Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation on Main Components and Fingerprint of Panax notoginseng Powder
-
摘要: 为探究电子束辐照灭菌对三七粉品质的影响,以三七粉为实验对象,研究不同辐照剂量(0、2、4、6、8、13 kGy)对其微生物数量、水分、灰分、醇溶性浸出物、主要活性成分、抗氧化能力及指纹图谱的影响。结果表明:电子束辐照能有效杀灭三七粉中的微生物,需氧菌总数的杀菌剂量的D10为2.04 kGy,当辐照剂量为4 kGy时微生物数量降至检测标准限度以下,抗氧化能力显著提高(P<0.05),水分、灰分、醇溶性浸出物、色泽、三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rb1、人参皂苷Rg1、指纹图谱等无明显变化(P>0.05)。因此,电子束辐照是一种有效的三七粉灭菌方式,13 kGy以内剂量的电子束辐照不会对其质量显著影响,且能提高其抗氧化活性。本研究为电子束辐照技术在三七粉及以三七粉为原料的其他加工产品中的质量控制提供理论参考。Abstract: In order to explore the effect of electron beam irradiation sterilization on the quality of Panax notoginseng powder, the effects of different irradiation doses (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 13 kGy) on the number of microorganisms, moisture content, total ash, alcohol-soluble extracts, active ingredients, the antioxidant capacity and fingerprint of Panax notoginseng powder were investigated. The results showed that electron beam irradiation could effectively kill microorganisms in Panax notoginseng powder, the D10 value of total aerobic microbial count was 2.04 kGy, and the number of microorganisms fell below the detection standard limit when the irradiation dose was 4 kGy. The antioxidant capacity was significantly improved (P<0.05). The moisture content, total ash, alcohol-soluble extracts, color, notoginsenoside R1, ginsenoside Rb1, ginsenoside Rg1 and fingerprint had no significant change. Therefore, electron beam irradiation was an effective sterilization method for Panax notoginseng powder. The dose of electron beam irradiation within 13 kGy did not significantly affect the quality of Panax notoginseng powder, and could improved its antioxidant activity. This study would provide a theoretical reference for the quality control of Panax notoginseng powder and other processed products based on the electron beam irradiation technology.
-
三七在《中国药典》2020版中定义为五加科植物三七Pananx notoginseng(Burk)F.H.Chen的干燥根和根茎[1]。根据现代药理研究表明,三七具有活血[2]、抗氧化[3]、止血[4]、抗炎[5]、保护神经[6]、抗肿瘤[7]、免疫调节[8]等作用。卫生部在2020年允许三七添加在保健食品当中;三七在2012年被国家食品药品监督管理局列入“可用于保健食品的物品名单”[9],在医药、保健、食品等多方面应用广泛。
然而,三七的根茎在土壤内,根茎生长不规则,表面有很多褶皱,导致微生物数量较多,三七粉在制作过程中也容易造成微生物污染,因此三七分的微生物控制是保证三七粉质量的一项重要因素[10]。目前三七粉常用的灭菌方式有湿热灭菌[11]、硫磺熏蒸、60Co-γ辐照灭菌[12]等,但高温会引起三七内皂苷含量的下降[13],硫磺熏蒸等存在熏蒸过度、影响药效等隐患。因此,选择一种绿色高效、处理过程温度变化较小的灭菌工艺来杀灭三七微生物是至关重要的。辐照作为一种冷杀菌技术,在市面上的运用越来越广泛。与60Co-γ射线相比电子束具有成本低、效率高、剂量控制更精确等优点,广泛用于食品、医药方面的辐照加工[14]。电子束辐照不会产生放射性,是利用电能产生电子束流发挥作用,用于食品上更容易让大众接受,虽然电子束的穿透力较60Co-γ射线更弱,但随着电子加速器设备的不断发展与完善,以及辐照方式的不断优化,电子束辐照有逐步取代60Co-γ射线辐照成为主流辐照技术的趋势[14]。关于电子束辐照在三七粉的中的应用国内外鲜见报道,电子束辐照灭菌是否适用于三七粉还有待探究。
因此,本实验采用电子束辐照处理三七粉,设置2、4、6、8、13 kGy五个辐照剂量,以未辐照组为对照,每组设定三个平行。以微生物数量、理化指标、色泽、活性成分、抗氧化活性为考察指标,建立辐照前后三七粉的指纹图谱,探究不同剂量的电子束辐照对三七粉的杀菌效果及品质的影响,为电子束辐照技术在三七粉及其类似产品上的应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
