Method Establishment for the Detection of Black Spot Disease on Winter Jujubes Based on Optical Properties
-
摘要: 本研究旨在探究冬枣果实黑斑病过程中光学特性的变化,并筛选出病害检测的特征波长。采用单积分球检测系统结合反向倍加(IAD)算法测定冬枣果实在黑斑病过程中短-中波近红外区域(900~1650 nm)内光学吸收和散射特性,通过光学特性与品质指标间的相关性分析获得特征波长,最后通过近红外光谱对特征波长的有效性进行了验证。研究结果表明,随着黑斑病的发展,冬枣果实的失重率和a*呈现明显的上升趋势,L*、可溶性固形物及叶绿素含量则随贮藏时间下降。冬枣果实的吸收系数(μa)和约化散射系数(μs')均表现出明显的下降趋势。μa和μs'分别在1400~1650和900~1360 nm与病害程度(病斑面积)和部分品质指标(失重率、L*、a*、可溶性固形物和叶绿素)呈现高度相关。与全波长和基于算法获得的特征波长模型相比,基于光学特性优选的10个特征变量建立的冬枣黑斑病判别模型效果最佳,建模集和预测集总体正确率分别达到92.53%和92.35%,证明了短-中波近红外光学信号识别不同病害程度冬枣果实的潜力及基于光学特性优选的特征波长的有效性。Abstract: The objective of this study is to investigate the variations of optical properties during the progression of black spot disease and select the characteristic wavelengths for disease detection. The optical absorption and scattering properties were measured on winter jujubes using a single integrating sphere detection system in the band range of 900~1650 nm combined with inverse adding-doubling (IAD) algorithm in this study. The characteristic wavelengths were obtained depending on the correlation analysis between optical properties absorption and physicochemical indicators. Finally, the effectiveness of characteristic wavelengths was verified using near-infrared spectroscopy. The results indicated that a* and weight loss increased with storage time, while L*, soluble solids content and chlorophyll showed a consistent decrease. Both the absorption coefficient (μa) and the reduced scattering coefficient (μs') of the winter jujubes showed a significant downward trend with the development of black spot disease. The μa and μs' curves were highly correlated with disease extent (spot area) and some quality indicators (weight loss, L*, a*, soluble solids content and chlorophyll) in the 1400~1650 and 900~1360 nm, respectively. The discriminant models built based on the 10 characteristic variables selected by optical properties performed best compared with the models based on full wavelengths and algorithm-based characteristic wavelengths, with an overall accuracy of 92.53% and 92.35% for the calibration and prediction set, respectively. This study demonstrated the potential of the short- and mid-wave infrared optical signal in the disease detection on winter jujubes and the effectiveness of characteristic wavelengths on the basis of optical properties.
-
冬枣(Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv. Dongzao)作为品质最好的鲜食枣品种之一,不仅皮薄肉厚、口感脆甜,风味独特,同时还因含有人体所需的多种氨基酸、维生素、微量元素以及其他生物活性物质而深受喜爱[1]。然而冬枣果实在采后易受到病原菌的侵染而引起腐烂,造成品质下降、商业损失严重等问题。由链格孢菌引起的冬枣黑斑病是冬枣果实最主要的采后病害之一[2]。受到链格孢菌侵染后,果实表面形成黑褐色病斑,同时果实内部品质也易腐烂,容易导致传染性病害。因此对冬枣黑斑病的识别与检测至关重要。
