Optimization of Fermentation Medium of Bacterial Cellulose Production by Gluconacetobacter and Effects of Exogenous Substances on Its Metabolism
-
摘要: 为了提高细菌纤维素(Bacterial Cellulose,BC)的产量,采用响应面法优化了木葡糖醋杆菌(Gluconacetobacter xylinus)的发酵培养基,基于优化结果探究了海藻酸钠(SA)、羧甲基纤维素钠(CMC-Na)、羧甲基纤维素(CMC)三种外源物质对BC合成过程中BC产量、总糖消耗、乙酸、丙酮酸等的影响。结果表明,最优培养基成分为葡萄糖4%、酵母浸粉1%、蛋白胨0.8%、MgSO4 1.9%、Na2HPO4 0.2%、乙酸0.4%、乙醇1.6%,BC产量为5.19 g/L。外源添加SA、CMC-Na、CMC后,总糖的消耗量分别提高了29.9%、22.82%和15.73%,BC终产量分别为6.72、6.01和5.1 g/L。相较于对照组,SA和CMC-Na组丙酮酸含量的增幅分别为29.02%和16.52%,促进了丙酮酸的积累与利用,提高了BC的积累量。CMC添加组乙酸的积累量最高为4.27 g/L,这与BC产量的下降有一定关系。Abstract: In order to improve the yield of bacterial cellulose (BC), the fermentation medium of the Gluconacetobacter xylinus was optimized by response surface methodology. Based on the optimization results, the effects of sodium alginate (SA), sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) on the yield of BC, total sugar consumption, acetic acid and pyruvic acid were investigated. The results showed that when the amounts of addition of glucose was 4%, yeast extract powder was 1%, peptone was 0.8%, MgSO4 was 1.9%, Na2HPO4 was 0.2%, acetic acid was 0.4%, ethanol was 1.6%, the actual yield of BC could reach 5.19 g/L. After adding SA, CMC-Na and CMC, the total sugar consumption increased by 29.9%, 22.82% and 15.73%, and the yield of BC was 6.72, 6.01 and 5.1 g/L, respectively. The content of pyruvic acid in SA group and CMC-Na group was increased by 29.02% and 16.52% compared with the control group. SA and CMC-Na promoted the accumulation and utilization of pyruvate acid, the yield of BC accumulation was increased. The highest acetic acid accumulation (4.27 g/L) was observed in the CMC addition group, which had a certain relationship to the lower yield of BC than the control group.
-
Keywords:
- Gluconacetobacter /
- bacterial cellulose yield /
- medium optimization /
- metabolism
-
细菌纤维素(BC)主要是由醋酸杆菌属(Acetobacter)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)、根瘤菌属(Rhizobium)、八叠球菌属(Sarcina)[1]等生产菌合成的不溶性直链多糖,它的直链之间彼此呈平行状,没有分支结构[2]。目前研究较多且能够大量合成BC的生产菌为木葡糖醋杆菌(Gluconacetobacter xylinum),原名木醋杆菌(Acetobacter xylinum)[3]。BC与植物纤维素不同之处在于BC不含果胶、半纤维素等物质,且具有高度多孔三维网络结构,因此BC具有高聚合度、高结晶度、可降解性[4]、较好的生物相容性等特点[5]。目前BC已成功应用于食品工业、生物医学、保鲜材料、复合材料[6-9]等领域。但由于其产量低、成本高、无法实现产业化生产,故极大地制约了BC的工业化推广应用[7]。目前,国内外对提高BC产量的研究开展了大量的工作,如菌种选育、改变生物反应器和发酵参数[8]、代谢机理研究等,以期降低BC生产成本、改良BC合成途径、拓宽BC应用范围。
微生物在发酵培养过程中需要利用大量的营养元素,如碳源、氮源、生长因子等,因此发酵培养过程中所用到的培养基成分能够直接影响到BC的合成[9]。此外,在木葡糖醋杆菌发酵过程中,多种添加物已被证实对菌体生长或合成纤维素具有一定的促进作用,如水溶性多糖[10]、木质素磺酸盐[11]、金属离子[12]等。
本研究采用实验室分离菌株为生产菌株,利用Plackett-Burman试验设计法和Box-Behnken试验设计法[13]得到合成BC的最优培养基配方,有效提高BC产量;在此基础上,通过添加SA、CMC-Na、CMC等水溶性多糖大分子作为合成体系的外源物质,对发酵过程中总糖含量、乙酸含量、丙酮酸含量等指标变化进行研究,以指标量化的方式,探究不同物质对细菌纤维素合成的影响机理,以期为进一步研究外源物质对BC合成的影响机理提供理论依据,为拓展BC的工业化应用提供一定的理论与实践基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
