Study on the Interaction Process between Rape Bee Pollen Polyphenols and Pancreatic Lipase by Ultraviolet andFluorescence Spectroscopy
-
摘要: 本文利用酶动力学方法测定了油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用,并通过紫外光谱、荧光光谱和同步荧光光谱分析了油菜蜂花粉多酚与胰脂肪酶的相互作用过程。结果表明,油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的活性具有一定的抑制作用,其半抑制浓度(IC50)为1.670±0.045 mg/mL,抑制类型为可逆性抑制中的混合型抑制。荧光光谱分析显示,随着油菜蜂花粉多酚浓度增加,胰脂肪酶的最大荧光发射强度逐渐降低,同时荧光最大发射波长从341 nm红移到349 nm。同步荧光光谱表明,多酚与胰脂肪酶结合时酶内部的疏水性降低,肽链的伸展程度增加;荧光猝灭机理结果显示,猝灭常数随温度升高从0.1000减小到0.0743,其结合过程为静态猝灭,且结合位点约为1个。综上,油菜蜂花粉多酚通过改变胰脂肪酶构象来抑制胰脂肪酶的活性,这为深入研究蜂花粉减脂机理提供了一定理论依据。Abstract: In this study, the inhibitory effect of rape bee pollen polyphenols on pancreatic lipase was measured by enzyme kinetics method, and the interaction between pancreatic lipase and rape bee pollen polyphenol extracts was analyzed by the ultravilolet, fluorescence spectra and synchronous fluorescence spectra. The results showed that rape bee pollen polyphenols had a certain inhibitory effect on the activity of pancreatic lipase, and the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was 1.670±0.045 mg/mL. The inhibitory type was a mixed inhibition of reversible inhibition. Fluorescence spectra showed that the maximal fluorescence intensity of pancreatic lipase gradually decreased with the increasing of rape bee pollen polyphenols concentration, and the maximal fluorescence peak had a redshift from 341 nm to 349 nm. Synchronous fluorescence spectra showed that the hydrophobicity inside the enzyme decreased and the stretch of the peptide chain increased when polyphenols bind to pancreatic lipase. The fluorescence quenching mechanism showed that the quenching constant decreased from 0.1000 to 0.0743 with increasing temperature, and the binding process was static quenching with about one binding site. In conclusion, the rape bee pollen polyphenols could inhibit the pancreatic lipase activity by changing the enzyme conformation, which provided a certain theoretical basis for the mechanism of bee pollen lipid reduction.
-
Keywords:
- rape bee pollen /
- polyphenols /
- pancreatic lipase /
- fluorescence spectrum /
- inhibitory effect
-
