Comparative Analysis of Characteristics and in Vitro Biological Activities of Cordyceps militaris Polysaccharide Prepared by Two Methods
-
摘要: 本研究以蛹虫草发酵液为材料,采用壳聚糖絮凝法和水提醇沉法分别制备了絮凝多糖(XDT)和醇沉多糖(CDT),并对两种方法制备所得多糖的得率、各组分含量、平均粒径和复溶性进行了对比分析,利用扫描电镜、傅里叶红外光谱和刚果红实验对其微观结构、官能团和空间构象进行表征,利用DPPH、超氧阴离子和羟自由基清除能力评价其抗氧化活性,以α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率评价其降血糖活性,以HepG2细胞增殖抑制率评价其抗肿瘤活性。结果表明:壳聚糖絮凝法制备多糖得率为3.58%,是醇沉法的1.91倍;两种多糖在扫描电镜下的微观结构存在差异,在红外光谱下吸收图谱相似,但XDT比CDT具有更多的三螺旋结构;XDT的平均粒径更小,复溶速度更快;体外抗氧化实验表明,在相同浓度下,对DPPH、超氧阴离子和羟自由基的清除能力,均表现为XDT>CDT;体外抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性实验表明,低浓度时,两种多糖的抑制率没有显著性差异,但随着浓度增加,在相同条件下,XDT的抑制活性明显强于CDT;体外抑制肿瘤细胞增殖能力实验表明,在相同处理浓度下,XDT对HepG2细胞的增殖抑制作用优于CDT。综上,壳聚糖絮凝法制备的蛹虫草多糖得率更高、平均粒径更小、复溶性更佳,XDT具备较强的体外抗氧化、降血糖和抗肿瘤活性。Abstract: Cordyceps militaris polysaccharides from the fermentation broth were prepared via chitosan flocculation and water extraction and alcohol precipitation methods to obtain the flocculated polysaccharide (XDT) and alcohol precipitation polysaccharide (CDT) respectively. The extraction yields, component content, average particle sizes and solubility of XDT and CDT were comparatively investigated. The microstructures, functional groups and spatial conformations were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier infrared spectroscopy and Congo red assay. The antioxidant activity was evaluated by scavenging ability of DPPH, superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical. The hypoglycemic activity was estimated by α-glucosidase inhibitory ability, and the antitumor cell activity was analyzed by inhibition of HepG2 cell proliferation. The results showed a yield of 3.58% for XDT, 1.91 times that of CDT. CDT and XDT exhibited different microstructures under electron microscopy, and similar absorption patterns under infrared spectrum, while XDT contained more triple helix structures than CDT. XDT displayed smaller average particle sizes but a faster dissolution rate than CDT. In vitro antioxidant tests showed that XDT exhibited significantly higher scavenging ability of DPPH, superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical than CDT at the same concentration. There was no significant difference between the XDT and CDT in the inhibition of α-glucosidase