Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of Sea-buckthorn Flavonoids on Acrylamide Formation by Using the Simulation System
-
摘要: 本研究旨在探究沙棘黄酮对丙烯酰胺生成的抑制作用及其机理。首先利用Asn-Glu模拟体系建立沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的量效关系;在此基础上,通过紫外吸收光谱、液相色谱-质谱和高效液相色谱测定美拉德反应三个阶段的产物,运用形成/消除动力学模型及机理动力学模型研究沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的机理。结果表明,沙棘黄酮对抑制丙烯酰胺生成有明显的效果,最高抑制率为62.1%;通过拟合形成/消除动力学模型发现沙棘黄酮显著降低丙烯酰胺的生成速率常数a、tcg(P<0.05),对消除速率常数τ没有显著影响(P>0.05),表明沙棘黄酮主要抑制丙烯酰胺的生成阶段,对丙烯酰胺的消除阶段没有影响;通过拟合机理动力学模型发现沙棘黄酮显著降低丙烯酰胺的生成速率k2和类黑素的生成速率k3(P<0.05),说明沙棘黄酮主要抑制了美拉德反应的第二阶段。综上,沙棘黄酮能有效抑制中间产物向丙烯酰胺和类黑素转化,可以作为食品添加剂应用于食品加工业中。
-
关键词:
- 丙烯酰胺 /
- 沙棘黄酮 /
- Asn-Glu模拟体系 /
- 抑制机理 /
- 动力学模型
Abstract: This study was designed to explore the inhibitory effect and mechanism of sea-buckthorn flavonoids on the formation of acrylamide. In order to study the inhibitory effect of sea-buckthorn flavonoids on the formation of acrylamide, the dose-effect relationship of sea-buckthorn flavonoids inhibiting the formation of acrylamide was investigated in the Asn-Glu simulation system. Then the formation/elimination kinetic model and mechanism kinetic model were used to evaluate the products of Maillard reaction by UV absorption spectrum, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and high performance liquid chromatography to explore the inhibitory mechanism of sea-buckthorn flavonoids on the formation of acrylamide. The results confirmed that sea-buckthorn flavonoids could effectively reduce the formation of acrylamide and achieve a maximum reduction rate 62.1%. The formation/elimination kinetic model demonstrated that sea-buckthorn flavonoids significantly reduced the formation rate constants a, tcg of acrylamide (P<0.05), and did not have a significant effect on eliminating rate constant τ (P>0.05), indicating that sea-buckthorn flavonoids mainly inhibited the formation stage of acrylamide, and had no effect on the elimination process. The mechanism kinetic model suggested that sea-buckthorn flavonoids actively reduced the production rate of acrylamide k2 and the production rate of melanin k3 (P<0.05), indicating that sea-buckthorn flavonoids mainly inhibited the second stage of Maillard reaction. In conclusion, sea-buckthorn flavonoids could effectively inhibit the conversion of intermediate products to acrylamide and melanoidin, and could be applied as a food additive in food processing industry. -
