Screening, Identification and Characterization of a Marine Chitinase-Producing Strain Gallaecimonas xiamenensis Chi34
-
摘要: 目的:海洋是自然界中含几丁质最多的生态系统,孵育了大量可降解利用几丁质的微生物,因此利用海洋微生物几丁质酶降解几丁质,是获得高附加值几丁寡糖的重要方法。本试验以连云港海域海泥为样品,以期筛选获得稳定的产几丁质酶菌株。方法:利用平板筛选法和摇瓶发酵复筛法筛选获得产几丁质酶菌株Chi34,利用形态学分析和16S rDNA序列分析对菌株进行鉴定,同时还研究了温度、pH、金属离子、EDTA及SDS等因素对Chi34几丁质酶的影响,最后通过TLC实验分析了Chi34几丁质酶降解几丁质胶体的产物。结果:菌株Chi34鉴定为厦门加西利亚单胞菌(Gallaecimonas xiamenensis),其几丁质酶酶活力为0.631 U/mL,最适反应温度为35 ℃,最适反应pH为6.0, Na+、Ca2+、Mn2+、K+对Chi34几丁质酶具有显著的激活作用,Cu2+、Fe3+、Ba2+、Zn2+、Cd2+、Co2+ 、EDTA和SDS等对Chi34几丁质酶有抑制作用,Chi34几丁质酶降解几丁质胶体得到的产物主要是几丁二糖和少量的几丁单糖。结论:本研究的几丁质酶能催化几丁质胶体产生几丁二糖和几丁单糖,可为几丁质的高值化利用提供一定的理论参考。Abstract: Objective: The marine ecosystem contains the most chitin in nature, which incubates a large number of microorganisms that can degrade and utilize chitin, therefore, the degradation of chitin by marine microbial chitinase is an important way to produce high value-added chitooligosaccharides. The aim of this study was to screen a stable chitinase-producing strain from the marine mud in Lianyungang. Methods: The chitinase-producing strain Chi34 was screened by plate screening and flask shaking fermentation re-screening and identified by morphological analysis and 16S rDNA sequence analysis. Then, effects of temperature, pH, metal ions, EDTA and SDS on Chi34 chitinase were studied. Finally, the TLC experiment was taken to analyze products of colloidal chitin hydrolyzed by Chi34 chitinase. Result: The isolated strain Chi34 was identified as Gallaecimonas xiamenensis and the activity of Chi34 chitinase was 0.631 U/mL. The optimum pH and temperature for the chitinolytic activity were 6.0 and 35 ℃, respectively. Chi34 chitinase was highly activated by Na+, Ca2+, Mn2+, and K+, while inhibited by Cu2+, Fe3+, Ba2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Co2+, EDTA, and SDS. The main products of chitin hydrolyzed by Chi34 chitinase were (GlcNAc)2 with little GlcNAc. Conclusion: The Chi34 chitinase could hydrolyze chitin to produce (GlcNAc)2 and GlcNAc, which would provide a certain theoretical reference for the high value utilization of chitin.