at low concentration, but XDT showed significantly higher inhibition than CDT as the increase of concentration. XDT was found to be a stronger inhibitor of HepG2 cells proliferation than CDT at the same treatment concentration. In summary, XDT showed higher yields, smaller average particle sizes, faster solubility, and higher antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and antitumor activity in vitro.
-
蛹虫草(Cordyceps militaris(L.ex Fr)Link)是一种常见的食药同源真菌,又名北冬虫夏草、东北草等,为虫草属(Cordyceps)大型真菌[1]。蛹虫草与冬虫夏草同属异种、同功效,属珍稀菌类,因其含有多糖、核苷类、蛋白质、多肽和氨基酸等多种活性成分,使其具有良好的免疫调节作用、抗氧化和延缓衰老的作用、抑菌作用、抗肿瘤作用、神经保护作用、降血脂保肝作用和降血糖作用等多种生理活性[2-5]。虫草多糖是蛹虫草中含量最丰富的活性成分之一,大量存在于蛹虫草的菌丝体和发酵液中,因其具有显著的抗氧化、抗肿瘤和降低血糖等活性,在医药、食品和保健品等领域应用前景广阔[6-8]。
水提醇沉法为多糖提取的常用方法,但此方法存在生产周期长,醇沉后的液体制剂容易产生沉淀,易导致有效成分流失等缺点[9]。壳聚糖为甲壳素的脱乙酰基产物,在昆虫,甲壳类动物的外壳中广泛存在,因其兼具吸附和絮凝作用及良好的生物相容性,被广泛用于医药、食品、化工和农业等领域[10-12]。许昕等[13]对比了壳聚糖絮凝法和水提醇沉法对牛蒡多糖的纯化效果,结果表明壳聚糖絮凝法制备的多糖纯度更高,对DPPH自由基清除能力更强,对氧化应激酵母细胞的保护作用更强,说明壳聚糖絮凝法制备的牛蒡多糖具有更好的抗氧化活性。侯静宇等[14]分别采用壳聚糖絮凝法和传统水提醇沉法制备了黑木耳多糖,对比了二者生物活性,发现壳聚糖絮凝法制备的黑木耳多糖具有更高的降血糖和抗肿瘤活性。王学军等[15]对杜仲叶水提液进行壳聚糖絮凝法纯化,该方法制备的多糖,对药效组分具有较高的保留率,所得药液的澄清度较好。此外壳聚糖絮凝法已用于香菇多糖、灰树花多糖和金针菇多糖等食用菌多糖制备过程中,且此法制备的多糖在纯度、多糖损失率、蛋白质清除率等方面均明显优于传统水提醇沉法[16-18]。但壳聚糖絮凝法制备所得食用菌多糖,其理化特性与生物学活性是否优于传统水提醇沉法,国内外鲜有文献报道。本实验室前期侯静宇等[19]优化了壳聚糖絮凝法制备蛹虫草多糖工艺参数,然而此法制备的多糖与传统水提醇沉法制备多糖在表观特征、结构和生物活性方面是否存在差异,还有待深入对比研究。
本研究以蛹虫草发酵后菌丝体为材料,通过壳聚糖絮凝法和水提醇沉法分别制备蛹虫草多糖,从多糖得率、结构特性、粒径、复溶性和体外抗氧化、降血糖及抗肿瘤活性等方面进行了对比分析,研究结果可为蛹虫草多糖的开发利用奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
蛹虫草菌株 现保藏于河北师范大学应用真菌实验室;纤维素酶(11000 U/mg)、木瓜蛋白酶(0.5~2 U/mg)、α-葡萄糖苷酶(0.35 U/mL)、壳聚糖(脱乙酰度>90%)、阿卡波糖、顺铂 索莱宝生物科技有限公司;人肝癌细胞HepG2(1×106 cells/T25培养瓶) 上海弘顺生物科技有限公司;GK5011 BCA法蛋白定量试剂盒 上海捷瑞生物工程有限公司;其他试剂 国产分析纯。
YH-M10000型电子天平 瑞安市英恒电器有限公司;1510-03461型酶标仪 赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司;Heraeus Fresco 21型离心机 赛默飞科技有限公司;90 Plus Zeta型粒度分析仪 美国布鲁克海文仪器公司;VERTEX 70型红外光谱仪 布鲁克(北京)科技有限公司;S-4800型扫描电子显微镜 日立(中国)有限公司;UV2501pc型紫外可见分光光度计 岛津(上海)实验器材有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蛹虫草多糖的制备方法
将在固体培养基(PDA 斜面培养基,其配方为:马铃薯 20%,葡萄糖 2%,琼脂 2%,MgSO4 0.1%,KH2PO4 0.1%)中生长的蛹虫草接种于液体发酵培养基(配方:葡萄糖 2%,蛋白胨 1.5%,KH2PO4 0.5%,MgSO4 0.1%),采用500 mL摇瓶发酵,装液量200 mL,初始pH6.5,摇床转速160 r/min,培养温度23 ℃,发酵周期为18 d。发酵后菌液用40目滤网过滤,超纯水反复冲洗3次。冷冻干燥箱中进行干燥,至恒重,收获菌丝体。
1.2.1.1 菌丝体多糖提取
