Effects of Billet-Making Methods on Volatile Flavor Components of Sanhua Plum Fruit Billets Based on Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectroscopy and Electronic Nose
-
摘要: 为研究不同制坯方式对三华李果坯挥发性成分的影响,采用电子鼻与气相色谱-离子迁移谱(Headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy,HS-GC-IMS)技术对食盐腌制、亚硫酸盐混合食盐腌制、乳酸菌发酵果坯及鲜果对照共4组样品的挥发性成分进行分析比较。结果表明,电子鼻线性判别分析(LDA)及基于HS-GC-IMS检测结果的主成分分析均可有效区分4组样品,鲜果经不同制坯方式处理后风味特征发生明显变化,各样品间差异显著。HS-GC-IMS在4组样品中共检测鉴定出49种挥发性化合物,相对含量较高的主要为醇类、酯类、醛类物质。相对气味活度值(ROAV)表明三种果坯间关键风味物质差异明显,发酵果坯挥发性风味物质总峰体积最高(194760),关键风味物质种类最多(10种),以短链醛类为主,从果坯风味丰富性角度出发,认为乳酸菌发酵法果坯风味品质较好。本研究结果为三华李制坯方式的选择提供有益参考。Abstract: In order to investigate the effect of billet-making methods on the volatile components of the Sanhua plum fruit billets, electronic nose and headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy (HS-GC-IMS) were used to analyze and compare the volatile components of four groups of samples of salt cured, sulfite mixed salt cured, lactic acid bacteria fermented fruit billets and fresh fruit control. The results showed that both the electronic nose linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and the principal component analysis based on the HS-GC-IMS assay results clearly distinguished the four groups of samples, the flavor characteristics of fresh fruits were significantly changed after different curing treatments, and the differences among fruit blanks samples were significant. HS-GC-IMS detected and identified a total of 49 volatile compounds in four groups of samples, and the high relative contents were mainly alcohols, esters and aldehydes. The relative odor activity value (ROAV) showed significant differences in key flavor substances among the three fruit billets, the lactic acid fermented fruit billet had the highest total peak volume of volatile flavor substances (194760) and the most types of key flavor substances (10), mainly short-chain aldehydes. From the perspective of flavor richness of fruit billets, the flavor quality of fruit billet by lactic acid fermentation was considered to be better. The results of this study provided an useful reference for the selection of the billet-making methods of Sanhua plums.
-
三华李(Prunus salicina Lindl. cv. Sanhua)为蔷薇科李属植物,营养丰富,肉质爽脆,酸甜可口,果肉中含有丰富的花色苷使其呈现紫红色,具有良好的抗氧化活性,是广式凉果的主要原料之一[1−2]。因鲜果上市时间短、产能集中,容易腐烂造成浪费。鲜果加工成果坯,以半成品(果坯)形式保藏,供产品周年生产使用,是凉果生产过程中的必备环节。食盐腌制、亚硫酸盐混合食盐腌制为果坯的传统加工方式,成本低,操作简单,但高盐腌制形成的高渗透压使原果汁大量流失造成原果风味物质逸散;亚硫酸盐的使用会使果品产生不愉快气味且存在食品安全风险;腌制液的排放还会对环境造成污染,因此新型的乳酸发酵法成为有潜力的制坯方法[3−4]。目前,关于果坯的研究主要关注相关的加工工艺及质量安全,黄志钰等[5]对乳酸发酵三华李果坯发酵液中的腐败菌进行分离鉴定,并优化发酵工艺。宋倩[6]以双华李果坯为原料,采用正交试验优化果坯脱硫工艺。张媛媛等[7]探究纳它霉素在青梅果坯糖渍过程中的抑菌效果。风味是评价果坯加工品质的重要指标,与凉果产品的品质密切相关,而目前有关制坯方式对三华李果坯挥发性成分的影响研究鲜见报道。
电子鼻是一种快速识别样品整体气味轮廓的仪器,其检测结果具有客观性、重复性、可视性等优点,但其无法判断样品之间气味差异的具体物质[8−9]。气相色谱-离子迁移谱(Headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy,HS-GC-IMS)是基于气相保留时间和离子迁移时间的差异,来区分挥发性化合物的新型分析技术,具有前处理简单,香气无需浓缩和富集,灵敏度高,可检测痕量挥发性物质,分析速度快的特点[10−11],在食品检测、鉴别、溯源、分级等各个领域发展迅速[12]。电子鼻和HS-GC-IMS两项技术联用,可发挥它们在便捷性、高效性以及灵敏性等方面的互补优势[13],更加全面分析不同制坯方式果坯的挥发性成分差异。
基于此,本研究采用电子鼻、HS-GC-IMS等技术系统地对食盐腌制、亚硫酸盐混合食盐腌制及乳酸菌发酵三华李果坯的挥发性风味成分进行分析,结合相对气味活度值确定果坯的关键香气成分组成,研究不同制坯方式对三华李果坯风味的影响,以期为三华李果坯加工方式的选择提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜三华李 购于广州市天平架水果批发市场;干酪乳杆菌(Lactobacillus casei)、植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)、肠膜状明串珠菌(Leuconostoc mesenteroides) 广东省微生物菌种保藏中心;MRS肉汤培养基 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;氯化钠、无水葡萄糖 均为食品级,市售;焦亚硫酸钠 食品级,广东兴达食品配料有限公司。
