Comparative Analysis of Ingredients and Key Differential Components between House Edible Bird's Nest and Cave Edible Bird's Nest
-
摘要: 屋燕和洞燕是燕窝(Edible bird's nest, EBN)的两种主要类型,但造成二者差异的关键组分尚不清晰。为了探究二者差异,实现对屋燕和洞燕样品的有效区分,本研究对四种屋燕和洞燕中的蛋白质、氨基酸、唾液酸和矿物质元素等营养成分以及亚硝酸盐和重金属元素等危害因子进行测定,并利用热图和偏最小二乘回归分析(Partial least squares regression, PLSR)进行聚类分析及关键差异组分的筛选。结果表明,蛋白质和唾液酸是燕窝中最重要的营养成分,分别占燕窝总量的63.09%~67.79%和7.22%~10.41%。亮氨酸、缬氨酸、苏氨酸和苯丙氨酸是燕窝中主要的必需氨基酸,丝氨酸、天冬氨酸和脯氨酸是主要的非必需氨基酸,且燕窝中必需氨基酸占总氨基酸的比例(45.76%~47.60%)高于联合国粮农组织/世界卫生组织(FAO/WHO)推荐的优质蛋白40%的标准。屋燕中蛋白质(66.70~67.79 g/100 g>63.09~66.28 g/100 g)和唾液酸(10.41 g/100 g>7.22~7.88 g/100 g)的含量均高于洞燕,而洞燕的氨基酸和矿物质元素含量显著高于屋燕(P<0.05)。另一方面,PLSR分析可以很好地将屋燕与洞燕区分开,且Se、Fe、I、Mn、Cu等微量元素是造成屋燕与洞燕差异的关键组分。洞燕在基础营养物质的含量上占据优势,且微量元素的检测可作为燕窝种类的区分依据。Abstract: House edible bird's nest and cave edible bird's nest are two main types of EBN. However, the key differential components, which can cause the differences of these EBN are not clear. In order to explore the differences between house EBN and cave EBN and effectively discriminate between different EBN samples, protein, amino acid, sialic acid, mineral elements and other nutritional components, as well as the hazard factors such as nitrite and heavy metal elements in four kinds of house EBN and cave EBN were determined, respectively. Moreover, cluster analysis and key differential components screening were carried out using heatmap and partial least squares regression (PLSR), respectively. The results showed that protein and sialic acid were the most important nutritional components, accounting for 63.09%~67.79% and 7.22%~10.41% in the total EBN, respectively. Leucine, valine, threonine and phenylalanine were the main essential amino acids in EBN, while serine, aspartic acid and proline were the main non-essential amino acids. In addition, the proportion of essential amino acids in total amino acids (45.76%~47.60%) was higher than 40% of the standard according to the high-quality protein recommendation from FAO/WHO. The contents of protein (66.70~67.79 g/100 g>63.09~66.28 g/100 g) and sialic acid (10.41 g/100 g<7.22~7.88 g/100 g) in house EBN were higher than those in cave EBN. The contents of amino acids and mineral elements in cave EBN were significantly higher than those in house EBN (P<0.05). On the other hand, house EBN and cave EBN could be well distinguished by PLSR analysis. Trace elements, such as Se, Fe, I, Mn, Cu, not only were the key differential components between the two EBN, but could be used as the basis to discriminate the origin of EBN species. Cave EBN has an advantage in the content of basic nutrients, and the detection of trace elements can serve as a basis for distinguishing different EBN samples.
-
燕窝(Edible bird's nest, EBN)是由雨燕科金丝燕在繁殖季节分泌出的唾液与羽毛在天然洞穴或墙壁中凝结筑就的巢穴,用于产卵及孵育雏燕。燕窝主要产于印度尼西亚、马来西亚、泰国和越南等东南亚国家以及中国南部[1]。燕窝在中国的食用历史可追溯到唐朝(公元618~907年)[2]。现代研究表明,蛋白质是燕窝中最主要的营养成分,占比高达50%。燕窝中还包含唾液酸、碳水化合物、氨基酸、矿物质元素等多种营养成分,具有美白、抗炎、抗氧化、抗病毒、促进骨骼健康、促进智力发育等多种功效[3−4]。传统上的燕窝指的是洞燕,即金丝燕在天然洞穴或悬崖峭壁上筑巢,由当地居民采摘并加工而成的食用燕窝。20世纪80年代以来,不少国家开始发展屋燕产业,通过模拟金丝燕栖息地建造燕屋,吸引金丝燕前来筑巢。屋燕的发展不仅方便农户采摘,也有利于燕窝原料品质的把控,逐渐成为燕窝主流产品[5−7]。
