Effects of Yeast-lactic Acid Bacteria Co-fermentation on the Quality of Navel Orange Beverage
-
摘要: 为研究酿酒酵母SC-125(Saccharomyces cerevisiae)与植物乳杆菌B-5(Lactobacillus plantarum)在混菌发酵中的发酵特性,以新鲜的金堂脐橙汁为原料,分别接种两种菌共发酵,探究发酵过程中活菌数、pH、还原糖、酒精度、总酚等基本理化指标变化,并对脐橙饮品DPPH自由基清除能力、羟基自由基清除能力进行检测,结合电子鼻与气相色谱-质谱联用技术(Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer,GC-MS)利用主成分分析脐橙饮品发酵过程中的风味物质。结果表明:在发酵0~36 h,与单菌株发酵制备脐橙饮品相比,共发酵脐橙饮品中的酵母菌迅速增加,达到8.0 CFU·mL−1,还原糖含量下降迅速;共发酵最终酒精度为5.33%,低于酿酒酵母SC-125单独发酵;共发酵的总酚含量、DPPH自由基和羟基自由基清除能力增加,分别达到355.5 mg·L−1、78.82%和77.08%;共发酵挥发性成分种类更加丰富,共检测出53种香气物质,其中特有的香气物质9种,分别是:甲酸异丙酯、十一酸乙酯、乙酸异丁酯、丁酸甲酯、四氢芳樟醇、1-十四醇、2-戊醇、十一醛、2-硝基丙烷;赋予脐橙饮品果仁香、椰香和玫瑰花香等特征香气。电子鼻的主成分分析表明:共发酵对W5S、W1S、W2S3个传感器更加灵敏,主要以氮氧化合物、短链烷烃、乙醇为主,该研究为脐橙饮品的开发提供了理论依据。
-
关键词:
- 脐橙饮品 /
- 酵母菌酿酒酵母SC-125 /
- 植物乳杆菌B-5 /
- 共发酵
Abstract: To study the fermentation characteristics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (SC-125) and Lactobacillus plantarum (B-5) in mixed bacterial fermentation, fresh Jintang navel orange juice was used as raw material and inoculated with the two bacteria separately for co-fermentation, to investigate the changes in the number of viable bacteria, pH, reducing sugar, alcohol, and The changes of basic physicochemical indexes such as viable bacteria, pH, reducing sugar, alcoholic content and total phenols were investigated, and the scavenging ability of DPPH and hydroxyl radicals of navel orange drinks were examined. The results showed that the yeast in the co-fermented navel orange beverage increased rapidly to 8.0 CFU·mL−1 and the reduced sugar content decreased rapidly during 0~36 h of fermentation compared with the navel orange drink prepared by single-strain fermentation. The final alcohol content of co-fermentation was 5.33%, which was lower than that of brewer's yeast SC-125 alone. The total phenolic content, DPPH radicals and hydroxyl radical scavenging capacity of co-fermentation increased, reaching 355.5 mg·L−1, 78.82%, and 77.08%, respectively. Co-fermentation volatile components were more abundant, with 51 aroma substances detected, including 9 unique aroma substances, namely: Isopropyl format, ethyl undecanoate, isobutyl acetate, methyl butyrate, tetrahydro linalool, 1-tetradecanol, 2-pentanol, undecylenic