丙烯酰胺(Acrylamide,AA)是一种广泛存在于各类热加工食品中的2A类致癌物质,因其具有神经毒性、生殖毒性、遗传毒性以及致癌性,从2002年一经发现,便得到世界各国食品研究人员的广泛关注[1]。研究发现,食品中丙烯酰胺的生成与美拉德反应有关,是天冬酰胺(Asn)的氨基残基和还原糖(如葡萄糖)的羰基在120 ℃以上生成的非酶促褐变反应副产物[2]。因此,可以通过减少丙烯酰胺前体(天冬酰胺和还原糖)或阻碍美拉德反应途径来抑制丙烯酰胺的生成。已证实蛋白质或氨基酸[3−4]、金属离子[5−6]及抗氧化剂[7−8]等对丙烯酰胺的生成具有不同程度的抑制作用。
近年来,黄酮类天然抗氧化剂—植物总黄酮及其黄酮单体抑制丙烯酰胺生成的研究被广泛报道,如花青素[9]、绿茶提取物[10]、竹叶黄酮[11]等能显著抑制烘炸食品中丙烯酰胺的生成。且Zhao等[12]研究原花青素B型二聚体原花青素及儿茶素和表儿茶素单体,发现聚合体原花青素最高抑制率达到81.07%,而其单体最高抑制率只有61.73%。同时蔡文[13]研究柑桔黄酮及其5种单体对丙烯酰胺生成的抑制,其中柑桔黄酮对丙烯酰胺的抑制率最高为58.42%,而其单体的抑制率约为20%~55%,结果表明植物总黄酮对模拟体系和食品体系中的丙烯酰胺抑制效果往往优于黄酮单体。而与纯度较高的黄酮单体的分离、提取相比,植物总黄酮的提取具有操作简单、耗时短、成本低、可进行规模化生产等优点[14],更适合作为食品添加剂应用于食品加工产业。
沙棘属药食两用植物,含有黄酮类化合物、维生素、脂肪酸、萜类甾醇类物质及有机酸等丰富的营养物质[15]。作为沙棘最重要的化学组分—黄酮类化合物分布于沙棘的各个部位,包括果实、根、茎、叶以及花等。已研究证实沙棘黄酮单体如槲皮素、异鼠李素和山奈酚等具有良好的抗氧化性,能有效抑制模拟体系中丙烯酰胺的生成,且抑制率约为20%~50%[16−17]。而沙棘总黄酮对丙烯酰胺生成的抑制效果及抑制机理尚未可知。因此本文利用Asn-Glu模拟体系探究沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的量效关系,通过紫外吸收光谱、液相色谱-质谱和高效液相色谱测定前体物质、中间产物和终产物,运用形成/消除动力学模型及机理动力学模型拟合探究其抑制机理,从而拓展沙棘黄酮在食品加工业的应用范围。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
沙棘黄酮(纯度≥65%) 陕西普兰特生物技术有限公司;丙烯酰胺标准品(纯度≥99%) 美国Sigma公司;葡萄糖 分析纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;天冬酰胺 分析纯,北京博奥拓科技有限公司。
KH-10水热合成反应釜 上海凌科实业发展有限公司;DHG-9070烘箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;LC-20A高效液相色谱系统 日本岛津;Qtrap5500三重四级杆液质联用仪 新加坡爱博才思仪器有限公司;UV-2600紫外可见分光光度计 苏州岛津仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 Asn-Glu模拟体系的建立
参照李金旺[18]的方法,稍作改动。称取0.2378 g葡萄糖和0.1802 g天冬酰胺放入10 mL的反应釜,加入2 mL超纯水溶解后,置于180 ℃的烘箱,加热60 min。将冷却后的样液于8000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,稀释10倍,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤,备用。
1.2.2 沙棘黄酮浓度对模拟体系中丙烯酰胺生成量的影响
分别取1000、100、10、1、0.1 μg/mL的沙棘黄酮乙醇溶液0.5 mL,加入到Asn-Glu模拟体系中,并加入超纯水,使总体积为2 mL,同时设立对照组(用乙醇溶液取代沙棘黄酮溶液)。模拟体系的后续反应操作同1.2.1。
1.2.3 沙棘黄酮添加量对模拟体系中丙烯酰胺生成量的影响
分别取0.25、0.5、0.75、1 mL的沙棘黄酮乙醇溶液(浓度为1.2.2所得沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的最适浓度)加入到Asn-Glu模拟体系中,并加入超纯水,使总体积为2 mL,同时设立对照组(即分别用0.25、0.5、0.75、1.00 mL的乙醇溶液取代沙棘黄酮溶液)。模拟体系的后续反应操作同1.2.1。
1.2.4 模拟体系中丙烯酰胺的测定及抑制率计算
参考Shen等[19]的方法,稍作改动。色谱柱:supersil AQ-C18色谱柱(4.6×250 mm,5 μm);进样量:5 μL;流速:1 mL/min;流动相:乙腈:甲醇:水=1:3:96;进样温度:30 ℃;检测波长:210 nm。
