Protective Effect of Sophora japonica L. Extract and Vitamin C Composition on Photodamage of HaCaT Cells Induced by Ultraviolet Irradiation
-
摘要: 本研究旨在探讨槐提取物和维生素C(Vitamin C,VC)对紫外线照射引起的HaCaT细胞光损伤的保护作用。通过体外培养HaCaT细胞并将其分为不同组别:对照组(未接受紫外辐照,无槐提取物、VC或二者组合物处理)、紫外线辐射组、125 μg/mL槐提取物(接受紫外辐照及槐提取物处理)、125 μg/mL维生素C(接受紫外辐照及维生素C处理)以及125 μg/mL组合物组(接受紫外辐照及组合物处理,槐提取物和VC质量比为1:1)。采用荧光染色和酶标仪检测技术来评估槐提取物、VC及二者组合物对紫外照射引起的HaCaT细胞产生的活性氧物质(ROS)和线粒体ROS的抑制率。利用免疫荧光染色和酶联免疫吸附法检测槐提取物、VC和组合物对紫外照射引起的HaCaT细胞中环丁烷嘧啶二聚体(Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers,CPDs)和细胞炎症因子IL-6的表达水平。结果显示,槐提取物、VC和组合物对UVA处理后HaCaT细胞生成的总ROS抑制率分别为38.23%±9.23%、27.20%±6.87%及64.13%±4.08%,与单独使用槐提取物或VC处理相比,组合物显著提高总ROS抑制率(P<0.01)。槐提取物、VC和组合物对线粒体ROS(Mitochondrial DNA,mtROS)的抑制率分别为50.29%±4.92%、38.81%±8.66%及84.74%±3.68%,与单独使用槐提取物或VC处理相比,组合物极显著提高mtROS抑制率(P<0.01)。此外,在UVB照射后,槐提取物、VC及组合物可极显著减少CPDs的生成(P<0.01),这种效应在组合物组效果更为显著(与槐提取物组比较P<0.05;与VC组比较P<0.01)。同时,槐提取物和组合物显著降低UVA照射后炎症因子IL-6的分泌(P<0.01;P<0.05),表明槐提取物及组合物具有抗炎作用。本研究结果表明槐提取物和维生素C组合物能减轻紫外线引起的氧化应激损伤和炎症反应,为未来体内研究和开发具有健康益处的槐提取物和VC组合物提供实验支持。Abstract: This study aims to investigate the protective effects of the extract of Sophora japonica L. (Sophora extract) and vitamin C (VC) on UV-induced damage in HaCaT cells. HaCaT cells were cultured in vitro and divided into different groups: Control group (without UV irradiation or treatment with Sophora extract, VC, or their combination), UV radiation group, 125 μg/mL Sophora extract group (with UV irradiation and treatment with Sophora extract), 125 μg/mL vitamin C group (with UV irradiation and treatment with VC), and 125 μg/mL combination group (with UV irradiation, Sophora extract and VC at a mass ratio of 1:1). The inhibitory effects of Sophora extract, VC, and their combination on reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and mitochondrial ROS in UV-irradiated HaCaT cells were measured using fluorescence staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Immunofluorescence staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were also employed to evaluate the expression levels of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and the inflammatory cytokine IL-6 in UV-irradiated HaCaT cells treated with Sophora extract, VC, or their combination. The results showed that the total ROS inhibition rates of Sophora extract, VC, and the combination in UVA-treated HaCaT cells were 38.23%±9.23%, 27.20%±6.87%, and 64.13%±4.08%, respectively. The combination significantly enhanced the total ROS inhibition rate compared to the individual treatments (P<0.01). The inhibition rates of mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) by Sophora extract, VC, and the combination were 50.29%±4.92%, 38.81%±8.66%, and 84.74%±3.68%, respectively. The combination significantly increased the mtROS inhibition rate compared to the individual treatments (P<0.01). After UVB irradiation, the CPDs content in HaCaT cells increased, and Sophora extract, VC, and their combination significantly reduced CPDs formation (P<0.01), with the combination showing a more pronounced effect compared to the Sophora extract group (P<0.05) and the VC group (P<0.01) alone. Furthermore, Sophora extract and the combination significantly reduced the secretion of the inflammatory cytokine IL-6 in HaCaT cells after UVA irradiation (P<0.01, P<0.05), indicating an anti-inflammatory capability. The results demonstrated that the combination of Sophora extract and Vitamin C could alleviate oxidative stress damage and inflammatory responses caused by UV radiation and provided experimental support for future in vivo studies and the development and utilization of health-promoting Sophora extract and VC combinations.
