Optimization of Frying Technology of Agaricus bisporus Recombinant Rice and Analysis of Its Flavor Components
-
摘要: 为改善炒米风味,提高炒米的营养价值,本研究以双孢菇粉和籼米粉为原料,通过挤压造粒和油炸处理获得双孢菇炒米,并利用响应面法优化工艺配方,再对其营养成分和风味成分进行分析。结果表明,双孢菇炒米最佳工艺配方为:油炸温度170 ℃,油炸时间79 s,双孢菇粉添加量5.90%。在此基础上进行验证实验,双孢菇炒米的综合评分为86.80±0.47,与理论预测值接近。营养成分结果显示,与空白炒米相比,双孢菇炒米总淀粉含量显著下降(P<0.05),而蛋白质、脂肪和膳食纤维含量均显著上升(P<0.05),氨基酸总量也有所提高,其中的谷氨酸、天冬氨酸和精氨酸对双孢菇炒米独特风味的形成有较高贡献。此外,电子鼻和气相色谱-离子迁移谱结果显示,空白重组米、空白炒米、双孢菇重组米和双孢菇炒米共检测出包括醛类、酯类、酮类、醇类、呋喃类和酸类等53种挥发性风味物质。与空白重组米相比,空白炒米中酮类和呋喃类物质的相对含量增加;与空白炒米相比,双孢菇炒米中醛类和酮类物质的相对含量增加;与双孢菇重组米相比,双孢菇炒米中酮类、酯类和呋喃类物质的相对含量增加。
-
关键词:
- 炒米 /
- 响应面 /
- 营养成分 /
- 电子鼻 /
- 气相色谱-离子迁移谱
Abstract: In order to improve the flavor and nutritional value of stir-fried rice, this study used Agaricus bisporus powder and indica rice powder as raw materials, and obtained Agaricus bisporus stir-fried rice by extrusion granulation and frying. Response surface methodology was used to optimize the technological formula, and then the nutritional components and flavor components were analyzed. The results showed that the best formula of stir-fried rice with Agaricus bisporus was as follows: The frying temperature 170 ℃, the frying time 79 s, and the addition of Agaricus bisporus powder 5.90%. On this basis, the comprehensive score of Agaricus bisporus stir-fried rice was 86.80±0.47, which was close to the theoretical prediction. The nutritional results showed that compared with the blank stir-fried rice, the total starch content of the stir-fried rice with Agaricus bisporus decreased significantly (P<0.05), while the contents of protein, fat and dietary fiber increased significantly (P<0.05), and the total amino acid content was also increased. Glutamic acid, aspartic acid and arginine made great contributions to the formation of the unique flavor of the stir-fried rice with Agaricus bisporus. In addition, the results of electronic nose and gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry showed that 53 volatile flavor substances including aldehydes, esters, ketones, alcohols, furans and acids were detected in blank recombinant rice, blank stir-fried rice, Agaricus bisporus recombinant rice and Agaricus bisporus stir-fried rice. Compared with blank recombinant rice, the relative contents of ketones and furans in blank stir-fried rice increased. Compared with blank stir-fried rice, the relative contents of aldehydes and ketones in Agaricus bisporus stir-fried rice increased. Compared with Agaricus bisporus recombinant rice, the relative contents of ketones, esters and furans in Agaricus bisporus stir-fried rice increased. -
双孢菇别名口蘑、白蘑菇,是目前世界上种植面积较为广泛且产量较多的一种食用菌[1−2]。双孢菇营养丰富,富含多种氨基酸、维生素和核苷酸,具有良好的食用价值和保健价值[3−4]。此外,双孢菇的挥发性风味成分十分丰富,1-辛烯-3-醇、1-辛烯-3-酮和3-辛醇等八碳化合物是其主要香气成分,具有浓郁的蘑菇风味,尤其是1-辛烯-3-醇在双孢菇中其含量占总挥发性成分的78%[5]。近年来,我国双孢菇产量不断提高,但其在产品加工与开发利用领域还亟待大力提升。因此,以双孢菇为原料,开发具有独特风味的蘑菇深加工产品,满足市场多样化消费需求尤为必要。
挤压重组米又叫人造米,通常是以谷物、淀粉等物质为原料,添加其他辅料,按一定比例配制后,通过挤压造粒、干燥等过程获得的具有原生大米相似的形态、质地和感官评价的米制品[6]。目前重组米多以马铃薯、豆类等为原辅料进行挤压加工。Sumardiono等[7]以西米、葛粉和绿豆粉为主要原料生产重组米,结果表明当使用50%(w/w)西米粉、30%(w/w)葛粉和20%(w/w)绿豆粉的组合时,重组米品质最好。Saha等[8]选择高直链淀粉米生产重组米,在测试的25个指标中,发现14个测定指标对重组米的感官接受度有显著影响。董状等[9]以富硒发芽糙米为原料,利用双螺杆挤压机挤压得到有机硒含量为1.661 mg/kg,感官评分高、口感佳、有米饭香气的重组米。然而,目前有关重组米加工方式研究,多以蒸煮为主,对其进行油炸等加工的研究较少,需要深入探讨炒米等休闲食品,以提升重组米开发利用途径。
炒米作为中国特有的传统小吃,在我国各地均有食用历史[10]。传统炒米通常以糯米或籼米为原料,具有助消化、清空肠道的作用。然而其在加工过程中营养物质流失较为严重,制作工艺复杂,不利于大规模工业化生产[11]。若将传统炒制工艺改为油炸加工炒米,将有利于产业化和规模化开发利用,进而扩大传统炒米加工产能[12]。
本研究以双孢菇粉和籼米粉为主要原料,经挤压造粒和油炸处理后得到双孢菇炒米,通过响应面法优化并获得双孢菇炒米的最佳工艺配方,同时对其营养成分和挥发性风味物质进行检测分析。本研究为传统炒米的生产以及双孢菇资源多元化开发均提供良好的指导和参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
双孢菇粉 双孢菇经烘干和粉碎机粉碎获得,菌菇原料来自阜南联美农产品有限公司;籼米粉 市售米粉;植物油 购自益海嘉里食品营销有限公司;茚三酮、氢氧化钠、浓盐酸、磺基水杨酸 均为分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
DSE32-1双螺杆挤压膨化机 济南盛润机械有限公司;DHG-9053A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海申贤恒温设备厂;750-T高速多功能粉碎机 永康市铂欧五金制品有限公司;多功能电热锅 湖北香江电器股份有限公司;TA质构仪 苏昊仪器设备有限公司;L-8900全自动氨基酸分析仪 日本日立公司;PEN3型电子鼻 德国AIRSENSE公司;FlavourSpec®风味分析仪 德国G.A.S.公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 双孢菇炒米工艺流程
将烘干的干双孢菇用粉碎机粉碎后,过120目筛得双孢菇粉。双孢菇粉和籼米粉根据国标[13]进行水分测定,按照所需水分含量添加水分(总水分含量为28%),搅拌均匀,得到原料混合粉。将混合粉倒入挤压膨化机,设置双螺杆挤压机的进料速率为13 Hz,螺杆旋转速率为13 Hz,切刀旋切速率为40 Hz,四区温度为80 ℃,采用双刀恒速模切刀,将挤出物料切成米粒状,得到双孢菇重组米。用恒温干燥箱在70 ℃干燥3 h,冷却后得到成品双孢菇重组米。将0.5 L植物油倒入多功能电热锅内,待电热锅内温度达到设置温度时,放入50 g双孢菇重组米,油炸时间为实验时间,油炸结束后将炒米用不锈钢粉篱捞出并放置在室温下冷却,即可得到双孢菇炒米成品。对照组制作只以籼米粉为原料,未添加双孢菇粉,工艺与双孢菇重组米和双孢菇炒米相同。
1.2.2 响应面试验
1.2.2.1 响应面试验设计
采用油炸温度(A)、油炸时间(B)、双孢菇粉添加量(C)为因素,由预实验中单因素实验结果得到各因素的水平范围,利用Box-Behnken响应面法设计试验,试验结果是以感官得分加质构得分的综合得分为响应值,响应面试验因素水平表见表1。
表 1 响应面试验设计表Table 1. Response surface test design table因素 符号 水平 −1 0 1 油炸温度(℃) A 165 170 175 油炸时间(s) B 68 75 82 双孢菇粉添加量(%) C 5 6 7 1.2.2.2 感官评分
由经培训的食品专业人员组建15人感官评价小组,对双孢菇炒米的外观形态、色泽、香味和口感四个评价指标进行打分,感官评分标准参考巫婷婷[10]并稍作修改,如表2所示。样本随机编号。
表 2 炒米感官评价标准Table 2. Sensory evaluation criteria for stir-fried rice评价指标 评分标准 得分(分) 饱满完整,没有褐变,膨化度好 21~25 外观形态(25分) 较光滑饱满,有点碎米粒,稍有褐变,
膨化度较好16~20 碎米粒较多,褐变严重,未膨化 0~15 色泽均匀一致,光泽好 21~25 色泽(25分) 光泽较差,边缘略有褐色 16~20 色泽发黑,光泽差 0~15 油炸香味浓郁,有双孢菇特有的香味,无异味 21~25 香味(25分) 没有明显的油炸食品的香味,双孢菇香味略淡 16~20 没有香味甚至带有糊味 0~15 硬脆度适中,口感酥脆,咀嚼感好 21~25 口感(25分) 偏硬或偏脆,咀嚼感一般 16~20 口感过硬,咀嚼感差 0~15 1.2.2.3 质构分析
