Screening and Identification of Selenium-tolerant Marine Strain and the Antibacterial Activity of Se Nanoparticles It Synthesized
-
摘要: 本研究从海洋菌株中筛选出一株对Na2SeO3 具有高还原能力的新型菌株,为纳米硒的生物合成提供新的还原体系。首先,对41株来自北冰洋沉积物的海洋菌株进行筛选,通过初筛、复筛,得到对Na2SeO3还原较强的菌株,并对其进行了种属鉴定。随后利用筛选出的菌株进行纳米硒(Selenium nanoparticles,SeNPs)的生物合成。利用傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FTIR),扫描电镜(Scanning electron microscope,SEM),X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction,XRD),粒度分析等对该菌株生物合成的SeNPs进行了表征,并对其抗菌活性进行了研究。结果表明,72号菌株对Na2SeO3的耐受能力最强,在300 mmol/L浓度条件下能够正常生长且将Na2SeO3还原为纳米硒。经鉴定该菌株为芽孢杆菌,命名为Bacillus sp. Q72。利用该菌株合成的纳米硒为球形颗粒,平均粒径为169.3 nm,电位为−48.1±0.5 mV,其表面存在着氨基和羟基等官能团。Bacillus sp. Q72菌株生物合成的纳米硒对大肠杆菌表现出更优的抑制活性,当纳米硒浓度为200 μg/mL时,对大肠杆菌的抑制率达到92.1%。Abstract: In this study, a novel strain with high Na2SeO3 reducing ability was screened from marine strains, providing a new reduction system for the biosynthesis of Se nanoparticles (SeNPs). Firstly, 41 marine strains from Arctic Ocean sediments were screened, and a strain with high selenium-tolerant was obtained and species identified. Subsequently, the screened marine strain was used for the biosynthesis SeNPs and the SeNPs were characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and particle size analysis. Furthermore, the antibacterial activities of SeNPs were also determined. The results showed that strain 72 had the strongest tolerance to Na2SeO3, which could grow in the presence of 300 mmol/L Na2SeO3 and reducing it to brick red SeNPs. Subsequently, strain 72 was identified and named as Bacillus sp. Q72. The SeNPs biosynthesized by this strain were spherical particles with an average size of 169.3 nm and a potential of −48.1±0.5 mV. There were amino and hydroxyl groups on their surface. The SeNPs produced by Bacillus sp. Q72 showed better inhibitory activity against E. coli. When the concentration of SeNPs was 200 μg/mL, the inhibitory rate against E. coli reached 92.1%.
-
Keywords:
- marine strains /
- Se nanoparticles /
- biosynthesis /
- antibacterial activity /
- screening /
- identify
-
纳米硒是一种具有纳米级尺寸的红色单质硒[1],具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗病毒以及抗癌等作用[2]。纳米硒合成方法主要有化学合成、生物合成以及物理合成。化学合成法是以无机硒如:SeO2、Na2SeO3、H2SeO3等为硒源,利用还原剂将其还原成单质硒[3];物理法常利用机械作用,包括摩擦、挤压、剪切、冲击、超声等处理固体原料制备纳米硒,或通过升华冷凝法改变硒分子间作用力制备纳米硒[4];生物法制备纳米硒,是利用微生物生长发育过程产生的有效物质还原硒盐(Na2SeO3、H2SeO3等),或利用植物提取物中的有效物质将Na2SeO3还原成红色纳米硒。