近年来,燕窝研究主要集中在燕窝成分、功效、真伪鉴别、加工工艺、质量控制等方向。其中燕窝营养价值的物质基础和真伪鉴别一直是燕窝行业的研究重点。从营养价值考虑,许多消费者认为暗红色的洞燕掺有金丝燕的血液,对人体健康有更高的益处,因此其价格甚至超出屋燕两倍[8−9]。但实际上屋燕与洞燕的营养差异还未被研究透彻。对于真伪鉴别,许多不法商家将便宜的白燕窝熏制、染色伪造成血燕(即洞燕),影响燕窝行业的发展[10]。可见,只有明确屋燕与洞燕营养差异才能更好的为燕窝原料筛选提供依据,阐明二者的区分方法对于消费者认知和燕窝行业的发展也至关重要。目前已有部分研究对屋燕与洞燕的化学组成进行了对比。研究表明,屋燕唾液酸含量高于洞燕,而洞燕含有更高的钙和亚硝酸盐[11]。Shim等[12]利用扫描电镜和光谱技术发现洞燕含有的方解石晶簇是造成屋燕与洞燕差异的关键。此外,有研究通过元素组成对屋燕和洞燕进行区分,如Ma等[13]对燕窝中矿物质元素进行检测,应用线性判别分析(Linear discriminant analysis, LDA)结合交叉验证建模发现以Na/Ca为变量的LDA预测模型能够准确区分屋燕与洞燕种类。同样Ang等[8]利用矿物质比率对屋燕和洞燕样本进行逻辑回归模型分析,补充Mg/K组成的模型也可准确区分燕窝种类。除矿物质元素外,Lee等[14]通过高效液相色谱(High performance liquid chromatography, HPLC)结合聚类分析、主成分分析和偏最小二乘判别分析,以氨基酸为指标建模应用于燕窝产区的鉴别。
然而,上述研究并未对屋燕与洞燕中的营养成分及危害因子进行全面检测对比,对于二者的差异,仅以某些特定的常量元素或氨基酸为指标进行区分过于片面,且并未阐明造成屋燕与洞燕营养差异的关键组分。基于此,本文以屋燕和洞燕为研究对象,利用HPLC、电感耦合等离子体质谱法(Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, ICP-MS)、氨基酸分析仪等多种技术手段对燕窝中主要的营养成分以及危害因子进行全面测定,探究二者组成成分的差异。对比以往研究,本研究创新地利用PLSR分析燕窝组成成分,筛选出了屋燕与洞燕组成成分的关键差异物,研究结果将有助于更好地区分屋燕与洞燕的营养差异,对揭示造成二者营养差异的关键组分有重要的参考价值。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
目前我国允许进口燕窝的国家仅有马来西亚、印度尼西亚、越南和泰国,其中以马来西亚为主。马来西亚、印度尼西亚和越南仅允许屋燕进口,《质检总局关于进口泰国燕窝产品检验检疫要求的公告》(2017年第66号)中明确规定我国仅允许泰国洞燕进口。因此本研究选用的4种燕窝原料分别采购于马来西亚与泰国:两种泰国洞燕为TL1-Cave EBN和TL2-Cave EBN,两种马来西亚屋燕为MAS1-House EBN和MAS2-House EBN。燕窝原料采购后储藏于干燥箱中待后续分析。
无水乙醇 色谱纯,上海安普实验科技有限公司;盐酸 分析纯,北京世纪科博科技发展有限公司;柠檬酸钠、硫酸氢钠、辛酸、硼酸、氢氧化钠 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;高氯酸 优级纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;16种氨基酸标准品(丙氨酸、丝氨酸、亮氨酸、天冬氨酸、异亮氨酸、甘氨酸、精氨酸、组氨酸、缬氨酸、脯氨酸、苏氨酸、苯丙氨酸、蛋氨酸、谷氨酸、赖氨酸、酪氨酸) 色谱纯,北京索莱宝科技有限公司;衍生液试剂 日本岛津公司;唾液酸 色谱纯,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。
Mettler AG135型分析天平 瑞士梅特勒公司;101-0AB型电热鼓风干燥箱 林茂科技(北京)有限公司;1260型液相色谱仪、Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18(4.6×150 mm,5 µm)毛细管色谱柱 美国Agilent公司;LC-16AAA型全自动氨基酸分析仪、Shim-pack Amino-Na(6.0×100 mm,5 µm)色谱柱 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蛋白质的检测
燕窝中蛋白质的检测参考国标《GB 5009.5-2016 食品中蛋白质的测定》中凯氏定氮法进行。
1.2.2 氨基酸的检测
1.2.2.1 样品制备
样品的制备方法参考穆闯录[15]的研究,取适量燕窝样品于105 ℃烘干2 h,用研钵研成细粉混匀。称取0.5 g燕窝干粉于水解管中,加入10 mL 6 mol/L盐酸溶液,充氮气后于110 ℃的电热鼓风干燥箱内水解22 h。水解结束后取出,冷却至室温。将水解液过滤至50 mL容量瓶中,去离子水定容混匀。准确吸取1 mL滤液至离心管中,40 ℃氮气吹干,用1 mL 0.2 mol/L柠檬酸钠缓冲溶液溶解后混匀,0.22 μm孔径有机滤膜过滤后上样检测。其中柠檬酸钠缓冲液制备方法为:称取19.6 g柠檬酸钠加入500 mL去离子水溶解,加入16.5 mL盐酸并用水稀释至1000 mL混匀,用6 mol/L盐酸溶液或500 g/L氢氧化钠溶液调节溶液pH2.2。
1.2.2.2 氨基酸自动分析仪检测方法
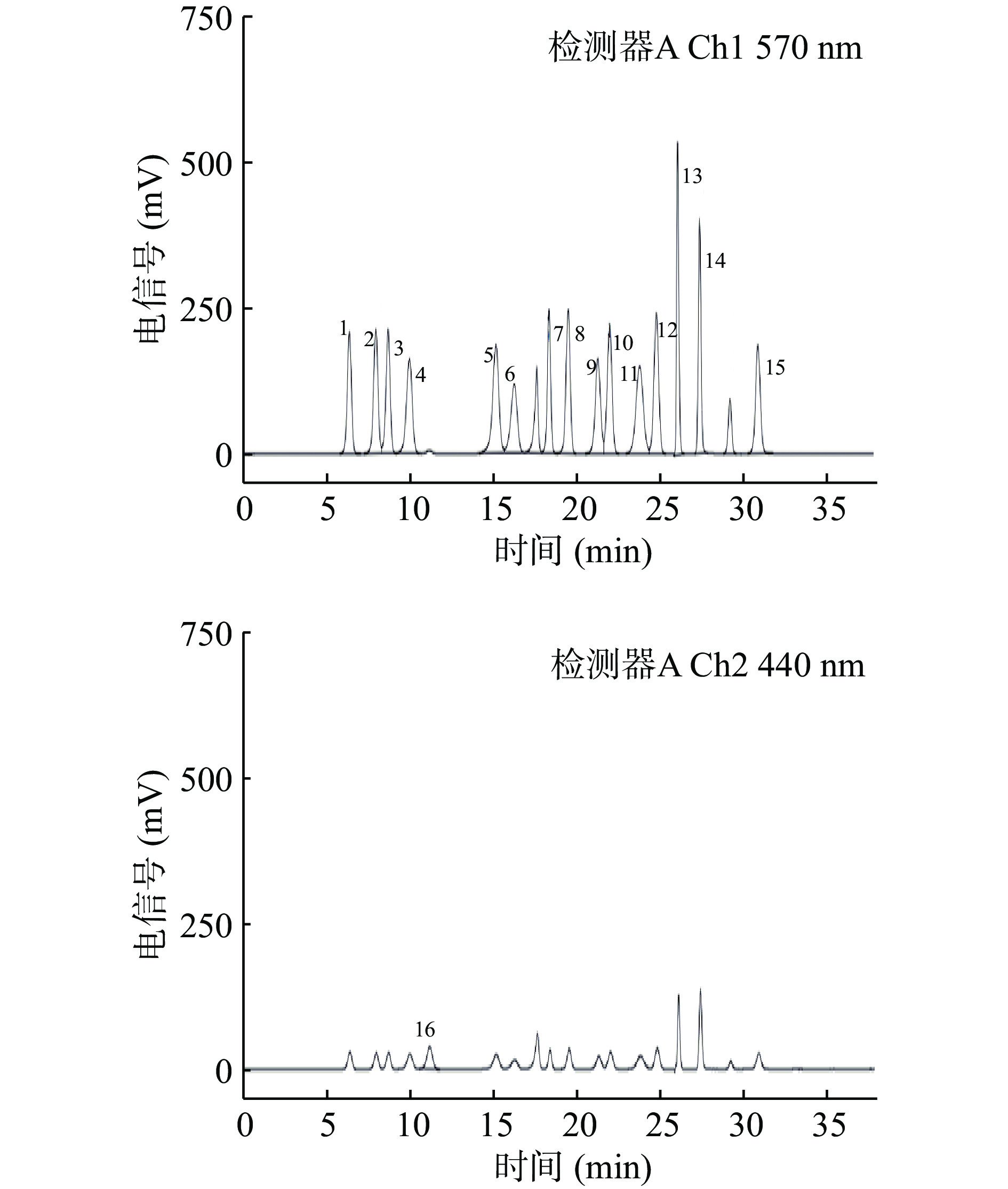
采用全自动氨基酸分析仪对燕窝原料中氨基酸组成进行检测,色谱柱型号为Shim-pack Amino-Na(6.0×100 mm,5 µm)。将混合氨基酸标准工作液注入氨基酸自动分析仪,参照《JJG1064—2011氨基酸分析仪检定规程及仪器说明书》调整仪器参数和洗脱液配比进行检测。各氨基酸标准品、混合氨基酸标准工作液与样品测定液分别以相同体积注入氨基酸分析仪,通过对比样品中检测出的氨基酸与氨基酸标准品的保留时间进行定性,以外标法通过峰面积计算样品氨基酸的浓度。流动相A、B均为柠檬酸钠溶液,流动相C为0.2 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液。其中流动相A的配制方法为:称取19.6 g柠檬酸钠溶解于800 mL去离子水中,添加55.3 g无水乙醇、22.75 g高氯酸、0.1 mL辛酸,转移至1 L容量瓶中水定容,抽滤备用,溶液pH约为3.24;流动相B的配制方法为:称取58.8 g柠檬酸钠、12.4 g硼酸溶解于900 mL去离子水中,加入0.1 mL辛酸、32.5 mL 4 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液,转移至1 L容量瓶中水定容,抽滤备用,溶液pH约为10.00。泵3为衍生液试剂。泵1、泵2流速分别为0.6、0.2 mL/min,进样量为20 μL,分离柱柱温为60 ℃,衍生柱柱温为130 ℃,检测器为紫外可见光检测器,检测波长为570 nm和440 nm。具体洗脱程序见表1。
