.021ab0.130
±0.010bcde55.4ab~73.9bc 2 0.19±0.01b 1.18±0.02b 0.27±0.01b 0.36±0.01b 0.79±0.02b 0.060
±0.002a0.286
±0.018ab0.109
±0.005abcd56.3c~73.4b 3 0.15±0.01a 1.06±0.01a 0.19±0.01a 0.27±0.01a 0.72±0.02a 0.060
±0.001a0.298
±0.016ab0.101
±0.001ab56.2c~72.4a 4 0.14±0.01a 1.15±0.01b 0.17±0.01a 0.23±0.03a 0.81±0.01b 0.054
±0.002a0.288
±0.036ab0.111
±0.003abcd56.1bc~73.1b XG 0.1 0.28±0.01d 1.44±0.01de 0.35±0.01bc 0.44±0.02cde 1.06±0.06de 0.096
±0.006bc0.288
±0.036ab0.138
±0.004def56.2c~73.8bc 0.2 0.30±0.02d 1.49±0.02e 0.32±0.05bc 0.41±0.03bcd 1.12±0.02e 0.099
±0.023bc0.299
±0.017ab0.135
±0.001cdef56.4c~73.7bc 0.3 0.30±0.01d 1.47±0.01e 0.34±0.02bc 0.40±0.01bc 1.09±0.04de 0.093
±0.007bc0.260
±0.004a0.148
±0.006ef56.3c~74.4c 0.4 0.30±0.01d 1.54±0.02e 0.37±0.02c 0.44±0.04cde 1.13±0.04e 0.108
±0.012c0.302
±0.040ab0.160
±0.006f55.9bc~73.9bc GOX 0.01 0.28±0.03d 1.48±0.05e 0.35±0.10bc 0.48±0.07e 1.05±0.02d 0.095
±0.005bc0.323
±0.003b0.112
±0.036abcd56.1bc~73.9bc 0.02 0.28±0.01d 1.44±0.02de 0.34±0.01bc 0.48±0.01de 1.08±0.03de 0.099
±0.001bc0.279
±0.011ab0.107
±0.003abc55.3a~73.5b 0.03 0.31±0.03d 1.45±0.13de 0.41±0.01c 0.56±0.02f 1.10±0.04de 0.099
±0.005bc0.3007
±0.005ab0.093
±0.011a55.4ab~73.5b 0.04 0.28±0.01d 1.48±0.01e 0.39±0.02c 0.58±0.01f 1.07±0.01de 0.102
±0.004bc0.332
±0.006b0.103
±0.005ab55.7abc~74.5c 注:C2(与蛋白质弱化相关)、C3(与淀粉老化相关),C4(糊化热胶稳定性)、C5(与淀粉回生相关)、CS(8分钟稠度值)、-α(弱化速度)、β(糊化速率),γ(酶解速度)、T0~T1(糊化温度范围)。 其他指标,如弱化速度(-α)、糊化速度(β)、酶解速度(γ)和糊化温度范围(T0~T1),均在Mixolab2完全测试中,如表3所示。与对照组相比,添加HPMC使面团-α值显著(P<0.05)降低,但添加XG和GOX的样品-α值无显著变化。三种改良剂对β值均无显著影响。与对照组相比,添加HPMC和GOX的面团γ值降低,添加XG的面团γ值无显著差异。Moreira等[22]发现HPMC降低了栗子粉的γ值。Liu等[26]发现HPMC可以提高马铃薯粉的γ值。因此,HPMC对不同原料制作的面团可能具有不同的作用效果。淀粉糊化延迟对于改善淀粉类食品的内部结构、质地和其他品质至关重要[27]。因此,2% HPMC和0.2% XG可以作为GBRF-WF馒头的改良剂。改良剂的添加导致最终温度显著(P<0.05)降低,当添加2%的HPMC时最明显,与Sudha等[28]之前的研究结果相同,添加1%的HPMC降低了全麦面团的最终糊化温度。糊化温度的变化可能是因为改良剂具有不同的化学成分以及直链淀粉、支链淀粉和改良剂之间的一些相互作用导致[29]。
2.3 改良剂对GBRF-WF面团吹泡特性的影响