由于化学合成法在制备过程中会使用到对人体和环境造成危害的有毒化学物质,物理法存在能量消耗大,易污染样品等问题,而生物合成法是在绿色环保理念下发展起来的一种简单、安全、更为环保的合成方法[5],因此备受人们关注,利用生物法合成纳米硒已成为国内外制备纳米硒的新趋势[6]。此外,生物合成的纳米硒生物相容性好,细胞活性高,尺寸小,粒径均匀,稳定性强[7],在食品包装[8]、功能性保健品[9]、抗肿瘤[10]、抗癌[11−12]、药物开发[13]等领域有着广泛的应用。
迄今为止,研究发现多种细菌、真菌等能够将硒酸盐或亚硒酸盐还原为单质硒,如枯草芽孢杆菌亚种 Bacillus subtilis subspecies stercoris XP、枯草芽孢杆菌Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Lxz41、链霉菌Streptomyces sp. ES2-5等[14−16],但来自海洋的菌株目前仅有少量报道[17−20]。海洋环境的特殊性和海洋物种复杂的生态功能赋予了海洋微生物不同于陆地微生物的代谢途径和适应机制[21]。海洋已成为具有特殊功能细菌的重要来源[22]。为了寻找具有高耐硒能力和还原能力的新菌株,本研究以41株来自北冰洋沉积物的菌株为研究对象,通过初筛和复筛,筛选出一株对Na2SeO3具有高耐受力和还原还原能力的菌株,并对其进行了鉴定。此外,对利用该菌株还原制备的纳米硒进行了表征,并进一步考察了其对两种食源性病原菌的抑菌活性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
41株来自北冰洋深海沉积物的海洋菌株 −80 ℃冻存于本实验;酵母粉 英国OXOID;蛋白胨 北京奥博星生物技术有限公司;NaCl(>99%)、琼脂 上海生工有限公司;无水乙醇(AR)、丙酮(AR)、溴化钾(SP)、蔗糖、盐酸、三羟甲基氨基甲烷盐酸溶液 天津市科密欧试剂有限公司;亚硒酸钠(Na2SeO3) 阿法埃莎(中国)化学有限公司。
AvantiJ-30高速低温冷冻离心机 美国Beckman公司;JY92-ⅡN超声波细胞破碎仪 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;D2F-2060真空干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;FTIR傅里叶红外光谱仪 北京北分瑞利分析仪器公司;XRD-6000型X-射线衍射仪 日本岛津公司;ZHWY-2102C恒温摇床 上海智城分析仪器公司;HORIBASZ-100激光粒度分析仪 日本HORIBA公司;ZWYD-2403恒温培养振荡器 上海智城分析仪器制造有限公司;ZXRD-A7080全自动新型鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;BXM-30R高温灭菌锅 上海博讯实业有限公司;920-Ⅱ洁净工作台 上海智城分析仪器公司;Milli-Qacademic超纯水制备系统 美国Millipore公司;JA50003N型电子天平 上海静科仪器公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌株的筛选
将冻存于−80 ℃的41株海洋菌株进行活化,随后用接种环挑取菌液于LB固体培养基(10 g/L NaCl、10 g/L蛋白胨、5 g/L酵母粉、1 L过膜海水、15 g/L琼脂粉)上划线,33 ℃倒置培养48 h得到单菌落。随后从LB固体培养基平板上挑取单菌落,转移到装有10 mL LB液体培养基的试管中,置于恒温摇床上180 r/min培养24 h。按照3%(v/v)的接种量将各菌液分别加入到含有150 mmol/L亚硒酸钠的LB液体培养基中,33 ℃,180 r/min条件下振荡培养24 h,观察体系颜色变化,筛选出能够还原Na2SeO3产纳米硒的菌株。随后,再次将能够还原Na2SeO3的菌株按照3%(v/v)的接种量加入到含有150 mmol/L Na2SeO3的LB液体培养基中,33 ℃,180 r/min条件下振荡培养48 h,测其OD值,每个菌株平行测定三次。根据OD值判断菌株在Na2SeO3存在条件下的生长情况,挑选出耐硒能力强的菌株。
将初筛出的各菌株菌液,按照3%(v/v)的接种量加入到含有10、20、40、60、80、100、200、300、400和500 mmol/L Na2SeO3的LB液体培养基中,33 ℃,180 r/min条件下振荡培养24 h,根据各菌株对不同溶度Na2SeO3的还原情况,复筛出还原能力最强的菌株。
1.2.2 菌株对亚硒酸钠还原能力的测定
