Analysis of Chemical Composition Differences of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' with Storage from 7 to 11 Years by Widely-Targeted Metabolomics Technology
-
摘要: 目的:研究不同陈化年限广陈皮化学成分的差异,为广陈皮的陈化机制提供一定的理论基础和科学依据。方法:采用UPLC-MS/MS广泛靶向代谢组学技术对3种陈化年限(7Y、9Y、11Y)广陈皮的化学成分进行检测和分析;使用PCA和OPLS-DA统计分析方法鉴定差异代谢物。结果:共鉴定出27类778个化合物,主要为黄酮类(121个)和萜类(90个)等成分,根据变量投影重要度(VIP)值大于1且P-value小于0.05,筛选出121个差异代谢物,其中陈化11Y组与陈化9Y组比较发现22类65个差异代谢物,陈化11Y组与陈化7Y组比较发现20类62个差异代谢物,陈化9Y组与陈化7Y组比较发现14类32个差异代谢物,陈化7~11年广陈皮差异代谢物的数量和种类趋于增多。陈化年限不同的广陈皮代谢物有较大差异。随着陈化时间的增加,陈化时间对黄酮类、萜类、氨基酸及其衍生物影响较大。与差异代谢物相关性最高的关键通路有:单萜类生物合成、黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成、氨基酸及其衍生物参与的代谢通路(丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢)。结论:采用广泛靶向代谢组学技术可以高效地对广陈皮化学成分进行组分鉴别和分析,为广陈皮陈化机制研究奠定了重要的技术基础。
-
关键词:
- 陈皮 /
- 广泛靶向代谢组学 /
- UPLC-MS/MS /
- 陈化 /
- 差异代谢物
Abstract: Objective: To analyze the differences of chemical composition of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' under different aging years, and to provide the theoretical and scientific basis for the aging mechanism of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi'. Methods: UPLC-MS/MS widely-targeted metabolomics technology was used to detect and analyze the chemical constituents of three kinds of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' aged seven years, nine years and eleven years. PCA and OPLS-DA statistical analysis methods were used to identify differential metabolites. Results: A total of 778 compounds of 27 categories were identified. Main components were flavonoids (121) and terpenoids (90). According to the VIP value greater than 1 and the P-value less than 0.05, 121 differential metabolites were screened, 65 differential metabolites of 22 categories between the 11-year aging group and 9-year aging group, 62 differential metabolites of 20 categories between the 11-year aging group and 7-year aging group, 32 differential metabolites of 14 categories between the 9-year aging group and 7-year aging group. The numbers and types of differential metabolites in Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' tended to increase after aging for 7~11 years. There were differences in metabolites of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' under different aging years. With the increase of aging time, the aging time had great influence on flavonoids, terpenoids, amino acid and derivatives. The key pathways with the highest correlation with differential metabolites were: Monoterpenoid biosynthesis, flavone and flavonol biosynthesis, the metabolic pathways involved in amino acid and derivatives (alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, cysteine and methionine metabolism). Conclusion: Widely-targeted metabolomics technology can be used to identify and analyze the chemical components of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' with high efficiency. It has established important technical foundation for researching the aging mechanism of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi'. -
