Effect of Storage Positions on the Volatile Flavor Compounds (VFCs) of Paddy Rice through Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectroscopy (GC-IMS) Analysis
-
摘要: 粮仓中的储藏位置对储粮品质特性有着较大的影响。本文通过气相离子迁移谱(GC-IMS)技术分析了18个月(18 M)储藏期内,粮仓中间冷心层和表层的稻谷中挥发性风味物质(VFCs)的组成变化,探讨了高大平房仓中位置效应对稻谷VFCs的影响规律。结果表明,稻谷中的VFCs随储藏时间的延长不断变化,且时间越长变化越大,尤其位于表层的稻谷变化趋势明显。与中间冷心层稻谷相比,储藏到12~18 M的表层稻谷中醛类和酯类含量较高,而醇类物质含量偏少。主成分(PCA)分析表明,储藏至12 M时,中间冷心层和表层稻谷的VFCs差异最为明显。其中,表层稻谷中戊醛、壬醛、乙酸乙酯、乙酸丙酯和乙酸丁酯等醛和酯类物质以及异辛醇含量明显高于中间冷心层;而反-2-己烯-醇、2-戊基呋喃、1-辛烯-3-醇、庚醇、1-丙醇、1-己醇、1-戊醇、异丁醇和2-庚酮等醇、酮类VFCs则在中间冷心层稻谷中含量更高。以上结果表明,粮仓中不同储粮位置对稻谷风味特性有较大影响,而表层受环境温度影响较大,风味品质变化也最为明显。
-
关键词:
- 气相色谱-离子迁移谱(GC-IMS) /
- 贮藏位置 /
- 贮藏时间 /
- 挥发性风味成分(VFCs) /
- 主成分分析(PCA)
Abstract: The storage positions in the granary has a great influence on the quality of stored grain. In the present study, the changes of volatile flavor compounds (VFCs) in paddy rice stored at middle cold core layer and top layer of the granary during 18 months of storage were analyzed by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy (GC-IMS), and the effect of storage location on the VFCs of paddy rice in high and big one-store granary were discussed. The results showed that the VFCs in paddy rice changed continuously with the storage time and the longer the time, the greater the change, especially for paddy rice stored at top layer. Compared with that stored at middle cold core layer, the contents of aldehydes and esters in paddy rice stored at top layer for 12 and 18 months were much higher, while that of the alcohols was relatively low, and the largest difference between middle cold core layer and top layer was found in paddy rice stored for 12 months by the principal component analysis (PCA). Among them, the contents of aldehydes and esters including valeraldehyde, nonanal, ethyl acetate, propyl acetate, butyl acetate and isooctanol at the top layer were significantly higher than that at the middle cold layer; while the contents of alcohol and ketone including trans 2-hexene alcohol, 2-pentylfuran, 1-octene-3-ol, heptanol, 1-propanol, 1-hexanol, 1-pentanol, isobutanol and 2-heptanone was higher in paddy rice stored at middle cold core layer. These results indicated that the storage location in the granary has great impact on the flavor characteristics of paddy rice, especially for that stored at top layer which was more affected by the ambient temperature. -