根据文献[14]所描述的方法进行适当修改,将双孢菇炒米放在质构仪载物台中部,使用P/2探头对双孢菇炒米进行质构分析,测前、测中和测后的探头速度分别设置为0.5、0.5和10 mm/s,每组平行测定10次,去除最大值和最小值,取其余8组的平均值。
1.2.2.4 综合评分方法
按照百分制的评分方法,综合评分中感官评价得分占总分的50%,质构得分占总分的50%。质构得分又由硬度和脆度各占50%组成,炒米的硬度与消化率与适口性相关,较高的硬度可能会对人的消化有影响,探针下降过程中第一个破裂点的压缩距离设为脆裂形变值,脆裂形变值越低表明脆度越大[15],较好的酥脆性会提高摄食乐趣。参照杨涛等[15]的方法稍作修改,选择线性插值法计算得分。
硬度:样品最大值Y硬max规定为1分,最小值规定为Y硬min为10分。将最终结果乘以10,换算为百分制。
(1) 脆度:样品最大值H脆max规定为1分,最小值规定为H脆min为10分。将最终结果乘以10,换算为百分制。
(2) 质构得分=硬度得分(50%)+脆度得分(50%)
综合得分=感官得分(50%)+质构得分(50%)
1.2.3 基本成分测定
称取粉碎后的空白炒米和双孢菇炒米,对其基本成分进行测定。蛋白质含量参照GB/T 5009.5-2016食品中蛋白质的测定中凯氏定氮法进行测定;脂肪含量参照GB/T5009.6-2016食品中脂肪的测定中索氏提取法进行测定;总膳食纤维含量参照GB 5009.88-2014酶重量法进行测定;总淀粉含量参照GB/T5009.9-2016食品中淀粉的测定中酶水解法进行测定。
1.2.4 水解氨基酸测定
参照GB 5009.124-2016食品中氨基酸的测定。
1.2.5 游离氨基酸测定
参考王纯等[16]的方法并稍作修改,称取0.1 g粉碎后的空白炒米和双孢菇炒米,加入10 mL 4%磺基水杨酸,放入超声波中浸提40 min,静置后取上清液于离心管中离心40 min,最后过0.22 μm水膜装入上样瓶中,使用全自动氨基酸分析仪进行测定。含量阈值比(RCT)=风味氨基酸含量/味觉阈值,RCT可以用来评价风味氨基酸对风味的贡献率,当RCT<1时,此种氨基酸对味觉特征无贡献;RCT≥1时,表示该氨基酸会影响相应的味觉特征,比值越高,影响越大[17]。
1.2.6 电子鼻测定
参考刘志云等[18]的样品处理方法,称取过100目筛的空白重组米、空白炒米、双孢菇重组米和双孢菇炒米四种样品粉末3 g,放入25 mL顶空瓶中,封口后置于室温下富集1 h,采用顶空上样法对样品进行香气分析。参数设置如下:进样间隔时间:1 s,预进样时间:5 s,归零时间:10 s,清洗时间:120 s,测量时间:100 s,初始注射流量:300 mL/min,传感器仓流量:300 mL/min。PEN3电子鼻配制传感器对不同类型化合物响应如表3所示。
表 3 PEN3电子鼻传感器敏感物质Table 3. Substances for sensing of PEN3 electronic nose sensor编号 传感器 敏感物质 S1 W1C 芳烃化合物 S2 W5S 氮氧化合物 S3 W3C 芳香分子氨 S4 W6S 对氢化物有选择性 S5 W5C 短链烷烃和芳香成分 S6 W1S 烷类 S7 W1W 无机硫化物 S8 W2S 醇类和醛酮类 S9 W2W 芳香成分和有机硫化物 S10 W3S 氨类和芳香成分 1.2.7 气相色谱-离子迁移谱测定
气相色谱-离子迁移谱单元分析条件:分析时间30 min,色谱柱为MXT-WAX(长30 m,内径0.53 mm,膜厚1 μm),柱温60 ℃,载气/漂移气N2,IMS温度45 ℃。自动顶空进样单元分析条件:进样体积200 μL,孵育时间150 min,孵育温度80 ℃,进样针温度85 ℃,孵化转速500 r/min。样品处理:取空白重组米、空白炒米、双孢菇重组米和双孢菇炒米四种样品粉末2 g置于20 mL顶空瓶中,在80 ℃的温度下孵育20 min后进样。使用分析软件VOCal内置的NIST数据库和IMS数据库对物质进行定性分析,用峰面积归一化法确定各种成分的相对含量。利用与FlavourSpec®风味分析仪器配套的分析软件中的VOCal以及内置的Reporter、Gallery Plot、Dynamic PCA三款插件,对样品挥发性物质的数据、图谱和动态主成分进行分析。
1.3 数据处理
响应面试验设计及其数据分析由Design Expert 8.0.6生成。利用Microsoft Excel 2010和IBM SPSS Statistics 25进行数据处理和分析,Origin 2021进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 响应面试验结果
2.1.1 响应面试验设计及结果
根据单因素的实验结果,利用Box-Behnken设计了17组试验,试验结果是以感官得分加质构得分的综合评分为响应值,响应面实验设计及结果如表4所示。
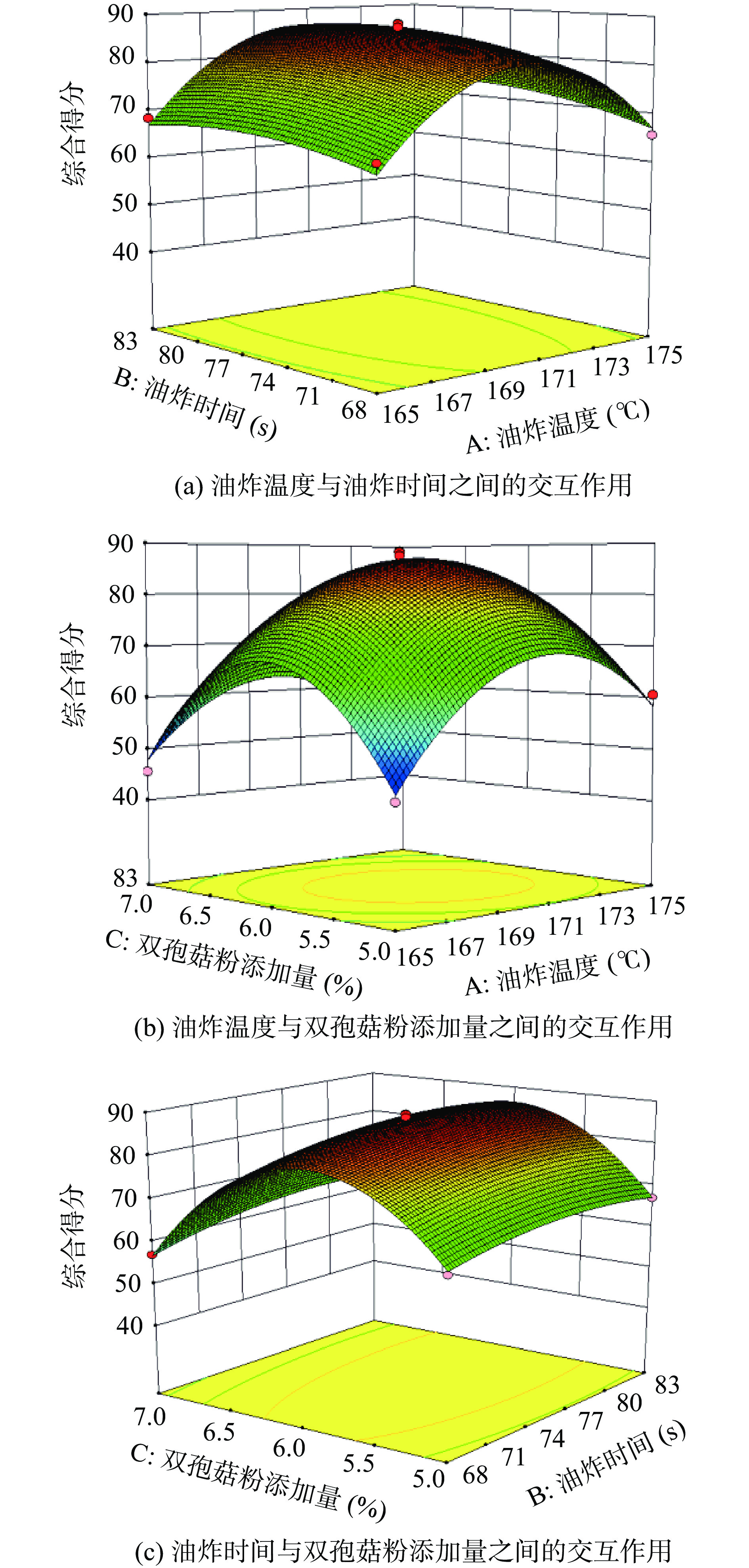
表 4 响应面试验设计及结果Table 4. Response surface design and results实验号 因素 综合评分 A B C 1 1 1 0 70.79 2 1 0 −1 60.63 3 0 0 0 88.31 4 0 0 0 85.62 5 −1 0 −1 45.25 6 0 −1 1 56.99 7 −1 1 0 68.36 8 0 0 0 87.48 9 −1 −1 0 65.92 10 0 0 0 88.13 11 0 1 1 64.40 12 1 0 1 46.65 13 1 −1 0 65.65 14 0 1 −1 67.00 15 0 −1 −1 64.23 16 −1 0 1 45.53 17 0 0 0 84.50 对数据进行回归拟合分析,结果如表5所示。对油炸温度、油炸时间和双孢菇粉添加量三个因素进行回归拟合得到二次回归方程为:Y=86.81+2.33A+2.22B−2.94C+0.67AB−3.56AC+1.16BC−16.39A2−2.74B2−20.91C2。系数的显著性和组合因素的交互作用强度由P值决定,P值越小,越显著。由方差分析可知,P<0.0001显示回归模型极显著,失拟项P>0.05表示不显著,说明模型与实验数据拟合充分。决定系数R2为0.9886,说明模型拟合性好,实验误差小。回归模型的校正决定系数R2adj为0.9740,说明该模型能解释97.40%的响应值变化,证明了模型的有效性。模型方差分析得出油炸温度(A)、油炸时间(B)、双孢菇粉添加量(C)、油炸温度与双孢菇粉添加量交互项(AC)及各因素的二次项对响应值有显著影响。得出影响产品综合得分的因素主次顺序为:C-双孢菇粉添加量>A-油炸温度>B-油炸时间。
表 5 回归模型方差分析表Table 5. Regression model variance analysis table回归项 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 3439.47 9 382.16 67.65 0.0001 ** A-油炸温度 43.52 1 43.52 7.71 0.0275 * B-油炸时间 39.38 1 39.38 6.97 0.0334 * C-双孢菇粉
添加量69.20 1 69.20 12.25 0.0100 * AB 1.81 1 1.81 0.32 0.5890 NS AC 50.80 1 50.80 8.99 0.0200 * BC 5.38 1 5.38 0.95 0.3616 NS A2 1130.41 1 1130.41 200.11 0.0001 ** B2 31.69 1 31.69 5.61 0.0497 * C2 1840.27 1 1840.27 325.78 0.0001 ** 残差 39.54 7 5.65 失拟项 28.36 3 9.45 3.38 0.1349 NS 误差项 11.18 4 2.79 总变异 3479.02 16 R2 0.9886 R2adj 0.9740 注:**差异极显著,P<0.01;*差异显著,P<0.05;NS差异不显著,P>0.05。 油炸温度、油炸时间和双孢菇粉添加量三因素之间相互作用的响应曲面图如图1所示。根据响应曲面图可以直观地反映出两种实验因素交互作用对响应值影响的大小。如果两因素交互作用对响应值影响越大,则响应曲面图越陡峭;如果两因素交互作用对响应值影响不显著,则响应曲面图越平缓。图1a和图1c的响应曲面图较为平缓,表明油炸温度和油炸时间两者交互作用不显著,油炸时间和双孢菇粉添加量两者交互作用不显著。图1b中响应面呈现一定程度的凸起,表明油炸温度与双孢菇粉添加量之间的交互作用显著。
利用Design-Expert 软件对该模型优化求解,对最佳配方预测参数为:油炸温度为170.43 ℃,油炸时间为78.51 s,双孢菇粉添加量为5.93%,综合得分87.45分。根据实际实验的可操作性,将工艺参数修正为:油炸温度为170 ℃,油炸时间为79 s,双孢菇粉添加量为5.90%。
2.1.2 验证实验
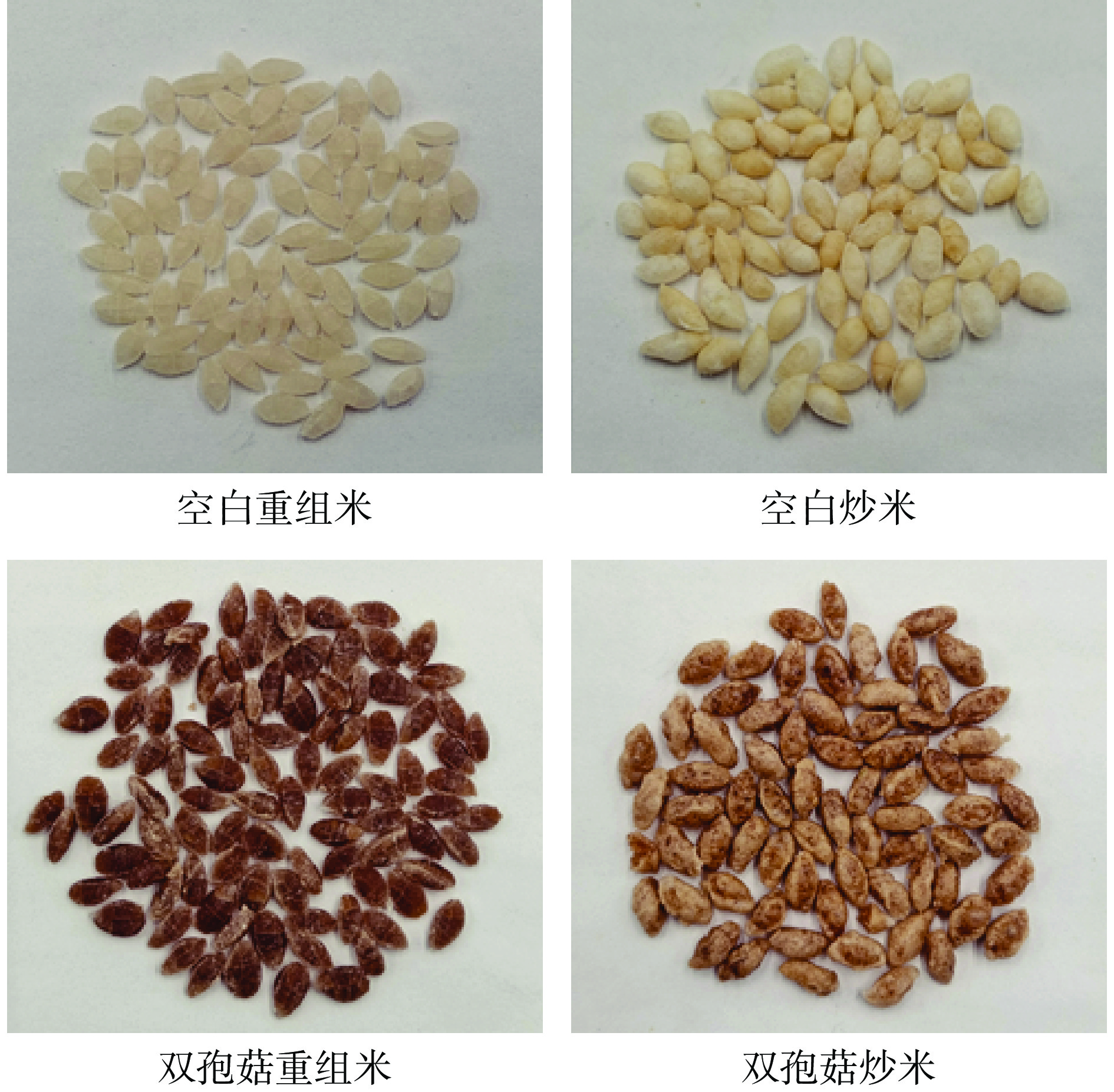
为验证最佳工艺条件的可靠性,根据上述最佳工艺配方重复试验3次进行t检验,三组数据平均值为86.803,标准偏差为0.465,标准误差平均值为0.269。在单个样本检验表中,显示了t统计量、自由度、相伴概率、均值偏差分别为2.409、2、0.138、0.647,t检验的相伴概率为0.138,大于显著性水平0.05,说明这三组数据与检验值差异不显著。优化后的产品对比分析如图2所示,可以看出双孢菇炒米的亮度低于空白炒米,且它的颜色更黄也更红。
2.2 基本组分测定
从表6数据可以看出,与空白炒米相比,双孢菇炒米的蛋白质、脂肪和总膳食纤维含量均显著增加(P<0.05),其中蛋白质含量增加了60.58%,总膳食纤维含量增加了58.29%,这跟双孢菇本身含有丰富的蛋白质和膳食纤维有关,与黄雨露[19]和张钰萌等[20]的研究结果一致。从表中也可以看出,与空白炒米相比,双胞菇炒米的总淀粉含量显著减少(P<0.05),是因为籼米粉中加入了双孢菇粉,使淀粉相对含量减少,该结果与靳羽慧[21]将金针菇粉加入面条的结果相似。综合分析得出,双孢菇粉的加入在一定程度上提高了炒米的营养价值。
表 6 炒米的基本成分表Table 6. Table of basic ingredients of stir-fried rice样品 蛋白质(g/100 g) 脂肪(g/100 g) 总膳食纤维(g/100 g) 总淀粉(g/100 g) 空白炒米 7.630±0.321b 6.909±0.296b 0.784±0.033b 81.779±0.414a 双孢菇炒米 12.252±0.339a 7.639±0.245a 1.241±0.136a 77.530±0.382b 注:同一列数据中不同字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。 2.3 水解氨基酸分析
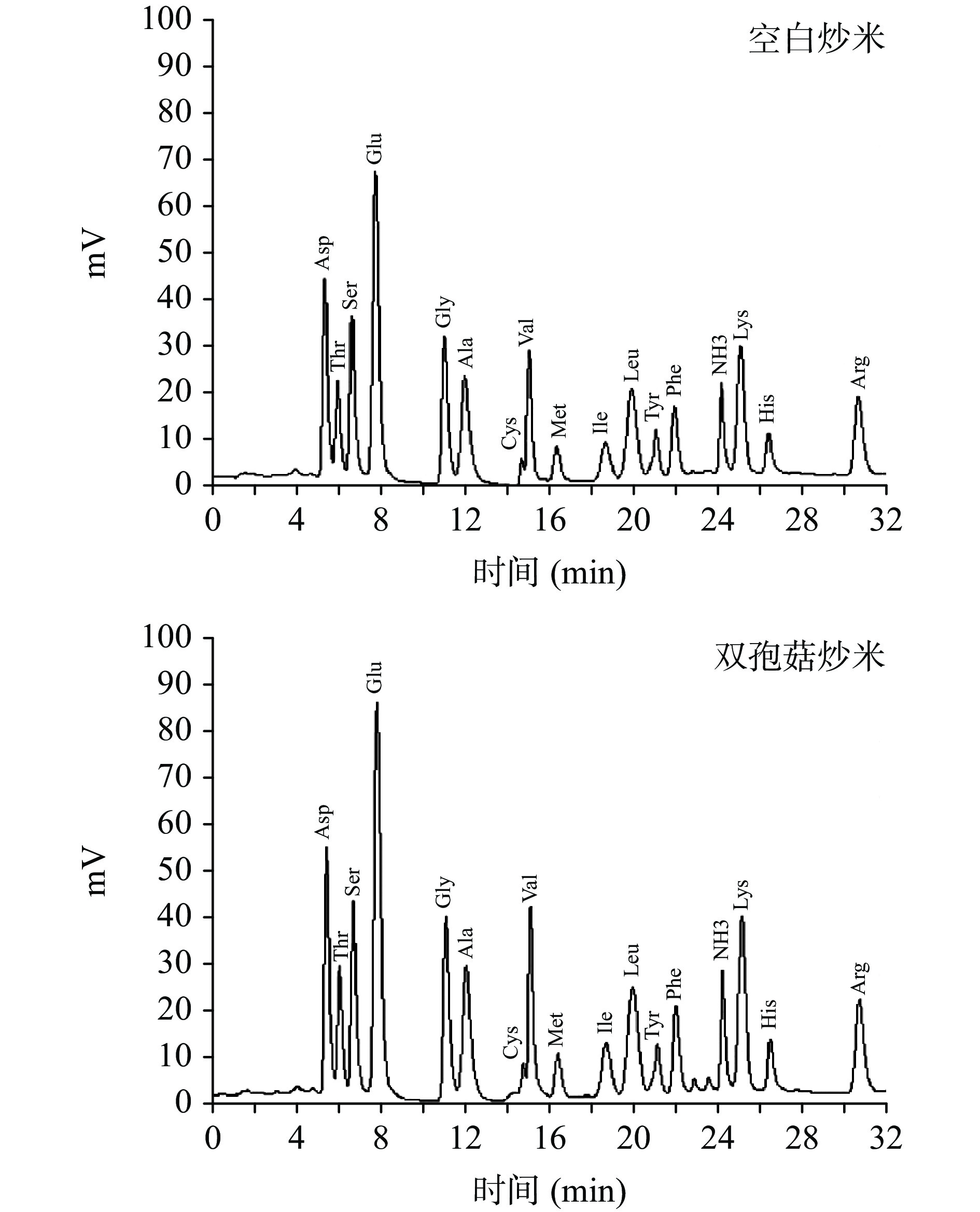
不同炒米的水解氨基酸图谱及含量分别如图3及表7所示,从表7数据可以看出,两种炒米均测得16种氨基酸,包括7种必需氨基酸和9种非必需氨基酸。空白炒米的必需氨基酸含量为31.33±2.07 mg/g,非必需氨基酸含量为40.60±0.21 mg/g,双孢菇炒米的必需氨基酸含量为38.16±6.62 mg/g,非必需氨基酸含量为46.91±4.88 mg/g,可以看出双孢菇炒米的必需氨基酸含量和非必需氨基酸含量均高于空白炒米。在FAO/WHO推荐的理想模式下,氨基酸组成中总必需氨基酸(TEAA)/总氨基酸(TAA)为40%,总必需氨基酸(TEAA)/总非必需氨基酸(TNEAA)达到60%即为优质的蛋白质[22]。两种炒米的EAA/TAA值均在44%左右,EAA/NEAA均在80%左右。