-
Keywords:
- Sophora japonica L. /
- vitamin C /
- HaCaT cells /
- antioxidant activity /
- inflammatory cytokines
-
随着生活水平的提升,人们对皮肤健康和管理的关注度与日俱增。紫外线辐射作为主要的外源性老化因素对皮肤的伤害长期存在,与人体皮肤的生理病理状态关系最为密切。维生素C(Vitamin C,VC),又称为抗坏血酸,是人体健康必需的微量营养素,天然VC主要来源于柑橘类水果和蔬菜[1],有提高免疫力、预防细菌和病毒感染等作用。作为人体内最重要的水溶性维生素之一,VC具有抗氧化、减轻炎性反应、光保护、抗衰老和抗色素沉着的作用,在皮肤健康方向也起着重要作用[2]。槐(Sophora japonica L.)是一种高大的多年生乔木,因其具有观赏、药用和食用价值而受到关注[3]。花/花芽具有外观美观、气味芳香、口感独特、保健功能优良等优点,在改善氧化应激,调节黑色素沉淀,修复紫外线辐射损伤等方向具有显著作用[4−6]。近年来的研究表明,槐米中提取的多糖具有保护HaCaT细胞免受UVB照射诱导的损伤[5]。槐花中的主要成分芦丁被认为可以降低顺铂导致的HMCs细胞的氧化损伤[7]。因此,VC和槐提取物有抗氧化功效,具有对皮肤的光保护作用。
此外,有研究表明芦丁和VC联用对超氧阴离子自由基的清除或对脂质过氧化的抑制呈浓度依赖性,且芦丁与VC组合可以产生超加性效应[8]。芦丁和VC组合物在紫外辐照的人类皮肤成纤维细胞中也表现出保护作用,二者联用对促炎信号蛋白的过度表达和DNA重组/表达有抑制作用[9]。Zhang等[10]的研究表明槐花和VC组合物显著提高运动训练小鼠血清中SOD活性,且其抗氧化能力较单一物料处理组具有更好的效果。可见,槐提取物与维生素C组合物有一定的协同抗氧化作用,可能对紫外线照射造成的皮肤光氧化损伤有效。
本实验室之前的实验研究表明,槐提取物和VC组合物可以促进紫外照射后皮肤成纤维细胞弹性蛋白的生成,且槐提取物和VC组合物的质量比为1:1时有协同增效的作用。为进一步探究槐提取物和VC特定比例组合物对人体皮肤细胞的影响,本研究以槐提取物和VC为实验材料,以HaCaT细胞为研究对象,通过检测槐提取物、VC及其组合物对UV导致的光损伤的抗氧化保护与抗炎的初步探究,为槐提取物和维生素C组合物的开发和利用提供实验支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
槐提取物 河南中大恒源生物科技股份有限公司(10%芦丁,水提、包埋、干燥等工艺制备);维生素C(合成) 帝斯曼江山制药(江苏)有限公司;胎牛血清(FBS)、0.25%胰蛋白酶/EDTA、青霉素/链霉素、DMEM培养基 Gibco公司;磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS) 普诺赛生命科技有限公司;6-羧基-2',7'-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(H2DCF-DA) Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;人白介素-6(IL-6)Elisa试剂盒 RD systems公司;MitoSOX™ Red Invitrogen公司;鼠源Anti-Thymine Dimer抗体 Abcam公司;Alexa Fluor 488标记山羊抗小鼠IgG(H+L)、抗荧光淬灭封片液(含DAPI) Beyotime Biotechnology公司;即用型正常山羊血清 武汉博士德生物工程有限公司;永生化人角质形成细胞(HaCaT) 普诺赛生命科技有限公司。
