Effects of Lentinan on Proliferation, Migration and Chemotherapy Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cells through the IL-6/STAT3/Notch Signaling Pathway
-
摘要: 目的:香菇多糖(Lentinan,LNT)已被证明对癌细胞具有直接的细胞毒性。然而,这种抗肿瘤作用机制尚不清楚。本研究旨在探讨香菇多糖对胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移及化疗敏感性的影响及其机制。方法:将胰腺癌Capan-1细胞随机分为对照组、IL-6组、IL-6+LNT组,MTT检测细胞存活率,Western blot检测p-STAT3、STAT3、Notch1和Hes1表达水平,Transwell实验检测细胞迁移。建立顺铂耐药细胞模型(Capan-1/DDP),检测各组顺铂半抑制浓度(IC50),分析Ki-67、MMP-9、MRP1和P-gp蛋白相对表达水平。选择Capan-1/DDP细胞株进行裸鼠成瘤实验,验证LNT对裸鼠体内瘤体的瘤重、IL-6/STAT3/Notch信号通路的影响。结果:7.5~240 µg/mL香菇多糖对胰腺癌细胞增殖有抑制作用;与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组增殖率显著降低,p-STAT3/STAT3、Notch1和Hes1表达和迁移水平(极)显著下调(P<0.05,P<0.01);与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组Capan-1/DDP细胞株增殖率极显著下调,IC50极显著降低,Ki-67、MMP-9、MRP1和P-gp表达水平显著下调(P<0.05,P<0.01)。体内实验显示,与IL-6组比较,顺铂+IL-6组、LNT+IL-6组瘤体体积、瘤重极显著下调,p-STAT3/STAT3、Notch1、Hes1表达水平(极)显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01)。结论:LNT抑制胰腺癌Capan-1细胞增殖、迁移和耐药,与调控IL-6/STAT3/Notch信号通路相关。Abstract: Objective: Lentinan (LNT) had been shown to have direct cytotoxicity on cancer cells. However, the mechanism of this anti-tumor effect was still unclear. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of lentinan on the proliferation, migration and chemosensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells and its mechanism. Methods: Capan-1 cells from pancreatic cancer were randomly divided into control group, IL-6 group and IL-6+LNT group. Cell survival rate was detected by MTT, expression levels of p-STAT3, STAT3, Notch1 and Hes1 were analyzed by Western blot, and cell migration was observed by Transwell test. The cisplatin resistant cell model (Capan-1/DDP) was established, and the semi-inhibitory concentration of cisplatin (IC50) was detected in each group, and the relative expression levels of Ki67, MMP-9, MRP1 