参照侯静宇等[19]建立的方法,将上述冻干后的菌丝体粉碎后,过40目筛,取20 g加入5%的复合酶水溶液800 mL(木瓜蛋白酶:纤维素酶=2:1),在50 ℃下浸提2 h后,再置于70 ℃下超声辅助提取70 min,离心,取上清液浓缩5倍,即可得到蛹虫草菌丝体粗多糖浸提液,于−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.1.2 壳聚糖絮凝法制备蛹虫草多糖
取粗多糖浸提液,加入1%壳聚糖-醋酸溶液,壳聚糖用量为1.4 mL/g,在絮凝温度为55 ℃,絮凝70 min,得到蛹虫草粗多糖纯化液,经55 ℃减压浓缩后,冷冻干燥,即得絮凝多糖XDT[19]。
1.2.1.3 水提醇沉法制备蛹虫草多糖
取粗多糖浸提液,加入无水乙醇,至其终浓度为80%,4 ℃静置过夜,真空抽滤得到粗多糖,随后用Sevag法去蛋白3次,冷冻干燥后得到醇沉多糖CDT[19]。
多糖得率(%)=(多糖冻干粉质量/原料干重)×100 1.2.2 蛹虫草多糖主要成分测定
取适量上述方法制备好的XDT和CDT两种多糖样品,采用苯酚-硫酸法测定样品中总糖含量[14],葡萄糖标准曲线的方程为Y=0.005X+0.0469,Y表示490 nm波长下吸光度值,X表示葡萄糖浓度(μg/mL),R2=0.999;采用BCA法检测样品中蛋白含量,测定步骤参考试剂盒说明书,蛋白质标准曲线的方程为Y=0.0037X+0.034,Y表示595 nm波长下吸光度值,X表示蛋白质浓度(μg/mL),R2=0.9991;采用咔唑-硫酸法[20]测定样品中糖醛酸含量,糖醛酸标准曲线的方程为Y=7.6856X+0.005,Y表示523 nm波长下吸光度值,X表示糖醛酸浓度(mg/mL),R2=0.9989;参考GB/T 5009.4-2016测定样品中灰分含量[21]。
1.2.3 蛹虫草多糖微观形态及结构特性分析
1.2.3.1 蛹虫草多糖扫描电镜分析
取制备的XDT和CDT两种多糖样品粉末粘于样品座的导电胶上后吹去浮样、喷金,进行冷场扫描电镜观察[22]。
1.2.3.2 蛹虫草多糖粒径测定
取制备的XDT和CDT两种多糖样品利用 Nano Brook 90Plus Zeta 仪测定多糖颗粒的粒径。
1.2.3.3 蛹虫草多糖傅里叶红外光谱分析
取制备的XDT和CDT两种多糖样品各1 mg与适量KBr混合研磨,真空压片制样,放入仪器中在4500~0 cm−1范围内进行红外光谱扫描。
1.2.3.4 蛹虫草多糖构象分析
取适量1.2.1制备的XDT和CDT两种多糖样品配成浓度1 g/L多糖溶液,并与刚果红溶液(5×10−6 mol/L)和不同浓度的NaOH溶液按体积比1:1:2混合并摇匀。在室温静置30 min后用分光光度计于400~600 nm范围下扫描,确定样品的最大吸收波长。结果分别以最大波长、NaOH浓度为纵、横坐标作图[23]。
1.2.4 两种蛹虫草多糖的复溶性比较
称取1.2.1制备的XDT和CDT两种多糖样品各0.1 g研磨成细粉,过40目筛,置于1 mL 70 ℃蒸馏水中,热水浴保持温度,每1 min观察两种多糖溶解情况并上下振摇10 s,直至无肉眼可见颗粒即为完全溶解[14, 24]。
1.2.5 两种蛹虫草多糖体外生物活性对比分析
1.2.5.1 抗氧化活性测定
分别配制浓度为1、2、4、6和8 mg/mL的XDT和CDT多糖溶液,阳性对照组以VC 代替多糖溶液,配制成相同浓度(现用现配)。
a.DPPH自由基清除能力的测定:参考国利超等[25]建立的方法,分别向样品溶液中加入2 mL 0.2 mmol/L DPPH-乙醇溶液振荡混匀,避光反应30 min,测定样品在517 nm波长处吸光度记为Ai;样品溶液中加入2 mL无水乙醇,测定吸光度记为Aj;DPPH-乙醇溶液和无水乙醇各2 mL混合,测定吸光度记为A0。
b.羟自由基清除能力的测定:参考Govindan等建立的方法[26],取样品溶液1.0 mL,加入6 mmol/L的FeSO4溶液、6 mmol/L的H2O2溶液、6 mmol/L的水杨酸-乙醇溶液各1 mL,37 ℃水浴1 h后在510 nm波长处测定吸光值记为Ai;蒸馏水代替样品溶液记为A0;用蒸馏水代替H2O2溶液记为Aj。
c.超氧阴离子自由基清除能力的测定:参考Najafabad等建立的方法[27],分别取100 μL样品溶液,加入100 μL浓度为50 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH8.2)缓冲液,置于25 ℃水浴加热20 min,取出后加入邻苯三酚-HCl(30 mmol/L),精确反应6 min,立即滴入7 μL浓度为4 mol/L HCl终止反应,在325 nm波长处测定吸光度值,记为Ai。以0.1 mol/L HCl代替邻苯三酚溶液,测定325 nm吸光值,记为Aj。以蒸馏水代替样品溶液作对照组在325 nm波长处测定吸光度值,记为A0,按下式计算清除率:
自由基清除率(%)=(1−Ai−AjAo)×100 1.2.5.2 抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性测定
取适量1.2.1制备的两种多糖样品复溶,以阿卡波糖作为阳性对照,参照侯静宇等[14]建立的方法进行α-葡萄糖苷酶活性测定,并计算抑制率。按下列公式计算α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制率:式中以A1表示加入样品的反应液的吸光值;A2表示不加样品的反应液的吸光值;A表示为加入样品但不加酶的反应液的吸光值。