将复筛得到的菌株进行活化,按照3%(v/v)的接种量加入到LB液体培养基中,再加入Na2SeO3溶液使体系中Na2SeO3的终浓度为5 mmol/L。将接好菌的LB培养基置于恒温摇床中33 ℃,180 r/min振荡培养,每隔2 h取1 mL上层清液于试管中,加入1 mL浓度为1 mol/L的抗坏血酸溶液,再加入1 mL浓度为4 mol/L的HCl溶液,在室温条件下静置10 min,在500 nm条件下,利用紫外分光光度计测量吸光度,将其带入标准曲线,得到体系中剩余Na2SeO3的量。
1.2.3 菌株鉴定
将冻存于−80 ℃的72号菌株进行活化,随后用接种环挑取菌液于固体培养基划线,最后倒置于33 ℃恒温培养箱中培养24~48 h,观察并记录菌落形态特征。选择长势较好的单菌落,置于内含10 μL无菌水的离心管中,100 ℃煮沸10 min,12000 r/min离心2 min,得到细菌DNA。以提取的DNA为模板,采用细菌通用引物[23]正向引物8F(5’-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3’)、反向引物1492R(5’-TACGGCTACCTTGTTAGGACT-3’),对菌株进行16S rDNA扩增。PCR扩增反应体系总体积为50 μL,包括:10 μmol/L 8F,10 μmol/L 1492R,10 ng/μL Template DNA,200 μmol/L dNTP Mixture,5 U/μL rTaq,4.0 μL 1×10 Loading Buffer,39.75 μL dd H2O。
PCR反应条件为:95 ℃预变性5 min,94 ℃变性30 s,退火50 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,循环以上条件32次;72 ℃延伸10 min,于4 ℃保存。扩增产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后,送至生工生物工程(上海)有限公司进行测序。
1.2.4 纳米硒的制备与分离
将72号菌株以3%(v/v)的接种量加入到装有LB液体培养基的1000 mL锥形瓶中,33 ℃,180 r/min培养24 h,10000 r/min离心10 min,然后倒出上清液,以同样的条件对上清液再次离心。合并两次离心的沉淀转移至离心管,用生理盐水清洗3次,每次洗完均以12000 r/min离心10 min去上清,沉淀用3 mL无菌水重悬,在冰浴条件下超声破壁30 min。破壁完成后用Tris-HCl和SDS(pH=8.3)溶液洗涤两次,12000 r/min条件离心10 min,再用无菌水洗涤一次,然后用无菌水重悬,按V(重悬液):V(正辛醇)为2:1的比例加入正辛醇,混匀后12000 r/min离心10 min,沉淀即为纳米硒颗粒,分别用氯仿、乙醇和无菌水各洗涤一次,12000 r/min离心10 min,沉淀用冷冻干燥仪干燥。
1.2.5 纳米硒的表征
采用傅里叶红外光谱仪测定样品的结构,将SeNPs粉末与溴化钾混合压片,室温下在400~4000 cm−1范围内测量其吸收光谱,扫描速度为5 kHz。采用X-射线衍射仪对制得的样品结晶状态进行分析,将SeNPs粉末置于载玻片的样品槽中,进行表面压片,随后将其置于X射线衍射仪中进行测试,扫描角度为10~80°,扫描速度为5°/min。采用扫描电子显微镜观察SeNPs的形态及组成,用乙醇分散制样。利用SZ-100纳米粒度仪测定SeNPs的粒径大小、分布以及Zeta电位。
1.2.6 纳米硒的抑菌活性
称取菌株还原得到的纳米硒0.2 g溶解于100 mL超纯无菌水,得到2 mg/mL的纳米硒母液,超声振荡混匀,过膜除菌。随后将纳米硒母液分别稀释至20、50、100、150、200 µg/mL的浓度梯度。将OD600=0.5的大肠杆菌和李斯特菌各100 µL分别加入96孔板中,再将不同浓度的纳米硒溶液接至各孔,37 ℃恒温培养4 h(三组平行实验及一组空白对照实验)。将实验组和空白组中的细菌悬浊液用无菌水稀释至原液的10−1、10−2、10−3和10−4,随后分别取2.5 μL稀释后的菌悬液滴至LB固体培养基平板,37 ℃过夜培养,观察并计数菌落形成单位(Colony Forming Unit,CFU)。根据空白组和不同浓度实验组的菌落数,依据式(1)计算SeNPs对两种细菌的抑制率:
(1) 1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS 27.0统计学软件进行数据统计分析,采用单样本T检验进行显著性分析。P<0.01表示差异极显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 耐硒海洋菌株的筛选
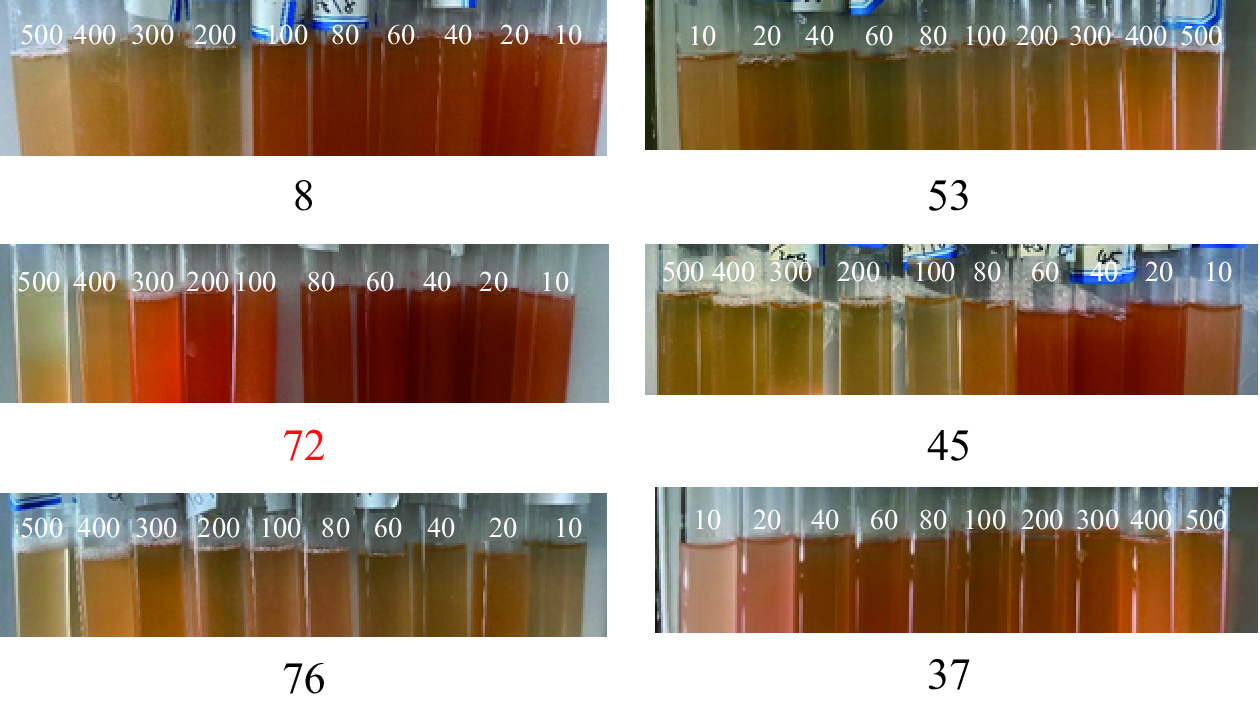
将实验室保存的41株分离自北冰洋沉积物的菌株加入到含有150 mmol/L Na2SeO3的LB液体培养基中进行培养,24 h后发现有30株能够还原Na2SeO3产生砖红色的纳米硒。随后检测了这30株菌在150 mmol/L Na2SeO3存在条件下48 h后的生长情况,结果如表1所示。27号和58号菌株的生长明显受到抑制,培养48 h后其OD值明显小于其它菌株,亦小于这两株菌株正常生长48 h后的OD值。6株菌株的OD值较高,分别为8号、37号、45号、53号、72号、76号,因此选择这6株菌株进行复筛。
