Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Bovine Bone Marrow Protein and Its Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties
-
摘要: 探讨牛骨髓蛋白(Bovine bone marrow protein, BBMP)酶解工艺并评价其理化性质和抗氧化活性,挖掘其潜在药用和保健功效物质基础,提升牛骨的综合利用价值。以水解度(DH)、蛋白含量、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼自由基(DPPH·)清除率为评价指标,结合结构表征,筛选最佳酶种。以酶解时间、酶添加量、pH、酶解温度为自变量,采用响应面法优化牛骨髓蛋白的酶解工艺,并研究其酶解物的理化性质和抗氧化活性。结果表明,最适蛋白酶为胃蛋白酶(Bovine bone marrow protein pepsin hydrolysate,BBMP-PH),最佳酶解工艺参数为酶解时间2 h,酶添加量2%,pH为3,酶解温度为37 ℃。在此条件下,DH、蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率分别为36.07%、37.05%及39.57%;四种因素对酶解效率的影响为:加酶量>酶解时间>酶解温度>pH。理化性质实验结果表明,BBMP-PH的等电点在pH6左右,并在等电点处溶解性、乳化性及乳化稳定性、持水性最弱,远离等电点时较高;当pH为2时,BBMP-PH溶解性最好,达94.72%,当pH为8时乳化性及乳化稳定性达1.11 m2/g和101.37%。BBMP-PH具有较强的DPPH·、羟自由基(·OH)、超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)、2, 2’-联氮-双-3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸自由基(ABTS+·)清除能力,半抑制浓度IC50分别为0.65、1.16、0.35、0.57 mg/mL,蛋白浓度为1 mg/mL时,总还原能力为0.88。本文为牛骨髓资源的高值化利用和多肽类功能食品的开发提供一定的参考。Abstract: The enzymatic hydrolysis of bovine bone marrow protein (BBMP) was optimized and its physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities were studied, aimed to explore the material basis of its potential medicinal and health benefits and enhance the comprehensive utilization value of beef bone. The degree of hydrolysis (DH), protein content, and 1,1-diphenyl-2-trinitrophenylhydrazine free radical (DPPH·) scavenging rate were used as evaluation indexes, combined with the results of structural characterization, the suitable enzyme was screened. The response surface methodology was used to the optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of bovine bone marrow protein as the hydrolysis time, enzyme concentration, pH, and temperature were independent variables. Then, the physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of the obtained hydrolysates were investigated. The results showed that pepsin was selected as the optimal protease for the preparation of BBMP pepsin hydrolysate (BBMP-PH). The optimum enzymatic hydrolysis conditions were time 2 h, enzyme concentration 2%, pH3, and temperature of 37 ℃. Under these conditions, the DH, protein content, and DPPH· scavenging rate were 36.07%, 37.05%, and 39.57%, respectively. The effects of four factors on the efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis were ordered as: Enzyme concentration>enzymatic hydrolysis time>enzymatic hydrolysis temperature>pH. The results of physicochemical properties showed that the isoelectric point (pI) of BBMP-PH was about pH6, and the solubility, emulsifying activity, emulsion stability, and water holding capacity of BBMP-PH were up to their lowest value at pI, and the better when far from the pI. When pH was 2, BBMP-PH has the highest solubility (94.72%), whereas pH8 for the emulsifying activity and emulsion stability (1.11 m2/g and 101.37%). BBMP-PH had strong scavenging ability of DPPH·, hydroxyl (·OH), superoxide anion (O2−·), and 2,2'-azo-bis-3-ethyl benzothiazoline 6-sulfonic acid (ABTS+·) free radicals, and the half inhibitory concentration IC50 were 0.65, 1.16, 0.35, 0.57 mg/mL, respectively. When the protein concentration was 1 mg/mL, the total reducing power was 0.88. This paper provides a reference for the high-value utilization of bovine bone marrow resources and the development of peptide-originated functional foods.
-