酶活抑制率(%)=(1−A1−A2A)×100 1.2.5.3 抑制肿瘤细胞增殖活性测定
参照侯静宇等[14]建立的方法,以顺铂作为阳性对照,采用CCK-8法检测细胞活性。根据下列公式计算处理后的细胞抑制率(%)。公式中,Ac表示对照孔吸光度;As表示实验孔吸光度;Ab表示空白孔吸光度。
细胞抑制率(%)=Ac−AsAc−Ab×100 1.3 数据处理
采用Excel及SPSS17.0软件进行统计分析,采用Duncan检验进行显著性分析,实验结果以“平均值±标准差”表示,每次实验重复3次。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 两种方法制备的蛹虫草多糖得率和主要成分含量分析
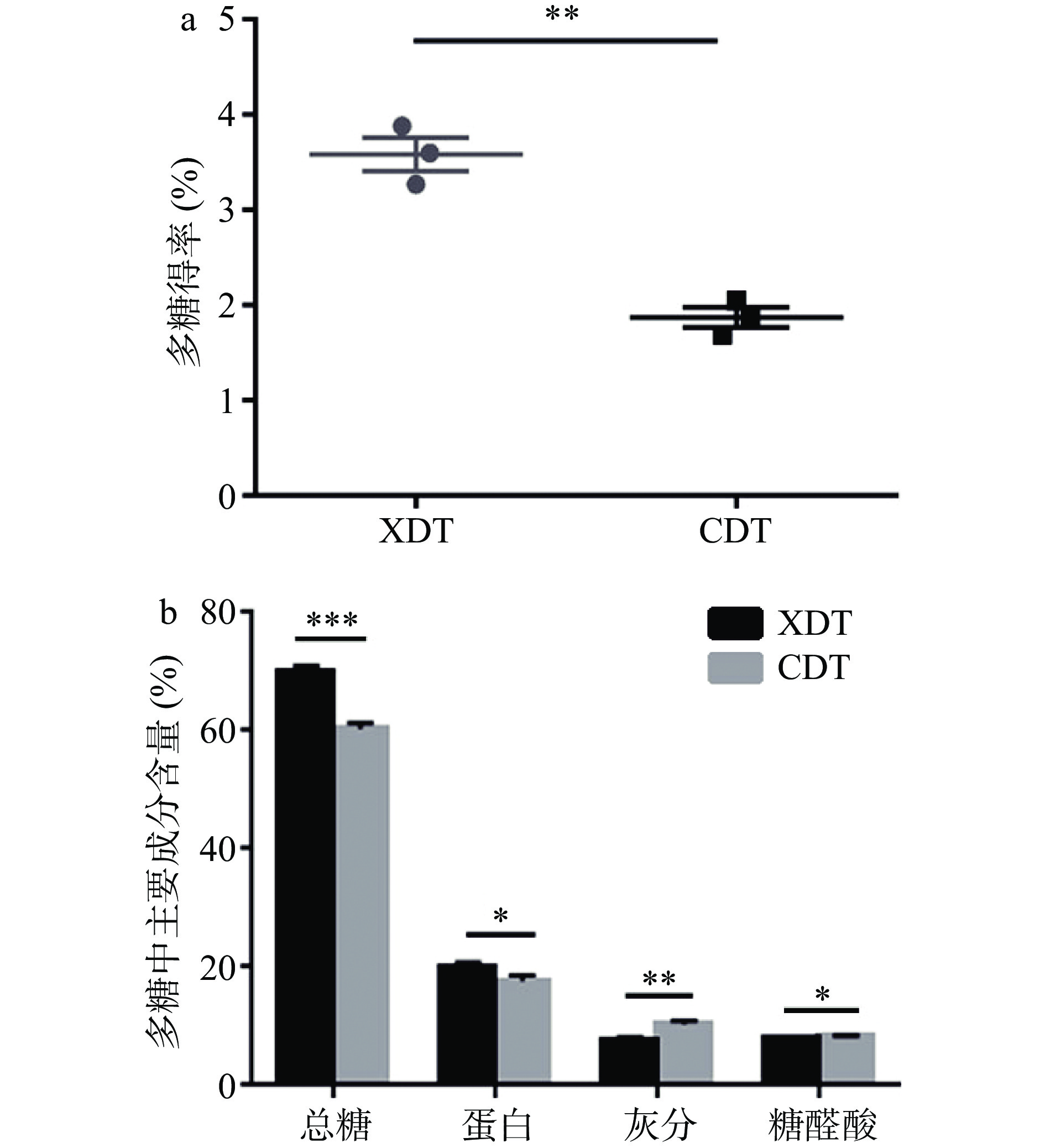
对两种方法制备的蛹虫草多糖得率进行分析,结果表明壳聚糖絮凝法制备所得絮凝多糖(XDT)得率可达3.58%,是醇沉多糖(CDT)的1.91倍,两者具有显著性差异(P<0.01)(图1a),这与文献中报道的,壳聚糖絮凝法制备的牛蒡多糖和黑木耳多糖得率显著高于水提醇沉法的结果类似[13-14]。可能是由于壳聚糖具有的电中和及吸附架桥作用,可有效去除多糖溶液中的杂质,使多糖得率显著提高[14]。
对两种蛹虫草多糖中主要成分含量进行分析可知,XDT和CDT两种方法制备多糖主要成分均为总糖、蛋白质和灰分,三者总含量分别占据总质量的95.31%和88.39%。其中,XDT的总糖含量为70.02%,是CDT的1.16倍,通过方差分析可知两者差异极其显著(P<0.001) (图1b),但是糖醛酸含量(图1b)相较于CDT有所降低,可能是由于壳聚糖中含有一定量的活性氨基,为天然存在的碱性多糖,容易与糖醛酸中的酸性基团产生静电吸引作用而产生絮凝[28],以沉淀形式析出,使其含量降低。XDT的蛋白质含量为19.83%,而CDT的蛋白质含量为17.66%,两者差异较为显著(P<0.05);XDT和CDT中灰分含量分别为7.63%和10.37%,两者差异显著(P<0.01)(图1b)。絮凝法制备的蛹虫草多糖中含有一定量的蛋白组分和灰分等成分,仍属于粗多糖,若无法满足纯度需求,可通过葡聚糖凝胶层析法、二乙氨基乙基纤维素52(DEAE-52)柱层析等方法进一步纯化,提高多糖纯度[9]。综上,与醇沉法相比较,絮凝法能够显著提高蛹虫草多糖的得率和多糖成分中的总糖含量占比。
2.2 两种蛹虫草多糖结构特性分析
2.2.1 蛹虫草多糖扫描电镜形态观察
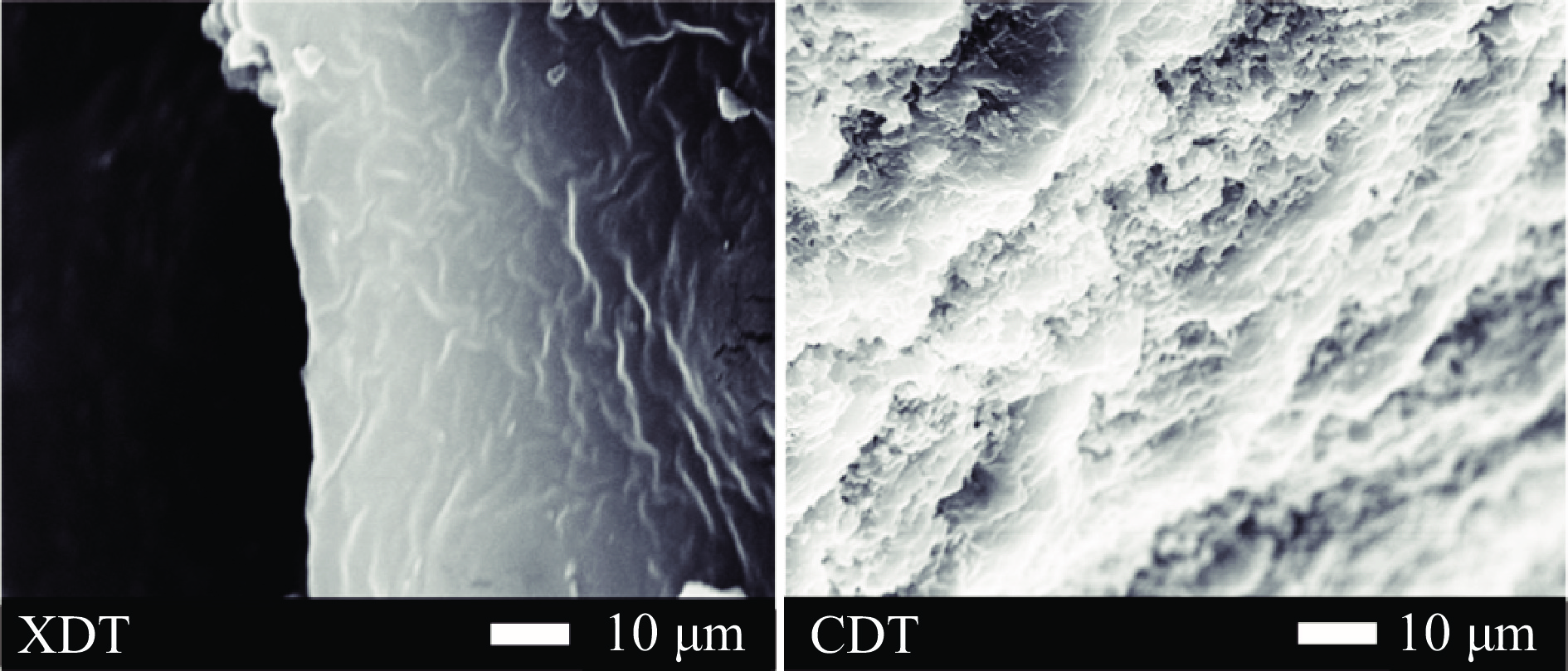
在扫描电镜下,XDT(图2)颗粒规整,表面光滑,具有鳞片纹路,结构紧密无明显褶皱;而CDT(图2)表面褶皱明显,具有疏松的网状结构,二者在扫描电镜下形态差异明显,可能由于两种多糖中各组分的含量占比不同,CDT中的蛋白类和糖醛酸含量低,多糖颗粒间的相互作用点较少,颗粒相互作用较小,使得多糖颗粒间的聚集程度降低,从而呈现出无规则的颗粒状态[29]。
2.2.2 蛹虫草多糖傅里叶红外光谱分析
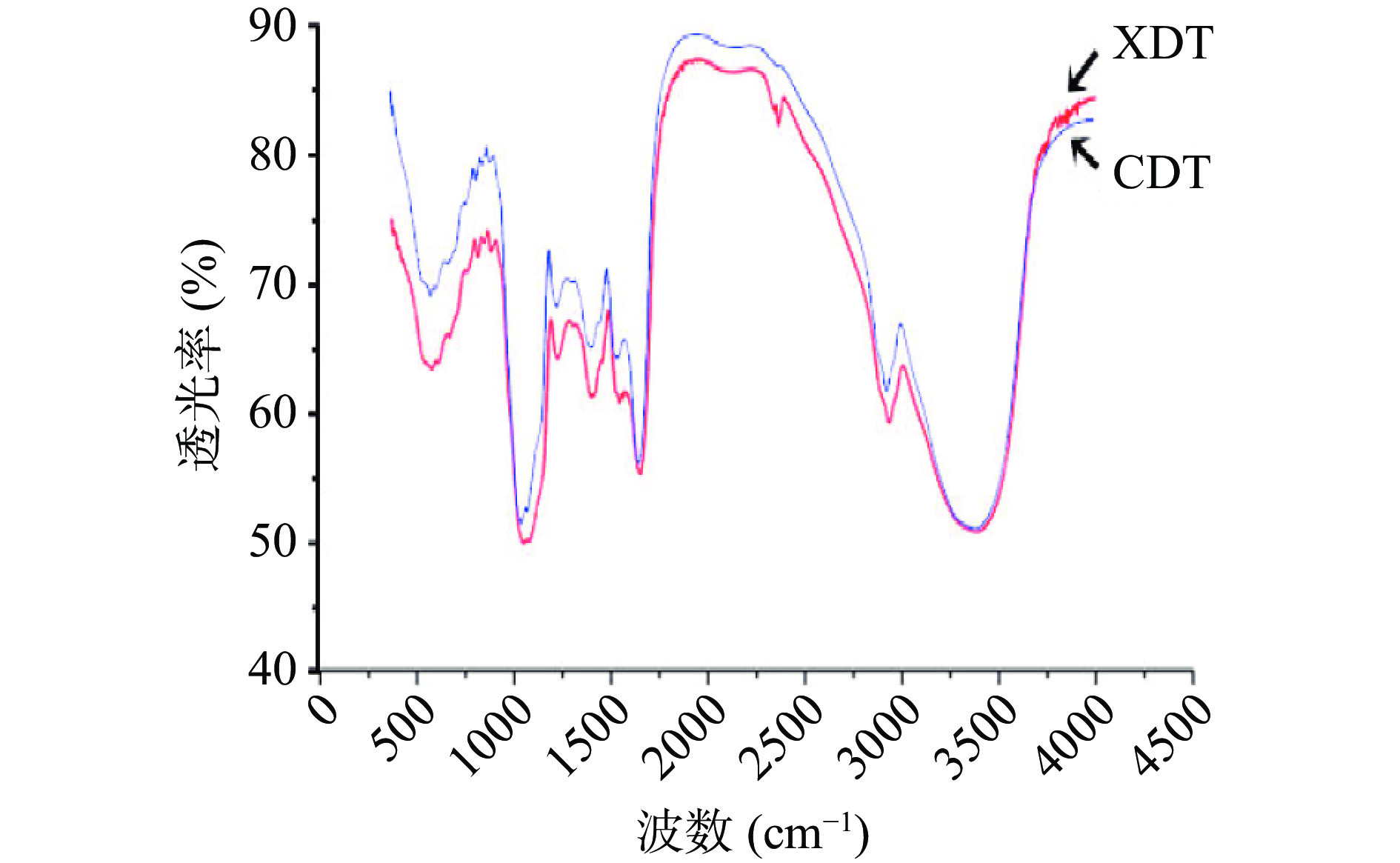
XDT和CDT红外图谱基本吻合,说明壳聚糖絮凝法和醇沉法制备的多糖的官能团没有明显差异(图3)。具体分析图谱可知,3500~3000 cm−1的一组峰是O-H和N-H的伸缩振动;3000~2800 cm−1的一组峰是糖类C-H伸缩振动。1700 cm−1附近的吸收峰为羧基的酯键C=O的伸缩振动;1600 cm−1附近的吸收峰是由酰胺基的C=O伸缩振动、N-H变角振动引起的;1400~1200 cm−1的一组峰是由糖类化合物的亚甲基、甲基C-H以及羧基C-O、O-H变角振动引起;1200~1000 cm−1的一组峰是吡喃糖环醚键、羟基以及环内醚C-O伸缩振动引起的。1100~1000 cm−1的一组峰为多糖的一级羟基变角、二级羟基变角振动;750和800 cm−1附近的吸收峰分别为吡喃环对称伸缩振动和C-H变角振动,两种方法制备的多糖在FT-IR光谱中测得的峰形相似,均具有多糖的特征吸收峰[7]。
2.2.3 蛹虫草多糖构象分析
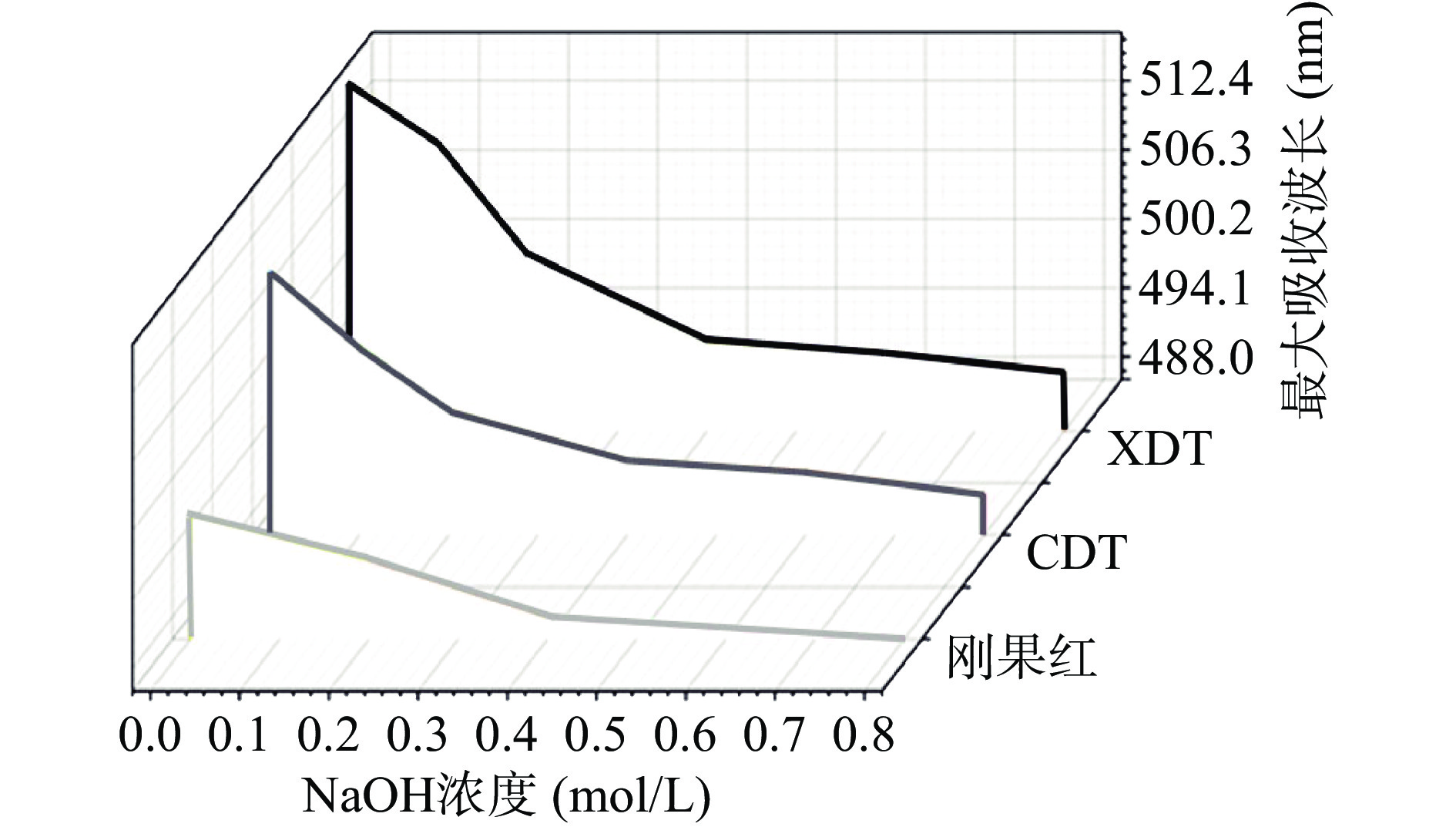
刚果红分子能够与多糖三螺旋结构中的β-葡聚糖结合,最大吸收峰由493 nm迁移至更高吸收波长,即发生红移,且三螺旋结构的含量与吸收值的增加呈现量效关系[30]。在0~0.8 mol/L范围内,XDT和CDT两种多糖最大吸收波长随NaOH浓度的改变而变化,两者均产生红移现象,说明两种多糖均具有规则的三螺旋结构(图4)。与CDT相比,XDT的红移现象更明显,说明其比CDT存在更多的三螺旋结构[30]。研究表明,三螺旋结构能够影响多糖的抗肿瘤、抗菌和免疫调节等方面生物活性[31-32]。刚果红实验结果显示,XDT比CDT具有更多的三螺旋结构,预示着XDT可能具有更高的生物活性[30]。
2.3 两种蛹虫草多糖的粒径分析
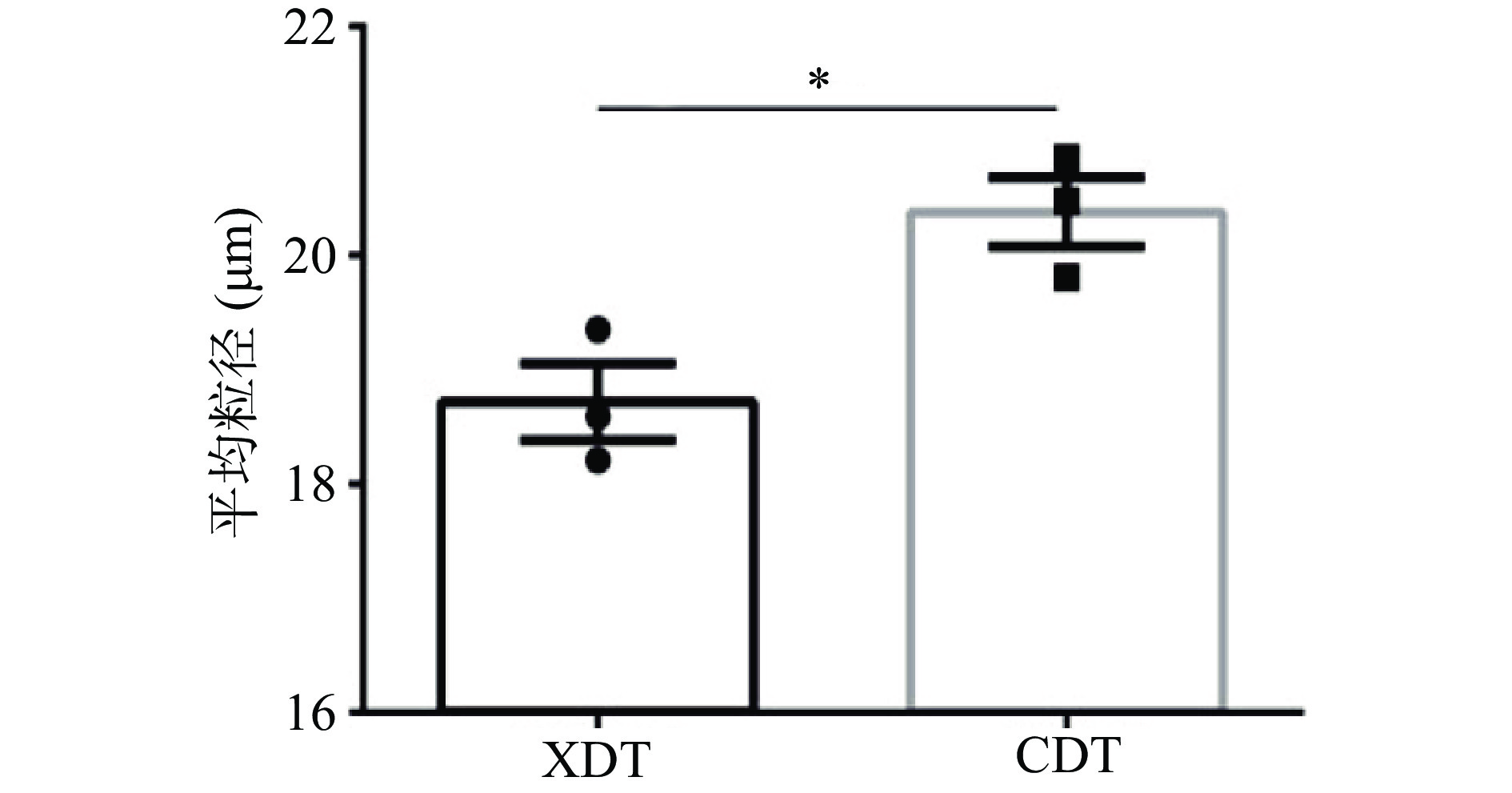