陈皮为芸香科柑橘属小乔木植物橘(Citrus reticulate Blanco)及其栽培变种的成熟果皮,最早记载于《神农本草经》,是药食同源类物质[1],具有理气健脾、燥湿化痰的功效[2]。2020年版《中国药典》收载陈皮和广陈皮2个药材品种,其中,广陈皮来源于橘的变种茶枝柑(Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi'),广东新会茶枝柑皮为广陈皮的上品[3]。现代研究表明,陈皮挥发油能温和刺激胃肠道平滑肌,促进消化液分泌,排除肠道积气,增加食欲[4];陈皮中的黄酮和多糖化合物能清除自由基,具有抗氧化活性[5−6],抗衰老;陈皮含有的维生素C能降低胆固醇、预防血管破裂或渗血,和维生素P服用,治疗坏血病,经常饮用橘皮茶,对动脉粥样硬化或维生素C缺乏者有益[7];橙皮苷能降低胆固醇,调节肠胃功能和抗血栓形成[4]。陈皮还具有抗肿瘤[8−9]、降血脂[10]、抗肝损伤[11]等多种药理作用,在临床上广泛用于治疗恶心呕吐、咳嗽、消化不良、贫血和呼吸道炎症综合征等[12−13]。陈皮主要含黄酮类[14]、挥发油类[13]、生物碱类[15]、多糖类[16]等成分,对陈皮化学成分的研究主要集中于对不同储存年限、不同产地黄酮[2,17−18]和挥发油成分[19−21]的分析。
《日用本草》云“陈皮多年者更妙”,陈皮久置时间不同,其成分和药理活性存有一定差别[22],对其变化趋势,不同学者研究不一。目前对于陈皮年份的鉴别常通过拉曼光谱[23]、性状鉴别[24]、近红外光谱[25−26]或测定其成分组成与含量[27−28]。采用性状鉴别,操作简单快速,但具有主观性,准确率低。近红外光谱和光谱学是一种快速、无损、绿色的年份鉴别方法,但需要多种预处理方法优化光谱,消除仪器或样品的干扰,且为单点检测,不能直观观察整个样本,对样本本质的评估会有偏差[29]。通过化学方法判别,能检测到的成分种类少,不能完全体现陈皮陈化过程中所有化学成分的变化。这些方法也不能阐述陈皮的陈化机制,代谢组学可以全面地对生物系统中小分子代谢物进行定性和定量研究,为一种发现生物过程活性驱动因素的技术,适合研究和分析传统中药,突显中药的药理生物活性和生化机制[30−32]。广泛靶向代谢组学技术通过多反应监测技术采集大量的数据并建立代谢物标本数据库实现对代谢物高通量、准确的定性定量[31],能深入阐述样本的生物活性过程及陈化机制。
颜仁梁等[33]利用UPLC-MS/MS结合广泛靶向代谢组学对陈化1年、3年和5年广陈皮化学成分的差异进行研究发现,在五年的陈化过程中,随着陈化时间的增加,广陈皮化学成分逐渐趋于稳定。随着存储年限再延长,广陈皮成分是否会产生新的差异有待进一步研究。本实验采用超高效液相色谱-串联质谱(UPLC-MS/MS)结合广泛靶向代谢组学对陈化7年以上3种不同年限(7年、9年、11年)的广陈皮化学成分进行组分鉴别分析,使用主成分分析(PCA)和正交偏最小二乘法-判别分析(OPLS-DA)等多元统计分析方法对不同陈化年限广陈皮化学成分差异代谢物进行定量分析,并对差异代谢物的代谢通路进行富集分析和拓扑分析,为深入研究广陈皮陈化机制提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
实验所用18个广陈皮样品 由广东食品药品职业学院颜仁梁副研究员提供;甲醇、乙腈 色谱级,德国CNW Technologies公司;甲酸 色谱级,德国SIGMA公司。
ExionLC AD超高效液相色谱仪 美国Sciex公司;QTrap 6500+高灵敏度质谱仪 美国Sciex公司;Heraeus Fresco17离心机 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;明澈D24 UV纯水仪 德国Merck Millipore公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 陈皮样品采集
实验所用陈皮样品均采自广东省江门市新会陈皮核心产区,经广东食品药品职业学院梁永枢副研究员鉴定为芸香科植物广陈皮茶枝柑干燥成熟果皮,陈化时间分别为2014年(7Y)、2012年(9Y)、和2010年(11Y)新会陈皮,分为3组,每组3个样品,每个样品分装成两份,共18份,每份各检验一次,并两两对比(11Y VS 9Y,11Y VS 7Y和9Y VS 7Y),7Y广陈皮采集地:广东省江门市新会区天马村、梅江、双水南岸;9Y广陈皮采集地:广东省江门市新会区茶坑村、围垦村、双水南岸;11Y广陈皮采集地:广东省江门市新会区天马村(2份样品)、茶坑村。
1.2.2 样品制备
样品处理方法、质谱与色谱条件参考文献报道方法[33−35]。将陈皮样本冷冻干燥后进行研磨(60 Hz,30 s),称取50 mg的样品,加入700 μL提取液(甲醇水,体积比3:1,−40 ℃ 预冷,含内标2-氯苯丙氨酸),涡旋30 s(35 Hz),匀浆4 min,冰水浴超声(35 Hz,5 min),重复匀浆超声3次,并在混匀仪上过夜(4 ℃),将样品于4 ℃,12000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液经0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤,并保存于进样瓶中,用于UPLC-MS/MS分析。
1.2.3 质控样品
质控样本(QC)由18份陈皮样本提取物混合制备而成,样品制备项下提取得到的陈皮上清液用提取液稀释10倍,涡旋30 s后,每个样本稀释液各取20 μL混合成QC样本,加入内标2-氯苯丙氨酸,QC样本内标浓度相同,在仪器分析过程中,每10个检测分析样本中插入一个质控样本,以监测分析过程的重复性。
1.2.4 分析条件
1.2.4.1 色谱条件
色谱柱:Waters Acquity UPLC HSS T3(1.8 μm,2.1×100 mm);柱温:40 ℃;进样体积:2 μL;流速:400 μL/min;流动相A:0.1%甲酸水溶液,流动相B:乙腈;梯度洗脱条件:0~0.5 min(保持2% B),0.5~10 min(2% B~50% B),10~11 min(50% B~95% B),11~13 min(保持95% B),13~13.10 min(95% B~2% B),13.1~15 min(保持2% B);自动进样器温度:4 ℃。
1.2.4.2 质谱条件
检测仪器:SCIEX 6500 QTRAP+三重四极杆质谱仪(IonDrive Turbo VESI 离子源),结合使用电喷雾电离(ESI)正离子和负离子模式进行检测。离子源参数:离子喷雾电压:+5500/−4500 V;气帘气流速:35 psi;离子源温度:400 ℃;GSI气体流速:60 psi;GSII 气体流速:60 psi;去簇电压:±100 V;以多反应监测 (MRM)模式进行质谱分析。
1.3 数据处理