表 7 不同炒米的水解氨基酸含量及比例Table 7. Content and proportion of hydrolyzed amino acids in different stir-fried rice氨基酸名称 空白炒米 双孢菇炒米 含量
(mg/g)占总氨基酸
的质量分数(%)含量
(mg/g)占总氨基酸
的质量分数(%)*苏氨酸(Thr) 2.55±0.01 3.55 3.11±0.34 3.67 *缬氨酸(Val) 3.35±0.03 4.66 4.58±0.72 5.38 *蛋氨酸(Met) 1.55±0.04 2.15 1.56±0.23 1.84 *异亮氨酸(Ile) 2.11±0.05 2.94 2.66±0.52 3.11 *亮氨酸(Leu) 5.42±0.11 7.54 6.11±0.80 7.18 *苯丙氨酸(Phe) 3.65±0.20 5.07 4.22±0.47 4.97 *赖氨酸(Lys) 12.69±1.64 17.62 15.91±3.54 18.60 必需氨基酸
EAA31.33±2.07 43.53 38.16±6.62 44.74 丝氨酸(Ser) 3.78±0.01 5.26 4.20±0.39 4.95 谷氨酸(Glu) 13.03±0.14 18.13 15.31±1.76 18.02 甘氨酸(Gly) 2.93±0.01 4.07 3.39±0.39 4.00 丙氨酸(Ala) 4.15±0.06 5.77 4.78±0.49 5.63 半胱氨酸(Cys) 1.00±0.08 1.39 1.53±0.03 1.81 酪氨酸(Tyr) 2.74±0.17 3.81 2.87±0.22 3.39 天冬氨酸(Asp) 6.14±0.04 8.53 7.04±0.72 8.29 组氨酸(His) 1.66±0.25 2.30 2.08±0.21 2.45 精氨酸(Arg) 5.19±0.01 7.22 5.71±0.67 6.72 非必需氨基酸NEAA 40.60±0.21 56.47 46.91±4.88 55.26 总氨基酸TAA 71.94±2.21 100.00 85.07±11.50 100.00 注:*代表必需氨基酸。 2.4 游离氨基酸分析
食品中含有两种氨基酸,一是作为蛋白质基本结构的水解氨基酸,另一部分是处于游离状态的氨基酸。由于水解氨基酸在食用过程中并不能立即水解,因此游离氨基酸的组成与含量对食品滋味的贡献更大[23]。从表8可知,空白炒米中的风味氨基酸含量甚微,总量仅为62.64±2.19 mg/100 g,含量最大的Pro也仅为11.78±0.40 mg/100 g,而双孢菇炒米中风味氨基酸含量则相对较高,总量为219.401±2.45 mg/100 g。由于不同氨基酸的味觉阈值不同,含量高的风味氨基酸并非一定对食品的风味贡献大,从含量阈值比(RCT)的计算结果来看,谷氨酸对双孢菇炒米风味的影响最大,其次是天冬氨酸和精氨酸。而精氨酸为苦味氨基酸,谷氨酸和天冬氨酸则可呈现鲜味,3种游离氨基酸是形成双孢菇炒米独特风味的原因之一。空白炒米中仅天冬氨酸影响其风味,使其呈现出鲜味。在各风味氨基酸中,每种样品的鲜味、甜味氨基酸含量总和与苦味氨基酸相比,差值越高,鲜味越浓[24]。双孢菇炒米的鲜味、甜味氨基酸与苦味氨基酸差值为125.31 mg/100 g,远大于空白炒米,说明双孢菇粉的添加可以很好地改善炒米的风味。
表 8 不同炒米中各种风味氨基酸的含量及RCTTable 8. Contents and RCT of flavor amino acids in different stir-fried rice氨基酸名称 味觉阈值 空白炒米 双孢菇炒米 含量
(mg/100 g)RCT 含量
(mg/100 g)RCT 天冬氨酸(Asp)a 3.00 6.50±0.14 2.17 18.95±0.01 6.32 谷氨酸(Glu)a 5.00 1.99±0.01 0.40 45.90±0.40 9.18 赖氨酸(Lys)a 50.00 0.60±0.01 0.01 3.68±0.04 0.07 鲜味氨基酸
总和8.99±0.01 68.54±0.35 苏氨酸(Thr)b 260.00 0.82±0.12 0.00 5.43±0.03 0.02 丝氨酸(Ser)b 150.00 2.01±0.46 0.01 11.28±0.39 0.08 甘氨酸(Gly)b 110.00 5.46±0.09 0.05 9.98±0.16 0.09 丙氨酸(Ala)b 60.00 7.84±0.25 0.13 33.61±0.07 0.56 组氨酸(His)b 20.00 0.01±0.01 0.00 1.52±0.04 0.08 脯氨酸(Pro)b 300.00 11.78±0.40 0.04 40.01±2.95 0.13 甜味氨基酸
总和27.93±1.31 101.83±2.27 亮氨酸(Leu)c 380.00 0.64±0.07 0.00 3.47±0.03 0.01 异亮氨酸(Ile)c 90.00 − 0.00 1.62±0.03 0.02 缬氨酸(Val)c 150.00 11.21±0.44 0.07 14.57±0.36 0.10 精氨酸(Arg)c 10.00 7.50±0.14 0.75 18.79±0.04 1.88 蛋氨酸(Met)c 30.00 2.72±0.08 0.09 2.57±0.03 0.09 鸟氨酸(Orn)c 20.00 0.33±0.13 0.02 4.03±0.03 0.20 苦味氨基酸
总和22.40±0.58 45.06±0.45 苯丙氨酸(Phe)d 150.00 0.00±0.00 0.00 0.53±0.02 0.00 酪氨酸(Tyr)d 260.00 2.27±0.08 0.01 3.25±0.01 0.01 半胱氨酸(Cys)d 2.00 0.93±0.05 0.47 0.19±0.27 0.10 芳香族氨基酸总和 3.20±0.14 3.97±0.29 鲜味、甜味氨基酸与
苦味氨基酸差值14.51±0.73 125.32±3.07 总量 62.64±2.19 219.40±2.45 注:a.鲜味氨基酸;b.甜味氨基酸;c.苦味氨基酸;d.芳香族氨基酸。 2.5 电子鼻分析
由图4可以看出,四种样品挥发性气味在W1W、W2W、W2S和W5S传感器的响应值较高。W1W、W2W、W2S和W5S所敏感的香气种类分别为无机硫化物、芳香成分和有机硫化物、醇类和醛酮类、氮氧化合物[25]。两种炒米与对应的重组米相比,炒米对W1C、W3C和W5C传感器响应值较高,对W5S、W2W、W2S、W1W和W1S的响应值均弱于重组米,雷达图中的总峰面积减小。结果表明,重组米经过高温短时油炸后,炒米的挥发性风味物质与重组米具有一定差异。
由图5可以看出,主成分1的贡献率为91.10%,主成分2的贡献率为6.65%,总成分贡献率97.75%,大于85.00%,说明该结果能够准确反映出样品的主要信息,可很好地表征各样品间的差异性。图中四种样品挥发性气味的区域无重叠现象,说明电子鼻可以有效地区分四种样品。
采用变量投影重要性分析值(variable importance in project,VIP)筛选能够表征四种样品差异性的标志物,其中VIP值大于1的成分是体现样品间差异的主要标志性成分,而VIP值小于1的成分对样品的区分影响较小[26]。VIP结果见表9,筛选得到2个VIP值大于1的物质,W3S(对氨类和芳香成分灵敏)和W6S(主要对氢化物有选择性)[25]。
表 9 挥发性物质的变量投影重要性分析值Table 9. Variable projection importance analysis value of volatile substances挥发性物质 VIP W3S 1.43667 W6S 1.43079 W1C 0.88233 W1W 0.86803 W2S 0.86572 W2W 0.86026 W5C 0.84872 W1S 0.84744 W5S 0.84583 W3C 0.84464 2.6 气相色谱-离子迁移谱分析
按照制备双孢菇炒米的最优配方和工艺,以无添加双孢菇粉的重组米和炒米作为对照,探究双孢菇炒米挥发性风味物质的变化规律。将四种样品利用气相色谱-离子迁移谱(GC-IMS)进行挥发性风味物质分析。
图6是对四种样品GC-IMS的二维谱图,图中横坐标表示漂移时间,纵坐标表示保留时间,红色垂直线表示反应离子峰(reaction ion peak,RIP),离子峰右侧的斑点代表不同的挥发性有机物质,颜色越红表示这种风味物质含量越高[27]。从图中可以看出挥发性物质主要集中在0~400 s的保留时间和0~10 s的漂移时间之间,且挥发性物质在这段保留时间内变化明显。
差异图能更加明显比较样品间风味物质的差异性,如图7所示。选择空白重组米的谱图作为参比,如果其余三个样品与空白重组米的挥发性物质一致,则扣减后的背景为白色,若该物质的浓度高于参比则为红色,该物质的浓度低于参比则为蓝色,且颜色越深,差异性越明显[28]。从图7中可以看出,红色部分比较多,说明双孢菇粉的加入,重组米和炒米的特征风味物质发生了很大变化,风味更加丰富。
为进一步直观分析四种样品的风味物质的差异性,运用Gallery Plot插件生成样品的挥发性物质指纹图谱,如图8所示。指纹图谱的每一行代表同一样品中的不同物质,每一列代表不同样品中相同的挥发性物质。且图中的亮点颜色越红,代表该物质浓度越高。一种化合物可能会在同一水平上产生1~2个斑点,这分别代表此物质的单体(-M)和二聚体(-D)[29]。
结合图8和表10可以得出四种样品共分离鉴定出53种挥发性风味物质,包括醛类16种、醇类7种、酮类10种、酯类13种、酸类1种、呋喃类3种和3种其他化合物。
表 10 不同米样挥发性风味物质分析Table 10. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds in different rice samples类别 化合物名称 CAS号 分子式 分子量 保留
指数保留时
间(s)迁移时
间(ms)相对含量(%) 英文 中文 空白
重组米空白
炒米双孢菇
重组米双孢
