Compound Enzyme Extraction of Platycodon grandiflorum Polysaccharides and Its Structure and Antioxidant Activity Characterization
-
摘要: 目的:优化复合酶法提取桔梗多糖工艺,并初步分析桔梗多糖的结构和体外抗氧化活性。方法:分别考察酶添加量、料液比、酶解时间、酶解温度对桔梗多糖提取率的影响,采用响应面法进行提取条件优化,利用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)测定多糖的分子量和单糖组成,应用核磁共振(NMR)和扫描电镜(SEM)对多糖的糖苷键和形貌进行分析,并对多糖清除自由基的能力和还原力进行研究。结果:桔梗多糖的最佳提取工艺为纤维素酶、果胶酶、木瓜蛋白酶的添加量为2%,酶解时间90 min,料液比1:30 g/mL,酶解温度50 ℃,在此条件下,多糖实际提取率为9.01%±0.07%,多糖含量达92%±0.76%。纯化后得到桔梗多糖组分PGP-W-1,分子量为6.2 kDa,由甘露糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖、半乳糖、木糖和阿拉伯糖按照摩尔比4.9:4.3:7.9:7.8:4.8:18.6组成,是一种具有α型糖苷键和β型糖苷键的吡喃型多糖。体外抗氧化试验显示PGP-W-1对DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基和羟基自由基清除率IC50值分别为2.14、2.25、0.78 mg/mL。结论:本研究优选出的桔梗多糖提取工艺切实可行,多糖提取效率高并表现出良好的体外抗氧化活性。Abstract: Objective: Optimize the extraction process of Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharides by compound enzyme method, and preliminarily analyze its structure and in vitro antioxidant activity. Methods: Response surface methodology was used to optimize the extraction conditions with the extraction rate of polysaccharides as the index and the addition amount of enzymes, solid-liquid ratio, enzymolysis time and enzymolysis temperature as the factors. The molecular weight and monosaccharide composition of purified polysaccharides were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), the glycosidic bonds and surface morphology of purified polysaccharides were analyzed by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), respectively, and the free radical scavenging ability and reducing power of purified polysaccharides were evaluated. Results: The optimum extraction conditions were as follows, the addition of cellulase, pectinase and papain was 2%, the enzymolysis time was 90 min, the solid-liquid ratio was 1:30 g/mL, the enzymolysis temperature was 50 ℃. Under these conditions, the actual extraction rate of polysaccharides was 9.01%±0.07%, and the purity of polysaccharides was 92%±0.76%. The purified polysaccharides component PGP-W-1 (6.2 kDa) was composed of mannose, rhamnose, glucose, galactose, xylose, and arabinose with a molar ratio of 4.9:4.3:7.9:7.8:4.8:18.6. NMR spectrum showed that