Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction and Purification of Resveratrol from Peanut Root
-
摘要: 研究了超声波辅助乙醇提取及大孔树脂初步纯化花生根中白藜芦醇的工艺条件。以花生根白藜芦醇的提取率为指标,考查了乙醇浓度、超声功率、超声时间和料液比对提取率的影响。结果表明,通过单因素实验和响应面法优化的最佳条件如下:乙醇浓度90%、超声功率290 W、超声时间12 min、料液比1:38(g/mL),白藜芦醇的含量为175.53±1.57 μg/g。通过方差分析发现:超声时间、超声功率和乙醇浓度对白藜芦醇含量的影响达到显著水平(P<0.05)。最佳条件下为树脂H103,上样浓度201.13 μg/mL,上样速率为1.0 mL/min,上样量为120 mL,洗脱溶剂为90%乙醇,洗脱流速为1.0 mL/min,洗脱量为160 mL,一次处理后,粗产品中白藜芦醇的含量为49.19%±0.81%,RSD为1.65%。超声辅助提取白藜芦醇和大孔树脂初步纯化白藜芦醇是可行的。Abstract: The process conditions of ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extraction of resveratrol in peanut roots and the purification of resveratrol by macroporous resin were studied. The effects of ethanol concentration, ultrasonic power, ultrasonic time and solid-liquid ratio on the extraction rate of resveratrol from peanut root were investigated. After optimization by single-factor experiments and response surface methodology, a promised yield of resveratrol (175.53±1.57 μg/g) was obtained under optimal conditions: Ethanol concentration 90%, ultrasonic power 290 W, ultrasonic time 12 min, and solid-liquid ratio 1:38 (g:mL). Analysis of variance was performed to find that the effects of ultrasonic time, ultrasonic power and ethanol concentration on the extracted content of resveratrol reached the significance level (P<0.05). Under the best conditions, the resin was H103, sample concentration 201.13 μg/mL, sample loading rate 1.0 mL/min, sample loading volume 120 mL, elution solvent 90% ethanol, elution flow rate 1.0 mL/min, elution volume 160 mL, after one treatment, the content of resveratrol in the product was 49.19%±0.81% and the RSD value was 1.65%. The ultrasonic-assisted extraction of resveratrol and the preliminary purification of resveratrol by macroporous resin would be promised and reliable, which would provide a reference for the rational development and comprehensive utilization of peanut roots and the standardization and industrial production of natural resveratrol.
-
Keywords:
- peanut root /
- resveratrol /
- ultrasonic /
- response surface optimization /
- macroporous resin
-
白藜芦醇,3,4',5-三羟基-1,2-二苯基乙烯,又名芪三酚,是某些植物在受外界刺激时产生的一种抗毒素,在消炎、抗氧化、抑制癌细胞生长、降血脂和预防心血管疾病等方面有比较显著的作用[1-2]。目前国内有关白藜芦醇的研究多集中以中药虎杖为提取原料,但虎杖为中药宝贵资源,提取成本较高。有研究表明花生根内含有丰富的白藜芦醇[3-5],但是作为花生采收后的副产物之一,花生根除少量作为燃料使用外,其余大部分被随意丢弃,造成资源浪费和环境污染[6-7]。