aldehyde, 2-nitropropane, giving navel orange drinks nutty, coconut and rose aromas. The principal component analysis of the electronic nose showed that the co-fermentation was more sensitive to three sensors, W5S, W1S and W2S, mainly nitrogen oxides, short chain alkanes and ethanol. This study would provide a theoretical basis for the development of navel orange beverages. -
脐橙(Navel orange)属蔷薇亚纲无患子目芸香科柑橘属,是柑橘品种中最优良的甜橙种类,含有多种常量和微量元素、维生素、氨基酸、膳食纤维等营养物质[1]。经常食用脐橙具有解油腻、分解脂肪、醒酒、促进肠道蠕动、清肠通便、增进食欲等功效[2]。
目前,脐橙饮品主要是单一酵母菌或酵母菌与非酿酒酵母菌发酵,研究主要集中在果酒[3]、果醋[4]以及发酵工艺的优化,针对脐橙饮品中酵母菌与乳酸菌共发酵特性的研究较少。酿酒酵母菌[5]和植物乳杆菌[6]共发酵是一个生物混合体系,体系中微生物之间大多具有生长代谢协调作用[7]。有相关研究报道,乳酸菌和酵母菌共发酵不但能够相互促进生长,而且可以获得某些纯种发酵不易得到的产物,这些物质赋予了饮品独特的风味和口感[8-10]。Sun等[11]研究了酵母菌LAIVIN RC212与乳酸菌PL18共同接种对樱桃酒化学和感官特性的影响,不仅使共发酵的挥发性物质更多,而且缩短了发酵时间;陈毅坚等[12]利用乳酸菌RSJ-1与酵母菌JMJ-1发酵新型乳制品,使苯乙醇和3-甲基丁醇等风味物质含量大大增加;马丽娟等[13]利用植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)和酿酒酵母(Saccharomyces cerevisiae)发酵菠萝汁,发现该饮品既保留了菠萝原有的营养物质和特有香气,还赋予一定的发酵风味。金晓帆[14]利用酵母菌DV10与植物乳杆菌(Saccharomyces cerevisiae)发酵芒果浆,使得醇类、酯类以及总酚含量增加,抗氧化能力更强。
本文以脐橙汁为原料,利用实验室保藏的酵母菌和乳酸菌菌株进行共菌发酵实验,以单一菌株发酵为对照,探究发酵过程中脐橙饮品的活菌数、酒精度、还原糖、总酚、抗氧化性、挥发性香气物质变化特性,为酿酒酵母和植物乳杆菌共发酵脐橙饮品的开发提供理论参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
脐橙 四川金堂脐橙果园,直径约75~80 mm,无公害;酵母菌(酿酒酵母SC-125)、乳酸菌(植物乳杆菌B-5) 均由西华大学古法发酵(酿造)生物技术研究所保藏;乳酸细菌培养基(MRS)、马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基(YPD) 青岛高科园海博生物技术有限公司;1,1-二苯-2-库基肼(DPPH试剂) 成都市科隆化学品有限公司;3,5-二硝基水杨酸 福晨(天津)化学试剂有限公司;仲辛醇 成都市科隆化学品有限公司;以上试剂均为分析纯。
FA1104型电子天平 上海舜宇恒平有限公司;BPH-9082型电热恒温培养箱 上海一恒科技有限公司;INFINITEF200型酶标仪 上海闪谱生物科技有限公司;GCMS-QP2020NX型气相色谱-质谱联用仪 岛津公司;5804R型冷冻离心机 Eppendorf公司;PEN3型电子鼻 德国AIRSENSE公司;G154DWS型全自动高压灭菌锅 致微(厦门)仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 脐橙饮品发酵试验
将脐橙鲜果的皮壳和核去掉,用榨汁机将果肉榨汁制备成果浆状,以3000 r/min离心30 min,120目分样筛过滤后取上清液置于250 mL发酵容器中,于60 ℃巴氏灭菌15 min。通过预实验,确定最佳接种量和种子液浓度,同时将酿酒酵母菌SC-125、植物乳杆菌B-5活化(酿酒酵母菌种子液浓度为106 CFU/mL,植物乳杆菌种子液浓度为108 CFU/mL)按2%的比例添加,30 ℃恒温静置发酵,设置三个平行,使用阿贝折光仪检测发酵状态,直至可溶性固形物稳定,主发酵结束。期间每隔12 h进行取样,在超净台收集脐橙发酵上清液,将其-50 ℃冷冻保存。
1.2.2 菌落计数方法
用PDA琼脂平板计数法和MRS琼脂平板计数法分别测定酿酒酵母SC-125和植物乳杆菌B-5协同发酵脐橙汁在不同发酵阶段的活细胞数。同时分别以两种菌株单独发酵脐橙为对照。活细胞数以每毫升菌落形成单位(CFU/mL)表示。
1.2.3 脐橙饮品理化指标的测定
可溶性固形物:手持糖度仪测定;pH:pH计测定;均参照GB/T 15038-2006的方法[15];还原糖含量:参照高文军等[16]的DNS法;总酚:福林酚法[17],以没食酸计。