三七原药材 太极集团四川绵阳制药有限公司提供,产地绵阳三台,采收后仅做晒干处理,室温下贮藏。经西南科技大学侯大斌教授鉴定为五加科植物三七Panax notoginseng(Burk.)F.H.Chen的干燥根;三七皂苷R1(纯度98%)、人参皂苷Rb1(纯度98%)、人参皂苷Rg1(纯度98%) 成都埃法生物科技有限公司;乙腈(色谱纯)、甲醇(色谱纯)、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH) 赛默飞科技(中国)有限公司;无水乙醇等其他试剂 分析纯,成都市科隆化学品有限公司。
SPECORD 200 PLUS紫外-可见分光光度计 德国Analytik Jena公司;5804R高速离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;RHCX-35超声波清洗器 济宁荣汇超声波设备有限公司;NH300色差仪 深圳市三恩时科技有限公司;GE60DA高压蒸汽灭菌锅 美国致微公司;DHG-9123A电热鼓风干燥箱 上海申贤恒温设备厂;UltiMate3000DGLC双三元、二维液相色谱仪系统 美国赛默飞世尔公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
三七样品粉碎过50目筛,粉碎后的样品采用聚乙烯自封袋(15 cm×20 cm)封装,每袋约100 g,平均厚度1.5 cm。包装好的样品送至四川润祥辐照技术有限公司(四川眉山),采用电子加速器(VF-ProAcc-10/20,10 MeV,20 kW)进行辐照处理。查阅资料[12,15-16],设定辐照剂量为2、4、6、8、13 kGy,以未辐照样品(CK)为对照组。辐照后样品置于室温避光保存,按《中国药典》2020版药材和饮片取样法取样检测[17]。
1.2.2 微生物数量检测
三七粉需氧菌总数(Total aerobic microbial count,TAMC)、霉菌和酵母菌总数(Total combined yeasts and molds count,TYMC)均按照《中国药典》2020版非无菌产品微生物限度检查通则1105进行测定[17],TAMC、TYMC含量检测结果以lg(CFU·g−1)表示。
1.2.3 理化性质的测定
三七粉样品按照《中国药典》2020版三七项下要求测定其水分、灰分、醇溶性浸出物含量[17]。
1.2.4 色泽测定
三七样品采用色差仪测定,记录其L*、a*、b*值,根据公式C=√a∗2+b∗2计算饱和度C;根据公式ρE=√ΔL*2+Δa∗2+Δb∗2计算总色差ρE值。
1.2.5 人参皂苷Rg1、人参皂苷Rb1、三七皂苷R1含量的测定
照《中国药典》2020版三七项下含量检测方法,参照高效液相色谱法(high performance liquid chromatography,HPLC),以乙腈-水为流动相,于203 nm下测定皂苷含量[1]。
1.2.6 黄酮含量的测定
参照刘格[18]的方法提取三七粉中的的总黄酮。取三七粉末1.0 g于磨口锥形瓶中,加入20 mL 70%的乙醇,超声提取1 h,过滤即得供试液。以芦丁为标准品,精确量取5 mL供试液,利用Al(NO3)3-NaNO2比色法测定总黄酮含量。
1.2.7 抗氧化活性的测定
1.2.7.1 DPPH自由基清除活性
参照徐宏化等[19]的方法并稍作修改,配制0.05 mmol/L的DPPH工作液,避光保存。用70%的乙醇配制1 mg/mL的VC标准液,用70%的乙醇溶液将VC标准液稀释至不同的浓度,分别取40 μL不同浓度的VC乙醇溶液,加入DPPH工作液10 mL,避光反应30 min,于517 nm下测定吸光度,得到标准曲线为Y=−0.1346X+0.5263,R2=0.9993。吸取40 μL样品供试液,至加入DPPH工作液10 mL开始,测定样品吸光度值,样品抗氧化活性以1 g三七粉达到所需VC的抗氧化能力表示(mg VC·g−1)。
1.2.7.2 ABTS自由基清除活性
参照文献[19]的方法稍作修改,将等体积的7 mmol/L的ABTS溶液和2.45 mmol/L的K2S2O8溶液混合均匀,置于4 ℃冰箱静置12 h后得到ABTS储备液。用无水乙醇稀释ABTS储备液,使其在734 nm下的吸光度值为0.700±0.020。以VC为对照品,配制不同浓度的VC乙醇溶液,取不同浓度的VC乙醇溶液50 μL,加入6 mLABTS溶液,避光反应6 min后,在734 nm下测定吸光度,得到标准曲线为Y=−0.6487X+0.6889,R2=0.9992。吸取50 μL样品供试液,至加入ABTS工作液6 mL开始,测定样品吸光度值,样品抗氧化活性以1 g三七粉达到所需VC的抗氧化能力表示(mg VC·g−1)。
1.2.8 三七样品辐照前后指纹图谱的建立
采用国家药典委员会制定的《中药指纹图谱相似性评价体系(2012版)》建立不同辐照剂量下三七样品的指纹图谱。
取三七样品0.3 g,加入25 mL甲醇,室温下超声30 min,取续滤液作为供试品溶液。洗脱条件:柱温:30 ℃;流速:0.8 mL/min;流动相:水(A)-乙腈(B);进样量:10 μL;检测波长:203 nm;洗脱梯度:0~10 min,20% B;10~42 min,20%~36% B;42~71 min,36%~94% B;71~83 min,94% B;81~83 min,94%~20% B;83~93 min,20% B。
1.3 数据处理
结果用SPSS 25进行方差分析,以平均值±标准差(Mean±SD)表示,采用多重比较分析是否有显著差异(P<0.05表示差异显著),图片均采用Origin 2021绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 电子束辐照对三七粉微生物数量的影响
表1为不同剂量电子束处理下三七粉微生物数量的变化。三七粉的初始TAMC为3.07 lg CFU·g−1,TYMC为2.12 lg CFU·g−1。采用电子束辐照处理后,微生物数量显著下降(P<0.05),当辐照剂量为2 KGy时,TAMC为2.54 lg CFU·g−1,TYMC未检出。辐照剂量为4 kGy时,TAMC、TYMC均未检出。当辐照剂量达到4 kGy及以上时,三七粉微生物数量符合现行《中国药典》要求。以辐照剂量为纵坐标,需氧菌总数的对数值(lgN)为横坐标得拟合方程(Y=−0.8925X+3.8271,R2=0.9437),根据拟合方程得到三七粉中需氧菌总数的杀菌剂量的D10值为2.04 kGy。徐远芳等[20]利用电子束辐照食用葛根粉,结果发现电子束辐照对葛根粉中的霉菌、大肠杆菌均有明显的杀菌效果,菌落总数的杀菌剂量的D10为2.68 kGy。此外,王海英等[21]在利用60Co-γ对三七粉进行辐照灭菌中发现,三七粉经5 kGy剂量辐照时,微生物数量达到检测标准限度以下,这与本实验结果存在差异,其原因其一可能是两种射线的穿透力不同,所需要的灭菌剂量不同;其二是因为三七粉的初始含菌量差异影响,初始含菌量越大,达到相同灭菌效果的所需剂量就越大,这种现象在Khawory等[22]的研究中也有体现。Kyung等[23]认为,辐照之所以能够杀死微生物,是因为通过辐射的间接作用,在一定程度上会破坏细胞中的蛋白质和酶,从而杀死微生物。Egea等[24]的研究中发现,辐照会破坏细胞内DNA的双螺旋结构,使DNA无法复制,从而导致细胞死亡。因此,电子束辐照能有效降低三七粉中的微生物数量,当辐照剂量为2.04 kGy时,能使微生物数量下降一个数量级。