PEN3电子鼻 德国Airsense公司; FlavourSpec®风味分析仪 德国G.A.S公司; AL104万分之一电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司; HH-6型数显恒温水浴锅 常州澳华仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 三华李果坯腌制方法
选取无病虫害及明显机械损伤的7~8成熟新鲜三华李果,洗净沥水待用。
乳酸菌发酵:将3株乳酸菌置于灭菌后的MRS肉汤培养基进行活化复壮,30 ℃静置发酵48 h,菌悬液浓度约为108 CFU/mL,按植物乳杆菌:干酪乳杆菌:肠膜明串珠菌=3:1:8比例进行复配,得到复合菌液。以果:水(质量比)1:1,按水重加入1.8%无水葡萄糖,1.7%氯化钠,2%复合菌液,室温密封发酵60 d,简称发酵果坯。
食盐腌制:按果重加入25%的食盐,室温条件下腌制60 d,简称盐腌果坯。
亚硫酸盐混合食盐腌制:按果重加入1%焦亚硫酸钠和25%的食盐,室温条件下腌制60 d,简称硫盐果坯。
1.2.2 电子鼻检测方法
将三种果坯及鲜果样品分别去核打浆,取5 g样品,60 ℃恒温水浴30 min,室温下平衡20 min,随后插入电子鼻探头吸取顶端气体,测定香气物质。电子鼻参数:采样间隔1 s,冲洗时间120 s,调零时间10 s,预采样时间5 s,检测时间120 s,载气流速、进样流速200 mL/min。每组样品做4次重复。PEN3型电子鼻由10种金属氧化物气体传感器阵列组成,如表1所示。
表 1 PEN3电子鼻传感器敏感物质Table 1. Sensitive substances of PEN3 electronic nose sensor阵列序号 传感器 性能描述 R1 W1C 芳烃成分,苯类灵敏 R2 W5S 灵敏度大,对氮氧化合物很灵敏 R3 W3C 芳香成分灵敏,氨类灵敏 R4 W6S 主要对氢化物有选择性 R5 W5C 短链烷烃芳香成分灵敏 R6 W1S 对甲基类灵敏 R7 W1W 对硫化物灵敏 R8 W2S 对醇类,醛酮类灵敏 R9 W2W 芳香成分,对有机硫化物灵敏 R10 W3S 对长链烷烃灵敏 1.2.3 HS-GC-IMS分析
顶空进样条件:取2 g样品移入20 mL顶空玻璃取样瓶中;顶空孵化温度60 ℃,孵化时间15 min,孵化转速500 r/min,进样体积500 μL,进样针温度:85 ℃。
GC条件:色谱柱(FS-SE-54-CB-1 15 m×0.53 mm,1 μm),色谱柱温60 ℃,运行时间30 min,载气为N2;载气流速:起始2.00 mL/min保持2 min,在2~20 min 线性增至100.00 mL/min,后保持10 min。
IMS条件:漂移管的温度为45 ℃;漂移气为N2;漂移气流速为150 mL/min。
化合物的定性定量分析:通过GC×IMS Library Search软件比对NIST数据库中化合物的保留指数和IMS数据库中化合物的迁移时间对挥发性化合物进行定性分析。通过IMS系统计算的峰体积对挥发性化合物进行定量分析。按峰体积归一化法计算各挥发性组分的相对含量。
1.2.4 相对气味活度值(Relative odor activity value,ROAV)
参考刘登勇等[14]的方法,引入参数ROAV,评价各化学物对风味的贡献,设定对样品风味贡献最大化合物:ROAVmax=100,其他化合物计算公式如下:
ROAVi≈CiCmax×TmaxTi×100 式中:Ci、Ti分别为各化合物的相对百分含量和对应的感觉阈值(μg/kg);Cmax、Tmax分别为对样品风味贡献最大组分的相对百分含量和感觉阈值(μg/kg)。
1.3 数据处理
使用Origin2018对数据进行统计分析及作图;使用软件Winmuster进行电子鼻数据LDA分析;使用GC-IMS仪器配套的分析软件VOCal及两款插件Reporter、Dynamic PCA分别从不同角度对样品挥发性化合物进行分析;VOCal 用于分析谱图和数据的定性定量,应用软件内置的NIST数据库和IMS数据库对物质进行定性分析;Reporter插件用于对比样品之间的谱图差异得到差异谱图;Dynamic PCA 插件用于动态主成分分析。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 基于电子鼻分析不同三华李果坯及鲜果的挥发性成分
2.1.1 传感器响应强度分析
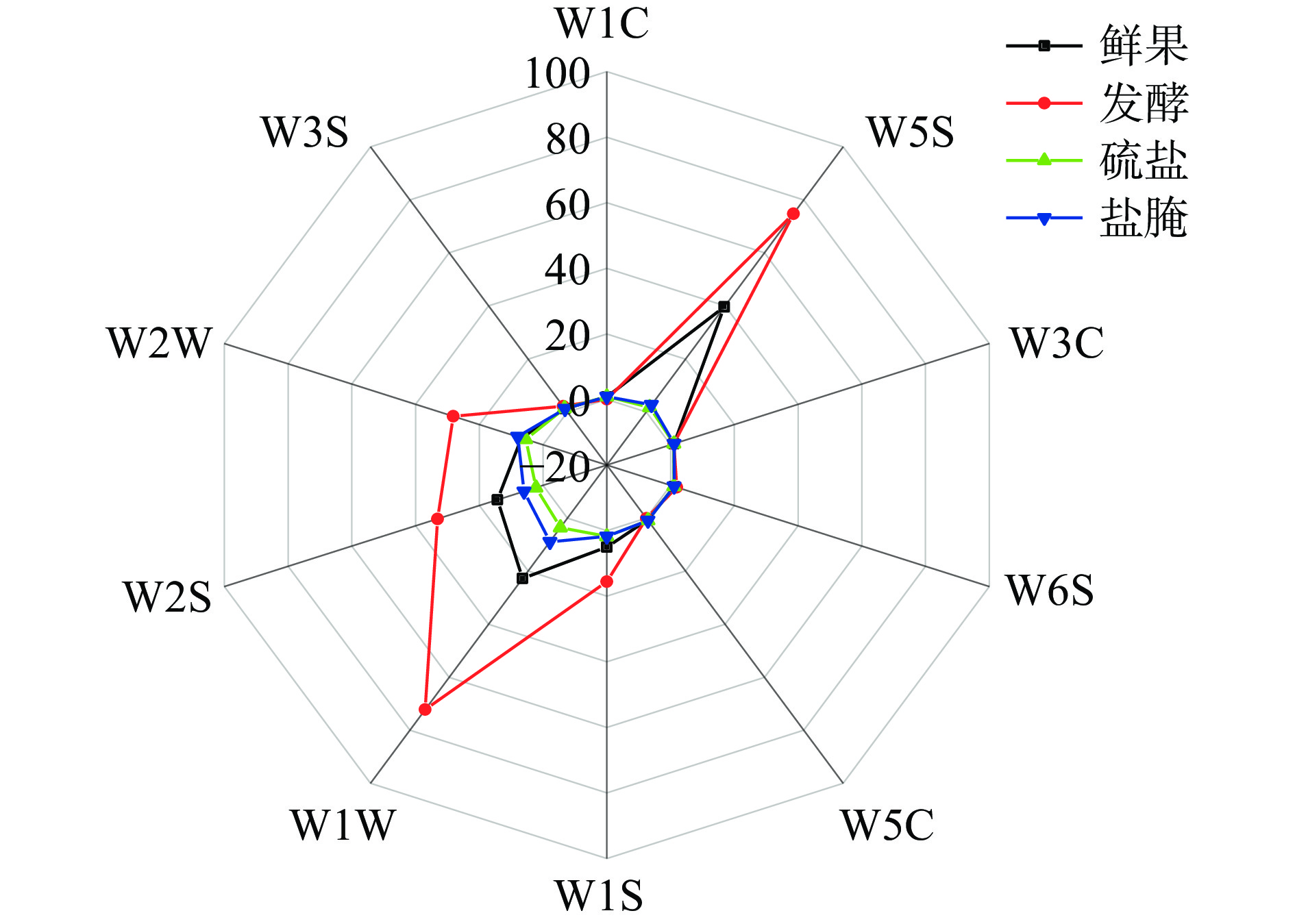
由图1可以看出,硫盐及盐腌果坯样品较鲜果样品各传感器响应强度均明显降低,在W5S、W1W、W2S差异较明显,其中硫盐果坯略低于盐腌果坯,说明食盐法及硫盐法腌制对三华李鲜果中的氮氧类、硫化物、醇和醛酮类化合物有较大影响。发酵果坯样品较鲜果样品各传感器响应强度均明显增加,在W5S、W1S、W1W、W2S、W2W差异较明显,说明乳酸发酵对三华李中的氮氧类、甲基类、硫化物、醇、醛酮类和芳香成分影响较大。
2.1.2 电子鼻线性判别LDA分析
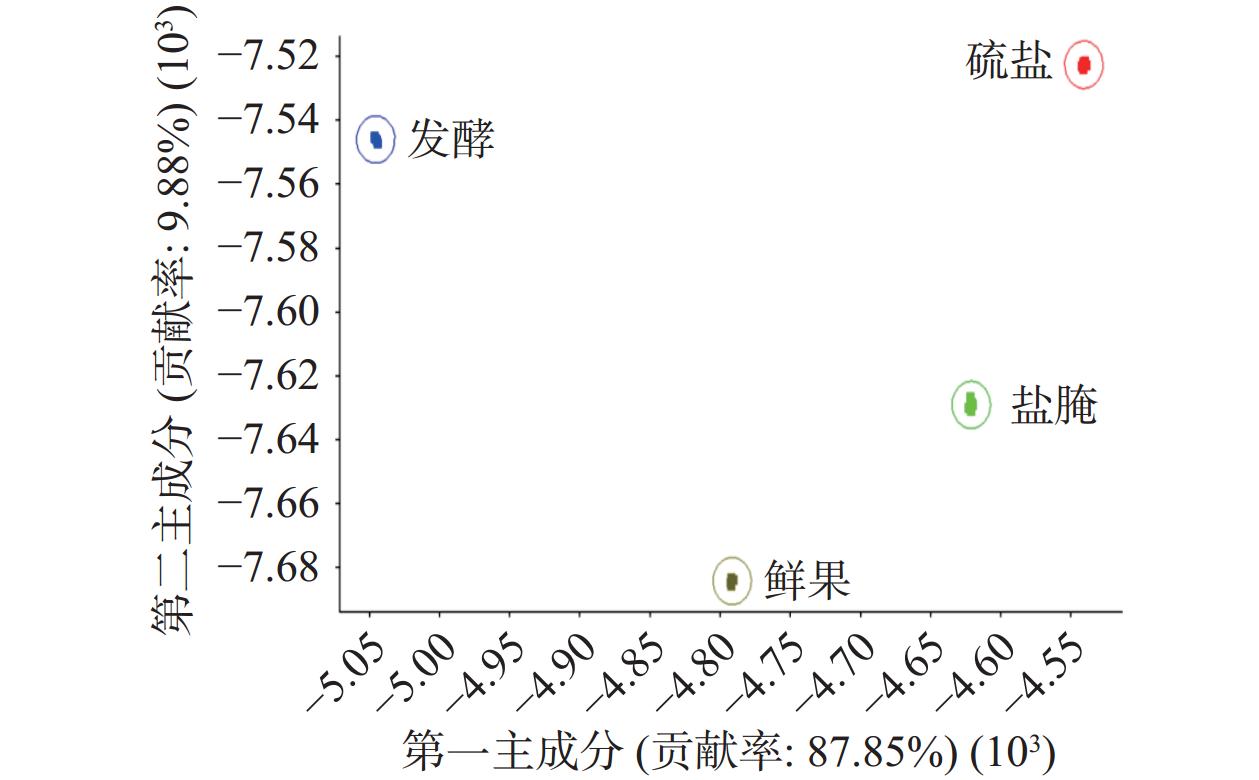
由图2可知,第一主成分(PC1)贡献率为87.85%,第二主成分(PC2)贡献率为9.88%,PC1和PC2贡献率之和达到97.73%,大于95%,可以有效反映各组样品绝大多数气味信息特征[15]。从LDA图可以看出,三种果坯及鲜果共4组样品之间无交叉区域,区分明显,说明经三种不同方式加工处理后,鲜果中挥发性成分均已发生显著变化,其中盐腌法果坯相对其他两种果坯,与鲜果香气特征轮廓较接近。
2.2 基于HS-GC-IMS分析三华李果坯及鲜果的挥发性成分
由于电子鼻是基于宏观角度对样品的挥发性物质特征轮廓进行整体解析,难以将样品中的挥发性成分定性定量,因此在电子鼻分析的基础上,采用HS-GC-IMS技术对果坯及鲜果挥发性香气成分种类及含量进行测定分析。
2.2.1 气相色谱离子迁移谱(HS-GC-IMS)差异对比
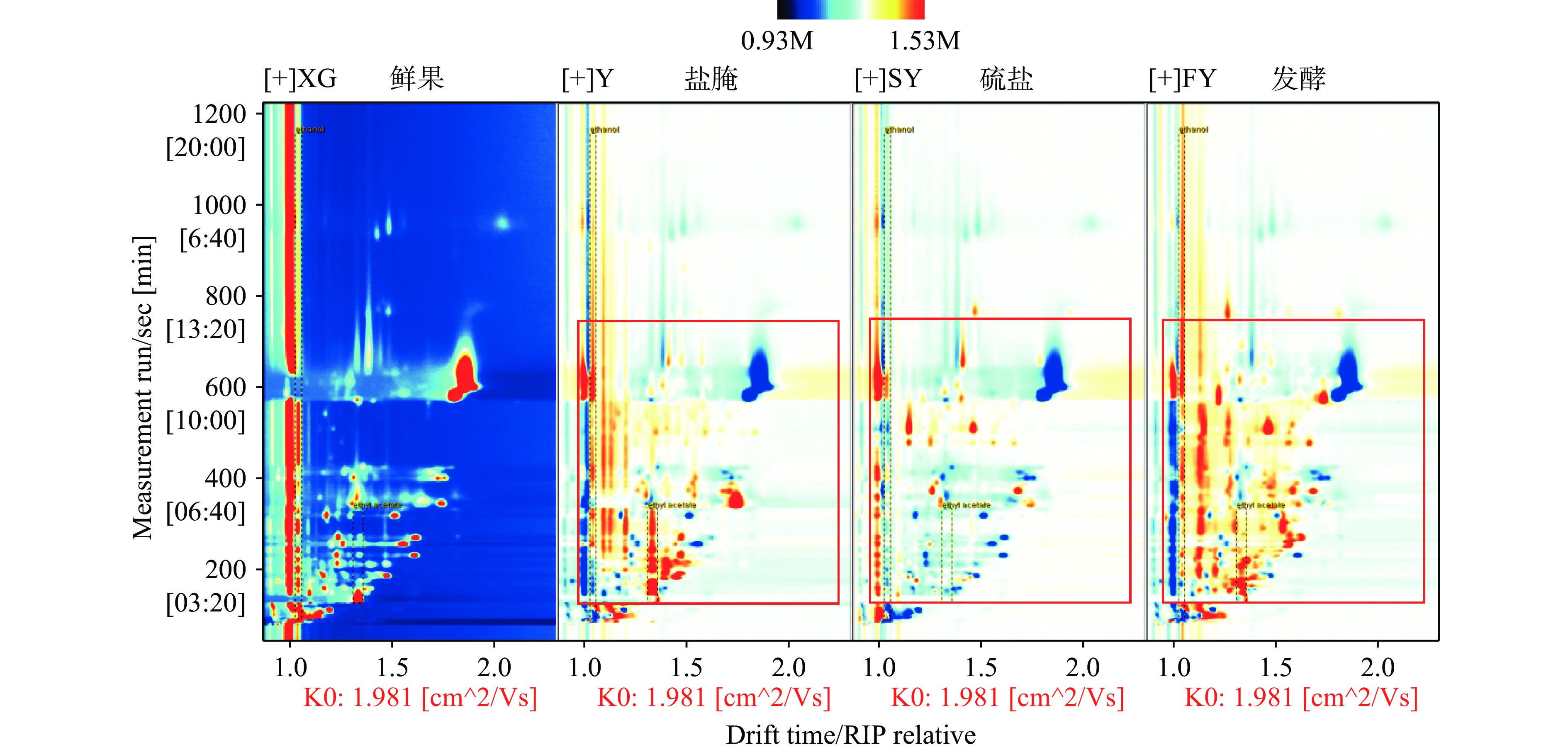
图3为三种果坯及鲜果的挥发性成分HS-GC-IMS差异对比图,差异对比图能够使各组样品间挥发性成分的差异可视化。以三华李鲜果的样品气味指纹谱图为参考,用不同果坯样品的谱图分别扣除参考谱图。果坯样品中的白色区域表示该物质与参照样品的浓度相同;蓝色区域表示该物质浓度低于参照样品,蓝色越深,则浓度越低;红色区域表示该物质浓度高于参照样品,红色越深,则浓度越高。从图3红框中可以看出,盐腌法果坯与鲜果挥发性风味物质存在差异,硫盐法果坯较鲜果挥发性风味物质种类及含量均大量减少,发酵法果坯挥发性风味物质无论种类还是浓度较鲜果均有增加。三种制坯方式均改变了三华李鲜果的挥发性风味物质,并且三种果坯之间,在挥发性风味物质的种类及含量上都存在较大差异。
2.2.2 三华李果坯及鲜果挥发性化合物的鉴定和分析