蜂花粉是蜜蜂采集显花植物花蕊内的花粉粒后混入自身腺体分泌物及花蜜的不规则扁球形团状物,再由蜜蜂的携粉足带回蜂巢,经脱粉器收集而来[1]。蜂花粉含有多种营养成分以及功能性物质,如蛋白质、多酚、脂肪、多糖及微量元素等[2]。作为传统的天然营养食品和理想的滋补品,蜂花粉具有一定的医疗和保健作用,如增强免疫力、抑制前列腺疾病、防癌作用和降脂减脂等功能[3−4],其中多酚类化合物是蜂花粉重要的功能活性成分[5]。
多酚化合物是指分子结构中含有若干个酚羟基的植物源化合物,主要包括黄酮类、单宁类、酚酸类和花色苷类。酚类化合具有降血脂、降血糖、清除自由基、抗动脉粥样硬化以及抗炎等功能,因而备受人们关注。杨佳林等[6]通过分离蜂花粉酸解液发现槲皮素和山奈酚为其主要抗氧化活性成分,另外研究表明山茶蜂花粉多酚对氧嗪酸钾诱导的高尿酸血症具有治疗作用[7]。近年来,已有一些与蜂花粉降脂相关的研究,Rzepecka-stojko等[8]证明了富含多酚的蜂花粉乙醇提取物可以减少动脉粥样硬化小鼠模型C57BL/6因高脂饮食引起的肝脏脂肪变性和退行性变化的发生,同时在给予蜂花粉多酚能够有效降低引起高脂饮食小鼠动脉粥样硬化有关物质的形成。Li等[9]利用玫瑰蜂花粉多糖对HepG 2细胞和高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠作用,研究其对胰岛素功能和脂质代谢的影响,结果表明蜂花粉多糖通过AMPK/mTOR介导的信号通路促进自噬,从而减轻肝脏脂肪变性和胰岛素抵抗,提示其可能是一种新的治疗肥胖和糖尿病药物。
胰脂肪酶是体内参与脂代谢的关键酶[10],它可以催化酯类生成脂肪酸和甘油,而胰脂肪酶抑制剂则通过抑制胰脂肪酶的活性来阻止脂肪的积累,从而达到减脂的功效[11]。因该类抑制剂具有不进入血液循环、不作用于神经系统、不抑制食欲等特点,备受人们的关注。来源于天然植物的胰脂肪酶抑制剂已经成为减肥保健产品的研究热点[12],其具有较其它非天然来源(如有机合成和微生物来源)诸多优点如活性稳定、副作用小等[13],愈来愈受到人们的重视。研究发现菠菜多酚水提取物对胰酶有较明显的抑制作用[14],任秀娟[15]和田强[16]等研究发现葡萄籽提取物原花青素等多酚类物质对胰脂肪酶有明显的抑制作用,且该抑制作用多为非竞争性抑制。但对于蜂花粉多酚的降脂机制尚未见报道。
由于研究植物多酚类物质与酶、血清白蛋白等蛋白质的相互作用能对于植物多酚物质的利用和人体吸收提供数据参考,因此本研究以油菜蜂花粉多酚为研究对象,首先利用超声波辅助乙醇提取法提取其中的多酚类物质,再分别利用酶动力学和荧光光谱技术探究其对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用过程。本实验结果为蜂花粉的降脂作用及进一步食品功能开发提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
干燥油菜蜂花粉 杭州天厨蜜源保健品有限公司提供,均于−20 ℃保存;脂肪酶 30000 U/g(来源于猪胰脏),北京百灵威科技有限公司;4-硝基苯基月桂酸酯(p-NPB) 上海阿拉丁试剂有限公司;福林酚试剂 生工生物公司(上海)股份有限公司;二甲亚砜、无水乙醇、Tris缓冲溶液及其他试剂 均为国产分析纯。
RF-5301PC型荧光分光光度计、UV-1800型紫外可见分光光度计 日本岛津公司;FlexA-200型酶标仪 杭州奥盛仪器有限公司;Rotavapor R-210型旋转蒸发仪 瑞士布奇公司;KQ-250DB型数控超声提取仪 昆山市超声仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 油菜蜂花粉多酚的提取和含量测定
油菜蜂花粉多酚的提取参照张燕新[17]的方法并稍有改进,取100 g油菜蜂花粉样品,研磨后过60目筛,按料液比1:10加入75%乙醇溶液在50 ℃下进行超声(功率200 W)提取1 h,重复提取三次合并滤液。旋转蒸发仪减压浓缩后,稀释至合适浓度再进行乙酸乙酯萃取,利用旋转蒸发仪蒸发至干后冷冻干燥得油菜蜂花粉多酚提取物备用。
总多酚含量测定采用福林酚法[18]并稍作改动,配制质量浓度为0.005、0.010、0.015、0.020、0.025 mg/mL的没食子酸标准品液,加入0.5 mL福林酚试剂与10%的Na2CO3溶液1.5 mL,避光反应后利用紫外分光光度计测定747 nm波长处的吸光度。以没食子酸质量浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,测定三次取平均值进行计算。得到拟合方程为y=66.82x+0.4517,其R2=0.9987,测得没食子酸计的油菜蜂花粉多酚含量为71.2%。
1.2.2 蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶活性的影响