表 1 电子束辐照对三七粉微生物数量的影响Table 1. Effects of high-energy electron beam irradiation on microbe quantity of Panax Notoginseng辐照剂量
(kGy)需氧菌总数
(lg CFU·g−1)霉菌和酵母总数
(lg CFU·g−1)CK 3.07 2.12 2 2.54 ND 4 ND ND 6 ND ND 8 ND ND 13 ND ND 注:ND表示在检测限1.0 CFU/g未检出。 2.2 电子束辐照对三七粉理化品质的影响
《中国药典》2020版规定三七粉水分含量必须低于14%,总灰分含量必须低于6%,醇溶性浸出物必须大于16%。由表2可知,三七粉水分含量范围为10.17%~10.65%、总灰分含量范围为2.94%~3.00%、醇溶性浸出物含量范围为17.10%~17.34%,均符合药典规定,且各处理组之间无显著差异,各含量与辐照剂量无明显相关性。于明等[25]在探究电子束辐照对天麻品质的影响时,把天麻的理化品质作为评价其质量优劣的一项重要指标。何毅等[26]以2、4、6 kGy电子束辐照处理川麦冬,结果发现电子束辐照对麦冬的水分、灰分、浸出物含量均无显著影响,与本实验研究结果一致。韩振明等[27]在利用60Co-γ处理蜈蚣药粉时,也发现蜈蚣药粉的水分、灰分、醇溶性浸出物受辐照的影响不大。但是,付孟等[28]利用电子束处理大黄中发现,辐照后大黄的水分、灰分含量无显著差异,但浸出物含量随着辐照剂量的增加而显著增加,与本实验结果存在差异,这可能与药材本身的性质有关。因此,13 kGy以下电子束辐照对三七粉的理化品质影响不显著。
表 2 电子束辐照对三七粉理化品质的影响Table 2. Effects of high-energy electron beam irradiation on physicochemical quality of Panax notoginseng2.3 电子束辐照对三七粉色泽的影响
药材的颜色与其品质密切相关,是评价中药材品质的直观指标。L*值代表亮度,a*代表红度值,b*代表黄度值,C值代表饱和度,∆E代表总色差。由表3可知,辐照后三七粉的a*值、b*值、C值均有降低,这说明在辐照后,三七粉的红度值、黄度值和饱和度均减小,在一定程度上说明三七粉在辐照后颜色变浅,但颜色的改变与辐照剂量的大小无关。Jung等[29]在研究电子束辐照辣椒粉的实验中发现辣椒粉的颜色变化与辐照剂量不呈线性关系,与本实验结果类似。Rather等[30]也认为,辐照导致的颜色改变没有明显的规律性。黄卉等[31]提出,颜色差异可以用总色差∆E辨别,当∆E<0.5时为极小差异,∆E值在0.5~1.5时表示稍有差异但不显著,当∆E>3存在显著差异,∆E>12表示不同颜色。本实验中不同处理组的∆E值均小于1,表示各组之间总体色差不显著。于明等[25]在研究电子束辐照对天麻色泽的影响中发现,电子束辐照对天麻的总色差值影响较小,与本实验研究结果类似。因此,说明13 kGy以下电子束辐照处理对三七粉的总体色泽无显著影响。
表 3 电子束辐照对三七粉色泽的影响Table 3. Effects of high-energy electron beam irradiation on the color of Panax notoginseng辐照剂量(kGy) 色泽指标 L *值 a *值 b *值 C ∆E CK 74.25±0.12a 3.64±0.02a 16.73±0.12a 17.12±0.11a 0.00 2 74.65±0.31a 3.09±0.04a 16.38±0.28a 16.67±0.07a 0.76 4 74.12±0.08a 3.22±0.07a 16.01±0.29a 16.33±0.29a 0.84 6 74.32±0.31a 3.32±0.06a 16.08±0.17a 16.42±0.17a 0.72 8 74.86±0.10a 3.16±0.05a 16.51±0.03a 16.81±0.01a 0.80 13 74.24±0.24a 3.52±0.05a 16.12±0.39a 16.50±0.39a 0.62 2.4 电子束辐照对三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1含量的影响
三七皂苷是三七的主要活性成分,三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1是药典规定的三七粉质量控制指标之一。有研究表明三七皂苷具有抗氧化[3]、抗癌[7]、降血脂[32]等作用,对乳腺癌[7]、肺纤维化[33]、高血脂[32]等多种疾病有较强的的抑制作用。现代药理学及临床研究表明,三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1对缓解血栓、保护血管有积极作用[32]。三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rg1还能抑制某些与炎症因子相关的信号通路,减少相关蛋白的表达,从而缓解炎症状态[34]。《中国药典》2020版三七项下规定,三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1的总量不得少于5.00%。本实验结果发现,在0、2、4、6、8、13 kGy剂量电子束辐照处理下,三种皂苷的总量为7.46%~7.68%,符合药典要求。三种皂苷的标准品色谱图如图1A所示,三七中三种皂苷的HPLC色谱图如图1B所示。其中,1号峰为三七皂苷R1,2号峰为人参皂苷Rg1,3号峰为人参皂苷Rb1。由图2可知,随辐照剂量的上升,三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rb1含量呈下降趋向,下降幅度均小于2.5%。