为满足无损、快速的检测需求,基于光谱技术检测果实病害已取得一定进展。Pham等[3]建立基于高光谱成像技术的冬枣缺陷识别方法,识别准确率可达96.3%以上;Pan等[4]通过高光谱成像中光谱信息对香梨黑斑病进行监测与识别,对不同病害天数的香梨果实的判别正确率可达97.50%。光谱技术可以获取光与果实组织产生交互过程的光谱信息,但由于果实组织具有复杂的化学和结构组成,导致光在果实组织中的传输过程比较复杂[5],因此,上述光谱技术不足以探明病害过程中光在果实组织中的传输规律。
组织的光学特性参数可以用于表征光在组织中的传输规律,反映果实组织中化学及结构的变化[6-7],其中吸收系数(μa)和约化散射系数(μs')常被用于定量表征组织光学吸收和散射的特性。Sun等[8]发现桃果实病害过程中的光学特性参数与内部品质及微观结构高度相关。Wang等[9]发现在可见波段(550~750 nm)范围内病害洋葱的吸收系数高于健康样本。此外,吸收系数也被证明对梨褐心病的检测至关重要[10]。上述研究均表明在病害过程中,果实组织存在一定的光学响应且利用光学信号进行病害检测具有一定可行性,然而对于冬枣黑斑病过程中光学特性变化却鲜有报道。与此同时,特征波段的筛选有助于剔除冗余及具有共线性的光学信号,进而提高检测的精度和稳定性。
因此,本研究选取陕西大荔冬枣为研究对象,探究冬枣果实发生黑斑病过程中理化指标的变化,同时采用单积分球技术结合反向倍加算法(IAD)探究冬枣果实发生黑斑病过程中短-中波近红外波段(900~1650 nm)光学特性的变化。最后,通过与品质指标的关联研究挑选病害检测的特征波段,建立基于近红外光谱的冬枣果实不同病害程度的判别模型以验证特征波段的有效性,以期为冬枣黑斑病的检测提供理论基础和实际指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大荔冬枣 产地为陕西大荔,采摘次日购于南京众彩物流有限公司。选择白熟期(果面无红色),大小均匀,表面无机械伤及病虫害的果实。其中用于内部品质以及光学特性研究的样本采摘时间为2021年10月21日,用于近红外光谱采集的样本采摘时间为2022年8月6日;链格孢菌(Alternaria alternata) 购自广东省微生物研究所,由南京农业大学食品科学与技术学院实验室提供,在4 ℃条件下保藏;马铃薯琼脂(PDA)培养基 上海盛思生化科技有限公司;次氯酸钠(分析纯)、无水乙醇(分析纯) 广东光华科技股份有限公司。
CTHI-250B型恒温恒湿箱 施都凯设备公司;CR-10便携式色差计 日本美能达公司;PAL-1手持式糖度仪、Easy ACID F5型酸度计 日本爱拓公司;UV1800紫外分光光度计 日本岛津公司;积分球系统:ASBN-W100-L卤素灯 上海复享光学股份有限公司;F240SMA-B准直镜 美国Thorlabs公司;SW2520光谱仪 上海五铃光电科技公司;4P-GPS-033-SL积分球 美国Labsphere公司;NIR2500近红外光谱仪、Y型传输光纤、校正白板 上海复享光学股份有限公司;卤素光源 台湾超微光学股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌悬液的制备及试验样本的处理
将保藏的链格孢菌接种至PDA培养基,28 ℃、90% RH条件下活化7 d,相同条件下进行二次活化。将少量无菌水倒入活化好的带菌PDA平板,用无菌玻璃棒刮下链格孢菌孢子后,再用4层无菌纱布过滤以去除菌丝,制成链格孢菌孢子悬液。最后在显微镜下利用血球计数板将悬液中的孢子浓度调整至1×105 个/mL。
挑选成熟度一致、大小均匀、果面无病害缺陷的冬枣样本。用2 %(v/v)次氯酸钠溶液浸泡2 min后用无菌水冲洗后自然风干备用。将冬枣样本均分为3组,即健康组、无菌水对照组和病害组,每组各挑选约2 kg冬枣样品备用。病害组和无菌水对照组果实均在赤道部位用无菌注射器针头制造一个直径和深度均为2 mm的伤口,病害组果实在伤口处接种5 μL上述孢子悬液,以模拟链格孢菌的侵染;无菌水对照组果实在伤口处接种5 μL无菌水,用于排除接种过程中机械损伤对果实造成的影响;健康组样本不做任何处理,用于排除贮藏过程对果实的影响。制备好的样品被置于恒温恒湿箱(20 ℃,90% RH)贮藏5 d,在贮藏0、1、2、3、4、5 d分别对不同处理组样品进行光学特性以及理化指标的测定。为减少个体差异,每次取样选取病害程度相似的果实。对于用于近红外光谱采集的样品,处理方法、贮藏条件以及取样时间同上。
1.2.2 理化指标的检测
在贮藏过程中,用电子天平测量各组冬枣样本的重量;用十字交叉法[11]测量病害组冬枣果实病斑区域的直径并计算面积;采用美能达CR-100型色差计对冬枣果实接种部位亮度(L*)、红色度(a*)和黄色度(b*)进行测定;可溶性固形物含量(Soluble solid content,SSC)用PAL-1手持式糖度仪进行测定,将接种部位附近的果肉挤汁进行测定,测定结果用百分比(%)表示;可滴定酸含量(Titratable acid,TA)用PAL-Easy ACID F5型酸度计进行测定[12],将接种部位附近的果肉挤汁进行测定,测定结果用百分比(%)表示。果皮叶绿素含量参考Sun等[13]的方法,结果以每克冬枣果皮中含叶绿素的毫克数表示。
1.2.3 光学特性检测
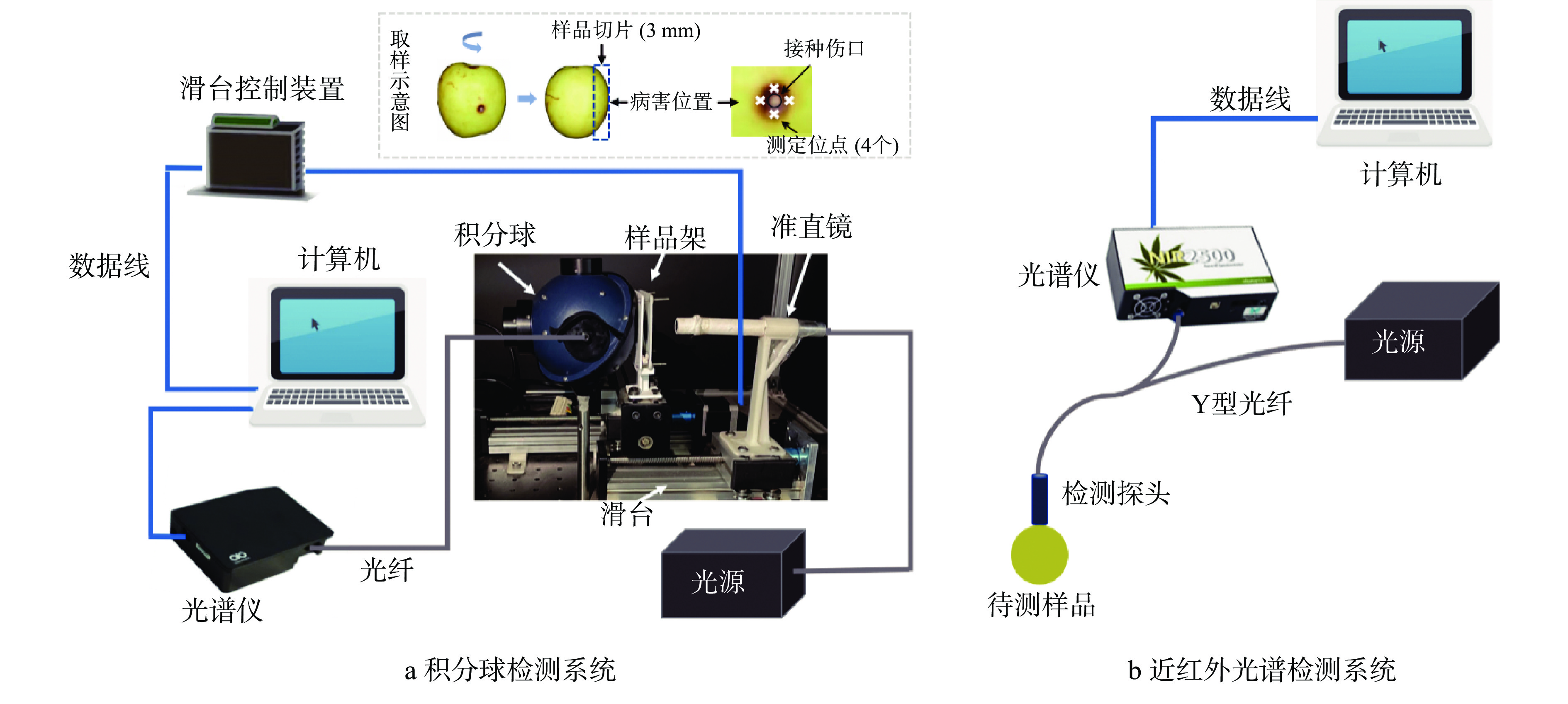
光学特性的检测采用的是实验室自主搭建的单积分球检测系统(图1a),主要由光源、准直镜、光谱仪、积分球、样品架、滑台控制器、滑台以及计算机构成。系统可以通过滑台调整样品架与积分球的相对位置来实现透射模式和反射模式的转换。系统在使用前已进行了精度验证[14]。
本研究选取赤道部位总厚度为3 mm的外层果实(包括果皮及果肉)(图1a)。每个样品切片用2片厚度为1 mm的石英玻璃片夹好后放置在积分球系统的样品架上,分别在透射和反射模式下获取冬枣样品的透射光谱和反射光谱,通过公式(1)和(2)分别计算反射率和透射率。最后利用IAD算法求解μa和μs′。每个冬枣果实的光学特性参数为与接种伤口相切的周围四个测定位点(图1a)光学特性参数的平均值。健康组(无伤口)在赤道部位对应位置进行检测。各处理组在每个取样时间测定5个样本并取平均值。
