Study on Lowering Uric Acid Effect and Component Analysis of Drug Food Homologous Compound Based on Zebrafish Model
-
摘要: 目的:探究芹菜籽、蒲公英、菊苣和玉米须四种药食同源中药联用下的降尿酸活性和作用机制,分析这四种中药复合提取物中具备降尿酸作用的主要效应成分。方法:随机选取5 dpf野生型AB品系斑马鱼,通过250 μmol/L氧嗪酸钾和10 μmol/L黄嘌呤钠盐诱导建立斑马鱼高尿酸模型,将已建立的斑马鱼模型随机分为对照组、模型组、别嘌醇组(136 µg/mL)和复方提取物低、中、高(250、500及1000 µg/mL)剂量组,每组30尾,连续干预24 h后,测定斑马鱼体内的尿酸荧光值和次黄嘌呤磷酸核糖转移酶1(HPRT1)、葡萄糖转运蛋白9(GLUT9)、有机阴离子转运体(OAT1)基因表达水平;采用超高液相色谱-串联高分辨质谱仪为主要手段,以乙腈-甲酸水为流动相,梯度洗脱,ESI离子源正、负离子扫描模式,结合软件数据库搜索及相关文献进行成分鉴定。结果:与模型组相比,复方提取物低、中、高剂量组均能极显著降低高尿酸斑马鱼模型的血尿酸水平(P<0.01),且能够有效上调高尿酸斑马鱼体内HPRT1、OAT1的相对表达量、下调GLUT9的相对表达(P<0.05);初步筛选鉴定出黄酮及其苷类、有机酸、香豆素、萜类等22种活性成分,均为复方提取物中具有降尿酸机制的效应物质。结论:复方提取物可能通过上调模型组斑马鱼体内HPRT1、OAT1的表达量、下调GLUT9的表达,发挥多方位降尿酸的作用;所筛选鉴定的化学成分为下一步筛选作用靶点提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 复方提取物 /
- 高尿酸血症 /
- 降尿酸 /
- 斑马鱼 /
- 超高液相色谱-串联高分辨质谱
Abstract: Objective: In order to explore the uric acid-lowering activity and mechanism of four traditional Chinese medicines, celery seed, dandelion, chicory and corn silk, and analysis of the main functional components with uric acid-lowering effect in these four kinds of traditional Chinese medicine compound extracts. Methods: Hyperuricemia model in zebrafish was induced by potassium oxazinate and sodium xanthine, then they were randomly divided into control group, model group, allopurinol group (136 µg/mL) and compound extract low, medium, high doses group (250, 500 and 1000 µg/mL), with 30 rats in each group. After continuous intervention for 24 h, the fluorescence level of uric acid and the gene expression levels of hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase1 (HPRT1), glucose transporter9 (GLUT9), and organic anion transporter (OAT1) in zebrafish were measured. Using liquid chromatography-series high resolution mass spectrometer as the main method, and acetonitrile formate water as the mobile phase, gradient elution, ESI ion source positive and negative ion scanning mode, and then combined with software database search and related literature for component identification. Results: Compared with the model group, the low, medium and high dose groups of the compound extract could reduce the blood uric acid level of the hyperuric acid zebrafish model (P<0.01), and could effectively up-regulate the relative expression of HPRT1 and OAT1 and down-regulate the relative expression of GLUT9 in the hyperuric acid zebrafish (P<0.05). At the same time, 22 active ingredients including flavonoids and their glycosides, organic acids, coumarins, and terpenes were initially screened and identified, all of which are effective substances in the compound extract with a uric acid-lowering mechanism. Conclusion: The compound extract may play a multifaceted role in lowering uric acid by up-regulating the gene expression of HPRT1, OAT1, and down-regulating the gene expression of GLUT9 in the model group of zebrafish. The chemical components screened and identified can provide a reference for the next step of screening the target.-
