Analysis of Nutritional and Flavor Components of Ten Strains of Pleurotus pulmonarius
-
摘要: 本研究对10个肺形侧耳Pleurotus pulmonarius菌株的子实体营养成分和呈味物质进行了分析评价,为肺形侧耳优良菌株的选育和开发利用提供一定的理论依据。以山东省内主要农林废弃物——苹果木屑和玉米芯作为基质对10个肺形侧耳菌株(5个野外采集菌株和5个商业栽培菌株)进行栽培,测定其粗蛋白、总糖、水解氨基酸、矿质元素和γ-氨基丁酸等营养成分以及游离氨基酸和5′-核苷酸等呈味物质的含量,并通过氨基酸评分AAS、化学评分CS和氨基酸比值系数RC、必需氨基酸指数EAAI和氨基酸比值系数评分SRCAA标准对其蛋白质营养品质进行评定。结果表明:10个供试肺形侧耳菌株的子实体中粗蛋白含量在30.00~36.07 g/100 g之间,总糖含量在31.10%~47.63%之间,γ-氨基丁酸含量在249.64~485.34 mg/kg之间,矿质元素含量丰富,必需氨基酸种类齐全、含量较高且组成均衡,尤其富含赖氨酸,通过必需氨基酸AAS、CS、RC、SRCAA和EAAI评定,发现供试肺形侧耳子实体蛋白质的营养价值与人体所需的营养水平较为接近,是一种较好的蛋白源,其中商品菌株的营养价值显著高于野生菌株。综合比较10个供试菌株发现,5个商业栽培菌株间的各项指标差异较小,品质普遍较高,其中菌株PL9表现最优,其蛋白营养价值和等鲜浓度值(EUC)明显高于另外4个菌株;5个野生菌株间的差异较为明显,个别菌株表现为单一营养物质含量较高。Abstract: In this study, the nutritional and flavor components of the fruit bodies of 10 Pleurotus pulmonarius strains were analyzed and the results would provide a certain theoretical basis for the development, utilization and deep processing of Pleurotus pulmonarius. The apple sawdust and corn cob were used as substrates for cultivation of 10 strains of Pleurotus pulmonarius (5 strains collected in the field and 5 commercial cultivation strains), and the crude protein, total sugar, hydrolyzed amino acids, mineral elements, γ-aminobutyric acid and other nutrients as well as free amino acids and 5'-nucleotides and other flavor substances of their fruit bodies were determined. And then the protein nutrition were evaluated by comparative analysis of the amino acid score (AAS), chemical score (CS), amino acid ratio coefficient (RC), essential amino acid index (EAAI) and score ratio coefficient amino acid (SRCAA). The results showed that the crude protein in the fruit bodies of the 10 tested Pleurotus pulmonarius strains was between 30.00 and 36.07 g/100 g. The total sugar content was between 31.10% and 47.63%. The γ-aminobutyric acid content was between 249.64 and 485.34 mg/kg. The minerals were rich. And the essential amino acids were rich and balance, especially rich in lysine. The nutritional value of Pleurotus pulmonarius was closed to the nutritional level required by the human body, suggesting it was a good protein source and the nutritional value of the commercial strains were significant super to the wild ones. Comprehensive comparison of 10 test strains found that the index differences among 5 commercial cultivated strains were small and the quality was generally high, among which PL9 showed the best performance, and its protein nutritional value and EUC value were significantly higher than those of the other 4 strains. The difference among the 5 wild strains was significant, and some strains showed a high content of a single nutrient.
-
肺形侧耳(Pleurotus pulmonarius),又名秀珍菇、味精菇,其味道鲜美,栽培基质广泛,可利用多种农林废弃物,且子实体富含蛋白质、矿质元素、氨基酸等营养成分和多糖、γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)、麦角甾醇等多种生理活性物质[1-3],具抗氧化、抗衰老和提高免疫力等功效[4-6],因此成为目前最具开发前景的珍稀食用菌种类之一,具广阔的市场前景。
随着人们生活水平和健康意识的不断提高,人们对食用菌营养成分和保健功效方面的需求也越来越高。研究发现,同种食用菌不同菌株间的子实体营养成分和呈味物质具较大差异[7-8],目前关于肺形侧耳不同菌株间营养成分和呈味物质的相关研究较少。山东省作为全国农业大省,农林废弃物资源丰富,但目前大部分都被焚烧或掩埋,造成严重的资源浪费和环境污染。肺形侧耳具有较强的生态适应性和木质纤维素降解能力,基于此,本研究选取10个肺形侧耳菌株(5个野外采集菌株和5个商业栽培品种),以苹果木屑和玉米芯等山东省主要农林废弃物作为栽培基质进行栽培出菇,并对不同菌株的子实体营养成分和呈味物质进行了较全面的分析和评价,以期为肺形侧耳优良菌株的选育和开发利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
肺形侧耳菌 共10个菌株,为国内各菌种保藏中心赠予,其中5个是野外采集菌株,5个为产量较高的商业栽培菌株。菌种保藏于山东农业大学菌物实验室,具体见表1;氨基酸标准品、5′-CMP(5′-胞苷酸)、5′-UMP(5′-尿苷酸)、5′-GMP(5′-鸟苷酸)、5′-IMP(5′-肌苷酸)、5′-AMP(5′-腺苷酸)等单核苷酸标准品 上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司;柠檬酸钠、氢氧化钠、硫酸铜、硫酸钾、硫酸、硼酸、甲基红指示剂、苯酚、高氯酸、盐酸标准滴定溶液、溴甲酚绿指示剂、四丁基硫酸氢铵、氢氧化钾、磷酸二氢钾等标准品 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;γ-氨基丁酸标准物质 上海源叶生物有限公司。
表 1 供试菌株Table 1. The tested strains菌株编号 菌株来源 PL1 云南勐海采集 PL2 云南麻栗坡老君山采集 PL3 云南大理鸡足山采集 PL4 云南普洱菜阳河自然保护区采集 PL5 云南楚雄禄丰县五台山采集 PL6 福建农林大学菌物研究中心 PL7 湖北嘉鱼环宇食用菌研究所 PL8 福建省漳州市龙海九湖食用菌研究所 PL9 福建省食用菌种质资源保藏管理中心 PL10 华中农大菌种中心 K9840凯氏定氮仪 济南海能仪器股份有限公司;FA-1004电子天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;8453紫外可见分光光度仪、1260液相色谱 Agilent公司;BR4I离心机、U3000液相色谱仪 Thermo公司;UB-7pH计 Denver公司;LA8080氨基酸自动分析仪 日本株式会社日立高新技术公司;MDS-6G多通量微波消解/萃取仪 上海新仪微波化学科技有限公司;iCAP-7000 全谱直读电感耦合等离子体发射仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;多功能粉碎机 浙江省永康市红太阳机电有限公司,附60目筛等。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 栽培出菇实验
该实验于2021年7月至11月在山东农业大学菌物实训基地进行接种栽培。栽培配方为:苹果木屑56%,玉米芯20%,麸皮20%,石灰2%,石膏1%,糖1%,含水量约为60%~62%。每个菌株接种20袋,接麦粒原种后置于发菌室进行菌丝培养,待菌袋长满经低温刺激后转移至菇房进行标准出菇管理。
1.2.2 样品预处理
将适时采收的肺形侧耳子实体鲜品于40 ℃烘干至含水量低于10%,粉碎过60目筛后置于干燥器中备用,后期实验研究对象为此干重子实体。
1.2.3 营养成分分析
粗蛋白、总糖、γ-氨基丁酸及水解氨基酸含量分别参照文献[9-12]进行测定。矿物质含量按照文献[13-14]测定。Cr含量、Pb含量及Cd含量分别按照文献[15-17]测定。