添加改良剂的GBRF-WF面团的吹泡特性参数如表4所示。面团的韧性(P)用于预测面团的气体保持能力[30]。随着HPMC和XG添加量的增加P值增大,且XG添加0.4%时影响最大,可能的原因是GBRF-WF面粉中的亲水胶体和蛋白质之间的相互作用造成的。与对照组相比,GOX的添加使P值略有减小,且当GOX含量为0.03%时,面团P值显著(P<0.05) 降低。同样,3%、4% HPMC的面团延伸性(L)显著(P<0.05) 增加,但对照组和其他改良剂处理的面团之间没有显著差异。标准品质面团的烘焙力(W)值一般高于160[31]。与对照组相比,除了1%的HPMC和添加GOX的样品,其他实验样品W值均显著增加。P/L比率可以预测面团的弹性阻力与延展性之间的平衡,亲水胶体有助于提高P/L比,除1% HPMC和0.1% XG的样品之外,添加亲水胶体对GBRF-WF面团的P/L值有显著(P<0.05) 影响。特别是,当XG添加量为0.2%、0.3%和0.4%时,P/L比率显著(P<0.05)增加,可能是因为XG和GBRF-WF面粉中的蛋白质之间的相互作用最强。与对照组相比,GOX的添加显著(P<0.05)降低了P/L比,但添加0.01% GOX的样品除外。结果显示,HPMC、XG和GOX可以通过多种机制改善面团品质,添加0.3% XG对面团吹泡特性作用效果最好。
表 4 不同改良剂的添加量对GBRF-WF面团吹泡特性参数的影响Table 4. Effects of different amounts of improver on alveograph characteristics of GBRF-WF dough改良剂
种类添加量
(%)P(mm) L(mm) W(×10−4 J) P/L Control 0 145.00±1.00b 25.00±1.00ab 167.00±1.00c 5.80±0.10c HPMC 1 144.00±1.00b 24.67±0.58ab 161.00±5.20b 5.78±0.04c 2 155.33±1.15c 26.00±1.00abc 179.33±1.15d 5.97±0.05cd 3 166.00±1.73e 30.00±1.00d 207.67±2.08f 6.00±0.02cd 4 173.33±0.58f 29.00±2.00cd 217.00±1.73h 5.99±0.02cd XG 0.1 146.00±1.73b 27.67±0.58bcd 180.00±3.46d 5.30±0.05ab 0.2 161.00±1.00d 26.00±2.00abc 186.00±2.00e 6.20±0.01d 0.3 162.00±2.00d 25.00±2.00ab 181.00±2.00d 6.48±0.10e 0.4 179.67±2.31g 26.00±1.00abc 212.00±2.00g 6.96±0.04f GOX 0.01 142.00±2.00ab 24.00±1.00a 157.00±1.00a 5.92±0.08c 0.02 143.00±3.00ab 26.00±1.00abc 167.33±2.31c 5.47±0.05b 0.03 139.33±1.15a 27.00±1.00abcd 168.00±1.73c 5.16±0.05a 0.04 143.00±1.73ab 27.00±1.00abcd 170.33±0.58c 5.31±0.03ab 2.4 改良剂对GBRF-WF馒头品质的影响
2.4.1 质构特性
质构是评价GBRF-WF馒头质量的重要属性之一,表5列举了改良剂对GBRF-WF馒头质地参数(硬度、弹性、咀嚼性和内聚性)的影响。添加改良剂后,相比对照组(76.27 N),实验组硬度整体下降,尤其是2%HPMC(32.28N)和0.2% XG(34.68N)的样本,表明改良剂对GBRF-WF馒头具有软化作用。Zhang等[32]同样发现,添加GOX降低了CSB的硬度,这可能与改良剂的添加强化了面筋网络有关。与对照组相比,实验组的GBRF-WF馒头弹性没有显著改变,添加4% HPMC、0.3%和0.4% XG、0.03和0.04% GOX后,样本弹性略有降低。咀嚼度随改良剂添加量的增加,呈现先减小后增加的趋势,含1%和2% HPMC的样本咀嚼度最低。内聚性可以量化食物内部结构阻力,内聚性低会导致馒头干燥、高度破碎,导致消费者对馒头的接受度下降[33]。与对照样品(0.51)相比,实验组样品内聚性整体提高(范围为0.52~0.60),表明添加改良剂的馒头样品具有更完整的基质。
表 5 不同改良剂的添加量对GBRF-WF馒头质构参数的影响Table 5. Effects of different amounts of improver on texture parameters of GBRF-WF steamed bread改良剂
种类添加量
(%)硬度(N) 弹性 咀嚼性(N) 内聚性 Control 0 76.27±1.29f 6.14±0.30a 223.23±5.71d 0.51±0.02a HPMC 1 44.81±1.84bc 6.82±0.85a 131.33±9.51a 0.54±0.04abc 2 32.28±3.57a 7.15±1.13a 127.57±1.32a 0.52±0.01ab 3 44.92±3.06bc 6.10±0.28a 190.00±3.80bcd 0.56±0.01abcd 4 49.50±2.01cd 5.69±0.12a 191.63±4.50bcd 0.57±0.01bcd XG 0.1 49.08±3.08cd 6.67±0.99a 