Research Progress on Food Derived Blood Glucose Regulating Peptides
-
摘要: 糖尿病已成为全球最严重的慢性疾病之一,亟需新型的预防、干预、调控手段。食物蛋白源小肽与参与血糖调节的受体、酶、生物分子,以及葡萄糖转运体相互作用,干预并调控血糖水平。它具有组织亲和力和特异性高、副作用低的优势,是一种前景广阔的糖尿病应对方案。本文综述了食源性血糖调节活性肽的作用机制、动植物食物来源、结构特征、制备和活性评价手段、构效关系研究方法,以及产业化推广的诸多挑战,包括DPP-IV抑制肽、α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制肽、α-淀粉酶抑制肽的序列特征,多种生物信息学技术(电子模拟、分子对接、定量构效关系等)联用分析降糖机制与活性位点。为未来研究提供了思路:a.从细胞通路、代谢组学角度明确机理,保障并强化体内功效;b.通过细胞和动物实验结合临床试验评估消化稳定性、生物利用度和安全性;c.采用新型载体技术,提高肽基活性物质的溶解度、稳定性和渗透性。本文期望为促进降糖功能食品的产业化应用提供理论和科学参考。Abstract: Diabetes mellitus has become one of the most serious chronic diseases all over the world, which need to be to prevented, intervened, regulated by innovative means. Food derived small peptides can regulate blood glucose by acting with receptors, enzymes, biological molecules and glucose transporters. They show high tissue affinities, significant specificities, with low side effects, which are promising strategies for diabetes mellitus. This survey summarizes the mechanisms, food protein sources, preparation and activity evaluation procedures, structure-activity relationships and challenges during commercial development of food derived blood glucose regulating peptides. Specifically, it includes the sequence characteristics of DPP-IV inhibitory peptide, α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides and α-amylase inhibitory peptides. Besides, the active sites are also discussed from different perspectives of sequence alignment: bioinformatics technologies such as in silico analysis, molecular structure alignment/docking, and quantitative structure activity relationship analysis. It may provide ideas for future research: a. Exploring the mechanism from the aspect of cell pathways and metabonomic to improve in vivo efficacy. b. Combining cell/animal experiments with clinical trials to evaluate digestive stability, bioavailability and safety. c. Innovative carriers to improve the solubility, stability and permeability of peptides. Supports for promoting the industrial application of diabetes functional foods are expected.
-
糖尿病已成为全球最严重和最常见的慢性疾病之一。2021年,全球20~79岁人群的糖尿病患病率约为10.5%(5.366亿人),支出约9660亿美元;2045年预估患病率将达12.2%(7.832亿人),预估支出10540亿美元[1]。糖尿病的病因包括胰岛素分泌缺乏、胰岛素受体功能损坏,或两者兼有。可分为四种类型:类型Ⅰ、类型Ⅱ、其他类型、妊娠糖尿病,其中Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型最常见。其并发症包括心血管疾病和癌症等[2]。糖尿病尚无法治愈,治疗方法包括口服降糖药、注射胰岛素、胰岛移植等。药物治疗的成本较高,低收入人群难以负担,且长期服药可能导致胰腺β细胞功能衰退等副作用,亟需新型的预防、干预、调控和治疗手段。
生物活性肽是蛋白质水解后释放的2~20个氨基酸长度的片段,可与人体代谢的某些酶和细胞受体相互作用[3],具有分子量低、结构简单,安全性、耐受性、选择性和效力高,代谢途径可预测等优点[4−5]。其中,血糖调节活性肽在维持血糖水平等生理稳态方面具有营养和药用潜力,可干预初期高血糖,从而预防糖尿病[6]。其结构特征与生物活性之间的量变规律具有重要的理论意义和应用价值。分子对接、定量构效关系模型等生物信息学手段,已被用于筛选和设计食源性血糖调节活性肽序列,并预测其活性[7]。本文整理归纳了近5年发表的多篇论文,综述了食源性血糖活性肽的研究和应用进展,探讨多种小肽的血糖调节机制及其构效关系,分析产业化推广的挑战性,以期探索血糖调节产品的新研发趋势。
1. 肽的血糖调节机制、食物来源与结构特征
1.1 调节机制
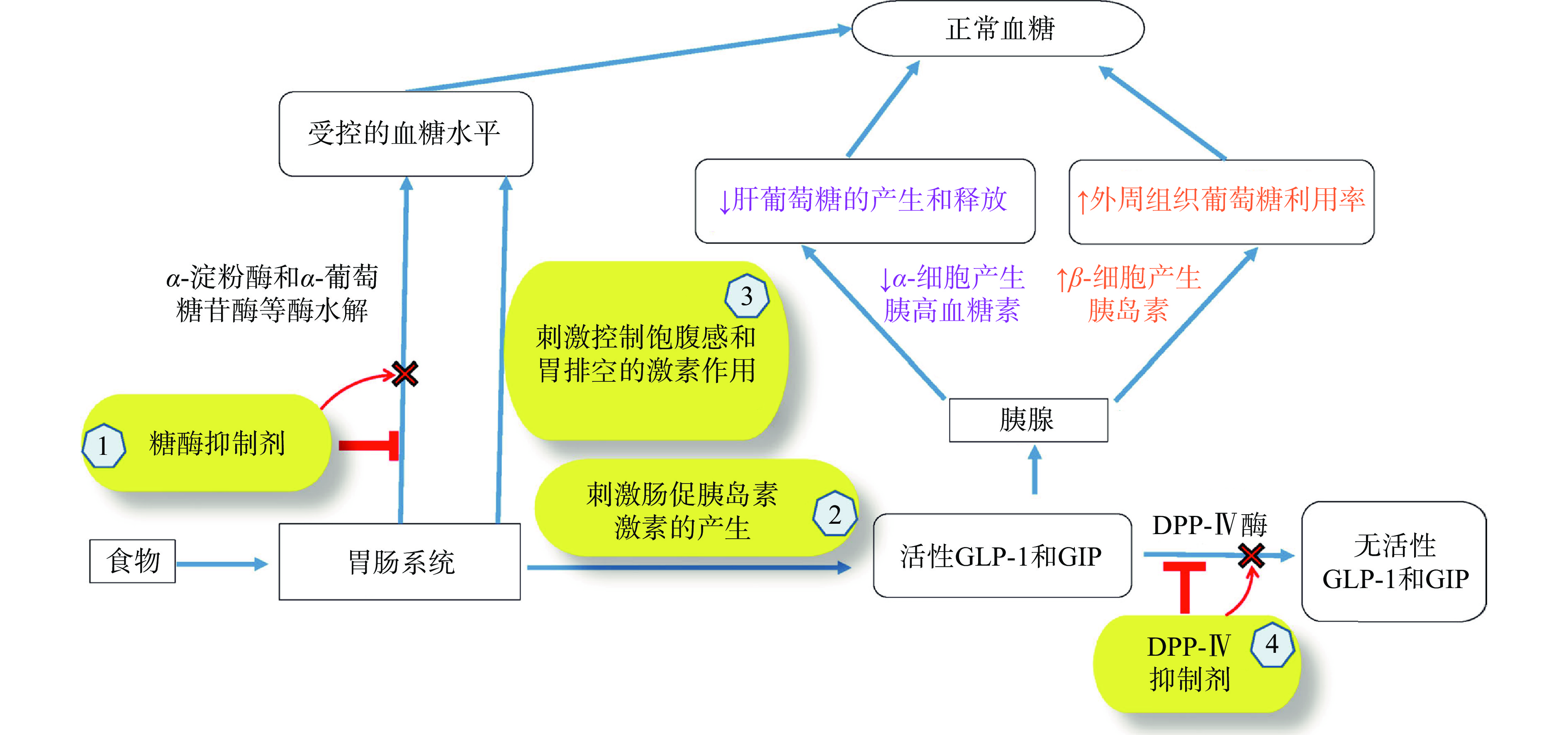
活性肽的血糖调节机制较为多样,目前主要有如下几类:a.通过抑制糖酶(α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶)的活性,抑制胰岛淀粉样多肽的纤维化聚集,或作为葡萄糖转运系统抑制剂、胰岛素模拟物等,如图1所示。肽可以通过氢键、极性和疏水性作用与酶活性位点和/或催化位点的氨基酸结合,阻止酶与底物相互作用。α-淀粉酶由胰腺和唾液腺分泌,水解淀粉等多糖中的α-D-(1-4)糖苷键,产生低聚糖。随后低聚糖被α-葡萄糖苷酶水解成单糖,消化吸收后造成血糖升高。b.肠促胰岛素分为胰高血糖素样肽-1(glucagon like peptide-1,GLP-1)和胃抑制肽(gastric inhibitory peptide,GIP),二者诱导约70%的餐后胰岛素分泌[8]。GLP-1可通过饮食达到降糖效果,应用前景良好。目前GLP-1受体激动剂或类似物的研究主要包括:修饰天然GLP-1、制备长效缓释制剂、植入式渗透泵、口服等非注射制剂[9],但未见公开的高纯度GLP-1促进肽。c.二肽基肽酶IV(dipeptidyl peptidase-IV,DPP-IV)会裂解肠促胰岛素,降低其水平,升高血糖。DPP-IV抑制剂与其他药物相比,副作用较小。已在细胞水平证实燕麦球蛋白源肽LQAFEPLR[10]、鲢鱼鳔蛋白源肽WGDEHIPGSPYH及其水解物IPGSPY具有良好的DPP-IV抑制活性[11]。小鼠模型证实了黑茶蛋白源肽AGFAGDDAPR有效抑制了DPP-IV并改善胰腺β细胞功能[12]。d.葡萄糖转运载体蛋白分为钠依赖性葡萄糖转运体(sodium-dependent glucose transporters,SGLT)和非钠依赖性葡萄糖转运体(glucose transporter,GLUT),分别有6种和5种亚型。活性肽通过促进GLUT异位和减少SGLT表达可发挥降糖活性,与胰岛素无关。现有研究集中在改善GLUT-4的易位障碍,提高其转移到细胞膜的数量。已在动物模型中验证[13],尚未进行临床试验。
1.2 血糖调节活性肽的食物来源与结构特征
蛋白质在自然状态下结构复杂,无法与其他分子结合,水解暴露了不同的氨基酸残基,形成了肽链的不同性质。肽的分子量和氨基酸序列会影响其性质,可能与残基的疏水性或官能团有关。而肽的蛋白质来源需要在评估活性的同时考虑环境和经济因素,优先选择油粕、内脏、皮肤等可持续的低值来源,提升经济附加值并减少污染。研究最多的植物来源是豆类和谷类,动物来源是乳类和海洋鱼类。表1是近5年报道的降糖活性肽序列及其来源,可见以下特征。
