Application of Photosensitive Chitosan-based Composite Films in the Preservation of Litopenaeus vannamei
-
摘要: -本文旨在研究一种复合膜-光动力技术的保鲜模式应用于南美白对虾,延缓对虾品质劣化。以壳聚糖为成膜基质,分别负载姜黄素、姜黄素/壳聚糖颗粒,制备了姜黄 素(PsC)和姜黄素/壳聚糖颗粒(PsG)复合膜,探究了两种复合膜的光敏特性,及其介导光动力杀菌(PsC-L/PsG-L)对南美白对虾的保鲜作用。分别使用PsC膜和PsG膜覆盖南美白对虾,经420 nm LED光源照射10 min后,在4 ℃贮藏0~4 d。贮藏期间,通过测定南美白对虾菌落总数、挥发性盐基氮、pH、质构、游离氨基酸等理化指标的变化,综合评价复合膜的保鲜作用。结果表明,在4 d的贮藏时间内,PsG-L与PsC-L可以影响南美白对虾菌落总数的生长。PsG-L可抑制南美白对虾TVB-N和pH的上升,延缓质地软化,保鲜效果优于PsC-L。PsG-L处理在2 d的贮藏时间内,保留鲜味氨基酸和降低苦味氨基酸含量的效果优于PsC-L。两种复合膜均具有光敏特性,在420 nm波长的光源驱动下具有光动力抑菌保鲜作用,对南美白对虾具有良好的保鲜效果。本研究成果为光动力非热杀菌技术在水产品保鲜中推广应用提供了支撑。Abstract: The purpose of this paper was to study the application of a fresh preservation mode of composite film-photodynamic technology to delay the quality deterioration of Litopenaeus vannamei. Composite films (PsC and PsG) were prepared by loading curcumin and curcumin/chitosan granules, respectively, onto chitosan as the film-forming matrix. For the preservation of Litopenaeus vannamei, the photosensitive characteristics of two composite films and their mediated photodynamic sterilization (PsC-L/PsG-L) were explored. Litopenaeus vannamei was covered by PsC films and PsG films, respectively, and kept them at 4 ℃ for 0~4 days after irradiating them with a 420 nm LED light source for 10 minutes. Throughout the storage period, the preservation impact of the composite films was examined comprehensively by assessing the changes in physicochemical indicators such as total bacterial colony, volatile salt nitrogen, pH, texture, and free amino acids in Litopenaeus vannamei. Results indicated that PsG-L and PsC-L might alter the development of microorganism of Litopenaeus vannamei over a 4 day storage period. PsG-L inhibited the increase of TVB-N and pH in Litopenaeus vannamei, delayed texture softening, and had a greater preservation effect than PsC-L. Over a 2 day storage period, PsG-L treatment was more successful than PsC-L in preserving fresh amino acids and reducing the amount of bitter amino acids. Both composite films exhibit photosensitive qualities and photodynamic inhibition of freshness induced by a light source with a wavelength of 420 nm, and they effectively preserve Litopenaeus vannamei. These findings give support for the promotion and deployment of photodynamic non-thermal sterilizing technology in the preservation of aquatic products.