游离氨基酸含量测定:精确称取样品100 mg,加入50 mL 0.1 mol/L盐酸溶液摇匀,40 ℃超声提取30 min,室温静置30 min后于5000 r/min离心3 min。取1 mL上清液于离心管中,以体积比1:1加入10%磺基水杨酸溶液,混合液4 ℃放置30 min后10000 r/min、4 ℃离心30 min,迅速移出上清液,由10 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液调节pH至2.0后过0.22 μm MCE微孔滤膜上氨基酸自动分析仪测定[18]。
5′-核苷酸的测定:精确称取100 mg混合均匀的样品于离心管中,加入15 mL 5%高氯酸,匀浆后于4 ℃,7000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,沉淀中加入10 mL 5%高氯酸再次匀浆提取,合并两次提取的上清液,用5 mol/L KOH调pH至6.75,超纯水定容至50 mL,0.22 μm滤膜过滤后经U3000液相色谱仪检测[19]。
1.2.4 蛋白质营养价值评价
氨基酸评分(AAS)根据Seligson等[20]的方法计算。SAA=w1/w2×100,式中:SAA为氨基酸评分;w1为待评价蛋白中某氨基酸含量,g/100 g;w2为参考蛋白模式中对应氨基酸含量,g/100 g。
化学评分(CS)根据FAO[21]的方法计算。SC=w1/w2×w3/w4×100,式中:SC为化学评分;w1为待评价蛋白中某一必需氨基酸含量,g/100 g;w2为待评价蛋白中必需氨基酸总含量,g/100 g;w3为参考蛋白中相应必需氨基酸含量,g/100 g;w4为待评价蛋白中必需氨基酸总含量,g/100 g。
必需氨基酸指数(EAAI)参考Oser[22]提出的方法计算。EAAI=(A/AE×B/BE×…×I/IE)1/n,式中:n为供试的必需氨基酸数量;A,B,…,I为待测蛋白质中的必需氨基酸含量;AE,BE,…,IE为鸡蛋蛋白质中的必需氨基酸含量,mg/g。
氨基酸比值系数(RC)和氨基酸比值系数分(SRCAA)根据朱圣陶等[23]的方法计算。CR=w1/w2×100,式中:CR为氨基酸的比值系数;w1为必需氨基酸含量的比值;w2为必需氨基酸含量比值的平均值。SRCAA=100−w1×100,式中:SRCAA为氨基酸的比值系数分;w1为氨基酸比值系数的变异系数。
1.2.5 等鲜浓度值(Equivalent Umami Concentration,EUC)计算
根据Mau等[24]的方法计算。Y=∑aibi+1218(∑aibi)(∑ajbj),式中:Y为等鲜浓度(g MSG/100 g);ai为鲜味氨基酸(谷氨酸或天冬氨酸)含量(g/100 g);aj为呈鲜核苷酸(5′-GMP、5′-IMP、5′-XMP、5′-AMP)含量(g/100 g);bi为呈鲜氨基酸相对谷氨酸的值(谷氨酸=1,天冬氨酸=0.077);bj为呈鲜核苷酸相对5′-肌苷酸的值(5′-GMP=2.3、5′-IMP=1、5′-XMP=0.61、5′-AMP=0.18);1218为协同作用常数。
1.3 数据处理
实验测定3次平行,数值结果表现为平均值±标准差形式。采用WPS Excel进行数据处理,IBM SPSS Statistics 21.0比较样品间的显著性,用Origin 2018作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 子实体营养成分分析
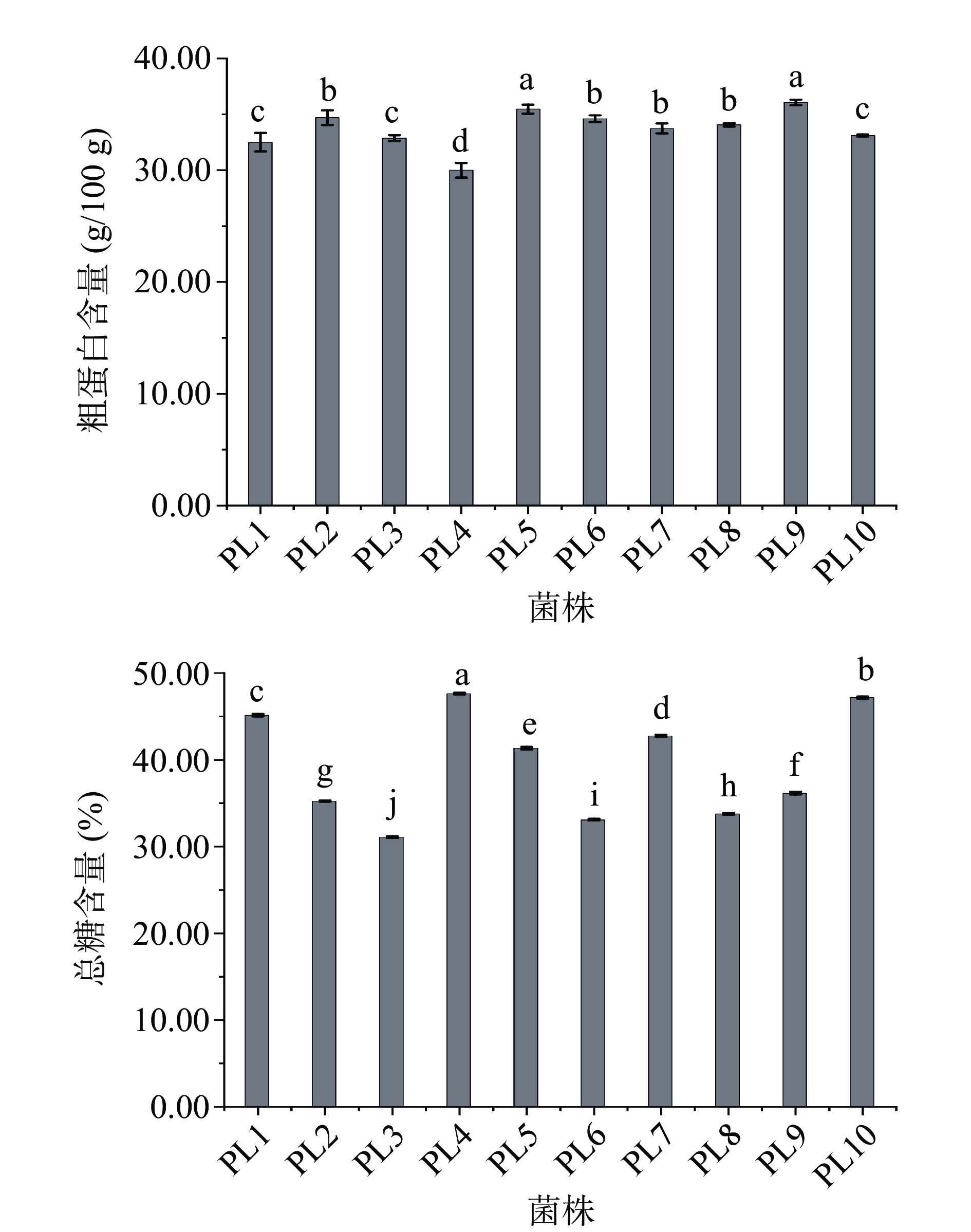
2.1.1 粗蛋白和总糖含量
10个供试肺形侧耳菌株子实体粗蛋白和总糖含量结果如图1所示。不同菌株的子实体中粗蛋白含量在30.00~36.07 g/100 g之间,其中菌株PL9含量最高,菌株PL4含量最低,比较发现商品菌株间的差异较小,而野生菌株间差异较大,推测原因可能是商品菌株大都基于商业需求选育,菌株间差异较小;10个供试菌株间的总糖含量差异显著(P<0.05),在31.10%~47.63%之间,其中菌株PL4含量最高,为47.63%,菌株PL3含量最低,仅为31.10%,两者相差16.53%,说明不同菌株总糖含量差异显著。
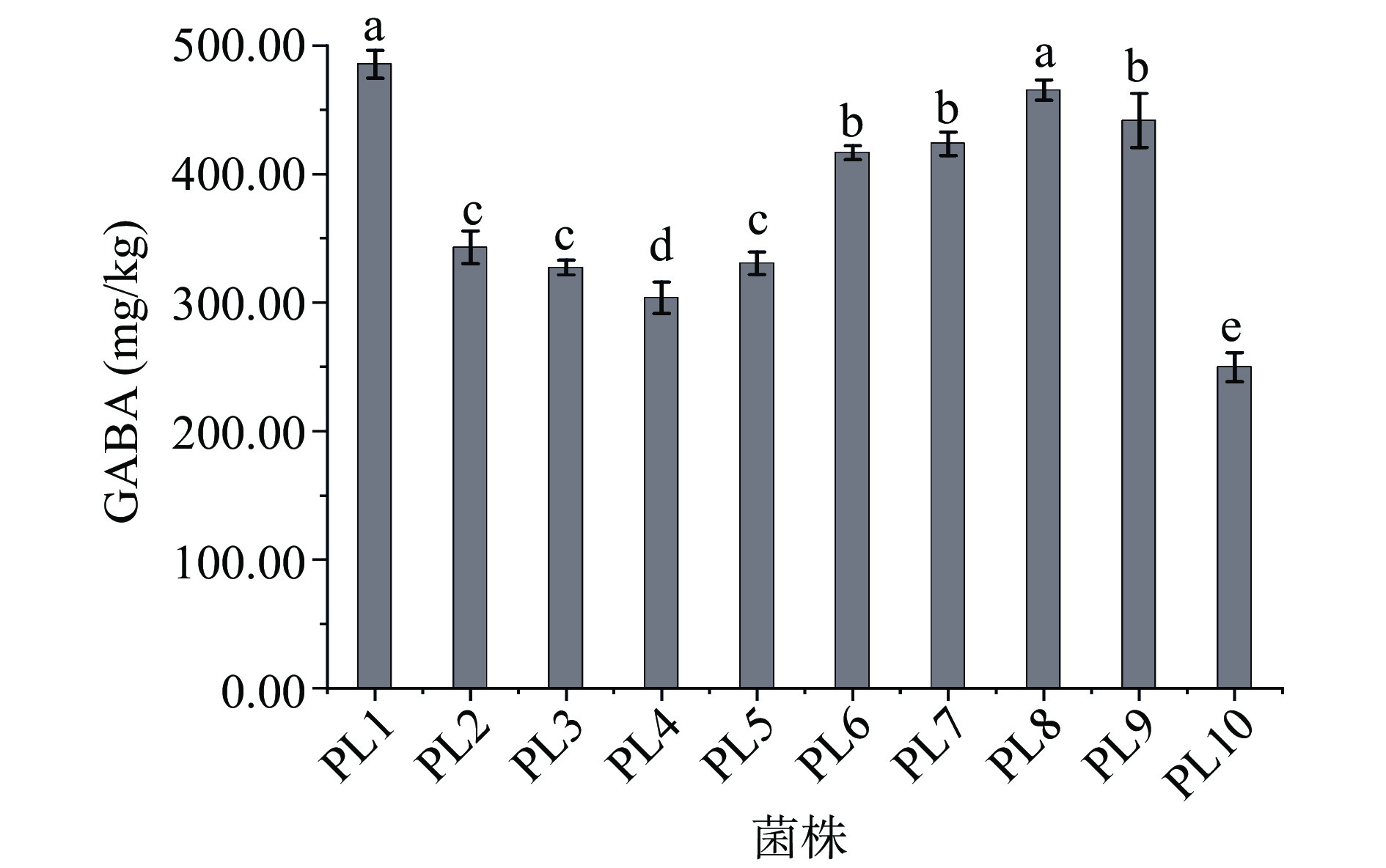
2.1.2 γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)含量
本研究发现10株供试肺形侧耳菌株的子实体中均含有GABA,结果如图2所示。不同菌株间GABA含量差异明显,在249.64~485.34 mg/kg之间,其中菌株PL1含量最高,菌株PL10含量最低,最高含量与最低含量相差接近一半,因此菌株PL1可作为高产GABA候选菌株用于GABA生产。除菌株PL1和PL10外,其余菌株都表现为商品菌株中GABA的含量普遍高于野生菌株。
2.2 子实中体矿物质元素和重金属含量分析
10个供试肺形侧耳菌株子实体中的矿物质元素和重金属含量如表2所示。所有供试菌株的子实体中均含有人体所必需的钙、镁、铁、锰、铜、锌等有益的矿物质元素,但不同菌株间含量存在较大差异,其中钙含量在2475.30~3682.64 mg/kg之间,镁含量在1021.14~1407.73 mg/kg之间,铁含量在136.59~563.95 mg/kg之间,锌含量在88.38~251.77 mg/kg之间,锰和铜的含量较低,分别在16.56~27.82和16.25~28.41 mg/kg之间。通过对供试菌株子实体中的重金属进行检测发现,所有样品中均未检测到Pb,而Cr和Cd两种重金属的含量分别在0.29~0.36和0.25~0.34 mg/kg之间,均远低于检测限量指标。
表 2 子实体中矿物质和重金属含量比较(mg/kg)Table 2. Comparison of mineral and heavy metal content in fruit bodies (mg/kg)元素 Ca Mg Fe Mn Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd PL1 3682.64±87.50a 1200.14±72.14b 563.95±24.67a 23.27±0.71a 25.84±1.68a 184.05±18.07b − 0.36±0.03a 0.34±0.03b PL2 3501.34±157.71a 1407.73±133.93a 519.39±52.19a 21.55±3.83a 28.41±2.97a 154.05±32.18b − 0.33±0.06a 0.31±0.05b PL3 2527.28±166.15c 1021.14±10.59b 482.69±24.67b 21.05±2.15a 17.32±0.84b 227.39±32.67a − 0.35±0.01a 0.28±0.02b PL4 3070.50±177.42b 1248.90±55.19b 541.05±105.14a 27.82±4.62a 23.09±3.60a 251.77±14.91a − 0.36±0.01a 0.27±0.07b PL5 3245.79±124.26a 1131.17±83.38b 159.91±4.89d 16.56±1.51c 22.85±0.72a 168.78±20.55b − 0.30±0.05a 0.42±0.00a PL6 3464.99±144.51a 1169.71±72.55b 171.79±6.93d 21.59±1.18a 19.77±2.93b 189.15±31.66a − 0.30±0.04a 0.31±0.02b PL7 2964.45±181.54c 1155.62±41.48b 292.70±21.54c 17.04±0.31c 16.58±1.14b 88.38±0.09e − 0.29±0.01b 0.30±0.03b PL8 2831.60±121.85c 1106.99±74.32b 136.59±14.70e 21.84±2.42a 24.99±3.54a 114.40±8.65d − 0.29±0.02b 0.29±0.03b PL9 2475.30±103.57c 1042.65±24.56b 161.26±9.02d 17.88±0.15b 16.25±0.49b 136.29±4.58c − 0.32±0.06a 0.25±0.05b PL10 2753.18±27.80c 1100.10±78.28b 333.23±107.63b 19.60±2.12a 18.02±0.40b 156.85±5.48b − 0.29±0.02b 0.29±0.02b 2.3 子实体氨基酸组成及含量分析
不同肺形侧耳菌株其氨基酸组成和含量各不相同,其中菌株PL9子实体中的总氨基酸含量最高,为26.04 g/100 g,菌株PL1的含量最低(表3)。综合分析发现,野生菌株的氨基酸总量普遍低于商品菌株。供试样品中必需氨基酸总量在7.97~9.70 g/100 g之间,必需氨基酸总量与氨基酸总量的比值(E/T)为0.36~0.38,且必需氨基酸总量与非必需氨基酸总量的比值(E/N)为0.55~0.61。根据世界卫生组织(WHO)和联合国粮农组织(FAO)所提出的理想模式,E/T在0.40,E/N在0.60以上时蛋白质氨基酸组成较优。