质谱数据:使用SCIEX Analyst Work Station Software (Version 1.6.3)对所有数据及目标化合物定量分析。 利用MSconventer 软件将质谱原始数据转成TXT格式,并使用自撰写R程序包结合自建数据库完成提峰、注释等工作。代谢组数据:先对单个峰基于四分位距对偏离值进行过滤以去除噪音,只保留单组空值不多于50%或所有组中空值不多于50%的峰面积数据;其次对原始数据中的缺失值进行模拟,数值模拟方法为最小值二分之一进行填补;最后对数据进行标准化处理,利用内标进行归一化。将处理好的数据导入SIMCA软件,进行主成分分析(PCA)和正交偏最小二乘法-判别分析(OPLS-DA)等多元统计分析,然后根据OPLS-DA模型第一主成分的变量投影重要度(Variable Importance in the Projection,VIP)大于1且t检验( t-test)的P值(P-value)小于0.05,进行差异性代谢物筛选。利用KEGG等数据库对差异代谢物的代谢途径进行富集分析和拓扑分析,找到与代谢物差异相关性最高的关键通路。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同年限广陈皮代谢组学的分析
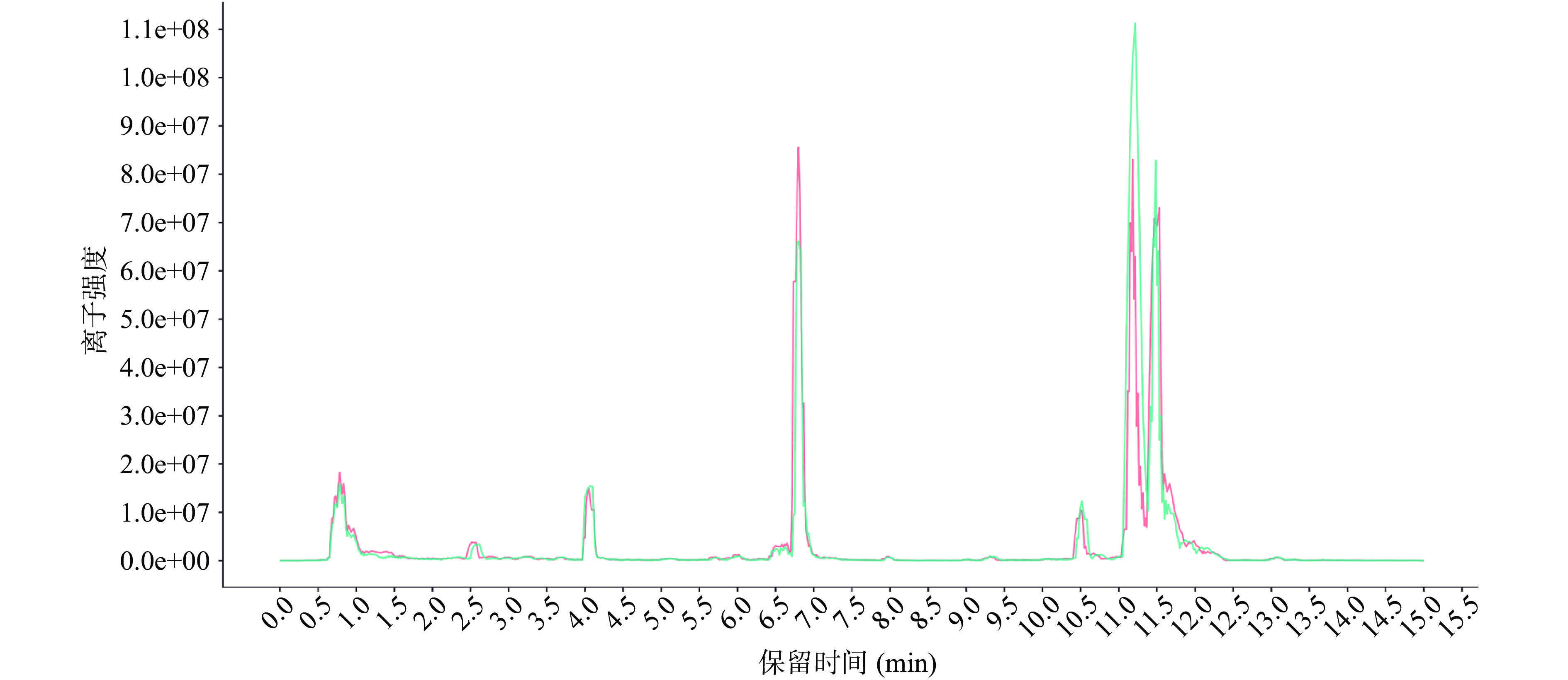
使用UPLC-MS/MS对混样质控QC 样品进行检测,对两次QC样本总离子流(TIC)出峰保留时间和峰面积进行重叠分析,判断代谢物提取和检测的重复性,为数据的质量提供保障[36]。QC样本的总离子流图如图1所示,QC样本TIC保留时间和峰面积重叠很好,表明仪器稳定性好,数据可靠。
对7年、9年和11年广陈皮代谢物进行质谱定性定量分析,从18个实验样本及QC样本中提取出779个峰(Peak),经预处理(见1.3数据处理)后778个峰被保留,代谢物高分辨二级质谱数据与公共数据库进行比对,利用质谱定性分析匹配得到物质名称,鉴定出27类778种化合物,分别属于黄酮类、植物激素类、氨基酸及其衍生物、萜类、生物碱类、其他类等27类化合物,其他类包括苯甲醛类、苯甲酸衍生物、吡咯烷类、二恶烷类、胍类、甲亚胺酸及其衍生物、芪类等,其中黄酮类和萜类化合物较多,如表1 所示。在 7 年、9 年和 11 年广陈皮均检出 778种化合物。
表 1 不同年限广陈皮中代谢物分类及峰面积占比Table 1. Metabolites classification and proportion of peak area of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' under different aging years代谢物类别 数量 峰面积占比(%) 代谢物类别 数量 峰面积占比(%) 氨基酸及其衍生物Amino acid and derivatives 44 8.152 植物激素phytohormone 14 0.116 吡啶及其衍生物Pyridines and derivatives 11 0.037 有机氧化合物Organooxygen compounds 11 0.442 其他类型other 74 0.987 有机酸及其衍生物Organic acids and derivatives 11 0.498 酚类Phenols 61 3.343 有机氮化合物Organooxygen compounds 9 0.134 核苷酸及其衍生物Nucleotide and its derivates 30 3.662 萜类Terpenes 90 1.215 黄酮Flavonoids 121 64.070 苯丙素类Phenylpropanoid 57 0.878 生物碱Alkaloids 87 1.962 醌类Quinones 12 0.017 羧酸类及其衍生物Carboxylic acids and derivatives 22 10.771 孕烯醇酮脂类Prenol lipids 7 0.038 糖类Carbohydrates 13 1.943 肉桂酸及其衍生物Cinnamic acids and derivatives 4 0.028 脂肪酰类Fatty acyls 28 1.151 酮酸及其衍生物Keto acids and derivatives 5 0.022 芳香类化合物Benzene and substituted derivatives 15 0.280 甾体及其衍生物Steroids and steroid derivatives 28 0.144 醇类和多元醇Alcohols and polyols 4 0.025 氧杂蒽酮Xanthones 6 0.003 维生素类Vitamins 5 0.065 吲哚及其衍生物Indoles and derivatives 5 0.014 查尔酮Chalcones 4 0.003 总计 778 100 2.2 不同年限广陈皮代谢组学差异分析
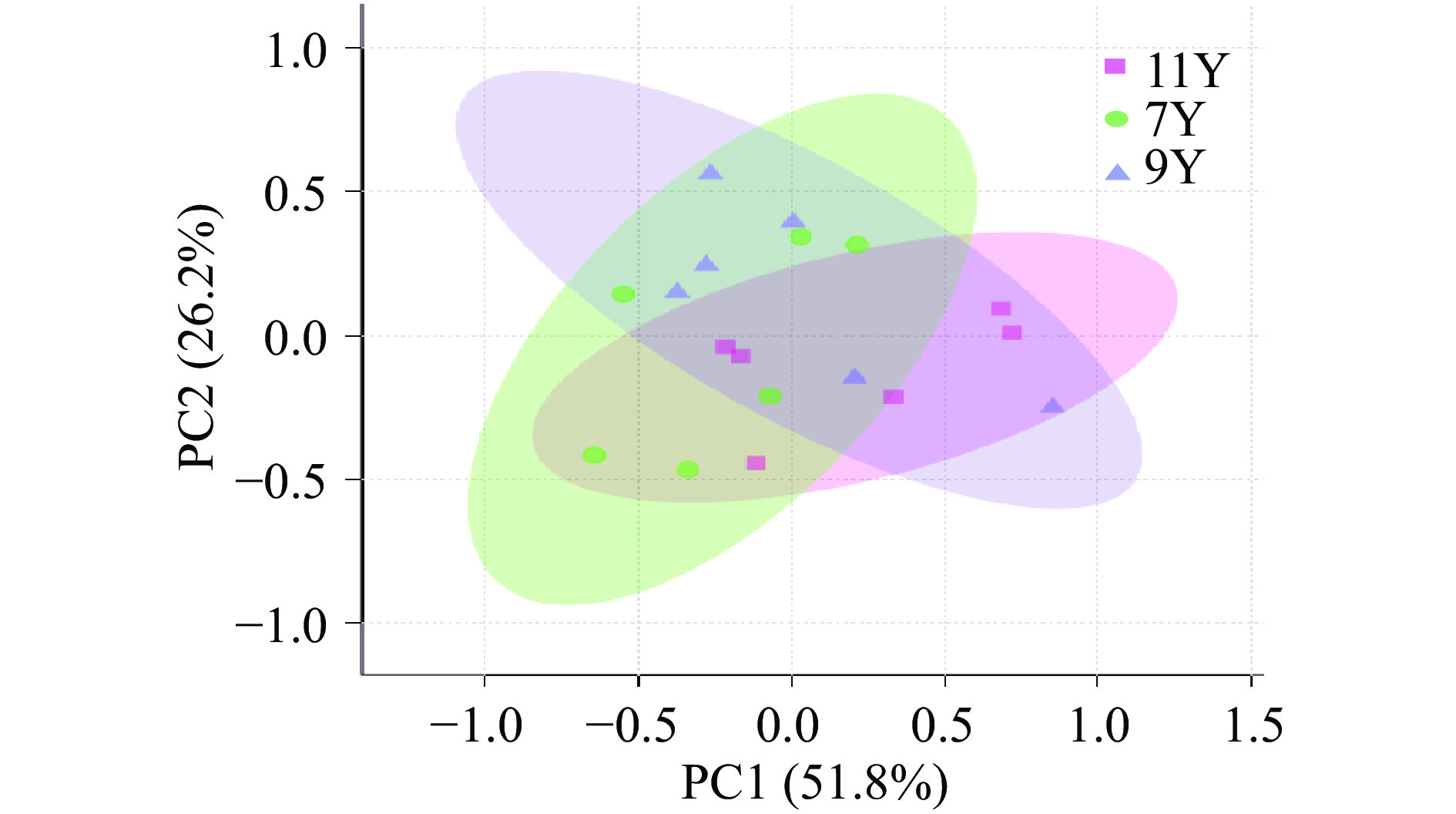
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)是一种无监督模型,可以揭示数据的内部结构,更好地解释数据变量[37],三组陈皮代谢组数据经标准化处理后进行PCA分析,结果见图2所示,第一主成分(PC1)的贡献率为51.8%,第二主成分(PC2)的贡献率为26.2%,R2X=0.544,样本全部处于95%置信区间内,三组广陈皮样本并没有区分开,有部分数据靠近,可能是由于品种相同、代谢物种类相近的原因造成。由于PCA是无监督分类模型,数据会受许多与分组信息无关的变量影响,因此,进行了有监督分类模型OPLS-DA。
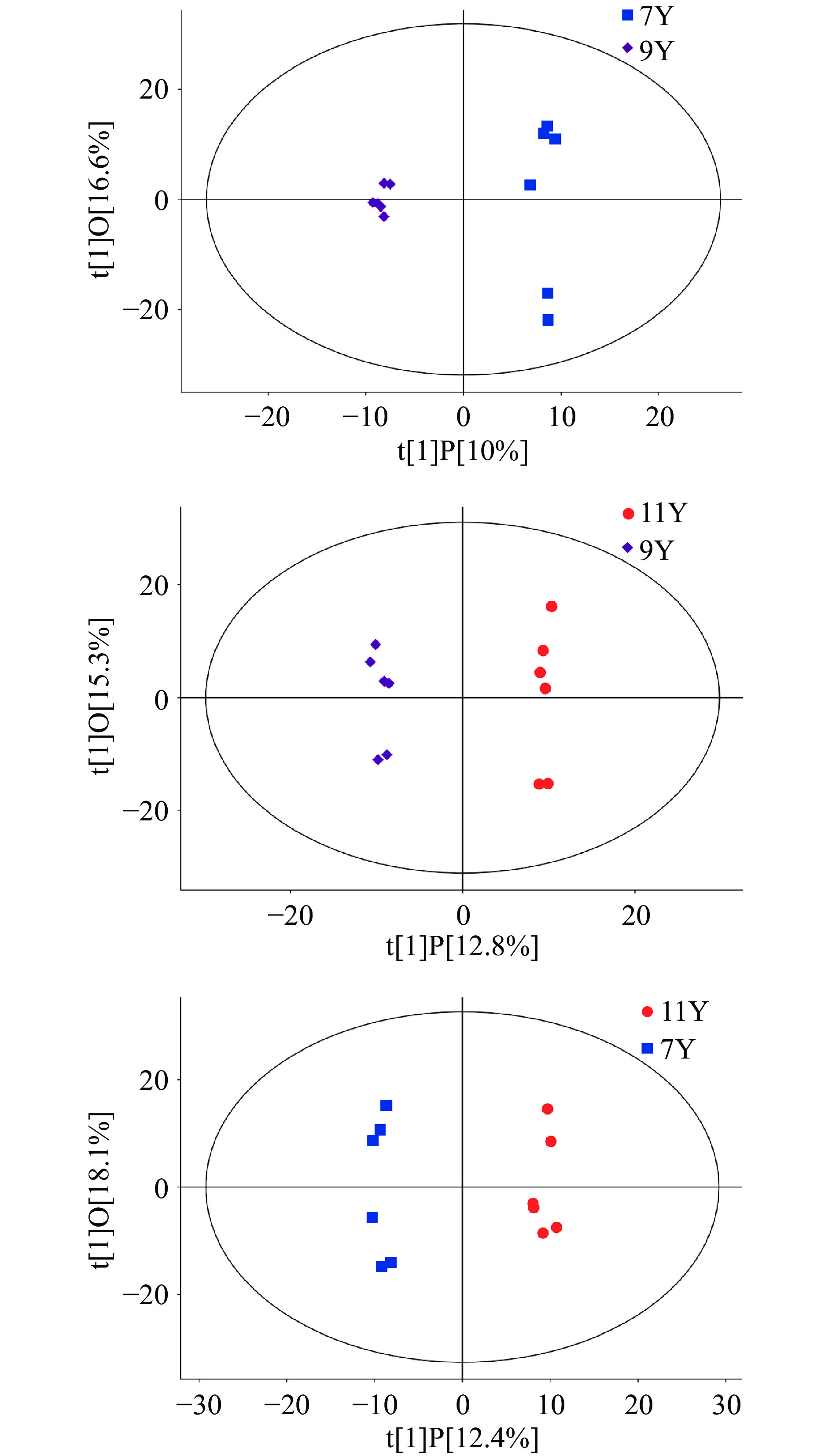
采用正交偏最小二乘法-判别分析(OPLS-DA)统计方法,可以过滤掉代谢物中与分类变量不相关的正交变量,并对非正交变量和正交变量分别分析,从而获取更加可靠的代谢物组间差异与实验组的相关程度信息[38]。OPLS-DA结果如图3和表2所示,从结果可以看出,样本全部处于95%置信区间内,Q2值大于等于0.4,说明OPLS-DA预测性可接受,各两组样本分布于左右侧置信区间内,样本点间没有重叠,区分效果较好。样本点之间分布相对分散,这可能与采样地点不同有关,由OPLS-DA结果可以看出,陈化时间、产地对广陈皮的代谢有一定的影响。
表 2 OPLS-DA模型参数和置换检验Table 2. OPLS-DA model parameters and permutation tests比较组 OPLS-DA模型参数 OPLS-DA置换检验(次数n=200) R2X
(cum)R2Y
(cum)Q2
(cum)R2Y(cum) Q2(cum) 11Y VS 9Y 0.281 0.995 0.503 0.99 −0.22 11Y VS 7Y 0.305 0.991 0.506 0.98 −0.23 9Y VS 7Y 0.266 0.994 0.4 0.99 −0.55 OPLS-DA置换检验随机模型(次数n=200)如表2所示,其模型Q2值均小于原模型的Q2值;Q2的回归线与纵轴的截距小于零;同时随着置换保留度逐渐降低,置换Y变量比例增大,随机模型的Q2逐渐下降。说明原模型具良好的稳健性,不存在过拟合现象,即OPLS-DA得分图结果准确。