-
Keywords:
- photodynamic /
- composite film /
- curcumin /
- chitosan /
- Litopenaeus vannamei
-
南美白对虾因其高蛋白、低脂肪的特性,受到广大消费者的青睐,产量和消费量逐年上升,2022年产养殖量达到210万吨[1]。目前,在运输及贮藏过程中,虾头黑变、微生物生长抑制不充分、营养成分流失严重是存在的主要问题[2−3]。为达到较好的贮藏效果,在低温条件下,复合气调保鲜、保鲜膜、生物制剂等方法用于保藏南美白对虾已逐渐成为趋势[4]。
单一成分的食品保鲜膜其功能存在局限性,负载不同类型的天然活性物质可提升薄膜的抑菌性、结构强度等[5−6]。以壳聚糖为成膜基质,添加姜黄素、花青素等天然成分,开发具有新的功能、可食用可降解、安全无毒的包装材料,有取代塑料基保鲜膜的可能性[7−10]。
光动力技术是一种利用可见光、光敏剂、氧气对食源性致病菌产生抑菌效果的非热杀菌技术[11−12]。已有报道将此技术应用在缢蛏[13]、虾仁[14]、牡蛎[15]等水产品的保鲜上,延长了贮藏期。但是,姜黄素等光敏剂(photosensitizer,Ps)具有较强的着色能力,影响食品的颜色品质,限制了此技术的推广应用[16−17]。将天然光敏剂加入薄膜中并介导光动力技术是一种具有良好发展前景的食品保鲜新思路。本研究将姜黄素(curcumin,C)、姜黄素/壳聚糖颗粒(curcumin-chitosan granule,G)作为功能物质,壳聚糖作为成膜基质,制备得到两种复合膜(PsC/PsG),进而构建复合膜-光动力杀菌体系,并将其应用于南美白对虾的保鲜。该研究评估了两种光敏性复合膜的功能特性,以期拓展光动力技术在食品领域的应用形式,丰富南美白对虾的保鲜方案。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
南美白对虾 购自于青岛金海利达水产市场;姜黄素 纯度>98%,西安圣青生物有限公司;壳聚糖 脱乙酰度90%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;平板计数琼脂 青岛海博生物技术有限公司;氧化镁 天津光复科技发展有限公司;其他化学试剂 国产分析纯试剂。
NR60CP型多功能色差仪 深圳三恩时科技有限公司;HZQ-X100电热恒温培养箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;8400型全自动凯氏定氮仪 美国福斯公司;ST3100型pH计 美国奥豪斯仪器有限公司;Model 680型酶标仪 美国 Bio-Rad公司;TMS-TOUCH型质构仪 FTC公司;L-8900全自动氨基酸分析仪 日本日立公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 姜黄素/壳聚糖颗粒制备
参照郑育[18]、LI等[19]的方法,稍作改进,将2 mL 2 mg/mL姜黄素溶液(curcumin, CUR)加入8 mL 2.5 mg/mL壳聚糖(chitosan, CTS)溶液中,磁力搅拌5 min,滴加1%三聚磷酸钠(TPP)溶液400 µL,使CTS:CUR:TPP=5:1:1(m:m:m),磁力搅拌30 min后得姜黄素/壳聚糖颗粒溶液。
1.2.2 光敏性复合膜制备
参照CHEN等[20]的方法进行改进,取0.4 mg/mL姜黄素溶液,加入1%壳聚糖溶液(0.3%甘油)中,使姜黄素浓度为8 μg/mL ,超声脱气15 min后,倒入12×12 cm模具中,40 ℃干燥8 h,得PsC膜。取1.2.1所得颗粒溶液替换姜黄素溶液,其他操作同PsC膜的制备,得PsG膜。两种膜避光干燥处保存。
1.2.3 复合膜经光照后的颜色变化
在光照功率10 W、膜-光间距15 cm的条件下,照射不同时间(0、2、5、10、15、20 min),使用色差计检测膜的颜色变化。
1.2.4 样品处理
购买鲜活南美白对虾,加冰猝死后,随机分为三组(每组36±3 g),在无菌器皿中放入三只虾,分别用市售PE保鲜膜(plastic wrap, PW)、PsC、PsG膜覆盖器皿,减少膜与样品的接触。PsC、PsG膜覆盖南美白对虾后使用420 nm LED光源照射(膜-光动力参数:光照功率10 W,膜-光间距15 cm,光照时间10 min,光功率密度为60 mW/cm2)。处理后各组样品均置于4 ℃冰箱中保存。在0、1、2、3、4 d取出贮藏样品,进行各指标的检测。
1.2.5 菌落总数的测定
按照GB 4789.2-2016《食品微生物学检验-菌落总数测定》进行测定,在每个取样日,将样品绞碎,取5 g虾肉置于45 mL的无菌生理盐水中,浸泡30 min后,取每个样品1 mL,进行梯度稀释,取三个合适梯度的稀释液100 μL涂布平板,37 ℃培养72 h后计数。
1.2.6 挥发性盐基氮、pH的测定
参照GB/T 5009.228-2016《食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》中自动凯氏定氮仪法测定挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N),取10 g虾肉在75 mL去离子水中浸泡30 min后,上机测定。