菇炒米醛类 (E)-2-Heptenal (E)-2-庚烯醛 C18829555 C7H12O 112.2 1330.5 689 1.2585 0.15 0.18 0.15 0.19 (E)-2-Hexenal 2-已烯醛 C6728263 C6H10O 98.1 1228.3 515.183 1.1824 0.35 0.33 0.29 0.35 heptanal 庚醛 C111717 C7H14O 114.2 1194.8 470.802 1.3368 0.59 0.49 0.77 0.55 (E)-2-Pentenal-M 反式-2-戊烯醛 C1576870 C5H8O 84.1 1144.4 412.687 1.1073 2.73 1.81 2.30 1.36 (E)-2-Pentenal-D 反式-2-戊烯醛二聚体 C1576870 C5H8O 84.1 1143.6 411.878 1.3616 0.47 1.77 0.32 1.52 Hexanal-M 正己醛 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 1101.1 368.677 1.2617 2.29 2.00 1.92 1.77 Hexanal-D 正己醛二聚体 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 1100.9 368.435 1.5633 5.89 5.47 4.92 4.95 Pentanal-M 正戊醛 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 999.3 295.573 1.1923 1.87 1.78 1.66 1.56 Pentanal-D 正戊醛二聚体 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 998.8 295.275 1.4224 4.08 4.17 4.51 3.81 2-methylbutanal-M 2-甲基丁醛 C96173 C5H10O 86.1 923.6 260.536 1.1651 1.20 0.73 1.18 1.09 2-Methylbutanal-D 2-甲基丁醛二聚体 C96173 C5H10O 86.1 926.3 261.694 1.4009 1.56 0.89 4.46 3.57 3-Methylbutanal 异戊醛 C590863 C5H10O 86.1 932.6 264.396 1.1781 0.70 0.28 0.42 0.50 Butanal-M 正丁醛 C123728 C4H8O 72.1 889.4 246.253 1.1243 1.78 1.82 1.74 1.67 Propionaldehyde-M 丙醛 C123386 C3H6O 58.1 827.7 222.47 1.0696 2.77 2.16 2.45 1.84 Propanal-D 丙醛二聚体 C123386 C3H6O 58.1 827.7 222.47 1.1445 7.21 7.68 6.17 6.87 2-Methylpentanal 2-甲基戊醛 C123159 C6H12O 100.2 754.6 197.259 1.2299 2.81 2.20 2.21 2.50 总和 36.45 33.76 35.47 34.10 醇类 Ethanol 乙醇 C64175 C2H6O 46.1 941 268.088 1.138 4.41 3.92 3.67 3.39 1-Pentanol 1-戊醇 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 1261.9 563.859 1.2563 0.19 0.07 0.33 0.07 1-Pentanol-D 1-戊醇二聚体 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 1262.2 564.337 1.5159 1.31 0.71 1.50 0.62 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol 3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇 C763326 C5H10O 86.1 1271.5 578.653 1.1788 0.04 0.14 0.04 0.12 Butan-1-ol-M 叔丁醇 C71363 C4H10O 74.1 1154.3 423.5 1.1824 2.58 2.19 2.21 1.95 Butan-1-ol-D 叔丁醇二聚体 C71363 C4H10O 74.1 1154.1 423.224 1.3826 2.76 2.36 2.05 2.03 1-Propanol 正丙醇 C71238 C3H8O 60.1 1051.7 330.863 1.1113 0.74 0.64 0.61 0.63 总和 12.03 10.03 10.41 8.81 酮类 Propan-2-one 丙酮 C67641 C3H6O 58.1 844.8 228.83 1.1147 10.36 8.40 8.11 7.39 Butan-2-one-M 2-丁酮 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 915.5 257.062 1.0605 1.45 1.12 1.49 1.21 Butanone-D 2-丁酮二聚体 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 914.3 256.579 1.2473 1.91 1.89 2.26 2.36 3-hydroxybutan-2-one (acetoin) 3-羟基-2-丁酮 C513860 C4H8O2 88.1 1296.5 619.443 1.0655 0.57 0.34 0.43 0.37 heptan-2-one 2-庚酮 C110430 C7H14O 114.2 1187.1 461.257 1.2658 0.33 0.24 0.44 0.33 2,3-pentanedione 2,3-戊二酮 C600146 C5H8O2 100.1 1076.9 349.257 1.2357 0.16 0.97 0.11 0.81 1-hydroxypropan-2-one-M 羟基丙酮 C116096 C3H6O2 74.1 1310.9 647.936 1.0617 0.16 1.02 0.12 1.61 1-hydroxypropan-2-one-D 羟基丙酮二聚体 C116096 C3H6O2 74.1 1310.1 646.26 1.2325 0.03 0.10 0.03 0.29 1-Penten-3-one-M 1-戊烯-3-酮 C1629589 C5H8O 84.1 1040.3 322.822 1.0788 0.13 0.88 0.05 0.75 1-Penten-3-one-D 1-戊烯-3-酮二聚体 C1629589 C5H8O 84.1 1039.8 322.525 1.3117 0.03 0.39 0.05 0.36 总和 15.13 15.35 13.09 15.48 酯类 Ethyl acetate-M 乙酸乙酯 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 892 247.315 1.0977 1.38 1.03 0.86 0.90 Ethyl acetate-D 乙酸乙酯二聚体 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 895.8 248.859 1.3359 9.33 8.12 7.96 7.37 Ethyl hexanoate 正己酸乙酯 C123660 C8H16O2 144.2 1244.1 537.612 1.3441 0.85 0.28 0.22 0.18 butyl acetate-M 乙酸丁酯 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 1089 358.482 1.2381 1.80 1.79 1.95 1.81 butyl acetate-D 乙酸丁酯二聚体 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 1088.3 357.996 1.6184 0.65 1.07 1.13 1.69 Isoamyl acetate-M 乙酸异戊酯 C123922 C7H14O2 130.2 1133.3 400.964 1.3058 0.62 0.73 0.57 0.66 Isoamyl acetate-D 乙酸异戊酯二聚体 C123922 C7H14O2 130.2 1133.6 401.206 1.7484 0.05 0.36 0.04 0.23 2-methylbutyl acetate 2-甲基丁基乙酸酯 C624419 C7H14O2 130.2 1153.1 422.123 1.3191 0.53 0.48 0.43 0.40 Butyl propionate-M 丙酸丁酯 C590012 C7H14O2 130.2 1149.4 418.165 1.286 0.23 0.24 0.33 0.36 Butyl propionate-D 丙酸丁酯二聚体 C590012 C7H14O2 130.2 1150.7 419.546 1.7225 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.12 Ethyl butanoate-M 丁酸乙酯 C105544 C6H12O2 116.2 1051.3 330.565 1.2083 0.45 0.84 0.32 0.80 Ethyl butanoate-D 丁酸乙酯二聚体 C105544 C6H12O2 116.2 1051.1 330.417 1.5598 0.06 0.27 0.04 0.29 Isobutyl butanoate 丁酸异丁酯 C539902 C8H16O2 144.2 1138.2 406.062 1.3247 3.36 3.28 3.07 3.20 总和 19.38 18.56 17.00 18.01 2-Ethylfuran 2-乙基呋喃 C3208160 C6H8O 96.1 971.3 281.821 1.3213 0.15 1.02 0.28 1.05 呋喃类 Tetrahydrofuran-M 四氢呋喃 C109999 C4H8O 72.1 881.2 242.975 1.0633 0.54 0.88 0.46 0.69 Tetrahydrofuran-D 四氢呋喃二聚体 C109999 C4H8O 72.1 881 242.869 1.2276 0.12 0.37 0.09 0.24 总和 0.81 2.27 0.83 1.98 酸类 Acetic acid 乙酸 C-4197 C2H4O2 60.1 1484.4 1116.398 1.0571 2.03 1.45 1.65 1.29 其他 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine 2,5-二甲基吡嗪 C123320 C6H8N2 108.1 1346.7 725.035 1.1074 0.04 0.11 0.02 0.15 1,2-Dimethoxyethane-M 乙二醇二甲醚 C110714 C4H10O2 90.1 912.5 255.807 1.1054 1.50 1.56 1.57 1.33 1,2-Dimethoxyethane-D 乙二醇二甲醚二聚体 C110714 C4H10O2 90.1 913.6 256.29 1.2898 1.49 1.67 1.41 1.89 通过图8可以看出,图中红色框中,空白炒米和双孢菇炒米中含有的(E)-2-庚烯醛、反式-2-戊烯醛二聚体、2,5-二甲基吡嗪、乙酸异戊酯、乙酸异戊酯二聚体、2,3-戊二酮、1-戊烯-3-酮、1-戊烯-3-酮二聚体、2-乙基呋喃、3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇、丁酸乙酯、丁酸乙酯二聚体、四氢呋喃、四氢呋喃二聚体等风味物质的含量较高。图中黄色框中,空白重组米和双孢菇重组米中含有的2-甲基丁醛、2-甲基丁醛二聚体、1-戊醇、正庚醛、2-庚酮等风味物质的含量较高。此外,(E)-2-庚烯醛、2-已烯醛、2-甲基戊醛、乙醇、叔丁醇、正丙醇、2-丁酮、3-羟基-2-丁酮、乙酸丁酯、2-甲基丁基乙酸酯、乙二醇二甲醚等风味物质在四种样品中均存在,且相对含量无较大差别。