Axio Vert. A1倒置荧光显微镜、LSM 880激光共聚焦显微镜 ZEISS公司;Spark®多模式微孔板酶标仪 TECAN公司;CL-3000L紫外交联仪 Analytik Jena公司;Forma 3111二氧化碳培养箱 Thermo Fisher Scientific公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 槐提取物及维生素C组合物对UV诱导的HaCaT细胞ROS的影响
1.2.1.1 细胞内总ROS水平的测定(酶标仪检测)
取对数生长期生长到80%的HaCaT细胞,以1.5×104个/孔接种于黑壁透明板底的96孔板。5% CO2的37 ℃培养箱中培养24 h。细胞随机分为对照组、模型组(UVA组)及槐提取物处理组(槐提取物组)、维生素C处理组(VC组)、槐提取物和VC组合物处理组(槐提取物+VC组,质量比为1:1)。弃去上清液,10 mmol/L PBS洗涤1次,模型组及不同实验组加入适量PBS覆盖细胞,模型组和各实验组置于10 J/cm2 UVA(波长为365 nm)照射[11],UVA照射结束后30 min,未接受辐照的对照组和UVA照射的模型组加入100 μL DMEM基础培养基继续培养,实验组加入100 μL DMEM基础培养基配制的125 μg/mL槐提取物溶液、125 μg/mL VC溶液、总浓度为125 μg/mL槐提取物和VC组合物溶液,对照组加入DMEM基础培养基。实验组的处理浓度按照实验室之前的研究得出。所有组别继续培养30 min。弃去上清,加入50 μL含5 μmol/L的H2DCF-DA的DMEM基础培养基,37 ℃避光孵育30 min。多模式微孔板酶标仪(激发光波长Ex/发射光波长Em=488/530)测定各孔荧光值,并按照下式计算细胞内ROS抑制率[12]:
抑制率(%)=(1−T−C0C−C0)×100 式中:T-受试样品荧光强度;C-模型组荧光强度;C0-对照组荧光强度。
1.2.1.2 细胞内总ROS水平的测定(荧光显微镜观察)
取对数期HaCaT细胞,以6×105个/孔接种于35 mm培养皿,后续操作与上述类似,H2DCF-DA探针处理后,PBS洗涤2次,荧光显微镜下拍照[13]。
1.2.2 线粒体ROS(Mitochondrial DNA,mtROS)水平的测定
取对数生长期生长到80%的HaCaT细胞,以1.5×104个/孔接种于共聚焦培养皿中,培养24 h。细胞随机分为对照组、模型组及实验组。模型组和实验组经10 J/cm2 UVA照射。模型组加入1 mL基础培养基,实验组加入1 mL DMEM基础培养基配制的125 μg/mL槐提取物溶液、125 μg/mL VC溶液、总浓度为125 μg/mL槐提取物和VC组合物溶液(质量比为槐提取物:VC=1:1)培养箱中孵育30 min。吸去培养基,PBS缓冲溶液洗3次;加入500 μL含MitoSOX™ Red终浓度为10 μmol/L的DMEM基础培养基,37 ℃孵育30 min。30 min后,吸去上清,用37 ℃预热PBS漂洗3次,加入1 mL PBS。激光共聚焦显微镜观察并拍照[14],Image-J软件分析各组的平均荧光强度(Mean fluorescence intensity,MFI),并计算mtROS抑制率,计算公式如实验方法1.2.1。
1.2.3 环丁烷嘧啶二聚体(Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers,CPDs)含量的测定