采用 HS-GC-IMS内置NIST数据库进一步定性分析,从鲜果及果坯中共鉴定出49种已知挥发性组分,如表2所示,包括酯类18种、醇类9种、醛类13种、酮类 4 种、萜烯类2种、酸类1种、杂环类1种、其它1种。由表3可知,相对含量较高的是醇类,在鲜果、发酵法果坯、硫盐法果坯和盐腌法果坯中分别占挥发性成分的64.10%、55.71%、55.68%及56.43%;其次是酯类,相对含量分别为31.48%、24.34%、29.36%及41.17%;醛类,相对含量分别为3.54%、12.39%、12.86%及1.89%。醇类、酯类和醛类是三华李鲜果及果坯的重要挥发性成分,这与李媛[4]研究三华李鲜果及发酵法果坯的挥发性风味物质的结果一致。不同制坯方式使得三华李果坯中挥发性风味成分种类及含量发生不同程度的变化。以峰体积代表各样品挥发性化合物含量高低[16],峰体积由大到小的顺序为:发酵法果坯(194760)>盐腌法果坯(184290)>鲜果(181750)>硫盐法果坯(105410)。可见,三华李鲜果经发酵后果坯挥发性香味成分含量明显增加,硫盐法腌制后挥发性香味成分含量显著降低,这与图3气相色谱离子迁移谱(HS-GC-IMS)差异对比结果相符。前人研究表明,乳酸菌发酵可为产品增添特殊的发酵香味,同时产生氨基酸短肽、醛类、酮类、酯类等成香成分,赋予产品奶油香、水果香[17−18]。而硫盐法果坯中因亚硫酸盐具有极强的抑菌性及还原性,使挥发性化合物发生加成、氧化还原等反应,减少新风味物质的产生,从而使果坯挥发性风味物质峰体积显著减少。
表 2 三华李鲜果及果坯挥发性化合物相对含量Table 2. Relative content of volatile compounds in Sanhua plum fresh fruit and fruit billets化合物名称 保留指数 保留时间(s) 迁移时间(ms) 相对含量(%) 鲜果 发酵 硫盐 盐腌 酯类 乙酸异戊酯-M 872.3 344.46 1.30 1.10 0.50 3.19 1.22 乙酸异戊酯-D 873 345.28 1.75 1.35 0.90 3.53 6.91 乙酸乙酯 598.7 134.66 1.33 10.45 16.03 15.90 23.74 丁酸丙酯-M 919.4 413.99 1.27 0.21 — 0.12 — 丁酸丙酯-D 918.8 412.95 1.69 0.28 — — — 乙酸丁酯 803.6 270.41 1.23 1.75 3.03 0.87 1.09 己酸乙酯 1014.6 586.49 1.81 10.09 — 0.98 0.31 辛酸乙酯-D 1200.9 959.45 2.03 0.50 — — — 辛酸乙酯-M 1197.1 951.82 1.48 0.52 — — — 乙酸甲酯 544 111.69 1.19 1.00 — — — 乙酸戊酯-D 912.2 401.27 1.76 0.51 — — 0.28 乙酸戊酯-M 913.3 403.25 1.31 0.50 — — 0.29 乙酸异丁酯-M 764 233.20 1.23 0.75 — 0.25 0.19 乙酸异丁酯-D 761.6 231.24 1.61 1.09 0.09 0.03 0.74 乙酸丙酯 706.3 186.67 1.47 1.31 0.65 1.20 4.92 乙酸苄酯 1174.7 906.98 1.32 — — — 0.13 丁酸丁酯-M 968.5 500.86 1.35 — — — 0.33 丁酸丁酯-D 968.3 500.39 1.83 — — — 0.13 丁酸己酯 1151.4 860.33 1.49 — — — 0.13 丙酸丁酯-D 905.5 389.45 1.72 — 0.03 0.10 0.09 丙酸丁酯-M 906.3 390.96 1.29 — 0.15 0.32 0.12 丁酸甲酯 740.6 214.31 1.15 — — 0.21 — 戊酸乙酯-D 897 374.49 1.68 — 0.65 1.37 0.30 戊酸乙酯-M 897 374.49 1.26 — 0.26 1.12 0.17 乳酸乙酯 822.3 290.61 1.54 — 1.34 — — 乙酸叶醇酯 1028.4 614.21 1.82 — 0.64 — — 醛类 正己醛 790.3 256.01 1.56 2.45 4.12 1.66 0.12 2-甲基丁醛 657.8 159.46 1.40 0.09 — — — 2-糠醛 860 331.25 1.09 0.06 0.14 0.15 0.46 庚醛 885.8 359.09 1.33 0.45 — — — 正辛醛 1007.9 573.17 1.41 0.16 0.06 0.90 0.18 壬醛-M 1104.6 766.56 1.47 0.17 0.16 1.03 0.16 壬醛-D 1105.2 767.83 1.93 — — 0.19 — 戊醛 693.4 176.24 1.19 — 0.16 0.73 — 苯甲醛-M 974.9 512.04 1.15 — 1.33 3.77 0.52 苯甲醛-D 972.8 508.42 1.47 — 3.50 3.10 0.19 E-2-己烯醛 835.2 304.45 1.18 0.09 0.08 0.09 — E-2-庚烯醛-M 956 478.77 1.25 0.08 0.42 0.84 0.17 E-2-庚烯醛-D 954.4 475.87 1.66 — 0.51 0.33 0.08 E-2-戊烯醛 747.2 219.67 1.35 — 1.33 0.06 — 2-甲基戊醛 774.1 241.34 1.52 — 0.13 — — E-2-辛烯醛-M 1065.4 688.12 1.33 — 0.28 — — E-2-辛烯醛-D 1064.7 686.73 1.82 — 0.11 — — 醇类 乙醇 512.3 98.34 1.05 34.59 53.80 51.85 55.14 E-2-己烯-1-醇-M 848.1 318.44 1.18 0.74 0.13 0.27 — E-2-己烯-1-醇-D 847.8 318.04 1.51 0.89 0.70 0.06 — 2-辛醇 1028.4 614.21 1.85 27.26 — — — 2-甲基-1-丙醇 660.2 160.47 1.17 0.40 — — — 2-甲基丁醇 741.7 215.21 1.23 0.19 — — 0.46 异辛醇-M 1049.9 657.22 1.41 — 0.23 1.94 0.58 异辛醇-D 1048.6 654.67 1.79 — 0.07 0.48 0.14 5-甲基-2-呋喃甲醇 956.5 479.54 1.57 — 0.30 0.35 — 苯甲醇 1015.7 588.80 1.32 — — 0.65 0.30 正戊醇 760.6 230.46 1.51 — 0.20 0.03 — 酮类 2-环己烯-1-酮 875.7 348.19 1.41 0.18 0.33 0.24 — 3-辛酮 989.8 538.40 1.31 — — 0.09 0.09 2-辛酮 1007.6 572.59 1.33 0.32 — — — 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 991.3 541.18 1.17 0.07 — — 0.20 萜烯类 β-蒎烯 974 510.60 1.22 0.10 — — — α-萜品烯-M 1011.6 580.52 1.22 — 2.62 0.89 — α-萜品烯-D 1010.1 577.59 1.73 — 3.08 0.30 — 酸类 丙酸 661.3 160.93 1.27 0.24 0.81 0.48 — 杂环化合物 2-戊基呋喃 993.6 545.20 1.25 0.03 — 0.12 — 其他 芳樟醇氧化物-M 1104.2 765.93 1.26 — 0.99 0.22 0.10 芳樟醇氧化物-D 1102.7 762.75 1.81 — 0.16 — — 表 3 主要的挥发性化合物种类的峰体积及相对含量Table 3. Peak volume and relative content of the main volatile compounds化合物种类 鲜果 发酵 硫盐 盐腌 峰体积 相对含量(%) 峰体积 相对含量(%) 峰体积 相对含量(%) 峰体积 相对含量(%) 醇类 116.49 64.10 108.51 55.71 58.69 55.68 104.22 56.43 酯类 57.22 31.48 47.41 24.34 30.95 29.36 75.87 41.17 醛类 6.44 3.54 24.14 12.39 13.56 12.86 3.48 1.89 烯烃类 0.17 0.09 11.16 5.73 1.25 1.19 0.00 0.00 酮类 1.05 0.58 0.65 0.33 0.35 0.33 0.54 0.29 其他 0.38 0.21 2.89 1.48 0.61 0.58 0.18 0.10 总计 181.75 — 194.76 — 105.41 — 184.29 — 注:峰体积(×103)。 