and P-gp were analyzed. Capan-1/DDP cell line was selected for tumor formation test in nude mice to verify the effects of LNT on tumor weight and IL-6/STAT3/Notch signaling pathway in nude mice. Results: Lentinan (7.5~240 µg/mL) could inhibit proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Compared with the IL-6 group, the expression levels of p-STAT3/STAT3, Notch1 and Hes1 in IL-6+LNT group were significantly down-regulated, the proliferation rate and the migration level was significantly dcreased (P<0.05, P<0.01). The proliferation rate of Capan-1/DDP cell line, IC50 and the expression levels of Ki-67, MMP-9, MRP1 and P-gp in IL-6+LNT group were significantly down-regulated (P<0.05, P<0.01). In vivo experiments, compared with IL-6 group, the tumor volume and tumor weight in cisplatin+IL-6 group and LNT+IL-6 group was significantly down-regulated, and expression levels of p-STAT3/STAT3, Notch1 and Hes1 were significantly decreased (P<0.05, P<0.01). Conclusion: LNT inhibits proliferation, migration and drug resistance of Capan-1 pancreatic cancer cells, which is related to the regulation of IL-6/STAT3/Notch signal pathway.
-
胰腺癌(Pancreatic cancer,PC)是最具侵袭性的消化系统致命癌症,预后严重,死亡率高,5年生存率小于5%[1]。虽然胰腺癌的发病机制和病因尚未完全阐明,但一些常见的胰腺癌危险因素已被报道,包括吸烟、肥胖、遗传、糖尿病、饮食,甚至胰腺炎和饮酒。胰腺癌的治疗包括手术、放射治疗、化疗和姑息治疗[2]。然而,复杂的胰腺癌手术或联合治疗并不能取得良好的疗效,迫切需要更有效的治疗方法[3]。而食品来源的活性物质具有毒副作用小等特点,因此,研究香菇多糖对胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移及化疗敏感性的影响及其机制,可以为胰腺癌的辅助治疗提供实验依据。
胰腺癌的发生不仅受到丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶11(STK11)、蛋白酶、丝氨酸1/蛋白酶、丝氨酸2 (PRSS1/PRSS2)、Pim-1等基因突变的高度影响,也受到炎症细胞、趋化因子和细胞因子为主的微环境的影响[4]。研究显示,白细胞介素-6(IL-6)与自身免疫性疾病、癌变等有关,并已证明其影响PC的发生、进展、预后和转移[5]。研究显示,Notch信号通路在癌症的进展、自我更新中起着重要作用,能调节肝癌细胞的增殖[6],而且Notch信号传导和IL-6相互作用在肝细胞癌、乳腺癌中作用已经得到证实,能有效的调控癌症的进展[7−8]。而调节IL-6/STAT3信号通路能有效调控药物对癌细胞的化学增敏作用[9],包括IL-6通过STAT3/Notch信号通路调节多发性骨髓瘤细胞系对硼替佐米的耐药及化学敏感性[10]。