2.3 不同年限广陈皮之间差异代谢分析
2.3.1 不同年限广陈皮差异代谢物鉴定与分析
利用 t 检验(t-test)的 P 值(P-value)和 OPLS-DA 模型第一主成分的变量投影重要度(Variable Importance in the Projection,VIP)筛选各组间的差异代谢物,VIP值可以衡量各代谢物组分含量对样本分类判别的影响强度和解释能力,辅助标志代谢物的筛选[33]。当代谢物同时满足P<0.05和VIP>1这两个条件时,则认为存有差异。其中11Y VS 9Y共筛选出22类65种差异代谢物,如表3所示,占比较多的是黄酮、萜类、生物碱和酚类,有38种差异代谢物上调和27种差异代谢物下调,上调物质多为黄酮、氨基酸及其衍生物和核苷酸及其衍生物类物质,下调物质多为生物碱和萜类,其中下调物质萜类为单萜和倍半萜,是挥发油的主要成分,具有挥发性。9Y VS 7Y筛选到14类32种差异代谢物,占比较多的是萜类、黄酮、氨基酸及其衍生物、酚类和生物碱,19个差异代谢物上调和13个差异代谢物下调,上调物质多为黄酮和酚类,下调物质多为萜类,为环烯醚萜和三萜类物质。其中高丽槐素、别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物、乙酸龙脑酯和Altholactone在9Y VS 7Y组中上调,在11Y VS 9Y下调;N,N-二甲基苯胺、3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸和Ipecoside变化与之相反。11Y VS 7Y筛选到20类62种差异代谢物,占比较多的是黄酮、萜类、氨基酸及其衍生物、苯丙素类和酚类,47种差异代谢物上调和15种差异代谢物下调,上调物质多为黄酮、氨基酸及其衍生物、苯丙素类和酚类,下调物质多为萜类,且多为三萜类物质。但高丽槐素、别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物、乙酸龙脑酯、Altholactone、N,N-二甲基苯胺、3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸和Ipecoside这些化合物在11Y VS 7Y中为非显著差异代谢物。3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸、锦葵色素3-O-葡糖苷、乳菇紫素、杜克苷A、右美托咪定、吴茱萸苦素和奇霉素在11Y VS 7Y、9Y VS 7Y组上调,茉莉酸变化与之相反,但这些化合物在11Y VS 9Y中为非显著差异代谢物。
表 3 不同年限广陈皮差异代谢物Table 3. Differential metabolites of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' under different aging years比较组 表达上调/下调 代谢物
11Y VS 9Y
上调黄酮:矢车菊素、维采宁2、桑皮酮H、葡萄糖基甘草苷、槲皮素、川橙皮素、二氢槲皮素;
生物碱:马山茶碱、灵芝酸L;萜类:左旋龙脑、alpha-松油醇、Ipecoside;酚类:Pinostilbenoside、香草酸、Myzodendrone;氨基酸及其衍生物:N-甲酰蛋氨酸、L-蛋氨酸、L-苏氨酸、同型丝氨酸;有机氮化合物:N,N-二甲基苯胺;核苷酸及其衍生物:1-甲基腺嘌呤、腺苷 5'-单磷酸、腺苷-2',3'-环磷酸、吉西他滨;吡啶及其衍生物:3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸、Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate下调 黄酮:高丽槐素、水黄皮素、7,8-二羟基黄酮;萜类:土木香内酯、桉叶油醇、乙酸龙脑酯、Alpha-山道年;
生物碱:别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物、去甲肾上腺素、蜀黍苷、迷迭香宁碱;酚类:Altholactone、6-姜酚
9Y VS 7Y
上调黄酮:甜橙黄酮、锦葵色素 3-O-葡糖苷、高丽槐素;萜类:乙酸龙脑酯、杜克苷A、吴茱萸苦素;
氨基酸及其衍生物:3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸;酚类:天麻素、Altholactone、构树宁C;生物碱:别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物;糖类:D-果糖-6-磷酸;芳香类化合物:右美托咪定;二恶烷类:奇霉素
下调黄酮:天竺葵素-3-O-葡萄糖苷;萜类:京尼平苷、Ipecoside、20(S)-人参皂苷Rh2;
氨基酸及其衍生物:L-蛋氨酸、L-谷氨酰胺;生物碱:4-甲基-5-噻唑乙醇;有机氮化合物:N,N-二甲基苯胺;吡啶及其衍生物:3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸;核苷酸及其衍生物:1-甲基腺嘌呤
11Y VS 7Y
上调黄酮:金合欢素、桔皮素、川橙皮素、锦葵色素 3-O-葡糖苷、3'-甲氧基芹菜苷、异金雀花素、桑皮酮H、汉黄芩素、3,9-二甲氧基紫檀碱、黄颜木素;萜类:吴茱萸苦素、杜克苷A、尼洛替星、奇壬醇;氨基酸及其衍生物:L-苏氨酸、L-蛋氨酸、3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸、N-甲酰蛋氨酸、苯乙酰甘氨酸、同型丝氨酸;苯丙素:异秦皮啶、松柏苷、牛蒡子苷元、8-香叶草氧基补骨脂素;酚类:1,2-二甲氧基苯、桑辛素 C、Pinostilbenoside、姜黄素;甲亚胺酸及其衍生物:十六酰胺乙醇;甾体:固甾酮;蝶啶及其衍生物:异黄蝶呤 下调 黄酮:7,8-二羟基黄酮;萜类:右旋香芹酮、泽渥萜、蒲公英赛醇、土木香内酯、氯化缬草素、日耳曼醇 2.3.2 不同年限广陈皮主要代谢成分比较分析
广陈皮陈化7~11年过程中,共发现778种化学成分、121种差异代谢物,差异代谢物占比约16%,而有约84%的成分保持稳定,不同陈化年限广陈皮代谢物有较大差异,11Y VS 9Y和11Y VS 7Y组筛选得到的差异代谢物种类和数量比9Y VS 7Y多,在7~11年这过程中,随着陈化时间的增加,广陈皮差异代谢物的数量和种类趋于增多,陈化时间对黄酮类、萜类、氨基酸及其衍生物影响较大。
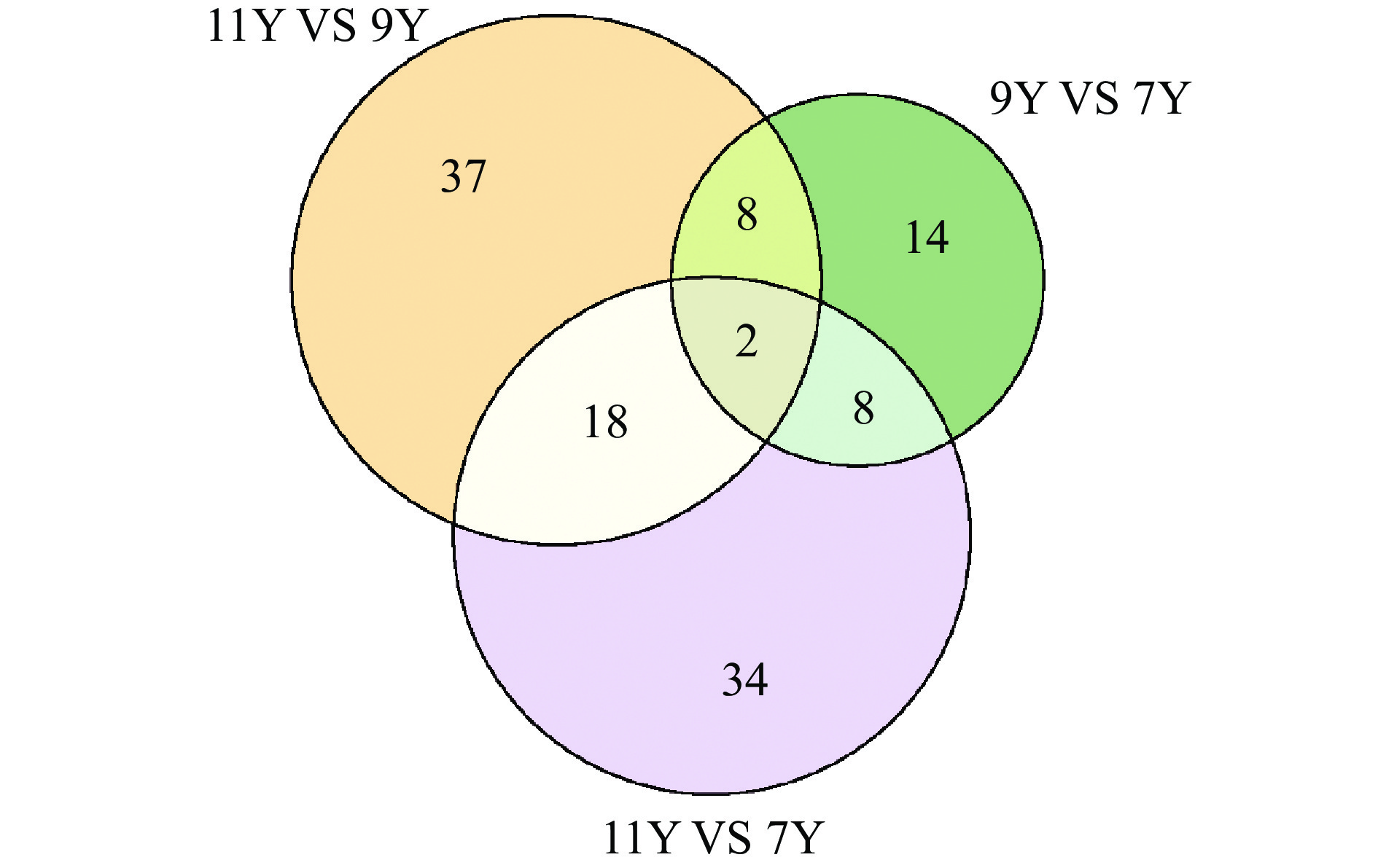
将各两组对比筛选得到的差异代谢物结果以韦恩图(Venn Plot)的方式进行展示,用于发现多组间差异代谢物,如图4所示。三组共同交集差异代谢物成分仅为1-Methyladenine(1-甲基腺嘌呤,核苷酸及其衍生物)和L-Methionine(L-蛋氨酸,氨基酸及其衍生物),而1-甲基腺嘌呤和L-蛋氨酸在9Y VS 7Y组中表现下调,在11Y VS 9Y和11Y VS 7Y组上调,各比较组间差异代谢物相差较大。
