Study on the Physicochemical Properties of Polysaccharide from Polygonatum sibiricum and Its Protective Effect on D-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Damage in Mice
-
摘要: 本研究从黄精根茎部位提取、分离纯化一种均一多糖组分,分析其理化性质和对氧化损伤的保护作用,并探讨其潜在的保护机制。采用水提醇沉、DEAE-纤维素阴离子交换柱与Sephadex G-100凝胶层析柱从黄精根茎提取、分离得到均一多糖组分PSP。采用苯酚硫酸法、间羟基联苯法、高效凝胶渗透色谱和傅里叶红外光谱等分析PSP的理化性质,并通过D-半乳糖诱导氧化损伤小鼠模型探究PSP的体内抗氧化作用。结果表明,PSP的碳水化合物含量为94.42%±14.73%,其分子量为5566.41 Da,含有β型的呋喃环或吡喃环果糖,以及较长的支链和较多的分支。与模型组相比,PSP高剂量组血清、脑组织、肝脏组织的SOD、GSH-Px与T-AOC水平显著升高(P<0.05),MDA水平显著降低(P<0.05);HE染色发现PSP处理组的肝脏损伤明显得到改善,且肝脏中Nrf2和HO-1的表达显著增强(P<0.05)。因此,结果表明黄精多糖PSP可能通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路保护小鼠的氧化损伤。Abstract: In this study, a homogeneous polysaccharide fraction was extracted and purified from the rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum, its physicochemical properties and protective effect against oxidative damage were analyzed, and its potential protective mechanism was initially explored. The homogeneous polysaccharide (PSP) was obtained by water extraction, alcohol precipitation, and separation on DEAE-52 cellulose and Sephadex G-100 columns. The phenol sulfate method, m-hydroxybiphenyl method, high performance gel permeation chromatography and Fourier infrared spectroscopy were used to analyze the physicochemical properties of PSP. The in vivo antioxidant effects of PSP were investigated in a mouse model of D-galactose induced oxidative damage. The results showed that the carbohydrate content of PSP was 94.42%±14.73% and its molecular weight was 5566.41 Da. PSP was also found to contain β-type furan or pyran fructose, as well as longer branched chains with more branches. Compared with the model group, the levels of SOD, GSH-Px and T-AOC significantly increased (P<0.05), and MDA levels significantly decreased (P<0.05) in serum, brain tissue and liver tissue of the PSP high dose groups, HE staining revealed that liver damage was significantly ameliorated and the expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 protein in the liver was significantly enhanced in the PSP-treated group (P<0.05). It could be concluded that PSP had a protective effect on oxidative damage in mice, and its protective mechanism might be related to the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