Keywords:
- compound extract /
- hyperuricemia /
- uric acid /
- zebrafish /
- UPLC-MS/MS
-
高尿酸血症是由于体内嘌呤代谢紊乱或尿酸排泄障碍引起的,以血尿酸水平升高为主要表现的代谢性疾病[1]。嘌呤代谢的关键酶异常和负责肾尿酸排泄的转运体异常是造成尿酸合成增加和排泄减少的关键因素[2],HPRT1(次黄嘌呤磷酸核糖转移酶1)功能缺陷导致过多嘌呤被分解成尿酸并从细胞中排出[3],是引起血尿酸浓度升高的主要原因之一;参与肾小管重吸收尿酸盐的转运体GLUT9(葡萄糖转运蛋白9),可使尿酸盐从肾小管细胞膜上被重吸收回血液中;而OAT1(有机阴离子转运体)作为尿酸排泄的转运体[4],其作用是将尿酸从血液吸收到肾小管细胞中,因此HPRT1、OAT1和GLUT9的异常表达和功能变化与高尿酸血症的发生有着紧密的联系。
据流行病学资料显示,高尿酸血症在世界各地的流行率相当高,特别是在中国,过去十年高尿酸症的流行率几乎翻了一番,达到13.0%[5],同时高尿酸血症也是引起多种严重负担性疾病的风险因素,如痛风、心血管疾病、糖尿病,甚至肾脏损伤等[6]。目前临床应用上降尿酸药有苯溴马隆、非布司他、别嘌醇等[7],虽然它们有明显的降尿酸作用,但需要一个较长的服用周期,一旦停药,就会恢复尿酸水平,同时长时间口服别嘌醇这类黄嘌呤氧化酶抑制剂会带来一定的不良反应,如史蒂文斯约翰逊综合征[8]、肝肾毒性[9]、骨髓抑制[10]和表皮坏死松解[11]等,具有一定的限制性。近年来,随着健康产业的不断升温,药食同源中药在医药和功能食品领域备受关注,众多研究表明,药食同源中药中含有黄酮类、酚酸类、皂苷等多种成分,毒副作用小,在降尿酸等药理活性方面具有显著优势。同时,合理配伍的药食同源复方合剂较之单方相比,具有多组分、多途径、多靶点的特点,因此从药理角度出发,选择合适的药食同源复方,多方位抑制尿酸的生成、促进尿酸的排泄,发挥积极的降尿酸作用。
多项药理研究显示,芹菜籽[12]、菊苣[13]、蒲公英[14]、玉米须[15]都具有降尿酸、抗痛风的功效。同时,随着基因组分析、活体成像和高通量小分子筛选等新技术的发展,斑马鱼模型被广泛应用于中药不同提取部位的药效评价、中药单体和活性成分高通量筛选、中药安全性评价等各个方面。因此,本实验探究由芹菜籽、蒲公英、玉米须、菊苣组成的药食同源复方(以下简称复方提取物)对黄嘌呤钠盐联合氧嗪酸钾诱导建立的高尿酸(HUA)斑马鱼模型的降尿酸作用及机制,并利用超高液相色谱-串联高分辨质谱仪(UPLC-MS/MS)和数据处理软件对样品中的中药化学成分进行分析,旨为天然药用植物联用治疗高尿酸血症提供新思路,为下一步筛选作用靶点提供成分参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
芹菜籽、菊苣、蒲公英、玉米须 均购自安徽润邦中药饮片有限公司;野生型AB品系斑马鱼 购自杭州环特生物科技有限公司,实验动物使用许可证号:SYXK(浙)2022-0004,斑马鱼饲养在28 ℃海水(水质:每升含200 mg海盐;电导率450~550 µS/cm;pH5~8.5)中,使用受精后5 d(5 dpf)的斑马鱼用于复方提取物最大耐受浓度测定和降尿酸功效评价。
氧嗪酸钾 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;黄嘌呤钠盐、二甲基亚砜、甲醇 美国Sigma公司;甲酸 中国国药集团;Amplex Red Uric尿酸试剂盒 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;RNA-Quick Purification Kit型RNA快速提取试剂盒 中国YiShan Biotech公司;FastKing cDNA第一链合成试剂盒 天根生化科技(北京)有限公司。
Heraeus Fresco17高速冷冻离心机 德国Thermo Fisher公司;T100普通PCR扩增仪、CFX Connect荧光定量PCR仪 新加坡BIO-RAD公司;Multiskan FC多功能酶标仪、ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3柱(2.1 m×100 mm,1.8 μm)色谱柱、Q Exactive Orbitrap高分辨液质联用仪、U3000超高液相色谱及自动进样器 中国赛默飞世尔科技公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 复方提取物的制备
经查询中国药典,初步确定药食同源复方用量。准确称取芹菜籽10 g,蒲公英8 g,菊苣5 g,玉米须5 g,粉碎后过40目筛,其中芹菜籽粉粹后采用0.5 mol/L的碳酸钠室温静置1 h除脂,取出芹菜籽与其他三种药材混匀,按照1:12(药材:酶解液体积)的比例加入物料比0.04%纤维素酶,调节pH5.0~5.5,60 ℃酶解4 h,收集酶解液过滤,减压浓缩,60 ℃真空干燥得到复方提取物浸膏。
1.2.2 复方提取物降尿酸活性与机制探究
1.2.2.1 斑马鱼最大耐受浓度测定(MTC)
随机抽样选取180尾5 dpf野生型AB品系斑马鱼,转入6孔板中,每孔处理30尾。除对照组外,每组分别给予复方提取物125、250、500、1000、2000 µg/mL浓度的水溶液,经过28 ℃处理24 h后,观察记录每组斑马鱼状态及死亡率。
1.2.2.2 斑马鱼造模、分组及给药