将丙烯酰胺标准品配制成1.0 mg/mL标准溶液,经准确稀释后配制成10.0、8.0、6.0、4.0、2.0 μg/mL的丙烯酰胺标液,进行高效液相色谱分析。以丙烯酰胺标液质量浓度(μg/mL)为横坐标,峰面积为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线,求得回归方程y=43.456x+6.582(R2=0.999),得到丙烯酰胺的含量计算公式如下:
X=25nCV1MV2 (1) 式中:X为丙烯酰胺的量,μmol;V1为反应液体积,mL;V2为测定液体积,mL;C为样品中丙烯酰胺的浓度,μg/mL;n为稀释倍数;M为丙烯酰胺的摩尔质量,g/mol。
沙棘黄酮对Asn-Glu模拟体系中丙烯酰胺的抑制率计算公式如下:
A(%)=X−X0X×100 (2) 式中:A为沙棘黄酮对丙烯酰胺的抑制率,%;X0为试验组测得的丙烯酰胺生成量,μmol;X为对照组中测得丙烯酰胺的生成量,μmol。
1.2.5 沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的形成/消除动力学研究
取100 μg/mL的沙棘黄酮溶液0.25 mL加入Asn-Glu模拟体系中,并加入超纯水,使总体积为2 mL(同时设立对照组),于180 ℃的烘箱内分别反应30、45、60、90、120、150 min。冷却后的样液于8000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液,稀释10倍后,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤,用HPLC测定丙烯酰胺含量。然后采用Origin 2021软件中的非线性最小二乘回归方法分别与三种形成/消除动力学模型(Logistic-Fermi动力学模型[20]、Logistic指数动力学模型[21]、形成/消除一级动力学模型[22])进行拟合,确定沙棘黄酮对丙烯酰胺的抑制作用是发生在形成阶段还是消除阶段。
1.2.5.1 Logistic-Fermi动力学模型
C(t)=Cg(t)⋅Cd(t) (3) Cg(t)=a1+exp[kg(tcg−t)]−a1+exp(kg⋅tcg) (4) Cd(t)=11+exp[kd(t−tcd)] (5) 式中:a、kg、tcg为与丙烯酰胺形成有关的温度依赖系数;kd、tcd为与丙烯酰胺消除有关的温度依赖系数。
1.2.5.2 Logistic指数动力学模型
Cf(t)=a1+exp[kf(tcf−t)]−a1+exp(kf⋅tcf) (6) Ce(t)=exp(−tτ) (7) 式中:a、kf、tcf为与丙烯酰胺形成有关的温度依赖系数;τ为特征性时间。
1.2.5.3 形成/消除一级动力学模型
dCdt=−kf⋅C (8) dCAAdt=kf⋅C−ke⋅CAA (9) dCDdt=−ke⋅CAA (10) 式中:kf为丙烯酰胺的生成速率,s−1;ke为丙烯酰胺的消除速率,s−1;C为天冬酰胺/葡萄糖的摩尔质量,mmol;CAA为丙烯酰胺的摩尔质量,mmol;CD为丙烯酰胺降解产物的摩尔质量,mmol。当t=0时C=1.2 mmol,其余物质的摩尔质量为零。
1.2.6 沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的机理动力学研究
取100 μg/mL的沙棘黄酮溶液0.25 mL加入Asn-Glu模拟体系中,并加入超纯水,使总体积为2 mL(同时设立对照组),于180 ℃的烘箱内分别反应30、45、60、90、120、150 min。冷却后的样液于8000 r/min离心5 min,留取上清液,稀释10倍后,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤,用于测定还原糖、天冬酰胺、类黑素和丙烯酰胺的含量。
1.2.6.1 还原糖含量测定
根据Lü等[23]的比色法,稍作改动。将冷却后的样液于8000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液稀释10倍后的1 mL样液,加入1 mL超纯水和3 mL的3,5-二硝基水杨酸溶液,震荡混匀,置于沸水浴中反应10 min,冷却后于25 mL容量瓶中定容。于540 mn波长下测其吸光度。计算公式如下:
X=25nCV1MV2 (11) 式中:X为还原糖的量,nmol;V1为反应液体积,mL;V2为测定液体积,mL;C为还原糖含量,mg/mL;n为稀释倍数;M为葡萄糖的摩尔质量,g/mol。
1.2.6.2 天冬酰胺含量测定
参考Bertuzzi等[24]的LC−MS方法,并做适当改正。色谱柱:supersil AQ-C18色谱柱(4.6×250 mm,5 μm);进样量:5 μL;流速:0.2 mL/min;流动相:A为0.2%(V/V)甲酸水溶液和B为0.1%甲酸乙腈梯度洗脱。
质谱条件:电喷雾正模式;喷雾毛细管电压4.2 kV;鞘气和辅助气体分别为35和12 psi;撇渣器6 V;加热毛细管的温度270 ℃。设置氩碰撞压力为1.5 mTorr;碰撞能量为15 V;碎片离子为116、87和74 m/z。
1.2.6.3 类黑素含量测定
参照Leong等[25]的比色法。取0.1 mL反应釜中的样品,再稀释100倍,于470 nm波长下测其吸光度,采用朗伯比尔定律计算反应液中类黑素的含量。计算公式如下:
C=nAVe⋅b (12) 式中:C为类黑素的生成量,mmol;n为稀释倍数;A为吸光度值;V为反应液体积,mL;e为摩尔吸光系数,L/(mol·cm);b为液层厚度,cm;其中e=282 L/(mol·cm),b=1 cm。
1.2.6.4 丙烯酰胺含量测定
丙烯酰胺的测定和计算方法同1.2.4。
1.2.6.5 机理动力学模型
参考Knol等[26]的机理动力学模型稍作改动。此模型用席夫碱表示美拉德反应的中间产物,用类黑素、丙烯酰胺和丙烯酰胺降解产物表示反应的终产物,由于本试验没有考虑还原糖与其他糖类的互相转化,所以将机理动力学模型简化,计算公式如下:
dCAsndt=−k1⋅CAsn (13) dCRdt=−k1⋅CR (14) dCSdt=k1⋅CR−(k1+k2)⋅CS (15) dCAAdt=k2⋅CS−k4⋅CAA (16) dCMdt=k3⋅Cs (17) dCDdt=k4⋅CAA (18) 式中:CAsn为天冬酰胺的量,mmol;CR为还原糖的量,mmol;CS为席夫碱的量,mmol;CAA为丙烯酰胺的量,mmol;CM为类黑素的量,mmol;CD为丙烯酰胺降解产物的量,mmol;k1为天冬酰胺-还原糖的反应速率,s−1;k2为丙烯酰胺的形成速率,s−1;k3为类黑素的形成速率,s−1;k4为丙烯酰胺的消除速率,s−1。当t=0时,CAsn=CR=1.2 mmol,Cs、CAA、CM、CD都等于0。
1.3 数据处理
设3次平行实验,结果用平均数±方差(¯x±s)表示;采用SPSS 26.0软件数据处理,并采用ANOVA以及最小显著性差异T检验对数据进行统计分析,P<0.05为显著性差异;采用Origin 2021软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 沙棘黄酮的浓度对模拟体系中丙烯酰胺生成量的影响
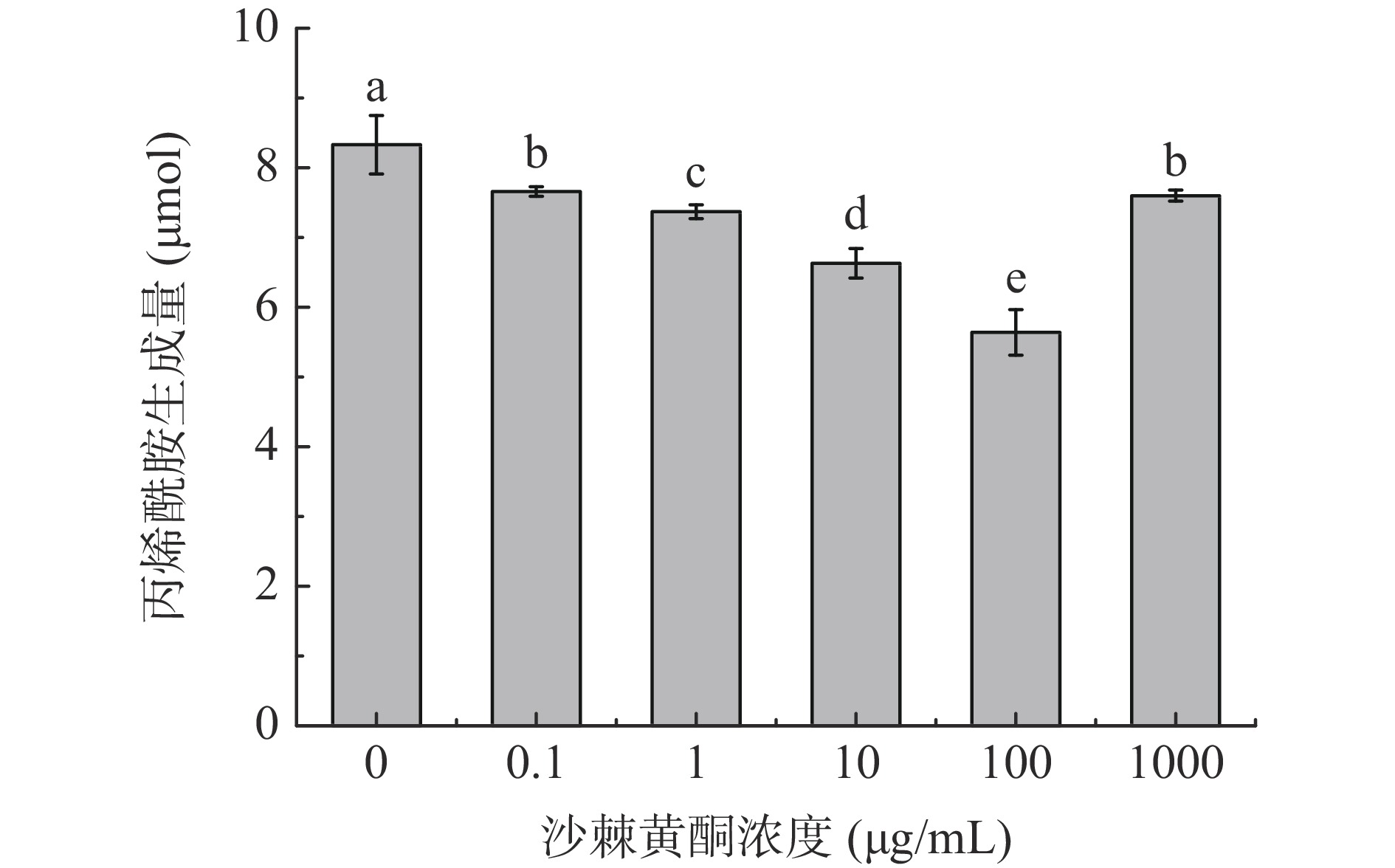
在0.1~1000 μg/mL浓度范围内,沙棘黄酮溶液可显著抑制模拟体系中丙烯酰胺的生成量(P<0.05)(图1)。但随沙棘黄酮浓度的不断增加,丙烯酰胺生成量先降低后升高,并在100 μg/mL时,达到最低生成量5.64 μmol。这与Zhang[27]研究黄酮类化合物—竹叶抗氧化剂和绿茶提取物对丙烯酰胺生成量抑制的变化趋势一致,这可能是因为3-氨基丙酰胺是一种通过天冬酰胺脱羧反应生成的瞬时中间体,是促成丙烯酰胺形成的重要的前体,抗氧化剂和3-氨基丙酰胺的反应作用可以减少丙烯酰胺的生成[28]。此外,丙烯酰胺含量与沙棘黄酮浓度之间的这种非线性关系也可能归因于沙棘黄酮的抗氧化和促氧化特性。
2.2 沙棘黄酮的添加量对模拟体系中丙烯酰胺生成量的影响
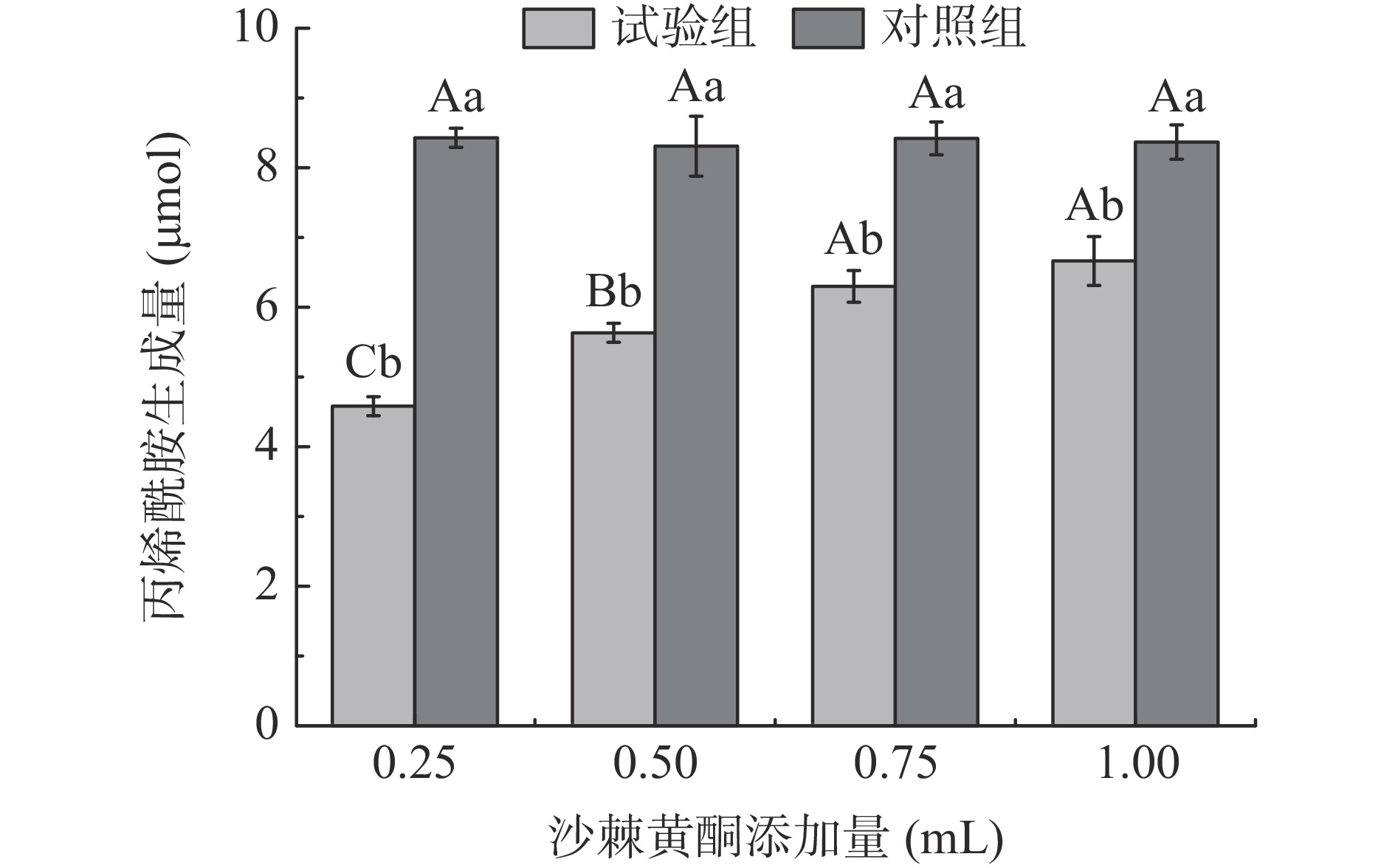
在上述沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的最适浓度100 μg/mL下,添加量0.25~1 mL(25~100 μg)范围内,试验组的丙烯酰胺生成量均显著低于对照组丙烯酰胺生成量(P<0.05)(图2)。随着沙棘黄酮溶液添加量的不断增加,在添加量为0.25~0.75 mL(25~75 μg)之间各试验组丙烯酰胺生成量呈现缓慢升高的趋势,但添加量0.75~1.00 mL(75~100 μg)范围差异不显著(P>0.05)。张翔宇[29]发现在模拟体系中添加芹菜黄酮0.1~1000 μg/mL(0.01~100 μg)处理后,其丙烯酰胺生成量增加,抑制率呈负相关。与本研究结果趋势一致。因此,选择添加量为0.25 mL进行后续试验。
综上,根据量效关系结果,当沙棘黄酮浓度为100 μg/mL,添加量为0.25 mL时,此时抑制率最高,为62.1%,选取其进行接下来的动力学分析。
2.3 沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺的形成/消除动力学分析
2.3.1 丙烯酰胺的形成/消除动力学曲线
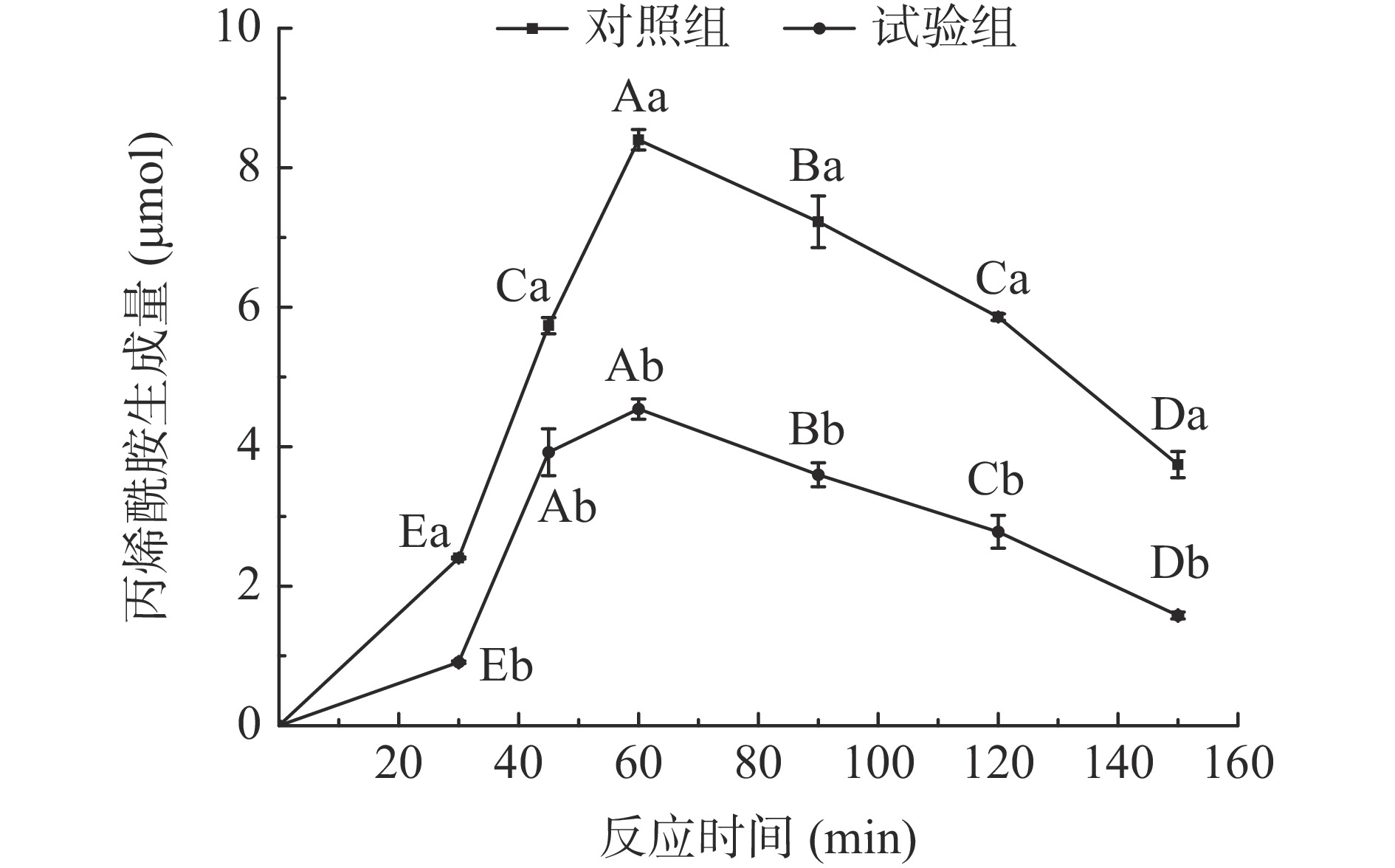
由图3可知,试验组的丙烯酰胺生成量显著低于对照组(P<0.05)。在0~150 min内,试验组和对照组丙烯酰胺生成量呈现相同的先增加后减少的趋势,并在60 min时达到最大生成量。研究结果与刘黄友[30]测定多种黄酮对丙烯酰胺的抑制的变化趋势相似,出现此种变化规律的原因可能是在60 min以前,丙烯酰胺生成速率大于降解速率,此时丙烯酰胺反应底物充足,其形成动力学占主导地位;60 min后,丙烯酰胺生成速率会小于降解速率,此阶段丙烯酰胺的消除反应占优势,且60 min后,试验组和对照组的降幅相似,推测沙棘黄酮在丙烯酰胺的降解阶段的作用不明显。
2.3.2 形成/消除动力学模型拟合及分析
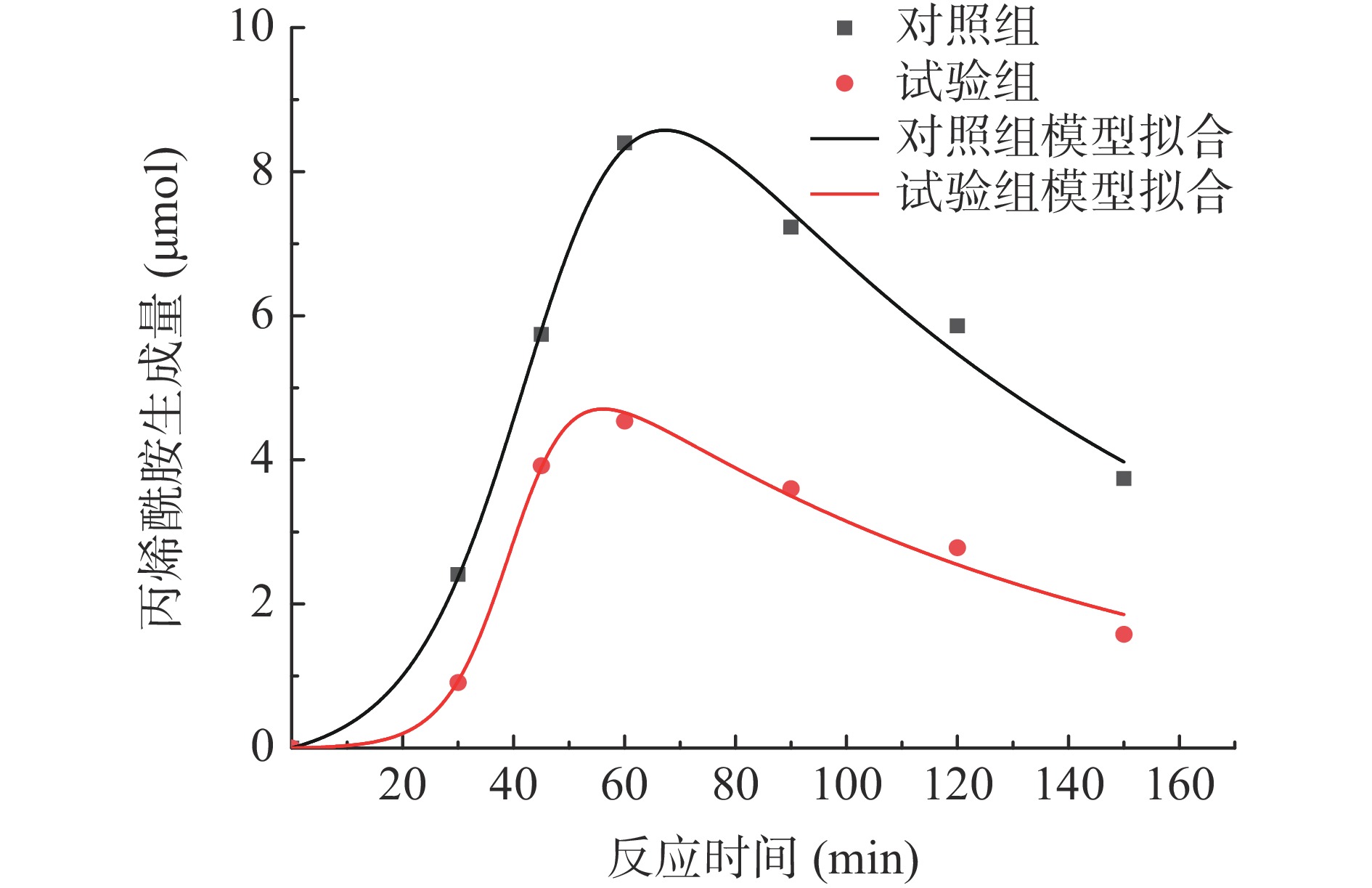
用Origin软件分别与三种形成/消除动力学模型进行非线性拟合。其中,与形成/消除一级动力学模型拟合,相关性系数R2=0.49,拟合没有意义;与Logistic-Fermi动力学模型拟合,相关性系数R2=0.98,模型的拟合度高,但动力学参数tcg<0,所以上述2个模型不适用。与Logistic指数动力学模型拟合(图4),相关性系数R2=0.98,且各种动力学参数均有意义,表明Logistic指数模型适用于分析模拟体系中丙烯酰胺生成的动力学过程。