两种方式得到的多糖在水溶液中的平均粒径具有显著差异,其中XDT的平均粒径为18.72±0.58 μm,而CDT的平均粒径为20.38±0.53 μm(图5)。多糖粒径的大小直接影响流变学性质、消化特性、改性效果和热力学性质,平均粒径作为体系内所有颗粒的均一值具有重要的参考意义,XDT平均粒径减少可能是由于在絮凝操作过程中,破坏了多糖分子间的氢键或范德华力,导致分子间相互作用减弱,从而使其粒径减小[33]。
2.4 两种蛹虫草多糖的复溶性分析
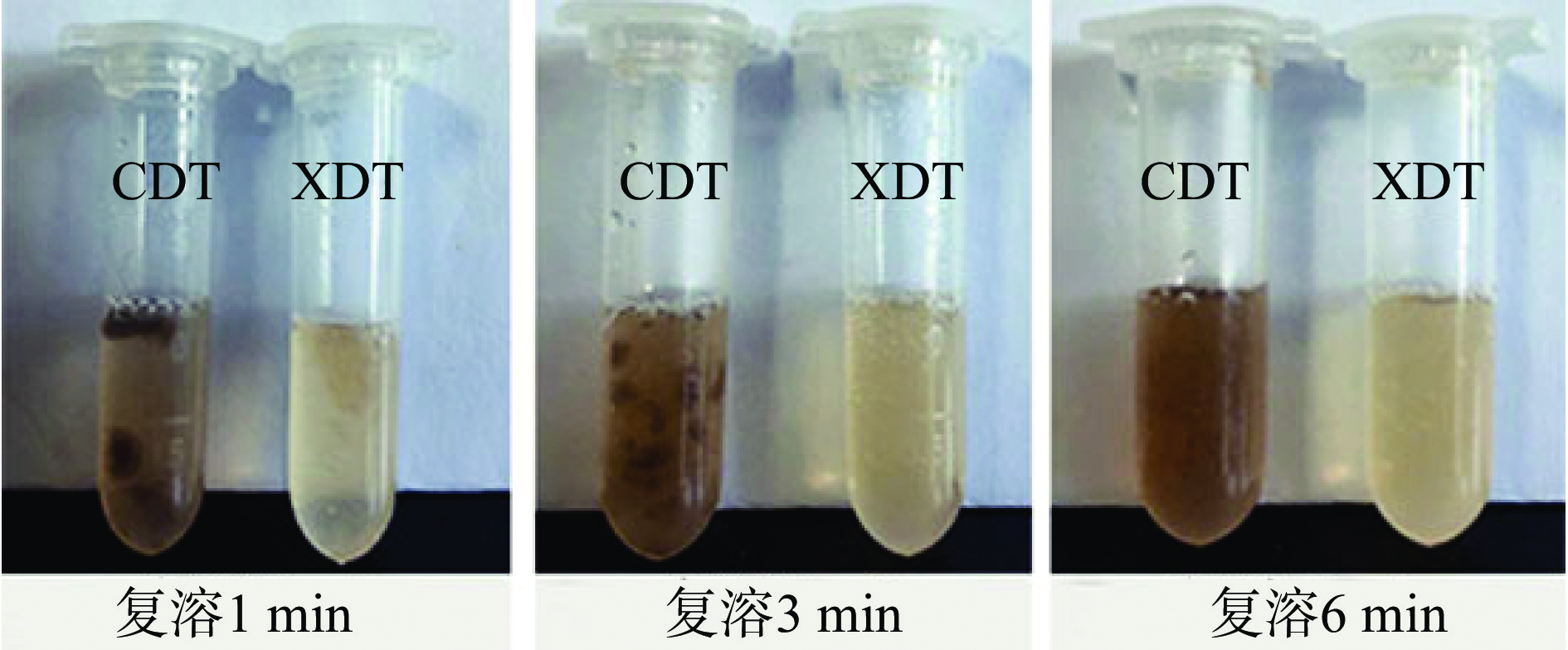
0~1 min时,XDT颗粒开始溶解并逐步向周围扩散,而CDT颗粒散布于溶液中,未发生明显溶解;2~3 min时,XDT基本溶解,CDT颗粒开始溶解,但相较于XDT溶解速度低;到6 min时,XDT完全溶解,溶解后颜色为浅黄色,液体清澈透亮;CDT复溶后溶液为灰色,液体浑浊,透光性差(图6)。与侯静宇等[14]制备的絮凝黑木耳多糖优于醇沉黑木耳多糖的结果类似。综上所述,XDT的复溶速度、复溶后溶液颜色和澄清度优于CDT。
2.5 两种蛹虫草多糖体外生物活性对比分析
2.5.1 体外抗氧化能力分析
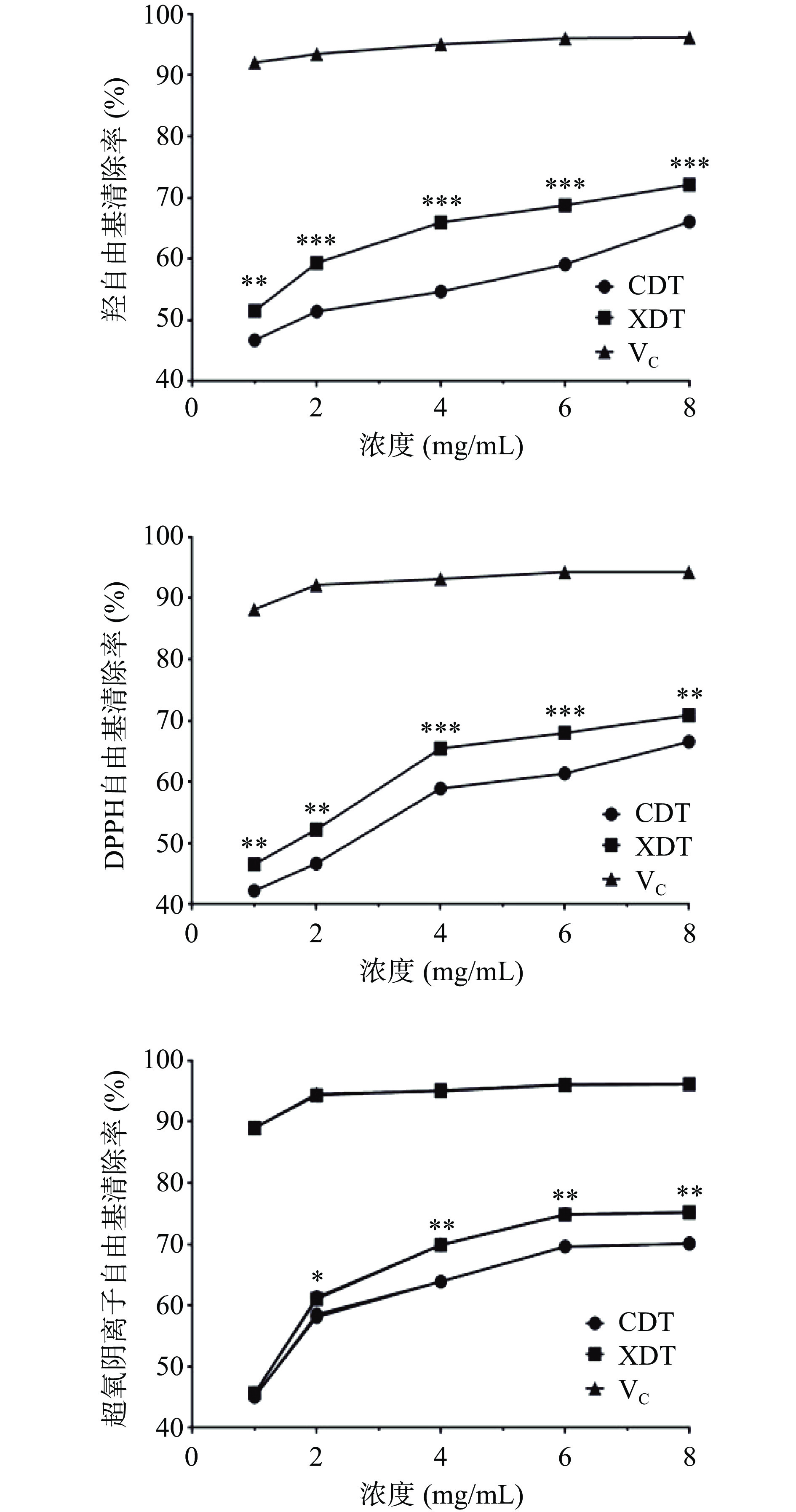
以维生素C为阳性对照,研究了XDT和CDT对DPPH和超氧阴离子和羟自由基的清除能力。两种多糖对三种自由基的清除能力随处理浓度的增加而逐渐升高,呈明显的量效关系。在处理浓度为1 mg/mL时,两种多糖对超氧阴离子自由基的清除能力无明显差异,在其余相同的处理浓度下,对三种自由基清除能力均表现为XDT>CDT。XDT在处理浓度为8 mg/mL时,对超氧阴离子的清除率达到最高值75.54%±0.73%,而CDT为69.93%±0.64%;在浓度为8 mg/mL时,XDT对羟自由基的清除作用达到最高值为71.17%±0.25%,高于CDT的66.67%±0.71%;XDT和CDT对于DPPH自由基的清除能力相比前两者较弱,在相同处理浓度下,XDT为72.17%±0.25%,而CDT为67.67%±0.65%(图7)。蛹虫草多糖的抗氧化活性与其还原力密切相关,还原力一般是由分子中具有供氢能力的物质提供,推测其机理为,具有还原性的物质可将其分子中的氢原子提供给DPPH和羟自由基,从而使其转变为非自由基产物,从而消除其对机体的损害,多糖中的糖醛酸,通过激发多糖链中端基碳的氢原子,使其具有较强的供氢能力,絮凝多糖中的糖醛酸含量明显高于醇沉多糖,可能使其具有更高的还原力,因此具有更强的抗氧化活性[8]。
2.5.2 体外α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性分析
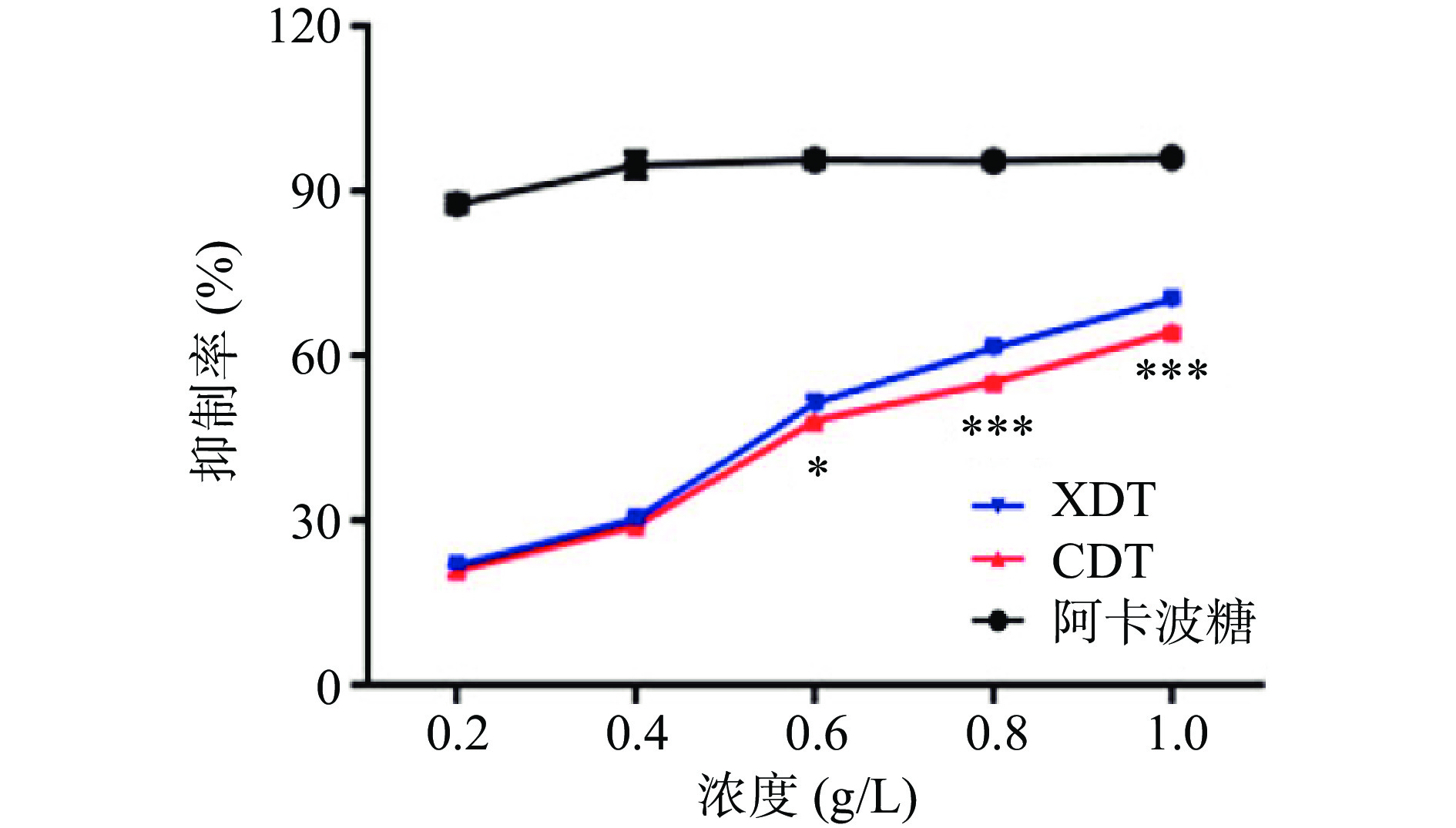
以阿卡波糖为阳性对照,研究了XDT和CDT对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制活性。两种多糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性随处理浓度的增加而逐渐升高,呈明显的量效关系。在0.2和0.4 g/L浓度时,两者的抑制率没有显著性差异(P>0.05),而随着浓度的增加,在相同浓度条件下,XDT的抑制活性明显强于CDT。当浓度达到0.8~1.0 g/L时,两者具有极其显著的差异(P<0.001)(图8)。α-葡萄糖苷酶是调控餐后血糖的重要靶点,抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性可有效降低餐后血糖,多糖的结构与其降血糖活性密切相关,其中高级结构、分子量和单糖组成均会影响其降血糖活性,如黄精多糖、猪苓多糖和马尾藻多糖中含有的三螺旋结构,与其降糖活性密切相关,而XDT比CDT含有更多的三螺旋结构,可能使XDT具有更强的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性[34]。此外,提取方法也会影响多糖的结构进而影响其生物活性,絮凝法操作步骤简单,不需要使用氯仿、酒精等有机试剂,可能有助于保持多糖的高级结构,保留其活性,使絮凝法制备的多糖具有较高的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性[14]。
2.5.3 体外抑制肿瘤细胞增殖能力分析
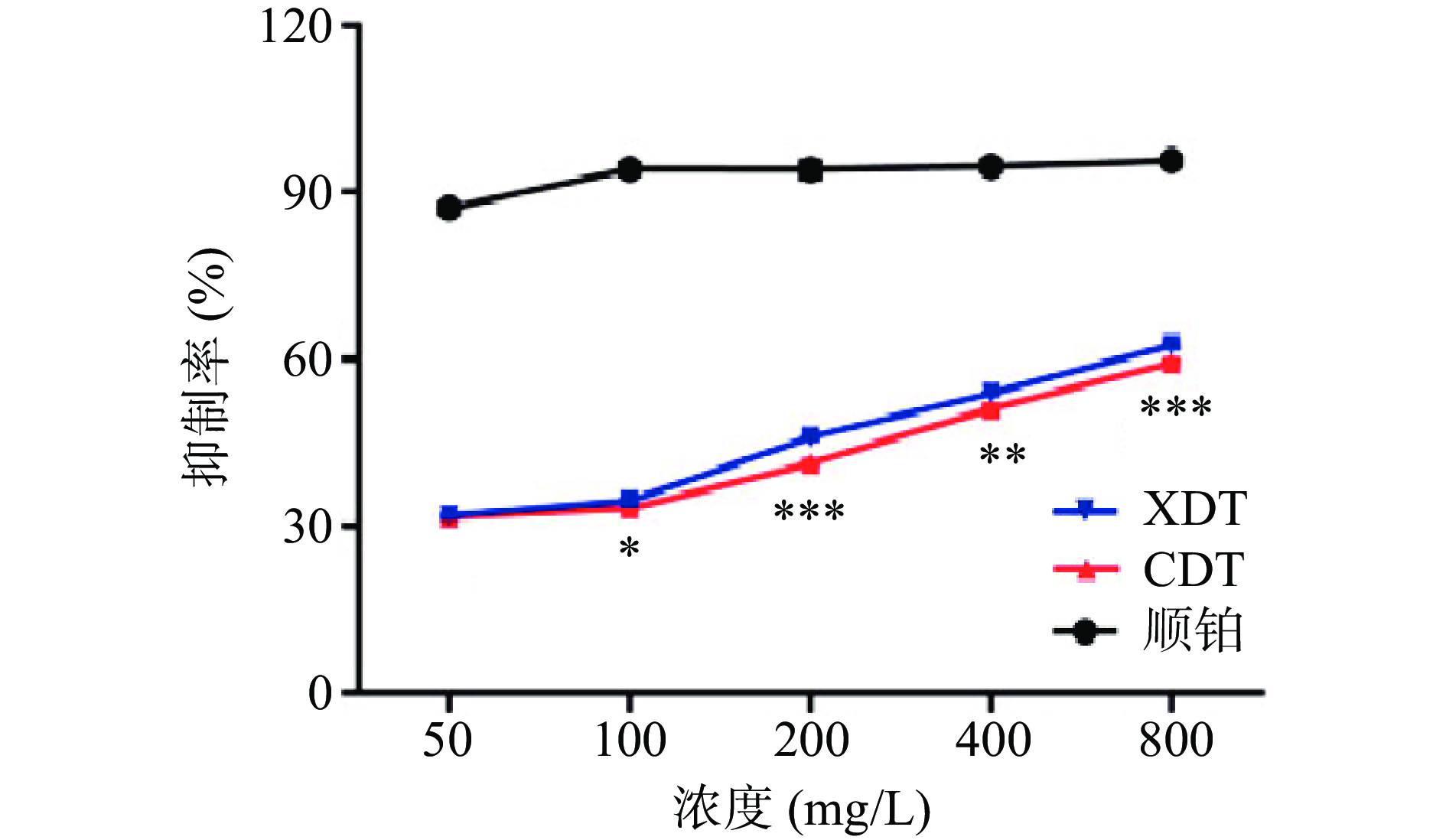
以顺铂为阳性对照,研究了XDT和CDT对HepG2细胞增殖的抑制能力。两种多糖对HepG2细胞增殖的抑制能力随着处理浓度的增大而升高,除低浓度50 mg/L以外,在相同处理浓度条件下对HepG2细胞的增殖抑制作用均为XDT>CDT,两者具有显著性差异(P<0.05),在200和800 mg/L下达到了极其显著的差异,最大浓度800 mg/L时,XDT对HepG2细胞的抑制率达到最大值62.56%±0.73%(图9)。研究表明,三螺旋结构能够影响多糖的抗肿瘤活性[32-33],前人从蛹虫草菌丝体和子实体中分离的两种多糖(CMPS-II和CBPS-II)可以通过上调凋亡因子的表达,并下调增殖细胞核抗原表达,达到抑制肿瘤细胞增殖的作用,这两种多糖均具有三螺旋骨架结构[7],XDT比CDT具有更强的抑制肿瘤细胞增殖能力,可能是由于XDT中具有更多的三螺旋结构。