木葡糖醋杆菌(Gluconacetobacter xylinus)K8-5 由兰州理工大学生命科学与工程学院赵萍老师课题组筛选并保藏;葡萄糖 天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;蛋白胨、酵母浸粉 上海迈瑞尔;K2HPO4、Na2HPO4、MgSO4 天津市北辰方正试剂厂;琼脂 天津大茂化学试剂厂;乙酸、乙醇 天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;斜面培养基:葡萄糖3%,酵母膏0.5%,MgSO4 1.5%,K2HPO4 0.15%,琼脂2%,pH自然;基础培养基:葡萄糖3%,酵母膏0.5%,MgSO4 1.5%,K2HPO4 0.15%,乙醇2%,pH自然。
DHP-9082 电热恒温培养箱 上海恒一科学仪器有限公司;YX280B 压力蒸汽灭菌锅 上海三申医疗器械有限公司;Cary50 紫外分光光度计 美国瓦里安公司;SHA-82恒温振荡器 上海贺帆仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌种的培养
菌种活化:挑取适量保存在4 ℃条件下的木葡糖醋杆菌接种于斜面培养基中,29 ℃静置培养7 d。种子培养:于种子培养基中接种2~3环斜面种子,29 ℃,150 r/min恒温振荡24 h。发酵培养:10%(v/v)种子液接入基础培养基,29 ℃静置培养7 d[14]。
1.2.2 木葡糖醋杆菌发酵培养基优化
1.2.2.1 单因素实验
实验前期参照1.1中基础培养基配方,通过控制变量法,已筛选出最优碳源为葡萄糖,最优氮源为酵母浸粉、蛋白胨,最优无机盐为Na2HPO4、MgSO4,最优有机酸为乙酸。以BC产量为指标,确定各因素的最佳添加范围。研究葡萄糖添加量(2%、3%、4%、5%、6%、7%、8%)、酵母浸粉或蛋白胨(0.2%、0.4%、0.6%、0.8%、1.0%、1.2%、1.4%)代替基础培养基中酵母膏、MgSO4添加量(0.5%、1.0%、1.5%、2.0%、2.5%、3.0%、3.5%)、Na2HPO4(0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%、0.6%、0.7%)代替K2HPO4、乙酸添加量(0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%、0.6%、0.7%)、乙醇添加量(1%、1.2%、1.4%、1.6%、1.8%、2.0%、2.2%)对BC产量的影响。考察某一因素时,其他固定条件为葡萄糖添加量3%、酵母膏添加量0.5%,MgSO4添加量1.5%,K2HPO4 添加量0.15%,乙醇添加量2%。
1.2.2.2 Plackett-Burman试验
根据单因素实验结果,利用Plackett-Burman试验对影响BC产量的7个因素为自变量,BC产量作为响应值,设计7个因素2个水平试验,水平设置如表1[15−16]。
表 1 Plackett-Burman 试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of Plackett-Burmanexperiments design水平 A
葡萄糖
(%)B
酵母浸粉
(%)C
蛋白胨
(%)D
MgSO4
(%)E
Na2HPO4
(%)F
乙酸
(%)G
乙醇
(%)低水平(−1) 2 0.2 0.2 0.5 0.1 0.1 1 高水平(+1) 8 1.4 1.4 3.5 0.7 0.7 2.2 1.2.2.3 Box-Behnken响应面设计试验
根据Box-Behnken试验设计原理,结合单因素及Plackett-Burman试验的结果,确定MgSO4、酵母浸粉、葡萄糖3个显著因素为Box-Behnken试验考察自变量,BC产量作为响应值,设计三因素三水平的响应面试验,因素水平及编码见表2。
表 2 Box-Behnken 试验因素水平及编码Table 2. Factors and levels of Box-Behnken experiments因素 编码 水平 −1 0 +1 葡萄糖(%) A 3 4 5 酵母浸粉(%) B 0.8 1 1.2 MgSO4(%) C 1.5 2 2.5 1.2.2.4 BC产量的测定
将发酵液中气液交界处生成的BC膜取出,用蒸馏水多次冲洗,后浸泡于0.1 mol/L的NaOH溶液中,煮沸30 min,冷却后再用0.5%的乙酸浸泡5 min,经蒸馏水多次冲洗至膜呈乳白色半透明,将处理后的纤维素膜75 ℃烘干至恒重,称量BC重量[17]。
1.2.3 添加外源物质对总糖含量、OD600、pH、乙酸含量、丙酮酸含量的影响
1.2.3.1 外源物质添加量的确定
在基础培养基中分别添加因素水平为0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6、0.7%(w/v)的SA、CMC-Na和CMC,经120 ℃、121 kPa灭菌30 min后按比例接种10%(v/v)的种子液,29 ℃条件下静置培养7 d,收取BC,确定BC产量,根据BC最大产量选择最优添加量。
1.2.3.2 发酵样液的制备
在优化培养基中分别添加外源物质(SA、CMC-Na和CMC),以空白添加为对照组,将种子液按10%(v/v)的接种量接种于培养基中,29 ℃静置培养7 d,每天对四组发酵液进行随机3次平行取样,共取7 d,测定其发酵指标(BC产量、OD600、总糖含量、pH、乙酸含量、丙酮酸含量)。
1.2.3.3 菌体生长情况的测定
将1%纤维素酶(10000 U/g)溶液置于柠檬酸缓冲溶液(pH5)中,将发酵液与纤维素酶溶液以1:1混合,50 ℃水浴2 h,室温静置后取两份上清液,将其中一份上清液用0.22 μm的微孔滤膜过滤除菌作为对照组[18],使用紫外分光光度计测定菌液在600 nm处的吸光度,以OD600值反映菌体生长发育情况[19]。
1.2.3.4 总糖的测定