胰脂肪酶活性测定及计算方法参考张静等[19]并稍作改动。将适量胰脂肪酶溶解于0.25 μmol/L的Tris缓冲溶液作为储备液,12000 r/min离心3 min后取上清液即为5 mg/mL的胰脂肪酶工作液,用二甲亚砜配制10 mmol/L的底物p-NPB溶液和不同质量浓度(0、0.142、0.356、0.570、0.712、1.068、1.424、2.136 mg/mL)的油菜蜂花粉多酚溶液。在酶标板中每孔加入10 μL的蜂花粉多酚提取物、30 μL胰脂肪酶溶液、20 μL Tris缓冲液作为实验组,不加胰脂肪酶和多酚提取物为空白组,不加多酚提取物为实验对照组,不加胰脂肪酶为溶剂对照组。设置酶标仪孵育温度为37 ℃并孵育15 min后,加入40 μL的底物溶液,轻轻吹打混匀后继续孵育15 min,并于405 nm处测定吸光度,通过公式(1)得到酶相对活性。以油菜蜂花粉多酚提取物的质量浓度为横坐标,纵坐标为酶相对活性,绘制曲线并进行多元线性拟合,再利用回归方程同时计算蜂花粉多酚的半抑制浓度(IC50),所有组别平行测定三次。
酶相对活性(%)=A1−A2A3−A4×100 (1) 式中,A1为实验组吸光度;A2为空白组吸光度;A3为实验对照组吸光度;A4为溶剂对照组吸光度。
1.2.3 油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的抑制类型判定
固定底物浓度为10 mmol/L不变,分别测定不同质量浓度的油菜蜂花粉多酚溶液(0、0.712、1.424 mg/mL)和不添加酶抑制剂时,不同酶浓度下的反应速率。以1.2.2中实验组体系进行反应,并以不加抑制剂为对照组。反应速率为反应后的体系吸光度与反应时间相除,以胰脂肪酶质量浓度为横坐标,反应速率为纵坐标绘制曲线,基于曲线斜率初步判断抑制类型[20]。
固定胰脂肪酶质量浓度为5 mg/mL和油菜蜂花粉多酚提取物浓度为IC50,加入不同浓度的底物p-NPB溶液(0.5、1、2、3、4 mg/mL),以1.2.2中实验组体系进行反应。以底物浓度的倒数(1/[S])为横坐标,纵坐标为反应速率的倒数(1/v),绘制Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线[21]。
1.2.4 油菜蜂花粉多酚作用于胰脂肪酶的紫外-可见吸收光谱分析测定
将胰脂肪酶工作液与不同质量浓度的油菜蜂花粉多酚溶液混匀,室温作用5 min后取适量反应液于石英比色皿,并在250~400 nm范围内进行紫外-可见吸收光谱扫描。
1.2.5 荧光发射光谱及同步荧光光谱分析测定
将不同浓度的油菜蜂花粉多酚提取物加入胰脂肪酶工作液中,调整油菜蜂花粉多酚提取物与胰脂肪酶的用量比。分别在不同温度(298和308 K)下振荡混匀并静置5 min,设置仪器的激发波长为280 nm,发射波长扫描范围300~500 nm,狭缝宽为5 nm进行荧光发射光谱扫描。
改变荧光光谱仪的激发波长和发射波长之间的波长差(Δλ)分别为15和60 nm,进行同步荧光光谱扫描,其余测量条件和发射光谱实验条件一致[22]。
1.2.6 荧光猝灭机理和结合常数分析
根据荧光光谱峰值,结合式(2)进行荧光猝灭机理和结合常数的分析,以F0/F为纵坐标,[Q]为横坐标绘制Stern-Volmer曲线,斜率即为猝灭常数(KSV)[23],通过计算得到双分子碰撞猝灭常数(Kq)。
F0F=1+Kqτ0[Q]=1+Ksv[Q] (2) 式中,F0为不加样品时的荧光强度;F为加入样品后的荧光强度;τ0为生物分子的荧光寿命(10−8);[Q]为样品的质量浓度。
1.3 数据处理
使用Microsoft Excel 2016软件进行数据处理,以及GraphPad Prism 8.0软件进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
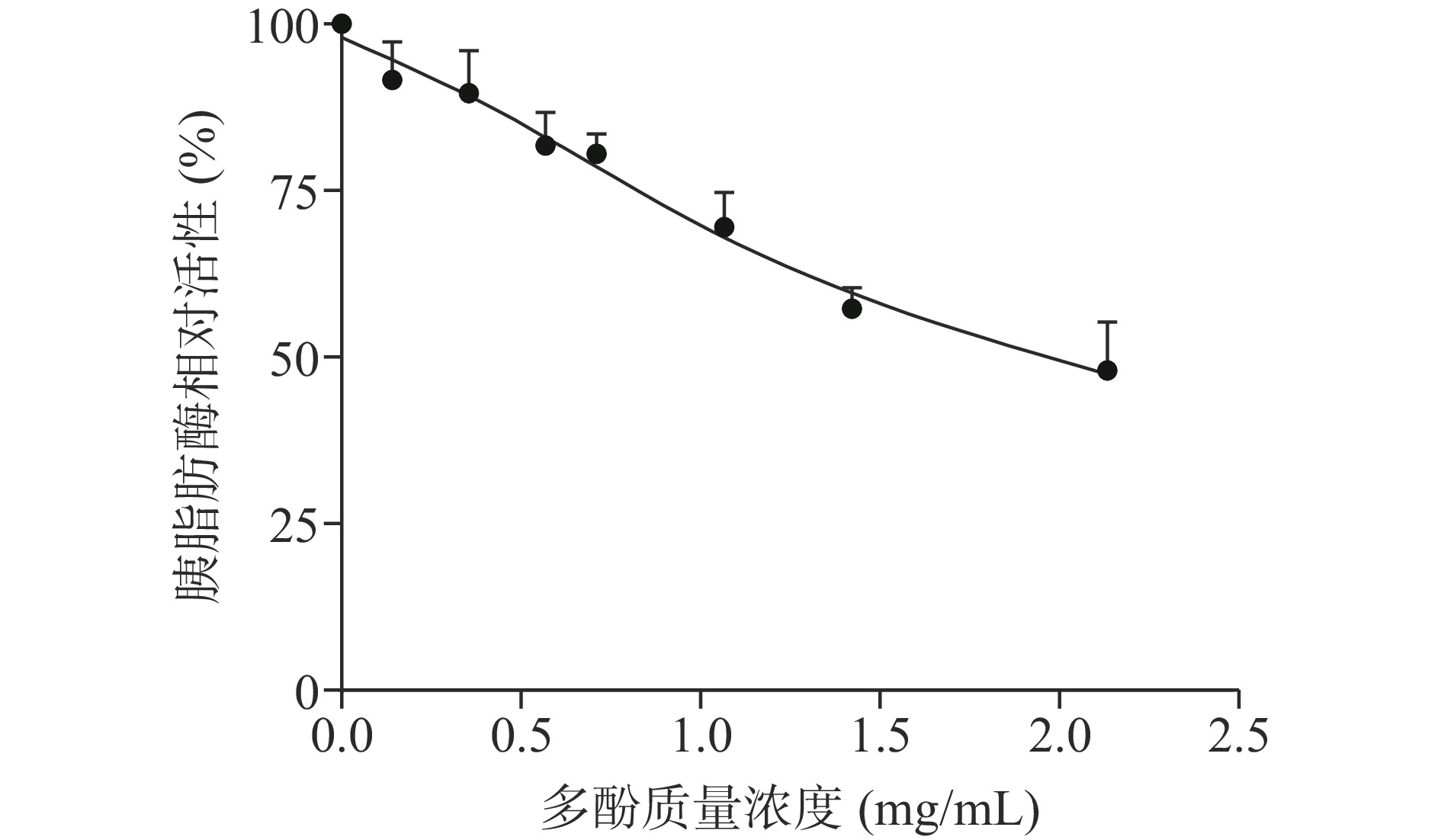
2.1 蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用
如图1所示,随着提取物的浓度增大,胰脂肪酶的活性也随之降低,呈现质量浓度依赖性,蜂花粉多酚引起胰脂肪酶的活性降低50%的质量浓度为1.670±0.045 mg/mL。由此可见,油菜蜂花粉多酚提取物对胰脂肪酶的具有较好的抑制效果。张静等[19]发现黑果枸杞花色苷提取物对胰脂肪酶的半抑制质量浓度为2.84±0.45 mg/mL,与本实验结果类似。
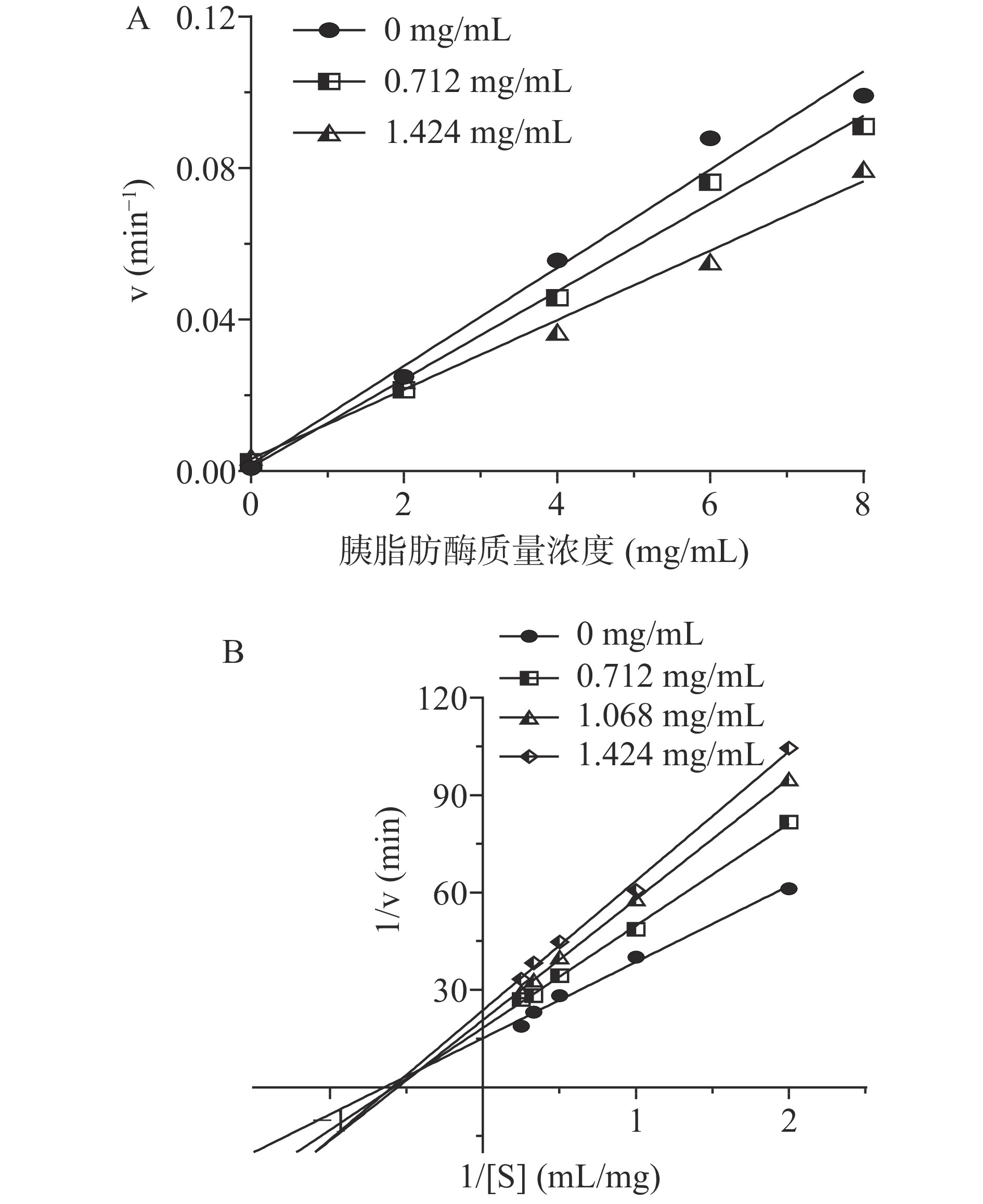
2.2 蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的抑制类型
底物浓度为10 mmol/L不变,改变酶浓度,以反应速率对酶的质量浓度进行作图,得到经过原点的直线。由图2A可知,随着蜂花粉多酚浓度增加,直线斜率逐渐降低,且曲线均经过原点,说明油菜蜂花粉多酚通过降低酶活性使得反应速率减小,而不是通过降低酶量,说明此过程为可逆性抑制过程[24]。固定胰脂肪酶的质量浓度,改变底物的浓度,Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线如图2B,曲线均相交于第二象限,为非竞争性与竞争性混合的抑制类型[25]。黄桂丽等[26]证实枇杷花多酚对胰脂肪酶的抑制类型为可逆混合型抑制,半抑制质量浓度为66.1±6.36 μg/mL,与本研究的结果比较类似,表明植物提取多酚对于胰脂肪酶的抑制类型具有一定相似性。