1.2.4 酒精度的测定
酒精度含量的测定参照Fulgencio等[18]通过外标法利用气相色谱测定白酒酒精度,其标准曲线方程为y=5255.3x−769.1,R2=0.998。
色谱条件:初始温度45 ℃,保持5 min,以3 ℃·min−1 升温至60 ℃,保持3 min,以20 ℃·min−1升温至200 ℃,保持5 min。色谱柱为Rtx-Wax毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm),载气为高纯度氦气,载气流速1.0 mL·min−1;进样口温度: 200 ℃。
1.2.5 脐橙饮品抗氧化能力测定
1.2.5.1 DPPH自由基清除率
取1 mL待测脐橙饮品溶液和1 mL 0.5 mmol·L−1的DPPH溶液,摇匀避光静置30 min,于517 nm处测定其吸光度值A1,同时用蒸馏水做空白对照,无水乙醇做阳性对照[19]。DPPH自由基清除率计算公式如式(1):
清除率(%)=[1−(A1−A2)A0]×100 (1) 式中:A0为蒸馏水代替脐橙饮品溶液的吸光度;A1为加入脐橙饮品溶液的吸光度;A2为无水乙醇代替DPPH溶液的吸光度。
1.2.5.2 羟基自由基清除率
参考Hui等[20]的方法,精确吸取9 mmol·L−1硫酸亚铁1 mL,加入1 mL 9 mmol·L−1水杨酸乙醇溶液,然后加入酒样1 mL,最后加入8.8 mmol·L−1的H2O2 1 mL,摇匀后在37 ℃的恒温水浴锅中反应30 min,在波长510 nm下测定吸光度A1,同时用甲醇做空白对照,蒸馏水代替H2O2做阳性对照。羟基自由基清除率计算公式如式(2):
清除率(%)=[1−(A1−A2)A0]×100 (2) 式中:A0为甲醇代替脐橙饮品溶液的吸光度;A1为加入脐橙饮品溶液的吸光度;A2为蒸馏水代替H2O2溶液的吸光度。
1.2.6 挥发性成分的分析
1.2.6.1 样品预处理
参照文献[21-22]的方法,基于HS-SPME/GC-MS对挥发性物质的分析,采用内标法进行半定量分析,内标选用浓度为0.4175 mg·L−1的仲辛醇。取3.8 mL发酵样品加入0.2 mL稀释的仲辛醇(用超纯水稀释1×105倍),置于顶空瓶中,加入1 g NaCl,加盖密封,放入60 ℃恒温水浴中平衡20 min,将老固相微萃取器插在样品瓶上,吸附20 min后拔出,插入气相色谱仪进样口,于220 ℃解吸3 min,进行GC-MS检测分析。
1.2.6.2 GC-MS检测条件
a.气相色谱条件:色谱柱为DB-Wax(30 mm×0.25 mm×0.25 μm),进样温度为240 ℃;程序升温:初始温度40 ℃保持2 min;以6 ℃·min−1升至240 ℃保持4 min;载气为氦气,线速为1.0 mL·min−1,不分流。
b.质谱条件:电离方式为电子电离(electron ionization,EI)源,电子能量为70 eV,灯丝流量为0.20 mA,离子源温度为200 ℃,接口温度为250 ℃。
1.2.7 电子鼻香气成分的测定
电子鼻可对特定香气成分进行响应,然后可以通过模式识别算法来执行区分和分类[23]。为了研究脐橙汁发酵过程中风味的变化,分析发酵中的风味变化,采用顶空吸气法[24]检测,比较气味的差异性,并使用Origin 2018进行主成分分析对其风味特征进行比较,表1为电子鼻的10个传感器性能。
表 1 电子鼻的10个传感器的性能Table 1. Ten sensors performance of the e-nose序号 传感器名称 敏感物质 1 W1C 芳香成分 2 W5S 对氮氧化合物很灵敏 3 W3C 氨水,对芳香成分灵敏 4 W6S 主要对氢气有选择性 5 W5C 烷烃芳香成分 6 W1S 对短链烷烃灵敏 7 W1W 对硫化物灵敏 8 W2S 对乙醇灵敏 9 W2W 对有机硫化物灵敏 10 W3S 对烷烃灵敏 1.3 数据处理
试验数据采用SPSS 20.0 进行显著性分析,柱状图折线图采用 Origin 2018进行绘制,每组试验三个平行,所有结果用平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
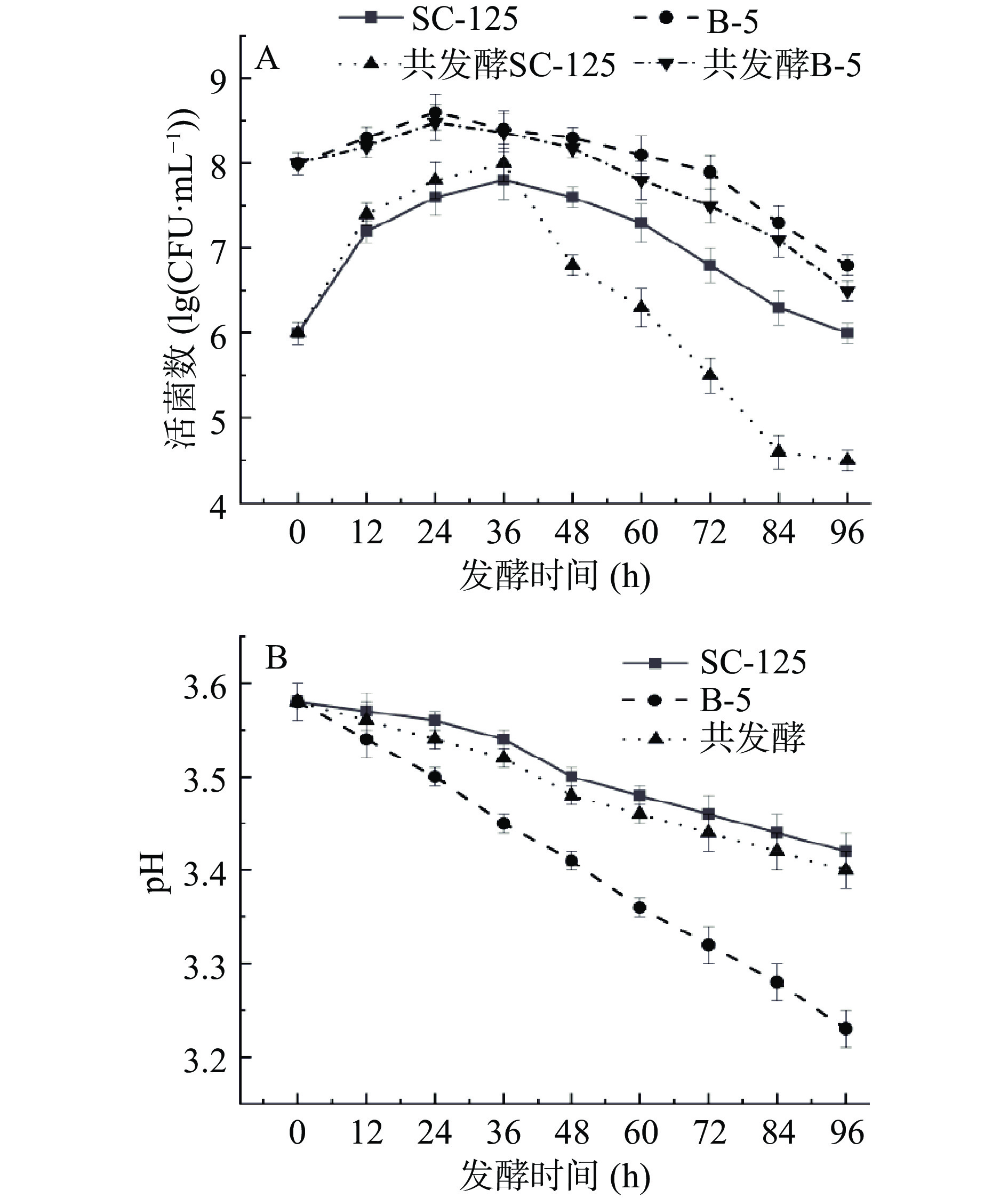
2.1 脐橙发酵过程中活菌数和pH的变化
在脐橙发酵初期,酵母菌SC-125和植物乳杆菌B-5都能很好的代谢脐橙中的有机质,表现出了较好的生长能力。如图1A所示,在共发酵前期,酵母菌SC-125迅速增加达约8.0 CFU·mL−1,这是由于脐橙汁中的还原糖为酵母菌提供了营养物质。尽管随着发酵时间的延长,共发酵酵母菌SC-125活菌数在降低,但共发酵中的植物乳杆菌B-5活菌数保持相对的稳定,其利用酵母代谢产物和还原糖等营养物质代谢产生了乳酸、氨基酸等[25],使饮品中的可滴定酸含量升高,导致pH下降(如图1B所示)。葡萄酒pH的最佳活性是2.5~3.8,三种不同菌种发酵饮品的pH均在此范围,而且都有下降趋势,pH的大小会影响最终产品中高级醇的含量,从而影响饮品的风味。
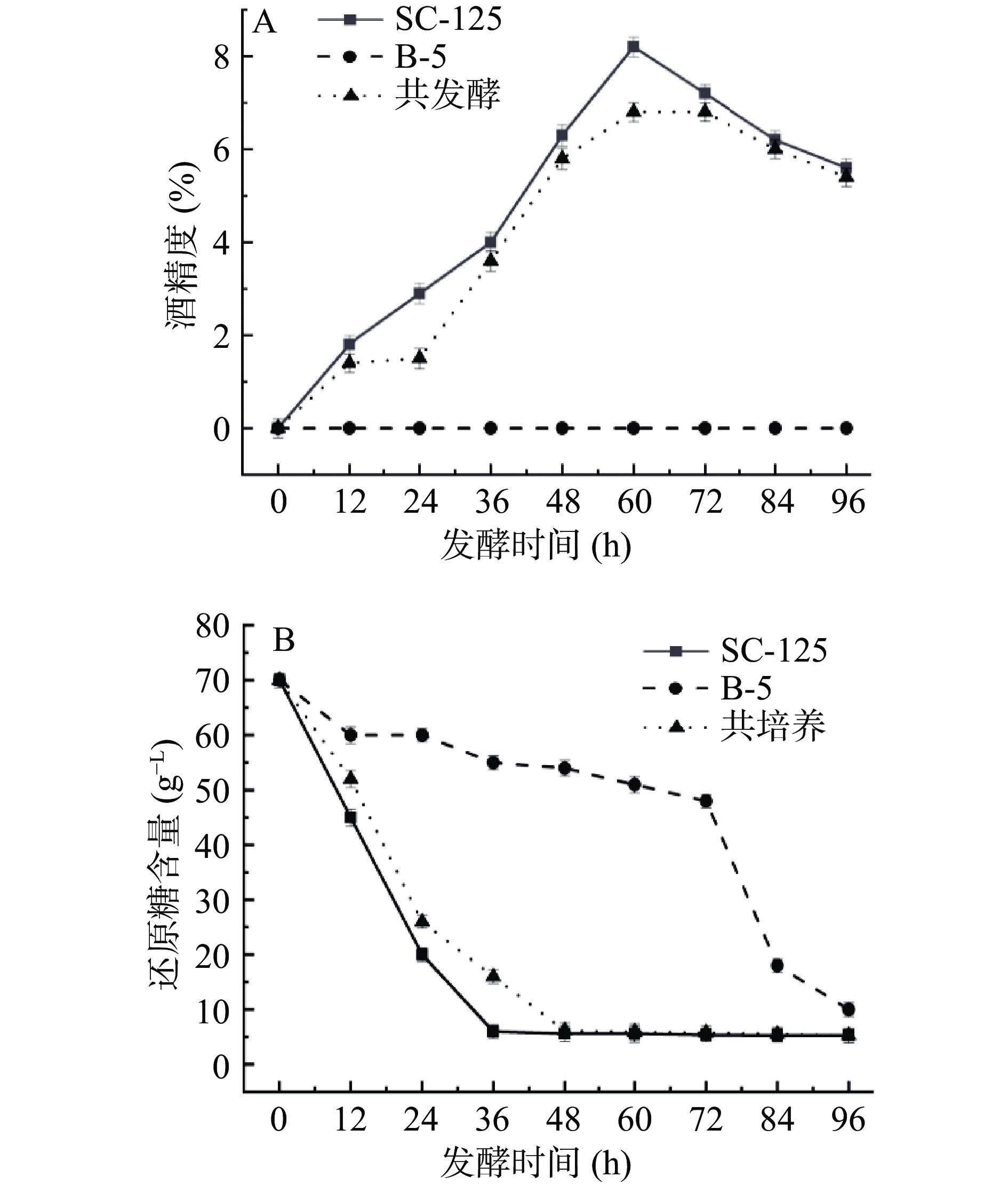
2.2 脐橙发酵过程中酒精度和还原糖含量的变化