-
Keywords:
- Polygonatum sibiricum /
- polysaccharide /
- isolation and purification /
- D-galactose /
- oxidative damage
-
《神农本草经》记载“黄精,味甘、平、无毒,主补中益气,除风湿,安五脏,久服轻身,延年不饥”[1]。《中国药典》2020版收藏了滇黄精(Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl.)、黄精(Polygonatum sibiricum Red.)或多花黄精(Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua)3种原生药,按形状不同,习称“大黄精”、“鸡头黄精”、“姜形黄精”[2]。黄精为百合科黄精属植物Polygonatum sibiricum Red.的干燥根茎,属于药食兼用的中药材。现代药理学研究证明,黄精具有降血压、降血糖、抗氧化、抗菌和抗炎等功效[3]。
黄精主要含有多糖、皂苷、多酚、黄酮、木质素、氨基酸、微量元素和挥发油等生物活性物质[4],多糖作为黄精的主要化学成分,具有抗癌[5]、抗肿瘤[6]、免疫调节[7]、预防抑郁[8]和阿尔兹海默症[9]等作用。已有研究表明,黄精多糖具有较好的抗氧化活性,如体外清除DPPH自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、羟基自由基等活性[10];体内研究发现黄精多糖能显著提高经训练所致疲劳大鼠或炎症性肠病小鼠血清中超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase, SOD)的含量,并减少丙二醛(Malondialdehyde, MDA)的产生[11]。另外,黄精酒制前后的水溶性多糖可以改善氧化损伤细胞内总超氧化物歧化酶(Total-SOD)和谷胱甘肽酶(Glutathione peroxidase, GSH-Px)活性,抑制MDA和活性氧(Reactive oxygen species, ROS)的升高,从而发挥抗氧化损伤作用[12]。目前,黄精多糖的抗氧化活性研究大多集中于黄精粗多糖,而对于黄精中均一多糖组分的抗氧化研究较为缺乏。
本研究采用传统的水提醇沉法提取得到黄精的粗多糖,后经DEAE-纤维素阴离子交换柱与Sephadex G-100凝胶层析柱分离纯化得到均一多糖组分PSP。通过建立D-半乳糖诱导的氧化损伤小鼠模型分析黄精多糖PSP对氧化损伤的保护作用,并对其潜在的保护机制进行初步探究,以期为黄精抗氧化作用机制的深入研究和天然抗氧化剂的开发奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
SPF级昆明种雄性小鼠8周龄70只(20±2 g) 饲养于安徽中医药大学实验动物中心[动物许可证号:SCXK(豫)2019-0002],动物实验由安徽中医药大学实验动物伦理委员会审议通过,审批编号AHUCM-mouse-2021128;黄精(鸡头黄精) 陕西秦岭山;D-半乳糖 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;维生素C(分析纯) 上海润捷化学试剂有限公司;正丁醇 上海苏懿化学试剂有限公司;T-AOC(总抗氧化能力)、SOD(超氧化物歧化酶)、GSH-Px(谷胱甘肽酶)、MDA(丙二醛)试剂盒 南京建成生物科技有限公司。HE染液套装 G1003,Servicebio;DEAE纤维素DE-52、葡聚糖凝胶G-100 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;葡聚糖分子量标品 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
FD-1B-50冷冻干燥机 上海比朗仪器制造有限公司;YHZ-212恒温振荡摇床 苏州国飞实验室仪器有限公司;GFL-230烤箱 天津市莱玻瑞仪器设备有限公司;Nikon Eclipse E100正置光学显微镜、Nikon DS-U3成像系统 日本尼康公司;凝胶色谱仪 日本岛津公司;DHL-A电脑数显恒流泵 上海沪西分析仪器厂有限公司;Multiskan Spectrum酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;NIcolet in10 MX傅立叶交换显微红外成像光谱仪 美国尼高力仪器公司;UV-8000紫外-可见分光光度计 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;普通玻璃层析柱(1.6×60 cm)、(1.6×80 cm) 上海琪特分析有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 粗多糖的提取
