Immunomodulatory Effect of Polysaccharide Extracted from Sanghuangporus baumi Mycelia in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages
-
摘要: 鲍姆纤孔菌(Sanghuangporus baumi)是一种药用真菌,具有很高的活性,本文研究在脂多糖(LPS)诱导下鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖对巨噬细胞RAW264.7的免疫调节作用。以鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖(SJ)为研究对象,利用脂多糖(LPS)诱导的巨噬细胞RAW264.7建立炎症模型,实验分为空白对照组,LPS模型组,SJ处理组(SJ+LPS),采用Cell Counting Kit-8(CCK8)法检测SJ对巨噬细胞RAW264.7的增殖作用;利用酶联免疫(ELISA)法测定SJ对巨噬细胞RAW264.7一氧化氮(NO)、白介素-6(IL-6)、白介素-1β(IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)细胞因子分泌量的影响。此外,采用免疫印迹(Western-Blot)技术,研究SJ对RAW 264.7细胞生成IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β和iNOS蛋白能力的影响。结果表明,不同浓度的SJ处理后巨噬细胞的活力与对照组相比分别增加了20.5%~50%;ELISA法结果表明:200 μg/mL组的SJ极显著(P<0.001)抑制在炎症模型下巨噬细胞RAW264.7产NO的能力,比LPS模型组巨噬细胞NO、TNF-α、IL-6和IL-β分泌量分别降低了21.62%、29.99%、35.5%和50.03%。SJ呈剂量依赖的方式极显著(P<0.001)抑制由LPS诱导的促炎介质IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β和iNOS表达,可减轻LPS引发的炎症反应,且与ELISA法检测到的细胞因子的分泌量变化结果相一致。综上,鲍姆纤孔菌多糖具有良好的免疫调节活性。Abstract: Sanghuangporus baumi is a kind of medicinal fungus with high activity. The aim of the present study was to investigate the immunoregulatory effects of Sanghuangporus baumi mycelia polysaccharides (SJ) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW264.7 cells. In this study, Sanghuangporus baumi mycelia polysaccharides (SJ) were taken as the study subjects, and LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages were used as the cell model. The experiment was divided into three groups: Control group, LPS (model) and LPS+SJ groups. A CCK-8 kit was used to detect the viability of RAW264.7 cells. The effects of SJ on nitric oxide, and cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) production in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages were measured by enzyme-linked immunoassay assay (ELISA). Furthermore, the effects of SJ on the protein levels of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) were investigated by Western-Blot analysis. The results indicated that SJ increased 20.5%~50% cell viability at different concentrations compared to the control group. SJ at 200 μg/mL potently inhibited the release of nitric oxide and cytokine production in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 (P<0.001), and compared with the LPS group, the secretion of NO, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β decreased by 21.62%, 29.99%, 35.5% and 50.03%, respectively. Moreover, SJ also reduced LPS-induced protein expression levels of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β and iNOS in a dose-dependent fashion (P<0.001), and alleviated the inflammatory damage induced by LPS. And it was consistent with the change of cytokine secretion detected by ELISA method. The results of the present study suggest that Sanghuangporus baumi mycelia polysaccharides (SJ) have good immunomodulatory.
-
Keywords:
- Sanghuangporus baumi /
- lipopolysaccharide /
- macrophages /
- cytokines
-
长期的炎症被认为与癌症、关节炎和神经退行性变等各种疾病的进展有关。尽管在疾病发生的过程中可以暂时通过药物来解决,但是由炎症引起的感染、以及抗炎类药物引起的并发症仍是引起死亡的主要因素之一[1]。所以,开发应用能够抑制炎症过度的天然、无毒副作用的替代药物以及能够增强宿主防御反应的免疫调节剂是非常迫切的。
桑黄是一种珍贵的功能性真菌,数百年来在包括中国、韩国和日本在内的几个东亚国家被广泛用作食物来源。具有抗肿瘤[2]、抗氧化[3]、降糖[4]、抗氧化[5]等多种生物活性。鲍姆纤孔菌(Sanghuangporus baumi)是桑黄的一个品种,一种著名真菌,幼时表面为褐色绒毛,老后细龟裂而变粗糙[6],其水提取物不仅具有增强小鼠免疫力的免疫调节活性[7],还可以缓解溃疡性结肠炎[8]以及通过分泌细胞因子来参与巨噬细胞的反应[9]。另一方面,鲍姆纤孔菌的子实体稀有,培养难度大,不可能获得大量的提取物。目前,越来越多的人开始对食药用菌进行液体发酵培养。菌丝深层培养具有快速、经济、易控制、无重金属污染、易于从菌丝体中提取生物活性物质等优点[10]。在过去的二十年中,从天然产物中获得的多糖由于其有前景的有益健康活性而引起了研究的极大关注。