$$ \mathrm{R}=\frac{{\mathrm{R}}_{\mathrm{s}}-{\mathrm{R}}_{\mathrm{d}}}{{\mathrm{R}}_{\mathrm{r}}-{\mathrm{R}}_{\mathrm{d}}}\times {\mathrm{R}}_{\mathrm{w}} $$ (1) $$ \mathrm{T}=\frac{{\mathrm{T}}_{\mathrm{s}}-{\mathrm{T}}_{\mathrm{d}}}{{\mathrm{T}}_{\mathrm{r}}-{\mathrm{T}}_{\mathrm{d}}} $$ (2) 式中:R代表冬枣样品的反射率;Rs、Rd、Rr分别代表样品、暗背景和白背景的反射光强;Rw=0.98为白板反射率;T代表冬枣样品的透射率;Ts、Td、Tr分别为样品、暗背景和白背景光强。
1.2.4 近红外光谱检测
实验室自主搭建的点光源近红外光谱检测系统主要由光源、光谱仪、Y型光纤以及计算机组成(图1b)。通过检测探头对冬枣果实接种部位附近位点(与积分球检测位点相同)进行光谱采集,计算平均值作为单个样本的近红外光谱。每个取样点随机选取40个冬枣样本进行光谱采集,共采集240个不同病害程度的冬枣样本的光谱信息。按照约7:3的比例划分建模集(174个样本)与预测集(66个样本)。
1.3 数据处理
Pearson线性相关性分析在IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0软件中进行,绘图在OriginPro2022b软件中进行。近红外光谱的预处理、特征波长的筛选以及判别模型的建立在Matlab R2016a软件中进行。为消除噪声、基线漂移、背景等冗余信息来提高光谱信息的有效性和模型检测的准确性和稳定性,在用于模型的建立之前在本研究采用自动标准化(Autoscale)方法对光谱信息进行预处理。模型效果用判别正确率表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 冬枣品质变化
2.1.1 病斑面积以及果皮色差的变化
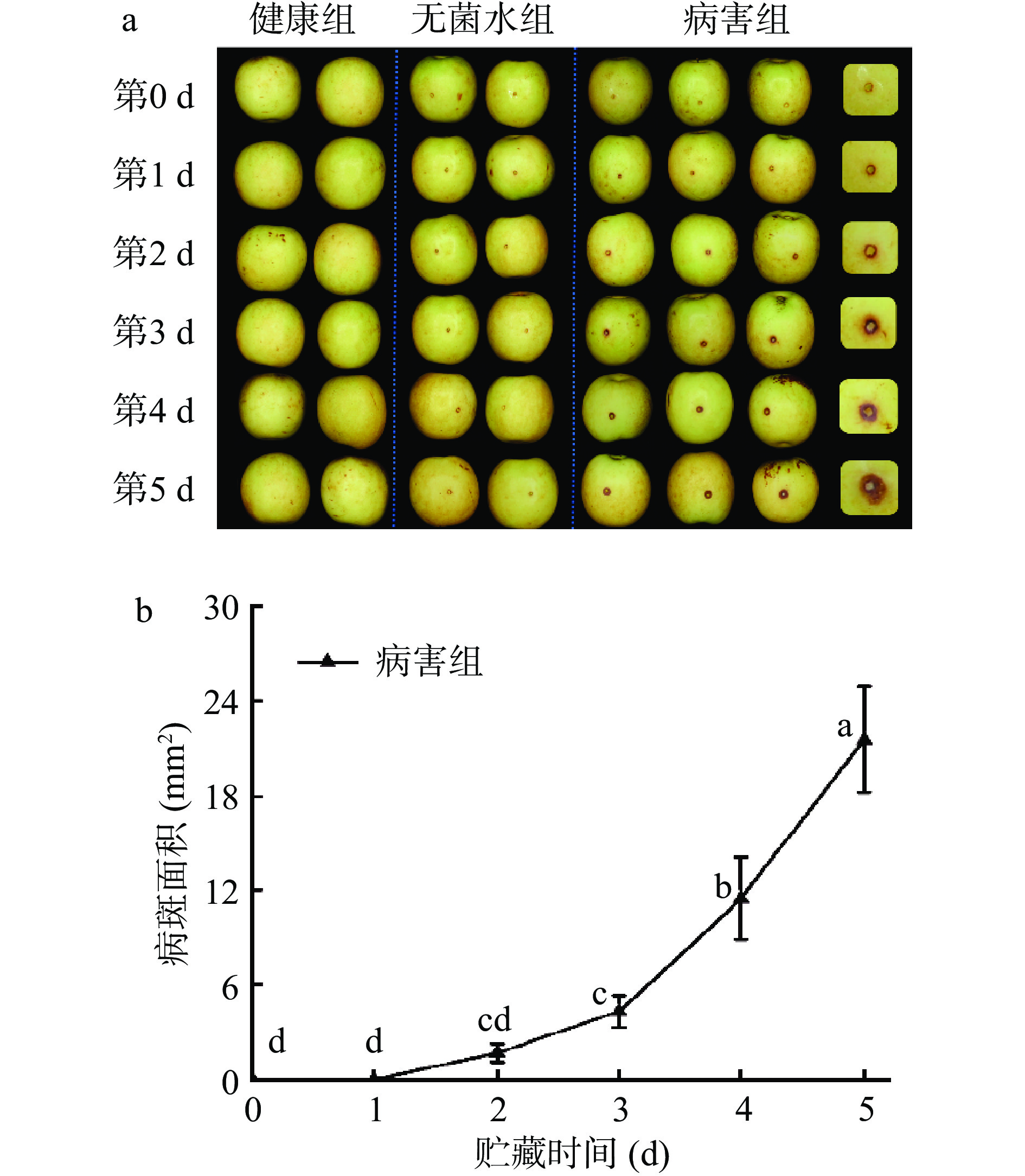
如图2所示,贮藏0~1 d病害组的冬枣样本接种部位附近还未发生明显变化(图2a),这是由于病原菌在此期间仍处于潜伏状态[15],然而随着病害程度的加深,接种部位逐渐形成黑褐色的病斑,在贮藏2~3 d病斑面积开始有显著变化(P<0.05)(图2b),且病斑面积随贮藏时间的延长逐渐增大,在贮藏4~5 d接种部位可以看到明显的菌丝,证明已经发生了严重病害。而健康组与无菌水对照组均未发生病害。三个处理组果皮色泽的变化如表1所示。由表可见,随着贮藏时间的延长三个处理组的L*值均呈现不同程度的下降,其中病害组的下降幅度最大。病害组的冬枣果皮L*值在贮藏3 d开始显著(P<0.05)低于两个未感染的处理组,在贮藏5 d降至57.64。研究表明,L*值越大则说明果实表面的颜色与新鲜的自然色越相近[16],L*值的下降也证实了果实新鲜度的不断下降。三个处理组的a*值则呈现不断上升的变化趋势,健康组和无菌水对照组的a*值分别从–3.6和–3.4升至–0.5和–0.2,病害组的a*值从–3.3升至5.3,在贮藏3 d开始呈现正值并且显著(P<0.05)高于两个对照组,这与上述观察一致,即从3 d开始接种位置处已出现肉眼可见的黑褐色病斑。然而对于b*值,随着果实病害的发生未发现明显的变化规律。
表 1 20 ℃贮藏期间冬枣样品颜色变化Table 1. Changes in skin color of winter jujubes during the storage at 20 ℃指标 时间(d) 健康组 无菌水对照组 病害组 L* 0 70.7±1.0Aa 68.3±2.2Aa 71.0±1.0Aa 1 70.0±1.2Aa 68.9±1.3Ab 68.4±0.6Ab 2 69.1±0.9Aab 68.2±0.5ABbc 67.1±1.1Bb 3 68.6±1.9Aab 67.8±0.5Abc 61.6±1.9Bc 4 67.6±0.8Aab 66.7±0.8Abc 57.4±1.4Bd 5 66.8±1.6Ab 65.9±1.4Ac 57.6±2.0Bd a* 0 –3.6±1.1Ac –3.4±1.1Ab –3.3±1.2Ac 1 –2.9±0.6Ac –2.0±0.2Aab –2.0±1.5Ab 2 –1.6±0.7Abc –1.4±1.2Aab –1.1±1.1Ab 3 –1.4±0.7Bbc –0.8±1.4Bab 2.5±1.3Aa 4 –1.0±0.8Bab –0.9±1.4Bab 3.2±0.2Aa 5 –0.5±0.5Ba –0.2±1.5Ba 5.3±1.1Aa b* 0 40.3±1.1Aa 41.1±0.8Aa 40.9±1.0Aa 1 40.7±0.7Aa 41.0±1.4Aa 40.3±1.5Aa 2 40.6±1.0Aa 41.1±1.1Aa 40.4±0.9Aa 3 40.3±1.1Aa 40.4±1.0Aa 40.7±0.9Aa 4 40.4±0.5Aa 40.7±1.4Aa 40.5±0.9Aa 5 40.0±0.7Aa 40.7±0.4Aa 39.2±1.2Aa 注:同行不同大写字母表示组别间存在显著差异(P<0.05),同列不同小写字母表示不同贮藏时间存在显著差异(P<0.05)。 2.1.2 失重率、SSC、TA及叶绿素含量的变化
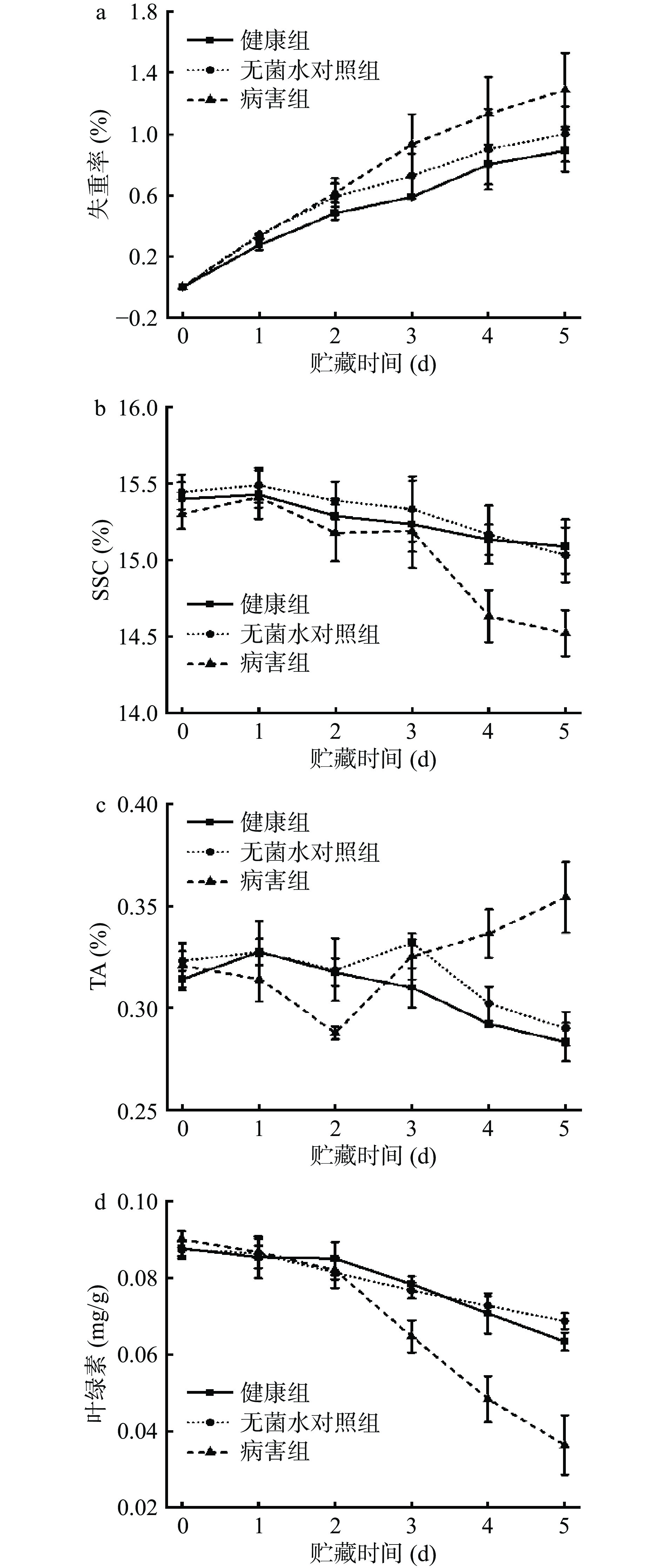