将发酵样液4000 r/min离心10 min后取上清液5 mL,加入5 mL 6 mol/L HCl溶液和30 mL蒸馏水,70 ℃水浴15 min,冷却后调pH至7~8,定容至100 mL,作为混合液备用。吸取混合液1 mL,DNS试剂2 mL,沸水浴2 min显色,流水迅速冷却后定容至25 mL,在540 nm处测定样品的吸光值,根据标准曲线计算总糖含量[20−21]。
1.2.3.5 乙酸及pH测定
样品处理:取一定量的发酵样液,经8000 r/mn离心后取上清液,稀释10倍,用0.22 μm的滤膜过滤后进样分析。色谱条件:SB-AQ色谱柱,流动相:pH2.5的磷酸二氢钾溶液,流速:0.5 mL/min,检测器波长:210 nm,柱温30 ℃,进样量:10 μL。pH的测定参考GB 5009. 237-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定[22]。
1.2.3.6 丙酮酸的测定
参考张继冉[23]的方法在320 nm处测定紫外吸收丙酮酸标准曲线。以丙酮酸含量为X轴,吸光值为Y轴,绘制丙酮酸标准曲线,标准曲线为y=0.2583x+0.0248(R2=0.9975)。发酵液经8000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液用NaOH溶液调pH为11.0,在320 nm处测其吸光值,根据标准曲线计算丙酮酸含量。
1.3 数据处理
使用 Design Expert 8.0.6、SPSS Statistics 21软件对试验数据进行处理以及显著性分析(P<0.05),使用Origin 2021软件作图,BC产量有效数据均取5次平行实验的平均值,其余有效数据均取3次平行实验的平均值。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 木葡糖醋杆菌培养基优化结果
2.1.1 单因素实验结果
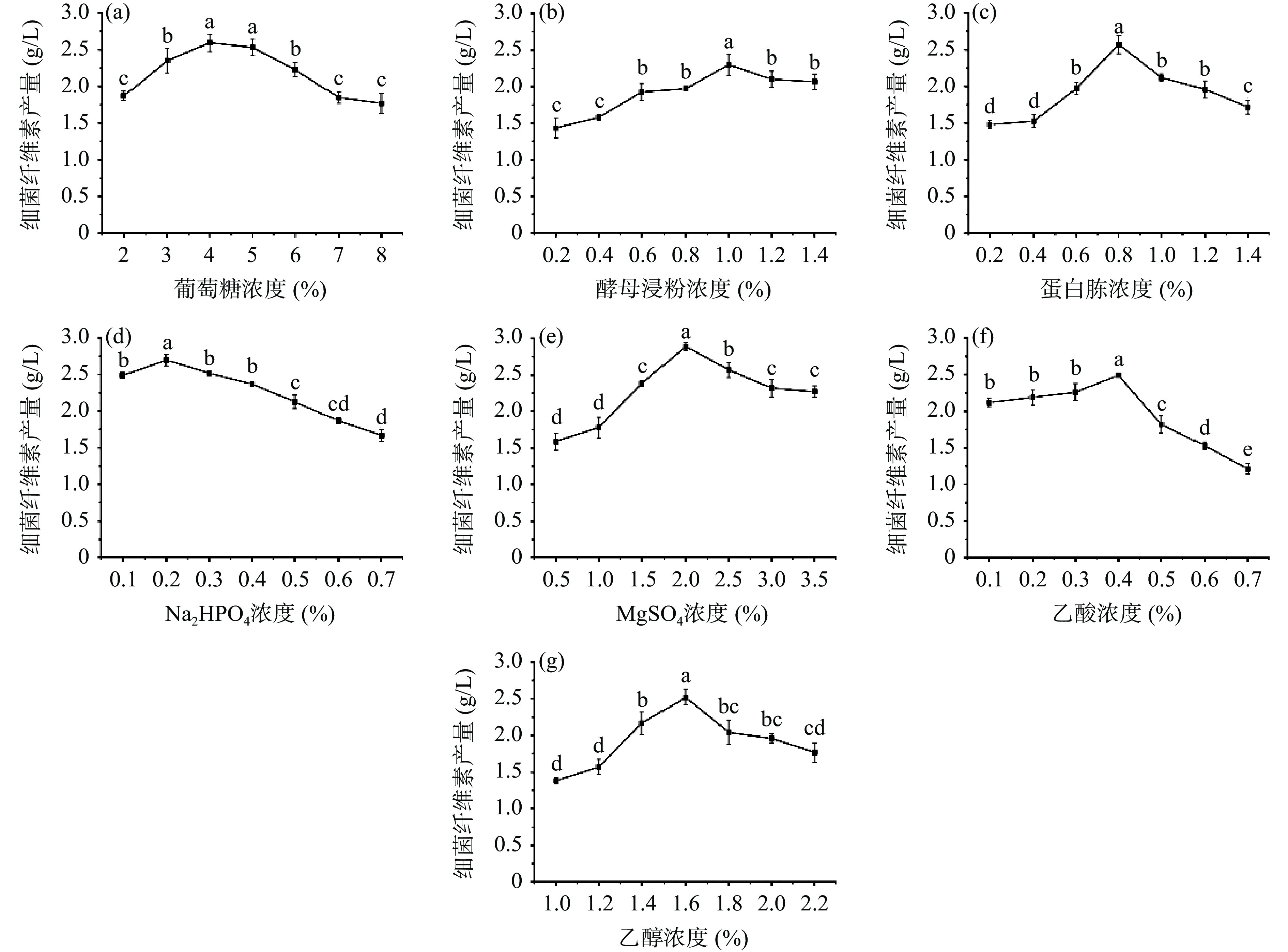
不同物质的添加量对BC产量的影响存在一定差异。葡萄糖作为唯一的碳源,为菌体生长和BC合成提供能量,如图1所示,当葡萄糖添加量为4%和5%时BC产量并不具有显著性差异(P>0.05),但当葡萄糖添加量增加时,BC产量呈下降趋势,因此选择葡萄糖的最佳添加量为4%;氮源是细胞代谢所必需蛋白质的主要成分,占细菌干细胞质量的8%~14%,当蛋白胨和酵母浸粉分别代替基础培养基中氮源时,对BC产量进行测定,结果表明当蛋白胨和酵母浸粉的添加量分别为0.8%和1%时,BC产量最高;无机盐可以作为酶的重要组成成分参与微生物的代谢,当MgSO4添加量为2%时,BC产量最高为2.89 g/L,且Na2HPO4添加量为0.2%时,BC产量最高;Liu等[24]研究表明,在BC合成过程中,乙醇或乙酸盐作为补充碳源,通过三羧酸循环产生ATP,可以有效提高BC产量,当乙醇添加量为1.6%时,BC合成量最大,当乙酸浓度大于0.4%时,BC合成被抑制,表明过量的乙酸浓度会对细胞生长造成抑制作用,故乙醇和乙酸的最佳添加量分别为1.6%和0.4%。选择上述各物质最佳添加量进行下一步实验。
![]() 图 1 不同添加物浓度对BC产量的影响注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图3同。Figure 1. Effects of different additive concentrations on yield of bacterial cellulose
图 1 不同添加物浓度对BC产量的影响注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图3同。Figure 1. Effects of different additive concentrations on yield of bacterial cellulose2.1.2 Plackett-Burman试验
根据单因素实验进行Plackett-Burman试验,如表3。由表4可知Plackett-Burman试验模型的P值为0.013<0.05,对BC产量影响最显著的三个因子为MgSO4、酵母浸粉、葡萄糖,固定其他因素,蛋白胨(0.8%)、乙酸(0.4%)、乙醇(1.6%)、Na2HPO4(0.2%)的添加量不变,进行下一步Box-Behnken试验。
表 3 Plackett-Burman试验设计与结果Table 3. Design and results of Plackett-Burman experiments实验号 A B C D E F G BC产量(g/L) 1 1 −1 1 1 1 −1 −1 2.31±0.11 2 1 −1 1 1 −1 1 1 3.75±0.27 3 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 0.29±0.05 4 −1 −1 −1 1 −1 1 1 2.51±0.18 5 −1 −1 1 −1 1 1 −1 0.12±0.05 6 1 −1 −1 −1 1 −1 1 0.78±0.09 7 −1 1 1 1 −1 −1 −1 4.18±0.16 8 −1 1 −1 1 1 −1 1 3.44±0.15 9 1 1 −1 −1 −1 1 −1 2.35±0.17 10 1 1 −1 1 1 1 −1 4.44±0.37 11 −1 1 1 −1 1 1 1 0.36±0.11 12 1 1 1 −1 −1 −1 1 2.42±0.08 表 4 Plackett-Burman试验的方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance of Plackett-Burman experiments因素 平方和 F值 P值 显著性 模型 25.3 12.99 0.0130 * A葡萄糖 2.21 7.95 0.0479 * B酵母浸粉 4.6 16.54 0.0153 * C蛋白胨 0.037 0.13 0.7324 D MgSO4 17.0.6 61.36 0.0014 ** E Na2HPO4 1.37 4.91 0.0909 F乙酸 1.008E−003 3.625E−003 0.9549 G乙醇 0.015 0.055 0.8255 注:*表示差异显著P<0.05,**表示差异极显著P<0.01;表6同。 2.1.3 Box-Behnken 响应面优化试验结果与分析