Logistic指数动力学参数分析表明,试验组与对照组中与丙烯酰胺生成相关的三个动力学参数a、kg、tcg均有显著性差异(P<0.05),与丙烯酰胺消除相关的τ没有显著性差异(P>0.05)(表1)。这说明沙棘黄酮可显著影响丙烯酰胺的形成速率,但对丙烯酰胺的消除速率没有影响,证实了2.3.1的推测。此结论与Zhang等[31]得出的竹叶黄酮可显著影响丙烯酰胺的生成速率这一结论相类似。
表 1 丙烯酰胺的Logistic指数动力学模型参数Table 1. Parameters of Logistic exponent kinetic model of acrylamideLogistic指数
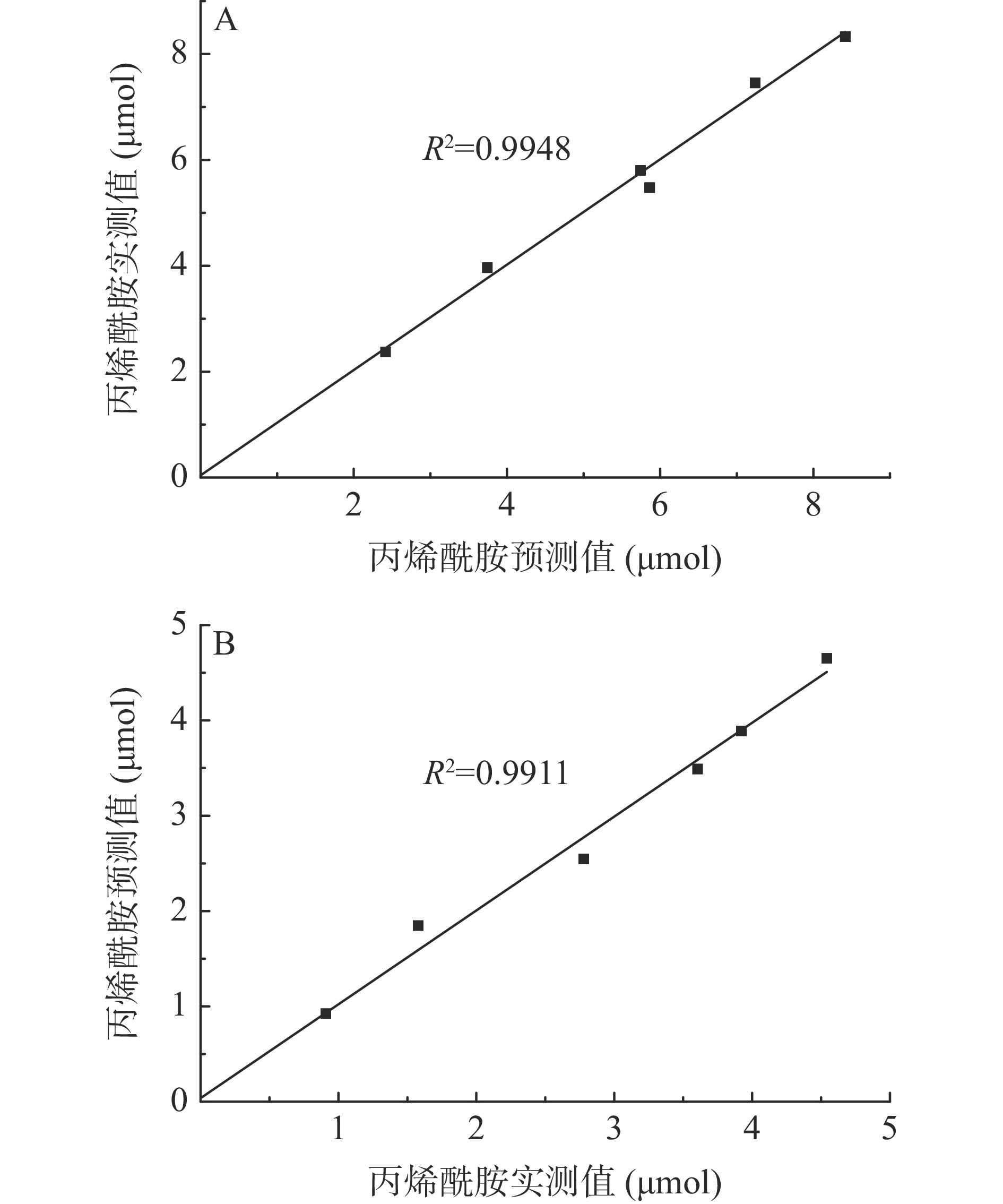
动力学模型a kg tcg τ R2 对照组 19.95±3.00a 0.099±0.01b 45.76±2.22a 93.57±11.63a 0.99 试验组 9.10±1.16b 0.174±0.03a 40.38±1.48b 94.28±11.90a 0.98 根据拟合得到的模型计算丙烯酰胺生成的预测值,通过绘制相关性散点图(图5),发现两组丙烯酰胺含量的预测值和实测值均有很强的相关性,相关系数分别为0.9948、0.9911,进一步说明了Logistic指数模型与数据拟合度高。
根据拟合得到的方程分析试验组和对照组丙烯酰胺生成量的预测值(表2),发现试验组的丙烯酰胺生成量始终低于对照组,且在56 min达到最大值,之后开始逐渐降低。而对照组则在67 min达到丙烯酰胺的最大生成量,之后开始逐渐降低。推测可能是沙棘黄酮的加入影响了美拉德反应进程,使得各阶段反应所需时间发生变化。
表 2 试验组与对照组丙烯酰胺生成量的预测值对比Table 2. Comparison of acrylamide predicted values of the proliferation group with the control group反应时间(min) 30 45 56 60 67 90 120 150 试验组丙烯酰胺含量预测值(μmol) 0.93 3.89 4.71 4.66 4.41 3.50 2.55 1.85 对照组丙烯酰胺含量预测值(μmol) 2.37 5.80 7.94 8.32 8.57 7.45 5.47 3.97 2.4 沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的机理动力学分析
2.4.1 还原糖动力学曲线
还原糖是丙烯酰胺生成的前体物质之一。在0~60 min内,试验组和对照组含量均大幅降低,之后逐渐平缓(图6),表明在0~60 min内,美拉德反应以丙烯酰胺的生成反应为主导,导致大量还原糖被消耗。与此同时,在30~60 min内,试验组的还原糖含量显著高于对照组(P<0.05),而之后的反应时间内,试验组还原糖含量虽然高于对照组,但差异不显著(P>0.05)(图6)。已有报道证实黄酮类物质能够结合反应性羰基或二羰基,从而竞争性抑制天冬酰胺和葡萄糖之间的美拉德反应[32],这与本研究沙棘黄酮减缓了还原糖的急剧下降的结果一致,表明沙棘黄酮对美拉德反应的抑制作用主要发生在丙烯酰胺的生成阶段。
2.4.2 天冬酰胺动力学曲线
天冬酰胺作为丙烯酰胺生成的另一个前体物质,在0~60 min内,模拟体系中试验组与对照组的天冬酰胺含量也均大幅降低,之后逐渐平缓(图7),且在45~60 min内,试验组的天冬酰胺含量显著高于对照组(P<0.05),而之后的反应时间内,试验组天冬酰胺含量虽然高于对照组,但差异不显著(P>0.05)。Bassama等[33]也证实了天冬酰胺的这种变化趋势,与葡萄糖的损失相比,天冬酰胺的损失更慢,这可能是由于天冬酰胺从缩合产物中的重组以及二葡糖基胺的形成。结合以上还原糖和天冬酰胺的动力学变化,进一步说明沙棘黄酮对美拉德反应的抑制作用主要发生在丙烯酰胺的生成阶段。
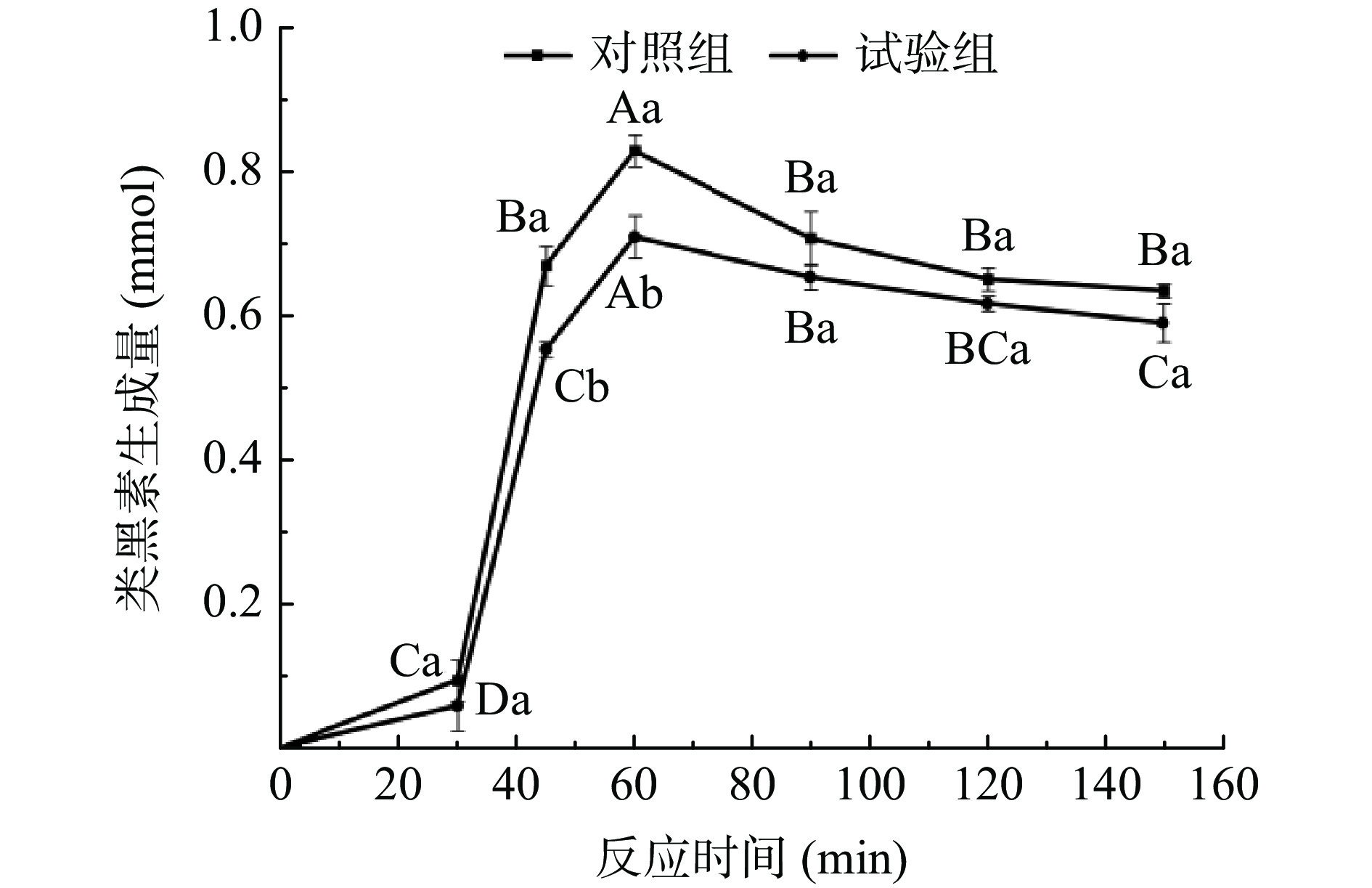
2.4.3 类黑素动力学曲线
类黑素是美拉德反应的中间产物之一。在0~150 min内,模拟体系中试验组与对照组的类黑素含量迅速升高,之后逐渐降低(图8)。这种趋势与报道过的文献[34]研究类似。整个反应过程中,试验组的类黑素含量低于对照组,表明沙棘黄酮对美拉德反应有抑制作用。在45~60 min内,试验组的类黑素含量显著低于对照组(P<0.05),而此时间段内,天冬酰胺和还原糖的含量显著高于对照组(P<0.05),说明试验组的沙棘黄酮对美拉德反应的抑制作用主要发生此阶段,即前体物质(还原糖和天冬酰胺)反应生成的中间产物向丙烯酰胺和类黑素转化的阶段。
2.4.4 机理动力学分析
机理动力学模型将美拉德反应过程分为三个不同阶段:即前体物质(还原糖和天冬酰胺)反应生成中间产物阶段、中间产物向丙烯酰胺和类黑素的转化阶段(即丙烯酰胺和类黑素的生成)、丙烯酰胺的消除和其他终产物生成阶段。根据机理动力学模型拟合得到的动力学参数(表3)分析发现,试验组的k2(与丙烯酰胺形成有关的速率常数)和k3(与类黑素形成有关的速率常数)均显著低于对照组(P<0.05),而k4(与丙烯酰胺消除有关的速率常数)与对照组无显著性差异(P>0.05),说明试验组沙棘黄酮的加入显著抑制了丙烯酰胺和类黑素的生成,但对丙烯酰胺的消除无显著影响,即沙棘黄酮主要对美拉德反应的第二阶段起抑制作用。