-
Keywords:
- chitinase /
- identification /
- Gallaecimonas xiamenensis /
- enzymatic properties
-
几丁质是一种线性糖类多聚物,由N-乙酰葡萄糖胺通过β-1,4糖苷键连接而成,也称为甲壳素,是第二大天然的有机化合物,是甲壳类动物壳、某些昆虫和其他节肢动物外骨骼的构成成分,几丁质也存在于大多数真菌和一些藻类的细胞壁中[1],是海洋生物圈中来源最丰富的碳源。据统计,几丁质每年的产量大约为1010~1011吨,其中,绝大部分是由海洋生态系统产生的[2~4]。几丁质的溶解性差,难以开发利用,而其降解产物——几丁寡糖因具有良好的溶解性、抗氧化性和抗肿瘤活性,被广泛应用于医药、食品添加剂、农业、保健品等行业,具有较高的商业价值[5]。因此,高效绿色便捷地制备几丁寡糖具有重要的经济意义,而生物酶降解几丁质生产几丁寡糖因具有高效、专一、绿色环保等优点,成为近年来开发几丁质及其衍生物的研究热点[3]。
在自然界中几丁质酶(Chitinase,EC 3.2.1.14)是降解天然几丁质关键性酶[6],几丁质经几丁质酶降解为聚合度低的几丁寡糖,从而被生物体加以利用。几丁质酶在环保、农业及食品、保健品等行业的应用都有相关报道,如Wang等[7]通过将Bacillus subtilis几丁质酶进行重组表达,成功应用于虾蟹壳废物的降解;Pseudomonas fluorescens几丁质酶经纯化后能够抑制茶蚊子的生长[8],经几丁质酶处理几丁质得到的几丁寡糖被广泛应用于食品、保健品[9]等。目前,可分泌几丁质酶的生物体分布较广,主要有Aeromonas media[10]、Serratia marcescens[11]等细菌、烟曲霉(Aspergillus fumigatus)[12]、绿色木霉[13]等真菌、以及病毒等。细菌来源几丁质酶因其生产成本低、产率高和良好的适应性,更受工业应用的青睐[14],而海洋环境因其具有陆地无法比拟的优势,海洋几丁质酶具备能够适应某些特殊条件下的工业生产潜质,有一定的工业应用前景[15]。目前,虽然国内外有很多关于海洋几丁质酶的报道,但大部分无法满足几丁寡糖工业生产需求[16],几丁寡糖产品依然是通过化学方法生产,因此,筛选出优质的海洋几丁质酶菌株在工业上利用海洋几丁质酶生产几丁寡糖仍具现实意义。
本课题组以连云港黄海海域海泥为样品,从中筛选得到一株产几丁质酶菌株,经形态学分析和分子生物学鉴定为厦门加西利亚单胞菌(Gallaecimonas xiamenensis),并对其酶学性质进行研究,以期为绿色生产几丁寡糖提供优良菌株,为几丁质废弃物高值化利用提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
海泥样品 采自江苏省连云港市在海一方公园海滩滩涂(34.76 °N,119.38 °E),此处虾蟹壳沉积物丰富,利于诱导微生物分泌几丁质酶。取样后,立即封袋,置于装有冰袋的泡沫箱中,运回实验室,4 ℃冰箱保存;细粉几丁质 BR纯,阿拉丁化学试剂有限公司;胰蛋白胨、酵母粉 BR纯,日本Oxoid;细菌通用引物(27F、1492R)、N-乙酰-氨基葡萄糖 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;细菌基因组DNA提取试剂盒 天根生化科技有限公司;PCR试剂盒 北京全式金生物技术有限公司;DNS试剂 福州飞净(Phygene)科技有限公司;几丁寡糖标准品 青岛博智汇力生物科技有限公司;其余常用试剂均为国药分析纯;富集培养基(g/L):细粉几丁质10,胶体几丁质1,KH2PO4 0.3,K2HPO4 0.7,ZnSO4 0.01,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5,FeSO4·7H2O 0.01,陈海水配制,pH自然;筛选培养基(g/L):几丁质胶体10,(NH4)2SO4 10,KH2PO4 0.3,K2HPO4 0.7,NaCl 5,MgSO4·7H2O 1.5,琼脂20,陈海水配制,pH自然;液体种子培养基(g/L):酵母提取物5,胰蛋白胨10,NaCl 10,pH自然;固体种子培养基(g/L):酵母提取物5,胰蛋白胨10,NaCl 10,琼脂20,pH自然;摇瓶发酵培养基(g/L):酵母提取物4,胰蛋白胨2,MgSO4·7H2O 4,KH2PO4 1.2,K2HPO4 2.8,胶体几丁质15,pH自然。
