Optimization of the Preparation Process of Plant-based Chocolate Mousse by Response Surface Methodology
-
摘要: 为积极落实“健康中国”战略,满足人们对绿色健康饮食的需求,本文使用鹰嘴豆水替代奶油打发制备植物基巧克力慕斯。文章研究了煮豆时间、零卡糖添加量和打发温度对鹰嘴豆水泡沫性能的影响,以单因素实验研究鹰嘴豆水添加量、零卡糖添加量和混合温度对慕斯感官品质的影响,并在此基础上以响应面试验优化慕斯制备工艺,并对慕斯营养成分进行检测,分别测定了蛋白质、脂肪和总糖含量。结果表明:鹰嘴豆水在煮豆时间40 min、零卡糖添加量10%、打发温度20 ℃条件下的泡沫性能最佳;慕斯的最优配方与工艺条件为鹰嘴豆水添加量27%、零卡糖添加量17%、混合温度27 ℃,该条件下慕斯的感官评分为89分,与预测值相近。营养成分检测结果显示每100 g慕斯的蛋白质、脂肪和总糖含量分别为5.4 g、13.7 g 和1.4 g,均符合国标要求。最优条件下制备的植物基巧克力慕斯与普通巧克力慕斯相比,感官品质更优,且蛋白质含量更高,脂肪含量更低。Abstract: To support the "Healthy China" strategy and to meet people's demands for a green, healthy diet, aquafaba is used instead of cream in plant-based chocolate mousse. The effects of the cooking time, the addition of zero-calorie sugar, and the whisking temperature on the foam properties of aquafaba were studied. A single factor experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of chickpea water addition, zero calorie sugar addition, and mixing temperature on the sensory quality of mousse. Based on this, a response surface methodology was designed using Box-Benhnken to optimize the mousse preparation process. Besides, an analysis of the nutritional composition of the mousse was performed, including content test of protein, fat and total sugar. It was determined that the foam properties of aquafaba were most optimal under the conditions of 40 min of cooking time, a 10% addition of zero-calorie sugar, and a whisking temperature of 20 ℃. Mousse's best formula and process conditions were 27% aquafaba, 17% zero-calorie sugar, and a 27 ℃ mixing temperature. Under these conditions, the sensory score of the mousse was 89 points, which was in line with the predicted value. Based on the nutrient composition test results, the amount of protein, fat, and total sugar in one hundred grams of mousse was 5.4 g, 13.7 g, and 1.4 g, respectively, which met the national standard requirements. A plant-based chocolate mousse prepared under optimal conditions is higher in protein, has a lower fat content, and has better sensory quality than conventional chocolate mousse.
-
Keywords:
- plant-based /
- mousse /
- aquabafa /
- nutrition /
- response surface
-
植物基食品是以植物蛋白替代动物蛋白制成的一类食品[1]。作为未来食品的代表,植物基食品在健康[2-3]、安全[4]、环保[5]和道德[6]等方面均较传统肉类食品具有显著优势,是满足消费者追求营养健康和可持续生活方式需求的新品类[7],也是未来食品科学发展的重要方向[8]。