动物骨骼是一种营养丰富的天然资源,含有蛋白、脂肪、软骨素以及矿物质等成分,且骨蛋白水解物中包括了人体所需的必需氨基酸,是一种优质蛋白来源[1]。近年来,从海洋动物和陆生动物副产物骨骼中制取胶原蛋白和制备活性多肽,并将其用于保健品和化妆品领域的研究逐渐深入,这对全产业链的增值带来便利。同时,骨骼提取物在降血压、免疫调节、骨病治疗、抗菌、抗氧化等活性[2-4]方面的发现促进了相关功能产品的研发和上市。随着保健食品加工技术的进步,越来越多的学者关注着动物骨类蛋白肽与相关产品的生物活性及应用方面的研究。因此,建立骨骼蛋白高值化利用技术评价体系,优化有效成分制备工艺,提高目标产物的含量在畜牧副产物循环利用、健康产品开发及产业链的升级等领域具有重要的意义。
较多研究表明动物骨骼含有丰富的活性胶原蛋白,且不同的畜禽骨骼含有的胶原蛋白含量有一定的差异。刘泓等[5]研究发现牦牛腿骨、黄牛腿骨、猪腿骨及鸡腿骨富含活性蛋白,蛋白含量在79.18%~90.43%范围内。张岩[6]研究得出,经过胰蛋白酶和碱性蛋白酶水解得到的鱿鱼多肽分子量小于经过氨肽酶水解得到的鱿鱼多肽,且抗氧化能力较强。由于胶原蛋白的分子量较大,结构较为复杂,导致其摄入人体后难以发挥本有的营养价值和功能[7]。因此需要对其进行适当的酶解,从而降低分子量。酶解法制备肽被誉为21世纪营养革命的潜在触发器[8]。酶解法具有温和、可控、周期短等特点,能满足食品经济发展和环保的工艺要求,对胶原蛋白的破坏作用相对较少,而且可维持所得胶原蛋白肽的活性。通过酸溶酶法及超声辅助酶法制备的牛骨胶原肽均显出较强的抗氧化活性[9]。同时,多项研究已证实动物来源骨胶原蛋白及肽具有较好的理化性质和抗氧化活性,在食品工业加工中具有较好的应用潜力。然而多数食药加工业通常使用全骨,未能将骨质和骨髓有效地分离,并且动物骨髓有效成分的针对性研究尚处于初步阶段。本课题组前期比较了牛骨质及骨髓的营养成分,得出牛骨髓蛋白含量显著高于其骨质蛋白,牛骨髓蛋白中的氨基酸含量高达466.24 mg/g[10],且含有丰富的Na、K、Ca、P、Mg等常量元素及Fe、Zn等微量元素[11]。目前,较多的研究集中于牛骨胶原蛋白肽的制备及生物活性研究,而对牛骨髓胶原蛋白肽的针对性研究仍然较少。
为了进一步提高牛骨的综合利用率及附加值,本文以牛骨髓为原料,以水解度、蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率为评价指标,结合结构表征筛选出酶解牛骨髓蛋白的最佳酶种,通过响应面法优化酶解工艺,并对其酶解物的理化性质和抗氧化活性进行研究,为后期分离纯化、肽序列鉴定及其食药功能的开发等方面提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
冷冻牛骨 购买于新疆阿勒泰地区,经新疆农业大学食品科学与药学学院巴吐尔·阿不力克木教授鉴定为新疆褐牛腿骨;牛血清蛋白E-BC-K318-M Elabscience公司;考马斯亮蓝G-250 上海蓝季科技发展有限公司;2,2-联苯基-1-苦基肼基自由 上海麦克林生化科技公司;碱性蛋白酶(400 U/mg)、胃蛋白酶(300 U/mg)、木瓜蛋白酶(800 U/mg)、中性蛋白酶(100 U/mg) 华迈科公司;花生油 益海嘉里金龙鱼粮油食品股份有限公司;所有有机溶剂 均为国产分析纯。
FA1004电子天平 常州市幸运电子设备有限公司;DF-101S集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器 上海兴创科学仪器设备有限公司;PHS-3CB pH计 上海越平科学仪器有限公司; BCD-208JDE冷藏冷冻箱 浙江星星冷链集成股份有限公司;T6新世纪紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;RE-52旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器有限公司;SF-TDL-40D离心机 上海菲恰尔分析仪器股份有限公司;XHF-DY高速分散器 宁波新芝生物有限公司;TGL-16M高度冷冻离心机 湖南湘鑫仪器仪表有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品预处理
取出冷冻的牛骨,用锯骨器将牛骨切开,初步洗净,除去骨髓中的残留碎片和多余的肉渣并洗去多余的血迹,将所得的牛骨髓冷冻至−20 ℃下硬化,再放置于捣药罐中按照1:6(g/mL)的固液比加入液氮进行冷冻粉碎,粉末保存在−40 ℃冰箱,备用。
1.2.2 牛骨髓蛋白(Bovine bone marrow protein,BBMP)的提取
参照文献[12]并略作修改,取100 g牛骨髓粉末,以蒸馏水作为溶剂提取BBMP,用磁力搅拌器在45 ℃回流提取3次,三次提取料液比及提取时间分别为1:10、1:7、1:5 g/mL及2、1、0.5 h,合并提取液。用分液漏斗分离油水层,收集水层,用石油醚脱脂3次,水溶液经适当浓缩,透析(3500 Da,48 h),真空冷冻干燥得到牛骨髓蛋白粉末。
1.2.3 酶的筛选
参照文献[9]并略作修改,称取200 mg牛骨髓蛋白粉末,加蒸馏水100 mL,再分别加入四种蛋白酶,酶加量均为2%,于各自最适水解条件水解2 h,各蛋白酶的水解条件见表1。待酶解结束,沸水灭酶15 min,冷却,pH调到7,4000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液测定其各酶解液的水解度、蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率,通过综合评分选择适宜的酶。
表 1 不同蛋白酶水解实验条件Table 1. Experimental conditions for different proteases酶种类 最适温度(℃) pH 加酶量(%) 碱性蛋白酶 55 9 2 胃蛋白酶 37 2 2 木瓜蛋白酶 60 6 2 中性蛋白酶 50 7 2 1.2.4 结构表征
1.2.4.1 紫外光谱(Ultraviolet Spectroscopy,UV)分析
将1 mg/mL的牛骨髓蛋白酶解物溶液在室温条件下用紫外分光光度计于200~400 nm波长范围内进行扫描,以蒸馏水为空白对照[13]。
1.2.4.2 红外光谱(Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy,FTIR)分析
取少量牛骨髓蛋白酶解物,与适量溴化钾混合,用压片法测定其4000~400 cm−1范围内的红外吸收光谱[13]。
1.2.4.3 SDS-PAGE分析
将20 mg/mL的牛骨髓蛋白酶解物溶液与4×蛋白质上样缓冲液3:1比例混合后煮沸5 min,冷却后将15 μL上样。分离胶15%,浓缩胶5%,采用直压恒流电源,75 V开始,在分离0.5 h后,将电压调节到120 V。结束后,用考马斯亮蓝染色2 h,脱色至透明后,拍照并进行观察分析[13]。
1.2.5 单因素实验
按照酶种筛选结果得出胃蛋白酶为最佳酶种,固定因素水平为酶解时间2 h,加酶量2%,pH2,酶解温37 ℃,在上述工艺条件下,通过测定酶解液的水解度、蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率来研究酶解时间(1、2、3、4、5 h)、加酶量(1%、2%、3%、4%、5%)、pH(1、2、3、4、5)、酶解温度(27、32、37、42、47 ℃)等因素对牛骨髓蛋白酶解效果的影响,重复试验3次。
1.2.6 响应面优化试验
根据单因素实验结果,运用Box-Behnken设计原理,以酶解时间(A)、加酶量(B)、pH(C)、酶解温度(D)为变量,进行四因素三水平的响应面试验,因素与水平设计见表2。
表 2 响应面试验因素与水平Table 2. Response surface test factors and levels水平 A 酶解时间(h) B 加酶量(%) C pH D 酶解温度(℃) −1 1 1 2 32 0 2 2 3 37 1 3 3 4 42 1.2.7 指标测定