近期,从桑黄属子实体、菌丝体和发酵液中提取和纯化的多糖被认为是负责各种健康促进作用的主要生物活性成分,包括免疫调节、抗肿瘤、抗炎、保肝、降血糖、降血脂、抗氧化和其他生物活性[11]。研究发现,从Phellinus linteus和Phellinus ignarius纯化的(1→3,6)-β-D-多糖可以显著降低TNF-α的生成,刺激高IL-10反应,并抑制RAW264.7细胞中IL-6的转录,表明其具有免疫抑制活性[12]。连续13 d口服500 mg/kg Phellinus linteus多糖能够显著改善了小鼠的健康状况,减轻了病理变化,下调了IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α和iNOS mRNA和蛋白质水平,并降低了DSS诱导的小鼠结肠组织中的MPO活性、MDA和NO水平[13]。最新研究表明,一种来自Phellinus baumii的杂多糖,命名为SHPS-1,能够抑制LPS诱导的RAW264.7巨噬细胞中的STAT-1通路和DSS诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎,具有较强的抗炎活性[14]。对于鲍姆纤孔菌多糖的研究大都集中在子实体多糖,对于菌丝多糖的药理和构效研究比较少。在前期研究工作中,实验室提取了菌丝化合物,发现其具有免疫调节作用[15]。在此基础上,本实验研究了鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖(SJ)对脂多糖诱导下的RAW264.7巨噬细胞的潜在免疫调节活性。利用脂多糖(LPS)诱导的巨噬细胞RAW264.7建立炎症模型,研究了不同浓度SJ对脂多糖诱导下RAW264.7细胞生成IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β和iNOS的影响。以此了解鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖(SJ)的抗炎活性,也为进一步临床应用免疫佐剂和免疫增强剂提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鲍姆纤孔菌 辽宁省农业科学院食用菌研究所;RAW264.7巨噬细胞 吉林农业大学食药用菌教育部工程研究中心;DMEM高糖培养基(pH7.2~7.4)、PBS磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.2~7.4)、胎牛血清 美国Gibco公司;脂多糖(LPS) 美国Sigma公司;Cell Counting Kit-8 CCK8 美国MP Biomedicals生物医药公司;BCA蛋白定量试剂盒 美国Thermo科技公司;一氧化氮检测试剂盒、细胞因子ELISA试剂盒 江苏酶联实业有限公司;RIPA组织细胞快速裂解液、Tris-HCl电泳缓冲液、SDS、过硫酸铵、TEMED、蛋白上样缓冲液、脱脂奶粉、PBS磷酸盐缓冲液、Tween-20 北京索莱宝生物有限公司;蛋白预染Marker Fermentas酶制剂公司;NC膜﹑发光液(ECL) 美国Millipore公司;抗体IL-6、TNF-α、iNOS、IL-1β、β-actin 英国Abcam抗体试剂公司;羊抗兔HRP标记二抗 上海碧云天生物科技有限公司;其他所有化学品和溶剂均为分析纯 国药化学试剂有限公司。
VS-1300U超净工作台 苏州智净净化设备有限公司;Cytoperm2型二氧化碳培养箱 美国Thermo公司;HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 常州市江南实验仪器厂;J6-M1低速离心机 美国BECMAN公司;1680多功能酶标仪 美国Biotek公司;BX51T-PHD-J11显微镜 日本奥林巴斯公司;XW-80A微型旋涡混合仪 上海沪西分析仪器厂;Mini Protean 3 Cell电泳仪 BIO-RAD 公司;TE77XP电转仪 美国HOEFER公司;Tanon-5200成像系统 上海Tanon科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验分组