人参皂苷Rg1含量在辐照处理下略有波动,但变化幅度小于1%。可见,电子束辐照对三七粉中三种皂苷的含量有影响,但无显著影响且结果都在药典要求范围内。肖满等[12]采用60Co-γ辐照三七粉,结果发现13 kGy以下剂量辐照对三种皂苷的含量无显著影响,与本实验研究结果类似。王海英等[21]利用60Co-γ射线对三七粉进行辐照灭菌,结果发现经5 kGy剂量辐照后,三七皂苷R1的含量无明显变化。蔡杨靖等[35]在实验中也发现,辐照对康尔心胶囊中的三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rg1、Rb1含量无显著影响。白羽[36]发现三七、西洋参、人参中的人参皂苷Rb1随着60Co-γ辐照剂量的增高而减少,但变化幅度也不大,与本实验结果类似,这可能是因为辐照导致部分大分子降解,导致成分含量减少。在本实验中,三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rb1的含量变化很小,因此可能是在实验过程中造成的误差,具体下降原因还需进一步实验验证。综上所述,电子束辐照对三七的三种皂苷含量影响不大,在可接受的范围内。
2.5 电子束辐照对黄酮含量的影响
现代药理研究表明,三七黄酮类物质具有抗病毒[37]、调节血糖血脂[32]、保肝、抗癌等作用[38],刘耀晨等[34]、张铁军等[32]在三七粉的质量标志物研究中也将黄酮类物质作为标志物之一。刘格[18]在综合评价不同产地三七药效质量中将黄酮类物质作为评价指标之一。由表4可知,在13 kGy以下剂量电子束辐照下,三七粉的总黄酮含量为1.25~1.27 mg RE/g,辐照后的总黄酮含量略有上升,但各处理组之间黄酮含量无显著影响(P>0.05)。何毅等[26]研究发现,6 kGy剂量以下电子束辐照对川麦冬的总黄酮含量影响不大。李俊杰等[39]采用电子束辐照灭菌昭通酱,结果发现昭通酱中的异黄酮类物质的含量无显著变化。顾可飞等[40]在利用电子束辐照甜高粱的实验中也得到了类似的结果,推测可能是因为黄酮类物质具有抗辐射能力,对低剂量辐照不敏感。相关研究表明,黄酮类物质的抗辐射功效对其他营养成分有一定的保护作用[41]。
表 4 电子束辐照对三七粉总黄酮含量及抗氧化活性的影响Table 4. Effect of electron beam irradiation on total flavonoids content and antioxidant activity of Panax notoginseng powder检测项目 辐照剂量(kGy) 0(CK) 2 4 6 8 13 总黄酮含量(mg RE/g) 1.25±0.01a 1.25±0.02a 1.26±0.02a 1.27±0.01a 1.26±0.02a 1.26±0.01a DPPH自由基清除活性(mg VC·g−1) 9.86±0.10d 9.96±0.07c 10.06±0.02b 10.35±0.02a 10.37±0.02a 10.39±0.03a ABTS自由基清除活性(mg VC·g−1) 3.51±0.08d 3.77±0.01c 3.79±0.01c 3.82±0.01bc 3.87±0.02b 3.99±0.01a 2.6 电子束辐照对三七粉抗氧化活性的影响
机体的氧化水平与抗氧化水平正常情况下是处于一个动态平衡当中的,当机体受到外界因素的影响或者机体自身异常时,这个平衡就会被破坏,即所谓的氧化应激。当氧化水平超过抗氧化水平时就会造成机体损伤,严重时会引起机体病变,例如阿兹海默症、糖尿病、高血压等[42]。近年来,随着天然植物抗氧化剂的深入研究,天然抗氧化剂已在水果、肉制品、蔬菜、医疗保健等多方面得到广泛应用。因此,植物的抗氧化能力是确定植物生物活性的指标之一。
表4反映了不同剂量电子束辐照处理对三七样品DPPH自由基清除活性及ABTS自由基清除活性的影响。由表4可知,电子束辐照导致样品的抗氧化活性显著增加(P<0.05)。随着辐照剂量的增加,DPPH自由基清除能力和ABTS自由基清除能力均逐步增加。当辐照剂量为13 kGy时,抗氧化活性达到最大值,与对照组相比DPPH自由基清除活性增加约5.37%,ABTS自由基清除活新增加约13.68%。Rather等[30]在探究电子束辐照对杏干和木瓜干的影响时,发现辐照导致抗氧化活性增强,与本研究结果一致。Krishnan等[43]也发现60Co-γ辐照能够增强大豆提取物的抗氧化活性。辐照能够破坏某些糖苷键,将大分子物质降解为小分子物质,从而导致抗氧化活性的增强[44]。本实验研究结果发现,辐照处理后皂苷含量略有下降,可能是因为辐照导致皂苷中某些键的断裂,产生了具有抗氧化活性的小分子,进而使抗氧化能力增强。抗氧化能力的大小是所有具有抗氧化活性物质共同作用的结果,例如黄酮、多酚、皂苷类物质均具有抗氧化活性。在本实验中,总黄酮含量在辐照后略有上升,可能是导致抗氧化活性增加的原因之一。辐照食品的抗氧化活性的增强也可能是酶活性的增加或组织中抗氧化剂化合物萃取率的增加,例如过氧化物酶活性的增强。Chawla等[45]认为辐照导致抗氧化活性的增强是因为在辐照过程中形成美拉德反应产物(MRPs),MRPs在食品中具有抗氧化潜力。因此,13 kGy以下剂量电子束辐照能够显著提高三七粉的抗氧化活性,但具体原因有待进一步研究。
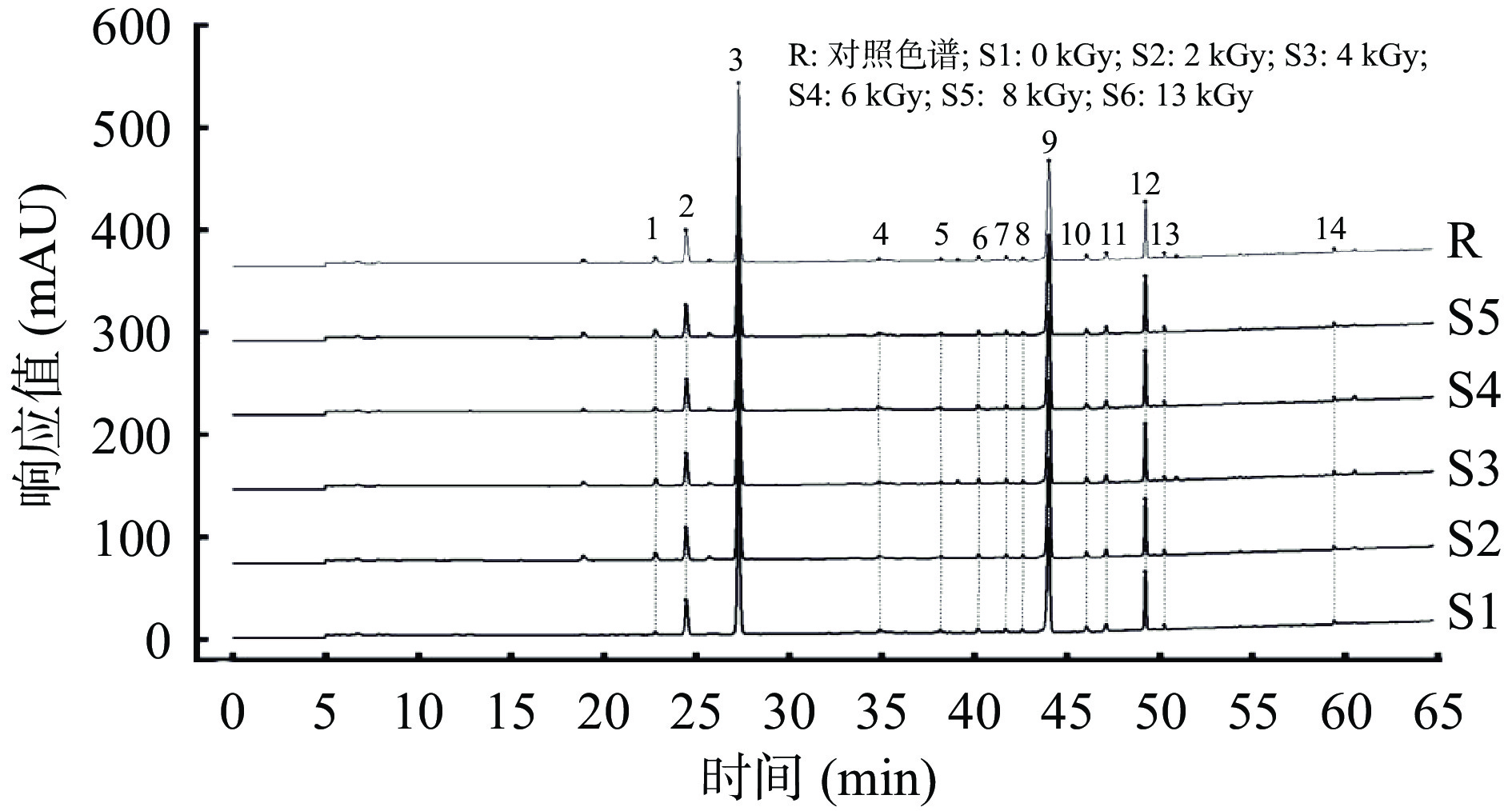
2.7 电子束辐照对三七粉指纹图谱的影响
中药指纹图谱是研究鉴定中药有效成分的有效方法,常用于中药材的质量控制、品质鉴定和新药研究等,已在社会上得到广泛的运用和认可[46]。本实验利用指纹图谱技术研究不同剂量电子束辐照对三七质量的影响,发现三七指纹图谱在8 kGy以下电子束辐照处理下无明显变化。如图3所示,本实验在HPLC图谱上选择标定了14个共有特征峰,在与对照品图谱比较下可确认2号峰为三七皂苷R1,3号峰为人参皂苷Rg1,9号峰为人参皂苷Rb1。采用中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统2.0软件分别对不同剂量电子束辐照三七的指纹图谱生成对照图谱R,并计算相似度(表5)。由表5可知,各处理组的三七样品特征峰相似度均能达到0.999以上,说明在13 KGy以下剂量电子束辐照不会对三七的化学成分产生显著影响。肖满等[12]研究发现,4、6、8 kGy剂量的60Co-γ辐照处理对三七粉的指纹图谱无显著影响,与本研究结果一致。徐远芳等[20]研究发现60Co-γ射线和电子束辐照处理均不会对葛根粉的指纹图谱产生显著影响。白羽辛等[46]的研究结果表明,辐照处理人参粉的指纹图谱相似度能达到0.9以上,与本研究结果类似。因此,13kGy以下剂量电子束辐照不会使三七粉的成分发生明显改变。