189.47±4.20bcd 0.53±0.01ab 0.2 34.68±1.38a 7.10±0.42a 145.17±2.55a 0.55±0.01abcd 0.3 53.62±1.30cde 6.04±0.46a 160.03±5.84abc 0.55±0.01abcd 0.4 56.53±3.97de 5.72±0.55a 208.77±2.93d 0.57±0.04abcd GOX 0.01 56.68±1.01de 6.45±0.34a 184.23±9.51bcd 0.56±0.02abcd 0.02 39.72±3.72ab 6.94±0.42a 155.17±5.47ab 0.60±0.03d 0.03 58.09±2.59de 5.88±0.24a 200.07±6.14cd 0.60±0.02d 0.04 59.24±2.37e 5.71±0.20a 217.13±7.10d 0.59±0.02cd 2.4.2 GBRF-WF馒头品质分析
添加改良剂对GBRF-WF馒头质量参数(比容、高径比、色泽和感官得分)的影响如表6所示。GBRF-WF馒头的比容值仅在添加2% HPMC和0.2% XG时显著(P<0.05)增大。最大比容(2.53 ml/g)是对照样品的1.17倍,这也证实了添加2% HPMC和0.2% XG通过与面粉蛋白质或淀粉分子之间相互作用而形成更稳定面团。除对照组和0.04% GOX的样品外,大多数样品的高径比均高于0.5,表明样品呈椭球形。2%HPMC(0.64)的样品高径比最大,对照组的样品最小0.40。相关研究表明,L*值被认为是影响馒头色泽的最重要参数[34−35]。添加HPMC显著(P<0.05)改善了GBRF-WF馒头L*值,而XG和GOX的添加对L*值没有显著影响,表明添加HPMC可以提高CSB的整体亮度,Mezaize等[36]也曾得到相同观点。不同的改良剂对GBRF-WF馒头感官得分结果有显著(P<0.05)影响,与不添加改良剂的馒头相比,添加HPMC、XG或GOX可以改善馒头的感官属性,从而获得更高的消费者可接受性分数,特别是含有2% HPMC和0.2% XG的GBRF-WF馒头更容易被消费者接受。但当改良剂含量增加时,感官得分有所下降,因此适当添加改良剂可GBRF-WF馒头感官品质。
表 6 改良剂对GBRF-WF馒头品质的影响Table 6. Effect of food additive on quality of GBRF-WF steamed bread改良剂种类 添加量(%) 比容(mL/g) 高径比 L* a* b* 感官得分(分) Control 0 2.16±0.05a 0.40±0.02a 69.81±0.55abc 1.93±0.15bcd 22.86±0.71cde 76.39±0.12a HPMC 1 2.41±0.06ab 0.59±0.01e 75.52±0.39d 1.29±0.08a 20.32±0.33a 84.10±0.30de 2 2.53±0.12b 0.64±0.02f 75.24±0.13d 1.83±0.08abc 22.94±0.42cde 85.11±0.63e 3 2.40±0.11ab 0.56±0.02cde 74.93±2.01d 1.77±0.35abc 22.50±0.94bcd 83.22±0.54cde 4 2.39±0.12ab 0.52±0.02bcd 75.31±1.04d 1.53±0.07ab 21.01±0.20ab 81.43±1.20c XG 0.1 2.43±0.18ab 0.57±0.03de 72.36±0.72c 1.85±0.17abc 21.58±0.51abc 83.46±0.49de 0.2 2.52±0.14b 0.60±0.02e 67.45±0.72a 3.01±0.90f 24.89±0.50e 84.93±0.55e 0.3 2.30±0.09ab 0.53±0.02cd 70.34±0.64bc 2.55±0.16ef 23.81±0.36de 82.27±0.76cd 0.4 2.20±0.03ab 0.51±0.03bc 68.93±0.69ab 2.75±0.58f 22.98±1.99cde 79.39±1.10b GOX 0.01 2.42±0.19ab 0.54±0.02cd 71.45±1.16bc 2.19±0.26cde 23.52±0.77cde 83.05±0.90cde 0.02 2.49±0.14ab 0.59±0.03e 69.32±0.59ab 2.17±0.11cde 23.18±0.49cde 84.88±0.51e 0.03 2.34±0.02ab 0.51±0.02bc 71.16±1.82bc 2.50±0.30def 23.77±0.47de 81.26±1.30c 0.04 2.28±0.02ab 0.47±0.03b 72.29±0.72c 1.99±0.15bcde 23.37±0.31cde 78.68±1.21b 3. 结论