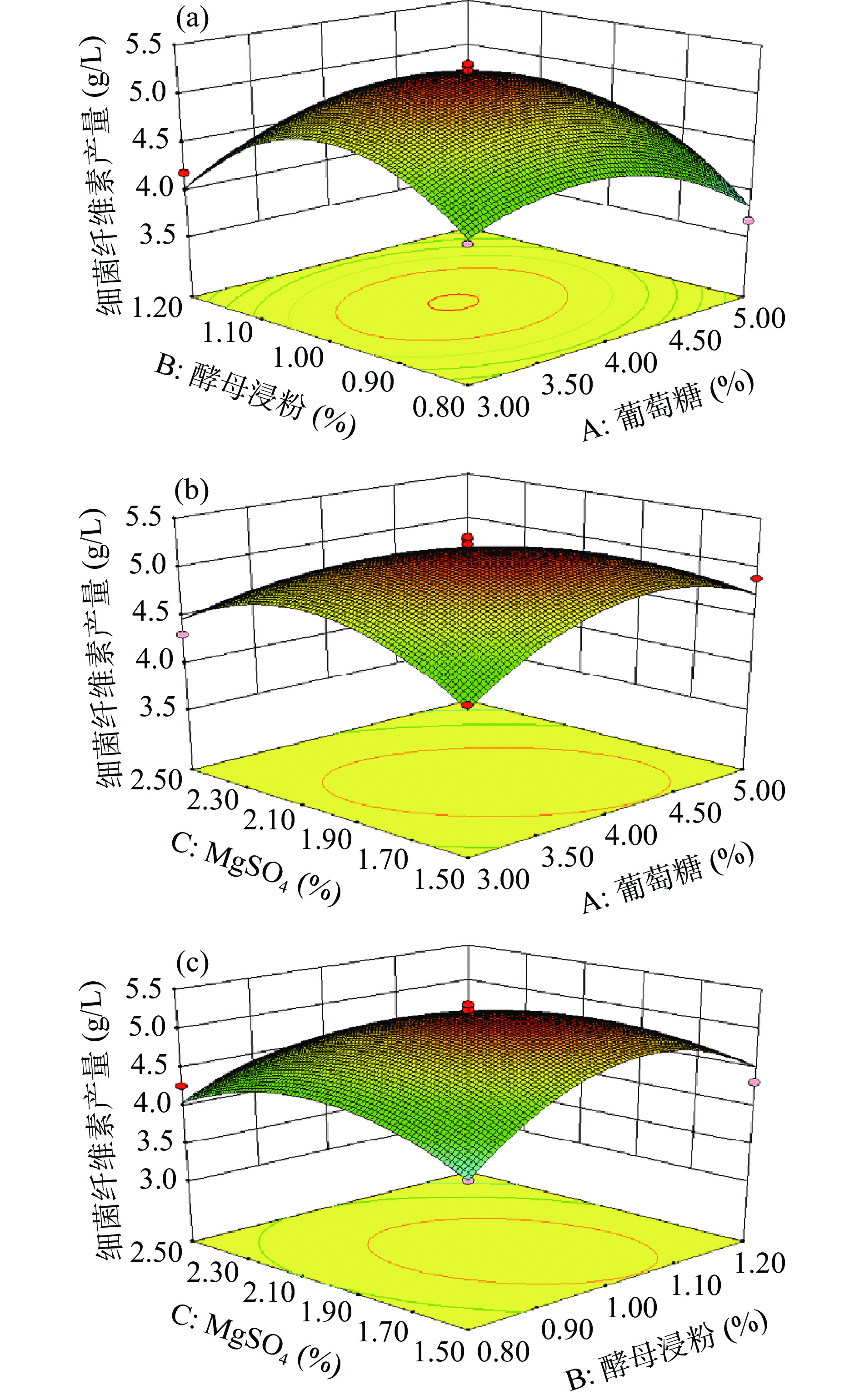
在Plackett-Burman试验基础上以MgSO4、酵母浸粉和葡萄糖的添加量为响应值,进行Box-Behnken试验,如表5。利用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件对实验数据进行多元回归拟合,最终得到BC产量高低响应面回归模拟方程为:
表 5 Box-Behnken 响应面试验设计与结果Table 5. Design and results of Box-Behnken response surface experiment实验号 葡萄糖 酵母浸粉 MgSO4 BC产量(g/L) 1 0 0 0 5.29±0.12 2 0 1 1 3.5±0.19 3 0 1 −1 4.32±0.18 4 1 1 0 4.08±0.31 5 0 0 0 5.24±0.08 6 0 0 0 5.19±0.04 7 −1 1 0 4.19±0.09 8 1 0 1 3.54±0.12 9 1 0 −1 4.89±0.19 10 −1 −1 0 4.21±0.03 11 0 −1 −1 3.98±0.15 12 1 −1 0 3.67±0.26 13 0 0 0 5.31±0.09 14 0 −1 1 4.27±0.15 15 0 0 0 4.99±0.18 16 −1 0 1 4.31±0.15 17 −1 0 −1 4.32±0.14 Y=5.20−0.11A−5.000E−003B−0.24C+0.11AB−0.33AC−0.28BC−0.46A2−0.71B2−0.48C2
由表6可知,A2、B2、C2对BC产量有极显著影响(P<0.01),C、AC、BC对BC产量有显著影响(P<0.05),A、B、AB影响不显著(P>0.05)。该模型P值为0.0006,表明回归模型影响极显著(P<0.01),失拟项为0.1087(P>0.05)不显著,决定系数R2=0.9565,校正系数R2adj=0.9005,说明该回归模型具有良好的拟合度和预测能力。
表 6 Box-Behnken 响应面试验结果方差分析Table 6. Analysis of variance of Box-Behnken response surface experiment results方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 Prob>F 显著性 模型 5.74 9 0.64 0.0006 ** A 0.09 1 0.09 0.1639 B 2.000E−004 1 5.356E−003 0.9437 C 0.45 1 0.45 0.0106 * AB 0.046 1 0.046 0.3026 AC 0.45 1 0.45 0.0104 * BC 0.31 1 0.31 0.0239 * A2 0.89 1 0.89 0.0018 ** B2 2.10 1 2.10 0.0001 ** C2 0.97 1 0.97 0.0014 ** 残差 0.26 7 0.037 失拟项 0.20 3 0.065 0.1087 纯误差 0.11 4 0.022 总和 6.58 16 R2=0.9565,R2adj=0.9005 2.1.4 响应面不同因素间交互作用分析
由图2可知,葡萄糖和酵母浸粉(AB)的等高线中心区域呈圆形,表明葡萄糖和酵母浸粉之间交互作用不明显,葡萄糖和MgSO4(AC)、酵母浸粉和MgSO4(BC)的交互作用的等高线中心区域显示为椭圆形,响应曲面坡度趋势陡峭,表明AC、BC的交互作用明显,对BC产量影响较大,响应面分析结果与方差分析结果一致。
2.1.5 验证实验
根据试验可得出BC产量的最大预测值为5.23 g/L,最终得到的预测培养基配方为:葡萄糖3.98%、酵母浸粉1.01%、蛋白胨0.8%、MgSO4 1.87%、Na2HPO4 0.2%、乙酸0.4%、乙醇1.6%,为了实际操纵可控,设置优化后培养基配方为葡萄糖4%、酵母浸粉1%、蛋白胨0.8%、MgSO4 1.9%、Na2HPO4 0.2%、乙酸0.4%、乙醇1.6%。按此培养基配方进行发酵,实际得到BC产量为5.19 g/L,与预测结果接近,因此,可以证明这个模型准确性较高,可预测实际发酵情况。
文献报道赵浩杰等[15]通过响应面法优化培养基后,最终BC产量为5.02±0.14 g/L;文章等[25]利用稀释后的白酒酿造副产物黄水为培养基,BC产量提高了53.2%,终产量为2.42 g/L;张丽平等[21]在基础培养基中添加乙醇及有机酸后,有效提高了BC产量,BC产量为3.012 g/L。本文响应面优化后实际BC产量为5.19±0.16 g/L,BC产量较高,具有较大优势。
2.2 外源物质对BC的影响
2.2.1 外源物质添加量的确定
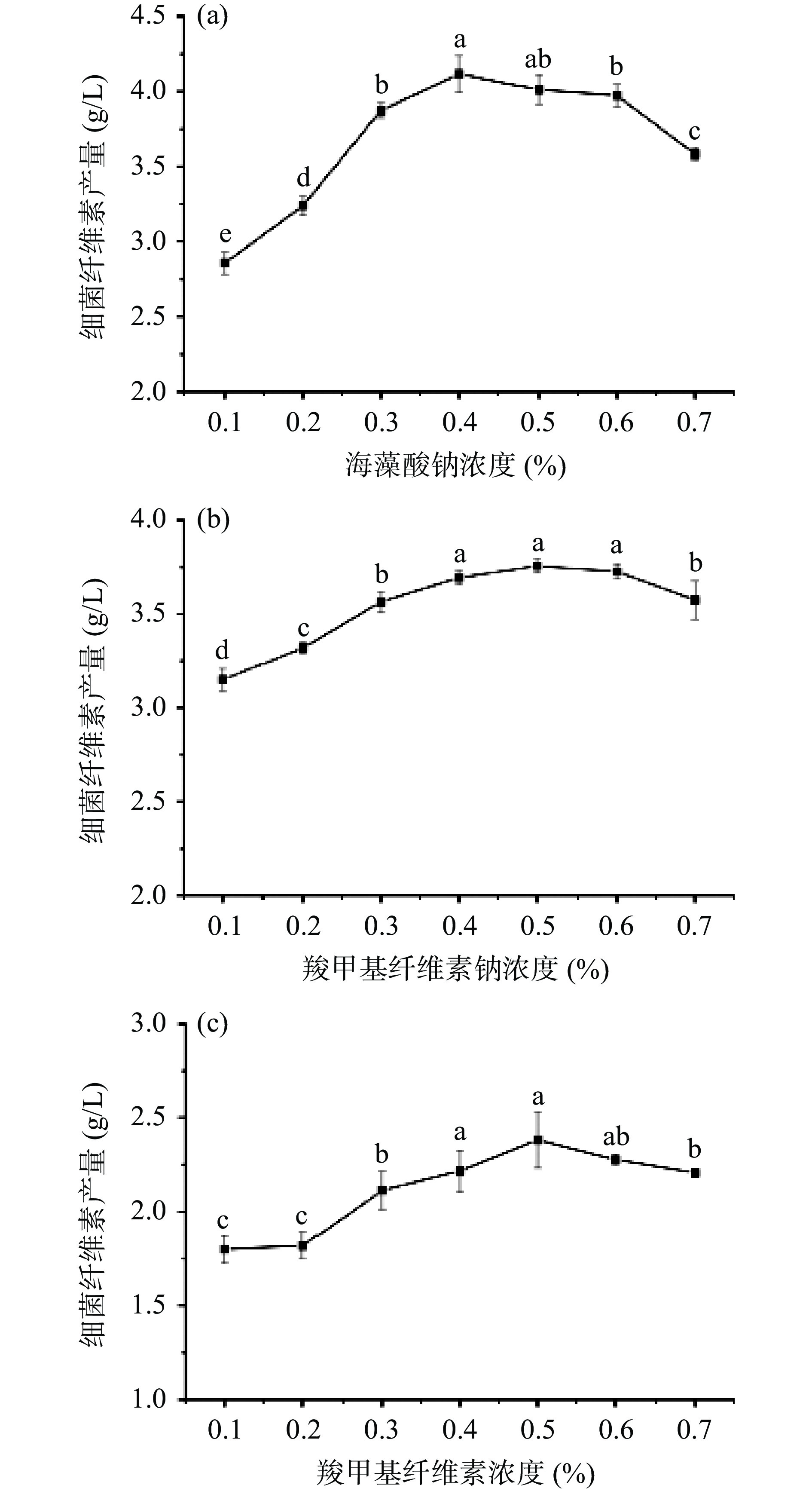
通过单因素实验,确定外源物质CMC-Na、SA、CMC的最佳添加量。由图3可知,当CMC-Na添加量为0.4%、0.5%、0.6%时,BC含量并不具有显著性差异(P>0.05),发酵环境中不同因素会对发酵结果产生不同影响,且三次平行实验结果显示CMC-Na添加量为0.5%时,BC合成量最大,故CMC-Na的最佳添加量为0.5%;随着SA添加量的增加,合成BC的促进作用较明显,SA的最佳添加量为0.4%;添加CMC后培养基体系粘度增大,BC产量误差较大,但当CMC添加量为0.5%时,BC产量最高。
2.2.2 外源物质对BC产量、OD600、总糖含量的影响
木葡糖醋杆菌发酵过程中,培养基中的一些外源物质可以直接与纤维素结合,干扰其结晶或与纤维素共结晶,部分外源物质也可以直接干扰细菌细胞,间接改变纤维素的生产[26]。
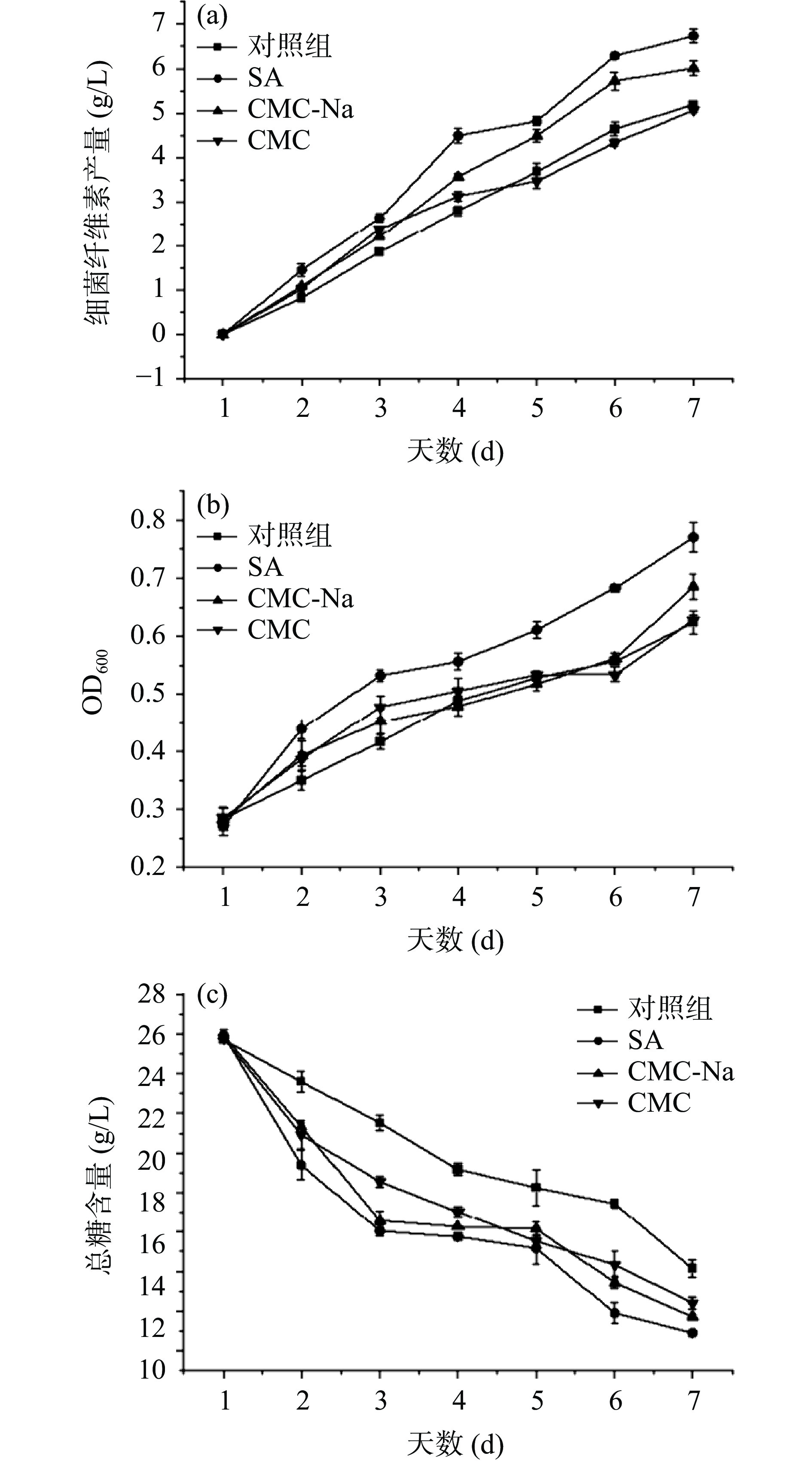