24孔板加入细胞爬片,HaCaT细胞以1.5×105个/孔的密度种于孔板,培养24 h。细胞随机分为对照组、模型组及实验组。模型组和实验组经30 mJ/cm2 UVB(波长为302 nm)照射[15−16]。实验组加入DMEM基础培养基配制的125 μg/mL槐提取物溶液、125 μg/mL VC溶液、125 μg/mL槐提取物和VC组合物溶液培养箱中孵育30 min。PBS洗涤3次。每孔加入1 mL预冷4%多聚甲醛,室温固定20 min;吸弃多聚甲醛,PBS漂洗3次,5 min/次。加入1 mL 0.1% PBST,室温放置15 min;PBS漂洗3次,5 min/次。每孔加入1 mL 2 mol/L盐酸(现配现用),室温放置10 min;吸弃盐酸,PBS漂洗3次,5 min/次。加入50 μL山羊血清封闭,覆盖盖玻片,室温封闭1 h。吸弃封闭液,加入5%牛血清蛋白(BSA)稀释的鼠源CPD抗体,覆盖盖玻片,置于抗体孵育湿盒中,4 ℃过夜。PBS漂洗3次,5 min/次。加入5% BSA稀释的荧光二抗(Alexa Fluor488标记的山羊抗鼠IgG),室温避光孵育1 h;吸弃二抗,PBS漂洗3次,5 min/次。用含DAPI的抗荧光淬灭剂封片。观察并拍照,Image-J软件分析各组的MFI。
1.2.4 细胞因子IL-6分泌水平的测定
HaCaT细胞按照5×106浓度接种于10 cm细胞培养皿中。10 J/cm2 UVA照射结束后DMEM基础培养基配制的125 μg/mL槐提取物溶液、125 μg/mL VC溶液、125 μg/mL槐提取物和VC组合物溶液,置于培养箱中继续培养6 h[17]。按照IL-6 Elisa检测试剂盒检测IL-6的含量。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据至少3次重复,实验结果用Graphpad8.0.0统计软件分析并绘图,结果以mean±SD表示,统计方法为单因素方差分析(One-way,ANOVA)。*P<0.05、**P<0.01、#P<0.05、##P<0.01。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 槐提取物和维生素C组合物对HaCaT细胞ROS的影响
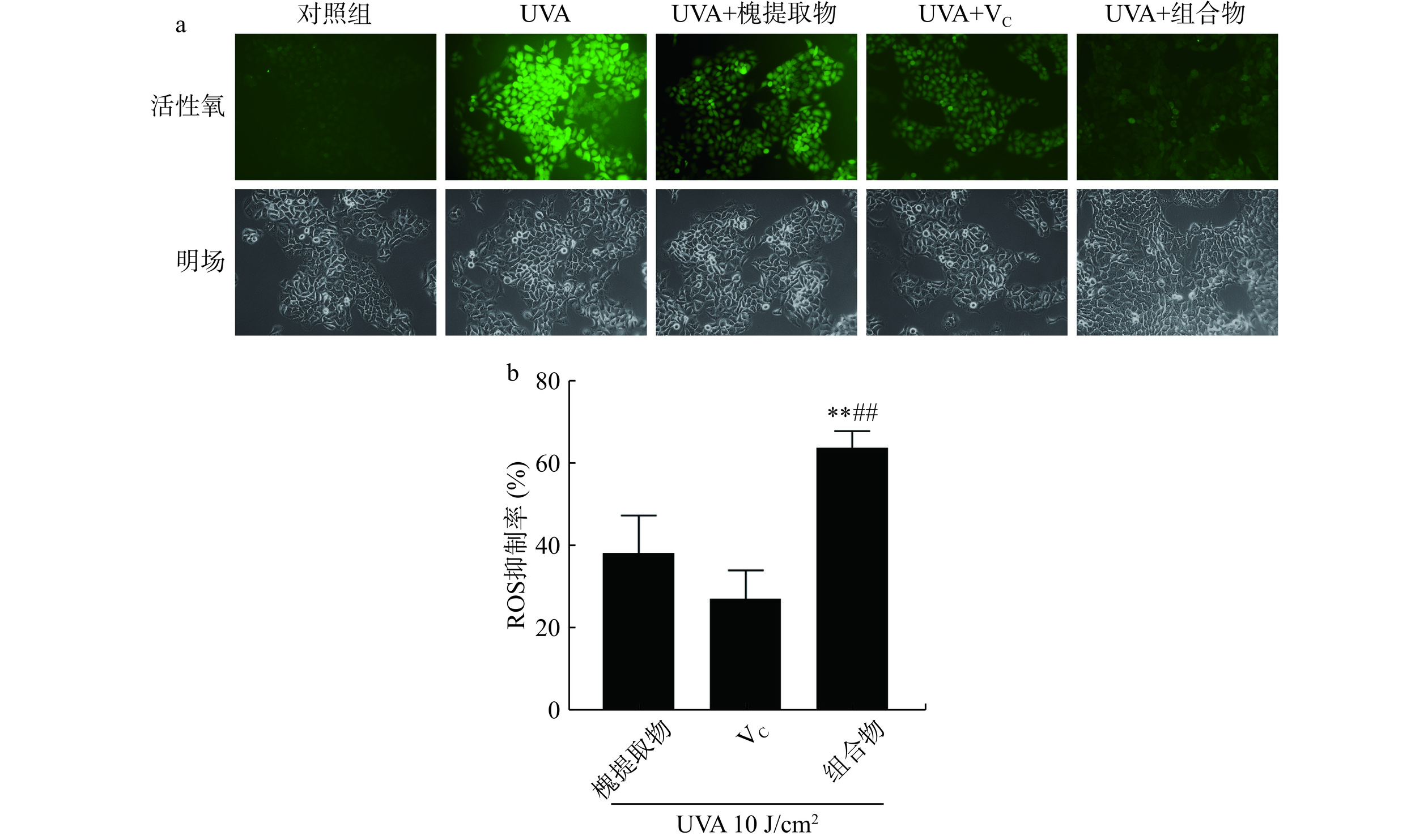
具有细胞膜渗透性的ROS荧光检测探针H2DCF-DA进入细胞后,被水解生成DCFH而无法穿过细胞膜,从而被装载到细胞内,ROS可将DCFH氧化成在激发时发出绿色荧光产物DCF,因此DCF的荧光强度可反映细胞内ROS水平[18]。如图1a所示,对照组几乎无荧光,UVA处理后绿色荧光强度明显增强,说明细胞内ROS含量明显增加,UVA诱导的氧化应激导致细胞内ROS含量增加。与UVA组相比,槐提取物、VC及组合物处理组荧光明显减弱,其中槐提取物和VC组合物组荧光最弱。结果表明,UVA照射增加细胞内ROS的含量,槐提取物、VC及组合物均可降低细胞中ROS含量,且组合物的ROS清除效果最好。如图1b所示,UVA处理后,槐提取物的ROS抑制率为38.23%±9.23%;VC的ROS抑制率为27.20%±6.87%;组合物的ROS抑制率为64.13%±4.08%,槐提取物、VC及其组合物显著降低UVA导致的ROS生成(对照组vs.槐提取物,P<0.01;对照组vs. VC,P<0.01;对照组vs.组合物,P<0.01)。结果表明,UVA照射后,组合物组ROS清除率极显著高于单一组分处理组(组合物vs.槐提取物,P<0.01;组合物vs.VC,P<0.01)。荧光显微法与酶标仪检测均显示槐提取物和VC组合物对于ROS的清除效果最好。多酚(包括芦丁)和VC可显著降低抗氧化蛋白(如硫氧还蛋白和戊二醛)在细胞中的表达,硫氧还蛋白还原酶是一种在氧化应激下恢复细胞中还原硫氧还蛋白水平的酶[9]。