研究表明,改良剂的类型和添加量对GBRF-WF面团特性和GBRF-WF馒头品质影响显著(P<0.05) 。改良剂(HPMC、XG和GOX)的添加有效增强了GBRF-WF面团的面筋网络。添加改良剂可显著(P<0.05) 改善GBRF-WF面团的热机械性能,HPMC、XG和GOX可以通过多种机制改善面团品质,0.3% XG对面团吹泡特性作用效果最好。此外,GBRF-WF馒头质量参数结果表明,添加改良剂后,馒头的比体积、质地参数、颜色和感官评分都得到了改善。综合考虑GBRF-WF面团的热机械性能、吹泡特性、破损淀粉值和GBRF-WF馒头质量,HPMC和XG改良剂对于生产优质GBRF-WF馒头具有良好的效果,同时也表明用GBRF替代部分WF制作馒头存在潜在的可能性,但WF和GBRF的最佳配比有待进一步研究。
-
表 1 GBRF-WF馒头感官评价表
Table 1 Sensory evaluation table of GBRF-WF Chinese steamed bread
项目 分值(分) 评分标准 色泽 15 颜色明亮均匀(10.1~15分),颜色暗淡不均匀(5.1~10分),
颜色灰暗不均匀(0~5分)外观 20 表面光滑、馒头立体圆润(16.1~20分),体积微缩、表面褶皱、
形状不饱满(10.1~16分),体积萎缩严重、表面褶皱程度大(0~10分)内部结构 10 纵切面气孔均匀且密集(7.1~10分),气孔大小适中,较不密集(4.1~7分),气孔少且大小不均匀(0~4分) 口味 15 有发酵香味、微甜、浓郁的发芽糙米香气(10.1~15分),甜味下降、发芽糙米香气较淡
(5.1~10分),无香气和甜味(0~5分)适口性 20 面质柔软适口(16.1~20分),面质柔软度轻微下降(10.1~16分),
面质稍硬、口感粗糙(0~10分)弹性 20 面体回弹速度快、能复原(16.1~20分),回弹性和复原度减弱(10.1~16分),
回弹弱、复原度差(0~10分)表 2 不同改良剂添加量对GBRF-WF面团混合测试参数的影响
Table 2 Effect of different amounts of improver on mixing test parameters of GBRF-WF dough
改良剂种类 添加量(%) 吸水率(%) 形成时间(min) 稳定时间(min) Control 0 62.52±0.02abc 5.29±0.24c 7.54±0.19d HPMC 1 67.81±0.02e 3.79±0.06b 5.82±0.14c 2 71.01±0.02f 2.72±0.01a 3.91±0.16b 3 74.60±0.03g 2.54±0.02a 3.15±0.13a 4 75.34±0.65h 2.49±0.17a 3.91±0.16b XG 0.1 62.79±1.04bcd 5.69±0.21c 7.58±0.28d 0.2 62.83±0.02bcd 7.47±0.95d 7.86±0.05d 0.3 63.13±0.23cd 8.20±0.05d 8.00±0.45de 0.4 63.23±0.40cd 8.20±1.25d 8.42±0.01e GOX 0.01 63.56±0.48d 5.55±0.22c 7.69±0.08d 0.02 61.96±0.03ab 5.74±0.11c 7.76±0.26d 0.03 61.90±0.35ab 7.72±0.17d 8.02±0.48de 0.04 61.72±0.03a 7.80±0.09d 7.96±0.08de 注:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),表3~表6同。 表 3 不同改良剂添加量对GBRF-WF面团加热冷却测试参数的影响
Table 3 Effect of different amounts of improver on parameters of GBRF-WF dough during complete tests
改良剂种类 添加量(%) C2(Nm) C3(Nm) C4(Nm) C5(Nm) CS(Nm) -α(Nm/min) β
(Nm/min)γ
(Nm/min)T0~T1 Control 0 0.28±0.01d 1.37±0.01cd 0.35±0.01bc 0.42
±0.01bcde1.03±0.01d 0.093
±0.001bc0.273
±0.013ab0.138
±0.004def56.1bc~74.6c HPMC 1 0.23±0.01c 1.31±0.01c 0.34±0.01bc 0.41±0.01bcd 0.90±0.01c 0.083
±0.001b0.293
±0.021ab0.130
±0.010bcde55.4ab~73.9bc 2 0.19±0.01b 1.18±0.02b 0.27±0.01b 0.36±0.01b 0.79±0.02b 0.060
±0.002a0.286
±0.018ab0.109