3. 讨论与结论
本研究采用壳聚糖絮凝法和传统水提醇沉法分别制备了蛹虫草多糖,对两种多糖的形态结构特征、复溶性和体外抗氧化、抗肿瘤及降糖活性等进行了比较。结果表明,与醇沉法相比较,絮凝法能够显著提高多糖的得率和多糖成分中的总糖含量占比;两种多糖物理特征上具有明显差异,扫描电镜观察发现,XDT颗粒大小、颜色均一度等指标显著优于CDT,粒径分析和多糖复溶性分析进一步地证实,XDT相较于CDT平均粒径更小,复溶速度更快;两种多糖的红外图谱没有明显差异,但XDT比CDT具有更多的三螺旋结构;XDT的体外抗氧化活性、α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性和抗肿瘤活性均优于CDT。
在实验过程中,我们对比分析了絮体(壳聚糖与多糖溶液絮凝后产生的沉淀)和壳聚糖颗粒的红外光谱图,初步发现与壳聚糖颗粒相比,絮体在1500~1100 cm−1附近处的吸收峰发生了明显偏差,这一区域出现的吸收峰,主要是由糖类化合物的亚甲基、甲基C-H以及羧基C-O变角等振动引起,这说明壳聚糖分子确实参与了絮凝作用[7],但具体的絮凝机制,需要进一步的实验验证。本研究仅对比了XDT和CDT的体外生物活性,但XDT在体内的生物活性是否优于CDT,还需进一步实验验证。综上,壳聚糖絮凝法制备蛹虫草多糖具有良好的应用前景,研究结果为蛹虫草多糖在抗氧化、抗肿瘤和降血糖等功效产品的开发提供了理论基础。
-
-
[1] 董彩虹, 李文佳, 李增智, 等. 我国虫草产业发展现状、问题及展望——虫草产业发展金湖宣言[J]. 菌物学报,2016,35(1):1−15. [DONG C H, LI W J, LI Z Z, et al. Cordyceps industry in China: current status, challenges and perspectives—Jinhu declaration for cordyceps industry development[J]. Mycosystema,2016,35(1):1−15. DONG C H, LI W J, LI Z Z, et al. Cordyceps industry in China: current status, challenges and perspectives—Jinhu declaration for cordyceps industry development[J]. Mycosystema, 2016, 35(1): 1−15.
[2] LIU Y, GUO Z J, ZHOU X W. Chinese cordyceps: Bioactive components, antitumor effects and underlying mechanism: A review[J]. Molecules,2022,27(19):6576. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196576
[3] 左锦辉, 贡晓燕, 董银卯, 等. 蛹虫草的活性成分和药理作用及其应用研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(21):330−339. [ZUO J H, GONG X Y, DONG Y M, et al. Research achievements in bioactive components, pharmacological effects and applications of Cordyceps militaris[J]. Food Science,2018,39(21):330−339. ZUO J H, GONG X Y, DONG Y M, et al. Research achievements in bioactive components, pharmacological effects and applications of Cordyceps militaris[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(21): 330−339.
[4] XU J, SHEN R, JIAO Z, et al. Current advancements in antitumor properties and mechanisms of medicinal components in edible mushrooms[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(13):2622. doi: 10.3390/nu14132622
[5] PHULL A R, AHMED M, PARK H J. Cordyceps militaris as a bio-functional food source: Pharmacological potential, anti-inflammatory actions and related molecular mechanisms[J]. Microorganisms,2022,10(2):405. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020405
