Study on the Spectrum Effect Relationship of Antioxidant Activity of Sedum aizoon L. Based on HPLC-ECD
-
摘要: 目的:基于谱效关系研究,寻找景天三七抗氧化活性的物质基础,为其质量控制提供一定的参考依据。方法:建立不同产地景天三七的HPLC-ECD(High performance liquid chromatography-Electrochemical Detection,HPLC-ECD)指纹图谱并进行相似度评价;通过偏最小二乘回归分析和灰色关联分析研究指纹图谱与其抗氧化活性之间的谱效关系。结果:建立了景天三七的HPLC-ECD指纹图谱,样品间的相似度较高,共标定17个共有峰,通过与对照品比对鉴别出了没食子酸、原儿茶酸、色氨酸、没食子酸甲酯、表没食子儿茶素、咖啡酸、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、鸢尾酚酮、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷等12种成分;谱效关系表明,没食子酸、原儿茶酸、表没食子儿茶素、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷的VIP值均大于1;其中没食子酸、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷的关联度接近于0.8。分子对接结果表明,表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷的Libdock Score较高。因此,表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷等化合物为景天三七抗氧化活性的关键成分。结论:结合化学计量学方法进行谱效关系研究,确定了景天三七抗氧化活性物质基础,可为景天三七的质量评价提供了一定的科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 景天三七 /
- 高效液相色谱指纹图谱 /
- 化学计量学 /
- 抗氧化活性 /
- 谱效关系
Abstract: Objective: To find the material basis of antioxidant activity of Sedum aizoon L. based on the study of spectrum-effect relationship, which provided a certain reference for its quality control. Method: The fringerprint of Sedum aizoon L. from different areas were established by high performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD) and the similarity of the samples were evaluated. At the same time, the spectrum-effect relationship between HPLC-ECD fingerprint of Sedum aizoon L. and antioxidant activity was studied by partial least squares regression analysis and grey correlation analysis. Results: The HPLC-ECD fingerprint of Sedum aizoon L was established. The similarity of the samples was high and 17 common peaks were obtained. Among them, the 12 components were identified with the standard solution, including gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, tryptophan, methyl gallate, epigallocatechin, caffeic acid, epigallocatechin gallate, iriflophene, myricitrin, isoquercitrin, rosmarinic acid and quercitrin. The spectrum relationship showed that the variables important in projection (VIP) scores of gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, epigallocatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, rosmarinic acid and quercitrin were greater than 1. Among them, the grey correlation degree of gallic acid, rosmarinic acid and quercitrin was nearly 0.8. Furthermore, epigallocatechin gallate, myricitrin, isoquercitrin, rosmarinic acid and quercitrin had higher libdock score in molecular docking. Therefore, epigallocatechin gallate, myricitrin, isoquercitrin, rosmarinic acid and quercitrin were the primary components contributing to the antioxidant activity of Sedum aizoon L.. Conclusion: The basis of antioxidant activity of Sedum aizoon L. was determined by the study of spectrum effect relationship with chemometrics, which provides a certain scientific basis for the quality evaluation of Sedum aizoon L.. -
景天三七(Sedum aizoon L)为景天科景天属的多年生草本植物[1],别名费菜、养心草、救心菜等,在我国主要分布于福建、江苏、河北、河南等地。景天三七可作药用,具有良好的抗氧化、抗炎、抗菌和止血等生物活性,用于止血止痛、消肿散瘀、宁心安神、消炎和高血压等病症[2-3]。据文献报道,民间广泛将景天三七作为药食两用的天然物用于高血脂、高血压和一些心脏疾病的防治,故被称为“救心菜”,中科院武汉植物园曾立项将其作为茎叶类蔬菜进行开发利用[4],并且被中国绿色食品发展中心认定为AA级绿色食品[5]。景天三七始载于《救荒本草》,其化学成分主要包括酚酸类、黄酮类、糖类、挥发油、生物碱以及三萜类等[6-7]。其中黄酮和酚酸类成分为景天三七中的主要活性成分[8],如原儿茶酸、咖啡酸、杨梅素、槲皮素、木犀草苷等[9-10]。