准低温储粮是通过自然或机械制冷方法控制温度,使粮食平均粮温处于20 ℃以下的准低温状态,提高粮食储藏稳定性的一种控温储粮技术。准低温储粮可以有效延缓储粮的品质陈化,降低粮食的呼吸强度和干物质损耗,延长粮食储藏期[1]。但在储粮过程中,粮库仓内温度会随外界环境温度的变化而发生不同程度的变化,尤其对粮堆表层、沿仓墙部分等受外界影响较大,为粮温变化的活跃区域,而粮堆的中心部分则受外界环境影响较小,形成粮堆的中间冷心层[2]。
在粮食储藏过程中,位于粮库不同位置的储粮品质会因这种温度波动的存在而产生差异性变化。王荣雪等[3]研究了江苏泰州高大平房仓储存的稻谷粮堆不同位置的品质差异,结果表明,稻谷粮堆不同位置的霉菌量、脂肪酸值和水分存在显著性差异。其中,中层稻谷的霉菌数量最多,其次是上层,下层最少;中层稻谷脂肪酸值和水分最高,同时中层尤其是中间位置水分最高,中下层东南位置稻谷水分含量最低。方宝庆等[4]也研究了稻谷粮堆不同位置稻谷的品质差异,结果表明,春夏交替季节粮堆上层稻谷的水分活度显著低于中下层,冬季粮堆上层稻谷的水分活度显著高于中下层;粮堆上层稻谷脂肪酸值高于中下层;粮堆上层稻谷霉菌量低于中下层;粮堆不同方位稻谷的水分活度、脂肪酸值、霉菌量均有一定差异。但目前尚未见粮仓储粮位置效应对稻谷风味品质特性影响的相关研究。
稻谷多以带壳形式贮藏,贮藏期间的品质变化难以直接观察得到,而通过对挥发性风味物质(VFCs)进行特异性分析是对其品质特性进行有效评价的重要方法之一。气相色谱-离子迁移谱联用技术(GC-IMS)是一种利用气相离子电场迁移速率差异分析鉴定特征风味成分的新技术。其以离子迁移谱仪(IMS)作为气相色谱的检测器,通过GC色谱保留时间和离子迁移谱相对迁移时间可以有效反映样品中VFCs的二维信息[5],具有高分离度、高分辨率、高灵敏度的优点,且对样品预处理和分析温度要求更低[6-7],更适用于VFCs的痕量检测。王熠瑶等[8]通过GC-IMS对贮藏脱壳糙米的风味变化进行了监测,刘强等[9]也用其分析了稻谷虫害致霉变引起的稻谷VFCs变化,ZHAO等[10]研究了茉莉花米在储藏过程中风味物质的变化情况,郭啸天[11]利用GC-IMS技术对不同储藏条件下粳稻谷的挥发性成分进行检测分析,为 4 ℃低温和 30 ℃充氮气调条件下粳稻谷储藏提供理论依据。
针对此,本文以高大平房仓中准低温储藏的晚籼稻为研究对象,通过GC-IMS技术对18 M储藏期间内粮库中表层和冷心层稻谷的VFCs随储藏时间的变化进行分析,研究粮仓位置效应对储藏稻谷风味品质特性的影响,并通过主成分分析(PCA)对不同样品的VFCs进行差异分析。旨在探讨位置效应对稻谷风味品质特性的影响,同时为稻谷储藏过程的品质评价提供一定理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
储粮品种为2017年12月收获入库的晚籼稻 产地为江苏省,入仓时的水分含量13.5%,杂质含量0.9%;试验仓房 为湖州直属库有限公司的高大平房仓,单个仓房容量为2640 t,仓库长30.0 m,宽21.0 m,堆粮线高6.0 m。稻谷贮藏周期18个月(18 M),期间每隔6个月取样一次。2-丁酮、2-戊酮、2-己酮、2-庚酮、2-辛酮、2-壬酮等均为分析纯 购于国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
粮仓安装YSWKF-15专用空调一台(江苏永昇空调有限公司)和BHKF-I-210内环流及热皮控温系统一套(中储粮成都储藏研究院)。控温工艺设定表层平均粮温超过21 ℃启动空调控温(夜间),储粮表层平均粮温超过23 ℃启动开内环流,低于22 ℃停止内环流;四周靠墙平均粮温超过22 ℃启动四周热皮控温环流风机,低于21 ℃停止热皮环流控温作业[12]。FlavourSpec® 1H1-00053型GC-IMS检测仪 配有 CTC自动顶空进样器,Laboratory Analytical Viewer(LAV)分析软件及 Library Search 定性软件,石英毛细管柱(15 m×0.53 mm,1 μm),德国G.A.S公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 稻谷取样
如图1,将粮库稻谷由下至上平均分为5层,每层平均分为4个块区,其中中间冷心组(A组)取中间三层各4个块区,共12个块区;表层(B组)取最上层14个块区的表层下0.1~0.2 m处样品;各组样品混匀后取平均样进行分析。分别于储藏的0、6、12和18个月取样,样品编号分别为:A-0、A-6、A-12、A-18;B-0、B-6、B-12、B-18。
1.2.2 样品的预处理
随机称取各组样品3 g,置于20 mL顶空瓶中,60 ℃孵育15 min,500 r/min振荡加热,SPME顶空气体进样后进行GC-IMS检测。每组样品三个平行。
1.2.3 挥发性风味物质的检测
贮藏过程中不同组稻谷VFCs的检测通过FlavourSpec®1H1-00053型气相离子迁移谱联用仪进行检测。根据金文刚等[13]的方法并作适当修改。GC色谱柱:FS-SE-54-CB-1,15 m×0.53 mm;柱温:60 ℃;石英毛细血管柱:(15 m×0.53 mm,1 µm);载气流速:2.0 mL/min的初始流速保持2 min;以2 mL/min 的速度升至15 mL/min,再以10 mL/min 的速度升至100 mL/min运行20 min。IMS漂移管长度:5 cm;管内线性电压: 400 V/cm;IMS温度:45 ℃;漂移气:N2(纯度≥99.999%);漂移气流速:150 mL/min;放射源:ß射线(氚,3H)。离子化模式:正负离子。顶空进样气体容积:500 μL,不分流模式;进样针温度:85 ℃;孵育转速:500 r/min;清洗时间:0.5 min。