1.2.7.1 水解度的测定
采用甲醛电位滴定法[14]测定水解度。吸取10 mL灭酶后的水解液于烧杯中,加5滴30%过氧化氢。将烧杯置于磁力搅拌器上,将pH计的电极插入烧杯内试样中适当位置。先用0.1 mol/L氢氧化钠缓慢调节pH至7.5左右,再用0.05 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液调节至pH=8.10,并且保持1 min不变。再缓慢加入15 mL甲醛溶液,反应1 min,用0.05 mol/L氢氧化钠标准溶液滴定至pH=8.10。记录消耗氢氧化钠标准溶液滴定的体积(V1)。按下式(1)计算水解度:
水解度(%)=(V1−V0)×V×C×14.01×6.251000×M×pro×100 (1) 式中:V1为1 mL水解液消耗的氢氧化钠溶液体积,mL;V0为1 mL空白液消耗的氢氧化钠溶液体积,mL;V为配料用水体积,mL;C为滴定用氢氧化钠溶液浓度,mol/L;14.01为氮的摩尔质量,g/mol;6.25为氮换算为蛋白质的系数;M为牛骨髓蛋白水解产物的质量,g;pro为牛骨髓蛋白水解产物的蛋白含量,%。
1.2.7.2 蛋白含量的测定
1 mL不同浓度的(0.1、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1 mg/mL)牛血清蛋白质溶液中分别加入3 mL考马斯亮蓝溶液,避光静置反应5 min,在595 nm处测吸光度。以蛋白浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线[15],得到回归方程:Y=1.0139X+0.692(R2=0.9996)。取浓度为1 mg/mL的样品溶液,按照上述蛋白标准曲线的试验步骤测定其蛋白含量。
蛋白含量(%)=C2C1×100 (2) 式中:C1是样品起始浓度,mg/mL;C2是供试品溶液中蛋白浓度,mg/mL。
1.2.7.3 抗氧化活性的测定
BBMP-PH对1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼自由基(DPPH·)、羟自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、ABTS+自由基清除率及总还原能力的测定采用文献[16-17]的方法,以维生素C为对照品。
1.2.7.4 综合评分的计算
基于综合评分选择适宜的酶,由于贡献值大小未知,因此综合评分设定总值为100%,水解度为主要考察指标占50%,蛋白含量占25%,DPPH·清除率占25%。按下式(3)~(6)计算综合评分:
Y水解度(%)=水解度测定水解度最大值×50% (3) Y蛋白含量(%)=蛋白含量测定蛋白含量最大值×25% (4) YDPPH⋅清除率(%)=DPPH⋅清除率测定DPPH⋅清除率最大值×25% (5) 综合评分=Y水解度+Y蛋白含量+YDPPH⋅清除率 (6) 1.2.7.5 等电点的测定
准确称取牛骨髓蛋白酶解物10 mg于离心管中,溶解于10 mL蒸馏水,加入盐酸(0.5 mol/L)或氢氧化钠(0.5 mol/L)分别调pH(2、4、6、8、10、12),测定不同pH条件下BBMP-PH在660 nm处的透光率,绘制pH与透光率的对应关系图[18]。
1.2.7.6 溶解性的测定
准确称取牛骨髓蛋白酶解物10 mg于离心管中,溶解于10 mL蒸馏水,加入盐酸(0.5 mol/L)或氢氧化钠(0.5 mol/L)分别调pH(2、4、6、8、10、12),混合6 min,离心(3500 r/min)25 min,测定上清液蛋白含量,按下式(7)计算溶解性[18]。
溶解性(%)=M2M1×100 (7) 式中:M1:悬浮液中加入的蛋白含量;M2:离心后上清液蛋白含量。
1.2.7.7 蛋白乳化性和乳化稳定性的测定
参照文献[16]测定其BBMP-PH的乳化性(EAI)与乳化稳定性(ESI)。准确称取牛骨髓蛋白酶解物10 mg于烧杯中,加入10 mL蒸馏水,分别将溶液pH调至2、4、6、8、10、12,再加5 mL花生油,10000 r/min的条件下高速均质2 min。分别在0 min(A0)和静置10 min(A10)时从烧杯底部取50 μL乳浊液与5 mL SDS(1%)溶液混合均匀,在500 nm处测定吸光度。用式(8)、式(9)计算EAI和ESI[18]:
EAI(m2/g)=2×2.303×A0×DFC×Φ(1−θ)×1000 (8) ESI(%)=A10A0×100 (9) 式中:DF为样品稀释倍数;C为蛋白质浓度,mg/mL;Φ为光程,设定为0.01;θ为乳状液的油体积分数,0.25。
1.2.7.8 持水性的测定
准确称取10 mg 牛骨髓蛋白酶解物记录为m0,将样品称入离心管中记录重量为m1,加10 mL蒸馏水溶解,将溶液pH分别调至2、4、6、8、10、12,漩涡混合6 min并于30 ℃恒温箱恒温30 min,离心(4000 r/min、30 min),除去上层清液,称重记为m2,按下式(10)计算持水性[19]。
持水性(g/g)=m2−m1m0 (10) 1.2.7.9 持油性的测定
准确称取10 mg牛骨髓蛋白酶解物记录为m0,将样品称入离心管中记录重量为m1,加入10 mL花生油,再漩涡混合5 min,直到样品持油量达到饱和,静置30 min,离心(4000 r/min、20 min),将上清液的油去掉,称离心管重量记为m2,按下式(11)计算持油性[18]。
持油性(g/g)=m2−m1m0 (11) 1.3 数据处理
每个样品重复测定3次,取平均值,采用SPSS 26.0、Origin 9.0、Design-Expert 8.0.6进行数据处理和分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 蛋白酶的筛选结果
2.1.1 不同酶对牛骨髓蛋白酶解效果的影响
由表3可知,牛骨髓蛋白通过四种蛋白酶进行酶解,结果表明胃蛋白酶水解物的水解度达到31.68%,显著高于木瓜蛋白酶水解物和中性蛋白酶水解物(P<0.05),可能是由于不同蛋白酶对肽键的作用部位不同,所以酶解产物的水解度有所不同[9];碱性蛋白酶水解物的蛋白含量达到38.91%,显著高于胃蛋白酶水解物和中性蛋白酶水解物(P<0.05);胃蛋白酶水解物的DPPH·清除率达到29.85%,显著高于其它三种蛋白酶(P<0.05)。代亚民[20]采用胃蛋白酶酶解牛骨蛋白,水解度仅为14.4%。因此,根据综合评分初步确定胃蛋白酶为最适用酶。
表 3 不同蛋白酶对牛骨髓蛋白酶解效果的影响Table 3. Effect of protease type on hydrolysis efficiency酶种类 水解度(%) 蛋白含量(%) DPPH·清除率(%) 综合评分(%) 碱性蛋白酶 29.75±2.63ab 38.91±2.84a 14.31±4.87c 83.94 胃蛋白酶 31.68±2.28a 24.27±1.73c 29.85±5.09a 90.59 木瓜蛋白酶 24.83±0.29c 37.92±0.44ab 19.64±2.48b 79.99 中性蛋白酶 24.04±2.18bc 33.83±2.62b 20.12±4.78b 76.53 注:同列字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.1.2 紫外光谱分析
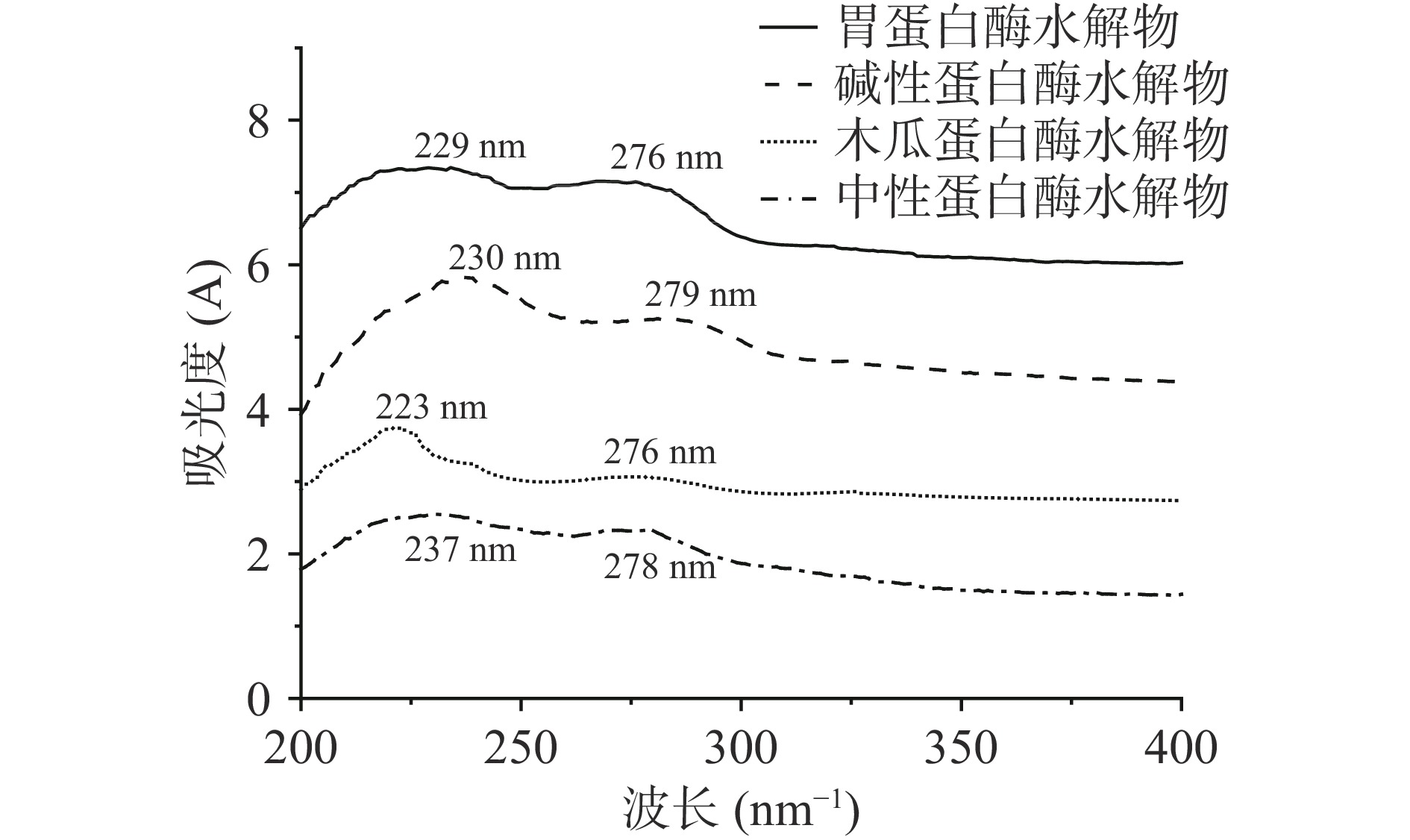
四种蛋白酶水解物的紫外扫描图谱如图1所示。四种蛋白酶水解物分别在229、230、223、237 nm处有最大的吸收峰,均符合胶原蛋白肽的特征吸收峰,280 nm附近也有微弱的吸收峰,说明牛骨髓胶原肽含有一定的酪氨酸[18]。综上,四种蛋白酶能够有效酶解牛骨髓蛋白。
2.1.3 傅里叶红外光谱分析
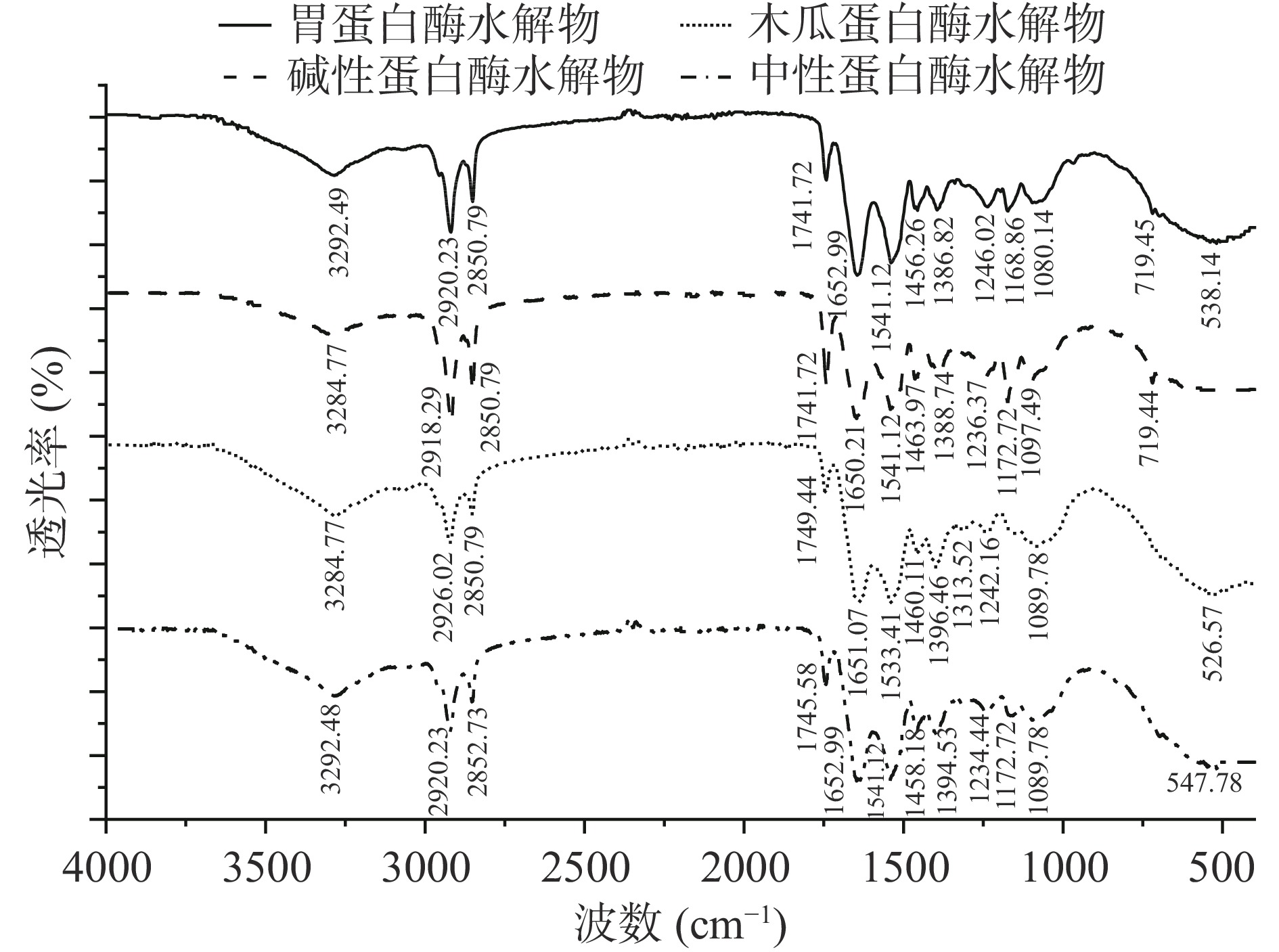