将RAW264.7细胞复苏后,混悬于含10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基中,37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养,2~3 d换液和传代1次。
取处于对数生长期的RAW264.7细胞(1×106 cells/mL)移于6孔板,37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养24 h。细胞分为空白对照组(Control)、模型组(LPS)、SJ 25、50、100和200 μg/mL组,各组设3个复孔。除空白对照组外,其余组加入0.1 μg/mL LPS,空白对照组添加含有0.1% DMSO的完全培养基,以上不同的组与巨噬细胞RAW264.7在37 ℃培养24 h。吸取各组上清液,3000 r/min离心10 min,−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ对巨噬细胞细胞活力的影响
CCK8法检测[16]SJ对RAW264.7细胞存活率的影响。取生长状态良好、密度达到80%~90%的RAW264.7细胞,密度为1×106 cells/mL接种于96孔板中,37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养24 h。实验分为空白对照组(Control)和不同鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ浓度组(25、50、100、200 μg/mL),每组平行6孔。菌丝多糖SJ用0.22 μm滤膜过滤。对照组换含10%胎牛血清DMEM培养基,SJ组分别加入不同浓度的菌丝多糖,放入37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中继续培养24 h。然后避光加入细胞培养液体积1/10的CCK-8于各孔中,继续培养2 h。用酶标仪于450 nm处测定其吸光度。
细胞存活率(%)=(OD实验组/OD对照组)×100 1.2.3 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ对巨噬细胞上清液中NO的生成量的影响
按照1.2.1实验分组进行实验,收集细胞培养上清液,按照酶联免疫吸附分析(ELISA)试剂盒测定NO水平。
1.2.4 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ对巨噬细胞中TNF-α、IL-6和IL-β分泌量的影响
RAW264.7细胞(5×105 cells/mL)接种于96孔板中培养至对数期,按照实验分组处理:空白对照组加入200 μL的完全培养液,LPS模型组加入培养液和脂多糖LPS(0.2 μg/mL)各100 μL,SJ处理组分别加入培养液和浓度为25、50、100、200 μg/mL的提取物溶液各100 μL,每组设3个重复。不同实验分组与巨噬细胞处理24 h后,4 ℃,3000 r/min离心10 min,收集上清液,−20 ℃保存。按照ELISA试剂盒说明书步骤,检测细胞因子TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β。
1.2.5 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ对巨噬细胞iNOS、IL-6、IL-β和TNF-α蛋白表达的影响
按照“1.2.1”实验分组,每组处理均和巨噬细胞RAW246.7共培养24 h,然后收集各组细胞进行裂解,裂解后的样品4 ℃, 12000 r/min离心15 min,取上清,进行蛋白质定量后,每孔上样量为15 μg蛋白,加入适量上样缓冲液,沸水浴10 min后离心取上清上样。将配制好的PAGE胶放入电泳槽中,加入适量电泳缓冲液进行电泳,当染料到达胶底部时切断电源,停止电泳,进行下一步转膜。分离后转移到PVDF膜上。5%脱脂奶粉室温封闭1 h,根据说明书稀释抗体,抗体iNOS、IL-6、TNF-α、IL-β和β-actin分别加入封闭液中稀释到所需浓度,和膜室温孵育2 h或4 ℃孵育过夜。与HRP标记的相应二抗37 ℃孵育1 h,ECL避光显色5 min。将其放入成像系统中进行扫描,以β-actin作为内参。