表 1 氨基酸检测洗脱程序(%)Table 1. Elution program of amino acids detection (%)时间
(min)泵1 泵2 泵3 流动相A
柠檬
酸钠溶液流动相C
氢氧
化钠溶液流动相B
柠檬
酸钠溶液衍生液 0~9 100 0 100 9~13 100~93 0~7 100 13~17.2 93~92 7~8 100 17.2~17.21 92~89 8~11 100 17.21~20.8 89 11 100 20.8~20.81 89~50 11~50 100 20.81~22 50~42 50~58 100 22~22.01 42~0 58~100 100 22.01~29.3 100 100 29.3~29.31 0~100 100~0 100 29.31~33 0~100 100~0 0 100 33~45 100 0 100 1.2.3 唾液酸的检测
1.2.3.1 样品制备
参考王羚郦等[16]的方法制备样品:称取10 mg燕窝干粉,加入0.5 mol/L的硫酸氢钠水溶液1 mL,于80 ℃水浴中水解30 min,水浴结束待其冷却至室温后进行衍生化反应。取上述溶液200 µL,加入20 mg/mL邻苯二胺盐酸盐(0.25 mol/L的硫酸氢钠溶液溶解)200 µL,再置于80 ℃水浴中加热40 min。水浴结束后冷却至室温,将该溶液于8000 r/min、4 ℃条件下离心5 min,经0.22 μm孔径有机滤膜过滤后上样检测。准确称取唾液酸标准品10 mg,加入0.5 mol/L的硫酸氢钠水溶液定容至2 mL,得到5 mg/mL的母液备用。通过对比样品中检测出的唾液酸与标准品的保留时间进行定性,以外标法定量。
1.2.3.2 HPLC分析
采用1260型液相色谱仪对燕窝原料中唾液酸进行检测,液相色谱柱型号为Agilent ZORBAX SB-C 18(4.6×150 mm,5 µm)。检测方法参照王羚郦等[16]并稍作修改,具体方法如下:流动相 A为水,B相为乙腈。流动相洗脱程序为:0~10 min, 10% B;10~11 min, 10%~95% B;11~20 min, 95% B;20~21 min, 95%~10% B;21~30 min, 10% B。流动相流速为1 mL/min,柱温为25 ℃,检测波长为330 nm,进样量为10 µL。
1.2.4 元素的检测
燕窝中钙、钠、镁、铁、锰、铜、锌、硒、砷的检测参考国标《GB 5009.268-2016 食品中多元素的测定》中电感耦合等离子体质谱法;磷的检测参考国标《GB 5009.87-2016 食品中磷的测定》中钼蓝分光光度法;碘的检测参考国标《GB 5009.267-2020 食品中碘的测定》中气相色谱法;汞的检测参考国标《GB 5009.17-2021 食品中总汞及有机汞的测定》中原子荧光光谱法;铅的检测参考国标《GB 5009.12-2017 食品中铅的测定》中石墨炉原子吸收光谱法;镉的检测参考国标《GB 5009.15-2014 食品中镉的测定》;铬的检测参考国标《GB 5009.123-2014 食品中铬的测定》。
1.2.5 亚硝酸盐的检测
燕窝中亚硝酸盐的检测参考国标《GB 5009.33-2016 食品中亚硝酸盐与硝酸盐的测定》中分光光度法。
1.3 数据处理
数据计算采用Excel 2019(Microsoft, USA)进行;显著性差异分析选用IBM SPSS 25.0(SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)中的Duncan test和T-test进行单因素方差分析,P<0.05表示差异显著。PLSR分析由SIMCA 14.1分析绘制,蛋白质及唾液酸柱状图由Sigma Plot 14.0分析绘制,箱线图、热图均由R 4.1.1分析绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蛋白质及唾液酸结果分析
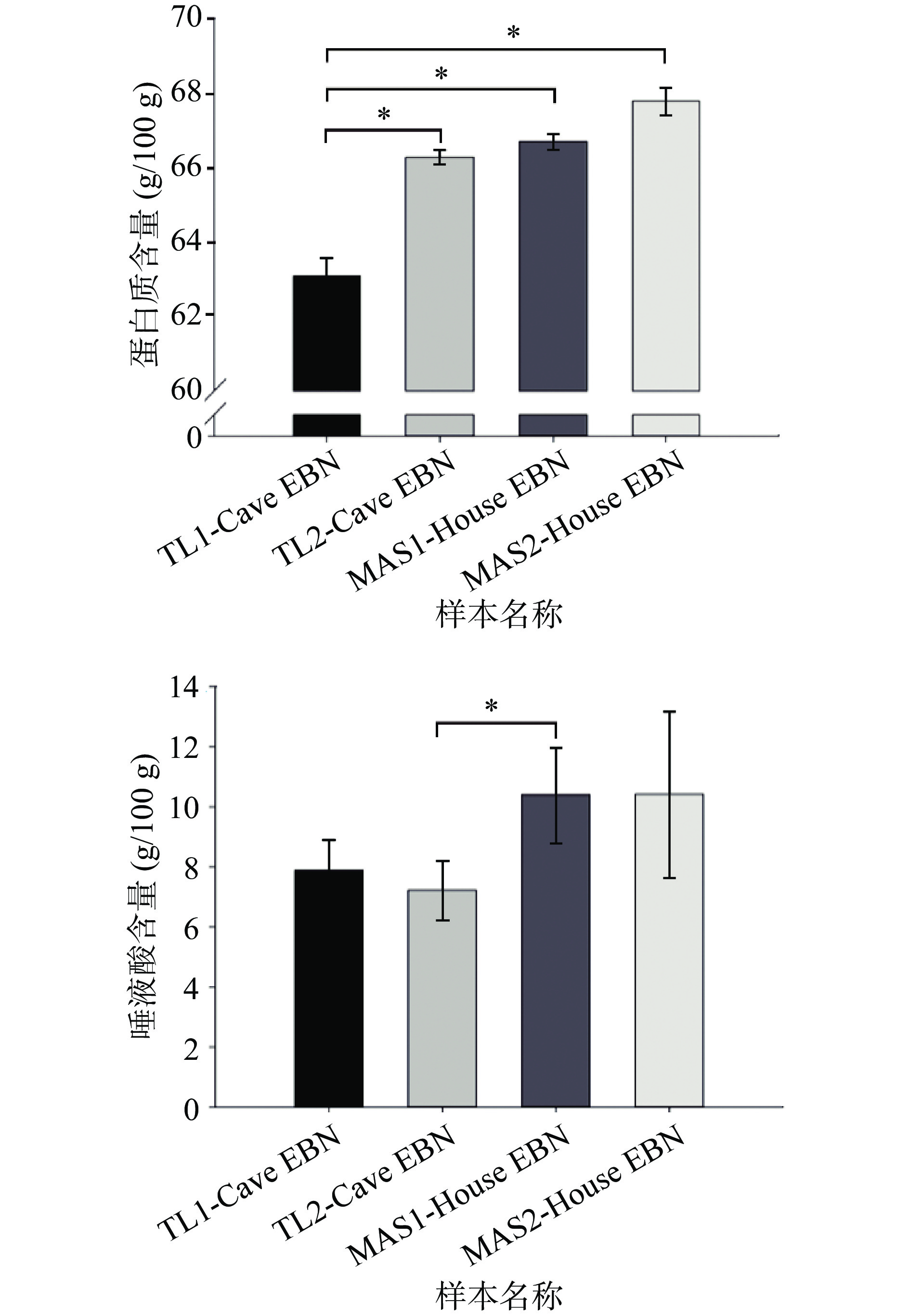
蛋白质和唾液酸是燕窝中重要的营养成分。从图1中可以看出4种燕窝原料蛋白质含量为63.09~67.79 g/100 g,略高于之前研究得出的燕窝蛋白含量在50%~60%之间[17]。相比于旱季,金丝燕在雨季的食物更加充沛,通常燕窝品质更高,加上金丝燕在旱季换羽,因而旱季采摘的燕窝沾有较多羽毛和杂质[18]。本研究所用样品均为雨季燕窝,这可能是燕窝蛋白质含量较高的重要原因。中国营养学会提出成年人膳食营养素参考摄入量(DRI)中蛋白质为男性65 g/d和女性55 g/d[19],因此每100 g燕窝可为人体每日提供充足的蛋白质营养。TL1-Cave EBN中蛋白质含量为63.09 g/100 g,显著低于其他3种燕窝样品(P<0.05)。虽然TL2-Cave EBN中蛋白质含量并未与两种屋燕蛋白质含量呈现显著差异(P>0.05),但还是可以看出屋燕中蛋白质含量高于洞燕,可能是因为研究所用原料未经挑拣除杂等加工处理,在人工干预下屋燕的栖息环境优于洞燕,因而羽毛和杂质更少。此外,产地不同也是造成燕窝蛋白含量差异的重要原因之一,特别是产地差异导致金丝燕生存的气候环境、饮食特点不同,进而影响着燕窝的品质[17]。蛋白质占据燕窝组成的50%以上,表明燕窝是良好的蛋白来源。因此后续进一步研究其氨基酸单体组成,以更好地表征燕窝的蛋白质来源。
唾液酸又名N-乙酰神经氨酸,是一类含有9-碳骨架的酸性单糖,在大脑中含量最高,是神经节苷脂的重要组成成分,对大脑和神经系统的产生和发育具有非常重要的作用[20]。燕窝是唾液酸的重要来源,许多研究将燕窝促进神经发育的功效归因于唾液酸的存在[21−22]。本研究中,4种原料唾液酸含量范围为7.22~10.41 g/100 g。屋燕与洞燕中唾液酸含量不同,虽然仅在MAS1-House EBN与TL2-Cave EBN样品间唾液酸含量呈现出显著差异(P<0.05),但整体来看屋燕中唾液酸含量高于洞燕。唾液酸含量受地理来源和生产环境的影响,马来西亚和泰国不同的气候特点导致金丝燕的生活习性差异,进而影响唾液酸含量[17]。除产地影响外,金丝燕的生存环境是造成该现象的关键原因。岩洞等自然环境下存在诸多不可控因素,微生物的生长、代谢水平高于屋燕,从而增加了微生物酶促反应导致唾液酸的降解[23]。
2.2 氨基酸结果分析