目前从花生根中提取白藜芦醇的方法主要有有机溶剂提取法、酶法和超临界CO2萃取等[8-10]。对白藜芦醇粗提物的纯化主要采用大孔树脂法、高速逆流色谱法和双水相萃取纯化等[11-13]。上述提取纯化的方法适于开展大规模工业化生产的很少[14-17],对花生根白藜芦醇提取工业化和产业化方面的参考价值较低。对花生根的综合利用研究应当以利于工业化和产业化为目标。因此,有必要建立一套完整且适于工业化生产花生根白藜芦醇的方法。而超声辅助溶剂提取则具有耗时短、效率高及适应性广等方面的优势[18-19]。大孔树脂纯化具有吸附、解吸较快、选择性高、吸附容量大和便于工业化生产等特点[20-21]。本研究拟采用超声波辅助提取联合大孔树脂初步纯化花生根白藜芦醇,以期为花生根的合理开发、综合利用和天然白藜芦醇的标准化及工业化生产提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
花生根粉 中花16,中国农业科学院油料作物研究所;白藜芦醇标准品 纯度98%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;乙腈 色谱级,Thermo Fisher;乙醇 分析纯,国药集团;大孔树脂H103 安徽三星树脂科技有限公司;层析柱 1.5×40 cm,上海沪西分析仪器厂有限公司。
Agilent 1260 Ⅱ高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦公司;ZLGZ-12冷冻干燥机 郑州科旺达生物仪器有限公司;JY92-IIN超声波细胞粉碎机 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;N-1300旋转蒸发仪 上海爱朗仪器有限公司;SPH-200B恒温摇床 上海世平实验设备有限公司;HL-1恒流泵 上海沪西分析仪器厂有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 白藜芦醇的提取方法
参考安宝树[22]的方法,花生根打粉后过40目筛,用乙醇提取,提取方式为超声波辅助提取。参考黄纪念等[23]的方法,固定提取温度为50 ℃,选取花生根粉与乙醇的不同配比即料液比(g:mL)、乙醇浓度(%)、超声波功率(W)及超声时间(min)四个实验因素,以白藜芦醇的含量为试验指标进行提取实验。
1.2.2 单因素实验
乙醇浓度:保持料液比、超声时间以及超声功率分别为1:30 g:mL、9 min和300 W,乙醇浓度分别为60%、70%、80%、90%和100%。考察不同乙醇浓度对花生根内白藜芦醇含量的作用。
超声时间:保持乙醇浓度、料液比以及超声功率分别为90%、1:30 g:mL和300 W,超声作用时间分别设置为3、6、9、12和15 min。考察不同超声时间对花生根内白藜芦醇含量的影响。
超声功率:保持乙醇浓度、料液比以及超声时间分别为90%、1:30 g:mL和9 min,超声功率分别设置为150、200、250、300和350 W。考察不同超声功率对花生根内白藜芦醇含量的影响。
料液比:保持乙醇浓度、超声时间以及超声功率分别为90%、9 min和300 W,料液比分别为1:10、1:20、1:30、1:40和1:50 g:mL。考察不同料液比对花生根内白藜芦醇含量的影响。
依据式(1)计算白藜芦醇含量(μg/g)。
(1) 式中:c为白藜芦醇质量浓度,μg/mL;v为待测溶液总体积,mL;m为花生根粉质量,g。
1.2.3 响应面试验
以单因素实验的结果为参考,选取乙醇浓度(A)、超声时间(B)、超声功率(C)以及料液比(D)作为影响因素,设计响应面试验方案。以白藜芦醇含量为实验指标,确定白藜芦醇的最佳提取工艺,同时对模型建议的最佳提取工艺进行验证实验[24]。以单因素实验的结果为参考选取合适的因素以及水平并进行编码,使用响应面模型对实验结果进行优化分析。因素水平表见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素水平设计Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface methodology水平 A.乙醇浓度
(%)B.超声时间
(min)C.超声功率
(W)D.料液比
(g:mL)−1 80 9 250 1:30 0 90 12 300 1:40 1 100 15 350 1:50 1.2.4 大孔树脂对白藜芦醇的分离纯化
参考吴佳等[25]和骆航等[26]的方法采用H103大孔树脂对花生根白藜芦醇进行初步纯化。
1.2.4.1 静态吸附动力学
称取0.5 g树脂,加入提取浓缩后质量浓度为247.49 μg/mL的粗提液原液25 mL,通过恒温摇床在25 ℃、150 r/min环境下振荡,每隔20 min测定白藜芦醇的含量。
1.2.4.2 静态吸附等温曲线
称取五份树脂,每份0.5 g,分别加入25 mL含有60%、70%、80%、90%和100%提取原液的白藜芦醇粗提液,通过恒温摇床在25 ℃、150 r/min环境下振荡,60 min后分别测定白藜芦醇的含量。
1.2.4.3 上样流速与上样体积
称取10 g树脂,湿法装柱[18,27],将质量浓度为70%提取原液的白藜芦醇粗提液400 mL,分别在0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5 mL/min的流速下收集流出液(10 mL/管),当上样液质量浓度为流出液质量浓度的10倍时确定上样体积。
1.2.4.4 洗脱流速与洗脱体积
称取10 g树脂,湿法装柱,使其吸附饱和,以纯化水清洗树脂至流出液中检测不到白藜芦醇,分别在0.25、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mL/min的流速下洗脱,以90%乙醇为洗脱剂,收集各流速条件下的洗脱液(10 mL/管),测定白藜芦醇的含量。