FT-IR是一种常用于阐明蛋白质二级结构官能团的定性分析技术[17],四种蛋白酶水解物的FT-IR光谱图如图2所示。
图2可知,四种蛋白酶水解物均在4000~400 cm−1呈现出蛋白类化合物的特征吸收峰,在3200~3300 cm−1处附近均出现强吸收峰,是典型的因N-H伸缩振动形成的酰胺A带的特征峰;出现在2900~2950 cm−1处的吸收峰是因C-N伸缩振动产生的酰胺B带的特征峰,分别在2924.21、2918.29 cm−1处有吸收峰;1600~1700 cm−1处归属于蛋白酰胺Ⅰ带的吸收峰,由C=O的伸缩振动引起,四种蛋白酶水解物的酰胺Ⅰ带分别在1655.79和1650.21 cm−1;1540和1450 cm−1左右出现的振动是酰胺II带,是由N-H键的面内弯曲振动和C-N键的伸缩振动引起的;在1380.86和1388.74 cm−1处出现的吸收峰是因C-N伸缩振动引起的酰胺Ⅲ带,1239.74和1236.37 cm−1处出现的吸收峰是因N-H面内弯曲振动引起的酰胺Ⅲ带。同时,1646~1664 cm−1处的吸收峰为α螺旋结构的特征峰。综上,牛骨髓蛋白四种蛋白酶水解物均显出了典型的蛋白吸收峰。
2.1.4 SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分析结果
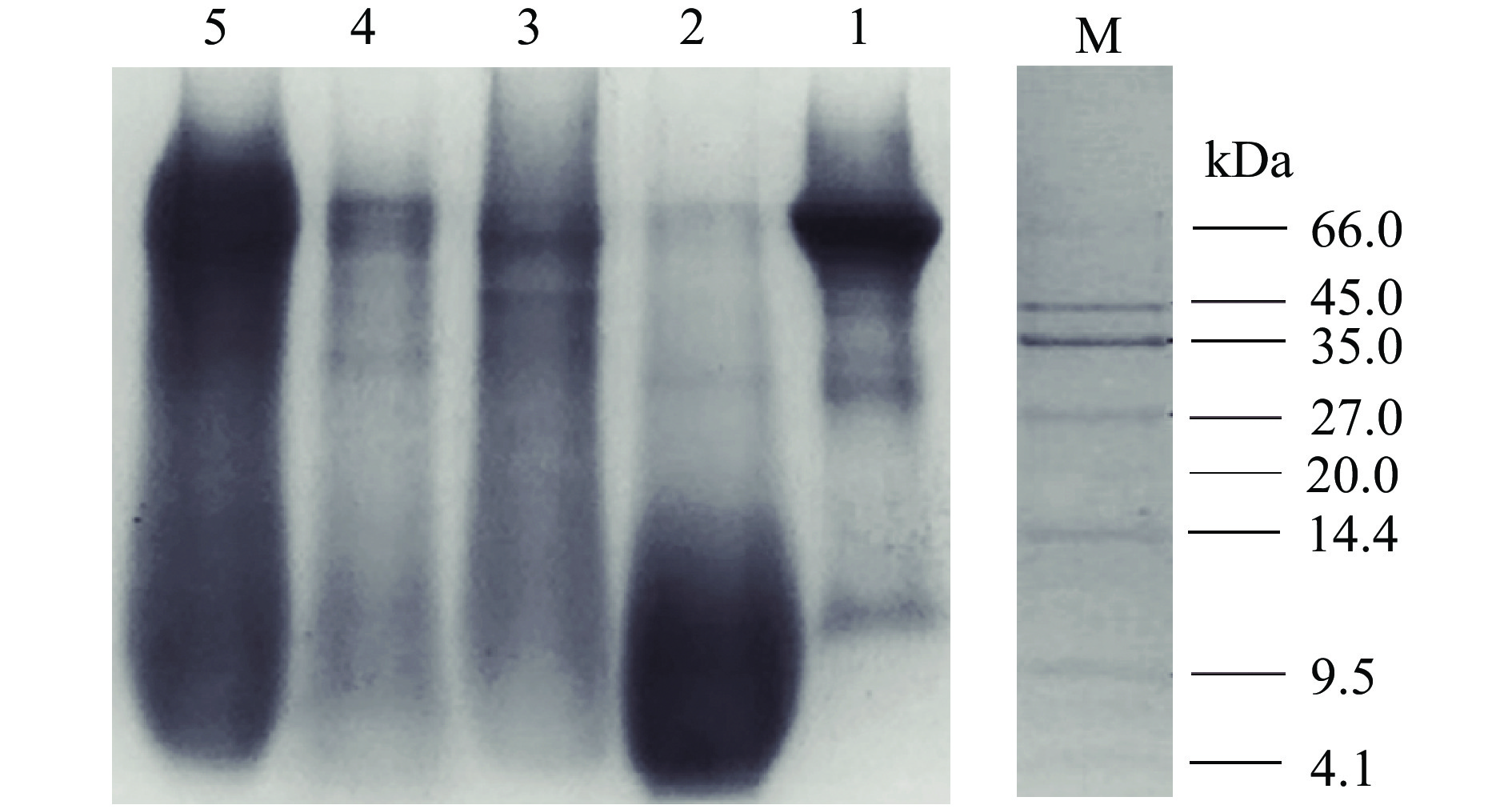
牛骨髓蛋白及其四种蛋白酶水解物的SDS-PAGE结果如图3所示。如图所示,BBMP及其水解物的相对分子质量主要分布在4.1~66.0 kDa。其中,水提蛋白的分子量较大,集中在66.0 kDa左右,也有10 kDa左右的亚基。经酶解处理后,胃蛋白酶水解物分子量降低较明显,肽段亚基降低到4.1~14.4 kDa处,主要在10 kDa以下较为集中。尹玉文等[21]对骨胶蛋白酶处理的牛骨制备酶解液,电泳显示其分子量为7.8~20.1 kDa,本实验得出经胃蛋白酶处理后能够得到分子量更小的牛骨髓胶原多肽。
因此,经结合不同酶种对水解度、蛋白含量、DPPH·清除能力的影响及UV、FT-IR、SDS-PAGE结果,得出胃蛋白酶能够更有效的制备分子量较低的牛骨髓胶原肽。综上,进一步选用响应面法优化BBMP的胃蛋白酶酶解工艺,为其生产应用能提供依据。
2.2 单因素实验结果
2.2.1 酶解时间对BBMP酶解效果的影响
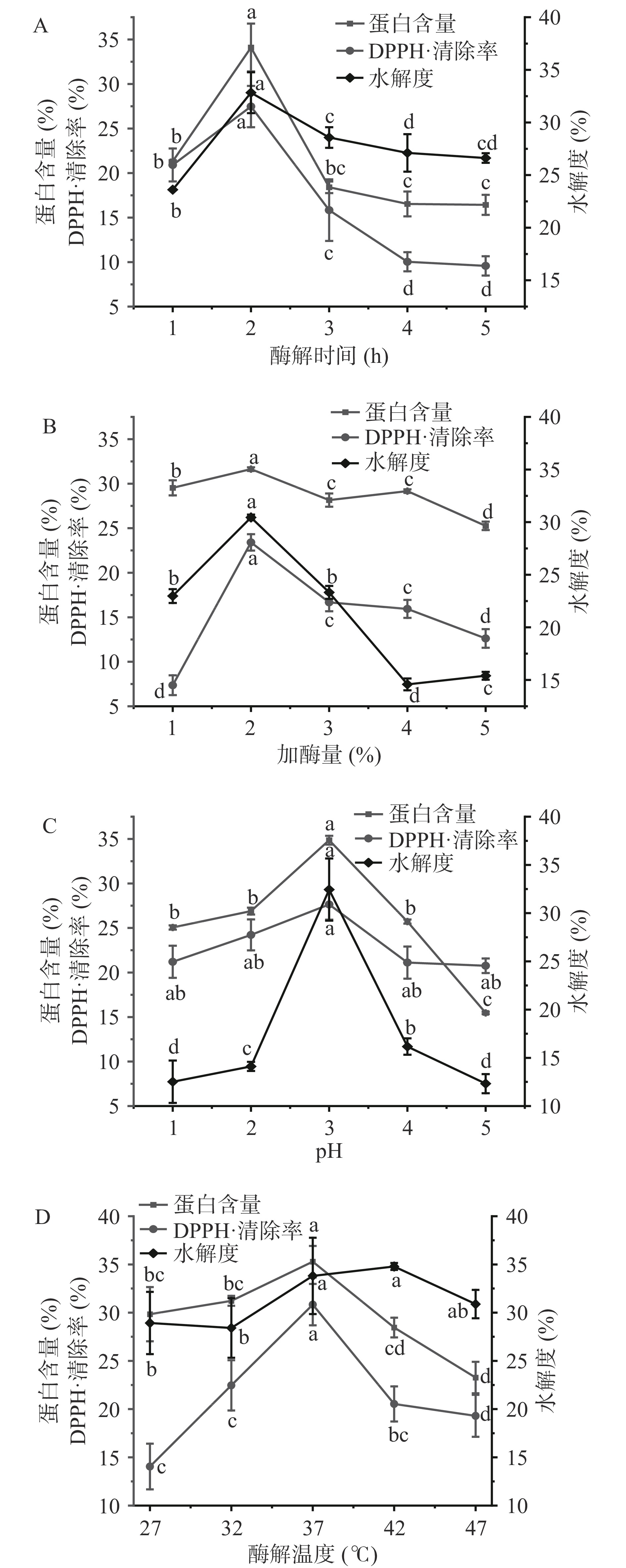
由图4A所示,随着酶解时间的延长,在1~2 h范围内蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率和水解度不断增加,当酶解时间为2 h时,蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率及水解度分别为34.11%、27.47%、32.83%达到最高值(P<0.05)。此后,各指标缓慢下降,可能由于酶解时间过长,导致酶失活。因此,选择1~3 h作为响应面分析的最佳时间范围。
2.2.2 加酶量对BBMP酶解效果的影响
由图4B所示,随着加酶量的增加,蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率和水解度呈现先升高后降低的趋势,加酶量达到2%时蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率及水解度分别为31.64%、23.40%、30.44% 达到最高值(P<0.05)。酶加量过高时可能导致酶解物的进一步降解。因此,选择1%~3%作为响应面分析的最佳酶用量范围。
2.2.3 pH对BBMP酶解效果的影响
由图4C所示,酶解物的蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率和水解度随着pH的增加呈现先升高后降低的趋势,pH为3时蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率及水解度分别为34.86%、27.64%、32.45% 达到最高值(P<0.05)。此后随着pH增加各指标逐渐降低。因此,选择pH2~4作为响应面分析的最佳pH范围。
2.2.4 酶解温度对BBMP酶解效果的影响
由图4D所示,随着酶解温度的升高,酶解物蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率呈现先升高后降低的趋势,水解度呈现平稳的趋势,当温度达到37 ℃时蛋白含量、DPPH·清除率及水解度分别为35.28%、30.83%、33.81% 达到最高值(P<0.05)。考虑到温度的升高导致蛋白质变性及酶失活,选择温度为32~42 ℃作为响应面分析的最佳温度范围。
2.3 Box-Behnken 响应面试验结果
2.3.1 响应面试验结果
响应面优化酶法制备牛骨髓胶原蛋白工艺试验结果见表4。水解度、蛋白含量和抗氧化活性是蛋白酶解的重要属性,对上述3个指标进行综合考虑,分别以水解度、蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率的权重系数设为0.5、0.25、0.25得出综合评分。
表 4 Box-Behnken试验设计及结果Table 4. Box-Behnken design with experimental results实验号 A 酶解
时间B 加
酶量C
pHD 酶解
温度Y1 水解
度(%)Y2 蛋白
含量(%)Y3 DPPH·
清除率(%)Y综合
评分(%)1 −1 −1 0 0 24.18 31.09 12.44 58.37 2 1 −1 0 0 24.79 15.93 29.68 60.10 3 −1 1 0 0 21.32 22.81 11.24 48.74 4 1 1 0 0 17.67 27.82 19.46 52.14 5 0 0 −1 −1 25.47 21.96 16.46 56.75 6 0 0 1 −1 19.57 20.70 27.86 55.23 7 0 0 −1 1 24.55 21.81 20.53 57.93 8 0 0 1 1 15.56 13.47 23.15 42.64 9 −1 0 0 −1 15.18 22.81 16.13 43.75 10 1 0 0 −1 16.74 26.86 26.29 54.47 11 −1 0 0 1 17.18 27.24 12.44 44.89 12 1 0 0 1 22.23 37.31 16.20 62.02 13 0 −1 −1 0 18.19 21.52 20.91 49.74 14 0 1 −1 0 19.41 20.41 15.83 47.55 15 0 −1 1 0 20.56 27.98 12.83 51.97 16 0 1 1 0 16.48 25.91 25.75 53.21 17 −1 0 −1 0 19.94 29.73 12.36 51.97 18 1 0 −1 0 18.85 28.24 11.43 49.06 19 −1 0 1 0 15.60 24.56 27.96 52.57 20 1 0 1 0 16.48 25.91 25.75 53.21 21 0 −1 0 −1 26.93 13.97 29.94 61.80 22 0 1 0 −1 17.87 20.04 11.52 42.71 23 0 −1 0 1 28.42 16.73 33.51 67.63 24 0 1 0 1 19.40 24.38 12.17 47.80 25 0 0 0 0 36.02 38.98 31.56 90.25 26 0 0 0 0 34.89 39.86 41.24 95.21 27 0 0 0 0 32.98 39.78 38.98 91.31 28 0 0 0 0 38.59 35.44 39.51 96.18 29 0 0 0 0 33.67 34.91 31.83 84.82 2.3.2 方差分析