表 3 子实体中氨基酸含量比较Table 3. Comparison of amino acid contents in fruit bodies氨基酸 含量(干重)(g/100 g) PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Asp 2.34±0.07 2.28±0.06 2.51±0.06 2.41±0.06 2.66±0.04 2.57±0.05 2.51±0.02 2.52±0.04 2.78±0.04 2.71±0.03 Thr 1.15±0.02 1.19±0.03 1.18±0.03 1.16±0.03 1.24±0.02 1.15±0.06 1.19±0.04 1.17±0.03 1.30±0.05 1.23±0.05 Ser 1.19±0.03 1.19±0.03 1.19±0.03 1.19±0.04 1.22±0.04 1.15±0.04 1.20±0.04 1.19±0.03 1.29±0.04 1.25±0.03 Glu 3.89±0.04 4.24±0.07 4.03±0.06 4.06±0.05 4.10±0.02 4.15±0.03 4.61±0.02 4.60±0.03 4.69±0.03 4.37±0.03 Gly 1.16±0.04 1.13±0.07 1.13±0.06 1.17±0.05 1.15±0.02 1.13±0.03 1.15±0.02 1.12±0.03 1.25±0.03 1.28±0.03 Ala 1.42±0.03 1.44±0.02 1.45±0.02 1.46±0.03 1.55±0.02 1.45±0.02 1.48±0.02 1.49±0.02 1.66±0.01 1.58±0.03 Cys 0.19±0.02 0.21±0.02 0.22±0.02 0.21±0.02 0.22±0.02 0.21±0.02 0.22±0.02 0.23±0.02 0.24±0.02 0.21±0.03 Val 1.29±0.02 1.37±0.02 1.27±0.02 1.34±0.02 1.36±0.02 1.31±0.02 1.35±0.02 1.33±0.02 1.47±0.02 1.37±0.03 Met 0.01±0.01 0.71±0.03 0.66±0.03 0.66±0.02 0.01±0.01 0.62±0.02 0.72±0.02 0.71±0.02 0.70±0.01 0.72±0.03 Ile 0.90±0.02 0.89±0.02 0.88±0.02 0.87±0.02 0.93±0.01 0.90±0.02 0.92±0.01 0.90±0.02 1.05±0.02 0.93±0.02 Leu 1.85±0.03 1.80±0.02 1.83±0.02 1.81±0.02 1.91±0.02 1.81±0.02 1.83±0.02 1.79±0.02 2.06±0.04 1.95±0.03 Tyr 0.74±0.02 0.75±0.03 0.71±0.02 0.78±0.01 0.78±0.02 0.75±0.02 0.80±0.02 0.74±0.02 0.81±0.02 0.78±0.02 Phe 1.19±0.02 1.22±0.01 1.20±0.01 1.19±0.02 1.24±0.02 1.21±0.02 1.24±0.02 1.20±0.02 1.37±0.03 1.25±0.02 Lys 1.58±0.02 1.58±0.02 1.51±0.02 1.52±0.04 1.61±0.02 1.59±0.03 1.56±0.03 1.52±0.03 1.75±0.03 1.67±0.03 His 0.55±0.02 0.60±0.02 0.56±0.02 0.59±0.03 0.60±0.02 0.55±0.04 0.59±0.04 0.60±0.04 0.61±0.04 0.60±0.04 Arg 1.52±0.04 1.49±0.02 1.49±0.03 1.48±0.03 1.84±0.09 1.63±0.04 1.60±0.04 1.60±0.02 1.80±0.03 1.75±0.02 Pro 1.04±0.05 1.11±0.03 1.06±0.04 1.10±0.02 1.07±0.04 1.09±0.03 1.13±0.02 1.06±0.05 1.22±0.04 1.13±0.03 EAA 7.97±0.11 8.77±0.09 8.52±0.12 8.55±0.09 8.30±0.06 8.60±0.05 8.80±0.05 8.63±0.04 9.70±0.10 9.12±0.12 TAA 22.02±0.23 23.22±0.21 22.89±0.26 23.00±0.10 23.50±0.21 23.29±0.09 24.09±0.05 23.80±0.11 26.04±0.23 24.78±0.31 NEAA 14.05±0.13 14.44±0.13 14.37±0.15 14.45±0.02 15.20±0.18 14.68±0.06 15.30±0.04 15.17±0.08 16.35±0.13 15.67±0.19 E/T 0.36±0.00 0.38±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.35±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.36±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.37±0.00 E/N 0.57±0.00 0.61±0.00 0.59±0.01 0.59±0.01 0.55±0.01 0.59±0.00 0.58±0.00 0.57±0.00 0.59±0.00 0.58±0.00 注:TAA:氨基酸总量;EAA:必需氨基酸总量;NEAA:非必需氨基酸。 对10个供试菌株的子实体蛋白质中氨基酸组成和含量进行鸡蛋模式和FAO/WHO模式转化(表4),结果表明,除菌株PL1和PL5的甲硫氨酸+半胱氨酸的含量较低外,其余氨基酸含量均大于FAO/WHO推荐值;10个供试菌株的赖氨酸含量均较高,占总氨基酸含量的6.39%~7.18%,几乎全部高于鸡蛋中的含量。赖氨酸作为人体第一必需氨基酸,在小麦、玉米和大米等谷类中含量较少,本研究中的肺形侧耳子实体中赖氨酸含量普遍较高,可作为人体获取赖氨酸的良好来源。
表 4 子实体中必需氨基酸组成分析(%)Table 4. Essential amino acid composition analysis in fruit bodies (%)氨基酸 菌株 鸡蛋 FAO/
WHOPL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Thr 5.22±0.06 5.14±0.08 5.14±0.07 5.04±0.11 5.26±0.11 4.95±0.24 4.94±0.15 4.93±0.13 5.00±0.17 4.96±0.12 5.10 4.00 Val 5.86±0.06 5.90±0.06 5.55±0.05 5.81±0.08 5.80±0.07 5.64±0.09 5.60±0.09 5.60±0.09 5.64±0.09 5.52±0.13 7.30 5.00 Met+Cys 0.94±0.06 3.96±0.19 3.81±0.15 3.81±0.03 0.99±0.11 3.56±0.11 3.90±0.12 3.96±0.11 3.62±0.08 3.74±0.13 5.50 3.50 Ile 4.10±0.10 3.85±0.07 3.86±0.06 3.78±0.05 3.94±0.05 3.88±0.12 3.80±0.05 3.77±0.12 4.02±0.09 3.75±0.02 5.50 3.50 Leu 8.39±0.09 7.77±0.13 1.99±0.05 7.87±0.06 8.11±0.12 7.79±0.09 7.60±0.08 7.53±0.06 7.91±0.07 7.85±0.03 8.80 7.00 Phe+Tyr 8.77±0.09 8.47±0.08 8.35±0.10 8.55±0.07 8.61±0.08 8.43±0.13 8.45±0.15 8.15±0.19 8.34±0.15 8.22±0.10 10.00 6.00 Lys 7.18±0.04 6.82±0.04 6.60±0.05 6.62±0.15 6.87±0.07 6.84±0.15 6.46±0.15 6.39±0.10 6.71±0.09 6.75±0.03 6.40 5.50 Total 40.45±0.17 41.91±0.20 41.30±0.30 41.49±0.28 39.59±0.39 41.10±0.18 40.76±0.20 40.33±0.11 41.25±0.14 40.79±0.14 49.70 35.00 2.4 子实体中蛋白质的营养价值评分
氨基酸评分(AAS)是目前应用广泛的一种食物蛋白质营养价值评价方法,它是实验蛋白质中某一必需氨基酸占WFO/FAO评分模式中相应氨基酸含量的百分比。当AAS的值越接近1时,实验样品的氨基酸组成就越接近WFO/FAO评分模式,蛋白质价值就越高。AAS低于1的为限制氨基酸,其中最低的为第一限制氨基酸。由表5可知,供试菌株中除菌株PL1和PL5的甲硫氨酸+半胱氨酸偏离较大之外,其他氨基酸均与评分模式氨基酸组成接近,其中第一限制氨基酸为异亮氨酸(菌株PL1和PL5第一限制氨基酸为甲硫氨酸+半胱氨酸)。10个供试菌株中PL9子实体中必需氨基酸的AAS值均大于或等于1,表明该菌株所含的氨基酸价值最高,利于消化吸收。综合比较发现,商品菌株的必需氨基酸得分更接近WFO/FAO评分模式,因此蛋白质品质相较更加优良。
表 5 子实体必需氨基酸氨基酸评分(AAS)(%)Table 5. Essential amino acid AAS scores in fruit bodies (%)氨基酸 菌株 PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Thr 1.31±0.02 1.28±0.02 1.28±0.02 1.26±0.03 1.32±0.03 1.24±0.06 1.23±0.04 1.23±0.03 1.25±0.04 1.24±0.03 Val 1.17±0.01 1.18±0.01 1.11±0.01 1.16±0.02 1.16±0.01 1.13±0.02 1.12±0.02 1.12±0.02 1.13±0.02 1.10±0.03 Met+Cys 0.27±0.02 1.13±0.06 1.09±0.04 1.09±0.01 0.28±0.03 1.02±0.03 1.11±0.04 1.13±0.03 1.03±0.02 1.07±0.04 Ile 1.03±0.03 0.96±0.02 0.96±0.02 0.95±0.01 0.99±0.01 0.97±0.03 0.95±0.01 0.94±0.03 1.00±0.02 0.94±0.01 Leu 1.20±0.01 1.11±0.02 1.14±0.01 1.12±0.01 1.16±0.02 1.11±0.01 1.09±0.01 1.08±0.01 1.13±0.01 1.12±0.00 Phe+Tyr 1.46±0.01 1.41±0.01 1.39±0.02 1.43±0.01 1.43±0.01 1.41±0.02 1.41±0.03 1.36±0.03 1.39±0.03 1.37±0.02 Lys 1.30±0.01 1.24±0.01 1.20±0.01 1.20±0.03 1.25±0.01 1.24±0.03 1.17±0.03 1.16±0.02 1.22±0.02 1.23±0.03 Total 1.16±0.00 1.20±0.01 1.18±0.01 1.19±0.01 1.13±0.01 1.17±0.01 1.16±0.01 1.15±0.00 1.18±0.00 1.17±0.00 化学评分(CS)用来评价待测蛋白质中某一必需氨基酸含量与标准鸡蛋蛋白中该必需氨基酸含量的接近程度,它与AAS一样,都是评价氨基酸的营养价值的指标。CS值越接近1,与鸡蛋模式氨基酸组成越接近,蛋白质价值就越高。由表6可知,菌株PL1、PL3、PL5、PL6和PL10的第一限制氨基酸为甲硫氨酸+半胱氨酸,其余菌株的第一限制氨基酸为异亮氨酸。供试菌株中苏氨酸和赖氨酸的CS值最接近1,其余氨基酸的CS值在0.65~1.12之间(PL1和PL5的甲硫氨酸+半胱氨酸的值除外)。综合比较10个供试菌株发现,野生菌株的CS值更加接近鸡蛋模式,表明在该评价指标下,野生菌株表现较优。