参考张瑛毓[16]和Zhang等[17]确立建立斑马鱼高尿酸(HUA)模型的方法,使用氧嗪酸钾250 μmol/L和黄嘌呤钠盐10 μmol/L处理5 dpf斑马鱼,28 ℃孵育24 h,诱导建立斑马鱼高尿酸模型。随机选取造模后的斑马鱼于6孔板中,每孔30尾,水浴给予低、中、高浓度(250、500及1000 µg/mL)浓度复方提取物水溶液,设置正常对照组和模型组,正常组对照组斑马鱼给与等体积养鱼用水,同时以别嘌呤醇水溶液为阳性对照,每组三个平行。参照Xiong等[18]确定阳性药别嘌呤醇的给药浓度为136 µg/mL。
1.2.2.3 检测指标
尿酸荧光值的测定:28 ℃处理1 d后,利用尿酸试剂盒,使用多功能酶标仪软件采集数据,分析斑马鱼体内尿酸荧光值。
测定HPRT1、OAT1、GLUT9基因相对表达量:利用RNA快速提取试剂盒对各组斑马鱼提取总RNA,紫外-可见光分光光度计测定总RNA浓度和纯度。取2.0 μg斑马鱼样品总RNA,按cDNA第一链合成试剂盒说明操作,合成20.0 μL cDNA,通过q-PCR检测β-actin、HPRT1、GLUT9和OAT1基因的表达。使用β-actin作为基因表达的内参来计算HPRT1、OAT1、GLUT9基因的RNA相对表达量。引物序列信息见表1。
表 1 引物序列信息Table 1. Primer sequence information基因 引物序列 β-actin Forward 5’-TCGAGCAGGAGATGGGAACC-3’ Reverse 5’-CTCGTGGATACCGCAAGATTC-3’ HPRT1 Forward 5’-CACGCTAACAGGAAAGAACG-3’ Reverse 5’-GGTGTCCTCTTCACCAGCAA-3’ OAT1 Forward 5’-GGACGATATCCTGCCAGCTC-3’ Reverse 5’-CGTCCTGTAAGGCCAGATCC-3’ GLUT9 Forward 5’-AGATCGAACGCAGCATCACA-3’ Reverse 5’-GCGTCATATTTCGGTTCCAGC-3’ 1.2.3 复方提取物有效成分分析
1.2.3.1 供试品溶液的制备
取样品200 mg,置于15 mL离心管内,加入10 mL 50%甲醇水溶液(v:v,水:甲醇=50:50),涡旋振荡5 min后,超声30 min,14000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液过0.22 µm微孔滤膜,待UPLC-MS/MS分析测定。
1.2.3.2 液相条件
色谱柱:ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3柱(2.1 m×100 mm,1.8 μm);柱温:35 ℃;进样体积:10 μL;流速:0.3 mL/min;流动相:A(0.1%甲酸水);B(乙腈),梯度洗脱程序见表2。
表 2 梯度洗脱流动相比例Table 2. Proportion of mobile phase eluted by gradient时间 流速(mL/min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0~5 0.3 3~5 97~95 5~8 0.3 5~8 95~92 8~20 0.3 8~15 92~85 20~30 0.3 15~16 85~84 30~45 0.3 16~40 84~60 45~70 0.3 40~3 60~97 1.2.3.3 质谱条件
采用Q Exactive Orbitrap高分辨质谱进行质谱数据采集,检测模式为Full MS-ddMS2,正离子和负离子模式分别扫描,扫描范围为m/z 100~1200,MS1分辨率设置为70000,MS2分辨率设置为17500,离子源电压为3.2 kV,毛细管离子传输管温度为320 ℃,辅助气加热温度为350 ℃,鞘气流速为40 L/min,辅助气流速为15 L/min,AGC Target设置为1e6,TopN设置为5,触发MS2扫描的碰撞能量采用阶梯式碎裂电压NCE,设置为30,40,50。
1.2.3.4 化学成分鉴定
采用Compound discover 3.2软件进行原始Raw质谱数据特征峰提取,特征峰元素匹配、分子式预测及同位素分布匹配的质量偏差均设置为5 ppm以内。利用BATMAN-TCM、GeneCards、中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)数据库进行特征峰鉴定。阳性结果筛选标准为质量偏差<5 ppm、符合同位素分布及mzVault best match数据库匹配得分>70分。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据采用SPSS 26.0分析,统计学处理结果采用平均值±标准差(mean±SE)表示,P<0.05表明差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 复方提取物对斑马鱼的最大耐受浓度
斑马鱼用125、250、500、1000 μg/mL的复方提取物进行药浴暴露处理,结果发现,实验组中斑马鱼均未发现异常行为和毒副作用,且表现出与空白对照组相似的活性状态;而当给药浓度达到2000 μg/mL时斑马鱼行动迟缓,整体状态不佳。因此,选择250、500、1000 μg/mL复方提取物水溶液作为实验的低、中、高剂量对斑马鱼进行降尿酸实验。
2.2 复方提取物对HUA斑马鱼降尿酸活性评价
斑马鱼的降尿酸功效如表3所示,模型组中斑马鱼的尿酸荧光值约为14984,与正常对照组相比明显升高,这表明成功构建了斑马鱼HUA模型。此外,由表可知,与模型组相比,复方提取物低、中、高浓度组中的尿酸荧光值均有一定程度的下降,其中高浓度复方提取物组中斑马鱼体内的尿酸荧光值仅约为5385,较模型组相比下降了64.06%(P<0.01),复方提取物对于HUA斑马鱼的降尿酸效果显著。同时复方提取物组与阳性药别嘌醇组相比,尿酸荧光值无显著差异(P>0.05),说明复方提取物的降尿酸功效能够达到阳性药物别嘌醇的水平。文献报道,芹菜籽、蒲公英、玉米须和菊苣均有不同程度的降尿酸功效[19-20],本实验结果也证实,复方提取物能够降低高尿酸斑马鱼体内尿酸水平;此外有研究表明[21],别嘌醇在降尿酸的同时具有一定的肾脏毒性等副作用,而许多天然植物药不仅毒性低[22],活性成分多样,而且降尿酸功效能够达到化学药的水平[23],这与本实验结果一致。