多糖的提取参照课题组原有的提取方法[13],并略作修改。称取100 g黄精粉末,加入80%乙醇在75 ℃的条件下震荡24 h除去脂肪、低聚糖、色素类等小分子物质。用4层200目脱脂棉纱布过滤,滤渣在50 ℃的烘箱中干燥24 h,后按1:30的料液比80 ℃水浴提取2 h,过滤。按照原有比例向滤渣中加入相同水量,继续提取2 h。合并滤液并浓缩至300 mL体积,向浓缩液中加入100 μL α-淀粉酶溶液(46 U/mL)于60 ℃反应2 h除去淀粉。离心除去沉淀,在所得上清液中加入无水乙醇,使乙醇的终浓度达到80%,4 ℃静置24 h。离心取沉淀,采用Sevage法脱去沉淀中的蛋白质。将脱完蛋白的糖液浓缩,透析,冷冻干燥后得到黄精粗多糖。
1.2.2 DEAE-纤维素阴离子交换柱(1.6 cm×60 cm)对粗多糖进行初步分离
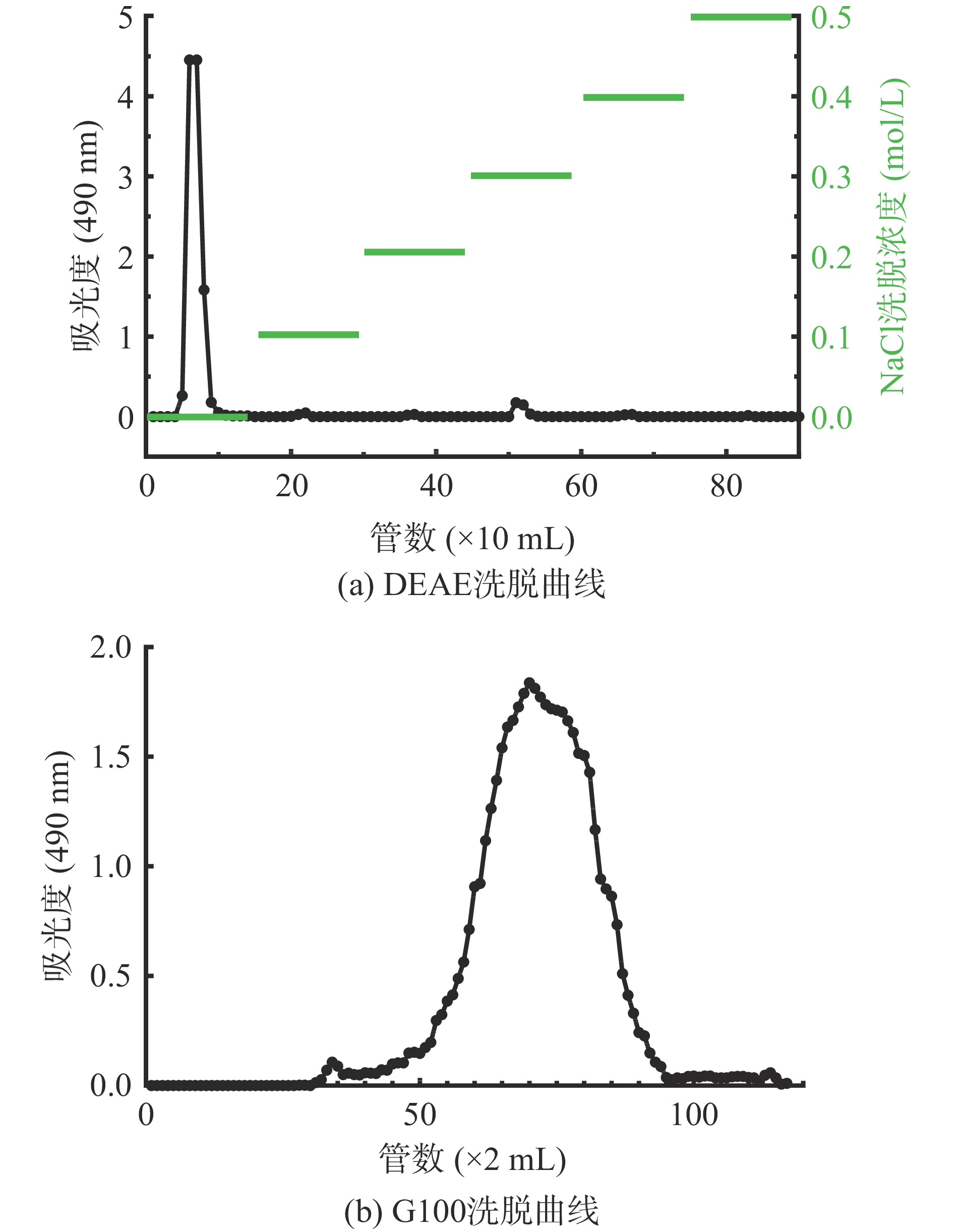
将200 mg黄精溶解于5 mL超纯水中,依次使用超纯水、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mol/L NaCl水溶液进行梯度洗脱(流速设置为5 mL/min,2 min/管),用自动收集器收集,采用苯酚硫酸法测定每管中洗脱液的吸光度,并绘制洗脱曲线。收集组分最高的洗脱液,冻干得到黄精多糖P1组分。
1.2.3 黄精多糖P1组分中成分的分离纯化
将50 mg P1组分溶解于3 mL水中,采用Sephadex G-100凝胶层析柱(1.6 cm×80 cm)对P1组分进行分离纯化,以超纯水作洗脱液,流速设置为0.2 mL/min,采用苯酚硫酸法测定每管中洗脱液(2 mL)的吸光度,并绘制洗脱曲线,将最终所得组分收集合并冻干得到PSP。
1.2.4 多糖的化学组成分析
1.2.4.1 碳水化合物测定
参照李媛媛等[14]的方法,以葡萄糖作为标准品,采用苯酚硫酸法测定PSP组分中碳水化合物含量,获得葡萄糖的标准曲线回归方程为:Y=17.721X+0.0641(R²=0.9929)。其中,X为葡萄糖溶液浓度,Y为吸光度。
1.2.4.2 糖醛酸含量测定
参照赵志强等[15]的方法,以D-半乳糖醛酸作为标准品,采用间羟基联苯法法测定PSP组分中糖醛酸的含量,获得D-半乳糖醛酸的标准曲线回归方程为:Y=10.345X−0.0303(R²=0.998)。其中,X为D-半乳糖醛酸溶液浓度,Y为吸光度。
1.2.4.3 蛋白质含量测定
参照张瑞平等[16]的方法,以牛血清白蛋白作为标准品,采用考马斯亮法测定PSP中蛋白质含量,获得牛血清白蛋白的标准曲线回归方程为:Y=5.6699X+0.0444(R²=0.9987)。其中,X为牛血清白蛋白溶液浓度,Y为吸光度。。
1.2.5 紫外分光光度法分析
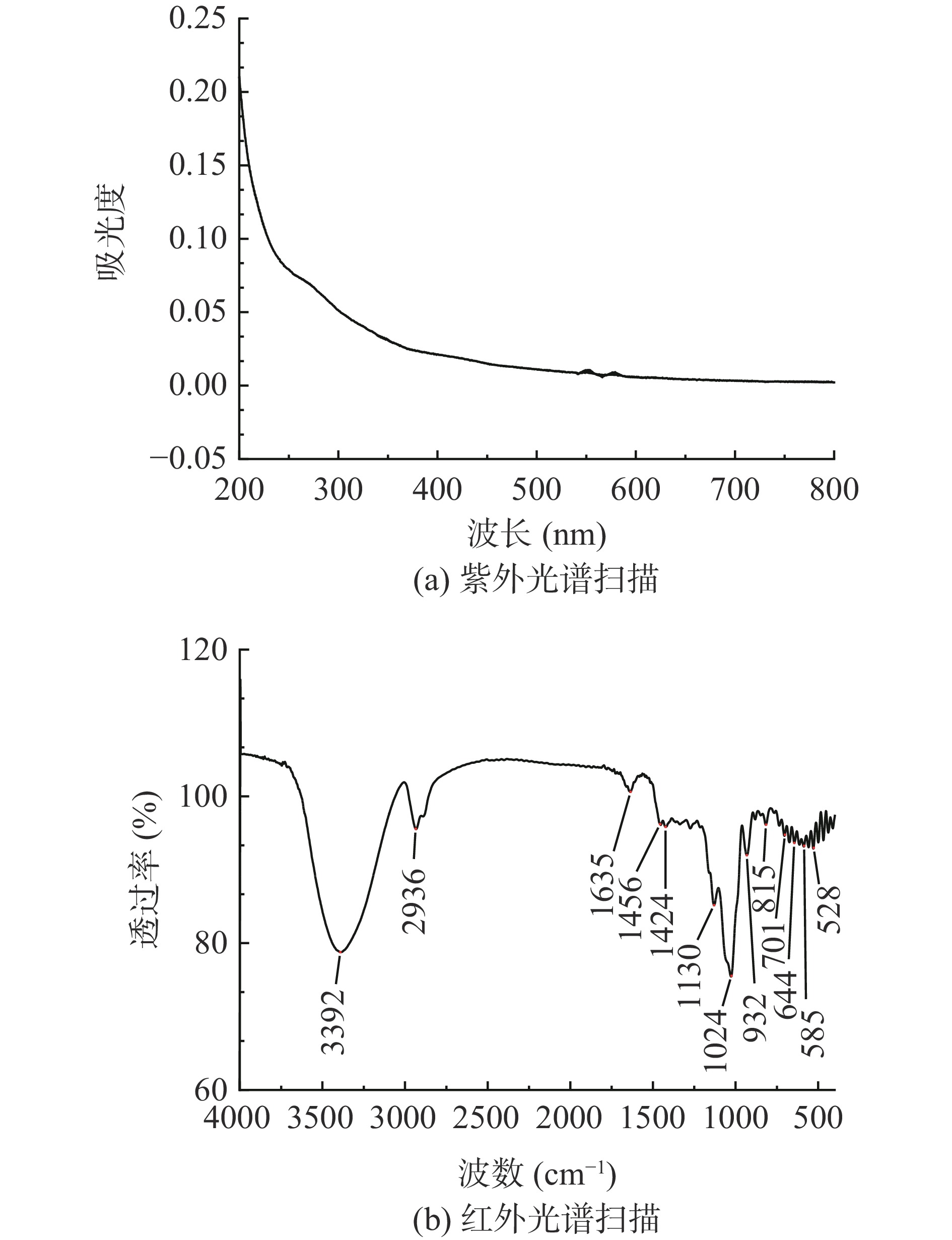
将PSP溶于纯水中,配制成0.1 mg/mL的溶液,在200~800 nm的波长区间扫描。
1.2.6 红外光谱分析
参照刘贵珍等[17]的方法,采用KBr压片法制样。用红外光谱仪在4000~400 cm−1区域进行扫描。利用OriginPro 2021软件进行数据处理。
1.2.7 分子量测定
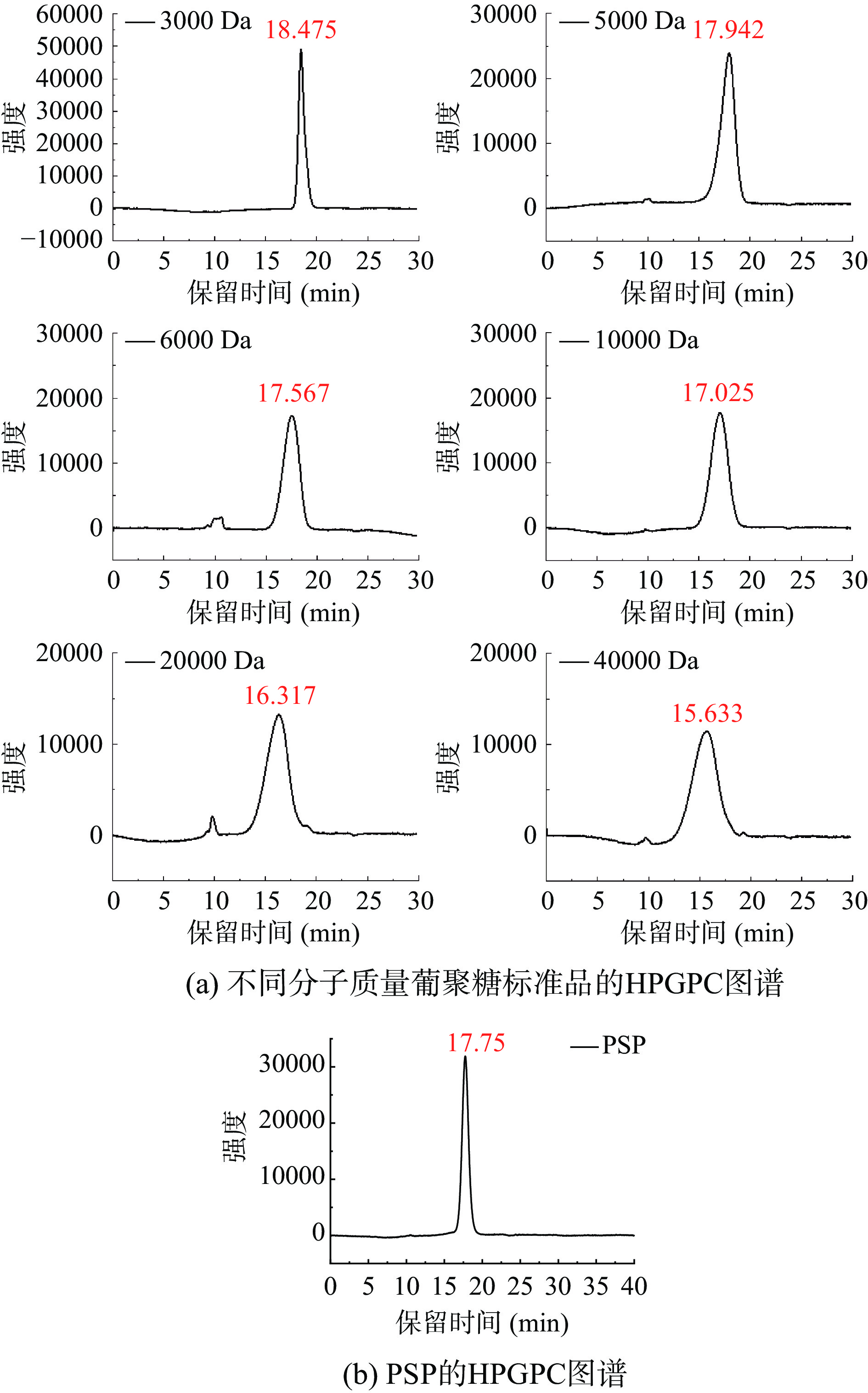
使用岛津凝胶色谱柱,对多糖的均一性和分子量进行分析,分析柱采用TSK G4000PWXL柱(7.8 mm×300 mm)。配制多糖溶液(5 mg/mL),以超纯水作流动相,流速为0.6 mL/min,在30 ℃的环境下用RID检测器检测。根据由不同分子量的葡聚糖标准品制成的校准曲线来确定分子量。
1.2.8 碘化钾试验
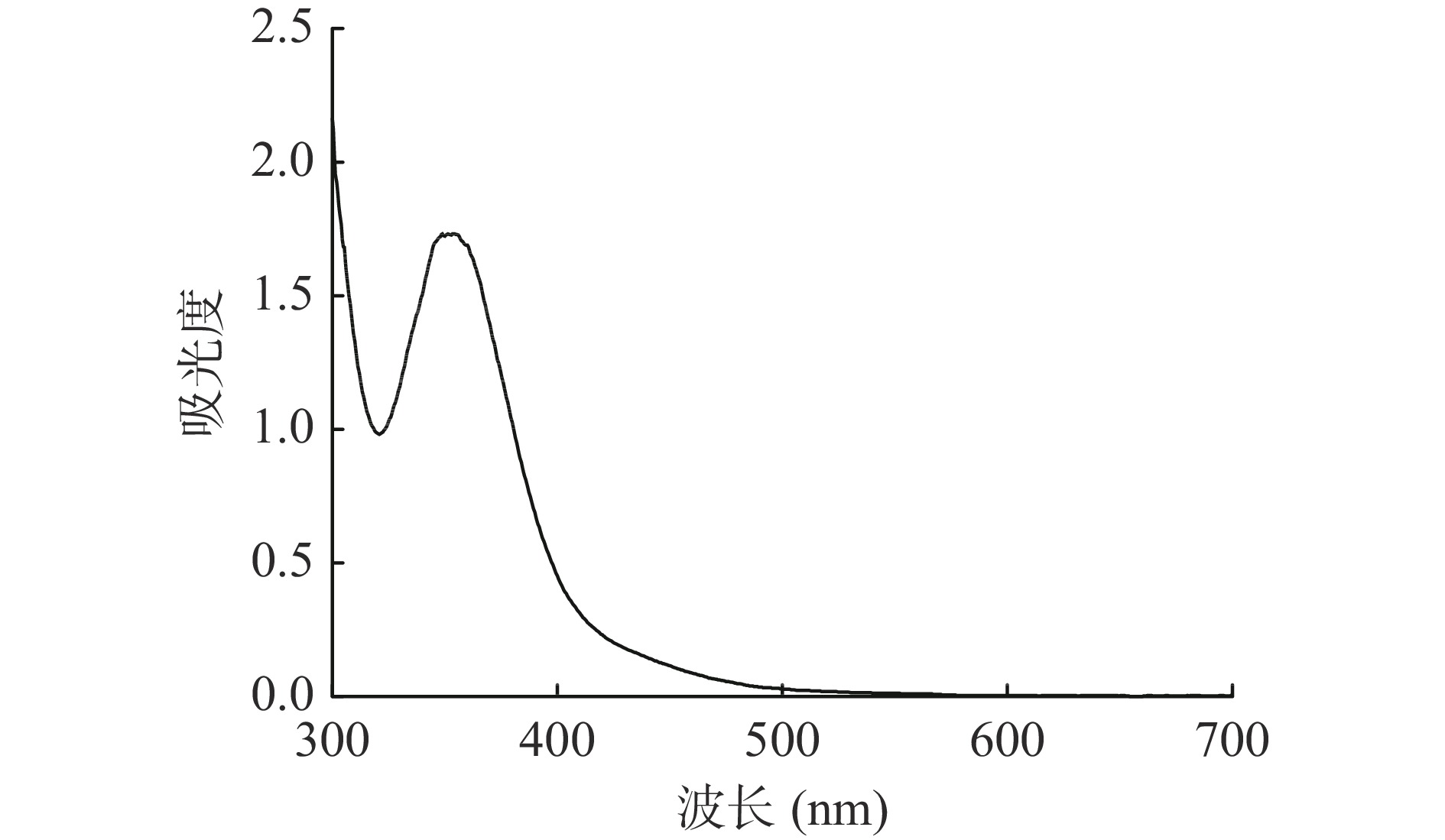
精密称取2 mg黄精多糖样品溶于1.2 mL含0.02% I2的KI溶液,稀释10倍,在300~700 nm区域进行波长扫描,观察350 nm处是否存在吸收峰,以此判断多糖的侧链和分支结构。
1.2.9 刚果红实验
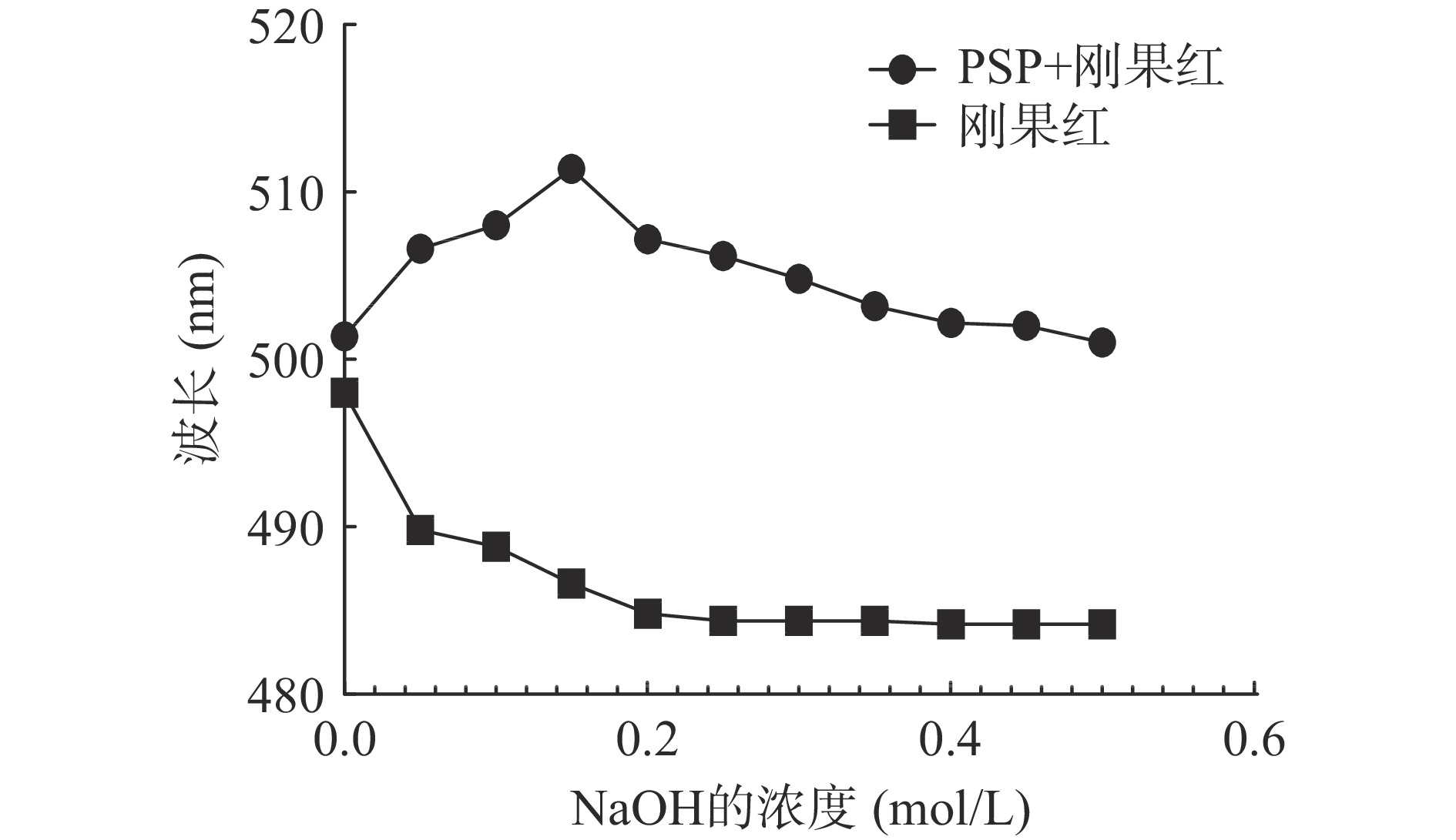
配制PSP溶液(2.5 mg/mL)与刚果红溶液(80 μmol/L)按1:1(v/v)的比例充分混合,通过加入NaOH溶液(4 mol/L),将混合物逐渐调整到不同NaOH浓度(0、0.05、0.1、0.15、0.2、0.25、0.3、0.35、0.4、0.45和0.5 mol/L)。通过紫外扫描(200~600 nm)记录不同浓度的刚果红多糖溶液的最大吸收波长。
1.3 动物实验
1.3.1 氧化损伤小鼠模型的构建与给药
70只SPF级小鼠适应性喂养一周,期间小鼠自由饮水、觅食普通饲料。适应期后,随机分为5组(每组14只):正常组(Control)、模型组(Model)、阳性组(Positive)、多糖低剂量组(PSP-L)、多糖高剂量组(PSP-H)。除正常组外,各组连续每天上午腹腔注射D-半乳糖(500 mg/kg)三周,下午6~7点灌胃黄精多糖PSP,多糖低剂量组灌胃50 mg/kg的多糖溶液,多糖高剂量组灌胃200 mg/kg的多糖溶液;阳性对照组上午注射D-半乳糖(500 mg/kg),下午灌胃维生素C(200 mg/kg)。
1.3.2 样本采集
小鼠禁食不禁水12 h,称重,采集小鼠血液,在4 ℃放置3 h,离心15 min(3500 g),取血清,分装保存备用;采血后立即处死小鼠,取出其肝脏、脾脏、肾脏、脑等组织,将脏器表面的血液用预冷的生理盐水洗净,随后用滤纸擦干表层水分,称重并计算脏器指数。随机选取部分肝脏、脑组织加入的4%多聚甲醛溶液固定;另一部分用液氮预冻后−80 ℃保存备用。按照公式(1)~(3)计算脏器指数。