现有对景天三七指纹图谱与活性的研究多是在抗炎、止血和安神等药理作用,如林珠灿等[9]采用HPLC指纹图谱法研究其抗炎活性成分;蔡扬帆等[10]采用HPLC法建立不同产地景天三七指纹图谱,筛选安神活性部位。或是单以相似度评价药材质量,如林珠灿等[11]对景天三七HPLC指纹图谱的研究。景天三七抗氧化活性多集中于总酚和总黄酮,如王佰灵等[12]对景天三七中总多酚提取工艺的优化及抗氧化研究,对具体作用成分的分析较少。或单以少数成分研究其抗氧化活性,如Gong等[13]以不同干燥方法研究对景天三七不同部位酚类化合物及抗氧化能力的影响。目前,景天三七与抗氧化活性的谱效关系尚未有明确报道,而液相色谱指纹图谱可以表征植物活性物质,是评价食源性植物质量和一致性的重要方法,结合谱效关系可筛选食源性植物中的生物活性成分[14]。常用的检测器中,电化学检测器因其选择性好、灵敏度高、响应快,且能够更快速检测分析具有高电化学活性、易氧化的化合物,如:酚酸、杂环化合物,目前已广泛应用于生物、化学和医学等领域[15-16]。
综上,本研究拟建立高效液相色谱-电化学检测(HPLC-ECD)指纹图谱,通过相似度评价对各批次样品进行质量评价;同时,测定1,1-二苯基-2-苦肼基(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)自由基清除活性、2,2-联氮-双-3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸(2,2'- azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid),ABTS)自由基清除活性以及铁离子还原能力(ferric reducing antioxidant power,FRAP),结合偏最小二乘回归分析和灰色关联分析等化学计量学方法,研究景天三七指纹图谱与抗氧化活性之间的谱效关系。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
景天三七 采集自贵州、重庆、云南、河南、河北、安徽、江苏等不同地区,经遵义医科大学孟令杰博士鉴定为景天科植物景天三七(Sedum aizoon L)的地上部分,经45 ℃烘干至恒重后粉碎。样品信息见表1;乙腈 色谱级,北京伊诺凯科技有限公司;没食子酸、原儿茶酸、色氨酸、没食子酸甲酯、表没食子儿茶素(epigallocatechin,EGC)、咖啡酸、杨梅苷、迷迭香酸、槲皮苷 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(epigallocatechin gallate,EGCG) 四川维克奇生物科技有限公司;异槲皮苷 成都普菲德生物技术有限公司;鸢尾酚酮 成都植标化纯生物技术有限公司;对照品纯度均大于97%;所有其余试剂均为分析纯。
表 1 景天三七样品信息Table 1. Information of Sedum aizoon L. samples样品编号 产地 收集时间 样品编号 产地 收集时间 样品编号 产地 收集时间 S1 贵州黔东南 2021.07 S9 河北廊坊 2021.07 S17 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S2 重庆丰都 2021.07 S10 河北定州 2021.07 S18 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S3 云南昆明 2021.07 S11 安徽芜湖 2021.07 S19 河北石家庄 2021.08 S4 湖南永州 2021.07 S12 山东曹县 2021.08 S20 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S5 河南商丘 2021.07 S13 山东曹县 2021.08 S21 山东临沂 2021.08 S6 河南周口 2021.07 S14 江苏沐阳 2021.08 S22 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S7 河南南阳 2021.07 S15 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S23 江苏苏州 2021.08 S8 河北南宫 2021.07 S16 江苏宿迁 2021.08 UltiMate 3000 bio-RS超高效液相色谱仪(配备Chromeleon 7.2工作站、ECD-3000 RS电化学检测器,检测池为安培检测池)、ST8R小型台式离心机、1510酶标仪 美国Thermo-fisher;ME104E/02电子分析天平、FE28型pH计 梅特勒-托利多;SB-5200DT型超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;Purelab Chorus 2超纯水系统 英国埃尔格。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 供试液的制备
参考文献[17-18],分别精密称取23批景天三七粉末(过60目筛)0.7 g,料液比按1 g:20 mL加入80%甲醇,超声提取30 min,放冷,再称定质量,用80%甲醇补足失重;于10000 r/min 离心5 min后,取上清液用0.22 μm有机滤膜过滤。
1.2.2 对照品溶液的配制
分别精密称取没食子酸、原儿茶酸、色氨酸、没食子酸甲酯、EGC、咖啡酸、EGCG、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸、槲皮苷等适量对照品,甲醇溶解,配制成质量浓度为1 mg/mL的标准品储备液,于−20 ℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2.3 色谱条件
色谱柱:XBridge BEH shield RP18色谱柱(3.0 mm×150 mm,2.5 μm);流动相:A:乙腈,B:50 mmol/L柠檬酸缓冲溶液(pH2.75),梯度洗脱:0~20 min,2.5%~25% A;20~25 min,25%~42.5% A;25~33 min,42.5%~75% A。体积流量:0.6 mL/min;柱温:45 ℃;检测电压:600 mV;进样体积:4 μL。
1.2.4 多成分含量测定
称取景天三七样品粉末,按“1.2.1”方法制备供试品溶液,按上述“1.2.3”色谱条件条件测定并记录峰面积,计算其含量。
1.2.5 抗氧化活性的测定
1.2.5.1 DPPH自由基清除能力的测定
参考文献[19-20],将样品提取液稀释80倍作为供试液,于2 mL离心管中加入60 μL供试液和140 μL 80%甲醇,再加入400 μL DPPH溶液(0.1 mg/mL),混合均匀后于室温下避光静置30 min。在波长517 nm处测定吸光值,DPPH自由基清除能力以Trolox当量(mg TE/g DW)表示。
1.2.5.2 ABTS自由基清除能力的测定
参考文献[19-20],配制ABTS溶液,734 nm处吸光度为0.70±0.02。样液稀释250倍作为供试液。分别取40 μL供试液和160 μL 80%甲醇,加入400 μL ABTS工作液,混合均匀后,于暗处反应30 min,734 nm处测定吸光度,计算Trolox当量(mg TE/g DW)。
1.2.5.3 铁离子还原能力(FRAP)的测定
参考文献[19-20],工作液由20 mmol/L FeCl3溶液、冰醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲溶液(pH3.6)和10 mmol/L TPTZ溶液按1:10:1配制而成。将提取液稀释60倍作为供试液,取60 μL供试液和40 μL 80%甲醇置于2 mL离心管中,加入300 μL TPTZ工作液,于37 ℃水浴中反应10 min,测定其在593 nm处的吸光度,FRAP以Trolox当量(mg TE/g DW)表示。
1.3 数据处理
采用中药指纹图谱相似度评价系统(2012版)建立HPLC-ECD指纹图谱;采用SPSS软件,对 23批样品进行系统聚类分析;采用SIMCA 14.1软件,建立PLSR模型;采用Excel进行GRA分析;参考文献[21-22],通过RCSB PDB数据库获取蛋白结构,将化合物与GSTP1、ROS-1、TNF、HO-2和NO-1导入Discover Studio 2016进行分子对接。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 指纹图谱方法学考察