表 3 复方提取物降尿酸功效评价(n=3)Table 3. Evaluation of the effect of compound extract on lowering uric acid (n=3)组别 浓度(µg/mL) 尿酸荧光值(mean±SE) 正常对照组 − 3816±156*** 模型对照组 − 14984±807 别嘌呤醇 136 5155±171*** 复方提取物 低 250 10958±884** 中 500 8485±788** 高 1000 5385±998** 注:与模型对照组比较,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 2.3 复方提取物对斑马鱼体内OAT1、GLUT9、HPRT1表达水平的影响
2.3.1 RNA提取结果及引物序列信息
样品处理结束后,提取斑马鱼总RNA,用紫外-可见光分光光度计测定RNA的浓度及A260/A280比值,A260/A280比值均在1.8~2.2之间,结果表明提取得到斑马鱼总RNA质量较好,可用于后续q-PCR实验。
2.3.2 复方提取物对尿酸合成(HPRT1)、重吸收(GLUT9)、排泄(OAT1)基因表达的影响
研究发现,过量的尿酸生成和排泄障碍是导致体内尿酸水平升高的主要原因,HPRT1是目前被熟知的能够影响尿酸合成增加的一大遗传因素,HPRT既催化嘌呤碱基的补救合成,又参与嘌呤类药物的代谢,是调控该类药物合成代谢途径的关键酶[24]。肾脏是尿酸排泄的主要器官,研究发现,在近曲小管的尿酸重吸收过程中GLUT9发挥着不可忽视的作用,甚至可能比URAT1的作用更为明显[25]。OAT1/OAT3是负责尿酸分泌的主要蛋白,且均在肾近曲小管细胞的基底外侧膜中高度表达,研究表明,OAT1蛋白通过有机离子与双羧酸的交换参与肾中尿酸的转运,特别在尿酸的分泌排泄方面表现突出。
各组斑马鱼体内HPRT1、GLUT9、OAT1基因表达水平如表4所示。与正常对照组相比,模型组中斑马鱼体内HPRT1、OAT1基因表达水平极显著下降(P<0.01),GLUT9基因表达水平极显著上升(P<0.01),使用250、500、1000 μg/mL复方提取物处理24 h后,与模型组相比,斑马鱼体内的HPRT1、OAT1基因表达水平均有上调趋势,GLUT9表达水平有下降趋势,其中高剂量复方提取物组中斑马鱼体内的HPRT1基因表达水平显著上调了约64%(P<0.05),OAT1极显著上调231%(P<0.01)。
表 4 样品处理后斑马鱼RNA相对表达量Table 4. Relative expression of zebrafish RNA after sample treatment组别 浓度(μg/mL) HPRT1相对表达量(mean±SE) OAT1相对表达量(mean±SE) GLUT9相对表达量(mean±SE) 正常对照组 − 1.89±0.09** 2.67±0.11*** 0.646±0.05** 模型对照组 − 1.00±0.07 1.00±0.06 1.00±0.02 别嘌呤醇 136 1.90±0.13** 1.72±0.08** 0.468±0.11** 复合提取物低剂量组 250 1.24±0.12* 2.31±0.30** 0.897±0.07*** 复合提取物中剂量组 500.00 1.44±0.16* 2.81±0.36** 0.785±0.06*** 复合提取物高剂量组 1000.00 1.64±0.17* 3.31±0.33** 0.681±0.05*** 注:与模型对照组比较,*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 李少鹏[26]考察芹菜籽提取物对高尿酸大鼠体内黄嘌呤氧化酶的影响,发现芹菜籽提取物对黄嘌呤氧化酶的活性有抑制作用,猜测可能是通过上调HPRT1的表达来抑制尿酸生成。Wang等[27]对玉米须的降尿酸活性成分进行筛选,发现玉米须在明显改善肾脏损伤,促进尿酸排泄的同时,还对高尿酸小鼠肝脏的黄嘌呤氧化酶有抑制作用;李丽玉[28]选用鹌鹑为实验对象建立HUA模型,研究菊苣对鹌鹑体内尿酸含量的影响,结果显示菊苣可能发挥抑制尿酸生成、促进尿酸排泄的作用,通过抑制腺苷脱氨酶活性、上调OAT3基因表达;姚江琪[29]研究发现,在小鼠肝脏中,蒲公英可以降低GLUT9的表达量。本实验结果表明,复方提取物可能通过抑制HUA斑马鱼体内的GLUT9,上调HPRT1和OAT1基因表达水平来降低HUA斑马鱼体内的血尿酸浓度,且其促进尿酸排泄的效果优于抑制尿酸生成。
2.4 复方提取物成分分析
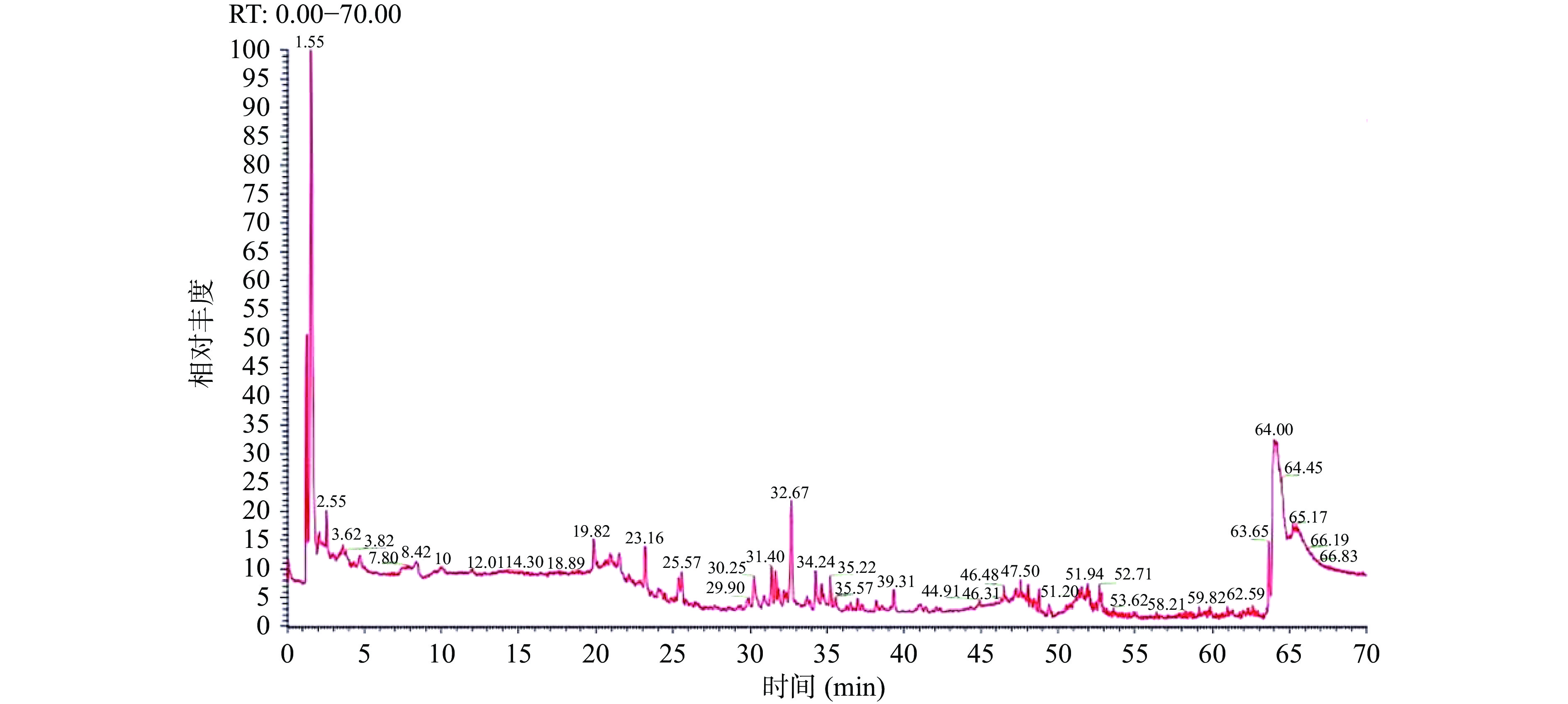
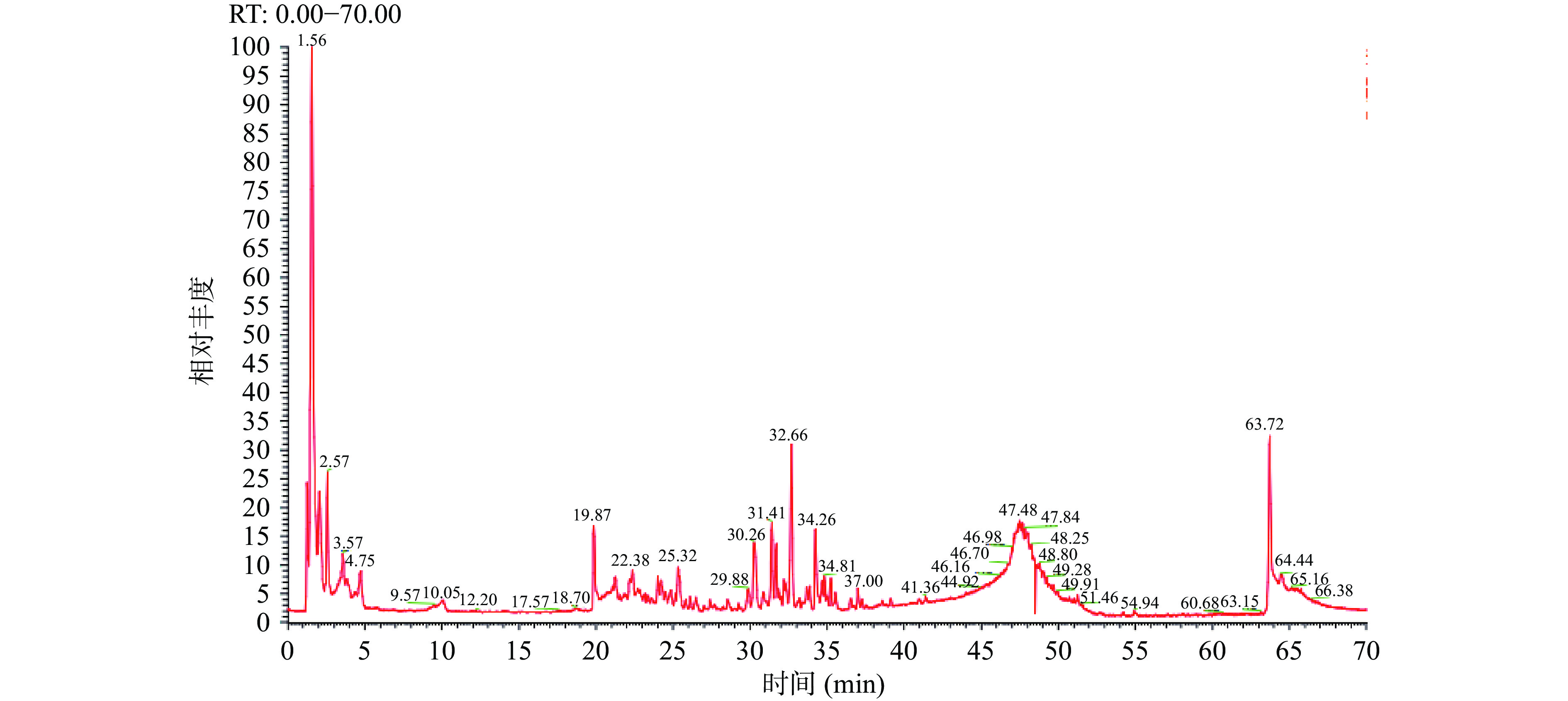
为了探究复合提取物中的主要功效性成分,根据“1.2.3”项下的方法,借助UPLC-MS/MS技术对复方提取物进行分析,其正负离子模式下基峰色谱图如图1、图2所示。根据“1.2.3.4”的方法对复方提取物中化学成分,进行了全面具体的解析,最终鉴定出83种化合物,其中数据库匹配度在90分以上的化学成分鉴定结果如表5所示。由表可知,复方提取物中含有黄酮及其苷类、酚酸、香豆素及其萜类等物质,其中黄酮类占比较多,包括芦丁、木犀草素、槲皮素、芹菜苷、山奈酚、芹菜素-7-O-葡萄糖苷等,有机酸类包括菊苣酸、绿原酸、咖啡酸等,香豆素及其萜类包括异鼠李素、秦皮甲素、山莴苣苦素、七叶内酯等。