传统慕斯蛋糕是指以牛奶、糖、蛋黄、食用胶和奶油为主要原料,经搅打、混合、注模、成型和冷冻而成的具有稳定泡沫结构的充气甜点,其中使用到的动物性原料主要包括牛奶、蛋黄和奶油。牛奶使慕斯更加细腻醇香;鸡蛋具有较好的凝聚和乳化作用,是稳定慕斯的重要成分;奶油打发后填充慕斯使其体积膨大,口感更为芬芳爽口[9-10]。开发新型植物基慕斯蛋糕,需将其中的动物性原料替换为植物性原料[11]。关于蛋糕制作过程中的植物性原料替代国内鲜有报道,但国外有所研究[12]。Rana等[13]研究了鹰嘴豆水代替鸡蛋制作海绵蛋糕的可能性。Lafarga等[14]发现鹰嘴豆烹饪过程中产生的粘性液体具有起泡、乳化和凝胶特性,Buhl等[15]将这种粘性液体命名为鹰嘴豆水(Aquafaba),鹰嘴豆水既指来自鹰嘴豆罐头中的液体,也包括煮沸鹰嘴豆过程中产生的液体。有报道称鹰嘴豆水作为一种纯素、无麸质和无胆固醇的流变添加剂[16],在无蛋蛋黄酱[17]、蛋白酥皮[18]、冰淇淋[19]和烘焙食品[20]等制备中表现出一定潜力,对植物基食品的开发具有重要意义。
为紧跟植物基食品的发展步伐,满足人们对绿色健康饮食的需求,丰富国内对鹰嘴豆水的研究,本研究选取最为常见且深受消费者喜爱的巧克力慕斯为研究对象,使用椰浆替代牛奶,鹰嘴豆水替代蛋黄和奶油,零卡糖替代白砂糖制备植物基巧克力慕斯,研究煮豆时间、零卡糖添加量和打发温度对鹰嘴豆水泡沫性能的影响,通过单因素实验和响应面试验进行配方和工艺优化研究,并对条件下制备的植物基巧克力慕斯进行营养成分分析,为营养健康植物基食品的研究与开发提供一定的参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鹰嘴豆 新疆天山北坡冷粮食品有限公司,2021年8月采收;零卡糖(赤藓糖醇99.71%、罗汉果甜苷0.25%、甜菊糖苷0.04%) 浙江华康药业股份有限公司;纯净水、黑巧克力、海藻胶、椰浆 市售;硫酸、硫酸铜、硫酸钾、氢氧化钠、盐酸、乙醇、无水乙醚、碘化钾等 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
YS20E高压锅 浙江苏泊尔集团有限公司;HM340打蛋器 青岛汉尚电器有限公司;C22-IJ59E电磁炉 浙江苏泊尔集团有限公司;BL4100S电子天平 美国Setra西特公司;ALS250-4A分析天平 德国科恩公司;SE-A6全自动脂肪测定仪 济南阿尔瓦仪器有限公司;KND-1000自动凯氏定氮仪 上海昕瑞仪器仪表有限公司;E2695高效液相色谱系统 美国Waters公司等。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 植物基巧克力慕斯制备工艺
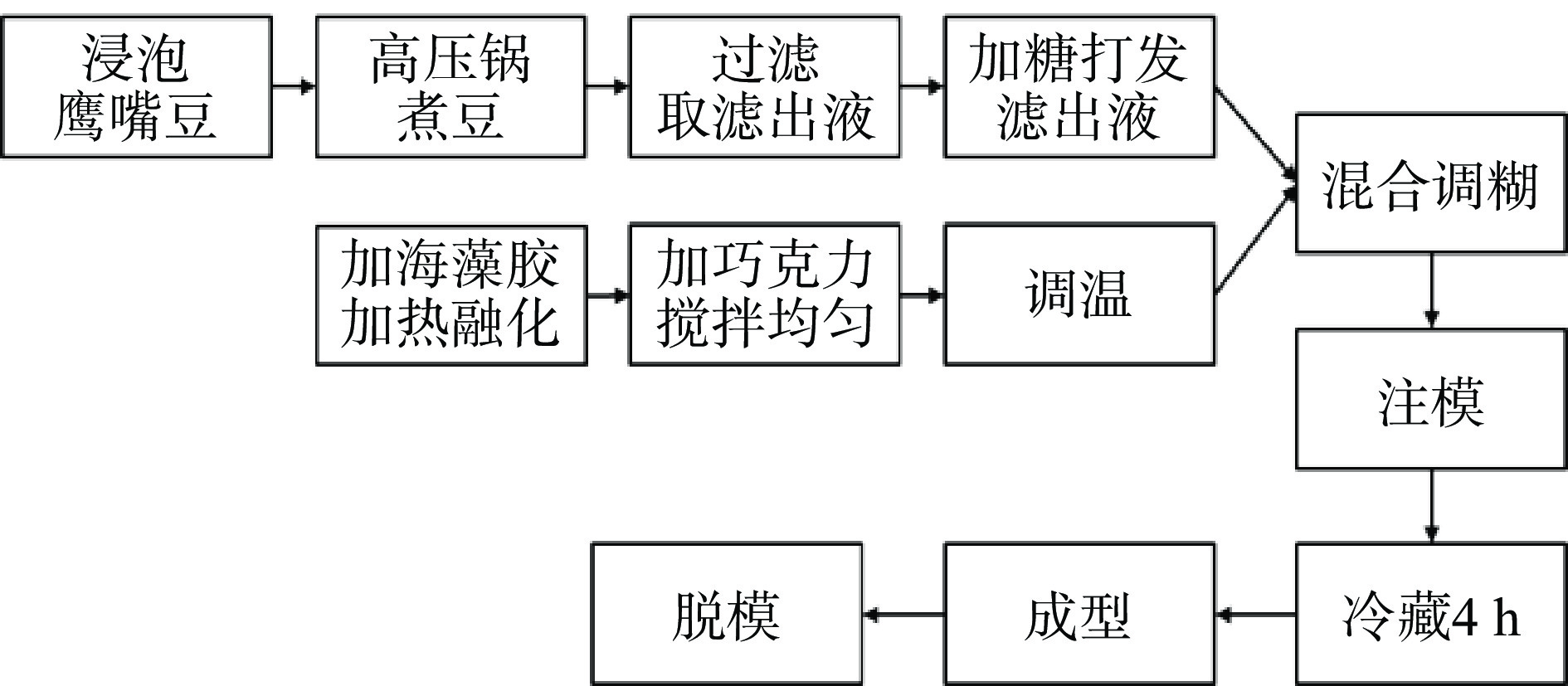
植物基巧克力慕斯制备主要工艺如图1所示:
鹰嘴豆水打发[14]:称取鹰嘴豆500 g,清水浸泡8 h,过滤并弃去滤液,泡发后的鹰嘴豆加入纯净水于高压锅中煮豆一定时间,过滤并将滤出液转移至不锈钢盆中,向滤出液中加入一定量零卡糖,用电动打蛋器高速打发至湿性发泡,拉起打蛋器时有弹性挺立,尾端稍弯曲。
慕斯基底调制:称取210 g椰浆加入一定量零卡糖,加热煮沸,加入4 g海藻胶加热融化,加入220 g黑巧克力搅拌均匀,水浴法对慕斯基底进行调温。
混合注模:将打发后的鹰嘴豆水泡沫加入到调制好的慕斯基底中,翻拌均匀,动作应轻而快,防止发生消泡。将混合均匀的慕斯糊倒入慕斯模具中,用刮刀抹平慕斯表面,放入冰箱冷藏4 h以上,取出后脱模。
1.2.2 单因素实验
取50 g鹰嘴豆,清水浸泡8 h,过滤并弃去滤液,泡发后的鹰嘴豆加入300 mL纯净水于高压锅中煮豆,取上清液并加入零卡糖共计20 mL进行打发实验。固定零卡糖添加量为10%,打发温度为20 ℃,考察鹰嘴豆煮豆时间(20、30、40、50和60 min)对泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响;固定鹰嘴豆煮豆时间为40 min,打发温度为20 ℃,考察零卡糖添加量(0、4%、8%、10%和12%)对泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响;固定零卡糖添加量为10%,鹰嘴豆煮豆时间为40 min,考察打发温度(0、10、20、30和40 ℃),对泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响,零卡糖添加量为零卡糖占含糖鹰嘴豆水总量的百分比。
以鹰嘴豆水打发最优条件为基础,固定零卡糖添加量为17%,混合温度为25 ℃,考察鹰嘴豆水添加量(15%、20%、25%、30%、35%)对慕斯感官品质的影响;固定鹰嘴豆水添加量为25%,混合温度为25 ℃,考察零卡糖添加量(11%、14%、17%、20%、23%)对慕斯感官品质的影响;固定鹰嘴豆水添加量为25%,零卡糖添加量为17%,考察基料混合温度(20、25、30、35、40 ℃)对感官品质的影响,鹰嘴豆水和零卡糖添加量均分别为占混合后慕斯糊总量的百分比。
1.2.3 响应面优化试验
在单因素实验的基础上,以感官评分为响应值,鹰嘴豆水添加量(A)、零卡糖添加量(B)以及混合温度(C)为三个影响因素,根据Box-Behnken试验设计[21]进行三因素三水平的响应面试验,试验的具体因素与水平设计详见表1。运用Design Expert 12.0.3软件进行实验设计以及响应面分析。
表 1 响应面试验因素及水平设计Table 1. Box-Behnken test factors and horizontal design水平 因素 A 鹰嘴豆水添加量(%) B 零卡糖添加量(%) C 混合温度(℃) −1 20 14 20 0 25 17 25 1 30 20 30 1.2.4 泡沫性能测定