表 5 不同剂量电子束辐照前后三七粉指纹图谱相似度计算结果Table 5. Calculation results of fingerprint similarity of Panax notoginseng powder before and after electron beam irradiation at different doses样品 CK 2 kGy 4 kGy 6 kGy 8 kGy 对照图谱R CK 1 0.999 0.999 0.999 0.999 0.999 2 kGy 0.999 1 1 1 1 1 4 kGy 0.999 1 1 0.999 0.999 1 6 kGy 0.999 1 0.999 1 1 1 8 kGy 0.999 1 0.999 1 1 1 13kGy 0.999 1 1 1 1 1 对照图谱R 0.999 1 1 1 1 1 3. 结论
本研究结果表明,电子束辐照能有效降低三七粉中的微生物数量,且辐照剂量越大,杀菌效果越明显,需氧菌总数的杀菌剂量的D10为2.04 kGy。当三七粉初始含菌量为TAMC 3.07 lg CFU·g−1、TYMC 2.12 lg CFU·g−1时,4 kGy剂量电子束能有效控制其微生物数量。随着辐照剂量增加,三七粉抗氧化能力显著提高,13 kGy辐照组较未辐照样品DPPH自由基清除活性提高5.37%(P<0.05),ABTS自由基清除活性增加13.68%(P<0.05);三七皂苷R1、人参皂苷Rb1含量略有下降,但变化不显著。电子束辐照对其水分、灰分、浸出物含量、色泽、总黄酮含量及指纹图谱无明显影响(P>0.05)。因此,电子束辐照能有效杀灭三七粉中的微生物,13 kGy以内剂量辐照对三七粉的主要活性成分及品质无显著影响,且能提高其抗氧化能力,并且有望在保证其品质的前提下延长保质期。今后拟进一步探究三七粉电子束辐照加工工艺,探寻更高效的加工方式,为电子束辐照技术在三七及其加工制品上的应用提供理论依据。
-
表 1 电子束辐照对三七粉微生物数量的影响
Table 1 Effects of high-energy electron beam irradiation on microbe quantity of Panax Notoginseng
辐照剂量
(kGy)需氧菌总数
(lg CFU·g−1)霉菌和酵母总数
(lg CFU·g−1)CK 3.07 2.12 2 2.54 ND 4 ND ND 6 ND ND 8 ND ND 13 ND ND 注:ND表示在检测限1.0 CFU/g未检出。 表 2 电子束辐照对三七粉理化品质的影响
Table 2 Effects of high-energy electron beam irradiation on physicochemical quality of Panax notoginseng
表 3 电子束辐照对三七粉色泽的影响
Table 3 Effects of high-energy electron beam irradiation on the color of Panax notoginseng
辐照剂量(kGy) 色泽指标 L *值 a *值 b *值 C ∆E CK 74.25±0.12a 3.64±0.02a 16.73±0.12a 17.12±0.11a 0.00 2 74.65±0.31a 3.09±0.04a 16.38±0.28a 16.67±0.07a 0.76 4 74.12±0.08a 3.22±0.07a 16.01±0.29a 16.33±0.29a 0.84 6 74.32±0.31a 3.32±0.06a 16.08±0.17a 16.42±0.17a 0.72 8 74.86±0.10a 3.16±0.05a 16.51±0.03a 16.81±0.01a 0.80 13 74.24±0.24a 3.52±0.05a 16.12±0.39a 16.50±0.39a 0.62 表 4 电子束辐照对三七粉总黄酮含量及抗氧化活性的影响
Table 4 Effect of electron beam irradiation on total flavonoids content and antioxidant activity of Panax notoginseng powder
检测项目 辐照剂量(kGy) 0(CK) 2 4 6 8 13 总黄酮含量(mg RE/g) 1.25±0.01a 1.25±0.02a 1.26±0.02a 1.27±0.01a 1.26±0.02a 1.26±0.01a DPPH自由基清除活性(mg VC·g−1) 9.86±0.10d 9.96±0.07c 10.06±0.02b 10.35±0.02a 10.37±0.02a 10.39±0.03a ABTS自由基清除活性(mg VC·g−1) 3.51±0.08d 3.77±0.01c 3.79±0.01c 3.82±0.01bc 3.87±0.02b 3.99±0.01a 表 5 不同剂量电子束辐照前后三七粉指纹图谱相似度计算结果
Table 5 Calculation results of fingerprint similarity of Panax notoginseng powder before and after electron beam irradiation at different doses
样品 CK 2 kGy 4 kGy 6 kGy 8 kGy 对照图谱R CK 1 0.999 0.999 0.999 0.999 0.999 2 kGy 0.999 1 1 1 1 1 4 kGy 0.999 1 1 0.999 0.999 1 6 kGy 0.999 1 0.999 1 1 1 8 kGy 0.999 1 0.999 1 1 1 13kGy 0.999 1 1 1 1 1 对照图谱R 0.999 1 1 1 1 1 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 一部[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020. Pharmacopoeia committee pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China: Volume I [S]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 12.