1.3 数据处理
本研究获得的所有数据均经统计学处理,数据结果以平均值±标准差表示。比较ANOVA单因素方差分析,统计软件采用SPSS16.0 for Windows,P<0.05,数据结果有统计学意义,采用GraphPad Prism 9软件绘图。
2. 结果与分析
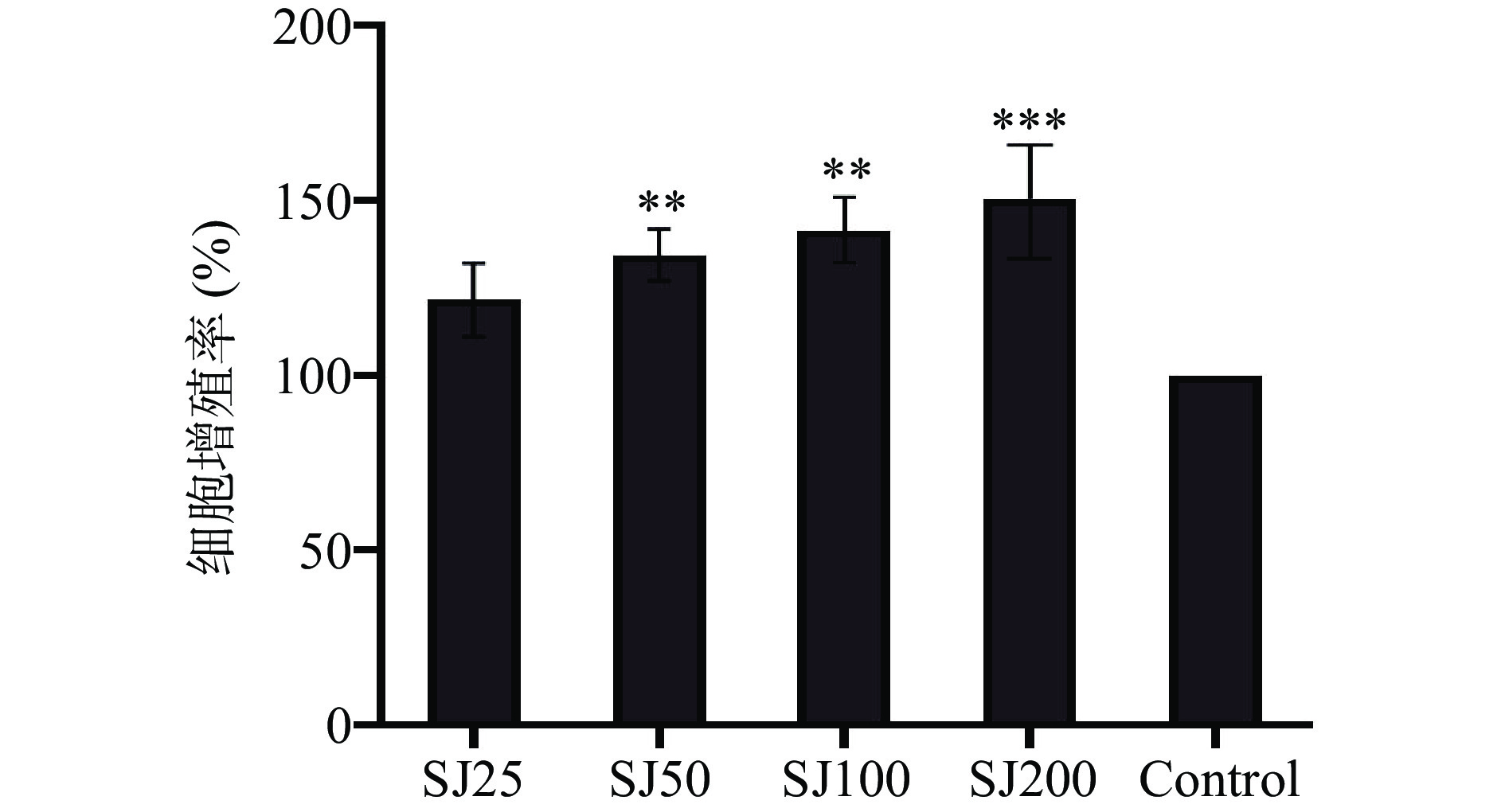
2.1 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ对巨噬细胞RAW264.7细胞活力的影响
不同处理按照1.2.1分组作用于RAW264.7细胞24 h后,用CCK-8比色法检测细胞增殖活力。如图1所示,当SJ作用到巨噬细胞后,可以增加细胞的数量,且呈浓度依赖性上升。不同浓度的SJ对巨噬细胞的活力与对照组相比分别增加了20.5%~50.0%。结果表明,SJ可以增加巨噬细胞RAW264.7细胞活力。
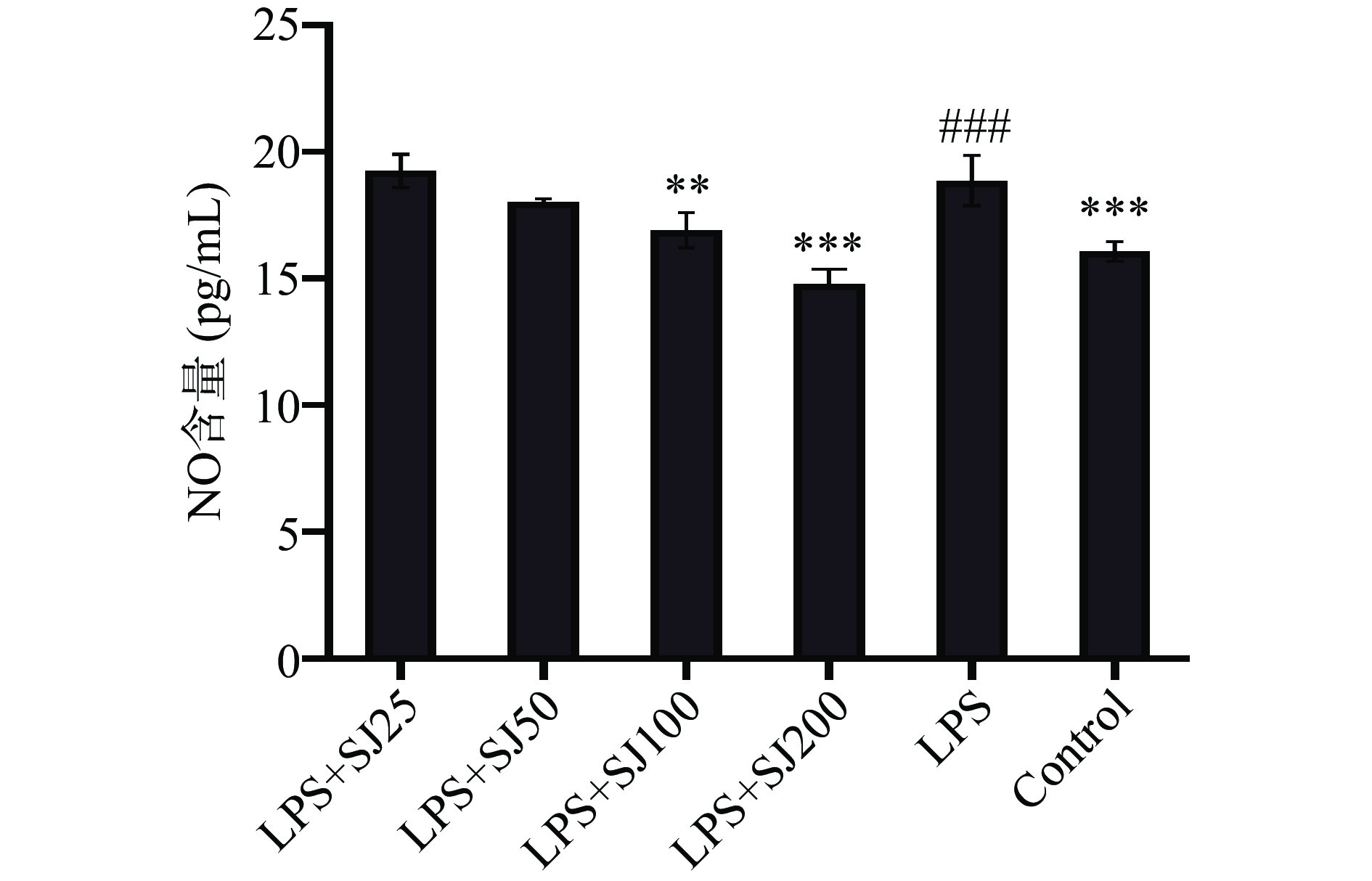
2.2 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ对LPS诱导下RAW264.7细胞释放NO的影响
图2显示,LPS组可以增加NO的释放,与单一LPS组相比,SJ(25、50、100和200 μg/mL)组NO分泌量显著减少(P<0.01)。同时,200 μg/mL组的SJ极显著( P<0.001)抑制在炎症模型下巨噬细胞RAW264.7产NO的能力,比单一LPS组巨噬细胞NO分泌量降低了21.62%。
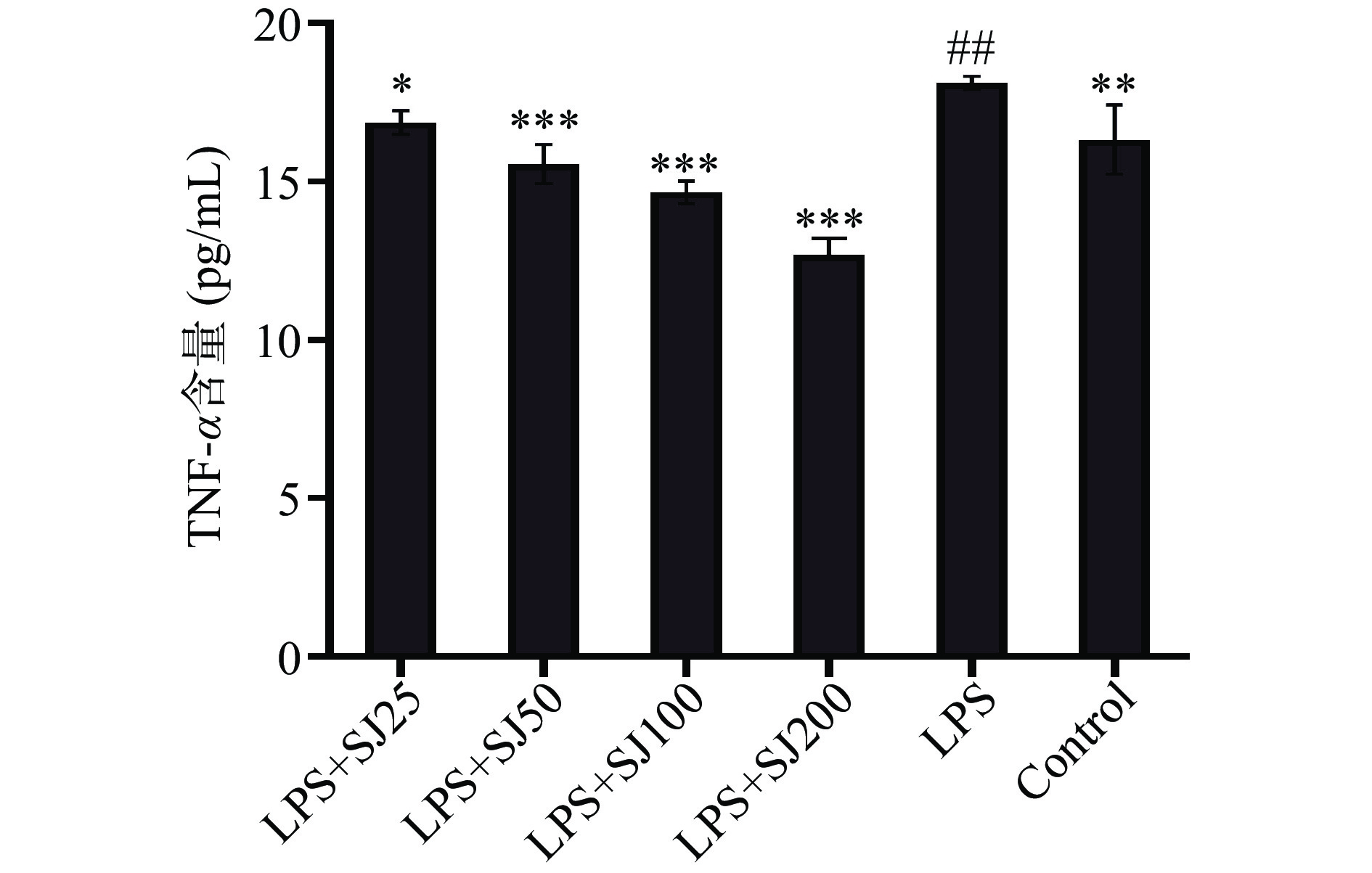
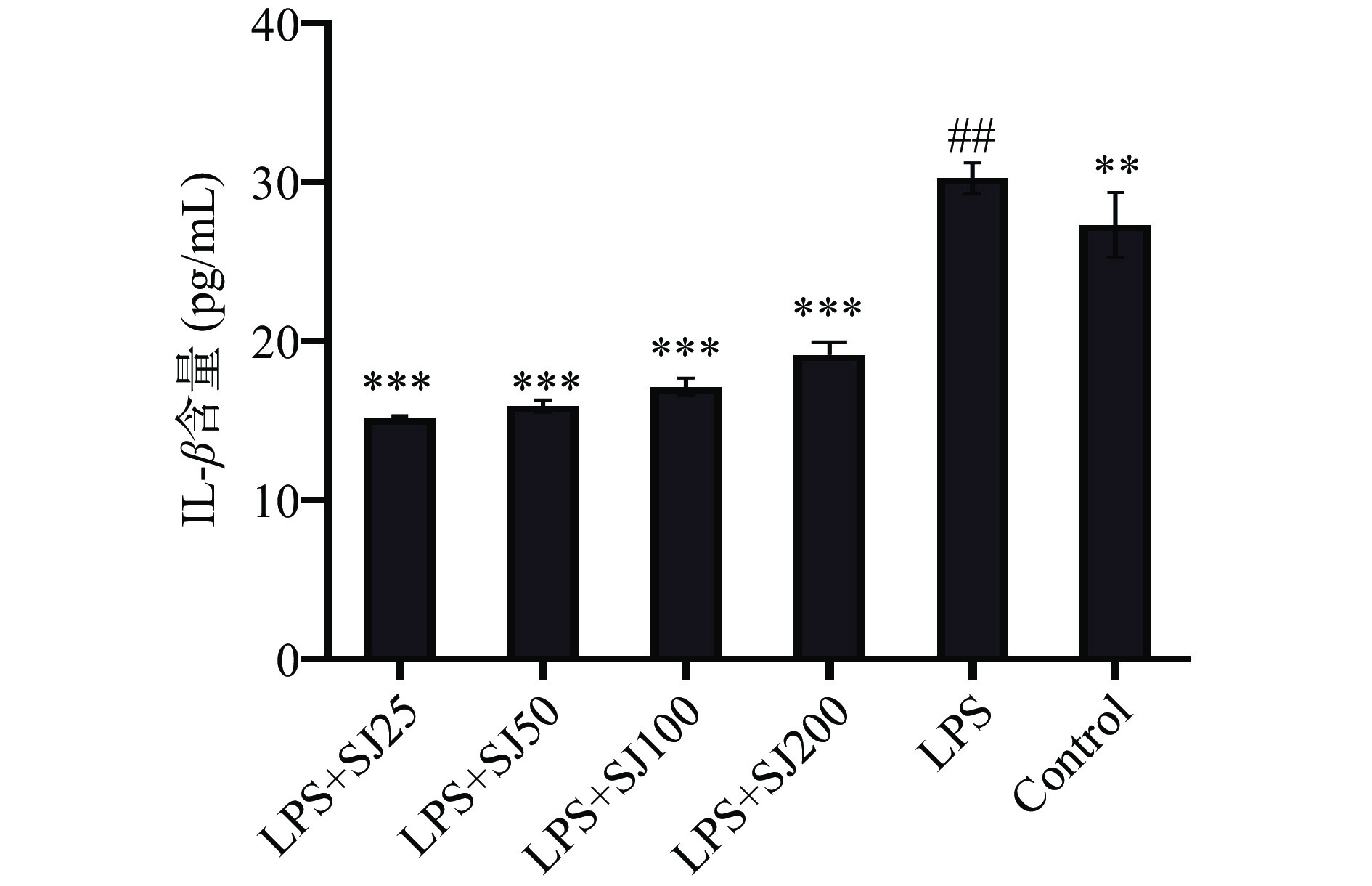
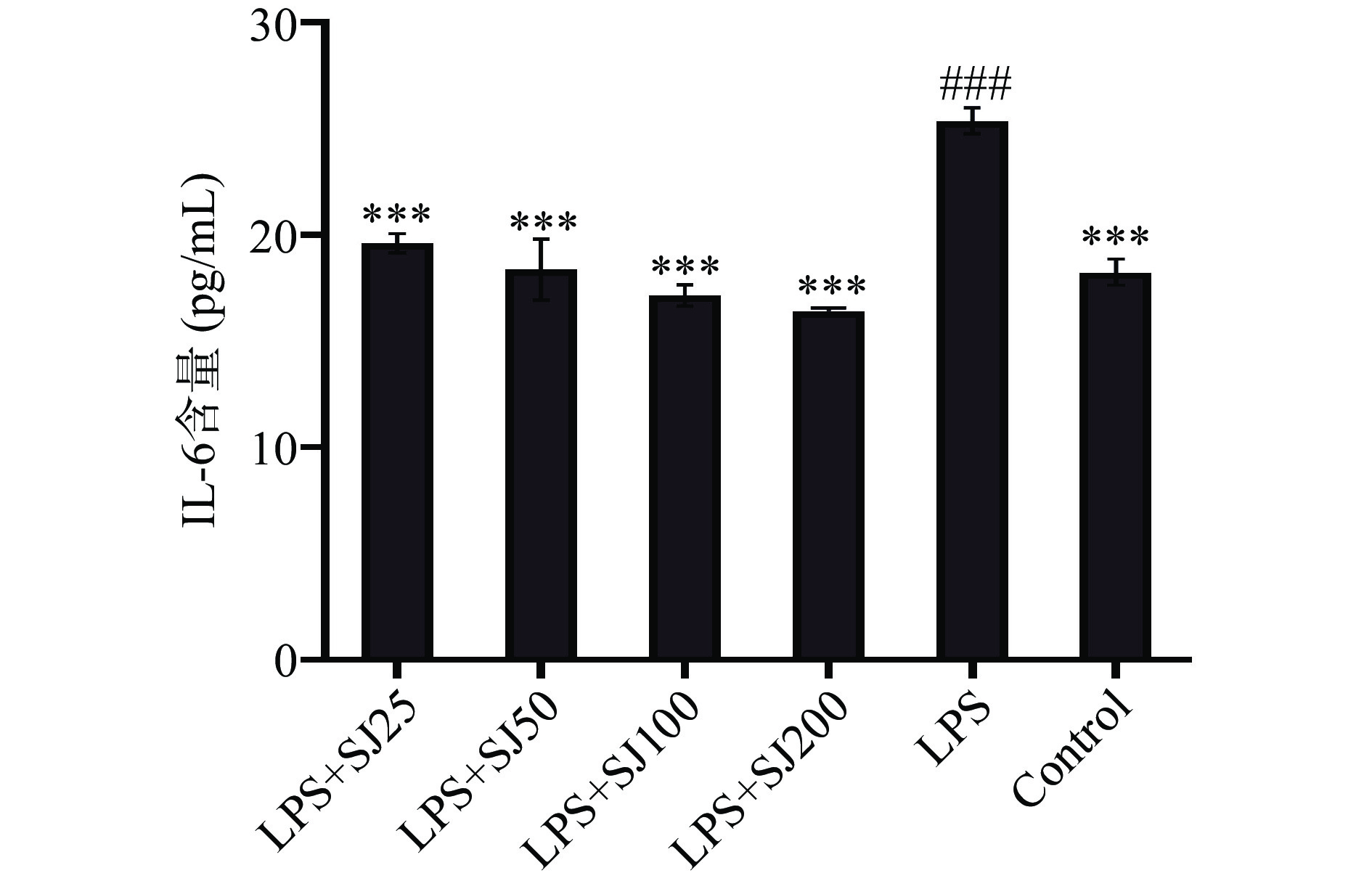
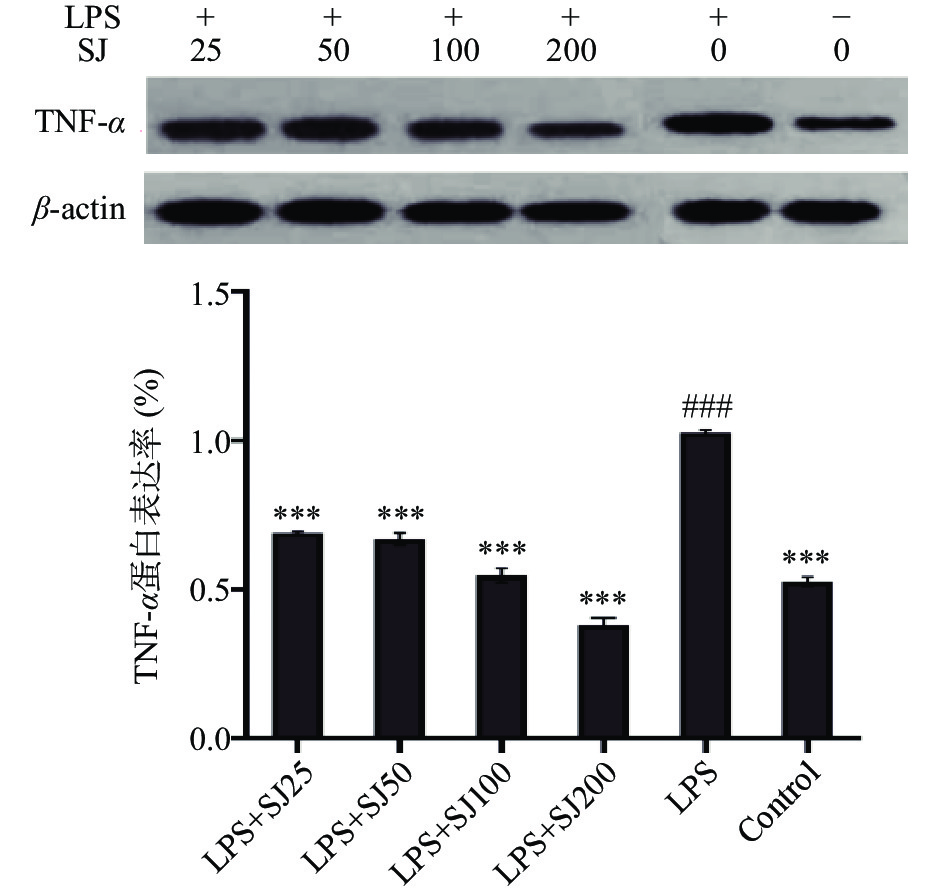
2.3 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖SJ对LPS诱导下RAW264.7细胞分泌TNF-α、IL-6和IL-β的影响
如图3~图5所示,与Control相比,LPS组中的TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β水平显著增加(P<0.01,P<0.001,P<0.01)。与LPS模型组相比,添加SJ各组均能够降低TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6的含量(P<0.05,P<0.001,P<0.001)。与LPS模型组相比,质量浓度为200 μg/mL的SJ处理组比LPS组巨噬细胞TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β分泌量降低了29.99%(P<0.001)、35.5%(P<0.001)、50.03%(P<0.001)。这表明鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖能够减少LPS诱导下巨噬细胞产炎症因子的能力。
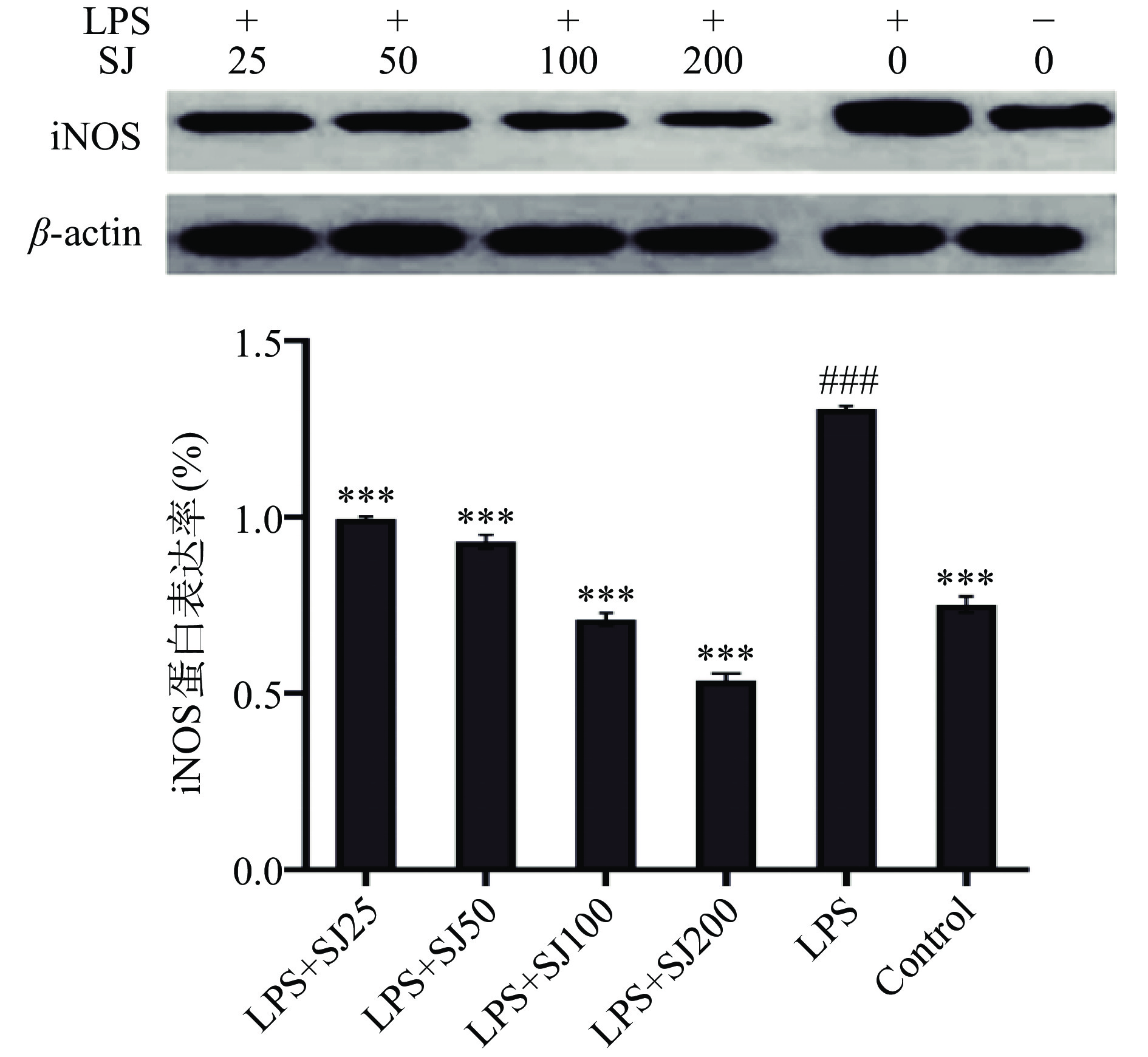
2.4 SJ对LPS诱导的RAW246.7巨噬细胞iNOS蛋白表达水平的影响
如图6所示,以不同处理组与内参蛋白量的比值作为相对表达率,与空白对照组比较,LPS组iNOS蛋白相对表达水平极显著升高(P<0.001),这表明在受到LPS诱导后巨噬细胞中iNOS表达量会上升,而加入SJ后,与LPS组比较,SJ处理组中所有组别iNOS中蛋白表达水平极显著降低(P<0.001),且具有一定的剂量效应关系。
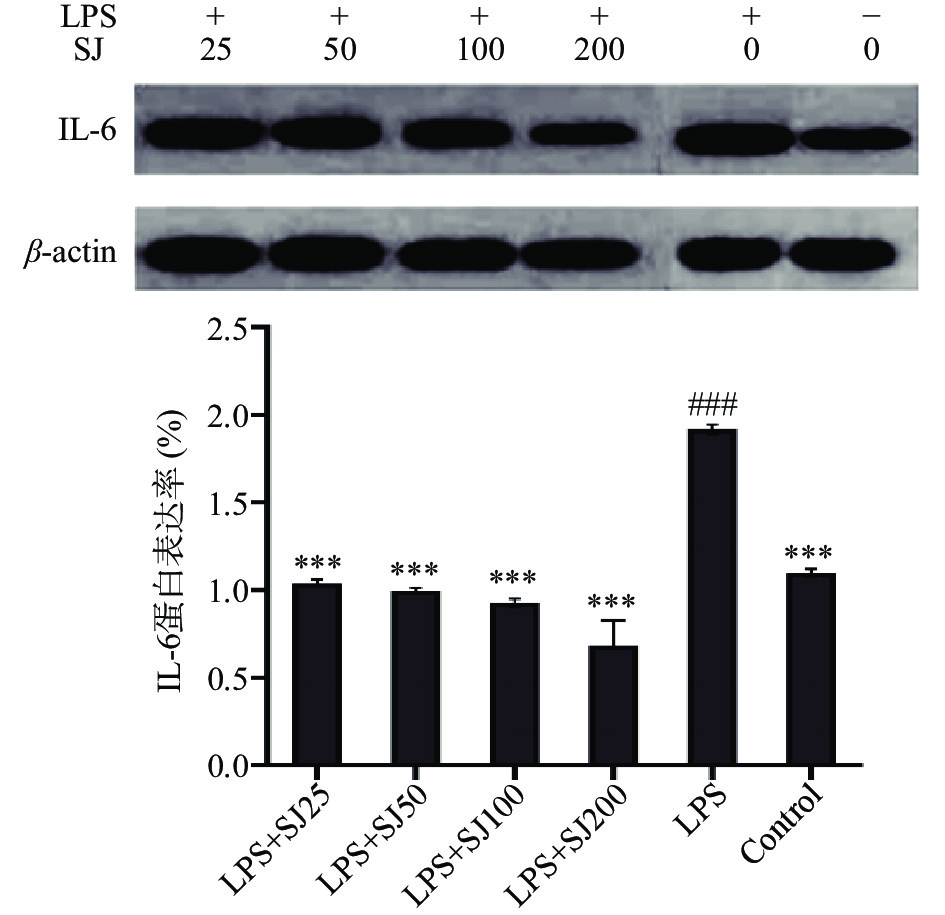