在Wang等[22]方法的基础上稍作调整测定鹰嘴豆水打发后的泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性。称取零卡糖溶解于鹰嘴豆水中并定容,取20 mL(记为V0)定容后鹰嘴豆水,于恒温水浴中保温30 min,转移至500 mL塑料量杯中,用电动打蛋器高速打发10 min,打发后泡沫体积记为V1,静置1 h,静置后剩余泡沫体积记为V2,泡沫膨胀率(FE,%)和泡沫稳定性(FS,%)的计算分别如式(1)和式(2):
FE=V1V0×100 (1) FS=V2V1×100 (2) 式中:V0是初使鹰嘴豆水体积,mL;V1是初使泡沫的体积,mL;V2是静置后的泡沫体积,mL。
1.2.5 感官评定
采用感官评定方法对慕斯进行评价。感官评定小组由10位食品专业人员组成,参照GB/T 31059-2014《裱花蛋糕》中对慕斯蛋糕的感官要求[23],建立分别从外观色泽、滋味气味、组织形态和口感四个方面进行评分,每个方面的评分各占25%,合计为总分,详见表2。取10位评委的平均分作为最终评分。
表 2 植物基巧克力慕斯感官评价表Table 2. The sensory evaluation form of plant-based chocolate mousse评价指标 评分标准 评分(分) 外观色泽 表面平整,色泽均匀一致,表面无裂痕 17~25 表面较平整,色泽较为均匀,表面有轻微裂痕 9~16 表面不平整,色泽不均匀,表面有轻微裂痕 0~8 滋味气味 甜度适口,气味浓郁
有该品种应有的风味、无异味17~25 甜度基本适口,气味不足
该品种应有的风味较淡,无明显异味9~16 甜度偏离,气味不足
无该品种应有的风味,有异味0~8 组织形态 组织形态完整,无变形,不析水
内部组织结构紧实,无大气孔17~25 组织形态较完整,略有变形,轻微析水
内部结构较紧实,有气孔9~16 组织形态较完整,略有变形,轻微析水
内部结构较紧实,有气孔0~8 口感 口感细腻,凉爽,无异味,无杂质 17~25 口感较为细腻,无异味,无杂质 9~16 口感不细腻,浓稠,有异味 0~8 1.2.6 成品营养成分测定
植物基巧克力慕斯中蛋白质、脂肪和总糖的测定分别参照GB 5009.5-2016《食品安全国家标准食品中蛋白质的测定》[24]、GB 5009.6-2016《食品安全国家标准食品中脂肪的测定》[25]和GB 5009.8-2016《食品安全国家标准食品中果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖、麦芽糖、乳糖的测定》[26]进行测定。
1.3 数据处理
每组试验均重复3次,使用Box-Benhnken进行试验设计,DesignExpert 12和SPSS 25.0软件进行数据统计分析,使用Origin 9.1软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 泡沫性能影响因素实验结果
鹰嘴豆水中含有糖、可溶性和不溶性纤维等碳水化合物、低分子量蛋白质、皂苷和一些美拉德反应产物[17]。这些成分使鹰嘴豆水具有一定的起泡性能[27]。不同的煮豆时间、零卡糖添加量和打发温度对鹰嘴豆水泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响结果如下。
2.1.1 煮豆时间对泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响
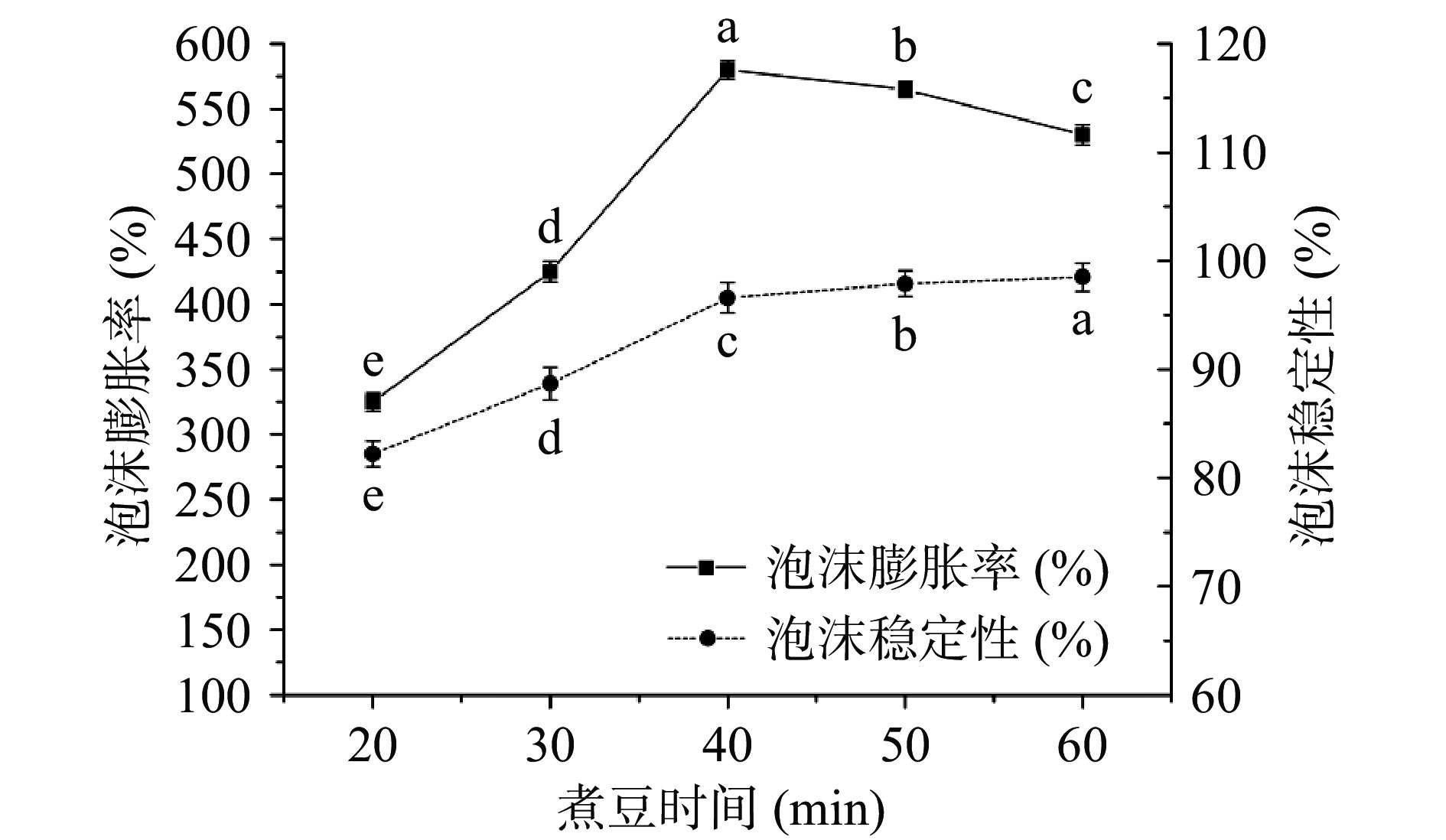
不同煮豆时间对鹰嘴豆水泡沫稳定性和泡沫膨胀率的影响结果如图2所示。
从图2中可以看出,随着煮豆时间的增加,泡沫膨胀率呈现先上升后下降的趋势,在40 min时达到最佳达580%,而泡沫稳定性持续上升。在煮豆过程中,具有起泡性能的蛋白质等成分不断析出,鹰嘴豆水中蛋白质浓度的提高使泡沫膨胀率得以提升,在煮豆时间为40 min时达到最大,而随着煮豆时间的继续增加,鹰嘴豆水的粘度也随之升高,过高的粘度对泡沫的膨胀产生了一定的抑制作用。而鹰嘴豆水粘度的增加,有助于抑制气体在泡沫间流动,从而提升泡沫的稳定性[17]。综合考虑煮豆时间对泡沫稳定性和泡沫膨胀率的影响,确定最佳煮豆时间为40 min。
2.1.2 零卡糖添加量对泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响
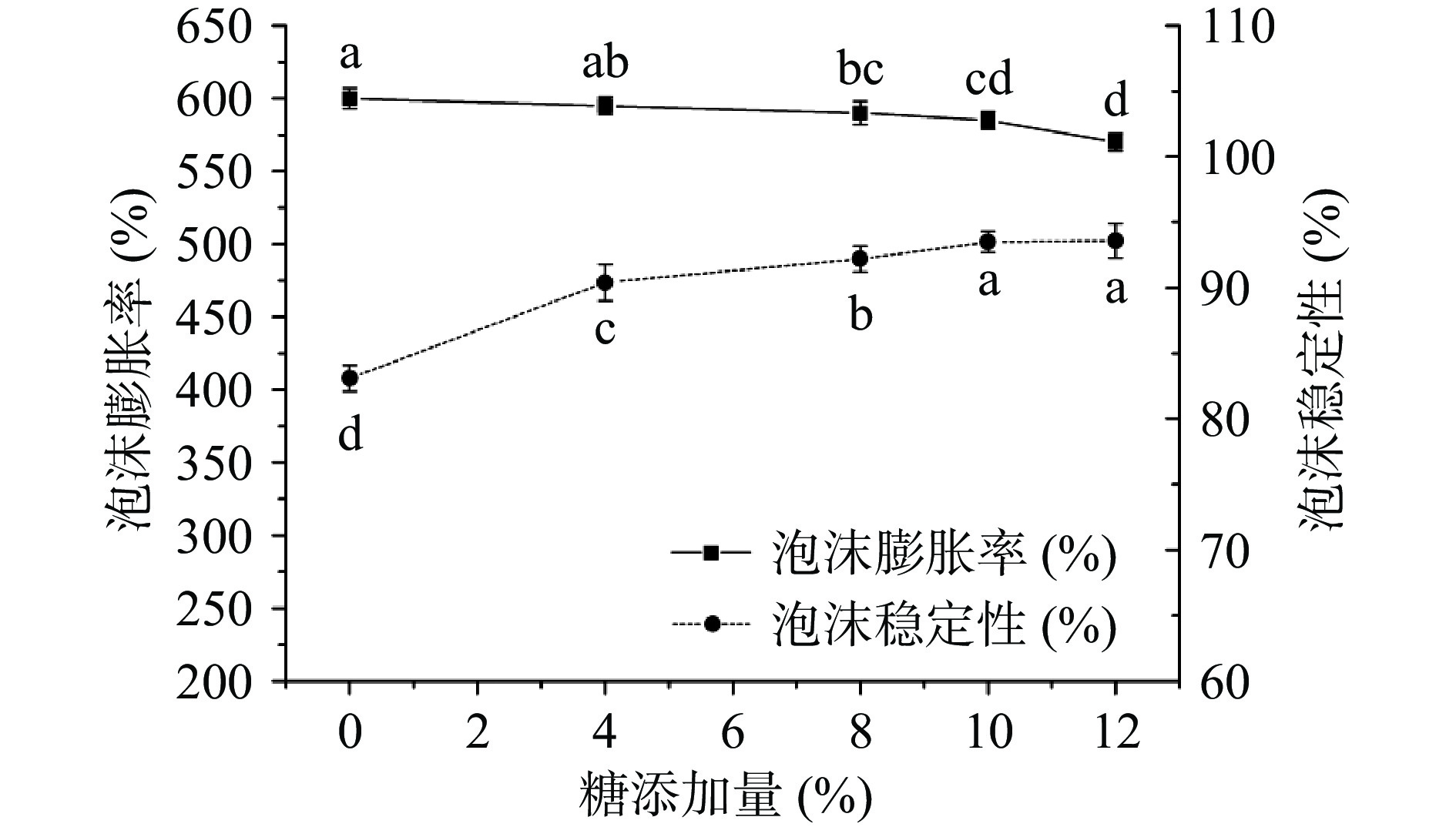
零卡糖的添加对鹰嘴豆水打发的泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响结果如图3所示。
从图3可以看出,随着零卡糖添加量的增加,泡沫膨胀率呈现下降趋势,而泡沫稳定性呈现上升趋势。零卡糖的主要成分为赤藓糖醇,赤藓糖醇的添加会增加蛋白液的粘度,阻碍蛋白分子从液相迁移至气液界面,从而对泡沫的形成产生一定的抑制作用,同时增强泡沫持水能力,泡沫更加稳定,这与Nastaj等[28]的研究结果相一致。综合考虑煮豆时间对泡沫稳定性和泡沫膨胀率的影响,当糖添加量超过10%,泡沫膨胀率下降更为显著(P<0.05),泡沫稳定性上升不显著(P>0.05),因此确定最佳零卡糖添加量为10%。
2.1.3 打发温度对泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响
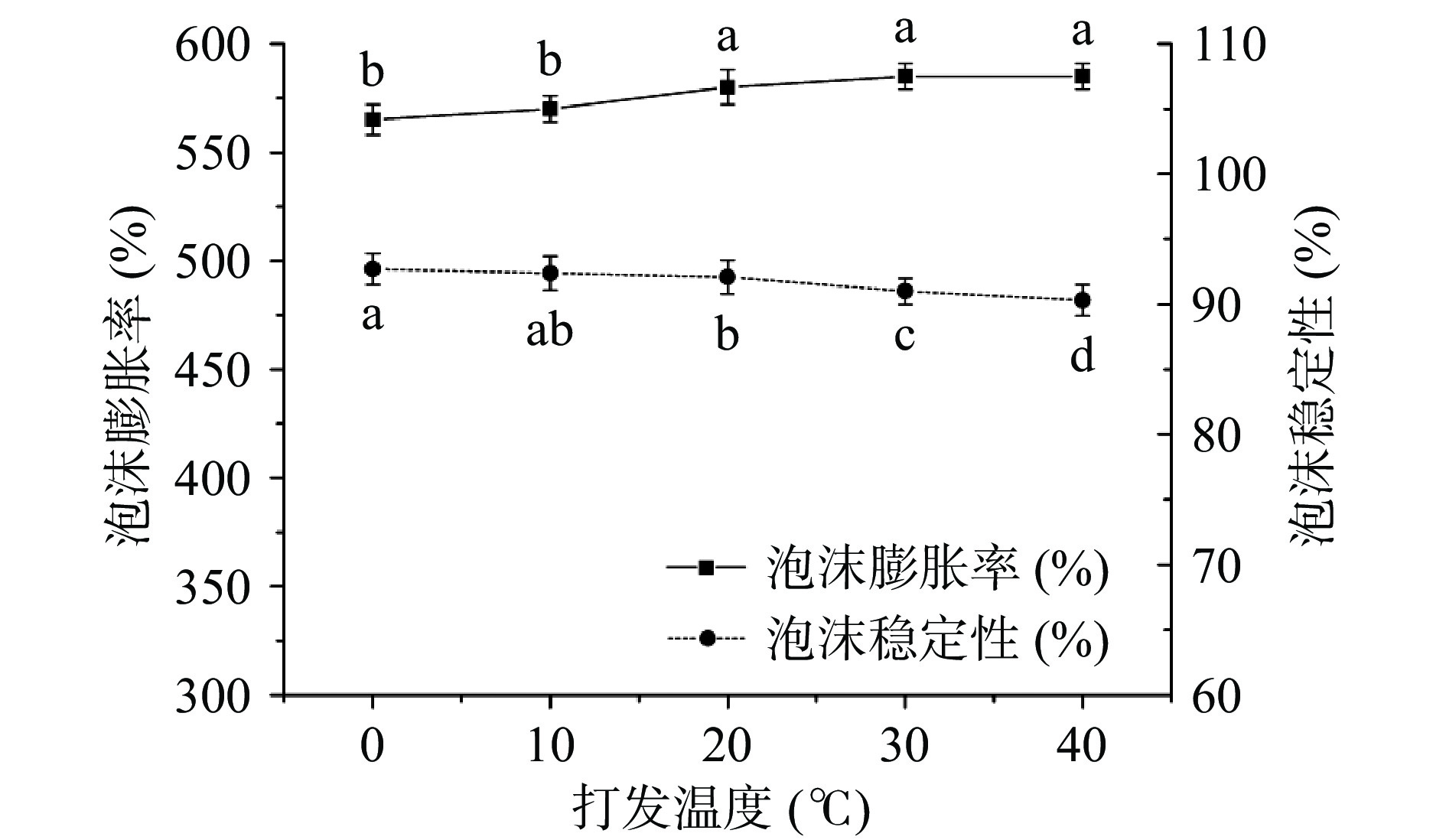
打发温度也是影响泡沫性质的一个因素,其对泡沫膨胀率和泡沫稳定性的影响如图4所示。