按照GB 5009.237-2016《食品pH值的测定》的方法测定pH,取2 g虾肉与去离子水混合(1:9,m:m),均质后静置30 min,测定上清液pH。
1.2.7 质构的测定
取三只对虾,剪取与虾头相近的第二节肌肉,采用质构仪测定其质构数据,取参数设定为:触发类型Auto(自动)、测试速率60 mm/min、力量感应元量程为100 N、起始力为0.5 N、形变百分量为50%,纵向压缩,两次压缩之间停留时间为5 s。压缩探头为不锈钢P/36R圆柱形。
1.2.8 游离氨基酸的测定
取贮藏2 d的样品绞碎,准确称量2 g虾肉于安瓿瓶中,加入15 mL 0.02 mol/L HCl,充分均质后超声5 min,5000 r/min,4 ℃离心10 min,收取上清液。将剩余残渣加入10 mL 0.02 mol/L稀盐酸后搅拌,5000 r/min,4 ℃离心5 min,合并上清液,定容至50 mL。定容后移取2 mL,加入2 mL体积分数5%磺基水杨酸溶液,10000 r/min,4 ℃离心10 min,上清液过0.22 μm水系滤膜于液相小瓶中,上机测定。
1.3 数据处理
实验进行三次重复,数据处理及统计采用SPSS 25.0进行分析,结果以平均值±标准偏差表示,方差分析采用Duncan的方法,P<0.05表示差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
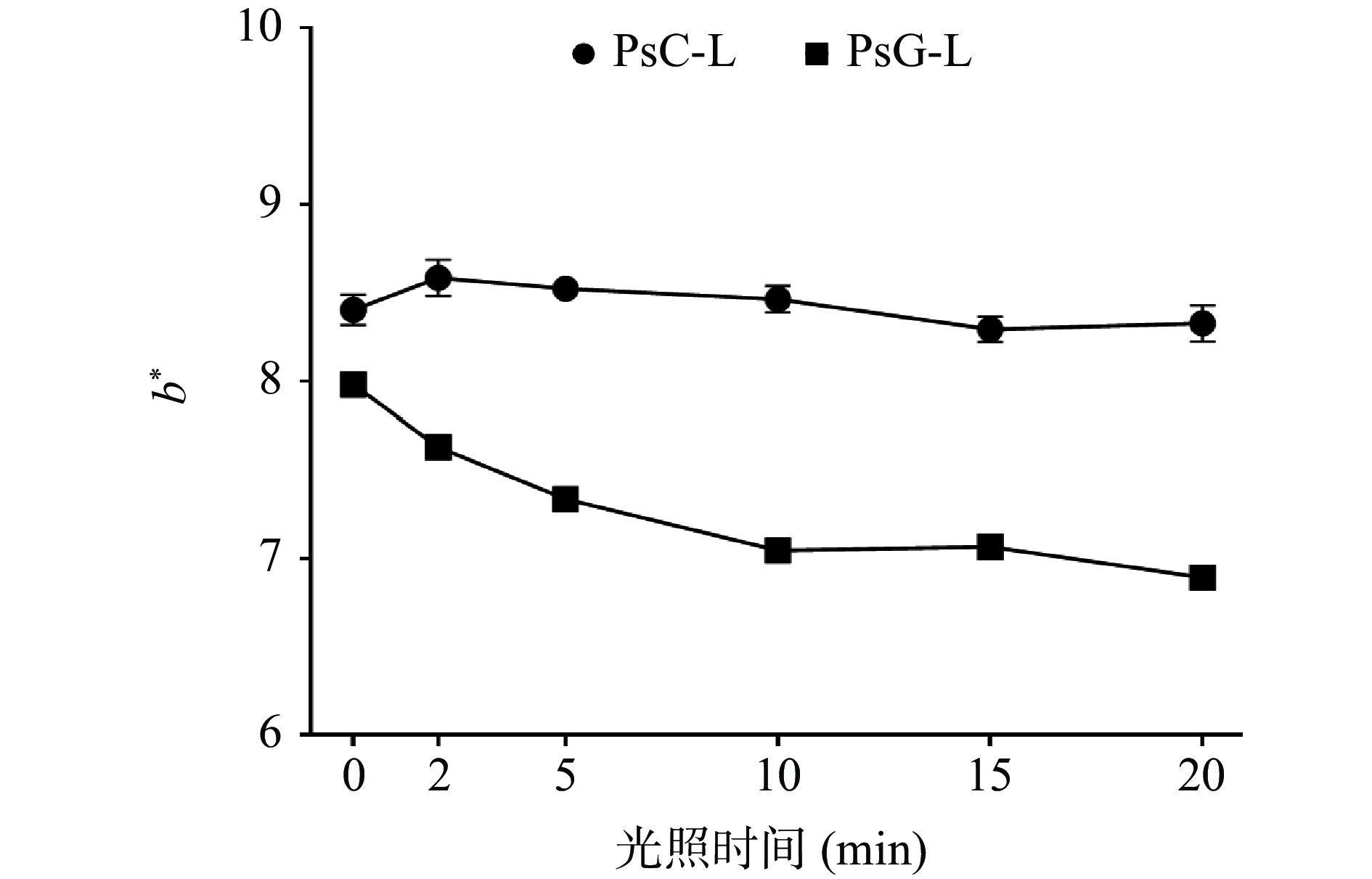
2.1 420 nm LED光源照射对复合膜色值影响研究
经光照射,姜黄素易分解,导致色值发生变化[21]。PsC和PsG膜经420 nm LED光源照射后色值变化如图1所示。照射前,PsC和PsG膜的L*值分别为44.74±0.31和46.24±0.21,a*值分别为−1.18±0.13和−1.64±0.11,b*值分别为8.40±0.09和7.98±0.06。照射后,两种膜的L*和a*无明显变化,b*的变化趋势不同。PsC和PsG膜的L*值分别为45.21±0.38和47.07±0.21;a*值分别为−1.09±0.06和−1.50±0.02;PsC膜的b*值在8.29~8.58范围内波动,b*变化与光照时间无明显关系;PsG膜的b*值明显下降,随光照时间延长,b*由7.98±0.06下降到6.89±0.07。结果表明,PsC和PsG膜初始b*不同,这可能与两种膜中游离姜黄素的含量不同有关[22]。通过离子交联法,姜黄素被包封在壳聚糖与三聚磷酸钠形成的体系中,导致PsG膜中的游离姜黄素含量减少。此外,PsG膜相较PsC膜更易在420 nm光源的照射下发生色值变化,这种不同的色度变化说明两种膜介导光动力的能力及光敏特性可能具有差异。
2.2 复合膜介导光动力对冷藏南美白对虾品质的影响
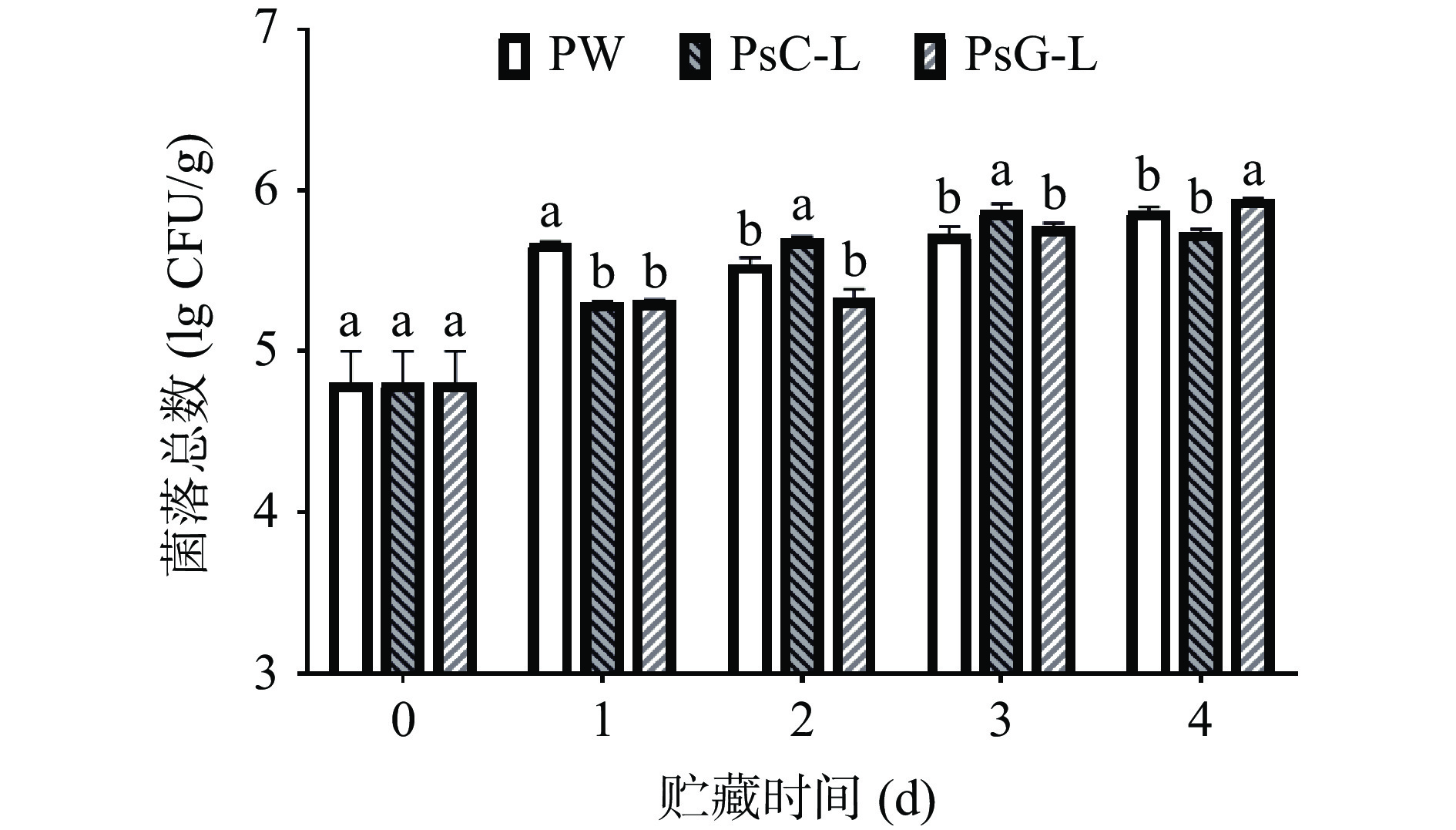
2.2.1 不同处理方式对冷藏南美白对虾菌落总数的影响
南美白对虾在冷藏期间,伴随着微生物的滋生,腐败希瓦氏菌、气单胞菌等腐败菌的生长易引起虾肉的腐败[23],从而产生食品安全问题[4]。复合膜介导光动力对冷藏南美白对虾的菌落总数的影响如图2所示。各组菌落总数在4 d内均未超过限值6 lg(CFU/g)。在贮藏过程中,PW组菌落总数前期增长较快,且整体菌落总数值较高。PW、PsG-L组在第4 d有菌落总数较高,分别为5.87±0.02、5.95±0.00 lg(CFU/g),PsC-L组在第3 d的菌落总数值最高,为5.88±0.04 lg(CFU/g)。结果表明,相较PW,PsC-L、PsG-L处理可显著抑制贮藏前期南美白对虾菌落总数的生长,且PsG-L延缓菌落总数生长的效果较优。保鲜膜无抑菌活性,所以在1 d的贮藏时间内,其菌落总数急剧上升,而由于其阻隔性能较好,贮藏环境中气体成分变化可能造成其菌落总数在1 d后先下降后持续上升[24]。PsC-L和PsG-L膜依靠壳聚糖、姜黄素及光动力的抑菌活性可延缓菌落总数的增长[25−26],PsC膜中壳聚糖、姜黄素在南美白对虾表面的释放可能使其菌落总数在4 d下降[27],而PsG膜较为稳定,活性成分迁移较少。
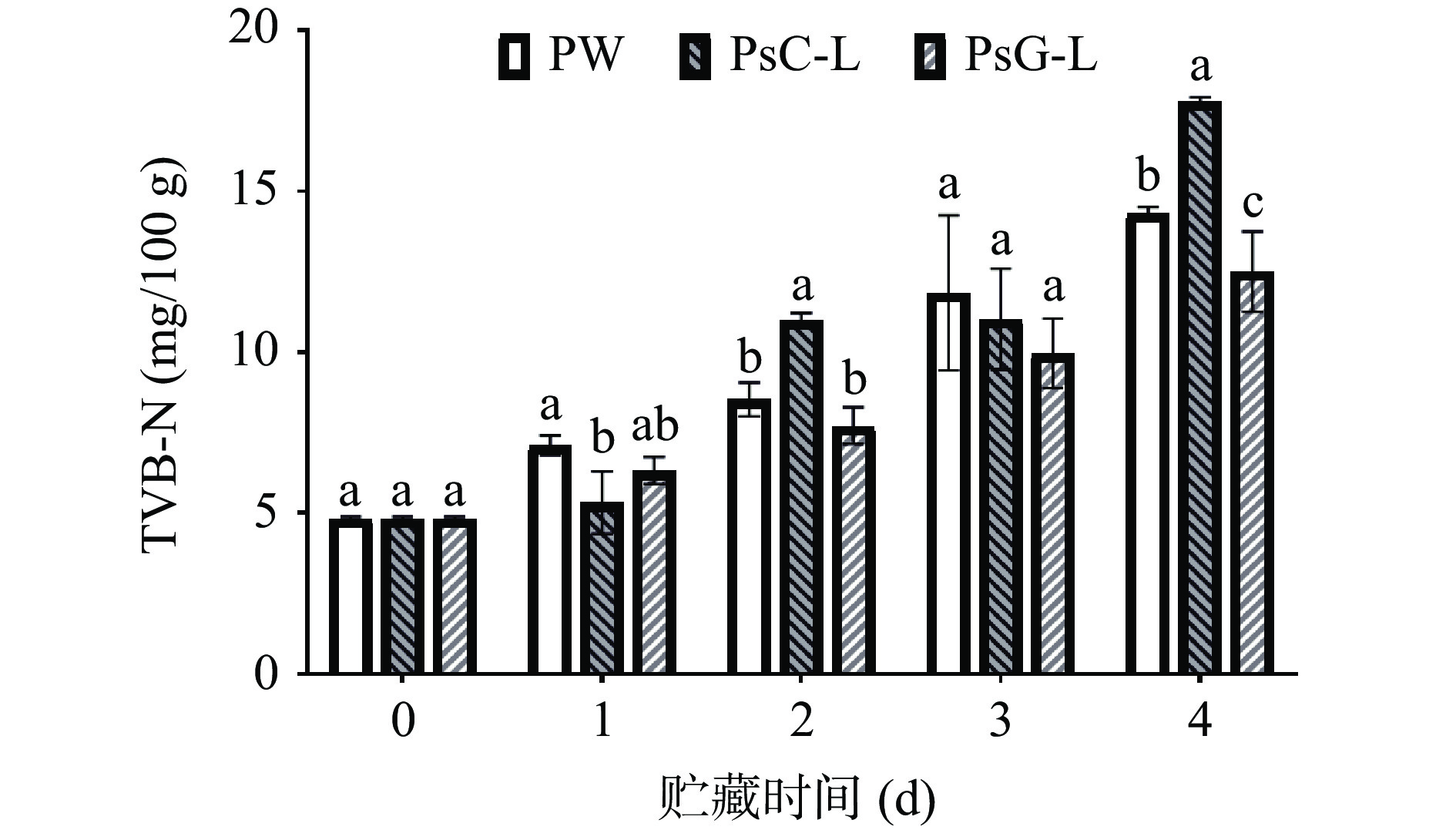
2.2.2 不同处理方式对冷藏南美白对虾挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)、酸碱值(pH)的影响
南美白对虾是一种高蛋白低脂肪的水产品,通过TVB-N、pH指标可反映虾肉的新鲜度[28]。在对虾鲜度的评定中,TVB-N值不超过15 mg/100 g为一级鲜度,15~20 mg/100 g为二级鲜度[29]。复合膜介导光动力对冷藏南美白对虾的挥发性盐基氮的影响如图3所示,随着贮藏时间的延长,各组南美白对虾的TVB-N值均呈上升趋势。在4 d,PW、PsC-L、PsG-L组TVB-N值分别14.31±0.19、17.80±0.12、12.50±1.25 mg/100 g。结果提示,4 ℃贮藏南美白对虾4 d后,PW、PsG-L组对虾仍为一级鲜度,PsC-L组对虾已为二级鲜度。PsG-L处理可显著的延缓TVB-N的产生,优于PW和PsC-L保鲜模式,LU等[30]发现光动力技术可以抑制丝氨酸蛋白酶和天冬氨酸蛋白酶的活性,从而抑制挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)、多肽氮(PeN)等的产生,延缓了蛋白质的降解。这说明PsG膜介导光动力的效果要显著优于PsC膜,与2.1中两种膜经光照后颜色变化不同的结果进行对照,膜颜色变化的程度可能与其介导光动力的能力相关。