氨基酸是组成蛋白质的基本结构单元,是人体进行正常代谢、维持生命的物质基础。本研究在燕窝中共检测到16种氨基酸,包括8种必需氨基酸(Essential amino acid, EAA):亮氨酸(Leucine, Leu)、异亮氨酸(Isoleucine, Ile)、组氨酸(Histidine, His)、缬氨酸(Valine, Val)、苏氨酸(Threonine, Thr)、苯丙氨酸(Phenylalanine, Phe)、蛋氨酸(Methionine, Met)、赖氨酸(Lysine, Lys)和8种非必需氨基酸(Non-essential amino acid, NEAA):丙氨酸(Alanine, Ala)、丝氨酸(Serine, Ser)、天冬氨酸(Aspartic acid, Asp)、甘氨酸(Glycine, Gly)、精氨酸(Arginine, Arg)、脯氨酸(Proline, Pro)、谷氨酸(Glutamic acid, Glu)、酪氨酸(Tyrosine, Tyr),16种氨基酸混标的分离色谱图见图2。
4种燕窝原料总氨基酸(Total amino acid, TAA)含量范围为43.82~47.04 g/100 g,具体含量见表2。在所有燕窝样品中,Leu、Val、Thr和Phe是主要的EAA,Ser、Asp和Pro是主要的NEAA,这与Chantakun等[11]和Chua等[24]的研究结果类似。此外,燕窝中几乎所有的氨基酸含量均比牛奶、鸡蛋高,特别是EAA含量(20.81~22.04 g/100 g)明显高于牛奶(2.9 g/100 g)、鸡蛋(11~17 g/100 g)和婴幼儿奶粉(9.6 g/100 g)[24],表明燕窝是良好的氨基酸来源,高含量的氨基酸有助于人体蛋白质的合成。值得注意的是,燕窝中存在的Lys在大多数植物蛋白质中都不存在[25],这表明燕窝可以为素食者提供更为完整的氨基酸。
表 2 燕窝中氨基酸组成及含量(g/100 g)Table 2. Composition and content of amino acids in EBN (g/100 g)种类 TL1-Cave EBN TL2-Cave EBN MAS1-House EBN MAS2-House EBN 丙氨酸 Ala 1.52±0.05a 1.47±0a 1.36±0.01b 1.47±0.01a 丝氨酸 Ser 3.56±0.03a 3.48±0ab 3.41±0.02b 3.44±0.06b 亮氨酸 Leu* 3.60±0.10a 3.50±0.04a 3.21±0.01b 3.55±0.01a 天冬氨酸 Asp 4.57±0.13a 4.35±0.06b 4.03±0.04c 4.51±0ab 异亮氨酸 Ile* 1.67±0.06a 1.61±0.03a 1.42±0.02b 1.65±0a 甘氨酸 Gly 1.91±0.05a 1.87±0.01a 1.70±0.03b 1.90±0.01a 精氨酸 Arg 3.19±0.08a 3.18±0.04a 2.89±0.03b 3.19±0a 组氨酸 His 3.37±0.25b 3.54±0.04ab 3.87±0.19a 2.72±0.01c 缬氨酸 Val* 3.72±0.13a 3.65±0.05a 3.21±0.05b 3.72±0.02a 脯氨酸 Pro 3.88±0.09a 3.84±0.07a 3.45±0.01b 3.83±0.01a 苏氨酸 Thr* 3.43±0.05a 3.29±0.02b 3.13±0.01c 3.27±0.01b 苯丙氨酸 Phe* 4.01±0.11a 3.89±0.03a 3.97±0.09a 3.67±0.05b 蛋氨酸 Met* 0.33±0a 0.28±0c 0.29±0b 0.29±0b 谷氨酸 Glu 3.37±0.11b 3.27±0.07bc 3.08±0.07c 3.59±0.01a 赖氨酸 Lys* 1.91±0.07a 1.85±0.04ab 1.75±0.03b 1.95±0a 酪氨酸 Tyr 3.01±0.08a 2.88±0.01ab 3.04±0.05a 2.74±0.08b 鲜味氨基酸 7.93±0.24ab(16.86%) 7.62±0.13b(16.58%) 7.12±0.11c(16.25%) 8.10±0a(17.81%) 甜味氨基酸 14.29±0.21a(30.38%) 13.95±0.10b(30.36%) 13.05±0.05c(29.78%) 13.90±0.06b(30.56%) 苦味氨基酸 24.81±0.01a(52.75%) 24.38±0.12b(53.06%) 23.65±0.09c(53.97%) 23.48±0.11c(51.63%) 必需氨基酸 EAA 22.04±0.05a 21.61±0.11b 20.86±0c 20.81±0.03c 非必需氨基酸 NEAA 25.00±0.04a 24.34±0.24a 22.96±0.25b 24.67±0.13a 总氨基酸 TAA 47.04±0.46a 45.96±0.35b 43.82±0.25c 45.48±0.17b EAA/TAA (%) 46.85±0.34b 47.03±0.13b 47.60±0.27a 45.76±0.09c 注:*必需氨基酸为Leu、Ile、His、Val、Thr、Phe、Met、Lys;非必需氨基酸为Ala、Ser、Asp、Gly、Arg、Pro、Glu、Tyr;鲜味氨基酸为Glu和Asp;甜味氨基酸为Ala、Pro、Gly、Ser和Thr;苦味氨基酸为Phe、Leu、Met、Val、Arg、Ile、Lys、His和Tyr;结果以平均值±标准差表示,每行中不同字母表示样本之间差异显著(P<0.05),表3同。 具体来看,TL1-Cave EBN总氨基酸含量最高,为47.04 g /100 g,除Glu和His外,该样品在其余氨基酸含量上均占据明显优势。TL2-Cave EBN总氨基酸含量次之,且洞燕总氨基酸含量高于屋燕。燕窝中EAA含量范围为20.81~22.04 g/100 g,且TL1-CaveEBN>TL2-Cave EBN>MAS1-House EBN>MAS2-House EBN,其中洞燕EAA含量显著高于屋燕(P<0.05)。EAA指人体无法合成或合成速率无法满足机体需求,需从食物中获取的氨基酸。4种燕窝原料必需氨基酸占总氨基酸的比率均在45.76%~47.60%之间,符合FAO/WHO推荐的优质蛋白质40%的标准。Shim等[12]认为岩洞大气中亚硝酸等活性氮成分含量更高,可硝酸化酪氨酸并使糖蛋白中存在的谷氨酸脱氨,从而降低洞燕中这些氨基酸的含量,这解释了洞燕在两种氨基酸上不占优势的原因。
氨基酸组成、比例及相互作用也是影响食品风味的重要因素,根据呈味特性可划分为鲜味、甜味和苦味氨基酸[26],目前少有文献对燕窝中呈味氨基酸组成进行分析,本研究对屋燕与洞燕呈味氨基酸含量及占比进行初探。3类呈味氨基酸在燕窝原料中分布规律一致,苦味氨基酸是燕窝中最主要的呈味氨基酸,占比高达50%,甜味氨基酸次之,最后是鲜味氨基酸。对比屋燕与洞燕呈味氨基酸含量,洞燕中甜味和苦味氨基酸含量显著高于屋燕(P<0.05),MAS2-House EBN中鲜味氨基酸含量(8.10 g/100 g)及占比(17.81%)均最高,其次是两种洞燕。Glu和Asp为主要的鲜味氨基酸,由于洞燕高含量活性氮的存在使Glu脱氨,因而洞燕中Glu含量显著低于MAS2-House EBN(P<0.05),使MAS2-House EBN的鲜味氨基酸含量更高。而其余氨基酸的味觉特点为甜味和苦味,相比于屋燕,洞燕在这些氨基酸的含量上均占据优势,因而甜味和苦味氨基酸含量更高。