2.3.3 不同年限广陈皮差异代谢物通路分析
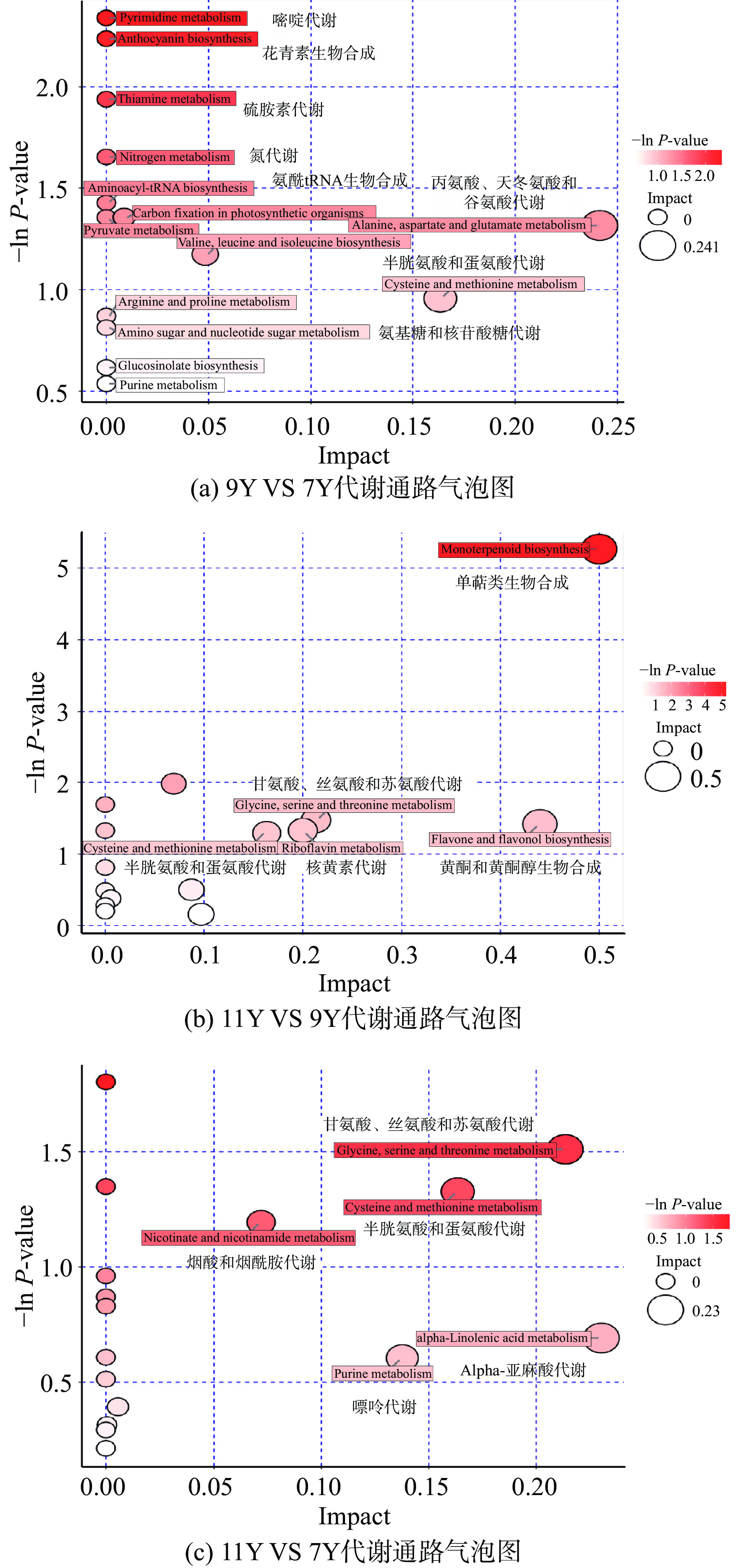
利用KEGG、HDMB和PubChem数据库对差异代谢物的代谢途径进行富集分析和拓扑分析,找到与代谢物差异相关性最高的关键代谢通路,通过分析发现:11Y VS 9Y有14种差异代谢物富集在15条通路中,9Y VS 7Y有7种差异代谢物富集14条通路中,11Y VS 7Y有12种差异代谢物富集17条通路中,代谢通路分析的结果以气泡图展示,如图5所示。有5条通路是11Y VS 9Y、9Y VS 7Y和11Y VS 7Y所共有,分别是:Valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis(缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸生物合成)、Cysteine and methionine metabolism(半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢)、Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis(氨酰tRNA生物合成)、Glucosinolate biosynthesis(葡萄糖苷酸生物合成)和Purine metabolism(嘌呤代谢)。这些差异代谢物参与的代谢途径可能与广陈皮陈化机制有关。
由图5综合可知,Monoterpenoid biosynthesis(单萜类生物合成)处的气泡颜色最深,而且最大,说明该通路对11年和9年广陈皮之间的差异影响最大,11Y VS 9Y中萜类成分为单萜和倍半萜;其次是黄酮类物质参与的代谢通路(黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成)、氨基酸及其衍生物参与的代谢通路(丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢)代谢通路对不同年限广陈皮陈化的影响较大,总之,陈化时间对黄酮类、萜类、氨基酸及其衍生物影响较大,随着陈皮储藏年限延长,三类化合物种类和数目也增多。
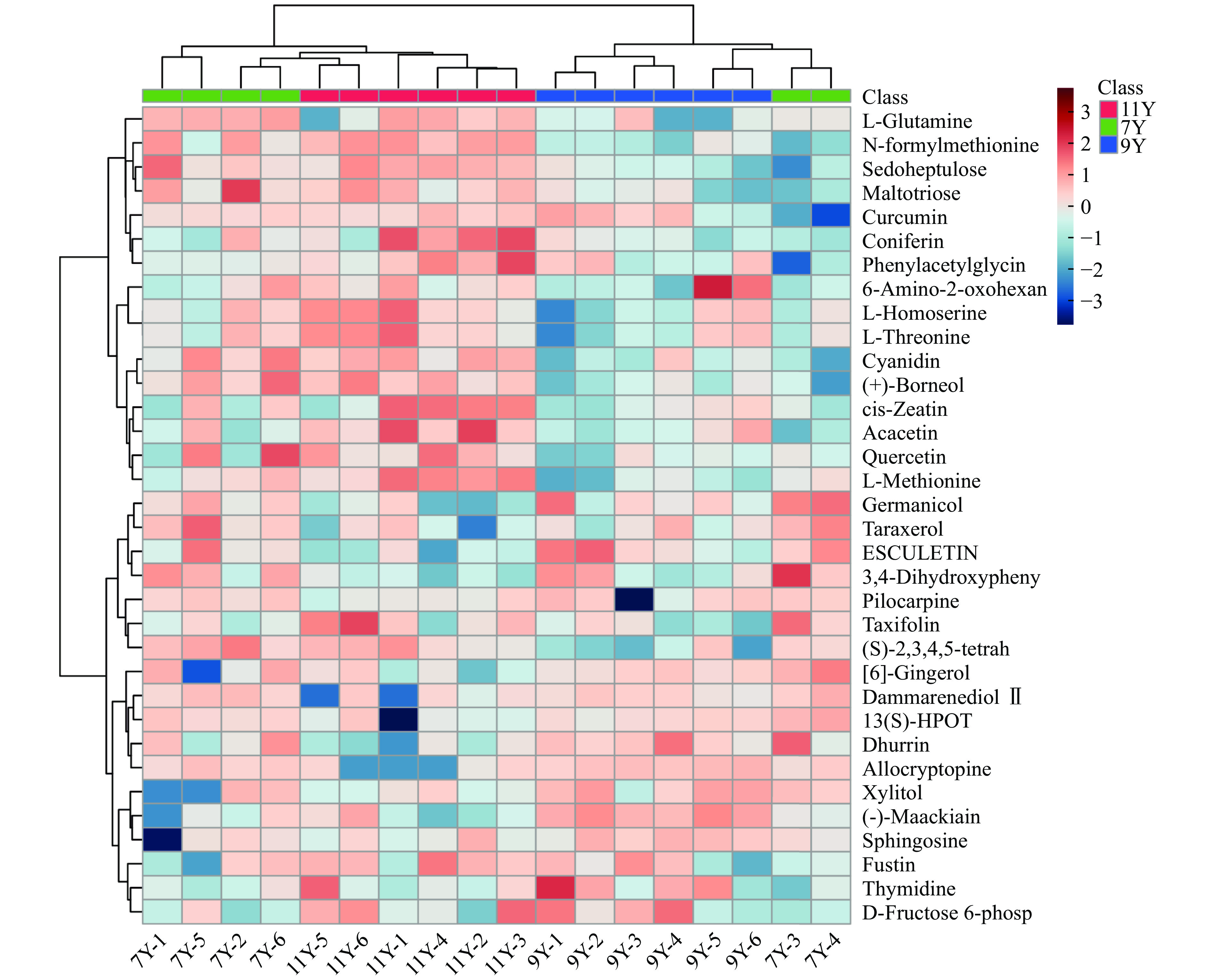
另外,筛选出的121种差异代谢物中有34个化合物能被注释到KEGG数据库现有的通路,主要包括17类34个差异代谢物,富集在45条通路中,6种黄酮(包括类黄酮)、6种氨基酸及其衍生物、4种单萜、1种核苷酸及其衍生物、1种糖类、1种脂肪酰类、2种苯丙素类、2种酚类、1种芳香类化合物、1种其他类、3种生物碱、1种植物激素、2种有机氧化合物、1种羧酸类及其衍生物、1种醇类和多元醇及1种有机氮化合物。差异代谢物被注释最多的是黄酮和氨基酸及其衍生物这2种类别,其中黄酮类物质主要参与黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成、类黄酮生物合成、次级代谢产物的生物合成等多条代谢通路;氨基酸及其衍生物主要参与缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸生物合成、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢、嘌呤代谢、氨酰tRNA生物合成、次级代谢产物的生物合成等多条代谢通路。聚类分析结果以热图表示,如图6所示,不同陈化年限广陈皮代谢物有较大差异,同型丝氨酸(Log2 FC:0.89)、槲皮素(Log2 FC:0.96)、矢车菊素(Log2 FC:1.05)、景天庚酮糖(Log2 FC:0.82)、L-苏氨酸(Log2 FC:0.89)、麦芽三糖(Log2 FC:1.26)、N-甲酰蛋氨酸(Log2 FC:2.18)等成分在11Y VS 9Y中上调;胸苷(Log2 FC:1.17)、鞘氨醇(Log2 FC:1.41)、D-果糖-6-磷酸(Log2 FC:0.82)、别隐品碱(Log2 FC:0.81)、高丽槐素(Log2 FC:1.62)等成分在9Y VS 7Y中上调;苯乙酰甘氨酸(Log2 FC:1.54)、N-甲酰蛋氨酸(Log2 FC:1.15)、L-苏氨酸(Log2 FC:0.78)、L-蛋氨酸(Log2 FC:1.04)、同型丝氨酸(Log2 FC:0.78)、黄颜木素(Log2 FC:0.61)、姜黄素(Log2 FC:0.91)、松柏苷(Log2 FC:1.95)、顺式玉米素(Log2 FC:1.95)、金合欢素(Log2 FC:1.40)、6-氨基-2-氧代己酸(Log2 FC:0.4)等成分在11Y VS 7Y中上调。
3. 讨论与结论
本研究运用超高效液相色谱-串联质谱广泛靶向代谢组学技术对7年、9年、11年广陈皮化学成分进行组分鉴别分析,共鉴定出27类778个化合物,主要为黄酮类(121个)和萜类(90个)等成分,高于利用顶空固相微萃取-全二维气相色谱-飞行时间质谱结合化学计量学方法检测到的约500种广陈皮化合物[39],778个化合物中共筛选出121种差异代谢物,说明7年到11年陈化过程中,约84%的成分保持稳定,约16%是差异代谢物,差异代谢物中黄酮类、氨基酸及其衍生物和萜类占比较多。与前文研究报道[33]的5年内广陈皮陈化后化学成分变化情况比较,检出了更多的成分,但7年后广陈皮化学成分变化较小,差异代谢物比例下降,主要是苷类变化较大,可能与苷类成分降解有关,具体机制有待进一步研究。
本实验三组间共同交集差异代谢物成分为1-Methyladenine(1-甲基腺嘌呤,核苷酸及其衍生物)和L-Methionine(L-蛋氨酸,氨基酸及其衍生物),各比较组间相差较大,可能是由于陈化时间或者产地不同等造成的。在本次研究中发现,高丽槐素、别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物、乙酸龙脑酯、Altholactone在9Y VS 7Y组中上调,在11Y VS 9Y下调;N,N-二甲基苯胺、3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸和Ipecoside与之变化相反。但高丽槐素、别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物、乙酸龙脑酯、Altholactone、N,N-二甲基苯胺、3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸和Ipecoside这些化合物在11Y VS 7Y中为非显著差异代谢物。3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸、锦葵色素3-O-葡糖苷、乳菇紫素、杜克苷A、右美托咪定、吴茱萸苦素和奇霉素在11Y VS 7Y、9Y VS 7Y组上调,茉莉酸变化与之相反,但这些化合物在11Y VS 9Y中为非显著差异代谢物。具体原因有待下一步深入研究。