±0.005abcd56.3c~73.4b 3 0.15±0.01a 1.06±0.01a 0.19±0.01a 0.27±0.01a 0.72±0.02a 0.060
±0.001a0.298
±0.016ab0.101
±0.001ab56.2c~72.4a 4 0.14±0.01a 1.15±0.01b 0.17±0.01a 0.23±0.03a 0.81±0.01b 0.054
±0.002a0.288
±0.036ab0.111
±0.003abcd56.1bc~73.1b XG 0.1 0.28±0.01d 1.44±0.01de 0.35±0.01bc 0.44±0.02cde 1.06±0.06de 0.096
±0.006bc0.288
±0.036ab0.138
±0.004def56.2c~73.8bc 0.2 0.30±0.02d 1.49±0.02e 0.32±0.05bc 0.41±0.03bcd 1.12±0.02e 0.099
±0.023bc0.299
±0.017ab0.135
±0.001cdef56.4c~73.7bc 0.3 0.30±0.01d 1.47±0.01e 0.34±0.02bc 0.40±0.01bc 1.09±0.04de 0.093
±0.007bc0.260
±0.004a0.148
±0.006ef56.3c~74.4c 0.4 0.30±0.01d 1.54±0.02e 0.37±0.02c 0.44±0.04cde 1.13±0.04e 0.108
±0.012c0.302
±0.040ab0.160
±0.006f55.9bc~73.9bc GOX 0.01 0.28±0.03d 1.48±0.05e 0.35±0.10bc 0.48±0.07e 1.05±0.02d 0.095
±0.005bc0.323
±0.003b0.112
±0.036abcd56.1bc~73.9bc 0.02 0.28±0.01d 1.44±0.02de 0.34±0.01bc 0.48±0.01de 1.08±0.03de 0.099
±0.001bc0.279
±0.011ab0.107
±0.003abc55.3a~73.5b 0.03 0.31±0.03d 1.45±0.13de 0.41±0.01c 0.56±0.02f 1.10±0.04de 0.099
±0.005bc0.3007
±0.005ab0.093
±0.011a55.4ab~73.5b 0.04 0.28±0.01d 1.48±0.01e 0.39±0.02c 0.58±0.01f 1.07±0.01de 0.102
±0.004bc0.332
±0.006b0.103
±0.005ab55.7abc~74.5c 注:C2(与蛋白质弱化相关)、C3(与淀粉老化相关),C4(糊化热胶稳定性)、C5(与淀粉回生相关)、CS(8分钟稠度值)、-α(弱化速度)、β(糊化速率),γ(酶解速度)、T0~T1(糊化温度范围)。 表 4 不同改良剂的添加量对GBRF-WF面团吹泡特性参数的影响
Table 4 Effects of different amounts of improver on alveograph characteristics of GBRF-WF dough
改良剂
种类添加量
(%)P(mm) L(mm) W(×10−4 J) P/L Control 0 145.00±1.00b 25.00±1.00ab 167.00±1.00c 5.80±0.10c HPMC 1 144.00±1.00b 24.67±0.58ab 161.00±5.20b 5.78±0.04c 2 155.33±1.15c 26.00±1.00abc 179.33±1.15d 5.97±0.05cd 3 166.00±1.73e 30.00±1.00d 207.67±2.08f 6.00±0.02cd 4 173.33±0.58f 29.00±2.00cd 217.00±1.73h 5.99±0.02cd XG 0.1 146.00±1.73b 27.67±0.58bcd 180.00±3.46d 5.30±0.05ab 0.2 161.00±1.00d 26.00±2.00abc 186.00±2.00e 6.20±0.01d 0.3 162.00±2.00d 25.00±2.00ab 181.00±2.00d 6.48±0.10e 0.4 179.67±2.31g 26.00±1.00abc 212.00±2.00g 6.96±0.04f GOX 0.01 142.00±2.00ab 24.00±1.00a 157.00±1.00a 5.92±0.08c 0.02 143.00±3.00ab 26.00±1.00abc 167.33±2.31c 5.47±0.05b 0.03 139.33±1.15a 27.00±1.00abcd 168.00±1.73c 5.16±0.05a 0.04 143.00±1.73ab 27.00±1.00abcd 170.33±0.58c 5.31±0.03ab 表 5 不同改良剂的添加量对GBRF-WF馒头质构参数的影响