2.3 元素结果分析
燕窝中的主要矿物质含量如表3所示。TL2-Cave EBN中矿物质元素含量最高(11.71 g/kg),其次是TL1-Cave EBN(11.33 g/kg)、MAS2-House EBN(6.60 g/kg)和MAS1-House EBN(5.54 g/kg)。Ca和Na是燕窝中最丰富的矿物质,含量范围分别为4706.67~9426.67 mg/kg和251~5049.67 mg/kg,其次是Mg(360.67~937.00 mg/kg),这与之前的研究结果一致[8,11]。三者均是人体必需的常量元素,Ca是骨骼和牙齿的主要成分,调控着神经传递和肌肉收缩,Na维持着人体电解质、渗透压的平衡,而Mg负责酶的激活[27],燕窝的高钙含量解释了其在提高骨密度、治疗骨关节炎方向的功效[28−29]。根据中国营养学会推荐,Na、Ca和Mg的成年人膳食营养素参考摄入量(DRI)分别为1500 、800和330 mg/d[19]。本研究结果显示,每100 g TL2-Cave EBN可为人体提供每天所需118%的Ca和28%的Mg,TL1-Cave EBN可提供30%的Na,可见燕窝是良好的矿物质来源。值得注意的是,本研究并未在燕窝样品中检测到P,可能是因为燕窝中P含量低于仪器检出限所致,相关文献报道燕窝中P含量也很低,仅为0.03~6.79 mg/100 g[30−31]。
表 3 燕窝中元素组成及含量(mg/kg)Table 3. Composition and content of mineral elements in EBN (mg/kg)种类 TL1-Cave EBN TL2-Cave EBN MAS1-House EBN MAS2-House EBN 钙 Ca 5890.00±173.49b 9426.67±28.87a 4706.67±263.12d 5280.00±209.52c 磷 P nd nd nd nd 镁 Mg 360.67±2.52d 937.00±12.17a 566.33±3.79c 813.67±5.86b 钠 Na 5049.67±182.77a 1313.33±15.28b 251.00±5.00d 491.33±9.02c 常量元素 11300.33±99.45b 11677.00±10.39a 5524.00±269.29d 6585.00±208.18c 铁 Fe 10.90±0.40b 16.07±0.21a 3.39±0.14c 3.59±0.12c 锌 Zn 3.46±0.16b 3.12±0.03c 7.39±0.04a 3.60±0.08b 铜 Cu 3.45±0.04c 3.12±0.05d 4.10±0.03a 3.66±0.17b 碘 I 2.54±0.10c 2.92±0.09b 3.47±0.16a 3.42±0.16a 硒 Se 0.58±0.01a 0.54±0.03a 0.37±0.03b 0.29±0.02c 锰 Mn 4.22±0.04a 3.47±0.18b 0.90±0.03d 2.60±0.07c 微量元素 25.15±0.35b 29.24±0.29a 19.62±0.36c 17.16±0.28d 除常量元素外,燕窝中含有Fe(3.39~16.07 mg/kg)、Zn(3.12~7.39 mg/kg)、Cu(3.12~4.10 mg/kg)、I(2.54~3.47 mg/kg)、Se(0.29~0.58 mg/kg)和Mn(0.90~4.22 mg/kg)6种微量元素,Fe是燕窝中含量最高的微量元素,在洞燕中的含量高出屋燕3~5倍,Fe2+的氧化是导致洞燕呈现红色的重要原因[32]。本研究显示每100 g燕窝可以为人体每天提供至少35%的Cu。Cu在人体侧脑室下区大量分布,能够促进神经系统以及脑部发育[33],这可能是燕窝促进神经发育的重要原因之一[21]。整体来看,洞燕在绝大多数矿物质元素含量上均高于屋燕,特别是常量元素含量是屋燕的近2倍,且均呈现出显著差异(P<0.05),可能是由于岩壁中矿物质渗入燕窝中或氧化所致[2,34],或洞燕因生活在洞穴等海边附近,食用的昆虫等食物中含更高含量的Na、Ca、Mg和K元素[35]。
2.4 危害因子结果分析
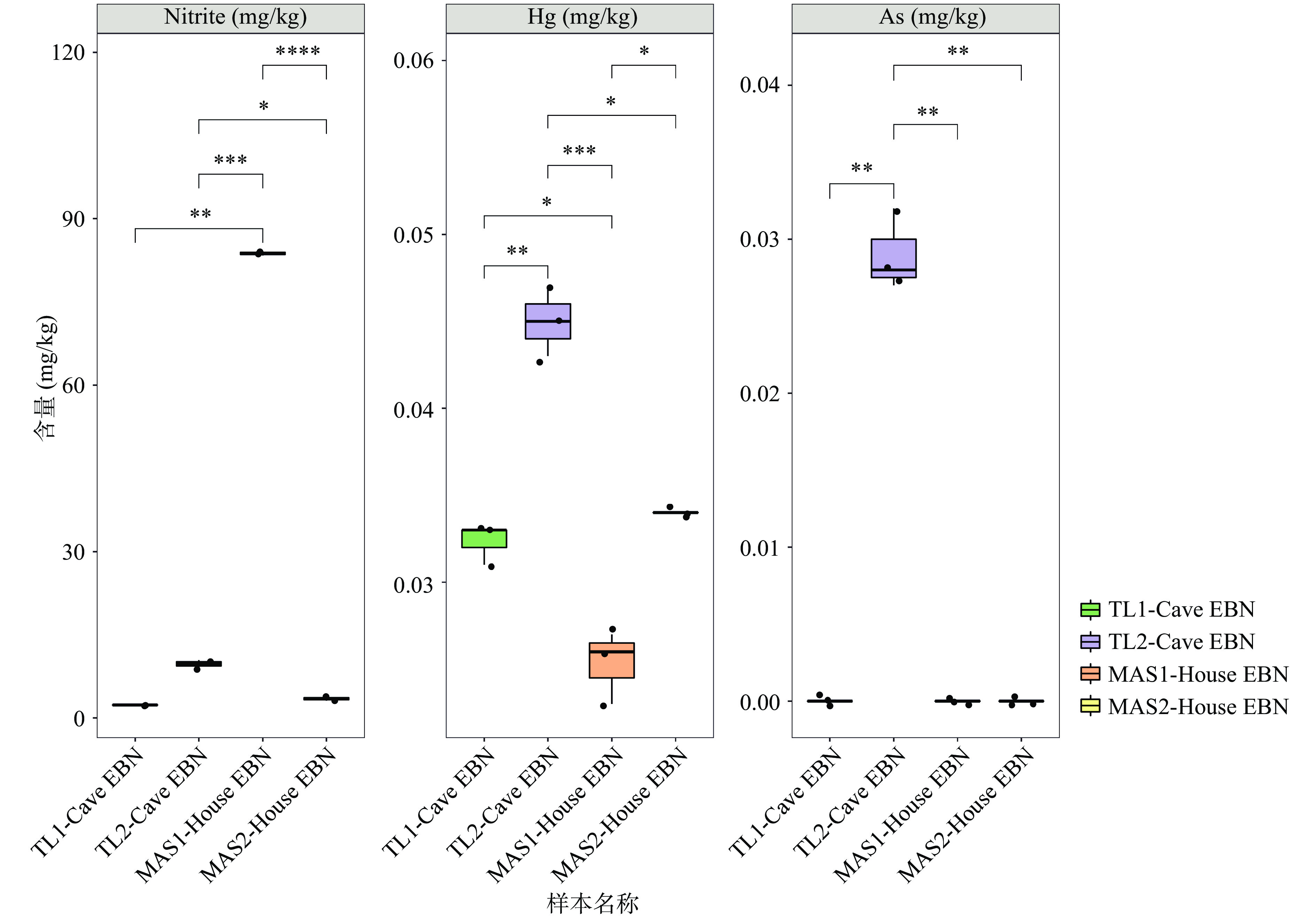
燕窝中主要的危害因子含量结果见图3。金丝燕排泄物产生NH3的氧化以及燕窝所处环境的污染是燕窝中亚硝酸盐的主要来源,此外,血燕的人工熏制过程也会导致亚硝酸盐的产生,如2011年发生的燕窝亚硝酸盐严重超标的“血燕”事件[36−37]。亚硝酸盐是剧毒物质,因此亚硝酸盐含量一直是评估燕窝安全性的关键指标之一。本研究检测的4种燕窝原料中MAS1-House EBN亚硝酸盐含量为83.74 mg/kg,已不符合我国燕窝进口规定亚硝酸盐含量不得超出30 mg/kg的标准[38]。推测可能是因为样本的进口周期长,原料贮藏条件稍有变动,导致该批次样品中亚硝酸盐含量过高。从整体数据所呈现的结果来看,MAS1-House EBN样本中其他生理生化指标并未受到亚硝酸盐含量的影响。通过本次检测,发现贮藏条件和时间的不同可能会对原料品质造成影响,因此后续实验将着重研究储存过程中原料品质和贮藏条件之间存在的关系。T2-Cave EBN中亚硝酸盐含量显著高于MAS2-House EBN(P<0.05),而另一种洞燕T1-Cave EBN并未与其表现出显著性差异(P>0.05)。由于屋燕环境更容易把控,而洞燕周围散布的粪便等排泄物会被细菌发酵产生亚硝酸盐,因此洞燕中亚硝酸盐含量往往比屋燕高[36]。此外,亚硝酸盐含量也影响着燕窝原料的颜色,通常认为高亚硝酸盐含量和铁氧化是使洞燕呈现红色的主要原因[9,39]。
除亚硝酸盐外,Cd、Cr、Hg、Pb、As等重金属也是衡量燕窝食用安全的关键因素,特别是Hg有剧毒,通过危害神经系统使大脑受损。本研究在四种燕窝原料中仅检测到Hg和As两种重金属元素,二者含量均低于0.05 mg/kg。TL2-Cave EBN中Hg含量显著高于两种屋燕(P<0.05),虽然TL1-Cave EBN中Hg含量略低于MAS2-House EBN,但并未呈现出显著性差异(P>0.05)。研究仅在TL2-Cave EBN中检测到As,燕窝原料中本不存在重金属,金丝燕的饮食和栖息环境的污染是造成燕窝中存在重金属元素的主要原因[40]。
2.5 聚类分析
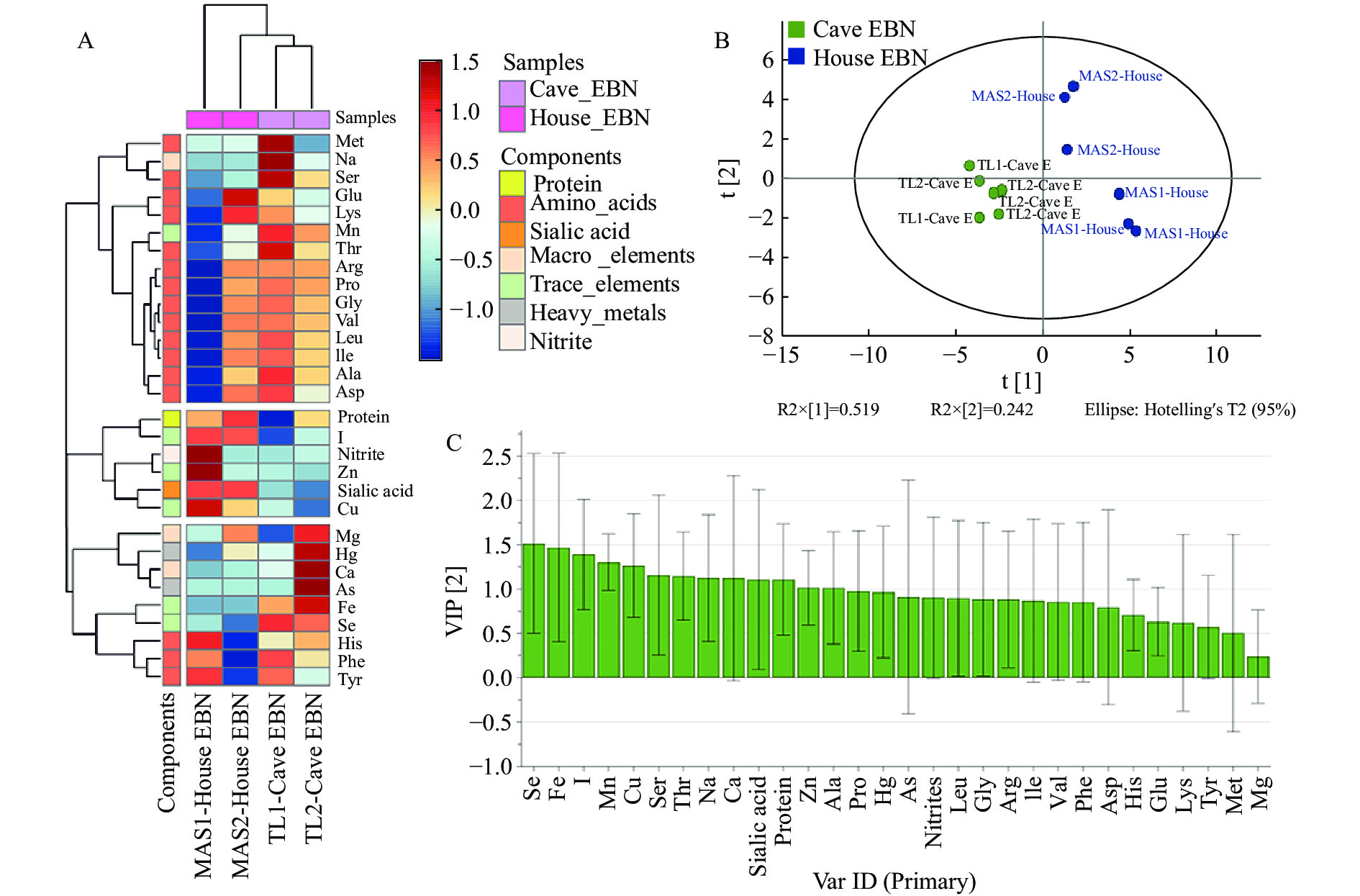
热图更直观地显示了4种燕窝原料在各组成成分上的的差异(图4 A)。具体来说80%以上的氨基酸均聚类在热图上半部分,与两种洞燕及MAS2-House EBN多呈现显著正相关,其中Met、Ser和Thr与TL1-Cave EBN样本相关性较强,可作为该样本的特征氨基酸。蛋白质、唾液酸、亚硝酸盐以及Cu、Zn、I三种元素位于热图中部,蛋白质和唾液酸与两种屋燕相关性更强,MAS1-House EBN中Zn和亚硝酸盐含量明显高于其他燕窝原料。His、Phe和Tyr均与MAS1-House EBN展现出了强相关性,三者均是具有环状结构的氨基酸,且Phe和Tyr存在着相似的合成代谢途径[41],这可能是导致该类化合物表现出强相关性的原因之一。此外,两种洞燕,特别是TL2-Cave EBN与多数矿物质元素呈现显著正相关关系。