肝脏指数(mg/g)=肝脏质量小鼠体重 (1) 肾脏指数(mg/g)=肾脏质量小鼠体重 (2) 脾脏指数(mg/g)=脾脏质量小鼠体重 (3) 1.3.3 血清、肝脏、脑组织匀浆抗氧化指标测定
血清、肝脏和脑组织匀浆液中的SOD、T-AOC、GSH-Px、MDA水平均按照试剂盒说明书方法测定。
1.3.4 肝脏HE染色
将浸泡在4%多聚甲醛中的肝脏进行常规的HE组织化学染色,以观察肝组织的病理变化情况,细胞核呈蓝色,细胞质呈红色。
1.3.5 免疫组化
采用常规的免疫组化方法评估黄精多糖低、高剂量组处理的小鼠对Nrf2、HO-1蛋白的表达。将样本脱蜡和水化后,将组织切片浸入柠檬酸(pH6.0)以进行抗原修复。此后,将切片在室温下用血清密封30 min,然后与一级抗Nrf2和抗HO-1抗体在4 ℃孵育过夜。用PBS(PH7.4)洗涤3次后,在室温下用二抗(HRP标记)覆盖切片50 min,并加入二氨基联苯胺(DAB)进行显色反应,对细胞核复染,切片用苏木精染色溶液复染,后在光学显微镜下观察[18]。
1.4 数据处理
所有实验统计数据图均采用Origin 2021、Graphpad Prism 8绘制而成,所有数据分析均采用单因素方差分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 PSP的分离纯化
黄精粗多糖DEAE的洗脱曲线见图1a,经DEAE-纤维素阴离子交换柱分离纯化后,收集水洗组分冷冻干燥后得水洗组分糖P1,得率为82.67%。采用Sephadex G-100凝胶层析柱对P1组分进一步分离,所得组分冷冻干燥后命名为PSP,洗脱曲线见图1b,得率为93.24%。制备PSP继续开展后续实验。
2.2 PSP的化学组成分析
将样品所测得的吸光度值带入标曲测得样品中所含碳水化合物的含量为94.42%±14.73%、糖醛酸的含量为6.21%±0.71%、蛋白质的含量为0.24%±0.032%,表明PSP是纯度较高的多糖。
2.3 PSP的分子量测定
由PSP的HPGPC图谱(见图2b)可推断,PSP是均一性较好的多糖组分。根据不同分子量葡聚糖标准品的保留时间(见图2a)与其对数值,可获得标准曲线:Y=−0.3927X+10.716(R²=0.9951),将样品的保留时间代入,算得PSP的分子量为5566.41 Da。
2.4 PSP的紫外光谱与红外光谱分析
紫外光谱扫描图见图3a,PSP在260和280 nm处未见明显的特征吸收峰存在,说明PSP中没有核酸和蛋白质的存在[19]。
红外光谱见图3b,在3392 cm−1附近的强而宽的吸收峰是由O-H的拉伸振动引起的[20],在2936 cm−1左右的峰值是C-H拉伸振动引起的,1635 cm−1附近的条带是由C=O所引起的,表明PSP中有糖醛酸的存在[21],这与化学组成分析结果相验证。1130 cm−1和1024 cm−1的吸收峰是由呋喃糖的C-O-C的伸缩振动引起的[22],在932和815 cm−1左右的吸收峰归属于含有β型糖苷键果糖的吸收峰 [21-23],在644和528 cm−1附近的吸收峰表明PSP中存在吡喃糖环骨架[13]。
2.5 PSP的碘化钾试验
PSP溶液与碘试剂混匀后用紫外光谱仪扫描,光谱图如图4所示,由于PSP与I2-KI的反应物最大吸收峰出现在350 nm处附近,而不是565 nm处,说明PSP中可能具有较长的侧链和较多的分支[24]。
2.6 PSP的构象分析
刚果红溶液可以与具有三股螺旋结构的多糖形成络合物,在弱碱性条件下络合物的最大吸收波长会上升,而较强碱性条件下复合物的最大吸收波长会下降,这种最大吸收波长的特征性变化用于判断样品中的螺旋结构[25]。PSP与刚果红溶液在碱性条件下最大吸收波长的变化见图5,与单独的刚果红溶液相比,PSP与刚果红的混合溶液在0~0.15 mol/L的NaOH溶液中,其最大的吸收波长发生明显上升,表明PSP中有三股螺旋结构的存在[26]。
2.7 PSP对氧化损伤小鼠体重及脏器指数的影响
为测定PSP在体内对氧化损伤的保护作用,建立了D-半乳糖诱导的小鼠氧化损伤模型。与对照组相比,D-半乳糖的注射显著降低了小鼠的体重,然而,低、高剂量组的多糖显著逆转了小鼠的体重减轻(P<0.05)。有研究表明,D-半乳糖的注射可引发脏器功能减弱与失调的免疫反应[27]。如表1中所示,氧化损伤模型组的脾脏指数显著低于正常组(P<0.05);与模型组相比,高剂量保护组显著提高了小鼠的脾脏指数(P<0.05);低剂量和高剂量的PSP均显著提高了肝脏指数(P<0.05);给药组的肾脏指数与模型组相比无显著性差异(P>0.05)。这些结果表明,多糖处理可改善由D-半乳糖注射诱导所引起的体重减轻和肝脏及脾脏指数的降低。
表 1 氧化损伤小鼠体重及脏器指数Table 1. Body weight and organ indices of mice with oxidative damage组别 第三周体重(g) 肝脏指数(mg/g) 肾脏指数(mg/g) 脾脏指数(mg/g) 正常组 42.15±0.77 61.21±2.02 16.26±0.76 8.12±1.28 模型组 36.87±1.70# 51.27±3.99# 11.77±0.92# 4.53±0.36# 阳性组 40.47±0.84* 59.84±1.08* 14.04±0.69 6.89±1.46 多糖高剂量组 40.50±0.64* 61.91±1.93* 13.83±0.40 7.02±0.65* 多糖低剂量组 40.20±0.85* 57.95±0.70* 13.34±2.34 6.82±1.04 注:“#”表示与正常组相比存在显著差异(P<0.05);“*”表示与模型组相比存在显著差异(P<0.05)。 2.8 PSP对氧化损伤小鼠脑、肝、血清中GSH-Px、MDA、SOD、T-AOC含量的影响