由图4a可知,添加外源物质后葡萄糖利用率明显提高,与对照组相比,添加SA和CMC-Na的细菌纤维素产量由5.19 g/L上升到6.74 g/L和6.01 g/L,增幅达到29.87%和15.8%;添加CMC后的BC产量为5.1 g/L,低于对照组,表明添加一定量的SA和CMC-Na可以有效提高BC产量,添加CMC后不但没有促进作用,反而抑制了BC的合成,这与钱子俊等[3]的研究结果类似。所有实验组中菌体浓度整体呈持续增长趋势(图4b)。添加外源物质后,发酵前期菌体浓度的增长速率均高于对照组,尤其是SA处理组菌体浓度上升趋势最为明显,表明加入适量外源物质可以缩短木葡糖醋杆菌发酵过程的适应期,使其迅速进入对数期,菌体迅速生长、繁殖,从而提高BC产量。在发酵过程中,葡萄糖主要用于BC合成途径以及糖酵解(EMP)途径和三羧酸循环(TCA),产生能量和菌体所需的蛋白质,同时产生各种有机酸与其他代谢副产物[27]。由图4c可看出,对照组以及添加SA、CMC-Na、CMC后的总糖消耗量分别为11.57、15.03、14.21、13.39 g/L,与对照组相比,添加外源物质后总糖消耗量和总糖消耗速率均大于对照组,表明添加外源物质后促进了碳源的消耗。发酵前3 d总糖快速消耗,后趋于平稳,主要是由于发酵前期菌体迅速繁殖,合成BC,碳源物质消耗速率加快。张丽平等[21]的研究表明,部分外源物质的添加可以减少无效碳循环,提高糖转化率,促进总糖消耗,提高BC合成途径的碳流量,与本文中添加SA和CMC-Na组研究结果类似。
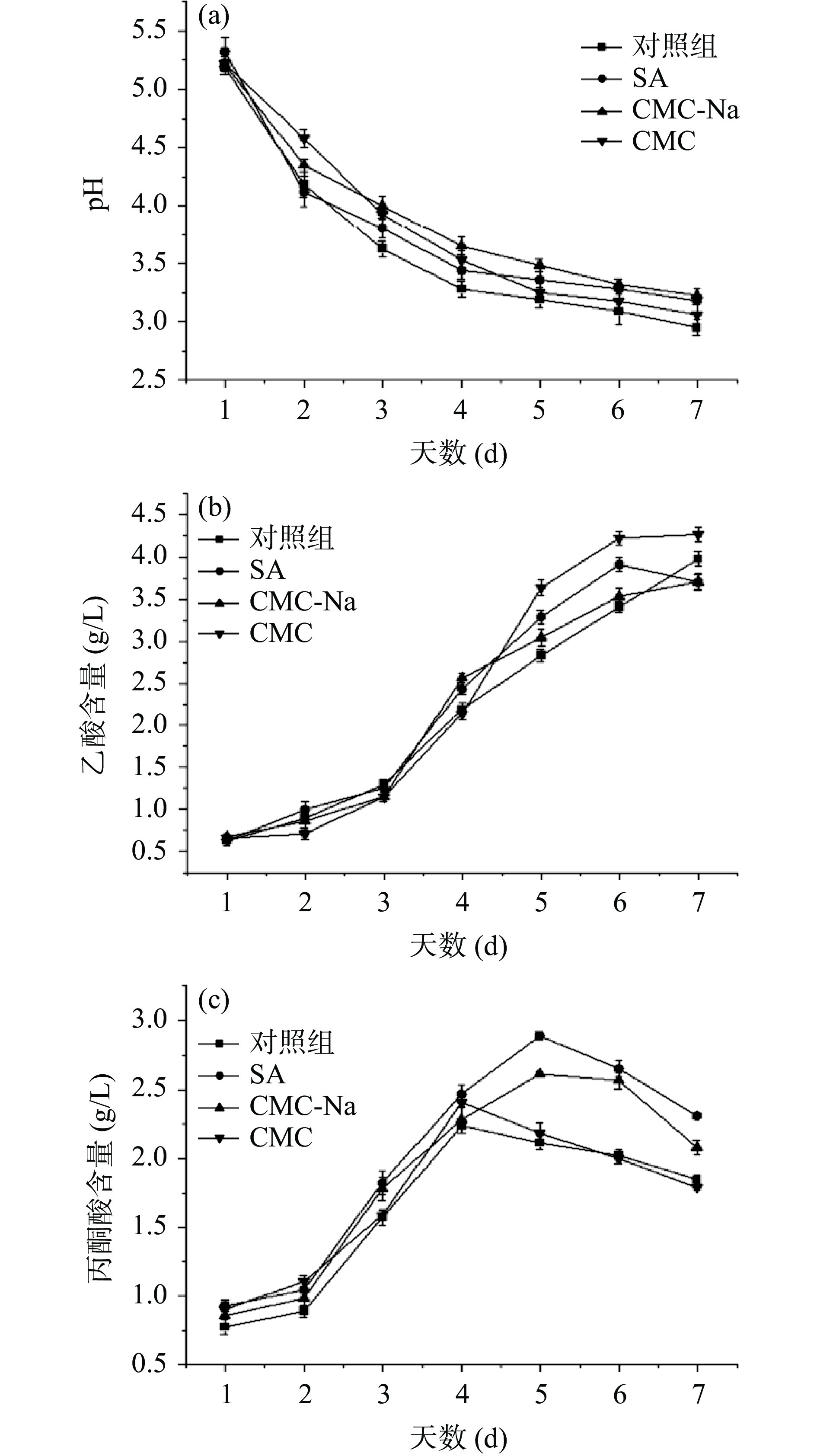
2.2.3 外源物质对发酵液pH、乙酸含量、丙酮酸含量的影响
由图5a可看出,添加不同外源物质对发酵液pH的变化影响有一定差异,发酵前期pH迅速下降,发酵中后期缓慢下降,这种现象与BC合成过程中乙酸、葡萄糖酸等物质的生成和后期消耗有关[28]。对照组pH下降趋势最明显,且发酵过程中pH均低于其他三组,可能是由于对照组中其他有机酸的积累量高于外源添加物组。李萧[29]的研究中发现,与添加外源物质组相比未添加外源物质的菌株利用碳源合成BC时,会生成大量的葡萄糖酸,使pH降低。吴敏等[30]研究发现添加外源物质可以减缓pH的下降,为菌体合成BC提供适宜的培养环境,从而促进BC合成,与本研究中SA与CMC-Na组结果类似。
由图5b乙酸含量变化图可看出,添加CMC后乙酸积累量最高为4.27 g/L,其次是对照组,而SA与CMC-Na组在发酵中后期乙酸积累量分别为3.85 g/L和3.87 g/L,高于对照组,但在终期低于对照组,表明SA与CMC-Na的添加促进了乙酸的部分积累,且一定量的乙酸可以作为底物,在发酵后期被利用,流向BC合成路径,促进BC合成。而CMC组乙酸积累量显著高于其他三组,BC合成被抑制,表明CMC的添加会促使菌株积累过量的乙酸,从而使细菌细胞的生长和纤维素的合成受到抑制。马霞等[31]研究有机酸对BC合成的影响规律时发现,当乙酸浓度高于临界值,会导致BC产量下降;李珏等[32]研究表明,汉逊氏葡糖醋杆菌(Gluconacetobacter hasenii)发酵生产BC时的最适乙酸浓度为3 g/L。
由图5c可知,4个组的丙酮酸含量整体呈先上升后下降的趋势,添加外源物质后丙酮酸积累量明显高于对照组,添加SA和CMC-Na后丙酮酸在第5 d达到最高积累量2.89 g/L和2.61 g/L,而CMC与对照组在第4 d最高达到2.41 g/L与2.24 g/L,当丙酮酸大量积累,EMP途径和TCA循环受到抑制,随后丙酮酸作为底物被消耗,经过糖异生后合成6-磷酸葡萄糖,使代谢流向BC合成途径,丙酮酸含量下降[21],SA与CMC-Na的添加促进了丙酮酸的积累与再利用,进而提升了BC的产量。
3. 结论
本文利用响应面优化试验,确定木葡糖醋杆菌合成BC的最佳培养基配方为葡萄糖4%、酵母浸粉1%、蛋白胨0.8%、MgSO4 1.9%、Na2HPO4 0.2%、乙酸0.4%、乙醇1.6%,此时,BC产量可达5.19 g/L。并在优化培养基中添加SA、CMC-Na和CMC三种物质,测定BC产量、总糖、乙酸、pH等指标。结果表明,与对照组相比,添加SA和CMC-Na后,消耗的碳源分别增加了3.46 g/L和2.64 g/L,同时也促进了丙酮酸的积累,使糖异生途径被加强,更多能量流向BC合成途径,最终BC产量分别为6.74 g/L和6.01 g/L,与对照组相比分别提高了29.87%和15.8%;添加CMC后乙酸含量最大为4.27 g/L,过量的乙酸积累量对细菌细胞的生长和纤维素的合成造成负面影响,BC产量为5.1 g/L,较对照组BC产量下降。后续将继续针对发酵液中各种有机酸对pH及BC产量的影响开展深入研究,以期为外源物质对木葡糖醋杆菌合成BC的影响提供理论基础,为细菌纤维素的规模化生产提供一定的参考。
-
图 1 不同添加物浓度对BC产量的影响
注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);图3同。
Figure 1. Effects of different additive concentrations on yield of bacterial cellulose
表 1 Plackett-Burman 试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of Plackett-Burmanexperiments design
水平 A
葡萄糖
(%)B
酵母浸粉
(%)C
蛋白胨
(%)D
MgSO4
(%)E
Na2HPO4
(%)F
乙酸
(%)G
乙醇
(%)低水平(−1) 2 0.2 0.2 0.5 0.1 0.1 1 高水平(+1) 8 1.4 1.4 3.5 0.7 0.7 2.2 表 2 Box-Behnken 试验因素水平及编码
Table 2 Factors and levels of Box-Behnken experiments
因素 编码 水平 −1 0 +1 葡萄糖(%) A 3 4 5 酵母浸粉(%) B 0.8 1 1.2 MgSO4(%) C 1.5 2 2.5 表 3 Plackett-Burman试验设计与结果
Table 3 Design and results of Plackett-Burman experiments