Table 5 Effects of different amounts of improver on texture parameters of GBRF-WF steamed bread
改良剂
种类添加量
(%)硬度(N) 弹性 咀嚼性(N) 内聚性 Control 0 76.27±1.29f 6.14±0.30a 223.23±5.71d 0.51±0.02a HPMC 1 44.81±1.84bc 6.82±0.85a 131.33±9.51a 0.54±0.04abc 2 32.28±3.57a 7.15±1.13a 127.57±1.32a 0.52±0.01ab 3 44.92±3.06bc 6.10±0.28a 190.00±3.80bcd 0.56±0.01abcd 4 49.50±2.01cd 5.69±0.12a 191.63±4.50bcd 0.57±0.01bcd XG 0.1 49.08±3.08cd 6.67±0.99a 189.47±4.20bcd 0.53±0.01ab 0.2 34.68±1.38a 7.10±0.42a 145.17±2.55a 0.55±0.01abcd 0.3 53.62±1.30cde 6.04±0.46a 160.03±5.84abc 0.55±0.01abcd 0.4 56.53±3.97de 5.72±0.55a 208.77±2.93d 0.57±0.04abcd GOX 0.01 56.68±1.01de 6.45±0.34a 184.23±9.51bcd 0.56±0.02abcd 0.02 39.72±3.72ab 6.94±0.42a 155.17±5.47ab 0.60±0.03d 0.03 58.09±2.59de 5.88±0.24a 200.07±6.14cd 0.60±0.02d 0.04 59.24±2.37e 5.71±0.20a 217.13±7.10d 0.59±0.02cd 表 6 改良剂对GBRF-WF馒头品质的影响
Table 6 Effect of food additive on quality of GBRF-WF steamed bread
改良剂种类 添加量(%) 比容(mL/g) 高径比 L* a* b* 感官得分(分) Control 0 2.16±0.05a 0.40±0.02a 69.81±0.55abc 1.93±0.15bcd 22.86±0.71cde 76.39±0.12a HPMC 1 2.41±0.06ab 0.59±0.01e 75.52±0.39d 1.29±0.08a 20.32±0.33a 84.10±0.30de 2 2.53±0.12b 0.64±0.02f 75.24±0.13d 1.83±0.08abc 22.94±0.42cde 85.11±0.63e 3 2.40±0.11ab 0.56±0.02cde 74.93±2.01d 1.77±0.35abc 22.50±0.94bcd 83.22±0.54cde 4 2.39±0.12ab 0.52±0.02bcd 75.31±1.04d 1.53±0.07ab 21.01±0.20ab 81.43±1.20c XG 0.1 2.43±0.18ab 0.57±0.03de 72.36±0.72c 1.85±0.17abc 21.58±0.51abc 83.46±0.49de 0.2 2.52±0.14b 0.60±0.02e 67.45±0.72a 3.01±0.90f 24.89±0.50e 84.93±0.55e 0.3 2.30±0.09ab 0.53±0.02cd 70.34±0.64bc 2.55±0.16ef 23.81±0.36de 82.27±0.76cd 0.4 2.20±0.03ab 0.51±0.03bc 68.93±0.69ab 2.75±0.58f 22.98±1.99cde 79.39±1.10b GOX 0.01 2.42±0.19ab 0.54±0.02cd 71.45±1.16bc 2.19±0.26cde 23.52±0.77cde 83.05±0.90cde 0.02 2.49±0.14ab 0.59±0.03e 69.32±0.59ab 2.17±0.11cde 23.18±0.49cde 84.88±0.51e 0.03 2.34±0.02ab 0.51±0.02bc 71.16±1.82bc 2.50±0.30def 23.77±0.47de 81.26±1.30c 0.04 2.28±0.02ab 0.47±0.03b 72.29±0.72c 1.99±0.15bcde 23.37±0.31cde 78.68±1.21b -
[1] POPPER L, SCHÄFER W, FREUND W. Future of flour:A compendium of flour improvement[M]. Clenze:Verlag Agrimedia, 2006, 309-318.