醛类是四种样品中含量最高的风味物质,主要来源于乳脂肪氧化反应,由于风味阈值比较低[30−31],风味特征明显。四种样品中丙醛及其二聚体的相对含量较高,占总峰面积的8.62%~9.98%,赋予产品青香[32]。与重组米相比,两种炒米的反式-2-戊烯醛二聚体相对含量较高,赋予炒米坚果香气[33]。双孢菇重组米和双孢菇炒米中2-甲基丁醛二聚体的相对含量分别为4.46%和3.57%,赋予产品咖啡和微甜的水果香味[34]。
酯类为食品提供花香、果香等香气[35],是四种样品中含量第二高的挥发性风味物质。在检测到的酯类化合物中,四种样品中乙酸乙酯及其二聚体的相对含量较高,占总峰面积的8.27%~10.71%,赋予产品菠萝的香气[36]。与重组米相比,两种炒米的丁酸乙酯及其二聚体的相对含量较高,赋予炒米凤梨香和果香[33]。双孢菇炒米中乙酸丁酯二聚体的相对含量为1.69%,赋予炒米香蕉和水果香[32];丙酸丁酯及其二聚体的相对含量为0.48%,赋予炒米苹果香[33],高于其它三种样品。
酮类是食品中重要的挥发性风味物质,且双孢菇炒米的酮类物质相对含量大于其它三种样品。其中,双孢菇炒米挥发性物质中2-丁酮二聚体的相对含量较高,达到2.36%,赋予双孢菇炒米果香味[37]。与重组米相比,两种炒米的2,3-戊二酮、羟基丙酮及其二聚体和1-戊烯-3-酮及其二聚体的相对含量较高,分别赋予炒米果香和辛辣气味[38]。在检测到的酮类化合物中,四种样品中丙酮的相对含量较高,占总峰面积的7.39%~10.36%,赋予产品微绿焦糖的香味[32]。
醇类化合物共检测到7种,与醛类、酯类等物质相比,相对含量较低,四种样品醇类化合物的相对含量在8.81%~12.03%之间。适当浓度的醇类化合物能起到衬托酯香的作用,提高协调性[38]。与重组米相比,两种炒米的3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇相对含量较高,赋予炒米甜果香[36]。
呋喃类化合物常见于焙烤类食品的香味成分中,提供了一种特殊的香味,在空白炒米和双孢菇炒米中占比较大,其中2-乙基呋喃的相对含量分别达到了1.02%和1.05%,其中四氢呋喃及其二聚体和2-乙基呋喃均具有豆香、果香及类似蔬菜的香韵,2-乙基呋喃还具有面包、麦芽的焦香香气[39]。
酸类化合物在食品中会降低产品总体的香气品质[40]。从表10可以看出,空白炒米和双孢菇炒米乙酸的相对含量低于空白重组米和双孢菇重组米,且双孢菇炒米酸类化合物的相对含量仅有1.29%,表明样品经油炸处理后,其酸类物质含量有效降低。
综上所述,四种样品的主要香气成分来源于醛类、酯类、醇类、酮类、醇类、和呋喃类等成分,在风味中起着重要的调和、协同或互补的作用。
主成分分析法(PCA)是一种多变量统计方法,可以检查多个变量的相关性。从图9可以看出,这4个样品的分布区域不同且互不重叠,说明四种样品的挥发性风味物质存在明显差异,其中空白炒米和双胞菇炒米两个样品的相似度相对较高且与空白重组米和双孢菇重组米的差异较大。PC1的主成分贡献率为59%,PC2主成分贡献率为28%,总贡献率为87%,超过了85%,说明能很好地反应原始数据的信息。
3. 结论
本研究通过响应面试验获得了双孢菇炒米的最佳工艺配方:油炸温度170 ℃,油炸时间79 s,双孢菇粉添加量5.90%。添加双孢菇粉后,双孢菇炒米总淀粉含量显著下降(P<0.05),而蛋白质、脂肪和膳食纤维含量均显著上升(P<0.05)。通过对炒米水解氨基酸和游离氨基酸的测定,表明双孢菇炒米的氨基酸总量提高,且谷氨酸、天冬氨酸和精氨酸是形成双孢菇炒米独特风味的原因之一。使用电子鼻和气相色谱-离子迁移谱分析空白重组米、空白炒米、双孢菇重组米和双孢菇炒米的香气特征,加入双孢菇粉后,炒米风味得到丰富,酮类、酯类和呋喃类物质的相对含量增加。本研究在挤压造粒的基础上添加了双孢菇粉,通过油炸处理的方式开发了一款营养丰富且风味独特的双孢菇炒米,为开发炒米类休闲食品提供重要的参考价值。
-
表 1 响应面试验设计表
Table 1 Response surface test design table
因素 符号 水平 −1 0 1 油炸温度(℃) A 165 170 175 油炸时间(s) B 68 75 82 双孢菇粉添加量(%) C 5 6 7 表 2 炒米感官评价标准
Table 2 Sensory evaluation criteria for stir-fried rice
评价指标 评分标准 得分(分) 饱满完整,没有褐变,膨化度好 21~25 外观形态(25分) 较光滑饱满,有点碎米粒,稍有褐变,
膨化度较好16~20 碎米粒较多,褐变严重,未膨化 0~15 色泽均匀一致,光泽好 21~25 色泽(25分) 光泽较差,边缘略有褐色 16~20 色泽发黑,光泽差 0~15 油炸香味浓郁,有双孢菇特有的香味,无异味 21~25 香味(25分) 没有明显的油炸食品的香味,双孢菇香味略淡 16~20 没有香味甚至带有糊味 0~15 硬脆度适中,口感酥脆,咀嚼感好 21~25 口感(25分) 偏硬或偏脆,咀嚼感一般 16~20 口感过硬,咀嚼感差 0~15 表 3 PEN3电子鼻传感器敏感物质
Table 3 Substances for sensing of PEN3 electronic nose sensor
编号 传感器 敏感物质 S1 W1C 芳烃化合物 S2 W5S 氮氧化合物 S3 W3C 芳香分子氨 S4 W6S 对氢化物有选择性 S5 W5C 短链烷烃和芳香成分 S6 W1S 烷类 S7 W1W 无机硫化物 S8 W2S 醇类和醛酮类 S9 W2W 芳香成分和有机硫化物 S10 W3S 氨类和芳香成分 表 4 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 4 Response surface design and results
实验号 因素 综合评分 A B C 1 1 1 0 70.79 2 1 0 −1 60.63 3 0 0 0 88.31 4 0 0 0 85.62 5 −1 0 −1 45.25 6 0 −1 1 56.99 7 −1 1 0 68.36 8 0 0 0 87.48 9 −1 −1 0 65.92 10 0 0 0 88.13 11 0 1 1 64.40 12 1 0 1 46.65 13 1 −1 0 65.65 14 0 1 −1 67.00 15 0 −1 −1 64.23 16 −1 0 1 45.53 17 0 0 0 84.50 表 5 回归模型方差分析表
Table 5 Regression model variance analysis table
回归项 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 3439.47 9 382.16 67.65 0.0001 ** A-油炸温度 43.52 1 43.52 7.71 0.0275 * B-油炸时间 39.38 1 39.38 6.97 0.0334 * C-双孢菇粉
添加量69.20 1 69.20 12.25 0.0100 * AB 1.81 1 1.81 0.32 0.5890 NS AC 50.80 1 50.80 8.99 0.0200 * BC 5.38 1 5.38 0.95 0.3616 NS A2 1130.41 1 1130.41 200.11 0.0001 ** B2 31.69 1 31.69 5.61 0.0497 * C2 1840.27 1 1840.27 325.78 0.0001 ** 残差 39.54 7 5.65 失拟项 28.36 3 9.45 3.38 0.1349 NS 误差项 11.18 4 2.79 总变异 3479.02 16 R2 0.9886 R2adj 0.9740 注:**差异极显著,P<0.01;*差异显著,P<0.05;NS差异不显著,P>0.05。 表 6 炒米的基本成分表
Table 6 Table of basic ingredients of stir-fried rice
样品 蛋白质(g/100 g) 脂肪(g/100 g) 总膳食纤维(g/100 g) 总淀粉(g/100 g) 空白炒米 7.630±0.321b 6.909±0.296b 0.784±0.033b 81.779±0.414a 双孢菇炒米 12.252±0.339a 7.639±0.245a 1.241±0.136a 77.530±0.382b 注:同一列数据中不同字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。 表 7 不同炒米的水解氨基酸含量及比例
Table 7 Content and proportion of hydrolyzed amino acids in different stir-fried rice
氨基酸名称 空白炒米 双孢菇炒米 含量
(mg/g)占总氨基酸
的质量分数(%)含量
(mg/g)占总氨基酸
的质量分数(%)*苏氨酸(Thr) 2.55±0.01 3.55 3.11±0.34 3.67 *缬氨酸(Val) 3.35±0.03 4.66 4.58±0.72 5.38 *蛋氨酸(Met) 1.55±0.04 2.15 1.56±0.23 1.84 *异亮氨酸(Ile) 2.11±0.05 2.94 2.66±0.52 3.11 *亮氨酸(Leu) 5.42±0.11 7.54 6.11±0.80 7.18 *苯丙氨酸(Phe) 3.65±0.20 5.07 4.22±0.47 4.97 *赖氨酸(Lys) 12.69±1.64 17.62 15.91±3.54 18.60 必需氨基酸
EAA31.33±2.07 43.53 38.16±6.62 44.74 丝氨酸(Ser) 3.78±0.01 5.26 4.20±0.39 4.95 谷氨酸(Glu) 13.03±0.14 18.13 15.31±1.76 18.02 甘氨酸(Gly) 2.93±0.01 4.07 3.39±0.39 4.00 丙氨酸(Ala) 4.15±0.06 5.77 4.78±0.49 5.63 半胱氨酸(Cys) 1.00±0.08 1.39 1.53±0.03 1.81 酪氨酸(Tyr) 2.74±0.17 3.81 2.87±0.22 3.39 天冬氨酸(Asp) 6.14±0.04 8.53 7.04±0.72 8.29 组氨酸(His) 1.66±0.25 2.30 2.08±0.21 2.45 精氨酸(Arg) 5.19±0.01 7.22 5.71±0.67 6.72 非必需氨基酸NEAA 40.60±0.21 56.47 46.91±4.88 55.26 总氨基酸TAA 71.94±2.21 100.00 85.07±11.50 100.00 注:*代表必需氨基酸。 表 8 不同炒米中各种风味氨基酸的含量及RCT
Table 8 Contents and RCT of flavor amino acids in different stir-fried rice
氨基酸名称 味觉阈值 空白炒米 双孢菇炒米 含量
(mg/100 g)RCT 含量
(mg/100 g)RCT 天冬氨酸(Asp)a 3.00 6.50±0.14 2.17 18.95±0.01 6.32 谷氨酸(Glu)a 5.00 1.99±0.01 0.40 45.90±0.40 9.18 赖氨酸(Lys)a 50.00 0.60±0.01 0.01 3.68±0.04 0.07 鲜味氨基酸
总和8.99±0.01 68.54±0.35 苏氨酸(Thr)b 260.00 0.82±0.12 0.00 5.43±0.03 0.02 丝氨酸(Ser)b 150.00 2.01±0.46 0.01 11.28±0.39 0.08 甘氨酸(Gly)b 110.00 5.46±0.09 0.05 9.98±0.16 0.09 丙氨酸(Ala)b 60.00 7.84±0.25 0.13 33.61±0.07 0.56 组氨酸(His)b 20.00 0.01±0.01 0.00 1.52±0.04 0.08 脯氨酸(Pro)b 300.00 11.78±0.40 0.04 40.01±2.95 0.13 甜味氨基酸