运用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件对表4中综合评分的数据进行统计分析后进行多元回归拟合,得到二次回归方程Y=91.55+2.81A–4.79B−0.096C+0.68D+0.42AB+0.13AC+1.60AD+0.86BC−0.18BD−3.44CD−19.88A2−18.19B2−21.06C2−18.71D2。
综合评分回归方程方差分析结果见表5,方程因变量与自变量之间的线性关系明显,回归模型极显著(P<0.01),失拟项不显著,回归系数R2=0.9203,说明该模型与试验拟合良好,以综合评分为响应值所建立的酶法制备牛骨髓胶原肽工艺模型是合理的。通过方差分析结果可以发现,B、A2、B2、C2、D2均对Y影响显著(P<0.05),表明酶解时间、酶添加量、pH、酶解温度对酶法制备牛骨髓胶原蛋白的水解度、蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率均有一定的影响。F值的大小反映因素对试验指标(因变量)的重要程度为,FB>FA>FD>FC。
表 5 回归模型方差分析Table 5. Analysis of variance of regression equation方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 Sig 模型 6743.90 14 481.71 11.55 <0.0001 ** A-酶解时间 94.98 1 94.98 2.28 0.1535 B-酶添加量 275.17 1 275.17 6.60 0.0223 * C- pH 0.11 1 0.11 2.651E−003 0.9597 D-酶解温度 5.61 1 5.61 0.13 0.7193 AB 0.69 1 0.69 0.017 0.8994 AC 0.068 1 0.068 1.638E−003 0.9683 AD 10.30 1 10.30 0.25 0.6270 BC 2.96 1 2.96 0.071 0.7939 BD 0.13 1 0.13 3.171E−003 0.9559 CD 47.38 1 47.38 1.14 0.3045 A2 2562.72 1 2562.72 61.44 <0.0001 ** B2 2146.37 1 2146.37 51.46 <0.0001 ** C2 2877.15 1 2877.15 68.98 <0.0001 ** D2 2269.87 1 2269.87 54.42 <0.0001 ** 残差 583.92 14 41.71 失拟项 502.04 10 50.20 2.45 0.2008 不显著 纯误差 81.88 4 20.47 注:*P<0.05为差异显著,**P<0.01为差异极显著。 各因素影响综合评分的交互作用见图5。图5中酶解时间、酶添加量、pH、酶解温度两两交互作用的等高线接近椭圆,说明交互作用明显。
2.3.3 最优工艺确定及验证试验
经Design-Expert 8.0.6软件分析,最终得到最优酶解工艺为酶解时间2.04 h、酶添加量1.92%、pH2.95、酶解温度37.23 ℃,此时预测的水解度、蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率分别为35.47%、37.68%及37.13%。考虑到实际运用时的可操作性,将酶解工艺参数修正为酶解时间2 h、酶添加量2%、pH3、酶解温度37 ℃,做3次平行试验进行验证,得到的水解度为36.07%±1.17%、蛋白含量为37.05%±1.29%、DPPH·清除率为39.57%±1.69%,此结果与预测值接近,说明水解度、蛋白含量及DPPH·清除率为指标,采用响应面法对胃蛋白酶酶解牛骨髓蛋白工艺条件进行优化是行之有效的。
2.4 牛骨髓蛋白酶解物的理化特性
2.4.1 等电点分析
胶原蛋白是一种两性电解质,等电点与其结构有着密切的关系,尤其是与其侧链上的酸性和碱性氨基酸数量有关[22]。胶原蛋白在等电点时,分子之间没有静电排斥,导致溶液的浑浊程度增加,透光率降低[16]。如图6A所示,BBMP-PH在不同的pH条件下透光率呈现先降低后升高的趋势,当pH为6时最低为19.57%。因此,可初步推断BBMP-PH的等电点在pH6左右。冯建慧等[23]研究报道采用酸法和酶法提取的鲢鱼鱼皮和鱼骨胶原蛋白的等电点在pH6.7左右,与本实验结果相似。
2.4.2 溶解性分析
如图6B所示,BBMP-PH的pH偏酸或偏碱时,溶解性较好。当pH为6时溶解性最低为79.02%,这是由于等电点附近的蛋白分子表面电荷几乎为零,极易导致蛋白颗粒聚集,溶解性降低并形成沉淀[24],这与杨恒[25]报道的鸡肺胶原蛋白在等电点附近溶解度最小,偏离等电点溶解度增大的结果一致。当pH为2时,BBMP-PH溶解性达到94.72%,表明在酸性环境中的溶解性高于碱性环境,可能是因为酸性环境有利于蛋白质与水的相互作用,结果与张鑫[26]研究的牛鼻胶原蛋白在酸性环境中的溶解度较高一致。
2.4.3 乳化性及乳化稳定性的分析
蛋白质在界面上的吸附能力对食品加工中乳剂的形成和稳定起着重要的作用[26]。如图6C,BBMP-PH的乳化性及乳化稳定性均随pH的增加先降后升再降,当pH在等电点6时最低为0.27 m2/g和69.23%,和溶解性表现出相似的曲线图,在等电点附近乳化性及乳化稳定性较差。当pH为8时乳化性和乳化稳定性最高1.11 m2/g和101.37%,与乌日古莫乐[27]报道吉尔利阁蒙古牛骨胶原蛋白在pH为8时乳化性及乳化稳定性最好的结果相似。
2.4.4 持水性的分析
如图6D所示,BBMP-PH的持水性呈现出先降后升的变化,强碱性环境下持水性下降。当pH达到等电点时持水性最低为3.81 g/g,这是由于蛋白质在等电点的总电荷值为零,分子之间的交互作用最强,结合和收缩蛋白的水化和膨胀率最低[28]。在pH8时,BBMP-PH的持水性最高为4.59 g/g,是因为远离等电点后蛋白间的相互作用变小,结合水的能力增大,表现为持水性增强[29]。
2.4.5 持油性的分析
BBMP-PH的持油性为13.65 g/g,大于驼掌胶原蛋白(6.22 g/g),可作为优良的蛋白质补充剂。
2.5 牛骨髓蛋白酶解物的抗氧化活性
2.5.1 DPPH·清除能力
DPPH为测定物质体外抗氧化活性的重要指标[30],不同浓度的BBMP-PH与维生素C对DPPH·清除能力如图7A所示。在0.1~1.0 mg/mL范围内,清除能力与浓度均呈正比关系。当浓度1 mg/mL时清除率达到69.93%,其半抑制浓度IC50值为0.65 mg/mL。郭佳俊等[31]利用碱性蛋白酶提取牛骨胶原蛋白肽的DPPH·清除率为37.33%,其清除能力显著小于BBMP-PH。
2.5.2 羟自由基(·OH)清除能力
·OH是体内产生的活性氧,能带给细胞很大的伤害,因此清除·OH是很有必要的[32]。如图7B所示,BBMP-PH在0.1~1.0 mg/mL浓度范围内的·OH清除能力随着浓度的升高逐渐增强,其半抑制浓度IC50值为1.16 mg/mL。魏洁琼等[9]比较了不同蛋白酶对牛骨胶原蛋白肽酶解效果的影响,得出浓度为5 mg/mL时碱性蛋白酶处理后的牛骨蛋白酶解物对·OH清除率达到70.86%。本研究中,经胃蛋白酶水解所得的BBMP-PH在浓度为1 mg/mL时,对·OH的清除能力达到51.23%,表明其具有较强的清除·OH的能力。
2.5.3 超氧阴离子自由基(O2−·)清除能力
如图7C所示, BBMP-PH在0.1~1.0 mg/mL浓度范围内随着浓度的增高,O2−·清除率也增高,当浓度为1.0 mg/mL时,BBMP-PH的O2−·清除率达到最高值为66.92%,其半抑制浓度IC50值为0.35 mg/mL。郭佳俊等[31]研究表明,酶解法提取的牛骨胶原蛋白肽浓度为5 mg/mL对O2−·的清除率为64.74%,由此可知,BBMP-PH的O2−·清除率高于牛骨蛋白酶解产物。
2.5.4 ABTS+·清除能力