表 1 初筛出的30株菌株在LB培养基和含有Na2SeO3 LB培养基中生长48 h后的OD值Table 1. OD values of 30 strains initially screened after 48 hours of growth in LB medium and LB medium containing Na2SeO3菌号 OD值
(LB)OD值
(含有
Na2SeO4的LB)菌号 OD值
(LB)OD值
(含有
Na2SeO4的LB)2 2.47±0.11 2.39±0.07 36 2.13±0.05 1.48±0.08 5 2.36±0.07 2.24±0.12 37 2.68±0.06 2.61±0.11 6 2.25±0.05 1.86±0.15 40 2.18±0.15 1.75±0.10 8 2.64±0.13 2.55±0.08 45 2.84±0.10 2.77±0.07 12 2.32±0.09 1.92±0.10 53 2.64±0.07 2.58±0.08 13 2.28±0.06 1.99±0.05 58 2.45±0.08 0.62±0.13 14 2.31±0.07 2.09±0.10 59 2.17±0.08 1.76±0.09 17 2.16±0.12 1.54±0.15 66 2.58±0.10 2.29±0.15 21 2.68±0.10 2.50±0.17 67 2.74±0.07 2.43±0.11 22 2.24±0.06 1.59±0.09 70 2.52±0.14 2.13±0.08 25 2.39±0.14 2.09±0.07 71 2.63±0.06 2.15±0.10 27 2.67±0.06 1.03±0.05 72 2.90±0.04 2.81±0.07 28 2.22±0.08 1.57±0.11 73 2.36±0.09 1.70±0.13 33 2.71±0.10 2.47±0.13 74 2.35±0.11 2.06±0.07 34 2.24±0.12 1.71±0.09 76 2.78±0.12 2.67±0.15 图1为8号、53号、72号、45号、76号、37号菌株分别在含有10、20、40、60、80、100、200、300、400和500 mmol/LNa2SeO3的LB液体培养基中的生长情况,由图可见,72号菌株对Na2SeO3的还原能力最强。当Na2SeO3浓度为300 mmol/L时,体系颜色依然较红,说明该菌株能够在较高浓度的Na2SeO3存在下生长且将其还原为砖红色纳米硒。因此,本实验选择了72号菌株作为生物合成纳米硒的菌株。
2.2 72 号菌株还原 Na2SeO3的能力
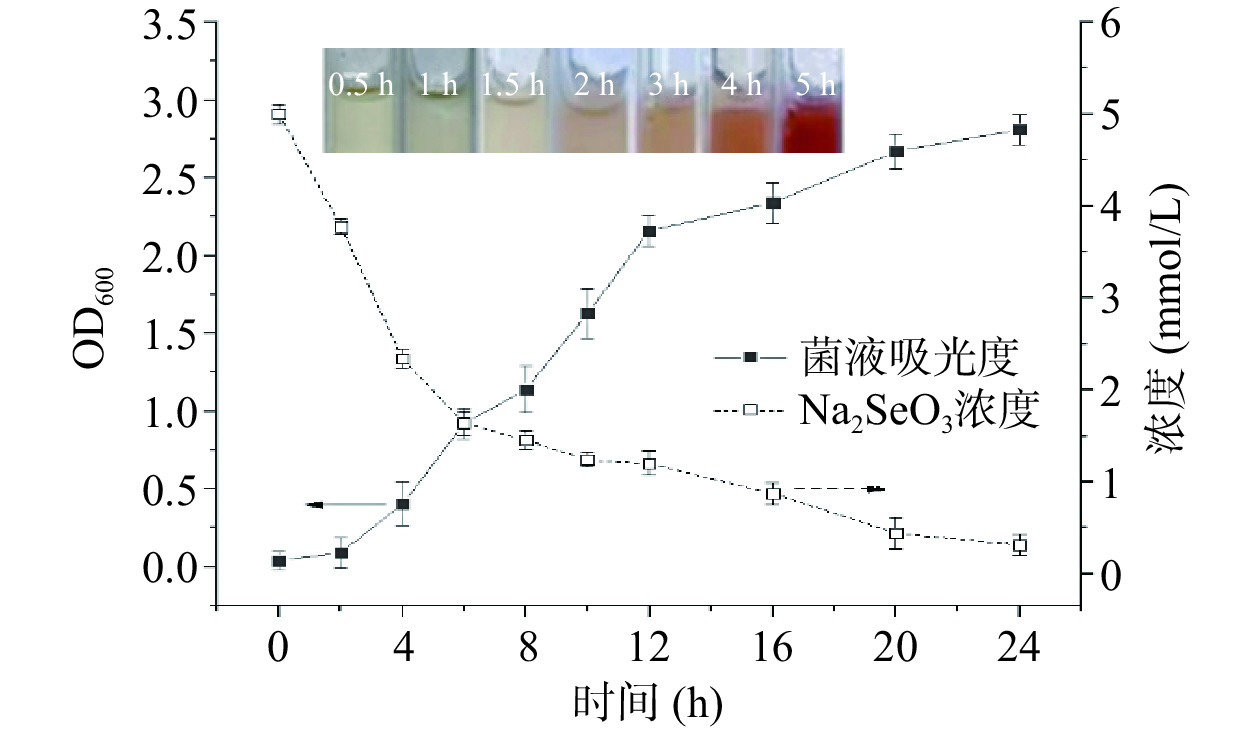
通过监测还原过程中体系Na2SeO3浓度的变化,定量研究了72号菌株对的Na2SeO3的还原能力,结果如图2所示。由图2可知,培养2 h后,体系已开始显示出红色,表明有纳米硒的生成,4 h后,体系中Na2SeO3的浓度已低于原始浓度的50%。72号菌对Na2SeO3的还原主要在其对数生长期进行。
2.3 菌株的鉴定
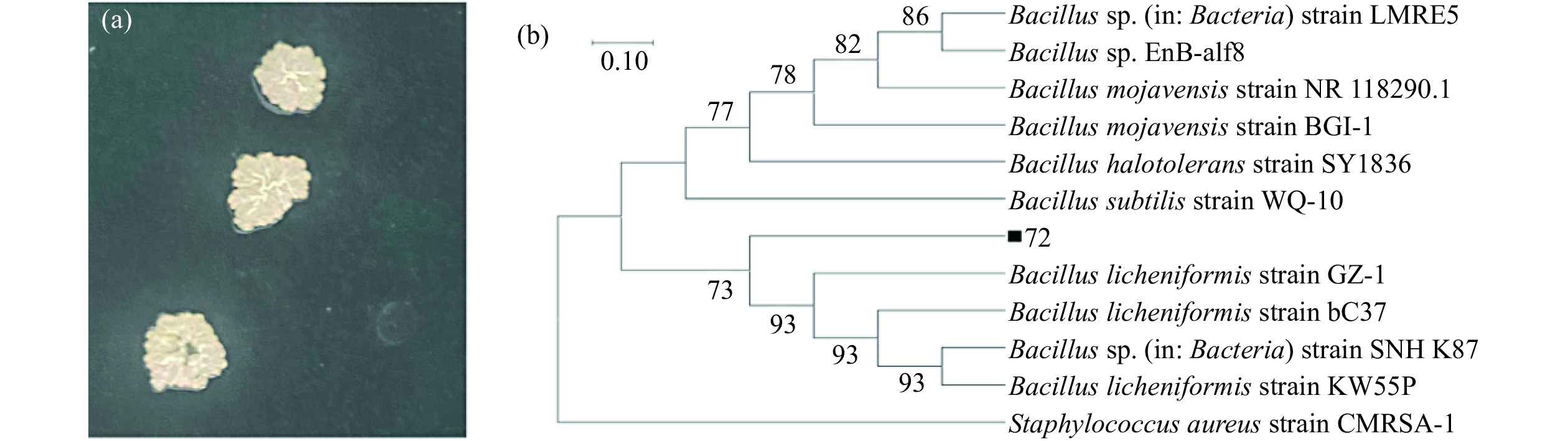
图3为72号菌株的聚落形态图和系统发育树。由图3(a)可知菌落呈乳白色、不透明,菌落边缘出现褶皱和收缩并向中间膨胀,采摘细菌时存在粘液分泌物。将72号菌株的16S rDNA序列与GenBank数据库中的16S rDNA序列做相似性比对,随后利用MEGA(5.0)中的邻接法构建系统发育树[24],结果如图3(b)所示。72号菌株的16SrDNA序列与芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)相关菌株的16SrDNA序列相似性较高,聚集为一簇,由此确定72号菌株为芽孢杆菌,将其命名为Bacillus sp. Q72。
2.4 纳米硒表征
2.4.1 红外光谱分析
利用傅里叶红外光谱检测纳米硒的表面官能团种类,结果如图4所示。在2940,1654,1538,1429,1077,748 cm−1,位置出现明显的特征吸收峰,其中在2940 cm−1的特征峰是由脂肪族中C-H伸缩振动产生;1654 cm−1处的峰由酰胺基中的C=O(酰胺Ⅰ带)伸缩振动产生;在1538 cm−1处的吸收峰是由苯环骨架的双键伸缩振动产生;1429 cm−1处的吸收峰是C-H变形振动造成的;1077 cm−1吸收峰可能是由胺中的C-N伸缩振动造成的;748 cm−1处具有特征吸收峰,属于取代苯环的弯曲振动吸收[25−27]。傅里叶红外光谱结果表明,由72号菌株还原Na2SeO3所得到的纳米硒表面存在着氨基和羟基等基团,说明在纳米硒合成过程中,含有这些官能团的生物分子,如脂类、蛋白质、碳水化合物等发挥着重要作用。
2.4.2 扫描电镜分析
图5为Bacillus sp. Q72及其产纳米硒的扫描电镜结果。由图5可见,72号菌株呈短棒状,长度约为1.0 μm左右(图5a),其产生的纳米硒为规则的球形颗粒(图5b)。图5c能谱分析结果显示,图5b黄色圆圈处的元素组成中包含35.13%的Se元素,证明菌体附近白色球状颗粒为纳米硒颗粒。