1.2.5 白藜芦醇含量的测定
色谱条件:高效液相色谱法(High performance liquid chromatography,HPLC)测定提取液中白藜芦醇含量[28]。色谱条件参考程杏安等[6]和叶梦娜等[29]的方法并略作修改:Symmetry C18色谱柱(150×3.9 mm,5 μm);流动相为乙腈/水(24.5/75.5,v/v);等度洗脱;DAD,检测波长306 nm;流速0.45 mL/min;柱温箱26 ℃;自动进样,进样量为10 μL。
标曲的制作:以吸收峰面积为纵坐标(y),白藜芦醇含量为横坐标(x),建立回归方程。对待测样品过0.22 μm有机滤膜后按色谱条件进样,平行测定三次,峰面积取平均值,并通过线性回归方程计算待测样品中白藜芦醇含量。通过计算得线性回归方程为y=43.06x+2.0378,R2=0.9997,表明白藜芦醇在3.92~39.2 μg/mL范围内线性关系良好。
1.2.6 样品纯度的测定
依照1.2.4实验确定的最佳条件,进行三次平行试验。收集洗脱液,经真空旋转蒸发、真空冷冻干燥得纯化产物,准确称重后用甲醇溶解,测定白藜芦醇的含量,依据式(2)计算纯度P。
(2) 式中:c为白藜芦醇质量浓度,mg/mL;V为待测溶液总体积,mL;W为白藜芦醇干粉质量,mg。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2019软件对单因素试验数据进行处理,采用SPSS 25软件对单因素进行P<0.05水平显著性分析,结果采用平均值±标准偏差表示。运用Design-Expert 13软件中的Box-Behnken中心试验设计,并对结果进行分析,采用Origin 2021软件绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
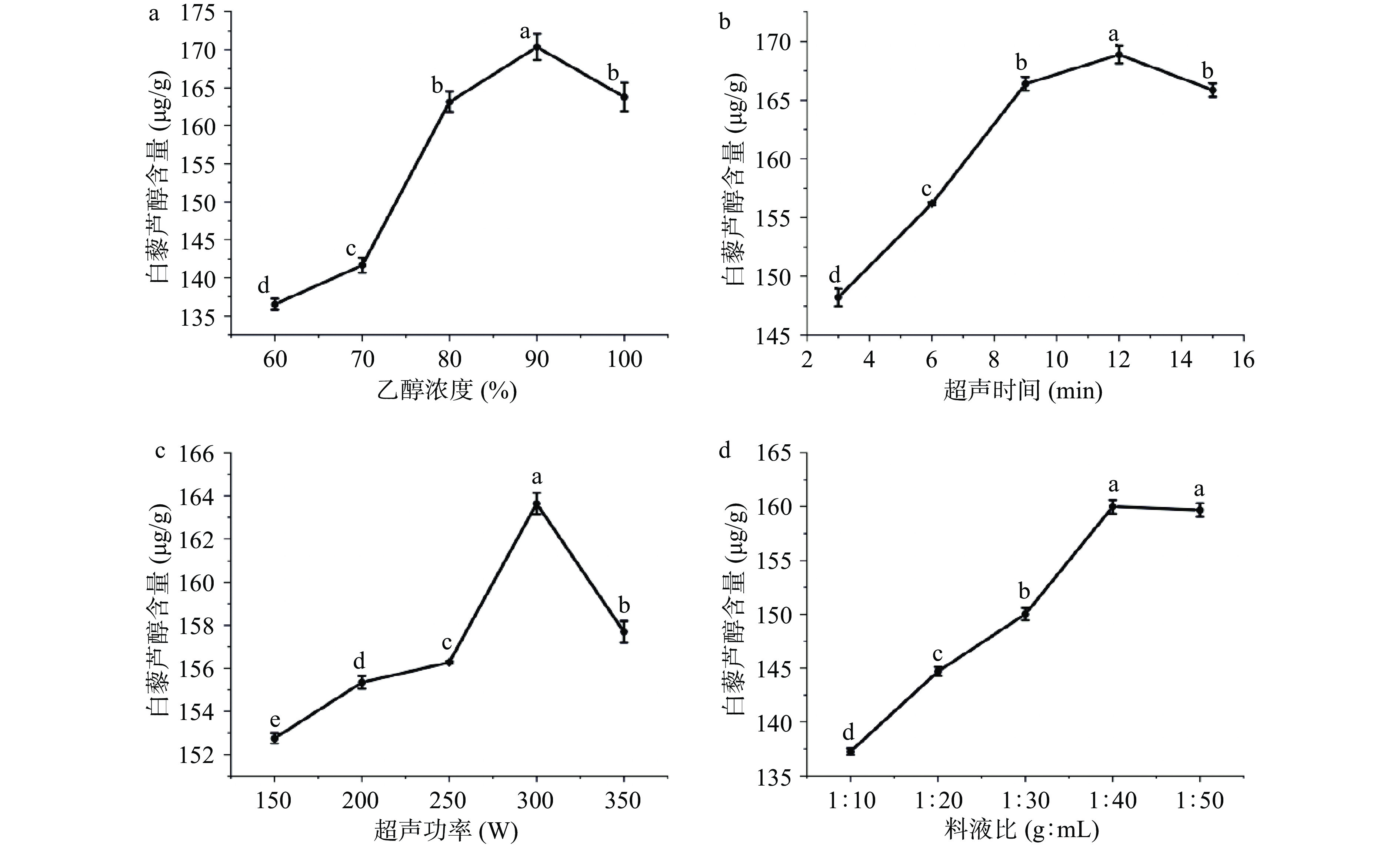
2.1.1 乙醇浓度对白藜芦醇含量的影响
如图1a所示,乙醇浓度的增加的同时,白藜芦醇的含量先增加后减少,90%乙醇时,含量达到最高170.35±1.72 μg/g,与其他水平具有显著性差异(P<0.05),而后开始下降。这可能是由于乙醇浓度的增加,醇溶性杂质及亲脂性物质溶出,与白藜芦醇竞争结合溶剂,导致白藜芦醇含量下降[30-31]。
2.1.2 超声时间对白藜芦醇含量的影响
由图1b所示,随着超声时间的增加,白藜芦醇含量迅速增加,12 min后达到顶峰168.86±0.74 μg/g,与其他水平具有显著性差异(P<0.05),而后开始下降,这可能是由于超声波的机械效应和空化效应促进细胞的破碎,促进白藜芦醇的溶出,继续增加超声时间,体系温度升高,而白藜芦醇在光、热条件下稳定性较弱,且时间越长,白藜芦醇部分被氧化,从而导致含量下降。
2.1.3 超声功率对白藜芦醇含量的影响
如图1c所示,超声功率的增加的同时,白藜芦醇含量上升,功率为300 W时,含量达到最高163.64±0.49 μg/g,与其他水平具有显著性差异(P<0.05),之后开始下降,这可能是由于随着功率的增加,超声波的机械效应和空化效应加强,促进白藜芦醇的溶出,继续增加超声功率,白藜芦醇受到破坏而含量下降。
2.1.4 料液比对白藜芦醇含量的影响
如图1d所示,料液比中提取溶剂增加的同时,白藜芦醇含量先增加后趋于稳定,到1:40 g:mL时达到最高,达到159.98±0.63 μg/g,除与1:50 g:mL水平无显著差异外(P>0.05)和其他水平均具有显著性差异(P<0.05),这可能是由于料液比在1:40 g:mL之前,溶剂的增加促进白藜芦醇的扩散溶出,料液比到达1:40 g:mL后,这种溶剂促溶达到动态平衡,使得白藜芦醇的提取量趋于稳定结果
2.2 响应面试验优化提取工艺
2.2.1 响应面试验结果
根据单因素实验结果进行响应面试验设计,实验结果如表2所示。
表 2 响应面试验方案与结果Table 2. Response surface experiment scheme and results实验号 乙醇浓度(A) 超声时间(B) 超声功率(C) 料液比(D) Y含量
(μg/g)1 0 −1 1 0 168.338 2 0 0 0 0 174.235 3 0 0 −1 1 163.159 4 0 0 0 0 178.156 5 −1 0 0 −1 160.112 6 0 −1 0 1 169.258 7 1 0 0 −1 173.225 8 0 −1 −1 0 171.962 9 0 0 1 1 165.572 10 0 −1 0 −1 170.784 11 −1 0 0 1 160.258 12 1 0 0 1 170.225 13 0 0 0 0 176.332 14 1 0 −1 0 170.152 15 0 0 1 −1 161.311 16 0 0 0 0 180.312 17 0 1 −1 0 165.728 18 1 0 1 0 155.483 19 1 1 0 0 167.791 20 0 1 1 0 160.789 21 −1 0 −1 0 161.148 22 −1 0 1 0 159.822 23 0 0 0 0 175.165 24 −1 −1 0 0 170.841 25 −1 1 0 0 158.516 26 0 1 0 1 168.892 27 0 1 0 −1 169.071 28 1 −1 0 0 163.021 29 0 0 −1 −1 169.675 利用软件Design Expert 13进行统计分析,建立白藜芦醇含量(R)与乙醇浓度(A)、超声时间(B)、超声功率(C)、液料比(D)之间的二次回归模型。得到回归方程如下:
Y=−821.23296+14.75721A−4.12544B+2.13831C+1.98605D+0.142458AB−0.006672AC−0.007865AD−0.002192BC+0.011225BD+0.005388CD−0.07726A2−0.380741B2−0.002963C2−0.038578D2
2.2.2 模型方差分析
由表3方差分析可得,模型失拟项不显著(P=0.3005>0.05),而模型P<0.01,表明模型方程高度显著,由此得模型的预测值与实际值比较相符,实验结果可靠,同时,本实验的变异系数1.82%,说明模型的置信度高,决定系数R2=0.8843,表明模型方程能够较好的反映真实的实验情况。该模型方程可以用来预测不同提取工艺下花生根白藜芦醇的含量。通过分析表3的P值可得乙醇浓度、超声时间、超声功率、乙醇浓度和超声时间、乙醇浓度和超声功率、乙醇浓度二次项、超声功率二次项、超声时间二次项和料液比二次项对含量的影响显著,即实验的影响因素对响应值并非简单的线性关系,而交互项以及二次项也存在显著影响。超声时间、超声功率和乙醇浓度对白藜芦醇提取含量的影响达到显著性水平,影响次序为超声功率(C)>乙醇浓度(A)>超声时间(B)。
表 3 模型的ANOVA分析结果Table 3. ANOVA analysis results of the model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 992.48 14 70.89 7.64 0.0003 ** A 71.05 1 71.05 7.66 0.0151 * B 45.7 1 45.7 4.93 0.0435 * C 77.57 1 77.57 8.36 0.0118 * D 3.87 1 3.87 0.4171 0.5288 AB 73.06 1 73.06 7.88 0.014 * AC 44.51 1 44.51 4.8 0.0459 * AD 2.47 1 2.47 0.2667 0.6136 BC 0.4323 1 0.4323 0.0466 0.8322 BD 0.4536 1 0.4536 0.0489 0.8282 CD 29.04 1 29.04 3.13 0.0986 A2 387.21 1 387.21 41.74 <0.0001 ** B2 76.16 1 76.16 8.21 0.0125 * C2 355.98 1 355.98 38.37 <0.0001 ** D2 96.54 1 96.54 10.41 0.0061 ** 残差 129.87 14 9.28 失拟项 106.24 10 10.62 1.8 0.3005 纯误差 23.64 4 5.91 总和 1122.36 28 注:“*”表示对结果影响差异显著(P<0.05);“**”表示对结果影响差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.2.3 响应面分析
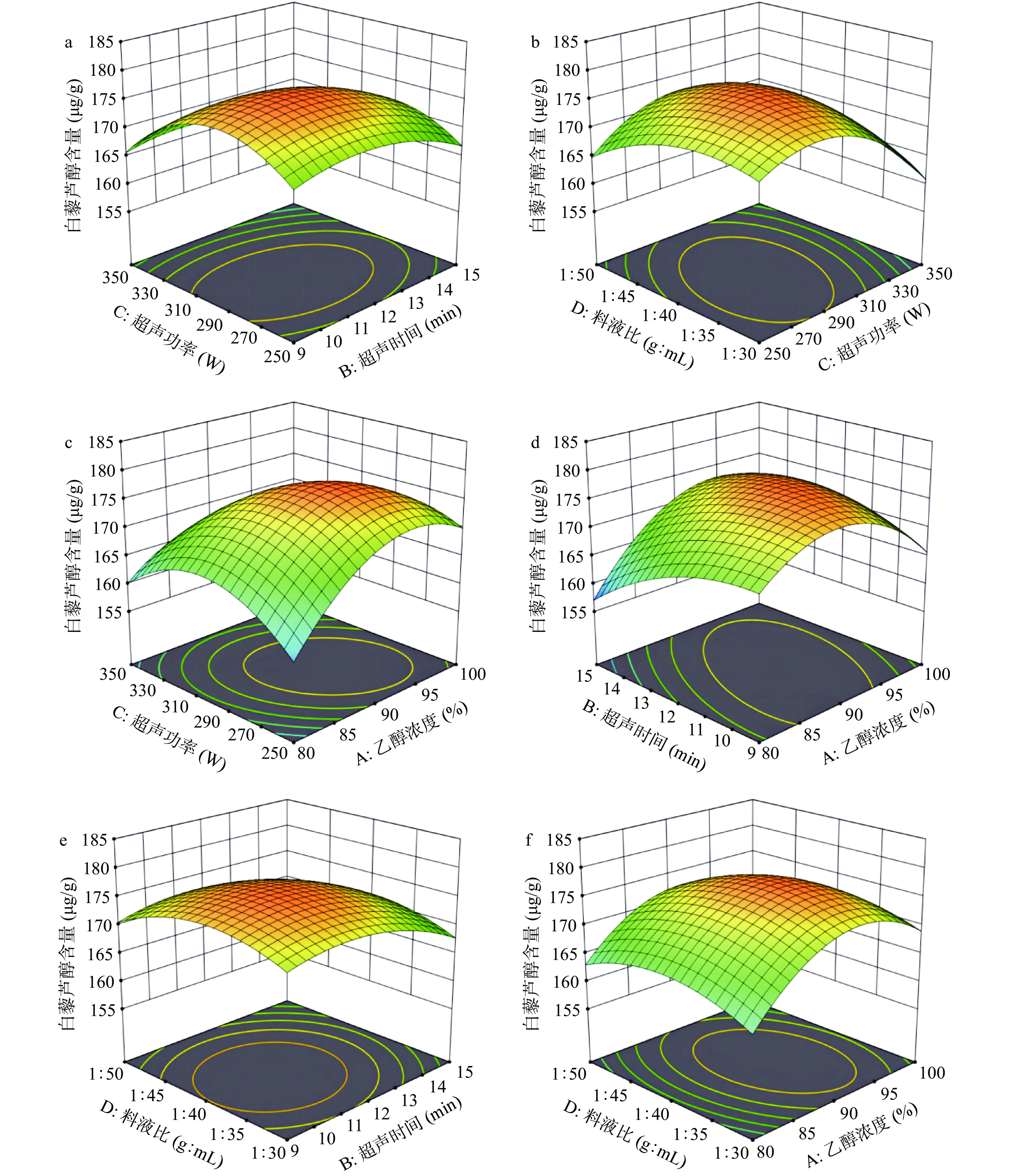
因素与因素间交互作用的曲面图和等高线图如图2a~图2f所示。曲面面的倾斜程度反映出实验值随实验条件变化而变化,曲面斜率越大, 实验条件的变化对白藜芦醇提取量影响程度越大,反之,越平缓影响则越小。等高线图呈圆形说明因素与因素的相互作用影响非显著,呈椭圆说明因素与因素的相互作用影响显著,且中心位置向边缘延伸,白藜芦醇含量逐渐减少[32-34]。分析图2并结合ANOVA表可知,各因素两两之间均存在交互作用,其中乙醇浓度和超声时间、乙醇浓度和超声功率之间的交互作用显著(P<0.05)。
2.2.4 最佳工艺验证
通过软件优化分析得出最佳提取工艺条件为超声功率288.078 W,超声时间11.472 min,料液比1:38.183 g:mL,乙醇浓度为91.695%,含量为177.574 μg/g。考虑到实验条件和实际操作,简化验证实验条件为超声功率290 W、超声时间12 min、料液比1:38 g:mL和乙醇浓度90%含量为175.53±1.57 μg/g,与预测值相近,模型可靠。提取结果高于陈琼玲[35]的溶剂提取和王岩等[36]的蒸汽爆破提取。
通过响应面实验优化得到的最优提取条件为超声功率290 W,超声时间12 min,料液比1:38 g:mL,乙醇浓度为90%,工艺稳定可靠。
2.3 大孔树脂对白藜芦醇的分离纯化
2.3.1 大孔树脂吸附与解吸实验
2.3.1.1 静态吸附动力学
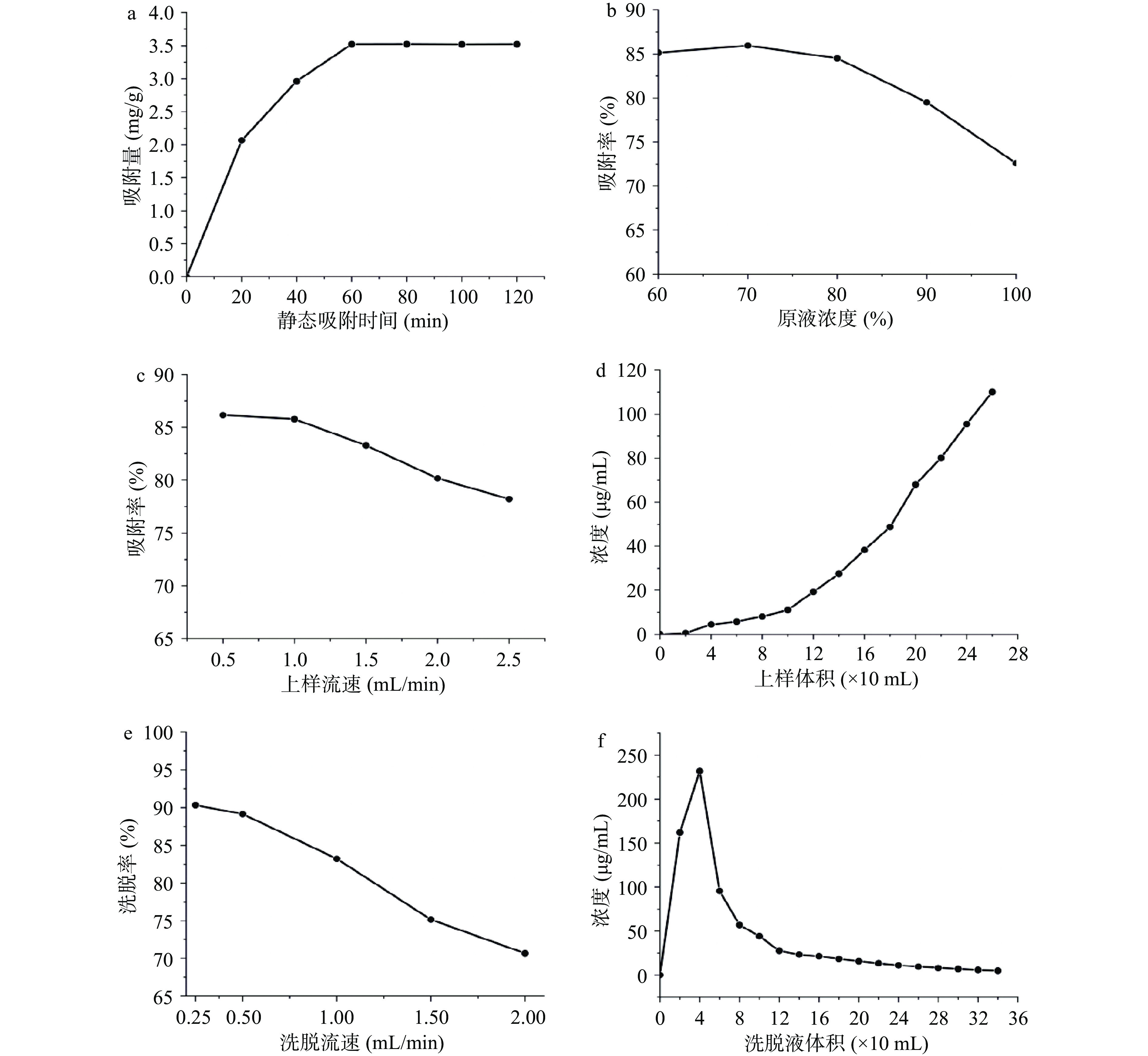
从图3a得,在前20 min内,曲线斜率较大,说明H103树脂对白藜芦醇的吸收较快,之后吸收速率变缓,到60 min以后,吸收量趋于稳定,说明树脂已基本吸附饱和。所以选择60 min为上样液的静态吸附时间。
2.3.1.2 静态吸附等温曲线
从图3b得,随着洗脱液乙醇浓度的增加,白藜芦醇解吸率先增加后逐渐降低,乙醇浓度为70%时,解吸率最高。原因可能是当乙醇浓度较低时不能破坏白藜芦醇与树脂之间的氢键,从而白藜芦醇较难被洗脱;而当乙醇浓度大于70%时,高浓度乙醇和白藜芦醇极性相差较大,故解吸率下降。所以选择70%乙醇作为解吸液。
2.3.1.3 上样流速与上样体积
从图3c得,上样流速为0.5和1.0 mL/min时,两者吸附率高且相近,综合吸附率和吸附时间,选择1.0 mL/min的流速上样。从图3d得,当流出液体积达到120 mL时,流出液中白藜芦醇浓度达到19.26 μg/mL,此时已接近上样浓度的1/10即达到泄漏点[25, 37]。
2.3.1.4 洗脱流速与洗脱体积