香菇多糖(Lentinan)是从香菇中分离出来的β-(1,3)-葡聚糖多糖,具有低毒和抗肿瘤、抗炎和免疫增强等多种活性,能通过增强宿主的免疫应答(特别是T淋巴细胞介导的应答间接发挥抗)肿瘤作用[11]。与单纯化疗相比,香菇多糖联合化疗可显著延长结直肠癌患者的生存率,改善免疫反应,减少不良反应,表明香菇多糖对抗肿瘤作用具有一定的辅助作用[12]。已有研究显示,香菇多糖治疗胰腺癌具有一定的效果[13],且胰腺癌组织中,IL-6/STAT3信号通路和Notch信号通路均处于激活状态[14−15],而香菇多糖能否通过IL-6/STAT3/Notch信号通路发挥抗癌作用并不明确。本研究重点分析香菇多糖对胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移及化疗敏感性的影响,并分析其机制,为香菇多糖的开发提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
BALB/c裸鼠 30只SPF级5~6周龄,雄性,体重(16~20 g),购自中国科学院上海动物实验中心,动物合格证号SCXK(沪)2017-0005。标准动物房饲养,温度(22±5)℃ , 湿度(57±8)%,光暗交替各 12 h,自由获得标准的饲料和水;人胰腺癌Capan-1细胞株 碧云天生物技术有限公司;干香菇 购自漯河市许慎市场;MTT试剂盒、IL-6 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;兔抗p- STAT3、STAT3、Notch1、Hes1、Ki-67、MMP-9、MRP1、P-gp、HRP标记的羊抗兔IgG二抗 美国Sigma公司。
DMIL LED倒置荧光显微镜 德国徕卡公司;ELx800全自动酶标仪 美国BioTek公司;Gel Doc XR+凝胶成像系统 美国BIO-RAD公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 香菇多糖的提取
准确称取500 g香菇,粉碎后过40目筛,料液比1:60(g:mL)加水混匀,70 ℃超声辅助提取2 h,提取2次,过滤,减压至250 mL,D101大孔树脂纯化,蒸馏水洗脱,浓缩至250 mL,加入终浓度为 80%乙醇,静置过夜,抽滤,溶解,二次醇沉,无水乙醇、丙酮冲洗,得香菇多糖。选择葡萄糖为标准品,苯酚-硫酸法检测多糖水平[16]。标准曲线方程为y=51.432x−0.0213(r=0.9998)。线性范围0.00287~0.01762 mg/mL,纯度为91.27%。溶于0.1%二甲基亚砜中,培养基稀释;动物实验进行时,采用PEG400溶解,生理盐水稀释,4 ℃ 保存备用。
1.2.2 细胞培养
Capan-1细胞培养于DMEM培养基中,添加10%胎牛血清、100单位/mL青霉素和100 μg/mL链霉素,37 ℃,5% CO2条件下标准加湿培养箱孵育。
1.2.3 MTT法检测细胞抑制率
选择对数生长期的细胞(5×103 个细胞/孔)转移到96孔板中,5% CO2培养箱中37 ℃孵育,贴壁后,加入终浓度分别为0、7.5、15、30、60、120、240 µg/mL的LNT的培养基溶液,空白对照组只加等量的培养基,另设置阳性对照组(60 µg/mL顺铂,预实验获得)、0.1%的二甲亚砜(DMSO)组(对照组)、空白对照组(完全培养液)和只加培养基无细胞的空白组,每组设置3个复孔,孵育48 h。每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液。充分混合后,37 ℃孵育4 h,除去上清,加入150 μL二甲亚砜溶液,37 ℃孵育30 min。随后,通过酶标仪检测490 nm处的光密度(OD)值。抑制率(%)=(OD对照组−OD给药组)×100/(OD对照组−OD空白组)。GraphPad Prism 8统计软件计算香菇多糖对Capan-1细胞的IC50。
1.2.4 细胞分组及增殖率检测
选取对数生长期胰腺癌细胞,随机分组:对照组,正常培养;IL-6 组:IL-6终浓度为50 ng/mL的培养基培养[9];IL-6+LNT组:含50 ng/mL IL-6和60 µg/mLLNT的培养基培养。培养48 h后,参照“1.2.3”采用MTT法检测增殖率,增殖率(%)=(OD给药组−OD空白组)×100/(OD对照组−OD空白组)。