[2] CHEN J, ZHANG X, LIU X, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes cerebral angiogenesis via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in ischemic mice[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2019,856:172418. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172418
[3] 姚娟, 林佳, 吴平安, 等. 基于抗氧化研究三七提取物对6-OHDA损伤PC12细胞的保护作用[J]. 中药药理与临床,2022,38(2):115−119. [YAO J, LIN J, WU P A, et al. Protective effect of Sanqi extract on 6-OHDA-injured PC12 cells based on antioxidation study[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2022,38(2):115−119. YAO J, LIN J, WU P A, et al. Protective effect of Sanqi extract on 6-OHDA-injured PC12 cells based on antioxidation study[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 38(2): 115-119.
[4] DING S, WANG M, FANG S, et al. D-dencichine regulates thrombopoiesis by promoting megakaryocyte adhesion, migration and proplatelet formation[J]. Front Pharmacol,2018,9:297. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00297
[5] 高利超, 徐兵, 刘永安, 等. 三七皂苷R1抑制TGF-β1/Smad3信号传导对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾脏纤维化和炎症细胞因子的调节作用研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志,2020,36(10):1188−1193. [GAO L C, XU B, LIU Y A, et al. Regulatory effect of notoginsenoside R1 on renal fibrosis and inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy rats via inhibiting of TGF-β12/Smad3 signal transduction[J]. Cellular & Molecular Immunology,2020,36(10):1188−1193. GAO L C, XU B, LIU Y A, et al. Regulatory effect of Notoginsenoside R1 on renal fibrosis and inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy rats via inhibiting of TGF-β12/Smad3 signal transduction[J]. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 2020, 36(10): 1188-1193.
[6] ZHOU Y J, CHEN J M, SAPKOTA K, et al. Pananx notoginseng saponins attenuate CCL2-induced cognitive deficits in rats via anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis effects that involve suppressing over-activation of NMDA receptors[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2020,127:110139. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110139
[7] KIM B K, EUN-YEONG L, EUN-JI H, et al. Panax notoginsenginhibits tumor growth through activating macrophage to M1 polarization[J]. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine,2018,46(6):1369−1385. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X18500726
[8] 赵文娟. 三七总皂苷调节哮喘小鼠气道炎症及Th亚群相关细胞因子的实验研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2012. ZHAO W J. Study on Panax notoginseng saponins adjust asthma mice airway inflammation and Thlymphocyte`s cytokines[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2012.
[9] 朱安妮, 田芷睿, 唐俊妮, 等. 三七保健酸乳的制备和工艺优化[J]. 食品工业,2016,37(3):177−182. [ZHU A N, TIAN Z R, TANG J N, et al. Preparation and optimization of fermented yoghurt with Panax notoginseng (Burk. ) F. H. Chen[J]. The Food Industry,2016,37(3):177−182. ZHU A N, TIAN Z R, TANG J N, et al. Preparation and Optimization of Fermented Yoghurt with Panax notoginseng (Burk. ) F. H. Chen[J]. The Food Industry, 2016, 37(3): 177-182.
[10] 白雯静, 李志俊, 周斌, 等. 三七药材中微生物污染的研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(8):3405−3409. [BAI W J, LI Z J, ZHOU B, et al. Study on microbial contamination of Panax notoginseng[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2021,12(8):3405−3409. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.08.065 BAI W J, LI Z J, ZHOU B, et al. Study on microbial contamination of Panax notoginseng[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2021, 12(8): 3405-3409. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.08.065
[11] MCCORMICK P J, SCHOENE M J, PEDEVILLE D, et al. Verification testing of biological indicators for moist heat sterilization[J]. Biomedical Instrumentation & Technology,2018,52(3):199−207.
[12] 肖满, 吴艳, 马江南, 等. 60Co-γ辐照灭菌对三七药材质量的影响[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2020,36(3):150−152,175. [XIAO M, WU Y, MA J N, et al. Influence of 60Co-γ irradiation sterilization on the quality of the medicinal material Panax notoginseng[J]. HuNan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,36(3):150−152,175. XIAO M, WU Y, MA J N, et al. Influence of 60Co-γ irradiation sterilization on the quality of the medicinal material Panax notoginseng[J]. HuNan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 36(3): 150-152, 175.
[13] 崔琳琳, 陈宁, 曹玲, 等. 三七生药粉乙醇灭菌工艺优化及不同灭菌方式对质量的影响[J]. 中国现代中药,2022,24(12):2462−2470. [CUI L L, CHENG N, CAO L, et al. Optimization of ethanol sterilization technology for Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma powder and impact of sterilization methods on quality[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2022,24(12):2462−2470. CUI L L, CHENG N, CAO L, et al. Optimization of ethanol sterilization technology for Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma powder and impact of sterilization methods on quality[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2022, 24(12): 2462-2470.
[14] 王梁燕, 洪奇华, 孙志明, 等. 电子束辐照技术在生命科学中的应用[J]. 核农学报,2018,32(2):283−290. [WANG L Y, HONG Q H, SUN Z M, et al. Application of electron beam irradiation in life sciences[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2018,32(2):283−290. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2018.02.0283 WANG L Y, HONG Q H, SUN Z M, et al. Application of electron beam irradiation in life sciences[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 32(2): 283-290. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2018.02.0283
[15] 白洁, 迟玉明, 金红宇, 等. 《中药辐照灭菌技术指导原则》解读[J]. 中成药,2017,39(7):1537−1538. [BAI J, CHI Y M, JIN H Y, et al. Interpretation of guiding principles of irradiation sterilization of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2017,39(7):1537−1538. BAI J, CHI Y M, JIN H Y, et al. Interpretation of guiding principles of irradiation sterilization of traditional chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2017, 39(7): 1537-1538.
[16] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T2209-2012 食品电子束辐照通用技术规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013. Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. NY/T2209-2012 General technical specification for food irradiation by electron beam[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013.