因此,槐提取物和VC可支持抗氧化系统。槐花/槐米中含有丰富的芦丁,芦丁作为一类黄酮类物质,通过增加抗氧化(如SOD、TrxR和Prx1/2)和炎症反应(如IL-17F、PAK2和YWHAZ)相关蛋白总表达的增加发挥保护作用[19]。此外,芦丁通过恢复照射后增加的p53、细胞色素c、细胞周期和凋亡调节蛋白2的生理水平,部分防止紫外线诱导的细胞凋亡[19]。VC可以抑制紫外辐照诱导的表皮角质形成细胞中SOD、CAT、GST和GSH-Px活性的降低,从而维持细胞内抗氧化防御系统[20-21]。一项关于芦丁和VC联用对紫外诱导氧化应激的HaCaT细胞保护作用的研究表明芦丁与VC组合物导致UVB照射的HaCaT细胞中超氧阴离子的生成减少约60%,优于芦丁和VC的单独作用[22]。本研究表明,槐提取物和VC对UVA紫外辐射导致的细胞氧化损伤也具有保护作用,二者单独使用可减少细胞ROS及mtROS的生成,对紫外辐照导致的氧化损伤起到保护作用。此外,本研究将槐提取物与VC进行特定比例配比,探究出一种对于对紫外线辐射导致的细胞氧化损伤具有更强保护作用的复合物。
2.2 槐提取物和维生素C组合物对HaCaT细胞mtROS的影响
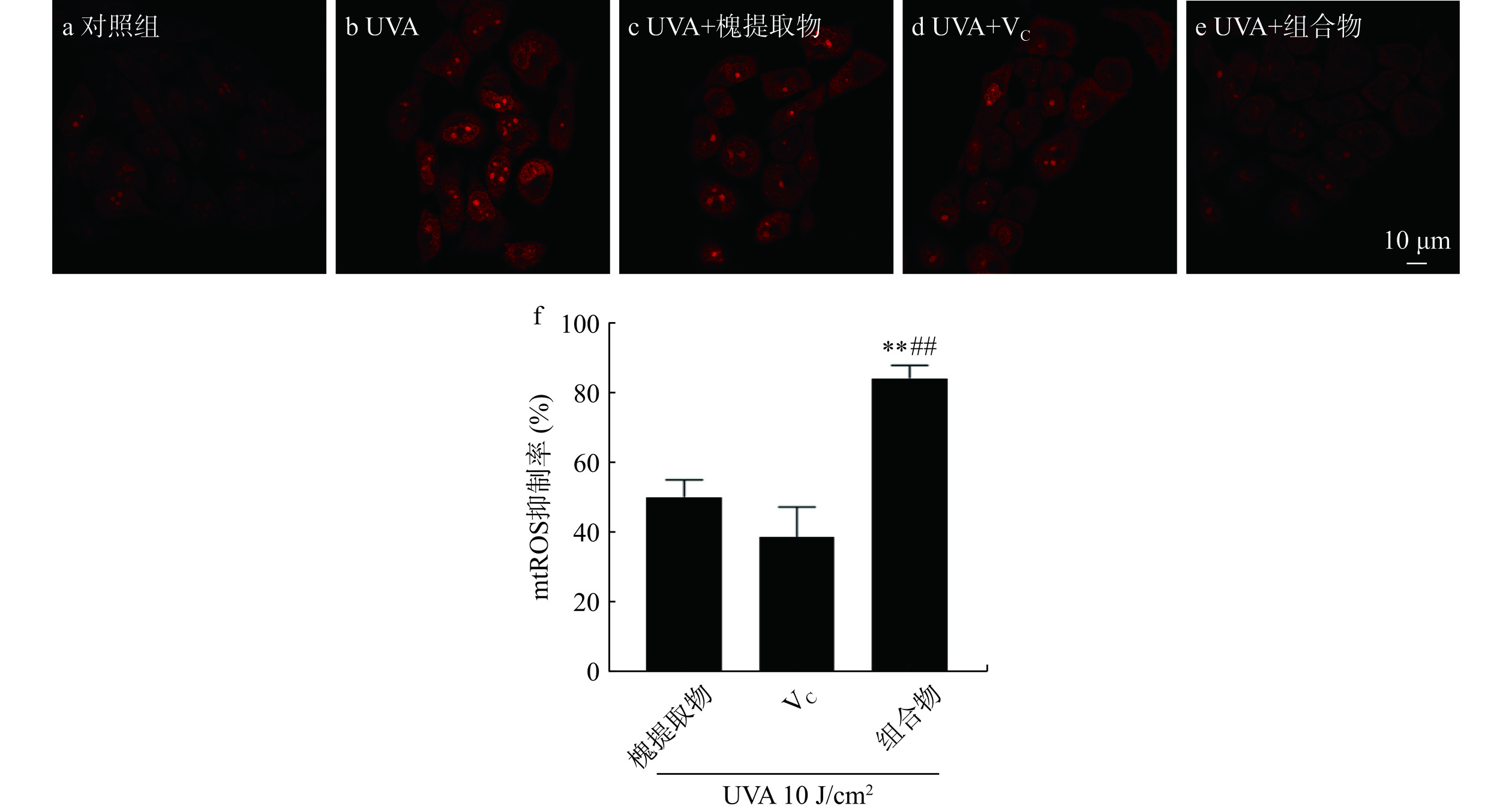
如图2所示,红色荧光表示线粒体内超氧阴离子含量,对照组几乎无荧光,UVA组的荧光强度显著增强,槐提取物、VC及组合物处理后荧光强度显著减弱,其中槐提取物和VC组合物处理组的荧光强度弱于单一物料处理组。UVA照射后,HaCaT细胞mtROS含量增加,分别给予槐提取物、VC及其组合物处理后mtROS抑制率分别为50.29%±4.92%、38.81%±8.66%、84.74%±3.68%,均可一定程度上减少线粒体ROS的生成,其中槐提取物和VC组合物处理组效果最佳(槐提取物+VC vs.槐提取物,P<0.01;槐提取物+VC vs. VC,P<0.01)。线粒体膜是细胞内ROS的重要来源[23]。研究表明,VC对线粒体具有多种有益作用,包括直接清除ROS以及基于分散在基质和膜中的其他线粒体抗氧化剂的再循环的关键作用[23]。VC对线粒体的复杂调节可能有助于多功能的抗氧化反应,从而为维生素提供核心作用,以充分控制与线粒体ROS产生增加相关的线粒体功能障碍[24]。本研究也表明,槐提取物、VC及其组合物可抑制mtROS的生成,且组合物具有一定的加成效果。
2.3 槐提取物和维生素C组合物对HaCaT细胞内CPDs水平的影响
如图3a所示,UVB照射后细胞中荧光强度明显增加,说明UVB导致细胞中的CPDs水平上升。与UVB照射组相比,槐提取物、VC及其组合物处理后CPDs的水平显著降低。对照组、模型组(UVB照射组)、槐提取物组、VC组及组合组的CPDs的荧光强度分别为:6.95±0.80、23.22±1.23、13.10±1.21、15.75±0.44、9.17±0.47。与对照组比较,UVB组细胞中CPDs含量显著升高(P<0.01),说明UVB损伤模型造模成功;与模型组比较槐提取物组、VC组和组合组CPDs含量均极显著下降(P<0.01);其中,槐提取物和维生素C组合组效果显著优于单一组分处理组(P<0.05)。以上结果表明,槐提取物、VC及其组合组均可降低UVB照射导致的细胞中高水平的CPDs,其中组合物对DNA损伤的保护作用最强。