从图3e得,在0.25和0.5 mL/min流速洗脱下,两者解吸率高且相近,综合解吸率和解吸时间,洗脱流速选择0.5 mL/min。从图3f得,160 mL时,洗脱液中白藜芦醇的量只有21.34 μg/mL,随着洗脱液体积的增加含量无明显变化,选择上样量为160 mL。
综上白藜芦醇的纯化工艺为:树脂H103,上样的质量浓度为70%原液质量浓度即201.13 μg/mL,上样速率为1.0 mL/min,上样量为120 mL,洗脱溶剂为90%乙醇,洗脱流速为1.0 mL/min,洗脱量为160 mL。
2.4 大孔树脂初纯物纯度的测定
由表4得,纯化后白藜芦醇初纯物纯度达到49.19%±0.81%,与骆航等[26]的纯化结果34.77%和武鹏程[38]的纯化结果39.61%相比均有所提高,且RSD值1.65%,表明工艺的纯化效果和重现性良好。
表 4 样品纯度的测定Table 4. Determination of sample purity序号 纯度
(%)平均值
(%)RSD
(%)1 49.98 49.19 1.65 2 48.36 3 49.24 3. 结论
通过单因素实验和响应面法优化确定最佳提取条件:乙醇浓度90%、超声功率290W、超声时间12 min、料液比1:38 g:mL,白藜芦醇的含量为175.53±1.57μg/g。优化后,经H103树脂一次处理,粗产品中白藜芦醇的纯度为49.19%±0.81%,RSD为1.65%。超声辅助提取白藜芦醇和大孔树脂初步纯化白藜芦醇是可行的,可为花生根的合理开发和综合利用以及天然白藜芦醇的标准化和工业化生产提供参考。
从实验室走向工厂,需要经历小试、中试等诸多环节。这对于工艺条件的稳定性要求更加严格,诸如提取时的溶剂挥发引起的料液比变化、纯化用的柱材料和上样的温度等因素可能因为规模的放大而成为重要影响因素,这在后续的研究中有必要进行考查。日常生活中,不同的应用场景对于白藜芦醇纯度的要求不同,后续可考虑对粗产品进行分级纯化,以得到满足不同需求的白藜芦醇产品。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface methodology
水平 A.乙醇浓度
(%)B.超声时间
(min)C.超声功率
(W)D.料液比
(g:mL)−1 80 9 250 1:30 0 90 12 300 1:40 1 100 15 350 1:50 表 2 响应面试验方案与结果
Table 2 Response surface experiment scheme and results
实验号 乙醇浓度(A) 超声时间(B) 超声功率(C) 料液比(D) Y含量
(μg/g)1 0 −1 1 0 168.338 2 0 0 0 0 174.235 3 0 0 −1 1 163.159 4 0 0 0 0 178.156 5 −1 0 0 −1 160.112 6 0 −1 0 1 169.258 7 1 0 0 −1 173.225 8 0 −1 −1 0 171.962 9 0 0 1 1 165.572 10 0 −1 0 −1 170.784 11 −1 0 0 1 160.258 12 1 0 0 1 170.225 13 0 0 0 0 176.332 14 1 0 −1 0 170.152 15 0 0 1 −1 161.311 16 0 0 0 0 180.312 17 0 1 −1 0 165.728 18 1 0 1 0 155.483 19 1 1 0 0 167.791 20 0 1 1 0 160.789 21 −1 0 −1 0 161.148 22 −1 0 1 0 159.822 23 0 0 0 0 175.165 24 −1 −1 0 0 170.841 25 −1 1 0 0 158.516 26 0 1 0 1 168.892 27 0 1 0 −1 169.071 28 1 −1 0 0 163.021 29 0 0 −1 −1 169.675 表 3 模型的ANOVA分析结果
Table 3 ANOVA analysis results of the model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 992.48 14 70.89 7.64 0.0003 ** A 71.05 1 71.05 7.66 0.0151 * B 45.7 1 45.7 4.93 0.0435 * C 77.57 1 77.57 8.36 0.0118 * D 3.87 1 3.87 0.4171 0.5288 AB 73.06 1 73.06 7.88 0.014 * AC 44.51 1 44.51 4.8 0.0459 * AD 2.47 1 2.47 0.2667 0.6136 BC 0.4323 1 0.4323 0.0466 0.8322 BD 0.4536 1 0.4536 0.0489 0.8282 CD 29.04 1 29.04 3.13 0.0986 A2 387.21 1 387.21 41.74 <0.0001 ** B2 76.16 1 76.16 8.21 0.0125 * C2 355.98 1 355.98 38.37 <0.0001 ** D2 96.54 1 96.54 10.41 0.0061 ** 残差 129.87 14 9.28 失拟项 106.24 10 10.62 1.8 0.3005 纯误差 23.64 4 5.91 总和 1122.36 28 注:“*”表示对结果影响差异显著(P<0.05);“**”表示对结果影响差异极显著(P<0.01)。 表 4 样品纯度的测定
Table 4 Determination of sample purity