[2] CHAROENTHAIKIJ P, JANGCHUD K, JANGCHUD A, et al. Germination conditions affect selected quality of composite wheat-germinated brown rice flour and bread formulations[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,75(6):S312−S318.
[3] CHO D H, LIM S T. Germinated brown rice and its bio-functional compounds[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,196:259−271. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.09.025
[4] 蒋静, 马涛. 营养液培养糙米发芽富集GABA工艺条件优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(5):195−199. [JIANG J, MA T. Technological conditions optimization of GABA enrichment of brown rice germination using nutrient water culture method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(5):195−199.] doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.05.063 JIANG J, MA T. Technological conditions optimization of GABA enrichment of brown rice germination using nutrient water culture method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(5): 195−199. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.05.063
[5] BEAULIEU J C, MOREAU R A, POWELL M J, et al. Lipid profiles in preliminary germinated brown rice beverages compared to non-germinated brown and white rice beverages[J]. Foods,2022,11(2):220. doi: 10.3390/foods11020220
[6] 王丹. 萌芽留胚糙米制备工艺研究[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学, 2017. [WANG D. Study on the Preparation technology of germination and leaving brown rice[D]. Guiyang:Guizhou University, 2017.] WANG D. Study on the Preparation technology of germination and leaving brown rice[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2017.
[7] LIU L, YANG W, CUI S W, et al. Effects of pentosanase and glucose oxidase on the composition, rheology and microstructure of whole wheat dough[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,84:545−551. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.06.034
[8] ITTHIVADHANAPONG P, JANTATHAI S, SCHLEINING G. Improvement of physical properties of gluten-free steamed cake based on black waxy rice flour using different hydrocolloids[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2016,53(6):2733−2741. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2245-5
[9] LI J X, ZHU Y P, YADAV M P, et al. Effect of various hydrocolloids on the physical and fermentation properties of dough[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,271:165−173. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.192
[10] XU J, ZHANG H, GUO X N, et al. The impact of germination on the characteristics of brown rice flour and starch[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2012,92(2):380−387. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4588
[11] WU P, LIU B, CHEN J S, et al. QTL analysis of textural property traits for Chinese northern-style steamed bread[J]. Euphytica,2011,179(2):265−276. doi: 10.1007/s10681-010-0304-y
[12] 北京市粮食科学研究院. GB/T 14614.4-2005小麦粉面团流变特性测定(吹泡仪法)[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2005. [Beijing Grain Science Research Institute. GB/T 14614.4-2005 Determination of rheological properties of wheat flour dough (Alveograph)[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2005.] Beijing Grain Science Research Institute. GB/T 14614.4-2005 Determination of rheological properties of wheat flour dough (Alveograph)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2005.