皮肤UVR暴露导致DNA损伤。CPDs是UVR诱导DNA损伤的代表产物,被认为是启动光致癌的分子触发器CPDs的生成主要与UVB有关,且主要生成于表皮层的细胞中[25−26]。核酸切除修复(NER)是紫外线诱导的DNA损伤的主要修复途径,细胞着色性干皮病蛋白A(XPA)在NER中其中不可或缺的作用[27−28]。研究表明VC可以上调细胞中sirtuin1(SirT1)蛋白的表达,而SirT1通过与XPA结合,将XPA维持在低乙酰化状态,下调细胞中紫外线诱导的CPDs的表达,在紫外线的NER途径中起到积极作用[29]。苹果提取物显著降低导致紫外线照射体外皮肤外植体和3D组织工程皮肤细胞中CPDs的形成,这种保护作用可能与苹果提取物中的芦丁相关[30]。研究表明芦丁和VC联用有增强皮肤细胞的抗UVB损伤的作用[9]。因此,两者联用对UVB导致的DNA损伤可能也有一定的加成效果。本研究也发现,UVB照射则使细胞中的CPDs含量显著增加。UVB照射后给予槐提取物、VC及其组合物,可减少HaCaT细胞中CPDs的生成,说明槐提取物、维生素C及其组合物可促进UVB诱导的DNA损伤修复,且组合物具有加成作用。
2.4 槐提取物和维生素C组合物对HaCaT细胞内IL-6水平的影响
UV作用于HaCaT细胞,可激活转录因子NF-κB,促进多种炎症因子如IL-1、IL-6、IL-8等的表达[31]。其中IL-6是炎症反应过程中的促发剂,可促进T细胞增殖与分化,刺激B细胞分化产生抗体,参与机体的免疫应答[32]。如图4所示,与对照组比较,UVA照射组细胞内IL-6含量极显著升高(P<0.01);与UVA组比较,槐提取物处理组及组合物处理组细胞内IL-6含量显著下降(P<0.05),槐提取物处理组IL-6水平下降最低(P<0.01),其次组合物处理组(P<0.05)。因此,组合物处理组在UVA诱导的角质形成氧化应激模型中虽具有抗炎作用,但效果并不优于单用槐提取物处理组抗炎作用。
在生物相关的相互作用机制中,植物提取物联合使用可通过多靶点效应发挥互补增效的作用,包括介导不同信号通路或同一通路的不同下游环节。本研究发现本研究发现槐提取物和VC均具有抗氧化活性和抗炎作用,VC对抑制ROS、mtROS的生成方面有优于槐提取物的趋势,其抗氧化活性更强,而槐提取物的抗炎作用强于VC。氧化应激与炎症反应间存在的错综复杂的调控通路,二者往往相互影响形成正反馈循环[33−34]。本文的研究结果表明,VC和槐提取物组合物抗氧化活性有明显提高,推测槐提取物和VC分别主要通过拮抗氧化应激和炎症反应发挥互补增效作用。然而,在抗炎方面本研究表明,VC有抗炎趋势,槐提取物有较好抗炎效果,VC和槐提取物联用后虽仍具有较好的抗炎作用,但与槐提取物相比,效果不突出。关于VC和槐提取物联用后抗氧化效果增强的机制需要进一步进行验证。
3. 结论
本文通过分析槐提取物、VC及其组合物对紫外照射处理的HaCaT细胞的抗氧化和细胞炎症因子分泌的影响。结果表明,槐提取物、VC及其组合物具有抑制由UVA诱导产生的ROS生成的作用,对细胞ROS抑制率分别为38.23%±9.23%、27.20%±6.87%及64.13%±4.08%,对mtROS抑制率分别为50.29%±4.92%、38.81%±8.66%及84.74%±3.68%。组合物对于ROS的抑制作用优于单一物料处理。槐提取物、VC及其组合物显著降低由UVB诱导产生的CPDs的含量,其中组合物效果最佳。此外,槐提取物及槐提取物和VC组合物显著减低炎症因子IL-6的分泌。该研究可为槐提取物及VC组合物的营养健康产品开发和应用提供实验支持。而未来的研究将聚焦在槐提取物和VC联用后抗氧化效果增强的机制进行深入研究与探讨。
-
-
[1] SANTOS K L B, BRAGANÇA V A N, PACHECO L V, et al. Essential features for antioxidant capacity of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C)[J]. Journal of Molecular Modeling,2021,28(1):1.