LDZM-80L-I立式高压灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂;KYC-100C摇床 上海新苗医疗器械制造有限公司;SW-CJ-1D超净工作台 浙江夏孚医疗科技有限公司;722型可见光分光光度计 上海光谱仪器有限公司;LRH-70F恒温培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;Nikon 90i全电动显微镜 日本尼康;Veriti 96孔梯度PCR扩增仪 美国ABI;LYNX 6000高速冷冻离心机 Thermo Scientific;C600全能凝胶成像系统 美国Azure。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 胶体几丁质的配制
参考Roberts等[17]的方法稍加改进。准确称取25 g几丁质粉末加入至150 mL蒸馏水中,充分搅拌成糊状后,在磁力搅拌器上边搅拌边缓慢加入150 mL预冷的80% H2SO4,搅拌过夜后,加入至2 L预冷的95%乙醇中,混匀,置于4 ℃冰箱,静置过夜后,4 ℃ 5000 r/min离心20 min,弃去乙醇,用去离子水反复洗涤、离心沉淀直至中性,收集洗净后的沉淀,加入500 mL去离子水,置于4 ℃下保存备用。
1.2.2 产几丁质酶海洋菌株的筛选
初筛:取1 g海泥样品加入至50 mL富集培养基中,在摇床中180 r/min 30 ℃培养5 d,富集后样品按10−1、10−2、10−3、10−4、10−5、10−6浓度梯度稀释,并涂布于筛选培养基上,每个浓度梯度涂布三个平板,30 ℃倒置培养3~5 d,每天观察菌落生长情况。挑取产生透明圈明显的菌落三区划线至LB固体培养基纯培养,分离出单菌落,用灭菌的牙签挑取单菌落接种至筛选培养基上,继续观察菌株生长情况和透明圈。
复筛:将产生透明圈明显的单菌落接种至LB液体培养基中,30 ℃培养24 h后,按1%的接种量接种至摇瓶发酵培养基中,发酵培养72 h,用DNS法测定粗酶液的酶活力。选取酶活力强的菌株进行下一步鉴定。
酶活力测定方法:用DNS法测定菌株的酶活力,参考文献[10]方法稍加改变。将菌株接种至发酵培养基中培养72 h,形成的混合液即为发酵液,取发酵液1 mL,12000 r/min 4 ℃离心5 min,得到的上清液即为粗酶液。将粗酶液与1%几丁质胶体、0.2 mol/L pH7.0的PBS缓冲液按体积比0.5 mL:0.5 mL: 1 mL混匀,37 ℃水浴保温30 min后,煮沸10 min终止反应,再加入0.5 mL DNS试剂,沸水浴中加热10 min显色,冷却至室温,定容至25 mL,在540 nm波长下测吸光度值。灭活的粗酶液按以上方法处理,作为对照,测定菌株粗酶液的酶活力。
酶活力定义:在37 ℃下,每分钟降解底物生成1 μmol N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖所需的酶的量作为一个活性单位。
1.2.3 产几丁质酶海洋菌株的鉴定
根据《常见细菌系统鉴定手册》和《伯杰氏细菌鉴定手册》进行形态学分析。利用16S rDNA技术进行分子生物学鉴定。将菌株接种至LB固体培养基中,30 ℃培养48 h,挑取单菌落进行菌株鉴定。用细菌全基因组DNA试剂盒提取菌株的全基因组DNA作为模板,以细菌通用引物(上游引物27F:5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3';下游引物1492R:5'-GGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3')为16S rDNA扩增引物。反应体系为PCR Premix 25 μL,dd H2O 22 μL,上下游引物各1 μL,模板 1 μL;反应程序:94 ℃预变性5 min,94 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸90 s,32个循环,末次延伸7 min。得到的PCR产物送至青岛擎科生物科技有限公司测序。将拼接序列提交至GenBank数据库进行BLAST比对分析,利用MEGA7.0软件进行同源性分析,构建系统发育树。