2.1.1 精密度试验
按“1.2.1”项下制备供试液,“1.2.3”项条件下连续进样6次。各共有峰保留时间RSD在0.05%~0.29%之间,峰面积的RSD在1.98%~6.20%之间。表明仪器精密度良好。
2.1.2 稳定性试验
按“1.2.1”项下制备供试液,分别于0、2、4、6、12、24 h进样一次。各共有峰保留时间RSD在0.07%~0.78%之间,峰面积的RSD在2.48%~7.18%。表明供试品溶液在24 h内稳定。
2.1.3 重复性试验
按“1.2.1”项下制备6份供试液,“1.2.3”项条件下进样分析。各共有峰保留时间RSD均在0.01%~0.39%之间,峰面积的RSD在0.29%~6.44%之间。表明方法重复性良好。
2.2 指纹图谱的建立及相似度评价
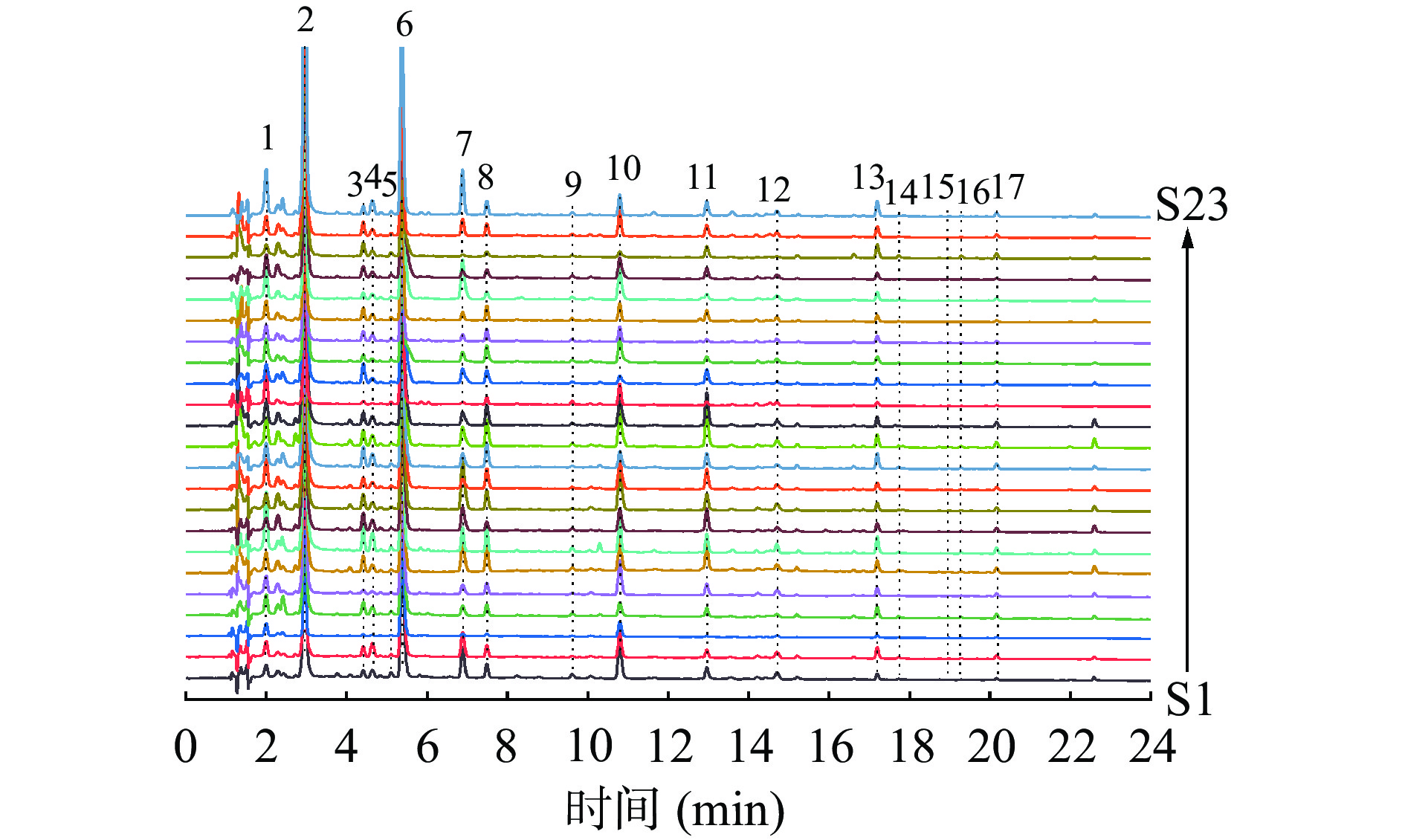
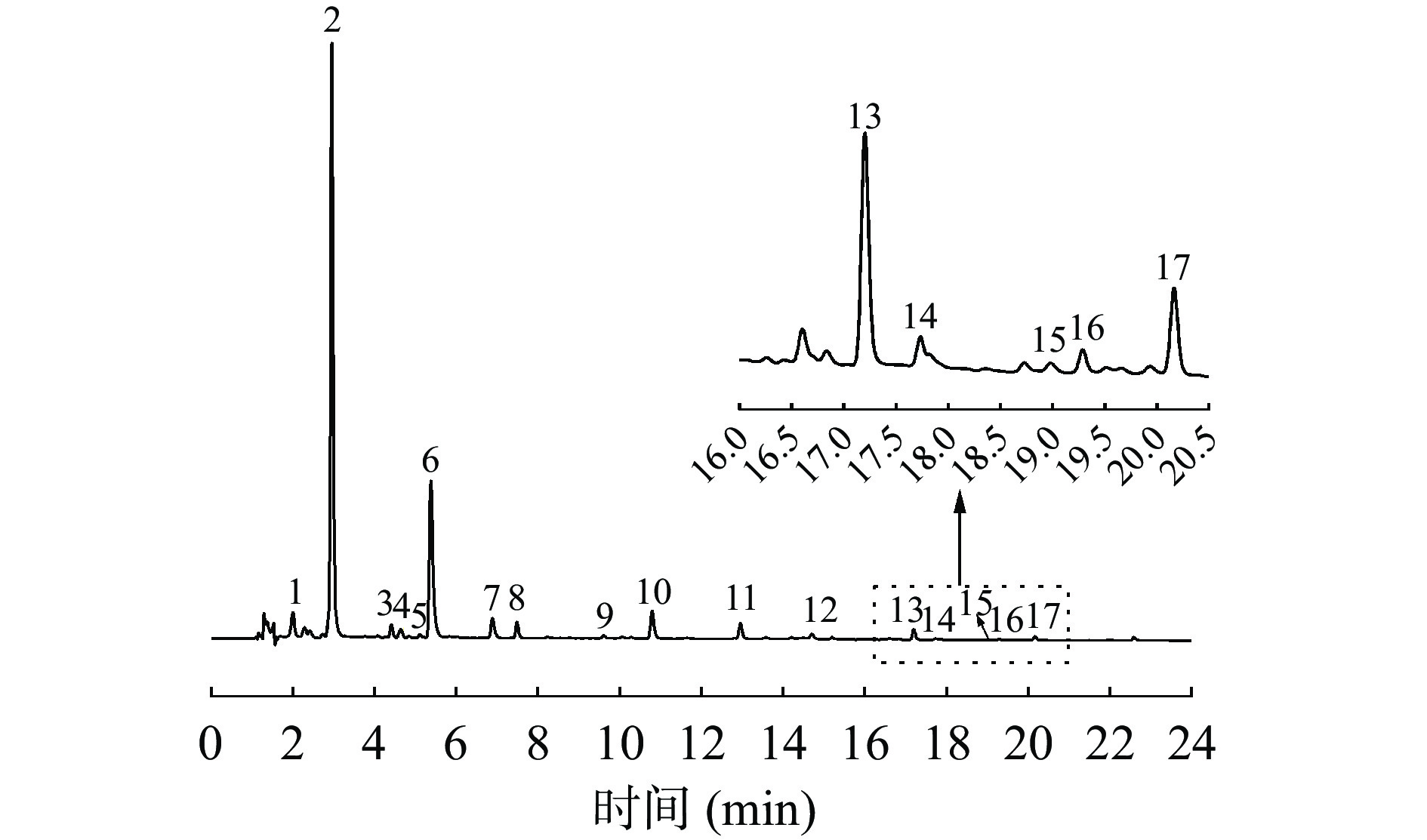
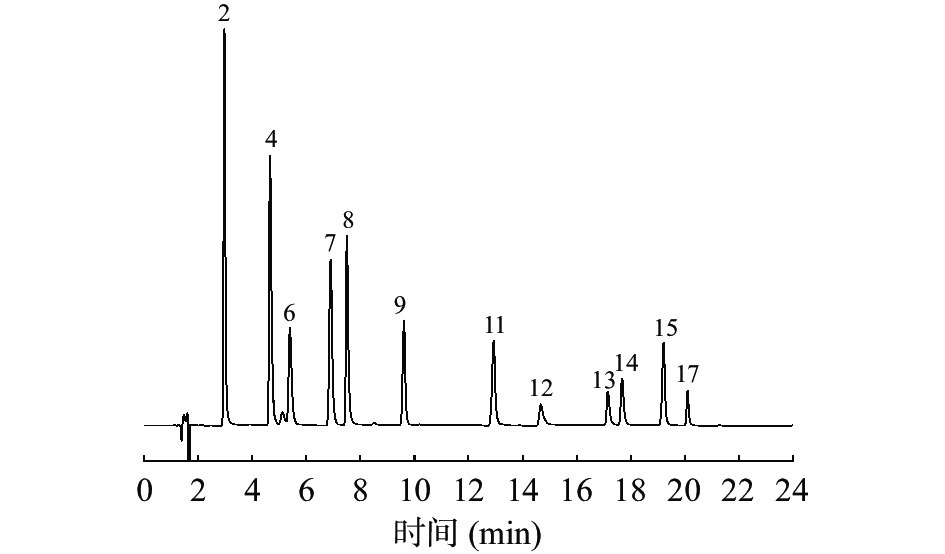
景天三七HPLC-ECD指纹图谱见图1,共标定17个共有峰。以S1为参照图谱,依次进行多点校正、峰匹配后以平均数法生成对照图谱(见图2)并进行相似度计算。通过图2与混合标准品溶液的色谱图比对(图3),2号峰为没食子酸,4号峰为原儿茶酸,6号峰为色氨酸,7号峰为没食子酸甲酯,8号峰为EGC,9号峰为咖啡酸,11号峰为EGCG,12号峰为鸢尾酚酮,13号峰为杨梅苷,14号峰为异槲皮苷,15号峰为迷迭香酸,17号峰为槲皮苷。各批样品的相似度结果见表2,其相似度较高,范围在0.852~1.000之间,表明各批景天三七样品间一致性较高。
表 2 23批景天三七的相似度结果Table 2. Similarity evaluation of 23 batches of Sedum aizoon L.样品编号 相似度 样品编号 相似度 样品编号 相似度 S1 0.997 S9 0.995 S17 0.999 S2 0.938 S10 1.000 S18 0.999 S3 0.852 S11 0.989 S19 0.883 S4 0.992 S12 0.991 S20 0.988 S5 0.997 S13 0.991 S21 0.996 S6 0.997 S14 0.967 S22 0.999 S7 0.999 S15 0.999 S23 0.997 S8 0.999 S16 0.994 2.3 多成分含量测定
2.3.1 线性关系
分别精密吸取“1.2.2”项下的对照品溶液,配制成不同浓度的混合对照品溶液,按上述色谱条件进样分析,记录峰面积。以对照品的浓度(μg/mL)为横坐标,峰面积为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,计算线性回归方程,见表3。12种化合物在线性范围内,线性关系良好,r在0.9990~0.9999范围内。
表 3 方法学考察Table 3. Method validation of the proposed method化合物 线性范围(μg/mL) 线性方程 r 平均加样回收率(%) RSD (%) 没食子酸 1.5~75 Y=1.0556X−0.2131 0.9999 97.76 3.92 原儿茶酸 0.1~10 Y=0.5784X+0.0143 0.9994 93.08 6.35 色氨酸 2.5~50 Y=0.6446X+0.5004 0.9995 98.71 4.85 没食子酸甲酯 0.2~10 Y=0.8211+0.0789 0.9993 97.21 3.16 EGC 0.5~25 Y=0.185X−0.0364 0.9993 99.35 6.34 咖啡酸 0.1~5 Y=0.46X−0.0185 0.9996 94.19 3.60 EGCG 0.3~150 Y=0.0649+0.0299 0.9996 97.63 2.01 杨梅苷 3.8~95 Y=0.0314X+0.0355 0.9990 98.61 5.95 异槲皮苷 2.5~50 Y=0.015X-0.0055 0.9997 96.07 5.56 迷迭香酸 0.01~5 Y=0.0558X+0.001 0.9994 94.74 2.14 鸢尾酚酮 2.5~50 Y=0.0513X+0.0425 0.9992 96.96 5.72 槲皮苷 0.8~40 Y=0.0142X+0.0096 0.9996 97.14 4.83 2.3.2 精密度试验
按“1.2.1”项下制备供试液,连续进样6次。各共有峰保留时间RSD在0.05%~0.26%之间,峰面积RSD在1.85%~5.93%之间。表明仪器精密度良好。
2.3.3 稳定性试验
按“1.2.1”项下制备供试液,分别于0、2、4、6、12、24 h进样一次。各共有峰保留时间RSD在0.12%~0.95%之间,峰面积RSD在2.15%~6.86%。表明供试品溶液在24 h内稳定。
2.3.4 重复性试验
按“1.2.1”项下制备6份供试液,进样分析。各共有峰保留时间RSD均在0.03%~0.28%之间,峰面积RSD在1.24%~6.25%之间。表明该方法重复性良好。
2.3.5 加样回收率试验
取同一批含量已知的景天三七粉末6份,每份约0.35 g,加入适量对照品,按“1.2.1 样品制备”方法制备供试液,进样测定,计算回收率。结果见表3,平均加样回收率在93.08%~99.35%之间,其RSD在2.01%~6.35%之间。
2.3.6 样品测定
含量测定结果见表4。其中,没食子酸、色氨酸、EGCG、杨梅苷和异槲皮苷的含量较高,其含量分别为207.52~2319.45、338.28~1136.17、25.97~2476.61、433.39~2675.31和7.69~759.54 μg/g;各批样品之间也存在较大差异。任平等[23]的研究表明,土壤元素中的钙、铜、铁对景天三七活性成分含量影响较大。同时,充足的降水量可保证植物的正常生长代谢和次生代谢物质的累积。多个温度因子对黄酮含量呈现负相关,因而适度低温有利于黄酮类物质的合成,并且较大的温差有利于景天三七谷甾醇、总黄酮和景天庚糖的累积,尤其是总黄酮含量的增加最为明显。何晶晶等[24]的研究结果表明,不同采收期的景天三七含量存在差异。因此,景天三七样品间的差异不仅与产地间的多种生态因子有关,同时还与采收季节有关,也可能是药材的成熟程度不同而导致。
表 4 23批景天三七中12种化合物含量测定结果(μg/g)Table 4. Contents of 12 compounds in 23 batches of Sedum aizoon L. (μg/g)编号 没食子酸 原儿茶酸 色氨酸 没食子酸甲酯 EGC 咖啡酸 EGCG 鸢尾酚酮 杨梅苷 异槲皮苷 迷迭香酸 槲皮苷 S1 1010.15 23.89 624.25 155.76 222.68 27.43 47.85 785.11 1006.99 186.93 15.93 132.95 S2 537.08 42.00 757.70 131.55 185.36 9.80 25.97 551.30 1878.03 307.16 16.38 244.93 S3 207.52 3.02 442.77 10.08 49.39 5.86 125.68 169.84 433.39 7.69 0.99 61.67 S4 783.22 23.41 684.69 50.06 178.04 20.29 579.07 292.50 1805.69 476.80 30.10 302.78 S5 1037.80 8.08 503.93 47.87 191.14 9.92 734.59 555.04 1296.53 174.31 31.01 268.53 S6 1577.07 23.17 746.70 168.46 496.17 21.08 1716.99 772.36 1864.05 483.12 