1.2.5 Western blot检测相关蛋白水平
参照“1.2.4”分组,孵育48 h,RIPA细胞裂解液裂解细胞,BCA法测定总蛋白水平。使用10% SDS-PAGE分离蛋白,并转移到PVDF膜上,5%脱脂奶粉封闭1 h。膜与一抗孵育过夜:p-STAT3(1:1000)、STAT3(1:1000)、Notch1(1:2000)、Hes1(1:2000),TBST洗涤三次,加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的羊抗兔IgG (1:1000),37 ℃孵育1 h,TBST洗涤三次,增强型化学发光试剂 (ECL)显现蛋白条带,Image J软件分析结果。
1.2.6 细胞迁移能力检测
参照“1.2.4”分组,将Capan-1细胞重悬于200 µL无FBS的培养基(1×105个细胞/孔)中,加入transwell小室顶室。下腔添加10% FBS的培养基。48 h后,细胞固定染色,显微镜下随机选取6个区域计数细胞数量。
1.2.7 细胞顺铂耐药模型的建立
对数生长期Capan-1细胞置于处于含有0.1 μg/mL顺铂(DDP)的培养基中培养2周,调整DDP浓度为0.2 μg/mL,继续培养2周,将DDP浓度分别调整至0.4、0.8 μg/mL,选择0.8 μg/mL DDP存在下稳定生长的细胞被为抗DDP的胰腺癌细胞Capan-1/DDP。
将Capan-1/DDP细胞接种到96孔板(5×103个细胞/孔),贴壁后分成3组,包括对照组、IL-6、IL-6+LNT组,每组加入DDP终浓度分别为10、20、30、40 μg/mL的培养基,孵育48 h,采用MTT法检测490 nm处的OD值,计算增殖率,GraphPad Prism 8软件计算顺铂半抑制浓度(IC50),Western blot检测Ki-67、MMP-9、MRP1和P-gp表达水平。
1.2.8 裸鼠急性毒性试验
确定裸鼠最小剂量(Dm)和最大剂量(Dn),确定r值为0.7(r值代表相关系数)。设置LNT剂量依次呈等比数列的5个组别,每组10只,各组裸鼠每天灌胃1次,持续观察14 d。应用SPSS 21.0软件中的Probit模块计算LD50。所有动物实验均经校动物伦理委员会批准(批准号:2021-01011)。
1.2.9 动物模型建立及分组
0.2 mL对数期Capan-1/DDP(1×107个/mL)细胞,接种于裸鼠侧腹,当肿瘤达到50~100 mm3时,分为模型组(生理盐水)、IL-6组(5 μg/kg,预实验确定)、顺铂+IL-6 组[顺铂(4 mg/kg,预实验确定)+IL-6(5 μg/kg)]、IL-6+LNT组[LNT(80 mg /kg)+IL-6(5 μg/kg)],每组8 只,均为腹腔给药,1次/3 d,每周用卡尺测量异种移植瘤的大小(计算体积=最短直径2×最长直径/2)。给药21 d后,裸鼠给予安乐死,记录肿瘤重量。Western blot检测肿瘤组织中p- STAT3、STAT3、Notch1和Hes1的水平。
1.3 数据处理
计量资料以±s表示,SPSS 21.0软件中的Probit模块计算LD50,采用GraphPad Prism 8的单因素方差分析进行多重比较,P<0.05为差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
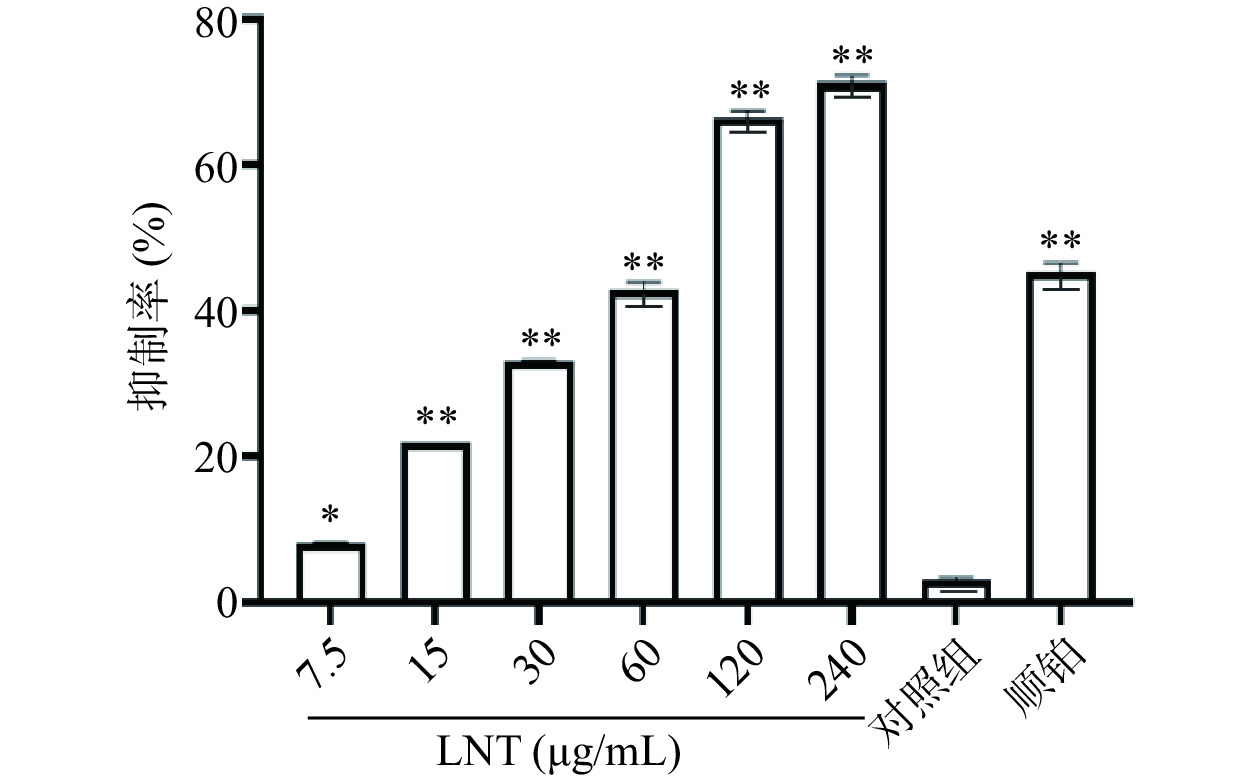
2.1 香菇多糖对胰腺癌细胞给药浓度的筛选
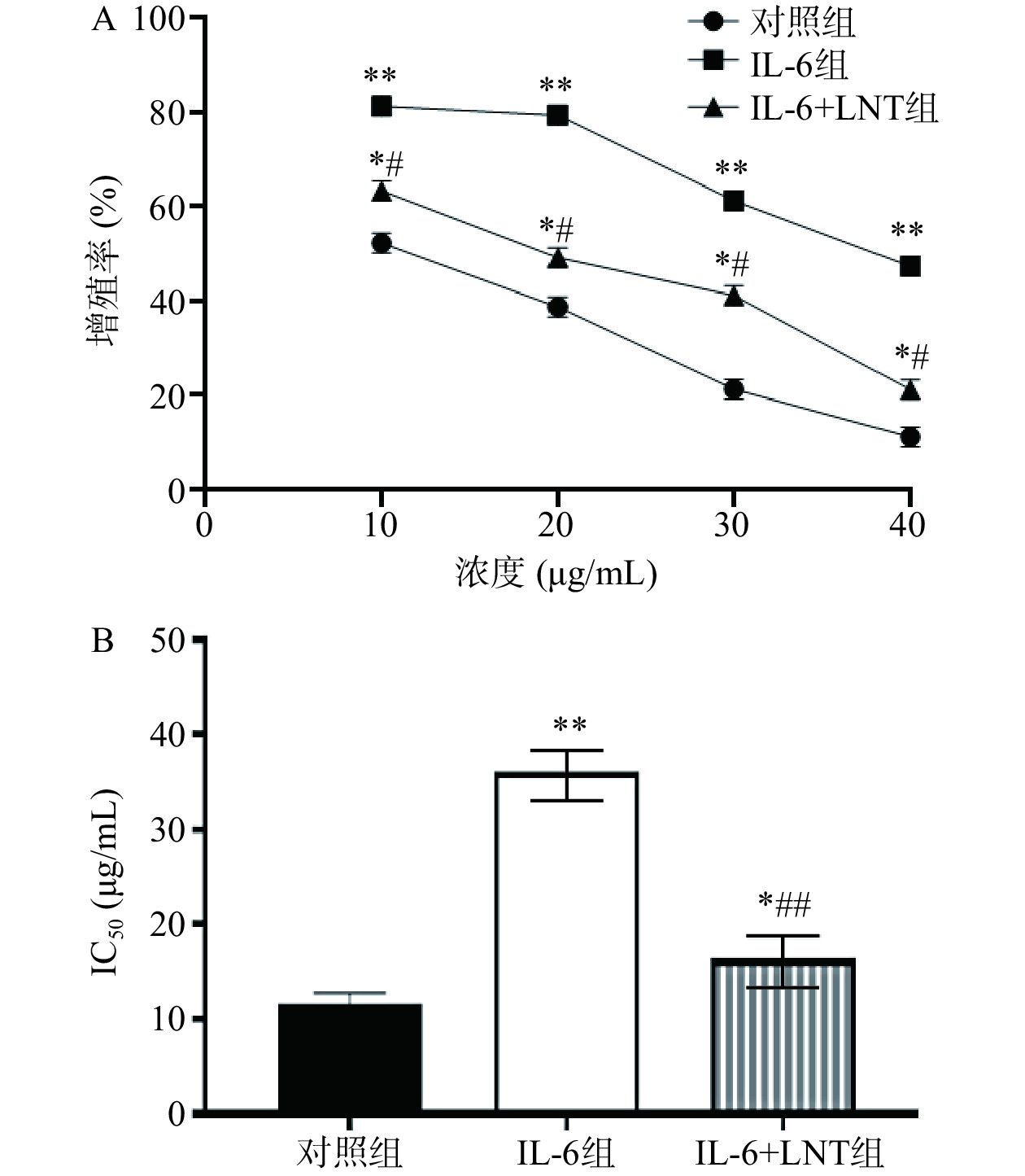
研究表明,香菇多糖是香菇中活性成分之一,具有抗病毒、抗肿瘤、调节免疫功能和刺激干扰素形成的作用[17]。香菇多糖由于其广谱的治疗特性、相对较低的毒性和成本,成为潜在和理想的联合化疗的免疫调节有效活性成分[18]。与相同浓度的顺铂比较,60 µg/mL的LNT对胰腺癌Capan-1细胞抑制率无统计学差异(P>0.05),说明相同浓度的LNT与顺铂存在相同的药效。从图1中可以看出,与对照组比较,7.5、15、30、60、120、240 µg/mL LNT组胰腺癌Capan-1细胞抑制率极显著增加(P<0.01)。通过GraphPad Prism 8统计软件计算香菇多糖对胰腺癌Capan-1细胞的IC50值为73.34 µg/mL,后续香菇多糖依据预实验浓度选择60 µg/mL。