混合型抑制是特异性抑制和酶催化作用同时存在的抑制类型,KI表示抑制剂与酶的复合物(EI)的离解常数,而KIS则表示抑制剂与酶-底物的复合物(EIS)分解出抑制剂(I)时的离解常数,KI与KIS的大小均与抑制剂的抑制作用效果呈反比[27]。根据Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线计算在有无油菜蜂花粉多酚存在时斜率的比值(1+[Q]/KI)以及纵轴截距的比值(1+[Q]/KIS)即可求得KI及KIS,计算结果见表1。当油菜蜂花粉多酚质量浓度一定时,1/KI>1/KIS,即多酚与胰脂肪酶的亲和力大于多酚与底物-酶复合物的亲和力[28],表明油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的抑制现象是竞争性与非竞争性抑制两种混合的结果。王燕飞等[29]发现米胚芽中的胰脂肪酶抑制剂是通过间接改变底物乳化来阻碍底物与酶的而结合,不直接与酶作用。
表 1 Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线参数Table 1. Lineweaver-Burk double reciprocal curve parameters[Q](mg/mL) 拟合方程 R2 KI(mg/mL) KIS(mg/mL) 0 y=23.474x+15.126 0.992 / / 0.712 y=31.485x+18.322 0.997 2.086 3.370 1.068 y=37.179x+21.805 0.998 1.829 2.419 1.424 y=39.859x+23.74 0.996 2.040 2.510 2.3 油菜蜂花粉多酚作用于胰脂肪酶的紫外-可见吸收光谱分析
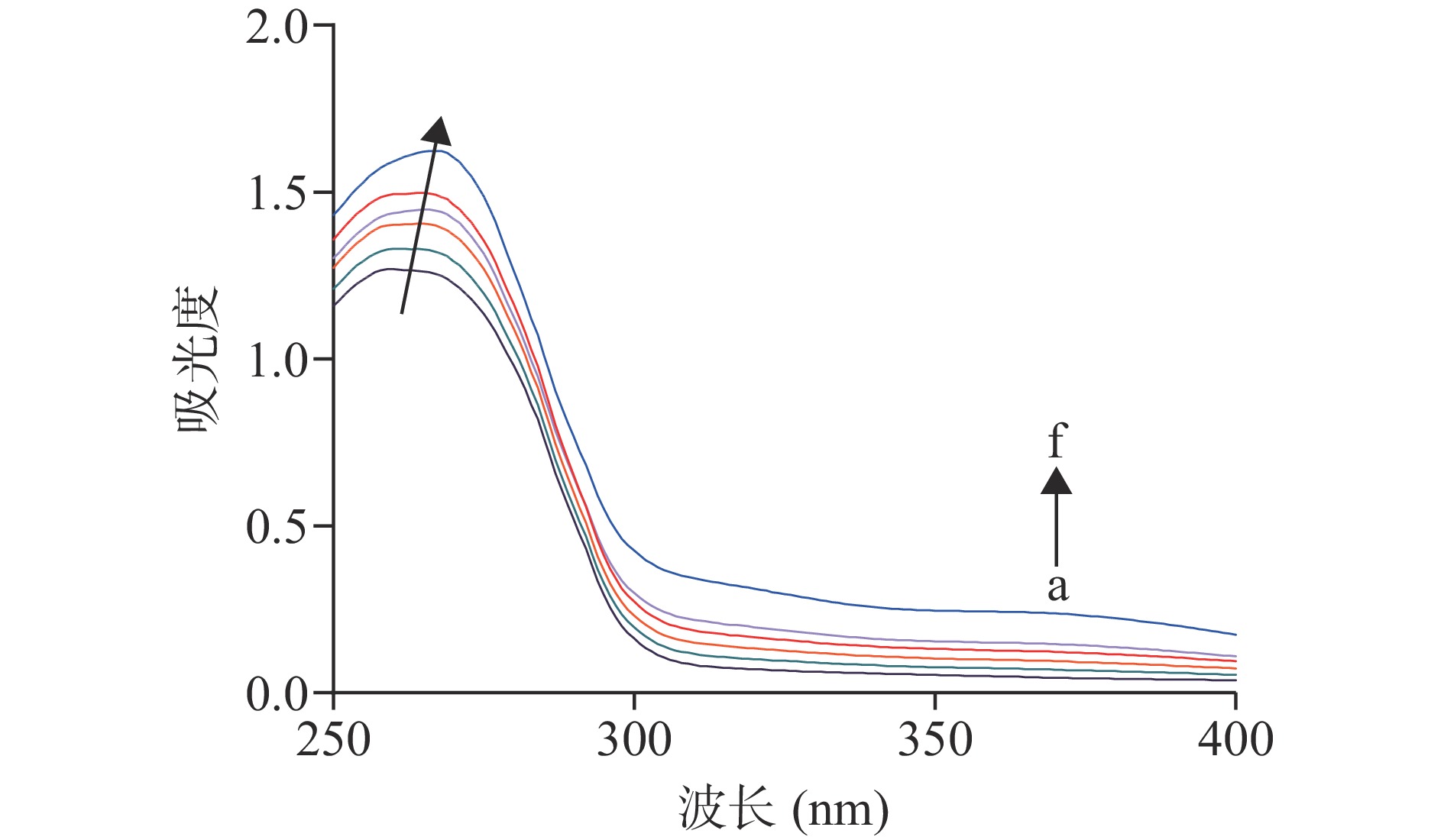
胰脂肪酶中含有芳香族氨基酸如酪氨酸、色氨酸和苯丙氨酸,这也决定了其在260 nm左右存在最大吸收波长。由图3可知,胰脂肪酶除了在260 nm处有最大吸收峰外同时随着油菜蜂花粉多酚浓度的增加,250~280 nm处的吸收峰值增强并出现了红移现象,这也说明了胰脂肪酶结构中的芳香族氨基酸微环境发生了改变,因此导致酶构象的改变。
2.4 油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的荧光光谱
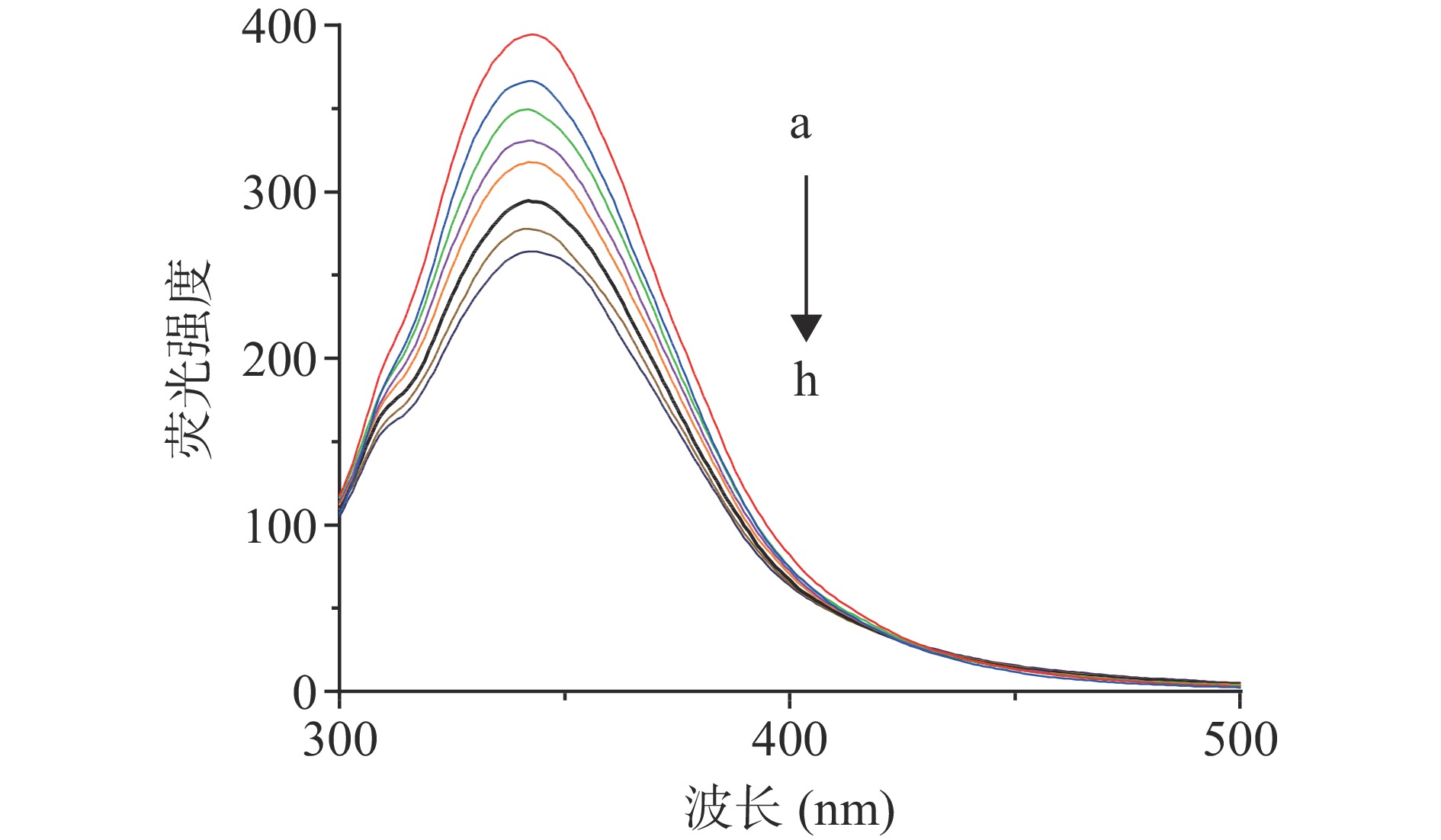
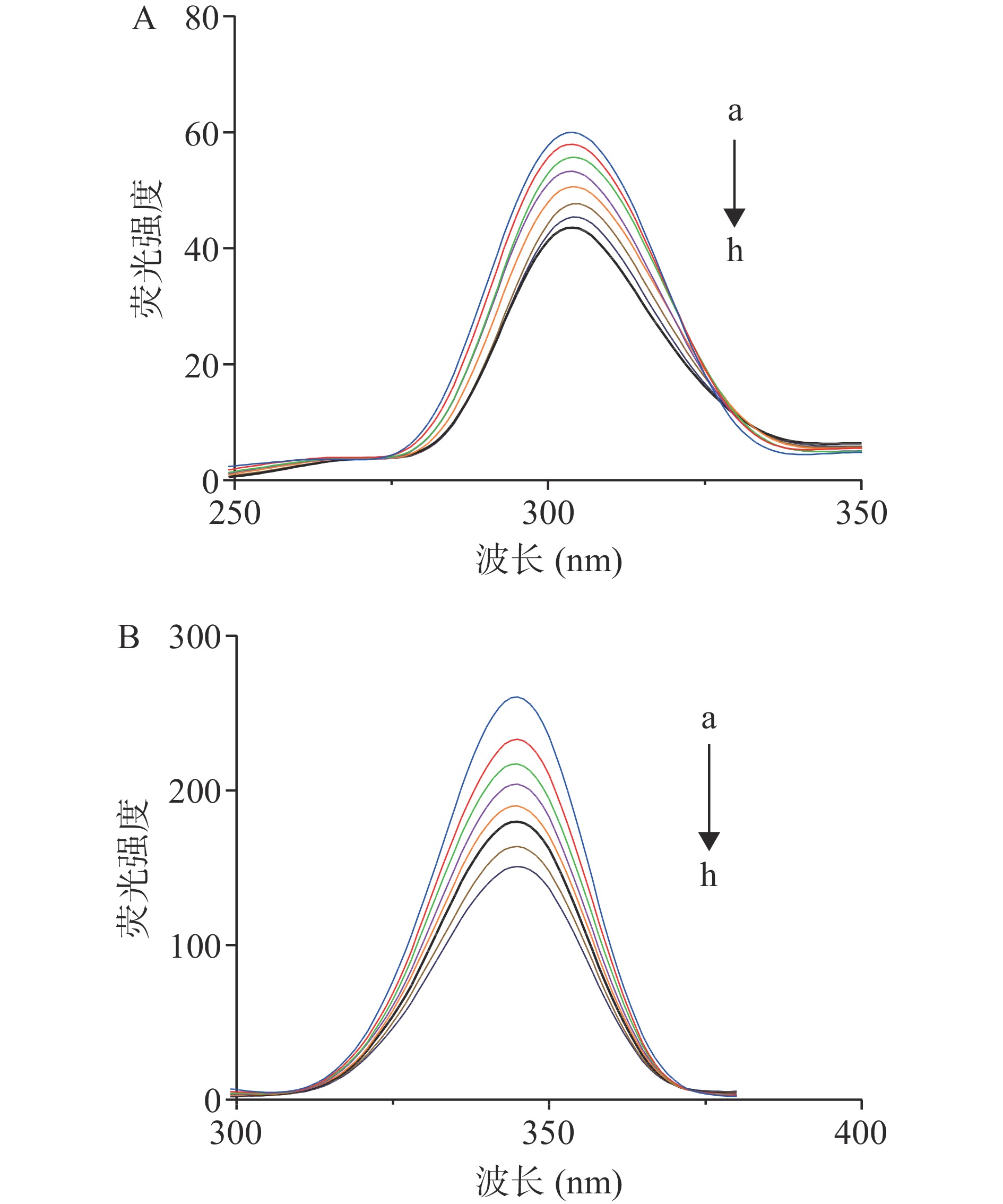
通过荧光猝灭实验分析油菜蜂花粉多酚与胰脂肪酶之间的相互作用,如图4所示,随着油菜蜂花粉多酚质量浓度的升高,胰脂肪酶的荧光强度呈现出递降的趋势,同时荧光峰位从341 nm红移到349 nm,说明油菜蜂花粉多酚使胰脂肪酶的构象发生了改变,即色氨酸、酪氨酸以及苯丙氨酸影响导致。
为进一步确定蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶构象的影响,利用同步荧光光谱来判断氨基酸残基构象及其所处环境的变化。如图5A和图5B分别是Δλ=15 nm和Δλ=60 nm时油菜蜂花粉多酚的加入对胰脂肪酶的影响。前者表示对胰脂肪酶中酪氨酸的光谱特性,后者则为色氨酸[30]。由图5可知,酪氨酸残基的最大发射波长基本保持不变,而色氨酸残基的最大发射波长略有红移,表明多酚的加入导致胰脂肪酶的构象发生变化,从而降低了色氨酸残基所处环境的疏水性,使得胰脂肪酶内部结构发生改变,肽链的伸展程度随之增加[31]。范金波等[32−33]、张国文等[34]采用荧光光谱法分别研究了绿原酸、咖啡酸和白杨素与胰脂肪酶的相互作用。结果表明这三种多酚与胰脂肪酶的结合均通过改变酶的结构从而抑制胰脂肪酶活性,同时金属离子在一定程度上抑制了这种结合。此外绿原酸、咖啡酸和白杨素均通过静态猝灭方式猝灭胰脂肪酶的内源性荧光。
2.5 荧光猝灭机理和结合常数分析
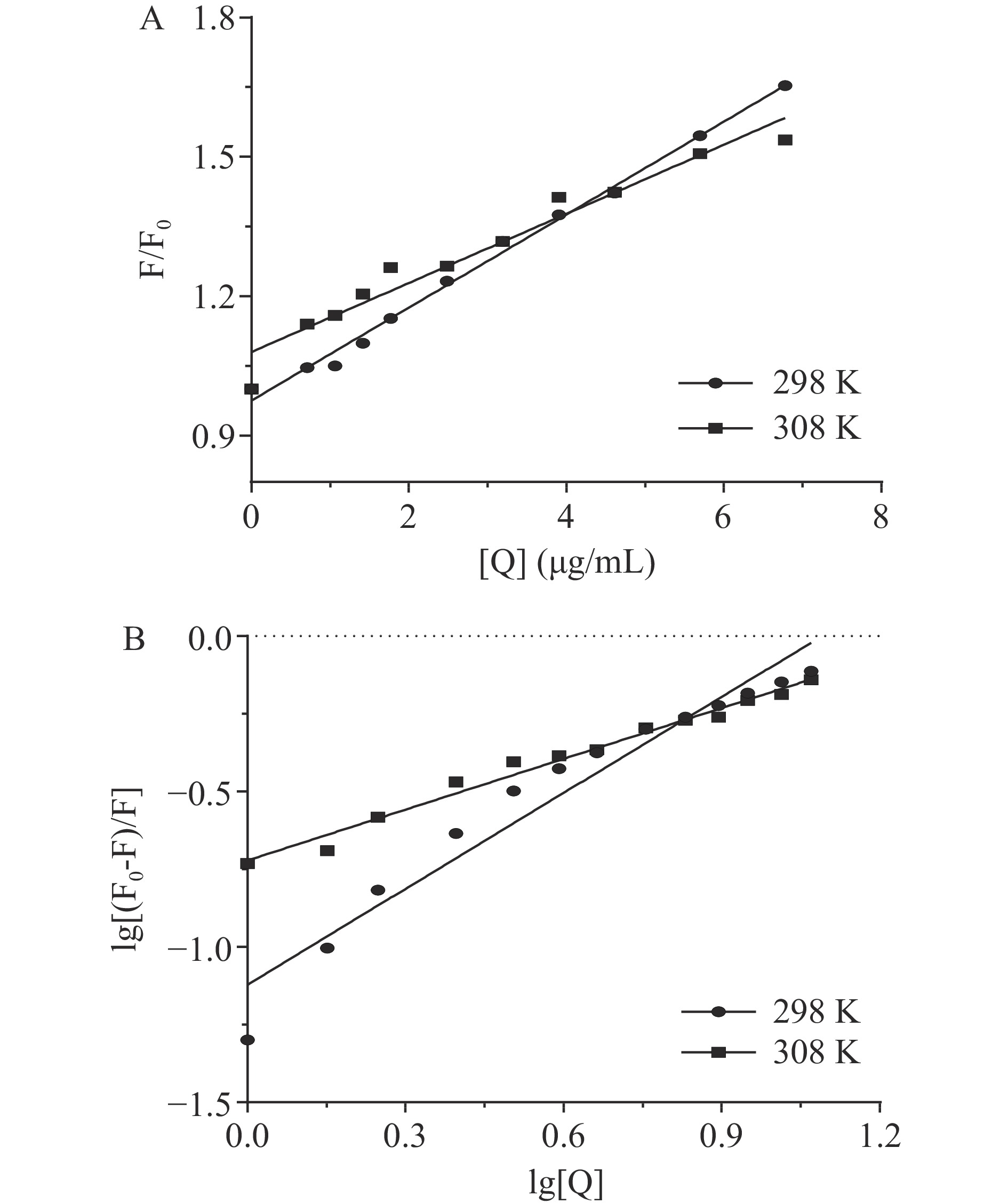
为探究胰脂肪酶和油菜蜂花粉多酚的互作模式,实验比较了不同温度下Stern-Volmer方程的变化曲线。分别测定298 K和308 K时胰脂肪酶的的荧光强度,据公式(2)绘制F0/F对[Q]的关系图见图6A,并将由Stern-Volmer曲线拟合得到的方程中各参数见表2。在荧光分析中,若已知猝灭为动态猝灭,则随温度升高,猝灭常数增大;若为静态猝灭,则减小[35]。由图6A可知,直线斜率随着温度升高而减小,提示其结合过程为静态猝灭。另外在298 K时,蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的KSV为0.1000 mg/mL,而在308 K时,KSV则为0.0743 mg/mL。当油菜蜂花粉多酚与胰脂肪酶的荧光猝灭主要为静态猝灭时,其猝灭规律符合公式(3)。