还原糖的利用表明了酵母进行酒精发酵和底物转化的能力[26],而微生物对糖的耐受性和利用率也成为发酵终点判断的重要指标之一。如图2所示,在发酵前期,酿酒酵母SC-125单独发酵和共培养的还原糖含量从70.31 g·L−1迅速下降,分别达到3.4和3.2 g/L,符合葡萄酒还原糖的标准[15],即4 g/L以下;脐橙饮品酒精度持续升高,0~96 h,酿酒酵母SC-125单独发酵的酒精度比共发酵的酒精度高,酒精度都在60 h时达到最高峰,说明植物乳杆菌B-5同型乳酸发酵利用还原糖生长繁殖,与酿酒酵母SC-125共发酵中能起到一定的降低酒精度的作用。整个发酵过程中,共发酵酒精度在0~6%左右,发酵终点酒精度为5.2%,与葡萄酒低醇标准6%以下相符。
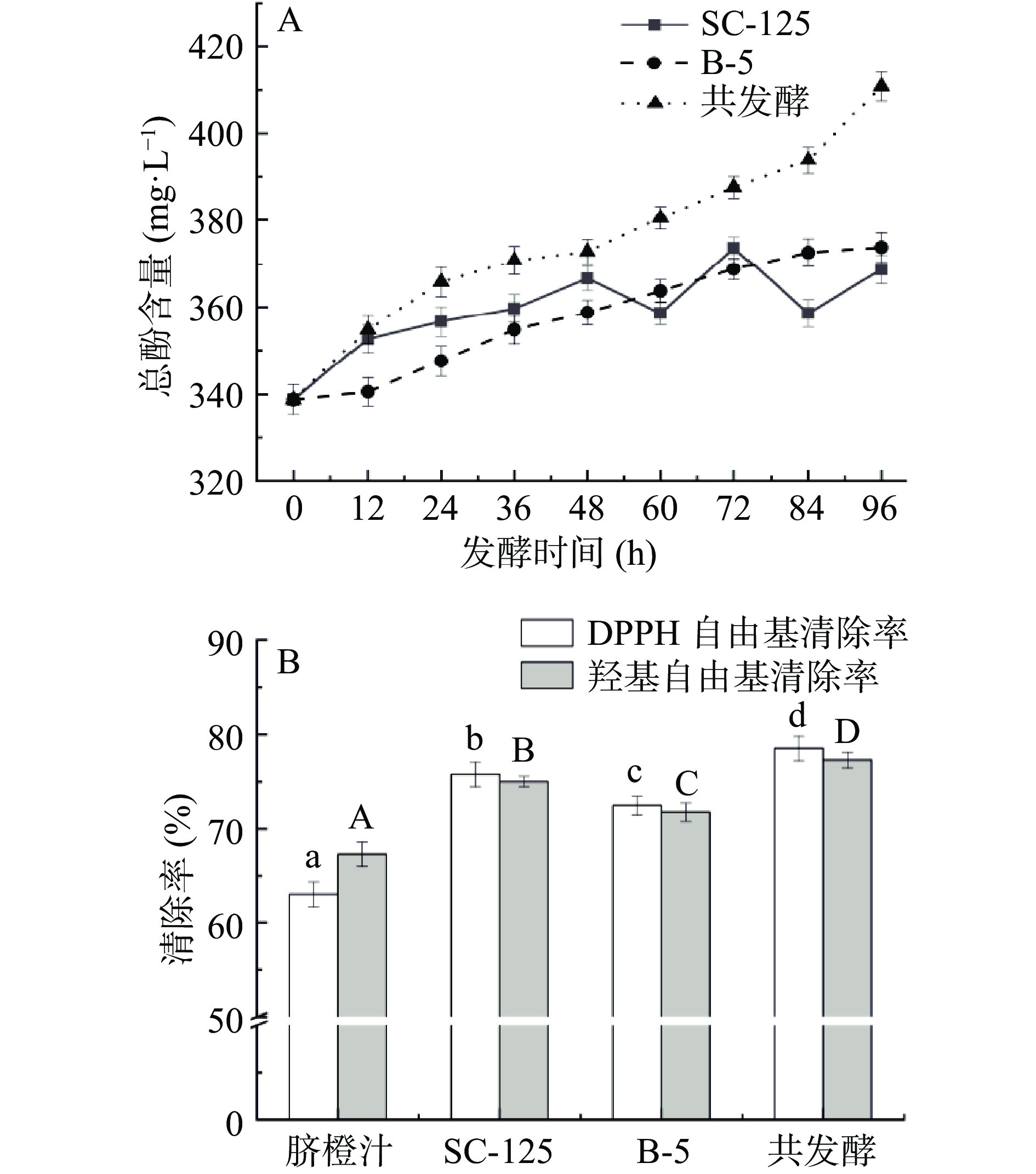
2.3 脐橙发酵过程中总酚含量的变化和脐橙饮品抗氧化能力分析
由于酵母细胞会对酚类物质产生吸附作用,随着发酵液环境的变化,又会产生解吸作用[27],从图3A可知,对照组酿酒酵母SC-125单独发酵过程中,总酚含量差异波动较大,而随着植物乳杆菌B-5的添加,共发酵总酚含量最高,共发酵总酚含量从338.78 mg·L−1上升到355.5 mg·L−1,相比对照组酵母SC-125总酚提高了7.73%。共发酵对DPPH自由基的清除率和羟基自由基清除率最高,这与总酚含量的变化是一致的,共发酵脐橙饮品的抗氧化能力与总酚含量呈正相关关系,这与王东伟等[28]的研究是一致的。如图3B所示,对照组酿酒酵母SC-125、对照组植物乳杆菌B-5以及共发酵对DPPH自由基的清除率分别由脐橙汁的62.67%提高到75.54%、72.45%、78.82%,对羟基自由基的清除率分别由初始的68.77%提高到74.71%、71.82%、77.08%。共发酵对DPPH自由基的清除率和羟基自由基清除率最高,。证明菌株的协同作用发酵有利于抗氧化活性的增加,且共发酵的抗氧化能力效果最佳。
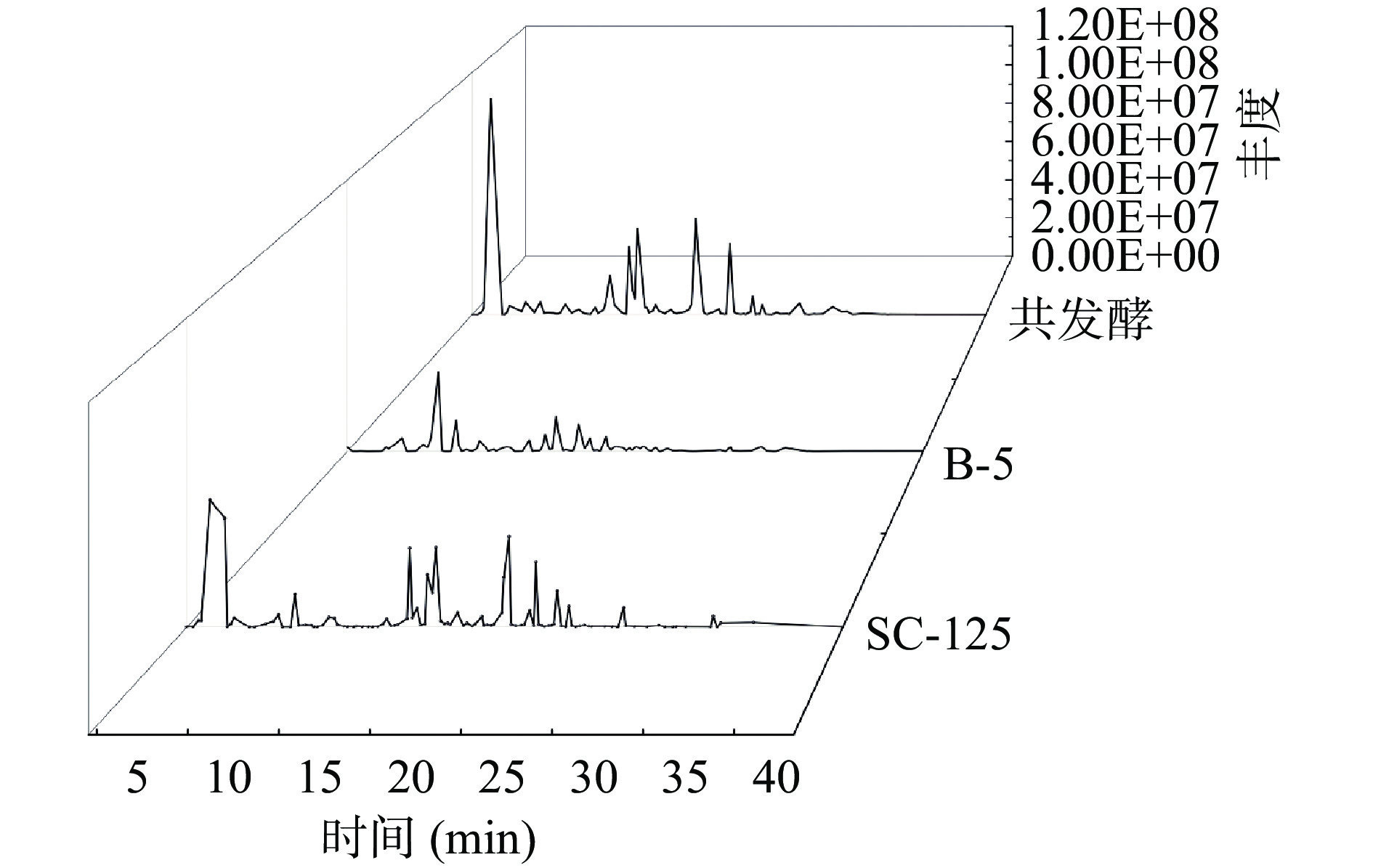
2.4 脐橙发酵饮品挥发性物质及电子鼻主成分分析
表 2 三种发酵方式的脐橙饮品挥发性物质的含量Table 2. Content of volatile substances in three kinds of fermented navel orange drinks中文名称 香气特征[29] 含量(μg·L−1) 酿酒酵母SC-125 植物乳杆菌B-5 共发酵 酯类 正己酸乙酯 曲香、菠萝香气 36.34 9.02 82.07 苯甲酸乙酯 水果芳香 4.08 3.55 25.46 辛酸乙酯 花香、酒香 35.98 10.16 65.24 乙酸苯乙酯 草莓香味 438.78 29.69 479.54 癸酸乙酯 白兰地、果香 93.42 − 273.51 月桂酸乙酯 油脂、水果香味 226.48 33.07 407.48 棕榈酸乙酯 果爵、奶油香气 25.47 5.12 50.23 乙酸乙酯 果子芳香 305.01 12.5 309.44 苯乙酸乙酯 蜂蜜香气 3.63 − 4.68 甲酸异丙酯 醚香、梨子味 − − 4.30 L(-)-乳酸乙酯 酒香气味 − 22.56 39.94 3-羟基己酸乙酯 水果香气 32.67 83.74 127.57 丙位壬内酯 桃杏气息 8.30 4.78 8.69 十一酸乙酯 果香、椰子香 − − 10.46 邻苯二甲酸二乙酯 特殊芳香 33.83 35.72 32.47 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 特殊芳香 3.90 − 4.66 乙酸异丁酯 水果香味 − − 10.59 乙酸异戊酯 香蕉香味 52.22 8.12 54.74 丁酸甲酯 苹果干酪香 − − 4.15 乙酸叶醇酯 青草气味 8.37 − 11.11 癸酸异戊酯 玫瑰香味 13.37 − 15.24 乙酸丁香酚酯 丁香似香 − 83.35 27.1 3-羟基丁酸乙酯 果香、葡萄香 − 3.65 − 丁酸己酯 混合水果香气 − 2.32 6.46 醇类 苯甲醇 芳香气味 17.16 31.94 37.04 芳樟醇 柠檬香 77.98 47.65 70.86 苯乙醇 玫瑰香 1460.74 827.61 1691.67 4-萜烯醇 胡椒、泥土香 304.39 136.82 235.53 松油醇 丁香香 43.58 104.48 179.13 异丁醇 酒香 21.05 8.74 61.87 异戊醇 苹果白兰地 923.95 344.59 1650.59 正己醇 酒香、果香 130.77 101.55 169.94 正辛醇 油脂、甘橘香 117.81 26.45 120.67 四氢芳樟醇 玫瑰、芜荽似香 − − 88.38 十一醇 柑橘、凤梨果香 82.63 12.67 169.18 紫苏醇 特殊香气 5.20 6.11 14.68 1-十四醇 蜡质气味 − − 23.76 2-戊醇 葡萄酒、醚香 − − 3.00 1-壬醇 玫瑰、橙香 19.32 11.87 27.69 十二醇 油脂气味 3.86 5.27 6.53 1-戊醇 略有气味 4.60 2.14 6.02 香茅醇 特殊香气 18.67 − 20.54 1-十六烷醇 玫瑰香 49.24 37.86 62.54 酸类 辛酸 水果香气 5365.36 4230.37 3630.29 庚酸 脂肪气味 1.89 1.96 1.05 油酸 植物油气味 65.62 28.75 24.53 9-癸烯酸 果香、乳香 149.09 210.78 108.63 醛酮类 正辛醛 果香、茉莉香 4.57 2.22 5.15 十一醛 木香橙皮香气 − − 35.72 3-羟基-2-丁酮 奶油香气 12.64 7.95 69.57 二氢香芹酮 药草气味 8.91 17.94 26.92 左旋香芹酮 留兰香香气 46.96 17.17 53.25 其他类 2-甲基吡嗪 牛肉、果仁香 24.65 13.25 32.17 2-硝基丙烷 令人愉快的气味 − − 42.33 注:“−”表示未检出。 通过对发酵结束后的样品进行HS-SPME/GC-MS进行分析,得到如图4及表2的结果。酿酒酵母SC-125单菌发酵共有41种挥发性成分,含有16种酯类、16种醇类、4种酸类、4种醛酮类、1种其他类;植物乳杆菌B-5单菌发酵共检测出38种,含有15种酯类、15种醇类、3种酸类、4种醛酮类、1种其他类;共发酵共检测出53种挥发性成分,包括23种酯类、19种醇类、4种酸类、5种醛酮类、2种其他类。相比于酿酒酵母SC-125和植物乳杆菌B-5,共发酵后有更多的风味物质,还产生特有的挥发性成分,如甲酸异丙酯、十一酸乙酯、乙酸异丁酯、丁酸甲酯、四氢芳樟醇、1-十四醇、2-戊醇、十一醛、2-硝基丙烷,这些物质赋予脐橙饮品醚香、梨子、苹果、干酪、玫瑰和木香橙皮等香气特征,这与之前的研究类似,即酵母菌与乳酸菌共发酵会产生更多的挥发性物质[30]。
酯类化合物对果酒的主体香型具有重要的作用,是构成果酒香气的重要物质[31]。共发酵酯类物质含量和种类高于酵母菌SC-125和植物乳杆菌B-5,其中酵母菌SC-125的酯类物质种类及含量高于植物乳杆菌B-5,主要产生的香气物质有乙酸苯乙酯、月桂酸乙酯、乙酸乙酯、癸酸乙酯、辛酸乙酯和3-羟基己酸乙酯,共发酵使这些物质的含量分别提高到479.54、407.48、309.44、273.51、65.24 、127.57 μg/L。乙酸苯乙酯[32]呈草莓香味,月桂酸乙酯呈油脂水果味,乙酸乙酯具有果子的芳香,癸酸乙酯具有白兰地和果香,辛酸乙酯具有花香和酒香,增加了脐橙饮品的复杂性。
醇类物质是果酒中的主要香气成分,主要通过糖代谢分解产生或是果酒中氨基酸转化形成[33]。对比三种发酵方式,醇类物质在种类和含量上均有不同,其中在共发酵中种类更多,含量最高,主要的醇类物质如:苯乙醇、4-萜烯醇[34]、异戊醇和正己醇。苯乙醇具有温和淡雅的玫瑰花气味,4-萜烯醇呈胡椒香和较淡的泥土香,异戊醇有苹果白兰地香气,正己醇微带酒香和果香。张毅坚等[12]的研究表明酵母菌与植物乳杆菌共培养增加了更多的醇类物质,使发酵制品具有更好的风味。
酸类物质是酵母代谢产生的次级物质,在本研究中,酸类物质主要有辛酸、庚酸、油酸和9-癸烯酸,共发酵的酸类物质含量比单菌发酵含量更少,这可能是共发酵中的酸与醇发生反应产生更多酯类物质[35]。
醛酮类和其他类物质在本试验中含量占比较少,如正辛醛、3-羟基-2-丁酮和2-甲基吡嗪,正辛醛呈果香、茉莉香气,3-羟基-2-丁酮呈奶油香气,2-甲基吡嗪有牛肉加热时的香味和果仁香味,这些物质与酯类、醇类和酸类物质相互协同,赋予了饮品更多的风味。
2.5 通过电子鼻比较脐橙饮品香气成分
由图5可知,第一主成分区分贡献率为83.9%,第二主成分区分贡献率为8.2%,两个主成分区分贡献率和为92.1%,大于90%,表明两个主成分已经基本代表了样品的主要信息特征[36],而且风味相互独立,整体区分度较好,其中W5S、W1S、W2S贡献较大,他们分别对氮氧化合物、短链烷烃、乙醇灵敏。PCA显示脐橙发酵饮品与脐橙原汁区分明显,共发酵与单菌发酵的脐橙饮品在第一主成分和第二主成分上虽然有交叉,但是雷达图可以明显看出,共发酵10个传感器得分均高于脐橙原汁和单菌,尤其在W5S、W1S、W2S三个传感器的得分更高,因此判断共发酵饮品香气物质相较于脐橙原汁以及单菌发酵饮品更加丰富。
3. 结论
本研究以金堂脐橙为发酵原料,首次利用酿酒酵母和植物乳杆菌发酵脐橙饮品,并比较了酿酒酵母SC-125和植物乳杆菌B-5单独发酵以及共发酵脐橙过程中各项指标的变化规律,结果表明:在共发酵前期酿酒酵母SC-125迅速繁殖,还原糖含量下降;酒精度持续上升后下降最终达到为5.33%,低于酿酒酵母SC-125单独发酵;其抗氧化能力强,共挥发性成分的种类更加丰富,特有成分赋予了共发酵的脐橙饮品椰子、坚果和醚香等香气;结合主成分分析,共发酵饮品对氮氧化合物、短链烷烃、乙醇更加灵敏。总体来说,酿酒酵母与植物乳杆菌协同发酵制备脐橙饮品口感酸甜适中,香气浓郁,为脐橙风味饮品提供了理论依据和技术参考。后续还可以针对脐橙饮品的发酵工艺进行优化,进一步探讨不同菌种接种量及其接种顺序等因素对脐橙饮品品质的影响。
-
表 1 电子鼻的10个传感器的性能
Table 1 Ten sensors performance of the e-nose