为了进一步区分屋燕与洞燕样品,筛选造成二者差异的关键组分,本研究进行PLSR分析,模型的Rx2为0.761,Ry2为0.968,Q2为0.923,表明该模型可以准确的解释不同燕窝原料在化合物组成上的差异。PLSR分析中前两个主成分提取了总方差的76.1%,可解释样本的大部分信息(图4 B)。不同燕窝原料根据化合物组成的差异可以很好地被分开,其中两种屋燕位于第一主成分正半轴,第二主成分可将两种屋燕进一步区分开。两种洞燕主要集中在第二和第三象限,与第一主成分呈现负相关关系,二者化合物组成及含量较为相似,并未作出进一步的区分。在这些对燕窝种类具有重要影响的化合物中,有13种物质的变量投影重要性(Variable importance in the projection, VIP)>1(图4 C),包括Se、Fe、I、Mn、Cu、Zn在内的6种微量元素,Ser、Thr和Ala在内的3种氨基酸,Ca和Na在内的2种常量元素以及唾液酸和蛋白质,它们对模型方差具有较高的贡献率,可以用来区分屋燕与洞燕种类。整体来看,矿物质元素对屋燕和洞燕成分组成的影响大于氨基酸、危害因子及其他营养成分,特别是微量元素Se、Fe、I、Mn和Cu贡献率更高,因此后续研究区分燕窝种类时可将微量元素含量作为关注重点。
3. 结论
本研究以4种屋燕和洞燕为实验原料,对燕窝中蛋白质、唾液酸、氨基酸和矿物质元素等营养成分以及亚硝酸盐、重金属元素进行了检测分析。结果表明,蛋白质和唾液酸是燕窝中最主要的营养物质(占比分别为63.09%~67.79%和7.22%~10.41%),且屋燕中蛋白质和唾液酸含量高于洞燕。燕窝还富含人体必需氨基酸,可作为人体优质蛋白质的来源,且洞燕中氨基酸含量高于屋燕(45.96~47.04 g/100 g>43.82~45.48 g/100 g)。不同种类燕窝矿物质元素组成及含量差异较大,特别是洞燕中Ca、Na、Fe、Mn含量显著高于屋燕。其中Se、Fe、I、Mn、Cu可作为区分屋燕与洞燕的关键指标,对燕窝种类进行鉴别时以上述5种微量元素为衡量指标可提高准确度。总的来说,不论从氨基酸还是矿物质元素含量角度分析,洞燕的营养价值均高于屋燕,特别是TL1-Cave EBN营养价值更高,可作为优质的燕窝原料。
对比以往研究中利用特定的常量元素建模区分燕窝种类,本研究利用回归分析筛出的微量元素更加准确,可应用于市面上洞燕真伪鉴别的重要依据,但后续还需要收集大量的样本做进一步的验证。燕窝富含对人体健康有益的高质量蛋白及必需氨基酸,暗示燕窝蛋白的功效不容忽视。目前关于燕窝中蛋白质的组成少有研究,屋燕与洞燕蛋白质组成差异还未见报道,具体哪种蛋白质发挥关键作用尚不明确,后续实验将重点挖掘燕窝中的活性蛋白组分并对其生理功能展开一系列研究。此外,燕窝贮藏条件对燕窝品质有重要影响,有必要对二者的线性关系开展研究,以得到燕窝贮藏的最适条件。
-
表 1 氨基酸检测洗脱程序(%)
Table 1 Elution program of amino acids detection (%)
时间
(min)泵1 泵2 泵3 流动相A
柠檬
酸钠溶液流动相C
氢氧
化钠溶液流动相B
柠檬
酸钠溶液衍生液 0~9 100 0 100 9~13 100~93 0~7 100 13~17.2 93~92 7~8 100 17.2~17.21 92~89 8~11 100 17.21~20.8 89 11 100 20.8~20.81 89~50 11~50 100 20.81~22 50~42 50~58 100 22~22.01 42~0 58~100 100 22.01~29.3 100 100 29.3~29.31 0~100 100~0 100 29.31~33 0~100 100~0 0 100 33~45 100 0 100 表 2 燕窝中氨基酸组成及含量(g/100 g)
Table 2 Composition and content of amino acids in EBN (g/100 g)
种类 TL1-Cave EBN TL2-Cave EBN MAS1-House EBN MAS2-House EBN 丙氨酸 Ala 1.52±0.05a 1.47±0a 1.36±0.01b 1.47±0.01a 丝氨酸 Ser 3.56±0.03a 3.48±0ab 3.41±0.02b 3.44±0.06b 亮氨酸 Leu* 3.60±0.10a 3.50±0.04a 3.21±0.01b 3.55±0.01a 天冬氨酸 Asp 4.57±0.13a 4.35±0.06b 4.03±0.04c 4.51±0ab 异亮氨酸 Ile* 1.67±0.06a 1.61±0.03a 1.42±0.02b 1.65±0a 甘氨酸 Gly 1.91±0.05a 1.87±0.01a 1.70±0.03b 1.90±0.01a 精氨酸 Arg 3.19±0.08a 3.18±0.04a 2.89±0.03b 3.19±0a 组氨酸 His 3.37±0.25b 3.54±0.04ab 3.87±0.19a 2.72±0.01c 缬氨酸 Val* 3.72±0.13a 3.65±0.05a 3.21±0.05b 3.72±0.02a 脯氨酸 Pro 3.88±0.09a 3.84±0.07a 3.45±0.01b 3.83±0.01a 苏氨酸 Thr* 3.43±0.05a 3.29±0.02b 3.13±0.01c 3.27±0.01b 苯丙氨酸 Phe* 4.01±0.11a 3.89±0.03a 3.97±0.09a 3.67±0.05b 蛋氨酸 Met* 0.33±0a 0.28±0c 0.29±0b 0.29±0b 谷氨酸 Glu 3.37±0.11b 3.27±0.07bc 3.08±0.07c 3.59±0.01a 赖氨酸 Lys* 1.91±0.07a 1.85±0.04ab 1.75±0.03b 1.95±0a 酪氨酸 Tyr 3.01±0.08a 2.88±0.01ab 3.04±0.05a 2.74±0.08b 鲜味氨基酸 7.93±0.24ab(16.86%) 7.62±0.13b(16.58%) 7.12±0.11c(16.25%) 8.10±0a(17.81%) 甜味氨基酸 14.29±0.21a(30.38%) 13.95±0.10b(30.36%) 13.05±0.05c(29.78%) 13.90±0.06b(30.56%) 苦味氨基酸 24.81±0.01a(52.75%) 24.38±0.12b(53.06%) 23.65±0.09c(53.97%) 23.48±0.11c(51.63%) 必需氨基酸 EAA 22.04±0.05a 21.61±0.11b 20.86±0c 20.81±0.03c 非必需氨基酸 NEAA 25.00±0.04a 24.34±0.24a 22.96±0.25b 24.67±0.13a 总氨基酸 TAA 47.04±0.46a 45.96±0.35b 43.82±0.25c 45.48±0.17b EAA/TAA (%) 46.85±0.34b 47.03±0.13b 47.60±0.27a 45.76±0.09c 注:*必需氨基酸为Leu、Ile、His、Val、Thr、Phe、Met、Lys;非必需氨基酸为Ala、Ser、Asp、Gly、Arg、Pro、Glu、Tyr;鲜味氨基酸为Glu和Asp;甜味氨基酸为Ala、Pro、Gly、Ser和Thr;苦味氨基酸为Phe、Leu、Met、Val、Arg、Ile、Lys、His和Tyr;结果以平均值±标准差表示,每行中不同字母表示样本之间差异显著(P<0.05),表3同。 表 3 燕窝中元素组成及含量(mg/kg)