从图4可以看出,随着打发温度的升高,泡沫膨胀率略有上升,这可能是由于较高的温度有利于蛋白质的展开,从而促进促进蛋白发泡。泡沫稳定性与温度呈现负相关,温度越低,蛋白气泡表面张力越强,更有利于泡沫的稳定[27]。综合考虑煮豆时间对泡沫稳定性和泡沫膨胀率的影响,当打发温度超过20 ℃时,泡沫膨胀率上升不显著(P>0.05),泡沫稳定性下降更为显著(P<0.05),因此确定最佳打发温度为20 ℃。
2.2 慕斯感官品质影响因素实验结果
2.2.1 鹰嘴豆水添加量对慕斯感官品质的影响
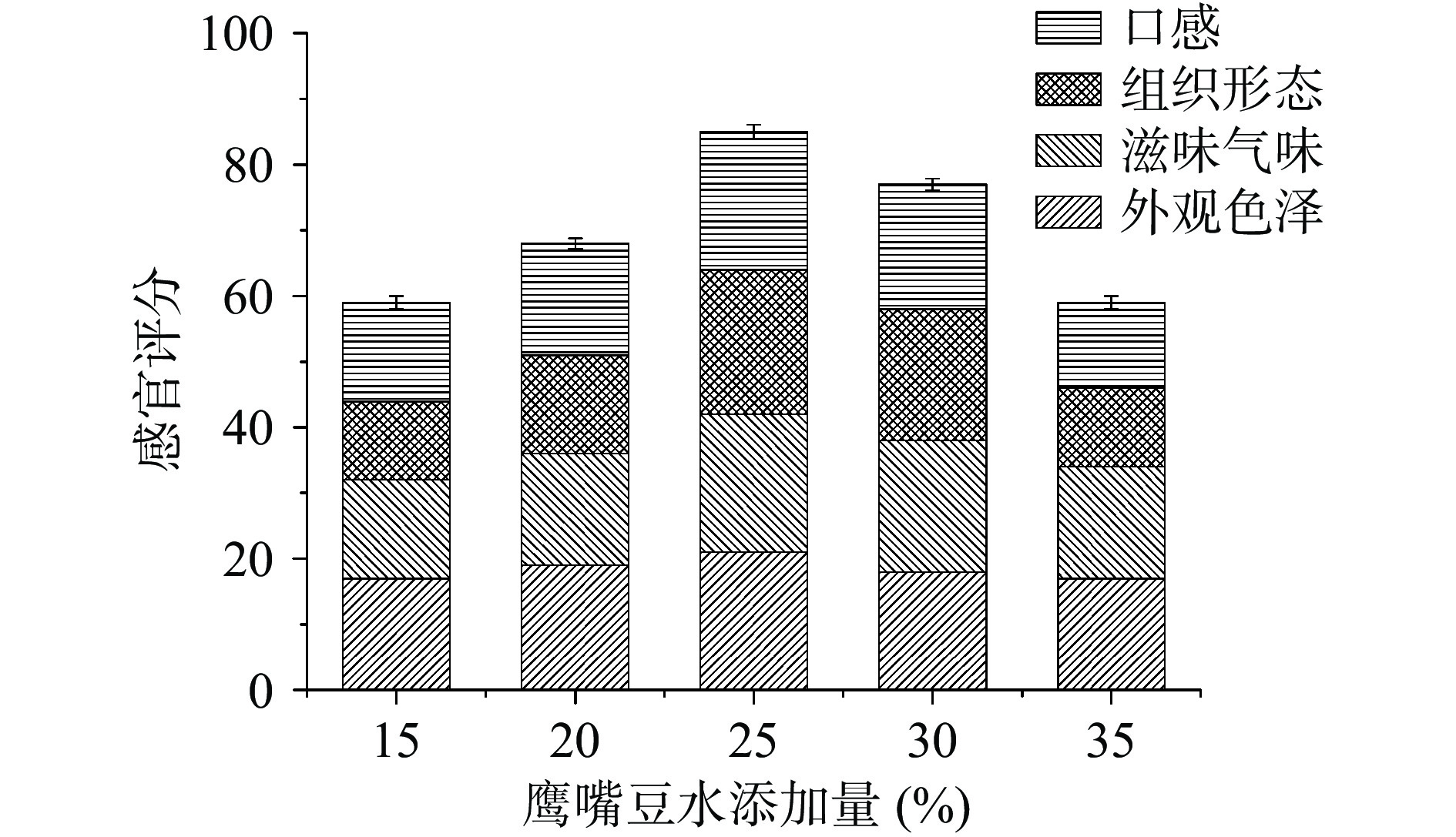
鹰嘴豆水添加量对慕斯感官品质的影响结果如图5所示。
从图5中可以看出,随着鹰嘴豆水添加量的增加,感官评分呈现先上升后下降的趋势。当其添加量为25%时,感官评分最高,为84。鹰嘴豆水添加量过少时,慕斯质地不够细腻;反之,其组织结构不够紧实,易析水。综上,鹰嘴豆水添加量选取20%、25%、30%三水平进行响应面设计。
2.2.2 零卡糖添加量对慕斯感官品质的影响
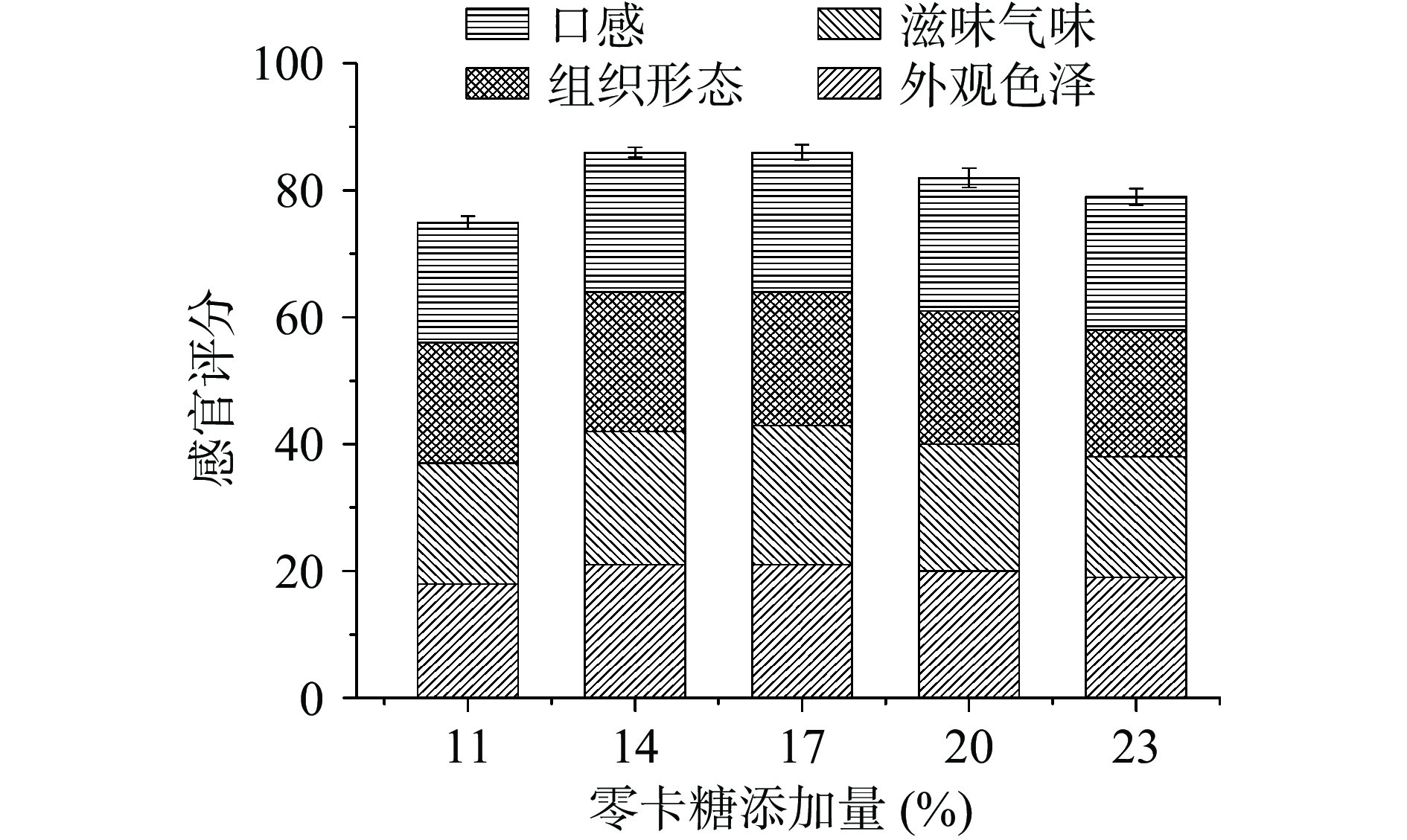
零卡糖添加量对慕斯感官品质的影响结果如图6所示。
从图6中可以看出,随着零卡糖添加量的增加,感官评分先上升后下降。当其添加量为11%时风味不足,口感偏苦,添加量为23%时,则甜味过重,口感腻人。零卡糖的添加量分别为14%和17%时,感官评分相近,在添加量为17%时达到最高。综上,零卡糖添加量选取14%、17%和20%三水平进行响应面设计。
2.2.3 基料混合温度对慕斯感官品质的影响
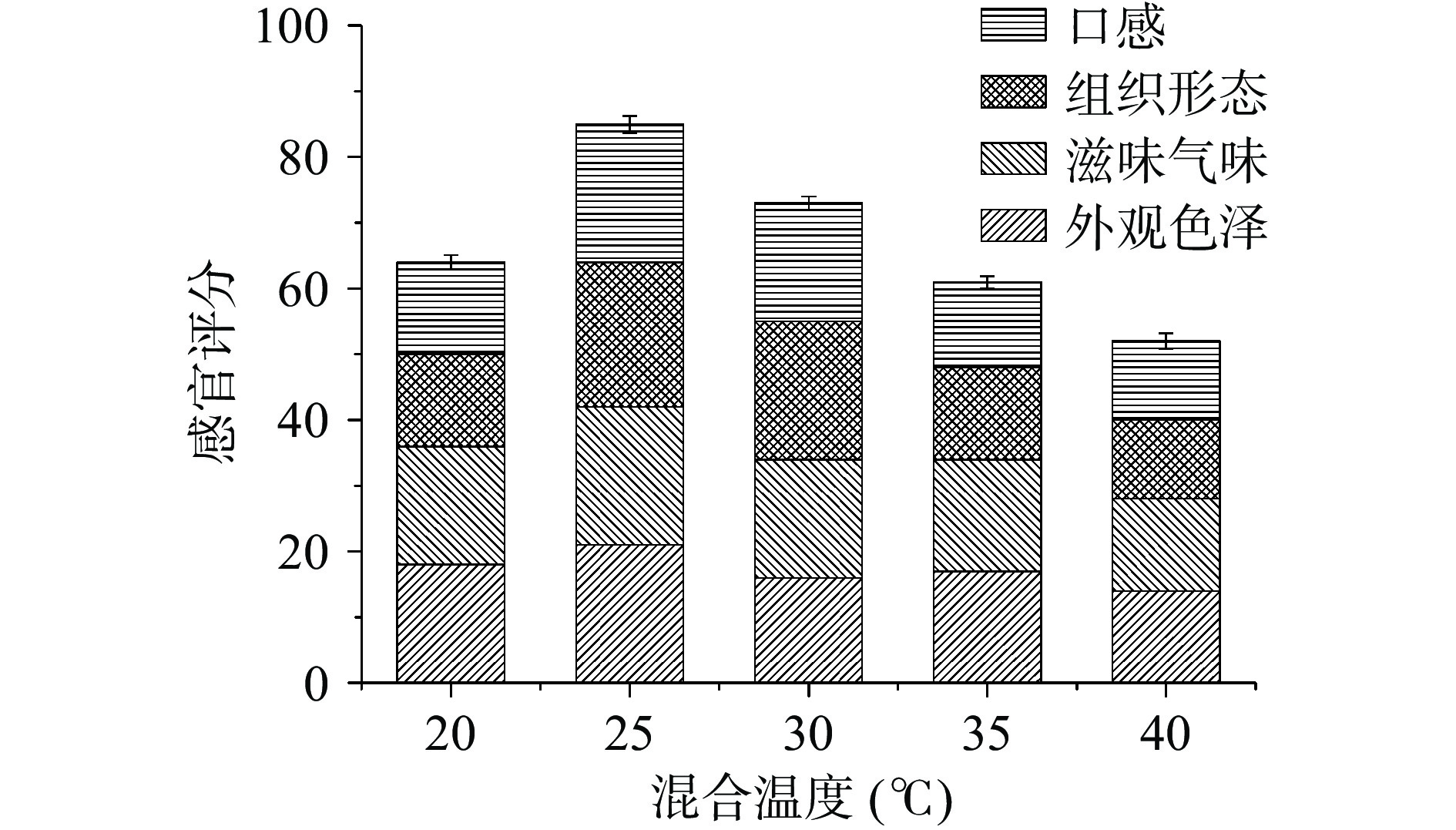
基料混合温度对慕斯感官品质的影响结果如图7所示。
从图7中可以看出,混合温度为25 ℃时,慕斯感官评分最高。高于此温度时,感官评分呈下降趋势,慕斯组织形态变化较为明显,逐步出现塌陷析水的现象,这可能是由于较高的温度影响了鹰嘴豆水泡沫的稳定性;低于此温度,感官评分也较低,慕斯的均匀度和细腻度较差,这是由于该温度下慕斯基底趋于凝固,导致混合效果受到影响[27]。综上,混合温度选取20、25和30 ℃进行响应面设计。
2.3 响应面优化设计与结果分析
2.3.1 响应面试验设计与结果
在单因素实验的基础上,根据Box-Behnken设计原理,以鹰嘴豆水添加量、零卡糖添加量以及混合温度为考察因素,感官评分为响应值,建立17组植物基巧克力慕斯工艺优化试验,试验结果见表3。
表 3 Box-Behnken试验设计和结果Table 3. Box-Behnken test design and results试验号 A 鹰嘴豆水
添加量B 零卡糖
添加量C 混合温度 Y 感官评分
(分)1 −1 −1 0 78 2 1 −1 0 82 3 −1 1 0 75 4 1 1 0 84 5 −1 0 −1 79 6 1 0 −1 83 7 −1 0 1 80 8 1 0 1 86 9 0 −1 −1 84 10 0 1 −1 80 11 0 −1 1 84 12 0 1 1 84 13 0 0 0 88 14 0 0 0 88 15 0 0 0 88 16 0 0 0 87 17 0 0 0 88 2.3.2 模型建立与方差分析
根据表4的试验数据,运用Design Expert软件进行二次多项回归拟合,得到响应值回归方程为:Y=87.80+2.88A−0.63B+C+1.25AB+0.50AC+BC−4.53A2−3.53B2−1.27C2,方差分析结果见表4。
表 4 感官评分的回归模型方差分析Table 4. Regression model analysis of variance for sensory score变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 247.07 9 27.45 63.00 <0.0001 ** A 鹰嘴豆水添加量 66.13 1 66.13 151.76 <0.0001 ** B 零卡糖添加量 3.12 1 3.12 7.17 0.0316 * C 混合温度 8.00 1 8 18.36 0.0036 ** AB 6.25 1 6.25 14.34 0.0068 ** AC 1.00 1 1.00 2.30 0.1736 BC 4.00 1 4.00 9.18 0.0191 * A² 86.21 1 86.21 197.87 <0.0001 ** B² 52.32 1 52.32 120.08 <0.0001 ** C² 6.84 1 6.84 15.71 0.0054 ** 残差 3.05 7 0.4357 失拟项 2.25 3 0.75 3.75 0.1171 误差项 0.80 4 0.20 总和 250.12 16 R2=0.9878 R2Adj=0.9721 信噪比=25.28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 从表4可以看出,该模型P值小于0.01,表明模型具有极显著性,失拟项F值为3.75,P值为0.1171,大于0.05,失效项不显著,相关系数R2和R2Adj分别为0.9878和0.9721,信噪比为25.28,远大于4,表明该模型拟合程度较好,模型可靠[29]。一次项A和C的影响极显著,一次项B影响显著(P<0.05);交互项AB极显著(P<0.01),BC显著(P<0.05),AC不显著(P>0.05);二次项A2、B2和C2均极显著(P<0.01)。由F值可知,三个因素对响应值感官评分的影响大小排序为鹰嘴豆水添加量(A)>混合温度(C)>零卡糖添加量(B)。
2.3.3 响应面分析
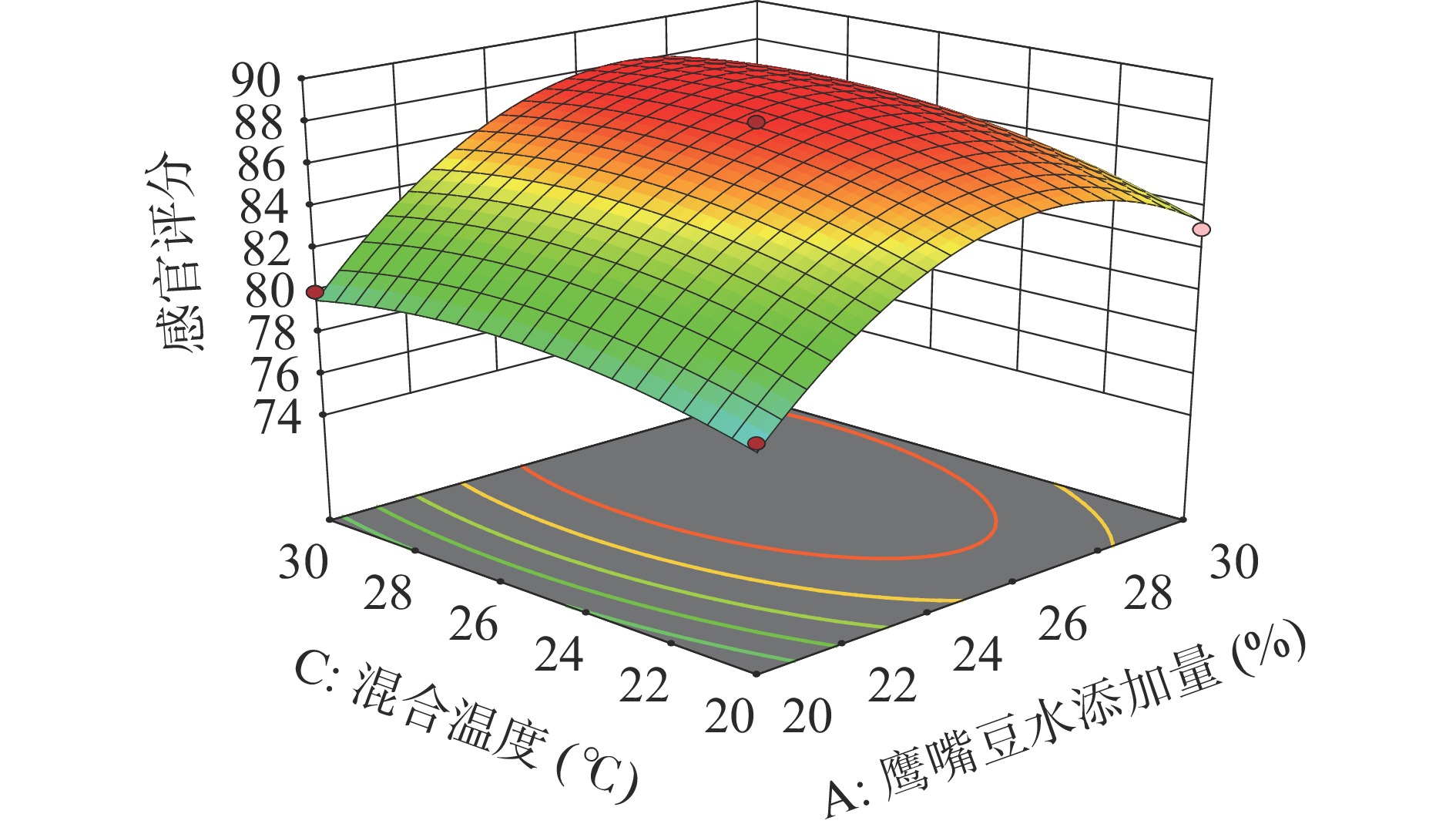
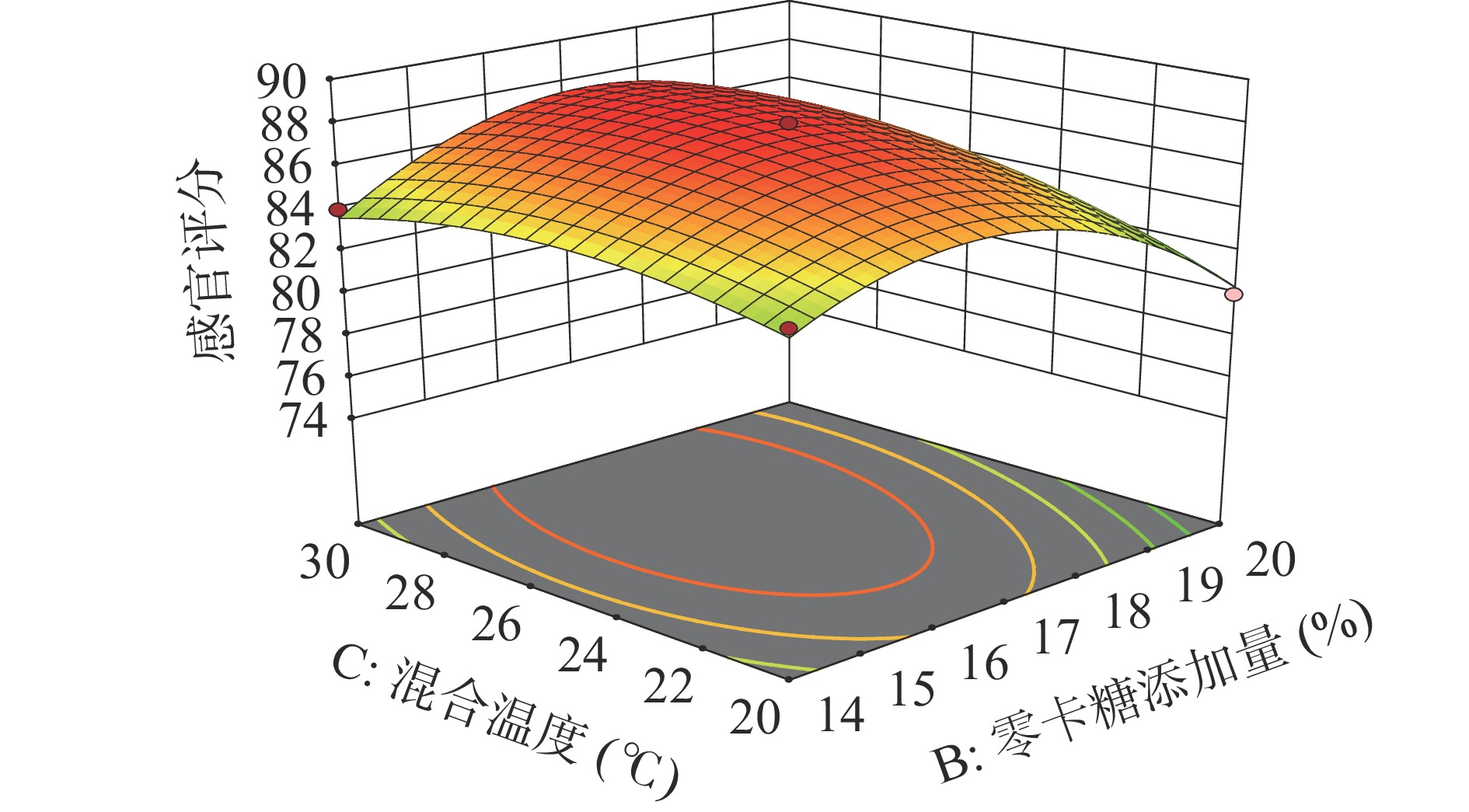