醇类物质是酯类化合物形成的前体物质,赋予水果清新的醇香味,可使李果香气更加丰满。三华李鲜果相对含量较高为乙醇(34.59%)、2-辛醇(27.26%)。三种果坯中相对含量最高均为乙醇(51.85%~55.14%),在挥发性成分相对含量中占比均过半。乙醇的阈值较高,高浓度下才会对三华李果坯总体风味起贡献作用。三种制坯方法均使乙醇相对含量大大增加,根据表3的峰体积及表2物质的相对含量,可计算出乙醇峰体积,发酵法果坯(104781)及盐腌法果坯(101617)较鲜果(62867)大幅增加,而硫盐法果坯(54566)较鲜果降低,这是因为醇类物质通常来自微生物的作用或者氨基酸的降解产物[19],硫盐法果坯中亚硫酸盐具有强还原性,抑制微生物的生长且与氨基酸、蛋白质结合生成双硫键化合物。
酯类物质一般具有较强的水果香和花香,对三华李鲜果及果坯风味的形成至关重要。鲜果中酯类物质相对含量较高的为乙酸乙酯(10.45%)、己酸乙酯(10.09%)。发酵法、硫盐法、盐腌法果坯中相对含量最高均为乙酸乙酯(16.03%、15.90%、23.74%),其赋予三华李鲜果及果坯类似桃、苹果等花果香气[20]。结合峰体积可知,与鲜果相比,硫盐法果坯乙酸乙酯峰体积降低,而发酵法、盐腌法果坯乙酸乙酯含量增加。可能是由于发酵法与盐腌法果坯醇类物质峰体积较高,约为硫盐法果坯的两倍,为酯类物质提供了充足的前体物质,在发酵、腌制过程中不断酯化生成酯类物质。发酵法果坯在发酵过程中酵母、乳酸菌等微生物也具有产酯香能力。陈思奇等[21]在研究刺梨果渣发酵香气变化情况时也发现类似的情况。
醛类物质挥发性强,阈值低,对三华李果坯的总体风味起到重要作用。三华李鲜果中醛类物质相对含量较高为正己醛(2.45%);发酵果坯中醛类物质相对含量较高为苯甲醛(4.83%)、正己醛(4.12%)、E-2戊烯醛(1.33%);硫盐法果坯中醛类物质相对含量较高为苯甲醛(6.87%)、正己醛(1.66%);盐腌法果坯中醛类物质种类最少,相对含量低,相对含量最高的醛类物质为苯甲醛(0.71%)。上述提到的醛类物质主要赋予李果青草香、水果香、酯香味。结合峰体积分析,鲜果经乳酸发酵后醛类物质种类及峰体积大幅增加,硫盐法与盐腌法果坯醛类物质种类及含量明显低于发酵果坯。研究指出,醛类物质含量与发酵菌株有密切关系,苯甲醛可由乳酸菌分泌的苯丙氨酸或色氨酸转化产生[22−23]。乳酸菌发酵过程中,部分前体物质在乳酸菌的代谢作用下发生不同程度的氧化降解形成醛类物质,使得果坯香气物质在发酵后含量及组成发生较大改变,风味丰度提高[24]。
2.2.3 三华李果坯及鲜果关键挥发性化合物分析及香味评价
仅用挥发性风味物质的相对含量来衡量三华李鲜果及果坯的总体香气不够全面和准确,还需结合挥发性风味物质的阈值进行判断。因此,在评价各组分对三华李果坯风味的贡献时,引入ROAV(相对气味活性值)进行计算分析。ROAV≥1 的成分为该样品关键性风味化合物,对果坯的总体风味起到主导作用,ROAV 值越大,对样品总体风味的贡献越大,0.1≤ROAV<1 的成分对样品的风味起到润饰作用。三华李鲜果及果坯中挥发性物质的阈值和香气描述参考文献[25−28]。
如表4可知,三华李鲜果中有10种关键风味物质,主要为醇类、酯类、醛类,2-辛醇(脂香)、辛酸乙酯(白兰地酒香、菠萝香)、庚醛(水果香)、2-甲基丁醛(水果、麦芽香)是三华李鲜果特有的关键风味物质。其中2-辛醇对鲜果香气的贡献率最大,在三种果坯中均检测不到该物质,可能在腌制过程与其他化合物发生酯化、还原等转化反应有关[29−30],与鲜果比较,果坯中的清新脂蜡香味减弱。盐腌法、硫盐法、发酵法3种果坯样品关键风味物质主要为醛类,E-2-庚烯醛、乙酸异戊酯、壬醛、辛醛、己醛、苯甲醛为共有的6种关键风味物质,风味总体呈现脂香、青草香、果香,但不同果坯间贡献率差异明显,E-2-庚烯醛是所有果坯样品中贡献度最大的关键风味物质,呈现脂香、青叶香、水果香,对果坯独特风味品质的形成有较大贡献。硫盐果坯共有8种关键风味物质,风味总体呈现脂香、青草香及部分橙香。盐腌果坯共有9种关键风味物质,风味总体呈现脂香、青草香及果香。发酵果坯共有10种关键风味物质,风味总体呈较浓郁脂香、青草香及水果香,其中E-2-辛烯醛(青叶、坚果香,脂香)、乙酸叶醇酯(香蕉香)、α-萜品烯(似柑橘、柠檬香)是发酵果坯特有的关键风味物质,赋予其独特风味。
表 4 三华李鲜果及果坯中已定性挥发性化合物的ROAV值Table 4. ROAV values of confirmed volatile compounds in Sanhua plum fresh fruit and fruit billets化合物名称 阈值(μg/kg) 气味描述 ROAV值 鲜果 发酵 硫盐 盐腌 醇类 2-辛醇 7.8 清新脂蜡香 100.00 — — — 酯类 己酸乙酯 8 青苹果,草莓香 36.10 — 5.26 7.55 乙酸丁酯 66 水果香 0.76 2.49 0.56 3.22 乙酸叶醇酯 13 香蕉香 — 2.64 — — 乙酸戊酯 50 水果香 0.58 — — 2.21 辛酸乙酯 19.3 白兰地酒香、菠萝香 1.52 — — — 乙酸乙酯 7500 水果香 — 0.12 — 0.61 丁酸丁酯 400 梨、菠萝样水果香气 — — — 0.22 乙酸异戊酯 30 新鲜果香、甜香 2.35 2.51 9.65 52.71 醛类 E-2-庚烯醛 0.5 脂香,青叶香,水果香 4.12 100.00 100.00 100.00 壬醛 1 青草味 4.71 8.43 64.91 31.25 辛醛 0.7 甜橙味、甜蜂蜜味 6.72 4.82 55.76 47.62 己醛 4.5 青草香、脂肪香 15.56 49.44 15.89 5.09 庚醛 3 水果清香味 9.11 — — — E-2-辛烯醛 3 青叶香,坚果香,脂香 — 7.12 — — 苯甲醛 100 樱桃香、坚果香、杏仁味 — 2.62 2.96 1.40 戊醛 12 水果面包香、油脂、木香味 — 0.75 2.63 — 2-甲基丁醛 2.2 水果香、麦芽香 1.20 — — — 其他 2-戊基呋喃 6 青豆香、果香 0.15 — 0.88 — 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 68 水果香气及柠檬草香气 — — — 0.55 α-萜品烯 85 具有柑橘和柠檬似香气 — 3.63 0.60 — β-蒎烯 16.6 木青气息,花、药草香气 0.16 — — — 通过对鲜果及3种果坯香气成分的比较,可以看出鲜果经不同方式腌制后,关键风味成分发生变化且三种果坯间关键风味物质差异明显。硫盐果坯表现稍逊,关键风味物质种类最少,且峰体积大幅降低。发酵法果坯关键风味物质种类最多,以短链醛类香气成分为主,具有独特的关键风味物质,特征明显,这与乳酸菌发酵过程中产生丰富多样的代谢产物有关[31]。从提高产品挥发性风味物质丰富性的角度出发,发酵法果坯风味品质更佳。