表 2 不同温度下油菜蜂花粉多酚与胰脂肪酶相互作用的Stern-Volmer方程和双对数曲线方程参数Table 2. Stern-Volmer equation and double logarithm curve equation parameters for the interaction between rape bee pollen polyphenols and pancreatic lipase at different temperatures温度 (K) Stern-Volmer 方程 双对数曲线方程 KSV (mg/mL) Kq (mg/(mL·s)) KA (mg/mL) n 298 F0/F=0.1[Q]+0.9751 lg[(F0−F)/F]=1.0288lg[Q]−1.1218 0.1000 1.000×107 0.0755 1.0288 308 F0/F=0.0743 [Q]+1.0796 lg[(F0−F)/F]=0.5993lg[Q]−0.7650 0.0743 0.743×107 0.1718 0.5993 lgF0−FF=lgKA+nlg[Q] (3) 式中,F0为未加入猝灭剂时的荧光强度;F为猝灭剂浓度等于[Q]时的荧光强度;KA为表观结合常数;n为结合位点数。
以lg[(F0-F)/F]对lg[Q]作图,见图6B及表2,结合图表可求得298 K时的油菜蜂花粉多酚与胰脂肪酶的表观结合常数KA的值为0.0755 mg/mL(298 K),0.1718 mg/mL(308 K),结合位点常数n值为1.0288(298 K),0.5993(308 K),说明油菜蜂花粉多酚与胰脂肪酶的结合位点在这两个温度下均仅有1个。
3. 结论
本文通过紫外-可见分光光度法和荧光光谱法探究油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的抑制活性和相互作用过程,发现油菜蜂花粉多酚能以静态猝灭方式与胰脂肪酶结合,而且能对胰脂肪酶的活性产生一定的抑制作用,引起酶活性降低50%时多酚的质量浓度为1.670±0.045 mg/mL,抑制类型为可逆性混合型抑制。此外,根据同步荧光光谱结果显示,随着油菜蜂花粉多酚的加入,胰脂肪酶中酪氨酸残基的最大发射波长基本保持不变,而色氨酸残基的最大发射波长略有红移,由此可见多酚的加入导致胰脂肪酶的构象发生了变化。Stern-Volmer猝灭常数Ksv随着温度升高而减小,表明结合过程为静态猝灭,且结合位点约为1个。综上所述,油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶存在明显抑制作用,多酚的存在可进一步阻碍膳食中脂肪的吸收,并使脂肪积累过程受到抑制。本实验也为蜂花粉多酚的降脂机制和进一步功能开发提供了理论依据,此外不同萃取方式得到的提取物及油菜蜂花粉多酚单体化合物对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制作用及二者的构效关系可作为后续研究的重点。
-
表 1 Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线参数
Table 1 Lineweaver-Burk double reciprocal curve parameters
[Q](mg/mL) 拟合方程 R2 KI(mg/mL) KIS(mg/mL) 0 y=23.474x+15.126 0.992 / / 0.712 y=31.485x+18.322 0.997 2.086 3.370 1.068 y=37.179x+21.805 0.998 1.829 2.419 1.424 y=39.859x+23.74 0.996 2.040 2.510 表 2 不同温度下油菜蜂花粉多酚与胰脂肪酶相互作用的Stern-Volmer方程和双对数曲线方程参数
Table 2 Stern-Volmer equation and double logarithm curve equation parameters for the interaction between rape bee pollen polyphenols and pancreatic lipase at different temperatures
温度 (K) Stern-Volmer 方程 双对数曲线方程 KSV (mg/mL) Kq (mg/(mL·s)) KA (mg/mL) n 298 F0/F=0.1[Q]+0.9751 lg[(F0−F)/F]=1.0288lg[Q]−1.1218 0.1000 1.000×107 0.0755 1.0288 308 F0/F=0.0743 [Q]+1.0796 lg[(F0−F)/F]=0.5993lg[Q]−0.7650 0.0743 0.743×107 0.1718 0.5993 -
[1] THAKUR M, NANDA V. Composition and functionality of bee pollen:A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,98:82−106.