鹰嘴豆水添加量(A)、零卡糖添加量(B)和混合温度(C)两两交互作用对感官评分影响的响应面图见图8~图10。由图可知鹰嘴豆水添加量和零卡糖添加量(AB)、零卡糖添加量和混合温度(BC)交互作用的响应曲面坡度趋势陡峭,表明这两组交互作用对感官评分影响显著,而鹰嘴豆水添加量和混合温度(AC)交互作用的响应曲面趋势平缓,对感官评分影响较小。响应面分析结果与方差分析结果一致。
2.3.4 最优条件与验证试验
通过Design Expert软件分析计算,得到植物基巧克力慕斯最优工艺条件为:鹰嘴豆水添加量26.75%、零卡糖添加量17.12%和混合温度27.39 ℃,在此条件下,感官评分预测值为88.53分。为方便试验操作,调整工艺条件为鹰嘴豆水添加量27%、零卡糖添加量17%和混合温度27 ℃进行3组验证试验,得到感官评分为89,与预测值接近。
2.4 成品营养成分测定结果
按照优化后的工艺条件制备植物基巧克力慕斯蛋糕,按照Gisslen[30]的方法制备普通巧克力慕斯,运用国标方法分别测定两种巧克力慕斯中蛋白质、脂肪和总糖含量,并将检测结果与GB/T 31059-2014《裱花蛋糕》中对慕斯蛋糕的理化检测要求[23]进行比对,结果详见表5。从表5中我们可以看出,两种巧克力慕斯每100 g的蛋白质、脂肪和总糖含量均符合国标要求。植物基巧克力慕斯相比普通巧克力慕斯,蛋白质含量较高、脂肪含量较低。此外,由于植物基巧克力在制备过程中使用了零卡糖代替白砂糖,因此在保证口感的同时,总糖含量也远低于普通巧克力慕斯。
表 5 巧克力慕斯营养成分比对Table 5. Nutrition facts comparison of chocolate mousse每100 g
慕斯含量普通巧克力
慕斯植物基巧克力
慕斯国标要求
GB/T
31059-2014能量(kcal) 211.5±1.3 150.5±1.4 − 蛋白质(g) 4.2±0.2 5.4±0.1 ≥3 脂肪(g) 15.1±0.1 13.7±0.2 ≥5 总糖(g) 14.7±0.1 1.4±0.1 ≤50 感官评分 88 89 − 3. 结论
通过鹰嘴豆水替代奶油打发制备植物基巧克力慕斯,首先通过单因素实验,确定了鹰嘴豆水的打发条件为:煮豆时间40 min、零卡糖添加量10%和打发温度20 ℃;其次通过单因素实验研究了鹰嘴豆水添加量、零卡糖添加量和基料混合温度对慕斯感官品质的影响,并在此基础上通过Box-Behnken响应面试验优化慕斯制备工艺,得到最佳的工艺条件为鹰嘴豆水添加量27%、零卡糖添加量17%和混合温度27 ℃,该条件下制备的慕斯表面平整,甜度适口,气味浓郁,口感细腻。与普通巧克力慕斯相比,植物基巧克力慕斯的品质更优、营养成分组成更优。在良好口感的基础上,更加营养健康,既满足了人们对绿色健康饮食的需求,也为植物基食品的开发和利用提供了新途径。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素及水平设计
Table 1 Box-Behnken test factors and horizontal design
水平 因素 A 鹰嘴豆水添加量(%) B 零卡糖添加量(%) C 混合温度(℃) −1 20 14 20 0 25 17 25 1 30 20 30 表 2 植物基巧克力慕斯感官评价表
Table 2 The sensory evaluation form of plant-based chocolate mousse
评价指标 评分标准 评分(分) 外观色泽 表面平整,色泽均匀一致,表面无裂痕 17~25 表面较平整,色泽较为均匀,表面有轻微裂痕 9~16 表面不平整,色泽不均匀,表面有轻微裂痕 0~8 滋味气味 甜度适口,气味浓郁
有该品种应有的风味、无异味17~25 甜度基本适口,气味不足
该品种应有的风味较淡,无明显异味9~16 甜度偏离,气味不足
无该品种应有的风味,有异味0~8 组织形态 组织形态完整,无变形,不析水
内部组织结构紧实,无大气孔17~25 组织形态较完整,略有变形,轻微析水
内部结构较紧实,有气孔9~16 组织形态较完整,略有变形,轻微析水
内部结构较紧实,有气孔0~8 口感 口感细腻,凉爽,无异味,无杂质 17~25 口感较为细腻,无异味,无杂质 9~16 口感不细腻,浓稠,有异味 0~8 表 3 Box-Behnken试验设计和结果
Table 3 Box-Behnken test design and results
试验号 A 鹰嘴豆水
添加量B 零卡糖
添加量C 混合温度 Y 感官评分
(分)1 −1 −1 0 78 2 1 −1 0 82 3 −1 1 0 75 4 1 1 0 84 5 −1 0 −1 79 6 1 0 −1 83 7 −1 0 1 80 8 1 0 1 86 9 0 −1 −1 84 10 0 1 −1 80 11 0 −1 1 84 12 0 1 1 84 13 0 0 0 88 14 0 0 0 88 15 0 0 0 88 16 0 0 0 87 17 0 0 0 88 表 4 感官评分的回归模型方差分析
Table 4 Regression model analysis of variance for sensory score