实验号 A B C D E F G BC产量(g/L) 1 1 −1 1 1 1 −1 −1 2.31±0.11 2 1 −1 1 1 −1 1 1 3.75±0.27 3 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 −1 0.29±0.05 4 −1 −1 −1 1 −1 1 1 2.51±0.18 5 −1 −1 1 −1 1 1 −1 0.12±0.05 6 1 −1 −1 −1 1 −1 1 0.78±0.09 7 −1 1 1 1 −1 −1 −1 4.18±0.16 8 −1 1 −1 1 1 −1 1 3.44±0.15 9 1 1 −1 −1 −1 1 −1 2.35±0.17 10 1 1 −1 1 1 1 −1 4.44±0.37 11 −1 1 1 −1 1 1 1 0.36±0.11 12 1 1 1 −1 −1 −1 1 2.42±0.08 表 4 Plackett-Burman试验的方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of Plackett-Burman experiments
因素 平方和 F值 P值 显著性 模型 25.3 12.99 0.0130 * A葡萄糖 2.21 7.95 0.0479 * B酵母浸粉 4.6 16.54 0.0153 * C蛋白胨 0.037 0.13 0.7324 D MgSO4 17.0.6 61.36 0.0014 ** E Na2HPO4 1.37 4.91 0.0909 F乙酸 1.008E−003 3.625E−003 0.9549 G乙醇 0.015 0.055 0.8255 注:*表示差异显著P<0.05,**表示差异极显著P<0.01;表6同。 表 5 Box-Behnken 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 5 Design and results of Box-Behnken response surface experiment
实验号 葡萄糖 酵母浸粉 MgSO4 BC产量(g/L) 1 0 0 0 5.29±0.12 2 0 1 1 3.5±0.19 3 0 1 −1 4.32±0.18 4 1 1 0 4.08±0.31 5 0 0 0 5.24±0.08 6 0 0 0 5.19±0.04 7 −1 1 0 4.19±0.09 8 1 0 1 3.54±0.12 9 1 0 −1 4.89±0.19 10 −1 −1 0 4.21±0.03 11 0 −1 −1 3.98±0.15 12 1 −1 0 3.67±0.26 13 0 0 0 5.31±0.09 14 0 −1 1 4.27±0.15 15 0 0 0 4.99±0.18 16 −1 0 1 4.31±0.15 17 −1 0 −1 4.32±0.14 表 6 Box-Behnken 响应面试验结果方差分析
Table 6 Analysis of variance of Box-Behnken response surface experiment results
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 Prob>F 显著性 模型 5.74 9 0.64 0.0006 ** A 0.09 1 0.09 0.1639 B 2.000E−004 1 5.356E−003 0.9437 C 0.45 1 0.45 0.0106 * AB 0.046 1 0.046 0.3026 AC 0.45 1 0.45 0.0104 * BC 0.31 1 0.31 0.0239 * A2 0.89 1 0.89 0.0018 ** B2 2.10 1 2.10 0.0001 ** C2 0.97 1 0.97 0.0014 ** 残差 0.26 7 0.037 失拟项 0.20 3 0.065 0.1087 纯误差 0.11 4 0.022 总和 6.58 16 R2=0.9565,R2adj=0.9005 -
[1] 赵鑫, 熊健力, 任叶琳, 等. 细菌纤维素合成与鉴定研究综述[J]. 化工进展,2020,39(S2):262−268 doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-0384 ZHAO X, XIONG J L, REN Y L, et al. Synthesis and identification of bacterial cellulose[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2020,39(S2):262−268. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-0384
[2] RADIMAN C, YULIANI G. Coconut water as a potential resource for cellulose acetate membrane preparation[J]. Polymer International,2008,57(3):502−508. doi: 10.1002/pi.2374
[3] 钱子俊, 张一瞳, 刘鹏, 等. 不同添加剂对木醋杆菌发酵细菌纤维素的影响[J]. 林业工程学报,2018,3(4):62−67 QIAN Z J, ZHANG Y T, LIU P. Effects of different additives on bacterial cellulose production by Gluconacetobacter xylinum[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2018,3(4):62−67.
[4] JI L, ZHANG F, ZHU L, et al. An in-situ fabrication of bamboo bacterial cellulose/sodium alginate nanocomposite hydrogels as carrier materials for controlled protein drug delivery[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,170:459−468. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.139