表 1 近5年(2017—2022年)报道的食源性血糖调节活性肽的来源、序列与活性评价方式Table 1. Sources, sequences and activity evaluations of food derived antidiabetic peptides reported in recent 5 years (2017—2022)血糖调节方式 来源 序列1 活性评价方式 文献 α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制 羽扇豆 SPRRF,FE,RR 体外,生物信息学 [48] 辣木籽 KETTTIVR 体外 [29] 牡丹籽粕 TFFM,FFFM,YYFM 体外 [49] 水牛乳酪蛋白 RNAVPITPTLNR,TKVIPYVRYL,YLGYLEQLLR,FALPQYLK 体外,生物信息学 [50] 鹰嘴豆 NGIF,QHNIGF,THMAGS,HAAM,NGGR,GE,QPHR 体外,生物信息学 [51] 小麦胚芽 LDLQR,AGGFR,LDNFR 体外 [28] 山茶籽 GHSLESIK,GLTSLDRYK,SPGYYDGR 体外,生物信息学 [52] 尾穗苋 FPFPR 体外,生物信息学 [53] 牛乳和骆驼乳酪蛋白 LPTGWLM,MFE,GPAHCLL 体外,生物信息学 [42] 骆驼乳乳清蛋白 CCGM,MFE 体外,生物信息学 [54] 中华鳖卵 HNKPEVEVR,ARDASVLK,SGTLLHK 体外,生物信息学 [55] 干腌火腿肌肉 EA,PP,VE,PE,AD,LGVGG,GGLGP,AEEEYPDL 体外 [40] 大豆 WLRL,SWLRL,LLPLPVLK,GSR,EAK 体外 [30−31] 米糠 YGIYPR等39条序列(6~20肽) 体外,生物信息学 [56] 黑茶 TAELLPR,CGKKFVR,AVPANLVDLNVPALLK,VVDLVFAAAK 体外,生物信息学 [37] α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制,
α-淀粉酶抑制橙种子 LVDVGNSDNQ等26条序列(10~14肽) 体外 [57] 骆驼乳乳清蛋白 PAGNFLMNGLMHR,PAVACCLPPLPCHM,MLPLMLPFTMGY,PAGNFLPPVAAAPVM 体外,生物信息学 [54] 胡桃楸 LPLLR 体外, Hep G2细胞 [38] 大鲵 CSSV,YSFR,SAAP,PGGP,LGGGN 体外 [58] α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制,
DPP-IV抑制黑茶 MSLYPR,QGQELLPSDFK 体外,生物信息学 [37] α-淀粉酶抑制 羽扇豆 RPR,PPGIP,LRP 体外,生物信息学 [48] 骆驼乳酪蛋白 FLWPEYGAL 体外,生物信息学 [42] 骆驼乳清蛋白 FCCLGPVPP 体外,生物信息学 [54] 斑豆 PPHMLP,PPHMGGP,PLPWGAGF,PLPLHMLP,LSSLEMGSLGALFVCM 生物信息学 [34] α-淀粉酶抑制,
DPP-IV抑制燕麦球蛋白 GDVVALPA,DVVALPAG 体外 [59] 骆驼乳 MPSKPPLL,KDLWDDFLGL 体外 [39] DPP-IV抑制 高粱醇溶蛋白 LPFYPQ,GPVTPPILG,LPFYPQGV 体外,生物信息学,Caco-2细胞 [60] 牛皮革胶原蛋白 GPVG,FGPGP,APGGAP,GPPGPT,GPVGPPG 体外,生物信息学 [61] 牦牛骨胶原蛋白 MGPR 体外,生物信息学,Hep G2细胞 [62] 罗非鱼皮肤胶原蛋白 WF,VW,WY,WG 生物信息学 [63] 鹰嘴豆 SFDLPAL,EVLSEVSF,VVFW 体外,生物信息学 [64] 榛子粕 PGHF,FMRWRDRFL,APGHF,NSMVGNMIFWFFFCILGQPMCVLLY,YHDLMNR,FFFPGPNK,LSVPNLYVWLCMFY,LILVSFSLCLLVLFNGCLG 体外,生物信息学 [15] 夏威夷果 AESE,EQVR,EQVK,EEDNK,EECK,EVEE 生物信息学 [65] 尾穗苋 FPFPPTLGY 体外,生物信息学 [53] 牛乳酪蛋白 HLPGRG,QNVLPLH,PLMLP 体外,生物信息学 [42] 绵羊皮胶原蛋白 GPAGPIGPV,GPAGPOGFPG 生物信息学 [66] 鲭鱼副产品 GPLGAAGP,GRDGEP,MTGTQGEAGR 体外,生物信息学 [67] 钝顶节螺藻藻胆蛋白 DIGYYLR等26条序列(7~27肽) 体外,Caco-2细胞 [68] α-乳白蛋白 LDQWLCEKL 体外 [69] 卵清蛋白 CF,KM,AM,GR,FR,LPR,PRM,ELPF,ADHPF 生物信息学 [21] 鸡蛋 MIR,ADF,FGR 生物信息学 [70] 大西洋鲑鱼皮胶原蛋白 LDKVFR 体外,生物信息学 [71] 沙丁鱼 NAPNPR等19条序列(4~9肽) 体外 [24] 大嘴鲈 VSM,ISW,VSW,ICY,ISD,ISE 体外,生物信息学 [72] 红茶 AGFAGDDAPR 体外,链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病小鼠 [12] 骆驼乳乳清蛋白 VPV,YPI,VPF,LAHKPL,ILDKEGIDY 体外 [73] 斑巴拉豆 LN,IN,VK,VQ,VD,LT,VE,VY,IP 体外 [74] 大豆 LPYP,IAVPGEVA,IAVPTGVA Caco-2细胞、体外血清 [16−17] 羽扇豆 LTFPGSAED Caco-2细胞、体外血清 [16] 纳豆 KL,LR 体外 [75] 牛乳蛋白 LKPTPEGDL,LPYPY, IPIQY,WR Caco-2细胞 [18] 马乳清蛋白 NLEIILR,TQMVDGGIMGKFR 体外 [19] 南极磷虾 PAL,KVEPLP 体外 [20] 上述三种活性 尾穗苋,藜麦,鼠尾草 IW,PW 生物信息学 [76] 燕麦种子 GDVVALPA,DVVALPAG 体外 [35] 钝顶螺旋藻 GVPMPNK,LRSELAAWSR,RNPFVFAPTLLTVAAR 体外, Hep G2细胞 [77] 发芽大豆 IKSQSES等26条序列(6~18肽) 体外 [78] 藜麦 IQAEGGLT,DKDYPK,GEHGSDGNV 体外 [41] 改善胰岛素抵抗 大豆 ISCNGVCSPFDIPPCGTPLCRCIPA GLFVGKCRHPYG C57BL/6J小鼠,3T3-L1小鼠前脂肪
细胞[45] 大鲵皮肤 GPPGPA Hep G2细胞,生物信息学 [79] 胡桃楸 LVRL,LRYL,VLLALVLLR Hep G2细胞 [80] 刺参 FRLPNGGL等58条序列 3T3-L1小鼠前脂肪细胞, Hep G2细胞 [81] 抑制胰岛素受体激动剂,SGLT-1、DPP-IV、GLUT-2 苦瓜 LIVA,TSEP,EKAI,LKHA,EALF,VAEK,DFGAS,EPGGGG 生物信息学 [43] 血糖调节 鲑鱼 IPVE,IVDI,IEGTL,VAPEEHPTL L6大鼠成肌细胞,FAO大鼠肝细胞 [46] 抑制DPP-IV,刺激胰岛素分泌 方鲷 IPV等22条序列(3~4肽)与VPDPR等15条序列(4~5肽) Caco-2细胞,BRIN-BD11细胞 [44] 抑制DPP-IV,增加INS-1胰岛素分泌 鲢鱼鱼鳔 WGDEHIPGSPYH 体外,生物信息学,Caco-2细胞,INS-1细胞 [11] 胰岛素调节 大西洋鲑鱼 IAY,IGY L6大鼠成肌细胞 [82] 抑制DPP-IV,α-葡萄糖苷酶、GLUT-2和GLUT-5 燕麦球蛋白 LQAFEPLR,EFLLAGNNK 体外,Caco-2细胞 [10] 抑制DPP-IV,调节胰岛分泌和GLP-1活性 大西洋鲑鱼皮明胶 GPAG,AVLGPK,AVLGPQ 体外,BRIN-BD11细胞,GLUTag细胞 [47] 阻断GLUT-2和SGLT-1 黑豆 AKSPLF,ATNPLF, FEELN,LSVSVL 体内和体外 [83] 注:1肽序列由氨基酸单字母符号表示。 1.2.1 DPP-IV抑制肽的来源与结构特征
DPP-IV抑制肽的蛋白来源很丰富,植物源包括海藻[14]、榛子粕[15]、燕麦球蛋白[10]、羽扇豆[16]和大豆[17],动物源有乳蛋白[18]、海洋鱼类,马乳[19]、南极磷虾[20]、蛋清[21]等。其分子量大多低于500 Da[22],结构特征较为清晰:序列中疏水性氨基酸的含量、N端氨基酸的疏水性与芳香环结构是重要特征[22],但并不仅限于此。肽链的N1位或N2位上存在脯氨酸、丙氨酸等疏水性氨基酸[23−24],或者N1位上存在异亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸等芳香族氨基酸[14]。C1位脯氨酸,支链上的亮氨酸和异亮氨酸[25]都与活性有关。氨基酸组成上富含疏水性氨基酸(丙氨酸、甘氨酸、异亮氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、蛋氨酸、色氨酸和缬氨酸),也可能出现亲水性氨基酸(苏氨酸、组氨酸、谷氨酰胺、丝氨酸、赖氨酸和精氨酸)[26]。表1所示的序列特征为C端的精氨酸、酪氨酸、苯丙氨酸和赖氨酸,N端的亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸和甘氨酸。
1.2.2 α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制肽的来源与结构特征