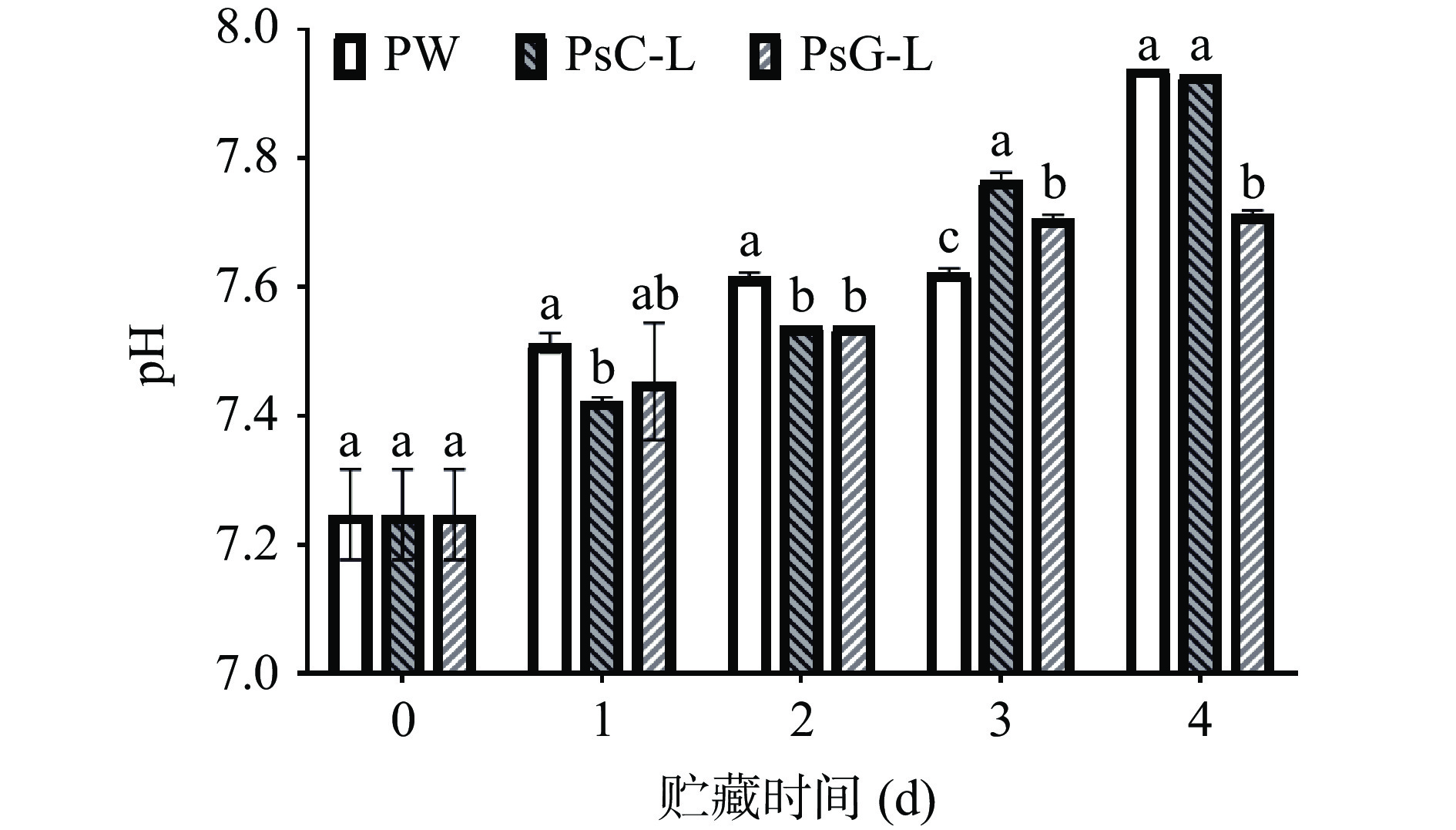
复合膜介导光动力对冷藏南美白对虾的pH的影响如图4所示,贮藏过程中,三组对虾pH均呈上升趋势。在1、2 d,PsC-L、PsG-L处理可有效延缓虾肉pH的上升,优于PW组,但PsC-L组样品在贮藏后期pH长较快。三组样品pH在第4 d分别达到7.94±0.00、7.93±0.00、7.71±0.01。这与菌落总数、TVB-N的变化趋势相似,故PsG-L处理后可能能够延缓虾肉蛋白质氧化等生化反应的发生,使虾肉pH升高较慢。
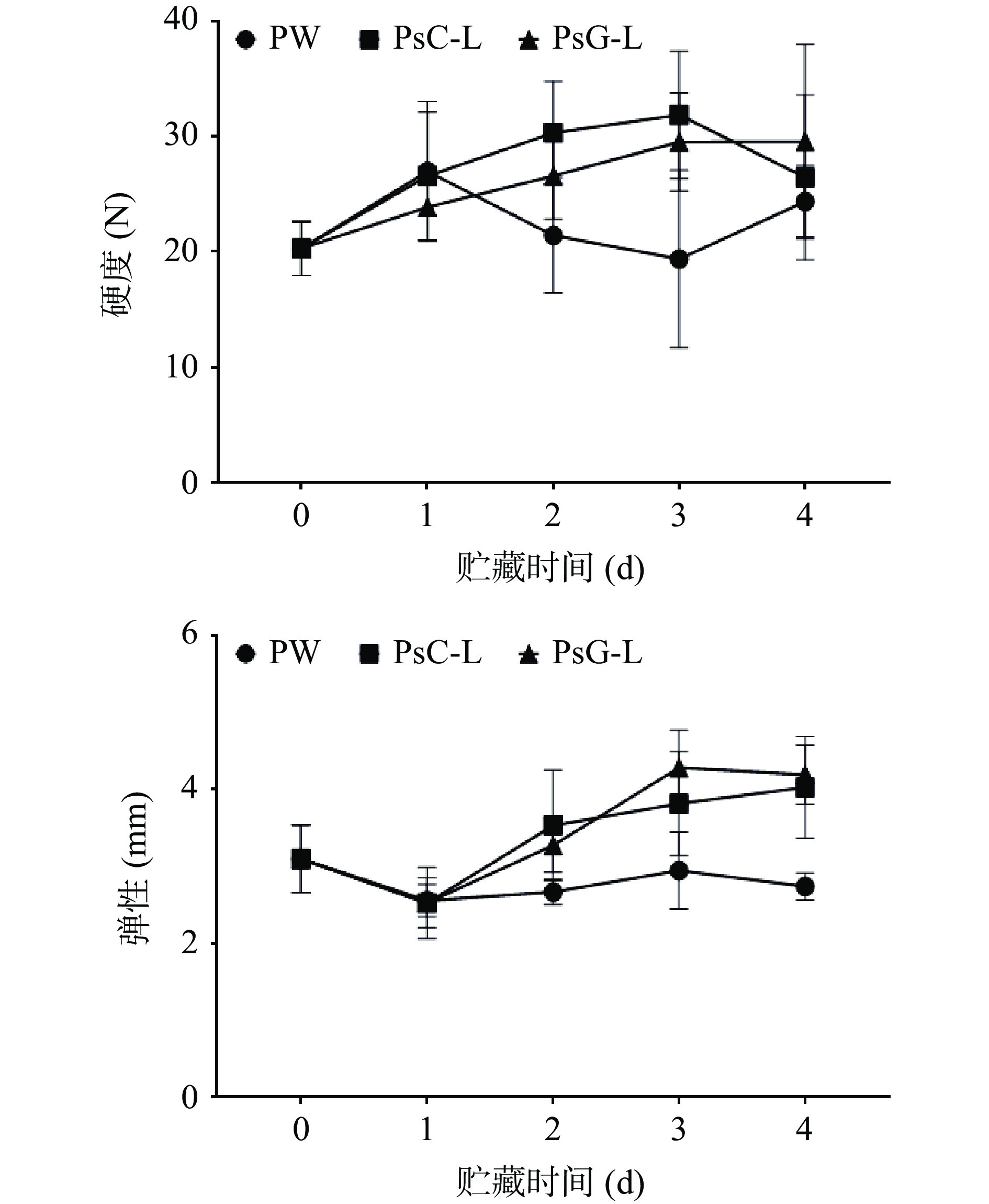
2.2.3 不同处理方式对冷藏南美白对虾质构的影响
南美白对虾在贮藏过程中,肌肉组成及结构会发生变化,最终导致虾体软化、弹性和食用口感下降[31]。复合膜介导光动力对冷藏南美白对虾的质构特性的影响如图5所示,各组虾的硬度变化趋势大致相同,均为先上升后下降, PW、PsC-L、PsG-L组分别在第1、3、3 d达到最高值,分别为26.96±6.04、31.87±5.53、29.55±8.43 N。而弹性的变化趋势与硬度有所不同,为先下降后上升,PW、PsC-L、PsG-L组均在1 d达到弹性最低点,分别为2.56±0.21、2.52±0.46、2.53±0.32 mm。结果说明,在贮藏期间,PsC-L,PsG-L两组对虾的硬度和弹性整体高于PW组的对虾。在南美白对虾贮藏期间,由于蛋白质的持水力下降,虾体会出现汁液流失以及水分的散失[32],而保鲜膜较两种光敏膜有更好的阻隔效果,来自于虾体的水分的释放会提升贮藏环境的湿度,这为微生物的生长繁殖提供了条件,这可能造成PW组虾体硬度下降较早。PsC、PsG膜以壳聚糖为基质,而壳聚糖膜其阻水性较为差[33],可能造成虾体水分散失,组织变得粗糙,硬度增大,弹性也随之有提升。
2.2.4 不同处理方式对冷藏南美白对虾呈味氨基酸的影响
游离氨基酸是水产品中呈味的基础物质,不同氨基酸呈现不同风味特征,对南美白对虾的风味有较大的影响[34]。呈味强度值(taste activity values, TAV)为食物基质中单个化合物的浓度与其对应的味觉阈值的比值,当TAV>1时,表明该呈味成分能独立对食品的滋味产生重要贡献,TAV值越高,该化合物对食物整体口味的贡献越大[35]。本研究中对贮藏2 d的南美白对虾的游离氨基酸含量进行了测定,结果如表1所示。在三组中检测到11种游离氨基酸,除甘氨酸外,PsC-L组样品的游离氨基酸含量高于其他两组,PsG-L组与PW组差异较小。由游离氨基酸含量计算得TAV值,结果如表2所示,其中,谷氨酸、甘氨酸、丙氨酸和精氨酸的TAV>1,在PsC-L组中谷氨酸、丙氨酸的TAV极显著高于另两组(P<0.01),PsG-L组谷氨酸的TAV显著高于PW组(P<0.05),这对样品的鲜味影响较大。结果提示,在贮藏2 d后,PsC-L组样品的蛋白质降解较多,游离氨基酸含量增加。而相较PW组,PsG-L处理可延缓鲜/甜味游离氨基酸的降解及苦味氨基酸的生成。
表 1 复合膜介导光动力对冷藏南美白对虾的游离氨基酸含量的影响Table 1. Effect of composite membrane-mediated photodynamics on the content of free amino acids in refrigerated shrimp氨基酸 滋味属性 含量(mg/100 g) PW PsC-L PsG-L 天冬氨酸(Asp) 鲜(+) 4.92±0.48 8.01±0.51 7.03±0.39 谷氨酸(Glu) 鲜(+) 58.50±4.51 71.40±4.32 64.57±1.21 甘氨酸(Gly) 甜/鲜(+) 319.78±21.46 304.42±17.97 299.84±5.63 丙氨酸(Ala) 甜/鲜(+) 138.42±8.80 161.98±7.23 144.66±5.81 精氨酸(Arg) 苦/甜(+) 296.05±17.33 296.38±19.07 277.86±2.90 甲硫氨酸(Met) 苦/甜/硫(−) 6.44±2.48 10.40±4.36 6.55±3.23 异亮氨酸(Ile) 苦(−) 8.49±1.73 12.75±1.26 9.40±1.98 亮氨酸(Leu) 苦(−) 12.08±1.17 16.17±0.71 13.95±1.35 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 苦(−) 3.42±0.42 4.59±1.61 3.63±0.15 赖氨酸(Lys) 苦(−) 26.24±1.60 28.24±1.85 24.27±0.53 组氨酸(His) 甜/苦(−) 10.17±0.59 11.58±0.60 10.62±0.42 表 2 呈味强度值Table 2. Taste activity values氨基酸 滋味属性 味觉阈值 TAV PW PsC-L PsG-L 天冬氨酸(Asp) 鲜(+) 100 0.05±0.00 0.08±0.01 0.07±0.00 谷氨酸(Glu) 鲜(+) 30 1.95±0.15 2.38±0.14** 2.15±0.04* 甘氨酸(Gly) 甜/鲜(+) 110 2.91±0.20 2.77±0.16 