水分、糖、酸是冬枣果实的主要营养成分,在病害发生的过程中,病害果实的失重率上升明显,且在接种后3 d开始显著(P<0.05)高于两个未感染病原菌的处理组(图3a),原因在于冬枣果实受病原菌的侵染后呼吸作用增强,果实中的水分消耗增大造成了失重率的显著上升。冬枣果实的SSC在接种病原菌后4 d显著(P<0.05)下降(图3b),这表明在严重病害的情况下果实内部糖类物质的生成途径受阻且快速分解[17]。TA含量在冬枣果实发生病害的过程中呈现先下降后上升的变化趋势,这不同于健康组以及无菌水对照组整体下降的变化趋势(图3c),其原因可能在于:果实内部的酸类物质在病害的初期随着果实的成熟衰老,其含量缓慢减少,病害发生后,果实内部代谢途径受阻,果实内部的酸类物质难以转化成糖类以及其他物质而积累,造成了TA的异常上升,这与病害桃果实中TA含量的变化相似[13]。冬枣果实受到病原菌的侵染后果皮叶绿素含量呈现显著的下降趋势(图3d),尤其是从接种后3 d起叶绿素含量较健康组和无菌水对照组显著(P<0.05) 减少,这是由于真菌侵染破坏了细胞中的叶绿体结构,从而导致叶绿素含量快速下降,于此同时病害部位开始失绿并发生褐变[18-19]。未感染病原菌的冬枣果皮中的叶绿素含量则逐步小幅减少,这表明冬枣在正常的成熟衰老过程中叶绿素也会逐渐分解。
2.1.3 病害冬枣理化指标的相关性分析
根据理化指标的变化情况可以看出,感染链格孢菌的冬枣果实的物理化学性质对比未感染的样本有显著差异且存在更大范围的波动,这说明病原菌侵染会显著影响果实的物理特性及化学组成。为研究病害发生过程中各理化指标间的关联性,对病害冬枣果实病斑面积以及其他品质指标的变化进行Pearson相关性分析。由表2可知,病害过程中水分的损失(失重率)与果皮颜色(L*、a*)(r=−0.974,P<0.01)以及叶绿素含量(r=−0.981,P<0.01)的变化密切相关,这与文献中报道的研究结果相一致[20]。于此同时,病斑面积作为病害程度的直观表征之一,与叶绿素含量的相关性最高(r=−0.956,P<0.01),这说明叶绿素是与病害最相关的指标,这与桃果实的研究结果相一致[13]。此外病斑面积与果皮色泽(L*、a*)、失重率和SSC均呈现显著(P<0.05)的线性相关,说明这些指标在病害发展过程中变化显著,可在一定程度上反映病害程度。
表 2 黑斑病冬枣样品各指标间相关性分析结果Table 2. Correlation analysis on physical and chemical indicators of winter jujubes with black spot disease指标 病斑面积 L* a* 失重率 SSC TA 叶绿素 病斑面积 1 –0.859* 0.907* 0.849* –0.947** 0.811 –0.956** L* 1 –0.974** –0.974** 0.891* –0.706 0.970** a* 1 0.974** –0.875* 0.743 –0.981** 失重率 1 –0.854* 0.591 –0.946** SSC 1 –0.727 0.947** TA 1 –0.799 叶绿素 1 注:由于病害组冬枣的果皮b*值未发生显著变化,因此未列入相关性分析;*和**分别表示显著相关(P<0.05)和极显著相关(P<0.01)。 2.2 光学特性的变化及其与理化指标间的相关性研究
2.2.1 光学吸收及散射特性的变化
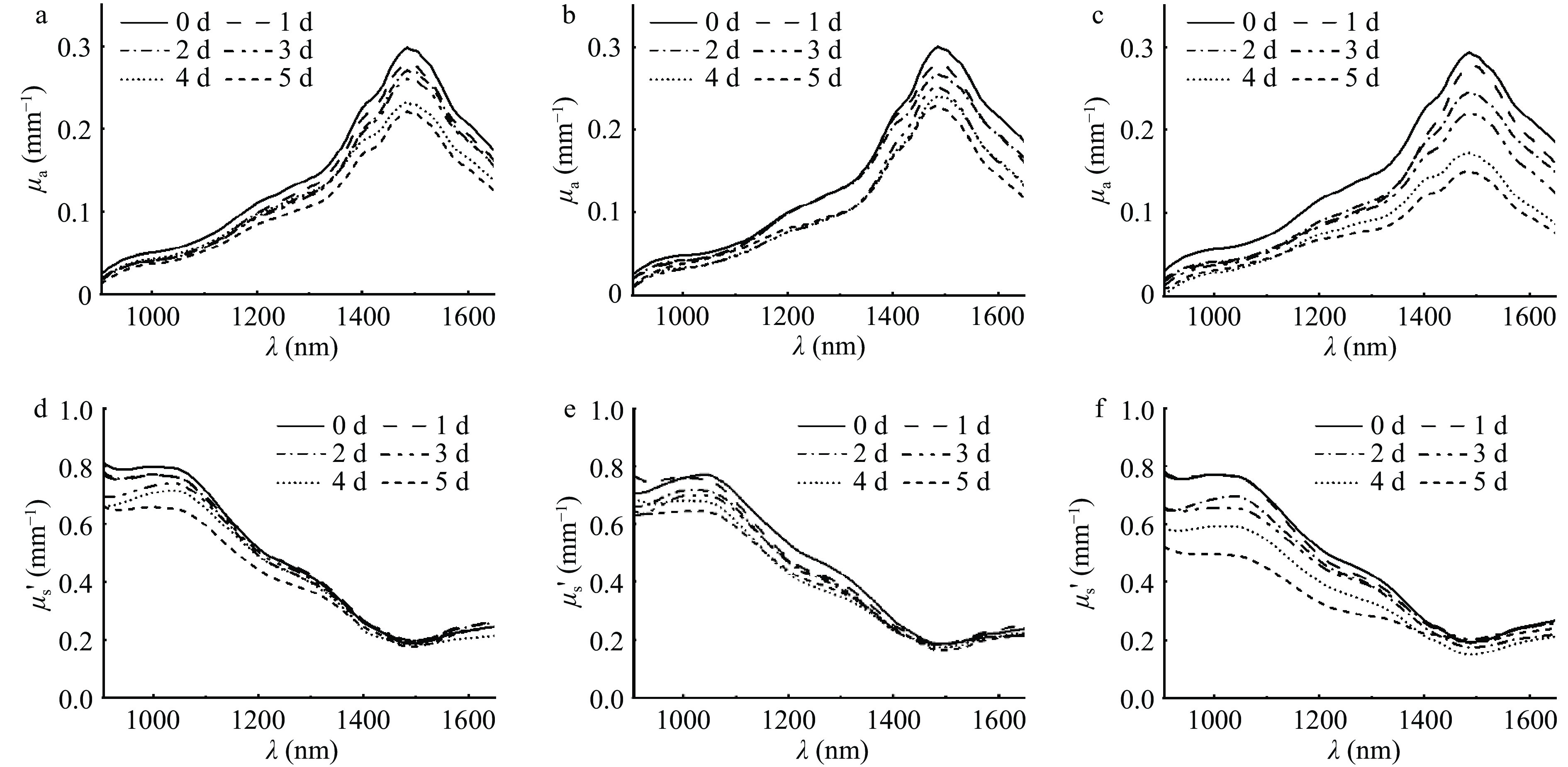
如图4a~图4c所示,三个处理组在不同贮藏时间的μa平均光谱曲线形状相似。在1480 nm附近呈现明显的水的吸收峰,与苹果[21]、梨[22]等水果的吸收系数类似。病害组冬枣果实的μa曲线随着贮藏时间的延长整体呈现明显的下降趋势,1480 nm处降幅最大,从贮藏初期的0.2708下降到贮藏5 d的0.1411 mm−1,在贮藏5 d显著(P<0.05) 低于健康组(μa=0.2033 mm−1)和无菌水对照组(μa=0.2051 mm−1)。这是由于病原菌的侵染导致水分的流失,与2.1.2中得到的结论相一致。而健康组和无菌水对照组的冬枣果实的μa仅出现了略微下降且不同贮藏时间下存在重叠。由图4d~图4f可知冬枣果实的μs'远高于μa,范围在0.2~0.8 mm−1之间,这是由于水果组织属于浑浊介质,其散射特性远大于吸收特性。μs'曲线没有明显的特征峰,且符合米氏散射定律,即μs'随波长的增加而减小[23]。随着贮藏时间的延长,病害组的冬枣果实的μs'呈现大幅减小的变化趋势,这是由于细胞壁是引起光散射的重要因素,然而在病原菌侵染的过程中细胞受到损伤的同时原本致密的细胞壁结构被严重破坏,导致了散射作用的降低[8]。结合两种光学特性参数的曲线图可以看出在900~1650 nm的波段范围内,随着波长的增加,冬枣果实的散射特性逐渐减弱,而吸收系数逐渐升高,最终占据主导地位。此外,健康组和无菌水对照组的吸收系数和约化散射系数的光谱曲线相似且随贮藏时间的延长变化幅度均较小,证明本研究中接种造成机械伤口产生的影响可以忽略。
2.2.2 光学特性与理化指标的相关性研究及特征波长筛选
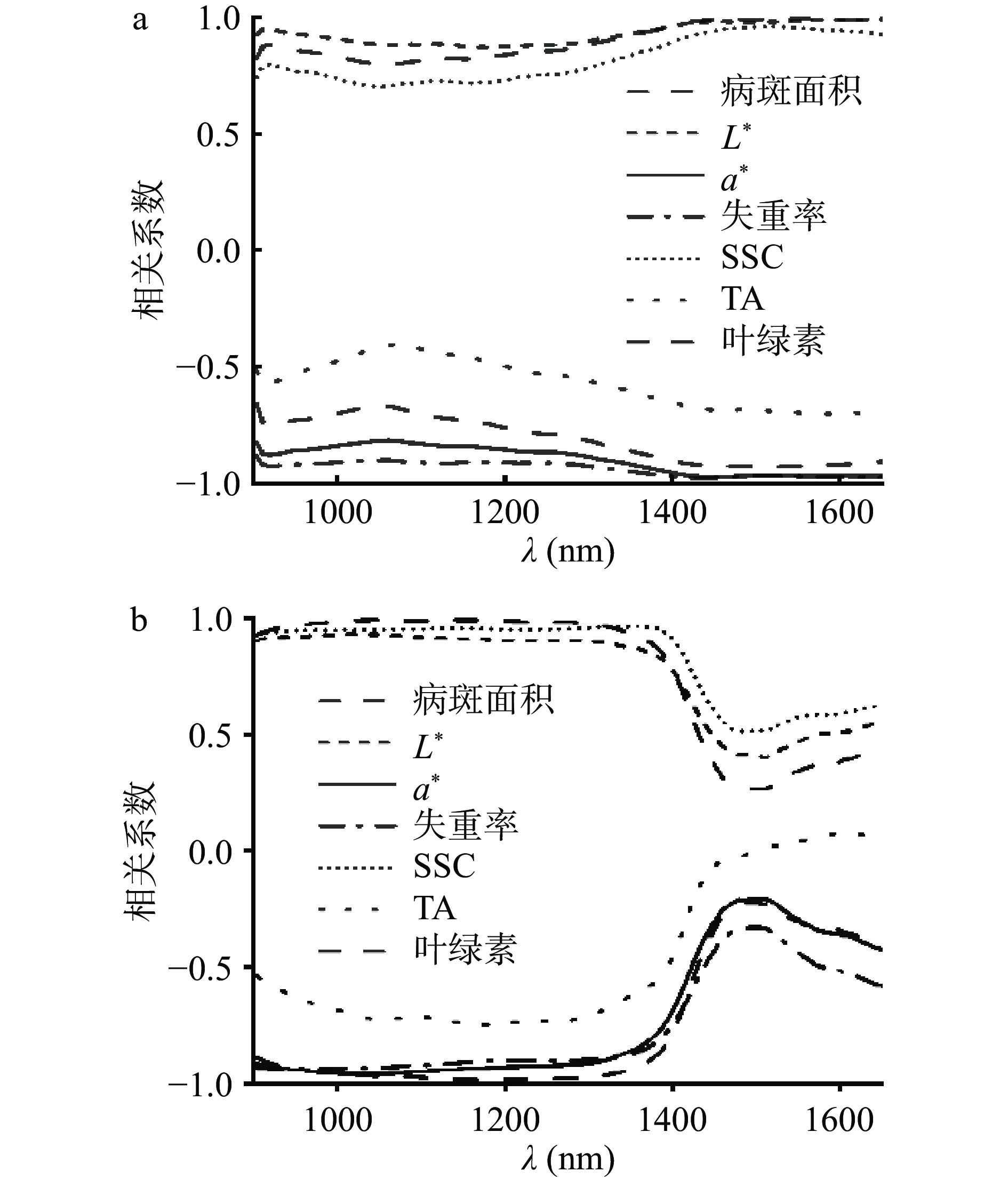
考虑到健康组和无菌水对照组的光学特性参数变化幅度不大,且本文重点在于探究病害期间的光学特性变化,因此仅对病害组的冬枣样品的光学特性与病斑面积以及理化指标进行了相关性分析。全波长范围内(900~1650 nm)病害组的冬枣样品各理化指标与光学特性参数的相关性曲线如图5所示。吸收和散射两种光学特性参数与L*、SSC和叶绿素含量呈正相关,与病斑面积、a*、失重率和TA呈负相关。
由图5a可知,所有品质指标在1400 nm附近与μa的相关系数(r)达到最大值并在1400~1650 nm波段范围内保持在稳定水平。在此波段内,除TA外其他指标均与μa高度相关,这表明在这一波段下光学吸收特性可以反映冬枣果实这些理化特性的变化,与2.1.3中提到的病斑面积、L*、a*、失重率、SSC以及叶绿素含量间的相关性结果相一致。在上述波段范围内,μa与叶绿素含量、L*、失重率以及a*的相关性最高,与Sun等[13]的研究结果一致。相关系数平均值分别为0.9831、0.9770、−0.9751以及−0.9717。前文的分析中得出叶绿素、L*、失重率以及a*之间存在极显著(P<0.01)的相关性能很好得解释这一现象,这些指标与μa的相关性系数的绝对值在1453、1498、1511和1557 nm处达到最大值,证明在这些波段下光学特性与品质变化的相关性最强。其中,a*和失重率在1453 nm处的相关系数达到最大值,分别是–0.9756和–0.9786;病斑面积(r=–0.9318)和SSC(r=0.9544)在1511 nm处的相关性最强;L*和叶绿素含量分别在1498和1556 nm处与μa的相关性最强,相关系数分别为0.9734和0.9878。在900~1360 nm波段范围内,μs'与除TA外的各指标高度相关(图5b),其与病斑面积的相关性最高,其次是叶绿素含量(平均相关系数分别为0.9700和0.9664),与失重率、L*、a*、SSC之间的平均相关系数的绝对值均在0.9088以上,一定程度上说明在这些波长下μs'能够较好地反映病害的发展。μs'与各品质指标的相关性系数的绝对值最大值分别出现在933、1020、1034、1047、1162和1360 nm处,对应的品质指标为失重率(r=−0.9451)、L*(r=0.9259)、a*(r=−0.9649)、叶绿素(r=0.9800)、病斑面积(r=−0.9901)和SSC(r=0.9581)。