表 6 子实体必需氨基酸化学评分(CS)Table 6. Essential amino acid CS in fruit bodies氨基酸 菌株 PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Thr 1.02±0.01 1.01±0.02 1.01±0.01 0.99±0.02 1.03±0.02 0.97±0.05 0.97±0.03 0.97±0.02 0.98±0.03 0.97±0.02 Val 0.80±0.01 0.81±0.01 0.76±0.01 0.80±0.01 0.79±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.76±0.02 Met+Cys 0.17±0.01 0.72±0.04 0.69±0.03 0.69±0.01 0.18±0.02 0.65±0.02 0.71±0.02 0.72±0.02 0.66±0.01 0.68±0.02 Ile 0.75±0.02 0.70±0.01 0.70±0.01 0.69±0.01 0.72±0.01 0.71±0.02 0.69±0.01 0.68±0.02 0.73±0.02 0.68±0.00 Leu 0.95±0.01 0.88±0.02 0.91±0.01 0.89±0.01 0.92±0.01 0.88±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.90±0.01 0.89±0.00 Phe+Tyr 0.88±0.01 0.85±0.01 0.83±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.84±0.01 0.85±0.02 0.82±0.02 0.83±0.02 0.82±0.01 Lys 1.12±0.01 1.07±0.01 1.03±0.01 1.03±0.02 1.07±0.01 1.07±0.02 1.01±0.02 1.00±0.02 1.05±0.01 1.05±0.01 Total 0.81±0.00 0.84±0.00 0.83±0.01 0.83±0.01 0.80±0.01 0.83±0.00 0.82±0.00 0.81±0.00 0.83±0.00 0.82±0.00 EAAI 71.77 85.20 83.84 84.07 70.95 83.09 82.88 82.26 83.66 82.67 必需氨基酸指数(EAAI)是一种蛋白质的必需氨基酸含量与标准蛋白质(通常是鸡蛋蛋白质)中的必需氨基酸含量比值的几何平均数,是评价食物蛋白质营养价值的指标之一。EAAI≤0.75不适合做蛋白源、0.75<EAAI≤0.85为可用蛋白源、0.85<EAAI≤0.95为良好蛋白源、EAAI≥0.95为优质蛋白源。本实验中,供试样品的EAAI值在70.95~85.20之间,根据以上评价标准,除菌株PL1和PL5外,其余8个菌株均为可用蛋白源,其中菌株PL2中必需氨基酸均衡性较好,为良好蛋白源。
2.5 氨基酸比值系数(RC)及氨基酸比值系数分(SRCAA)评价
氨基酸比值系数(RC)用来评估氨基酸在氨基酸平衡上做的贡献,RC>1表示该氨基酸过剩,RC<1表示该氨基酸相对不足;RC越集中,越接近1,蛋白质的营养价值越高。氨基酸比值系数分(SRCAA)表示氨基酸平衡做出的贡献大小,该值越接近100,蛋白质营养价值越高。如果食物中氨基酸组成与氨基酸模式一致,则RC都应等于1,SRC为100。由表7可知,本研究的供试菌株中,除菌株PL1的苏氨酸和赖氨酸,菌株PL5的苏氨酸及所有菌株的苯丙氨酸+酪氨酸含量相对过剩之外,其余样品的氨基酸含量皆相对不足。供试菌株的SRCAA值在69.06~90.12之间,其中菌株PL8的SRCAA值最高,为90.12,表明该菌株在所有供试菌株中的蛋白质营养价值最高。
表 7 子实体必需氨基酸RC、SRCAATable 7. Essential amino acid RC, SRCAA in fruit bodies氨基酸 菌株 PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 RC Thr 1.03 0.94 0.96 0.94 1.05 0.93 0.94 0.94 0.94 0.94 Val 0.92 0.87 0.83 0.87 0.93 0.85 0.85 0.86 0.85 0.84 Met+Cys 0.21 0.83 0.81 0.81 0.23 0.77 0.84 0.86 0.78 0.81 Ile 0.81 0.71 0.72 0.71 0.79 0.73 0.72 0.72 0.76 0.71 Leu 0.94 0.82 0.85 0.84 0.93 0.84 0.82 0.82 0.85 0.85 Phe+Tyr 1.15 1.04 1.04 1.06 1.15 1.06 1.07 1.04 1.05 1.04 Lys 1.03 0.91 0.90 0.90 1.00 0.94 0.89 0.89 0.92 0.93 SRCAA(%) 69.06 89.48 89.63 88.86 69.62 88.81 89.26 90.12 89.97 89.42 2.6 子实体中呈味氨基酸和5′核苷酸分析
呈味氨基酸与呈味核苷酸是食用菌中重要的非挥发性风味物质,当二者同时存在时可以产生协同效应,显著提高食用菌的鲜味。游离氨基酸是呈味氨基酸中一类重要的味觉活性物质,根据其呈味特性的不同,又可将其分为鲜味、甜味、苦味和无味四类。鲜味氨基酸和甜味氨基酸是赋予食用菌良好口感的重要因素,由表8可知,10个供试菌株中呈味氨基酸含量为甜味氨基酸>鲜味氨基酸>苦味氨基酸,甜味氨基酸总量介于47.02%~61.33%之间。呈味核苷酸是赋予食用菌特有鲜味的另一个因素,包括大量单核苷酸如5'-鸟苷酸、5'-肌苷酸、5'-黄苷酸、5'-腺苷酸,尤其5'-鸟苷酸含量最为丰富。供试肺形侧耳菌株子实体中5'-核苷酸总量为1195.16~1553.25 mg/kg,其中5′-AMP含量普遍较高。采用等鲜浓度值(EUC)来进行分析评价供试菌株的鲜味,结果如表9所示,EUC值在14.11~30.11 g MSG/100 g之间,处于Mau划分第3水平。综合比较分析发现商品菌株的5′-核苷酸总量、鲜味核苷酸及EUC值均普遍高于野生菌株,但本实验中的EUC值普遍较低,显著低于之前的研究结果[25],表明不同栽培基质对肺形侧耳的EUC值影响较大。
表 8 子实体呈味氨基酸含量比较Table 8. Comparison of flavor amino acid in fruit bodies氨基酸 含量(g/100 g) PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Asp 0.10 0.09 0.25 0.15 0.28 0.28 0.19 0.24 0.19 0.28 Glu 0.56 0.36 0.60 0.50 0.53 0.63 0.66 0.66 0.61 0.61 鲜味氨基酸MSG-like UAA 0.66 0.45 0.85 0.65 0.81 0.91 0.85 0.90 0.80 0.89 甜味氨基酸Sweet SAA 0.99 1.57 1.08 1.22 1.34 1.38 1.53 1.52 1.40 1.39 苦味氨基酸Bitter BAA 0.23 0.37 0.24 0.28 0.51 0.32 0.40 0.38 0.34 0.32 无滋味氨基酸Tasteless 0.13 0.17 0.12 0.15 0.19 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.21 0.22 氨基酸总量Total TAA 2.00 2.56 2.29 2.30 2.85 2.76 2.94 2.96 2.75 2.82 UAA/TAA(%) 33.00 17.58 37.12 28.26 28.42 32.97 28.91 30.41 29.09 31.56 SAA/TAA(%) 49.50 61.33 47.16 53.04 47.02 50.00 52.04 51.35 50.91 49.29 BAA/TAA(%) 11.50 14.45 10.48 12.17 17.89 11.59 13.61 12.84 12.36 11.35 (UAA+SAA)/BAA(%) 82.50 78.91 84.28 81.30 75.44 82.97 80.95 81.76 80.00 80.85 注:鲜味(Asp+Glu);甜味(Ser+Gly+Thr+Ala+Pro);苦味(His+Ile+Leu+Phe+Arg+Met+Val);无滋味(Cys+Lys+Tyr)。 表 9 子实体5′-核苷酸的含量及EUC评价Table 9. Content of 5′-nucleotides and EUC value evaluation of fruit bodies项目 含量(干重)(mg/kg) PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 5′-CMP 45.25 78.47 25.35 84.15 49.16 58.52 64.46 44.48 86.51 53.84 5′-UMP 346.40 385.03 365.17 359.64 355.06 325.32 339.94 270.46 389.78 357.42 5′-AMP 764.15 794.01 912.49 698.66 796.53 920.48 894.84 840.77 970.99 875.50 5′-GMP 89.29 71.52 69.05 46.49 63.47 59.63 53.56 43.44 92.49 59.25 5′-IMP 6.48 7.48 8.48 6.22 9.48 12.48 10.48 11.48 13.48 11.10 鲜味核苷酸 859.92 873.01 990.02 751.37 869.48 992.59 958.88 895.69 1076.96 945.85 Total 1251.57 1336.51 1380.54 1195.16 1273.70 1376.43 1363.28 1210.63 1553.25 1357.11 EUC 24.28 14.11 24.99 15.01 19.99 24.68 24.03 21.44 30.11 23.24 注:鲜味核苷酸(5′-GMP、5′-IMP和5′-AMP)。 3. 讨论与结论