序号 纯度
(%)平均值
(%)RSD
(%)1 49.98 49.19 1.65 2 48.36 3 49.24 -
[1] LÜ X, CONG Z, LIU Z, et al. Improvement of the solubility, photostability, antioxidant activity and UVB photoprotection of trans-resveratrol by essential oil based microemulsions for topical application[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology,2018,48:346−354. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2018.10.017
[2] XIANG-TAO, HUANG, XI, et al. Resveratrol: Review on its discovery, anti-leukemia effects and pharmacokinetics[J]. Chemico-biological interactions, 2019.
[3] CHEN J, JIANG X, YANG G, et al. Green and efficient extraction of resveratrol from peanut roots using deep eutectic solvents[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 2018.
[4] HASAN M M, CHA M, BAJPAI V K, et al. Production of a major stilbene phytoalexin, resveratrol in peanut (Arachis hypogaea) and peanut products: A mini review[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology,2013,12(3):209−221. doi: 10.1007/s11157-012-9294-7
[5] 张磊, 孙奎香, 孙庆杰, 等. 反相高效液相色谱法测定不同品种花生白藜芦醇含量[J]. 粮食与油脂,2012,25(2):33−34. [ZHANG L, SUN K X, SUN Q J, et al. Determination of resveratrol in different peanut species by RP-HPLC[J]. Cereas and Oils,2012,25(2):33−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2012.02.010 ZHANG L, SUN K X, SUN Q J, et al. Determination of resveratrol in different peanut species by RP-HPLC[J]. Cereas and Oils, 2012, 25(2): 33-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2012.02.010
[6] 程杏安, 东方云, 张汉辉, 等. 花生根茎中白藜芦醇提取工艺的优化及含量测定[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(12):182−187. [CHENG X A, DONG FY, ZHANG H H, et al. Pretreatment optimization and content filtering in different growth stages of peanut root, stem extraction of resveratrol[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(12):182−187. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.12.028 CHENG X A, DONG FY, ZHANG H H, et al. Pretreatment optimization and content filtering in different growth stages of peanut root, stem extraction of resveratrol[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(12): 182-187. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.12.028
[7] 姜瑞清. 花生根中白藜芦醇的分离纯化工艺研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2008. JIANG R Q. Study on purification of Resveratrol from peanut root through the silica gel column chromatography[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2008.