光学特性与理化指标间的相关性分析结果印证了2.2.1中的实验结果,即散射在900~1360 nm占主导地位,然而随着波长的增大果实组织对于光的吸收作用逐渐增强,1400~1650 nm波段的吸收系数包含更多反映果实组织的物理化学性质变化的信息,这证明了在短-中波近红外波段范围内光学技术在冬枣病害检测中的可行性。与此同时,由全波段的相关性分析可知,光学特性参数与病害发展过程中各品质指标的相关性系数在933、1020、1034、1047、1162、1360、1453、1498、1511和1557 nm波长处有最大值,证明这些波段下的光学信息与病害发展过程高度相关,优选为基于光学技术检测冬枣黑斑病的特征波长,在后续的研究中将通过近红外光谱技术对基于光学特性筛选到的特征波长的有效性进行验证。
2.3 基于近红外光谱的特征波长验证及病害冬枣的判别
在实际检测中全波长光谱通常存在易引入噪声、含有冗余信息、计算量大等缺点,造成检测效率以及准确率的降低[24],特征波长的筛选有利于有效信息的提取,同时简化模型、减少计算量,这说明特征波长的科学性和有效性至关重要。在2.2.2部分的相关性分析中筛选获得了10个特征波长,本节将采用无损的近红外光谱技术对光学特性优选波长的有效性进行验证,同时采用算法进行特征波长的筛选,将基于光学特性得到的特征波长建立的判别模型结果与全波长和基于算法得到的特征波长得到的检测结果对比总结,以期为光学技术检测冬枣黑斑病提供信息指导。
2.3.1 光谱分析
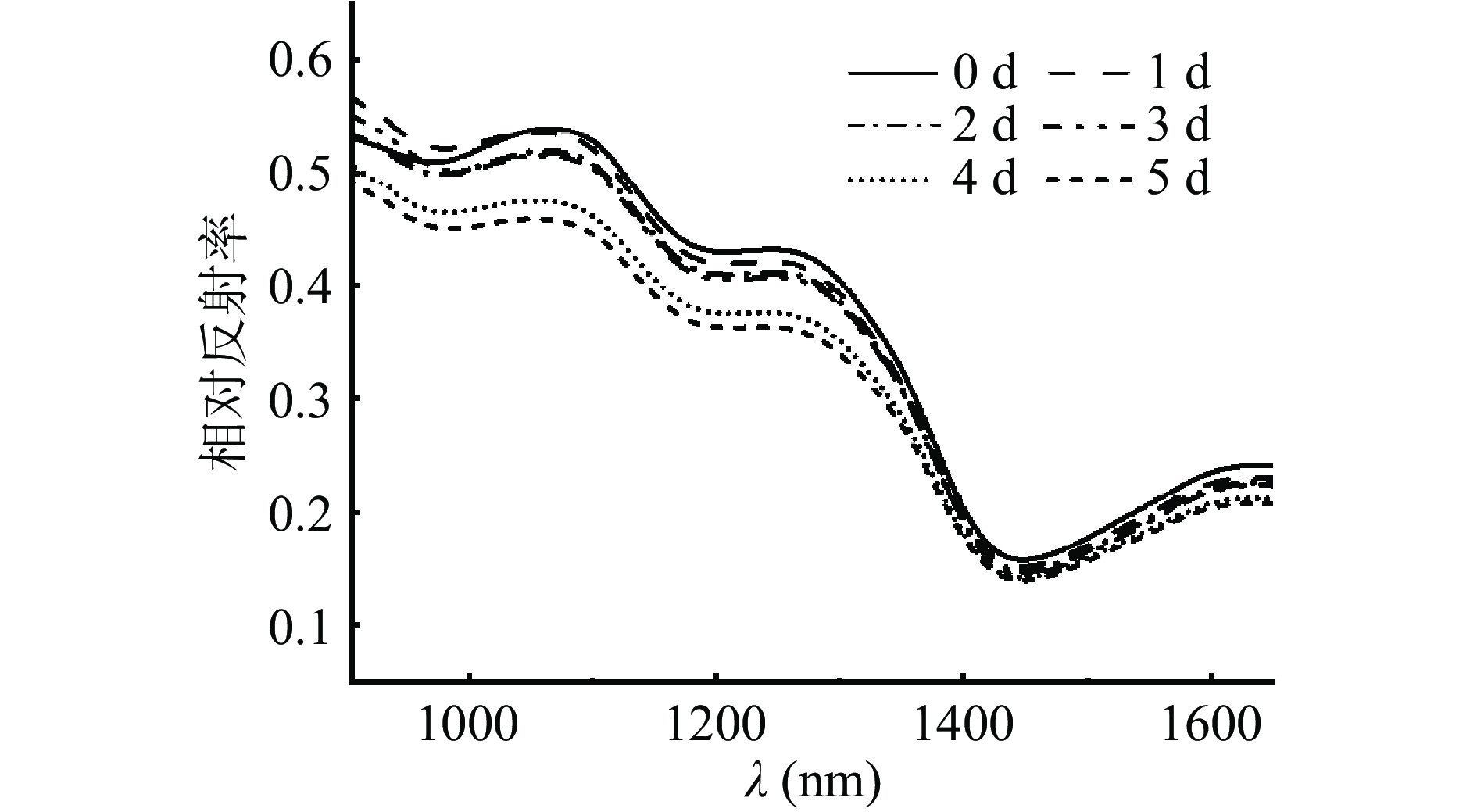
接种后不同贮藏天数的冬枣样品的近红外光谱曲线如图6所示。冬枣样品的光谱在900~1650 nm区域内主要呈现3个水的吸收峰,分别位于980 nm(O-H二级倍频)、1190 nm(O-H键的合频吸收峰)以及1440 nm(O-H键伸缩振动一级倍频)[25-26]。上述这些波长在水果果实内部品质及病害检测中常被认为是近红外区域的关键波段,如在苹果[27]、梨[28]等的果实检测中起到了重要作用。随着病害的发展,冬枣果实的相对反射率呈现逐步下降趋势,尤其是在接种病原菌后贮藏4 d起呈现明显的下降趋势。这主要是由于随着果实组织结构的逐渐受损,光将被更多地吸收和散射,造成了反射光的减少[29]。在西红柿的相关研究研究中也获得了类似的结果[30]。与此同时,表面亮度的降低也导致了反射光谱的下降,这也印证了2.1.1部分果皮L*随病害程度的加深不断降低这一发现。为更好地对不同病害程度的果实进行判别,同时结合病害发展规律(图2),将贮藏0~1 d的冬枣样品定义为未发生病害的样本,贮藏2~3 d的样本定义为轻微病害,贮藏4~5 d的样本定义为严重病害。
2.3.2 特征波段的筛选
通过2.2.2可知,病害期间光学特性参数与不同品质指标间在一定波长范围内存在较高的相关性,相关性系数的大小可以表征光学特性与品质变化的关联性,将光学特性与品质指标间的存在最强相关的波长定义为特征波长,在900~1650 nm范围优选10个特征波长,分别是933、1020、1034、1047、1162、1360、1453、1498、1511和1557 nm。
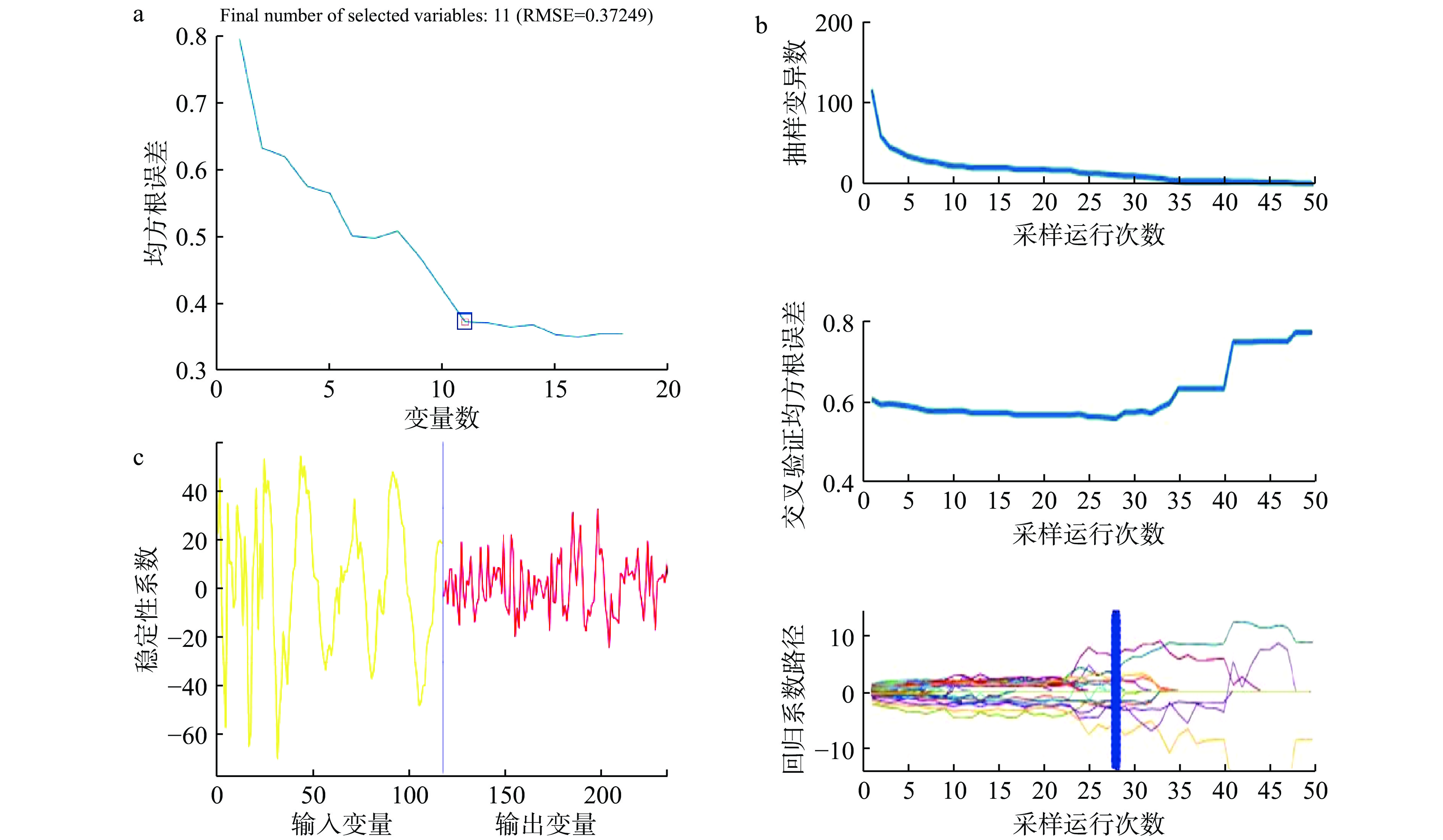
为更好得验证基于光学特性参数得到的特征波长的有效性和可靠性,本研究还引入3种特征波长筛选算法,分别是连续投影算法(SPA)、竞争性自适应重加权算法(CARS)和无信息变量消除法(UVE)对全波长下的光谱数据进行特征波长的筛选。图7展示了3种算法筛选特征波长的过程。
SPA是一种前向的特征波段筛选算法,提取的特征波段共线性小、冗余度低[24]。均方根误差的大小是SPA算法挑选特征变量的依据,由图7a可见均方根误差在特征变量数为9时处在较低水平且随变量数的增多均方根误差趋于平稳,因此SPA算法在900~1650 nm波段范围内共选取到11个特征波长,分别是907、913、920、933、966、985、1024、1186、1289、1379和1411 nm。
CARS算法的原理与达尔文的“适者生存”的原则相似[31],多次重复筛选将不适应模型的波长删除,最终得到最优特征波长组合,由图7b可见在采样运行次数为28时,交叉验证均方根误差最小说明在后面的采样中开始剔除了关键信息[32]。CARS算法在900~1650 nm波段范围内共选取到9个特征波长,分别是907、926、966、979、1005、1011、1031、1102及1128 nm。
UVE算法筛选特征波段的过程如图7c所示,竖线左右两侧分别为全光谱117个波数及117个随机变量的稳定性分布曲线,两条水平虚线代表保留阈值的上下限,虚线内的波长作为冗余波长变量被剔除[33],仅保留在水平虚线外侧的有效变量,UVE算法共筛选了38个特征波长,分别是907、920、926、933、966、1005、1011、1030、1056、1063、1070、1076、1096、1102、1109、1115、1146、1135、1173、1180、1186、1193、1180、1186、1193、1199、1206、1264、1360、1418、1424、1475、1482、1488、1495、1501、1584、1590 nm。
2.3.3 基于全波长及特征波长的病害冬枣的判别模型的建立