[2] LI Q Q, WANG K, MARCUCCI M C, et al. Nutrient-rich bee pollen:A treasure trove of active natural metabolites[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,49:472−484. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.09.008
[3] TUOHETI T, RASHEED H A, MENG L, et al. High hydrostatic pressure enhances the anti-prostate cancer activity of lotus bee pollen via increased metabolites[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2020,261:113057. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113057
[4] 郑慧, 梁倩倩, 陈希平, 等. 蜂花粉保健功能及产品开发研究进展[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(4):230−236 doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2019.04.042 ZHENG H, LIANG Q Q, CHEN X P, et al. Research progress of bee pollen health care function and product development[J]. Food & Machinery,2019,35(4):230−236. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2019.04.042
[5] RZEPECKA-STOJKO A, STOJKO J, KUREK-GORECK A, et al. Polyphenols from bee pollen:Structure, absorption, metabolism and biological activity[J]. Molecules,2016,21(2):21732−21749.
[6] 杨佳林, 孙丽萍, 徐响, 等. 油菜蜂花粉黄酮醇的测定及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(3):79−82 YANG J L, SUN L P, XU X, et al. Hydrolyzed rape bee pollen ethanol extract qualitative and quantitative analysis of flavonol and antioxidant activity evaluation[J]. Food Science,2010,31(3):79−82.
[7] XU Y Y, CAO X R, ZHAO H A, et al. Impact of Camellia japonica bee pollen polyphenols on hyperuricemia and gut microbiota in potassium oxonate-induced mice[J]. Nutrients,2021,13(8):2665−2685. doi: 10.3390/nu13082665
[8] RZEPECKA-STOJKO A, KABALA-DZIK A, KUBINA R, et al. Protective effect of polyphenol-rich extract from bee pollen in a high-fat diet[J]. Molecules,2018,23(4):805−823. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040805
[9] LI X Z, GONG H Q, YANG S W, et al. Pectic bee pollen polysaccharide from Rosa rugosa alleviates diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance via induction of ampk/mtor-mediated autophagy[J]. Molecules,2017,22(5):699. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050699
[10] KLEIN S. Long-term pharmacotherapy for obesity[J]. Obesity Research,2004,12(12):163−166.
[11] BIRARI R B, BHUTANI K K. Pancreatic lipase inhibitors from natural sources:Unexplored potential[J]. Drug Discovery Today,2007,12(19-20):879−889. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2007.07.024