28.79 360.56 S7 2261.78 39.79 1033.68 93.35 399.95 25.90 1114.10 546.83 2675.31 310.18 28.70 411.50 S8 1142.77 32.91 659.16 125.46 147.09 19.10 1442.95 469.60 1448.08 319.52 35.43 354.28 S9 1264.30 20.93 685.20 276.02 321.43 11.58 1023.02 657.10 1266.34 262.15 21.98 253.19 S10 1542.07 18.76 906.47 53.52 347.82 12.71 1215.22 608.82 1151.66 203.13 21.39 222.36 S11 1804.02 42.47 620.55 77.11 416.58 12.93 879.94 421.10 2597.91 510.29 17.29 362.86 S12 2319.45 34.19 853.57 110.32 482.88 18.10 2476.61 870.11 2155.40 449.08 42.79 418.57 S13 1919.34 27.22 710.42 75.57 353.88 18.41 2145.62 593.87 1675.01 403.24 26.90 344.03 S14 721.13 2.72 849.78 10.98 111.40 26.28 215.42 317.49 682.00 83.72 6.36 76.77 S15 1042.84 14.72 672.41 93.00 241.50 17.83 985.61 248.69 1175.77 188.58 14.85 189.54 S16 883.68 9.23 374.06 54.15 295.58 15.03 404.60 414.94 1386.69 208.62 8.89 181.51 S17 748.41 14.90 338.28 27.54 180.80 16.31 232.48 278.29 1270.59 188.58 15.25 148.21 S18 962.61 15.79 700.48 37.71 229.43 16.58 840.06 350.46 1195.62 200.93 21.57 138.44 S19 611.54 16.05 1136.17 219.95 119.06 18.60 444.49 543.61 1402.90 284.93 19.18 198.20 S20 863.82 18.06 806.48 39.24 152.51 22.98 628.86 637.25 1080.54 213.01 17.47 103.47 S21 908.69 17.56 428.62 13.50 119.72 10.89 703.94 360.43 2357.61 759.54 9.75 355.08 S22 850.25 18.71 596.91 76.56 218.85 13.78 832.63 390.47 2149.33 293.99 26.81 294.76 S23 1716.12 40.33 853.13 195.65 215.28 22.81 937.23 461.10 2650.80 375.79 14.13 274.33 2.4 抗氧化活性评价
体外抗氧化活性的测定结果见表5。DPPH、ABTS自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力的范围分别为5.87~100.92、25.57~274.66和8.54~122.12 mg TE/g DW。其中,S12的抗氧化活性最强;抗氧化活性较弱的样品为S3和S14,二者原儿茶酸、没食子酸甲酯、EGC、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷的含量均较低,故而活性较弱。因此这几种成分可能与景天三七的抗氧化活性密切相关。
表 5 23批景天三七抗氧化能力测定结果Table 5. Results of antioxidant activity in 23 batches of Sedum aizoon L.编号 DPPH(mg TE/g DW) FRAP(mg TE/g DW) ABTS(mg TE/g DW) 编号 DPPH(mg TE/g DW) FRAP(mg TE/g DW) ABTS(mg TE/g DW) S1 54.43 55.25 134.64 S13 83.98 95.80 210.81 S2 50.01 52.18 137.26 S14 17.06 19.19 54.79 S3 5.87 8.54 25.57 S15 63.95 62.44 138.75 S4 69.49 72.14 162.88 S16 40.46 39.30 77.96 S5 58.64 57.37 124.67 S17 38.10 37.87 85.83 S6 79.03 85.35 189.91 S18 37.25 36.47 95.19 S7 82.05 92.97 206.96 S19 50.92 55.85 116.79 S8 83.90 85.50 192.53 S20 48.34 50.38 117.76 S9 83.45 86.05 178.45 S21 64.31 66.18 149.15 S10 65.84 72.37 170.67 S22 54.28 67.99 134.20 S11 67.62 90.41 190.96 S23 72.61 85.73 182.83 S12 100.92 122.12 274.66 2.5 化学计量学分析
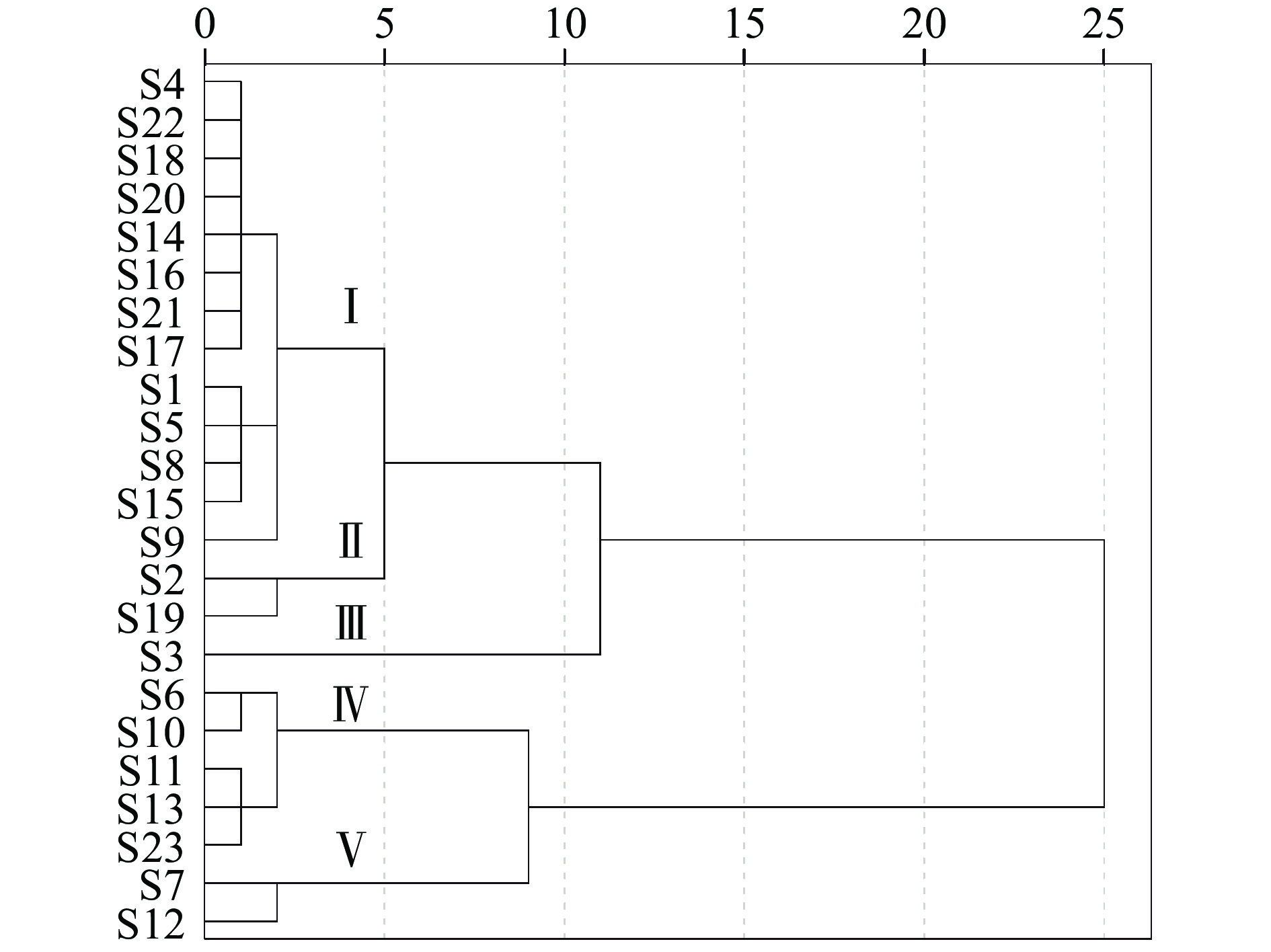
2.5.1 聚类分析
如图4所示,当平方欧氏距离为5时,23批样品可被分为五类,第Ⅰ类包括S1、S4、S5、S8、S9、S14、S15、S16、S17、S18、S20、S21、S22,化合物间的含量差异较小,且含量较高。其中,多数样品的产地为江苏,与湖南、山东、贵州、河南、河北等地的样品有少许交叉,而江苏一带为亚热带季风气候-温带季风气候。夏季高温多雨,降水量充足,有利于生物活性物质的积累。第Ⅱ类仅含S2和S19;而样品S3被单独分为第Ⅲ类,S3中大多数化合物含量均低于其他样品,故而被单列为一类。研究表明,适度的低温和较大的温差,有利于黄酮类化合物的合成。S3样品产地为云南省昆明市,全年温差较小,日照长;多数化合物含量均为最低,故而证实了温差对景天三七中活性成分的含量有一定影响;第Ⅳ类包括S6、S10、S11、S13、S23,该类中样品产地较为分散,但均为邻省,差异较小而聚为一类;第Ⅴ类为S7和S12,二者的成分含量差异较小,且含量较高,同为邻省。综上,景天三七中活性成分的含量与产地有一定关联,但关联性较小,可能是受其生长环境、生态因子的影响而产生了样品之间的差异,过度的土壤酸化可能会抑制景天三七的生长,出现功能紊乱,锌、镁、锰和速效钾等土壤因素影响会其活性物质的合成量;其次,景天三七的营养物质含量还与光照强度有关,过强或过弱的光照均会抑制其生长。
2.5.2 偏最小二乘回归分析
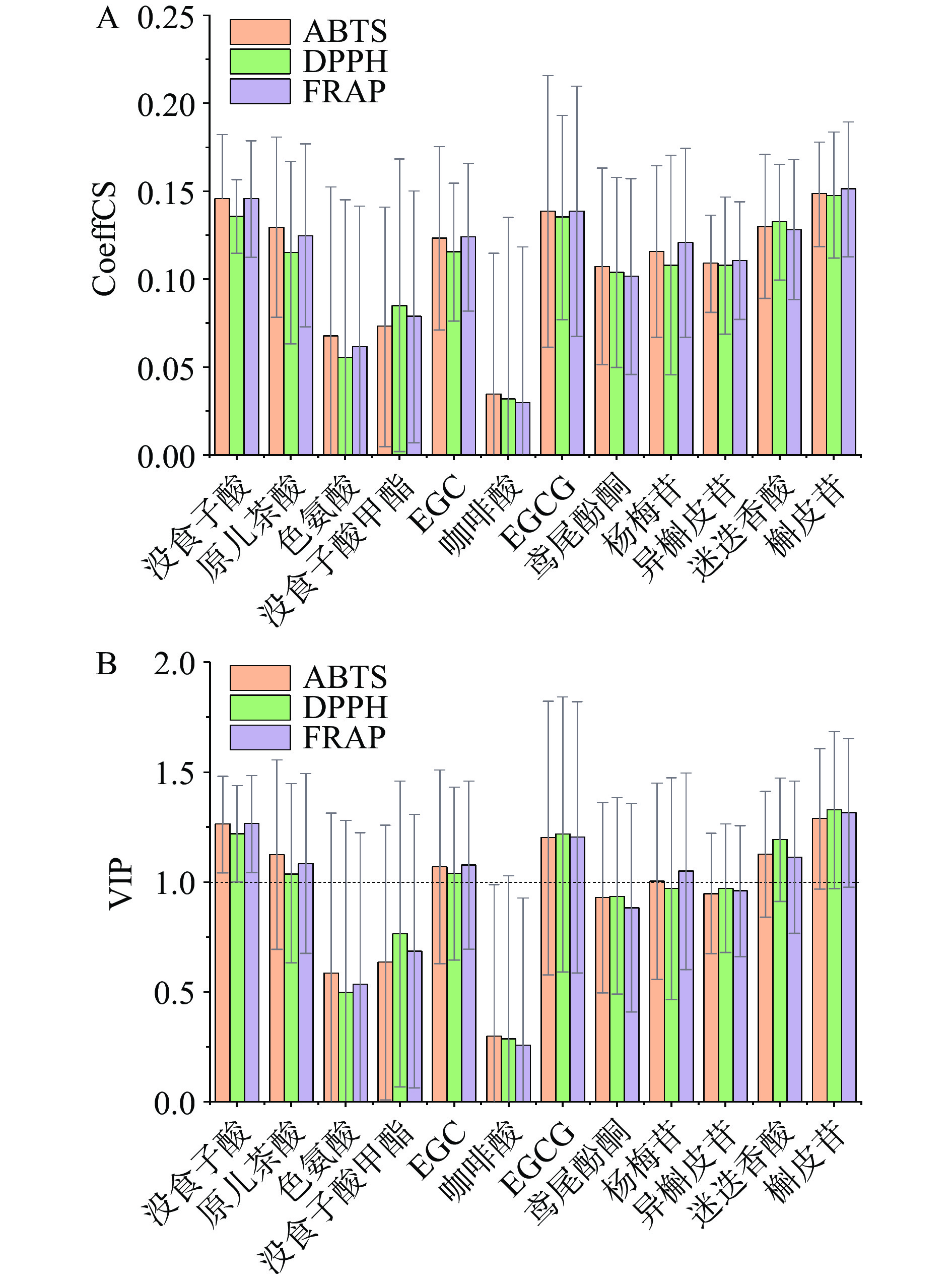
图5A结果表明,12种化合物均与ABTS、DPPH自由基清除能力及FRAP呈正相关,没食子酸、原儿茶酸、EGC、EGCG、鸢尾酚酮、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷与抗氧化活性的相关性较好,3种体外抗氧化活性测定指标间的相关性差异较小。