由表3可知,对于PLS-DA模型,基于光学特性优选变量建立的判别模型具有与全波长模型相当的判别效果,建模集和预测集的正确率分别达到了91.95%和90.84%;对于SVM-DA模型,基于光学特性优选变量模型具有最佳的判别正确率,建模集和预测集的正确率分别为92.53%和92.35%,较全波长模型的判别效果更优,这说明光学特优选变量剔除无关变量的同时获得了较为全面有效的信息,证明了利用光学特性获得的特征波长的有效性。
表 3 基于全波长和特征波长的冬枣病害判别的PLS-DA及SVM-DA模型结果Table 3. Discrimination accuracy of diseased winter jujubes at different levels based on PLS-DA and SVM-DA models using the spectral information at the full wavelengths and the characteristic wavelengths模型 变量 建模集正确率(%) 预测集正确率(%) 无明显病害 轻微病害 严重病害 总体 无明显病害 轻微病害 严重病害 总体 PLS-DA 全波长 (117) 98.28 86.21 89.66 91.38 95.24 90.91 86.36 90.84 光学特性优选
变量 (10)98.28 86.21 91.38 91.95 95.24 86.36 90.91 90.84 SPA (11) 98.28 91.38 91.38 93.68 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 CARS (9) 98.28 86.21 93.10 92.53 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 UVE (38) 98.28 84.48 89.66 90.80 95.24 81.82 90.91 89.32 SVM-DA 全波长 (117) 98.28 89.66 91.34 93.10 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 光学特性优选
变量 (10)98.28 87.93 91.38 92.53 95.24 86.36 95.46 92.35 SPA (11) 96.55 86.21 81.03 87.93 95.24 77.27 86.36 86.29 CARS (9) 98.28 89.66 93.10 93.68 95.24 86.36 90.91 90.84 UVE (38) 98.28 86.21 91.38 91.95 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 注:特征波长一栏中括号内数值代表变量数。 基于光学特性优选变量建立的判别模型效果略优于基于3种算法获得的特征波长的模型。对比利用光学特性和利用算法获得的特征波长,发现光学特性优选波段基本跨越了全波段范围(900~1650 nm),并多数分布在近红外光谱曲线的3个吸收谷(980、1190和1450 nm)附近。然而利用SPA算法和CARS算法得到的特征波长全部分布在1400 nm以前的波长范围,完全丢失了1400~1650 nm范围内的光谱信息,这可能是导致模型效果略差的原因[34]。UVE算法获得的特征波长虽跨越了全波长范围,且在3个吸收峰附近波长处均筛选到了特征波长,然而基于UVE算法获取的特征变量数(38)远大于其他方法获得的特征波长数,因此基于UVE算法获取的特征波长可能带入了冗余的信息,因此在两个模型中都未获得比光学特性优选变量模型更好的判别效果。由此可见,在光谱检测中特征波长的筛选是至关重要的。利用光学特性优选的10个波长(933、1020、1034、1047、1162、1360、1453、1498、1511、1557 nm)对应的光谱信息能够剔除无关变量并有效反映总体信息,可以实现冬枣黑斑病发病过程病害的识别和监测,证明了利用光学特性筛选的特征波长的科学性和有效性。
3. 结论
本研究探究了冬枣黑斑病发生过程中果实理化指标以及其在短-中波近红外区域内光学特性(吸收和散射)的变化规律,同时通过相关性分析筛选出特征波长,并由此建立基于近红外光谱信息的冬枣病害判别模型以验证特征波长的有效性。结果表明,随着病害加深,在900~1650 nm波段范围冬枣果实的μa和μs'均呈下降趋势。μa和μs'分别在1400~1650 nm和900~1360 nm波段范围与病斑面积、失重率、L*、a*、SSC以及叶绿素含量高度相关,证实了光学信号在冬枣病害检测中的可行性,同时通过相关系数筛选得到10个优选波长(933、1020、1034、1047、1162、1360、1453、1498、1511、1557 nm)。优选波长有效性的验证试验结果表明,基于光学特性优选波段建立的模型在两种模型(PLS-DA和SVM-DA)中均表现出最佳的判别效果,建模集和预测集的正确率分别达到了92.53%和92.35%,这为特征波长的有效性提供了有力证明,为基于光学的无损检测方法识别冬枣病害奠定了理论基础。
-
表 1 20 ℃贮藏期间冬枣样品颜色变化
Table 1 Changes in skin color of winter jujubes during the storage at 20 ℃