1.2.4 菌株Chi34几丁质酶的酶学性质研究
1.2.4.1 温度对菌株Chi34几丁质酶酶活力和稳定性的影响
将粗酶液与底物几丁质胶体按体积比1:1混匀,分别置于20、25、30、35、40、45、50、55、60 ℃下孵育30 min,在pH为7.0的PBS缓冲液中测定其酶活力,以最高酶活力为100%,其他计算相对酶活力,测定菌株Chi34几丁质酶的最适反应温度。将粗酶液分别在25、30、35、40、45、50、60 ℃下孵育2 h,在pH为7.0的PBS缓冲液中测定其酶活力,以最高酶活力为100%,其他计算相对酶活力,研究温度对菌株Chi34几丁质酶稳定性的影响。
1.2.4.2 pH对菌株Chi34几丁质酶酶活力和稳定性的影响
将粗酶液、底物液分别和不同pH的缓冲液按1:1:2的体积比混匀,在37 ℃下保温30 min,分别测定不同pH下Chi34几丁质酶的酶活力,以最高酶活力为100%,其他计算相对酶活力,研究Chi34几丁质酶的最适反应pH。将粗酶液与不同pH的缓冲液按1:2的体积比混匀,37 ℃下孵育2 h,分别测定pH对几丁质酶稳定性的影响。其中pH4.0~6.0的缓冲液为柠檬酸-柠檬酸钠缓冲液,pH7.0~8.0的缓冲液为磷酸盐缓冲液,pH9.0的缓冲液为甘氨酸-NaOH缓冲液。
1.2.4.3 金属离子及EDTA、SDS对菌株Chi34几丁质酶酶活力的影响
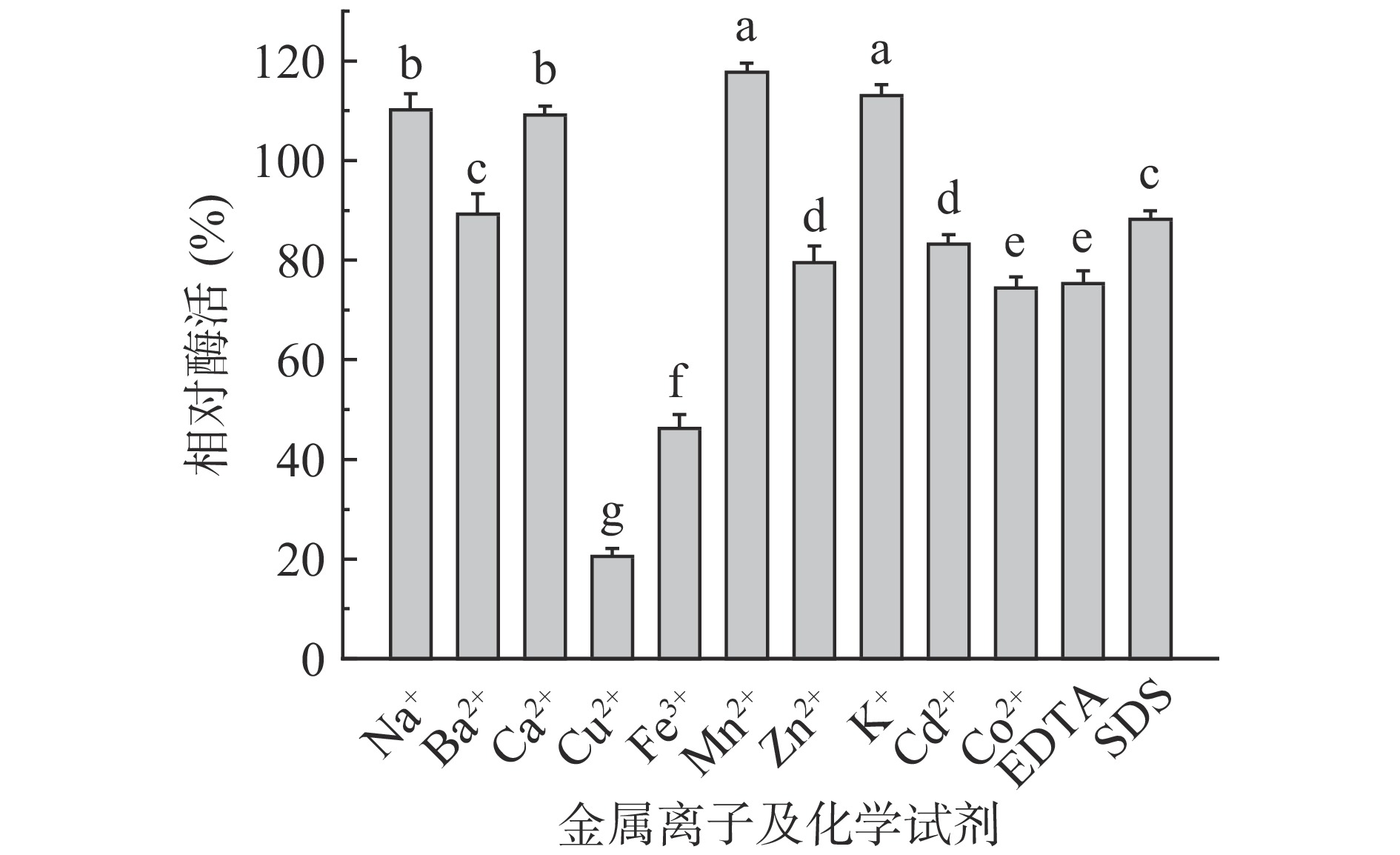
分别将金属离子Na+、K+、Ba2+、Ca2+、Cu2+、Cd2+、Co2+、Fe3+、Mn2+、Zn2+及化学试剂EDTA、SDS与粗酶液、几丁质胶体混匀,使各金属离子及EDTA、SDS的终浓度为3 mmol/L,在37 ℃水浴下保温30 min,分别测定其酶活力,以未加金属离子和EDTA、SDS的粗酶液酶活力为100%,计算相对酶活力,研究以上金属离子和EDTA、SDS对几丁质酶活力的影响。
1.2.4.4 菌株Chi34几丁质酶降解几丁质胶体产物分析
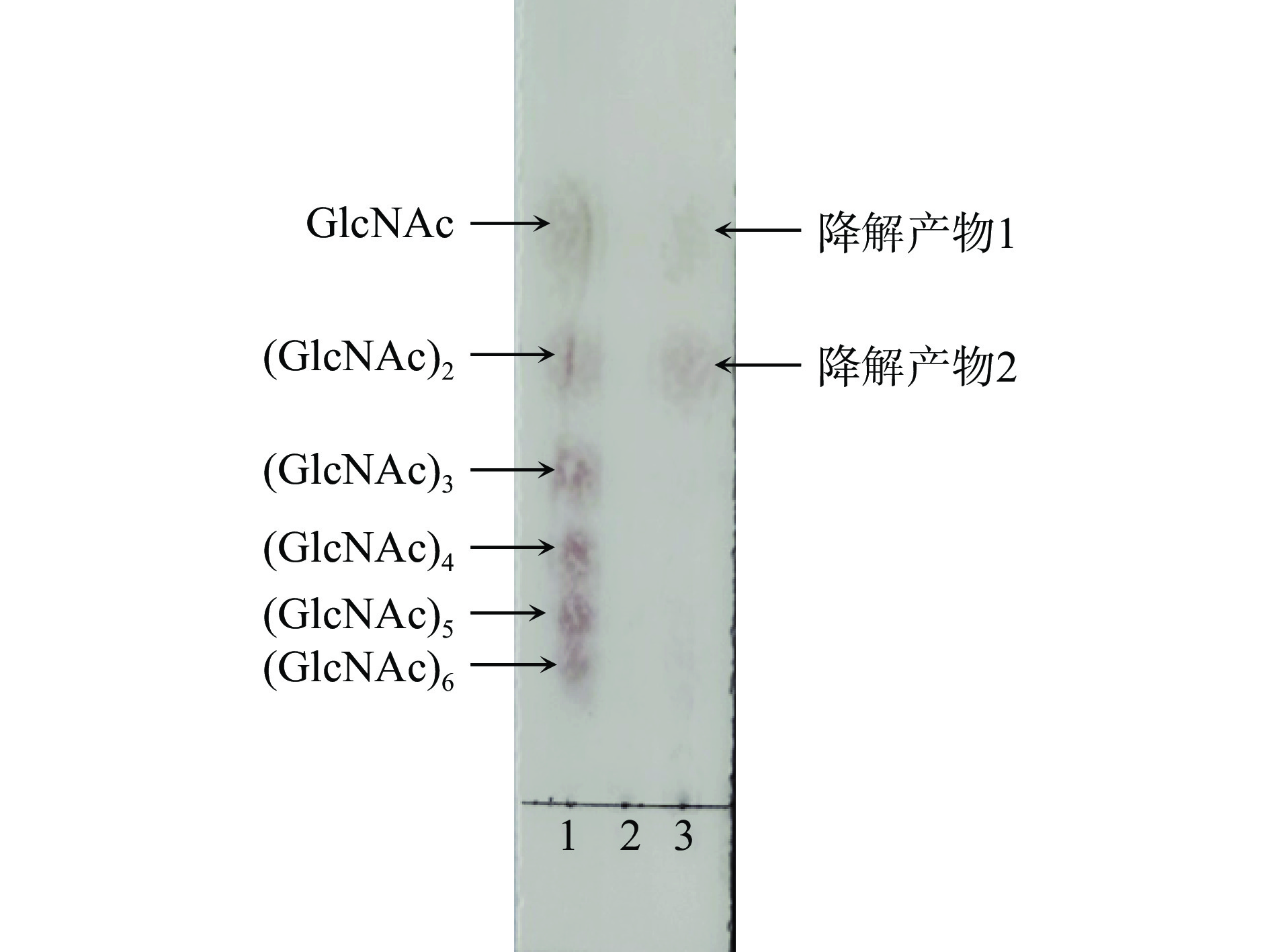
利用薄层层析法(TLC)进行菌株Chi34几丁质酶降解几丁质胶体产物分析。取粗酶液0.5 mL与0.5 mL 1%几丁质胶体混和,在37 ℃水浴锅中孵育24 h,离心,取上清液进行TLC实验。灭活的粗酶液按照相同的方法处理,作为对照。以体积比为5:2:3的正丁醇、乙醇、水混合液为展开剂,二苯胺1 g、苯胺1 mL、丙酮50 mL、和磷酸5 mL混合物为显色剂,80 ℃显色10 min,观察降解产物。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均设置3组平行实验,数据采用SPSS 26软件进行统计分析,以Oringin 2019作图,使用MEGA 7.0软件构建系统发育树。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 产几丁质酶海洋菌的筛选
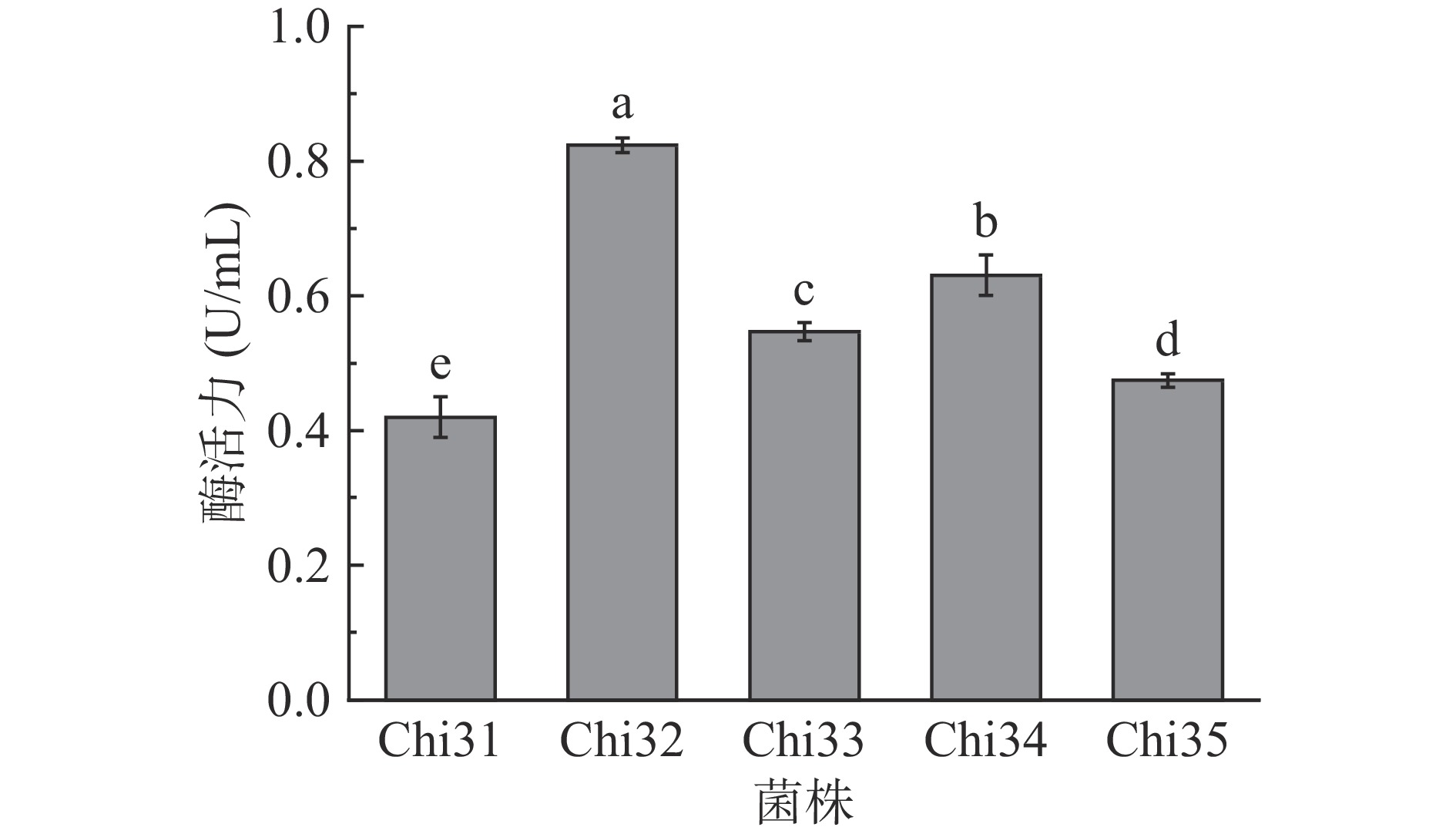
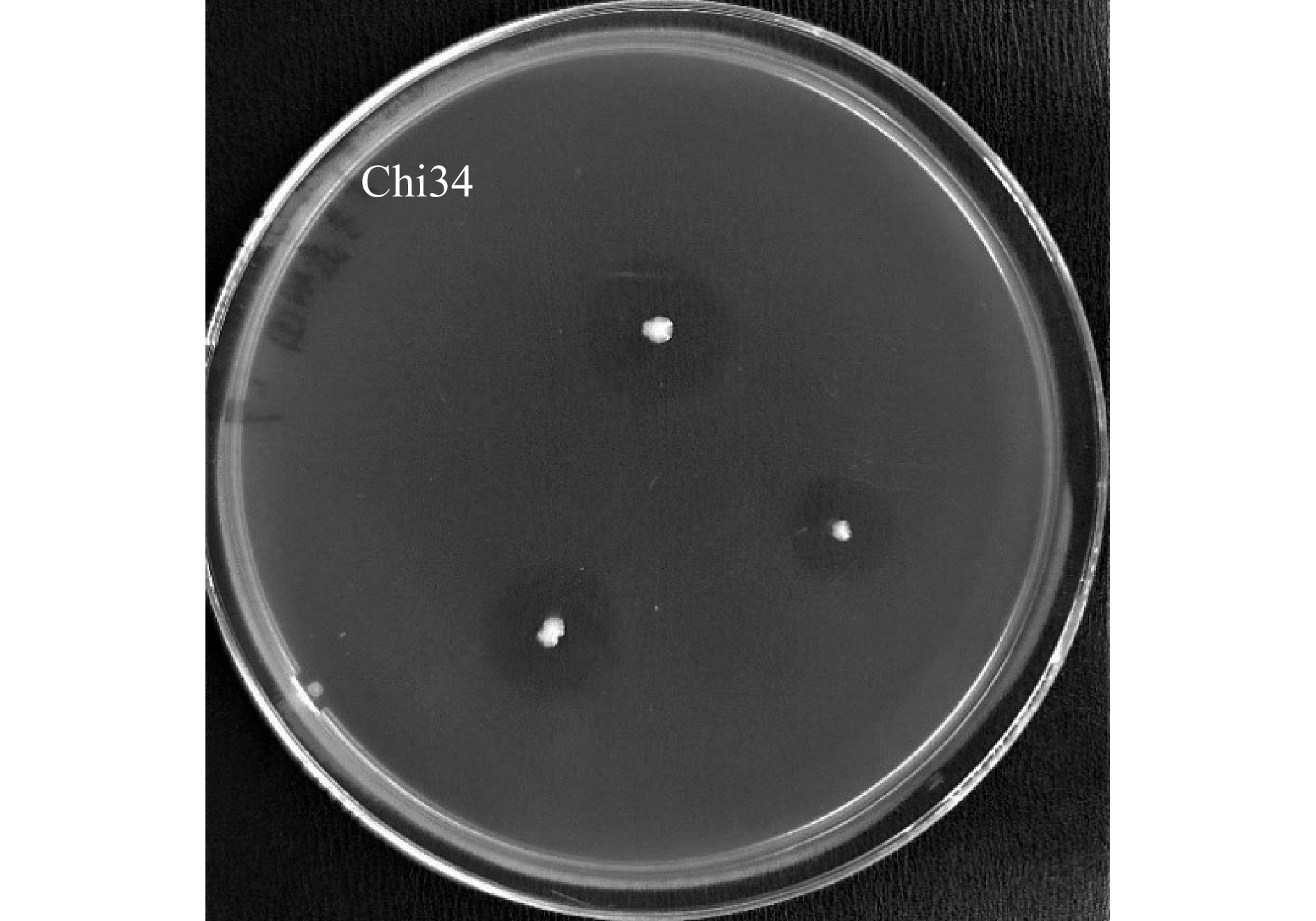
利用平板透明圈筛选法从海泥样品中筛选得到5株产几丁质酶菌株(表1),通过摇瓶发酵复筛,发现菌株Chi32的酶活力显著高于其他菌株(P<0.05)(图1),但是在后续的实验过程中发现该菌株不稳定,在传至几代后,几丁质酶活力下降比较大,而菌株Chi34在几丁质平板培养3 d后能产生明显的透明圈(图2),酶活力也明显高于其他剩余菌株,且长势快,遗传性能稳定,所以选取Chi34进行下一步研究。
表 1 菌落及透明圈直径Table 1. Diameter of colonies and transparent circles菌株 菌落直径(mm) 透明圈直径(mm) 酶活力(U/mL) Chi31 3.06±0.21a 7.06±0.12c 0.420±0.030e Chi32 1.52±0.04d 7.03±0.09c 0.824±0.011a Chi33 2.55±0.03b 7.03±0.08c 0.547±0.013c Chi34 2.01±0.05c 10.98±0.11a 0.631±0.030b Chi35 2.03±0.07c 7.99±0.10b 0.475±0.010d 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著,P<0.05。 2.2 菌株Chi34的鉴定