VIP值越大,说明该自变量对因变量的贡献率越大,当VIP值>1时,自变量与因变量呈显著相关。没食子酸、原儿茶酸、EGC、EGCG、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷的VIP值均大于1(图5B),与DPPH、ABTS自由基清除能力和FRAP具有显著相关性。其中,槲皮苷>没食子酸>EGCG>迷迭香酸,原儿茶酸与EGC的抗氧化能力差异较小。董馨等[25]推测酚羟基化合物的构效关系为邻三酚羟基>邻对三酚羟基>间三酚羟基,邻二酚羟基>对二酚羟基>间二酚羟基。黄酮类化合物结构中B环酚羟基活性高于A环,且B环上3,4-邻苯二酚结构活性最强[26]。槲皮苷具有邻二酚羟基和间二酚羟基,其中3,4-邻苯二酚活性较强,虽然含量不及没食子酸,其活性却略强于没食子酸,但二者差异较小;没食子酸具有邻三酚羟基,且其含量较高,为景天三七中的主要活性成分,ECCG具有两个邻三酚羟基和1个间二酚羟基,迷迭香酸具有2个邻二酚羟基。因此,本研究对体外抗氧化活性的研究与前人的研究结果基本一致。
2.5.3 灰色关联分析
关联度越大,化学成分的抗氧化活性作用越强。结果表明(表6),各化合物与体外抗氧化活性的关联度均大于0.6,均与体外抗氧化活性密切相关,是多种化合物共同作用的结果。对ABTS自由基清除能力贡献较大的共有峰(关联度>0.7)主要有:没食子酸>迷迭香酸>槲皮苷>EGC>异槲皮苷>原儿茶酸>EGCG>杨梅苷>鸢尾酚酮,其中没食子酸的关联度高达0.8168,对抗氧化活性的影响较大。槲皮苷、迷迭香酸、没食子酸、鸢尾酚酮、EGC、杨梅苷和异槲皮苷的关联度均大于0.7,对DPPH自由基清除能力的贡献较大,相关性较显著,其中的槲皮苷关联度大于0.8。除色氨酸、没食子酸甲酯、咖啡酸外,其余9种化合物与FRAP的关联度较大,其中没食子酸、槲皮苷和迷迭香酸的关联度均大于0.8,对FRAP的贡献极大。
表 6 12种化合物与抗氧化活性的灰色关联结果Table 6. Results of gray correlation between 12 compounds and antioxidant activity化合物 ABTS 排名 DPPH 排名 FRAP 排名 平均关联度 平均排名 没食子酸 0.8168 1 0.7646 3 0.8185 1 0.8000 1 原儿茶酸 0.7714 6 0.7192 7 0.7547 6 0.7484 6 色氨酸 0.6916 10 0.6414 11 0.6720 10 0.6683 11 没食子酸甲酯 0.6622 12 0.6277 12 0.6563 12 0.6487 12 EGC 0.7781 4 0.7276 5 0.7697 4 0.7585 4 咖啡酸 0.6640 11 0.6750 10 0.6710 11 0.6700 10 EGCG 0.7472 7 0.6765 9 0.7345 8 0.7194 9 鸢尾酚酮 0.7336 9 0.7346 4 0.7334 9 0.7339 8 杨梅苷 0.7369 8 0.7201 6 0.7450 7 0.7340 7 异槲皮苷 0.7773 5 0.7010 8 0.7676 5 0.7486 5 迷迭香酸 0.7981 2 0.7802 2 0.8025 3 0.7936 3 槲皮苷 0.7926 3 0.8015 1 0.8052 2 0.7998 2 以ABTS、DPPH和FRAP三者的关联度之和来看,景天三七中体外抗氧化活性较强的前5种化合物为:没食子酸、槲皮苷、迷迭香酸、EGC和异槲皮苷,该结果与偏最小二乘回归分析结果有些许差异,但可以确定的是没食子酸、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷与抗氧化活性的关联度极大,可将其作为一个质控指标。而没食子酸甲酯和咖啡酸,它们虽具有酚羟基结构,但其含量较低,发挥的作用较小,故而关联度较小。而HPLC-ECD中较为特殊的一个色谱峰为色氨酸,其含量较高,但是与抗氧化活性的关联度较小。其他化合物均为酚类化合物,在体外具有很强的抗氧化作用,主要抗氧化能力存在于酚环中的双键,羟基侧链和糖基化都有助于清除自由基活性。而色氨酸在结构上不同,由于吲哚环的不稳定性,在ECD上可以被氧化[27],与自由基结合生成稳定物质而发挥抗氧化作用。基于吲哚环和异吲哚环在ECD上的良好响应,常用来分析氨基酸类化合物[28]。但是,其抗氧化能力相对于酚类化合物较差。如钩藤中的钩藤碱和利血平均为吲哚类生物碱[29-30],钩藤碱的主要药理活性体现在心血管系统和中枢神经系统的保护作用[31],利血平主要药理活性为降压作用,而抗氧化并不是它们的主要活性。
2.6 分子对接
结果以Libdock Score表示(见表7),Libdock Score 越高,小分子与受体结合的活性越高。12种化合物均能与活性靶点的关键活性氨基酸残基结合,与各靶点的对接结果基本一致,表明对接参数较为合理,结果可靠。EGC、EGCG、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷与各个靶点的对接评分较高,其中与NO-1靶点的LibDock Score最高。EGC、EGCG、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷与NO-1的对接结果见图6。活性成分与靶点蛋白NO-1的氨基酸残基主要通过氢键、Pi-Alkyl键、pi-pi Stacked结合。综上,12种化合物均能与GSTP1、ROS-1、TNF、HO-1和NO-1蛋白相结合,从而发挥抗氧化作用,具有良好的自由基清除能力。
表 7 12种化合物的LibDock评分Table 7. LibDock Score of 12 compounds化合物 GSTP1 ROS-1 TNF HO-1 NO-1 没食子酸 69.7776 62.2938 67.1806 67.7897 75.4297 原儿茶酸 56.4386 57.0903 63.7542 70.1692 73.359 色氨酸 83.5447 69.3485 81.0263 86.9675 90.2187 没食子酸甲酯 72.5958 61.9535 70.6559 70.9126 80.2272 EGC 100.262 92.4051 109.624 106.326 115.547 咖啡酸 58.184 44.0605 51.6091 54.8233 60.413 EGCG 142.132 117.058 131.735 131.702 145.839 鸢尾酚酮 80.1019 64.7981 80.9352 74.911 85.2199 杨梅苷 116.557 106.696 119.567 109.226 123.865 异槲皮苷 118.205 104.135 125.782 113.899 127.767 迷迭香酸 129.061 109.115 118.374 115.742 133.845 槲皮苷 105.966 96.5478 121.308 114.845 121.889 3. 结论
综上,本研究成功建立了景天三七HPLC-ECD指纹图谱,结合多种化学计量方法对不同产地的景天三七进行质量评价及抗氧化作用的谱效关系研究。其中,没食子酸、EGCG、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷等具有良好的体外抗氧化活性。分子对接研究结果表明,EGCG、杨梅苷、异槲皮苷、迷迭香酸和槲皮苷等化合物具有良好的自由基清除活性,且能与GSTP1、ROS-1、TNF、HO-1和NO-1蛋白相结合。综上,本研究可为景天三七抗氧化活性质量标志物的筛选和质量控制提供了一定的参考依据。
-
表 1 景天三七样品信息
Table 1 Information of Sedum aizoon L. samples