PGP-W-1 was pyranose ring with α- and β-glycoside bond. The IC50 values of the PGP-W-1 on DPPH free radicals, ABTS+ free radicals and hydroxyl free radicals were 2.14, 2.25, and 0.78 mg/mL, respectively. Conclusion: The optimized extraction process of Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide was feasible with high extraction efficiency and showed excellent antioxidant activity in vitro.
-
桔梗,又名土人参,是属于双子叶植物纲、桔梗科、桔梗属的多年生草本植物[1],广泛分布于我国的四川、广西、贵州、陕西等地。桔梗味苦、性平,具有丰富的食用和药用价值,其主要成分有多糖、皂苷、黄酮、挥发油等[2],其根可入药,有宣肺排脓、止咳祛痰等作用[3]。桔梗多糖富集于桔梗根部细胞中[4],作为桔梗中重要的生物活性物质之一[5],桔梗多糖在抗肿瘤[6]、抗氧化[7]、增强免疫[8]以及降血糖[9]等方面都发挥着重要作用。
桔梗根部细胞及木质层主要由纤维素、木质素构成[10],细胞内层和细胞壁中还含有大量果胶[11],传统的回流提取方法难以剔除其中粗纤维、蛋白质和胶质等杂质[12],不利于多糖高效提取。复合酶法提取作为一种新型提取工艺,其提取条件温和,提取效率高,将相应的生物酶混合使用能有效破坏植物细胞壁[13],分解纤维素、蛋白质和果胶等杂质,从而提高多糖溶出率。针对桔梗根结构特点,本实验选用纤维素酶、果胶酶和木瓜蛋白酶进行配比组合,通过单因素实验和响应面法优化建立了一种新型复合酶法提取桔梗多糖的工艺。在此基础上,对所提取的桔梗粗多糖分离纯化,并对纯化后的多糖组分进行结构和抗氧化活性的初步分析,以期为桔梗多糖的高效提取及其进一步深入研究提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
桔梗根 河北安国中药材交易专业市场;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基肼(DPPH)、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)、磷酸钠、钼酸铵 分析纯,天津市鼎盛鑫化工有限公司;纤维素酶(50 U/mg)、果胶酶(500 U/mg)、木瓜蛋白酶(800 U/mg) 分析纯,上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
TDA-8002型恒温水浴锅 天津市中环实验电炉有限公司;Heraeus Megafuge 8R型离心机 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;SpectraMax-M5型多功能读板机 美国Molecular Devices公司;Agilent 1100 Series高效液相色谱仪 美国Agilent公司;Alltech 3300 ELSD检测器 美国Grace公司;HT7700透射电子显微镜 日本Hitachi公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 桔梗预处理
将购买的新鲜桔梗根在阳光下晾晒三日,粉碎过60目筛后,以石油醚为提取剂,80 ℃水浴下回流3 h,干燥滤渣得脱脂桔梗粉末,收集进行后续多糖提取。
1.2.2 单一酶的最适添加量实验
固定酶解温度50 ℃,时间60 min,料液比1:25 g/mL,以多糖得率为指标,选择木瓜蛋白酶、纤维素酶以及果胶酶按照质量比为0.5%、1%、1.5%、2%、2.5%进行实验。
1.2.3 复合酶配比正交试验
根据单一酶实验结果,以多糖得率为指标,进行正交试验筛选最佳复合酶配比,因素水平见表1。
表 1 正交试验因素水平设计Table 1. Orthogonal experimental factor horizontal design水平 X:纤维素酶(%) Y:果胶酶(%) Z:木瓜蛋白酶(%) 1 1.5 1.5 1 2 2 2 1.5 3 2.5 2.5 2 1.2.4 复合酶提取工艺单因素实验
结合筛选出最佳的复合酶比例,从影响多糖得率的因素中选取酶解温度(30、40、50、60、70 ℃)、料液比(1:20、1:25、1:30、1:35、1:40 g/mL)、酶解时间(30、60、90、120、150 min),对复合酶法提取桔梗多糖进行单因素优化实验,其中各因素固定水平为酶解温度50 ℃,酶解时间60 min,料液比1:25 g/mL。
1.2.5 复合酶提取工艺响应面优化试验
为了继续优化桔梗多糖的复合酶法提取工艺,结合单因素实验的结果,选取酶解温度(A)、料液比(B)、酶解时间(C)为影响因素,以多糖得率为指标进行三因素三水平的响应面试验设计,因素水平如表2。