1.3 数据处理
应用GC×IMS Library Search软件内置的NIST数据库和IMS数据库对VFCs进行定性分析,采用LAV(Laboratory Analytical Viewer)和插件Reporter、Gallery Plot进行图谱分析,采用Dynamic PCA插件对样品进行动态主成分分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 储藏稻谷VFCs的GC-IMS谱图分析
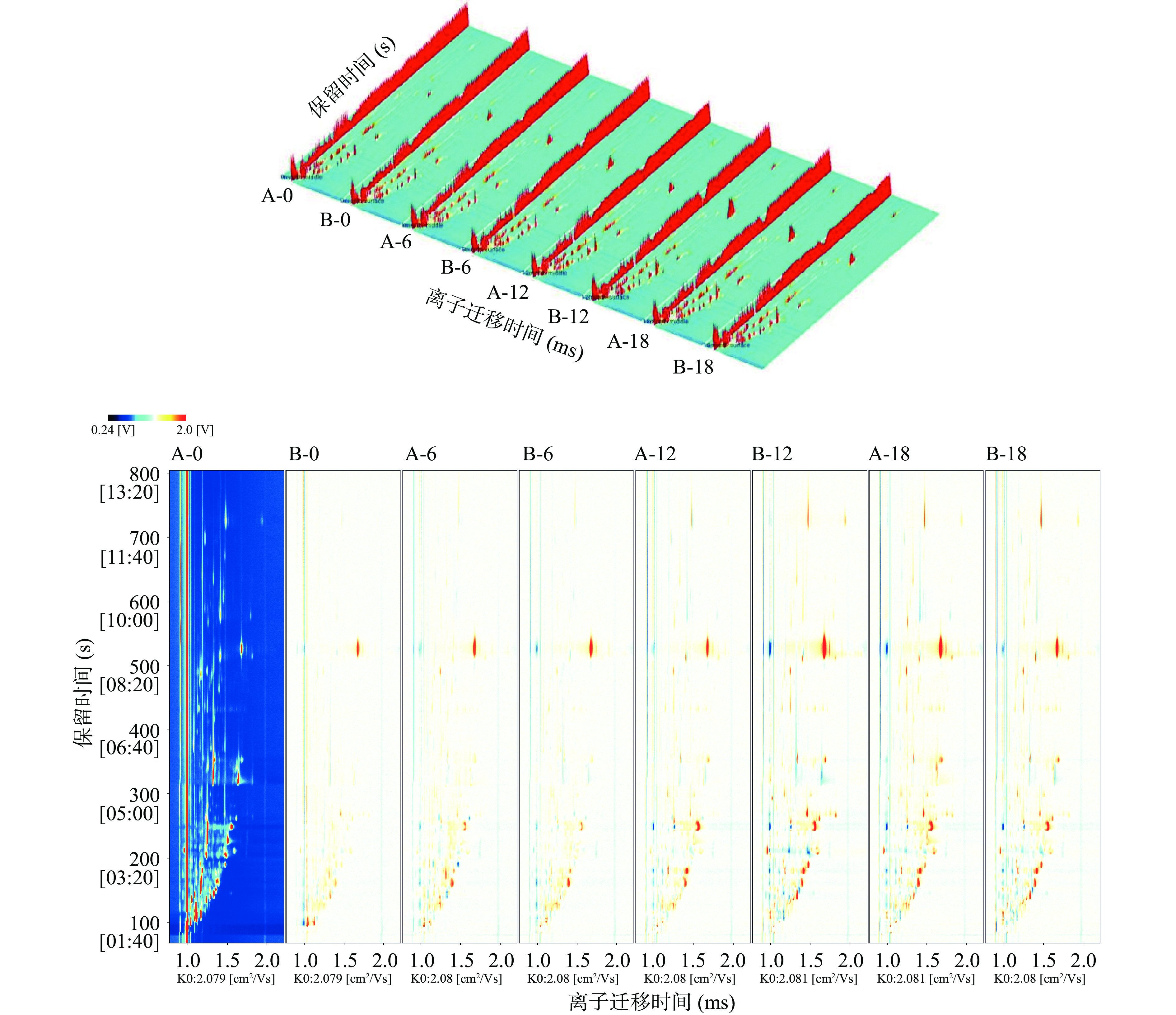
图2显示了8组稻谷中VFCs的GC-IMS图谱,其中水平X轴、Z轴和Y轴分别表示气相色谱仪检测VFCs的保留时间(s)、离子迁移时间(ms)和不同的离子峰强度[14]。可以看出,不同组稻谷VFCs随贮藏时间变化趋势有差异,同组不同贮藏时间的稻谷样品可鉴别的VFCs种类较相似,但离子迁移信号强度略有不同。
进一步通过差异对比模式对三维谱图进行降维处理获得Z-X俯视图谱。俯视谱上的每个点表征了特定VFCs。选取其中一个样品的谱图(A-0)作为参照,依次从其他各组样品的光谱图中扣除信号峰,具有相同有机化合物的样品,扣减后背景变为白色,若该组样品信号高于参照组则显示为红色,反之呈现为蓝色。可以看到,从左到右图谱上的点越来越密,红色也逐渐加深,表明A组中间冷心层和B组粮堆表层的VFCs种类和含量均随着稻谷储藏时间的延长而增加。对比分析发现,贮藏6 M时,A组和B组的VFCs差异很小,但当贮藏时间为12 M时,两个组中VFCs种类和含量差异较大,且表层稻谷VFCs较中间冷心层含量更高。可能是由于粮堆表层更容易与空气接触,也更容易受到外界环境温度变化的影响而发生脂肪氧化、淀粉或蛋白质的水解等一系列化学反应,导致了更多VFCs的产生[15-16]。
2.2 储藏稻谷VFCs的GC-IMS定性分析
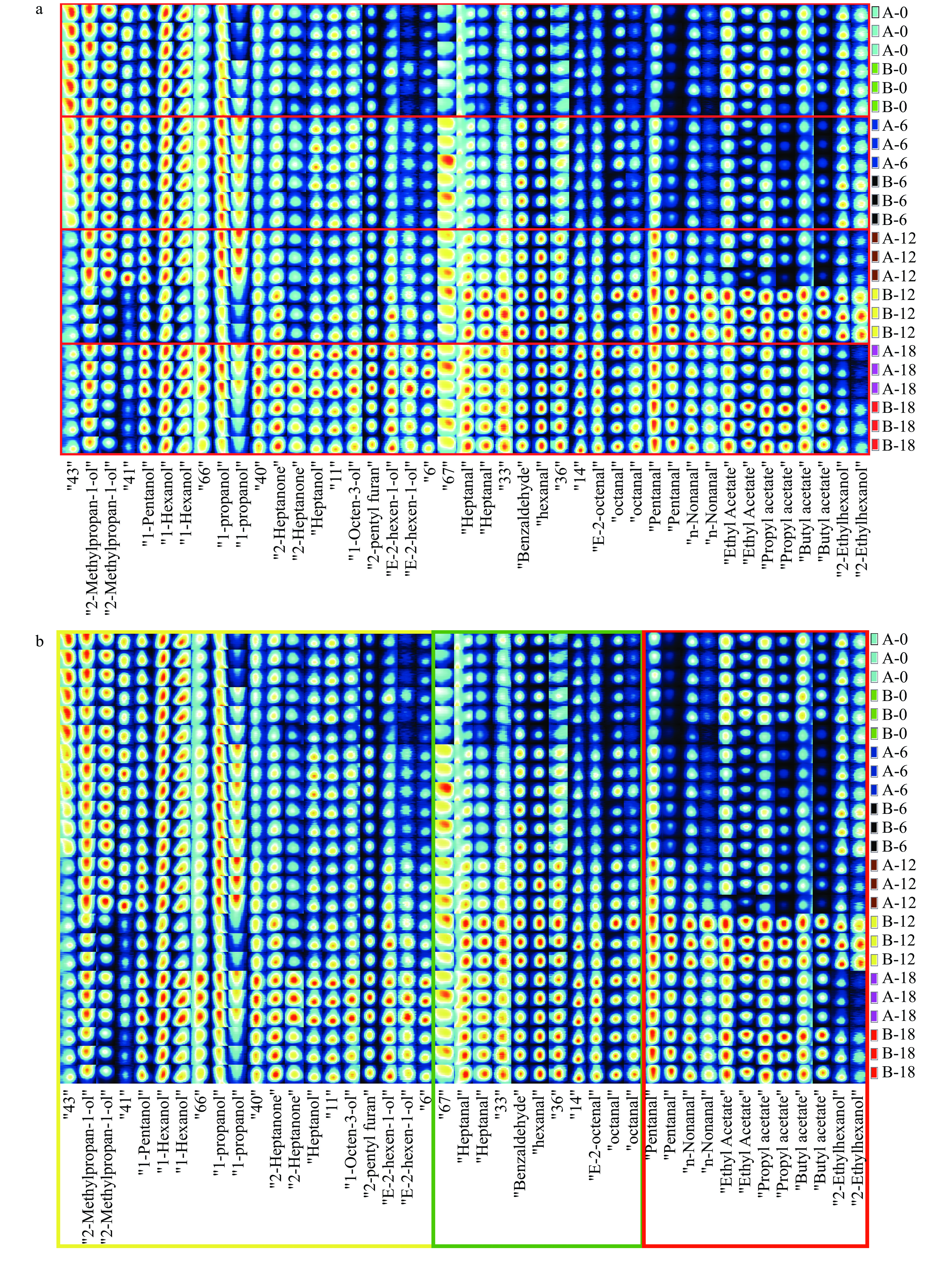
为了对比不同组贮藏稻谷样品间VFCs种类差异,通过内置的Gallery Plot插件选取VFCs库中的所有离子峰进行指纹比对。图3a为各样品VFCs中选取的43种变化明显的特征离子峰的指纹对比图谱,图谱中特征VFCs在不同样本间的变化放大对比于图3b。
图3a中每一行代表该贮藏期稻谷样品的全部信号峰,每一列代表某一VFCs在不同稻谷样品中的信号峰。蓝色表示含量较少,红色表示含量较高。可以看出,稻谷样品随贮藏时间和取样位置的不同呈现明显的变化。贮藏开始稻谷中VFCs的种类较少,只检测到几种醇类:2-甲基丙醇、1-戊醇、1-己醇和1-丙醇;储藏18 M开始,挥发性风味物质的种类及含量均呈现逐渐增加趋势,尤其是醛类、酯类、醇类。可能是由于储藏过程中,稻谷中脂质在脂肪酶作用下水解产生甘油和脂肪酸,并继续氧化分解成酮类、醛类、醇类小分子物质,同时产生陈化稻谷味[17-18]。其中,反式-2-己烯-1-醇、戊醛、己醛、庚醛、苯甲醛、十六醛、 正辛醛、反式-2-辛醛、壬醛、乙酸乙酯、乙酸丙酯、乙酸丁酯、2-乙基己醇的含量均逐渐增加。己醛与稻米的异味有关,通常被认为是稻米脂质氧化的标志[19]。此外,1-丙醇仅在贮藏6M时的稻谷表层和中间冷心层中都存在,在贮藏12M和18M时只存在于A组中间冷心层;2-乙基己醇仅在贮藏12M的表层样品中含量明显较多,在其他组的信号峰强度弱,含量较低;2-庚酮、庚醇、反-2-己烯-醇、1-辛烯-3-醇和2-戊基呋喃在贮藏18M组的信号峰强度最强,含量最多,在其他组的信号峰均呈现很淡的蓝色,含量较少。2-戊基呋喃为亚油酸氧化产物,在低浓度下有一种特有的坚果味,而在高浓度下具有氧化大豆油味,对稻谷风味有不利影响[20-22]。郭啸天[11]的研究结果显示,1-辛烯-3-醇、1-戊醇、己醛、1-己醇、2-戊基呋喃、辛醛、壬醛在各储藏条件下均随着储藏时间的延长呈现增强趋势,这与本研究结果一致。康文翠等[23]的研究结果表明,对不同储藏时间的苏软香型米的贡献率较高的物质有壬醛,正己醛和2-戊基呋喃,这些风味物质也均在贮藏12 M以上的稻谷中检出。综上,1-丙醇可作为表征稻谷准低温储藏半年的标志性风味物质;2-乙基己醇可以作为表征稻谷准低温储藏一年的标志性风味物质;反-2-己烯-醇、1-辛烯-3-醇和2-戊基呋喃等可以作为表征稻谷准低温储藏1.5年的标志性风味物质。
值得注意的是,图3b显示稻谷储存到12 M及以后时,位于粮堆表层的稻谷中的戊醛、壬醛、乙酸乙酯、乙酸丙酯、乙酸丁酯和异辛醇等醛、酯类VFCs含量明显高于中间冷心层位置贮藏的稻谷(红框),而反-2-己烯-醇、2-戊基呋喃、1-辛烯-3-醇、庚醇、1-丙醇、1-己醇、1-戊醇、异丁醇和2-庚酮等醇、酮类VFCs则在中间冷心层稻谷中含量更高(黄框)。酯类主要是通过有机酸和醇的酯化形成的,具有水果香气[24],醛类则通常由不饱和脂肪酸氧化产生,具有水果和植物香气以及较低的阈值,对稻米的风味有重要影响[25–27]。醇类主要是由脂肪酸的二级过氧化氢物分解产生,赋予了稻谷花香、草本以及甜味[26–28],如己醇和1-辛烯-3-醇,是大米中最丰富的挥发物之一,而酮类物质主要是脂质氧化产物[29]。绿框中的特征VFCs物质包括辛醛、反-2-辛烯醛、己醛、苯甲醛和庚醛等,则随稻谷贮藏时间延长逐渐增加,且两组样品基本无差异。中间冷心层和粮堆表层之间风味物质的差异可能是由于位置不同,粮堆的温度、接触的空气面积、水分含量不同等因素导致的。