2.4.3 XRD分析
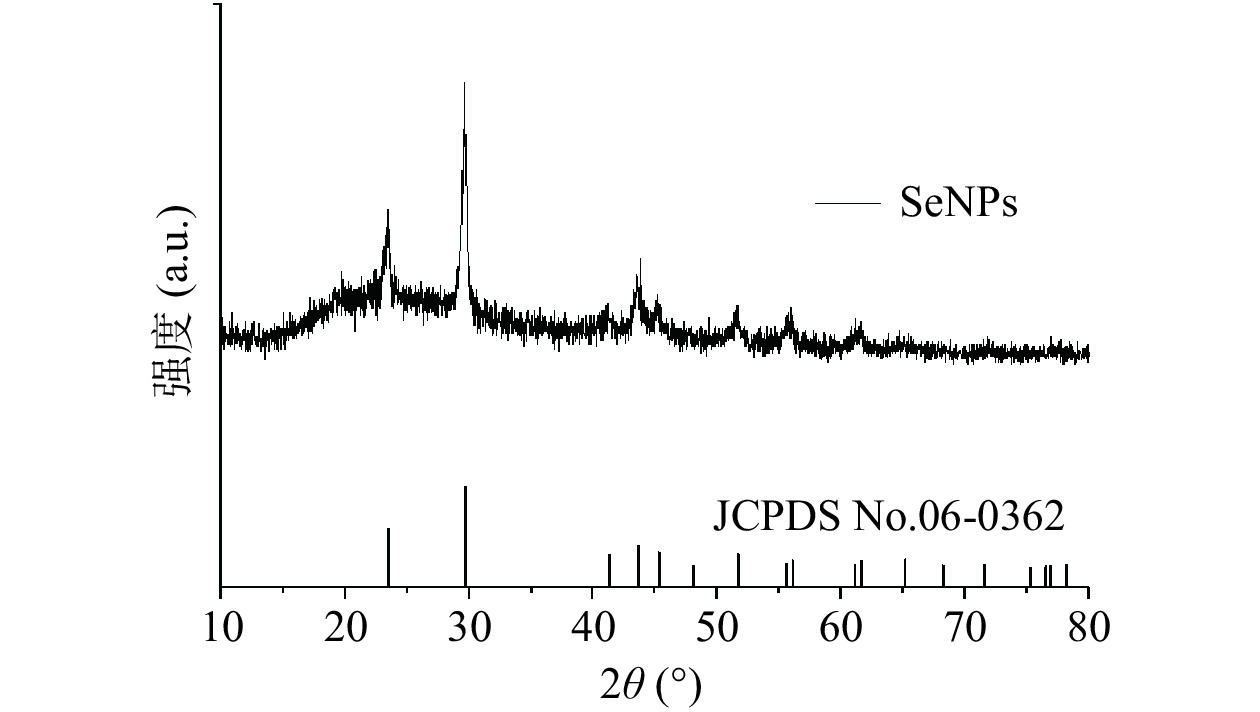
纳米硒的XRD光谱如图6所示,由图6可知由Bacillussp.Q72还原的纳米硒在20~30°之间具有较强的射峰,2θ值处显示出23.4°(100)和29.6°(101)处的尖峰,显示纳米颗粒结构中存在结晶硒[28]。此外,与纳米硒的六方形标准卡(JCPDS No.06-0362)对比可知,在41.2°、43.6°、45.4°、51.7°、55.9°、61.5°和65.4°处都有明显的衍射峰,这与六方晶形结构的(110)、(102)、(111)、(201)和(202)晶面一一对应[29]。由XRD图可以看出与(101)面对应的29.6°处的衍射峰强度最大,72号菌株合成的纳米硒晶体颗粒是以(101)面为主导。
2.4.4 粒度和电位分析
纳米硒的粒径、粒径分布及Zeta电位如图7所示。研究表明5~200 nm的纳米硒具有更加明显的生物效应[30−32],Zeta电位越小,其生物活性越好[33]。到目前为止,已报道多种芽孢杆菌在有氧或厌氧条件下能够将亚硒酸盐还原成SeNPs,如Ullah等[26]利用Bacillus subtilis BSN313生物合成的SeNPs平均粒径为590 nm,电位为−26.9 mV;Bao等[34]报道Bacillus oryziterrae ZYKT菌株生物合成SeNPs的粒径主要分布在100~500 nm之间;Lampis等[35]利用Bacillus mycoides SeITE01菌株合成的SeNPs粒径分布在50~400 nm。Bacillus sp. Q72菌株生物合成的纳米硒的平均粒径为169.3 nm,电位为−48.1±0.5 mV,其粒径分布较窄,具有良好的稳定性,可作为生物材料进行进一步的应用。
2.5 抑菌活性
图8为Bacillus sp. Q72生物合成的纳米硒对大肠杆菌和李斯特菌的抑菌活性图。大肠杆菌是一种重要的人畜共患致病菌,属于兼性厌氧型的革兰氏阴性杆菌[36−37],李斯特菌是我国主要的食源性致病菌之一,是一种兼性厌氧型的革兰氏阳性菌[38−39]。图8a~图8b用20~200 μg/mL不同浓度的纳米硒处理后,大肠杆菌和李斯特菌的菌落形成情况。从中可见,随着纳米硒浓度的增加,相同稀释倍数下,各菌液中的菌落数明显减小,纳米硒对两种致病菌的生长均表现出明显的抑制。图8c是纳米硒对大肠杆菌和李斯特菌的抑制率随浓度变化图,与对照组相比(0 μg/mL),Bacillus sp. Q72还原产生的纳米硒对两种致病菌的抑制率随浓度的增加而提高。纳米硒对大肠杆菌表现出更加明显的抑制活性,在20~150 μg/mL的浓度范围中对大肠杆菌的抑制率表现出极显著差异(P<0.01),在50~100 μg/mL浓度范围内对李斯特菌的抑制率表现出极显著差异(P<0.01)。纳米硒浓度为200 μg/mL时,其对大肠杆菌的抑制率可达到92.1%。
3. 结论
本研究通过初筛和复筛,从41株来自北冰洋深海沉积物的海洋菌株中,筛选出了一株对Na2SeO3还原能力较强的菌株。经鉴定,该菌株为芽孢杆菌,将其命名为Bacillus sp. Q72,其还原Na2SeO3产生的纳米硒为球形颗粒,平均粒径为169.3 nm,电位为−48.1±0.5Mv,具有较好的稳定性。Bacillus sp. Q72菌株合成的纳米硒对大肠杆菌和李斯特菌的生长均有明显抑制作用,对革兰氏阴性菌大肠杆菌的抑制效果更为明显。傅里叶红外光谱测定表明,纳米硒颗粒表面存在着氨基和羟基等基团,说明在纳米硒合成过程中,含有这些官能团的生物分子,如脂类、蛋白质、碳水化合物等发挥着重要作用。有关介导Bacillus sp. Q72合成纳米硒的的生物活性分子及其对亚硒酸盐的合成机制,将在后续实验中进一步深入探究。
-
表 1 初筛出的30株菌株在LB培养基和含有Na2SeO3 LB培养基中生长48 h后的OD值
Table 1 OD values of 30 strains initially screened after 48 hours of growth in LB medium and LB medium containing Na2SeO3
菌号 OD值
(LB)OD值
(含有
Na2SeO4的LB)菌号 OD值
(LB)OD值
(含有
Na2SeO4的LB)2 2.47±0.11 2.39±0.07 36 2.13±0.05 1.48±0.08 5 2.36±0.07 2.24±0.12 37 2.68±0.06 2.61±0.11 6 2.25±0.05 1.86±0.15 40 2.18±0.15 1.75±0.10 8 2.64±0.13 2.55±0.08 45 2.84±0.10 2.77±0.07 12 2.32±0.09 1.92±0.10 53 2.64±0.07 2.58±0.08 13 2.28±0.06 1.99±0.05 58 2.45±0.08 0.62±0.13 14 2.31±0.07 2.09±0.10 59 2.17±0.08 1.76±0.09 17 2.16±0.12 1.54±0.15 66 2.58±0.10 2.29±0.15 21 2.68±0.10 2.50±0.17 67 2.74±0.07 2.43±0.11 22 2.24±0.06 1.59±0.09 70 2.52±0.14 2.13±0.08 25 2.39±0.14 2.09±0.07 71 2.63±0.06 2.15±0.10 27 2.67±0.06 1.03±0.05 72 2.90±0.04 2.81±0.07 28 2.22±0.08 1.57±0.11 73 2.36±0.09 1.70±0.13 33 2.71±0.10 2.47±0.13 74 2.35±0.11 2.06±0.07 34 2.24±0.12 1.71±0.09 76 2.78±0.12 2.67±0.15 -
[1] 薛冰, 谢超新, 程水源, 等. 微生物转化法制备纳米硒及有机硒的研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(10):31−37. [XUE Bing, XIE Chaoxin, CHENG Shuiyuan, et al. Research progress in the preparation of nano-selenium and organic selenium by microbial transformation[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(10):31−37.] XUE Bing, XIE Chaoxin, CHENG Shuiyuan, et al. Research progress in the preparation of nano-selenium and organic selenium by microbial transformation[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47(10): 31−37.
[2] 苏华华, 王艳华. 纳米硒的制备及生物医学应用研究进展[J]. 生物技术通讯,2020,31(5):621−626. [SU Huahua, WANG Yanhua. Preparation of nanoselenium and research progress in biomedical applications[J]. Biotechnology Communications,2020,31(5):621−626.] SU Huahua, WANG Yanhua. Preparation of nanoselenium and research progress in biomedical applications[J]. Biotechnology Communications, 2020, 31(5): 621−626.
[3] 王振宇, 魏凌峰, 蔡杰, 等. 纳米硒的合成研究及其在食品与农业中的应用[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(12):26−33. [WANG Zhenyu, WEI Lingfeng, CAI Jie, et al. Synthesis of nanoselenium and its application in food and agriculture[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(12):26−33.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2021.12.spkj202112006 WANG Zhenyu, WEI Lingfeng, CAI Jie, et al. Synthesis of nanoselenium and its application in food and agriculture[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(12): 26−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2021.12.spkj202112006
[4] 苏文, 杨辉, 董腾达, 等. 纳米硒制备方法研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(1):280−284. [SU Wen, YANG Hui, DONG Tengda, et al. Research progress of nanoselenium preparation method[J]. Food Industry,2021,42(1):280−284.] SU Wen, YANG Hui, DONG Tengda, et al. Research progress of nanoselenium preparation method[J]. Food Industry, 2021, 42(1): 280−284.
[5] 杨颖, 厉舒祯, 范书伶, 等. 贪铜杆菌Cupriavidus sp. SHE细胞上清液合成纳米硒[J]. 生物工程学报,2020,36(6):1162−1169. [YANG Ying, LI Shuzhen, FAN Shuling, et al. Cupriavidus sp. Synthesis of nanoselenium from SHE cell supernatant[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology,2020,36(6):1162−1169.] YANG Ying, LI Shuzhen, FAN Shuling, et al. Cupriavidus sp. Synthesis of nanoselenium from SHE cell supernatant[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2020, 36(6): 1162−1169.
[6] 鲍唯. 细菌合成纳米硒微颗粒用于肿瘤化动力治疗[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学, 2020. [BAO Wei. Bacterial synthesis of nanoselenium microparticles for kinetic therapy of tumor[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2020.] BAO Wei. Bacterial synthesis of nanoselenium microparticles for kinetic therapy of tumor[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[7] 殷婷婷, 李志慧, 苏佳贺, 等. 生物法制备纳米硒的研究进展和应用前景[J]. 中国农学通报,2022,38(8):33−41. [YIN Tingting, LI Zhihui, SU Jiahe, et al. Research progress and application prospect of biological preparation of nanoselenium[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2022,38(8):33−41.] YIN Tingting, LI Zhihui, SU Jiahe, et al. Research progress and application prospect of biological preparation of nanoselenium[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(8): 33−41.
[8] 刘明珠, 魏凌峰, 蔡杰, 等. 多糖-纳米硒在食品包装中应用的研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(3):1−7. [LIU Mingzhu, WEI Lingfeng, CAI Jie, et al. Research progress on the application of polysaccharide-nanoselenium in food packaging[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(3):1−7.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.3.spkj202203001 LIU Mingzhu, WEI Lingfeng, CAI Jie, et al. Research progress on the application of polysaccharide-nanoselenium in food packaging[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 47(3): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.3.spkj202203001
[9] 叶园园, 蔡杰, 李楠, 等. 纳米硒在食品领域中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(10):11−18. [YE Yuanyuan, CAI Jie, LI Nan, et al. Research progress on the application of nanoselenium in the field of food[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(10):11−18.] YE Yuanyuan, CAI Jie, LI Nan, et al. Research progress on the application of nanoselenium in the field of food[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(10): 11−18.
[10] 刘晓庆, 魏凌峰, 贾继来, 等. 纳米硒多糖载体的构建及其抗肿瘤应用的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(21):454−460. [LIU Xiaoqing, WEI Lingfeng, JIA Jilai, et al. Research progress on the construction of nanoselenium polysaccharide carriers and their anti-tumor applications[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(21):454−460.] LIU Xiaoqing, WEI Lingfeng, JIA Jilai, et al. Research progress on the construction of nanoselenium polysaccharide carriers and their anti-tumor applications[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(21): 454−460.
[11] 王皓, 王玉丽, 孙洁洁, 等. 纳米硒在医药领域中的应用研究进展[J]. 国际药学研究杂志,2020,47(5):337−341,346. [WANG Hao, WANG Yuli, SUN Jiejie, et al. Research progress on the application of nanoselenium in the field of medicine[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research,2020,47(5):337−341,346.] WANG Hao, WANG Yuli, SUN Jiejie, et al. Research progress on the application of nanoselenium in the field of medicine[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2020, 47(5): 337−341,346.
[12] 周驰. 纳米硒的生物合成及其抑菌活性的研究[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2018. [ZHOU Chi. Biosynthesis of nanoselenium and its bacteriostatic activity[D]. Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University, 2018.] ZHOU Chi. Biosynthesis of nanoselenium and its bacteriostatic activity[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2018.
[13] 杨锐, 余雍和, 程水源, 等. 耐硒芽孢杆菌的筛选及其亚硒酸盐还原机制的探究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(22):105−111. [YANG Rui, YU Yonghe, CHENG Shuiyuan, et al. Screening of Bacillus selenium-resistant and its reduction mechanism of selenite[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(22):105−111.] YANG Rui, YU Yonghe, CHENG Shuiyuan, et al. Screening of Bacillus selenium-resistant and its reduction mechanism of selenite[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(22): 105−111.
[14] 朱燕云, 孔祥平, 吴娥娇, 等. 耐高盐枯草芽孢杆菌XP合成球形纳米硒及其抑制草莓病原真菌生物活性[J]. 生物工程学报,2021,37(8):2825−2835. [ZHU Yanyun, KONG Xiangping, WU Ejiao, et al. Synthesis of spherical nanoselenium byBacillus subtilis XP and its inhibition of biological activity of strawberry pathogenic fungi[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology,2021,37(8):2825−−2835.] ZHU Yanyun, KONG Xiangping, WU Ejiao, et al. Synthesis of spherical nanoselenium by Bacillus subtilis XP and its inhibition of biological activity of strawberry pathogenic fungi[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2021, 37(8): 2825−−2835.
[15] 利军, 马英辉, 卢美欢. 纳米硒合成细菌Lxz-41的鉴定、培养条件优化及其在富硒猕猴桃栽培中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(21):110−117. [LI Jun, MA Yinghui, LU Meihuan. Identification and optimization of culture conditions of nanoselenium synthetic bacteria lxz-41 and its application in the cultivation of selenium-rich kiwifruit[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(21):110−117.] LI Jun, MA Yinghui, LU Meihuan. Identification and optimization of culture conditions of nanoselenium synthetic bacteria lxz-41 and its application in the cultivation of selenium-rich kiwifruit[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(21): 110−117.
[16] TAN Y Q, YAO R, WANG R, et al. Reduction of selenite to Se(0) nanoparticles by filamentous bacterium Streptomyces sp. ES2-5 isolated from a selenium mining soil[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2016,15:157. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0554-z
[17] ZHANG L Y, LI Z T, ZHANG L, Lei Z, et al. High-efficiency reducing strain for producing selenium nanoparticles isolated from marine sediment[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(19):11953. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911953
[18] ASHENGROPH M, HOSSEINI S R. A newly isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SRB04 for the synthesis of selenium nanoparticles with potential antibacterial properties[J]. International Microbiology: The Official Journal of the Spanish Society for Microbiology,2020,24:103−114.