[17] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典: 四部[S]. 2020版. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020. Pharmacopoeia committee pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China: Volume Ⅳ [S]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 524−528.
[18] 刘格. 不同产地三七药材质量综合评价研究[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2020. LIU G. Study on quality comprehensive evaluation of Panax notoginseng from different producing areas[D]. Beijing: Beiiing University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.
[19] 徐宏化, 程慧, 王正加, 等. 美国山核桃总多酚与总黄酮含量及抗氧化活性[J]. 核农学报,2016,30(1):72−78. [XU H H, CHENG H, WANG Z J, et al. The study of total polyphenols, total flavonoids and antioxidant capacity in Pecan [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh. ) K. Koch] Kernerls[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2016,30(1):72−78. XU H H, CHENG H, WANG Z J, et al. The study of total polyphenols, total flavonoids and antioxidant capacity in Pecan [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh. ) K. Koch] Kernerls[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 30(1): 72-78.
[20] 徐远芳, 李文革, 邓钢桥, 等. 60Co-γ射线和电子束辐照灭菌对葛根提取物抗氧化活性及指纹图谱的影响[J]. 核农学报,2020,34(08):1713−1721. [XU Y F, LI W G, DENG G Q, et al. Effect of 60Co-γ ray and electron beam irradiation sterilization on antioxidant activity and fingerprint of Pueraria extract[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020,34(08):1713−1721. XU Y F, LI W G, DENG G Q, et al. Effect of 60Co-γ ray and electron beam irradiation sterilization on antioxidant activity and fingerprint of Pueraria extract[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(08): 1713-1721.
[21] 王海英, 孙彩华. 60Co-γ射线辐照灭菌对三七粉中三七皂苷R1含量的影响[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2018,35(6):875−877. [WANG H Y, SUN C H. Effect of the 60Co-γ ray irradiation sterilization on the content of notoginsenoside R1 in Sanqi powder[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy,2018,35(6):875−877. WANG H Y, SUN C H. Effect of the 60Co-γ ray irradiation sterilization on the content of Notoginsenoside R1 in Sanqi powder[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2018, 35(06): 875-877.
[22] KHAWORY M H, SAIN A A, ROSLI M A A, et al. Effects of gamma radiation treatment on three different medicinal plants: Microbial limit tes, total phenolic content, in vitro cytotoxicity effect and antioxidant assay[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes,2020,157:109013. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.109013
[23] KYUNG H K, RAMAKRISHNAN S R, KWON J H. Dose rates of electron beam and gamma ray irradiation affect microbial decontamination and quality changes in dried red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) powder[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(2):632−638.
[24] EGEA M I, SANXHEZ-BEL P, MMRTIAZEN-MADRID M C, et al. The effect of beta ionization on the antioxidant potential of 'Búlida' apricot and its relationship with quality[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2007,46(1):63−70. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2007.04.002
[25] 于明, 王丹, 王钢, 等. 电子束辐照对天麻粉灭菌效果及品质的影响[J]. 核农学报,2022,36(11):2175−2182. [YU M, WANG D, WANG G, et al. Effects of electron beam irradiation on sterilization and quality of Gastrodia rhizoma powder[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2022,36(11):2175−2182. YU M, WANG D, WANG G, et al. Effects of electron beam irradiation on sterilization and quality of Gastrodia rhizoma powder[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 36(11): 2175-2182.
[26] 何毅, 王丹, 梅星月, 等. 电子束辐照对川麦冬品质及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 核农学报,2021,35(8):1816−1824. [HE Y, WANG D, MEI X Y, et al. Effects of electron-beam irradiation on quality and antioxidant properties of Ophiopogon japonicus[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2021,35(8):1816−1824. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.08.1816 HE Y, WANG D, MEI X Y, et al. Effects of electron-beam irradiation on quality and antioxidant properties of Ophiopogon japonicus[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(8): 1816-1824. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.08.1816
[27] 韩振明, 关永霞, 张微, 等. 60Co-γ射线辐照灭菌对蜈蚣药粉品质的影响研究[J]. 中国药业,2021,30(9):42−45. [HAN Z M, GUAN Y X, ZHANG W, et al. Effect of 60Co-γ rays irradiation sterilization on the quality of Scolopendra subspinipes mutilans medicinal powder[J]. China Pharmaceuticals,2021,30(9):42−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2021.09.012 HAN Z M, GUAN Y X, ZHANG W, et al. Effect of 60Co-γ Rays irradiation sterilization on the quality of Scolopendra Subspinipes mutilans medicinal powder[J]. China Pharmaceuticals, 2021, 30(9): 42-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2021.09.012
[28] 付孟, 王丹, 何毅, 等. 电子束辐照对大黄品质及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 核农学报,2022,36(9):1789−1796. [FU M, WANG D, HE Y, et al. Effects of electron-beam irradiation on quality and antioxidant properties of Rheum palmatum L J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2022,36(9):1789−1796.
[29] JUNG K, SONG B S, KIM M J, et al. Effect of X-ray, gamma ray, and electron beam irradiation on the hygienic and physicochemical qualities of red pepper powder[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,63(2):846−851. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.04.030
[30] RATHER S A, HUSSAIN P R, SURADKAR P P, et al. Comparison of gamma and electron beam irradiation for using phyto-sanitary treatment and improving physico-chemical quality of dried apricot and quince[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences,2019,12(1):245−259. doi: 10.1080/16878507.2019.1650223
[31] 黄卉, 郑陆红, 李来好, 等. 不同预冷温度对鲈鱼冰藏期间质构和色差的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(24):302−308. [HUANG H, ZHENG L H, LI H L, et al. Effects of different precooling temperature on texture and color of Micropterus salmoides during ice storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(24):302−308. HUANG H, ZHENG L H, LI H L, et al. Effects of different precooling temperature on texture and color of Micropterus salmoides during ice storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(24): 302−308.
[32] 张铁军, 郭海彪, 许浚, 等. 三七粉质量标志物研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2022,24(1):1−8. [ZHANG T J, GUO H B, XU J, et al. Study on quality marker of Panax notoginseng powder[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology,2022,24(1):1−8. ZHANG T J, GUO H B, XU J, et al. Study on quality marker of Panax notoginseng Powder[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2022, 24(1): 1-8.