从营养方面来看,10个肺形侧耳菌株的子实体营养丰富但不同菌株间差异显著,其中粗蛋白含量在30.00~36.07 g/100 g之间,高于已报道的杏鲍菇[26](19.05~25.62 g/100 g),香菇[27](19.72~25.26 g/100 g),金针菇[28](15.32~23.81 g/100 g)等食用菌;总糖含量在31.10%~47.63%之间,普遍高于已报道的食用菌[29]。γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)广泛分布于动植物、微生物体中,是谷氨酸在谷氨酸脱氢酶作用下形成的一种非蛋白氨基酸,是人类神经系统中重要的活性物质,具有降压、改善肝功能、抗衰老、抗疲劳、促进睡眠、治疗糖尿病等作用[30]。张亚青[31]对市售的11种食用菌进行测定发现,秀珍菇中GABA的含量较高,本研究中GABA含量在249.64~485.34 mg/kg之间;不同菌株间各矿质元素的含量差异较显著,这与李杰庆等[32]的研究一致,表明不同菌株对不同矿质元素的吸收能力是不同的,食用菌在生长过程中会对Fe、Mn、Cu、Zn等元素有一定选择性吸收,因此可以作为补充这些必需元素的良好食物来源[33]。
通过对供试样品氨基酸组成分析与评价,结果发现肺形侧耳子实体中氨基酸种类齐全,含量丰富,其必需氨基酸含量占总氨基酸含量40%以上,接近WHO和FAO理想模式,属于较优质的蛋白质。蛋白质的营养价值与其氨基酸组成密切相关,食物蛋白质中的氨基酸越接近人体蛋白质的组成,且能被人体消化吸收,其营养价值越高。本研究采用国际通用的营养评价方法,对供试肺形侧耳蛋白质营养价值进行AAS、CS、EAAI和SRCAA评价。样品的EAAI值在70.95~85.20之间,根据评价标准,除菌株PL1和PL5子实体外,其余8个菌株子实体均为可用蛋白源,其中菌株PL2子实体必需氨基酸均衡性最好;SRCAA值在69.06~90.12之间,菌株PL8子实体最接近100,说明该菌株子实体蛋白营养价值最均衡。
通过以上测定指标得出肺形侧耳是一种营养价值较高的食用菌,含有丰富的糖类、蛋白质、矿物质和γ-氨基丁酸等营养成分,且必需氨基酸占比接近FAO/WHO氨基酸理想模式,具有较高的营养价值和保健食品开发前景。综合比较本研究的10个供试菌株发现,5个商业栽培菌株间的各项指标差异较小,品质普遍较高,其中菌株PL9表现最优,其蛋白营养价值和EUC值明显高于另外4个菌株;5个野生菌株间的差异较为显著,个别菌株表现为单一营养物质含量较高,如菌株PL1的γ-氨基丁酸含量显著高于其他供试菌株,菌株PL4的总糖含量较高,菌株PL2的蛋白营养价值较高等。由此表明,不同菌株间营养和风味成分含量具显著差异,今后应加强肺形侧耳种质资源的保护和创新利用,为专用特用品种的选育和满足人们的多元化消费需求奠定基础。
-
表 1 供试菌株
Table 1 The tested strains
菌株编号 菌株来源 PL1 云南勐海采集 PL2 云南麻栗坡老君山采集 PL3 云南大理鸡足山采集 PL4 云南普洱菜阳河自然保护区采集 PL5 云南楚雄禄丰县五台山采集 PL6 福建农林大学菌物研究中心 PL7 湖北嘉鱼环宇食用菌研究所 PL8 福建省漳州市龙海九湖食用菌研究所 PL9 福建省食用菌种质资源保藏管理中心 PL10 华中农大菌种中心 表 2 子实体中矿物质和重金属含量比较(mg/kg)
Table 2 Comparison of mineral and heavy metal content in fruit bodies (mg/kg)
元素 Ca Mg Fe Mn Cu Zn Pb Cr Cd PL1 3682.64±87.50a 1200.14±72.14b 563.95±24.67a 23.27±0.71a 25.84±1.68a 184.05±18.07b − 0.36±0.03a 0.34±0.03b PL2 3501.34±157.71a 1407.73±133.93a 519.39±52.19a 21.55±3.83a 28.41±2.97a 154.05±32.18b − 0.33±0.06a 0.31±0.05b PL3 2527.28±166.15c 1021.14±10.59b 482.69±24.67b 21.05±2.15a 17.32±0.84b 227.39±32.67a − 0.35±0.01a 0.28±0.02b PL4 3070.50±177.42b 1248.90±55.19b 541.05±105.14a 27.82±4.62a 23.09±3.60a 251.77±14.91a − 0.36±0.01a 0.27±0.07b PL5 3245.79±124.26a 1131.17±83.38b 159.91±4.89d 16.56±1.51c 22.85±0.72a 168.78±20.55b − 0.30±0.05a 0.42±0.00a PL6 3464.99±144.51a 1169.71±72.55b 171.79±6.93d 21.59±1.18a 19.77±2.93b 189.15±31.66a − 0.30±0.04a 0.31±0.02b PL7 2964.45±181.54c 1155.62±41.48b 292.70±21.54c 17.04±0.31c 16.58±1.14b 88.38±0.09e − 0.29±0.01b 0.30±0.03b PL8 2831.60±121.85c 1106.99±74.32b 136.59±14.70e 21.84±2.42a 24.99±3.54a 114.40±8.65d − 0.29±0.02b 0.29±0.03b PL9 2475.30±103.57c 1042.65±24.56b 161.26±9.02d 17.88±0.15b 16.25±0.49b 136.29±4.58c − 0.32±0.06a 0.25±0.05b PL10 2753.18±27.80c 1100.10±78.28b 333.23±107.63b 19.60±2.12a 18.02±0.40b 156.85±5.48b − 0.29±0.02b 0.29±0.02b 表 3 子实体中氨基酸含量比较
Table 3 Comparison of amino acid contents in fruit bodies
氨基酸 含量(干重)(g/100 g) PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Asp 2.34±0.07 2.28±0.06 2.51±0.06 2.41±0.06 2.66±0.04 2.57±0.05 2.51±0.02 2.52±0.04 2.78±0.04 2.71±0.03 Thr 1.15±0.02 1.19±0.03 1.18±0.03 1.16±0.03 1.24±0.02 1.15±0.06 1.19±0.04 1.17±0.03 1.30±0.05 1.23±0.05 Ser 1.19±0.03 1.19±0.03 1.19±0.03 1.19±0.04 1.22±0.04 1.15±0.04 1.20±0.04 1.19±0.03 1.29±0.04 1.25±0.03 Glu 3.89±0.04 4.24±0.07 4.03±0.06 4.06±0.05 4.10±0.02 4.15±0.03 4.61±0.02 4.60±0.03 4.69±0.03 4.37±0.03 Gly 1.16±0.04 1.13±0.07 1.13±0.06 1.17±0.05 1.15±0.02 1.13±0.03 1.15±0.02 1.12±0.03 1.25±0.03 1.28±0.03 Ala 1.42±0.03 1.44±0.02 1.45±0.02 1.46±0.03 1.55±0.02 1.45±0.02 1.48±0.02 1.49±0.02 1.66±0.01 1.58±0.03 Cys 0.19±0.02 0.21±0.02 0.22±0.02 0.21±0.02 0.22±0.02 0.21±0.02 0.22±0.02 0.23±0.02 0.24±0.02 0.21±0.03 Val 1.29±0.02 1.37±0.02 1.27±0.02 1.34±0.02 1.36±0.02 1.31±0.02 1.35±0.02 1.33±0.02 1.47±0.02 1.37±0.03 Met 0.01±0.01 0.71±0.03 0.66±0.03 0.66±0.02 0.01±0.01 0.62±0.02 0.72±0.02 0.71±0.02 0.70±0.01 0.72±0.03 Ile 0.90±0.02 0.89±0.02 0.88±0.02 0.87±0.02 0.93±0.01 0.90±0.02 0.92±0.01 0.90±0.02 1.05±0.02 0.93±0.02 Leu 1.85±0.03 1.80±0.02 1.83±0.02 1.81±0.02 1.91±0.02 1.81±0.02 1.83±0.02 1.79±0.02 2.06±0.04 1.95±0.03 Tyr 0.74±0.02 0.75±0.03 0.71±0.02 0.78±0.01 0.78±0.02 0.75±0.02 0.80±0.02 0.74±0.02 0.81±0.02 0.78±0.02 Phe 1.19±0.02 1.22±0.01 1.20±0.01 1.19±0.02 1.24±0.02 1.21±0.02 1.24±0.02 1.20±0.02 1.37±0.03 1.25±0.02 Lys 1.58±0.02 1.58±0.02 1.51±0.02 1.52±0.04 1.61±0.02 1.59±0.03 1.56±0.03 1.52±0.03 1.75±0.03 1.67±0.03 His 0.55±0.02 0.60±0.02 0.56±0.02 0.59±0.03 0.60±0.02 0.55±0.04 0.59±0.04 0.60±0.04 0.61±0.04 0.60±0.04 Arg 1.52±0.04 1.49±0.02 1.49±0.03 