[5] 张艳, 孙怡然, 于飞, 等. 细菌纤维素及其复合材料在环境领域应用的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报,2021,38(8):2418−2427 doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210402.002 ZHANG Y, SUN Y R, YU F, et al. Research progress on the application of bacterial cellulose and its composites in environmental field[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(8):2418−2427. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210402.002
[6] AREVALO GALLEGOS A M, CARRERA S H, PARRA R, et al. Bacterial cellulose:A sustainable source to develop value-added products-A review[J]. BioResources,2016,11(2):5641−5655. doi: 10.15376/biores.11.2.Gallegos
[7] 杨颖, 贾静静, 陆胜民, 等. 细菌纤维素高产菌株的鉴定及产物分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2012,12(7):216−221 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7848.2012.07.032 YANG Y, JIA J J, LU S M, et al. Identification and product characteristics analysis of cellulose-producing strain[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2012,12(7):216−221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7848.2012.07.032
[8] BLANCO PARTE F G, SANTOSO S P, CHOU C C, et al. Current progress on the production, modification, and applications of bacterial cellulose[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology,2020,40(3):397−414. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1713721
[9] 尤勇. 乙醇、乙酸、乳酸对木葡萄糖醋杆菌合成细菌纤维素的影响及其功能分析[D]. 天津:天津科技大学, 2019 YOU Y. Function exploration of ethanol, acetic acid and lactic acid on the synthesis of bacterial cellulose in Gluconacetobacter xylinus[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[10] JUNG J Y, PARK J K, CHANG H N. Bacterial cellulose production by Gluconacetobacter hansenii in an agitated culture without living non-cellulose producing cells[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology,2005,37(3):347−354. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.02.019
[11] KESHK S, SAMESHIMA K. Influence of lignosulfonate on crystal structure and productivity of bacterial cellulose in a static culture[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology,2006,40(1):4−8. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.07.037
[12] ZHU H, JIA S, WAN T, et al. Biosynthesis of spherical Fe3O4/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites as adsorbents for heavy metal ions[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,86(4):1558−1564. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.06.061
[13] 毋锐琴. 高产细菌纤维素菌株的筛选及发酵工艺优化[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2008 WU R Q. Selection of strain with high-yield bacterial cellulose and optimization of fermentation process[D]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University, 2008.