变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 247.07 9 27.45 63.00 <0.0001 ** A 鹰嘴豆水添加量 66.13 1 66.13 151.76 <0.0001 ** B 零卡糖添加量 3.12 1 3.12 7.17 0.0316 * C 混合温度 8.00 1 8 18.36 0.0036 ** AB 6.25 1 6.25 14.34 0.0068 ** AC 1.00 1 1.00 2.30 0.1736 BC 4.00 1 4.00 9.18 0.0191 * A² 86.21 1 86.21 197.87 <0.0001 ** B² 52.32 1 52.32 120.08 <0.0001 ** C² 6.84 1 6.84 15.71 0.0054 ** 残差 3.05 7 0.4357 失拟项 2.25 3 0.75 3.75 0.1171 误差项 0.80 4 0.20 总和 250.12 16 R2=0.9878 R2Adj=0.9721 信噪比=25.28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 5 巧克力慕斯营养成分比对
Table 5 Nutrition facts comparison of chocolate mousse
每100 g
慕斯含量普通巧克力
慕斯植物基巧克力
慕斯国标要求
GB/T
31059-2014能量(kcal) 211.5±1.3 150.5±1.4 − 蛋白质(g) 4.2±0.2 5.4±0.1 ≥3 脂肪(g) 15.1±0.1 13.7±0.2 ≥5 总糖(g) 14.7±0.1 1.4±0.1 ≤50 感官评分 88 89 − -
[1] 李兆丰, 孔昊存, 刘延峰, 等. 未来食品: 机遇与挑战[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(4):1−13. [LI Zhaofeng, KONG Haocun, LIU Yanfeng, et al. Future food: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Journal of China Food Science and Technology,2022,22(4):1−13. LI Zhaofeng, KONG Haocun, LIU Yanfeng, et al. Future food: Opportunities and challenges[J]. Journal of China Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(4): 1-13.
[2] WILLET T, ROCKSTRO M, LOKE N, et al. Food in the anthropocene: The EAT–Lancet commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems[J]. Lancet,2019,393(10170):447−492. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31788-4
[3] MARCO S, MICHAEL C, DANIEL M D, et al. Options for keeping the food system within environmental limits[J]. Nature,2018,562(7728):519−525. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0594-0
[4] MOHAMMADI C, ALINIA-AHANDANI E. Plant-based diets and cardiovascular disease[J]. Open Journal of Cardiology & Diseases,2020,3(2):1−3.
[5] CLARK M, TILMAN D. Comparative analysis of environmental impacts of agricultural production systems, agricultural input efficiency and food choice[J]. Environmental Research Letters,2017,12(6):064016. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/aa6cd5
[6] CP A, MP A, JGAB C. Consumer perceptions of conventional and alternative protein sources: A mixed-methods approach with meal and product framing[J]. Appetite,2020,156:104860.
[7] ALCORTA A, PORTA A, TÁRREGA A, et al. Foods for plant-based diets: Challenges and innovations[J]. Foods,2021,10(2):293. doi: 10.3390/foods10020293
[8] 中国食品科学技术学会植物基食品分会. 植物基食品的科学共识(2022年版)[J]. 中国食品学报, 2022, 22(10): 8 Plant-Based Foods Society of The Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology. Scientific consensus on plant-based foods (2022 Edition)[J] Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(10): 8.