1.48±0.03 1.84±0.09 1.63±0.04 1.60±0.04 1.60±0.02 1.80±0.03 1.75±0.02 Pro 1.04±0.05 1.11±0.03 1.06±0.04 1.10±0.02 1.07±0.04 1.09±0.03 1.13±0.02 1.06±0.05 1.22±0.04 1.13±0.03 EAA 7.97±0.11 8.77±0.09 8.52±0.12 8.55±0.09 8.30±0.06 8.60±0.05 8.80±0.05 8.63±0.04 9.70±0.10 9.12±0.12 TAA 22.02±0.23 23.22±0.21 22.89±0.26 23.00±0.10 23.50±0.21 23.29±0.09 24.09±0.05 23.80±0.11 26.04±0.23 24.78±0.31 NEAA 14.05±0.13 14.44±0.13 14.37±0.15 14.45±0.02 15.20±0.18 14.68±0.06 15.30±0.04 15.17±0.08 16.35±0.13 15.67±0.19 E/T 0.36±0.00 0.38±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.35±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.36±0.00 0.37±0.00 0.37±0.00 E/N 0.57±0.00 0.61±0.00 0.59±0.01 0.59±0.01 0.55±0.01 0.59±0.00 0.58±0.00 0.57±0.00 0.59±0.00 0.58±0.00 注:TAA:氨基酸总量;EAA:必需氨基酸总量;NEAA:非必需氨基酸。 表 4 子实体中必需氨基酸组成分析(%)
Table 4 Essential amino acid composition analysis in fruit bodies (%)
氨基酸 菌株 鸡蛋 FAO/
WHOPL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Thr 5.22±0.06 5.14±0.08 5.14±0.07 5.04±0.11 5.26±0.11 4.95±0.24 4.94±0.15 4.93±0.13 5.00±0.17 4.96±0.12 5.10 4.00 Val 5.86±0.06 5.90±0.06 5.55±0.05 5.81±0.08 5.80±0.07 5.64±0.09 5.60±0.09 5.60±0.09 5.64±0.09 5.52±0.13 7.30 5.00 Met+Cys 0.94±0.06 3.96±0.19 3.81±0.15 3.81±0.03 0.99±0.11 3.56±0.11 3.90±0.12 3.96±0.11 3.62±0.08 3.74±0.13 5.50 3.50 Ile 4.10±0.10 3.85±0.07 3.86±0.06 3.78±0.05 3.94±0.05 3.88±0.12 3.80±0.05 3.77±0.12 4.02±0.09 3.75±0.02 5.50 3.50 Leu 8.39±0.09 7.77±0.13 1.99±0.05 7.87±0.06 8.11±0.12 7.79±0.09 7.60±0.08 7.53±0.06 7.91±0.07 7.85±0.03 8.80 7.00 Phe+Tyr 8.77±0.09 8.47±0.08 8.35±0.10 8.55±0.07 8.61±0.08 8.43±0.13 8.45±0.15 8.15±0.19 8.34±0.15 8.22±0.10 10.00 6.00 Lys 7.18±0.04 6.82±0.04 6.60±0.05 6.62±0.15 6.87±0.07 6.84±0.15 6.46±0.15 6.39±0.10 6.71±0.09 6.75±0.03 6.40 5.50 Total 40.45±0.17 41.91±0.20 41.30±0.30 41.49±0.28 39.59±0.39 41.10±0.18 40.76±0.20 40.33±0.11 41.25±0.14 40.79±0.14 49.70 35.00 表 5 子实体必需氨基酸氨基酸评分(AAS)(%)
Table 5 Essential amino acid AAS scores in fruit bodies (%)
氨基酸 菌株 PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Thr 1.31±0.02 1.28±0.02 1.28±0.02 1.26±0.03 1.32±0.03 1.24±0.06 1.23±0.04 1.23±0.03 1.25±0.04 1.24±0.03 Val 1.17±0.01 1.18±0.01 1.11±0.01 1.16±0.02 1.16±0.01 1.13±0.02 1.12±0.02 1.12±0.02 1.13±0.02 1.10±0.03 Met+Cys 0.27±0.02 1.13±0.06 1.09±0.04 1.09±0.01 0.28±0.03 1.02±0.03 1.11±0.04 1.13±0.03 1.03±0.02 1.07±0.04 Ile 1.03±0.03 0.96±0.02 0.96±0.02 0.95±0.01 0.99±0.01 0.97±0.03 0.95±0.01 0.94±0.03 1.00±0.02 0.94±0.01 Leu 1.20±0.01 1.11±0.02 1.14±0.01 1.12±0.01 1.16±0.02 1.11±0.01 1.09±0.01 1.08±0.01 1.13±0.01 1.12±0.00 Phe+Tyr 1.46±0.01 1.41±0.01 1.39±0.02 1.43±0.01 1.43±0.01 1.41±0.02 1.41±0.03 1.36±0.03 1.39±0.03 1.37±0.02 Lys 1.30±0.01 1.24±0.01 1.20±0.01 1.20±0.03 1.25±0.01 1.24±0.03 1.17±0.03 1.16±0.02 1.22±0.02 1.23±0.03 Total 1.16±0.00 1.20±0.01 1.18±0.01 1.19±0.01 1.13±0.01 1.17±0.01 1.16±0.01 1.15±0.00 1.18±0.00 1.17±0.00 表 6 子实体必需氨基酸化学评分(CS)
Table 6 Essential amino acid CS in fruit bodies
氨基酸 菌株 PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Thr 1.02±0.01 1.01±0.02 1.01±0.01 0.99±0.02 1.03±0.02 0.97±0.05 0.97±0.03 0.97±0.02 0.98±0.03 0.97±0.02 Val 0.80±0.01 0.81±0.01 0.76±0.01 0.80±0.01 0.79±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.77±0.01 0.76±0.02 Met+Cys 0.17±0.01 0.72±0.04 0.69±0.03 0.69±0.01 0.18±0.02 0.65±0.02 0.71±0.02 0.72±0.02 0.66±0.01 0.68±0.02 Ile 0.75±0.02 0.70±0.01 0.70±0.01 0.69±0.01 0.72±0.01 0.71±0.02 0.69±0.01 0.68±0.02 0.73±0.02 0.68±0.00 Leu 0.95±0.01 0.88±0.02 0.91±0.01 0.89±0.01 0.92±0.01 0.88±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.90±0.01 0.89±0.00 Phe+Tyr 0.88±0.01 0.85±0.01 0.83±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.86±0.01 0.84±0.01 0.85±0.02 0.82±0.02 0.83±0.02 0.82±0.01 Lys 1.12±0.01 1.07±0.01 1.03±0.01 1.03±0.02 1.07±0.01 1.07±0.02 1.01±0.02 1.00±0.02 1.05±0.01 1.05±0.01 Total 0.81±0.00 0.84±0.00 0.83±0.01 0.83±0.01 0.80±0.01 0.83±0.00 0.82±0.00 0.81±0.00 0.83±0.00 0.82±0.00 EAAI 71.77 85.20 83.84 84.07 70.95 83.09 82.88 82.26 83.66 82.67 表 7 子实体必需氨基酸RC、SRCAA
Table 7 Essential amino acid RC, SRCAA in fruit bodies
氨基酸 菌株 PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 RC Thr 1.03 0.94 0.96 0.94 1.05 0.93 0.94 0.94 0.94 0.94 Val 0.92 0.87 0.83 0.87 0.93 0.85 0.85 0.86 0.85 0.84 Met+Cys 0.21 0.83 0.81 0.81 0.23 0.77 0.84 0.86 0.78 0.81 Ile 0.81 0.71 0.72 0.71 0.79 0.73 0.72 0.72 0.76 0.71 Leu 0.94 0.82 0.85 0.84 0.93 0.84 0.82 0.82 0.85 0.85 Phe+Tyr 1.15 1.04 1.04 1.06 1.15 1.06 1.07 1.04 1.05 1.04 Lys 1.03 0.91 0.90 0.90 1.00 0.94 0.89 0.89 0.92 0.93 SRCAA(%) 69.06 89.48 89.63 88.86 69.62 88.81 89.26 90.12 89.97 89.42 表 8 子实体呈味氨基酸含量比较