[14] 李艳. 细菌高产菌株筛选鉴定与发酵工艺优化[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2013 LI Y. Selection and identification of strain with high-yield bacterial cellulose and optimization of fermentation process[D]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University, 2013.
[15] 赵浩杰, 王光翟, 廖博文, 等. 响应面法优化动态发酵细菌纤维素菌株HS01培养基[J]. 纤维素科学与技术,2020,28(4):1−9, 27 doi: 10.16561/j.cnki.xws.2020.04.02 ZHAO H J, WANG G Z, LIAO B W, et al. Optimization of fermentation medium of shake flask for bacterial cellulose producing strain Komagataeibacter hansenii HS01 by response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Cellulose Science and Technology,2020,28(4):1−9, 27. doi: 10.16561/j.cnki.xws.2020.04.02
[16] 林杉, 赵萍, 付云娜, 等. 羊肚菌胞外多糖液态发酵培养基配方优化及其体外降血糖活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(20):196−203 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120191 LIN S, ZHAO P, FU Y N, et al. Optimization of liquid fermentation medium formulation of Morchella eohespera exopolysaccharide and its hypoglycemic activity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(20):196−203. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120191
[17] MARTINS D, FERREIRA D D C, GAMA M, et al. Dry bacterial cellulose and carboxymethyl cellulose formulations with interfacial-active performance:Processing conditions and redispersion[J]. Cellulose,2020,27(11):6505−6520. doi: 10.1007/s10570-020-03211-9
[18] 李元敬. 细菌纤维素发酵优化及代谢途径调控[D]. 哈尔滨:黑龙江大学, 2011 LI Y J. Optimization of bacterial cellulose fermentation and regulation of metabolic pathways[D]. Harbin:Heilongjiang University, 2011.
[19] 李孔翰, 陈玲琳, 周建森, 等. TAT-SOD在长期保藏的重组毕赤酵母中表达的条件优化[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2020,39(8):51−58 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2020.08.007 LI K H, CHEN L L, ZHOU J S, et al. Optimization of TAT-SOD expression conditions in long-term preserved recombinant Pichia pastoris[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2020,39(8):51−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2020.08.007
[20] 贾青慧, 卢红梅, 陈莉, 等. 增效因子对木醋杆菌产细菌纤维素发酵液中物质变化的影响[J]. 中国酿造,2016,35(1):14−18 JIA Q H, LU H M, CHEN L, et al. Effect of synergistic factor on the substances change of fermentation liquid with bacterial cellulose-producing Acetobacter xylinum[J]. China Brewing,2016,35(1):14−18.
[21] 张丽平, 卢红梅, 戴锐, 等. 乙醇及有机酸对木醋杆菌合成细菌纤维素的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(4):161−165, 169 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.04.059 ZHANG L P, LU H M, DAI R, et al. Study on the function of ethanol and organic acid to Acetobacter xylinum synthetic bacterial cellulose[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(4):161−165, 169. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2014.04.059
[22] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会 GB 5009.237-2016 食品pH值的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016 National Health and Family Planning Commission GB 5009.237-2016 Determination of food pH value[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.
[23] 张继冉. 丙酮酸发酵工艺的优化及其快速测定方法的研究[D]. 开封:河南大学, 2011 ZHANG J R. Optimations on parameters control of pyruvate fermentation and studies on rapid detection of pyruvic acid[D]. Kaifeng:Henan University, 2011.
[24] LIU M, LIU L, JIA S, et al. Complete genome analysis of Gluconacetobacter xylinus CGMCC 2955 for elucidating bacterial cellulose biosynthesis and metabolic regulation[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):6266. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24559-w
[25] 文章, 何朝玖, 陈才, 等. 以黄水为培养基生产细菌纤维素[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(9):100−107 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020070020 WEN Z, HE Z J, CHEN C, et al. Production of bacterial cellulose using “yellow water”as medium [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(9):100−107. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020070020
[26] RUKA D R, SIMON G P, DEAN K M. In situ modifications to bacterial cellulose with the water insoluble polymer poly-3-hydroxybutyrate[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,92(2):1717−1723. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.11.007
[27] 李萧, 王淼. Komagataeibacter rhaeticus 3-15全基因组及葡萄糖脱氢酶基因缺失体的构建[J]. 工业微生物,2020,50(2):7−14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2020.02.002 LI X, WANG M. Whole genome and construction of glucose dehydrogenase gene deletion in Komagataeibacter rhaeticus 3-15[J]. Industrial Microbiology,2020,50(2):7−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2020.02.002
[28] CHAWLA P R, BAJAJ I B, SURVASE S A, et al. Microbial cellulose:Fermentative production and applications[J]. Food Technology & Biotechnology, 2009, 47(2):107−24.
[29] 李萧. 莱蒂亚驹形杆菌315生物合成细菌纤维素[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2020 LI X. The bacterial cellulose biosynthesis of Komagataeibacter rhaeticus 315[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2020.
[30] 吴敏, 喻少帆, 曹献英, 等. 添加海藻酸钠对椰子水体系合成细菌纤维素的影响[J]. 精细化工,2011,28(5):456−460 doi: 10.13550/j.jxhg.2011.05.010 WU M, YU S F, CAO X Y, et al. Effect of different additive amount of sodium alginate in coconut water culture system on bacterial cellulose produced by Acetobacter xylinum [J]. Fine Chemicals,2011,28(5):456−460. doi: 10.13550/j.jxhg.2011.05.010
[31] 马霞, 贾士儒, 关凤梅, 等. 有机酸对木醋杆菌合成细菌纤维素的影响规律[J]. 纤维素科学与技术,2003(1):34−37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8405.2003.01.007 MA X, JIA S R, GUAN F M, et al. Effect of organic acid on the production of Acetobacter xylinum cellulose [J]. Journal of Cellulose Science and Technology,2003(1):34−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8405.2003.01.007
[32] 李珏, 董梦娜, 吴延鸽, 等. 葡糖酸醋杆菌JR-02产细菌纤维素发酵工艺优化[J]. 中国酿造,2018,37(3):42−48 LI J, DONG M N, WU Y G, et al. Optimization of fermentation process of Gluconacetobacter hasenii JR-02 for bacterial cellulose production [J]. China Brewing,2018,37(3):42−48.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 龙正玉,邹金浩,杨怀谷,任国谱,曹清明,唐道邦. 肉制品发酵技术对肉品品质的调控及应用研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(03): 354-362 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 白婷,王卫,吉莉莉,张佳敏,刘达玉. 浅发酵香肠产品特性及其与中式香肠和西式发酵肠的比较. 成都大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(02): 137-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张佳敏,袁波,王卫,叶富云,唐春,翁德晖. 品质改良剂对浅发酵腊肠产品特性的影响及主成分分析. 食品工业科技. 2021(18): 244-251 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