[19] SANDHYA M V S, RAJKUMAR K, BURGULA S. Efficient eco-friendly approach towards bimetallic nanoparticles synthesis and characterization using Exiguobacterium aestuarii by statistical optimization[J]. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews,2019,12:420−434. doi: 10.1080/17518253.2019.1687762
[20] Wang T, Zhao H Y, Bi Y G, et al. Preparation and antioxidant activity of selenium nanoparticles decorated by polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme[J]. Journal of Food Science,2021,86:977−986. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15605
[21] BAKER S, HARINI B P, RAKSHITH D, et al. Marine microbes:invisible nanofactories[J]. Journal of Pharmacy Research,2013,6:383−388. doi: 10.1016/j.jopr.2013.03.001
[22] CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports,2020,37:175−223. doi: 10.1039/C9NP00069K
[23] 冯震, 蒋波, 李芳, 等. 细菌DNA特征序列鉴定法在常见种属中的鉴定水平研究[J]. 药物分析杂志,2019,39(11):1924−1932. [FENG Zhen, JIANG Bo, LI Fang, et al. Identification level of bacterial DNA signature sequence identification method in common species[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2019,39(11):1924−1932.] FENG Zhen, JIANG Bo, LI Fang, et al. Identification level of bacterial DNA signature sequence identification method in common species[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2019, 39(11): 1924−1932.
[24] KURODA M, YAMASHITA M, MIWA E, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of the srdBCA operon, encoding the respiratory selenate reductase complex, from the selenate-reducing bacterium Bacillus selenatarsenatis SF-1[J]. Journal of bacteriology,2011,193(9):2141−2148. doi: 10.1128/JB.01197-10
[25] YILAMZ M T, ISPIRLI H, TAYLAN O, et al. A green nano-biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles with Tarragon extract:Structural, thermal, and antimicrobial characterization[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,141:110969. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.110969
[26] ULLAH A, YIN X Y, WANG F H, et al. Biosynthesis of selenium nanoparticles (via Bacillus subtilis BSN313), and their isolation, characterization, and bioactivities[J]. Molecules,2021,26:5559. doi: 10.3390/molecules26185559
[27] LI S K, SHEN Y H, XIE A J, et al. Rapid, room-temperature synthesis of amorphous selenium/protein composites using Capsicum annuum L extract[J]. Nanotechnology,2007,18:405101. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/18/40/405101
[28] AN C H, TANG K B, LIU X M, et al. Large-scale synthesis of high quality trigonal selenium nanowires[J]. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2003,17:3250−3255.
[29] SENTHIL K C K, AGILAN S, VELAUTHAPILLAI D, et al. Synthesis and characterization of selenium nanowires[J]. Nanotechnology,2011,18:405101.
[30] 王丽红, 杨辉, 苏文, 等. 植物乳杆菌LP21绿色合成纳米硒及对溶藻弧菌的抑菌活性[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(2):217−223. [WANG Lihong, YANG Hui, SU Wen, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum LP21 green synthetic nanoselenium and its bacteriostatic activity against Vibrio algaelyticum[J]. Food Science,2022,43(2):217−223.] WANG Lihong, YANG Hui, SU Wen, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum LP21 green synthetic nanoselenium and its bacteriostatic activity against Vibrio algaelyticum[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(2): 217−223.
[31] PENG D G, ZHANG J S, LIU Q L, et al. Size effect of elemental selenium nanoparticles (Nano-Se) at supranutritional levels on selenium accumulation and glutathione S-transferase activity[J]. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry,2007,101(10):1457−1463. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.06.021
[32] TANG L, JIA X E, JIANG X F, et al. In vitro study on the individual and synergistic cytotoxicity of adriamycin and selenium nanoparticles against Bel7402 cells with a quartz crystal microbalance[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2009,24(7):2268−2272. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2008.10.030
[33] YE X G, CHEN Z Z, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Construction, characterization, and bioactive evaluation of nano-selenium stabilized by green tea nano-aggregates[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,129:109475. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109475
[34] BAO P, XIAO K Q, WANG H J, et al. Characterization and potential applications of a selenium nanoparticle producing and nitrate reducing bacterium Bacillus oryziterrae sp. nov[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6:34054. doi: 10.1038/srep34054
[35] LAMPIS S, ZONARO E, BERTOLINI C, et al. Delayed formation of zero-valent selenium nanoparticles by Bacillus mycoides SeITE01 as a consequence of selenite reduction under aerobic conditions[J]. Microbial Cell Factories 2014, 13:35.
[36] 吴光燕, 陆海燕, 杨娟, 等. 一例大肠杆菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 农业开发与装备,2022,251(11):200−201. [WU Guangyan, LU Haiyan, YANG Juan, et al. Isolation and identification of a case of E. coli[J]. Agricultural Development and Equipment,2022,251(11):200−201.] WU Guangyan, LU Haiyan, YANG Juan, et al. Isolation and identification of a case of E. coli[J]. Agricultural Development and Equipment, 2022, 251(11): 200−201.
[37] ANANTH A, KEERTHIKA V, RUBY R M. Synthesis and characterization of nano-selenium and its antibacterial response on some important human pathogens[J]. Current Science,2019,116(2):285−290. doi: 10.18520/cs/v116/i2/285-290
[38] 万圣, 吕磊, 叶承华, 等. 1株非典型李斯特菌的鉴定分析[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2023,33(1):48−50,54. [WAN Sheng, LÜ Lei, YE Chenghua, et al. Identification and analysis of 1 strain of Atypical Listeria[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory and Laboratory,2023,33(1):48−50,54.] WAN Sheng, LÜ Lei, YE Chenghua, et al. Identification and analysis of 1 strain of Atypical Listeria[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory and Laboratory, 2023, 33(1): 48−50,54.
[39] 刘欣, 王真, 王园, 等. 持久性单增李斯特菌的抗逆表型及相关功能基因的研究进展[J/OL].食品与发酵工业: 1-9[2023-10-30]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.034407. [LIU Xin, WANG Zhen, WANG Yuan, et al. Research progress on anti-stress phenotypes and related functional genes of Listeria monocytogenes persistence[J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industry: 1-9[2023-10-30]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.034407.] LIU Xin, WANG Zhen, WANG Yuan, et al. Research progress on anti-stress phenotypes and related functional genes of Listeria monocytogenes persistence[J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industry: 1-9[2023-10-30]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.034407.





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