[2] ZENG X, RAN L. Research progress of promoting effect of Vitamin C on skin health[J]. Journal of Modern Medicine & Health,2020,36(19):3108−3110.
[3] WANG J R, SONG X H, LI L Y, et al. Metabolomic analysis reveals dynamic changes in secondary metabolites of Sophora japonica L. during flower maturation[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2022,13:916410. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.916410
[4] MIHAYLOVA D, SCHALOW S. Antioxidant and stabilization activity of a quercetin-containing flavonoid extract obtained from Bulgarian Sophora japonica L.[J]. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology,2013,56(3):431−438. doi: 10.1590/S1516-89132013000300011
[5] LO Y H, LIN R D, LIN Y P, et al. Active constituents from Sophora japonica exhibiting cellular tyrosinase inhibition in human epidermal melanocytes[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2009,124(3):625−629. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.04.053
[6] HOROSANSKAIA E, TAN M N, VU T D, et al. Crystallization-based isolation of pure rutin from herbal extract of Sophora japonica L.[J]. Organic Process Research & Development,2017,21(11):1769−1778.
[7] ZHANG Y, WANG Q, WANG Y D, et al. Effect of rutin on cisplatin-induced damage in human mesangial cells via apoptotic pathway[J]. Human and Experimental Toxicology,2019,38(1):118−128. doi: 10.1177/0960327118785233
[8] NÈGRE-SALVAYRE A, AFFANY A, HARITON C, et al. Additional antilipoperoxidant activities of alpha-tocopherol and ascorbic acid on membrane-like systems are potentiated by rutin[J]. Pharmacology,1991,42(5):262−272. doi: 10.1159/000138807
[9] GĘGOTEK A, JAROCKA-KARPOWICZ I, SKRZYDLEWSKA E. Cytoprotective effect of ascorbic acid and rutin against oxidative changes in the proteome of skin fibroblasts cultured in a three-dimensional system[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(4):1074. doi: 10.3390/nu12041074
[10] ZHANG J, XIONG Z Y, WANG J H. Flos-sophorae and Vitamin C on synergistic antioxidative ability of trained mouse[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2004,32(4):87−89.
[11] KARADENIZ F, OH J H, KIM H R, et al. Camellioside A, isolated from Camellia japonica flowers, attenuates UVA-induced production of MMP-1 in HaCaT keratinocytes via suppression of MAPK activation[J]. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine,2020,21(1):16.
[12] HAN B K, YOO B S. Propolis inhibits UVA-induced apoptosis of human keratinocyte HaCaT cells by scavenging ROS[J]. Toxicological Research,2016,32(4):345−351. doi: 10.5487/TR.2016.32.4.345
[13] ZHANG Y, LI T, PAN M, et al. SIRT1 prevents cigarette smoking-induced lung fibroblasts activation by regulating mitochondrial oxidative stress and lipid metabolism[J]. Journal of Translational Medicine,2022,20(1):1−13. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03207-4
[14] PIAO M J, AHN M J, KANG K A, et al. Phloroglucinol enhances the repair of UVB radiation-induced DNA damage via promotion of the nucleotide excision repair system in vitro and in vivo[J]. DNA Repair,2015,28:131−138. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.02.019
[15] ZHANG C, XIE X, YUAN Y, et al. MiR-664 protects against UVB radiation-induced HaCaT cell damage via downregulating ARMC8[J]. Dose-Response, 2020, 18(2):155932582092923.
[16] KAWANO A, KADOMATSU R, ONO M, et al. Autocrine regulation of UVA-induced IL-6 production via release of ATP and activation of P2Y receptors[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(6):e0127919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127919
[17] 上海日用化学品行业协会. T/SHRH032-2020 化妆品紧致、抗皱功效测试-体外角质形成细胞活性氧(ROS)抑制检测方法[S]. 上海: 中国标准出版社, 2020. [Shanghai Daily Chemistry Trade Association. T/SHRH031-2020 Anti-wrinkly and firming lifting efficacy test of cosmetics-in vitro test method of reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibition with keratinocytes[S]. Shanghai: Standards Press of China, 2020.] Shanghai Daily Chemistry Trade Association. T/SHRH031-2020 Anti-wrinkly and firming lifting efficacy test of cosmetics-in vitro test method of reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibition with keratinocytes[S]. Shanghai: Standards Press of China, 2020.