不同样品VFCs间的相似度的分析结果见表1。不同取样组间检测得到的VFCs相似度基本都高于80%,于6 M时达到最高相似度93%。而同组取样稻谷不同贮藏时间之间的相似度明显较小,其中,取样自中间冷心层(A组)的稻谷随着储藏时间的延长,相似度逐渐下降,于第18 M时达到最低79%。说明储藏时间越久,样品组间相似度差距越大。这一变化规律在表层稻谷(B组)样品中更为明显,其储藏18 M的样品与初始样品相似度仅有68%,可以看出取样表层稻谷能够快速鉴别储藏导致的VFCs变化。
表 1 不同稻谷贮藏组间VFCs的相似度(%)Table 1. Similarity of VFCs between different paddy rice samples (%)Sample-ID A-0 B-0 A-6 B-6 A-12 B-12 A-18 B-18 A-0 100 85 88 92 83 80 79 79 B-0 85 100 88 87 81 70 70 68 A-6 88 88 100 93 89 79 81 78 B-6 92 87 93 100 88 82 81 79 A-12 83 81 89 88 100 82 83 81 B-12 80 70 79 82 82 100 85 93 A-18 79 70 81 81 93 85 100 89 B-18 79 68 78 79 81 93 89 100 进一步根据HS-GC-IMS光谱中各风味物质的漂移时间和保留指数对样品进行分析,结果如表2所示。可以看出,稻谷样品中共检测出46种稻谷特征性VFCs,包括丁内酯、壬醛、正辛醛、正辛醛、1-己醇、正己醛等及其二聚体(同种物质的单体和二聚体形态不同,CAS 号和化学式均相同)[30]。
表 2 稻谷样品中VFCs的GC-IMS基础定性结果Table 2. GC-IMS basic qualitative results of VFCs in paddy rice samples编号 化合物名称 CAS号 分子式 分子量 保留时间(s) 离子迁移时间(ms) 1 γ-丁内酯 C96480 C4H6O2 86.1 372.895 1.0803 2 γ-丁内酯二聚体 C96480 C4H6O2 86.1 372.287 1.2995 3 壬醛 C124196 C9H18O 142.2 729.386 1.4811 4 壬醛二聚体 C124196 C9H18O 142.2 729.386 1.944 5 正辛醛 C124130 C8H16O 128.2 517.035 1.4135 6 正辛醛二聚体 C124130 C8H16O 128.2 519.127 1.8257 7 正辛醛 C111717 C7H14O 114.2 355.348 1.3397 8 庚醛二聚体 C111717 C7H14O 114.2 357.165 1.6904 9 1-己醇 C111273 C6H14O 102.2 327.945 1.3257 10 1-己醇二聚体 C111273 C6H14O 102.2 327.945 1.6419 11 正己醛 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 249.306 1.255 12 正己醛二聚体 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 251.455 1.5624 13 乙酸丁酯 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 265.635 1.2351 14 乙酸丁酯二聚体 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 263.917 1.6188 15 1-戊醇 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 231.07 1.2533 16 1-戊醇二聚体 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 227.606 1.5087 17 反式-2-己烯-1-醇 C928950 C6H12O 100.2 301.054 1.1791 18 反式-2-己烯-1-醇二聚体 C928950 C6H12O 100.2 299.322 1.5137 19 乙酸丙酯 C109604 C5H10O2 102.1 193.653 1.1665 20 乙酸丙酯二聚体 C109604 C5H10O2 102.1 192.268 1.4785 21 乙醇 C64175 C2H6O 46.1 101.278 1.044 22 丙酮 C67641 C3H6O 58.1 110.585 1.1153 23 1-丁醇 C71363 C4H10O 74.1 166.057 1.1812 24 戊醛 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 183.555 1.183 25 戊醛二聚体 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 180.577 1.4212 26 苯甲醛 C100527 C7H6O 106.1 434.252 1.1495 27 反-2-辛烯醛 C2548870 C8H14O 126.2 637.194 1.3319 28 2-乙基己醇 C104767 C8H18O 130.2 581.417 1.4172 29 2-乙基己醇二聚体 C104767 C8H18O 130.2 579.552 1.7986 30 乙酸乙酯 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 145.794 1.0967 31 乙酸乙酯二聚体 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 143.463 1.3344 32 2-戊基呋喃 C3777693 C9H14O 138.2 492.617 1.2478 33 正庚醇 C5353533