2.2.4 三华李果坯及鲜果挥发性化合物PCA分析
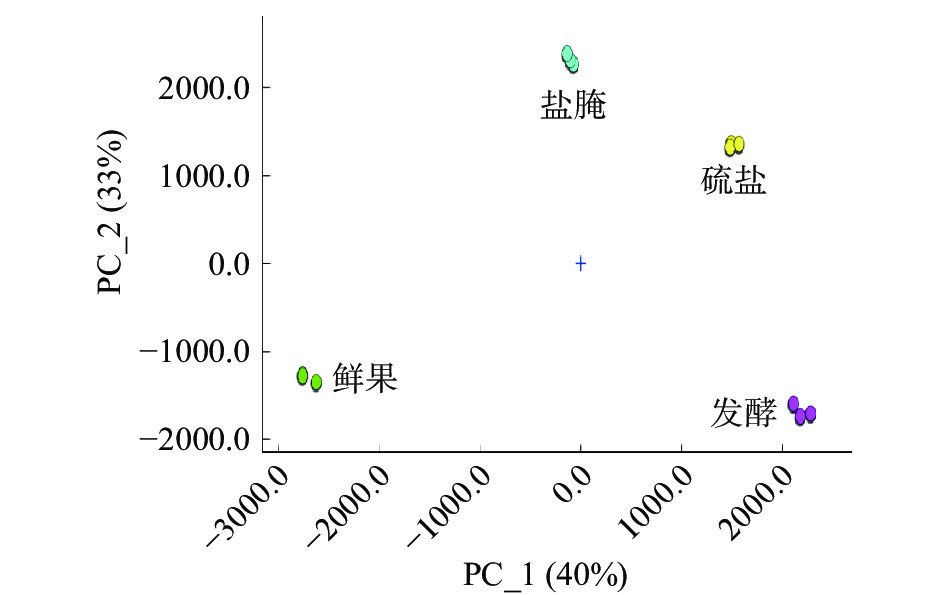
使用仪器软件自带的Dynamic PCA分析插件对HS-GC-IMS的测定结果进行分析,由图4可知,第一主成分PC1贡献率为40%,第二主成分PC2贡献率为33%,PC1与PC2的贡献率之和为73%,数据降维后所得综合变量在二维空间能较好地代表原始数据所反映的信息。通过二维空间的数据分布差异可以直观地观察到样品间的差异性,4组样品间无交叉区域,间距明显,说明鲜果经过盐腌法、硫盐法、发酵法制坯后,挥发性化合物发生明显变化,不同果坯间也有明显差别。从空间距离看,盐腌法果坯较其他两种果坯与鲜果距离较近,说明盐腌法果坯相比其他两种果坯与鲜果挥发性化合物相似度较高。该结果与电子鼻LDA分析和HS-GC-IMS差异谱图结果一致。
3. 结论
采用电子鼻结合HS-GC-IMS技术以三华李鲜果为对照,分析不同制坯方式对三华李果坯风味物质的影响。电子鼻线性判别分析及主成分分析可以很好地区分鲜果及三种果坯样品的风味,经不同制坯方式处理后,鲜果的挥发性风味物质发生明显变化,三种果坯间风味物质差异明显。传感器W5S、W1S、W1W、W2S、W2W在分析时发挥主要区分作用,发酵果坯样品的响应值显著高于硫盐法及盐腌法果坯。通过GC-IMS从四组样品中共鉴定出49种挥发性成分,以酯类(18种)、醇类(9种)、醛类(13种)、酮类(4种)为主。发酵果坯风味物质总峰体积最高为194760,其次是盐腌法果坯184290,而硫盐法果坯最低仅105410。ROAV结果表明3种果坯样品关键风味物质主要为醛类,E-2-庚烯醛、乙酸异戊酯、壬醛、辛醛、己醛、苯甲醛为共有的6种关键风味物质,但不同果坯间贡献率差异明显。乳酸发酵果坯特征风味物质种类最多,以短链醛类化合物为主,阈值低,总体风味呈现青草香、果香(香蕉、樱桃)及脂香,从风味丰富性角度认为乳酸发酵果坯风味品质更好。由于实验条件限制,本研究只能通过查阅文献获得挥发性成分的气味描述,若条件允许,可结合采用气相色谱-嗅觉测量(Gas chromatography-olfactometry,GC-O)检测技术,将色谱分析和感官分析相结合更全面分析三华李果坯的风味特征。
-
表 1 PEN3电子鼻传感器敏感物质
Table 1 Sensitive substances of PEN3 electronic nose sensor
阵列序号 传感器 性能描述 R1 W1C 芳烃成分,苯类灵敏 R2 W5S 灵敏度大,对氮氧化合物很灵敏 R3 W3C 芳香成分灵敏,氨类灵敏 R4 W6S 主要对氢化物有选择性 R5 W5C 短链烷烃芳香成分灵敏 R6 W1S 对甲基类灵敏 R7 W1W 对硫化物灵敏 R8 W2S 对醇类,醛酮类灵敏 R9 W2W 芳香成分,对有机硫化物灵敏 R10 W3S 对长链烷烃灵敏 表 2 三华李鲜果及果坯挥发性化合物相对含量
Table 2 Relative content of volatile compounds in Sanhua plum fresh fruit and fruit billets
化合物名称 保留指数 保留时间(s) 迁移时间(ms) 相对含量(%) 鲜果 发酵 硫盐 盐腌 酯类 乙酸异戊酯-M 872.3 344.46 1.30 1.10 0.50 3.19 1.22 乙酸异戊酯-D 873 345.28 1.75 1.35 0.90 3.53 6.91 乙酸乙酯 598.7 134.66 1.33 10.45 16.03 15.90 23.74 丁酸丙酯-M 919.4 413.99 1.27 0.21 — 0.12 — 丁酸丙酯-D 918.8 412.95 1.69 0.28 — — — 乙酸丁酯 803.6 270.41 1.23 1.75 3.03 0.87 1.09 己酸乙酯 1014.6 586.49 1.81 10.09 — 0.98 0.31 辛酸乙酯-D 1200.9 959.45 2.03 0.50 — — — 辛酸乙酯-M 1197.1 951.82 1.48 0.52 — — — 乙酸甲酯 544 111.69 1.19 1.00 — — — 乙酸戊酯-D 912.2 401.27 1.76 0.51 — — 0.28 乙酸戊酯-M 913.3 403.25 1.31 0.50 — — 0.29 乙酸异丁酯-M 764 233.20 1.23 0.75 — 0.25 0.19 乙酸异丁酯-D 761.6 231.24 1.61 1.09 0.09 0.03 0.74 乙酸丙酯 706.3 186.67 1.47 1.31 0.65 1.20 4.92 乙酸苄酯 1174.7 906.98 1.32 — — — 0.13 丁酸丁酯-M 968.5 500.86 1.35 — — — 0.33 丁酸丁酯-D 968.3 500.39 1.83 — — — 0.13 丁酸己酯 1151.4 860.33 1.49 — — — 0.13 丙酸丁酯-D 905.5 389.45 1.72 — 0.03 0.10 0.09 丙酸丁酯-M 906.3 390.96 1.29 — 0.15 0.32 0.12 丁酸甲酯 740.6 214.31 1.15 — — 0.21 — 戊酸乙酯-D 897 374.49 1.68 — 0.65 1.37 0.30 戊酸乙酯-M 897 374.49 1.26 — 0.26 1.12 0.17 乳酸乙酯 822.3 290.61 1.54 — 1.34 — — 乙酸叶醇酯 1028.4 614.21 1.82 — 0.64 — — 醛类 正己醛 790.3 256.01 1.56 2.45 4.12 1.66 0.12 2-甲基丁醛 657.8 159.46 1.40 0.09 — — — 2-糠醛 860 331.25 1.09 0.06 0.14 0.15 0.46 庚醛 885.8 359.09 1.33 0.45 — — — 正辛醛 1007.9 573.17 1.41 0.16 0.06 0.90 0.18 壬醛-M 1104.6 766.56 1.47 0.17 0.16 1.03 0.16 壬醛-D 1105.2 767.83 1.93 — — 0.19 — 戊醛 693.4 176.24 1.19 — 0.16 0.73 — 苯甲醛-M 974.9 512.04 1.15 — 1.33 3.77 0.52 苯甲醛-D 972.8 508.42 1.47 — 3.50 3.10 0.19 E-2-己烯醛 835.2 304.45 1.18 0.09 0.08 0.09 — E-2-庚烯醛-M 956 478.77 1.25 0.08 0.42 0.84 0.17 E-2-庚烯醛-D 954.4 475.87 1.66 — 0.51 0.33 0.08 E-2-戊烯醛 747.2 219.67 1.35 — 1.33 0.06 — 2-甲基戊醛 774.1 241.34 1.52 — 0.13 — — E-2-辛烯醛-M 1065.4 688.12 1.33 — 0.28 — — E-2-辛烯醛-D 1064.7 686.73 1.82 — 0.11 — — 醇类 乙醇 512.3 98.34 1.05 34.59 53.80 51.85 55.14 E-2-己烯-1-醇-M 848.1 318.44 1.18 0.74 0.13 0.27 — E-2-己烯-1-醇-D 847.8 318.04 1.51 0.89 0.70 0.06 — 2-辛醇 1028.4 614.21 1.85 27.26 — — — 