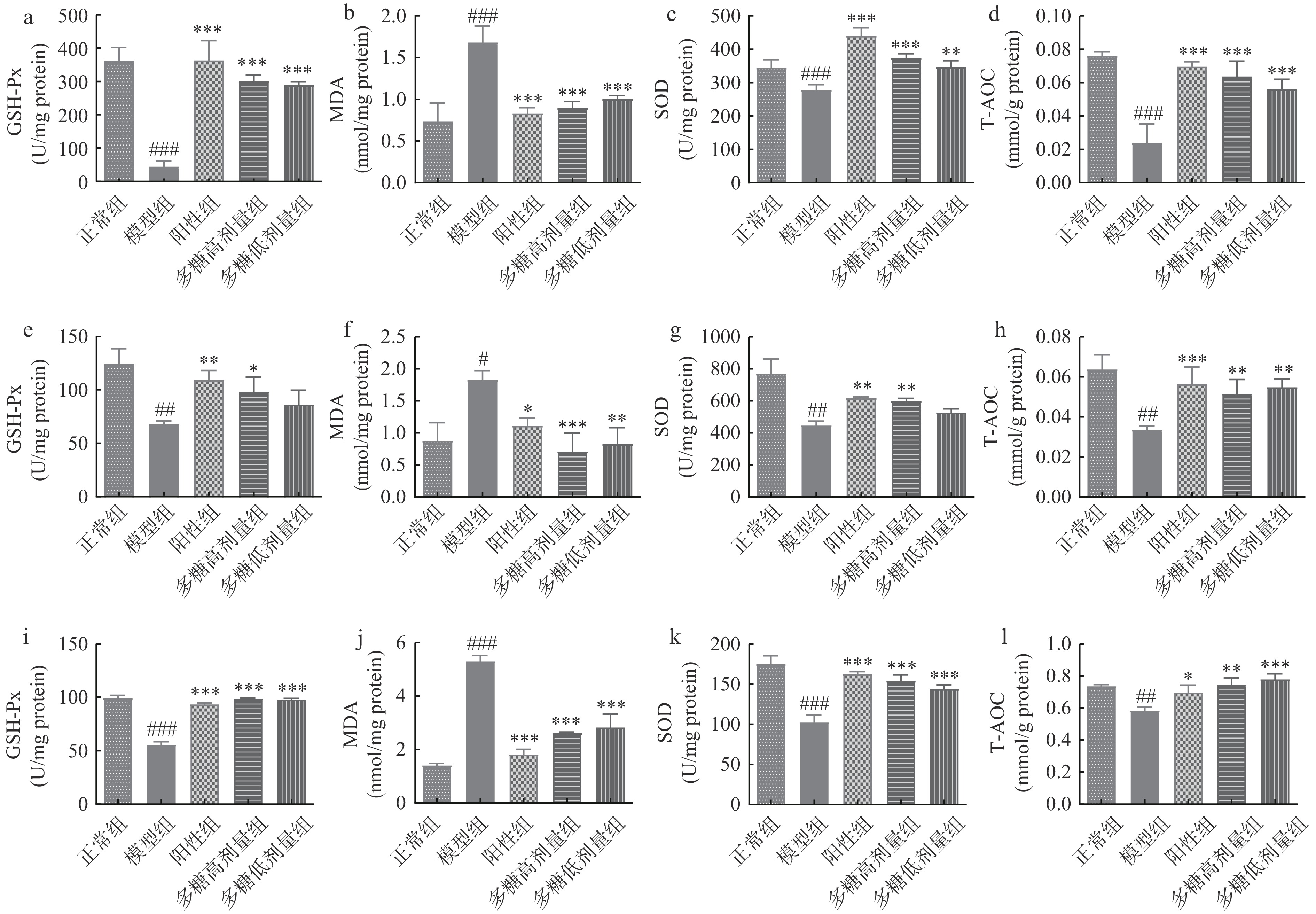
生物体的抗氧化能力与健康存在着紧密联系,当生物体的总抗氧化能力遭到破坏或降低时,容易引发各种疾病[28]。GSH-Px作为机体内部一种重要的过氧化物分解酶,其主要的功能是保护细胞膜的结构及功能的完整,防止机体受过氧化物的干扰及损害[29]。SOD是一种抗氧化金属酶,分布范围较广,几乎存在于所有生物细胞中,能够催化超氧阴离子自由基歧化生成氧和过氧化氢,在机体氧化与抗氧化平衡中起到至关重要的作用[30],MDA可以反映机体脂质过氧化速率和强度,能间接反映组织过氧化损伤程度[31-32],其含量的测定通常与SOD含量的测定互相配合[33]。T-AOC反应测定对象中各种抗氧化物质和抗氧化酶等构成总抗氧化水平[34]。
对小鼠脑、肝脏及血清中的GSH-Px、MDA、SOD、T-AOC测定发现(图6a-d, e-h, i-l),与正常组相比,模型组小鼠脑脑组织中GSH-Px的含量显著下降(P<0.05),MDA的含量显著上升(P<0.05),SOD的含量显著下降(P<0.05),T-AOC显著下降(P<0.05),均能够说明模型组小鼠的已产生氧化衰老症状,表明D-半乳糖诱导小鼠氧化损伤模型造模成功。与模型组相比,虽然多糖低剂量组肝脏中GSH-Px与SOD的表达量无显著差异,但是其T-AOC表达显著提升(P<0.05),MDA的含量显著降低(P<0.05)。此外,在脑和血清中GSH-Px、SOD与T-AOC的表达均有显著提升(P<0.05),MDA的表达显著降低(P<0.05)。多糖高剂量组小鼠的脑、肝脏及血清中的GSH-Px、SOD与T-AOC的表达均有显著提升(P<0.05),MDA的表达显著降低(P<0.05),表明高剂量的黄精多糖对D-半乳糖诱导的氧化损伤具有明显的保护作用。
2.9 PSP对氧化损伤小鼠肝脏组织形态的影响
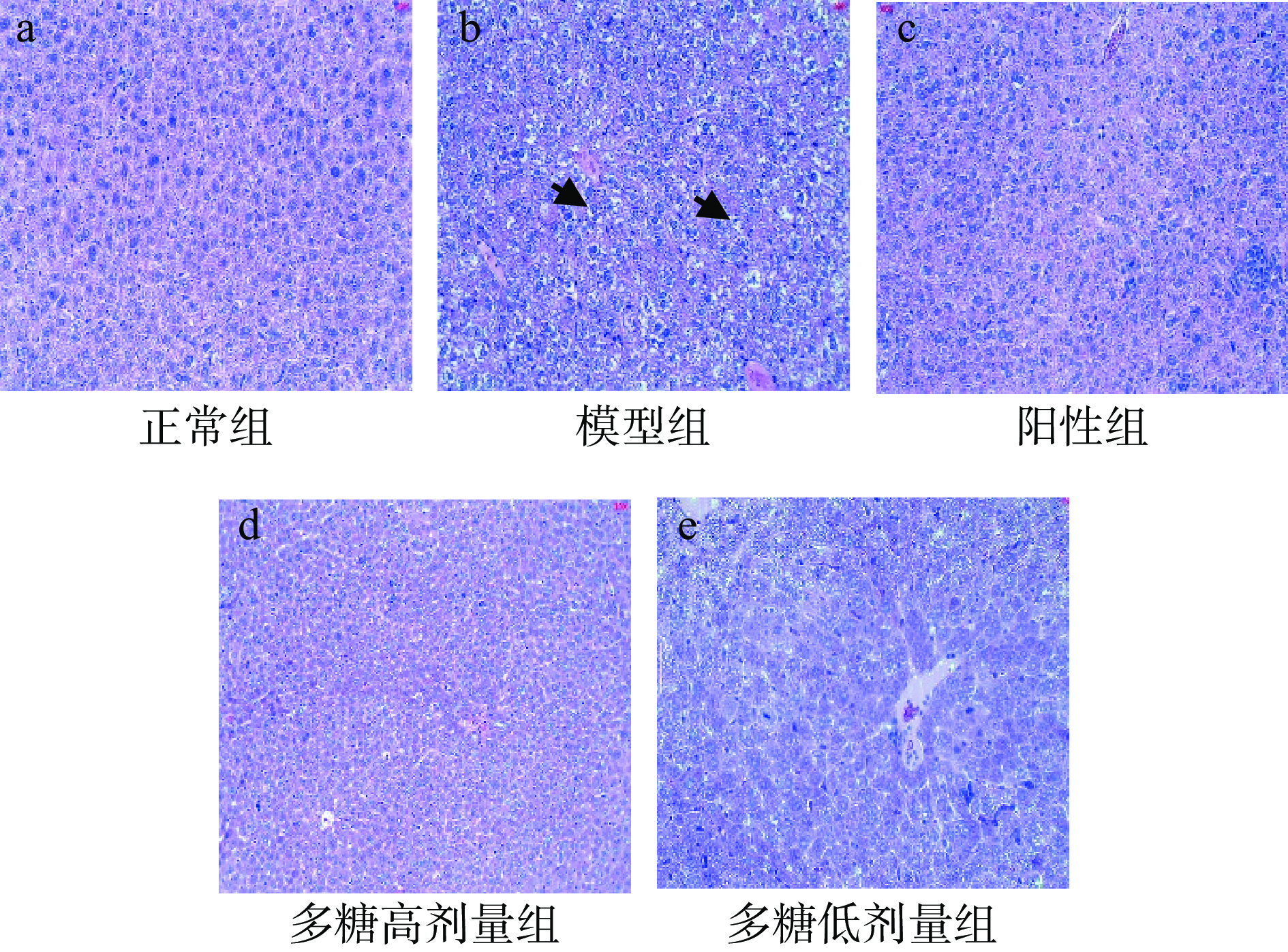
经过HE染色,肝脏组织切片细胞中所存在的脂类物质被二甲苯溶解成为空泡(见图7)。正常组的小鼠肝细胞排列齐整,形态饱满,细胞核呈圆形,周围的细胞质丰富,细胞膜清晰。模型组小鼠的细胞排列顺序紊乱、肝小叶的结构被破坏,可见大量的脂肪空泡,部分细胞核氧化应激损伤严重,颜色变浅或消失,表明模型小鼠的肝脏发生了严重的脂肪变性,肝脏氧化应激损伤程度严重。从小鼠肝脏的HE染色图可以看出,与模型组相比,多糖高剂量组的空泡数量明显减少,细胞排列整齐,大多数细胞核呈圆形,胞膜清晰,表明高剂量的黄精多糖对小鼠的肝脏细胞具有较好的保护作用[18]。
2.10 PSP对氧化损伤小鼠肝脏HO-1和Nrf2蛋白表达的影响
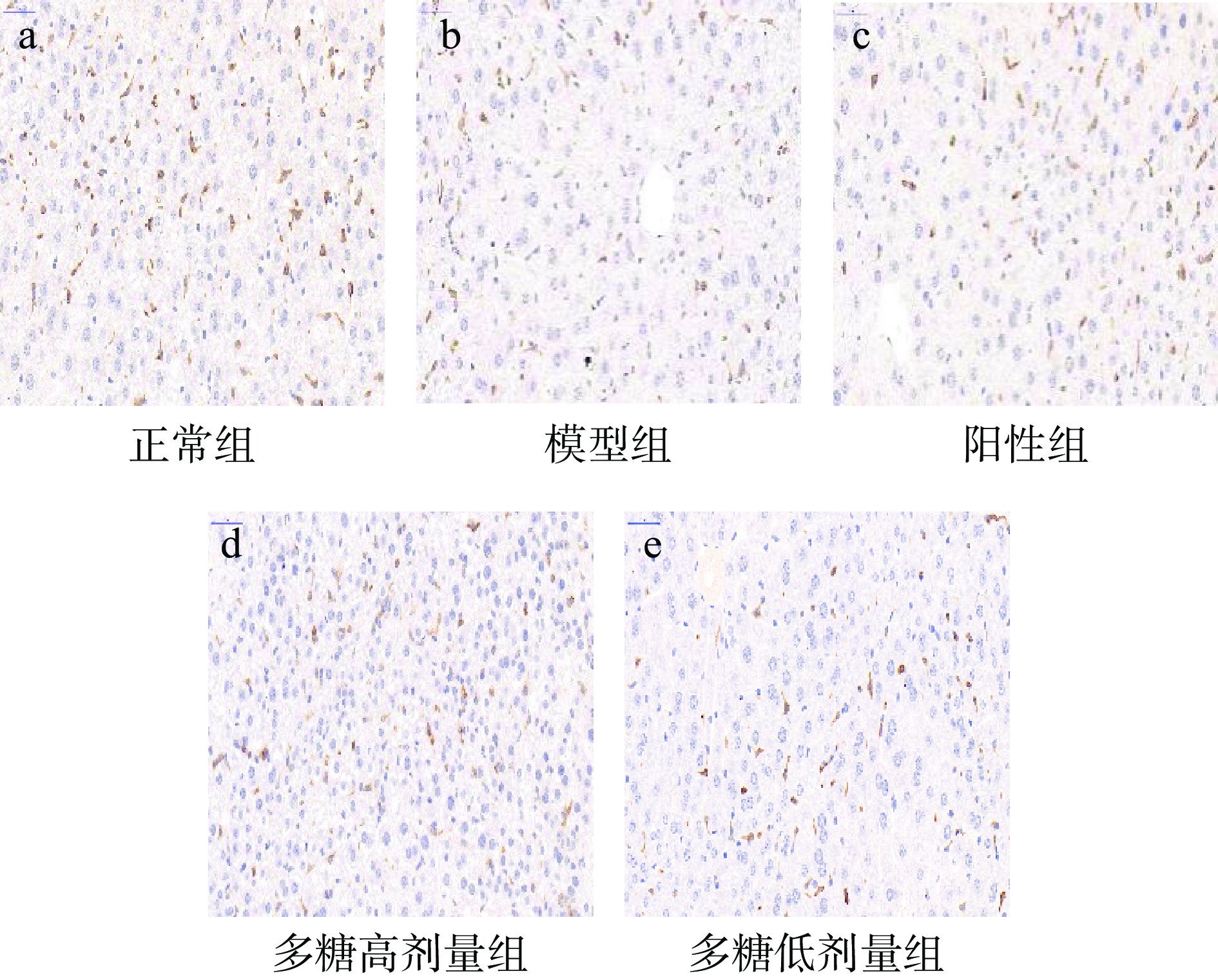
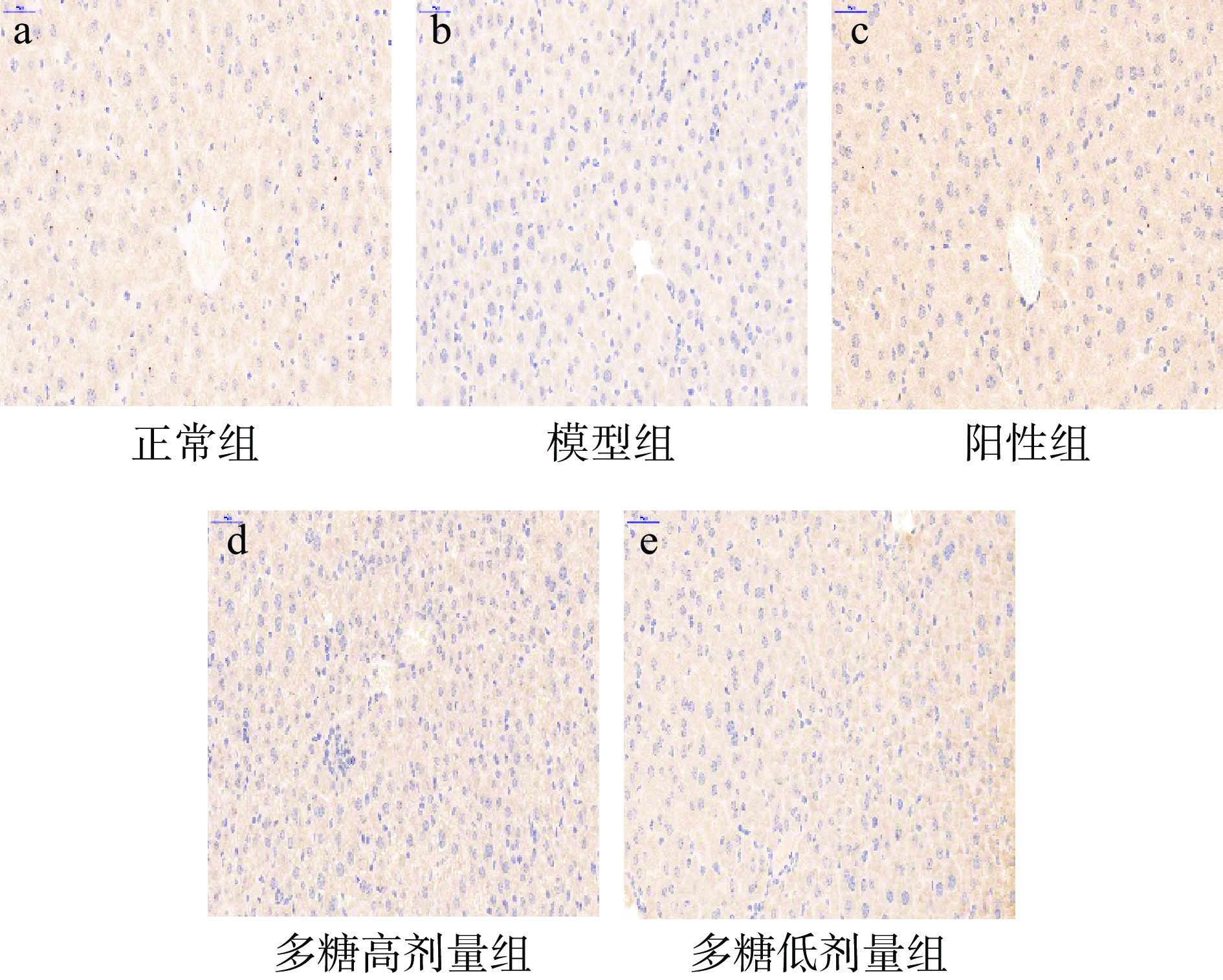
Nrf2/HO-1信号通路是细胞抗氧化防御机制的一个重要组成部分,在保护机体免受氧化损伤中起着重要作用,当ROS过量产生时,Nrf2被激活易位到细胞核,识别并激活ARE,进而诱导HO-1等下游抗氧化基因的表达[35]。HO-1是防止氧化应激最关键的蛋白。有研究表明,Nrf2/HO-1信号通路的激活可能是预防D-半乳糖诱导的小鼠氧化损伤的一个潜在途径[36]。小鼠肝脏HO-1染色情况如图8所示。
本文采用免疫组化的方法检测肝脏中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的表达(见图9~图10)。结果表明,与正常组相比,模型组的Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的表达显著降低,表明模型组造模成功;与模型组相比,低、高剂量黄精多糖能够显著增加Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的表达(P<0.05),表明黄精多糖很有可能是通过Nrf2/HO-1信号通路发挥对肝脏的保护作用。
3. 结论
经凝胶色谱测得PSP的分子量为5566.41 Da;PSP的化学组成分析发现,PSP中碳水化合物、糖醛酸及蛋白质的含量分别为94.42±14.73%、6.21±0.71%、0.24±0.032%;红外光谱分析显示PSP中存在呋喃环与吡喃环构型,且存在β型糖苷键的果糖;碘化钾实验验证了PSP中存在较长的侧链和较多的分支。
动物实验结果表明,与模型组比,高剂量的黄精多糖能够显著提高小鼠肝脏组织、脑组织、血清中GSH-Px、SOD和T-AOC含量,降低MDA水平;肝脏的HE染色及免疫组化学分析显示,黄精多糖对肝脏的氧化损伤细胞有着显著的保护效果且能够显著增强Nrf2、HO-1的表达。由此可以推断,黄精多糖对D-半乳糖诱导的氧化损伤具有一定的保护作用,且其发挥氧化损伤保护作用的机制可能与Nrf2/HO-1信号通路有关。