总和27.93±1.31 101.83±2.27 亮氨酸(Leu)c 380.00 0.64±0.07 0.00 3.47±0.03 0.01 异亮氨酸(Ile)c 90.00 − 0.00 1.62±0.03 0.02 缬氨酸(Val)c 150.00 11.21±0.44 0.07 14.57±0.36 0.10 精氨酸(Arg)c 10.00 7.50±0.14 0.75 18.79±0.04 1.88 蛋氨酸(Met)c 30.00 2.72±0.08 0.09 2.57±0.03 0.09 鸟氨酸(Orn)c 20.00 0.33±0.13 0.02 4.03±0.03 0.20 苦味氨基酸
总和22.40±0.58 45.06±0.45 苯丙氨酸(Phe)d 150.00 0.00±0.00 0.00 0.53±0.02 0.00 酪氨酸(Tyr)d 260.00 2.27±0.08 0.01 3.25±0.01 0.01 半胱氨酸(Cys)d 2.00 0.93±0.05 0.47 0.19±0.27 0.10 芳香族氨基酸总和 3.20±0.14 3.97±0.29 鲜味、甜味氨基酸与
苦味氨基酸差值14.51±0.73 125.32±3.07 总量 62.64±2.19 219.40±2.45 注:a.鲜味氨基酸;b.甜味氨基酸;c.苦味氨基酸;d.芳香族氨基酸。 表 9 挥发性物质的变量投影重要性分析值
Table 9 Variable projection importance analysis value of volatile substances
挥发性物质 VIP W3S 1.43667 W6S 1.43079 W1C 0.88233 W1W 0.86803 W2S 0.86572 W2W 0.86026 W5C 0.84872 W1S 0.84744 W5S 0.84583 W3C 0.84464 表 10 不同米样挥发性风味物质分析
Table 10 Analysis of volatile flavor compounds in different rice samples
类别 化合物名称 CAS号 分子式 分子量 保留
指数保留时
间(s)迁移时
间(ms)相对含量(%) 英文 中文 空白
重组米空白
炒米双孢菇
重组米双孢
菇炒米醛类 (E)-2-Heptenal (E)-2-庚烯醛 C18829555 C7H12O 112.2 1330.5 689 1.2585 0.15 0.18 0.15 0.19 (E)-2-Hexenal 2-已烯醛 C6728263 C6H10O 98.1 1228.3 515.183 1.1824 0.35 0.33 0.29 0.35 heptanal 庚醛 C111717 C7H14O 114.2 1194.8 470.802 1.3368 0.59 0.49 0.77 0.55 (E)-2-Pentenal-M 反式-2-戊烯醛 C1576870 C5H8O 84.1 1144.4 412.687 1.1073 2.73 1.81 2.30 1.36 (E)-2-Pentenal-D 反式-2-戊烯醛二聚体 C1576870 C5H8O 84.1 1143.6 411.878 1.3616 0.47 1.77 0.32 1.52 Hexanal-M 正己醛 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 1101.1 368.677 1.2617 2.29 2.00 1.92 1.77 Hexanal-D 正己醛二聚体 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 1100.9 368.435 1.5633 5.89 5.47 4.92 4.95 Pentanal-M 正戊醛 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 999.3 295.573 1.1923 1.87 1.78 1.66 1.56 Pentanal-D 正戊醛二聚体 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 998.8 295.275 1.4224 4.08 4.17 4.51 3.81 2-methylbutanal-M 2-甲基丁醛 C96173 C5H10O 86.1 923.6 260.536 1.1651 1.20 0.73 1.18 1.09 2-Methylbutanal-D 2-甲基丁醛二聚体 C96173 C5H10O 86.1 926.3 261.694 1.4009 1.56 0.89 4.46 3.57 3-Methylbutanal 异戊醛 C590863 C5H10O 86.1 932.6 264.396 1.1781 0.70 0.28 0.42 0.50 Butanal-M 正丁醛 C123728 C4H8O 72.1 889.4 246.253 1.1243 1.78 1.82 1.74 1.67 Propionaldehyde-M 丙醛 C123386 C3H6O 58.1 827.7 222.47 1.0696 2.77 2.16 2.45 1.84 Propanal-D 丙醛二聚体 C123386 C3H6O 58.1 827.7 222.47 1.1445 7.21 7.68 6.17 6.87 2-Methylpentanal 2-甲基戊醛 C123159 C6H12O 100.2 754.6 197.259 1.2299 2.81 2.20 2.21 2.50 总和 36.45 33.76 35.47 34.10 醇类 Ethanol 乙醇 C64175 C2H6O 46.1 941 268.088 1.138 4.41 3.92 3.67 3.39 1-Pentanol 1-戊醇 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 1261.9 563.859 1.2563 0.19 0.07 0.33 0.07 1-Pentanol-D 1-戊醇二聚体 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 1262.2 564.337 1.5159 1.31 0.71 1.50 0.62 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol 3-甲基-3-丁烯-1-醇 C763326 C5H10O 86.1 1271.5 578.653 1.1788 0.04 0.14 0.04 0.12 Butan-1-ol-M 叔丁醇 C71363 C4H10O 74.1 1154.3 423.5 1.1824 2.58 2.19 2.21 1.95 Butan-1-ol-D 叔丁醇二聚体 C71363 C4H10O 74.1 1154.1 423.224 1.3826 2.76 2.36 2.05 2.03 1-Propanol 正丙醇 C71238 C3H8O 60.1 1051.7 330.863 1.1113 0.74 0.64 0.61 0.63 总和 12.03 10.03 10.41 8.81 酮类 Propan-2-one 丙酮 C67641 C3H6O 58.1 844.8 228.83 1.1147 10.36 8.40 8.11 7.39 Butan-2-one-M 2-丁酮 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 915.5 257.062 1.0605 1.45 1.12 1.49 1.21 Butanone-D 2-丁酮二聚体 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 914.3 256.579 1.2473 1.91 1.89 2.26 2.36 3-hydroxybutan-2-one (acetoin) 3-羟基-2-丁酮 C513860 C4H8O2 88.1 1296.5 619.443 1.0655 0.57 0.34 0.43 0.37 heptan-2-one 2-庚酮 C110430 C7H14O 114.2 1187.1 461.257 1.2658 0.33 0.24 0.44 0.33 2,3-pentanedione 2,3-戊二酮 C600146 C5H8O2 100.1 1076.9 349.257 1.2357 0.16 0.97 0.11 0.81 1-hydroxypropan-2-one-M 羟基丙酮 C116096 C3H6O2 74.1 1310.9 647.936 1.0617 0.16 1.02 0.12 1.61 1-hydroxypropan-2-one-D 羟基丙酮二聚体 C116096 C3H6O2 74.1 1310.1 646.26 1.2325 0.03 0.10 0.03 0.29 1-Penten-3-one-M 1-戊烯-3-酮 C1629589 C5H8O 84.1 1040.3 322.822 1.0788 0.13 0.88 0.05 0.75 1-Penten-3-one-D 1-戊烯-3-酮二聚体 C1629589 C5H8O 84.1 1039.8 322.525 1.3117 0.03 0.39 0.05 0.36 总和 15.13 15.35 13.09 15.48 酯类 Ethyl acetate-M 乙酸乙酯 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 892 247.315 1.0977 1.38 1.03 0.86 0.90 Ethyl acetate-D 乙酸乙酯二聚体 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 895.8 248.859 1.3359 9.33 8.12 7.96 7.37 Ethyl hexanoate 正己酸乙酯 C123660 C8H16O2 144.2 1244.1 537.612 1.3441 0.85 0.28 0.22 0.18 butyl acetate-M 乙酸丁酯 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 1089 358.482 1.2381 1.80 1.79 1.95 1.81 butyl acetate-D 乙酸丁酯二聚体 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 1088.3 357.996 1.6184 0.65 1.07 1.13 1.69 Isoamyl acetate-M 乙酸异戊酯 C123922 C7H14O2 130.2 1133.3 400.964 1.3058 0.62 0.73 0.57 0.66 Isoamyl acetate-D 乙酸异戊酯二聚体 C123922 C7H14O2 130.2 1133.6 401.206 1.7484 0.05 0.36 0.04 0.23 2-methylbutyl acetate 2-甲基丁基乙酸酯 C624419 C7H14O2 130.2 1153.1 422.123 1.3191 