[13] MA S, LI L, WANG X X, et al. Effect of mechanically damaged starch from wheat flour on the quality of frozen dough and steamed bread[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,202:120−124. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.075
[14] FLANDER L, SALMENKALLIO-MARTTILA M, SUORTTI T, et al. Optimization of ingredients and baking process for improved wholemeal oat bread quality[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2007,40(5):860−870. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2006.05.004
[15] LUO D L, LIANG X, XU B C, et al. Effect of inulin with different degree of polymerization on plain wheat dough rheology and the quality of steamed bread[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2017,75:205−212. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2017.04.009
[16] LIU X L, MU T H, YAMUL K D, et al. Evaluation of different hydrocolloids to improve dough rheological properties and bread quality of potato–wheat flour[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2017,54(6):1597−1607. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2591-y
[17] ZHU F, SAKULNAK R, WANG S N. Effect of black tea on antioxidant, textural, and sensory properties of Chinese steamed bread[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:1217−1223. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.110
[18] WANG P, YANG R Q, GU Z X, et al. Comparative study of deterioration procedure in chemical-leavened steamed bread dough under frozen storage and freeze/thaw condition[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,229:464−471. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.122
[19] LIU X L, MU T H, SUN H N, et al. Influence of potato flour on dough rheological properties and quality of steamed bread[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2016,15(11):2666−2676. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61388-6
[20] FRIEND C P, WANISKA R D, ROONEY L W. Effects of hydrocolloids on processing and qualities of wheat tortillas[J]. Cereal chemistry (USA),1993,70(3):252−256.
[21] GHARAIE Z, AZIZI M H, BARZEGAR M, et al. Effects of hydrocolloids on the rheological characteristics of dough and the quality of bread made from frozen dough[J]. Journal of Texture Studies,2015,46(5):365−373. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12136
[22] MOREIRA R, CHENLO F, TORRES M D. Rheology of commercial chestnut flour doughs incorporated with gelling agents[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(5):1361−1371. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.12.015
[23] APRODU I, BANU I. Influence of dietary fiber, water, and glucose oxidase on rheological and baking properties of maize based gluten-free bread[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2015,24(4):1301−1307. doi: 10.1007/s10068-015-0167-z
[24] PRIMO-MARTÍN C, MARTÍNEZ-ANAYA M A. Influence of pentosanase and oxidases on water-extractable pentosans during a straight breadmaking process[J]. Journal of Food Science,2003,68(1):31−41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2003.tb14110.x
[25] COURTIN C M, DELCOUR J A. Arabinoxylans and endoxylanases in wheat flour bread-making[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2002,35(3):225−243. doi: 10.1006/jcrs.2001.0433
[26] LIU X L, MU T H, SUN H N, et al. Influence of different hydrocolloids on dough thermo-mechanical properties and in vitro starch digestibility of gluten-free steamed bread based on potato flour[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,239:1064−1074. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.047
[27] WADA K, TAKAHASHI K, SHIRAI K, et al. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) applied to examining gelatinization of starches in foods[J]. Journal of Food Science,1979,44(5):1366−1368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1979.tb06440.x
[28] SUDHA M L, RAO G V. Influence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose on the rheological and microstructural characteristics of whole wheat flour dough and quality of puri[J]. Journal of Texture Studies,2009,40(2):172−191. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4603.2009.00175.x
[29] SHARMA R, OBEROI D P S, SOGI D S, et al. Effect of sugar and gums on the pasting properties of cassava starch[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2009,33(3):401−414. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4549.2008.00283.x
[30] GRAÇA C, FRADINHO P, SOUSA I, et al. Impact of Chlorella vulgaris on the rheology of wheat flour dough and bread texture[J]. LWT,2018,89:466−474. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.11.024
[31] KAYA Y, SAHIN M. Non-parametric stability analyses of dough properties in wheat[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015,35:509−515. doi: 10.1590/1678-457X.6642
[32] ZHANG T, CUI Q, ZHANG F, et al. Effects of microencapsulated glucose oxidase on wheat flour dough properties and Chinese steamed bread quality[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2018,53(7):1657−1665.
[33] LINDARTE ARTUNDUAGA J, GUTIÉRREZ L F. Effects of replacing fat by betaglucans from Ganoderma lucidum on batter and cake properties[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,56(1):451−461. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3507-1
[34] MA S, WANG X X, ZHENG X L, et al. Improvement of the quality of steamed bread by supplementation of wheat germ from milling process[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2014,60(3):589−594. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2014.07.010
[35] WU M Y, SHIAU S Y. Effect of the amount and particle size of pineapple peel fiber on dough rheology and steamed bread quality[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2015,39(6):549−558. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.12260
[36] MEZAIZE S, CHEVALLIER S, LE BAIL A, et al. Optimization of gluten-free formulations for french-style breads[J]. Journal of Food Science,2009,74(3):E140−E146.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 何芮迪,翟立公,潘苗苗,何礼喜,尹雪斌,杨丽萍. 低血糖生成指数食物研究进展及其潜在利用价值. 中国科学:生命科学. 2025(03): 518-528 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