如图7D所示,BBMP-PH在0.1~1.0 mg/mL浓度范围内随着浓度的增高,ABTS+·清除率也增高。当浓度为1 mg/mL时,清除率达到 62.16%。徐红萍等[33]经超声波辅助酶解制备东海海参胶原蛋白低聚肽,当低聚肽浓度为8 mg/mL,其对ABTS+·的清除率达87.20%。本研究结果得出BBMP-PH清除ABTS+·的IC50值为0.57 mg/mL,说明具有较强的抗氧化活性。
2.5.5 总还原能力
生物大分子化合物的总还原能力与抗氧化活性之间具有显著的相关性[34]。如图7E所示,0.1~1.0 mg/mL浓度范围内BBMP-PH总还原能力明显低于阳性对照维生素C。当浓度1.0 mg/mL时BBMP-PH总还原能力最高为0.88,表明被测蛋白的总还原能力较弱。随着浓度的升高BBMP-PH总还原能力有所提高。
3. 结论
胃蛋白酶较适合于牛骨髓蛋白的酶解,酶解后理化性质及抗氧化活性进一步增强。最优条件为:酶解时间2 h、酶添加量2%、pH3、酶解温度37 ℃,此时胶原肽的水解度为36.07%、蛋白含量为37.05%、DPPH·清除率为39.57%。pH对牛骨髓胶原蛋白溶解性、乳化性、乳化稳定性及持水性的影响较为显著。当pH接近其等电点时,BBMP-PH的溶解性、乳化性及乳化稳定性、持水性最低。BBMP-PH在非等电点的酸性和碱性条件下的理化特性相应得到提升,随pH的增大其乳化性及乳化稳定性、持水性提高,当pH为8时乳化性及乳化稳定性达到1.11 m2/g和101.37%,持水性最高为4.59 g/g,持油性为13.65 g/g。抗氧化实验结果显示,BBMP-PH对DPPH·、·OH、O2−·、ABTS+·均具有清除能力和还原能力,且呈剂量效应关系。酶解处理可有效提高牛骨髓蛋白的理化特性及抗氧化能力,进一步扩大其在食品、医药等领域的开发应用范围。
-
表 1 不同蛋白酶水解实验条件
Table 1 Experimental conditions for different proteases
酶种类 最适温度(℃) pH 加酶量(%) 碱性蛋白酶 55 9 2 胃蛋白酶 37 2 2 木瓜蛋白酶 60 6 2 中性蛋白酶 50 7 2 表 2 响应面试验因素与水平
Table 2 Response surface test factors and levels
水平 A 酶解时间(h) B 加酶量(%) C pH D 酶解温度(℃) −1 1 1 2 32 0 2 2 3 37 1 3 3 4 42 表 3 不同蛋白酶对牛骨髓蛋白酶解效果的影响
Table 3 Effect of protease type on hydrolysis efficiency
酶种类 水解度(%) 蛋白含量(%) DPPH·清除率(%) 综合评分(%) 碱性蛋白酶 29.75±2.63ab 38.91±2.84a 14.31±4.87c 83.94 胃蛋白酶 31.68±2.28a 24.27±1.73c 29.85±5.09a 90.59 木瓜蛋白酶 24.83±0.29c 37.92±0.44ab 19.64±2.48b 79.99 中性蛋白酶 24.04±2.18bc 33.83±2.62b 20.12±4.78b 76.53 注:同列字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 4 Box-Behnken试验设计及结果
Table 4 Box-Behnken design with experimental results
实验号 A 酶解
时间B 加
酶量C
pHD 酶解
温度Y1 水解
度(%)Y2 蛋白
含量(%)Y3 DPPH·
清除率(%)Y综合
评分(%)1 −1 −1 0 0 24.18 31.09 12.44 58.37 2 1 −1 0 0 24.79 15.93 29.68 60.10 3 −1 1 0 0 21.32 22.81 11.24 48.74 4 1 1 0 0 17.67 27.82 19.46 52.14 5 0 0 −1 −1 25.47 21.96 16.46 56.75 6 0 0 1 −1 19.57 20.70 27.86 55.23 7 0 0 −1 1 24.55 21.81 20.53 57.93 8 0 0 1 1 15.56 13.47 23.15 42.64 9 −1 0 0 −1 15.18 22.81 16.13 43.75 10 1 0 0 −1 16.74 26.86 26.29 54.47 11 −1 0 0 1 17.18 27.24 12.44 44.89 12 1 0 0 1 22.23 37.31 16.20 62.02 13 0 −1 −1 0 18.19 21.52 20.91 49.74 14 0 1 −1 0 19.41 20.41 15.83 47.55 15 0 −1 1 0 20.56 27.98 12.83 51.97 16 0 1 1 0 16.48 25.91 25.75 53.21 17 −1 0 −1 0 19.94 29.73 12.36 51.97 18 1 0 −1 0 18.85 28.24 11.43 49.06 19 −1 0 1 0 15.60 24.56 27.96 52.57 20 1 0 1 0 16.48 25.91 25.75 53.21 21 0 −1 0 −1 26.93 13.97 29.94 61.80 22 0 1 0 −1 17.87 20.04 11.52 42.71 23 0 −1 0 1 28.42 16.73 33.51 67.63 24 0 1 0 1 19.40 24.38 12.17 47.80 25 0 0 0 0 36.02 38.98 31.56 90.25 26 0 0 0 0 34.89 39.86 41.24 95.21 27 0 0 0 0 32.98 39.78 38.98 91.31 28 0 0 0 0 38.59 35.44 39.51 96.18 29 0 0 0 0 33.67 34.91 31.83 84.82 表 5 回归模型方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of variance of regression equation
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 Sig 模型 6743.90 14 481.71 11.55 <0.0001 ** A-酶解时间 94.98 1 94.98 2.28 0.1535 B-酶添加量 275.17 1 275.17 6.60 0.0223 * C- pH 0.11 1 0.11 2.651E−003 0.9597 D-酶解温度 5.61 1 5.61 0.13 0.7193 AB 0.69 1 0.69 0.017 0.8994 AC 0.068 1 0.068 1.638E−003 0.9683 AD 10.30 1 10.30 0.25 0.6270 BC 2.96 1 2.96 0.071 0.7939 BD 0.13 1 0.13 3.171E−003 0.9559 CD 47.38 1 47.38 1.14 0.3045 A2 2562.72 1 2562.72 61.44 <0.0001 ** B2 2146.37 1 2146.37 51.46 <0.0001 ** C2 2877.15 1 2877.15 68.98 <0.0001 ** D2 2269.87 1 2269.87 54.42 <0.0001 ** 残差 583.92 14 41.71 失拟项 502.04 10 50.20 2.45 0.2008 不显著 纯误差 81.88 4 20.47 注:*P<0.05为差异显著,**P<0.01为差异极显著。 -