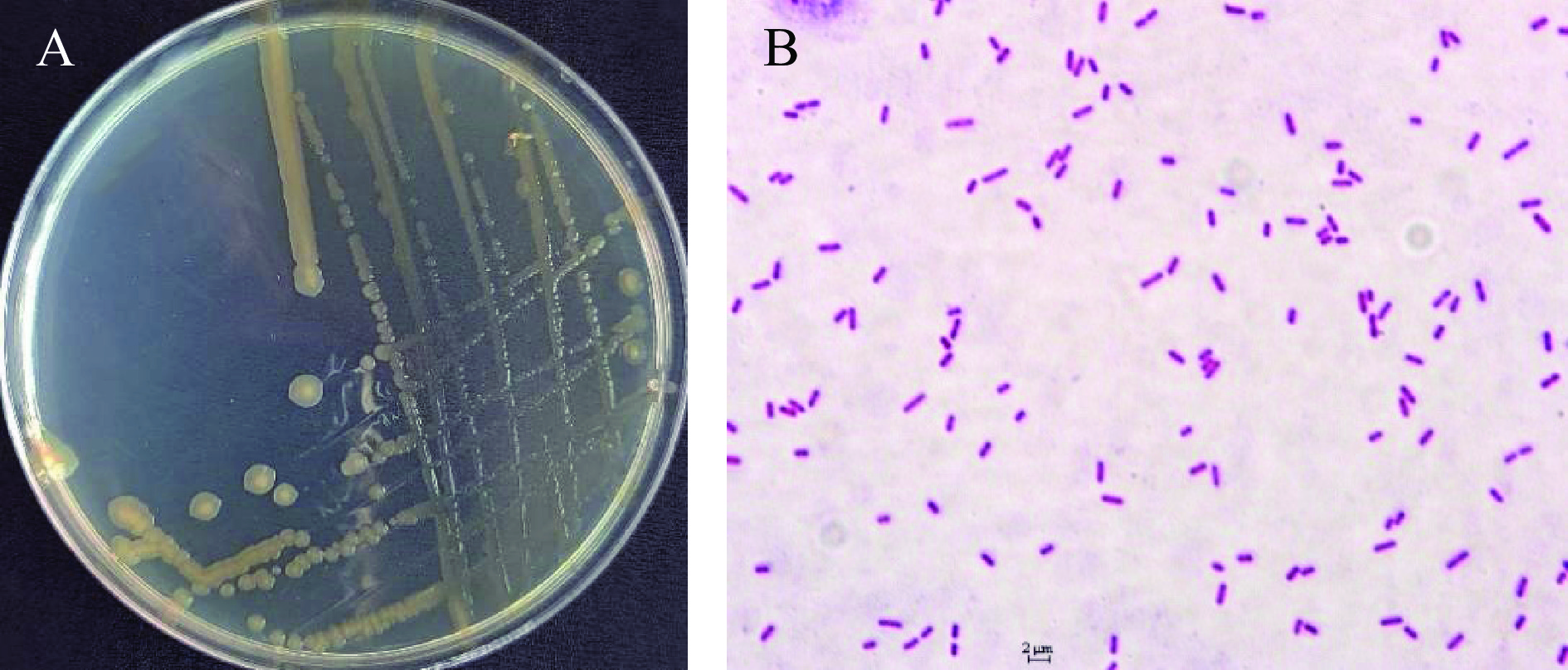
菌株Chi34在LB固体培养基30 ℃培养48 h后,菌落为淡黄色,圆形,表面光滑,中间凸起,边缘规整,易挑起(图3A);革兰氏染色阴性,短杆状,菌体长度约为1.72±0.24 μm,直径约为0.9±0.1 μm(图3B)。
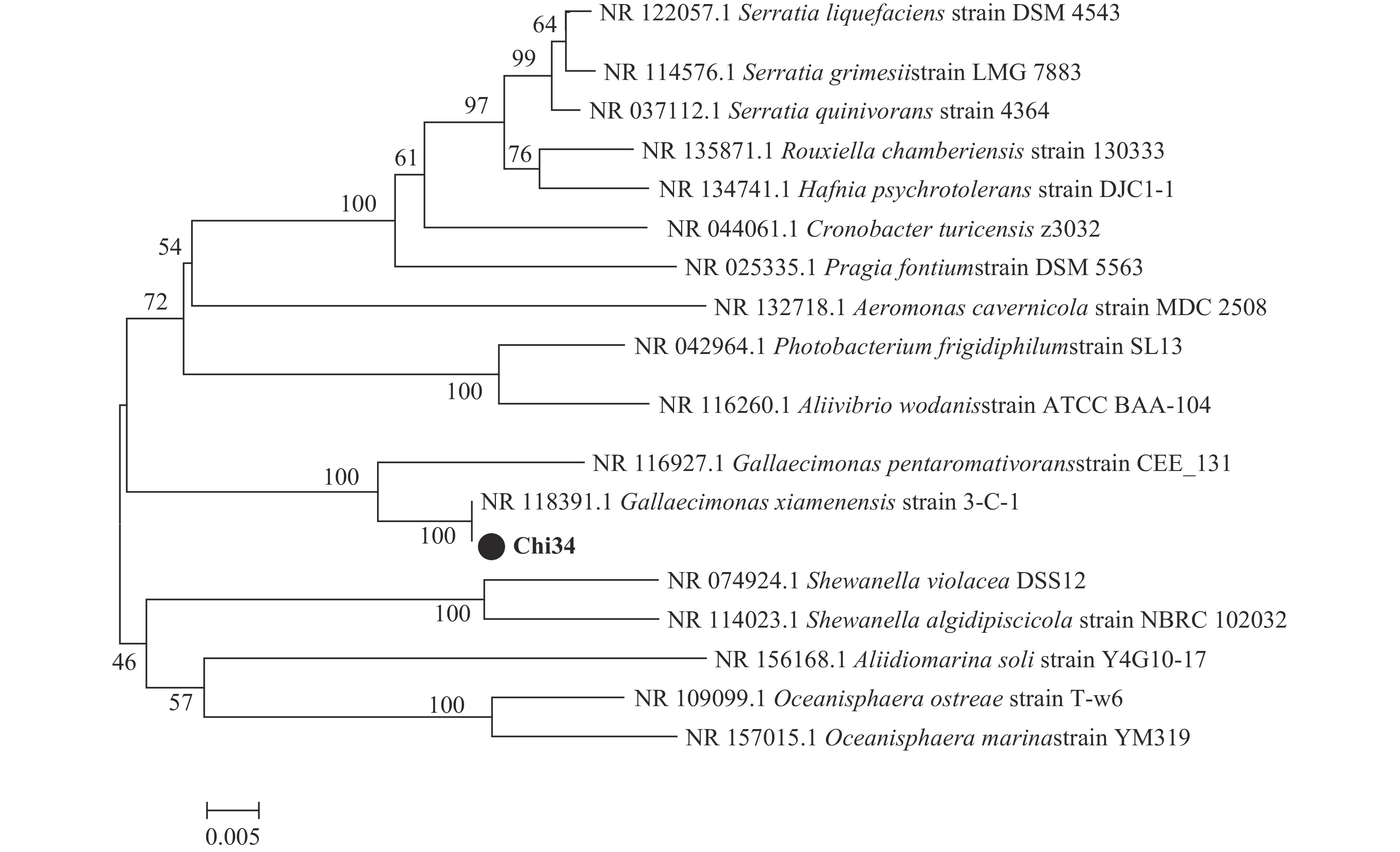
以菌株Chi34全基因组DNA作为模板,进行16S rDNA序列扩增,扩增产物用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,在1000~2000 bp之间有一条单一电泳条带。将扩增产物送至生物公司测序拼接后,得到总长为1442 bp的序列,把序列提交至GenBank(登录号:OP020592),利用BLAST进行同源比对,结果显示与菌株Gallaecimonas xiamenensis 16S rDNA同源性较高。利用MEGA 7.0软件构建系统发育树(图4),菌株Chi34与Gallaecimonas xiamenensis亲缘关系最近。综合形态学及16S rDNA结果分析,该菌属厦门加西利亚单胞菌(Gallaecimonas xiamenensis)。目前,尚未见Gallaecimonas xiamenensis产几丁质酶的报道。
2.3 菌株Chi34几丁质酶酶学性质研究
2.3.1 温度对菌株Chi34几丁质酶酶活力和稳定性的影响
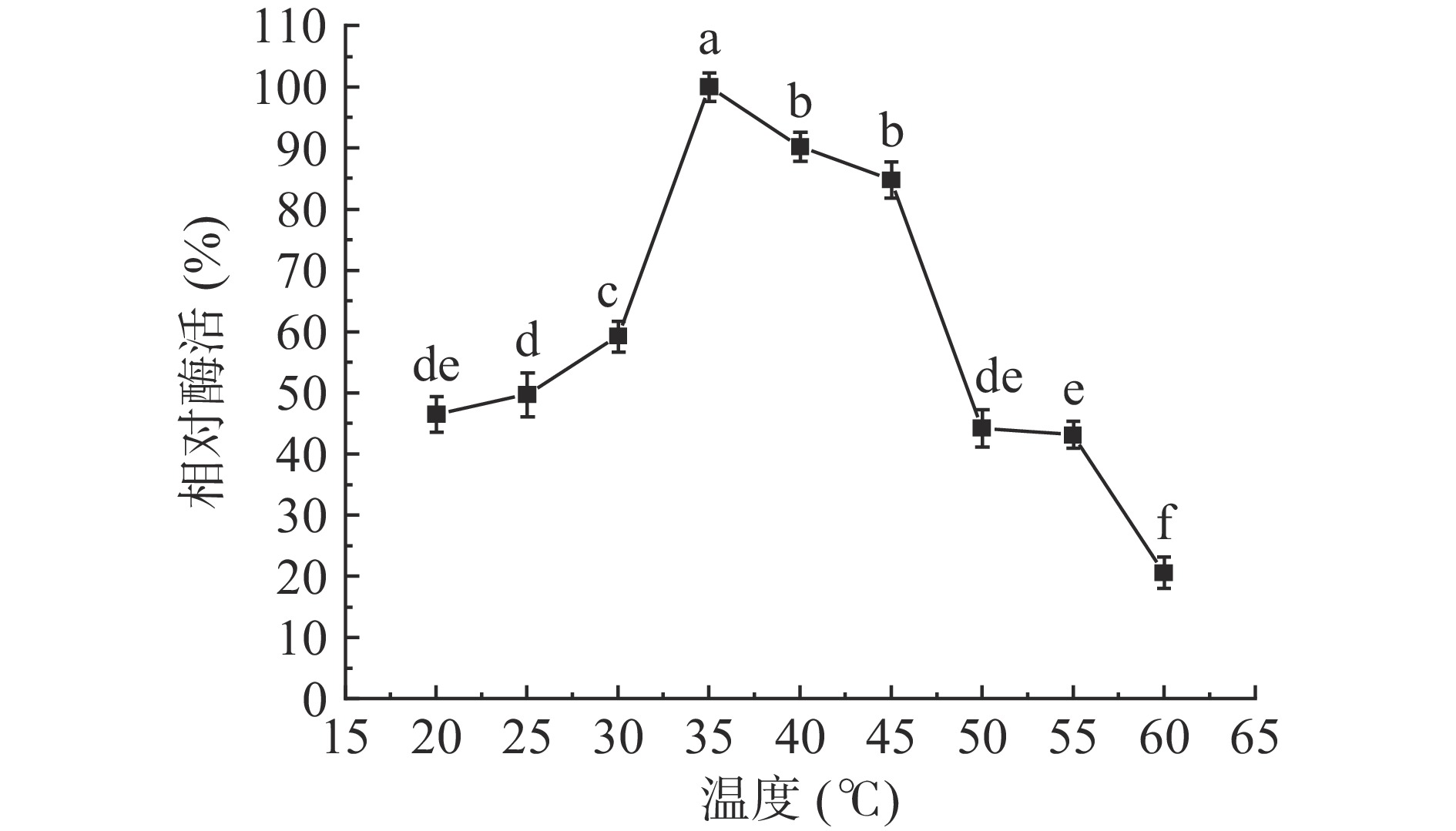
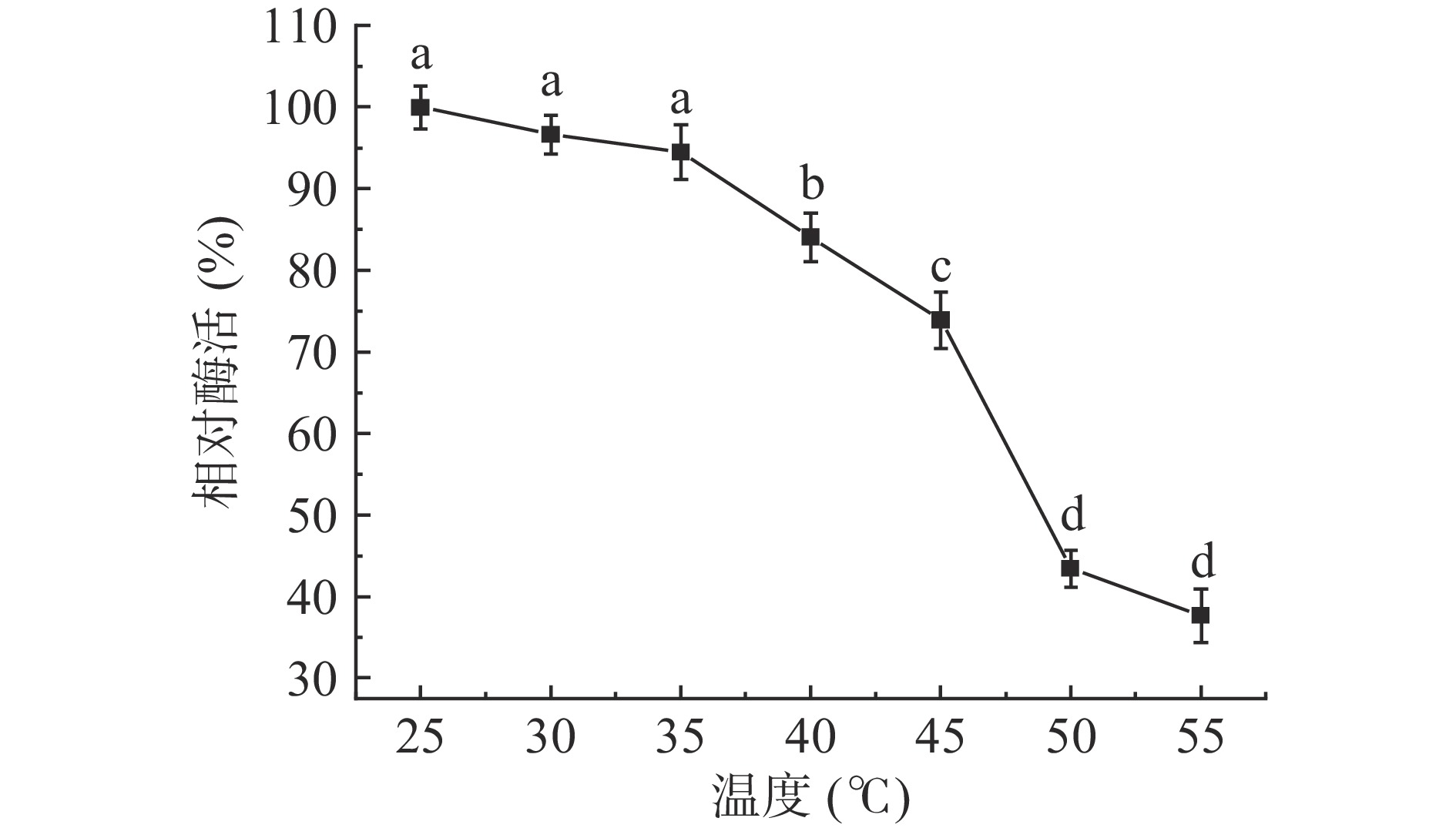
酶在催化反应的过程中受温度影响变化较大,一方面,随着温度的升高,反应速率加快;另一方面,温度升高,会使酶变性失活。目前报道的海洋细菌几丁质酶的最适温度在25~85 ℃[18]。菌株Chi34几丁质酶其最适反应温度为35 ℃(图5),在35 ℃时显著高于其他温度的酶活力(P<0.05);在25~40 ℃保温2 h后,残余酶活力均保持80%以上,温度高于40 ℃之后,残余酶活力随温度升高而降低,55 ℃后残余酶活力低于40%(图6)。
2.3.2 pH对菌株Chi34几丁质酶酶活力和稳定性的影响
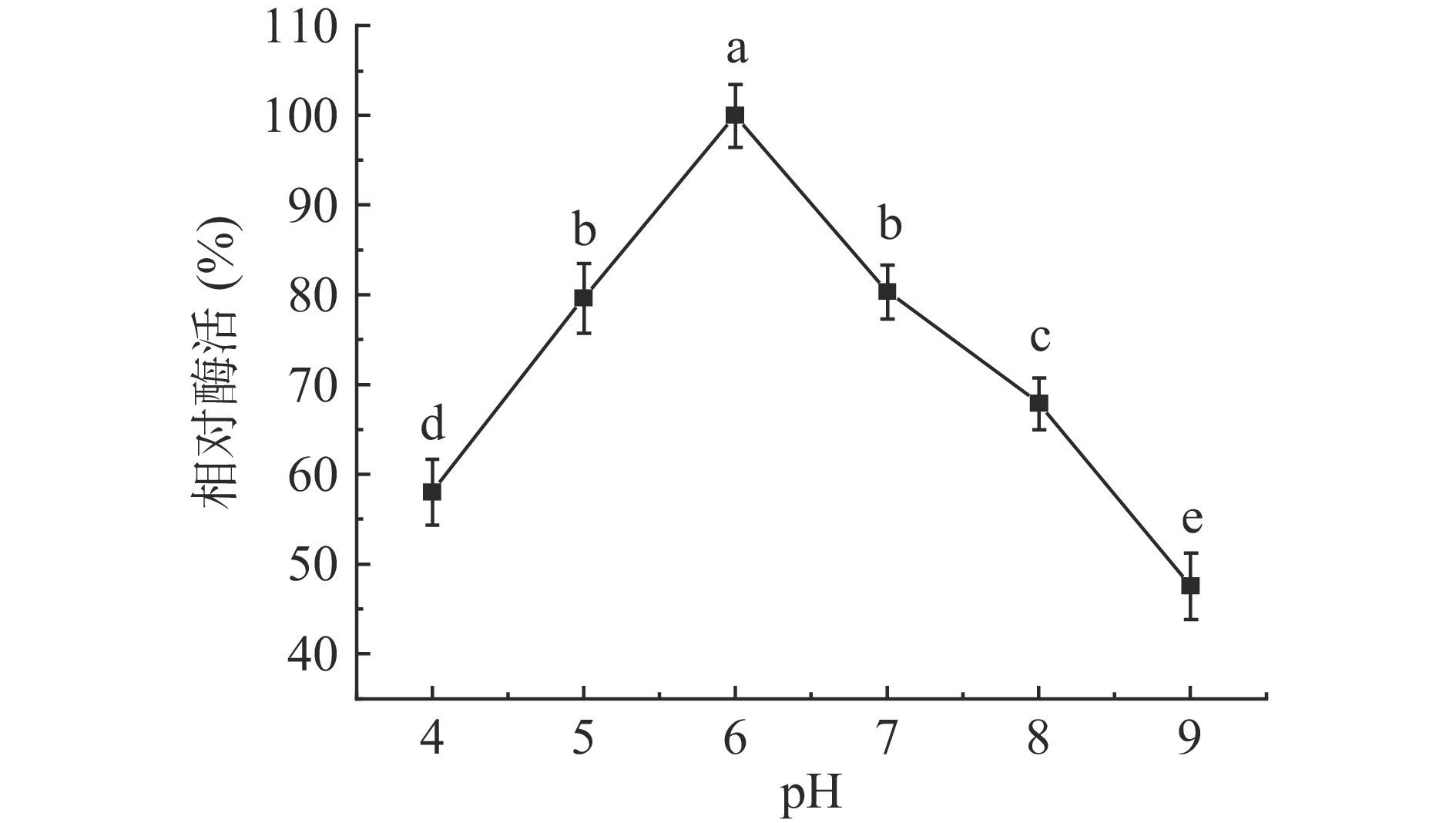
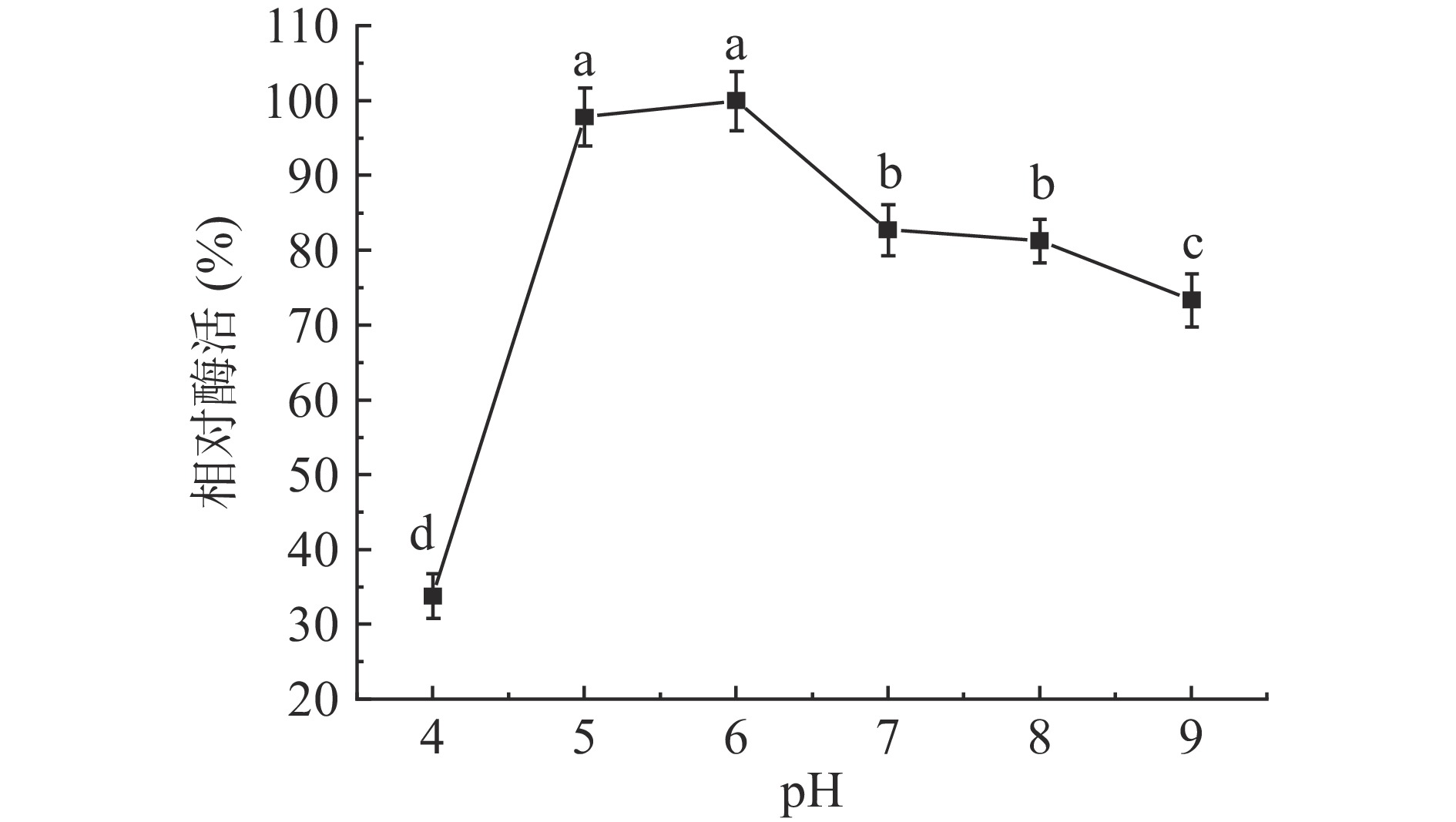
酶的分子结构中存在很多极性基团,在一定pH的缓冲体系中,pH影响酶的解离状态,底物和酶的电荷状态也受pH影响;同时,pH还能影响酶活性中心的构象,从而影响酶活力的大小[19]。从图7实验结果可知,Chi34几丁质酶的最佳反应pH约为6.0,酶活力显著高于其他pH下的酶活力(P<0.05);图8结果显示,Chi34几丁质酶在pH为5.0~6.0的缓冲液中孵育2 h,其残余酶活力没有显著性差异,在pH为5.0~8.0的缓冲液中孵育2 h,其残余酶活力保持在80%以上。
2.3.3 金属离子和EDTA、SDS对Chi34几丁质酶活力的影响
在酶促反应的过程中,金属离子和某些化学试剂将影响酶活力,如K+、Na+、Ca2+等金属离子对几丁质酶有激活作用,而 Ba2+、Cu2+、Co2+、Cd2+等能抑制几丁质酶活力[20]。如图9,在离子浓度为3 mmol/L时,Na+、Ca2+、Mn2+、K+对Chi34几丁质酶具有明显的激活作用,其中K+ 和Mn2+对Chi34几丁质酶的激活作用显著(P<0.05),而Cu2+、Fe3+、Ba2+、Zn2+、Cd2+、Co2+等对Chi34几丁质酶具有不同程度的抑制作用,且Cu2+的抑制作用最显著,相比于未加金属离子的粗酶液活性,其相对酶活力低于30%。另外,EDTA和SDS对Chi34几丁质酶均有抑制作用。
2.3.4 菌株Chi34几丁质酶降解几丁质胶体产物分析
以几丁寡糖混合物(含几丁单糖~几丁六糖)为标准物,灭活粗酶液为对照进行TLC实验,结果显示,Chi34几丁质酶降解几丁质胶体主要产物是几丁二糖,以及少量的几丁单糖(图10)。菌株Chi34分泌的几丁质酶主要为外切几丁质酶,外切几丁酶含外切几丁二糖酶和N-乙酰氨基糖苷水解酶,外切几丁质酶作用端是在几丁质分子链的非还原端或还原端,以两个糖为单位水解底物几丁质,终产物为几丁二糖,几丁二糖最终被N-乙酰氨基糖苷水解酶水解为几丁单糖[5,11,21-22]。
3. 讨论
近年来,随着人类对海洋资源的开发和利用,越来越多的海洋几丁质酶被发掘,海洋几丁质酶来源不同,其酶学性质也不同[16]。本研究筛选得到的菌株Chi34为厦门加西利亚单胞菌,是Gallaecimonas属,目前尚未见厦门加西利亚单胞菌属产几丁质酶的报道。Chi34几丁质酶的酶活力为0.631 U/mL(631 U/L),高于严佳佳等[23]分离的副溶血性弧菌几丁质酶活性80 U/L,低于陈立功等[24]分离得到的Photobacterium sp.几丁质酶活力0.932 U/mL,也明显低于章晓洋等[25]筛选的Photobacterium sp. LYM-1酶活力15.37±0.55 U/mL、Vibrio sp. WM-1酶活力40.82±6.03 U/mL和Shewanella sp. ZXY-1酶活力25.64±3.29 U/mL。各海洋几丁质酶的酶活力存在差异,其原因与海洋细菌的种属及其分泌几丁质酶种类、底物诱导水平和海洋细菌生长环境等因素有很大的关系。细菌种属不同,其体内几丁质酶基因表达水平不同,分泌的几丁质酶种类差异大,导致几丁质酶结构不同,结合域、催化域也不同,最终其酶活力存在差异[26]。Chi34几丁质酶最适反应温度为35 ℃,低于40 ℃时比较稳定,与丁志雯等报道的CZW019[27]相似,与陈立功等[28]报道的Photobacterium sp. LG-1几丁质酶最适温度35 ℃一致,低于Serratia marcescens[29]几丁质酶最适温度45 ℃、Streptomyces sp.[30]几丁质酶最适温度50 ℃、Bacillus sp. DAU101[3]几丁质酶最适温度65 ℃和Bacillus altitudinis KA15[31]几丁质酶最适温度85 ℃,进一步说明海洋菌株种类不同,所产几丁质酶最适反应温度也不尽相同。绝大多数海洋几丁质酶的最适反应pH主要在3.5~9.0之间[32-33],Chi34几丁质酶最适pH为6.0,在pH为5.0~8.0的范围内保持较高的酶活力,接近于海水的pH,符合海洋几丁质酶的pH特性;Na+、K+和Ca2+和Mn2+能够激活Chi34几丁质酶,其中Mn2+对Chi34几丁质酶激活作用最显著,与Stenotrophomonas rhizophila[34]相似;Cu2+、Fe3+、Ba2+、Zn2+、Cd2+、Co2+、EDTA和SDS对Chi34几丁质酶有抑制作用。Chi34几丁质酶的最适反应温度适中,最佳反应pH在弱酸性环境,反应条件比较温和,在宽泛的pH和温度范围内也能维持较高的活性。另外,Chi34几丁质酶能够催化胶体几丁质降解产生聚合度较低的几丁二糖,并伴随着少量的几丁单糖,在生产几丁二糖和几丁单糖中具有一定的应用前景。
4. 结论
本研究从连云港黄海海域在海一方公园海泥样中筛选出一株产几丁质酶菌株Chi34,经形态学分析和分子生物学分析鉴定为Gallaecimonas xiamenensis(厦门加西利亚单胞菌),菌株Chi34产几丁质酶能力稳定,酶活力为0.631 U/mL。Chi34几丁质酶最佳反应温度为35 ℃,最适pH为6.0,是酸性几丁质酶,在25~40 ℃有较高的酶活力;Na+、Ca2+、Mn2+、K+对Chi34几丁质酶具有明显的激活作用,Cu2+、Fe3+、Ba2+、Zn2+、Cd2+、Co2+、EDTA和SDS等具有不同程度的抑制作用,其降解几丁质胶体的主要产物是几丁二糖,及少量的几丁单糖。在后续的研究中,本课题组将把如何提高菌株Chi34几丁质酶的活力及降解虾蟹壳能力为研究重点,进一步挖掘Gallaecimonas xiamenensis Chi34几丁质酶的潜能,为实现其工业化生产几丁寡糖奠定理论基础。
-
表 1 菌落及透明圈直径
Table 1 Diameter of colonies and transparent circles