2.73±0.05 丙氨酸(Ala) 甜/鲜(+) 60 2.31±0.15 2.70±0.12** 2.41±0.10 精氨酸(Arg) 苦/甜(+) 50 5.92±0.35 5.93±0.38 5.56±0.06 甲硫氨酸(Met) 苦/甜/硫(−) 30 0.21±0.08 0.35±0.15 0.22±0.11 异亮氨酸(Ile) 苦(−) 90 0.09±0.02 0.14±0.01 0.10±0.02 亮氨酸(Leu) 苦(−) 190 0.06±0.01 0.09±0.00 0.07±0.01 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 苦(−) 30 0.11±0.01 0.15±0.05 0.12±0.01 赖氨酸(Lys) 苦(−) 50 0.52±0.03 0.56±0.04 0.49±0.01 组氨酸(His) 甜/苦(−) 20 0.51±0.03 0.58±0.03 0.53±0.02 注:显著性分析以PW组为对照组,“**”为P<0.01,“*”为P<0.05。 3. 结论
对比市售保鲜膜,在2 d的贮藏时间内,PsC-L处理可以产生更好的保鲜效果,而贮藏后期,保鲜效果变差。在4 d的贮藏时间内,PsG-L处理可以影响菌落总数的生长,显著延缓TVB-N、pH的上升,延缓虾的质地软化。在2 d的贮藏时间内,相较PW处理,PsG-L处理可延缓鲜味氨基酸的降解,减少苦味氨基酸的生成。总之,PsG-L处理可有效延缓南美白对虾的品质劣化,将姜黄素/壳聚糖颗粒添加到壳聚糖膜中介导光动力相比姜黄素与壳聚糖混合后介导光动力在保鲜效果上有显著提升。薄膜保鲜与光动力复合应用在水产品保鲜是可行的。
-
表 1 复合膜介导光动力对冷藏南美白对虾的游离氨基酸含量的影响
Table 1 Effect of composite membrane-mediated photodynamics on the content of free amino acids in refrigerated shrimp
氨基酸 滋味属性 含量(mg/100 g) PW PsC-L PsG-L 天冬氨酸(Asp) 鲜(+) 4.92±0.48 8.01±0.51 7.03±0.39 谷氨酸(Glu) 鲜(+) 58.50±4.51 71.40±4.32 64.57±1.21 甘氨酸(Gly) 甜/鲜(+) 319.78±21.46 304.42±17.97 299.84±5.63 丙氨酸(Ala) 甜/鲜(+) 138.42±8.80 161.98±7.23 144.66±5.81 精氨酸(Arg) 苦/甜(+) 296.05±17.33 296.38±19.07 277.86±2.90 甲硫氨酸(Met) 苦/甜/硫(−) 6.44±2.48 10.40±4.36 6.55±3.23 异亮氨酸(Ile) 苦(−) 8.49±1.73 12.75±1.26 9.40±1.98 亮氨酸(Leu) 苦(−) 12.08±1.17 16.17±0.71 13.95±1.35 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 苦(−) 3.42±0.42 4.59±1.61 3.63±0.15 赖氨酸(Lys) 苦(−) 26.24±1.60 28.24±1.85 24.27±0.53 组氨酸(His) 甜/苦(−) 10.17±0.59 11.58±0.60 10.62±0.42 表 2 呈味强度值
Table 2 Taste activity values
氨基酸 滋味属性 味觉阈值 TAV PW PsC-L PsG-L 天冬氨酸(Asp) 鲜(+) 100 0.05±0.00 0.08±0.01 0.07±0.00 谷氨酸(Glu) 鲜(+) 30 1.95±0.15 2.38±0.14** 2.15±0.04* 甘氨酸(Gly) 甜/鲜(+) 110 2.91±0.20 2.77±0.16 2.73±0.05 丙氨酸(Ala) 甜/鲜(+) 60 2.31±0.15 2.70±0.12** 2.41±0.10 精氨酸(Arg) 苦/甜(+) 50 5.92±0.35 5.93±0.38 5.56±0.06 甲硫氨酸(Met) 苦/甜/硫(−) 30 0.21±0.08 0.35±0.15 0.22±0.11 异亮氨酸(Ile) 苦(−) 90 0.09±0.02 0.14±0.01 0.10±0.02 亮氨酸(Leu) 苦(−) 190 0.06±0.01 0.09±0.00 0.07±0.01 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 苦(−) 30 0.11±0.01 0.15±0.05 0.12±0.01 赖氨酸(Lys) 苦(−) 50 0.52±0.03 0.56±0.04 0.49±0.01 组氨酸(His) 甜/苦(−) 20 0.51±0.03 0.58±0.03 0.53±0.02 注:显著性分析以PW组为对照组,“**”为P<0.01,“*”为P<0.05。 -