目前已从多种来源中获得α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制肽,包括大麻籽[27]、小麦胚芽[28]、辣木籽[29]、大豆[30−31]等。α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性的有无和大小由特征氨基酸及其序列位置决定,可能包括N端的丝氨酸、苏氨酸、酪氨酸、赖氨酸和精氨酸,C2位的脯氨酸,以及C端的甲硫氨酸或丙氨酸[25]。含有疏水性氨基酸[27]、必需氨基酸和支链氨基酸[27]的肽链,通过疏水等相互作用对α-葡萄糖苷酶表现出强烈的抑制活性,尤其是亮氨酸和脯氨酸[27,30]。表1显示最主要的结构特征是C端的精氨酸、赖氨酸和甲硫氨酸,N端的亮氨酸、脯氨酸和甘氨酸。
1.2.3 α-淀粉酶抑制肽的来源与结构特征
α-淀粉酶体外抑制活性肽的来源包括小茴香籽、孜然籽[32]、罗勒种子、斑豆[33−34]、多种乳类等。对其结构特征的阐释相对较少,侧重以局部的氨基酸结构描述,揭示特征氨基酸及其位点的可能作用[32]。需进一步研究,以建立更成熟的表征模型。已知序列中通常含有亮氨酸、脯氨酸、甘氨酸、苯丙氨酸、丙氨酸、亮氨酸和缬氨酸等疏水性氨基酸[34−35],以及半胱氨酸、蛋氨酸、组氨酸和丝氨酸等亲水性氨基酸[34]。例如N端存在甘氨酸[33]、脯氨酸和亮氨酸[34],C端存在亮氨酸,以及两端存在苯丙氨酸[33]。同时,有支链(赖氨酸、苯甲氨酸、酪氨酸和色氨酸)和阳离子残基的肽更易与α-淀粉酶结合[36]。表1中α-淀粉酶抑制肽序列两端都富含疏水性的脯氨酸和亮氨酸。
1.2.4 其他血糖调节活性肽的来源与结构特征
同一条序列可能具有多种降糖活性。例如,黑茶[37]、胡桃楸种子[38]、骆驼乳[39]、西班牙干腌火腿[23,40]小肽具有两种活性,而燕麦种子[35]、藜麦[41]、牛乳[42]、骆驼乳小肽等同时具有上述三种活性。在抑制DPP-IV活性的同时,苦瓜肽限制了SGLT-1、GLUT-2表达[43],鲢鱼鳔源肽WGDEHIPGSPYH及其水解物IPGSPY促进了胰岛素分泌[11],方鲷源肽增强了BRIN-BD11细胞的胰岛素分泌活性[44]。此外,小肽还可以改善胰岛素抵抗[45]、调节葡萄糖摄取和/或肝糖原形成[46]、介导 P13K/AKT、MAPK通路提高胰岛素敏感性[47]等。
2. 食源性血糖调节活性肽的制备、活性评价与构效关系
2.1 肽段释放
生物活性肽常见的制备方法有酶水解、微生物发酵、化学水解、化学合成等。化学水解法副产物较多,可能有毒性[3]。酶解法选用来自微生物的食品级蛋白酶,特异性和安全性高,是目前的首选工艺。酶作用在肽链内部/两端,分别为内/外肽酶。内肽酶将蛋白分解成多肽,随后经外肽酶分解成更小的肽和游离氨基酸。酶解低值鱼类制备活性肽已实现中试生产[84]。然而,酶解方法学仍受到经验等多因素影响。可利用实验设计质量、响应面法,针对每个底物/蛋白质优化关键参数(温度、时间、pH、酶的活性和稳定性、复合酶解顺序等)[73]。发酵法的产量低,产品不稳定,和酶法一样会生成次级代谢产物等杂质。化学合成法是定向合成已知的氨基酸序列,操作复杂,成本高,安全性存疑,主要用于药物研发和机制探究。对于食源性肽基物质来说,酶-菌耦合技术工具[85]、非热辅助预处理(高压、超声波、微波、脉冲电场等)和亚临界水解[86]等新技术也可以提高酶解效率。
2.2 分离纯化
水解产物是不同大小肽段、副产物和残留试剂的混合物,可能会互相拮抗,必须进行纯化浓缩。纯化是基于肽序列和分子的物理化学性质(分子量、极性或电荷)进行分离,应用最广泛的有超滤、色谱和透析。超滤以膜过滤为基础,同时完成分离和浓缩。通过选择截留分子量分离活性最高的组分,便于放大生产。但重现性差,疏水性肽和膜易相互作用,导致膜污染和堵塞[87]。色谱法分辨率高,常用的方法有尺寸排阻色谱(size exclusion chromatography,SEC)、反相色谱(reversed-phase chromatography,RPC)和离子交换色谱(ion-exchange chromatography,IEC),分别利用肽段的分子量、疏水特性和静电特性[3]。但色谱技术可能造成肽失活,且耗时、昂贵,不利于商业化。为了克服各技术弊端,并进行准确的分离纯化,多维色谱组合以及多种分离方法联用是未来的方向。如综合运用电渗析、多级循环膜反应器、色谱与超滤技术[87]。主要的挑战是操作成本的增加,以及流动相在多维系统中的不相容性,如正相和反相色谱、亲水和疏水色谱。例如,Najafian等[88]使用正交三维的分离方法从发酵鱼提取物中鉴定了生物活性肽AIPPHPYP和IAEVFLITDPK。
2.3 序列鉴定
鉴定序列后才能验证肽组分的实际活性,进而评价生物利用度、稳定性和功能性等。肽序列鉴定常采用质谱技术,包括电喷雾电离质谱(electrospray spray ionization mass spectrometry,ESI-MS)[40]、快速原子轰击质谱(fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry,FAB-MS)、基质辅助激光解吸/电离质谱(matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry,MALDI-MS)。然而质谱手段也有局限性:高活性小肽(<4个氨基酸长度)接近质谱的检测极限[89];酶的非特异性切割;产物的复杂性(游离氨基酸、中小肽、多肽、低聚物、未消化蛋白质)会造成干扰[3]。
2.4 活性评价
血糖调节活性评价方法分为体外评价、体内验证和生物信息学分析。体外评价通常是测定DPP-IV、α-葡萄糖苷酶、α-淀粉酶的抑制活性[5],相对成熟可靠,已有大量研究(表1)。但体内的环境会影响降糖肽的作用方式与效果,需要细胞或动物实验来验证。细胞培养技术较为经济、快速,常用小鼠前脂肪细胞(3T3-L1、3T3-F442A)、C2C12小鼠成肌细胞、GLUTag小鼠肠内分泌细胞、β-TC-6小鼠胰腺细胞、L6大鼠成肌细胞、INS-1大鼠胰岛细胞瘤细胞、FAO大鼠肝细胞、HepG2细胞,Caco-2细胞、BRIN-BD11细胞等。目前已进行常见降糖活性和通路的胞内研究,例如HepG2细胞中的PI3K和AMPK通路,肽与α-葡萄糖苷酶相互作用[29];WGDEHIPGSPYH和IPGSPY对Caco-2和INS-1细胞的DPP-IV抑制活性与胰岛素促进作用[11];三肽IAY和IGY在L6细胞内浓度2.8 pM时显示出抑制活性[82]。但细胞试验的结果不能直接推及到体内,体内验证通常以链脲佐菌素等化学物质诱导的糖尿病大鼠、小鼠模型,或者糖尿病人为对象。例如,海参水解物通过触发PI3K/Akt信号通路改善糖尿病大鼠的胰岛素抵抗[13]。单一的动物模型无法完全反映人体的病理特征,且大多数体内验证仅达到水解物验证或组学筛选鉴定层面,少见高度纯化肽序列的临床验证。生物信息学方法从多肽的结构特性入手,研究分子靶点和作用机制。比传统方法节约时间,经济成本更低,但是准确性仍待提高,需要结合体内外实验进行验证[90]。目前相关研究大多停留在体外阶段,体内的降糖作用是应用推广的关键。
2.5 生物信息学分析
生物信息学分析对于活性肽的鉴定、表征和生产具有重要作用[91]。不仅可分析其活性和作用机理,还可评估胃肠消化敏感性、毒性和过敏性[90],时间和经济成本更低。常用的方法包括数学建模、计算机模拟(in silico analysis)、分子对接(molecular docking)和定量构效关系(quantitative structure-activity relationship,QSAR)。
2.5.1 计算机模拟
计算机模拟分析已知的蛋白序列和酶切割位点,筛选特定的肽序列,并预测其生物活性、结构和物理化学特性,再通过传统方法验证。BIOPEP数据库可预测蛋白序列中的活性肽,或模拟蛋白酶的作用[92];BLAST比对新肽是否存在于前体蛋白的序列中;PepDraw可以预测多肽的理化性质;ExPASy或Enzyme Predictor可进行虚拟水解,即电子模拟消化[91]。优点是便捷可行,缺点是易受底物蛋白质的复杂结构和反应条件影响。
2.5.2 分子对接
分子对接技术模拟了两个分子结合形成稳定复合物时的最优构象,可探索肽序列如何与酶结合。在RCSB PDB等蛋白质数据库中找到人体源α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶和DPP-IV的不同晶体结构,筛选最佳活性化合物[22],确定互相作用位点。大豆源三肽GSR、EAK均能进入α-葡萄糖苷酶分子的活性口袋,分别和酶的活性位点形成4个、5个氢键,配体和受体之间产生强烈的范德华力和阴离子-π相互作用[93]。苦瓜源六肽EPGGGG通过范德华力和静电作用与胰岛素以及SGLT1受体蛋白相互作用[43]。然而,受限于不完整的分子结构等缺点,分子对接尚不能准确预测结合亲和力。可以将生物大数据集成到评分函数中来改进。
2.5.3 定量构效关系
定量构效关系(QSAR)可以定量描述结构和活性的关系,根据分子特征预测活性并探索作用机制,已用于筛选、设计和鉴定新分子。QSAR(主要是2D-QSAR和3D-QSAR)已广泛应用于生物活性肽的研究,建模过程包括数据集收集、结构表征、变量选择、模型构建、模型验证和评估等[7]。建模所需数据集依赖于生物信息学数据库,已公开了几十个。然而,数据集和描述符的有限性、数据的异质性、以及分子构象的柔性仍造成局限,结构表征的新方法与描述符整合是未来的研究方向。
2.5.4 多技术联用