4C7H16O 116.2 462.914 1.4009 34 1-辛烯-3-醇 C3391864 C8H16O 128.2 476.832 1.1543 35 异丁醇 C78831 C4H10O 74.1 150.266 1.1693 36 异丁醇二聚体 C78831 C4H10O 74.1 151.009 1.3619 37 甲乙酮 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 137.084 1.0581 38 甲乙酮二聚体 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 135.413 1.2435 39 1-丙醇 C71238 C3H8O 60.1 126.315 1.1089 40 1-丙醇二聚体 C71238 C3H8O 60.1 126.501 1.2539 41 2-己酮 C591786 C6H12O 100.2 241.518 1.1903 42 2-庚酮 C110430 C7H14O 114.2 344.392 1.2644 43 2-庚酮二聚体 C110430 C7H14O 114.2 343.893 1.6265 44 3-羟基-2-丁酮 C513860 C4H8O2 88.1 197.251 1.0582 45 2-甲基丁醇 C137326 C5H12O 88.1 206.782 1.2307 46 2-甲基丁醇二聚体 C137326 C5H12O 88.1 206.169 1.4755 2.3 PCA分析
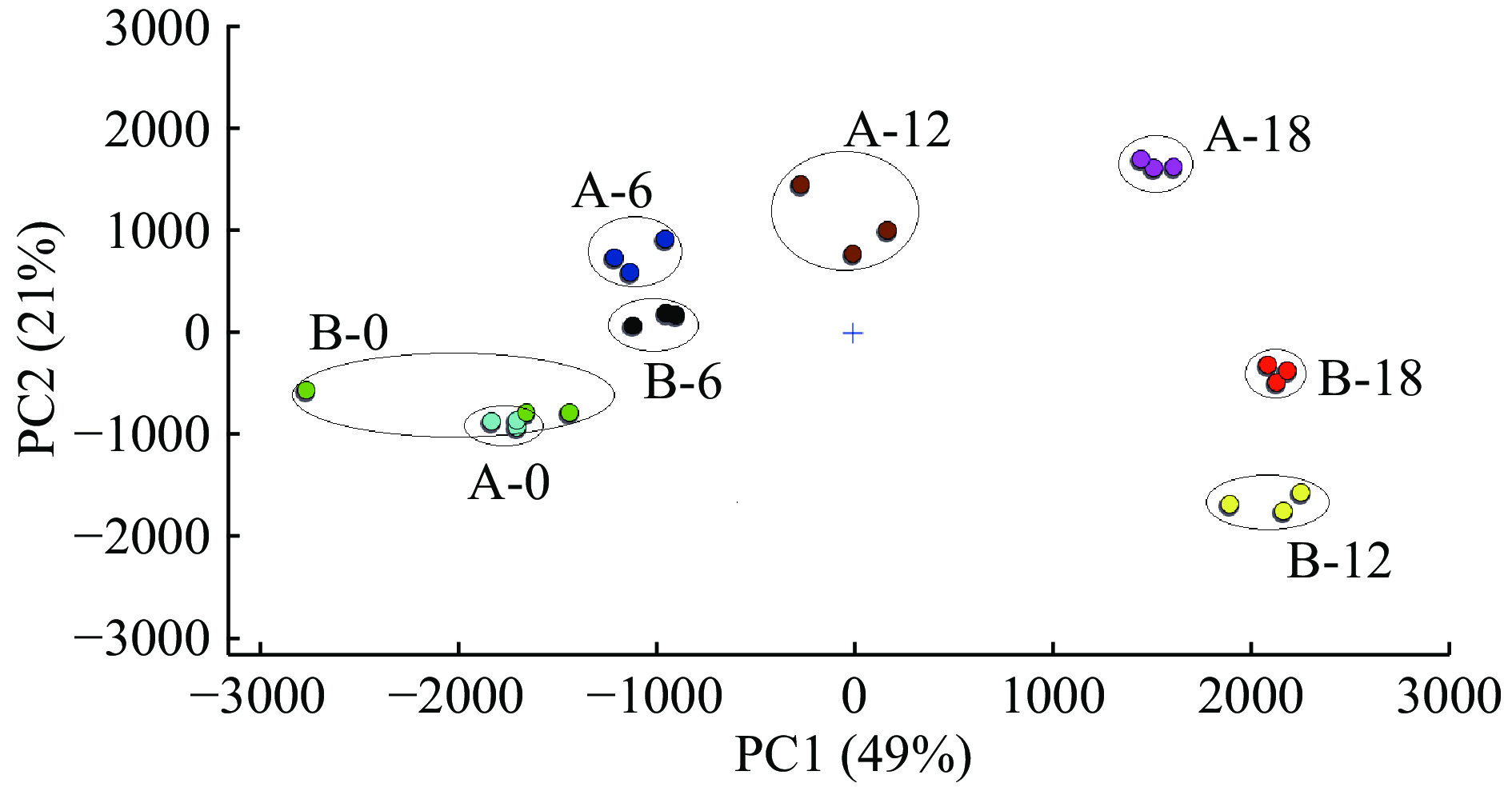
为了分辨出不同储藏期与稻谷所处位置对其中VFCs的影响,对样品VFCs的高维数组变量进行降维处理,根据贡献率的大小得到具有代表性的综合指标并进一步进行可视化动态主成分分析[31]。图4显示使用PCA的第一、二主成分因子占总主成分因子的70%,有较高累积贡献率,而稻谷储存到6 M时,取自中间冷心层和表层的稻谷风味仍保持相似,但12 M开始,二者的风味差异显著。
3. 结论
粮仓的储粮位置会通过环境温度、空气接触面等效应影响稻谷的风味特性,且这种影响与储藏时间相关。储存6 M时,中间冷心层和表层稻谷的VFCs相似,而到12 M时二者的风味差异最大。储存12~18 M,表层稻谷中戊醛、壬醛、乙酸乙酯、乙酸丙酯、乙酸丁酯和异辛醇等含量较高;而中间冷心层中反-2-己烯-醇、2-戊基呋喃、1-辛烯-3-醇、庚醇、1-丙醇、1-己醇、1-戊醇、异丁醇和2-庚酮等含量较高;辛醛、反-2-辛烯醛、己醛、苯甲醛和庚醛等在两组样品中均随储存时间延长而逐渐增加,但不同取样点间差异不显著。运用GC-IMS对其他带壳谷物风味变化的监测对设计品质无损监测设备有潜在指导意义,有待进一步探索。
-
表 1 不同稻谷贮藏组间VFCs的相似度(%)
Table 1 Similarity of VFCs between different paddy rice samples (%)
Sample-ID A-0 B-0 A-6 B-6 A-12 B-12 A-18 B-18 A-0 100 85 88 92 83 80 79 79 B-0 85 100 88 87 81 70 70 68 A-6 88 88 100 93 89 79 81 78 B-6 92 87 93 100 88 82 81 79 A-12 83 81 89 88 100 82 83 81 B-12 80 70 79 82 82 100 85 93 A-18 79 70 81 81 93 85 100 89 B-18 79 68 78 79 81 93 89 100 表 2 稻谷样品中VFCs的GC-IMS基础定性结果
Table 2 GC-IMS basic qualitative results of VFCs in paddy rice samples
编号 化合物名称 CAS号 分子式 分子量 保留时间(s) 离子迁移时间(ms) 1 γ-丁内酯 C96480 C4H6O2 86.1 372.895 1.0803 2 γ-丁内酯二聚体 C96480 C4H6O2 86.1 372.287 1.2995 3 壬醛 C124196 C9H18O 142.2 729.386 1.4811 4 壬醛二聚体 C124196 C9H18O 142.2 729.386 1.944 5 正辛醛 C124130 C8H16O 128.2 517.035 1.4135 6 正辛醛二聚体 C124130 C8H16O 128.2 519.127 1.8257 7 正辛醛 C111717 C7H14O 114.2 355.348 1.3397 8 庚醛二聚体 C111717 C7H14O 114.2 357.165 1.6904 9 1-己醇 C111273 C6H14O 102.2 327.945 1.3257 10 1-己醇二聚体 C111273 C6H14O 102.2 327.945 1.6419 11 正己醛 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 249.306 1.255 12 正己醛二聚体 C66251 C6H12O 100.2 251.455 1.5624 13 乙酸丁酯 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 