表 2 响应面试验因素水平设计Table 2. Experimental factor level of response surface水平 A :酶解温度(℃) B :料液比(g/mL) C:酶解时间(min) −1 40 1:25 60 0 50 1:30 90 1 60 1:35 120 1.2.6 桔梗多糖的含量及得率计算
多糖的含量测定采用苯酚-硫酸比色法[14]。以葡萄糖标准液浓度为横坐标,OD620 nm为纵坐标,得到葡萄糖标准曲线:y=0.0438x–0.0052,R2=0.9993。桔梗多糖得率计算公式为:
$$\rm 多糖提取得率(\text{%})=M_1\times M_2/M_3\times 100 $$ 式中:M1为桔梗多糖质量,g;M2为桔梗多糖含量,%;M3为桔梗粉末质量,g。
1.2.7 桔梗多糖的分离纯化
配制使用5 mg/mL的多糖溶液,经0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤后,采用DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow和Sephacryl S-300层析柱对桔梗粗多糖进行分离纯化,苯酚-硫酸比色法监测多糖含量,绘制洗脱曲线。合并主峰洗脱液,透析冻干后即得纯化多糖组分。
1.2.8 桔梗多糖分子量测定
通过HPLC-ELSD法计算桔梗多糖分子量[15]。色谱条件:Agilent 1100 Series高效液相色谱仪,Alltech 3300 ELSD检测器;色谱柱:Agilent PL aquael-OH Mixed-H柱(4.60 mm×150 mm, 8 μm);流动相为超纯水;进样量20 μL。
1.2.9 桔梗多糖单糖组成测定
采用PMP柱前衍生化法结合HPLC测定单糖组成[16]。具体步骤为:取200 µL质量浓度为4 mg/mL的多糖溶液,加入100 µL三氟乙酸(4 mol/L)溶液,N2封管,于110 ℃烘箱中水解2 h。水解完成后,加入400 µL甲醇于70 ℃条件下用N2吹干,重复3次以去除三氟乙酸。加入100 μL NaOH(0.3 mol/L)溶解残渣,再加入100 μL 的0.5 mol/L PMP-甲醇溶液于70 ℃孵育60 min。冷却至室温后,加入100 μL的0.3 mol/L HCl溶液调节pH。使用超纯水定容至2 mL,再加入2 mL氯仿进行萃取,保留上层水相,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤后进样分析。色谱条件:Agilent 1100 Series高效液相色谱仪,DAD检测器;色谱柱:Hypersl OD 25柱(4.60 mm×250 mm,5 μm);柱温27 ℃;流速0.9 mL/min;流动相:0.05 mol/L磷酸二氢钾溶液(pH6.8)-乙腈(84:16);检测波长250 nm;进样量20 μL。比较样品与混合标准单糖图谱,确定单糖组成和含量。
1.2.10 桔梗多糖核磁共振分析
25 mg桔梗多糖溶解于0.6 mL D2O中,然后用Bruker AscendTM 600 NMR核磁共振仪记录1H和13C光谱。MestNova软件用于数据分析。
1.2.11 桔梗多糖的扫描电镜观察
取少量干燥多糖,经电流镀金后使用HT7700透射电子显微镜测定并拍照,在1000、2000和5000倍下观察其表面形态。
1.2.12 桔梗多糖体外抗氧化活性分析
1.2.12.1 总还原力测定
根据Chen等[17]的方法稍作修改。取pH 6.6浓度为0.2 mol/L的H3PO4盐缓冲液2.5 mL,与1 mL浓度为10 mg/mL的K3[Fe(CN)6]混合。在混合液加入不同浓度的桔梗多糖溶液,50 ℃下反应20 min后,加入1.0 mL 10%的Cl3CCOOH溶液,离心分离。取上层清液2.5 mL,加入2.5 mL去离子水和2.5 mL 0.1%的FeCl3,混合后,测定吸光度A(700 nm)。维生素C为阳性对照组,蒸馏水为空白对照组。
1.2.12.2 DPPH自由基清除能力
根据Wang等[18]的方法稍作修改。取2.0 mL桔梗多糖溶液与3.0 mL DPPH-乙醇溶液(7 mmol/L)混合。混合液在黑暗条件下静置30 min,然后在517 nm处测定吸光度,记为A1;以乙醇替代多糖溶液测得的吸光度记为A0;蒸馏水代替DPPH-乙醇溶液测得吸光度为A2;维生素C作为阳性对照组,桔梗多糖的DPPH自由基清除能力为:
$$ \text{DPPH}\text{自由基清除率}(\text{%})=[(\text{1}{-}(\text{A}_\text{1}-\text{A}_\text{2})\text{/A}_\text{0}]\times\text{100} $$ 1.2.12.3 ABTS+自由基清除能力