Table 3 Composition and content of mineral elements in EBN (mg/kg)
种类 TL1-Cave EBN TL2-Cave EBN MAS1-House EBN MAS2-House EBN 钙 Ca 5890.00±173.49b 9426.67±28.87a 4706.67±263.12d 5280.00±209.52c 磷 P nd nd nd nd 镁 Mg 360.67±2.52d 937.00±12.17a 566.33±3.79c 813.67±5.86b 钠 Na 5049.67±182.77a 1313.33±15.28b 251.00±5.00d 491.33±9.02c 常量元素 11300.33±99.45b 11677.00±10.39a 5524.00±269.29d 6585.00±208.18c 铁 Fe 10.90±0.40b 16.07±0.21a 3.39±0.14c 3.59±0.12c 锌 Zn 3.46±0.16b 3.12±0.03c 7.39±0.04a 3.60±0.08b 铜 Cu 3.45±0.04c 3.12±0.05d 4.10±0.03a 3.66±0.17b 碘 I 2.54±0.10c 2.92±0.09b 3.47±0.16a 3.42±0.16a 硒 Se 0.58±0.01a 0.54±0.03a 0.37±0.03b 0.29±0.02c 锰 Mn 4.22±0.04a 3.47±0.18b 0.90±0.03d 2.60±0.07c 微量元素 25.15±0.35b 29.24±0.29a 19.62±0.36c 17.16±0.28d -
[1] FAN Q, LIU X, WANG Y, et al. Recent advances in edible bird's nests and edible bird's nest hydrolysates[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,42:e67422. doi: 10.1590/fst.67422
[2] JAMALLUDDIN N H, TUKIRAN N A, AHMAD F N, et al. Overview of edible bird's nests and their contemporary issues[J]. Food Control,2019,104:247−255. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.04.042
[3] WONG Z C F, CHAN G K L, WU L, et al. A comprehensive proteomics study on edible bird's nest using new monoclonal antibody approach and application in quality control[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2018,66:145−151. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2017.12.014
[4] 简叶叶, 李庆旺, 黄知几, 等. 燕窝的营养功效与真伪鉴别研究进展[J]. 亚热带农业研究,2016,12(2):136−144 doi: 10.13321/j.cnki.subtrop.agric.res.2016.02.012 JIAN Y Y, LI Q W, HUANG Z J, et al. Advances in nutrition, functions and authenticity identification of cubilose[J]. Subtropical Agriculture Research,2016,12(2):136−144. doi: 10.13321/j.cnki.subtrop.agric.res.2016.02.012
[5] SANKARAN R. The status and conservation of the edible-nest swiftlet ( Collocalia fuciphaga) in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands[J]. Biological Conservation,2001,97(3):283−294. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3207(00)00124-5
[6] LEE T, WANI W, LEE C, et al. Edible bird's nest:The functional values of the prized animal-based bioproduct from southeast Asia-a review[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:626233. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.626233
[7] 郭丽丽. 表征属性识别技术在燕窝真伪鉴别中的应用研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2014 GUO L L. Study on the application of representative characteristics recognition technology in authentication of edible bird's nest[D]. Beijing:China Agricultural University, 2014.