[9] LINA, CASALE, ARAGON-ALEGRO, et al. Potentially probiotic and synbiotic chocolate mousse[J]. Swiss Society of Food Science and Technology,2007:669−675.
[10] STANLEY G. The Technology of Dairy Products[M]. 1998.
[11] 中国食品科学技术学会. T/CIFST002-2021植物基食品通则[M]. 北京. 2021 China Institute of Food Science and Technology. T/CIFST002-2021 General principles of plant-based foods[M]. Beijing, 2021.
[12] GROSSMANN L, KINCHLA A J, NOLDEN A, et al. Standardized methods for testing the quality attributes of plant-based foods: Milk and cream alternati[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2021,20:2206−2233. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12718
[13] RANA M, HE Y, YOUNG S Y, et al. Aquafaba, wastewater from chickpea canning, functions as an egg replacer in sponge cake[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,53(10):2247−2255. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.13813
[14] LAFARGA T, VILLARÓ S, BOBO G, et al. Optimisation of the pH and boiling conditions needed to obtain improved foaming and emulsifying properties of chickpea aquafaba using a response surface methodology[J]. International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science,2019,18:100177. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgfs.2019.100177
[15] BUHL T F, CHRISTENSEN C H, HAMMERSHOJ M. Aquafaba as an egg white substitute in food foams and emulsions: Protein composition and functional behavior[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,96(NOV):354−364.
[16] HE Y, MEDA V, REANEY M J T, et al. Aquafaba, a new plant-based rheological additive for food applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,111:27−42.
[17] RAIKOS V, HAYES H, HE N. Aquafaba from commercially canned chickpeas as potential egg replacer for the development of vegan mayonnaise: Recipe optimization and storage stability[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,55(5):1935−1942.
[18] STANTIALL S E, DALE K J, CALIZO F S, et al. Application of pulses cooking water as functional ingredients: The foaming and gelling abilities[J]. European Food Research & Technology,2018(1):244.
[19] LIN A, CASAL E, ARAGON-ALEGR O, et al. Potentially probiotic and synbiotic chocolate mousse[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2007,40(4):669−675. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2006.02.020