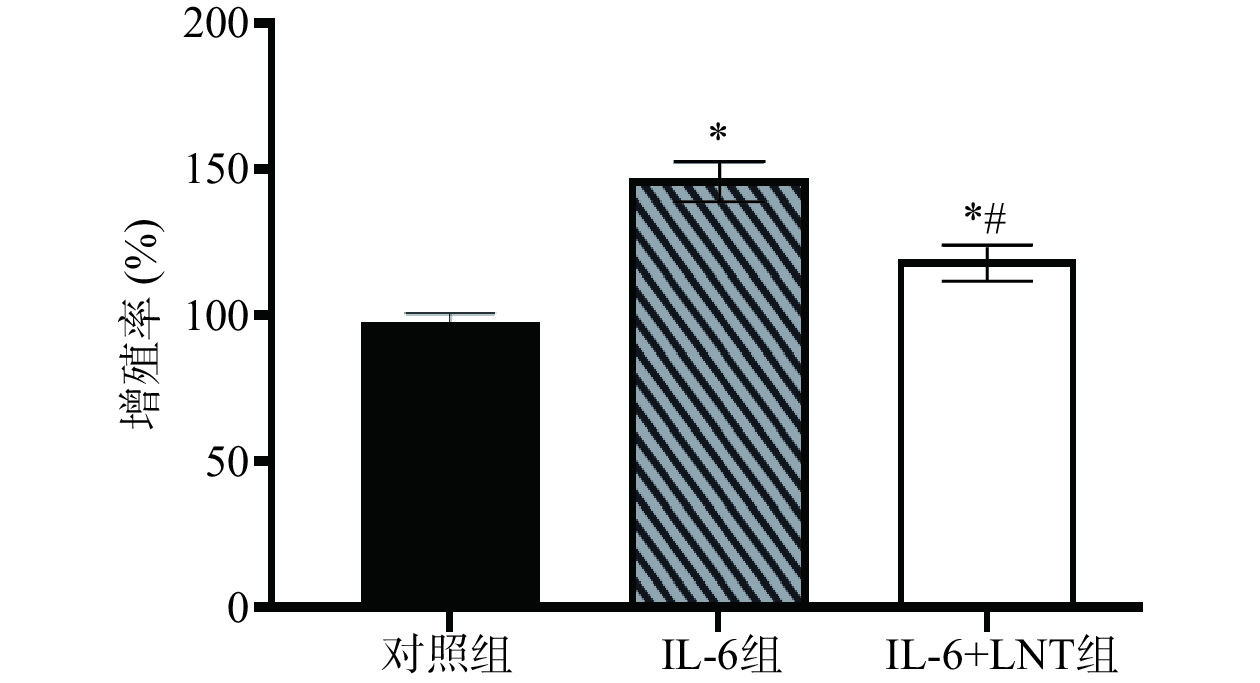
2.2 LNT对胰腺癌Capan-1细胞增殖的影响
在肿瘤细胞中STAT3激活与IL-6和Notch信号通路相关。高水平的IL-6诱导STAT3磷酸化,从而激活Notch信号通路,促进细胞增殖。通过阻断STAT3磷酸化,低水平的STAT3磷酸化能切断IL-6和Notch信号通路之家的联系[19]。而Notch信号通路对癌细胞的增殖具有一定的影响,对癌症的进展发挥重要的作用[20]。同样,在本研究中,与对照组比较,IL-6组增殖率显著上调(P<0.05)(图2),提示高水平的IL-6通过激活STAT3/Notch信号调控胰腺癌Capan-1细胞增殖,而LNT可以通过抑制IL-6/STAT3/Notch信号通路抑制Capan-1细胞增殖。
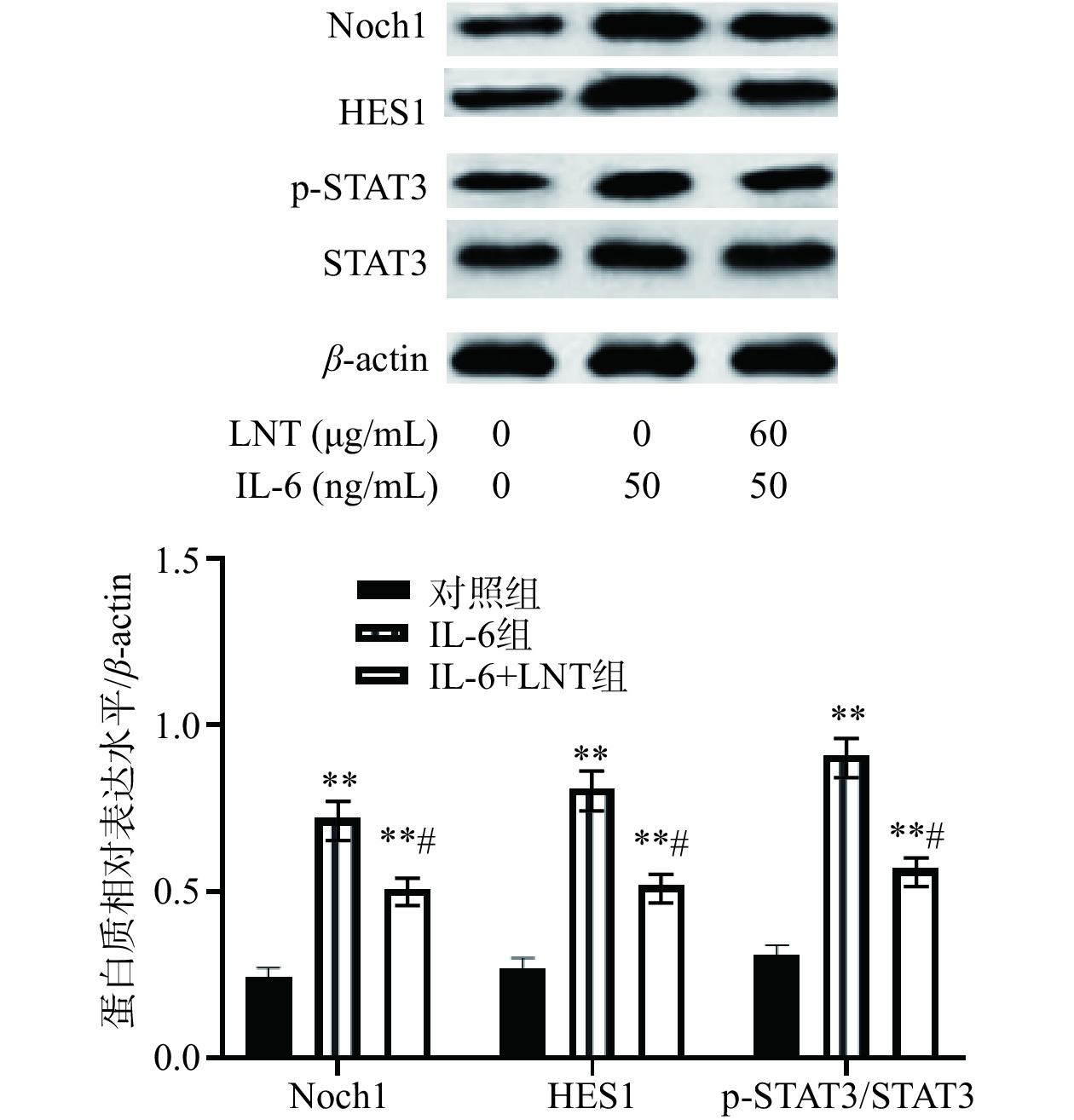
2.3 香菇多糖对胰腺癌Capan-1细胞中的 STAT3/Notch信号通路的影响
已有研究表明,在部分癌细胞中,IL-6通过STAT3磷酸化激活Notch信号通路,而Notch信号通路可以促进肿瘤细胞的自我更新和增殖[21]。由图3可知,与对照组比较,IL-6组p-STAT3/STAT3表达水平极显著上调(P<0.01),表明IL-6可以促进STAT3 磷酸化,而p-STAT3可以以二聚体的形式调控Notch1及其下游Hes1表达水平,而60 µg/mL LNT可以逆转IL-6对STAT3/Notch信号通路的影响。与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组p-STAT3/STAT3、Notch1和Hes1表达水平显著降低(P<0.05),说明LNT能够通过靶向STAT3/Notch信号通路对Capan-1细胞产生影响。
![]() 图 3 LNT对 STAT3/Notch信号通路的影响注:与对照组相比,**P<0.01;与IL-6组比较,#P<0.05,图6同。Figure 3. Effect of LNT on STAT3/Notch signal pathway
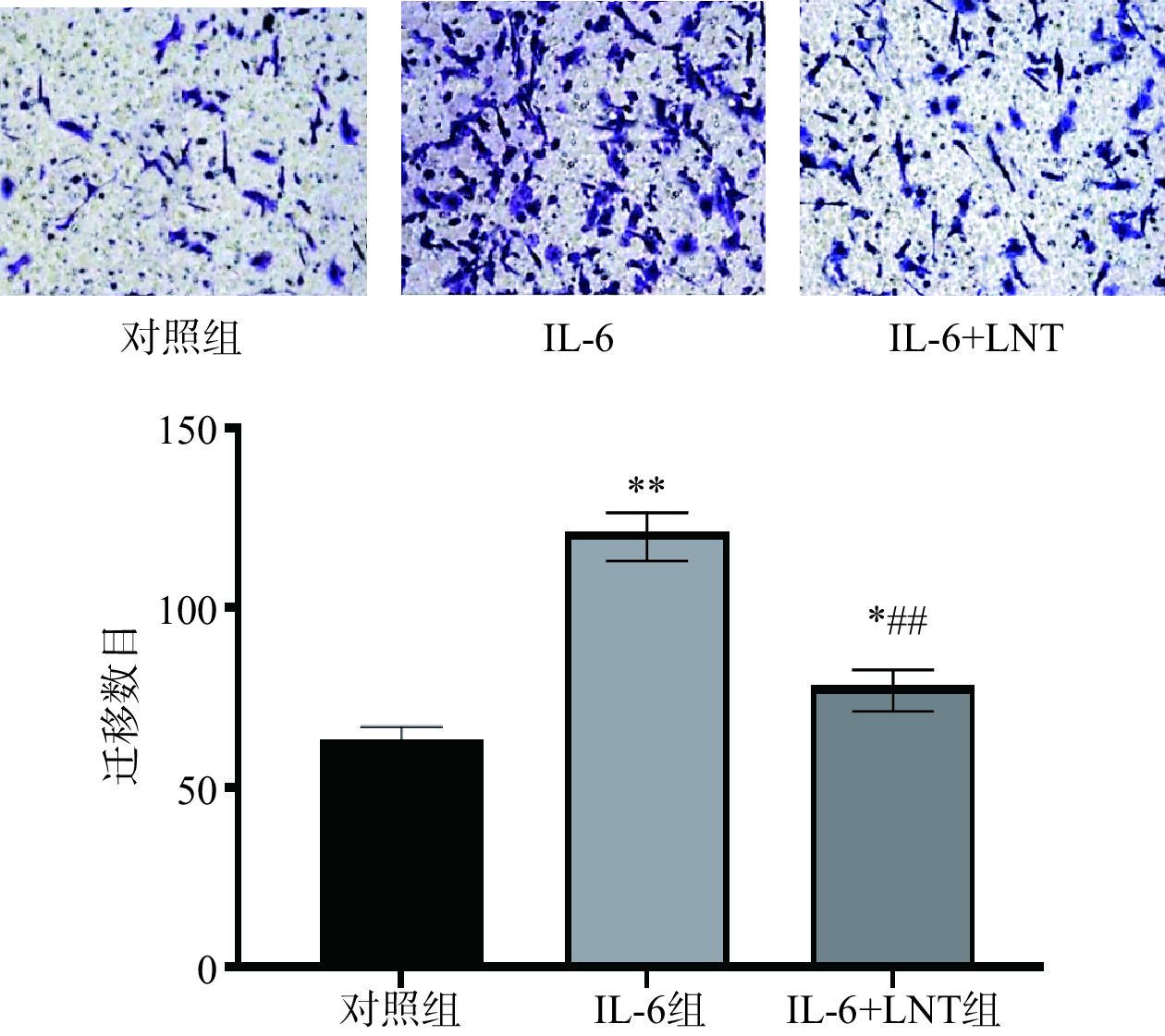
图 3 LNT对 STAT3/Notch信号通路的影响注:与对照组相比,**P<0.01;与IL-6组比较,#P<0.05,图6同。Figure 3. Effect of LNT on STAT3/Notch signal pathway2.4 LNT对胰腺癌Capan-1细胞迁移的影响
研究显示,肿瘤微环境中的促炎因子IL-6具有激活IL-6/STAT3信号通路,促进癌症发展的特征,包括癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[22−23]。本研究中,与对照组比较,细胞迁移率极显著增加(P<0.01)(图4),说明IL-6能刺激胰腺癌细胞迁移。而采用LNT处理后,与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组Capan-1胰腺癌细胞迁移数目显著减少(P<0.05),表明LNT可以逆转IL-6通过STAT3通路对Capan-1胰腺癌细胞迁移的影响。
2.5 LNT对胰腺癌Capan-1对顺铂耐药的影响
本研究中,伴随顺铂浓度的增加,对照组、IL-6组以及IL-6+LNT组Capan-1/DDP细胞增殖率(极)显著下调(P<0.05,P<0.01)(图5),说明10~40 μg/mL的顺铂能有效抑制Capan-1/DDP细胞增殖,并显示明显的浓度梯度依赖性。通过IC50值比较发现,与对照组比较,IL-6组顺铂对Capan-1/DDP细胞的IC50值极显著增加(P<0.01),说明IL-6能促进Capan-1/DDP细胞的耐药性,这与相关报道一致[24],因为IL-6作为一种炎症相关的肿瘤细胞因子,能通过激活IL-6/STAT3信号通路,激活下游一系列因子,导致癌细胞增殖、耐药、侵袭和转移等恶性行为的发生[25]。而采用LNT处理后,与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组顺铂对Capan-1/DDP细胞的IC50值呈现极显著下调(P<0.01),胰腺癌细胞耐药明显逆转,说明LNT可能对治疗胰腺癌以及降低耐药性具有一定的调控潜力。