-
表 1 氧化损伤小鼠体重及脏器指数
Table 1 Body weight and organ indices of mice with oxidative damage
组别 第三周体重(g) 肝脏指数(mg/g) 肾脏指数(mg/g) 脾脏指数(mg/g) 正常组 42.15±0.77 61.21±2.02 16.26±0.76 8.12±1.28 模型组 36.87±1.70# 51.27±3.99# 11.77±0.92# 4.53±0.36# 阳性组 40.47±0.84* 59.84±1.08* 14.04±0.69 6.89±1.46 多糖高剂量组 40.50±0.64* 61.91±1.93* 13.83±0.40 7.02±0.65* 多糖低剂量组 40.20±0.85* 57.95±0.70* 13.34±2.34 6.82±1.04 注:“#”表示与正常组相比存在显著差异(P<0.05);“*”表示与模型组相比存在显著差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 杨德, 薛淑静, 卢琪, 等. 黄精药理作用研究进展及产品开发[J]. 湖北农业科学,2020,59(21):5−9. [YANG De, XUE ShuJing, LU Qi, et al. Research progress and product development of Polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science,2020,59(21):5−9. YANG De, XUE ShuJing, LU Qi, et al. Research progress and product development of Polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science, 2020, 59(21): 5-9.
[2] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 319 National pharmacopoeia committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[S]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 319.
[3] ZHAO H, WANG Q L, HOU S B, et al. Chemical constituents from the rhizomes of Polygonatum sibiricum red. And anti-inflammatory activity in raw 264.7 macrophage cells[J]. Natural Product Research,2019,33(16):2359−2362. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1440220
[4] 吴丰鹏, 李芹英, 吴彦超, 等. 九蒸九制对黄精多糖单糖组成及其抗氧化性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(2):42−46. [WU Fengpeng, LI Qinying, WU Yanchao, et al. Effects of nine-steam-nine-bask on the monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activities of polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(2):42−46. WU Fengpeng, LI Qinying, WU Yanchao, et al. Effects of nine-steam-nine-bask on the monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activities of polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2021, 42(2): 42-46.
[5] LONG T, LIU Z, SHANG J, et al. Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides play anti-cancer effect through TLR4-MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,111:813−821. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.070
[6] XIE Y, JIANG Z, YANG R, et al. Polysaccharide-rich extract from Polygonatum sibiricum protects hematopoiesis in bone marrow suppressed by triple negative breast cancer[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2021,137:111338.