菌株 菌落直径(mm) 透明圈直径(mm) 酶活力(U/mL) Chi31 3.06±0.21a 7.06±0.12c 0.420±0.030e Chi32 1.52±0.04d 7.03±0.09c 0.824±0.011a Chi33 2.55±0.03b 7.03±0.08c 0.547±0.013c Chi34 2.01±0.05c 10.98±0.11a 0.631±0.030b Chi35 2.03±0.07c 7.99±0.10b 0.475±0.010d 注:同列不同小写字母表示差异显著,P<0.05。 -
[1] ESSGHAIER B, HEDI A, BEJJI M, et al. Characterization of a novel chitinase from a moderately halophilic bacterium, Virgibacillus marismortui strain M3-23[J]. Annals of Microbiology,2012,62(2):835−841. doi: 10.1007/s13213-011-0324-4
[2] LOPAMUDRA R, ANANTA N P, SAMIR R M, et al. Purification and characterization of an extracellular thermo-alkali stable, metal tolerant chitinase from Streptomyces chilikensis RC1830 isolated from a brackish water lake sediment[J]. Biotechnology Reports,2019,24:e00311.
[3] PAN Mengyan, LI Jianghua, LÜ Xueqin, et al. Molecular engineering of chitinase from Bacillus sp. DAU101 for enzymatic production of chitooligosaccharides[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology,2019,124:54−62. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2019.01.012
[4] GAO L, SUN J, SECUNDO F, et al. Cloning, characterization and substrate degradation mode of a novel chitinase from Streptomyces albolongus ATCC 27414[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,261:329−336. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.068
[5] WEI Guoguang, ZHANG Alei, CHEN Kequan, et al. Enzymatic production of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine from crayfish shell wastes pretreated via high pressure homogenization[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,171:236−241. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.028
[6] CHAVAN S B, DESHPANDE M V. Chitinolytic enzymes: An appraisal as a product of commercial potential[J]. Biotechnology Progress,2013,29(4):833−846. doi: 10.1002/btpr.1732
[7] WANG Di, LI Anjie, HAN Hongyu, et al. A potent chitinase from Bacillus subtilis for the efficient bioconversion of chitin-containing wastes[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018:863−868.