表 3 沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的机理动力学参数估计Table 3. Estimation of mechanism dynamics parameter estimation of seabuckthorn flavonoid inhibits acrylamide动力学参数 k1 k2 k3 k4 对照组 0.026±0.005a 4.115±0.214a 2.881±0.273a 0.0895±0.006a 试验组 0.021±0.003a 2.104±0.357b 1.098±0.315b 0.0679±0.002a 3. 结论
本试验利用Asn-Glu模拟体系证实沙棘黄酮对丙烯酰胺的生成有较好的抑制效果,抑制率最高为62.1%。同时,进一步阐明了沙棘黄酮在模拟体系中对丙烯酰胺抑制的动力学过程,即沙棘黄酮主要抑制丙烯酰胺的生成阶段,但对消除过程没有影响;且沙棘黄酮对丙烯酰胺的抑制作用主要发生在美拉德反应的第二阶段,而对美拉德反应的第三阶段无显著影响。综上所述,沙棘黄酮作为天然植物抗氧化剂,可以有效的降低食品加工过程中的丙烯酰胺生成。这不仅为食品中危害物质的防控提供思路,同时也为黄酮类化合物在食品加工方面的应用提供理论基础。但关于沙棘黄酮单体对丙烯酰胺抑制机理及应用还需要进一步探讨。
-
表 1 丙烯酰胺的Logistic指数动力学模型参数
Table 1 Parameters of Logistic exponent kinetic model of acrylamide
Logistic指数
动力学模型a kg tcg τ R2 对照组 19.95±3.00a 0.099±0.01b 45.76±2.22a 93.57±11.63a 0.99 试验组 9.10±1.16b 0.174±0.03a 40.38±1.48b 94.28±11.90a 0.98 表 2 试验组与对照组丙烯酰胺生成量的预测值对比
Table 2 Comparison of acrylamide predicted values of the proliferation group with the control group
反应时间(min) 30 45 56 60 67 90 120 150 试验组丙烯酰胺含量预测值(μmol) 0.93 3.89 4.71 4.66 4.41 3.50 2.55 1.85 对照组丙烯酰胺含量预测值(μmol) 2.37 5.80 7.94 8.32 8.57 7.45 5.47 3.97 表 3 沙棘黄酮抑制丙烯酰胺生成的机理动力学参数估计
Table 3 Estimation of mechanism dynamics parameter estimation of seabuckthorn flavonoid inhibits acrylamide
动力学参数 k1 k2 k3 k4 对照组 0.026±0.005a 4.115±0.214a 2.881±0.273a 0.0895±0.006a 试验组 0.021±0.003a 2.104±0.357b 1.098±0.315b 0.0679±0.002a -
[1] YEDIER S K, ŞEKEROGLU Z A, ŞEKEROGLU V, et al. Cytotoxic, genotoxic, and carcinogenic effects of acrylamide on human lung cells[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2022,161:112852. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.112852
[2] GIULIA S, PATRIZIA R, CHIARA C, et al. Acrylamide in coffee:What is known and what still needs to be explored. A review[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,393:133406. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133406
[3] 周艳玲, 梁文娟, 高晴, 等. 氨基酸对葡萄糖-天冬酰胺模拟体系中丙烯酰胺形成的抑制作用研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(8):2565−2572 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.8.spaqzljcjs202208025 ZHOU Y L, LIANG W J, GAO Q, et al. Inhibitory effects of amino acids on the formation of acrylamide in glucose-asparagine simulation system[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2022,13(8):2565−2572. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.8.spaqzljcjs202208025