![]() 图 5 LNT抑制胰腺癌Capan-1对顺铂耐药的影响注:与对照组比较,**P<0.01;与IL-6组比较,#P<0.05,##P<0.01,图8同。Figure 5. Effect ofLNT inhibits cisplatin resistance in pancreatic cancer Capan-1
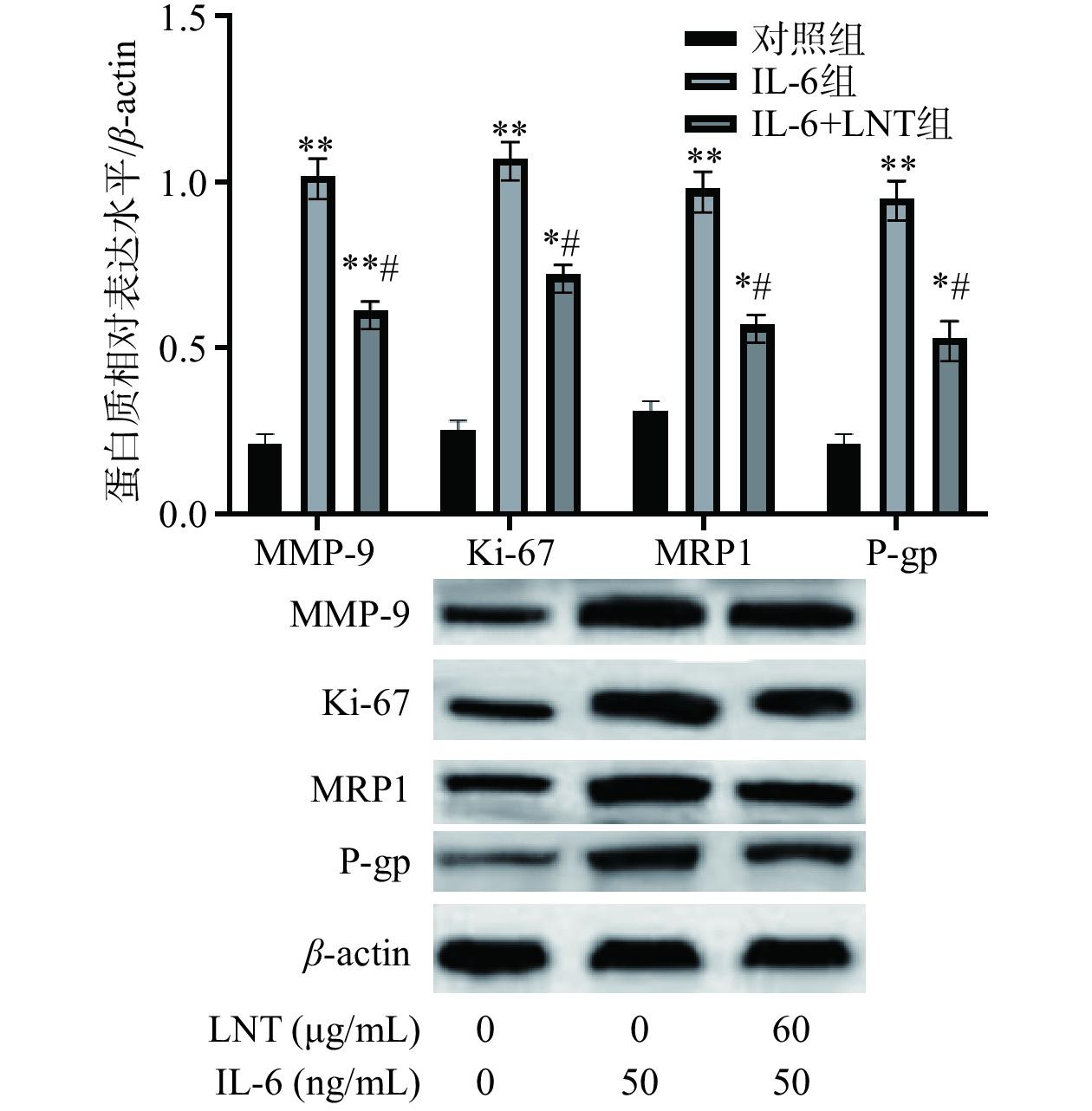
图 5 LNT抑制胰腺癌Capan-1对顺铂耐药的影响注:与对照组比较,**P<0.01;与IL-6组比较,#P<0.05,##P<0.01,图8同。Figure 5. Effect ofLNT inhibits cisplatin resistance in pancreatic cancer Capan-12.6 LNT抑制胰腺癌Capan-1中 Ki-67、MMP-9、P-gp和 MRP1的表达
Ki-67在细胞周期的G1、S、G2和M阶段保持活性,为细胞增殖的标记物,而MMP-9是基质金属蛋白酶最复杂的形式之一,具有降解细胞外基质(ECM)成分的能力,同样MRP1的表达与癌细胞耐药有关,并激活多药耐药家族的有效成员p -糖蛋白(P-gp)的表达[26−28]。本研究中,与对照组比较,Ki-67、MMP-9、MRP1 和 P-gp表达水平(极)显著上调(P<0.05,P<0.01)(图6),说明IL-6能通过Ki-67、MMP-9蛋白的表达促进胰腺癌细胞增值和迁移,并加强其耐药性。而采用LNT处理后,与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组Ki-67、MMP-9、MRP1 和 P-gp表达水平显著降低(P<0.05),进一步验证了LNT抑制Capan-1增值、迁移和耐药的原因,同时也间接说明IL-6可能通过STAT3/Notch通路调节Capan-1胰腺癌细胞增殖、迁移和耐药。
2.7 LNT对裸鼠急性毒性试验
本实验最大给药量为6000 mg/kg,灌胃后,出现发抖、怕冷,扎堆,半小时后恢复正常,无死亡发生,根据外源化学物相对毒性分级标准,一次经口LD50在5000 mg/kg以上为无毒,因此实际香菇多糖无毒。按照预实验最终取剂量为80 mg/kg。
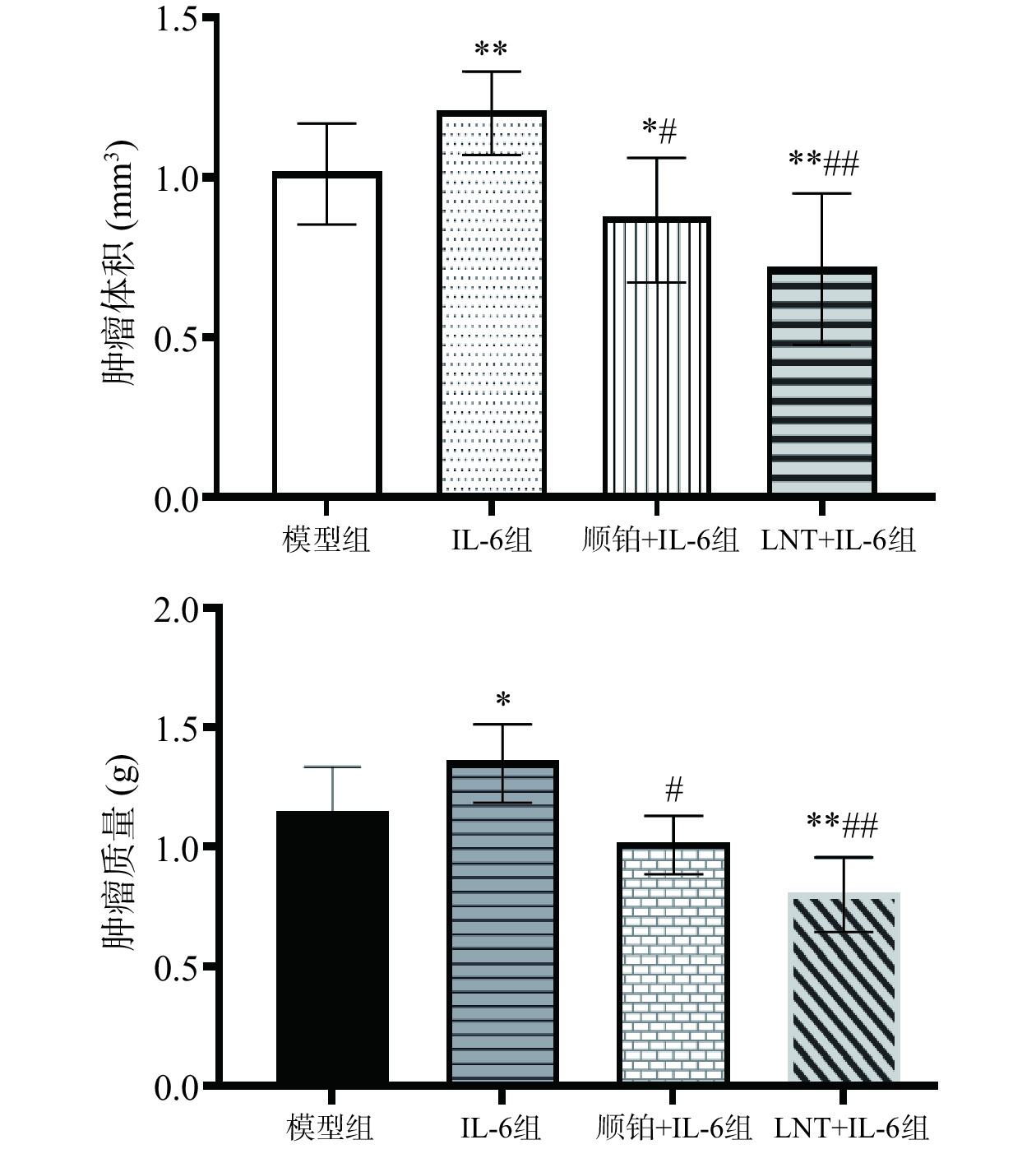
2.8 LNT对胰腺癌移植瘤顺铂耐药的影响
由图7可知,本研究中,与模型组比较,IL-6组瘤体体积、瘤重(极)显著上调(P<0.05,P<0.01),说明IL-6促进了肿瘤的增殖;而与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组瘤体体积、瘤重极显著下调(P<0.01),说明LNT可以发挥抑制IL-6致瘤作用,下调瘤重水平。这与相关研究一致[29],LNT是从香菇中分离出来的β-(1,3)-葡聚糖多糖,已知具有低毒性和抗肿瘤活性,并有可能通过增强宿主的免疫能力、降低炎症水平间接发挥抗肿瘤作用[30]。
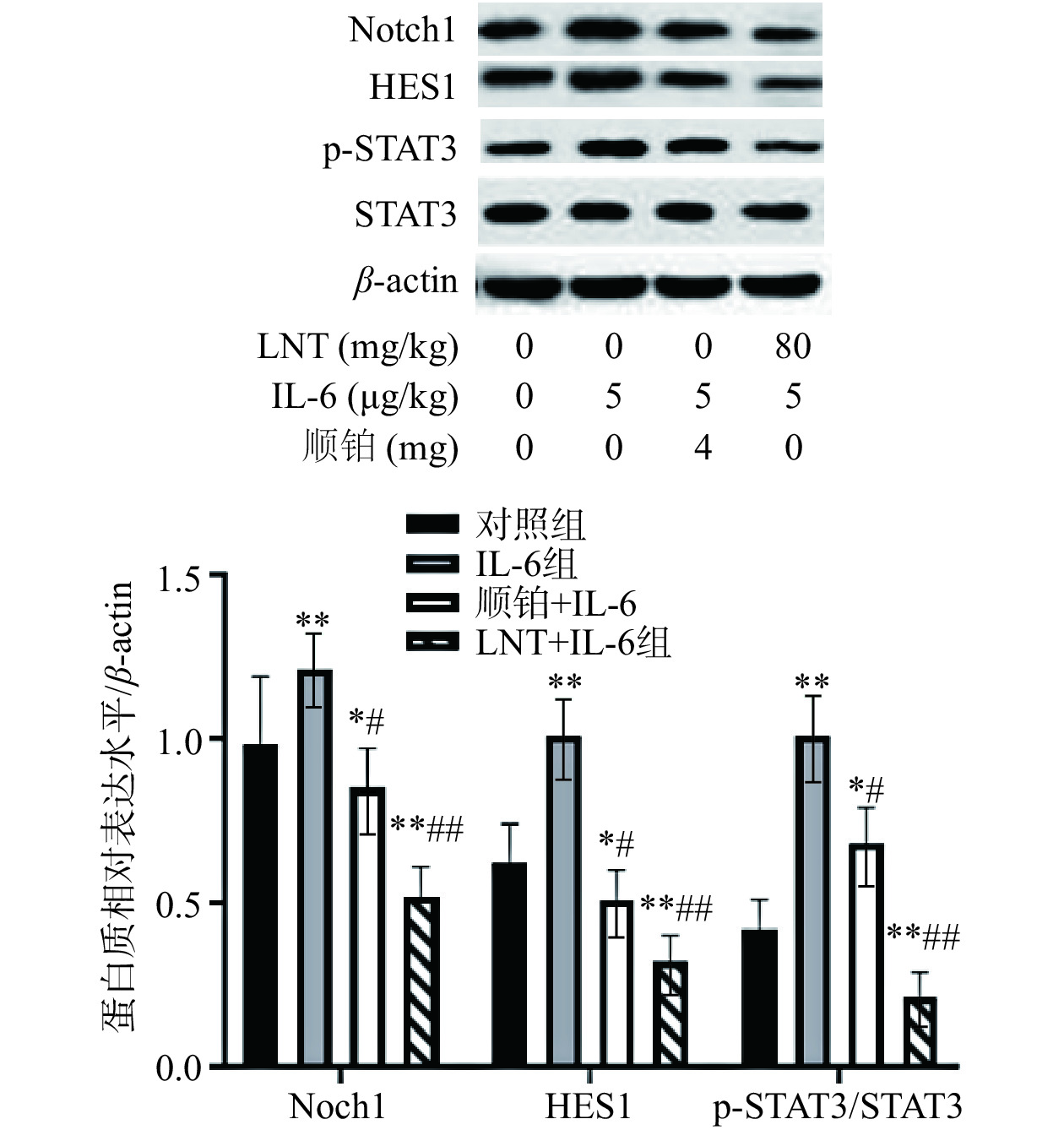
2.9 IL-6 对胰腺癌移植瘤 STAT3/Notch信号通路的作用
在这项研究中,与对照组比较,IL-6组Notch1、Hes1表达水平极显著上调(P<0.01)(图8),证明了IL-6靶向Notch信号后,能导致肿瘤细胞中STAT3出现过度激活,并进一步对Notch1、Hes1产生影响。而LNT和顺铂处理后,与IL-6组比较,IL-6+LNT组p-STAT3/STAT3、Notch1、Hes1表达水平(极)显著下调(P<0.05,P<0.01),说明LNT和顺铂能下调IL-6对致瘤性的影响。
3. 结论
本实验旨在研究LNT对人胰腺癌的直接抗肿瘤作用及其对化疗敏感性的影响,并分析体内外机制。本研究中7.5~240 µg/mL香菇多糖显著(P<0.05)抑制胰腺癌Capan-1细胞增值和迁移,下调p-STAT3/STAT3、Notch1和Hes1表达水平,说明LNT香菇多糖能通过调控IL-6/STAT3/Notch信号通路影响Capan-1的增殖和迁移。针对Capan-1/DDP耐药株结果表明,LNT能下调其对顺铂的IC50,说明LNT增强了Capan-1/DDP对顺铂的耐药敏感性。此外,通过体内实验表明,LNT能下调瘤体体积、瘤重,降低p-STAT3/STAT3、Notch1、Hes1表达水平,这些结果都表明LNT能有效抑制IL-6/STAT3/Notch信号通路,抑制癌细胞增殖,增加耐药敏感性。本研究通过体内外实验阐明了LNT抗胰腺癌的基本机制,为LNT作为一种辅助抗癌药提供了新的认识,为胰腺癌的发生机制、临床治疗提供参考,同时也为香菇多糖的进一步开发提供依据。