[1] 农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站, 中国水产学会. 《2023中国渔业统计年鉴》[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2023:22−24 Fisheries Administration of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center, Chinia Society of Fisheries. 2023 China fishery statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2023:22−24.]
[2] 林婷, 杨胜平, 谢晶, 等. 虾黑变形成机制及其抑制方法研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报,2020,36(6):1605−1611 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2020.06.034 LIN T, YANG S P, XIE J, et al. Research progress on mechanisms of melanosis development and anti-melanosis methods in shrimps[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2020,36 (6):1605−1611.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2020.06.034
[3] 陈胜军, 陶飞燕, 潘创, 等. 虾产品低温贮藏保鲜技术研究进展[J]. 中国渔业质量与标准,2020,10(1):68−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1833.2020.01.008 CHENG S J, TAO F Y, PAN C, et al. Research progress on low temperature storage and preservation technology of shrimp products[J]. Chinese Fishery Quality and Standards,2020,10 (1):68−75.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1833.2020.01.008
[4] 钱韻芳, 杨胜平, 谢晶, 等. 气调包装凡纳滨对虾特定腐败菌致腐败能力研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2015,15(1):85−91 QIAN Y F, YANG S P, XIE J, et al. Studies on the putrefaction potential of the specific spoilage organisms from modified atmosphere packaged of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2015,15 (1):85−91.]
[5] 杨旭, 方健, 覃敏, 等. 壳聚糖/结冷胶双层膜制备工艺优化及表征[J]. 中国塑料,2022,36(11):14−23 YANG X, FANG J, QIN M, et al. Preparation process optimization and characterization of chitosan/gellan gum bilayer films[J]. China Plastics,2022,36 (11):14−23.]
[6] MOREIRA M D R, ROURA S I, PONCE A. Effectiveness of chitosan edible coatings to improve microbiological and sensory quality of fresh cut broccoli[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2011,44(10):2335−2341. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.04.009
[7] TOSATI J V, DE O E F, OLIVEIRA J V, et al. Light-activated antimicrobial activity of turmeric residue edible coatings against cross-contamination of Listeria innocua on sausages[J]. Food Control, 2018, 84:177−185.
[8] MA S, MOSER D, HAN F, et al. Preparation and antibiofilm studies of curcumin loaded chitosan nanoparticles against polymicrobial biofilms of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,241:116254. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116254