2.5 SJ对LPS诱导的RAW246.7巨噬细胞促炎因子IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α蛋白表达水平的影响
如图7~图9所示,以β-actin作为内参蛋白,与空白对照组比较,LPS组巨噬细胞中的IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α蛋白的表达量会极显著(P<0.001,P<0.001,P<0.001)增加,加入与SJ干预后均有一定程度的降低。与LPS组比较,SJ的浓度25~200 μg/mL均能显著降低在LPS诱导下IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α蛋白表达量(P<0.001,P<0.001,P<0.001)。表明鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖干预后能在蛋白表达水平上抑制细胞炎症因子IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α的表达,降低机体炎症反应,从而发挥抗炎作用。
3. 讨论与结论
炎症是机体由内部或外部刺激诱发的复杂生物过程,参与多种疾病的病理进程[17]。巨噬细胞是免疫细胞的主体,在炎症的启动、维持和消退过程中具有重要的生物学功能。病原体或炎性刺激物激活的巨噬细胞会诱导先天免疫反应,并产生导致炎症的促炎介质[18]。
小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞RAW264.7可用于炎性细胞因子的产生、吞噬作用、细胞信号转导、毒理学等多种研究,并且RAW264.7对脂多糖的诱导很敏感[19]。炎症的形成是细胞与炎症介质之间相互作用的结果,脂多糖刺激巨噬细胞使其活化,并导致促炎介质的分泌,当巨噬细胞过度产生的促炎介质时,可诱发多种炎症相关疾病[20-21]。
iNOS是NO生成的限速酶,是介导NO生成的上层因子,在炎症反应过程中可大量产生[22]。NO过量产生会引起急性和慢性炎症,导致细胞死亡、组织损伤等病理变化[23]。因此,调节iNOS基因的表达是治疗涉及NO参与的炎症性疾病最直接、最关键的方式。本研究发现,SJ可以显著减少LPS诱导的RAW264.7巨噬细胞中NO的过量产生,表明SJ通过抑制NO的产生来抑制炎症。进一步研究发现,SJ通过显著抑制iNOS的表达来抑制NO过量产生。
iNOS基因的启动子包括NF-κB、激活蛋白-1和转录激活因子等识别位点。巨噬细胞中NF-κB的活化可使iNOS的表达水平明显增加,导致NO释放量持续升高,进而使得巨噬细胞分泌促炎细胞因子TNF-α[24]。TNF-α是由单核细胞-巨噬细胞受到促炎因子的刺激后合成和释放的一种关键性促炎性蛋白[25]。IL-6和IL-1β在先天性和适应性免疫反应中起重要作用,机体适量的分泌IL-6和IL-1β有助于感染的恢复,但是TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β等促炎性细胞因子的过度表达,不仅会诱导NO及iNOS的过度产生,还会导致多种器官的衰竭和功能的丧失[26]。因此,抑制巨噬细胞的炎症反应被认为是控制炎症反应的一种治疗干预措施。ELISA实验结果显示,与对照组相比,RAW264.7巨噬细胞经LPS诱导后TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的释放量显著增加,而SJ显著抑制了LPS诱导的RAW264.7巨噬细胞中TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的产生,且呈剂量依赖性(P<0.05)。为了进一步验证上述结果,笔者对TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β进行了Western-Blot分析。发现SJ显著下调LPS处理后TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的蛋白表达水平,在细胞蛋白水平显示出鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖的抗炎活性。