[8] ANG K, SEOW E, FAM P, et al. Classification of edible bird's nest samples using a logistic regression model through the mineral ratio approach[J]. Food Control,2022,137:108921. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.108921
[9] BUT P H, JIANG R W, SHAW P C. Edible bird's nests-how do the red ones get red?[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2013,145(1):378−380. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.10.050
[10] YEO B H, TANG T K, WONG S F, et al. Potential residual contaminants in edible bird's nest[J]. Front Pharmacol,2021,12:631136. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.631136
[11] CHANTAKUN K, KISHIMURA H, KUMAGAI Y, et al. Physicochemical properties of house and cave edible bird's nest from Southern Thailand[J]. ScienceAsia,2022,48(2):136. doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2022.017
[12] SHIM K S, LEE S Y. Calcite deposits differentiate cave from house-farmed edible bird's nest as shown by SEM-EDX, ATR-FTIR and raman microspectroscopy[J]. Chemistry-An Asian Journal,2020,15(16):2487−2492. doi: 10.1002/asia.202000520
[13] MA X T, ZHANG J K, LIANG J, et al. Element analysis of house-and cave-EBN (edible bird's nest) traceability by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) integrated with chemo-metrics[J]. Materials Express,2020,10(7):1141−1148. doi: 10.1166/mex.2020.1742
[14] LEE T H, LEE C H, AZMI N A, et al. Amino acid determination by HPLC combined with multivariate approach for geographical classification of Malaysian edible bird's nest[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2022,107:104399. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104399
[15] 穆闯录. 不同泌乳阶段牛羊乳及母乳中蛋白质和总氨基酸分析及评价[D]. 咸阳:西北农林科技大学, 2017 MU C L. Comparative analysis and evaluation of protein and total amino acid in different stages in cows', goats' and breast milk[D]. Xianyang:Northwest A&F University, 2017.
[16] 王羚郦, 李远彬, 邱子博, 等. 25种燕窝样品中唾液酸含量的测定与分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(19):64−67 WANG L L, LI Y B, QIU Z B, et al. Determination and analysis of sialic acid in 25 kinds of edible bird' nest[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2013,19(19):64−67.
[17] HUANG X W, LI Z H, ZOU X B, et al. Geographical origin discrimination of edible bird's nests using smart handheld device based on colorimetric sensor array[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2020,14(1):514−526. doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00251-z
[18] TAN K H, CHIA F C, HAN K. Impact of swiftlet's moult season on the value of edible bird nests[C]//. HongKong, China:2014.
[19] 中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量速查手册:2013版[M]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2014:12−24 Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese DRIs Handbook[M]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2014:12−24.
[20] WANG B. Sialic acid is an essential nutrient for brain development and cognition[J]. Annual Review of Nutrition,2009,29(1):177−222. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.28.061807.155515
[21] MAHAQ O, RAMELI M A P, EDWARD M J, et al. The effects of dietary edible bird nest supplementation on learning and memory functions of multigenerational mice[J]. Brain and Behavior,2020,10(11):e01817. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1817
[22] XIE Y, ZENG H, HUANG Z, et al. Effect of maternal administration of edible bird's nest on the learning and memory abilities of suckling offspring in mice[J]. Neural Plasticity,2018,2018:1−13.
[23] QUEK M C, CHIN N L, YUSOF Y A, et al. Characterization of edible bird's nest of different production, species and geographical origins using nutritional composition, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities[J]. Food Research International,2018,109:35−43. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.03.078
[24] CHUA Y G, CHAN S H, BLOODWORTH B C, et al. Identification of edible bird's nest with amino acid and monosaccharide analysis[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2014,63(1):279−289.
[25] 杜强. 卵形鲳鲹赖氨酸和蛋氨酸需求量及饲料中鱼粉替代的研究[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2012 DU Q. Dietary lysine and methionine requirements and substitution of fish meal in diets for juvenile Trachinotus ovatus[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2012.
[26] 黄百祺, 黄创成, 吴巨贤, 等. 4种龟肉酶解液的氨基酸及呈味特性比较[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(8):12−17 doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.08.003 HUANG B Q, HUANG C C, WU J X, et al. Comparison of amino acids and taste characteristics in four kinds of emydidae meat enzymatic hydrolysate[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(8):12−17. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.08.003
[27] 佚名. 人体中常量元素与微量元素的功能[J]. 化工进展,1998(6):62 Anon. Functions of macro and trace elements in human body[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,1998(6):62.
[28] MATSUKAWA N, MATSUMOTO M, BUKAWA W, et al. Improvement of bone strength and dermal thickness due to dietary edible bird's nest extract in ovariectomized rats[J]. Bioscience Biotechnology & Biochemistry,2011,75(3):590−592.
[29] CHUA K H, LEE T H, NAGANDRAN K, et al. Edible bird's nest extract as a chondro-protective agent for human chondrocytes isolated from osteoarthritic knee: In vitro study[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2013,13(1):19. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-19
[30] MOHAMAD I R, MOHAMAD N N, ABU B M Z, et al. The authentication and grading of edible bird’s nest by metabolite, nutritional, and mineral profiling[J]. Foods,2021,10(7):1574. doi: 10.3390/foods10071574
[31] 马雪婷, 张九凯, 陈颖, 等. 燕窝多元素的分布及溯源信息研究[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(2):66−71 MA X T, ZHANG J K, CHEN Y, et al. Study on the distribution characteristics and traceability information of multi-elements in edible bird's nest[J]. Food&Machinery,2019,35(2):66−71.
[32] WONG Z C F, CHAN G K L, DONG T T H, et al. Origin of red color in edible bird's nests directed by the binding of Fe ions to acidic mammalian chitinase-like protein[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(22):5644−5653. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01500
[33] LIU L L, RIJIN R M, ZHENG W. Copper modulates adult neurogenesis in brain subventricular zone[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(17):9888. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179888
[34] HALIMI N M, KASIM Z M, BABJI A S. Nutritional composition and solubility of edible bird nest ( Aerodramus fuchiphagus)[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings,2014,1614(1):476−481.
[35] SAENGKRAJANG W, MATAN N, MATAN N. Nutritional composition of the farmed edible bird's nest ( Collocalia fuciphaga) in Thailand[J]. Journal of Food Composition & Analysis,2013,31(1):41−45.
[36] 王文枝, 李立, 蒋萍萍, 等. 燕窝中亚硝酸盐研究现状[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(22):8927−8932 WANG W Z, LI L, JIANG P P, et al. Research status of nitrite in bird's nest[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2021,12(22):8927−8932.
[37] ISA M. Prevalence of nitrite (NO2) and nitrate (NO3) in edible bird's nest harvested from swiftlet ranches in the state of Johor[J]. Journal of Food Science,2013,78(12):1940−1947. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12313
[38] NINGRUM S G, PALGUNAD B U, SASMITA R. Evaluation of nitrite concentration in edible bird's nest (white, yellow, orange, and red blood)[J]. Makara Journal of Science,2022,26(1):68−72.
[39] PAYDAR M, WONG Y L, WONG W F, et al. Prevalence of nitrite and nitrate contents and its effect on edible bird nest's color[J]. Journal of Food Science,2013,78(10-11-12):T1940−T1947.
[40] DAI Y, CAO J, WANG Y, et al. A comprehensive review of edible bird's nest[J]. Food Research International,2020,140:109875.
[41] 吴凤礼, 王晓霜, 宋富强, 等. 芳香族化合物微生物代谢工程研究进展[J]. 生物工程学报,2021,37(5):1771−1793 doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200725 WU F L, WANG X S, SONG F Q, et al. Advances in metabolic engineering for the production of aromatic chemicals[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology,2021,37(5):1771−1793. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200725
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陈亮,郭江涛,李倩,徐锋,陈滕. 基于OBE面向科教融合的药物分析学教学改革研究. 广东化工. 2024(06): 177-178+152 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王雪,潘兆平,陈嘉序,郝丹丹,苏志鹏,马双双,肖佳豪,付复华. 茶枝柑与不同品种温州蜜柑果皮的非靶向代谢组学比较与分析. 食品科学. 2024(14): 133-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋娟,康三江,张海燕,曾朝珍,袁晶,慕钰文,苟丽娜. 基于高温高湿条件下苹果加工过程中代谢产物的多样性分析. 寒旱农业科学. 2024(08): 711-723+785 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