7~11年广陈皮陈化期间,陈化年限不同的广陈皮代谢物有较大差异,随着陈化时间的增加,广陈皮差异代谢物的数量和种类趋于增多,陈化时间对黄酮类、萜类、氨基酸及其衍生物影响较大。在差异代谢物涉及的代谢通路方面,与代谢物差异相关性最高的关键通路有:单萜类生物合成、黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成、氨基酸及其衍生物参与的代谢通路(丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢),为陈化机制研究奠定坚实基础。
由于本实验仅对7年到11年内的广陈皮样品进行研究,随着存储年限再延长,差异代谢物是否会有新的变化,需要进一步检测研究。但随着陈化时间越长,样本取样难度也越大,特别是收集新会区同一产地不同陈化年限的样本,另外,虽然陈化7~11年的广陈皮还有较多的差异化学成分,但这些差异化学成分是否对其品质是产生显著影响,需要结合体内外药理实验或临床试验进一步验证。
-
表 1 不同年限广陈皮中代谢物分类及峰面积占比
Table 1 Metabolites classification and proportion of peak area of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' under different aging years
代谢物类别 数量 峰面积占比(%) 代谢物类别 数量 峰面积占比(%) 氨基酸及其衍生物Amino acid and derivatives 44 8.152 植物激素phytohormone 14 0.116 吡啶及其衍生物Pyridines and derivatives 11 0.037 有机氧化合物Organooxygen compounds 11 0.442 其他类型other 74 0.987 有机酸及其衍生物Organic acids and derivatives 11 0.498 酚类Phenols 61 3.343 有机氮化合物Organooxygen compounds 9 0.134 核苷酸及其衍生物Nucleotide and its derivates 30 3.662 萜类Terpenes 90 1.215 黄酮Flavonoids 121 64.070 苯丙素类Phenylpropanoid 57 0.878 生物碱Alkaloids 87 1.962 醌类Quinones 12 0.017 羧酸类及其衍生物Carboxylic acids and derivatives 22 10.771 孕烯醇酮脂类Prenol lipids 7 0.038 糖类Carbohydrates 13 1.943 肉桂酸及其衍生物Cinnamic acids and derivatives 4 0.028 脂肪酰类Fatty acyls 28 1.151 酮酸及其衍生物Keto acids and derivatives 5 0.022 芳香类化合物Benzene and substituted derivatives 15 0.280 甾体及其衍生物Steroids and steroid derivatives 28 0.144 醇类和多元醇Alcohols and polyols 4 0.025 氧杂蒽酮Xanthones 6 0.003 维生素类Vitamins 5 0.065 吲哚及其衍生物Indoles and derivatives 5 0.014 查尔酮Chalcones 4 0.003 总计 778 100 表 2 OPLS-DA模型参数和置换检验
Table 2 OPLS-DA model parameters and permutation tests
比较组 OPLS-DA模型参数 OPLS-DA置换检验(次数n=200) R2X
(cum)R2Y
(cum)Q2
(cum)R2Y(cum) Q2(cum) 11Y VS 9Y 0.281 0.995 0.503 0.99 −0.22 11Y VS 7Y 0.305 0.991 0.506 0.98 −0.23 9Y VS 7Y 0.266 0.994 0.4 0.99 −0.55 表 3 不同年限广陈皮差异代谢物
Table 3 Differential metabolites of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' under different aging years
比较组 表达上调/下调 代谢物
11Y VS 9Y
上调黄酮:矢车菊素、维采宁2、桑皮酮H、葡萄糖基甘草苷、槲皮素、川橙皮素、二氢槲皮素;
生物碱:马山茶碱、灵芝酸L;萜类:左旋龙脑、alpha-松油醇、Ipecoside;酚类:Pinostilbenoside、香草酸、Myzodendrone;氨基酸及其衍生物:N-甲酰蛋氨酸、L-蛋氨酸、L-苏氨酸、同型丝氨酸;有机氮化合物:N,N-二甲基苯胺;核苷酸及其衍生物:1-甲基腺嘌呤、腺苷 5'-单磷酸、腺苷-2',3'-环磷酸、吉西他滨;吡啶及其衍生物:3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸、Pyridoxamine 5'-phosphate下调 黄酮:高丽槐素、水黄皮素、7,8-二羟基黄酮;萜类:土木香内酯、桉叶油醇、乙酸龙脑酯、Alpha-山道年;
生物碱:别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物、去甲肾上腺素、蜀黍苷、迷迭香宁碱;酚类:Altholactone、6-姜酚
9Y VS 7Y
上调黄酮:甜橙黄酮、锦葵色素 3-O-葡糖苷、高丽槐素;萜类:乙酸龙脑酯、杜克苷A、吴茱萸苦素;
氨基酸及其衍生物:3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸;酚类:天麻素、Altholactone、构树宁C;生物碱:别隐品碱、育亨酸一水化合物;糖类:D-果糖-6-磷酸;芳香类化合物:右美托咪定;二恶烷类:奇霉素
下调黄酮:天竺葵素-3-O-葡萄糖苷;萜类:京尼平苷、Ipecoside、20(S)-人参皂苷Rh2;
氨基酸及其衍生物:L-蛋氨酸、L-谷氨酰胺;生物碱:4-甲基-5-噻唑乙醇;有机氮化合物:N,N-二甲基苯胺;吡啶及其衍生物:3,4,5,6-四氢吡啶-2-羧酸;核苷酸及其衍生物:1-甲基腺嘌呤
11Y VS 7Y
上调黄酮:金合欢素、桔皮素、川橙皮素、锦葵色素 3-O-葡糖苷、3'-甲氧基芹菜苷、异金雀花素、桑皮酮H、汉黄芩素、3,9-二甲氧基紫檀碱、黄颜木素;萜类:吴茱萸苦素、杜克苷A、尼洛替星、奇壬醇;氨基酸及其衍生物:L-苏氨酸、L-蛋氨酸、3-羟基-3-甲基谷氨酸、N-甲酰蛋氨酸、苯乙酰甘氨酸、同型丝氨酸;苯丙素:异秦皮啶、松柏苷、牛蒡子苷元、8-香叶草氧基补骨脂素;酚类:1,2-二甲氧基苯、桑辛素 C、Pinostilbenoside、姜黄素;甲亚胺酸及其衍生物:十六酰胺乙醇;甾体:固甾酮;蝶啶及其衍生物:异黄蝶呤 下调 黄酮:7,8-二羟基黄酮;萜类:右旋香芹酮、泽渥萜、蒲公英赛醇、土木香内酯、氯化缬草素、日耳曼醇 -