[33] LIU L, NING B, CUI J, et al. miR-29c is implicated in the cardioprotective activity of Panax notoginseng saponins against isopro-terenol-induced myocardial fibrogenesis[J]. Journal of ethnophar-macology,2017,198:1−4. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.036
[34] 刘耀晨, 张铁军, 郭海彪, 等. 三七的研究进展及其质量标志物预测分析[J]. 中草药,2021,52(9):2733−2745. [LIU Y C, ZHANG T J, GUO H B, et al. Research progress on Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma and predictive analysis on its Q-Marker[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52(9):2733−2745. LIU Y C, ZHANG T J, GUO H B, et al. Research progress on Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma and predictive analysis on its Q-Marker[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(9): 2733-2745.
[35] 蔡杨靖, 潘云. 60Co-γ射线辐照灭菌对康尔心胶囊指纹图谱和有效成分含量的影响[J]. 中国药师,2020,23(6):1188−1192. [CAI Y J, PAN Y. Influence of 60Co-γ rays radiation sterilization on the fingerprint chromatography and contents of effective constituents in Kangerxin capsules[J]. China Pharmacist,2020,23(6):1188−1192. CAI Y J, PAN Y. Influence of 60Co-γ Rays radiation sterilization on the fingerprint chromatography and contents of effective constituents in Kangerxin capsules[J]. China Pharmacist, 2020, 23(6): 1188-1192.
[36] 白羽. 60Co-γ射线辐照对中药化学成分影响及辐照中药鉴定的热释光分析法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2014. BAI Y. Effect of Gamma irradiation on the ingredients of herbs and detection analysis methods for irradiated herbs by thermoluminescence[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2014.
[37] 许德星, 万发银, 张静怡, 等. 三七总黄酮通过miR-223-3p/FOXO1分子轴缓解病毒性心肌炎炎症反应和细胞损伤[J]. 病毒学报,2021,37(4):781−789. [XU D X, WAN F Y, ZHANG J Y, et al. Radix notoginseng flavone alleviated inflammatory response and cell damage of viral myocarditis via miR-223-3p/FOXO1 axis[J]. Chinese Journal of Virology,2021,37(4):781−789. doi: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003897 XU D X, WAN F Y, ZHANG J Y, et al. Radix notoginseng flavone alleviated inflammatory response and cell damage of viral myocarditis via miR-223-3p/FOXO1 axis[J]. Chinese Journal of Virology, 2021, 37(4): 781-789. doi: 10.13242/j.cnki.bingduxuebao.003897
[38] 黄周艳, 刘玟君, 陈勇, 等. 三七黄酮研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(1):81−84. [HUANG Y Z, LIU W J, CHENG Y, et al. Research progress of Panaxnotoginseng flavonoids[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of TCM,2020,22(1):81−84. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2020.01.022 HUANG Y Z, LIU W J, CHENG Y, et al. Research progress of Panaxnotoginseng flavonoids[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of TCM, 2020, 22(1): 81-84. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2020.01.022
[39] 李俊杰, 张帮磊, 师睿, 等. 电子束辐照灭菌对昭通酱挥发性成分的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(4):326−336. [LI J J, ZHANG B L, SHI R, et al. Effect of electron beam irradiation sterilization on volatile components of Zhaotong soybean paste[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(4):326−336. LI J J, ZHANG B L, SHI R, et al. Effect of electron beam irradiation sterilization on volatile components of Zhaotong soybean paste[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(4): 326-336.
[40] 顾可飞, 秦秋伟, 张栩. 电子束辐照技术对甜高粱鲜品营养品质的影响[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(10):315−319. [GU K F, QIN Q W, ZHANG X. Effect of electron beam irradiation on nutritional quality of fresh sweet sorghum[J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(10):315−319. GU K F, QIN Q W, ZHANG X. Effect of electron beam irradiation on nutritional quality of fresh sweet sorghum[J]. The Food Industry, 2021, 42(10): 315-319.
[41] 刘力源, 陈敏, 赵海田, 等. 天然产物抗辐射活性研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(17):269−274. [LIU L Y, CHENG M, ZHAO H T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the radioprotective effect of natural products[J]. Food Science,2018,39(17):269−274. LIU L Y, CHENG M, ZHAO H T, et al. Recent advances in understanding the radioprotective effect of natural products[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(17): 269-274.
[42] 项昌培, 周瑞, 张毅, 等. 三七中皂苷类成分及其抗脑缺血分子机制研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2020,45(13):3045−3054. [XIANG C P, ZHOU R, ZHANG Y, et al. Research progress on saponins in Panax notoginseng and their molecular mechanism of anti-cerebral ischemia[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020,45(13):3045−3054. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200302.403 XIANG C P, ZHOU R, ZHANG Y, et al. Research progress on saponins in Panax notoginseng and their molecular mechanism of anti-cerebral ischemia[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2020, 45(13): 3045-3054. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200302.403
[43] KRISHNAN V, GOTHWAL S, DAHUJA A, et al. Enhanced nutraceutical potential of gamma irradiated black soybean extracts. Food Chemistry, 2018, 245: 246-253.
[44] VARIYAR P S, LIMAYE A, SHARMA A. Radiation-induced enhancement of antioxidant contents of soybean (Glycine max Merrill)[J]. Famlilies in Society the Journal of Contemporary Social Services,2004,52(11):3385−3388.
[45] CHAWLA S P, CHANDER R, AND SHARMA A. Antioxidant formation by γ-irradiation of glucose–amino acid model systems[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,103(4):1297−1304. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.10.035
[46] 白羽辛, 王玥玥, 贡济宇, 等. 不同灭菌方式人参粉的皂苷含量、指纹图谱分析及灭菌效果评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(10):229−235. [BAI Y X, WANG Y Y, GONG J Y, et al. Fingerprint analysis of saponins contents of ginseng powder in different sterilization methods and evaluation of sterilization effect[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(10):229−235. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060074 BAI Y X, WANG Y Y, GONG J Y, et al. Fingerprint analysis of saponins contents of ginseng powder in different sterilization methods and evaluation of sterilization effect[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(10): 229−235. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020060074
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 田齐聪,于敏,刘守国,焦连庆,时晓宇,姜先慧,张凤清. 多维度定性定量评价电子束辐照灭菌对黄芪质量的影响. 核农学报. 2025(01): 77-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 姜榃,于敏,焦连庆,田齐聪,庄新慧,姜先慧,田义新. 多维度评价电子束辐照灭菌对白花蛇舌草质量的影响. 核农学报. 2024(10): 1922-1929 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郑玉霄,杨晨,胥新元,彭艳梅,李跃辉. 基于CiteSpace的中药辐照灭菌研究现状与热点的可视化分析. 中国医药导报. 2024(23): 152-158 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