鲍姆纤孔菌属于桑黄的一个品种,主要寄生在丁香属的植物上,研究表明,已经从桑黄属药用真菌中分离和鉴定出了多糖、黄酮类化合物、三萜类化合物、多酚、类固醇、香豆素、生物碱和吡喃类化合物,其中多糖的报道最多[27-28]。本研究从鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝体中提取多糖SJ,利用脂多糖建立炎症模型来研究其对巨噬细胞的免疫调节活性,由本实验所得结果可知SJ可通过抑制促炎性细胞因子及炎症介质的含量体现其抗炎活性。结果表明:SJ可以显著的抑制NO、TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β的分泌量,并呈剂量依赖性趋势。SJ同样可呈剂量依赖的抑制脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞中IL-6和TNF-α和IL-1β和iNOS蛋白的表达水平;表明SJ对脂多糖诱导的小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞中相关炎性细胞因子蛋白的表达水平与细胞因子分泌水平的调节作用相一致;进一步说明SJ可通过抑制iNOS/NO信号通路的激活进而降低NO的生成,进而抑制炎症介质TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β生成发挥其抗炎作用。本实验从细胞水平探讨了鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖的抗炎作用机制,为鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝多糖在临床上进一步推广应用提供实验依据。为进一步开发利用鲍姆纤孔菌和人类健康生活提供了依据。
-
-
[1] HEROLD K, MROWKA R. Inflammation-dysregulated inflammatory response and strategies for treatment[J]. Acta Physiol (Oxf),2019,226(3):e13284.
[2] LUAN F, PENG X, ZHAO G, et al. Structural diversity and bioactivity of polysaccharides from medicinal mushroom Phellinus spp.: A review[J]. Food Chem,2022(397):133731.
[3] WANG H, MA J X, ZHOU M, et al. Current advances and potential trends of the polysaccharides derived from medicinal mushrooms Sanghuang[J]. Front Microbiol,2022(13):965934.
[4] AJITH T. Antidiabetic properties of medicinal mushrooms with special reference to Phellinus species: A review[J]. The Natural Products Journal,2021,11:120−126. doi: 10.2174/2210315510666200124124540
[5] ZHANG J J, CHEN B S, DAI H Q, et al. Sesquiterpenes and polyphenols with glucose-uptake stimulatory and antioxidant activities from the medicinal mushroom Sanghuangporus Sanghuang[J]. Chin J Nat Med,2021,19(9):693−699.