根据施利奇等[19]的方法稍作修改。将5 mmol/L过硫酸钾溶液与7 mmol/L ABTS溶液等体积比例混合,并在室温静置过夜。使用蒸馏水稀释混合液,直至734 nm波长下吸光度达到0.70±0.02。将桔梗多糖溶液与4 mL配制好的ABTS溶液混合,反应6 min后,测量反应后的吸光度A1(734 nm)。以蒸馏水替代多糖溶液测得的吸光度记为A0。以蒸馏水替代ABTS溶液测得的吸光度记为A2。维生素C作为阳性对照组,桔梗多糖的ABTS+自由基清除能力计算公式为:
$$ \text{ABTS}^+\text{自由基清除率}(\text{%})=[(\text{1}{-}(\text{A}_\text{1}-\text{A}_\text{2})\text{/A}_\text{0}]\times\text{100} $$ 1.2.12.4 羟基自由基清除能力
根据孙艳等[20]的方法稍作修改。取1.0 mL浓度为9 mmol/L的FeSO4溶液与1.0 mL浓度为9 mmol/L的水杨酸CH3CH2OH溶液混合,然后加入1.0 mL桔梗多糖溶液。加入1.0 mL浓度为8.8 mmol/L的H2O2后,将混合溶液于室温孵育30 min,然后在510 nm处测量吸光度,记为A1。蒸馏水混合多糖溶液的吸光度记为A2。蒸馏水代替多糖溶液反应的吸光度记为A0。维生素C作为阳性对照组,桔梗多糖的OH自由基清除能力计算公式为:
$$ \text{OH}\text{自由基清除率}(\text{%})=[(\text{1}{-}(\text{A}_\text{1}-\text{A}_\text{2})\text{/A}_\text{0}]\times\text{100} $$ 1.3 数据处理
通过GraphPad 5.0软件进行处理,测定结果以平均值±标准差(n=3)表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析。P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单一酶的多糖提取效果
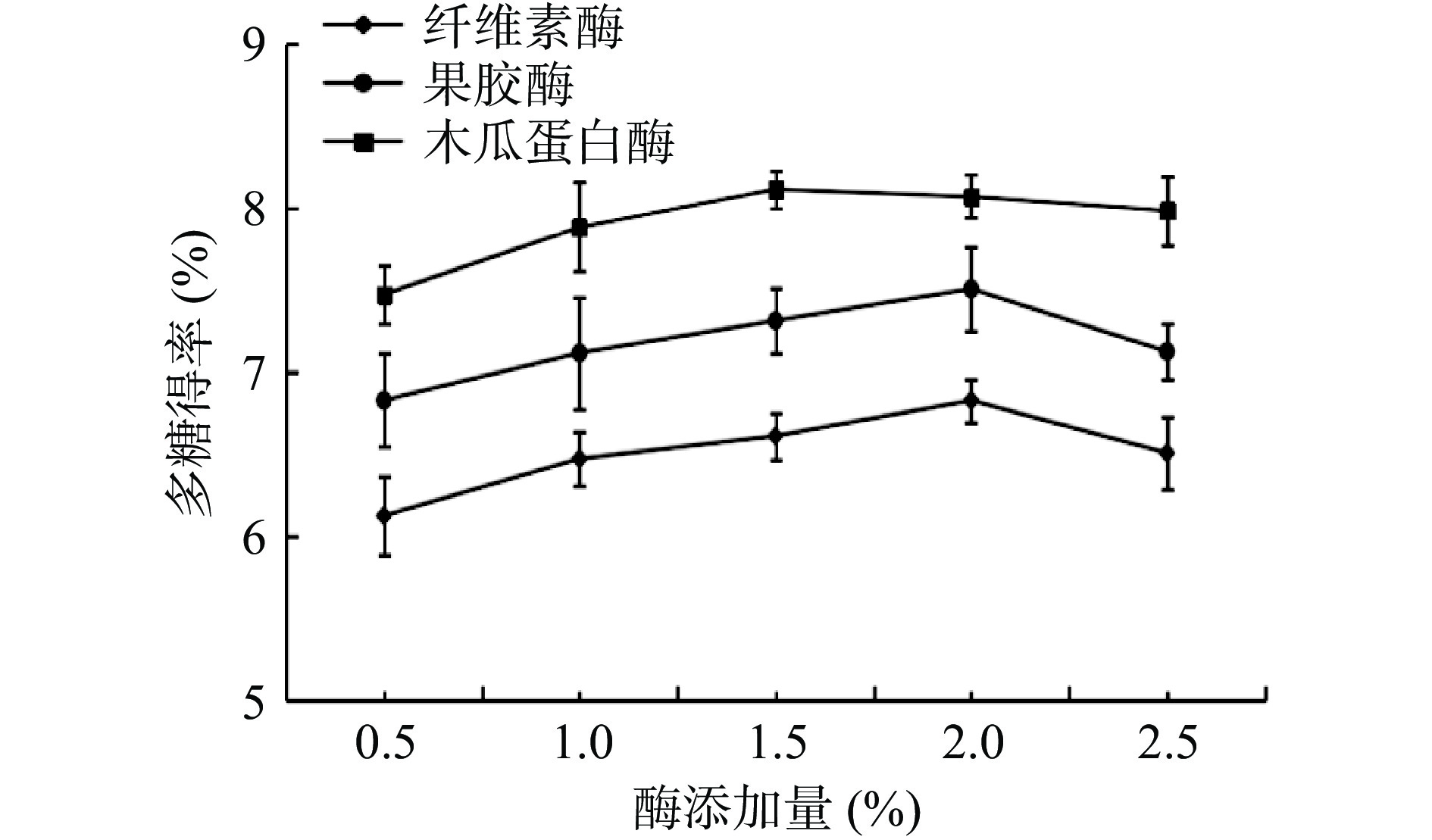
单一酶辅助提取结果如图1,木瓜蛋白酶提取桔梗多糖得率最佳,纤维素酶提取桔梗多糖得率最低。单一酶提取桔梗多糖的最佳加入量为纤维素酶2%、果胶酶为2%、木瓜蛋白酶为1.5%。
2.2 复合酶配比对多糖提取效果的影响
复合酶法提取桔梗多糖的正交试验结果如表3所示。由极差分析可知,改变纤维素酶的用量对多糖得率影响最大,果胶酶次之,木瓜蛋白酶影响最小。根据多糖得率进行筛选,可得到最佳复合酶配比为:纤维素酶2%、果胶酶2%、木瓜蛋白酶2%,此条件下的多糖得率达到8.251%。
表 3 复合酶配比正交试验结果Table 3. Orthogonal experimental results of compound enzyme ratio实验号 X:纤维素酶 Y:果胶酶 Z:木瓜蛋白酶 Y:多糖得率(%) 1 1 1 1 6.447 2 1 2 2 7.035 3 1 3 3 6.792 4 2 1 2 7.583 5 2 2 3 8.251 6 2 3 1 7.191 7 3 1 3 6.934 8 3 2 1 6.707 9 3 3 2 6.335 k1 6.758 6.988 6.782 k2 7.675 7.331 6.984 k3 6.658 6.772 7.325 R 1.016 0.558 0.544 2.3 复合酶提取单因素实验结果
2.3.1 料液比对桔梗多糖得率的影响
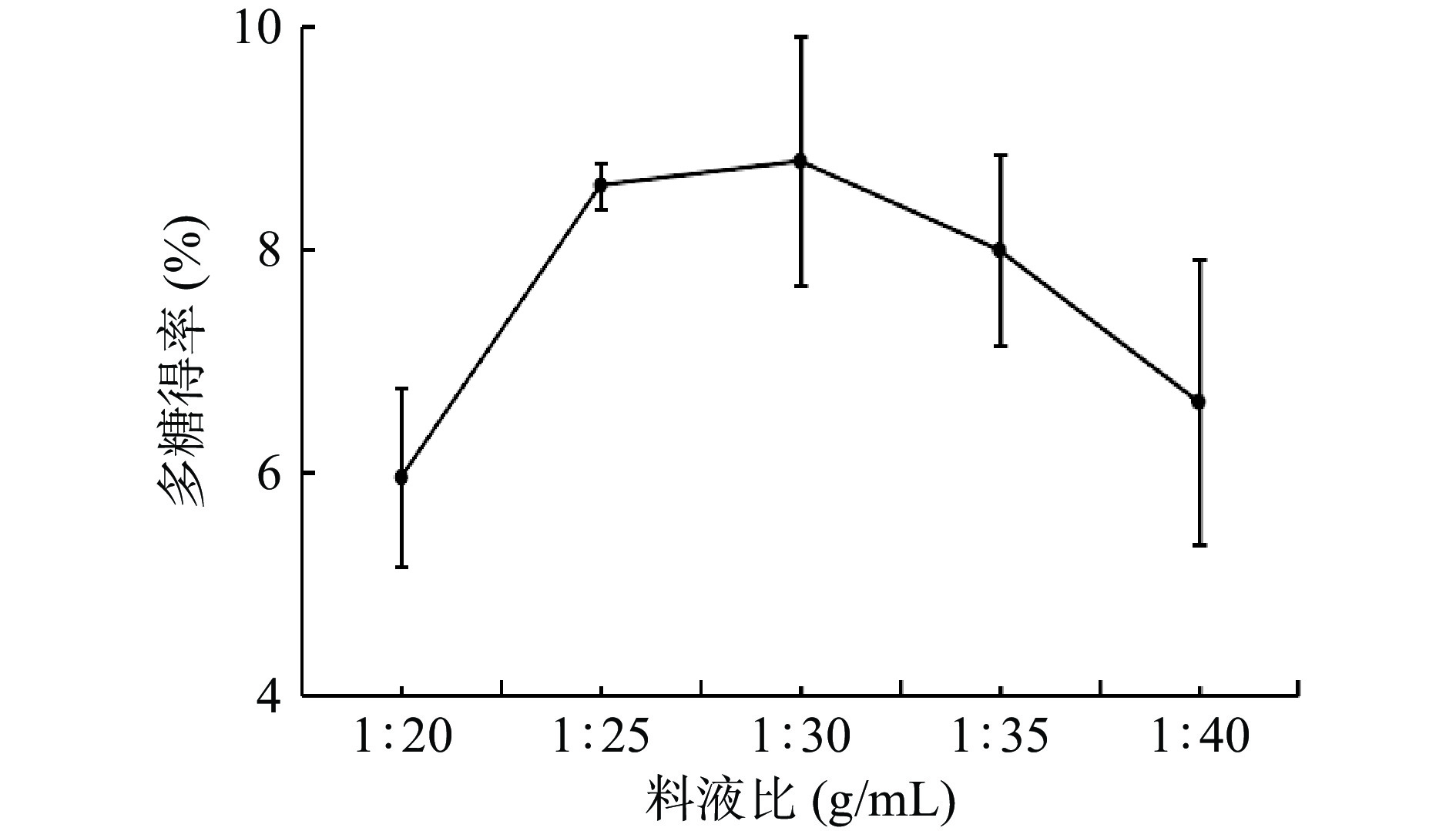
根据图2可以看出,随着溶剂的增加,当料液比达到1:30 g/mL时桔梗多糖得率达到顶峰,可能是由于溶剂增多扩大了复合酶和桔梗粉末的接触面积[21],使多糖更容易提取;随后出现下降趋势,可能由于随着溶剂的进一步增加,溶剂中的酶浓度逐渐被稀释[22],导致得率降低。选择料液比为1:25、1:30、1:35 g/mL进行后续响应面试验。
2.3.2 酶解时间对桔梗多糖得率的影响
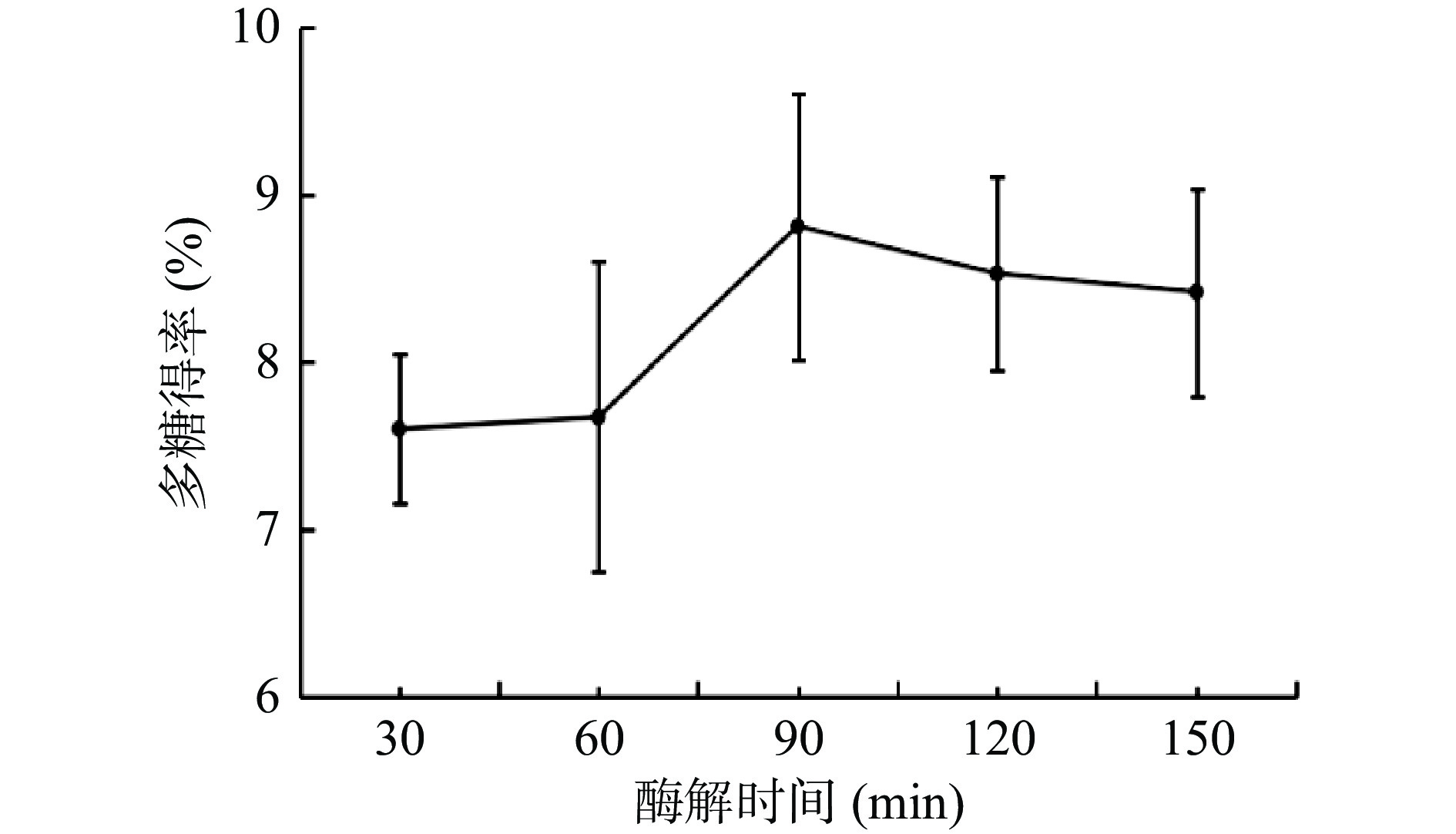
根据图3可以看出,当酶解时间达到90 min时桔梗多糖得率达到顶峰,此时复合酶和桔梗粉末充分反应。随着时间的进一步增加,得率出现下降趋势,这是因为酶解时间过长,酶催化活性减弱,反而不利于多糖提取[23]。选择酶解时间为60、90、120 min进行后续响应面试验。
2.3.3 酶解温度对桔梗多糖得率的影响
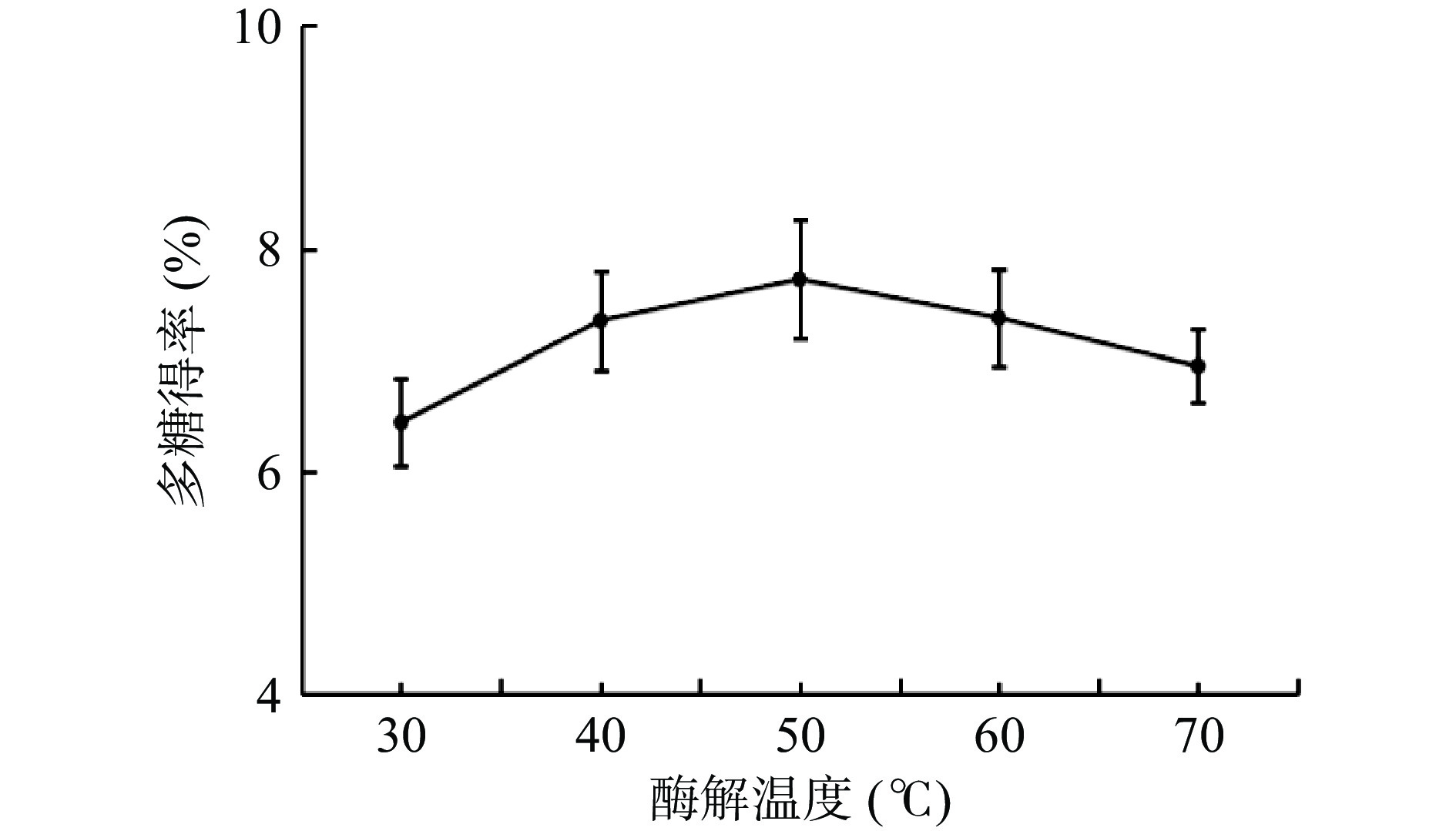
根据图4可以看出,在酶解温度30~50 ℃内,随着温度的增加,多糖得率逐步上升。当酶解温度达到50 ℃时桔梗多糖得率达到顶峰,该温度可能是复合酶在实验条件下的最适温度。当酶解温度继续超过50 ℃,多糖得率出现下降趋势,这是由于过高的温度导致酶失活[24]。因此选择酶解温度为40、50、60 ℃进行后续响应面试验。
2.4 复合酶提取工艺响应面试验优化结果
2.4.1 响应面优化试验结果
采用Design-Expert.8.0.6软件对数据进行回归拟合,得桔梗多糖得率Y对各因素的多项回归方程为:Y=9.49+0.29A+0.37B–0.041C−0.38AB−0.14AC−0.32BC−1.07A2−0.92B2−1.41C2,实验结果如表4。