[8] SUGANTHI M, SENTHILKUMAR P, ARVINTH S, et al. Chitinase from Pseudomonas fluorescens and its insecticidal activity against Helopeltis theivora[J]. Journal of General & Applied Microbiology,2017,63(4):222−227.
[9] HOU Furong, MA Xiaobin, FAN Lihua, et al. Enhancement of chitin suspension hydrolysis by a combination of ultrasound and chitinase[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,231:115669. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115669
[10] DING Zhiwen, LI Tian, CHENG Meng, et al. Purification and characterization of a chitinase from Aeromonas media CZW001 as a biocatalyst for producing chitinpentaose and chitinhexaose[J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 2023,70(1):281-289.
[11] SOPHANIT M, IDA R B, CATHERINE L, et al. Development of enzyme cocktails for complete saccharification of chitin using mono-component enzymes from Serratia marcescens[J]. Process Biochemistry,2017,56:132−138. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2017.02.021
[12] HE Bin, YANG Liyan, YANG Dengfeng, et al. Biochemical purification and characterization of a truncated acidic, thermostable chitinase from marine fungus for N-acetylglucosamine production[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology,2022,10:1013313.
[13] MEDHAT A A T, GEORGE S I. Anticancer and antifungal efficiencies of purified chitinase produced from Trichoderma viride under submerged fermentation[J]. The Journal of General and Applied Microbiology,2020,66(1):32−40. doi: 10.2323/jgam.2019.04.006
[14] DUTTA B, DESKA J, BANDOPADHYAY R, et al. In silico characterization of bacterial chitinase: Illuminating its relationship with archaeal and eukaryotic cousins[J]. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology,2021,19(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s43141-021-00121-6
[15] DAS S, DEY P, ROY D, et al. N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine production by a chitinase of marine fungal origin: A case study of potential industrial significance for valorization of waste chitins[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2019,187(1):407−423. doi: 10.1007/s12010-018-2822-3
[16] FU Xing, GUO Yunxue, JIN Yongguo, et al. Bioconversion of chitin waste using a cold-adapted chitinase to produce chitin oligosaccharides[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,133:109863. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109863
[17] ROBERTS W K, SELITRENNIKOFF C P. Plant and bacterial chitinases differ in antifungal activity[J]. Microbiology,1988,134(1):169−176. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-1-169
[18] 张新月, 张月琪, 王凤彪, 等. 海洋细菌来源几丁质酶的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(22):383−389. [ZHANG Xinyue, ZHANG Yueqi, WANG Fengbiao, et al. Research progress of microbial chitinase from marine bacteria[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(22):383−389. ZHANG Xinyue, ZHANG Yueqi, WANG Fengbiao, et al. Research progress of microbial chitinase from marine bacteria[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(22): 383-389.
[19] 李甜, 丁志雯, 刘耀东, 等. 产壳聚糖酶海洋Paenibacillus chitinolyticus CLT08的鉴定及酶学性质研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(7):132−138. [LI Tian, DING Zhiwen, LIU Yaodong, et al. Identification and enzymatic properties of chitosanase producing marine Paenibacillus chitinolyticus strain CLT08[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(7):132−138. LI Tian, DING Zhiwen, LIU Yaodong, et al. Identification and enzymatic properties of chitosanase producing marine Paenibacillus chitinolyticus strain CLT08[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(7): 132-138.
[20] 张瑶心, 王亮节, 郑文, 等. 产几丁质酶的无色杆菌ZWW8的发酵产酶及酶学性质研究[J]. 生物技术通报,2021,37(4):96−106. [ZHANG Yaoxin, WANG Liangjie, ZHENG Wen, et al. Study on enzyme production of a chitinase-producing strain Achromobacter sp. ZWW8 by fermentation and its enzymatic characterization[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2021,37(4):96−106. ZHANG Yaoxin, WANG Liangjie, ZHENG Wen, et al. Study on enzyme production of a chitinase-producing strain Achromobacter sp. ZWW8 by fermentation and its enzymatic characterization[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2021, 37(04): 96-106.
[21] ZHOU Jie, CHEN Jianhao, XU Ning, et al. The broad-specificity chitinases: Their origin, characterization, and potential application[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2019,103:3289−3295. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09718-x
[22] NHUNG N T, NICOLAS D. Combining chitinase C and N-acetylhexosaminidase from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) provides an efficient way to synthesize N-acetylglucosamine from crystalline chitin[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2016,220:25−32. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.12.038
[23] 严佳佳, 尤田, 张雪梅, 等. 一种海洋几丁质酶产生菌的筛选及酶学性质研究[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业: 1−11[2022-11-26]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.033466. YAN Jiajia, YOU Tian, ZHANG Xuemei, et al. Screening of a marine chitinase-producing bacterium and study on its enzymatic properties[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries: 1−11[2022-11-26]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.033466.
[24] 陈立功, 吴家葳, 张庆芳, 等. 产低温几丁质酶菌株的筛选、鉴定与产酶条件优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(23):85−90,98. [CHEN Ligong, WU Jiawei, ZHANG Jinping, et al. Screening and identification of a cold-adapted chitinolytic bacterium strain and optimization of its chitinase fermentation conditions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(23):85−90,98. CHEN Ligong, WU Jiawei, ZHANG Jinping, et al. Screening and identification of a cold-adapted chitinolytic bacterium strain and optimization of its chitinase fermentation conditions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(23): 85-90, 98.
[25] 章晓洋, 张译文, 朱思瑶, 等. 三株产几丁质酶菌株的筛选、产酶条件优化及水解虾壳的研究[J/OL]. 食品工业科技: 1−16 [2022-11-26]. https://doi.org/10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022050078. ZHANG Xiaoyang, ZHANG Yiwen, ZHU Siyao, et al. Screening and optimization of three chitinase-producing strains and their application in the hydrolysis of shrimp shells[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−16 [2022-11-26]. https://doi.org/10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022050078.
[26] 冯俊丽, 朱旭芬. 微生物几丁质酶的分子生物学研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2004,30(1):102−108. [FENG Junli, ZHU Xufen. Molecular biology of microbial chitinase[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric & Life Sci),2004,30(1):102−108. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-9209.2004.01.022 FENG Junli, ZHU Xufen. Molecular biology of microbial chitinase[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agric. & Life Sci. ), 2004, 30(1): 102-108. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-9209.2004.01.022
[27] 丁志雯, 刘耀东, 黄志发, 等. 产几丁质酶海洋细菌Dyadobacter sp. CZW019的筛选、鉴定及酶学性质研究[J]. 江苏海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2021,30(2):22−29. [DING Zhiwen, LIU Yaodong, HUANG Zhifa, et al. Screening, identification and enzymatic properties of a chitinase-producing marine bacteria Dyadobacter sp. CZW019[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Ocean University (Natural Science Edition),2021,30(2):22−29. DING Zhiwen, LIU Yaodong, HUANG Zhifa, et al. Screening, identification and enzymatic properties of a chitinase-producing marine bacteria Dyadobacter sp. CZW019[J]. Journal of Jiangsu Ocean University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 30(02): 22-29.
[28] 陈立功, 吴家葳, 张金平, 等. 海洋来源产低温几丁质酶菌株的诱变选育及酶学性质研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(10):105−111. [CHEN Ligong, WU Jiawei, ZHANG Jinping, et al. Mutation breeding and enzymatic properties of cold-adapted chitinolytic strain Photobacterium sp. from marine[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(10):105−111. CHEN Ligong, WU Jiawei, ZHANG Jinping, et al. Mutation breeding and enzymatic properties of cold-adapted chitinolytic strain Photobacterium sp. from marine[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(10): 105−111.
[29] LI Jincheng, ZHENG Jiamin, LIANG Yanhui, et al. Expression and characterization of a chitinase from Serratia marcescens[J]. Protein Expression and Purification,2020,171:105613. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2020.105613
[30] KARTHIK N, BINOD P, PANDEY A. Purification and characterization of an acidic and antifungal chitinase produced by a Streptomyces sp.[J]. Bioresource Technol,2015,188:195−201. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.03.006
[31] ASMANI K L, BOUACEM K, OUELHADJ A, et al. Biochemical and molecular characterization of an acido-thermostable endo-chitinase from Bacillus altitudinis KA15 for industrial degradation of chitinous waste[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2020,495:108089. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2020.108089
[32] FU Xing, YAN Qiaojuan, WANG Jing, et al. Purification and biochemical characterization of novel acidic chitinase from Paenicibacillus barengoltzii[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,91:973−979. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.06.050
[33] MAKHDOUMI A, DEHGHANI-JOYBARI Z, MASHREGHI M, et al. A novel halo-alkali-tolerant and thermo-tolerant chitinase from Pseudoalteromonas sp. DC14 isolated from the Caspian Sea[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology,2015,12(12):3895−3904. doi: 10.1007/s13762-015-0848-4
[34] JANKIEWICZ U, BARANOWSKI B, SWIONTEK B M, et al. Purification, characterization and cloning of a chitinase from Stenotrophomonas rhizophila G22[J]. 3 Biotech,2020,10(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-2007-y
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 任章成,郭泽美,李乐,袁莹. 植物多酚生物活性研究进展. 现代食品. 2023(22): 108-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