多种生物信息学技术联用是研究的发展方向。Ibrahim等用BIOPEP数据库对4210条3~5肽进行虚拟消化,使用AutoDock Vina对844条抗性肽进行分子对接,以肽与人体源α-葡萄糖苷酶(PDB ID:3L4Y)、α-淀粉酶(PDB ID:4GQR)的结合自由能为指标,筛选出SVPA和SEPA序列[94]。Mora等使用CPPpred、PeptideRanker、BIOPEP-UWM、AllerTOP、ToxinPred等工具分别表征伊比利亚干腌火腿源α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制肽的渗透性、生物活性、耐消化性、过敏性和毒性[40]。Çaglar等[15]使用PeptideRanker、BIOPEP数据库以及分子对接工具,从榛子粕源肽中筛选出7条DPP-IV抑制潜力序列,并利用PepSite2软件推测活性残基与DPP-IV之间的作用机制。Rolin[82]通过小分子靶点预测平台Swiss Target Prediction预测鲑鱼源肽IAY和IGY是μ型、δ型和κ型阿片受体激动剂的肽模拟物。目前降糖活性的预测主要从序列比对、分子结构比对、分子对接三方面进行,提高准确性需要扎实的理论基础辅以有效的运算模型设计,体内外的活性验证也不可或缺。
3. 产业化面临的挑战
许多食物衍生肽显示出体外血糖调节潜力,而在复杂的食品基质中对动物模型和人体的作用有限。肽的安全性、生物利用度、生物活性和效力[6],以及食品基质的影响,都是产业化推广面临的挑战,需要通过研究进行评估。
3.1 消化稳定性差
探究肽的特性及其消化稳定性、生物利用度之间的关系,是应用推广的基础。口服活性肽类在进入体循环前暴露于40余种酶,必须对肠道菌群、刷状缘和血清肽酶具有抗性,同时能够穿过肠膜[95]。分子量、酸碱性质、疏水性和C/N端氨基酸组成,以及外部因素(pH、离子强度)都可能影响其消化稳定性[96]。通常认为小分子对pH值的耐受性好,能穿透胃肠道,但是低分子肽也可能在模拟消化过程中的结构稳定性较弱[97]。通过新型活性物质载体技术:微胶囊、乳液包埋、天然聚合物、纳米载体,以及化学修饰、筛选共存成分等手段,都可提高肽的稳定性。例如,Pugliese等[98]将IAVPTGVA和LTFPGSAED封装到RADA16肽形成稳定的纳米凝胶,提高其稳定性和DPP-IV抑制活性。
3.2 生物利用度低
肽的功能性受限于生物利用度,而生物利用度的影响因素有:肽的结构和组成(大小、质量分布、疏水性)、包埋技术、个体因素(饮食、基因、肠道菌群)、作用机制等。通过体外模拟消化后的剩余活性评估生物利用度,精度有限,且因底物和酶而异[74]。通常在细胞和人体血清模型中评估生物利用度,并最终进行动物试验以及临床试验[95]。例如,通过单层Caco-2细胞评估发现分子量较小、中性或带负电的肽转运速率较高[16]。而关于疏水性的影响,目前还未形成统一结论。利用壳聚糖等基质提高肽类的上皮细胞渗透性,或者对氨基酸进行化学修饰可能有助于提高其生物利用度。
3.3 毒性和过敏性问题
肽一般不与DNA或染色体直接作用,故假设食物源肽可以安全口服。但经过胃肠道的作用存在释放毒性肽序列的可能性。同时,尚未明晰肽的多个分子靶点是否导致副作用。Parthasarathi等[99]总结了ToxinPred等毒性预测工具。毒性肽中半胱氨酸、脯氨酸、组氨酸和天冬酰胺的含量相对较高,毒性与N端的精氨酸或丝氨酸残基有关,而亮氨酸、赖氨酸和异亮氨酸出现最少[100]。某些蛋白质片段对消化水解具有抗性,保留了部分致敏性,产生了过敏肽[4]。针对过敏原和基序,已建立AlgPred服务器、BIOPEP-UWM数据库[92]和过敏蛋白结构数据库SDAP等。利用非热加工技术改变结构表位[101],或D-氨基酸等衍生物均可生产低致敏性产品。
3.4 半衰期短
肽在组织中的分布是循环持续时间的函数,因此肽在血液中的半衰期至关重要。而天然肽的血浆半衰期短[102]。肽一旦接触肠粘膜,胃酸和血液中的肽酶迅速将肽转化为氨基酸并排出体外。已有研究利用不可降解的聚合物和聚合物基质来增加肽和蛋白的半衰期,减少频繁给药;或者基于已知结构,修饰易被酶切割的氨基酸位点,改善其理化性质以降低降解率,例如利拉鲁肽;另外,通过BioEPDB数据库中的序列信息结合PLifePred等工具可以预测肽段的血液稳定性[103]。
3.5 食品基质的影响
肽容易发生相互作用,并与其他分子作用,生成衍生化合物(例如呋喃、生物胺、丙烯酰胺、亚硝胺)。热处理或非热处理(高压、微波、超声波)、干燥等加工技术,储存时发生的美拉德反应[104],氢键或疏水等其他作用[3],可能造成肽和蛋白质的聚集或沉淀,影响其稳定性和功能性。因此,应提高蛋白质水解产物在食品配方中的储存稳定性。利用高纤维基质,或聚合物、凝胶进行胶囊化,乳液包埋等新技术,可能有利于提高肽的功能性和感官接受性。总体来说,肽对加工和储存抗性的研究尚未成熟。
4. 总结与展望
血糖调节活性肽有丰富的食物来源,但其理论研究以及产品研发仍有不足,最明显的是作用机制尚未明晰,同时缺乏临床验证。可从以下几方面关注如何强化其体内活性:
表征体内作用机制。多数研究仅完成生物信息学分析,尚未阐明血糖调节肽的靶器官以及作用机制,无法保证生物利用度。分子对接等手段可以识别肽的低能构象和目标酶催化位点,预测肽与靶分子结构域之间的相互作用(氢键、静电和疏水相互作用等)。但仍然需要从细胞通路、代谢组学等新角度明确机理,寻找新靶点。
克服活性评估的异质性。虚拟筛选方法尚未成熟,多数活性评估仅采用体外方法,部分涉及细胞实验和动物模型,临床研究很少。而体外方法的目标酶与人体的同源性有限。活性肽也可能在肠道、血液和肝脏中分解、代谢和受损,并与机体内的其他非靶向酶相互作用而失活。因此,需要分析实验动物的体征变化,结合组织学、病理学等手段,进行初步的药代动力学研究,最终通过临床试验评估肽的消化稳定性、生物利用度和安全性,保障并强化体内功效。
促进研究成果转化。新仪器与工业应用存在技术壁垒。肽的纯化、鉴定和表征需要LC-MS、LC-NMR、X射线结晶学等新仪器技术;而工业化的放大生产需要微胶囊、乳液包埋、天然聚合物、纳米载体等载体技术,以提高肽的溶解度、稳定性和渗透性。在保证安全性的前提下,也考虑利用粗水解物直接生产降低成本和难度。
-
表 1 近5年(2017—2022年)报道的食源性血糖调节活性肽的来源、序列与活性评价方式
Table 1 Sources, sequences and activity evaluations of food derived antidiabetic peptides reported in recent 5 years (2017—2022)
血糖调节方式 来源 序列1 活性评价方式 文献 α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制 羽扇豆 SPRRF,FE,RR 体外,生物信息学 [48] 辣木籽 KETTTIVR 体外 [29] 牡丹籽粕 TFFM,FFFM,YYFM 体外 [49] 水牛乳酪蛋白 RNAVPITPTLNR,TKVIPYVRYL,YLGYLEQLLR,FALPQYLK 体外,生物信息学 [50] 鹰嘴豆 NGIF,QHNIGF,THMAGS,HAAM,NGGR,GE,QPHR 体外,生物信息学 [51] 小麦胚芽 LDLQR,AGGFR,LDNFR 体外 [28] 山茶籽 GHSLESIK,GLTSLDRYK,SPGYYDGR 体外,生物信息学 [52] 尾穗苋 FPFPR 体外,生物信息学 [53] 牛乳和骆驼乳酪蛋白 LPTGWLM,MFE,GPAHCLL 体外,生物信息学 [42] 骆驼乳乳清蛋白 CCGM,MFE 体外,生物信息学 [54] 中华鳖卵 HNKPEVEVR,ARDASVLK,SGTLLHK 体外,生物信息学 [55] 干腌火腿肌肉 EA,PP,VE,PE,AD,LGVGG,GGLGP,AEEEYPDL 体外 [40] 大豆 WLRL,SWLRL,LLPLPVLK,GSR,EAK 体外 [30−31] 米糠 YGIYPR等39条序列(6~20肽) 体外,生物信息学 [56] 黑茶 TAELLPR,CGKKFVR,AVPANLVDLNVPALLK,VVDLVFAAAK 体外,生物信息学 [37] α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制,
α-淀粉酶抑制橙种子 LVDVGNSDNQ等26条序列(10~14肽) 体外 [57] 骆驼乳乳清蛋白 PAGNFLMNGLMHR,PAVACCLPPLPCHM,MLPLMLPFTMGY,PAGNFLPPVAAAPVM 体外,生物信息学 [54] 胡桃楸 LPLLR 体外, Hep G2细胞 [38] 大鲵 CSSV,YSFR,SAAP,PGGP,LGGGN 体外 [58] α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制,
DPP-IV抑制黑茶 MSLYPR,QGQELLPSDFK 体外,生物信息学 [37] α-淀粉酶抑制 羽扇豆 RPR,PPGIP,LRP 体外,生物信息学 [48] 骆驼乳酪蛋白 FLWPEYGAL 体外,生物信息学 [42] 骆驼乳清蛋白 FCCLGPVPP 体外,生物信息学 [54] 斑豆 PPHMLP,PPHMGGP,PLPWGAGF,PLPLHMLP,LSSLEMGSLGALFVCM 生物信息学 [34] α-淀粉酶抑制,