[7] SUN T, ZHANG H, LI Y, et al. Physicochemical properties and immunological activities of polysaccharides from both crude and wine-processed Polygonatum sibiricum[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,143:255−264. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.166
[8] SHEN F, SONG Z, XIE P, et al. Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide prevents depression-like behaviors by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular and synaptic damage[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,275:114164. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114164
[9] ZHANG H, CAO Y, CHEN L, et al. A polysaccharide from Polygonatum sibiricum attenuates amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,117:879−886. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.034
[10] LI X, CHEN Q, LIU G, et al. Chemical elucidation of an arabinogalactan from rhizome of Polygonatum sibiricum with antioxidant activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,190:730−738. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.038
[11] 薛学彬, 房树华, 汪华君. 黄精多糖体外抗氧化作用及其对小鼠炎症性肠病的作用研究[J]. 中国现代医生,2017,55(29):27−30,34. [XUE Xuebin, FANG Shuhua, WANG Huajun. Study on the antioxidant effect in vitro of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides and its effect on inflammatory bowel disease in mice[J]. China Modern Doctor,2017,55(29):27−30,34. XUE Xuebin, FANG Shuhua, WANG Huajun. Study on the antioxidant effect in vitro of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides and its effect on inflammatory bowel disease in mice[J]. China Modern Doctor, 2017, 55(29): 27-30, 34.
[12] 孙婷婷, 刘洋, 魏明, 等. 黄精酒制前后水溶性多糖抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2023,41(2):78−84,263−265. [SUN TingTing, LIU Yang, WEI Ming, et al. Antioxidant activity of water-soluble polysaccharides from crude and wine-processed Polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2023,41(2):78−84,263−265. SUN TingTing, LIU Yang, WEI Ming, et al. Antioxidant activity of water-soluble polysaccharides from crude and wine-processed Polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine: 2023, 41(2): 78-84,263-265.