[12] 姜运耀, 吕国英, 李燕飞, 等. 植物来源的胰脂肪酶抑制剂研究进展[J]. 中国生化药物杂志,2012,33(2):199−202 JIANG Y Y, LÜ G Y, LI Y F, et al. Research advances in pancreatic lipase inhibitors from plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemical Pharmaceutics,2012,33(2):199−202.
[13] SLANC P, DOLJAK B, KREFT S, et al. Screening of selected food and medicinal plant extracts for pancreatic lipase inhibition[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2009,23(6):874−877. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2718
[14] SUTANA R, ALASHI A M, ISLAM K, et al. Inhibitory activities of polyphenolic extracts of bangladeshi vegetables against α-amylase, α-glucosidase, pancreatic lipase, renin, and angiotensin-converting enzyme[J]. Foods,2020,9(7):844−857. doi: 10.3390/foods9070844
[15] 任秀娟, 马海乐. 葡萄籽提取物脂肪酶抑制活性筛选及抑制机理的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2009,30(6):181−186 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2009.06.106 REN X J, MA H L. Study on inhibitory screening and mechanism of grape seed on pancreatic lipases[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2009,30(6):181−186. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2009.06.106
[16] 田强, 吴子健, 黄道荣, 等. 葡萄籽中胰脂肪酶抑制物提取工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发,2010,31(4):41−44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2010.04.012 TIAN Q, WU Z J, HUANG D R, et al. Optimizing conditions for the isolation of pancreatic lipase inhibitive substance from grape seeds[J]. Food Research and Development,2010,31(4):41−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2010.04.012
[17] 张燕新. 云南三种蜂花粉多酚的制备及抑制黑色素瘤B16细胞生物活性研究[D]. 昆明:昆明理工大学, 2016 ZHANG Y X. Preparation of three kinds of bee pollen polyphenols from Yunnan and their bioactivity against melanoma B16 cells[D]. Kunming:Kunming University of Science and Technology. 2016.
[18] 杨佳林. 油菜蜂花粉酚类化合物的分离及其抗氧化活性研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2010 YANG J L. Purification of phenolic compounds in rape seed pollen (Brassica capestris) and its antioxidant activity[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2010.