265.635 1.2351 14 乙酸丁酯二聚体 C123864 C6H12O2 116.2 263.917 1.6188 15 1-戊醇 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 231.07 1.2533 16 1-戊醇二聚体 C71410 C5H12O 88.1 227.606 1.5087 17 反式-2-己烯-1-醇 C928950 C6H12O 100.2 301.054 1.1791 18 反式-2-己烯-1-醇二聚体 C928950 C6H12O 100.2 299.322 1.5137 19 乙酸丙酯 C109604 C5H10O2 102.1 193.653 1.1665 20 乙酸丙酯二聚体 C109604 C5H10O2 102.1 192.268 1.4785 21 乙醇 C64175 C2H6O 46.1 101.278 1.044 22 丙酮 C67641 C3H6O 58.1 110.585 1.1153 23 1-丁醇 C71363 C4H10O 74.1 166.057 1.1812 24 戊醛 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 183.555 1.183 25 戊醛二聚体 C110623 C5H10O 86.1 180.577 1.4212 26 苯甲醛 C100527 C7H6O 106.1 434.252 1.1495 27 反-2-辛烯醛 C2548870 C8H14O 126.2 637.194 1.3319 28 2-乙基己醇 C104767 C8H18O 130.2 581.417 1.4172 29 2-乙基己醇二聚体 C104767 C8H18O 130.2 579.552 1.7986 30 乙酸乙酯 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 145.794 1.0967 31 乙酸乙酯二聚体 C141786 C4H8O2 88.1 143.463 1.3344 32 2-戊基呋喃 C3777693 C9H14O 138.2 492.617 1.2478 33 正庚醇 C5353533
4C7H16O 116.2 462.914 1.4009 34 1-辛烯-3-醇 C3391864 C8H16O 128.2 476.832 1.1543 35 异丁醇 C78831 C4H10O 74.1 150.266 1.1693 36 异丁醇二聚体 C78831 C4H10O 74.1 151.009 1.3619 37 甲乙酮 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 137.084 1.0581 38 甲乙酮二聚体 C78933 C4H8O 72.1 135.413 1.2435 39 1-丙醇 C71238 C3H8O 60.1 126.315 1.1089 40 1-丙醇二聚体 C71238 C3H8O 60.1 126.501 1.2539 41 2-己酮 C591786 C6H12O 100.2 241.518 1.1903 42 2-庚酮 C110430 C7H14O 114.2 344.392 1.2644 43 2-庚酮二聚体 C110430 C7H14O 114.2 343.893 1.6265 44 3-羟基-2-丁酮 C513860 C4H8O2 88.1 197.251 1.0582 45 2-甲基丁醇 C137326 C5H12O 88.1 206.782 1.2307 46 2-甲基丁醇二聚体 C137326 C5H12O 88.1 206.169 1.4755 -
[1] 韩越, 胡月英. 低温储粮技术的研究现状与思考[J]. 粮油仓储科技通讯,2019,35(6):30−34. [HAN Y, HU Y Y. Research status and thinking of low-temperature grain storage technology[J]. Scientific and Technological Communication of Grain and Oil Storage,2019,35(6):30−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1943.2019.06.009 HAN Y, HU Y Y. Research status and thinking of low-temperature grain storage technology[J]. Scientific and Technological Communication of Grain and Oil Storage, 2019, 35(6): 30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1943.2019.06.009
[2] 冯儒. 空调准低温储粮技术在稻谷仓储中应用的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018 FENG R. Research on the application of air conditioning quasi low temperature grain storage technology in rice storage[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018.