2-甲基-1-丙醇 660.2 160.47 1.17 0.40 — — — 2-甲基丁醇 741.7 215.21 1.23 0.19 — — 0.46 异辛醇-M 1049.9 657.22 1.41 — 0.23 1.94 0.58 异辛醇-D 1048.6 654.67 1.79 — 0.07 0.48 0.14 5-甲基-2-呋喃甲醇 956.5 479.54 1.57 — 0.30 0.35 — 苯甲醇 1015.7 588.80 1.32 — — 0.65 0.30 正戊醇 760.6 230.46 1.51 — 0.20 0.03 — 酮类 2-环己烯-1-酮 875.7 348.19 1.41 0.18 0.33 0.24 — 3-辛酮 989.8 538.40 1.31 — — 0.09 0.09 2-辛酮 1007.6 572.59 1.33 0.32 — — — 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 991.3 541.18 1.17 0.07 — — 0.20 萜烯类 β-蒎烯 974 510.60 1.22 0.10 — — — α-萜品烯-M 1011.6 580.52 1.22 — 2.62 0.89 — α-萜品烯-D 1010.1 577.59 1.73 — 3.08 0.30 — 酸类 丙酸 661.3 160.93 1.27 0.24 0.81 0.48 — 杂环化合物 2-戊基呋喃 993.6 545.20 1.25 0.03 — 0.12 — 其他 芳樟醇氧化物-M 1104.2 765.93 1.26 — 0.99 0.22 0.10 芳樟醇氧化物-D 1102.7 762.75 1.81 — 0.16 — — 表 3 主要的挥发性化合物种类的峰体积及相对含量
Table 3 Peak volume and relative content of the main volatile compounds
化合物种类 鲜果 发酵 硫盐 盐腌 峰体积 相对含量(%) 峰体积 相对含量(%) 峰体积 相对含量(%) 峰体积 相对含量(%) 醇类 116.49 64.10 108.51 55.71 58.69 55.68 104.22 56.43 酯类 57.22 31.48 47.41 24.34 30.95 29.36 75.87 41.17 醛类 6.44 3.54 24.14 12.39 13.56 12.86 3.48 1.89 烯烃类 0.17 0.09 11.16 5.73 1.25 1.19 0.00 0.00 酮类 1.05 0.58 0.65 0.33 0.35 0.33 0.54 0.29 其他 0.38 0.21 2.89 1.48 0.61 0.58 0.18 0.10 总计 181.75 — 194.76 — 105.41 — 184.29 — 注:峰体积(×103)。 表 4 三华李鲜果及果坯中已定性挥发性化合物的ROAV值
Table 4 ROAV values of confirmed volatile compounds in Sanhua plum fresh fruit and fruit billets
化合物名称 阈值(μg/kg) 气味描述 ROAV值 鲜果 发酵 硫盐 盐腌 醇类 2-辛醇 7.8 清新脂蜡香 100.00 — — — 酯类 己酸乙酯 8 青苹果,草莓香 36.10 — 5.26 7.55 乙酸丁酯 66 水果香 0.76 2.49 0.56 3.22 乙酸叶醇酯 13 香蕉香 — 2.64 — — 乙酸戊酯 50 水果香 0.58 — — 2.21 辛酸乙酯 19.3 白兰地酒香、菠萝香 1.52 — — — 乙酸乙酯 7500 水果香 — 0.12 — 0.61 丁酸丁酯 400 梨、菠萝样水果香气 — — — 0.22 乙酸异戊酯 30 新鲜果香、甜香 2.35 2.51 9.65 52.71 醛类 E-2-庚烯醛 0.5 脂香,青叶香,水果香 4.12 100.00 100.00 100.00 壬醛 1 青草味 4.71 8.43 64.91 31.25 辛醛 0.7 甜橙味、甜蜂蜜味 6.72 4.82 55.76 47.62 己醛 4.5 青草香、脂肪香 15.56 49.44 15.89 5.09 庚醛 3 水果清香味 9.11 — — — E-2-辛烯醛 3 青叶香,坚果香,脂香 — 7.12 — — 苯甲醛 100 樱桃香、坚果香、杏仁味 — 2.62 2.96 1.40 戊醛 12 水果面包香、油脂、木香味 — 0.75 2.63 — 2-甲基丁醛 2.2 水果香、麦芽香 1.20 — — — 其他 2-戊基呋喃 6 青豆香、果香 0.15 — 0.88 — 6-甲基-5-庚烯-2-酮 68 水果香气及柠檬草香气 — — — 0.55 α-萜品烯 85 具有柑橘和柠檬似香气 — 3.63 0.60 — β-蒎烯 16.6 木青气息,花、药草香气 0.16 — — — -
[1] 李依娜, 邹颖, 余元善, 等. 不同酚酸对三华李清汁贮藏期间色泽稳定性的比较分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(7):165−172,16. [LI Y N, ZOU Y, YU Y S, et al. Comparative analysis of color stability of Sanhuali clear juice during storage with different phenolic acids[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(7):165−172,16. LI Y N, ZOU Y, YU Y S, et al . Comparative analysis of color stability of Sanhuali clear juice during storage with different phenolic acids[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020 ,36 (7 ):165 −172,16 .[2] 李媛, 郭卓钊, 郭美媛, 等. 三华李与蓝莓花色苷抗氧化活性及抑制 α-淀粉酶活性比较研究[J]. 轻工科技,2020,36(6):20−23. [LI Y, GUO Z Z, GUO M Y, et al. Comparative study on antioxidant activity and α-amylase inhibiting activity of anthocyanin from plum and blueberry[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology,2020,36(6):20−23. LI Y, GUO Z Z, GUO M Y, et al . Comparative study on antioxidant activity and α-amylase inhibiting activity of anthocyanin from plum and blueberry[J]. Light Industry Science and Technology,2020 ,36 (6 ):20 −23 .[3] 白卫东, 梁娇, 杨婉媛, 等. 广式凉果的降硫技术研究进展[J]. 农产品加工, 2019(23):86−89. [BAI W D, LIANG J, YANG W Y, et al. Research progress on sulfur reduction technology of Guang-style cold fruits[J]. Agricultural Product Processing, 2019(23):86−89. BAI W D, LIANG J, YANG W Y, et al. Research progress on sulfur reduction technology of Guang-style cold fruits[J]. Agricultural Product Processing, 2019(23): 86−89.