-
图 3 LNT对 STAT3/Notch信号通路的影响
注:与对照组相比,**P<0.01;与IL-6组比较,#P<0.05,图6同。
Figure 3. Effect of LNT on STAT3/Notch signal pathway
图 5 LNT抑制胰腺癌Capan-1对顺铂耐药的影响
注:与对照组比较,**P<0.01;与IL-6组比较,#P<0.05,##P<0.01,图8同。
Figure 5. Effect ofLNT inhibits cisplatin resistance in pancreatic cancer Capan-1
-
[1] PARK J K, HANK T, SCHERBER C M, et al. Primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer cells exhibit differential migratory potentials[J]. Pancreas,2020,49(1):128−134. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001459
[2] CHANG C D, CHAO M W, LEE H Y, et al. In silico identification and biological evaluation of a selective MAP4K4 inhibitor against pancreatic cancer[J]. Journal of EnzymeInhibition and Medicinal Chemistry,2023,38(1):2166039.
[3] YANG B S, QUAN Y N, ZHAO W L, et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)-pyrrolo[2, 3-d]pyrimidine derivatives as CDK inhibitors[J]. Journal of EnzymeInhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 2023, 38(1):2169282.
[4] RUPERT J E, NARASIMHAN A, JENGELLEY D H A, et al. Tumor-derived IL-6 and trans-signaling among tumor, fat, and muscle mediate pancreatic cancer cachexia[J]. Journal of Experimental Medicine,2021,218(6):e20190450. doi: 10.1084/jem.20190450
[5] MACE T A, SHAKYA R, PITARRESI J R, et al. IL-6 and PD-L1 antibody blockade combination therapy reduces tumour progression in murine models of pancreatic cancer[J]. Gut,2018,67(2):320−332. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-311585
[6] MA T, WANG D Y, WU J J, et al. KCTD10 functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by triggering the Notch signaling pathway[J]. American Journal of Translational Research,2023,15(1):125−137.