[6] YAN J K, WANG W Q, WU J Y. Recent advances in Cordyceps sinensis polysaccharides: Mycelial fermentation, isolation, structure, and bioactivities: A review[J]. Journal of Functional Food,2014(6):33−47.
[7] MIAO M, YU W Q, LI Y, et al. Structural elucidation and activities of Cordyceps militaris-derived polysaccharides: A review[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022(9):898674.
[8] LEE C T, HUANG K S, SHAW J F, et al. Trends in the immunomodulatory effects of Cordyceps militaris: Total extracts, polysaccharides and cordycepin[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2020(11):575704.
[9] 赵炳杰, 郭岩彬. 食用菌多糖的提取纯化及生物活性研究进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志,2022,42(Z1):146−159. [ZHAO B J, GUO Y B. Advances in extraction, purification and bioactivity of polysaccharides from edible fungi[J]. China Biotechnology,2022,42(Z1):146−159. ZHAO B J, GUO Y B. Advances in extraction, purification and bioactivity of polysaccharides from edible fungi[J]. China Biotechnology, 2022, 42(Z1): 146−159.
[10] PENG W, LI D, DAI K, et al. Recent progress of collagen, chitosan, alginate and other hydrogels in skin repair and wound dressing applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,208:400−408. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.002
[11] DUTTA J, TRIPATHI S, DUTTA P K. Progress in antimicrobial activities of chitin, chitosan and its oligosaccharides: A systematic study needs for food applications[J]. Food Science and Technology International,2012,18(1):3−34. doi: 10.1177/1082013211399195
[12] CHEN Q, QI Y, JIANG Y, et al. Progress in research of chitosan chemical modification technologies and their applications[J]. Marine Drugs,2022,20(8):536. doi: 10.3390/md20080536
[13] 许昕, 侯静宇, 王立安. 壳聚糖絮凝法纯化牛蒡多糖的工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(24):178−184. [XU X, HOU J Y, WANG L A. Optimization of purification process of polysaccharide from Arctium lappa L. by chitosan flocculation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(24):178−184. XU X, HOU J Y, WANG L A. Optimization of purification process of polysaccharide from Arctium lappa l.by chitosan flocculation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(24): 178−184.