[3] 王荣雪, 杨正源, 寇林, 等. 高大平房仓储存稻谷粮堆不同位置霉菌区系、脂肪酸值和水分差异性研究[J]. 粮食科技与经济,2018,43(6):91−93. [WANG R X, YANG Z Y, KOU L, et al. Study on the difference of mold flora, fatty acid value and water content in different positions of rice grain piles stored in large warehouse[J]. Food Science and Technology and Economy,2018,43(6):91−93. doi: 10.16465/j.gste.cn431252ts.20180623 WANG R X, YANG Z Y, KOU L, et al. Study on the difference of mold flora, fatty acid value and water content in different positions of rice grain piles stored in large warehouse [J]. Food Science and Technology and Economy, 2018, 43(6): 91-93. doi: 10.16465/j.gste.cn431252ts.20180623
[4] 方宝庆, 葛志文, 高瑀珑, 等. 不同储藏时间稻谷在粮仓不同位置的品质及霉菌差异分析[J]. 江苏农业科学,2018,46(10):195−199. [FANG B Q, GE Z W, GAO Y L, et al. Analysis on the quality and mold difference of rice stored at different positions in the granary at different times[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science,2018,46(10):195−199. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2018.10.050 FANG B Q, GE Z W, GAO Y L, et al. Analysis on the quality and mold difference of rice stored at different positions in the granary at different times[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2018, 46(10): 195-199. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2018.10.050
[5] 何珊. 气相-离子迁移谱在食品风味检测中的应用[J]. 农产品加工,2021(14):80−85,90. [HE S. Application of gas phase ion migration spectroscopy in food flavor detection[J]. Processing of Agricultural Products,2021(14):80−85,90. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2021.07.050 HE S. Application of gas phase ion migration spectroscopy in food flavor detection[J]. Processing of agricultural products, 2021(14): 80-85, 90. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2021.07.050
[6] 刘娟, 赵欢蕊, 付咪咪, 等. 基于气相色谱-离子迁移谱对百里香挥发性成分的分析[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(4):153−156,164. [LIU J, ZHAO H R, FU M M, et al. Analysis of volatile components of thyme based on gas chromatography ion transfer spectroscopy[J]. China Condiment,2021,46(4):153−156,164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.04.030 LIU J, ZHAO H R, FU M M, et al. Analysis of volatile components of thyme based on gas chromatography ion transfer spectroscopy[J]. China Condiment, 2021, 46(4): 153-156, 164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.04.030
[7] 钱鑫, 李占明, 宋嘉慧, 等. 气相色谱-离子迁移谱法检测农产食品中挥发性有机化合物的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(18):7184−7190. [QIAN X, LI Z M, SONG J H, et al. Research progress in detection of volatile organic compounds in agricultural food by gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2021,12(18):7184−7190. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.18.012 QIAN X, LI Z M, SONG J H, et al. Research progress in detection of volatile organic compounds in agricultural food by gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry [J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection, 2021, 12(18): 7184-7190. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.18.012
[8] 王熠瑶, 张烝彦, 孙俊, 等. 基于GC-IMS技术分析糙米储藏过程中风味物质变化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(6):250−255. [WANG Y Y, ZHANG Z Y, SUN J, et al. Analysis of changes in flavor substances of brown rice during storage based on GC-IMS technology[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2020,46(6):250−255. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022672 WANG Y Y, ZHANG Z Y, SUN J, et al. Analysis of changes in flavor substances of brown rice during storage based on GC-IMS technology[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2020, 46(6): 250-255. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022672
[9] 刘强, 倪小颖, 丁海臻, 等. 基于气相离子迁移谱技术的稻谷中玉米象快速定量检测分析[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(6):162−169. [LIU Q, NI X Y, DING H Z, et al. Rapid quantitative detection and analysis of corn weevil in rice based on gas phase ion mobility spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2022,37(6):162−169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.06.024 LIU Q, NI X Y, DING H Z, et al. Rapid quantitative detection and analysis of corn weevil in rice based on gas phase ion mobility spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2022, 37(6): 162-169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.06.024
[10] ZHAO Q Y, XUE Y, SHEN Y. Changes in the major aroma-active compounds and taste components of Jasmine rice during storage[J]. Food Research International,2020,133(7):109160.
[11] 郭啸天. 充氮气调与低温冷藏对粳稻谷稳定性的影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京财经大学, 2021 GUO X T. Study on the influence of nitrogen filled regulation and low-temperature refrigeration on the stability of japonica rice[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, 2021.
[12] 闵炎芳, 张坚, 张学良, 等. 浙北地区籼稻准低温储藏应用工艺研究[J]. 粮食储藏,2019,48(4):7−13. [MIN Y F, ZHANG J, ZHANG X L, et al. Study on application technology of quasi low temperature storage of indica rice in northern Zhejiang[J]. Grain Storage,2019,48(4):7−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6958.2019.04.003 MIN Y F, ZHANG J, ZHANG X L, et al. Study on application technology of quasi low temperature storage of indica rice in northern Zhejiang[J]. Grain Storage, 2019, 48(4): 7-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6958.2019.04.003
[13] 金文刚, 刘俊霞, 赵萍, 等. 基于顶空气相色谱-离子迁移谱分析洋县不同色泽糙米蒸煮后挥发性风味物质差异[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(18):258−264. [JIN W G, LIU J X, ZHAO P, et al. Based on headspace gas chromatography ion transfer spectroscopy, the difference of volatile flavor substances in different color brown rice of Yangxian County after cooking was analyzed[J]. Food Science,2022,43(18):258−264. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210927-324 JIN W G, LIU J X, ZHAO P, et al. Based on headspace gas chromatography ion transfer spectroscopy, the difference of volatile flavor substances in different color brown rice of Yangxian County after cooking was analyzed[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(18): 258-264. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210927-324
[14] GERHARDT N, BIRKENMEIER M, SANDERS D, et al. Resolution-optimized headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS) for non-targeted olive oil profiling[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2017,409(16):3933−3942. doi: 10.1007/s00216-017-0338-2
[15] HAO L, ZHONG X M, WEN C K, et al. A novel colorimetric sensor array based on boron-dipyrromethene dyes for monitoring the storage time of rice[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,268:300−306. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.097
[16] 丁超, 常乐, 郭啸天, 等. 基于GC-IMS对充氮贮藏粳稻风味特性影响研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2023,38(1):123−131. [DING C, CHANG L, GUO X T, et al. Study on the influence of GC-IMS on flavor characteristics of japonica rice stored with nitrogen[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2023,38(1):123−131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2023.01.017 DING C, CHANG L, GUO X T, et al. Study on the influence of GC-IMS on flavor characteristics of japonica rice stored with nitrogen[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2023, 38(1): 123-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2023.01.017
[17] 周显青, 祝方清, 张玉荣, 等. 不同储藏年限稻谷的储藏特性、生理生化指标及其糊化特性分析[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(12):108−114, 124. [ZHOU X Q, ZHU F Q, ZHANG Y R, et al. Analysis on storage characteristics, physiological and biochemical indexes and pasting characteristics of rice with different storage years[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2020,35(12):108−114, 124. ZHOU X Q, ZHU F Q, ZHANG Y R, et al. Analysis on storage characteristics, physiological and biochemical indexes and pasting characteristics of rice with different storage years[J] Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2020, 35(12): 108-114, 124.
[18] WANG Y R, HA J H. Determination of hexanal in rice using an automated dynamic headspace sampler coupled to a gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer[J]. Journal of Chromatographic Science,2013,51(5):446−452. doi: 10.1093/chromsci/bms161
[19] LIU K, LI Y, CHEN F, et al. Lipid oxidation of brown rice stored at different temperatures[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2017,52(1):188−195.
[20] HU X Q, LU L, GUO Z L, et al. Volatile compounds, affecting factors and evaluation methods for rice aroma: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,97:136−146.