表 4 响应面试验设计及结果Table 4. Response surface experimental design and results实验号 A B C Y:多糖得率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 6.319 2 1 0 1 7.053 3 1 −1 0 7.817 4 0 0 0 9.289 5 −1 1 0 7.917 6 0 1 1 7.081 7 0 −1 1 7.072 8 0 1 −1 7.868 9 0 0 0 9.563 10 0 −1 −1 6.587 11 0 0 0 9.354 12 −1 0 1 6.927 13 0 0 0 9.408 14 0 0 0 9.815 15 1 1 0 7.915 16 −1 0 −1 6.657 17 1 0 −1 7.350 2.4.2 拟合模型的建立和数据分析
对模型进行方差分析,二项式回归方程系数显著性检验的结果见表5。整体模型的P<0.0001,表明该二次方程模型极显著,说明该模型具有统计学意义。A、B、AB、BC、A2、B2 、C2的P值均小于0.05,表示模拟项显著。失拟项P值不显著(P>0.05),模型相关系数R2=0.9234>0.9,说明该模型拟合度较好,预测值与实测值之间有较好的相关性。各因素对多糖得率的影响大小依次为:料液比(B)>酶解温度(A)>酶解时间(C)。
表 5 二项式回归方程系数显著性检验Table 5. Significance of coefficients in second order regression equation方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 21.58 9 2.40 63.62 <0.0001 ** A-酶解温度 0.67 1 0.67 17.77 0.0040 ** B-料液比 1.11 1 1.11 29.57 0.0010 ** C-酶解时间 0.014 1 0.014 0.36 0.5680 AB 0.56 1 0.56 14.92 0.0062 ** AC 0.080 1 0.080 2.13 0.1876 BC 0.40 1 0.40 10.73 0.0136 * A2 4.86 1 4.86 128.98 <0.0001 ** B2 3.56 1 3.56 94.40 <0.0001 ** C2 8.42 1 8.42 223.52 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.26 7 0.038 失拟项 0.087 3 0.029 0.66 0.6184 纯误差 0.18 4 0.044 总和 21.84 16 注:*P< 0.05为显著差异;**P< 0.01为极显著差异。 2.4.3 响应曲线分析及最佳工艺条件确定
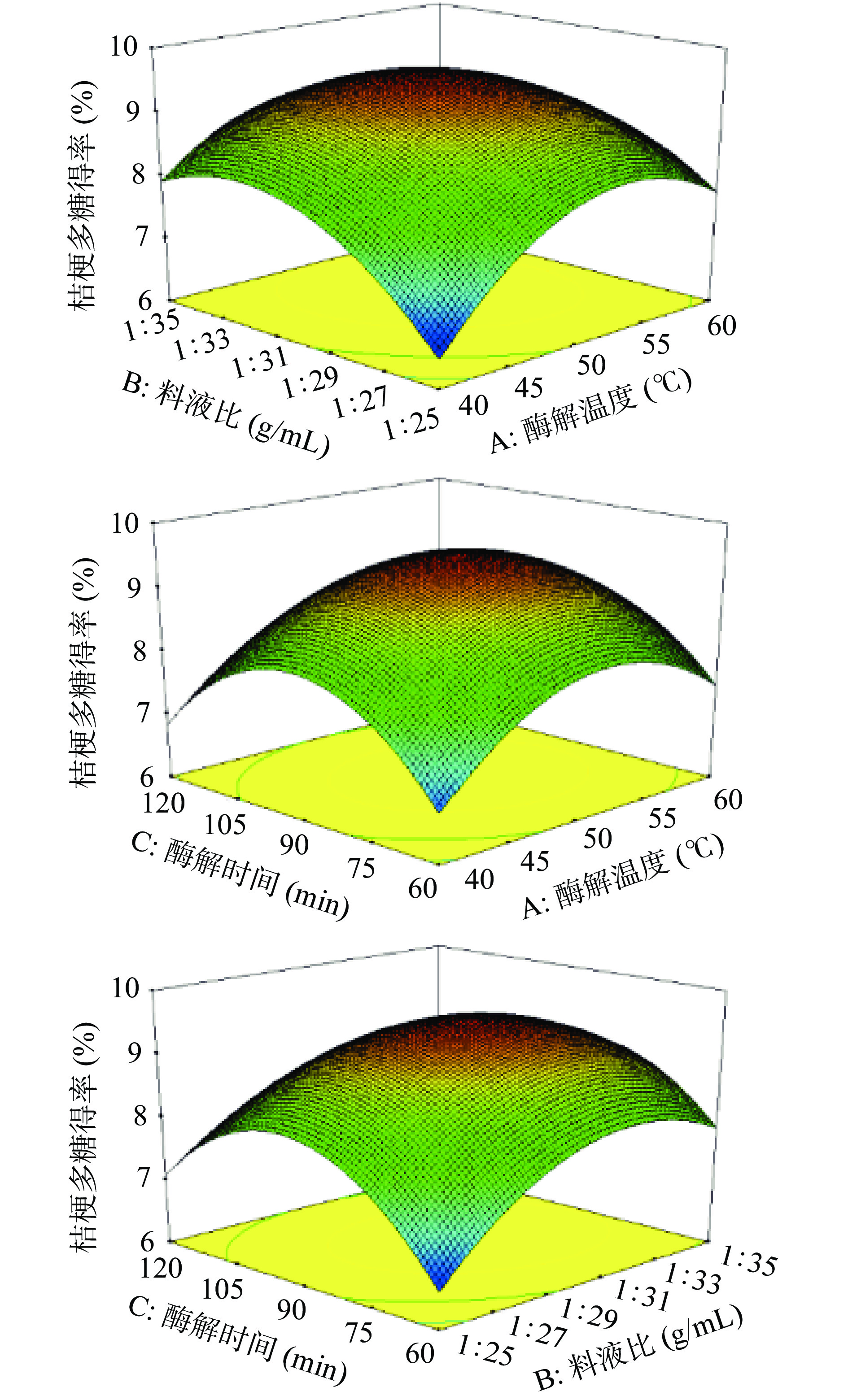
以Design-Expert 8.0.6的三维响应曲面来找出最佳优化工艺,并判定料液比、酶解温度和酶解时间对桔梗多糖得率的影响。如图5所示,响应曲面坡度的陡峭程度表示随着影响因素的变化,各因素对桔梗多糖得率的交互作用程度和影响[25],结合表5的实验结果可知,A和B、B和C交互作用对得率影响显著(P<0.05),A与C交互作用对得率影响不显著(P>0.05)。
通过回归模型的分析,以多糖得率为评价指标,确定复合酶法提取桔梗多糖的最佳工艺参数为:酶解时间88.78 min,料液比1:30.94 mL/g,酶解温度51.04 ℃,桔梗多糖得率的最大预测值为9.53%。为操作简便,将工艺修正为酶解时间90 min,料液比1:30 g/mL,酶解温度50 ℃。在上述条件下,多糖实际得率为9.01%,预测值与实际值相对误差较小,具有一定的实用价值。
2.5 桔梗多糖的分离纯化
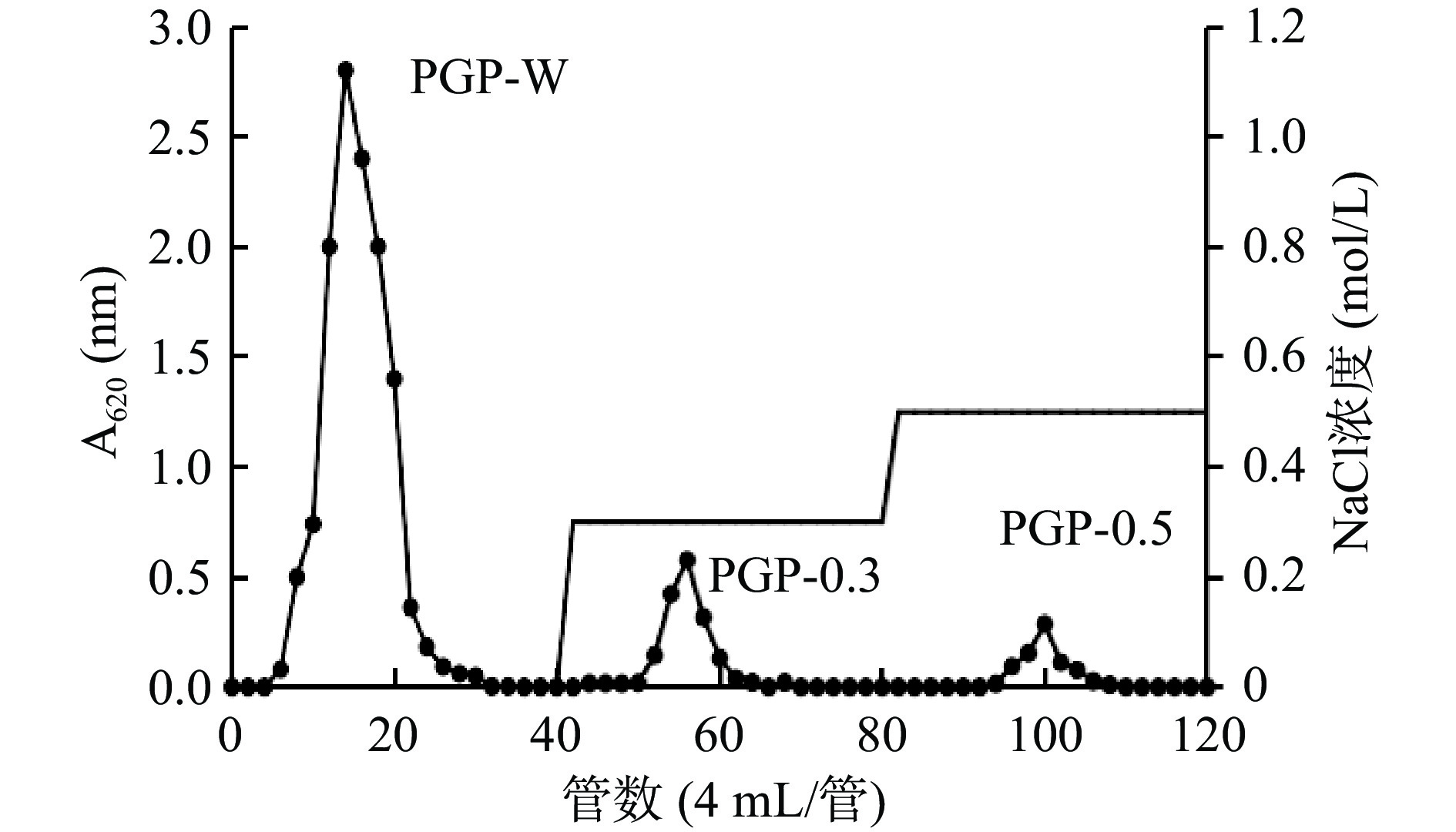
从桔梗根中提取的粗多糖经DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow离子柱层析洗脱,得到三个组分,按洗脱液浓度命名为:PGP-W、PGP-0.3、PGP-0.5。由图6可看出,0.3和0.5 mol/L NaCl洗脱得到的峰形较低,表明桔梗多糖主要由中性多糖构成。
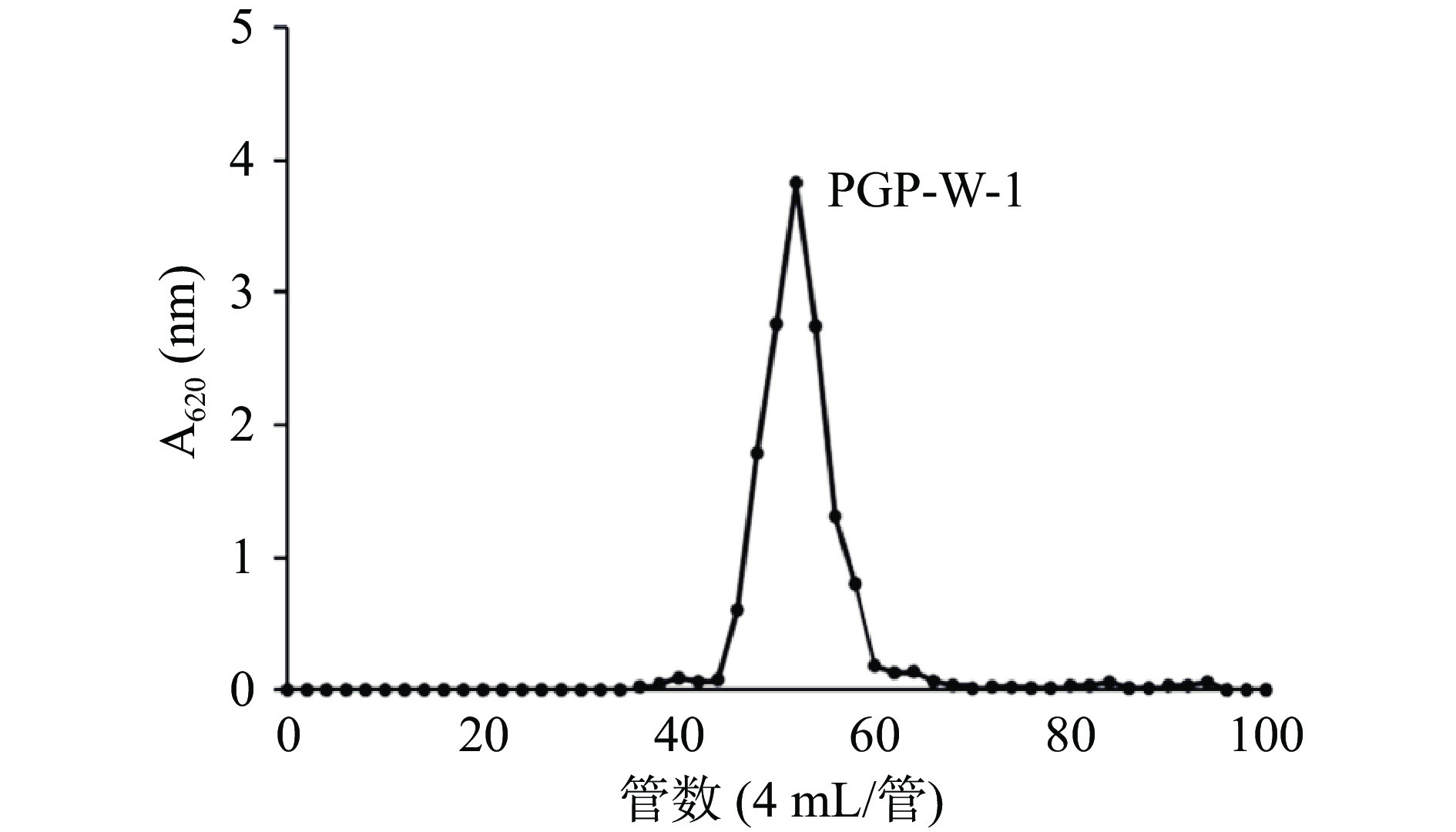
将超纯水洗脱的组分命名为PGP-W,继续以Sephacryl S-300凝胶柱纯化。由图7可看出,洗脱曲线表现出近似尖锐的对称峰,表明此时得到的桔梗多糖组分较纯。合并峰对应的洗脱液,浓缩干燥后得到桔梗纯化多糖PGP-W-1,进行后续研究。
2.6 PGP-W-1纯度鉴定及分子量测定
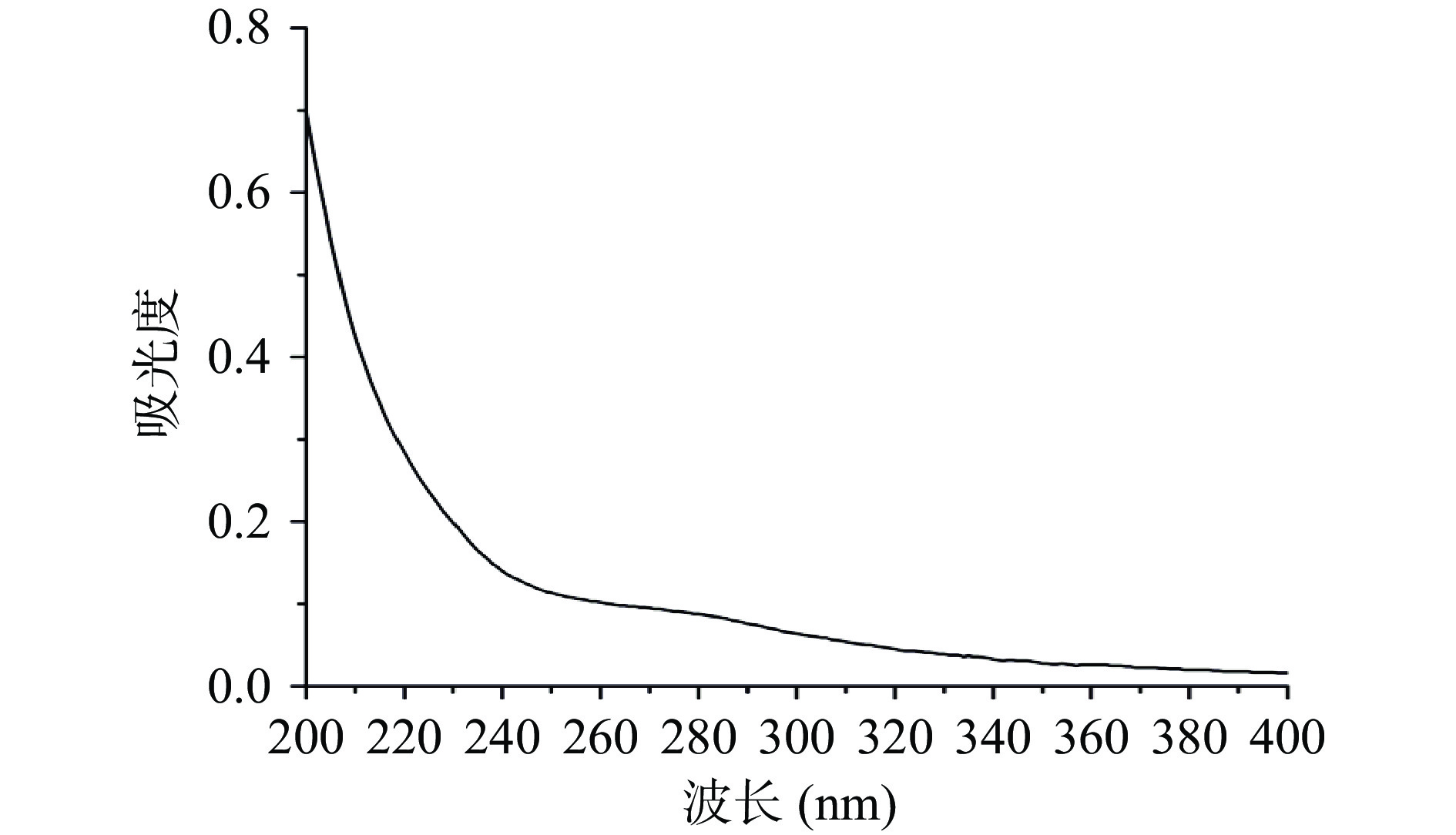
经测定PGP-W-1的总糖含量为96.8%,蛋白质含量为1.92%,表明PGP-W-1具有很高的纯度。紫外-可见光谱显示PGP-W-1在260和280 nm波长均未观察到明显的吸收峰(图8),进一步说明PGP-W-1的纯度较高,与上述结果一致。