Table 8 Comparison of flavor amino acid in fruit bodies
氨基酸 含量(g/100 g) PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 Asp 0.10 0.09 0.25 0.15 0.28 0.28 0.19 0.24 0.19 0.28 Glu 0.56 0.36 0.60 0.50 0.53 0.63 0.66 0.66 0.61 0.61 鲜味氨基酸MSG-like UAA 0.66 0.45 0.85 0.65 0.81 0.91 0.85 0.90 0.80 0.89 甜味氨基酸Sweet SAA 0.99 1.57 1.08 1.22 1.34 1.38 1.53 1.52 1.40 1.39 苦味氨基酸Bitter BAA 0.23 0.37 0.24 0.28 0.51 0.32 0.40 0.38 0.34 0.32 无滋味氨基酸Tasteless 0.13 0.17 0.12 0.15 0.19 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.21 0.22 氨基酸总量Total TAA 2.00 2.56 2.29 2.30 2.85 2.76 2.94 2.96 2.75 2.82 UAA/TAA(%) 33.00 17.58 37.12 28.26 28.42 32.97 28.91 30.41 29.09 31.56 SAA/TAA(%) 49.50 61.33 47.16 53.04 47.02 50.00 52.04 51.35 50.91 49.29 BAA/TAA(%) 11.50 14.45 10.48 12.17 17.89 11.59 13.61 12.84 12.36 11.35 (UAA+SAA)/BAA(%) 82.50 78.91 84.28 81.30 75.44 82.97 80.95 81.76 80.00 80.85 注:鲜味(Asp+Glu);甜味(Ser+Gly+Thr+Ala+Pro);苦味(His+Ile+Leu+Phe+Arg+Met+Val);无滋味(Cys+Lys+Tyr)。 表 9 子实体5′-核苷酸的含量及EUC评价
Table 9 Content of 5′-nucleotides and EUC value evaluation of fruit bodies
项目 含量(干重)(mg/kg) PL1 PL2 PL3 PL4 PL5 PL6 PL7 PL8 PL9 PL10 5′-CMP 45.25 78.47 25.35 84.15 49.16 58.52 64.46 44.48 86.51 53.84 5′-UMP 346.40 385.03 365.17 359.64 355.06 325.32 339.94 270.46 389.78 357.42 5′-AMP 764.15 794.01 912.49 698.66 796.53 920.48 894.84 840.77 970.99 875.50 5′-GMP 89.29 71.52 69.05 46.49 63.47 59.63 53.56 43.44 92.49 59.25 5′-IMP 6.48 7.48 8.48 6.22 9.48 12.48 10.48 11.48 13.48 11.10 鲜味核苷酸 859.92 873.01 990.02 751.37 869.48 992.59 958.88 895.69 1076.96 945.85 Total 1251.57 1336.51 1380.54 1195.16 1273.70 1376.43 1363.28 1210.63 1553.25 1357.11 EUC 24.28 14.11 24.99 15.01 19.99 24.68 24.03 21.44 30.11 23.24 注:鲜味核苷酸(5′-GMP、5′-IMP和5′-AMP)。 -
[1] 杨润亚, 李维焕, 吕芳芳. 秀珍菇子实体多糖的提取工艺优化及体外抗氧化性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2012,31(10):1093−1099. [YANG R Y, LI W H, LU F F. Optimization of the extraction technique and the antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Pleurotus geesteranus[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2012,31(10):1093−1099. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2012.10.014 YANG R Y, LI W H, LU F F. Optimization of the extraction technique and the antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Pleurotus geesteranus[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2012, 31(10): 1093-1099. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2012.10.014
[2] 张晓玉, 张博, 辛广, 等. 秀珍菇营养成分、生物活性及贮藏保鲜的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2016,7(6):2314−2319. [ZHANG X Y, ZHANG B, XIN G, et al. Research progress on nutrition constituents, bioactivity and storage preservation of Pleurotus geesteranus[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2016,7(6):2314−2319. ZHANG X Y, ZHANG B, XIN G, et al. Research progress on nutrition constituents, bioactivity and storage preservation of Pleurotus geesteranus[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2016, 7(6): 2314-2319.
[3] 张亚青, 张羡, 付佳伟, 等. 原生质体紫外诱变法选育高产γ-氨基丁酸秀珍菇菌株[J]. 浙江科技学院学报,2019,31(3):198−205. [ZHANG Y Q, ZHANG X, FU J W, et al. Breeding of GABA-rich Pleurotus geesteranus strains through an ultraviolet ray-mediated protoplast mutagenesis method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Science and Technology,2019,31(3):198−205. ZHANG Y Q, ZHANG X, FU J W, et al. Breeding of GABA-rich Pleurotus geesteranus strains through an ultraviolet ray-mediated protoplast mutagenesis method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, 2019, 31(3): 198-205.
[4] CHATCHAI T, SARANYU K, KHAJEELAK C, et al. Antioxidant properties and cytotoxicity of crude polysaccharides from Lentinus polychrous Lév[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,128(3):634−639. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.077
[5] WANG Q, LI H, CHEN T T, et al. Yield, polysaccharides content and antioxidant properties of Pleurotus abalonus and Pleurotus geesteranus produced on asparagus straw as substrate[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2012,134:222−226. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2011.11.005
[6] 孙玉军, 江昌俊, 任四海. 秀珍菇多糖对D-半乳糖致衰老小鼠的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(5):251−256. [SUN Y J, JIANG C J, REN S H. Protective effect of polysaccharides from the fruiting body of Pleurotus geesteranus against D-galactose-induced aging mice[J]. Food Science,2017,38(5):251−256. SUN Y J, JIANG C J, REN S H. Protective effect of polysaccharides from the fruiting body of Pleurotus geesteranus against D-galactose-induced aging mice[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(5): 251-256.