序号 传感器名称 敏感物质 1 W1C 芳香成分 2 W5S 对氮氧化合物很灵敏 3 W3C 氨水,对芳香成分灵敏 4 W6S 主要对氢气有选择性 5 W5C 烷烃芳香成分 6 W1S 对短链烷烃灵敏 7 W1W 对硫化物灵敏 8 W2S 对乙醇灵敏 9 W2W 对有机硫化物灵敏 10 W3S 对烷烃灵敏 表 2 三种发酵方式的脐橙饮品挥发性物质的含量
Table 2 Content of volatile substances in three kinds of fermented navel orange drinks
中文名称 香气特征[29] 含量(μg·L−1) 酿酒酵母SC-125 植物乳杆菌B-5 共发酵 酯类 正己酸乙酯 曲香、菠萝香气 36.34 9.02 82.07 苯甲酸乙酯 水果芳香 4.08 3.55 25.46 辛酸乙酯 花香、酒香 35.98 10.16 65.24 乙酸苯乙酯 草莓香味 438.78 29.69 479.54 癸酸乙酯 白兰地、果香 93.42 − 273.51 月桂酸乙酯 油脂、水果香味 226.48 33.07 407.48 棕榈酸乙酯 果爵、奶油香气 25.47 5.12 50.23 乙酸乙酯 果子芳香 305.01 12.5 309.44 苯乙酸乙酯 蜂蜜香气 3.63 − 4.68 甲酸异丙酯 醚香、梨子味 − − 4.30 L(-)-乳酸乙酯 酒香气味 − 22.56 39.94 3-羟基己酸乙酯 水果香气 32.67 83.74 127.57 丙位壬内酯 桃杏气息 8.30 4.78 8.69 十一酸乙酯 果香、椰子香 − − 10.46 邻苯二甲酸二乙酯 特殊芳香 33.83 35.72 32.47 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 特殊芳香 3.90 − 4.66 乙酸异丁酯 水果香味 − − 10.59 乙酸异戊酯 香蕉香味 52.22 8.12 54.74 丁酸甲酯 苹果干酪香 − − 4.15 乙酸叶醇酯 青草气味 8.37 − 11.11 癸酸异戊酯 玫瑰香味 13.37 − 15.24 乙酸丁香酚酯 丁香似香 − 83.35 27.1 3-羟基丁酸乙酯 果香、葡萄香 − 3.65 − 丁酸己酯 混合水果香气 − 2.32 6.46 醇类 苯甲醇 芳香气味 17.16 31.94 37.04 芳樟醇 柠檬香 77.98 47.65 70.86 苯乙醇 玫瑰香 1460.74 827.61 1691.67 4-萜烯醇 胡椒、泥土香 304.39 136.82 235.53 松油醇 丁香香 43.58 104.48 179.13 异丁醇 酒香 21.05 8.74 61.87 异戊醇 苹果白兰地 923.95 344.59 1650.59 正己醇 酒香、果香 130.77 101.55 169.94 正辛醇 油脂、甘橘香 117.81 26.45 120.67 四氢芳樟醇 玫瑰、芜荽似香 − − 88.38 十一醇 柑橘、凤梨果香 82.63 12.67 169.18 紫苏醇 特殊香气 5.20 6.11 14.68 1-十四醇 蜡质气味 − − 23.76 2-戊醇 葡萄酒、醚香 − − 3.00 1-壬醇 玫瑰、橙香 19.32 11.87 27.69 十二醇 油脂气味 3.86 5.27 6.53 1-戊醇 略有气味 4.60 2.14 6.02 香茅醇 特殊香气 18.67 − 20.54 1-十六烷醇 玫瑰香 49.24 37.86 62.54 酸类 辛酸 水果香气 5365.36 4230.37 3630.29 庚酸 脂肪气味 1.89 1.96 1.05 油酸 植物油气味 65.62 28.75 24.53 9-癸烯酸 果香、乳香 149.09 210.78 108.63 醛酮类 正辛醛 果香、茉莉香 4.57 2.22 5.15 十一醛 木香橙皮香气 − − 35.72 3-羟基-2-丁酮 奶油香气 12.64 7.95 69.57 二氢香芹酮 药草气味 8.91 17.94 26.92 左旋香芹酮 留兰香香气 46.96 17.17 53.25 其他类 2-甲基吡嗪 牛肉、果仁香 24.65 13.25 32.17 2-硝基丙烷 令人愉快的气味 − − 42.33 注:“−”表示未检出。 -
[1] 武松伟, 梁珊珊, 谭启玲, 等. 柑橘营养特性与“以果定肥”[J]. 华中农业大学学报,2021,40(1):12−21. [WU S W, NIANG S S, TAN Q L, et al. Nutritional characteristics of citrus and "determining fertilizer by fruit"[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2021,40(1):12−21. WU S W, NIANG S S, TAN Q L, et al. Nutritional characteristics of citrus and "determining fertilizer by fruit" [J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021, 40(1): 12-21.