[14] 侯静宇, 国利超, 鲁玉佳, 等. 两种不同方法制备的黑木耳多糖性质比较[J]. 菌物学报,2020,39(7):1429−1436. [HOU J Y, GUO LC, LU Y J, et al. Optimization of preparation method and property analysis of Auricularia heimuer polysaccharide[J]. Mycosystema,2020,39(7):1429−1436. HOU J Y, GUO LC, LU Y J, et al. Optimization of preparation method and property analysis of Auricularia heimuer polysaccharide[J]. Mycosystema, 2020, 39(7): 1429−1436
[15] 王学军, 徐恒, 程敏, 等. 以壳聚糖为絮凝剂的杜仲叶水提液澄清工艺优化[J]. 国际药学研究杂志,2018,45(2):150−153, 162. [WANG X J, XU H, CHENG M, et al. Optimization technology of the clarification process for the water-extracted solution of Folium Eucommiae with chitosan flocculant[J]. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research,2018,45(2):150−153, 162. WANG X J, XU H, CHENG M, et al. Optimization technology of the clarification process for the water-extracted solution of Folium Eucommiae with chitosan flocculant[J]. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research, 2018, 45(2): 150−153+162.
[16] 谢红旗, 刘东波, 肖深根, 等. 壳聚糖絮凝纯化香菇多糖的研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2010,22(1):77−80, 125. [XIE H Q, LIU D B, XIAO S G et al. Study on purification of lentinan by flocculation of chitosan[J]. Research and Development of Natural Products,2010,22(1):77−80, 125. XIE H Q, LIU D B, XIAO S G et al. Study on purification of lentinan by flocculation of chitosan[J]. Research and Development of Natural Products, 2010, 22(1): 77−80+125.
[17] 满宁, 孙盼, 韩伟. 灰树花子实体多糖的微波提取及絮凝纯化工艺[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版),2015,37(6):99−104. [MAN N, SUN P, HAN W. Application of microwave−flocculation technology in extraction and purification of polysaccharides from Grifola frondose[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition),2015,37(6):99−104. MAN N, SUN P, HAN W. Application of microwave−flocculation technology in extraction and purification of polysaccharides from Grifola frondose[J]. Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 37(6): 99−104.
[18] 罗文锋, 韩伟. 金针菇多糖的壳聚糖絮凝工艺优化[J]. 食用菌学报,2015,22(2):68−71. [LUO W F, HAN W. Optimization of chitosan-based flocculation and purification of polysaccharides from aqueous extracts of Flammulina velutipes[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi,2015,22(2):68−71. LUO W F, HAN W. Optimization of chitosan-based flocculation and purification of polysaccharides from aqueous extracts of flammulina velutipes[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2015, 22(2): 68−71.
[19] 侯静宇, 赵佳启, 张金秀, 等. 壳聚糖絮凝蛹虫草菌丝体多糖工艺优化及其失活动力学分析[J]. 菌物学报,2020,39(12):2346−2354. [HOU J Y, ZHAO J Q, ZHANG J X, et al. Optimization of chitosan flocculation of Cordyceps militaris polysaccharide and analysis of inactivation mechanics of chitosan[J]. Mycosystema,2020,39(12):2346−2354. HOU J Y, ZHAO J Q, ZHANG J X, et al. Optimization of chitosan flocculation of Cordyceps militaris polysaccharide and analysis of inactivation mechanics of chitosan[J]. Mycosystema, 2020, 39(12): 2346−2354.
[20] 郑婷婷, 严亮, 张文杰, 等. 水碱连续提取黄皮疣柄牛肝菌粗多糖的理化性质及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(15):84−89. [ZHENG T T, YAN L, ZHANG E J, et al. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of water-alkai continuous extraction of crude polysaccharides from Leccinellum crocipodium (letellier.) watliag[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(15):84−89. ZHENG T T, YAN L, ZHANG E J, et al. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of water-alkai continuous extraction of crude polysaccharides from Leccinellum crocipodium (letellier. ) watliag[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(15): 84−89.
[21] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB/T 5009.4-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中灰分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 China’s National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB/T 5009.4−2016. National food safety standard Determination of ash in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[22] 秦利鸿, 曹建波, 易伟松. 绿茶多糖的扫描电镜制样新方法及原子力显微镜观察[J]. 电子显微学报,2009,28(2):162−167. [QING L H, CAO J B, YI W S. A new method for scanning electron microscope samples of polysaccharides distilled from green tea and observation of ultrafine structure of them with atomic force microscope[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society,2009,28(2):162−167. QING L H, CAO J B, YI W S. A new method for scanning electron microscope samples of polysaccharides distilled from green tea and observation of ultrafine structure of them with atomic force microscope[J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2009, 28(2): 162−167.
[23] 贾俊强, 沈健, 陈炼, 等. 蛹虫草多糖的酶法修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(1):114−120. [JIA J Q, SHEN J, CHEN L, et al. Enzymatic modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Cordyceps militaris fruit bodies[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(1):114−120. JIA J Q, SHEN J, CHEN L, et al. Enzymatic modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Cordyceps militaris fruit bodies[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(1): 114−120.
[24] 杨生兵. 灰树花子实体和发酵菌丝体成分及多糖比较研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2012 YANG S B. Comparative study on components and polysaccharides of fruiting body and fermented mycelium of grifola frondosa[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2012.
[25] 国利超, 吕建华, 姚澜, 等. 朱红栓菌提取物抗氧化、抗肿瘤活性评价及相关化学成分分析[J]. 菌物学报,2018,37(6):772−781. [GUO L C, LÜ J H, YAO L, et al. Antioxidant and anti-tumor activities and main chemical constituent analysis of Trametes cinnabarina fruiting body extract[J]. Mycosystema,2018,37(6):772−781. GUO L C, LV J H, YAO L, et al. Antioxidant and anti-tumor activities and main chemical constituent analysis of Trametes cinnabarina fruiting body extract[J]. Mycosystema, 2018, 37(6): 772−781.
[26] GOVINDAN S, JOHNSON E, CHRISTOPHER J, et al. Antioxidant and anti-aging activities of polysaccharides from Calocybe indica var. APK2[J]. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology,2016,68(6):329−334. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2016.04.001
[27] NAJAFABAD A M, JAMEI R. Free radical scavenging capacity and antioxidant activity of methanolic and ethanolic extracts of plum (Prunus domestica L.) in both fresh and dried samples[J]. Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine,2014,4(4):343−353.
[28] 袁毅桦. 基于壳聚糖与海藻酸钠的改性聚合物的制备结构与性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012 YUAN Y H. Preparation, structure and properties of modified polymers based on chitosan and sodium alginate[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2012.
[29] 陈薛, 左欣欣, 徐安安, 等. 不同茶树品种鲜叶多糖的理化性质和抗氧化活性比较研究[J]. 茶叶科学,2022,42(6):806−818. [CHEN X, ZUO X X, XU A A, et al. Comparative study on the physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides in different tea cultivars[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2022,42(6):806−818. CHEN X, ZUO X X, Xu A A, et al. Comparative study on the physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides in different tea cultivars[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2022, 42(6): 806-818.
[30] 王志, 谢婷, 李冬芝, 等. 酵母三股螺旋结构β-葡聚糖测定方法研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2014,30(11):213−217, 222. [WANG Z, XIE T, LI D Z, et al. Method to determine the triple-helical β-glucan content in yeast[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2014,30(11):213−217, 222. WANG Z, XIE T, LI D Z, et al. Method to determine the triple-helical β-glucan content in yeast[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2014, 30(11): 213-217+222.
[31] YANG X, WEI S, LU X, et al. A neutral polysaccharide with a triple helix structure from ginger: Characterization and immunomodulatory activity[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,350:129261. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129261
[32] MENG Y, ZHANG H, HU N, et al. Construction of silver nanoparticles by the triple helical polysaccharide from black fungus and the antibacterial activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,182:1170−1178. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.130
[33] REN Y P, LIU S X. Effects of separation and purification on structural characteristics of polysaccharide from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.)[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2022,552(2):286−291.
[34] 杨玉洁, 刘静宜, 谭艳, 等. 多糖降血糖活性构效关系及作用机制研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(23):355−363. [YANG Y J, LIU J Y, TAN Y, et al. Progress in understanding the structure-activity relationship and hypoglycemic mechanism of polysaccharides[J]. Food Science,2021,42(23):355−363. YANG Y J, LIU J Y, TAN Y, et al. Progress in understanding the structure-activity relationship and hypoglycemic mechanism of polysaccharides[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(23): 355-363.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张涛,周芷夷,邓文奇,张婷,马杰,王艺诺,于俊飞,周建中. 苦杏仁多肽/壳聚糖复合膜的制备及其对奶酪的保鲜效果. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(06): 232-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