[8] LU H M, NI W D, LIANG Y Z, et al. Supercritical CO2 extraction of emodin and physcion from polygonum cuspidatum and subsequent isolation by semipreparative chromatography[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2015,29(14):2136−2142.
[9] YU M, LIU H, SHI A, et al. Preparation of resveratrol-enriched and poor allergic protein peanut sprout from ultrasound treated peanut seeds[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2016,28:334−340. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2015.08.008
[10] 吴桂玲, 周丽, 邓维先. 虎杖有效成分的提取方法研究进展[J]. 粮食与油脂,2022,35(6):16−18. [WU G L, ZHOU L, DENG W X. Research progress on extraction methods of effective components of polygonum cuspidatum[J]. Cereas and Oils,2022,35(6):16−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2022.06.005 WU G L, ZHOU L, DENG W X. Research progress on extraction methods of effective components of polygonum cuspidatum [J]. Cereas and Oils, 2022, 35(6): 16-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2022.06.005
[11] DENG J C, LI L H, YANG X Q, et al. High-purity isolation of trans-resveratrol from rhizma polygoni cuspidati by high-speed counter-current chromatography[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2013,690-693:1335−1339. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.690-693.1335
[12] 冯涛, 刘鹏, 刘海燕, 等. 白藜芦醇分子印迹聚合物的应用及性能研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(16):37−41. [FENG T, LIU P, LIU H Y, et al. Application and performance study of molecular imprinted polymer of resveratrol[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(16):37−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.16.010 FENG T, LIU P, LIU H Y, et al. Application and performance study of molecular imprinted polymer of resveratrol [J]. Food Research and Development, 2016, 37(16): 37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.16.010
[13] 鄢玉芬, 陶明宝, 杨森, 等. 白藜芦醇纯化工艺研究进展[J]. 亚太传统医药,2018,14(6):83−87. [YAN Y F, TAO M B, YANG S, et al. Advances in study on the purification technology of resveratro[J]. ASIA-PACIFIC Traditional Medicine,2018,14(6):83−87. YAN Y F, TAO M B, YANG S, et al. Advances in Study on the Purification Technology of Resveratro[J]. ASIA-PACIFIC Traditional Medicine, 2018, 14(6): 83-87.
[14] 梁浩, 李瑞敏, 袁其朋. 天然活性异硫氰酸酯类化合物的研究进展[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版),2015,42(2):1−12. [LIANG H, LI R M, YUAN Q P. Recent progress in the study of natural active isothiocyanates[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition),2015,42(2):1−12. LIANG H, LI R M, YUAN Q P. Recent progress in the study of natural active isothiocyanates [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 42(2): 1-12.
[15] 张颖, 刘义梅. 虎杖中白藜芦醇提取工艺研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2019,10(7):1884−1889. [ZHANG Y, LIU Y M. Research progress on the extraction process of resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2019,10(7):1884−1889. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2019.07.023 ZHANG Y, LIU Y M. Research progress on the extraction process of resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum [J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2019, 10(7): 1884-1889. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2019.07.023
[16] 毛俊霞. 葡萄叶中白藜芦醇的提取和分离纯化研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2013. MAO J X. Study on extraction, separation and purification of resveratrol from grape leaves[D]. Xi'an: Shanxi Normal University, 2013.
[17] 田华勤. 葡萄渣提取物和亚麻籽油对湖羊羔羊生产性能和养分消化代谢的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2016. TIAN H Q. Effects of grape pomace extract and linseed oil on growth performance and nutrient digestibility of Hu lambs[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2016.
[18] GUO H, ZHANG Q, CHEN J, et al. Large scale purification of puerarin from Puerariae Lobatae Radix through resins adsorption and acid hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Chromatography B-Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences,2015,980:8−15. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.12.014
[19] BABAZADEH A, TAGHVIMI A, HAMISHEHKAR H, et al. Development of new ultrasonic–solvent assisted method for determination of trans-resveratrol from red grapes: Optimization, characterization, and antioxidant activity (ORAC assay)[J]. Food Bioscience,2017,20:36−42. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2017.08.003
[20] JIA W, CHEN Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Separation and purification of resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum by macroporous adsorption resin mixed-bed technology[J]. Separation Science and Technology,2020,55(8):1473−1484. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2019.1604755
[21] WANG R, ZHAO Y, CHEN Z. Separation and purification of resveratrol by liquid extraction assistance macroporous adsorption resin mixed-bed technology[J]. Separation Science and Technology,2021,56(18):3106−3118. doi: 10.1080/01496395.2020.1851260
[22] 安宝树, 沙见浩, 罗星. 花生植株白藜芦醇提取工艺的优化[J]. 贵州农业科学,2017,45(6):114−118. [AN B S, SHA J H, LUO X. Optimization of resveratrol extraction process from roots, stem sand leaves of peanut[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2017,45(6):114−118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2017.06.027 AN B S, SHA J H, LUO X. Optimization of resveratrol extraction process from roots, stem sand leaves of peanut [J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(6): 114-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2017.06.027
[23] 黄纪念, 孙强, 宋国辉, 等. 超声提取花生根中白藜芦醇的工艺研究[J]. 中国食物与营养,2010(10):38−41. [HUANG J N, SUN Q, SONG G H, et al. Study on extraction of resveratrol from peanut root with ultrasonic[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2010(10):38−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2010.10.011 HUANG J N, SUN Q, SONG G H, et al. Study on extraction of resveratrol from peanut root with ultrasonic [J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2010(10): 38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2010.10.011
[24] 辛科颖, 孙向明, 胡扬, 等. 响应面法优化大孔树脂纯化菟丝子总黄酮工艺[J]. 中国药学杂志,2022,57(7):530−538. [XIN K Y, SUN X M, HU Y, et al. Optimization of purification process of total flavonoids from cuscuta chinensis by macroporous resin by response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2022,57(7):530−538. XIN K Y, SUN X M, HU Y, et al. Optimization of purification process of total flavonoids from cuscuta chinensis by macroporous resin by response surface methodology [J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 2022, 57(7): 530-538.