[1] 徐健, 曾万祥, 王晓东, 等. 陈皮的化学成分与药理学作用研究进展[J]. 中国野生植物资源,2022,41(10):72−76 XU Jian, ZENG Wanxiang, WANG Xiaodong, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of tangerine peel[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources,2022,41(10):72−76.
[2] 余祥英, 陈晓纯, 李玉婷, 等. 不同产地和不同贮藏年限陈皮的化学成分研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(12):3809−3817 YU Xiangying, CHEN Xiaochun, LI Yuting, et al. Research progress on the chemical composition of Citri Reticulatae of different regions and different storage time[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2020,11(12):3809−3817.
[3] LAI C L, WU H, NI G J. Traditional Chinese medicine Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae from Guangdong and Xinhui textual criticism[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi,2017,42(4):789−794.
[4] 王春燕. 浅谈陈皮的药理作用及临床应用[J]. 中国中医药现代远程教育,2013,11(3):120−131 WANG Chunyan. Discussion on the pharmacological effects and clinical applications of tangerine peel[J]. Chinese Medicine Modern Distance Education of China,2013,11(3):120−131.
[5] 莫云燕, 黄庆华, 殷光玲, 等. 新会陈皮多糖的体外抗氧化作用及总糖含量测定[J]. 今日药学,2009,19(10):22−25 MO Yunyan, HUANG Qinghua, YIN Guangling, et al. In vitro antioxidative effect and determination of polysaccharides from Xinhui tangerine peel[J]. Pharmacy Today,2009,19(10):22−25.
[6] 余祥英, 郑佳楠, 陈晓纯, 等. 不同干燥方式对陈皮中7种黄酮含量及抗氧化性的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(7):2075−2083 YU Xiangying, ZHENG Jianan, CHEN Xiaochun, et al. Effects of drying methods on the content of 7 kinds of flavonoids and antioxidant activity in Citri Retriculatae Pericarpium[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(7):2075−2083.
[7] 叶忠孝. 药食两用话橘皮[J]. 食品与生活,2008(1):39 YE Zhongxiao. Tangerine peel for food and medicine[J]. Food and Life,2008(1):39.
[8] CHENG L , WANG F, CAO Y X, et al. Rapid profiling of potential antitumor polymethoxylated flavonoids in natural products by integrating cell biospecific extraction with neutral loss/diagnostic ion filtering-based high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Phytochem Anal, 2022, 33(6):895−905.
[9] BIAN X Q , XIE X Y , CAI J L, et al. Dynamic changes of phenolic acids and antioxidant activity of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium during aging processes[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022, 373(Pt A):131399.
[10] YU J J, SU J, YAN M Q, et al. Correlation between lipid-lowering efficacy and components of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi,2019,44(15):3335−3342.
[11] WU J X, YE X T, YANG S H, et al. Systems pharmacology study of the anti-liver injury mechanism of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12:618846.
[12] YU X, SUN S, GUO Y Y, et al. Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium (Chenpi): Botany, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of a frequently used traditional Chinese medicine[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2018, 220:265−282.