[7] ELBAKRY M M M, ELBAKWRY N M, HAGAG S A, et al. Pomegranate peel extract sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to ionizing radiation, induces apoptosis and inhibits mapk, jak/stat3, β-catenin/notch, and socs3 signaling[J]. Integrative Cancer Therapies, 2023, 22:15347354221151021.
[8] TAO S F, CHEN Q, LIN C, et al. Linc00514 promotes breast cancer metastasis and M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages via Jagged1-mediated notch signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research,2020,39(1):191.
[9] PENG C Y, YU C C, HUANG C C, et al. Magnolol inhibits cancer stemness and IL-6/Stat3 signaling in oral carcinomas[J]. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association,2022,121(1):51−57. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.01.009
[10] VAN DUIJNEVELDT G, GRIFFIN M D W, PUTOCZKI T L. Emerging roles for the IL-6 family of cytokines in pancreatic cancer[J]. Clinical Science,2020,134(16):2091−2115. doi: 10.1042/CS20191211
[11] ZHANG M, ZHANG Y R, ZHANG L J, et al. Mushroom polysaccharide lentinan for treating different types of cancers:A review of 12 years clinical studies in China[J]. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science,2019,163:297−328.
[12] LIU H J, QIN Y, ZHAO Z H, et al. Lentinan-functionalized selenium nanoparticles target tumor cell mitochondria via TLR4/TRAF3/MFN1 pathway[J]. Theranostics,2020,10(20):9083−9099. doi: 10.7150/thno.46467
[13] SHIMIZU K, WATANABE S, WATANABE S, et al. Efficacy of oral administered superfine dispersed lentinan for advanced pancreatic cancer[J]. Hepato-Gastroenterology,2009,56(89):240−244.
[14] HU B, ZHANG K D, LI S B, et al. HIC1 attenuates invasion and metastasis by inhibiting the IL-6/STAT3 signalling pathway in human pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Letters,2016,376(2):387−398. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.04.013
[15] CHEN S Y, CAI K, ZHENG D J, et al. RHBDL2 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of pancreatic cancer by stabilizing the N1ICD via the OTUD7B and activating the notch signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death & Disease,2022,13(11):945.
[16] 张彩芳, 秦令祥, 周婧琦, 等. 基于响应面法优化双酶耦合超高压提取香菇多糖工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2022,33(9):69−74. [ZHANG C F, QIN L X, ZHOU J Q, et al. Optimization of double enzymes coupling ultra high pressure extraction process of lentinan by response surface method and its antioxidant activity[J]. China Food Additives,2022,33(9):69−74.] ZHANG C F, QIN L X, ZHOU J Q, et al. Optimization of double enzymes coupling ultra high pressure extraction process of lentinan by response surface method and its antioxidant activity[J]. China Food Additives, 2022, 33(9): 69−74.
[17] 苏华, 赵玉梅, 陈静, 等. 香菇多糖联合AC方案、紫杉醇对晚期三阴性乳腺癌患者生存情况及PF4、MK、Ki-67表达的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2023,8(4):55−57. [SU H, ZHAO Y M, CHEN J, et al. Effects of lentinan combined with AC regimen and paclitaxel on survival and expression of PF4, MK and Ki-67 in patients with advanced triple negative breast cancer[J]. Clinical Research and Practice,2023,8(4):55−57.] SU H, ZHAO Y M, CHEN J, et al. Effects of lentinan combined with AC regimen and paclitaxel on survival and expression of PF4, MK and Ki-67 in patients with advanced triple negative breast cancer[J]. Clinical Research and Practice, 2023, 8(4): 55−57.
[18] MENG M J, HUO R, WANG Y, et al. Lentinan inhibits oxidative stress and alleviates LPS-induced inflammation and apoptosis of BMECs by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 222(Pt B):2375−2391.
[19] IBRAHIM S A, GADALLA R, EI-GHONAIMY E A, et al. Syndecan-1 is a novel molecular marker for triple negative inflammatory breast cancer and modulates the cancer stem cell phenotype via the IL-6/STAT3, Notch and EGFR signaling pathways[J]. Molecular Cancer,2017,16(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0621-z
[20] HUNG L, HU B, NI J B, et al. Retraction note:Transcriptional repression of SOCS3 mediated by IL-6/STAT3 signaling via DNMT1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis[J]. 2023, 42(1):18.
[21] JI N, YU Z L. IL-6/Stat3 suppresses osteogenic differentiation in ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament via miR-135b-mediated BMPER reduction[J]. Cell and Tissue Research,2023,391(1):145−157. doi: 10.1007/s00441-022-03694-x
[22] 杜晓鹃, 李学军, 李素婷, 等. IL-6调控TLR4/NF-κB炎症信号促进人胰腺癌细胞增殖的实验研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2019, 46(15):2810-2815. [DU X J, LI X J, LI S T, et al. IL-6 promotes the proliferation of human pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cells via the activation of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2019, 46(15):2810-2815.] DU X J, LI X J, LI S T, et al. IL-6 promotes the proliferation of human pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 cells via the activation of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine, 2019, 46(15): 2810-2815.
[23] HE Y L, GUO X R, LAN T Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the function of liver in rats with acute-on-chronic liver failure via downregulating Notch and Stat1/Stat3 signaling[J]. Stem Cell Research & Therapy,2021,12(1):396.
[24] 谢娅, 张嘉琳, 李亚南, 等. 二甲双胍通过抑制IL-6/NF-κB/P-gp改善卵巢癌PARP抑制剂耐药[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2023,58(2):175−182. [XIE Y, ZHANG J L, LI Y N, et al. Metformin improves PARP inhibitor resistance in ovarian cancer by inhibiting IL-6/NF-κB/P-gp[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University(Medical Sciences),2023,58(2):175−182.] XIE Y, ZHANG J L, LI Y N, et al. Metformin improves PARP inhibitor resistance in ovarian cancer by inhibiting IL-6/NF-κB/P-gp[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University(Medical Sciences), 2023, 58(2): 175−182.
[25] ZOU M H, ZHANG X Q, XU C H. IL6-induced metastasis modulators p-STAT3, MMP-2 and MMP-9 are targets of 3,3'-diindolylmethane in ovarian cancer cells[J]. Cellular Oncology,2016,39(1):47−57. doi: 10.1007/s13402-015-0251-7
[26] MIYAKE M, NAKAI D. Effect of proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 on efflux transport of rebamipide in Caco-2 cells[J]. Xenobiotica,2017,47(9):821−824. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2016.1229085
[27] ZHAO X F, LI Y F, DU K, et al. Involvement of human and canine MRP1 and MRP4 in benzylpenicillin transport[J]. PLoS One,2019,14(11):e0225702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225702
[28] YIN Z, MA T T, LIN Y, et al. IL-6/STAT3 pathway intermediates M1/M2 macrophage polarization during the development of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry,2018,119(11):9419−9432. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27259
[29] 张晶, 苏畅, 孔凡铭, 等. 基于IKKβ/NF-κB通路探究香菇多糖联合顺铂对乳腺癌的干预作用[J]. 现代药物与临床,2022,37(9):1932−1937. [ZHANG J, SU C, KONG F M, et al. Explore the intervention effect of lentinan combined with cisplatin on breast cancer based on IKKβ/NF-κB pathway[J]. Drugs & Clinic,2022,37(9):1932−1937.] ZHANG J, SU C, KONG F M, et al. Explore the intervention effect of lentinan combined with cisplatin on breast cancer based on IKKβ/NF-κB pathway[J]. Drugs & Clinic, 2022, 37(9): 1932−1937.
[30] LI M, DU X, YUAN Z, et al. Lentinan triggers oxidative stress-mediated anti-inflammatory responses in lung cancer cells[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry,2022,477(2):469−477. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04293-0





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