[25] 吴佳, 王燕, 刘婷, 等. 大孔树脂对刺葡萄酒渣中提取的白藜芦醇的纯化工艺研究[J]. 中国酿造,2017,36(3):144−149. [WU J, WANG Y, LIU T, et al. Purification process of resveratrol from Vitis davidii Foex wine residues by macroporous resin[J]. China Brewing,2017,36(3):144−149. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2017.03.029 WU J, WANG Y, LIU T, et al. Purification process of resveratrol from Vitis davidii Foex wine residues by macroporous resin [J]. China Brewing, 2017, 36(3): 144-149. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2017.03.029
[26] 骆航, 孙兴力, 李华生, 等. 大孔树脂分离纯化虎杖白藜芦醇和蒽醌类成分的工艺优化[J]. 山西中医药大学学报,2021,22(3):5. [LUO H, SUN X L, LI H S, et al. Process optimization on separation and purification of resveratrol and anthraquinone from Polygonum cuspidatum by macroporous resin[J]. Journal of Shanxi College of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,22(3):5. LUO H, SUN X L, LI H S, et al. Process optimization on separation and purification of resveratrol and anthraquinone from Polygonum cuspidatum by macroporous resin [J]. Journal of Shanxi College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 22(3): 5.
[27] 李霞. 苦参生物碱的吸脱附研究及氧化苦参碱的分离[D]. 济南: 山东大学化学工艺, 2013. LI X. Adsorption and desorption study of alkaloids from Sophora flavescens Ait. and separation of oxymatrine[D]. Jinan: Chemical Technology of Shandong University, 2013.
[28] CVETKOVIĆ Ž S, NIKOLIĆ V D, SAVIĆ I M, et al. Development and validation of an RP-HPLC method for quantification of trans-resveratrol in the plant extracts[J]. Hemijska industrija,2015,69(6):679−687. doi: 10.2298/HEMIND140917004C
[29] 叶梦娜, 冯杉, 刘晓敏, 等. 花生根中白藜芦醇的提取与含量测定[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(7):73−75. [YE M N, FENG S, LIU X M, et al. Optimization of extraction technology and determination of resveratrol from peanut root[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(7):73−75. YE M N, FENG S, LIU X M, et al. Optimization of extraction technology and determination of resveratrol from peanut root [J]. Food Industry, 2020, 41(7): 73-75.
[30] 旷慧, 迟超, 吕长山, 等. 红树莓多酚的醇法提取工艺优化[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(10):88−93. [KUANG H, CHI C, LÜ C S, et al. Optimization of ethanol extraction process for polyphenols from red raspberry[J]. Food Science,2016,37(10):88−93. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201610015 KUANG H, CHI C, LÜ C S, et al. Optimization of ethanol extraction process for polyphenols from red raspberry [J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(10): 88-93. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201610015
[31] 张兴荣, 张学林, 贺连智, 等. 构树叶总黄酮提取工艺优化及成分分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(2):213−220. [ZHANG X R, ZHANG X L, HE L Z, et al. Optimization of extraction process and component analysis of the flavonoids from Broussonetia papyrifera leaves[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(2):213−220. ZHANG X R, ZHANG X L, HE L Z, et al. Optimization of extraction process and component analysis of the flavonoids from Broussonetia papyrifera leaves [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2021, 37(2): 213-220.
[32] 王冉, 李健, 黎晨晨, 等. 响应面法优化东北红松针总黄酮的超声辅助乙醇提取工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(4):143−149. [WANG R, LI J, LI C C, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extraction of total flavonoids from Pinus koraiensis needles by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(4):143−149. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.04.027 WANG R, LI J, LI C C, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extraction of total flavonoids from Pinus koraiensis needles by response surface methodology [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(4): 143-149. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.04.027
[33] 贺银菊, 杨再波, 彭莘媚, 等. 响应面优化紫果西番莲维生素C的超声辅助提取工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(1):119−124. [HE Y J, YANG Z B, PENG X M, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of vitamin c in the purple passionfruit by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(1):119−124. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.01.020 HE Y J, YANG Z B, PENG X M, et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of vitamin c in the purple passionfruit by response surface methodology [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(1): 119-124. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.01.020
[34] 王锦秀, 赵晴晴, 徐心怡, 等. 响应面优化超声波辅助酸法提取百香果皮果胶工艺及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(13):162−170. [WANG J X, ZHAO Q Q, XU X Y, et al. Optimization of response surface for ultrasonic acid extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(13):162−170. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021090363 WANG J X, ZHAO Q Q, XU X Y, et al. Optimization of response surface for ultrasonic acid extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel and its antioxidant activity [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(13): 162-170. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021090363
[35] 陈琼玲. 花生根白藜芦醇提纯, 纳米脂质体制备及抗肿瘤活性[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. CHENG Q L. Study on purification of reveratrol from peanut root, preparation and antitumor activity of reveratrol nanoliposomes[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013.
[36] 王岩, 王磊, 刘志军, 等. 蒸汽爆破提取花生根白藜芦醇及功能特性[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(5):172−176. [WANG Y, WANG L, LIU Z J, et al. Functional property of resveratrol with steam explosion from peanut root[J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(5):172−176. WANG Y, WANG L, LIU Z J, et al. Functional Property of Resveratrol with Steam Explosion from Peanut Root [J]. The Food Industry, 2021, 42(5): 172-176.
[37] LOBO DE SÁ F D, HEIMESAAT M M, BERESWILL S, et al. Resveratrol prevents campylobacter jejuni-induced leaky gut by restoring occludin and claudin-5 in the paracellular leak pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:640572. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.640572
[38] 武鹏程. 花生芽中白藜芦醇的提取纯化、抗氧化及抑制酶活性研究[D]. 阿拉尔: 塔里木大学, 2021. WU P C. Research on extraction and purification, antioxidant and inhibitory enzyme activity of resveratrol from peanut sprout[D]. Alaer: Tarim University, 2021.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 杜晓仪,杨继国,徐玉娟,吴继军,余元善,邹波,彭健,李璐. 不同益生菌对三华李发酵果汁品质及其体外消化特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(02): 143-151 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