指标 时间(d) 健康组 无菌水对照组 病害组 L* 0 70.7±1.0Aa 68.3±2.2Aa 71.0±1.0Aa 1 70.0±1.2Aa 68.9±1.3Ab 68.4±0.6Ab 2 69.1±0.9Aab 68.2±0.5ABbc 67.1±1.1Bb 3 68.6±1.9Aab 67.8±0.5Abc 61.6±1.9Bc 4 67.6±0.8Aab 66.7±0.8Abc 57.4±1.4Bd 5 66.8±1.6Ab 65.9±1.4Ac 57.6±2.0Bd a* 0 –3.6±1.1Ac –3.4±1.1Ab –3.3±1.2Ac 1 –2.9±0.6Ac –2.0±0.2Aab –2.0±1.5Ab 2 –1.6±0.7Abc –1.4±1.2Aab –1.1±1.1Ab 3 –1.4±0.7Bbc –0.8±1.4Bab 2.5±1.3Aa 4 –1.0±0.8Bab –0.9±1.4Bab 3.2±0.2Aa 5 –0.5±0.5Ba –0.2±1.5Ba 5.3±1.1Aa b* 0 40.3±1.1Aa 41.1±0.8Aa 40.9±1.0Aa 1 40.7±0.7Aa 41.0±1.4Aa 40.3±1.5Aa 2 40.6±1.0Aa 41.1±1.1Aa 40.4±0.9Aa 3 40.3±1.1Aa 40.4±1.0Aa 40.7±0.9Aa 4 40.4±0.5Aa 40.7±1.4Aa 40.5±0.9Aa 5 40.0±0.7Aa 40.7±0.4Aa 39.2±1.2Aa 注:同行不同大写字母表示组别间存在显著差异(P<0.05),同列不同小写字母表示不同贮藏时间存在显著差异(P<0.05)。 表 2 黑斑病冬枣样品各指标间相关性分析结果
Table 2 Correlation analysis on physical and chemical indicators of winter jujubes with black spot disease
指标 病斑面积 L* a* 失重率 SSC TA 叶绿素 病斑面积 1 –0.859* 0.907* 0.849* –0.947** 0.811 –0.956** L* 1 –0.974** –0.974** 0.891* –0.706 0.970** a* 1 0.974** –0.875* 0.743 –0.981** 失重率 1 –0.854* 0.591 –0.946** SSC 1 –0.727 0.947** TA 1 –0.799 叶绿素 1 注:由于病害组冬枣的果皮b*值未发生显著变化,因此未列入相关性分析;*和**分别表示显著相关(P<0.05)和极显著相关(P<0.01)。 表 3 基于全波长和特征波长的冬枣病害判别的PLS-DA及SVM-DA模型结果
Table 3 Discrimination accuracy of diseased winter jujubes at different levels based on PLS-DA and SVM-DA models using the spectral information at the full wavelengths and the characteristic wavelengths
模型 变量 建模集正确率(%) 预测集正确率(%) 无明显病害 轻微病害 严重病害 总体 无明显病害 轻微病害 严重病害 总体 PLS-DA 全波长 (117) 98.28 86.21 89.66 91.38 95.24 90.91 86.36 90.84 光学特性优选
变量 (10)98.28 86.21 91.38 91.95 95.24 86.36 90.91 90.84 SPA (11) 98.28 91.38 91.38 93.68 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 CARS (9) 98.28 86.21 93.10 92.53 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 UVE (38) 98.28 84.48 89.66 90.80 95.24 81.82 90.91 89.32 SVM-DA 全波长 (117) 98.28 89.66 91.34 93.10 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 光学特性优选
变量 (10)98.28 87.93 91.38 92.53 95.24 86.36 95.46 92.35 SPA (11) 96.55 86.21 81.03 87.93 95.24 77.27 86.36 86.29 CARS (9) 98.28 89.66 93.10 93.68 95.24 86.36 90.91 90.84 UVE (38) 98.28 86.21 91.38 91.95 95.24 86.36 86.36 89.32 注:特征波长一栏中括号内数值代表变量数。 -
[1] 高伟, 李秀莲. 冬枣采后黑斑病病原菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 农业开发与装备,2016,172(4):80−81. [GAO W, LI X L. Isolation and identification of postharvest black spot pathogens of jujube[J]. Agricultural Development and Equipment,2016,172(4):80−81. GAO W, LI X L. Isolation and identification of postharvest black spot pathogens of jujube[J]. Agricultural Development and Equipment, 2016, 172(4): 80-81.
[2] 张乐乐, 常璐璐, 王小佳, 等. 褪黑素诱导采后冬枣抗黑斑病的研究[J]. 保鲜与加工,2021,21(12):1−9. [ZHANG L L, CHANG L L, WANG X J, et al. Study on resistance to Alternaria rot of postharvest winter jujube induced by melatonin[J]. Storage and Process,2021,21(12):1−9. ZHANG L L, CHANG L L, WANG X J, et al. Study on resistance to Alternaria rot of postharvest winter jujube induced by melatonin[J]. Storage and Process, 2021, 21(12): 1-9.