[7] 王鸿磊, 陈润臣, 孙玮, 等. 国内外12个双孢菇菌株子实体的营养成分[J]. 贵州农业科学,2020,48(10):64−68. [WANG H L, CHEN R C, SUN W, et al. Nutritional components of 12 Agaricus bisporus strains fruibody at home and abroad[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(10):64−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2020.10.014 WANG H L, CHEN R C, SUN W, et al. Nutritional components of 12 Agaricus bisporus strains fruibody at home and abroad[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(10): 64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2020.10.014
[8] 谢丽源, 兰秀华, 唐杰, 等. 不同羊肚菌品种氨基酸营养评价及等鲜浓度值差异分析[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2020,32(6):1023−1029,979. [XIE L Y, LAN X H, TANG J, et al. Nutritional evaluation of different amino acids and difference analysis of equivalent umami concentration in Morchella spp[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2020,32(6):1023−1029,979. XIE L Y, LAN X H, TANG J, et al. Nutritional evaluation of different amino acids and difference analysis of equivalent umami concentration in Morchella spp[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2020, 32(6): 1023-1029, 979.
[9] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 National food safety standard. Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[10] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 15672-2009 食用菌中总糖含量的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 15672-2009 Determination of total sugar content in edible mushrooms[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009.
[11] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. γ-氨基丁酸: QB/T 4587-2013[S]. 北京: 中国轻工出版社, 2013 Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China. γ-Aminobutyric acid: QB/T 4587-2013[S]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2013.
[12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.124-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National food safety standards. Determination of amino acids in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[13] 国家林业局. LY/T 1270-1999 森林植物与森林枯枝落叶层全硅、铁、铝、钙、镁、钾、钠、磷、硫、锰、铜、锌的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1999 State Forestry Administration. LY/T 1270-1999 Determination of total silicon, iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, phosphorus, sulfur, manganese, copper, and zinc in forest plants and forest litter layer[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1999.
[14] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T 1676-2008 蔬菜、水果及制品中矿质元素的测定 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2008 Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. NY/T 1676-2008 Determination of mineral elements in vegetables, fruits and products. Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2008.
[15] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.123-2014 食品安全国家标准 食品中铬的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.123-2014 National food safety standard. Determination of chromium in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014.
[16] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.12-2017食品安全国家标准 食品中铅的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.12-2017 National food safety standard-Determination of lead in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
[17] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.15-2014 食品安全国家标准 食品中铅的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.12-2014 National food safety standard. Determination of lead in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014.
[18] 余昌霞, 陈明杰, 李传华, 等. 不同培养基质对草菇营养成分及呈味物质的影响[J]. 菌物学报,2018,37(12):1731−1740. [YU C X, CHEN M J, LI C H, et al. Effects of culture substrates on nutritional and flavor components of Volvariella volvacea[J]. Mycosystema,2018,37(12):1731−1740. YU C X, CHEN M J, LI C H, et al. Effects of culture substrates on nutritional and flavor components of Volvariella volvacea[J]. Mycosystema, 2018, 37(12): 1731-1740.
[19] LI W, LI X B, YANG Y, et al. Effect of different carbon sources and C/N values on nonvolatile taste components of Pleurotus eryngii[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2015,50(11):2360−2366. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.12901
[20] SELIGSON F H, MACKEY L N. Variable predictions of protein quality by chemical score due to amino acid analysis and reference pattern[J]. The Journal of Nutrition,1984,114(4):682−691. doi: 10.1093/jn/114.4.682
[21] FAO/WHO expert consultation. Protein quality evaluation report of the joint FAO/WHO expert consultation held in Bethseda[C]. Rome, 1989.
[22] OSER B L. Method for integrating essential amino acid content in the nutritional evaluation of protein[J]. Journal of the American Dietetic Association,1951,27(5):396−402. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8223(21)30758-1
[23] 朱圣陶, 吴坤. 蛋白质营养价值评价——氨基酸比值系数法[J]. 营养学报,1988,10(2):187−190. [ZHU S T, WU K. Nutritional evaluation of protein-ratio coefficient amino acid[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,1988,10(2):187−190. doi: 10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.1988.02.015 ZHU S T, WU K. Nutritional evaluation of protein-ratio coefficient amino acid[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 1988, 10(2): 187-190. doi: 10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.1988.02.015
[24] MAU J L, CHYAU C C, LI J Y, et al. Flavor compounds in straw mushrooms Volvariella volvacea harvested at different stages of maturity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1997,45(12):4726−4729. doi: 10.1021/jf9703314
[25] 汪乔, 王祥锋, 杨晓君, 等. 不同栽培基质对肺形侧耳营养成分及呈味物质的影响[J]. 菌物学报,2021,40(12):3182−3195. [WANG Q, WANG X F, YANG X J, et al. Effects of culture substrates on nutritional and flavor components of Pleurotus pulmonarius[J]. Mycosystema,2021,40(12):3182−3195. WANG Q, WANG X F, YANG X J, et al. Effects of culture substrates on nutritional and flavor components of Pleurotus pulmonarius[J]. Mycosystema, 2021, 40(12): 3182-3195.
[26] 陈洪雨, 鲍大鹏, 康前进, 等. 5种市售工厂化栽培杏鲍菇的氨基酸组成及蛋白质营养分析[J]. 上海农业学报,2019,35(4):9−15. [CHEN H Y, BAO D P, KANG Q J, et al. Amino acid composition and protein nutrition analysis of 5 commercial industrial cultivated Pleurotus eryngii samples[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai,2019,35(4):9−15. CHEN H Y, BAO D P, KANG Q J, et al. Amino acid composition and protein nutrition analysis of 5 commercial industrial cultivated Pleurotus eryngii samples[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2019, 35(4): 9-15.
[27] 李巧珍, 宋春艳, 刘建雨, 等. 香菇自交选育新菌株及其亲本子实体的氨基酸特征及蛋白质营养价值[J]. 食用菌学报,2019,26(3):51−57. [LI Q Z, SONG C Y, LIU J Y, et al. Amino acid profile and protein nutritional value of Lentinula edodes Huxiang F2 and its self-breeding progenies[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi,2019,26(3):51−57. LI Q Z, SONG C Y, LIU J Y, et al. Amino acid profile and protein nutritional value of Lentinula edodes Huxiang F2 and its self-breeding progenies[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2019, 26(3): 51-57.
[28] 陆欢, 王瑞娟, 刘建雨, 等. 不同品种金针菇的营养成分分析与评价[J]. 食品与机械,2021,37(6):69−75, 96. [LU H, WANG R J, LIU J Y, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutrient components of different strains of Flammulina filiformis[J]. Food & Machinery,2021,37(6):69−75, 96. LU H, WANG R J, LIU J Y, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutrient components of different strains of Flammulina filiformis[J]. Food & Machinery, 2021, 37(6): 69-75, 96.
[29] 靳羽慧, 邓楚君, 赵慧, 等. 3种常见食用菌营养成分和嘌呤物质含量分析[J]. 中国食用菌,2018,37(4):62−65,81. [JIN Y H, DENG C J, ZHAO H, et al. Analytical determination on nutrients and purine contents of three common edible mushrooms[J]. Edible Fungi of China,2018,37(4):62−65,81. doi: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2018.04.015 JIN Y H, DENG C J, ZHAO H, et al. Analytical determination on nutrients and purine contents of three common edible mushrooms[J]. Edible Fungi of China, 2018, 37(4): 62-65, 81. doi: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2018.04.015
[30] ABDELAZEZ A, ABDELMOTAAL H, EVIVIE S E, et al. Screening potential probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus brevis strains in vitro and intervention effect on type I diabetes in vivo[J]. BioMed Research International, 2018.
[31] 张亚青. 高产γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)食用菌资源的筛选与利用[D]. 杭州: 浙江科技学院, 2020 ZHANG Y Q. Screening and utilization of γ-amino butyric acid edible mushroom resources[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[32] 李杰庆, 孙景, 李涛, 等. 食(药)用真菌矿质元素研究进展[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2017,32(5):929−946. [LI J Q, SUN J, LI T, et al. Research progress of mineral elements in edible (or medicinal) fungi[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science),2017,32(5):929−946. LI J Q, SUN J, LI T, et al. Research progress of mineral elements in edible (or medicinal) fungi[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2017, 32(5): 929-946.
[33] 鲍长俊, 常惟丹, 庄永亮, 等. 灰褐牛肝菌(Boletus griseus)子实体的营养评价及蛋白质组分分析[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(20):83−89. [BAO C J, CHANG W D, ZHUANG Y L, et al. Nutritional characteristics and protein composition of fruiting bodies of Boletus griseus[J]. Food Science,2017,38(20):83−89. BAO C J, CHANG W D, ZHUANG Y L, et al. Nutritional characteristics and protein composition of fruiting bodies of Boletus griseus[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(20): 83-89.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张时馨,陈荟,耿阳阳. 不同菌材栽培糙皮侧耳营养品质综合评价. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(09): 321-331 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郭显会,李膳利,王杰,余彬情,石荣光,李星,李琳琪,孙厚静,陆兰芳,周剑南. 1株野生肺形侧耳菌丝生物学特性及驯化栽培. 食用菌. 2024(06): 18-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 闫静,王伟科,周祖法,周小华. 多孢自交选育秀珍菇新菌株研究. 北方园艺. 2024(23): 114-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 龚娜,刘国丽,陈珣,马晓颖,肇莹,肖军. 一株野生肺形侧耳的鉴定及其液体发酵培养基的优化. 浙江农业学报. 2024(11): 2535-2545 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