表 5 部分复方提取物化学成分鉴定信息Table 5. Identification information of chemical constituents of compound extractsNO TR(min) 化合物 分子式 理论值(m/z) 测定值(m/z) 二级质谱(m/z) 1 31.583 芦丁 C27H30O16 609.1456 609.1421 609,151,300 2 20.729 芹菜素 C15H10O5 285.0399 285.0381 265,151,167 3 24.673 芹菜苷 C26H28O14 565.295 565.210 269,431,271 3 24.377 山奈酚-3-O-桑布双糖苷 C26H28O15 581.0501 581.0497 449,187,153 4 28.72 木犀草素 C15H10O6 285.0399 285.0392 285,133,151 5 1.722 柯伊利素 C16H12O6 301.2741 301.2654 254,266 6 21.41 芹菜素-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C21H12O10 473.4510 433.4539 266,338 7 1.765 木犀草苷 C21H20O11 447.0932 447.0856 285 8 18.924 山奈酚 C15H10O6 285.0404 285.0409 257,229 9 24.901 菊苣酸 C22H18O12 473.0721 473.0740 473,179,293 10 18.924 绿原酸 C16H18O9 353.0872 353.0795 191 11 24.49 咖啡酸 C19H8O4 179.0342 179.0344 179,135 12 29.173 异绿原酸B C25H24O12 515.1190 515.1186 515,353 13 21.701 槲皮素 C15H10O7 130.0348 130.0246 301,151 14 24.963 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 C27H30O15 595.1657 595.1549 449,287,153 15 25.982 木犀草素-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C21H20O11 447.0927 447.0918 151,133 16 25.622 阿魏酸 C10H10O4 193.0501 193.0503 193,134 17 30.944 槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 C21H20O12 463.0877 463.0871 463,151 18 25.894 异绿原酸A C25H24O12 515.1190 515.1179 515,353 19 24.673 异鼠李素 C16H12O7 310.0505 310.0525 253,151 20 34.985 秦皮甲素 C15H16O9 339.0231 339.0210 176.9,133 21 25.982 山莴苣苦素 C23H22O7 409.2450 409.2447 226,151 22 32.951 七叶内酯 C9H6O4 177.0118 177.0182 177,133,121 现代中医临床用药多以组方为主,与单一药物相比,中药复方具有多成分、多靶点以及有效成分不明确的特性,因此,分析中药成分是研究药效物质的基础,也是控制中药复方质量的关键因素。本实验以UPLC-MS/MS平台为基础,结合在线数据库及文献,对由芹菜籽、蒲公英、玉米须、菊苣组成的复方提取物进行成分鉴定,发现了芹菜素、槲皮素、木犀草素、山奈酚、绿原酸、七叶内酯、秦皮素等单一功效成分。Feng等[30]论述了天然化合物降低尿酸的潜在活性和作用机制,发现木犀草素、芹菜素等黄酮类成分能抑制黄嘌呤氧化还原酶(XOR),调节GLUT9、尿酸阴离子转运蛋白1(URAT1)、乳腺癌抗性蛋白(BCRP/ABCG2)和OAT1,使血尿酸降低;Wang等[31]研究发现,酚酸类物质如绿原酸、菊苣酸等,可以通过抑制小鼠肝脏黄嘌呤氧化酶活性,起到抑制尿酸生成的作用;另有研究报道,香豆素可以抑制黄嘌呤氧化酶活性[32];Chen 等[33]经体外实验证实七叶内脂、秦皮素是有效抑制黄嘌呤氧化酶活性的药物,能够降低血尿酸水平。本研究表明,复方提取物中含有黄酮及其苷类、有机酸、香豆素及其萜类等多种类活性物质,这些成分之间相互配合、相互作用,共同发挥复方提取物多方位降尿酸的功效。
3. 结论
本研究结果表明,由芹菜籽、蒲公英、玉米须、菊苣组成的药食同源复方提取物对HUA斑马鱼体内尿酸水平具有显著的调节作用,复方提取物可能通过上调HUA斑马鱼体内的HPRT1和OAT1的表达、下调GLUT9的表达来抑制体内尿酸的生成,促进尿酸排泄。与单味药材相比,几种药材联用可以通过多通路、多靶点、协同增效来发挥降尿酸的功效,较单味药材机制更多,可适用于临床多种不同类型高尿酸血症人群使用。此外,本研究还利用UPLC-MS/MS联用技术,结合在线数据库和相关文献对复方提取物中的化学成分实现了快速识别鉴定,了解了复方提取物中的主要效应成分。综上,芹菜籽、蒲公英、玉米须、菊苣联用后具有调节高尿酸斑马鱼体内尿酸水平的作用,为下一步降尿酸复方产品的开发提供理论依据,同时提取物的成分分析能够快速、准确地从复杂混合物中寻找及发现活性成分,为下一步探究活性靶点带来一定的参考价值。
-
表 1 引物序列信息
Table 1 Primer sequence information
基因 引物序列 β-actin Forward 5’-TCGAGCAGGAGATGGGAACC-3’ Reverse 5’-CTCGTGGATACCGCAAGATTC-3’ HPRT1 Forward 5’-CACGCTAACAGGAAAGAACG-3’ Reverse 5’-GGTGTCCTCTTCACCAGCAA-3’ OAT1 Forward 5’-GGACGATATCCTGCCAGCTC-3’ Reverse 5’-CGTCCTGTAAGGCCAGATCC-3’ GLUT9 Forward 5’-AGATCGAACGCAGCATCACA-3’ Reverse 5’-GCGTCATATTTCGGTTCCAGC-3’ 表 2 梯度洗脱流动相比例
Table 2 Proportion of mobile phase eluted by gradient