[4] 李媛. 基于发酵法的高花色苷三华李果坯保藏工艺研究[D]. 广州:华南农业大学, 2017. [LI Y. Research on the preservation process of high anthocyanin Sanhua plum fruit blanks based on fermentation method[D]. Guangzhou:South China Agricultural University, 2017. LI Y. Research on the preservation process of high anthocyanin Sanhua plum fruit blanks based on fermentation method[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2017.
[5] 黄志钰, 沈雪玉, 陈珣琳, 等. 三华李果坯发酵液中腐败真菌分离鉴定、相关抑菌剂效价评定及发酵工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(14):113−120. [HUANG Z Y, SHEN X Y, CHEN X L, et al. Isolation and identification of spoilage fungi in the fermentation broth of plum fruit blanks, evaluation of the efficacy of relevant inhibitors and optimization of the fermentation process[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(14):113−120. HUANG Z Y, SHEN X Y, CHEN X L, et al . Isolation and identification of spoilage fungi in the fermentation broth of plum fruit blanks, evaluation of the efficacy of relevant inhibitors and optimization of the fermentation process[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (14 ):113 −120 .[6] 宋倩. 双华李脱硫工艺研究及其清咽功能凉果的研发[D]. 广州:华南农业大学, 2016. [SONG Q. Research on the desulfurization process of Shuanghua plum and the development of its cool fruit with clear throat function[D]. Guangzhou:South China Agricultural University, 2016. SONG Q. Research on the desulfurization process of Shuanghua plum and the development of its cool fruit with clear throat function[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2016.
[7] 张媛媛, 吴璇, 俞坤, 等. 纳他霉素在青梅果胚糖渍过程中的抑菌效果研究[J]. 食品科技,2015,40(7):276−280. [ZHANG Y Y, WU X, YU K, et al. Study on the antibacterial effect of natamycin in the canning process of plum fruit embryos[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015,40(7):276−280. ZHANG Y Y, WU X, YU K, et al . Study on the antibacterial effect of natamycin in the canning process of plum fruit embryos[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015 ,40 (7 ):276 −280 .[8] LAN Y L, WU J, WANG X J, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant capacity and flavor profile change of pomegranate wine during fermentation and aging process[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,232:777−787. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.030
[9] XI H, HUANG Y, GÓRSKA-HORCZYCZAK E, et al. Rapid analysis of Baijiu volatile compounds fingerprint for their aroma and regional origin authenticity assessment[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,337:128002. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128002
[10] GERHARDT N, BIRKENMEIER M, SANDERS D, et al. Resolution-optimized headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) for non-targeted olive oil profiling[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2017,409(16):3933−3942. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0338-2
[11] CHEN T, QI X P, CHEN M J, et al. Discrimination of Chinese yellow wine from different origins based on flavor fingerprint[J]. Acta Chromatographica,2019,32(2):1−6.