DPP-IV抑制燕麦球蛋白 GDVVALPA,DVVALPAG 体外 [59] 骆驼乳 MPSKPPLL,KDLWDDFLGL 体外 [39] DPP-IV抑制 高粱醇溶蛋白 LPFYPQ,GPVTPPILG,LPFYPQGV 体外,生物信息学,Caco-2细胞 [60] 牛皮革胶原蛋白 GPVG,FGPGP,APGGAP,GPPGPT,GPVGPPG 体外,生物信息学 [61] 牦牛骨胶原蛋白 MGPR 体外,生物信息学,Hep G2细胞 [62] 罗非鱼皮肤胶原蛋白 WF,VW,WY,WG 生物信息学 [63] 鹰嘴豆 SFDLPAL,EVLSEVSF,VVFW 体外,生物信息学 [64] 榛子粕 PGHF,FMRWRDRFL,APGHF,NSMVGNMIFWFFFCILGQPMCVLLY,YHDLMNR,FFFPGPNK,LSVPNLYVWLCMFY,LILVSFSLCLLVLFNGCLG 体外,生物信息学 [15] 夏威夷果 AESE,EQVR,EQVK,EEDNK,EECK,EVEE 生物信息学 [65] 尾穗苋 FPFPPTLGY 体外,生物信息学 [53] 牛乳酪蛋白 HLPGRG,QNVLPLH,PLMLP 体外,生物信息学 [42] 绵羊皮胶原蛋白 GPAGPIGPV,GPAGPOGFPG 生物信息学 [66] 鲭鱼副产品 GPLGAAGP,GRDGEP,MTGTQGEAGR 体外,生物信息学 [67] 钝顶节螺藻藻胆蛋白 DIGYYLR等26条序列(7~27肽) 体外,Caco-2细胞 [68] α-乳白蛋白 LDQWLCEKL 体外 [69] 卵清蛋白 CF,KM,AM,GR,FR,LPR,PRM,ELPF,ADHPF 生物信息学 [21] 鸡蛋 MIR,ADF,FGR 生物信息学 [70] 大西洋鲑鱼皮胶原蛋白 LDKVFR 体外,生物信息学 [71] 沙丁鱼 NAPNPR等19条序列(4~9肽) 体外 [24] 大嘴鲈 VSM,ISW,VSW,ICY,ISD,ISE 体外,生物信息学 [72] 红茶 AGFAGDDAPR 体外,链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病小鼠 [12] 骆驼乳乳清蛋白 VPV,YPI,VPF,LAHKPL,ILDKEGIDY 体外 [73] 斑巴拉豆 LN,IN,VK,VQ,VD,LT,VE,VY,IP 体外 [74] 大豆 LPYP,IAVPGEVA,IAVPTGVA Caco-2细胞、体外血清 [16−17] 羽扇豆 LTFPGSAED Caco-2细胞、体外血清 [16] 纳豆 KL,LR 体外 [75] 牛乳蛋白 LKPTPEGDL,LPYPY, IPIQY,WR Caco-2细胞 [18] 马乳清蛋白 NLEIILR,TQMVDGGIMGKFR 体外 [19] 南极磷虾 PAL,KVEPLP 体外 [20] 上述三种活性 尾穗苋,藜麦,鼠尾草 IW,PW 生物信息学 [76] 燕麦种子 GDVVALPA,DVVALPAG 体外 [35] 钝顶螺旋藻 GVPMPNK,LRSELAAWSR,RNPFVFAPTLLTVAAR 体外, Hep G2细胞 [77] 发芽大豆 IKSQSES等26条序列(6~18肽) 体外 [78] 藜麦 IQAEGGLT,DKDYPK,GEHGSDGNV 体外 [41] 改善胰岛素抵抗 大豆 ISCNGVCSPFDIPPCGTPLCRCIPA GLFVGKCRHPYG C57BL/6J小鼠,3T3-L1小鼠前脂肪
细胞[45] 大鲵皮肤 GPPGPA Hep G2细胞,生物信息学 [79] 胡桃楸 LVRL,LRYL,VLLALVLLR Hep G2细胞 [80] 刺参 FRLPNGGL等58条序列 3T3-L1小鼠前脂肪细胞, Hep G2细胞 [81] 抑制胰岛素受体激动剂,SGLT-1、DPP-IV、GLUT-2 苦瓜 LIVA,TSEP,EKAI,LKHA,EALF,VAEK,DFGAS,EPGGGG 生物信息学 [43] 血糖调节 鲑鱼 IPVE,IVDI,IEGTL,VAPEEHPTL L6大鼠成肌细胞,FAO大鼠肝细胞 [46] 抑制DPP-IV,刺激胰岛素分泌 方鲷 IPV等22条序列(3~4肽)与VPDPR等15条序列(4~5肽) Caco-2细胞,BRIN-BD11细胞 [44] 抑制DPP-IV,增加INS-1胰岛素分泌 鲢鱼鱼鳔 WGDEHIPGSPYH 体外,生物信息学,Caco-2细胞,INS-1细胞 [11] 胰岛素调节 大西洋鲑鱼 IAY,IGY L6大鼠成肌细胞 [82] 抑制DPP-IV,α-葡萄糖苷酶、GLUT-2和GLUT-5 燕麦球蛋白 LQAFEPLR,EFLLAGNNK 体外,Caco-2细胞 [10] 抑制DPP-IV,调节胰岛分泌和GLP-1活性 大西洋鲑鱼皮明胶 GPAG,AVLGPK,AVLGPQ 体外,BRIN-BD11细胞,GLUTag细胞 [47] 阻断GLUT-2和SGLT-1 黑豆 AKSPLF,ATNPLF, FEELN,LSVSVL 体内和体外 [83] 注:1肽序列由氨基酸单字母符号表示。 -
[1] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas:Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2022,183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
[2] PIZZATO M, TURATI F, ROSATO V, et al. Exploring the link between diabetes and pancreatic cancer[J]. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy,2019,19(8):681−687. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2019.1642109
[3] RIVERO-PINO F, ESPEJO-CARPIO F J, GUADIX E M. Antidiabetic food-derived peptides for functional feeding:Production, functionality and in vivo evidences[J]. Foods,2020,9(8):983. doi: 10.3390/foods9080983
[4] LIU L, LI S S, ZHENG J X, et al. Safety considerations on food protein-derived bioactive peptides[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,96:199−207.
[5] 张廷新, 李富强, 张楠, 等. 降糖肽的制备、生物学效应及其构效关系研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(8):433−442 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021040219 ZHANG Tingxin, LI Fuqiang, ZHANG Nan, et al. Advances in preparation, biological effect and structure-activity relationship of hypoglycemic peptides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(8):433−442. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021040219
[6] ACQUAH C, DZUVOR C K, TOSH S, et al. Anti-diabetic effects of bioactive peptides:recent advances and clinical implications[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2022,62(8):2158−2171. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1851168
[7] BO W C, CHEN L, QIN D Y, et al. Application of quantitative structure-activity relationship to food-derived peptides:Methods, situations, challenges and prospects[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,114:176−188.
[8] NAUCK M A, BALLER B, MEIER J J. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes,2004,53(suppl_3):S190−S196. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.suppl_3.S190
[9] 王清. 胰高血糖素样肽-1类似物的合成及活性研究[D]. 岳阳:湖南理工学院, 2019 WANG Qing. Synthesis and activity of glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs[D]. Yueyang:Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, 2019.
[10] WANG F, ZHANG Y Y, YU T T, et al. Oat globulin peptides regulate antidiabetic drug targets and glucose transporters in Caco-2 cells[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,42:12−20. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.061
[11] HONG H, ZHENG Y Y, SONG S J, et al. Identification and characterization of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from silver carp swim bladder hydrolysates[J]. Food Bioscience,2020,38:100748. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100748
[12] LU Y T, LU P, WANG Y, et al. A novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory tea peptide improves pancreatic β-cell function and reduces α-cell proliferation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(2):322. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020322
[13] WANG T T, ZHENG L, ZHAO T T, et al. Anti-diabetic effects of sea cucumber ( Holothuria nobilis) hydrolysates in streptozotocin and high-fat-diet induced diabetic rats via activating the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,75:104224. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104224
[14] ADMASSU H, GASMALLA M A A, YANG R, et al. Bioactive peptides derived from seaweed protein and their health benefits:Antihypertensive, antioxidant, and antidiabetic properties[J]. Journal of Food Science,2018,83(1):6−16. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14011
[15] ÇAĞLAR A F, GÖKSU A G, ÇAKIR B, et al. Tombul hazelnut ( Corylus avellana L.) peptides with DPP-IV inhibitory activity: In vitro and in silico studies[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2021,12:100151.
[16] LAMMI C, BOLLATI C, FERRUZZA S, et al. Soybean-and lupin-derived peptides inhibit DPP-IV activity on in situ human intestinal Caco-2 cells and ex vivo human serum[J]. Nutrients,2018,10(8):1082. doi: 10.3390/nu10081082
[17] AIELLO G, FERRUZZA S, RANALDI G, et al. Behavior of three hypocholesterolemic peptides from soy protein in an intestinal model based on differentiated Caco-2 cell[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,45:363−370. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.04.023
[18] LACROIX I M, CHEN X-M, KITTS D D, et al. Investigation into the bioavailability of milk protein-derived peptides with dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitory activity using Caco-2 cell monolayers[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(2):701−709.
[19] SONG J J, WANG Q, DU M, et al. Identification of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from mare whey protein hydrolysates[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2017,100(9):6885−6894. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11828
[20] JI W, ZHANG C H, JI H W. Two novel bioactive peptides from antarctic krill with dual angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory activities[J]. Journal of Food Science,2017,82(7):1742−1749. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13735
[21] SALIM M A S M, GAN C-Y. Dual-function peptides derived from egg white ovalbumin:Bioinformatics identification with validation using in vitro assay[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64:103618. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103618
[22] LIU R, CHENG J M, WU H. Discovery of food-derived dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides:A review[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(3):463. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030463
[23] GALLEGO M, ARISTOY M-C, TOLDRÁ F. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides generated in Spanish dry-cured ham[J]. Meat Science,2014,96(2):757−761. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.09.014
[24] RIVERO-PINO F, ESPEJO-CARPIO F J, GUADIX E M. Production and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from discarded Sardine pilchardus protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,328:127096. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127096
[25] IBRAHIM M A, BESTER M J, NEITZ A W, et al. Structural properties of bioactive peptides with α-glucosidase inhibitory activity[J]. Chemical Biology & Drug Design,2018,91(2):370−379.
[26] NONGONIERMA A B, FITZGERALD R J. Features of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from dietary proteins[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2019,43(1):e12451. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12451
[27] REN Y, LIANG K, JIN Y Q, et al. Identification and characterization of two novel α-glucosidase inhibitory oligopeptides from hemp ( Cannabis sativa L.) seed protein[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2016,26:439−450. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.07.024
[28] LIU W W, LI H Y, WEN Y Y, et al. Molecular mechanism for the α-glucosidase inhibitory effect of wheat germ peptides[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(50):15231−15239. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06098
[29] WANG X F, FAN Y Z, XU F R, et al. Characterization of the structure, stability, and activity of hypoglycemic peptides from Moringa oleifera seed protein hydrolysates[J]. Food & Function,2022,13(6):3481−3494.
[30] WANG R C, ZHAO H X, PAN X X, et al. Preparation of bioactive peptides with antidiabetic, antihypertensive, and antioxidant activities and identification of α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from soy protein[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2019,7(5):1848−1856.
[31] JIANG M Z, YAN H, HE R H, et al. Purification and a molecular docking study of α-glucosidase-inhibitory peptides from a soybean protein hydrolysate with ultrasonic pretreatment[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2018,244(11):1995−2005. doi: 10.1007/s00217-018-3111-7
[32] SIOW H L, GAN C Y. Extraction, identification, and structure-activity relationship of antioxidative and α-amylase inhibitory peptides from cumin seeds ( Cuminum cyminum)[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2016,22:1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.01.011
[33] NGOH Y Y, GAN C Y. Enzyme-assisted extraction and identification of antioxidative and α-amylase inhibitory peptides from Pinto beans ( Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Pinto)[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,190:331−337. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.120
[34] NGOH Y-Y, GAN C-Y. Identification of Pinto bean peptides with inhibitory effects on α-amylase and angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activities using an integrated bioinformatics-assisted approach[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,267:124−131. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.166
[35] FUENTES L R, RICHARD C, CHEN L Y. Sequential alcalase and flavourzyme treatment for preparation of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV inhibitory peptides from oat protein[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2021,87:104829. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104829
[36] ARISE R O, IDI J J, MIC-BRAIMOH I M, et al. In vitro Angiotesin-1-converting enzyme, α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant activities of Luffa cylindrical (L.) M. Roem seed protein hydrolysate[J]. Heliyon,2019,5(5):e01634. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01634
[37] ZHAO B L, SU K Y, MAO X L, et al. Separation and identification of enzyme inhibition peptides from dark tea protein[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2020,99:103772. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103772
[38] WANG J, WU T, FANG L, et al. Anti-diabetic effect by walnut ( Juglans mandshurica Maxim.)-derived peptide LPLLR through inhibiting α-glucosidase and α-amylase, and alleviating insulin resistance of hepatic HepG2 cells[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,69:103944. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.103944
[39] MUDGIL P, KAMAL H, YUEN G C, et al. Characterization and identification of novel antidiabetic and anti-obesity peptides from camel milk protein hydrolysates[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,259:46−54. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.082
[40] MORA L, GONZÁLEZ-ROGEL D, HERES A, et al. Iberian dry-cured ham as a potential source of α-glucosidase-inhibitory peptides[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,67:103840. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.103840
[41] VILCACUNDO R ,VILLALUENG C M, LEDESMA B H. Release of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from quinoa ( Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,35:531−539. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.06.024
[42] MUDGIL P, KAMAL H, KILARI B P, et al. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion of camel and bovine casein hydrolysates:Identification and characterization of novel anti-diabetic bioactive peptides[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,353:129374. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129374
[43] ARIF R, AHMAD S, MUSTAFA G, et al. Molecular docking and simulation studies of antidiabetic agents devised from hypoglycemic polypeptide-P of Momordica charantia[J]. BioMed Research International,2021,2021:5561129.
[44] HARNEDY-ROTHWELL P A, MCLAUGHLIN C M, O'KEEFFE M B, et al. Identification and characterisation of peptides from a boarfish ( Capros aper) protein hydrolysate displaying in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory and insulinotropic activity[J]. Food Research International,2020,131:108989. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.108989
[45] WU Y H, ZHAO R, LI M X, et al. Novel soybean peptide iglycin ameliorates insulin resistance of high-fat diet fed C57BL/6J mice and differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes with improvement of insulin signaling and mitochondrial function[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2022,11(6):1565−1572. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.06.014
[46] HENAUX L, PEREIRA K D, THIBODEAU J, et al. Glucoregulatory and anti-inflammatory activities of peptide fractions separated by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membranes from salmon protein hydrolysate and identification of four novel glucoregulatory peptides[J]. Membranes,2021,11(7):528. doi: 10.3390/membranes11070528
[47] HARNEDY P A, PARTHSARATHY V, MCLAUGHLIN C M, et al. Atlantic salmon ( Salmo salar) co-product-derived protein hydrolysates:A source of antidiabetic peptides[J]. Food Research International,2018,106:598−606. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.01.025
[48] FADIMU G J, FARAHNAKY A, GILL H, et al. In-silico analysis and antidiabetic effect of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from lupin protein hydrolysate:Enzyme-peptide interaction study using molecular docking approach[J]. Foods,2022,11(21):3375. doi: 10.3390/foods11213375
[49] WEI R T, LIN L K, LI T T, et al. Separation, identification, and design of α‐glucosidase inhibitory peptides based on the molecular mechanism from Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’ seed protein[J]. Journal of Food Science,2022,87(11):4892−4904. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16340
[50] ZHAO Q, WEI G Q, LI K L, et al. Identification and molecular docking of novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from hydrolysates of Binglangjiang buffalo casein[J]. LWT,2022,156:113062. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.113062
[51] RIVERO-PINO F, ESPEJO-CARPIO F J, GUADIX E M.Unravelling the α-glucosidase inhibitory properties of chickpea protein by enzymatic hydrolysis and in silico analysis[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,44:101328. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101328
[52] FENG J, MA Y L, SUN P, et al. Purification and characterisation of α‐glucosidase inhibitory peptides from defatted camellia seed cake[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2021,56(1):138−147.
[53] KAMAL H, MUDGIL P, BHASKAR B, et al. Amaranth proteins as potential source of bioactive peptides with enhanced inhibition of enzymatic markers linked with hypertension and diabetes[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2021,101:103308. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2021.103308
[54] BABA W N, MUDGIL P, KAMAL H, et al. Identification and characterization of novel α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from camel whey proteins[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2021,104(2):1364−1377. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19271
[55] QIU L Y, DENG Z Y, ZHAO C D, et al. Nutritional composition and proteomic analysis of soft-shelled turtle ( Pelodiscus sinensis) egg and identification of oligopeptides with alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity[J]. Food Research International,2021,145:110414. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110414
[56] URAIPONG C, ZHAO J. In vitro digestion of rice bran proteins produces peptides with potent inhibitory effects on α‐glucosidase and angiotensin I converting enzyme[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2018,98(2):758−766. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8523
[57] MAZLOOMI S N, MAHOONAK A S, MORA L, et al. Pepsin hydrolysis of orange by-products for the production of bioactive peptides with gastrointestinal resistant properties[J]. Foods,2021,10(3):679. doi: 10.3390/foods10030679
[58] RAMADHAN A H, NAWAS T, ZHANG X W, et al. Purification and identification of a novel antidiabetic peptide from Chinese giant salamander ( Andrias davidianus) protein hydrolysate against α-amylase and α-glucosidase[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2017,20(sup3):S3360−S3372. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2017.1354885
[59] FUENTES L R. Development and characterization of peptides with antidiabetic activities from oat protein[D]. Edmonton, Alberta:University of Alberta, 2021.
[60] DAI L Y, KONG L X, CAI X, et al. Analysis of the structure and activity of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory oligopeptides from sorghum kafirin[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(6):2010−2017. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04484
[61] HE L, WANG X Y, WANG Y R, et al. Production and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from discarded cowhide collagen[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022:134793.
[62] LIU C Y, GUO Z T, YANG Y L, et al. Identification of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from yak bone collagen by in silico and in vitro analysis[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2022,248(12):3059−3069. doi: 10.1007/s00217-022-04111-x
[63] MUNAWAROH H S H, GUMILAR G G, BERLIANA J D, et al. In silico proteolysis and molecular interaction of tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus) skin collagen-derived peptides for environmental remediation[J]. Environmental Research,2022,212:113002. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113002
[64] MARTÍNEZ K A A, MEJIA E G. Comparison of five chickpea varieties, optimization of hydrolysates production and evaluation of biomarkers for type 2 diabetes[J]. Food Research International,2021,147:110572. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110572
[65] ZHAO L, ZHANG M X, PAN F, et al. In silico analysis of novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides released from Macadamia integrifolia antimicrobial protein 2 (MiAMP2) and the possible pathways involved in diabetes protection[J]. Current Research in Food Science,2021,4:603−611. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2021.08.008
[66] WANG B B, YU Z, YOKOYAMA W, et al. Collagen peptides with DPP-IV inhibitory activity from sheep skin and their stability to in vitro gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,42:101161. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101161
[67] MIRZAPOUR-KOUHDASHT A, MOOSAVI-NASAB M, LEE C W, et al. Structure-function engineering of novel fish gelatin-derived multifunctional peptides using high-resolution peptidomics and bioinformatics[J]. Scientific Reports,2021,11:7401. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86808-9
[68] LI Y C, AIELLO G, BOLLATI C, et al. Phycobiliproteins from Arthrospira Platensis (Spirulina):A new source of peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(3):794. doi: 10.3390/nu12030794
[69] JIA C L, HUSSAIN N, UJIROGHENE O J, et al. Generation and characterization of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory peptides from trypsin-hydrolyzed α-lactalbumin-rich whey proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,318:126333. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126333
[70] ZHAO W Z, ZHANG D, YU Z P, et al. Novel membrane peptidase inhibitory peptides with activity against angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV identified from hen eggs[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64:103649. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103649
[71] JIN R T, TENG X Y, SHANG J Q, et al. Identification of novel DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from Atlantic salmon ( Salmo salar) skin[J]. Food Research International,2020,133:109161. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109161
[72] WANG K, YANG X X, LOU W Y, et al. Discovery of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitory peptides from Largemouth bass ( Micropterus salmoides) by a comprehensive approach[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2020,105:104432. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104432
[73] NONGONIERMA A B, CADAMURO C, GOUIC LE A, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory properties of a camel whey protein enriched hydrolysate preparation[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,279:70−79. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.142
[74] MUNE M A M, MINKA S R, HENLE T. Investigation on antioxidant, angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory activity of Bambara bean protein hydrolysates[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,250:162−169. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.001
[75] SATO K, MIYASAKA S, TSUJI A, et al. Isolation and characterization of peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) inhibitory activity from natto using DPPIV from Aspergillus oryzae[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,261:51−56. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.029
[76] ZAMUDIO F V, HIDALGO-FIGUEROA S N, ANDRADE R R O, et al. Identification of antidiabetic peptides derived from in silico hydrolysis of three ancient grains:Amaranth, Quinoa and Chia[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,394:133479. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133479
[77] HU S, FAN X, QI P, et al. Identification of anti-diabetes peptides from Spirulina platensis[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,56:333−341. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.03.024
[78] GONZÁLEZ-MONTOYA M, HERNÁNDEZ-LEDESMA B, MORA-ESCOBEDO R, et al. Bioactive peptides from germinated soybean with anti-diabetic potential by inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, α-amylase, and α-glucosidase enzymes[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2018,19(10):2883. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102883
[79] ZHOU M, REN G Y, ZHANG B, et al. Screening and identification of a novel antidiabetic peptide from collagen hydrolysates of Chinese giant salamander skin:network pharmacology, inhibition kinetics and protection of IR-HepG2 cells[J]. Food & Function,2022,13(6):3329−3342.
[80] WANG J, WU T, FANG L, et al. Peptides from walnut ( Juglans mandshurica Maxim.) protect hepatic HepG2 cells from high glucose-induced insulin resistance and oxidative stress[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(9):8112−8121.
[81] GONG P X, WANG B K, WU Y C, et al. Release of antidiabetic peptides from Stichopus japonicas by simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,315:126273. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126273
[82] ROLIN J. Identification and aspects of commercial production of anti-diabetic peptide(s) from salmon protein hydrolysates [D]. Halifax:Dalhousie University, 2020.
[83] MOJICA L, DE MEJIA E G, GRANADOS-SILVESTRE M Á, et al. Evaluation of the hypoglycemic potential of a black bean hydrolyzed protein isolate and its pure peptides using in silico, in vitro and in vivo approaches[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,31:274−286. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.02.006
[84] VÁZQUEZ J A, FRAGUAS J, MIRÓN J, et al. Valorisation of fish discards assisted by enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial bioconversion:Lab and pilot plant studies and preliminary sustainability evaluation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,246:119027. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119027
[85] 徐磊, 王清爽, 高珊, 等. 菌酶协同处理提高脱脂薏米水提取液营养价值[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(12):303−309[XU Lei, WANG Qingshuang, GAO Shan, et al. Improving nutrition value of the defatted adlay water extract by using fermentation with enzyme[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(12):303−309. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.12.036 XU Lei, WANG Qingshuang, GAO Shan, et al . Improving nutrition value of the defatted adlay water extract by using fermentation with enzyme[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020 ,36 (12 ):303 −309 . doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.12.036[86] ULUG S K, JAHANDIDEH F, WU J P. Novel technologies for the production of bioactive peptides[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,108:27−39.
[87] ACQUAH C, CHAN Y W, PAN S, et al. Structure‐informed separation of bioactive peptides[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2019,43(1):e12765. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12765
[88] NAJAFIAN L, BABJI A S. Fractionation and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from fermented fish (pekasam)[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2018,12(3):2174−2183. doi: 10.1007/s11694-018-9833-1
[89] GALLEGO M, TOLDRÁ F, MORA L. Quantification and in silico analysis of taste dipeptides generated during dry-cured ham processing[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,370:130977. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130977
[90] YAP P G, GAN C Y. In vivo challenges of anti-diabetic peptide therapeutics:Gastrointestinal stability, toxicity and allergenicity[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,105:161−175.
[91] TU M L, CHENG S Z, LU W H, et al. Advancement and prospects of bioinformatics analysis for studying bioactive peptides from food-derived protein:Sequence, structure, and functions[J]. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2018,105:7−17. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2018.04.005
[92] MINKIEWICZ P, IWANIAK A, DAREWICZ M. BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides:Current opportunities[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(23):5978. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235978
[93] 江明珠. 超声波预处理辅助酶解制备大豆降糖肽及其作用机理[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2018[JIANG Mingzhu. Preparation and hypoglycemic mechanism of soybean peptides by ultrasonic pretreatment with enzymatic hydrolysis[D]. Zhenjiang:Jiangsu University, 2018. JIANG Mingzhu. Preparation and hypoglycemic mechanism of soybean peptides by ultrasonic pretreatment with enzymatic hydrolysis[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2018.
[94] IBRAHIM M A, BESTER M J, NEITZ A W, et al. Rational in silico design of novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides and in vitro evaluation of promising candidates[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2018,107:234−242.
[95] TOLDRÁ F, GALLEGO M, REIG M, et al. Recent progress in enzymatic release of peptides in foods of animal origin and assessment of bioactivity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(46):12842−12855. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b08297
[96] WANG B, XIE N N, LI B. Influence of peptide characteristics on their stability, intestinal transport, and in vitro bioavailability:A review[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2019,43(1):e12571. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12571
[97] XIE N N, LIU S S, WANG C, et al. Stability of casein antioxidant peptide fractions during in vitro digestion/Caco-2 cell model:Characteristics of the resistant peptides[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2014,239:577−586. doi: 10.1007/s00217-014-2253-5
[98] PUGLIESE R, BOLLATI C, GELAIN F, et al. A supramolecular approach to develop new soybean and lupin peptide nanogels with enhanced dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(13):3615−3623. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b07264
[99] PARTHASARATHI R, DHAWAN A. In silico approaches for predictive toxicology[M]. In vitro toxicology. Elsevier. 2018:91−109.
[100] GUPTA S, KAPOOR P, CHAUDHARY K, et al. In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins[J]. PloS one,2013,8(9):e73957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073957
[101] EKEZIE F G C, CHENG J H, SUN D W. Effects of nonthermal food processing technologies on food allergens:A review of recent research advances[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,74:12−25.
[102] WANG J, YIN T L, XIAO X W, et al. StraPep:A structure database of bioactive peptides[J]. Database,2018,2018:bay038.
[103] GÜLSEREN İ, VAHAPOGLU B. The stability of food bioactive peptides in blood:An overview[J]. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics,2022,28:1−7. doi: 10.1007/s10989-021-10311-y
[104] FU Y, ZHANG Y H, SOLADOYE O P, et al. Maillard reaction products derived from food protein-derived peptides:Insights into flavor and bioactivity[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020,60(20):3429−3442. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1691500
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 孟烨,昝丽霞,张文夷,高宁,杜小平. 酶法制备植源性生物活性肽及其生理活性的研究进展. 农业技术与装备. 2024(03): 189-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