时间 流速(mL/min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0~5 0.3 3~5 97~95 5~8 0.3 5~8 95~92 8~20 0.3 8~15 92~85 20~30 0.3 15~16 85~84 30~45 0.3 16~40 84~60 45~70 0.3 40~3 60~97 表 3 复方提取物降尿酸功效评价(n=3)
Table 3 Evaluation of the effect of compound extract on lowering uric acid (n=3)
组别 浓度(µg/mL) 尿酸荧光值(mean±SE) 正常对照组 − 3816±156*** 模型对照组 − 14984±807 别嘌呤醇 136 5155±171*** 复方提取物 低 250 10958±884** 中 500 8485±788** 高 1000 5385±998** 注:与模型对照组比较,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 表 4 样品处理后斑马鱼RNA相对表达量
Table 4 Relative expression of zebrafish RNA after sample treatment
组别 浓度(μg/mL) HPRT1相对表达量(mean±SE) OAT1相对表达量(mean±SE) GLUT9相对表达量(mean±SE) 正常对照组 − 1.89±0.09** 2.67±0.11*** 0.646±0.05** 模型对照组 − 1.00±0.07 1.00±0.06 1.00±0.02 别嘌呤醇 136 1.90±0.13** 1.72±0.08** 0.468±0.11** 复合提取物低剂量组 250 1.24±0.12* 2.31±0.30** 0.897±0.07*** 复合提取物中剂量组 500.00 1.44±0.16* 2.81±0.36** 0.785±0.06*** 复合提取物高剂量组 1000.00 1.64±0.17* 3.31±0.33** 0.681±0.05*** 注:与模型对照组比较,*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 表 5 部分复方提取物化学成分鉴定信息
Table 5 Identification information of chemical constituents of compound extracts
NO TR(min) 化合物 分子式 理论值(m/z) 测定值(m/z) 二级质谱(m/z) 1 31.583 芦丁 C27H30O16 609.1456 609.1421 609,151,300 2 20.729 芹菜素 C15H10O5 285.0399 285.0381 265,151,167 3 24.673 芹菜苷 C26H28O14 565.295 565.210 269,431,271 3 24.377 山奈酚-3-O-桑布双糖苷 C26H28O15 581.0501 581.0497 449,187,153 4 28.72 木犀草素 C15H10O6 285.0399 285.0392 285,133,151 5 1.722 柯伊利素 C16H12O6 301.2741 301.2654 254,266 6 21.41 芹菜素-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C21H12O10 473.4510 433.4539 266,338 7 1.765 木犀草苷 C21H20O11 447.0932 447.0856 285 8 18.924 山奈酚 C15H10O6 285.0404 285.0409 257,229 9 24.901 菊苣酸 C22H18O12 473.0721 473.0740 473,179,293 10 18.924 绿原酸 C16H18O9 353.0872 353.0795 191 11 24.49 咖啡酸 C19H8O4 179.0342 179.0344 179,135 12 29.173 异绿原酸B C25H24O12 515.1190 515.1186 515,353 13 21.701 槲皮素 C15H10O7 130.0348 130.0246 301,151 14 24.963 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 C27H30O15 595.1657 595.1549 449,287,153 15 25.982 木犀草素-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C21H20O11 447.0927 447.0918 151,133 16 25.622 阿魏酸 C10H10O4 193.0501 193.0503 193,134 17 30.944 槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 C21H20O12 463.0877 463.0871 463,151 18 25.894 异绿原酸A C25H24O12 515.1190 515.1179 515,353 19 24.673 异鼠李素 C16H12O7 310.0505 310.0525 253,151 20 34.985 秦皮甲素 C15H16O9 339.0231 339.0210 176.9,133 21 25.982 山莴苣苦素 C23H22O7 409.2450 409.2447 226,151 22 32.951 七叶内酯 C9H6O4 177.0118 177.0182 177,133,121 -
[1] YANG Y J, YAN D G, CHENG H Z, et al. Discovery of novel 1, 2, 4-triazole derivatives as xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitors with hypouricemic effects[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2022,129(9):106162−106103.