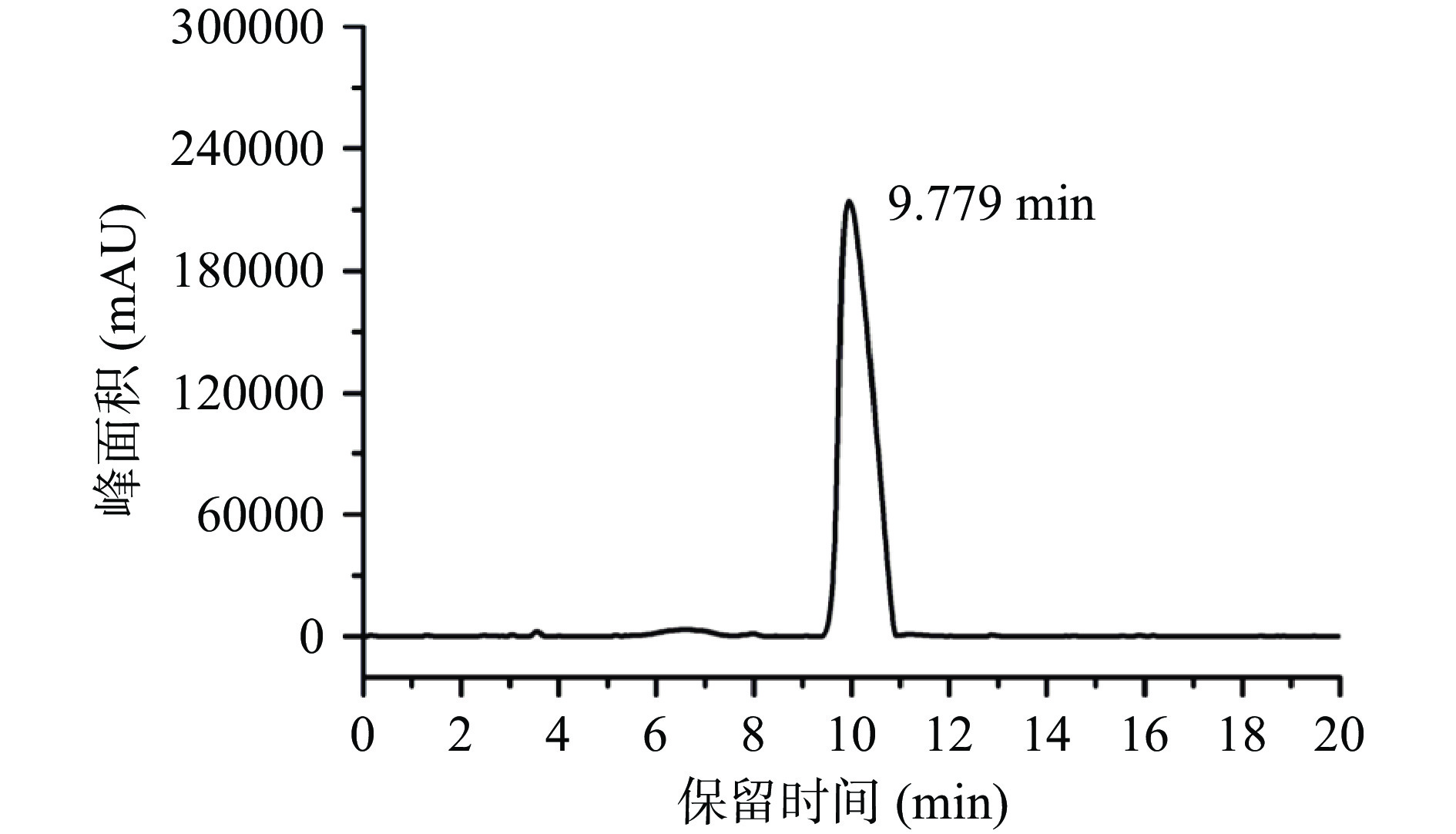
使用HPLC-ELSD系统检测PGP-W-1的均一性和分子量,如图9所示,单一对称的峰表示PGP-W-1分子量分布均一。以葡聚糖标准品的保留时间为横坐标,分子量对数值为纵坐标绘制标准曲线:lgMw=−1.0279t+13.69(R2=0.9998)。根据PGP-W-1保留时间(9.779 min)计算出桔梗多糖分子量为6.2 kDa。
2.7 桔梗多糖单糖组成分析
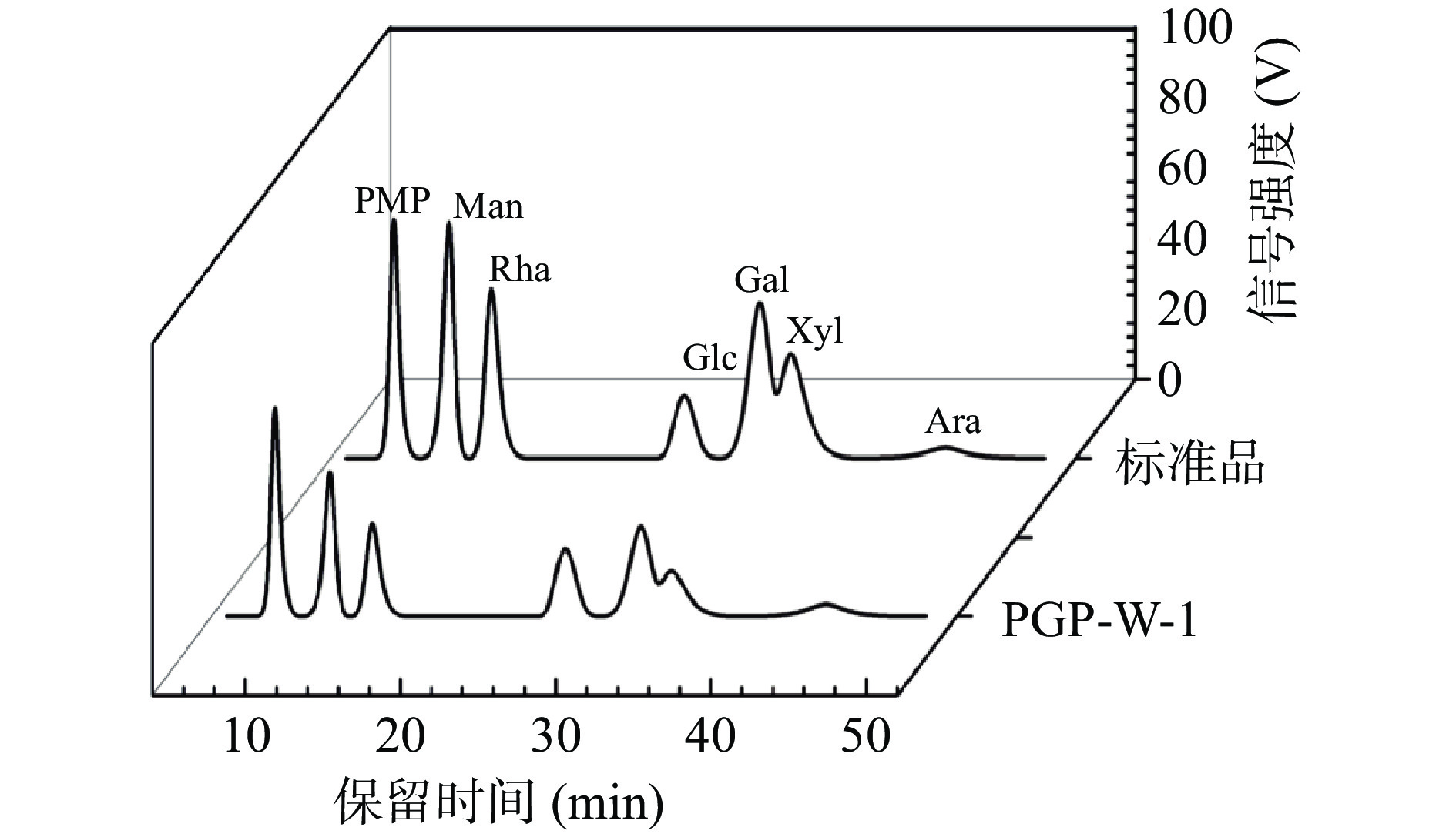
如图10所示,通过与单糖标准品曲线对比得出,PGP-W-1由甘露糖(Man),鼠李糖(Rha),葡萄糖(Glc),半乳糖(Gal),木糖(Xyl),阿拉伯糖(Ara)六种单糖组成,对应摩尔比为4.9:4.3:7.9:7.8:4.8:18.6。
2.8 桔梗多糖NMR图谱
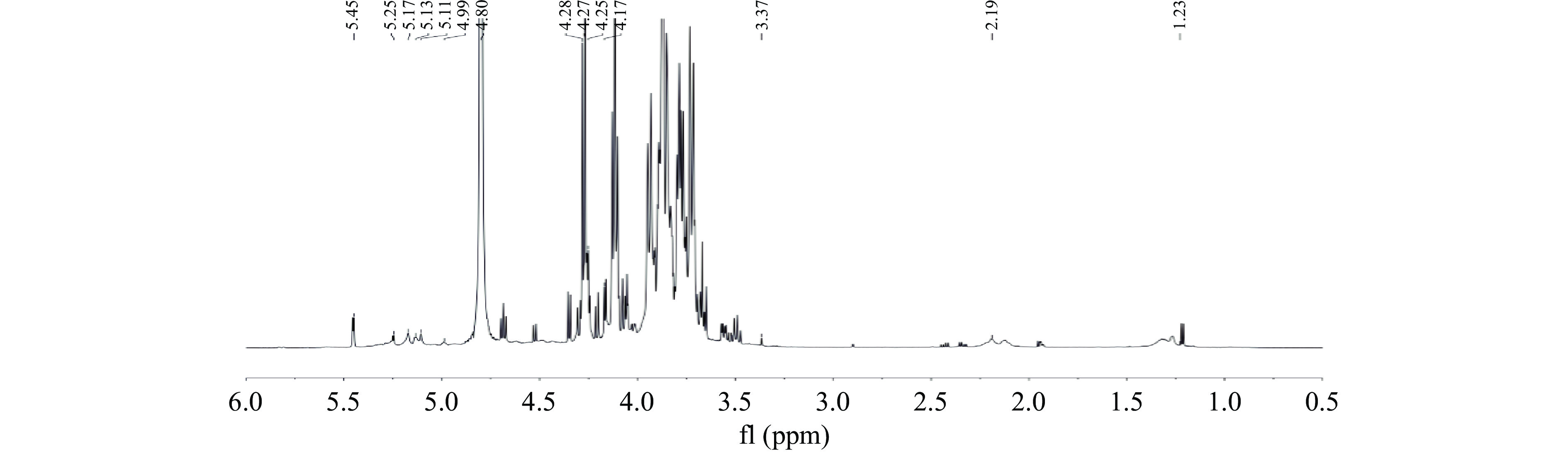
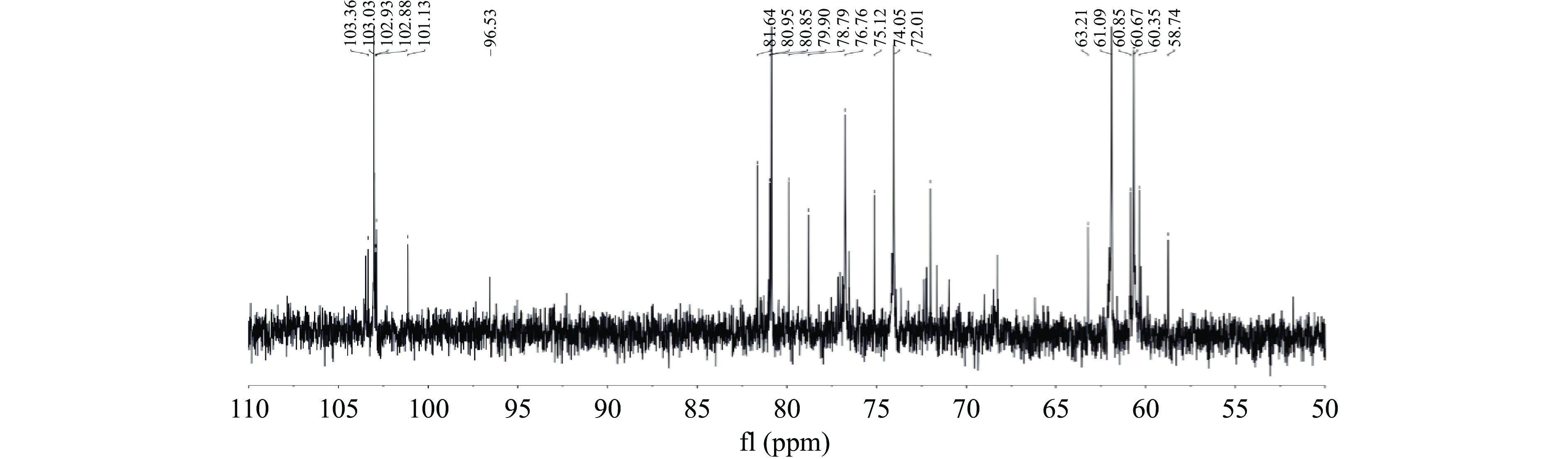
核磁共振图谱提供了碳水化合物的详细结构信息,包括糖苷键的构型和连接方式。图11和图12展示了PGP-W-1在δH 3.0~5.5 ppm和δC 60~110 ppm处的典型多糖信号,可看出PGP-W-1同时具有α型糖苷键和β型糖苷键[26]。
1H-NMR图谱中,δH 4.80 ppm处的强信号峰是D2O溶剂峰,δH 3.2~4.3 ppm范围内出现的重叠信号为糖苷键上H-2~H-6的质子信号积累。δH 1.23 ppm为鼠李糖残基的甲级质子信号峰[27];δH 5.45 ppm为α-1,4-Glcp的H-1信号;δH 5.25 ppm为α-1,3-Araf的H-1信号;δH 5.17 ppm为T-α-Araf的H-1信号;δH 4.68 ppm为β-1,4-Glcp的H-1信号;δH 4.52 ppm为β-1,3,4-Xylp的H-1信号[28]。
13C-NMR图谱中异头碳区域存在6个较为明显的信号峰,分别为:δC 103.36 ppm、δC 103.03 ppm、δC 102.93 ppm、δC 102.88 ppm、δC 101.13 ppm、δC 96.53 ppm,表明多糖中至少存在六种多糖残基,这与单糖组成的结果一致,其中,δC 60~90 ppm 范围内出现的重叠信号为糖苷键上C-2~C-6的质子信号积累[29],其中,δC103.03 ppm的C-1信号与δC 74.05 ppm的C-2信号相结合归属于β-1,6-Glcp,δC 96.53 ppm的C-1信号与δC 75.12 ppm的C-6信号相结合归属于α-1,4-Manp [30]。此外,在δC 170~180 ppm间未检测到信号峰,表明PGP-W-1不含糖醛酸,是一种中性多糖。PGP-W-1在δC 90 ppm处无明显信号,表明糖残基为吡喃型糖环。
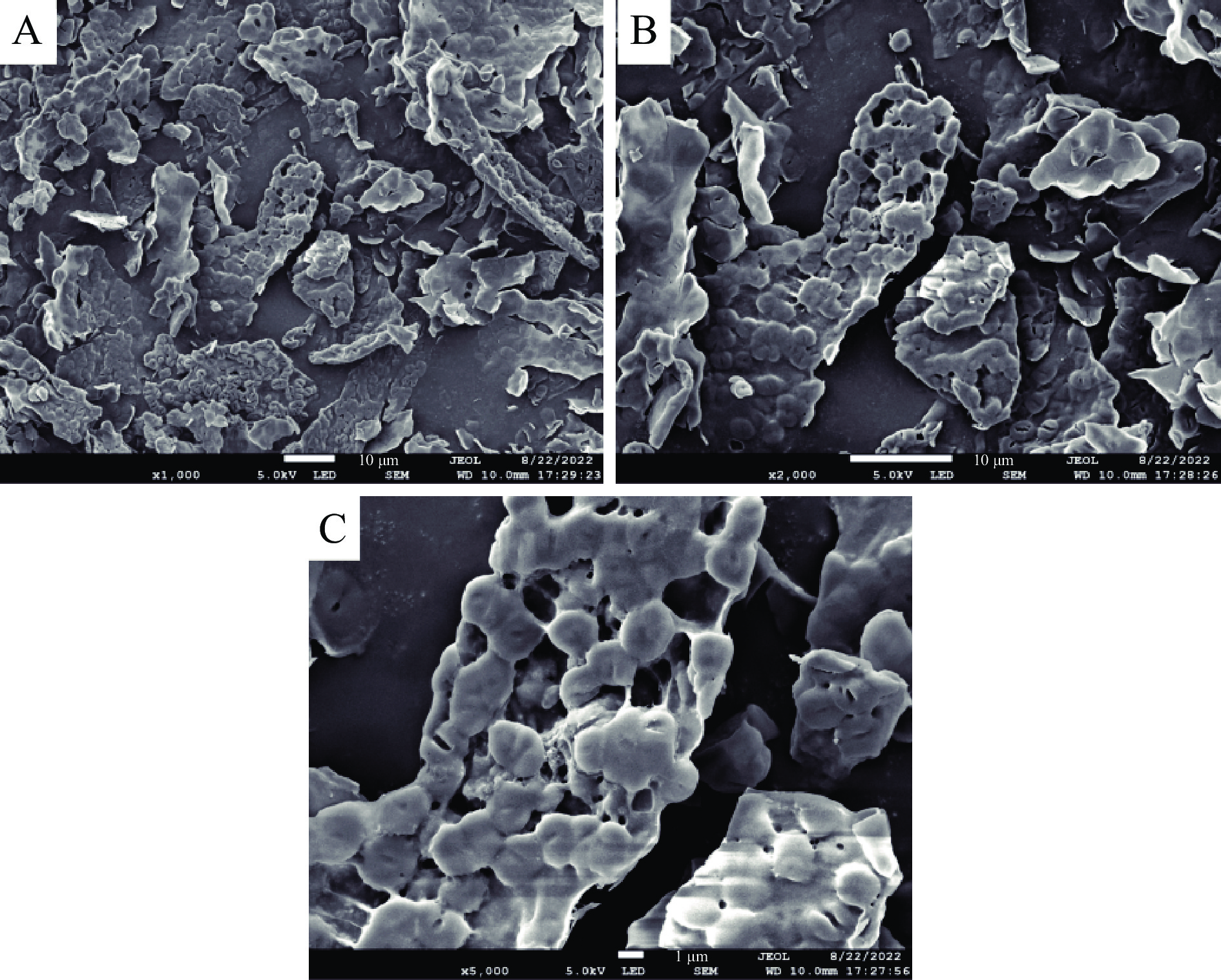
2.9 桔梗多糖的形貌特征
通过扫描电镜在1000、2000、5000倍下观察了桔梗多糖的表面形貌。如图13所示,放大1000倍时,多糖呈无规律的碎片状,且形状大小不一。放大2000倍时,多糖表面边缘褶皱且不规律。放大5000倍时,可看出多糖呈光滑、层状、片状形貌,表面有边缘褶皱。
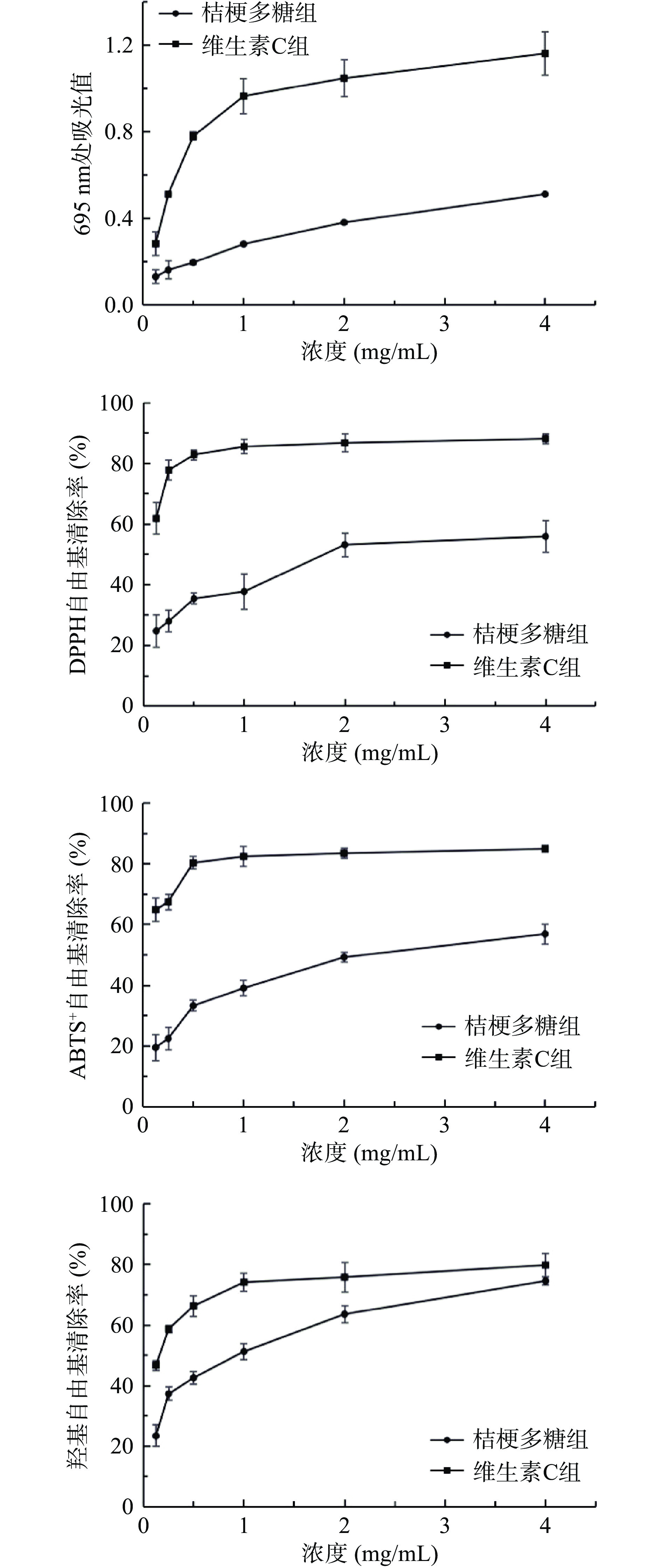
2.10 桔梗多糖体外抗氧化活性
由图14可知,在相同浓度条件下,PGP-W-1总还原力弱于维生素C。在0.125~4 mg/mL范围内,PGP-W-1和维生素C对DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基及羟基自由基的清除能力表现出剂量依赖性,其中,PGP-W-1清除DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基以及羟基自由基的IC50值分别为2.14、2.25、0.78 mg/mL。在浓度为4 mg/mL时,PGP-W-1清除DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基及羟基自由基的能力达到维生素C组的63.42%,66.99%,93.45%,表明PGP-W-1具有一定的抗氧化能力。
3. 结论
在单因素实验基础上,通过响应面法优化得到了复合酶提取桔梗多糖的最佳工艺,纤维素酶、果胶酶、木瓜蛋白酶的添加量为2%,酶解时间90 min,料液比1:30 mL/g,酶解温度50 ℃,在此条件下,多糖实际提取率为9.01%±0.07%,多糖含量达92%±0.76%。该工艺提取技术简易,产品纯度高,是一种提取桔梗多糖的高效方法,适合用于工业化生产。