[2] 牛静琪, 徐维盛, 赵佳, 等. 国产脐橙与进口脐橙的营养成分比较研究[C]//中国营养学会第十五届全国营养科学大会论文汇编, 2022: 891 NIU J Q, XU W S, ZHAO J, et al, Comparative study on nutritional components of domestic and imported navel oranges [C]. Collection of Papers of the 15th National Conference on Nutrition Science of the Chinese Society of Nutrition, 2022: 891.
[3] 李杰民, 吴翠琼, 何彩梅, 等. 干型富川脐橙果酒酿造技术研究[J]. 酿酒科技,2019(12):60−64. [LI J M, WU C Q, HE C M, et al. Research on brewing technology of dry Fuchuan navel orange fruit wine[J]. Brewing Technology,2019(12):60−64. LI J M, WU C Q, HE C M, et al. Research on brewing technology of dry Fuchuan navel orange fruit wine[J]. Brewing Technology, 2019(12): 60-64.
[4] 邢晓莹, 于迪, 乔羽, 等. 山楂果醋混合菌种发酵工艺及香气成分的HS-SPME/GC-MS分析[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(01):146−152. [XING X Y, YU D, QIAO Y, et al. Fermentation process of hawthorn fruit vinegar by mixed strains and analysis of aroma components by HS-SPME/GC-MS[J]. Chinese Condiment,2021,46(01):146−152. XING X Y, YU D, QIAO Y, et al. Fermentation process of hawthorn fruit vinegar by mixed strains and analysis of aroma components by HS-SPME/GC-MS [J]. Chinese Condiment, 2021, 46 (01): 146-152.
[5] 牟志勇, 杨昳津, 王光强, 等. 酵母菌的益生功能及在食品中的应用[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(15):309−318. [M0U Z Y, YANG Y J, WANG G Q, et al. The probiotic function of yeast and its application in food[J]. Food Science,2021,42(15):309−318. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200609-123 M0U Z Y, YANG Y J, WANG G Q, et al. The probiotic function of yeast and its application in food[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(15): 309-318. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200609-123
[6] 成晓苑. 乳酸菌在发酵食品中的应用研究[J]. 粮食科技与经济,2020,45(11):126−127. [CHENG X Y. Research on the application of lactic acid bacteria in fermented food[J]. Food Technology and Economics,2020,45(11):126−127. CHENG X Y. Research on the application of lactic acid bacteria in fermented food[J]. Food Technology and Economics, 2020, 45(11): 126-127.
[7] EFRIWATI, SUWANTO A, RAHAYU G et al. Population dynamics of yeasts and I acticacid Bacteria (LAB) during tempeh production[J]. Hayati Journal of Biosciences,2013,20(2):57−64. doi: 10.4308/hjb.20.2.57
[8] 赵修报, 程立坤, 付强, 等. 乳酸菌和酵母菌混合发酵制备谷物发酵饮料的工艺研究[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(2):198−202. [ZHAO X B, CHEN L K, FU Q, et al. Study on the technology of cereal fermented beverage by mixed fermentation of lactic acid bacteria and yeast[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(2):198−202. ZHAO X B, CHEN L K, FU Q, et al. Study on the technology of cereal fermented beverage by mixed fermentation of lactic acid bacteria and yeast[J]. China Brewing, 2021, 40(2): 198-202.
[9] SANTOS C C, LIBECK B S, SCHWANR F. Co-culture fermentation of peanut-soy milk for the development of a novel functional beverage[J]. International Journal of Food Scienceand Technology,2014,186(3):32−41.
[10] ALINEGALVAO T M, CINTIA L R, DIASD R, et al. Combination of probiotic yeast and lactic acid bacteria as starter culture to produce maize-based beverages[J]. Food Research Intereational,2018,111:187−197. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.04.065
[11] SUN SY, GONG HS, ZHAO K, et al. Co-inoculation of yeast and lactic acid bacteria to improve cherry wines sensory quality[J]. International Journal of Food Scienceand Technology,2013,48(9):1783−1790. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.12151
[12] 陈毅坚, 张建前, 胡秋月, 等. 乳酸菌与酵母菌混菌发酵新型乳制品的研究[J]. 中国乳品工业,2021,49(6):27−32. [CHEN Y J, ZHANG J Q, HU Q Y, et al. Study on new dairy products fermented by mixed bacteria of lactic acid bacteria and yeast[J]. China Dairy Industry,2021,49(6):27−32. CHEN Y J, ZHANG J Q, HU Q Y, et al. Study on new dairy products fermented by mixed bacteria of lactic acid bacteria and yeast[J]. 2021, 49(6): 27-32.
[13] 马立娟, 王超, 杜丽平, 等. 植物乳杆菌和酿酒酵母发酵菠萝汁的性能比较及产物分析[J]. 中国酿造,2018,37(3):72−77. [MA L J, WANG C, DU L P, et al. Performance comparison and product analysis of pineapple juice fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Chinese Brewing,2018,37(3):72−77. MA L J, WANG C, DU L P, et al. Performance comparison and product analysis of pineapple juice fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Chinese Brewing, 2018, 37(3): 72-77.
[14] 金晓帆. 乳酸菌和酵母菌混合发酵芒果浆的研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2019 JIN X F. Study on the mixed fermentation of mango pulp with lactic acid bacteria and yeast[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2019.
[15] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 15038-2006 葡萄酒果酒通用试验方法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006 General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 15038-2006 General test method for wine and fruit wine[S]. China Standard Press, 2006.
[16] 高文军, 李卫红, 王喜明, 等. 3, 5-二硝基水杨酸法测定蔓菁中还原糖和总糖含量[J]. 中国药业,2020,29(09):113−116. [GAO W J, LI W H, WANG X M, et al. Determination of reducing sugar and total sugar in Brassica chinensis by 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid method[J]. China Pharmaceutical,2020,29(09):113−116. GAO W J, LI W H, WANG X M, et al. Determination of reducing sugar and total sugar in Brassica chinensis by 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid method[J]. China Pharmaceutical, 2020, 29(09): 113-116.