[9] 李天密, 屈思佳, 韩俊华. 壳聚糖/姜黄素/γ-聚谷氨酸可食性复合膜的制备及对培根和火腿的保鲜效果[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(17):270−276 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180910-095 LI T M, QU S J, HAN J H. Preparation of chitosan/curcumin/γ-polyglutamic acid edible composite film and its preservation effect on bacon and sausage[J]. Food Science,2019,40(17):270−276.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180910-095
[10] 延梦瑶, 沈文, 刘树兴, 等. 负载姜黄素纳米粒子冷鲜肉抗氧化可食用膜的制备及表征[J]. 陕西科技大学学报,2022,40(2):54−60, 67 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5811.2022.02.009 YAN M Y, SHEN W, LIU S X, et al. Preparation and characterization of antioxidant edible films incorporated with curcumin nanoparticles for chilled meat[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology,2022,40(2):54−60, 67.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5811.2022.02.009
[11] ZHANG X, WU J, XU C S, et al. Inactivation of microbes on fruit surfaces using photodynamic therapy and its influence on the postharvest shelf-life of fruits[J]. Food Science and Technology International,2020,26(8):696−705. doi: 10.1177/1082013220921330
[12] 于金珅, 张芳. 姜黄素介导的光动力技术对鲜切马铃薯的杀菌效果[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(4):259−263, 270 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060050 YU J S, ZHANG F. Effects of curcumin-mediated photodynamic technology on bactericidal efficacy of fresh-cut potatoes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(4):259−263, 270.] doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060050
[13] 林以琳, 李世洋, 赖丹宁, 等. 姜黄素介导光动力减菌技术对缢蛏的保鲜效果[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(16):320−326 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.16.038 LIN Y L, LI S Y, LAI D N, et al. Effects of curcumin-mediated of anti-microbial photodynamic technology on preservation of rezor clam[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(16):320−326.] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.16.038
[14] 王凡. 基于光动力技术的明胶/壳聚糖/姜黄素抑菌复合膜的制备及其对虾仁品质的影响[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2022 WANG F. Development of gelatin/chitosan/curcumin antibacterial composite film based on photodynamic technology and its effect on the quality of shrimps[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2022.]