[2] HELGET N, MIKULS T R. Long-term adherence to urate-lowering therapy in gout: A glass half empty or a glass half full?[J]. The Journal of Rheumatology,2022,10(27):34−36.
[3] YONG T Q, LIANG D L, XIAO C, et al. Hypouricemic effect of 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester in hyperuricemic mice through inhibiting XOD and down-regulating URAT1[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2022,153(9):113303−113304.
[4] MA J W, BIAN X Y, SU Q, et al. The urate-lowering efficacy of febuxostat and its relationship with residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients with hyperuricemia[J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi,2022,102(36):2874−2880.
[5] 冯文韬. 清热利湿通络法治疗急性痛风性关节炎的临床观察[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2017. FENG W T. Clinical observation on the treatment of acute gouty arthritis by clearing heat and dispelling dampness and regulating collaterality[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 2017.
[6] 陈玲. 四种降尿酸药物有效性与安全性的网状Meta分析[D]. 大理: 大理大学, 2019. CHEN L. Network meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of four uric acid lowering drugs[D]. Dali: Dali University, 2019.
[7] 李丹, 张剑勇. 痛风现代流行病学及降尿酸药物研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2016,5(4):73−76. [LI D, ZHANG J Y. Modern epidemiology of gout and research progress of uric acid lowering drugs[J]. Rheumatology and Arthritis,2016,5(4):73−76. LI D, ZHANG J Y. Modern epidemiology of gout and research progress of uric acid lowering drugs[J]. Rheumatology and Arthritis, 2016, 5(4): 73-76.
[8] 何俊锋. 非布司他与别嘌醇在痛风治疗中降尿酸有效性和安全性比较[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2017,10(17):12−13. [HE J F. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of febuxostol and allopurinol in the treatment of gout[J]. Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use,2017,10(17):12−13. HE J F. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of febuxostol and allopurinol in the treatment of gout[J]. Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use, 2017, 10(17): 12-13.
[9] 裴媛, 王瑞. HLA-B~*5801基因多态性与别嘌醇致皮肤不良反应的文献分析[J]. 中国药物警戒,2019,16(3):154−156. [PEI Y, WANG R. Literature analysis of HLA-B~*5801 gene polymorphism and adverse reactions caused by allopurinol[J]. Chinese Pharmacovigilance,2019,16(3):154−156. PEI Y, WANG R. Literature analysis of HLA-B~*5801 gene polymorphism and adverse reactions caused by Allopurinol[J]. Chinese Pharmacovigilance, 2019, 16(3): 154-156
[10] 周新朋. 加味四妙散治疗慢性肾脏病Ⅲ~Ⅳ期高尿酸血症临床观察[D]. 济南: 山东中医药大学, 2014. ZHOU X P. Clinical observation of Jiawei Simiao powder in treating stage Ⅲ~Ⅳ hyperuricemia of chronic kidney disease[D]. Jinan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014.
[11] 陈一萍, 张劼, 周嘉, 等. 别嘌醇药物不良反应风险因素研究进展[J]. 广西医科大学学报,2019,36(1):137−141. [CHEN Y P, ZHANG J, ZHOU J, et al. Research progress of risk factors of adverse drug reactions allopurinol[J]. Journal of Guangxi Medical University,2019,36(1):137−141. CHEN Y P, ZHANG J, ZHOU J, et al. Research progress of risk factors of adverse drug reactions allopurinol[J]. Journal of Guangxi Medical University, 2019, 36(1): 137-141.
[12] HANG N T, TU U T, VAN P N. Green extraction of apigenin and luteolin from celery seed using deep eutectic solvent[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2022,207(10):114406.
[13] POUILLE C L, OUZAZ S, ROELS E, et al. Chicory: Understanding the effects and effectors of this functional food[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(5):957−958. doi: 10.3390/nu14050957
[14] CHOI J Y, JANG T W, SONG P H, et al. Combination effects of metformin and a mixture of lemon balm and dandelion on high-fat diet-induced metabolic alterations in mice[J]. Antioxidants,2022,11(3):580−582. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030580
[15] TIAN J, XU J, XU W, et al. Screening of active ingredient of Stigmatamaydis inhibitrg xanthine oxidase and its effect[J]. Journal of Jilin University,2011,37(3):433−436.
[16] 张瑛毓. 斑马鱼高尿酸血症模型构建及降尿酸功能食药材筛选[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. ZHANG Y Y. Construction of hyperuricemia model of zebrafish and screening of urico-lowering functional food herbs[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020.
[17] ZHANG Y Y, LI Q, WANG F Z, et al. A zebrafish (danio rerio) model for high-throughput screening food and drugs with uric acid-lowering activity[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2019,508(2):494−498. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.050
[18] XIONG X Y, LIANG J, SHENG Y G, et al. A natural complex product Yaocha reduces uric acid level in a live zebrafish model[J]. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods,2020,102(3):106−108.
[19] 刘涛. 薏仁木瓜化浊汤对高尿酸血症小鼠的降尿酸作用及其机制研究[D]. 广州: 广东药科大学, 2020. LIU T. Effect and mechanism of coix seed papaya turbidite decoction on reducing uric acid in hyperuricemia mice[D]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2020.
[20] LING D K, CHENG Y. A Chinese herbal medicine Ermiao wan reduces serum uric acid level and inhibits liver xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase in mice[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2004,93(3):325−330.