[17] 吴澎, 贾朝爽, 李向阳, 等. 响应面分析优化福林酚法测定樱桃酒中总酚的含量[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(20):200−206,211. [WU P, JIA Z S, LI X G, et al. Determination of total phenols in cherry wine by response surface methodology optimization of Folin phenol method[J]. Food Industry Technology,2018,39(20):200−206,211. WU P, JIA Z S, LI X G, et al. Determination of total phenols in cherry wine by response surface methodology optimization of Folin phenol method[J]. Food Industry Technology, 2018, 39(20): 200-206, 211.
[18] FULGENCIO A, RESENDE G, TEIXEIRA M, et al. Determination of alcohol content in beers of different styles based on portable near-infrared spectroscopy and multivariate calibration[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2021,15:307−316.
[19] KAEWKOD T, BOVONSOMBUT S, TRAGOOLPIA Y. Efficacy of kombucha obtained from green, oolong, and black teas on inhibition of pathogenic bacteria, antioxidation, and toxicity on colorectal cancer cell line[J]. Microorganisms,2019,7(12):700. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7120700
[20] HUI Y, JIN-LI H, CHUANG W. Anti-oxidation and anti-aging activity of polysaccharide from Malus micromoles Makino fruit wine[J]. International Journal of Biologicals Macromolecules,2019,121:1203−1212. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.096
[21] 蔡婷, 宋菲菲, 秦佳, 等. 天然野樱桃果酒的酿造及香气成分分析[J]. 中国酿造,2015,34(06):145−149. [CAI T, SONG FF, QIN J, et al. Brewing and aroma component analysis of natural wild cherry wine[J]. Chinese Brewing,2015,34(06):145−149. CAI T, SONG FF, QIN J, et al. Brewing and aroma component analysis of natural wild cherry wine[J]. Chinese Brewing, 2015, 34(06): 145-149.
[22] DESOUZA M P, BATAGLION, G A, DEALMEIDA, R A, et al. Phenolic and aroma compositions of pitomba fruit (Talisa esculenta Radek.) assessed by LC-MS/MS and HS-SPME/GC-MS[J]. Food Research International,2016,83:87−94. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.01.031
[23] TAN J, XU J. Applications of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) in food quality-related properties determination: A review[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture,2020,4:104−115. doi: 10.1016/j.aiia.2020.06.003
[24] 缪璐, 何善廉, 莫佳琳, 等. 电子鼻技术在朗姆酒分类识别中的应用研究[J]. 广西糖业,2016(4):24−33. [MIAO L, HE S L, MO J L, et al. Research on the application of electronic nose technology in rum classification and recognition[J]. Guangxi Sugar Industry,2016(4):24−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4732.2016.04.005 MIAO L, HE S L, MO J L, et al. Research on the application of electronic nose technology in rum classification and recognition[J]. Guangxi Sugar Industry, 2016(4): 24-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4732.2016.04.005
[25] SWIEGERS J H, BARTOWSKY E J, HENSCHKE P, et al. Yeast and bacterial modulation of wine aroma and flavour[J]. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research,2005,11(2):139−173. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0238.2005.tb00285.x
[26] WANG Z, XU K, CAI R, et al. Construction of recombinant Fusan yeasts for the production of cider with low alcohol and enhanced aroma[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2020,246:745−757. doi: 10.1007/s00217-020-03436-9
[27] 叶萌祺. 苹果酒酿造过程香气物质调控及FT-NIRS分析方法研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2015 YE M Q. Control of aroma substances in cider brewing process and FT-NIRS analysis method[D]. Xianyang: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2015.
[28] 王东伟, 黄燕芬, 肖默艳, 等. 猕猴桃果酒发酵条件优化及其抗氧化特性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2019,10(6):1619−1625. [WANG D W, HUANG Y F, XIAO M, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions and antioxidant properties of kiwifruit wine[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2019,10(6):1619−1625. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2019.06.034 WANG D W, HUANG Y F, XIAO M, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions and antioxidant properties of kiwifruit wine[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection, 2019, 10(6): 1619-1625. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2019.06.034
[29] 马博文. 巴斯德毕赤酵母和酿酒酵母混菌发酵黄桃酒工艺优化及风味的研究[D]. 上海: 上海应用技术大学, 2020 MA B W. Study on technology optimization and flavor of yellow peach wine by mixed fermentation of Pichia pastoris and Saccharomyces cerevisiae[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Applied Technology, 2020.
[30] 赵一凡. 梨酒的酿造工艺研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2019 ZHAO Y F. Research on brewing technology of pear wine[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[31] ZHANG S R, XING X, CHU Q, et al. Impact of co-culture of Lactobacillus plantarum and Oenococcus oeniat different ratios on malolactic fermentation, volatile and sensory characteristics of mulberry wine[J]. LWT,2022,169:113995. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113995
[32] 张雁凌, 张雁南, 刘刚. 乳酸菌和酵母菌的添加对低盐酱油品质的影响[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(12):45−47,51. [ZHANG Y L, ZHANG Y N, LIU G. Effect of lactic acid bacteria and yeast on the quality of low-salt soy sauce[J]. Chinese Condiment,2020,45(12):45−47,51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.12.010 ZHANG Y L, ZHANG Y N, LIU G. Effect of lactic acid bacteria and yeast on the quality of low-salt soy sauce[J]. Chinese Condiment, 2020, 45(12): 45-47, 51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.12.010
[33] 孙佳勰, 康文怀, 李慧, 等. 桑葚果酒发酵过程中的香气成分变化[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(8):307−316,201. [SUN J X, KANG W H, LI H, et al. Changes of aroma components in mulberry wine during fermentation[J]. Modern Food Technology,2020,36(8):307−316,201. SUN J X, KANG W H, LI H, et al. Changes of aroma components in mulberry wine during fermentation[J]. modern food technology, 2020, 36(8): 307-316, 201.
[34] 蔡健, 施佳康. 黄桃酸奶的加工工艺研究[J]. 食品科技,2011(2):76−79. [CAI J, SHI J K. Study on processing technology of yellow peach yoghurt[J]. Food Science and Technology,2011(2):76−79. CAI J, SHI J K. Study on processing technology of yellow peach yoghurt. Food Science and Technology, 2011(2): 76-79.
[35] 谭琰俐, 吴泳, 刘品, 等. 基于HS-SPME-GC-MS的不同醋龄河溪香醋香气成分比较[J]. 食品与机械,2022,38(8):80−86. [TAN Y L, WU Y, LIU P, et al. Comparison of aroma components of hexi vinegar of different vinegar ages based on HS-SPME-GC-MS[J]. Food and Machinery,2022,38(8):80−86. TAN Y L, WU Y, LIU P, et al. Comparison of aroma components of hexi vinegar of different vinegar ages based on HS-SPME-GC-MS [J]. Food and Machinery, 2022, 38(8): 80-86.
[36] ZHU D S, REN X J, WEI L W, et al. Collaborative analysis on difference of apple fruits flavour using electronic nose and electronic tongue[J]. Scientia Horticulture,2019,26:178−183.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 杜晓仪,杨继国,徐玉娟,吴继军,余元善,邹波,彭健,李璐. 不同益生菌对三华李发酵果汁品质及其体外消化特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(02): 143-151 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