[3] PHAM Q T, LIOU N S. The development of on-line surface defect detection system for jujubes based on hyperspectral images[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2022,194:106743. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2022.106743
[4] PAN T T, CHYNGYZ E, SUN D W, et al. Pathogenetic process monitoring and early detection of pear black spot disease caused by Alternaria alternata using hyperspectral imaging[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2019,154:96−104. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.04.005
[5] 张连顺, 张春平, 王新宇, 等. 生物组织光学特性参数无损测量实验研究[J]. 光电子激光,2004(6):746−749. [ZHANG L S, ZHANG C P, WANG X Y, et al. Experiment research for non-invasive measurement of optical parameters of biological tissue[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics Laser,2004(6):746−749. ZHANG L S, ZHANG C P, WANG X Y, et al. Experiment research for non-invasive measurement of optical parameters of biological tissue[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics Laser, 2004(6): 746-749.
[6] 潘磊庆, 方莉, 周彬静, 等. 光学参数测量系统和原理及其在果蔬品质检测方面的研究进展[J]. 南京农业大学学报,2021,44(3):401−411. [PAN L Q, FANG L, ZHOU B J, et al. System and principle of optical properties measurement and advances on quality detection of fruits and vegetables[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2021,44(3):401−411. PAN L Q, FANG L, ZHOU B J, et al. System and principle of optical properties measurement and advances on quality detection of fruits and vegetables[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021, 44(3): 401-411.
[7] WEI K, MA C, SUN K, et al. Relationship between optical properties and soluble sugar contents of apple flesh during storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2020,159:111021. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111021
[8] SUN Y, LU R, WANG X. Evaluation of fungal infection in peaches based on optical and microstructural properties[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2020,165:111181. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111181
[9] WANG W, LI C, GITAITIS R D. Optical properties of healthy and diseased onion tissues in the visible and near-infrared spectral region[J]. Transactions of the Asabe,2014,57:1771−1782.
[10] ZERBINI P E, GRASSI M, CUBEDDU R, et al. Nondestructive detection of brown heart in pears by time-resolved reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2002,25:87−97. doi: 10.1016/S0925-5214(01)00150-8
[11] 陈维维, 赵晓梅, 叶凯, 等. 草酸处理对库尔勒香梨黑斑病抑制效果的研究[J]. 保鲜与加工,2016,16(2):38−43. [CHEN W W, ZHAO X M, YE K, et al. Inhibition effect of oxalic acid treatment on black spot of Kuerle pear[J]. Storage and Process,2016,16(2):38−43. CHEN W W, ZHAO X M, YE K, et al. Inhibition effect of oxalic acid treatment on black spot of Kuerle pear [J]. Storage and Process, 2016, 16(2): 38-43.
[12] 张琴, 周丹丹, 彭菁, 等. 油桃采后结合态香气变化规律及其与可溶性糖的关联性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(6):206−214. [ZHANG Q, ZHOU D D, PENG J, et al. Changes of bound aroma compounds and their relationship between soluble sugars in nectarines during postharvest storage[J]. Food Science,2021,42(6):206−214. ZHANG Q, ZHOU D D, PENG J, et al. Changes of bound aroma compounds and their relationship between soluble sugars in nectarines during postharvest storage[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(6): 206-214.
[13] SUN Y, LU R, PAN L, et al. Assessment of the optical properties of peaches with fungal infection using spatially-resolved diffuse reflectance technique and their relationships with tissue structural and biochemical properties[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,321:126704. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126704
[14] MA C, FENG L, PAN L, et al. Relationships between optical properties of peach flesh with firmness and tissue structure during storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2020,163:111134. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111134
[15] CHO J S, LEE H J, PARK J H, et al. Image analysis to evaluate the browning degree of banana (Musa spp.) peel[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:1028−1033. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.103
[16] 何萌, 王丹, 马越, 等. 不同清洗剂对鲜切马铃薯贮藏过程品质变化的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(15):328−331. [HE M, WANG D, MA Y, et al. Effect of fresh-cut potatoes after washing with different sanitizers on storage quality change[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(15):328−331. HE M, WANG D, MA Y, et al. Effect of fresh-cut potatoes after washing with different sanitizers on storage quality change[J] Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(15): 328-331.
[17] WAND L, WU H, QIN G, et al. Chitosan disrupts Penicillium expansum and controls postharvest blue mold of jujube fruit[J]. Food Control,2014,41:56−62. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.12.028
[18] HAYAMA H, TATSUKI M, ITO A, et al. Ethylene and fruit softening in the stony hard mutation in peach[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2006,41:16−21. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2006.03.006
[19] 孙晔. 基于高光谱成像技术的水蜜桃果实病害检测研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2018: 81 SUN Y. Detection of fungal infection in honey peaches using hyperspectral imaging technology[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2018: 81.
[20] 胡新宇. 荔枝采后生理与常温保鲜的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2001: 2−3 HU X Y. Postharvest physiology and room temperature preservation of litchi[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2001: 2−3.
[21] FANG L, WEI K, FENG L, et al. Optical absorption and scattering properties at 900~1650 nm and their relationships with soluble solid content and soluble sugars in apple flesh during storage[J]. Foods,2020,9(12):1881. doi: 10.3390/foods9121881
[22] XIA Y, TIAN X, LI J, et al. Prediction and comparison of models for soluble solids content determination in 'Ya' pears using optical properties and diffuse reflectance in 900-1700 nm spectral region[J]. Ieee Access,2019,7:179199−179211. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2959028
[23] LU R, CEN H, HUANG, M, et al. Spectral absorption and scattering properties of normal and bruised apple tissue[J]. Transactions of the Asabe,2010,53:263−269. doi: 10.13031/2013.29491
[24] 戈永慧, 宋进, 潘磊庆, 等. 基于高光谱成像检测猕猴桃冷害的研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报,2022,45(2):386−394. [GE Y H, SONG J, PAN L Q, et al. Research on detecting chilling injury of kiwifruit based on hyperspectral imaging technology[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2022,45(2):386−394. GE Y H, SONG J, PAN L Q, et al. Research on detecting chilling injury of kiwifruit based on hyperspectral imaging technology[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2022, 45(02): 386-394.
[25] 孙世鹏, 彭俊, 李瑞, 等. 基于近红外高光谱图像的冬枣损伤早期检测[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(2):301−305. [SUN S P, PENG J, LI R, et al. Early detection of mechanical damage in Chinese winter jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Mill. cv. Dongzao) using nir hyperspectral images[J]. Food Science,2017,38(2):301−305. SUN S P, PENG J, LI R, et al. Early detection of mechanical damage in Chinese winter jujube (Zizyphus jujuba Mill. cv. Dongzao) using nir hyperspectral images[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(2): 301-305.
[26] FRIEND J, RHODES M J C. Recent advances in the biochemistry of fruits and vegetables[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1981: 41-61.
[27] LU R F, GUYER D E, BEAUDRY R M, et al. Determination of firmness and sugar content of apples using near-infrared diffuse reflectance[J]. Journal of Texture Studies,2000,31(6):615−630. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4603.2000.tb01024.x
[28] LEE W H, KIM M S, LEE H, et al. Hyperspectral near-infrared imaging for the detection of physical damages of pear[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2014,130:1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.12.032
[29] LIU G, HE J, WANG S, et al. Application of near-infrared hyperspectral imaging for detection of external insect infestations on jujube fruit[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2016,19(1):41−52.
[30] SUN Y, PESSANE I, PAN L Q, et al. Hyperspectral characteristics of bruised tomatoes as affected by drop height and fruit size [J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology Template, 2021, 141: 110863.
[31] 吴剑飞. 高光谱技术识别煤岩的特征波段筛选方法研究[J]. 黑龙江工程学院学报,2022,36(2):13−19. [WU J. Wavelength variable selection methods for identification of coal and rock based on hyperspectral technology[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Institute of Technology,2022,36(2):13−19. WU J. Wavelength variable selection methods for identification of coal and rock based on hyperspectral technology[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Institute of Technology, 2022, 36(2): 13-19.
[32] 王浩云, 宋进, 潘磊庆, 等. 优化BP神经网络提高高光谱检测调理鸡肉菌落总数精度[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(5):302−309. [WANG H Y, SONG J, PAN L Q, et al. Improving hyperspectral detection accuracy of total bacteria in prepared chicken using optimized BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(5):302−309. WANG H Y, SONG J, PAN L Q, et al. Improving hyperspectral detection accuracy of total bacteria in prepared chicken using optimized BP neural network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(5): 302-309.
[33] 樊书祥, 黄文倩, 李江波, 等. 特征变量优选在苹果可溶性固形物近红外便携式检测中的应用[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2014,34(10):2707−2712. [FAN S X, HUANG W Q, LI J B, et al. Application of characteristic NIR variables selection in portable detection of soluble solids content of apple by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2014,34(10):2707−2712. FAN S X, HUANG W Q, LI J B, et al. Application of characteristic NIR variables selection in portable detection of soluble solids content of apple by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2014, 34(10): 2707-2712.
[34] LIU Q, SUN K, PENG J, et al. Identification of bruise and fungi contamination in strawberries using hyperspectral imaging technology and multivariate analysis[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2018,11(5):1518−1527. doi: 10.1007/s12161-017-1136-3
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴莎莎,王振杰,江梦薇,兰维杰,屠康,李晏,袁栋栋,潘磊庆. 基于多成熟度光谱信息融合的阿森泰克苹果品质预测模型研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(07): 294-305 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