[1] 任戈一, 马雪莲, 潘丽, 等. 不同提取工艺下牛骨胶原蛋白的结构特性[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(14):27−33. [REN G Y, MA X L, PAN L, et al. Structural characteristics of bovine bone collagen under different extraction processes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(14):27−33. REN G Y, MA X L, PAN L, et al. Structural characteristics of bovine bone collagen under different extraction processes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(14): 27-33.
[2] 鲁速. 牛骨胶原蛋白肽功效研究进展[J]. 现代养生,2021,21(14):7−10. [LU S. Research progress on the efficacy of bovine bone collagen peptide[J]. Modern Health Preservation,2021,21(14):7−10. LU S. Research progress on the efficacy of bovine bone collagen peptide[J]. Modern Health Preservation, 2021, 21(14): 7-10.
[3] HU G H, WANG D B, SUN L N, et al. Isolation, purification and structure identification of a calcium-binding peptide from sheep bone protein hydrolysate[J]. Foods,2022,11(17):2655. doi: 10.3390/foods11172655
[4] 凌嘉阳, 曾晓房. 畜禽类骨胶原蛋白及其肽的研究进展[J]. 肉类工业,2021(6):51−57. [LING J Y, ZENG X F. Research progress of animal bone collagen like protein and its peptide[J]. Meat Industry,2021(6):51−57. LING J Y, ZENG X F. Research progress of animal bone collagen like protein and its peptide[J]. Meat Industry, 2021(6): 51-57.
[5] 刘泓, 郭玉杰, 许雄. 不同畜禽骨蛋白肽的制备、理化特性表征及其生物活性[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(13):2629−2642. [LIU H, GUO Y J, XU X, et al. Preparation, physicochemical characterization and biological activity of different animal bone protein peptides[J]. China Agricultural Sciences,2022,55(13):2629−2642. LIU H, GUO Y J, XU X, et al. Preparation, physicochemical characterization and biological activity of different animal bone protein peptides [J] China Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 55 (13): 2629-2642.
[6] 张岩. 鱿鱼多肽的制备及其美拉德产物抗氧化活性研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2019 ZHANG Y. Study on the preparation of squid peptides and the antioxidant activity of Maillard products [D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2019.
[7] 叶孟亮. 牦牛骨胶原蛋白肽抗骨质疏松作用机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2019 YE M L. Study on the anti osteoporosis mechanism of yak bone collagen peptide[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019.
[8] YAO Y M, WANG M Y, LIU Y, et al. Insights into the improvement of the enzymatic hydrolysis of bovine bone protein using lipase pretreatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,302:125199.
[9] 魏洁琼, 余群力, 韩玲, 等. 牛骨胶原蛋白肽制备工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2020,55(5):203−211. [WEI J J, YU Q L, HAN L, et al. Optimization of preparation process and analysis of antioxidant activity of bovine bone collagen peptide[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University,2020,55(5):203−211. WEI J J, YU Q L, HAN L, et al. Optimization of preparation process and analysis of antioxidant activity of bovine bone collagen peptide[J]. Lanzhou: Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 2020, 55 (5): 203-211.
[10] 帕尔哈提·柔孜, 帕丽达·买买提, 高彦华. 4种动物骨骼氨基酸组成及其营养价值评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(11):144−151. [PAERHATI R Z, PALIDA M M T, GAO Y H, et al. Analysis of amino acids composition and nutrition evaluation of 4 types of animals bone[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(11):144−151. PAERHATI R Z, PALIDA M M T, GAO Y H, et al. Analysis of amino acids composition and nutrition evaluation of 4 types of animals bone[J]. Food Research and Development, 2018, 39(11): 144-151.