[6] HE P, ZHANG Y, LI N. The phytochemistry and pharmacology of medicinal fungi of the genus Phellinus: A review[J]. Food Funct,2021,12(5):1856−1881. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02342F
[7] JHY A, YSLA B, SKK C, et al. Phellinus baumii enhances the immune response in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice[J]. Nutrition Research,2020,75:15−31. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2019.12.005
[8] YS A, JH A, SHI Z A, et al. Chemical structure and anti-inflammatory activity of a branched polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus baumii[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,268:118214. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118214
[9] ZUO K, TANG K, LIANG Y, et al. Purification and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of extracellular polysaccharopeptide from sanghuang mushroom, Sanghuangporus lonicericola[J]. J Sci Food Agric,2021,101(3):1009−1020. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10709
[10] WANG Z, ZHOU F, QUAN Y. Antioxidant and immunological activity in vitro of polysaccharides from Phellinus nigricans mycelia[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2014(64):139−143.
[11] LUO J, LIU J, SUN Y, et al. Medium optimization, preliminary characterization and antioxidant activity in vivo of mycelial polysaccharide from Phellinus baumii Pilat[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,81(3):533−540.
[12] SUABJAKYONG P, NISHIMURA K, TOIDA T, et al. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus and Phellinus igniarius on the IL-6/IL-10 cytokine balance of the mouse macrophage cell lines (RAW 264.7)[J]. Food Funct,2015,6(8):2834−2844. doi: 10.1039/C5FO00491H
[13] HU T, LIN Q, GUO T, et al. Polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus linteus mycelia exerts anti-inflammatory effects via MAPK and PPAR signaling pathways[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2018(200):487−497.
[14] SUN Y, HUO J, ZHONG S, et al. Chemical structure and anti-inflammatory activity of a branched polysaccharide isolated from Phellinus baumii[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2021(268):118214.
[15] 马晓颖, 吕立涛, 杨涛, 等. 鲍姆纤孔菌菌丝三萜对小鼠巨噬细胞免疫调节活性的影响[J]. 中国食用菌,2021,40(3):79−86,93. [MA X Y, LÜ L T, YANG T, et al. Effects of Mycelium triterpenes extractions from fermentation of Sanghuangporus baumii on the immunomodulatory activity of mouse macrophages[J]. Edible Fungi of China,2021,40(3):79−86,93. doi: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2021.03.016 MA X Y, LÜ L T, YANG T, et al. Effects of Mycelium triterpenes extractions from fermentation of sanghuangporus baumii on the immunomodulatory activity of mouse macrophages[J]. Edible Fungi Of China, 2021, 40(3): 79-86, 93. doi: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2021.03.016
[16] 李磊, 杨雨晗, 王双, 等. 细胞活性检测方法之比较[J]. 生物学杂志,2011,28(1):87−90,93. [LI L, YANG Y H, WANG S, et al. Comparison of cell activity detection methods[J]. Journal of Biology,2011,28(1):87−90,93. LI L, YANG Y H, WANG S, et al. Comparison of cell activity detection methods [J] Journal of Biology, 2011, 28(1): 87-90,93.
[17] LI X X, ZHENG X, LIU Z, et al. Cryptotanshinone from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) inhibited inflammatory responses via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Medicine,2020(15):20.
[18] KIM N, LERTNIMITPHUN P, JIANG Y, et al. Andrographolide inhibits inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated macrophages and murine acute colitis through activating AMPK[J]. Biochem Pharmacol,2019,170:113646. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113646
[19] 李静, 武万强, 杨靖亚. 紫草素可抑制在 RAW264.7 巨噬细胞和斑马鱼幼虫中由脂多糖诱导的炎症反应[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2023,58(1):38−45. [LI J, WU W Q, YANG J Y. Shikotin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in RAW264.7 macrophages and zebrafish larvae[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University,2023,58(1):38−45. LI J, WU W Q, YANG J Y. Shikotin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in RAW264.7 macrophages and zebrafish larvae [J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University,2023,58(1):38-45.
[20] DING L P, HAN Y, CHENG X, et al. Effects of hypoxia combined with LPS on the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and BNIP3 in primary cultured astrocyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology,2021,37(6):632−637.
[21] LIU X, YAO S, BI J, et al. Protective effects and regulatory mechanisms of melatonin in a neonatal mouse model of LPS-induced inflammation[J]. Neurosci Lett,2022(772):136483.
[22] MAN M Q, WAKEFIELD J S, MAURO T M, et al. Regulatory role of nitric oxide in cutaneous inflammation[J]. Inflammation,2022,45(3):949−964. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01615-8
[23] FAN H, WU Q, PENG L P, et al. Phyllolobiumchinense fisch flavonoids (PCFF) suppresses the M1 polarization of LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by inhibiting NF-κB/iNOS signaling pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2020,11(2):864.
[24] 寇育乐, 王文霸, 闫曙光, 等. 基于NF-κB/NLRP3信号通路和肺泡巨噬细胞活化研究肺肠合治法抑制炎症反应治疗急性肺损伤的作用机制[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(1):151. [KOU Y L, WANG W B, YAN S G, et al. Based on NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway and activation of alveolar macrophage study on the mechanism of lung intestine combined therapy in treating acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammatory response[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,47(1):151. KOU Y L, WANG W B, YAN S G, et al. Based on NF-κ B/NLRP3 signaling pathway and activation of Alveolar macrophage Study on the mechanism of lung intestine combined therapy in treating acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammatory response [J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 47(1): 151
[25] 曾晓艳, 郑沛, 曹玮龙, 等. 五步蛇蛇毒化学成分分析及其抗肿瘤活性筛选研究[J]. 中国药师,2022,25(3):439−444. [ZENG X Y, ZHENG P, CAO W L, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents and screening of antitumor activity of snake venom from agkistrodon acutus[J]. China Pharm,2022,25(3):439−444. ZENG X Y, ZHENG P, CAO W L, et al, analysis of chemical constituents and screening of antitumor activity of snake venom from agkistrodon acutus [J] China Pharm, 2022, 25(3): 439-444.
[26] TU P C, PAN Y L, LIANG Z Q, et al. Mechanical stretch promotes macrophage polarization and inflammation via the RhoA-ROCK/NF-κB pathway [J]. BiomedResInt, 2022 : 6871269
[27] ZHAO C, LIAO Z S, WU X Q, et al. Isolation, purification, and structural features of a polysaccharide from Phellinus linteus and its hypoglycemic effect in alloxan-induced diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Food Science,2014,79(5):1002−1010.
[28] WANG Y Y, MA H, DING Z C, et al. Three-phase partitioning for the direct extraction and separation of bioactive exopolysaccharides from the cultured broth of Phellinus baumii[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2019,123:01−209. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.219
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李向辉,宋幸辉,杨星宇,马霞. 包载PLGA的蒲公英多糖纳米粒对Raw264.7细胞免疫效果的评价. 中国兽医杂志. 2025(03): 110-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王艺学,赵辉,李彪,卢睿加,段江波,丁祥. 花脸香蘑E70菌株发酵条件优化及其胞外多糖生物活性. 食品研究与开发. 2024(20): 125-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 伍根瑞,马建成,李继兴,罗娅,包爽,王重娟,吴明一. 粗根荨麻多糖对巨噬细胞吞噬功能和极化的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(23): 358-365 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