[13] BAI J B, GE J C, ZHANG W J, et al. Physicochemical, morpho-structural, and biological characterization of polysaccharides from three polygonatum spp[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11(60):37952−37965. doi: 10.1039/D1RA07214E
[14] 李媛媛, 李奉楠, 杨小明, 等. 桑黄菌丝体多糖的分离纯化及抗氧化、抗肿瘤活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(11):127−135. [LI Yanyuan, LI Fengnan, YANG Xiaoming, et al. Fractionation, purification and antioxidant, antitumor activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius mycelia[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2023,44(11):127−135. LI Yanyuan, LI Fengnan, YANG Xiaoming, et al. Fractionation, purification and antioxidant, antitumor activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius mycelia [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2023, 44(11): 127-135.
[15] 赵志强, 朱叙丞, 冯真颖等. 沙棘果多糖的理化特征及其体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(13):30−38. [ZHAO Zhiqiang, ZHU Xucheng, FENG Zenying et al. Physicochemical characteristic and antioxidant activity in vitro of Seabuckthorn fruit polysaccharide[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2023,44(13):30−38. ZHAO Zhiqiang, ZHU Xucheng, FENG Zenying et al. Physicochemical characteristic and antioxidant activity in vitro of Seabuckthorn fruit polysaccharide[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2023, 44(13): 30-38.
[16] 张瑞平, 任昭辉, 张皓楠, 等. 香加皮多糖的分离纯化、单糖组成及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(13):71−78. [ZHANG Ruiping, REN Zhaohui, ZHANG Haonan, et al. Isolation, purification, monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from cortex periplocae[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2023,44(13):71−78. ZHANG Ruiping, REN Zhaohui, ZHANG Haonan, et al. Isolation, purification, monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from cortex periplocae[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2023, 44(13): 71-78.
[17] 刘贵珍, 杨志伟. 不同取代度羧甲基化罗汉果多糖的制备及生理活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(13):224−232. [Liu Guizhen, Yang Zhiwei. Preparation and physiological activity of carboxymethylated Siraitia grosvenorii polysaccharide with different degrees of substitution[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2023,44(13):224−232. Liu Guizhen, Yang Zhiwei. Preparation and Physiological Activity of Carboxymethylated Siraitia grosvenorii Polysaccharide with Different Degrees of Substitution[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2023, 44(13): 224-232.
[18] TENG H, ZHANG Y, JIN C, et al. Polysaccharides from steam-processed Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua protect against D-galactose-induced oxidative damage in mice by activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2023,103(2):779−791. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12189
[19] 羡荣华, 蒲铎文, 樊梓鸾, 等. 老山芹多糖的分离纯化、结构表征及体外降糖活性研究[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业: 1−9. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.032678. XIAN Ronghua, PU Duowen, FAN Ziluan, et al. Isolation, purification, structure characterisation and hypoglycemic activity analysis of polysaccharides from Heraclenm dissectum[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry: 1−9. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.032678.
[20] XIE S Z, YANG G, JIANG X M, et al. Polygonatum cyrtonema hua polysaccharide promotes glp-1 secretion from enteroendocrine l-cells through sweet taste receptor-mediated camp signaling[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(25):6864−6872. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02058
[21] ZHAO P, ZHOU H, ZHAO C, et al. Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of fructans from Polygonatum odoratum and P. cyrtonema[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,214:44−52. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.014
[22] ZHANG J, CHEN H, LUO L, et al. Structures of fructan and galactan from Polygonatum cyrtonema and their utilization by probiotic bacteria[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,267:118219. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118219
[23] XIE S Z, ZHANG W J, LIU W, et al. Physicochemical characterization and hypoglycemic potential of a novel polysaccharide from Polygonatum sibiricum Red through PI3K/Akt mediated signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2022, 93.
[24] 陈冠, 张岩, 冯文茹, 等. 苦豆子多糖溶液构象的研究[J]. 现代药物与临床,2015,30(3):237−240. [CHEN Guan, ZHANG Yan, FENG Wenru, et al. Conformation of Sophora alopecuroides polysaccharide solution[J]. Modern Drugs and Clinics,2015,30(3):237−240. CHEN Guan, ZHANG Yan, FENG Wenru, et al. Conformation of Sophora alopecuroides polysaccharide solution[J]. Modern Drugs and Clinics, 2015, 30(3): 237-240.
[25] GIESE E C, DEKKER R F H, BARBOSA A M, et al. Triple helix conformation of botryosphaeran, a (1→3;1→6)-β-D-glucan produced by Botryosphaeria rhodina MAMB-05[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2008,74(4):953−956. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.04.038
[26] 张子依. 紫甘薯多糖的制备及结构初步分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨商业大学, 2020 ZHANG Ziyi. Study on preparation and structure of sweet potato polysaccharide[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce, 2020.
[27] WANG W, LI X, CHEN K, et al. Extraction optimization, characterization and the antioxidant activities in vitro and in vivo of polysaccharide from Pleurotus ferulae[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,160:380−389. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.158
[28] 张丽, 陈冠华, 方柔, 等. 毛细管电泳法测定过氧化氢酶与天然抗氧化剂协同清除羟自由基作用[J]. 分析化学,2013,41(10):1571−1576. [ZHANG Li, CHEN Guanhua, FANG Rou, et al. Determination of synergistic effect of catalase and natural antioxidants for scavenging hydroxylradical by capillary electrophoresis[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2013,41(10):1571−1576. ZHANG Li, CHEN Guanhua, FANG Rou, et al. Determination of synergistic effect of catalase and natural antioxidants for scavenging hydroxylradical by capillary electrophoresis[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(10): 1571-1576.
[29] 刘刚, 王辉, 张洪. 松茸多糖对D-半乳糖所致小鼠衰老模型的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报,2012,28(10):1439−1442. [LIU Gang, WANG Fang, ZHANG Hong. Anti-aging effect of polysaccharide from tricholomamatsutake on D-galactose-induced aging mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology,2012,28(10):1439−1442. LIU Gang, WANG Fang, ZHANG Hong. Anti-aging effect of polysaccharide from tricholomamatsutake on D-galactose-induced aging mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology, 2012, 28(10): 1439-1442.
[30] GUO Y, PAN D, LI H, et al. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity of selenium exopolysaccharide produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,138(1):84−89. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.029
[31] HERMANN E, JÖRG S R, HELMWARD Z. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes[J]. Pergamon,1991,11(1):81−128.
[32] ZHU S Y, JIANG N, TU J, et al. Antioxidant and anti-aging activities of silybum marianum protein hydrolysate in mice treated with D-galactose[J]. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences,2017,30(9):623−631.
[33] 刘群群, 王燕, 李飞艳, 等. 两地牛蒡根总黄酮的体外和体内抗氧化活性研究[J]. 农产品加工,2021(13):9−16. [LIU Qunqun, WANG Yan, LI Feiyan, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of total flavoniods of burdock root fromtow places in vitro and in vivo[J]. Agricultural Products Processing,2021(13):9−16. LIU Qunqun, WANG Yan, LI Feiyan, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of total flavoniods of burdock root fromtow places in vitro and in vivo[J]. Agricultural Products Processing, 2021, (13): 9-16.
[34] FAN S, XIONG T, LEI Q, et al. Melatonin treatment improves postharvest preservation and resistance of guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.)[J]. Foods,2022,11(3):262.
[35] 申思楠, 牟珍妮, 唐丽, 等. 寿胎丸通过调控Nrf2信号通路减轻人绒毛膜滋养层细胞的氧化损伤治疗复发性流产[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(3):44−51. [SHEN Sinan, Mou Zhenni, Tang L, et al. Shoutai pills can reduce oxidative damage of human chorionic trophoblast cells by regulating Nrf2 signaling pathway to treat recurrent abortion[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulary,2023,29(3):44−51. SHEN Sinan, Mou Zhenni, Tang L, et al. Shoutai pills can reduce oxidative damage of human chorionic trophoblast cells by regulating Nrf2 signaling pathway to treat recurrent abortion[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulary, 2023, 29(3): 44-51.
[36] WEI W, SHURUI C, ZIPENG Z, et al. Aspirin suppresses neuronal apoptosis, reduces tissue inflammation, and restrains astrocyte activation by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway[J]. Neuroreport,2018,29(7):524−531. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000969
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 刘春阳,白金波,杨尚青,史进阳,秦亚敏,吴德玲,解松子. 枳椇子多糖的酸提取工艺优化及其理化性质与抗氧化活性研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(09): 148-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邓钰文,欧阳琳,王珊,谢瑜,廖贻华,彭彩云,龚力民. 黄精药食同源价值研究进展. 湖南中医药大学学报. 2024(05): 912-920 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 何云婧,杨忠琴,亢丽郦,谢永美,王战国,李经中. 模糊数学综合评价法优化黄精山楂果糕制备工艺及品质分析. 中国调味品. 2024(12): 21-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