[21] YAN W, LIU Q, WANG Y, et al. Inhibition of lipid and aroma deterioration in rice bran by infrared heating[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology: An International Journal,2020,13(10):1677−1687. doi: 10.1007/s11947-020-02503-z
[22] 王逸欢. 陈粳米饭异味成因剖析及饭煲调控式浸泡处理改良作用[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021 WANG Y H. Analysis on the cause of the peculiar smell of aged japonica rice and the improvement effect of the controlled soaking treatment of rice cooker[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[23] 康文翠, 林颢, 满忠秀. 基于GC-MS与多变量分析方法的不同储藏期大米挥发特征气味的分析[J]. 中国粮油学报,2018,33(5):94−101. [KANG W C, LIN H, MAN Z X. Analysis of volatile characteristic odor of rice in different storage periods based on GC-MS and multivariable analysis method[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2018,33(5):94−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2018.05.016 KANG W C, LIN H, MAN Z X. Analysis of volatile characteristic odor of rice in different storage periods based on GC-MS and multivariable analysis method[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2018, 33(5): 94-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2018.05.016
[24] LIU H H, CHIEN J T, KUO M I. Ultra high pressure homogenized soy flour for tofu making[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2013,32(2):278−285. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.01.005
[25] 贾梦, 刘金光, 康学栋, 等. 海南特色米中营养成分及挥发性风味物质的分布特征[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(7):31−38. [JIA M, LIU J G, KANG X D, et al. Distribution characteristics of nutrients and volatile flavor substances in Hainan characteristic rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2022,37(7):31−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.07.006 JIA M, LIU J G, KANG X D, et al. Distribution characteristics of nutrients and volatile flavor substances in Hainan characteristic rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2022, 37(7): 31-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.07.006
[26] 谷航, 陈通, 陈明杰, 等. 气相-离子迁移谱联用技术评定大米霉变程度的应用研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2019,34(9):118−124. [GU H, CHEN T, CHEN M J, et al. Study on the application of gas phase ion mobility spectrometry to evaluate the degree of rice mildew[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2019,34(9):118−124. GU H, CHEN T, CHEN M J, et al. Study on the application of gas phase ion mobility spectrometry to evaluate the degree of rice mildew[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2019, 34(9): 118-124.
[27] 龚霄, 陈廷慧, 胡小军, 等. 基于GC-IMS技术的百香果果啤风味分析[J]. 食品与机械,2022,38(11):46−52,75. [GONG X, CHEN Y H, HU X J, et al. Flavor analysis of passion fruit beer based on GC-IMS technology[J]. Food and Machinery,2022,38(11):46−52,75. doi: 10.13652/j.spjx.1003.5788.2022.80465 GONG X, CHEN Y H, HU X J, et al. Flavor analysis of passion fruit beer based on GC-IMS technology[J]. Food and Machinery, 2022, 38(11): 46-52, 75. doi: 10.13652/j.spjx.1003.5788.2022.80465
[28] 陈翠莹, 昝学梅, 杨柳, 等. 基于GC-IMS分析不同加工方式对糙米挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(12):1−12. [CHEN C Y, ZAN X M, YANG L, et al. The effect of different processing methods on volatile flavor compounds of brown rice was analyzed based on GC-IMS[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2022,37(12):1−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.12.002 CHEN C Y, ZAN X M, YANG L, et al. The effect of different processing methods on volatile flavor compounds of brown rice was analyzed based on GC-IMS[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils, 2022, 37(12): 1-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.12.002
[29] 王子妍, 窦博鑫, 贾健辉, 等. GC-IMS结合PCA分析不同焙炒程度留胚米挥发性化合物指纹差异[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(8):212−218. [WANG Z Y, DOU B X, JIA J H, et al. The fingerprint difference of volatile compounds in different degrees of roasting of embryo rice was analyzed by GC-IMS and PCA[J]. Food Science,2023,44(8):212−218. WANG Z Y, DOU B X, JIA J H, et al. The fingerprint difference of volatile compounds in different degrees of roasting of embryo rice was analyzed by GC-IMS and PCA[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(8): 212-218
[30] XIA Q, MEI J, YU W, et al. High hydrostatic pressure treatments enhance volatile components of pre-germinated brown rice revealed by aromatic fingerprinting based on HS-SPME/GC–MS and chemometric methods[J]. Food Research International,2017,91:103−114. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.12.001
[31] LOPEZ-FERIA S, CARDENAS S, VALCARCEL M. Simplifying chromatographic analysis of the volatile fraction of foods[J]. Trac-Trends in Analytical Chemistry,2008,27(9):794−803. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2008.07.006
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 张新圻,朱顺华,钟秀来,罗庆,熊爱生,谭国飞. 不同水芹种质资源的形态、花青素含量及相关基因表达量分析. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(02): 105-113 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张博,王雨婷,刘洁,李加会,吴鸿飞. 经典药对“瓜蒌-薤白”治疗痰瘀互结心血管疾病的血清代谢组学研究. 中国中药杂志. 2024(01): 232-242 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 罗庆,张新圻,李梦瑶,朱顺华,熊爱生,谭国飞. 药食同源植物水芹的研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报. 2024(08): 1221-1233 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 邢啸林,陈丹,况勇,徐文娟,黄然,甘德芳. 水芹SSR分子标记开发与遗传多样性分析. 江苏农业学报. 2024(07): 1285-1296 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李冬霞,张凡,王洧,南建. 水芹贮藏保鲜和开发利用研究进展. 农产品加工. 2023(02): 66-69+72 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 朱顺华,罗庆,李梦瑶,孟平红,钟秀来,王堃,陈志峰,谭国飞,熊爱生. 水芹雄性不育材料的鉴定及营养品质分析. 植物科学学报. 2023(03): 343-348 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 倪子怡,许海,詹旭,朱广伟,程新良,胡亮,王裕成,郑文婷. 刈割对千岛湖生态浮床植物生长与氮素净化效率的影响. 环境工程学报. 2023(08): 2494-2504 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘杰,刘吉祥,常雅军,陈婷,刘晓静,孙林鹤,姚东瑞. LC-SIM-Orbitraq测定无土栽培水芹不同器官中有机酸含量. 中国瓜菜. 2023(09): 80-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 王丹,万娜,黄金妮,陈敏妮,杨兹伟,汤祝华. 多壁碳纳米管净化-色谱质谱技术测定水芹中多农药残留. 食品科技. 2023(09): 276-284 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 刘吉祥,杜凤凤,孙林鹤,王巍,赵慧君,姚东瑞,常雅军. 无土栽培水芹不同器官的氨基酸特征及其资源化利用潜力分析. 中国蔬菜. 2022(07): 34-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 季青霞,陈伟,毕艳红,赵祥杰,白青云,王朝宇. 超声波辅助提取水芹中黄酮类化合物的工艺研究. 包装与食品机械. 2022(06): 25-30+38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