0.53 0.48 0.43 0.40 Butyl propionate-M 丙酸丁酯 C590012 C7H14O2 130.2 1149.4 418.165 1.286 0.23 0.24 0.33 0.36 Butyl propionate-D 丙酸丁酯二聚体 C590012 C7H14O2 130.2 1150.7 419.546 1.7225 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.12 Ethyl butanoate-M 丁酸乙酯 C105544 C6H12O2 116.2 1051.3 330.565 1.2083 0.45 0.84 0.32 0.80 Ethyl butanoate-D 丁酸乙酯二聚体 C105544 C6H12O2 116.2 1051.1 330.417 1.5598 0.06 0.27 0.04 0.29 Isobutyl butanoate 丁酸异丁酯 C539902 C8H16O2 144.2 1138.2 406.062 1.3247 3.36 3.28 3.07 3.20 总和 19.38 18.56 17.00 18.01 2-Ethylfuran 2-乙基呋喃 C3208160 C6H8O 96.1 971.3 281.821 1.3213 0.15 1.02 0.28 1.05 呋喃类 Tetrahydrofuran-M 四氢呋喃 C109999 C4H8O 72.1 881.2 242.975 1.0633 0.54 0.88 0.46 0.69 Tetrahydrofuran-D 四氢呋喃二聚体 C109999 C4H8O 72.1 881 242.869 1.2276 0.12 0.37 0.09 0.24 总和 0.81 2.27 0.83 1.98 酸类 Acetic acid 乙酸 C-4197 C2H4O2 60.1 1484.4 1116.398 1.0571 2.03 1.45 1.65 1.29 其他 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine 2,5-二甲基吡嗪 C123320 C6H8N2 108.1 1346.7 725.035 1.1074 0.04 0.11 0.02 0.15 1,2-Dimethoxyethane-M 乙二醇二甲醚 C110714 C4H10O2 90.1 912.5 255.807 1.1054 1.50 1.56 1.57 1.33 1,2-Dimethoxyethane-D 乙二醇二甲醚二聚体 C110714 C4H10O2 90.1 913.6 256.29 1.2898 1.49 1.67 1.41 1.89 -
[1] 蔡健, 王薇. 蘑菇的营养保健作用和保鲜技术[J]. 中国食物与营养,2004(3):22−23. [CAI J, WANG W. The healthy function and storage technique of fungus[J]. Chinese Food and Nutrition,2004(3):22−23. CAI J, WANG W . The healthy function and storage technique of fungus[J]. Chinese Food and Nutrition,2004 (3 ):22 −23 .[2] 吴锦文. 食用菌的化学成分和营养价值[J]. 农业新技术,1982(2):54−56. [WU J W. Chemical composition and nutritional value of edible fungi[J]. New Agricultural Technology,1982(2):54−56. WU J W . Chemical composition and nutritional value of edible fungi[J]. New Agricultural Technology,1982 (2 ):54 −56 .[3] 王世东. 双抱菇、草菇、滑子菇栽培与加工新技术[M]. 中国农业出版社, 2005. [WANG S D. New cultivation and processing techniques of Agaricus bisporus, Volvariella volvacea and Pholiota nameko[M]. China Agricultural Press, 2005. WANG S D. New cultivation and processing techniques of Agaricus bisporus, Volvariella volvacea and Pholiota nameko[M]. China Agricultural Press, 2005.
[4] 吴素玲, 孙晓明, 王波, 等. 双孢蘑菇子实体营养成分分析[J]. 中国野生植物资源,2006,25(2):47−52. [WU S L, SUN X M, WANG B, et al. Analysis of nutritional components of Agaricus bisporus fruiting body[J]. China Wild Plant Resources,2006,25(2):47−52. WU S L, SUN X M, WANG B, et al . Analysis of nutritional components of Agaricus bisporus fruiting body[J]. China Wild Plant Resources,2006 ,25 (2 ):47 −52 .[5] 谷镇, 杨焱. 食用菌呈香呈味物质研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(5):363−367. [GU Z, YANG Y. Research progress of aroma and flavor substances in edible fungi[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2013,34(5):363−367. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.05.012 GU Z, YANG Y . Research progress of aroma and flavor substances in edible fungi[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2013 ,34 (5 ):363 −367 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.05.012[6] 王清莲, 张云亮, 高帅, 等. 重组米产品研究及展望[J]. 农产品加工,2021(4):78−82. [WANG Q L, ZHANG Y L, GAO S, et al. Research and prospect of recombinant rice products[J]. Agricultural Products Processing,2021(4):78−82. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2021.02.051 WANG Q L, ZHANG Y L, GAO S, et al . Research and prospect of recombinant rice products[J]. Agricultural Products Processing,2021 (4 ):78 −82 . doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2021.02.051[7] SUMARDIONO S, JOS B, ANTONI M F Z, et al. Physicochemical properties of novel artificial rice produced from sago, arrowroot, and mung bean flour using hot extrusion technology[J]. Heliyon,2022,8(2):e08969. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08969
[8] SAHA S, ROY A. Selecting high amylose rice variety for puffing:A correlation between physicochemical parameters and sensory preferences[J]. Measurement:Food,2022,5:100021. doi: 10.1016/j.meafoo.2021.100021
[9] 董状, 吕庆云, 沈汪洋, 等. 富硒发芽糙米及其挤压米制作工艺优化[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(6):174−180. [DONG Z, LÜ Q Y, SHEN W Y, et al. Optimization of processing technology of selenium-enriched germinated brown rice and its extruded rice[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(6):174−180. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.06.029 DONG Z, LÜ Q Y, SHEN W Y, et al . Optimization of processing technology of selenium-enriched germinated brown rice and its extruded rice[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021 ,46 (6 ):174 −180 . doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.06.029[10] 巫婷婷. 炒米加工工艺参数优化及大米淀粉特性变化研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2011. [WU T T. Optimization of the process conditions for the stir-fried yin m and study for the change of rice starch characteristic[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University, 2011. WU T T. Optimization of the process conditions for the stir-fried yin m and study for the change of rice starch characteristic[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2011.