[4] NAN X, NAN S, ZENG X, et al. Inhibition kinetics and mechanism of glutathione and quercetin on acrylamide in the low-moisture Maillard systems[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2021,84(6):984−990. doi: 10.4315/JFP-20-411
[5] KUMARI A, BHATTACHARYA B, AGARWAL T, et al. Integrated approach towards acrylamide reduction in potato-based snacks:A critical review[J]. Food Research International,2022,156:111172. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111172
[6] RIFAI L, SALEH F A. A review on acrylamide in food:Occurrence, toxicity, and mitigation strategies[J]. International Journal of Toxicology,2020,39(2):93−102. doi: 10.1177/1091581820902405
[7] MEKAWI E M, SHAROBA A M, RAMADAN M F. Reduction of acrylamide formation in potato chips during deep-frying in sunflower oil using pomegranate peel nanoparticles extract[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2019,13(4):3298−3306. doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00252-y
[8] CHEN G, WANG J, LI Y. Extracts of sorghum bran, grape seed, and green tea:Chromatographic comparison of phenolic profiles and mitigation effect on acrylamide in antioxidant-fortified bread[J]. Food Chemistry Advances,2022,1:100082. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2022.100082
[9] WANG P, JI R, JI J, et al. Changes of metabolites of acrylamide and glycidamide in acrylamide-exposed rats pretreated with blueberry anthocyanins extract[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,274:611−619. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.058
[10] FU Z, YOO M J Y, ZHOU W, et al. Effect of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) extracted from green tea in reducing the formation of acrylamide during the bread baking process[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,242:162−168. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.050
[11] 钱雪洁. 竹叶黄酮对焙烤和油炸食品中丙烯酰胺生成的抑制性研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2012 QIAN X J. Bamboo leaf flavonoids inhibitory generated acrylamide in food baking and frying[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University, 2012.
[12] ZHAO L, ZHOU T, YAN F, et al. Synergistic inhibitory effects of procyanidin B2 and catechin on acrylamide in food matrix[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,296:94−99. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.102
[13] 蔡文. 柑桔黄酮提取纯化及其抑制食品中丙烯酰胺形成的机理研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2014 CAI W. Extraction and purification research of citrus flavonoids and its inhibitory mechanism on acrylamide formation in foods[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2014.
[14] LIU X, LIU Y, SHAN C, et al. Effects of five extraction methods on total content, composition, and stability of flavonoids in jujube[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2022,14:100287.
[15] CIESAROVA Z, MURKOVIC M, CEJPEK K, et al. Why is sea buckthorn ( Hippophae rhamnoides L.) so exceptional? A review[J]. Food Research International,2020,133:109170. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109170
[16] 张琳娜. 黄酮化合物对Glu-Asn反应体系中丙烯酰胺、羟甲基糠醛生成的影响[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2019 ZHANG L N. Effects of flavonoids on the formation of AM and HMF in Glu-Asn system[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2019.
[17] MILDNER-SZKUDLARZ S, ROZANSKA M, PIECHOWSKA P, et al. Effects of polyphenols on volatile profile and acrylamide formation in a model wheat bread system[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,297:125008. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125008
[18] 李金旺. 大蒜粉抑制丙烯酰胺的作用机理研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2016 LI J W. Inhibition mechanism of garlic powder on acrylamide formation[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2016.
[19] SHEN Y, ZHAO S, ZHAO X, et al. In vitro adsorption mechanism of acrylamide by lactic acid bacteria[J]. LWT,2019,100:119−125. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.10.058
[20] 周梦舟, 丁城, 关亚飞, 等. 原花青素抑制丙烯酰胺的动力学[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(3):123−128 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201803019 ZHOU M Z, DING C, GUAN Y F, et al. Inhibitory kinetics of acrylamide by procyanidins[J]. Food Science,2018,39(3):123−128. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201803019
[21] 景雨纯. 荞麦提取物对丙烯酰胺的抑制作用和机制研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2020 JING Y C. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of buckwheat extract on acrylamide[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2020.
[22] ZHU Y, LUO Y, SUN G, et al. Inhibition of acrylamide by glutathione in asparagine/glucose model systems and cookies[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,329:127171. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127171
[23] LÜ X, WANG P, WANG T, et al. Development and validation of an improved 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone method for quantitative determination of reducing sugar ends in chitooligosaccharides[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,343:128532. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128532
[24] BERTUZZI T, MARTINELLI E, MULAZZI A, et al. Acrylamide determination during an industrial roasting process of coffee and the influence of asparagine and low molecular weight sugars[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,303:125372. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125372
[25] LEONG L P, WEDZICHA B L. A critical appraisal of the kinetic model for the Maillard browning of glucose with glycine[J]. Food Chemistry,2000,68(1):21−28. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00146-6
[26] KNOL J J, VAN LOON W A M, LINSSEN J P H, et al. Toward a kinetic model for acrylamide formation in a glucose-asparagine reaction system[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2005,53(15):6133−6139. doi: 10.1021/jf050504m
[27] ZHANG Y. Effect of natural antioxidants on kinetic behavior of acrylamide formation and elimination in low-moisture asparagine-glucose model system[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2008,85:105−115. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.07.013
[28] ZHANG Y, CHEN X, CHENG J, et al. The reduction effect of dietary flavone C-and O-glycosides on the formation of acrylamide and its correlation and prediction with the antioxidant activity of Maillard reaction products[J]. RSC Advances,2014,4(46):24147−24155. doi: 10.1039/C4RA02793K
[29] 张翔宇. 芹菜黄酮对Asn-Glc模拟体系中丙烯酰胺的抑制作用[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2016 ZHANG X Y. Inhibitory effect of cerely flavonoids on acrylamide formation in the model system of asparagine and glucos[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2016.
[30] 刘黄友. 天然植物黄酮对美拉德模拟体系中丙烯酰胺及5-羟甲基糠醛的协同抑制研究[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2018 LIU H Y. Inhibition of acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation by natural plant flavonoids in the Maillard systems[D]. Jilin: Jilin University, 2018.
[31] ZHANG Y, YING T. Reduction of acrylamide and its kinetics by addition of antioxidant of bamboo leaves (AOB) and extract of green tea (EGT) in asparagine-glucose microwave heating system[J]. Journal of Food Science,2008,73(2):60−67. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00619.x
[32] SHAO X, BAI N, HE K, et al. Apple polyphenols, phloretin and phloridzin:New trapping agents of reactive dicarbonyl species[J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology,2008,21(10):2042−2050. doi: 10.1021/tx800227v
[33] BASSAMA J, OHUOBRAT P, BN P, et al. Acrylamide kinetic in plantain during heating process:Precursors and effect of water activity[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(5):1452−1458. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.03.018
[34] ZHANG Y, WANG Q, HUANG M, et al. Unravelling the effect of flavonoids on the kinetic profiles of acrylamide in the Maillard reaction[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(102):84084−84092. doi: 10.1039/C5RA14692E





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