[12] 邓静, 罗晶晶, 朱开宪, 等. 基于电子鼻和气相色谱-离子迁移谱法分析不同等级俄色绿茶香气物质差异[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2023,14(1):236−243. [DENG J, LUO J J, ZHU K X, et al. Analysis of differences in aroma substances between different grades of Russian green tea based on electronic nose and gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2023,14(1):236−243. DENG J, LUO J J, ZHU K X, et al . Analysis of differences in aroma substances between different grades of Russian green tea based on electronic nose and gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2023 ,14 (1 ):236 −243 .[13] 阳丹, 陈小爱, 杨玉洁, 等. 基于电子鼻、HS-GC-IMS、HS-SPME-GC-MS技术联用分析不同发酵年份老香黄挥发性成分差异[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(11):313−323. [YANG D, CHEN X A, YANG Y J, et al. Analysis of differences in volatile components of old aromatic yellow in different fermentation years based on electronic nose, HS-GC-IMS, HS-SPME-GC-MS technique coupling[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022,38(11):313−323. YANG D, CHEN X A, YANG Y J, et al . Analysis of differences in volatile components of old aromatic yellow in different fermentation years based on electronic nose, HS-GC-IMS, HS-SPME-GC-MS technique coupling[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022 ,38 (11 ):313 −323 .[14] 刘登勇, 周光宏, 徐幸莲. 确定食品关键风味化合物的一种新方法:“ROAV”法[J]. 食品科学,2008(7):370−374. [LIU D Y, ZHOU G H, XU X L. "ROAV" method: A new method for determining key odor compounds of Rugao Ham[J]. Food Science,2008(7):370−374. LIU D Y, ZHOU G H, XU X L . "ROAV" method: A new method for determining key odor compounds of Rugao Ham[J]. Food Science,2008 (7 ):370 −374 .[15] LIU Q, ZHAO N, ZHOU D D, et al. Discrimination and growth tracking of fungi contamination in peaches using electronic nose[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,262:226−234. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.100
[16] 李睿, 王海燕, 李星, 等. 不同加工方式荣昌猪肉风味差异性评价[J]. 肉类研究,2021,35(11):31−37. [LI R, WANG H Y, LI X, et al. Evaluation on flavor difference of Rongchang pork with different processing methods[J]. Meat Research,2021,35(11):31−37. LI R, WANG H Y, LI X, et al . Evaluation on flavor difference of Rongchang pork with different processing methods[J]. Meat Research,2021 ,35 (11 ):31 −37 .[17] 赖婷, 刘汉伟, 张名位, 等. 乳酸菌发酵对果蔬中主要活性物质及其生理功能的影响研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2015,34(3):1−4. [LAI T, LIU H W, ZHANG M W, et al. Research progress on the effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the main active substances and their physiological functions in fruits and vegetables[J]. China Brewing,2015,34(3):1−4. LAI T, LIU H W, ZHANG M W, et al . Research progress on the effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on the main active substances and their physiological functions in fruits and vegetables[J]. China Brewing,2015 ,34 (3 ):1 −4 .[18] 李依娜, 邹颖, 余元善, 等. 不同乳酸菌发酵对菠萝浆品质的影响[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(2):111−116. [LI Y N, ZOU Y, YU Y S, et al. Effects of different lactic acid bacteria on the quality of pineapple pulp[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(2):111−116. LI Y N, ZOU Y, YU Y S, et al . Effects of different lactic acid bacteria on the quality of pineapple pulp[J]. China Brewing,2021 ,40 (2 ):111 −116 .[19] 刘永逸, 林华, 杨超, 等. 不同发酵方式对酸豆角品质和风味的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(14):43−51. [LIU Y Y, LIN H, YANG C, et al. Effects of different fermentation methods on quality and flavor of sour bean[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(14):43−51. LIU Y Y, LIN H, YANG C, et al . Effects of different fermentation methods on quality and flavor of sour bean[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (14 ):43 −51 .[20] 王银, 田真, 杨晨晨, 等. 基于顶空气相色谱-离子迁移谱对乳杆菌及产香酵母发酵红枣汁的香气成分分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(3):266−272. [WANG Y, TIAN Z, YANG C C, et al. Aroma composition analysis of fermented red date juice by Lactobacillus and aroma yeast based on headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(3):266−272. WANG Y, TIAN Z, YANG C C, et al . Aroma composition analysis of fermented red date juice by Lactobacillus and aroma yeast based on headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022 ,48 (3 ):266 −272 .[21] 陈思奇, 孟满, 杜勃峰, 等. 混菌发酵刺梨果渣风味组分及香气特征的变化分析与评价[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(10):60−66. [CHEN S Q, MENG M, DU B F, et al. Analysis and evaluation of changes in flavor components and aroma characteristics of mixed bacteria fermented prickly pear pomace[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(10):60−66. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.10.013 CHEN S Q, MENG M, DU B F, et al . Analysis and evaluation of changes in flavor components and aroma characteristics of mixed bacteria fermented prickly pear pomace[J]. China Brewing,2019 ,38 (10 ):60 −66 . doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.10.013[22] 刘磊, 汪浩, 张名位, 等. 龙眼乳酸菌发酵工艺条件优化及其挥发性风味物质变化[J]. 中国农业科学,2015,48(20):4147−4158. [LIU L, WANG H, ZHANG M W, et al. Optimization of fermentation process conditions of longan lactic acid bacteria and their changes in volatile flavor substances[J]. China Agricultural Science,2015,48(20):4147−4158. LIU L, WANG H, ZHANG M W, et al . Optimization of fermentation process conditions of longan lactic acid bacteria and their changes in volatile flavor substances[J]. China Agricultural Science,2015 ,48 (20 ):4147 −4158 .[23] DI C R, FILANNINO P, GOBBETTI M. Lactic acid fermentation drives the optimal volatile flavor-aroma profile of pomegranate juice[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2017,248:56−62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.02.014
[24] 刘晓辉, 万晶琼, 吴函殷, 等. 益生菌固态发酵红茶风味品质的分析[J]. 饮料工业,2021,24(1):29−35. [LIU X H, WAN J Q, WU H Y, et al. Analysis of the flavor quality of probiotic solid fermented black tea[J]. Beverage Industry,2021,24(1):29−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7871.2021.01.011 LIU X H, WAN J Q, WU H Y, et al . Analysis of the flavor quality of probiotic solid fermented black tea[J]. Beverage Industry,2021 ,24 (1 ):29 −35 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7871.2021.01.011[25] ZHU J C, WANG L Y, XIAO Z B, et al. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in mulberry fruits by application of gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O), odor activity value (OAV), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and flame photometric detection (FPD)[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,245:775−785. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.11.112
[26] 里奥·范·海默特. 化合物香味阈值汇编[M]. 刘强, 昌德寿, 汤峨(译). 第二版. 北京:科学出版社, 2015. [VAN HEIMERT L. Compilation of flavour threshold values in water and other media[M]. LIU Q, CHANG D S, TANG E (Translation). 2nd Edition. Beijing:Science Press, 2015. VAN HEIMERT L. Compilation of flavour threshold values in water and other media[M]. LIU Q, CHANG D S, TANG E (Translation). 2nd Edition. Beijing: Science Press, 2015.
[27] 刘威, 张永瑞, 鲁静, 等. 不同加工工艺刺槐花代用茶香气成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(1):250−256. [LIU W, ZHANG Y R, LU J, et al. Analysis of aroma components of different processing processes of acacia flower tea substitutes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(1):250−256. LIU W, ZHANG Y R, LU J, et al . Analysis of aroma components of different processing processes of acacia flower tea substitutes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (1 ):250 −256 .[28] ZHU Y F, CHEN J, CHEN X J, et al. Use of relative odor activity value (ROAV) to link aroma profiles to volatile compounds: application to fresh and dried eel ( Muraenesox cinereus)[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2020,23(1):2257−2270. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2020.1856133
[29] 余元善, 肖更生, 陈卫东, 等. 凉果半成品的加工方式和存在的问题[J]. 现代食品科技,2007(4):60−63. [YU Y S, XIAO G S, CHEN W D, et al. Processing methods and problems of semi-finished products of cold fruits[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2007(4):60−63. YU Y S, XIAO G S, CHEN W D, et al . Processing methods and problems of semi-finished products of cold fruits[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2007 (4 ):60 −63 .[30] MOZZI F, RAYA R R, VIGNOLO G M. Vegetable and fruit fermentation by lactic acid bacteria[M]. JohnWiley & Sons, Ltd, 2015.
[31] KAPRASOB R, KERDCHOECHUEN O, LAOHAKUNJIT N, et al. Fermentation-based biotransformation of bioactive phenolics and volatile compounds from cashew apple juice by select lactic acid bacteria[J]. Process Biochemistry,2017,59: 141−149.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 蔡梦婷,刘荔,黄若楠,孙学宁,曾名湧. 亲水胶体调控全牡蛎-大豆分离蛋白热诱导凝胶的形成机制. 食品工业科技. 2024(23): 129-139 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