[15] WU J, HOU W, CAO B, et al. Virucidal efficacy of treatment with photodynamically activated curcumin on murine norovirus bio-accumulated in oysters[J]. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamics Therapy,2015,12(3):385−392. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2015.06.005
[16] 智锦锦, 王志广, 吴双杰, 等. 姜黄素介导光动力处理牡蛎的安全性评价[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(8):288−296 doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2022.8.1241 ZHI J J, WANG Z G, WU S J, et al. Safety evaluation of curcumin-mediated photodynamic treatment of oysters[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022,38(8):288−296.] doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2022.8.1241
[17] 陈梦奇, 周鸣睿, 韩娅红. 姜黄素在食品中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2022,33(10):292−300 doi: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2022.10.037 CHEN M Q, ZHOU M R, HAN Y H. Research progress on the application of curcumin in food[J]. China Food Additives,2022,33(10):292−300.] doi: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2022.10.037
[18] 郑育. 新型姜黄素纳米颗粒的制备及其对高糖环境下GMCs作用机制研究[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2017 ZHENG Y. Preparation of new curcumin nanoparticles and its effect and mechanism on gmcs in high glucose[D]. Jinan:Shandong University, 2017.]
[19] LI T M, ZHAO Y L, MATTHEWS K, et al. Antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus of curcumin-loaded chitosan spray coupled with photodynamic treatment[J]. LWT, 2020, 134: 110073.
[20] CHEN L, DONG Q, SHI Q, et al. Novel 2, 3-dialdehyde cellulose-based films with photodynamic inactivation potency by incorporating the beta-cyclodextrin/curcumin inclusion complex[J]. Biomacromolecules,2021,22(7):2790−2801. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00165
[21] LIU J R, WANG H L, WANG P F, et al. Films based on κ-carrageenan incorporated with curcumin for freshness monitoring[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,83:134−142. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.05.012
[22] CVEK M, PAUL U C, ZIA J, et al. Biodegradable films of pla/ppc and curcumin as packaging materials and smart indicators of food spoilage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2022,14(12):14654−14667.
[23] 王航. 草鱼贮藏过程中品质变化规律及特定腐败菌的研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2016 WANG H. Quality changes and the specific spoilage organisms of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets during storage[D]. Beijing:China Agricultural University, 2016.]
[24] 凌萍华, 谢晶. 南美白对虾气调包装工艺及保鲜效果评价[J]. 包装工程,2010,31(9):10−14 doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2010.09.004 LING P H, XIE J. Evaluation of techniques and freshness keeping effect of modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) on Pacific white shrimp[J]. Packaging Engineering,2010,31(9):10−14.] doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2010.09.004
[25] HU J, LIN S, TAN B K, et al. Photodynamic inactivation of Burkholderia cepacia by curcumin in combination with EDTA[J]. Food Research International,2018,111:265−271. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.05.042
[26] LAI D, ZHOU A, TAN B K, et al. Preparation and photodynamic bactericidal effects of curcumin-beta-cyclodextrin complex[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,361:130117. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130117
[27] 胡奇杰, 王东旭, 谷贵章. 复配生物涂膜保鲜液对冷藏南美白对虾的保鲜效果研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(2):763−768 doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.02.065 HU Q J, WANG D X, GU G Z. Study on the preservative effect of compound biological coating liquid on frozen South American white prawn[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2021,12(2):763−768.] doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.02.065
[28] 孙新玉. 可食性胶原蛋白/姜黄素活性缓释膜的制备、性质分析及对草鱼肉片保鲜的机理研究[D]. 福州:福州大学, 2018 SUN X Y. Preparation, characterization of edible collagen/curcumin film with sustained release activity and its mechanism of grass carp fillets preservation[D]. Fuzhou:Fuzhou University, 2018.]
[29] 邸珍涛, 王永妍, 马莉, 等. 汽爆柚皮对南美白对虾的保鲜效果[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(8):2448−2456 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.8.spaqzljcjs202208010 DI Z T, WANG Y Y, MA L, et al. Fresh-keeping effects of steam-exploded pomelo peel on Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(8):2448−2456.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.8.spaqzljcjs202208010
[30] LU N, WANG Z G, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of curcumin-based photodynamic method on protein degradation of oysters[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2021,56(8):4050−4061.
[31] 姜鹤. 虾贝类内源酶性质及保鲜研究[D]. 大连:大连工业大学, 2016 JIANG H. Study on the digestive enzyme properties of shrimp and shellfish and preservation[D]. Dalian:Dalian Polytechnic University, 2016.]
[32] 裴诺. 壳聚糖/淀粉功能性复合膜的制备及其在南美白对虾保鲜中的应用[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2022 PEI N. Preparation of chitosan/starch functional composite membrane and its application in preservation of Penaeus vannamei[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2022.]
[33] 李莹, 杨欣悦, 王雪羽, 等. 壳聚糖基复合膜的成膜机理和特性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技. 2022,43(7):430−438 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021040015 LI Y, YANG X Y, WANG X Y, et al. Research progress on the film-forming mechanism and characteristics of chitosan-based composite membranes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry. 2022,43(7):430−438.] doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021040015
[34] 沈思远, 施文正, 曲映红, 等. 热风微波联合干燥过程中南美白对虾滋味物质变化研究[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2021,39(3):52−61 doi: 10.12301/j.issn.2095-6002.2021.03.006 SHEN S Y, SHI W Z, QU Y H, et al. Changes of taste substances of Litopenaeus vannamei during hot air-microwave combined drying[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2021,39(3):52−61.] doi: 10.12301/j.issn.2095-6002.2021.03.006
[35] CHEN D, ZHANG M. Non-volatile taste active compounds in the meat of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis)[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,104(3):1200−1205.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 杜露露,陈浩,何双庆,胡贤锋. 天然复合膜在食品保鲜中的应用现状及展望. 现代农业科技. 2025(02): 156-159+163 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵士豪,窦梦思,巨浩羽,曹倩倩,刘晓柳. 可食性抑菌保鲜膜及其在水产品保藏中的应用研究进展. 华中农业大学学报. 2025(01): 239-245 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 路冠茹,李达,赵高乾. 黄酮接枝壳聚糖/聚乳酸复合膜的制备及保鲜效果研究. 食品科技. 2024(06): 56-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