[18] D'AGOSTINO A, DI PALMA T, CECCHINI GUALANDI S. Fluorescence spectroscopy for the diagnosis of endometritis in the mare[J]. Animals (Basel),2022,12(9):1157. doi: 10.3390/ani12091157
[19] GĘGOTEK A, DOMINGUES P, SKRZYDLEWSKA E. Proteins involved in the antioxidant and inflammatory response in rutin-treated human skin fibroblasts exposed to UVA or UVB irradiation[J]. Journal of Dermatological Science,2018,90(3):241−252. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.02.002
[20] JAGETIA G C, RAJANIKANT G K, RAO S K, et al. Alteration in the glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase and lipid peroxidation by ascorbic acid in the skin of mice exposed to fractionated γ radiation[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2003,332(1):111−121.
[21] ZAIDI S M K R, BANU N. Antioxidant potential of Vitamins A, E and C in modulating oxidative stress in rat brain[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2004,340(1-2):229−233. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2003.11.003
[22] GEGOTEK A, AMBROEWICZ E, JASTRZB A, et al. Rutin and ascorbic acid cooperation in antioxidant and antiapoptotic effect on human skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts exposed to UVA and UVB radiation[J]. Archives of dermatological research,2019,311(3):203−219. doi: 10.1007/s00403-019-01898-w
[23] SCHOFIELD J H, SCHAFER Z T. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and mitophagy:A complex and nuanced relationship[J]. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling,2021,34(7):517−530.
[24] FIORANI M, GUIDARELLI A, CANTONI O. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species:The effects of mitochondrial ascorbic acid vs untargeted and mitochondria-targeted antioxidants[J]. International Journal of Radiation Biology,2021,97(8):1055−1062. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1721604
[25] VECHTOMOVA Y, TELEGINA T, BUGLAK A, et al. UV radiation in DNA damage and repair involving DNA-photolyases and cryptochromes[J]. Biomedicines,2021,9(11):1564. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111564
[26] HEGEDS C, T JUHÁSZ, FIDRUS E, et al. Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers from UVB exposure induce a hypermetabolic state in keratinocytes via mitochondrial oxidative stress[J]. Redox Biology,2021,38(2):101808.
[27] FAN W, LUO J. SIRT1 regulates UV-induced DNA repair through deacetylating XPA[J]. Molecular Cell,2010,39(2):247−258. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.006
[28] BORSZÉKOVÁ PULZOVÁ L, WARD T A, CHOVANEC M. XPA:DNA repair protein of significant clinical importance[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(6):2182. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062182
[29] JEONG J H, KIM M B, KIM C, et al. Inhibitory effect of Vitamin C on intrinsic aging in human dermal fibroblasts and hairless mice[J]. Food Science & Biotechnology, 2018, 27:555–564 .
[30] MARTINS R M, ALVES G A D, MARTINS S S, et al. Apple extract (Malus sp. ) and rutin as photochemopreventive agents:evaluation of ultraviolet B-induced alterations on skin biopsies and tissue-engineered skin[J]. Rejuvenation Research,2020,23(6):465−475. doi: 10.1089/rej.2019.2219
[31] 马月丹. 绞股蓝总皂苷干预光老化HaCaT细胞对HSF细胞p38MAPK信号通路的影响[D]. 沈阳:辽宁中医药大学, 2014. [MA Y D. Gypenosides intervention photoaging HaCaT cells to HSF cells in p38MAPK signal pathway[D]. Shenyang:Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014.] MA Y D. Gypenosides intervention photoaging HaCaT cells to HSF cells in p38MAPK signal pathway[D]. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014.
[32] 张荣利. Toll受体在UVB诱导N-κB激活中的作用及其在光线相关性皮肤病中意义的初步观察[D]. 西安:第四军医大学, 2014. [ZHANG R L. A tentative study on functions of TLRs in the UVB-induced activation of NF-κB and its significances in the UV-related skin disease[D]. Xi’an:Fourth Military Medical University, 2014.] ZHANG R L. A tentative study on functions of TLRs in the UVB-induced activation of NF-κB and its significances in the UV-related skin disease[D]. Xi’an: Fourth Military Medical University, 2014.
[33] WANG Y, WANG L, WEN X, et al. NF-κB signaling in skin aging[J]. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development,2019,184:111160. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2019.111160
[34] HUSSAIN T, TAN B, YIN Y, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation:What polyphenols can do for us?[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2016,2016:7432797.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 韩婕珺,洪铮怡,龚天贵,王斌,张蓝月. 牡丹籽乙醇提取物对UVB诱导HaCaT细胞光老化的保护作用及机制研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(15): 351-359 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 肖检妹,吴月亮,崔苏菲,张美玲,万彧,王兵,王军伟,熊程. 不同光质条件下植物AsA合成积累的研究进展. 辣椒杂志. 2024(02): 7-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