[21] LYNCH E D, GU R, PIERCE C, et al.Reduction of acute cisplatin ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats by oret al. Reduction of acute cisplatin ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats by oral administration of allopurinol and ebselen[J]. Hearing Research,2005,201(2):81−89.
[22] LI F, ZHANG Y Z, ZHANG D, et al. Correction: Molecular mechanisms involved in drug-induced liver injury caused by urate-lowering Chinese herbs: A network pharmacology study and biology experiments[J]. PloS One,2020,15(3):231−216.
[23] 綦艳, 邓幸飞, 李聪, 等. 降尿酸功效食品开发及产业发展研究现状[J]. 食品安全导刊,2022(17):113−115. [QI Y, DENG X F, LI C, et al. Research status and industry development of functional foods to reducing uric acid[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2022(17):113−115. QI Yan, DENG Xingfei, LI Cong, et al.Research status and industry development of functional foods to reducing uric acid[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2022(17): 113-115
[24] EIKAN M, IKAN M, TAKAYASU M, et al. HPRT-related hyperuricemia with a novel p. V35M mutation in HPRT1 presenting familial juvenile gout[J]. CEN Case Reports,2020,9(3):15−18.
[25] NOVIKOV A, FU Y L, HUANG W, et al. SGLT2 inhibition and renal urate excretion: role of luminal glucose, GLUT9, and URAT1[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology,2019,316(1):F173−F185. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00462.2018
[26] 李少鹏. 芹菜籽提取物抗急性痛风性关节炎及高尿酸血症的活性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019. LI S P. Effect of celery seed extract on acute gouty arthritis and hyperuricemia[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019.
[27] WANG X Z, YUAN L Y, ZHI J B, et al. Screening of uric acid-lowering active components of corn silk polysaccharide and its targeted improvement on renal excretory dysfunction in hyperuricemia mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2021,9(86):104698−104700.
[28] 李丽玉. 基于肾脏排泄途径的菊苣降尿酸作用机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2015. LI L Y. Study on uric acid lowering mechanism of chicory based on renal excretion pathway[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2015.
[29] 姚江奇. 蒲公英精酿啤酒开发及其抑制小鼠尿酸升高的功效研究[D]. 杨林: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. YAO J Q. Development of dandelion craft beer and its inhibitory effect on uric acid in mice[D]. Yanglin: Northwest A&F University, 2012.
[30] FENG S M, WU S J, XIE F, et al. Natural compounds lower uric acid levels and hyperuricemia: Molecular mechanisms and prospective[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,123(5):87−102.
[31] WANG Y, LIN Z J, LIN B, et al. Cichorium intybus L. promotes intestinal uric acid excretion by modulating ABCG2 in experimental hyperuricemia[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2017,14(1):33−35.
[32] 刘雪梅. 具有XOI活性的食源性植物多酚提取物的筛选、降尿酸活性评价及功效因子靶向鉴定[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. LIU X M. Screening, evaluation of uric acid lowering activity and targeted identification of efficacy factors of foodborne plant polyphenol extracts with XOI activity[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019.
[33] CHEN L, CHEN S, YUAN C, et al. Structure-activity relationship of coumarin derivatives on xanthine oxidase-inhibiting and free radical-scavenging activities[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology,2008,75(6):1416−1425. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2007.11.023
-
期刊类型引用(14)
1. 张琪婧,耿振甲,李敏,王俊秋,钱思颖,师聪. 覆盆子总黄酮的酶辅助闪式提取及其抗氧化、降血糖和降血脂活性分析. 粮食与油脂. 2025(01): 115-120+126 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邹滨,包海鹰,赵立智,刘颖,韩晨,王青春. 粗毛纤孔菌不同提取物对免疫抑制小鼠免疫功能的影响. 食用菌学报. 2024(01): 62-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郭刚军,胡小静,付镓榕,马尚玄,董超,徐文婷,魏元苗,贺熙勇. 超声波-微波联合辅助提取澳洲坚果青皮多糖工艺优化及其抗氧化活性. 中国南方果树. 2024(03): 87-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 巫永华,黄莉莉,王解语,张文莉,陈安徽,郭红伟,张建萍,刘恩岐. 深共熔溶剂提取桑黄黄酮及体外降血糖、结合胆酸盐能力分析. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(11): 128-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵小亮,牟翮,张晶,张伟杰. 苦参多糖的提取工艺优化及体外抗氧化、降血脂活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(13): 212-220 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 陈静颖,陶玉贵,葛飞,谷燕. 响应面法优化微波-超声协同提取低聚糖的工艺研究. 安徽工程大学学报. 2024(04): 26-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 许梦粤,田鑫,王君可,武傲雪,邹芷怡,吴佳辉,王红波. 菜豆多糖与香菇多糖结构特征以及体外重要生物活性综合对比评价. 食品科学. 2024(23): 2318-2327 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王昱文,段涵怡,董悦君,范怡然,杨颖,赵佳迪,杨雪. 黄芩黄酮的微波-超声法提取及降胆固醇活性评价. 饲料工业. 2023(11): 98-104 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 张金朋,赵硕,郭晓帆,陈玉凤,齐永秀,刘媛媛. 五味子总木脂素超声波微波协同辅助提取工艺及其主要成分含量. 山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院)学报. 2023(05): 327-332 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 魏奇,钟鑫荣,翁馨,陈美霞,刘盛荣,张维瑞. 食用菌多糖制备工艺及其生物活性研究进展. 宁德师范学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 180-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 李湘利,刘静,邓英立,王森,王晓强. 超声-微波协同提取鸡枞菌多糖的工艺优化及抗氧化性. 食品科技. 2022(01): 184-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 姜欣洋,梁金月,史继童,刘兰玲,张珊珊,赵盼,颜培正,赵东升. 补骨脂乙醇提取物活性成分与抗氧化及胆酸盐结合能力的关联性分析. 食品工业科技. 2022(13): 381-388 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 李志军,包海鹰. 中药桑黄粗毛纤孔菌的化学成分与药理作用研究进展. 菌物研究. 2022(03): 203-213 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 蔡小雨,李雪晗,于美翠,巫小慧,王玉青,李梦瑶. 食药用菌多糖抑菌作用研究进展. 食品安全导刊. 2021(29): 183-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(15)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