[19] 张静, 米佳, 禄璐, 等. 黑果枸杞花色苷提取物对胰脂肪酶活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(5):8−14 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190620-234 ZHANG J, MI J, LU L, et al. Effect of anthocyanins extract from Lycium ruthenicum murr. fruit on pancreatic lipase activity[J]. Food Science,2020,41(5):8−14. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190620-234
[20] 张忠. 茶多酚对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制作用[J]. 食品工业, 2013, 34(8):168−170 ZHANG Z. The inhibition effect of tea polyphenol on pancreatic lipase[J]. The Food Industry, 2013, 34(8):168−170.
[21] 江慧芳, 王雅琴, 刘春国. 三种脂肪酶活力测定方法的比较及改进[J]. 化学与生物工程,2007,24(8):72−75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2007.08.022 JIANG H F, WANG Y Q, LIU C G. Comparison and improvement of three determination methods for of lipase activity[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering,2007,24(8):72−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2007.08.022
[22] 王燕, 吕达, 郭明, 等. 全氟辛酸与血清蛋白分子间作用的紫外-荧光光谱分析法建立及理论模建研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2018,38(2):494−501 WANG Y, LV D, GUO M, et al. Study on the intermolrcular interaction between perfluorooctanoic acid and serum protein by UV-fluorescence spectrometry and the establishment of theoretical models[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2018,38(2):494−501.
[23] LI X, CAI J J, YU J L, et al. Inhibition of in vitro enzymatic starch digestion by coffee extract[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,358(6):129837−129843.
[24] LIN M Z, CHAI W M, ZHENG Y L, et al. Inhibitory kinetics and mechanism of rifampicin on α-glucosidase:Insights from spectroscopic and molecular docking analyses[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,122:1244−1252.
[25] ZHENG L, LEE J, YUE L M, et al. Inhibitory effect of pyrogallol on alpha-glucosidase:Integrating docking simulations with inhibition kinetics[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules:Structure, Function and Interactions, 2018, 112:686−693.
[26] 黄桂丽, 王毓宁, 马佳佳, 等. 枇杷花多酚对脂肪酶的抑制作用[J]. 江苏农业学报,2021,37(1):192−196 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2021.01.025 HUANG G L, WANG Y N, MA J J, et al. Inhibitory effect of loqual flowers polyphenolics on lipase activity[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2021,37(1):192−196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2021.01.025
[27] HUANG Q, CHAI W M, MA Z Y, et al. Antityrosinase mechanism of ellagic acid in vitro and its effect on mouse melanoma cells[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2019,43(11):12996−13005.
[28] 陈宇霞, 张凯, 龚盛昭. 茯苓提取物对酪氨酸酶抑制动力学及刺激性研究[J]. 日用化学工业,2017,47(6):317−321 doi: 10.13218/j.cnki.csdc.2017.06.004 CHEN Y X, ZHANG K, GONG S Z. Tyrosinase activity inhibition kinetics and skin irritation of extracts of Poria cocos extract[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics,2017,47(6):317−321. doi: 10.13218/j.cnki.csdc.2017.06.004
[29] 王燕飞, 郭贯新, 张晖. 米胚芽中脂肪酶抑制剂提取工艺及其性质的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2004,25(2):85−87 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2004.02.032 WANG Y F, GUO G X, ZHANG H. Inhibitory mechanism studies of pancreatic lipase inhibitor derived from rice germ[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2004,25(2):85−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0306.2004.02.032
[30] 李朕, 尚丽平, 邓琥, 等. 色氨酸和酪氨酸的三维荧光光谱特征参量提取[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2009,29(7):1925−1928 doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)07-1925-04 LI Z, SHANG L P, DENG H, et al. Extraction of characteristic parameters of three-dimensional fluorescence spectra of tyrosine and tryptophan[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2009,29(7):1925−1928. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2009)07-1925-04
[31] 冯素玲, 袁道琴. 阿魏酸哌嗪与牛血清白蛋白相互作用的研究[J]. 分析试验室,2009,28(7):78−82 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2009.07.021 FENG S L, YUAN D Q. Study on interaction between piperazine ferulate and bovine serum albumin[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2009,28(7):78−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2009.07.021
[32] 范金波, 李鑫芮, 葛春辉, 等. 荧光光谱法研究绿原酸与胰脂肪酶相互作用[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2017,53(6):106−110 FAN J B, LI X R, GE C H, et al. Study on the interaction between chlorogenic acid and pancreatic lipase by fluorescence spectrometry[J]. Food and Fermentation Science & Technology,2017,53(6):106−110.
[33] 范金波, 王晓露, 姜海静, 等. 荧光光谱法研究咖啡酸与胰脂肪酶相互作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(2):152−155 FAN J B, WANG X L, JIANG H J, et al. Study on the interaction between caffeic acid and pancreatic lipase by fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(2):152−155.
[34] 张国文, 黎沙, 朱苗. 白杨素对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用及机制[J]. 南昌大学学报(理科版),2021,45(6):545−552 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0464.2021.06.006 ZHANG G W, LI S, ZHU M. Inhibitory interaction and mechanism of chrysin on pancreatic lipase[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Natural Science),2021,45(6):545−552. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0464.2021.06.006
[35] 周玉玳, 戴双雄, 佟斌, 等. 光谱学与分子对接结合解释生物大分子与配体间作用机制的研究进展[J]. 影像科学与光化学,2021,39(3):337−347 doi: 10.7517/issn.1674-0475.201204 ZHOU Y D, DAI S X, TONG B, et al. Recent progress of the interaction mechanism between biomacromolecules with ligands based on combining spectroscopy analysis with molecular docking[J]. Imaging Science and Photochemistry,2021,39(3):337−347. doi: 10.7517/issn.1674-0475.201204
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 张乾坤,康桦华,刘梦竹,涂杜,徐志宏. 肉品保鲜包装材料与新技术研究进展. 包装工程. 2024(03): 126-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王金霞,杨波,罗瑞明,李荣,陈雪妍,张倩,胡丽筠. 宰后贮藏期间滩羊肉线粒体氧化磷酸化与色泽稳定性的关系. 食品科学. 2024(08): 202-209 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王华安,刘启超,黄得草,张利军,刘美玉. 中高氧气调包装对冷鲜鸭肉品质的影响. 农产品加工. 2024(21): 36-40+46 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵红波,叶磊海,杨黎耀,郎欢,陆燕萍,柴振林,欧菊芳. 冷鲜猪肉在贮藏过程中生物胺含量变化及不同包装方式对生物胺含量变化的影响研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(12): 126-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘文轩,罗欣,杨啸吟,张一敏,朱立贤,毛衍伟,梁荣蓉,马伟民,杨振刚. 脂肪含量对雪花牛排在高氧气调包装贮藏期间肉色稳定性的影响. 现代食品科技. 2022(02): 110-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 霍霞飞,张德权,苏媛媛,古明辉,陈丽,李少博,王卫,郑晓春. 三甲胺和二甲胺表征冷鲜羊肉新鲜度. 肉类研究. 2022(07): 13-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周立,张锐,王卫,张佳敏,王素,侯成立,白婷. 不同气调包装对冷鲜羊肉保鲜效果研究. 包装工程. 2022(21): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 马红艳,张德权,陈丽,郑晓春. 荧光特征分子表征冷鲜羊肉新鲜度. 农业工程学报. 2022(22): 270-279 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