样品编号 产地 收集时间 样品编号 产地 收集时间 样品编号 产地 收集时间 S1 贵州黔东南 2021.07 S9 河北廊坊 2021.07 S17 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S2 重庆丰都 2021.07 S10 河北定州 2021.07 S18 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S3 云南昆明 2021.07 S11 安徽芜湖 2021.07 S19 河北石家庄 2021.08 S4 湖南永州 2021.07 S12 山东曹县 2021.08 S20 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S5 河南商丘 2021.07 S13 山东曹县 2021.08 S21 山东临沂 2021.08 S6 河南周口 2021.07 S14 江苏沐阳 2021.08 S22 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S7 河南南阳 2021.07 S15 江苏宿迁 2021.08 S23 江苏苏州 2021.08 S8 河北南宫 2021.07 S16 江苏宿迁 2021.08 表 2 23批景天三七的相似度结果
Table 2 Similarity evaluation of 23 batches of Sedum aizoon L.
样品编号 相似度 样品编号 相似度 样品编号 相似度 S1 0.997 S9 0.995 S17 0.999 S2 0.938 S10 1.000 S18 0.999 S3 0.852 S11 0.989 S19 0.883 S4 0.992 S12 0.991 S20 0.988 S5 0.997 S13 0.991 S21 0.996 S6 0.997 S14 0.967 S22 0.999 S7 0.999 S15 0.999 S23 0.997 S8 0.999 S16 0.994 表 3 方法学考察
Table 3 Method validation of the proposed method
化合物 线性范围(μg/mL) 线性方程 r 平均加样回收率(%) RSD (%) 没食子酸 1.5~75 Y=1.0556X−0.2131 0.9999 97.76 3.92 原儿茶酸 0.1~10 Y=0.5784X+0.0143 0.9994 93.08 6.35 色氨酸 2.5~50 Y=0.6446X+0.5004 0.9995 98.71 4.85 没食子酸甲酯 0.2~10 Y=0.8211+0.0789 0.9993 97.21 3.16 EGC 0.5~25 Y=0.185X−0.0364 0.9993 99.35 6.34 咖啡酸 0.1~5 Y=0.46X−0.0185 0.9996 94.19 3.60 EGCG 0.3~150 Y=0.0649+0.0299 0.9996 97.63 2.01 杨梅苷 3.8~95 Y=0.0314X+0.0355 0.9990 98.61 5.95 异槲皮苷 2.5~50 Y=0.015X-0.0055 0.9997 96.07 5.56 迷迭香酸 0.01~5 Y=0.0558X+0.001 0.9994 94.74 2.14 鸢尾酚酮 2.5~50 Y=0.0513X+0.0425 0.9992 96.96 5.72 槲皮苷 0.8~40 Y=0.0142X+0.0096 0.9996 97.14 4.83 表 4 23批景天三七中12种化合物含量测定结果(μg/g)
Table 4 Contents of 12 compounds in 23 batches of Sedum aizoon L. (μg/g)
编号 没食子酸 原儿茶酸 色氨酸 没食子酸甲酯 EGC 咖啡酸 EGCG 鸢尾酚酮 杨梅苷 异槲皮苷 迷迭香酸 槲皮苷 S1 1010.15 23.89 624.25 155.76 222.68 27.43 47.85 785.11 1006.99 186.93 15.93 132.95 S2 537.08 42.00 757.70 131.55 185.36 9.80 25.97 551.30 1878.03 307.16 16.38 244.93 S3 207.52 3.02 442.77 10.08 49.39 5.86 125.68 169.84 433.39 7.69 0.99 61.67 S4 783.22 23.41 684.69 50.06 178.04 20.29 579.07 292.50 1805.69 476.80 30.10 302.78 S5 1037.80 8.08 503.93 47.87 191.14 9.92 734.59 555.04 1296.53 174.31 31.01 268.53 S6 1577.07 23.17 746.70 168.46 496.17 21.08 1716.99 772.36 1864.05 483.12 28.79 360.56 S7 2261.78 39.79 1033.68 93.35 399.95 25.90 1114.10 546.83 2675.31 310.18 28.70 411.50 S8 1142.77 32.91 659.16 125.46 147.09 19.10 1442.95 469.60 1448.08 319.52 35.43 354.28 S9 1264.30 20.93 685.20 276.02 321.43 11.58 1023.02 657.10 1266.34 262.15 21.98 253.19 S10 1542.07 18.76 906.47 53.52 347.82 12.71 1215.22 608.82 1151.66 203.13 21.39 222.36 S11 1804.02 42.47 620.55 77.11 416.58 12.93 879.94 421.10 2597.91 510.29 17.29 362.86 S12 2319.45 34.19 853.57 110.32 482.88 18.10 2476.61 870.11 2155.40 449.08 42.79 418.57 S13 1919.34 27.22 710.42 75.57 353.88 18.41 2145.62 593.87 1675.01 403.24 26.90 344.03 S14 721.13 2.72 849.78 10.98 111.40 26.28 215.42 317.49 682.00 83.72 6.36 76.77 S15 1042.84 14.72 672.41 93.00 241.50 17.83 985.61 248.69 1175.77 188.58 14.85 189.54 S16 883.68 9.23 374.06 54.15 295.58 15.03 404.60 414.94 1386.69 208.62 8.89 181.51 S17 748.41 14.90 338.28 27.54 180.80 16.31 232.48 278.29 1270.59 188.58 15.25 148.21 S18 962.61 15.79 700.48 37.71 229.43 16.58 840.06 350.46 1195.62 200.93 21.57 138.44 S19 611.54 16.05 1136.17 219.95 119.06 18.60 444.49 543.61 1402.90 284.93 19.18 198.20 S20 863.82 18.06 806.48 39.24 152.51 22.98 628.86 637.25 1080.54 213.01 17.47 103.47 S21 908.69 17.56 428.62 13.50 119.72 10.89 703.94 360.43 2357.61 759.54 9.75 355.08 S22 850.25 18.71 596.91 76.56 218.85 13.78 832.63 390.47 2149.33 293.99 26.81 294.76 S23 1716.12 40.33 853.13 195.65 215.28 22.81 937.23 461.10 2650.80 375.79 14.13 274.33 表 5 23批景天三七抗氧化能力测定结果
Table 5 Results of antioxidant activity in 23 batches of Sedum aizoon L.