桔梗粗多糖经DEAE-Sepharose Fast Flow和Sephacryl S-300层析柱纯化后,得到均一组分PGP-W-1,紫外光谱显示其纯度较高,基本不含核酸和蛋白质等杂质。PGP-W-1是分子量为6.2 kDa的中性多糖,由甘露糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖、半乳糖、木糖和阿拉伯糖组成。核磁共振图谱显示PGP-W-1为吡喃糖环,同时具有α型糖苷键和β型糖苷键。体外抗氧化试验显示PGP-W-1对DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基和羟基自由基清除率IC50值分别为2.14、2.25、0.78 mg/mL,表明桔梗多糖具有作为天然抗氧化剂的潜力。该研究为复合酶法在桔梗多糖提取中的应用提供了理论基础,同时为桔梗在工业生产中的资源利用提供了重要参考。
-
表 1 正交试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Orthogonal experimental factor horizontal design
水平 X:纤维素酶(%) Y:果胶酶(%) Z:木瓜蛋白酶(%) 1 1.5 1.5 1 2 2 2 1.5 3 2.5 2.5 2 表 2 响应面试验因素水平设计
Table 2 Experimental factor level of response surface
水平 A :酶解温度(℃) B :料液比(g/mL) C:酶解时间(min) −1 40 1:25 60 0 50 1:30 90 1 60 1:35 120 表 3 复合酶配比正交试验结果
Table 3 Orthogonal experimental results of compound enzyme ratio
实验号 X:纤维素酶 Y:果胶酶 Z:木瓜蛋白酶 Y:多糖得率(%) 1 1 1 1 6.447 2 1 2 2 7.035 3 1 3 3 6.792 4 2 1 2 7.583 5 2 2 3 8.251 6 2 3 1 7.191 7 3 1 3 6.934 8 3 2 1 6.707 9 3 3 2 6.335 k1 6.758 6.988 6.782 k2 7.675 7.331 6.984 k3 6.658 6.772 7.325 R 1.016 0.558 0.544 表 4 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 4 Response surface experimental design and results
实验号 A B C Y:多糖得率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 6.319 2 1 0 1 7.053 3 1 −1 0 7.817 4 0 0 0 9.289 5 −1 1 0 7.917 6 0 1 1 7.081 7 0 −1 1 7.072 8 0 1 −1 7.868 9 0 0 0 9.563 10 0 −1 −1 6.587 11 0 0 0 9.354 12 −1 0 1 6.927 13 0 0 0 9.408 14 0 0 0 9.815 15 1 1 0 7.915 16 −1 0 −1 6.657 17 1 0 −1 7.350 表 5 二项式回归方程系数显著性检验
Table 5 Significance of coefficients in second order regression equation
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 21.58 9 2.40 63.62 <0.0001 ** A-酶解温度 0.67 1 0.67 17.77 0.0040 ** B-料液比 1.11 1 1.11 29.57 0.0010 ** C-酶解时间 0.014 1 0.014 0.36 0.5680 AB 0.56 1 0.56 14.92 0.0062 ** AC 0.080 1 0.080 2.13 0.1876 BC 0.40 1 0.40 10.73 0.0136 * A2 4.86 1 4.86 128.98 <0.0001 ** B2 3.56 1 3.56 94.40 <0.0001 ** C2 8.42 1 8.42 223.52 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.26 7 0.038 失拟项 0.087 3 0.029 0.66 0.6184 纯误差 0.18 4 0.044 总和 21.84 16 注:*P< 0.05为显著差异;**P< 0.01为极显著差异。 -
[1] CHO B O, CHOI J, KANG H J, et al. Anti-obesity effects of a mixed extract containing Platycodon grandiflorum, Apium graveolens and green tea in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice[J]. Experimental Theraeutic Medicine,2020,19(4):2783−2791.