[13] QIN K M, ZHENG L J, CAI H, et al. Characterization of chemical composition of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae volatile oil by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2013, 2013:237541.
[14] YU Q, TAO Y X, HUANG Y T, et al. Aged Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachi' attenuates oxidative damage induced by tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) in HepG2 cells[J]. Foods, 2022, 11(3):273.
[15] FU M Q, ZOU B, AN K J, et al. Anti-asthmatic activity of alkaloid compounds from Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae ( Citrus reticulata 'Chachi')[J]. Food Function,2019,10(2):903−911. doi: 10.1039/C8FO01753K
[16] COLODEL C, VRIESMANN L C, DE OLIIVEIRA PETKOWIICZ C L. Cell wall polysaccharides from Ponkan mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco cv. Ponkan) peel[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2018, 195:120−127.
[17] 杨放晴, 何丽英, 杨丹, 等. 不同陈化时间广陈皮中黄酮类成分的UPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(12):125−132 YAGN Fangqing, HE Liying, YANG Dan, et al. Analysis and identification of flavonoids in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium with different aging time by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS[J].Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2021,27(12):125−132.
[18] 潘志维, 颜庆佳. 不同陈化年限广陈皮中类黄酮含量测定及其抗氧化能力研究[J]. 中国处方药,2022,20(10):24−26 PAN Zhiwei, YAN Qingjia. Determination of flavonoids content and antioxidant ability in Citrus reticulata peel with different aging years[J]. Journal of China Prescription Drug,2022,20(10):24−26.
[19] 侯焕瑶, 杨子夜, 倪力军, 等. 不同年份新会陈皮中挥发性成分的分析与高品质陈皮精油的精制[J]. 中国调味品,2023,48(2):1−8 HOU Huanyao, YANG Ziye, NI Lijun, et al. Analysis of volatile components in Xinhui Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium stored for different years and refining high-quality essential oil from Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium[J]. China Condiment,2023,48(2):1−8.
[20] 陈彤, 曹庸, 刘飞, 等. GC-MS指纹图谱结合主成分分析法评价不同产地陈皮挥发油的质量[J]. 现代食品科技,2017,33(2):217−222 CHEN Tong, CAO Yong, LIU Fei, et al. Quality evaluation of tangerine peel volatile oils from different origins by GC-MS fingerprint and PCA[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2017,33(2):217−222.
[21] ZHOU X , HUANG Q H, MO Y Y, et al. Analysis on the volatile oil of Xinhui Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae in different years by GC/MS[J]. Zhong Yao Cai,2009,32(1):24−26.
[22] 李晓芳, 高慧, 朱绍光, 等. 基于指纹图谱结合多元统计分析的不同贮藏年限对广陈皮成分影响研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022,24(11):4233−4244 LI Xiaofang, GAO Hui, ZHU Shaoguang, et al. Study on the effect of different storage life on the composition of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium based on fingerprint and multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2022, 24(11):4233−4244.
[23] 李静敏, 辛志昂, 聂青青, 等. 基于拉曼光谱的广陈皮年份检测方法[J]. 食品工业,2023,44(1):279−285 LI Jingmin, XIN Zhiang, NIE Qingqing, et al. Age detection method of Citrus reticulata based on raman spectroscopy[J]. The Food Industry,2023,44(1):279−285.
[24] 王福, 李丹, 吴蓓, 等. 广陈皮外观性状与活性成分变化的相关性研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2021,32(3):761−763 WANG Fu, LI Dan, WU Bei, et al. Study on the correlation between the appearance character and the change of active component of the broad-leaved skin[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2021,32(3):761−763.
[25] 余梅. 基于近红外光谱技术的陈皮产地、年份和掺假的无损鉴别研究[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2021 YU Mei. Nondestructive identification of the origin, aging year and adulteration of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium based on near infrared spectroscopy technology[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2021.
[26] 郭宇晨, 彭心影, 余向阳. 近红外与光谱成像技术在食品智能快检中的应用[C]. 健康食品研发与产业技术创新高峰论坛暨2022年广东省食品学会年会论文集, 2023: 6 GUO Yuchen, PENG Xinying, YU Xiangyang, et al. Application of near-infrared spectroscopy and spectral imaging technology in intelligent and rapid inspection of food[C]. Proceedings of the Health Food R&D and Industrial Technology Innovation Summit Forum and the 2022 Annual Meeting of Guangdong Food Society, 2023: 6.
[27] 梁天一, 杨娟, 董浩, 等. 基于GC-IMS技术鉴别不同年份新会陈皮中的挥发性风味物质[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(4):168−173 LIANG Tianyi, YANG Juan, DONG Hao, et al. ldentification of volatile flavor substances in Xinhui tangerine peel in different years based on GC-IMS technology[J]. China Condiment,2020,45(4):168−173.
[28] 胡继藤, 唐铁鑫, 杨宜婷, 等. 利用FTIR和GC-MS鉴别不同贮藏年份新会陈皮的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2014,25(7):1646−1648 HU Jiteng, TANG Tiexin, YANG Yiting, et al. Identification of Xinhui tangerine peel in different storage years by FTIR and GC-MS[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2014,25(7):1646−1648.
[29] 鲍一丹, 吕阳阳, 朱红艳, 等. 陈皮年份的高光谱技术鉴别研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2017,37(6):1866−1871 BAO Yidan, LÜ Yangyang , ZHU Hongyan, et al. Identification and classification of different producing years of dried tangerine using hyperspectral technique with chemometrics models[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(6):1866−1871.
[30] RINSCHE M M, IVANISEVIC JULIJANA, GIERA MARTIN, et al. Identification of bioactive metabolites using activity metabolomics[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology ,2019,20(6):353−367. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0108-4
[31] LI J, YAN G H, DUAN X W, et al. Research progress and trends in metabolomics of fruit trees[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022, 13:881856.
[32] WANG M, CHEN L, LIU D, et al. Metabolomics highlights pharmacological bioactivity and biochemical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions ,2017,273:133−141. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.06.011
[33] 颜仁梁, 梁永枢, 沈小钟. 基于UPLC-MS/MS广靶代谢组学技术分析不同陈化年限广陈皮化学成分的差异[J]. 广东药科大学学报,2022,38(6):106−114 YAN Renliang, LIANG Yongshu, SHEN Xiaozhong, et al. Difference of compounds in Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium "Chachi” under different aging years analyzed by metabonomics technology based on UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University,2022,38(6):106−114.
[34] 胡媛, 吴蓓, 易达, 等. 基于广泛靶向代谢组学技术与高通量测序技术探究广陈皮陈化机制[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2022,34(4):553−562 HU Yuan, WU Bei, YI Da, et al. Integration of high throughput sequencing and widely targeted metabolomics reveals the aging mechanism of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae 'Chachiensis'[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2022,34(4):553−562.
[35] 李峰庆, 王福, 杨放晴, 等. 利用UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS法测定川陈皮与其混伪品中的黄酮类成分[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2020,32(8):1324−1330 LI Fengqing, WANG Fu, YANG Fangqing, et al. Analysis of flavonoids in Chuan Citrus Reticulata Pericarpium and its adulterant using UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS [J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2020,32(8):1324−1330.
[36] 茶凤官, 刘颖, 高峻, 等. 基于靶向代谢组学分析嫁接对茶树代谢物的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(21):45−51 CHA Fengguan, LIU Ying, GAO Jun, et al. Analysis on the effects of grafting on tea plant metabolites based on targeted metabolomics[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(21):45−51.
[37] JOLLIFFE I T. Principal component analysis[M]. New York:Springer, 2002:487.
[38] LÜ L N, LIU R, ZHOU D W. Application of OPLS in fundamental study of non-invasive measurement of human blood glucose concentration with near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi,2005,25(12):1950−1954.
[39] 曹烙文, 李华, 黄豆, 等. HS/SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS结合化学计量学方法鉴别分析新会陈皮[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报,2021,52(1):49−61 CAO Luowen, LI Hua, HUANG Dou, et al. HS/SPME-GC×GC-TOFMS combined with chemometric methods for differentiation of Xinhui Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2021,52(1):49−61.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 陈亮,郭江涛,李倩,徐锋,陈滕. 基于OBE面向科教融合的药物分析学教学改革研究. 广东化工. 2024(06): 177-178+152 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王雪,潘兆平,陈嘉序,郝丹丹,苏志鹏,马双双,肖佳豪,付复华. 茶枝柑与不同品种温州蜜柑果皮的非靶向代谢组学比较与分析. 食品科学. 2024(14): 133-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋娟,康三江,张海燕,曾朝珍,袁晶,慕钰文,苟丽娜. 基于高温高湿条件下苹果加工过程中代谢产物的多样性分析. 寒旱农业科学. 2024(08): 711-723+785 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