编号 DPPH(mg TE/g DW) FRAP(mg TE/g DW) ABTS(mg TE/g DW) 编号 DPPH(mg TE/g DW) FRAP(mg TE/g DW) ABTS(mg TE/g DW) S1 54.43 55.25 134.64 S13 83.98 95.80 210.81 S2 50.01 52.18 137.26 S14 17.06 19.19 54.79 S3 5.87 8.54 25.57 S15 63.95 62.44 138.75 S4 69.49 72.14 162.88 S16 40.46 39.30 77.96 S5 58.64 57.37 124.67 S17 38.10 37.87 85.83 S6 79.03 85.35 189.91 S18 37.25 36.47 95.19 S7 82.05 92.97 206.96 S19 50.92 55.85 116.79 S8 83.90 85.50 192.53 S20 48.34 50.38 117.76 S9 83.45 86.05 178.45 S21 64.31 66.18 149.15 S10 65.84 72.37 170.67 S22 54.28 67.99 134.20 S11 67.62 90.41 190.96 S23 72.61 85.73 182.83 S12 100.92 122.12 274.66 表 6 12种化合物与抗氧化活性的灰色关联结果
Table 6 Results of gray correlation between 12 compounds and antioxidant activity
化合物 ABTS 排名 DPPH 排名 FRAP 排名 平均关联度 平均排名 没食子酸 0.8168 1 0.7646 3 0.8185 1 0.8000 1 原儿茶酸 0.7714 6 0.7192 7 0.7547 6 0.7484 6 色氨酸 0.6916 10 0.6414 11 0.6720 10 0.6683 11 没食子酸甲酯 0.6622 12 0.6277 12 0.6563 12 0.6487 12 EGC 0.7781 4 0.7276 5 0.7697 4 0.7585 4 咖啡酸 0.6640 11 0.6750 10 0.6710 11 0.6700 10 EGCG 0.7472 7 0.6765 9 0.7345 8 0.7194 9 鸢尾酚酮 0.7336 9 0.7346 4 0.7334 9 0.7339 8 杨梅苷 0.7369 8 0.7201 6 0.7450 7 0.7340 7 异槲皮苷 0.7773 5 0.7010 8 0.7676 5 0.7486 5 迷迭香酸 0.7981 2 0.7802 2 0.8025 3 0.7936 3 槲皮苷 0.7926 3 0.8015 1 0.8052 2 0.7998 2 表 7 12种化合物的LibDock评分
Table 7 LibDock Score of 12 compounds
化合物 GSTP1 ROS-1 TNF HO-1 NO-1 没食子酸 69.7776 62.2938 67.1806 67.7897 75.4297 原儿茶酸 56.4386 57.0903 63.7542 70.1692 73.359 色氨酸 83.5447 69.3485 81.0263 86.9675 90.2187 没食子酸甲酯 72.5958 61.9535 70.6559 70.9126 80.2272 EGC 100.262 92.4051 109.624 106.326 115.547 咖啡酸 58.184 44.0605 51.6091 54.8233 60.413 EGCG 142.132 117.058 131.735 131.702 145.839 鸢尾酚酮 80.1019 64.7981 80.9352 74.911 85.2199 杨梅苷 116.557 106.696 119.567 109.226 123.865 异槲皮苷 118.205 104.135 125.782 113.899 127.767 迷迭香酸 129.061 109.115 118.374 115.742 133.845 槲皮苷 105.966 96.5478 121.308 114.845 121.889 -
[1] 谭波, 何席呈, 李婷, 等. 景天三七化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国民族民间医药,2018,27(17):49−52. [TAN B, HE X C, LI T, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and medical functions of Phedimus aizoon[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy,2018,27(17):49−52. TAN B, HE X C, LI T, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and medical functions of Phedimus aizoon[J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy, 2018, 27(17): 49-52.
[2] 周文, 强毅, 鲁秀兰, 等. 响应面法优化费菜多酚的提取工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(22):249−253. [ZHOU W, QIANG Y, LU X L, et al. Optimization of polyphenol extraction from Sedum Aizoon L. by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(22):249−253. ZHOU W, QIANG Y, LU X L, et al. Optimization of polyphenol extraction from Sedum Aizoon L. by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(22): 249-253.
[3] 胡月, 王鸿飞, 刘飞, 等. 费菜总黄酮分离纯化工艺的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(17):213−221. [HU Y, WANG H F, LIU F, et al. Separation and purification process of total flavonoids from Sedum aizoon leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(17):213−221. HU Y, WANG H F, LIU F, et al. Separation and purification process of total flavonoids from Sedum aizoon leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(17): 213-221.
[4] 刘晔峰, 马峥嵘, 吴晓琴, 等. 养心草的有效成分及功能性化合物研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2012,27(8):2135−2138. [LIU Y F, MA Z R, WU X Q, et al. Research progress of active principle and functional compounds of Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2012,27(8):2135−2138. LIU Y F, MA Z R, WU X Q, et al. Research progress of active principle and functional compounds of Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2012, 27(8): 2135-2138.
[5] 薛桂新. 养心草发酵茶饮料的研究[J]. 中国酿造,2015,34(10):151−155. [XUE G X. Research of fermented Sedum kamtschaticum tea beverage[J]. China Brewing,2015,34(10):151−155. XUE G X. Research of fermented Sedum kamtschaticum tea beverage[J]. China Brewing, 2015, 34(10): 151-155.
[6] 韩瑞杰, 赵晨, 陈豪杰, 等. 景天三七化学成分研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2021,36(7):4223−4226. [HAN R J, ZHAO C, CHEN H J, et al. Study on chemical constituents from Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2021,36(7):4223−4226. HAN R J, ZHAO C, CHEN H J, et al. Study on chemical constituents from Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2021, 36(7): 4223-4226.
[7] LI M, QI Z, HAO Y, et al. New adducts of iriflophene and flavonoids isolated from Sedum aizoon L. with potential antitumor activity[J]. Molecules,2017,22(11):1859−1866. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111859
[8] 熊燕, 杜彩霞, 段玉书, 等. 黔产景天三七的化学成分及药理活性研究[J]. 中草药,2019,50(22):5404−5410. [XIONG Y, DU C X, DUAN Y S, et al. Chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Sedum aizoon form Guizhou province[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2019,50(22):5404−5410. XIONG Y, DU C X, DUAN Y S, et al. Chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Sedum aizoon form Guizhou province[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(22): 5404-5410.
[9] 林珠灿, 张龙, 张睿卓, 等. 基于炎症细胞模型的景天三七醋酸乙酯部位抗炎活性及其HPLC指纹图谱的研究(英文)[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences,2015,24(10):647−653. [LIN Z C, ZHANG L, ZHANG R Z, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of ethyl acetate extract of Sedum aizoon L. in LPSstimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and its HPLC fingerprint[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences,2015,24(10):647−653. [LIN Z C, ZHANG L, ZHANG R Z, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of ethyl acetate extract of Sedum aizoon L. in LPSstimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and its HPLC fingerprint[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2015, 24(10): 647-653.
[10] 蔡扬帆, 房英娟, 林珠灿, 等. 景天三七宁心安神活性部位HPLC指纹图谱的研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2014,29(10):3275−3278. [CAI Y F, FANG Y J, LIN Z C, et al. HPLC fingerprint analysis on active site of calming the heart for tranquillization of Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2014,29(10):3275−3278. CAI Y F, FANG Y J, LIN Z C, et al. HPLC fingerprint analysis on active site of calming the heart for tranquillization of Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2014, 29(10): 3275-3278.
[11] 林珠灿, 林丹, 许飞, 等. 养心草药材HPLC指纹图谱研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2010,25(9):1499−1502. [LIN Z C, LIN D, XU F, et al. Studies on HPLC fingerprint of Herba Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2010,25(9):1499−1502. LIN Z C, LIN D, XU F, et al. Studies on HPLC fingerprint of Herba Sedum aizoon L[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2010, 25(9): 1499-1502.
[12] 王佰灵, 罗伦, 邱婧然, 等. 景天三七总多酚提取工艺的优化及活性研究[J]. 化学研究与应用,2021,33(8):1485−1493. [WANG B L, LUO L, QIU J R, et al. Optimization of extraction process of total polyphenol from Sedum aizoon L. and activities study[J]. Chemical Research and Application,2021,33(8):1485−1493. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2021.08.009 WANG B L, LUO L, QIU J R, et al. Optimization of extraction process of total polyphenol from Sedum aizoon L. and activities study[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2021, 33(8): 1485-1493. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2021.08.009
[13] GONG J, QIU S, WENG Q, et al. Effect of different drying methods on phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity in different fractions of Sedum aizoon L.[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2020,44(9):e14723.