[11] 帕尔哈提·柔孜, 艾合米丁·外力, 陈志慧, 等. 新疆 4 种动物骨质和骨髓中蛋白、常量及微量元素比较分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(12):39−46. [PAERHATI R Z, AIHEMIDING W L, CHEN ZH H, et al. Comparative analysis of protein, major and trace elements in bone and bone marrow of 4 kinds of animals in Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2018,24(12):39−46. PAERHATI R Z, AIHEMIDING W L, CHEN ZH H, et al. Comparative analysis of protein, major and trace elements in bone and bone marrow of 4 kinds of animals in Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2018, 24(12): 39-46.
[12] 吾哈丽妮萨·麦麦提托合提, 帕尔哈提·柔孜, 杨晓君, 等. 响应面优化马骨髓蛋白的提取工艺及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(12):151−159. [WUHALINISA M M T T H T, PAERHATI R Z, YANG X J, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of horse bone marrow protein by response surface methodology[J]. Food Industry Technology,2021,42(12):151−159. WUHALINISA M M T T H T, PAERHATI R Z, YANG X J, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of horse bone marrow protein by response surface methodology[J]. Food Industry Technology, 2021, 42(12): 151-159.
[13] 赵熙成. 延边黄牛骨胶原蛋白肽的制备、结构表征及体外功效作用[D]. 吉林: 延边大学, 2021 ZHAO X CH. Preparation, structural characterization and in vitro efficacy of Yanbian cattle bone collagen peptide[D]. Jilin: Yanbian University, 2021.
[14] 刘丽红, 雷清华. 茚三酮比色法与甲醛滴定法测定棉籽粕蛋白水解度的比较[J]. 化学工程与装备,2012(11):160−163. [LIU L H, LEI Q H. Comparison of ninhydrin colorimetric method and formaldehyde titration method for determining the degree of hydrolysis of cottonseed meal protein[J]. Chemical Engineering and Equipment,2012(11):160−163. LIU L H, LEI Q H. Comparison of ninhydrin colorimetric method and formaldehyde titration method for determining the degree of hydrolysis of cottonseed meal protein[J]. Chemical Engineering and Equipment, 2012 (11): 160-163.
[15] 则拉莱·司玛依, 帕尔哈提·柔孜, 吾哈丽妮萨·麦麦提托合提, 等. 三种甘草种子蛋白的提取方法、结构及抗氧化活性比较研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(18):227−234. [ZELALAI S M Y, PAERHATI R Z, WUHALINISA M M T T H T, et al. Comparative study on extraction methods, structures and antioxidant activities of three Glycyrrhiza seed protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(18):227−234. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.029069 ZELALAI S M Y, PAERHATI R Z, WUHALINISA M M T T H T, et al. Comparative study on extraction methods, structures and antioxidant activities of three Glycyrrhiza seed protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(18): 227-234. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.029069
[16] ROZI P, ABDUWAILI A, MUTAILIFU P, et al. Sequential extraction, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,131:97−106. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.029
[17] WU SH ZH, HE ZH P, WANG Q Q, et al. Response surface optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of peptides of chinese pecan (Carya cathayensis) and analysis of their antioxidant capacities and structures[J]. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics,2021,27:1239−1251. doi: 10.1007/s10989-021-10164-5
[18] 宋乐. 驼掌胶原蛋白的提取及其理化性质研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2020 SONG L. Study on extraction and physicochemical properties of camel palm collagen[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2020.
[19] HOU H, LI B, ZHANG Z, et al. Moisture absorption and retention properties, and activity in alleviating skin photodamage of collagen polypeptide from marine fish skin[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,135(3):1432−1439. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.009
[20] 代亚民. 牛骨的酶解条件与酶解物抗氧化活性的研究[D]. 成都: 西华大学, 2013 DAI Y M. Study on enzymatic hydrolysis conditions of beef bone and antioxidant activity of enzymatic hydrolysates[D]. Chengdu: Xihua University, 2013.
[21] 尹玉文, 高鸣阳, 张艳森, 等. 响应面法优化提取牛骨蛋白酶解物及其对酵母增殖的影响[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(6):34−38. [YIN Y W, GAO M Y, ZHANG Y S, et al. Optimization of extraction of bovine bone hydrolysate by response surface methodology and its effect on yeast proliferation[J]. Food Industry,2022,43(6):34−38. YIN Y W, GAO M Y, ZHANG Y S, et al. Optimization of extraction of bovine bone hydrolysate by response surface methodology and its effect on yeast proliferation[J]. Food Industry, 2022, 43(6): 34-38.
[22] 吴坤远. 马面鲀鱼皮胶原结构、功能及流变性能的研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2020 WU K Y. Studies on the structure, function and rheological properties of collagen from the skin of puffer fish [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2020.
[23] 冯建慧, 吴晓洒, 蔡路昀, 等. 鲢鱼鱼皮和鱼骨胶原蛋白的提取及理化性质分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2017,17(7):102−108. [FENG J H, WU X S, CAI L Y, et al. Extraction and physicochemical properties analysis of silver carp skin and bone collagen[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2017,17(7):102−108. FENG J H, WU X S, CAI L Y, et al. Extraction and physicochemical properties analysis of silver carp skin and bone collagen[J]. Chinese Journal of Food, 2017, 17 (7): 102-108.
[24] DAI L, GUO N, LIU Y, et al. Analysis of the binding sites with NL-101 to amino acids and peptides by HPLC/MS/MS[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters,2019,30(1):103−106. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.12.023
[25] 杨恒. 超声辅助对鸡肺胶原蛋白提取工艺、理化性质及其酶解产物抗氧化活性的影响[D]. 南京: 南京财经大学, 2020 YANG H. Effects of ultrasound on extraction process, physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of chicken lung collagen[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Finance and Economics, 2020.
[26] 张鑫. 牛胶原蛋白的功能特性及多肽的抗氧化活性研究[D]. 济南: 齐鲁工业大学, 2021 ZHANG X. Functional properties of bovine collagen and antioxidant activity of polypeptides[D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Technology, 2021.
[27] 乌日古莫乐. 吉尔利阁蒙古牛骨胶原蛋白的提取及理化特性研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2015 WURIGUMOLE. Study on extraction of collagen from Gi Er Li Go Mongolia bovine bone and its physical and chemical properties[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2015.
[28] 安兆祥, 蔡志鹏, 黄占旺, 等. 黑木耳蛋白提取工艺优化及其功能特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(18):157−166. [AN Z X, CAI Z P, HUANG Z W, et al. Optimization of the extraction process of Auricularia auricula protein and its functional properties[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(18):157−166. AN Z X, CAI Z P, HUANG ZH W, et al. Optimization of the extraction process of Auricularia auricula protein and its functional properties [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2021, 42 (18): 157-166.
[29] BIKAKI M, SHAH R, MULLR A, et al. Heat induced hydrolytic cleavage of the peptide bond in dietary peptides and proteins in food processing[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,357:129621. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129621
[30] XIAO J X, LI Y F, CHEN B B, et al. Enzymatic preparation and antioxidative activity of hydrolysate from rice bran protein[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2020,14(6):3163−3174. doi: 10.1007/s11694-020-00563-5
[31] 郭佳俊, 袁江涛, 刘贵珊. 牛骨胶原蛋白肽的超声辅助提取及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(10):185−192. [GUO J J, YUAN J T, LIU G S. Ultrasonic assisted extraction and antioxidant activity of bovine bone collagen peptide[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(10):185−192. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.031714 GUO J J, YUAN J T, LIU G SH. Ultrasonic assisted extraction and antioxidant activity of bovine bone collagen peptide[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(10):185-192. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.031714
[32] ZHU K, ZHOU H, QIAN H. Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase[J]. Process Biochemistry,2006,41(6):1296−1302. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.12.029
[33] 徐红萍, 谢辉, 梁建灏, 等. 超声波辅助酶解制备东海海参胶原蛋白低聚肽及其活性的研究[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2018,37(5):388−393. [XU H P, XIE H, LIANG J H, et al. Preparation and activity of collagen oligopeptides from Holothurian sea cucumber by ultrasonic assisted enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science Edition),2018,37(5):388−393. XU H P, XIE H, LIANG J H, et al. Preparation and activity of collagen oligopeptides from Holothurian sea cucumber by ultrasonic assisted enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 37 (5): 388-393.
[34] ABDUWAILI A, ROZI P, MUTAILIFU P, et al. Effects of different extraction techniques on physicochemical properties and biological activities of polysaccharides from Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk[J]. Process Biochemistry,2019,83:189−197. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.05.020





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