[20] ABERATHNE P, NAVARATNE S B, WICKRAMASINGHE I. Development of ready to bake plant based cake mixture for vegetarians and egg allergens[J]. Tropical Agricultural Research and Extension,2015(4):153−158.
[21] 徐向宏, 何明珠. 试验设计与Design-Expert、SPSS应用[M]. 科学出版社, 2010 XU Xianghong, HE Mingzhu. Experimental design and application of Design-Expert and SPSS[M]. Science Press, 2010.
[22] WANG G, WANG T. Improving foaming properties of yolk-contaminated egg albumen by basic soy protein[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,74(8):C581−C587.
[23] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 中国国家标准化委员会. GB/T 31059-2014裱花蛋糕[M]. 北京; 中国标准出版社. 2014 General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 31059-2014 Decorative cake[M]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2014.
[24] 中国人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.5-2016食品安全国家标准食品中蛋白质的测定[M]. 北京; 中国标准出版社. 2016 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the P. R. C. GB 5009.5-2016 National standard for food safety-determination of protein in food[M]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[25] 中国人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.6-2016食品安全国家标准食品中脂肪的测定[M]. 北京; 中国标准出版社. 2016 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the P. R. C. GB 5009.6-2016 National standard for food safety-determination of fat in food[M]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[26] 中国人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.8-2016食品安全国家标准食品中果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖、麦芽糖、乳糖的测定[M]. 北京; 中国标准出版社. 2016 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the P. R. C. GB 5009.8-2016 National standard for food safety-determination of fructose glucose sucrose maltose and lactose in food[M]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[27] SHIM Y Y, MUSTAFA R, SHEN J et al. Composition and properties of aquafaba: Water recovered from commercially canned chickpeas[J]. Journal of Visualized Experiments Jove,2018,132(1−14).
[28] NASTAJ M, SOOWIEJ B G, TERPIOWSKI K, et al. Effect of erythritol on physicochemical properties of reformulated high protein meringues obtained from whey protein isolate[J]. International Dairy Journal, 2020, 105(104672).
[29] KHURI A I, CORNELL J A. Response surfaces: Designs and analyses: Second edition[M]. 2018.
[30] GISSLEN W. The professional bakeshop[M]. 2013.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 胡玥,孙红男,张苗,木泰华. 食物源肽与淀粉相互作用的研究进展. 食品科学. 2023(09): 163-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