[2] 董增, 曹稳根, 段红, 等. 桔梗多糖提取、分离纯化以及生物活性研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2018,37(8):3534−3539. [DONG Z, CAO W G, DUAN H, et al. [Study on extraction, isolation, purification and biological activity of polysaccharides from Platycodon grandiflorum[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2018,37(8):3534−3539. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.037.003534 DONG Z, DONG W G, DUAN H, et al. [Study on extraction, isolation, purification and biological activity of polysaccharides from Platycodon grandiflorum [J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2018, 37(8): 3534−3539. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.037.003534
[3] HE J Q, ZHENG M X, YING H Z, et al. PRP1, a heteropolysaccharide from Platycodonis Radix, induced apoptosis of HepG2 cells via regulating miR-21-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,158:542−551. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.193
[4] JI M Y, BO A, YANG M, et al. The pharmacological effects and health benefits of Platycodon grandiflorus-a medicine food homology species[J]. Foods,2020,9(2):142. doi: 10.3390/foods9020142
[5] LI Q Q, YANG T, ZHAO S, et al. Distribution, biotransformation, pharmacological effects, metabolic mechanism and safety evaluation of platycodin D: A comprehensive review[J]. Current Drug Metabbolism,2022,23(1):21−29. doi: 10.2174/1389200223666220202090137
[6] ZHANG J, LI Y, LI Y, et al. Structure, selenization modification, and antitumor activity of a glucomannan from Platycodon grandiflorum[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,220:1345−1355. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.029
[7] ZHENG P, FAN W, WANG S, et al. Characterization of polysaccharides extracted from Platycodon grandiflorus (Jacq. ) A. DC. affecting activation of chicken peritoneal macrophages[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,96:775−785. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.077
[8] PARK M J, RYU H S, KIM J S, et al. Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide induces dendritic cell maturation via TLR4 signaling[J]. Food and Chemistry Toxicology,2014,72:212−220. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.07.011
[9] ZHANG S, CHAI X, HOU G, et al. Platycodon grandiflorum (Jacq. ) A. DC.: A review of phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and traditional use[J]. Phytomedicine,2022,106:154422. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154422
[10] ZHANG L, WANG Y, YANG D, et al. Platycodon grandiflorus-an ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacol,2015,164:147−161. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.052
[11] NADAR S S, RAO P, RATHOD V K. Enzyme assisted extraction of biomolecules as an approach to novel extraction technology: A review[J]. Food Research International,2018,108:309−330. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.03.006
[12] SHENG Y, LIU G, WANG M, et al. A selenium polysaccharide from Platycodon grandiflorum rescues PC12 cell death caused by H2O2 via inhibiting oxidative stress[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,104:393−399. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.06.052
[13] CHEN R, LUO S, WANG C, et al. Effects of ultra-high pressure enzyme extraction on characteristics and functional properties of red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus) peel pectic polysaccharides[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,121:107016. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107016
[14] DUBOIS M, GILLES K A, HAMILTION J K, et al. Coloimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1956,28(3):350−356. doi: 10.1021/ac60111a017
[15] LIN T T, LIU Y, LAI C J S, et al. The effect of ultrasound assisted extraction on structural composition, antioxidant activity and immunoregulation of polysaccharides from Ziziphus jujuba Mill var. spinosa seeds[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2018,125:150−159. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.08.078
[16] LI W, ZHANG Y Q, SANG L T, et al. Effects of different extraction techniques on the structural, physicochemical, and bioactivity properties of heteropolysaccharides from Platycodon grandiflorum roots[J]. Process Biochemistry,2023,127:33−43. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2023.02.001
[17] CHEN R, TAN L, JIN C G, et al. Extraction, isolation, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2015,77:434−443. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.08.006
[18] WANG H, CHEN J, REN P, et al. Ultrasound irradiation alters the spatial structure and improves the antioxidant activity of the yellow tea polysaccharide[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2021,70:105355. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105355
[19] 施利奇, 张彦青, 戚务勤, 等. 酸枣水提物不同提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(11):182−190. [SHI L Q, ZHANG Y Q, QI W Q, et al. Optimization of different extraction process of sour jujube juice and study on its antioxidant[J]. Food & Machinery,2019,35(11):182−190. SHI L Q, ZHANG Y Q, QI W Q, et al. Optimization of different extraction process of sour jujube juice and study on its antioxidant [J]. Food & Machinery, 2019, 35(11): 182-190.
[20] 孙艳, 崔旭盛, 刘静, 等. 酸枣仁黄酮的提取工艺优化及其抗秀丽隐杆线虫氧化损伤活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(8):143−150. [SUN Y, CUI X S, LIU J, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from Ziziphus jujuba Mill var. spinosa leaves and its antioxidant damage activity in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(8):143−150. SUN Y, CUI X S, LIU J, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from Ziziphus jujuba Mill var. spinosa leaves and its antioxidant damage activity in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(8): 143−150.
[21] 向丽. 复合酶提取桔梗多糖及其抗氧化活性研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2021 XIANG L. Researches on the extraction and antioxidant activity of glycoprotein from Platycodon Grandiflorum [D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[22] 王歆彤, 李朋月, 吴兰芳, 等. 知母多糖复合酶提取工艺优化及其免疫活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(11):218−227. [WANG X T, LI P Y, WU L F, et al. Optimization of multi-enzymatic extraction of polysaccharide from Anemarrhena asphodeloides bunge and its immunomodulatory activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(11):218−227. WANG X T, LI P Y, WU L F, et al. Optimization of multi-enzymatic extraction of polysaccharide from Anemarrhena asphodeloides bunge and its immunomodulatory activity [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(11): 218−227.
[23] 蒋德旗, 蒋夏荣, 夏家朗, 等. 复合酶提取金樱子根多糖工艺的优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 中成药,2018,40(11):2421−2425. [JIANG D R, JIANG X R, XIA J L, et al. Polysaccharides from Rosa laevigata roots, their compound enzyme extraction technique optimization and the antioxidant activity[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2018,40(11):2421−2425. JIANG D R, JIANG X R, XIA J L, et al. Polysaccharides from Rosa laevigata roots, their compound enzyme extraction technique optimization and the antioxidant activity [J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2018, 40(11): 2421−2425.
[24] 陈雪花, 杨万根. 响应面法优化超声波协同酶法提取杜仲叶多糖工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,41(22):193−220. [CHEN X H, YANG W G. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted enzymatic extraction of polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides oliver leaves by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,41(22):193−220. CHEN X H, YANG W G. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted enzymatic extraction of polysaccharides from Eucommia ulmoides oliver leaves by response surface methodology [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 41(22): 193−220.
[25] NUERXIATI R, ABUDUWAILI A, MUTAILIFU P, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction, characterization and biological activities of polysaccharides from Orchis chusua D. Don (Salep)[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,141:431−443. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.112
[26] ZHAO Q, LIU H M, LV T T, et al. Structure, rheological, thermal and antioxidant properties of cell wall polysaccharides from Chinese quince fruits[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,147:1146−1155. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.083
[27] WU M Q, LI W, ZHANG Y L, et al. Structure characteristics, hypoglycemic and immunomodulatory activities of pectic polysaccharides from Rosa setate x Rosa rugosa waste[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,253:117190. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117190
[28] YAO H Y Y, WANG J Q, YIN J Y, et al. A review of NMR analysis in polysaccharide structure and conformation: Progress, challenge and perspective[J]. Food Research International,2021,143:110290. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110290
[29] XU L S, ZHANG Y J, WANG L Z. Structure characteristics of a water-soluble polysaccharide purified from dragon fruit (Hylocereus undatus) pulp [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2016, 146: 224-230.
[30] POPOV S V, OVODOVA R G, GOLOVCHENKO V V, et al. Pectic polysaccharides of the fresh plum Prunus domestica L. isolated with a simulated gastric fluid and their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,143:106−113. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.07.049
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 李超,张欢,汲晨锋. 桔梗化学成分、药理作用及现代应用研究进展. 中国药学杂志. 2025(01): 9-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 于纯淼,廖贤,陈小倩,李艾欣,陈佳,于苗苗. 复合酶法提取诺丽多糖的工艺优化及其体外抗氧化活性. 食品研究与开发. 2025(03): 142-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李金婷,钱心燚,雍一丹,吴萌萌,孙华锴,王雅楠,陈安徽,邵颖,尼再中. 蝉花多糖酶法辅助双水相提取工艺优化及其抗氧化、降血糖和降血脂活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(12): 179-188 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. Lanying Zhang,Xinrui Wang,Jingze Zhang,Dailin Liu,Gang Bai. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology and product application of Platycodon grandiflorum: A review. Chinese Herbal Medicines. 2024(03): 327-343 .  必应学术
必应学术
5. 陈卫,谷彩花,毕晶晶,叶兆伟,张亚欣,白向茹,马晓辉,陈琼. 商桔梗多糖提取工艺优化及其吸湿保湿、抗氧化性能研究. 饲料工业. 2024(17): 113-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 袁思琪,翟茜,严建业,王元清. Box-Behnken设计优化竹节参多糖酶法提取工艺. 亚太传统医药. 2024(11): 75-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘忠群,谢晓岑,罗晶晶,谢曦,彭宏,王蓉,宋彦廷,胡文婷. 超声辅助复合酶法提取长茎葡萄蕨藻藻渣多糖及其降脂功能. 现代食品科技. 2024(11): 97-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 许梦粤,曾长立,王红波. 药食同源植物多糖提取方法、结构解析和生物活性研究进展. 食品研究与开发. 2023(19): 216-224 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