[14] CHANG Y, ZHANG D, ZHENG Y, et al. Screening of anti-lipase components of artemisia argyi leaves based on spectrum-effect relationships and HPLC-MS/MS[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:675396. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.675396
[15] 罗敏, 顾雯, 何婷, 等. 超高效液相色谱-电化学检测法测定女贞子中的3种成分[J]. 中国药学杂志,2020,55(24):2006−2011. [LUO M, GU W, HE T, et al. Determination of three constituent in Ligustri lucidi fructus by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detection[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,2020,55(24):2006−2011. LUO M, GU W, HE T, et al. Determination of three constituent in Ligustri lucidi fructus by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electrochemical detection[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 2020, 55(24): 2006-2011
[16] 淳泽利, 朱娅, 陈荣祥. UPLC-ECD法同时测定不同产地女贞子中9种成分的含量[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(8):305−311. [CHUN Z L, ZHU Y, CHEN R X. Simultaneous determination of nine components in Ligustri lucidi fructus from different habitats by UPLC-ECD[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(8):305−311. CHUN Z L, ZHU Y, CHEN R X. Simultaneous determination of nine components in Ligustri lucidi fructus from different habitats by UPLC-ECD[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(8): 305−311.
[17] 王文晓, 杨诺, 高欢, 等. HPLC法同时测定冠心丹参片中10种成分[J]. 中成药,2021,43(5):1141−1144. [WANG X W, YANG N, GAO H, et al. Simultaneous determination of ten constituents in Guanxin Danshen Tablets by HPLC[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2021,43(5):1141−1144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.05.005 WANG X W, YANG N, GAO H, et al. Simultaneous determination of ten constituents in Guanxin Danshen Tablets by HPLC[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2021, 43(5): 1141-1144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.05.005
[18] ZHANG Q W, LIN L G, YE W C. Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: A comprehensive review[J]. Chinese Medicine,2018,13(3):20.
[19] 罗敏, 何婷, 龚磊, 等. 夏枯草中16种酚类化合物含量的测定及其与抗氧化活性的相关性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(1):299−306. [LUO M, HE T, GONG L, et al. Determination of 16 phenolic compounds in Prunella vulgaris and analysis their correlation with antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(1):299−306. LUO M, HE T, GONG L, et al. Determination of 16 phenolic compounds in Prunella Vulgaris and analysis their correlation with antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(1): 299-306.
[20] ZHANG P, CHUN Z L, SHAO Q J, et al. valuation of the phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of Lophatherum gracile Brongn based on chemical fingerprinting by HPLC with electrochemical detection[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2021,44(20):3777−3788.
[21] 李轩豪, 刘兰茹, 龙伟, 等. 基于计算药理学的藏药三果汤散抗氧化研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2018,33(9):4139−4142. [LI X H, LIU R L, LONG W, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of Tibetan medicine Sanguotang Powder based on computational pharmacology[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2018,33(9):4139−4142. LI X H, LIU R L, LONG W, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of Tibetan medicine Sanguotang Powder based on computational pharmacology[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2018, 33(9): 4139-4142.
[22] 高燕, 陶培, 王毓杰, 等. 基于网络药理学的肉苁蓉苯乙醇苷抗氧化活性分子机制研究[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2022,39(17):2204−2015. [GAO Y, TAO P, WANG Y J, et al. Molecular mechanism of antioxidant activity of phenylethanoid glycosides from Cistanches herba based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy,2022,39(17):2204−2015. [GAO Y, TAO P, WANG Y J, et al. Molecular mechanism of antioxidant activity of phenylethanoid glycosides from Cistanches herba based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2022, 39(17): 2204-2015.
[23] 任平, 付博, 刘晨, 等. 景天三七主要活性成分与土壤、气象因子的相关性[J]. 生态环境学报,2019,28(5):908−917. [REN P, FU B, LIU C, et al. Correlation between the active components and soil and meteorological factors of Sedum aizoon[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2019,28(5):908−917. REN P, FU B, LIU C, et al. Correlation between the active components and soil and meteorological factors of Sedum aizoon[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 28(5): 908-917.
[24] 何晶晶, 杜江. 景天三七中槲皮苷、槲皮素及山萘酚含量的高效液相色谱法同时测定[J]. 时珍国医国药,2016,27(3):524−526. [HE J J, DU J. Simultaneous determination of quercetin, quercetin, and kaempferol in Jingtian Sanqi by high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Shi Zhen Guoyi Guoyao,2016,27(3):524−526. HE J J, DU J. Simultaneous determination of quercetin, quercetin, and kaempferol in Jingtian Sanqi by high-performance liquid chromatography [J]. Shi Zhen Guoyi Guoyao, 2016, 27 (3): 524-526.
[25] 董馨, 王弘, 马飞祥, 等. 基于在线HPLC-自由基清除检测-ESI-IT-TOF-MSn技术的蓝刺头抗氧化成分筛选及其构效关系研究(英文)[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Science,2021,30(4):267−279. [DONG X, WANG H, MA F X, et al. A strategy for structure-activity relationship study on antioxidants in Echinops latifolius tausch extracts by online HPLC-radical scavenging detection coupled with ESI-IT-TOF-MSn[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Science,2021,30(4):267−279. doi: 10.5246/jcps.2021.04.022 DONG X, WANG H, MA F X, et al. A strategy for structure-activity relationship study on antioxidants in Echinops latifolius tausch extracts by online HPLC-radical scavenging detection coupled with ESI-IT-TOF-MSn[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Science, 2021, 30(4): 267-279. doi: 10.5246/jcps.2021.04.022
[26] 孙静, 黄芸, 孙桂波, 等. 河北香菊中黄酮类成分体外抗氧化活性研究及构效关系探讨[J]. 中国中药杂志,2012,37(13):1958−1962. [SUN J, HUANG, Y, SUN G B, et al. Study onin vitro antioxidant activity of flavonoids contained in Hebei balmy chrysanthemum and structure-activity relationship[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2012,37(13):1958−1962. SUN J, HUANG, Y, SUN G B, et al. Study on in vitro antioxidant activity of flavonoids contained in Hebei balmy chrysanthemum and structure-activity relationship[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2012, 37(13): 1958-1962.
[27] XU N J, CHEN G Q, LIU H. Antioxidative categorization of twenty amino acids based on experimental evaluation[J]. Molecules,2017,22(12):2066. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122066
[28] DU T T, CUI T, QIU H M, et al. Simultaneous determination of tryptophan, kynurenine, kynurenic acid and two monoamines in rat plasma by HPLC-ECD/DAD[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2018,158:8−14. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.05.032
[29] 于潇, 祝琳琳, 刘婕, 等. 钩藤中单萜吲哚类生物碱成分及其药理活性的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2021,52(19):6052−6065. [YU X, ZHU L L, LIU J, et al. Research progress on monoterpenoid indole alkaloids in Uncariae ramulus cum uncis and their pharmacological activities[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52(19):6052−6065. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.19.029 YU X, ZHU L L, LIU J, et al. Research progress on monoterpenoid indole alkaloids in Uncariae ramulus cum uncis and their pharmacological activities[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2021, 52(19): 6052-6065. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.19.029
[30] 王明阳, 唐颖, 刘芳, 等. 钩藤总生物碱提取工艺的优化[J]. 遵义医科大学学报,2020,43(5):656−661. [WANG M Y, TANG Y, LIU F, et al. Optimization of the extraction technology of total alkaloids from Uncaria rhynchophylla[J]. Journal of Zunyi Medicine University,2020,43(5):656−661. WANG M Y, TANG Y, LIU F, et al. Optimization of the extraction technology of total alkaloids from uncaria rhynchophylla[J]. Journal of Zunyi Medicine University, 2020, 43(5): 656-661.
[31] 柳威, 邓林华, 赵英强. 钩藤提取物及钩藤碱的药理研究进展[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2021,32(6):899−904. [LIU W, DENG L H, ZHAO Y Q. Research progress on pharmacological effects of Uncaria extract and rhynchophylline[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology,2021,32(6):899−904. LIU W, DENG L H, ZHAO Y Q. Research progress on pharmacological effects of Uncaria Extract and Rhynchophylline[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2021, 32(6): 899-904.
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 孟新涛,许铭强,张婷,古丽米热·祖努纳,牛逍瞳,郭金宝,刘国庆,马燕. 基于GC-IMS技术分析新疆不同品种核桃油挥发性成分的差异. 中国油脂. 2025(03): 102-109 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 古丽米热·祖努纳,孟新涛,叶朵朵,付慧鑫,乔雪,乔雅洁,张婷. 不同储藏温度下鲜羊肉品质及风味的变化. 现代食品科技. 2025(03): 203-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 乔雪,乔雅洁,付慧鑫,孟新涛,张婷. 低压静电场辅助解冻对牛肉品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(17): 48-56 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨秉坤,剧柠,丁雨红,郭蓉,龚绵红. 沙棘酸奶挥发性风味物质的GC-IMS表征. 食品工业科技. 2023(13): 308-315 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 张凡,张宇帆,苏心悦,徐文雅,安焕炯,马倩云,孙剑锋,王颉,王文秀. 基于顶空气相离子迁移谱的干腐病马铃薯挥发性成分分析. 食品科学. 2022(06): 317-323 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王福成,米思,李劲松,王雨行,王向红. 基于气相色谱-离子迁移谱技术分析不同包装条件对黄瓜风味的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(08): 296-304 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 马姗,于文龙,焦英帅,刘卫华,王向红. 不同减菌处理对凡纳对虾贮藏期间品质的影响. 食品科技. 2022(03): 116-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