[11] 解菲, 赵宁, 江帆, 等. 炒米理化特性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(23):7−13. [XIE F, ZHAO N, JIANG F, et al. Physicochemical properties of chaomi[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(23):7−13. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.23.002 XIE F, ZHAO N, JIANG F, et al . Physicochemical properties of chaomi[J]. Food Research and Development,2021 ,42 (23 ):7 −13 . doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.23.002[12] 徐文泱, 王凯, 文欣. 炒米加工过程中二氧化硫含量的变化[J]. 粮食与油脂,2022,35(2):55−58,68. [XU W Y, WANG K, WEN X. Change of sulfur dioxide content in the production of stir-fried rice[J]. Cereals and Oils,2022,35(2):55−58,68. XU W Y, WANG K, WEN X . Change of sulfur dioxide content in the production of stir-fried rice[J]. Cereals and Oils,2022 ,35 (2 ):55 −58,68 .[13] 中华人民共和国国家标准. GB 5009.3-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Standard of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.3-2016 National Standard for Food Safety Determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016. National Standard of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.3-2016 National Standard for Food Safety Determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[14] 王洁洁, 邵子晗, 韩晶, 等. 挤压重组紫薯米工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(8):137−142,150. [WANG J J, SHAO Z J, HAN J, et al. Optimization of process and antioxidant activity of extruded recombinant purple potato rice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(8):137−142,150. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.08.022 WANG J J, SHAO Z J, HAN J, et al . Optimization of process and antioxidant activity of extruded recombinant purple potato rice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020 ,41 (8 ):137 −142,150 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.08.022[15] 杨涛, 徐雪野, 张新振, 等. 挤压香菇炒米的工艺优化及其风味成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(7):178−187. [YANG T, XU X Y, ZHANG X Z, et al. Process optimization and flavor composition analysis of fried rice with extruded mushrooms[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2023,44(7):178−187. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022060090 YANG T, XU X Y, ZHANG X Z, et al . Process optimization and flavor composition analysis of fried rice with extruded mushrooms[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2023 ,44 (7 ):178 −187 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022060090[16] 王纯, 戴艳军, 孙玥, 等. 不同品种菌菇加工脆片适宜性评价[J]. 食品与机械,2021,37(4):171−175,238. [WANG C, DAI Y J, SUN Y, et al. Evaluation of the suitability of different varieties of mushroom for processing crisps[J]. Food and Machinery,2021,37(4):171−175,238. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2021.04.032 WANG C, DAI Y J, SUN Y, et al . Evaluation of the suitability of different varieties of mushroom for processing crisps[J]. Food and Machinery,2021 ,37 (4 ):171 −175,238 . doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2021.04.032[17] 蒋谨, 徐颖, 朱庚伯. 人类味觉与氨基酸味道[J]. 氨基酸和生物资源,2002,24(4):1−3. [JIANG J, XU Y, ZHU G B. Human taste and amino acid taste[J]. Amino Acid and Biological Resources,2002,24(4):1−3. doi: 10.14188/j.ajsh.2002.04.023 JIANG J, XU Y, ZHU G B . Human taste and amino acid taste[J]. Amino Acid and Biological Resources,2002 ,24 (4 ):1 −3 . doi: 10.14188/j.ajsh.2002.04.023[18] 刘志云, 胡秋辉. 香菇粉和豆沙复配曲奇特征风味物质分析[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(20):95−101. [LIU Z Y, HU Q H. Analysis of characteristic flavor substances of compound cookies with mushroom powder and bean paste[J]. Food Science,2016,37(20):95−101. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201620016 LIU Z Y, HU Q H . Analysis of characteristic flavor substances of compound cookies with mushroom powder and bean paste[J]. Food Science,2016 ,37 (20 ):95 −101 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201620016[19] 黄雨露. 双孢菇籼米复合冲调粉的制备及其特性研究[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2019. [HUANG Y L. Preparation and characteristics of Agaricus bisporus-indica rice compound blending powder[D]. Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University, 2019. HUANG Y L. Preparation and characteristics of Agaricus bisporus-indica rice compound blending powder[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2019.
[20] 张钰萌, 鲍雨婷, 孙玥, 等. 双孢菇面包复合改良剂优化及其对面包品质的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2022,38(3):212−216. [ZHANG Y M, BAO Y T, SUN Y, et al. Optimization of compound improver for Agaricus bisporus bread and its influence on bread quality[J]. Food and Machinery,2022,38(3):212−216. doi: 10.13652/j.spjx.1003.5788.2022.90016 ZHANG Y M, BAO Y T, SUN Y, et al . Optimization of compound improver for Agaricus bisporus bread and its influence on bread quality[J]. Food and Machinery,2022 ,38 (3 ):212 −216 . doi: 10.13652/j.spjx.1003.5788.2022.90016[21] 靳羽慧. 金针菇对面条品质特性的影响[D]. 新乡:河南科技学院, 2018. [JIN Y H. Effect of flammulina velutipes on quality characteristics of noodles[D]. Xinxiang:Henan University of Science and Technology, 2018. JIN Y H. Effect of flammulina velutipes on quality characteristics of noodles[D]. Xinxiang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[22] 马宁, 陈雨婷, 方东路, 等. 猴头菇-青稞预糊化粉的添加对桃酥品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(20):46−53. [MA N, CHEN Y T, FANG D L, et al. Effect of Hericium erinaceus-highland barley pregelatinized powder on peach cake quality[J]. Food Science,2020,41(20):46−53. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200507-068 MA N, CHEN Y T, FANG D L, et al . Effect of Hericium erinaceus-highland barley pregelatinized powder on peach cake quality[J]. Food Science,2020 ,41 (20 ):46 −53 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200507-068[23] 鲁敏, 安华明, 赵小红. 无籽刺梨与刺梨果实中氨基酸分析[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(14):118−121. [LU M, AN H M, ZHAO X H. Analysis of amino acids in seedless Rosa roxburghii and Rosa roxburghii fruits[J]. Food Science,2015,36(14):118−121. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-2015140023 LU M, AN H M, ZHAO X H . Analysis of amino acids in seedless Rosa roxburghii and Rosa roxburghii fruits[J]. Food Science,2015 ,36 (14 ):118 −121 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-2015140023[24] 冯耐红, 侯东辉, 杨成元, 等. 不同品种小米主要营养成分及氨基酸组分评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(8):224−229. [FENG N H, HOU D H, YANG C Y, et al. Evaluation of main nutritional components and amino acid components of different varieties of millet[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2020,41(8):224−229. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.08.035 FENG N H, HOU D H, YANG C Y, et al . Evaluation of main nutritional components and amino acid components of different varieties of millet[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2020 ,41 (8 ):224 −229 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.08.035[25] 肖文敏, 唐小燕, 任志红, 等. 基于电子鼻技术的茶鲜叶农残快速诊断[J]. 茶叶通讯,2021,48(3):484−493. [XIAO W M, TANG X Y, REN Z H, et al. Rapid diagnosis of pesticide residues in fresh tea leaves based on electronic nse technology[J]. Journal of Tea Communication,2021,48(3):484−493. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-525X.2021.03.016 XIAO W M, TANG X Y, REN Z H, et al . Rapid diagnosis of pesticide residues in fresh tea leaves based on electronic nse technology[J]. Journal of Tea Communication,2021 ,48 (3 ):484 −493 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-525X.2021.03.016[26] LIU R C, LI R, WANG Y, et al. Analysis of volatile odor compounds and aroma properties of European vinegar by the ultra-fast gas chromatographic electronic nose[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2022,112:104673. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104673
[27] 李娟, 任芳, 甄大卫, 等. 气相色谱-离子迁移谱分析乳制品挥发性风味化合物[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(10):235−240. [LI J, REN F, ZHEN D W, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds dairy products by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2021,42(10):235−240. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200503-020 LI J, REN F, ZHEN D W, et al . Analysis of volatile flavor compounds dairy products by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (10 ):235 −240 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200503-020[28] TIAN X, LI Z J, CHAO Y Z, et al. Evaluation by electronic tongue and headspace-GC-IMS analyses of the flavor compounds in dry-cured pork with different salt content[J]. Food Research International,2020,137:109456. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109456
[29] ZHANG Q, DING Y, GU S, et al. Identification of changes in volatile compounds in dry-cured fish during storage using HS-GC-IMS[J]. Food Research International,2020,137:109339. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109339
[30] VAZQUEZ-LANDAVERDE P A, VELAZQUEZ G, TORRES J A, et al. Quantitative determination of thermally derived off-flavor compounds in milk using solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2005,88(11):3764−3772. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)73062-9
[31] PAN D D, WU Z, PENG T, et al. Volatile organic compounds profile during milk fermentation by Lactobacillus pentosus and correlations between volatiles flavor and carbohydrate metabolism[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2014, 97(2):624-631.
[32] 刘丽丽, 杨辉, 荆雄, 等. 基于GC-IMS和电子鼻技术分析贮酒容器对凤香型白酒香气成分的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(4):257−263. [LIU L L, YANG H, JING X, et al. Based on GC-IMS and electronic nose technology, the influence of wine containers on aroma components of Fengxiang liquor was analyzed[J]. Food Science,2022,43(4):257−263. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210203-062 LIU L L, YANG H, JING X, et al . Based on GC-IMS and electronic nose technology, the influence of wine containers on aroma components of Fengxiang liquor was analyzed[J]. Food Science,2022 ,43 (4 ):257 −263 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210203-062[33] 陈丽兰, 杨心怡, 乔明锋, 等. 基于GC-IMS、GC-MS和OAV法分析花椒粉颗粒度对花椒油挥发性香气成分的影响[J/OL]. 食品工业科技:1−14. [2022-12-22]. doi:10.13386/j. issn1002-0306.2022050344. CHEN L L, YANG X Y, QIAO M F, et al. Based on GC-IMS, GC-MS and OAV methods, the effect of pepper powder granularity on volatile aroma components of pepper oil was analyzed[J/OL]. Food Industry Science and Technology:1−14[2022-12-22]. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022050344. 2022-12-22]. doi: 10.13386/j. issn1002-0306.2022050344. CHEN L L, YANG X Y, QIAO M F, et al. Based on GC-IMS, GC-MS and OAV methods, the effect of pepper powder granularity on volatile aroma components of pepper oil was analyzed[J/OL]. Food Industry Science and Technology: 1−14[2022-12-22]. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022050344.
[34] 郑敏怡. 红烧乳鸽加工过程中品质变化的研究[D]. 广州:仲恺农业工程学院, 2019. [ZHENG M Y. Study on quality change of braised pigeon during processing[D]. Guangzhou:Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2019. ZHENG M Y. Study on quality change of braised pigeon during processing[D]. Guangzhou: Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2019.
[35] KHAIRY H L, SAADOON A F, ZZAMAN W, et al. Identification of flavor compounds in rambutan seed fat and its mixture with cocoa butter determined by SPME-GCMS[J]. Journal of King Saud University-Science,2018,30(3):316−323. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2017.03.001
[36] 王震, 叶宏, 朱婷婷, 等. 清香型白酒风味成分的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(7):232−244. [WANG Z, YE H, ZHU T T, et al. Research progress of flavor components of fen-flavor liquor[J]. Food Science,2022,43(7):232−244. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210316-217 WANG Z, YE H, ZHU T T, et al . Research progress of flavor components of fen-flavor liquor[J]. Food Science,2022 ,43 (7 ):232 −244 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210316-217[37] VALERO E, VILLAMIEL M, MIRALLES B, et al. Changes in flavor and volatile components during storage of whole and skimmed UHT milk[J]. Food Chemistry,2001,72(1):51−58. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00203-X
[38] 张秀玲, 汲润, 李凤凤, 等. 发酵工艺对蓝靛果酒功能性及香气成分的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(10):189−198. [ZHANG X L, JI R, LI F F, et al. Effect of fermentation technology on the functionality and aroma components of Lonicera edulis fruit wine[J]. Food Science,2022,43(10):189−198. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210618-213 ZHANG X L, JI R, LI F F, et al . Effect of fermentation technology on the functionality and aroma components of Lonicera edulis fruit wine[J]. Food Science,2022 ,43 (10 ):189 −198 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210618-213[39] YANG Y, WANG B, FU Y, et al. HS-GC-IMS with PCA to analyze volatile flavor compounds across different production stages of fermented soybean whey tofu[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,346:128880. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128880
[40] 刘静, 薛佳俐, 冯翠萍. 不同干制方式对香菇挥发性成分的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(18):224−229. [LIU J, XUE J L, FENG C P. Effects of different drying methods on volatile flavor compounds in Lentinus edodes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(18):224−229. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.18.039 LIU J, XUE J L, FENG C P . Effects of different drying methods on volatile flavor compounds in Lentinus edodes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018 ,39 (18 ):224 −229 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.18.039 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王震,赵欣蕊,王立东. 重组米加工及其品质特性研究进展. 粮食与油脂. 2025(03): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:



