Effects of Freezing Temperature and Freezing Center Temperature on the Quality of Frozen Dough Noodles
-
摘要: 冷冻面团技术广泛运用于面制品的工业化生产中,然而冷冻面团技术在应用过程中仍然会存在缺陷,导致冷冻面团以及最终成品品质的劣变。在本研究中,利用差示扫描量热法(DSC)分析了面团冷冻过程中热特性的变化,研究了不同冷冻温度和冷冻中心温度对面条冷冻面团与最终面条品质的影响,从而确定最佳的冷冻温度和冷冻中心温度。结果表明,相较于−20 ℃,−30与−40 ℃的冷冻速率分别为−0.44、−0.51 ℃·min−1,冷冻速率较快,中心温度降至−18 ℃耗时较短,通过最大冰晶生成带的时间最短,形成的冰晶体积较小较为均匀。面团的可冻结水含量与面条的蒸煮损失率在−30 ℃时降至最低,−30与−40 ℃的冻结条件下,吸水率与感官得分并未出现显著性差异(P>0.05),面条的剪切力、硬度、弹性、咀嚼性随着冷冻温度的降低在−30 ℃达到最大值,而粘附性无显著性差异(P>0.05),在−18 ℃的冷冻中心温度下,面条冷冻面团的可冻结水含量最少,冷冻面团面条的蒸煮损失率、吸水率最低、质构特性最好,感官得分最高。本研究为工业上提高面条冷冻面团品质提供参考。Abstract: Frozen dough technology is widely used in the industrial production of flour products, however, frozen dough technology in the application process will still be flawed, resulting in frozen dough and final product quality deterioration. In this study, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) was used to analyze the changes of thermal characteristics during dough freezing. The effects of different freezing temperatures and freezing center temperatures on the quality of frozen dough and final noodles were studied to determine the optimal freezing temperature and freezing center temperature. The results showed that compared with −20 ℃, the freezing rates of −30 and −40 ℃ were −0.44 and −0.51 ℃·min−1, respectively, with faster freezing rates, shorter freezing time for the central temperature to drop to −18 ℃, shortest time to pass through the maximum ice crystal generation zone, and smaller and more uniform ice crystal volume formed. The frozen water content of dough and the cooking loss rate of noodles decreased to the lowest at −30 ℃. Under the freezing conditions of −30 and −40 ℃, there was no significant difference in water absorption and sensory score (P>0.05). The shear force, hardness, elasticity and chewiness of noodles reached the maximum at −30 ℃ with the decrease of freezing temperature, while there was no significant difference in adhesion (P>0.05). At the freezing center temperature of −18 ℃, the frozen water content of frozen dough was the least, the cooking loss rate, water absorption rate of frozen dough noodles were the lowest, the texture characteristics were the best, and the sensory score was the highest. This study would provide a reference for improving the quality of frozen noodle dough in industry.
-
冷冻面团技术因其方便快捷,已经被广泛应用于面包、馒头等的工业化生产中[1]。然而冷冻面团技术在使用时,仍然会存在很大缺陷。面团在冷冻的过程中,水分会冻结成冰晶,由于冰晶的形成会对面团的面筋结构造成破坏[2],又由于储存和运输过程中温度的波动导致重结晶的发生[2],冰晶的增加会对面团造成机械性损伤,破坏面团的面筋结构,使得面团的持气性下降,品质降低[3]。因而,冰晶的含量和大小对最终产品的品质有重要的影响。为了避免冷团对面团品质的破坏,必须要控制冰晶的形成[4]。
为了控制冰晶的形成,大多数研究主要从生产工艺入手,通过控制冷冻温度、时间、速度等,使面团冷冻过程中冰晶的分布更加均匀,改善冷冻面团在冻藏过程中出现的萎缩、冻裂等质量问题。白妮[5]认为冷冻速率决定了冰晶的形成类型、大小、含量与分布,对最终产品的品质有决定性影响。Meziani等[6]研究发现较快的冷冻速率能够保持较好的面筋结构的完整性,冷冻温度在−30 ℃时面团的流变学特性较好。Yang等[7]发现较低的冷冻温度,冷冻速率越快,对非发酵冷冻面团的流变学特性与蛋白质结构方面的影响较小。陈丽[3]也发现冷冻温度越低,平均的冰晶面积和冰晶占比呈下降的趋势。冷冻温度越低,面团的冷冻速率越快,面团中冰晶的体积越小、分布越均匀,对最终产品品质的影响越小。
目前,利用差示扫描量热仪(DSC)分析面团可冻结水含量的研究较多,针对冰晶形成的相关研究则较少,冷冻至不同中心温度对冷冻面团与最终产品品质的影响的相关研究也较少,因此,在本研究中,利用差示扫描量热法(DSC)研究了面团中的冰晶形成,同时研究不同冷冻温度和不同冷冻中心温度对冷冻面团面条的影响。利用差示扫描量热法(DSC)研究了完整面团中的冰晶形成现象,从而确定最佳的冷冻温度和冷冻中心温度。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
高筋小麦粉(水分12.54%,湿面筋31.51%,蛋白质11.23%,粗脂肪0.76%,灰分0.52%) 五得利面粉集团有限公司;食盐 中盐黑龙江盐业有限公司。
DW-86L338J超低温保存箱 青岛海尔生物医疗股份有限公司;SJJ-B10Q1厨师机 小熊电器股份有限公司;BJM-2G电动压面机 极度空间家居有限公司;JD200-3电子天平 沈阳天平仪器有限公司;TMS-Touch 250N质构仪 美国Food Technology Corporation;BPG-9070A电热鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器股份有限公司;差示扫描量热仪DSC4000 PerkinElmer公司;UT320D K/J型热电偶 优利德科技(东莞)有限公司;C22-F8电磁炉 浙江九阳股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 面团的配方及面条的制作工艺
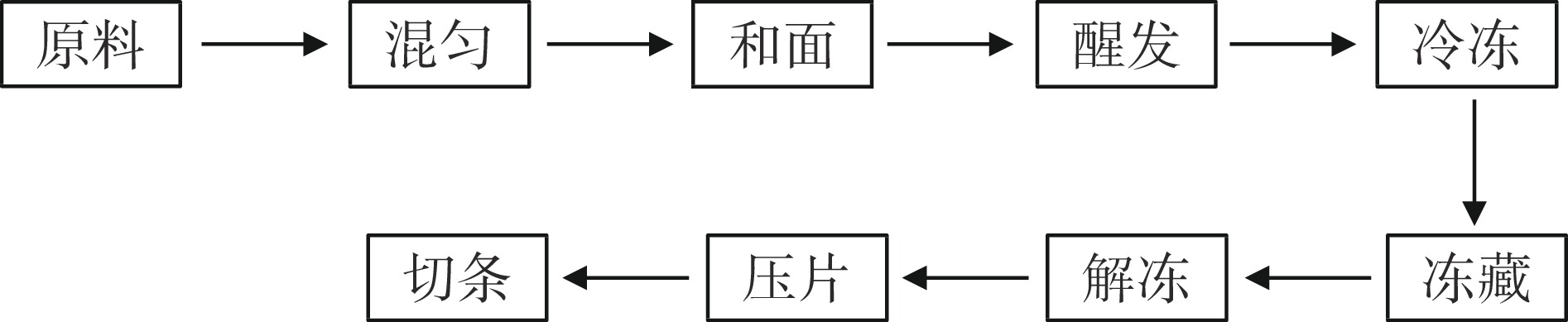
参照郑子懿[8]冷冻面条的制作方法略作修改制作冷冻面团面条,其制作工艺流程如图1所示:
参照Kondakci等[9]的面条面团的制作工艺,称取面粉100 g、水35 g、盐2 g,放入和面机中,启动和面机搅拌,慢速和面2 min后,再快速和面3 min,再慢速和面2 min,将面絮包上保鲜膜,置于温度25 ℃,湿度70%醒发箱中静置醒发。将醒发好的面团放入自封袋中,置于超低温冰箱速冻至中心温度达−18 ℃,再转移到冰箱中在−18 ℃的温度下冻藏一星期后进行解冻。解冻好的面团参照SB/T 10137-93[10]进行压片,共压5次,轧距依次为4、3、2、1 mm,每轧距均对折合片两次。最终面条厚1 mm,宽2 mm,长20 cm。
1.2.2 面条冷冻面团冷冻温度曲线的绘制
参考杨静洁等[11]的试验方法,将K型热电偶插入面条面团中心,并用保鲜膜密封,装入密封袋中,将面团分别放在−20、−30、−40 ℃下冷冻至面团中心温度达到−18 ℃,每5 min记录一次热电偶的数值,得到在这3个冷冻温度下面条冷冻面团中心温度变化的数据,将记录数据录入Excel表格中绘制面条冷冻面团冷冻温度曲线。冷冻中心温度则为面团中心温度达到−10、−14、−18、−22、26 ℃时的热电偶上显示的温度数值。
1.2.3 冷冻速率计算公式
参考Meziani等[12]的冷冻速率计算方法,基于面团的冷冻温度曲线计算样品的FR(freezing rate):
FR=(Tt−Ti)/Δt 式中:Tt为样品的终点温度;Ti为样品的起始温度;Δt为起始温度到达终点温度所需要的时间。
1.2.4 面条冷冻面团热特性的测定
利用DSC测定面条冷冻面团的热特性。参考Choongjin等[13]的实验方法,分别从面团的中心部位采集重量在14.8~24.2 mg的面团样品,将样品放入铝制坩埚中密封。用一个空坩埚为参照,初始温度设置为25 ℃,并在不同冷冻温度所测得的冷冻速率下进行,直到达到−18 ℃。利用Pyris 7 DSC数据处理软件,在热分析图上测定起始(Tonset)、峰值(Tpeak)和结束(Tend)温度值。
1.2.5 面团可冻结水含量的测定
参考徐云峰[14]的实验方法略作修改,将冻藏一周的冷冻面团解冻后在面团中心部位取10~15 mg冷冻面团样品立即放入铝制坩埚中密封,避免水分流失,以空坩埚做空白。
可冻结水含量的测定:用液氮冷却至在−30 ℃,恒温5 min,从−30 ℃升温到5 ℃,升温速率为5 ℃/min,吹入20 mL/min的氮气以防止水分冷凝,测定样品的相变焓,并用105 ℃恒温烘干法测定样品的水分含量,用Fw表示面团的可冻结水含量。根据下列公式计算样品中的可冻结水含量:
Fw=ΔHmΔfusHm×WA 式中:ΔHm为样品中冰的融化焓(J/g);ΔfusHm为纯水结成冰的融化潜热(334 J/g);WA为样品的水分含量(%)。
1.2.6 面条质构特性的测定
利用食品物性仪,将冷冻面团面条放沸水中煮制最佳蒸煮时间(面条白芯消失时)后捞出,用冷水淋洗1 min,控干水分,每次测试取3根面条平行置于载物台上进行测试,每个样品测定7次,取平均值。
TPA测定:采用探头为HDP/PFS型,校准距离为15 mm,测试前、中、后速度均为48 mm/min,形变量为75%,触发力为0.3 N,时间间隔为1 s。
剪切力测定:本实验采用的质构仪所配探头:Code A/LKD,测定前速度:30 mm/min,测定速度:30 mm/min,测定后速度:60 mm/min,触发力:0.3 N,压缩率:90%。
1.2.7 面条蒸煮品质的测定
1.2.7.1 面条干物质损失率的测定
取20根长度相等的面条,在锅中煮至面条断生后的冷冻面团面条取出,将剩余的面汤放至常温后,转入500 mL容量瓶,用蒸馏水冲洗锅并将蒸馏水一起转入容量瓶并定容至500 mL;摇匀,量取100 mL面汤倒入已干燥恒重已知质量的250 mL烧杯中,将烧杯放入105 ℃烘箱内,直至烧杯恒重,烧杯质量的增加即面汤中的干物质,同时做三次平行实验。下面的计算公式计算干物质损失率:
干物质损失率(%)=2.5MG×(1−W)×100 式中:M为100 mL面汤中干物质质量,g;G为煮前冷冻面条的质量,g;W为冷冻面条水分含量。
1.2.7.2 面条吸水率的测定
将面条煮至最佳蒸煮时间(面条内部白芯消失时)的冷冻面团面条取出,用冷水淋洗1 min,然后用滤纸吸干表面水分静置5 min,称重,冷冻面团面条吸水率根据公式计算:
吸水率(%)=Z−GG×100 式中:G为煮前冷冻面条的质量,g;Z为煮后冷冻面团面条质量,g。
1.2.8 面条感官品质的测定
由10名专业人员组成的评价小组,分别参照面条感官评分标准表对冷冻面团面条进行打分,10个打分结果取平均值[15-16]。冷冻面团面条感官评分标准(满分100分)见表1。
表 1 面条感官评分标准Table 1. Sensory evaluation criteria for noodles项目 满分 评分标准 色泽 10 面条的颜色、亮度。颜色为白色或奶黄色,亮度好:8.5~10分;亮度一般:6~8.4分;颜色暗、亮度差:1~5.9分 表观状态 10 面条表面光滑和膨胀程度。表面光滑细密:8.5~10分;表面较光滑、较细密:6.0~8.4分;表面粗糙且发生变形、膨胀:1~5.9分 适口性 20 咬断面条所需要的力的大小。咬力适中:17~20分;微硬或微软:12~16分;过硬或过软:1~11分 韧性 25 咀嚼时的咬劲及弹性大小。有咬劲且弹性好:21~25分;较有咬劲、较有弹性:15~20分;咬紧差、缺乏弹性:1~14分 粘性 25 咀嚼时的黏牙程度。不黏牙、爽口:21~25分;稍黏牙、较爽口:15~20分;样品发黏、爽口性差:10~14分 光滑性 5 品尝时口感的光滑程度。口感光滑:4.3~5分;较光滑:3~4.2分;不光滑:1~2.9分 食味 5 样品的味道。麦香味浓郁:4.3~5分;麦香味较浓郁、无异味:3~4.2分;有异味:1~2.9分 1.3 数据处理
除特殊说明外,所有数据平行测定三次,利用Origin Pro 2018与Excel 2010进行绘图,采用SPSS 22.0进行数据处理与分析,数据以“平均值±偏差”表示,以P<0.05表示数据之间的显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同冷冻温度下的面团冷冻温度曲线
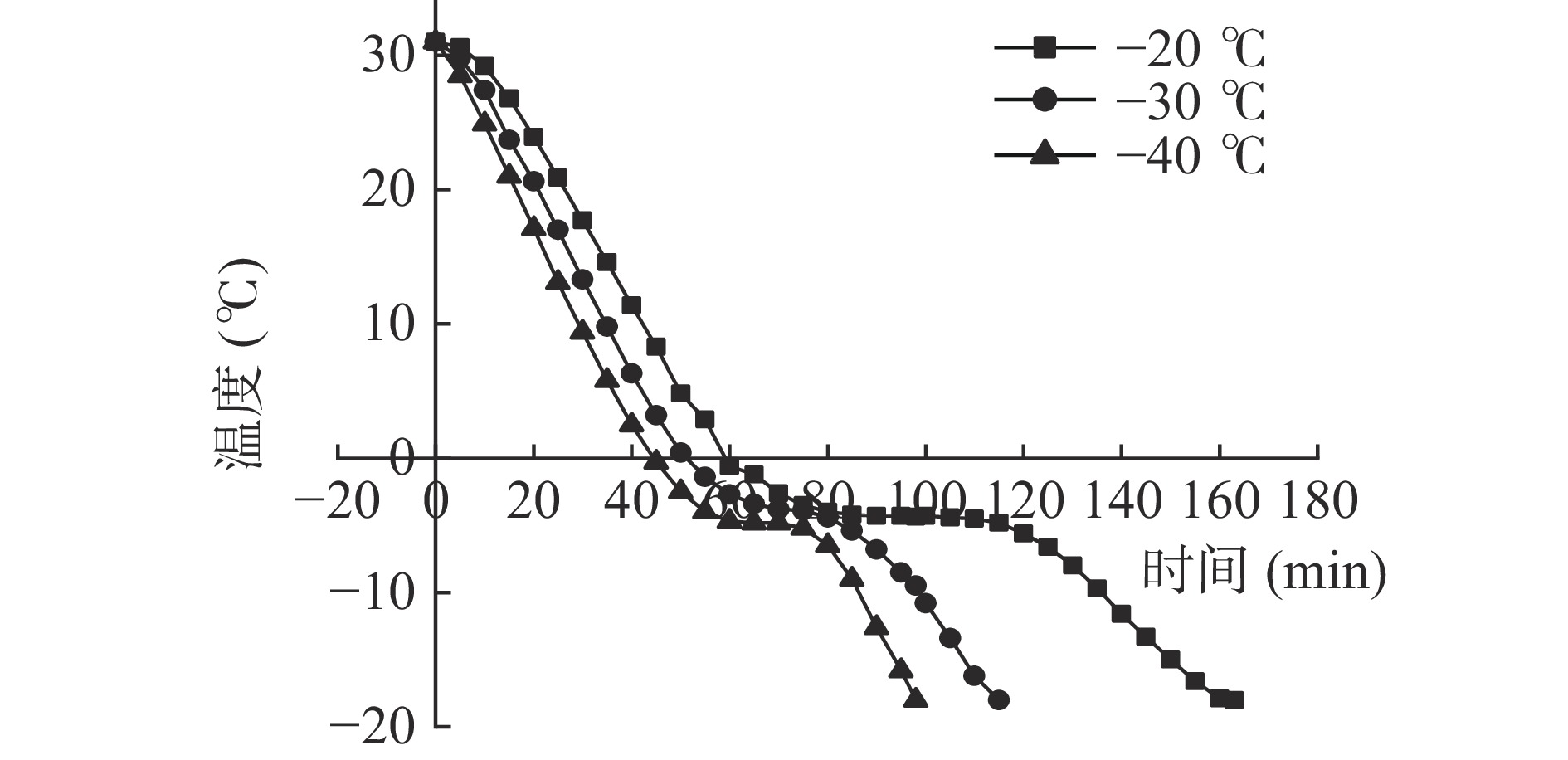
面条面团在冷冻的过程中,由于冰点降低,会在零度以下的温度下冻结[17]。由于原料含量和面团醒发程度的误差,实际冻结温度会略有不同。图2展示了不同冷冻温度下面团的冷冻温度曲线。其中,冷冻温度曲线一般分为三个阶段:预冷阶段、相变阶段和过冷阶段[18]。预冷阶段面团的温度迅速降至冰点,相变阶段的曲线近乎水平,但此刻面团内部开始大量形成晶核,且部分晶核生长称为冰晶,因此也被称为最大冰晶生成带,可冻结水转变成冰晶,并且冷冻速率的加快或冷冻时间的缩短皆可刺激小冰晶的产生,因此相变阶段是最关键的阶段。已有大量文献证实,较快的冷冻速率导致较短的相变时间,使形成的冰晶体积更小分布更加均匀,对面团结构所造成的物理伤害越小,越有利于提高冷冻面团的品质[19-21]。
从图2可以看出,−20 ℃的最大冰晶生成带的温度区间为−0.6~−4.8 ℃,用时55 min,其中心温度降至−18 ℃全程耗时160 min。−30 ℃的最大冰晶生成带的温度区间为−2.7~−5.4 ℃,用时25 min,全程耗时115 min。−40 ℃的最大冰晶生成带的温度区间为−4~−5.2 ℃,用时20 min,而−40 ℃组中心温度降至−18 ℃仅耗时95 min,耗时最短,其冷冻的效率最高。面条面团在−20、−30、−40 ℃的冷冻温度下,冷冻速率分别为−0.31、−0.44、−0.51 ℃min−1,显然更快的FR可以更加快速地通过最大冰结晶生成带,能够保持面团面筋结构的完整性。这是因为冷冻速度较慢时,面团需要较长的时间降到冰点以下,导致冰晶的形成不稳定,其他水分子的热运动导致其分散,从而形成更大的冰晶,对面团结构造成严重的机械损伤[22]。
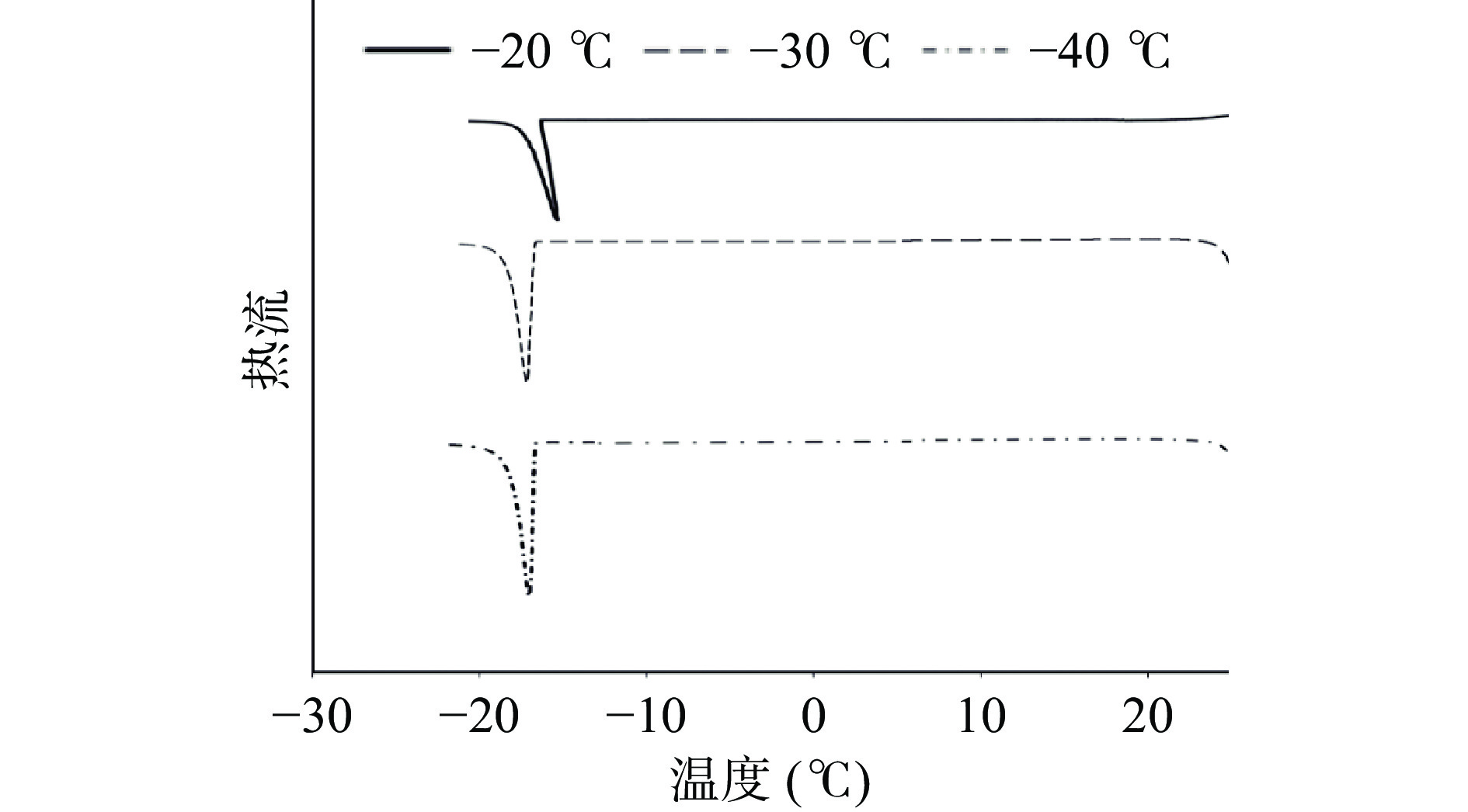
2.2 不同冷冻温度下面团冷冻过程中冰晶的形成
采用DSC模拟面团冷冻过程,根据面条面团在不同的冷冻温度下的冷冻速率模拟冷冻过程,验证不同的冷冻温度下的FR对面条冷冻面团热特性的影响,结果如图3所示。在温度下降的过程中会出现一处尖锐峰,它代表了面团中水分冰晶冻结的放热峰,从图3可以看出,随着冷冻温度的降低,冰晶形成峰明显滞后,该滞后现象说明冷冻温度越低,冷冻速率越快,面团的冰点不断降低,使得面团能够快速通过最大冰晶生成带,从而形成小而均匀的冰晶,降低对面团的损伤。将图3的分析结果转化成图4的柱状图。在图4中,Tpeak代表峰值温度,Tonset与Tend分别为起始温度与终点温度,基于图4的结果,可以看出,在不同的冷冻温度下,冷冻面团的Toneset值、Tpeak值与Tend值在−20~−30 ℃显著降低(P<0.05),而−30与−40 ℃的冷冻温度下并无显著差异(P>0.05)。在DSC下模拟不同冷冻温度下的冷冻速率面条冷冻面团的相变温度在−14.9~−17.3 ℃之间,低于之前实践实验冷冻面条冷冻面团过程中所观察到相变温度。造成这种差异的原因可能是因为样品量太大,扫描速度越大,出峰温度越高。
2.3 不同冷冻温度对冷冻面团品质及面条品质的影响
2.3.1 冷冻温度对面团可冻结水含量的影响
冷冻面团的品质受面团中可冻结水分含量的影响,面团中的可冻结水主要由自由水和一部分结合水组成,其它的一些结合水和与大分子结合的水则是非可冻结水[23]。可冻结水含量越少,面团在冻结的过程中就能形成越少的冰晶,面团的品质则越高[24]。利用DSC测定冷冻面团中的可冻结水含量,通过计算曲线峰值下的面积,即测得的熔化焓ΔH(J/g)用以反映样品中可冻结水的含量。通过对不同冷冻温度下冻藏一周的冷冻面团的可冻结水含量的计算结果进行分析,结果见表2。由表2可知,不同的冷冻温度对面条冷冻面团的可冻结水含量有显著的影响,当冷冻温度为−30 ℃时,面条冷冻面团可冻结水含量最少。面条面团的含水量大约为34%左右,水分又分为游离水和结合水[25],在面团冷冻的过程中主要由游离水结冰放热。在面团冻结的过程中,由于冰晶的形成对面团结构造成了机械性的损伤,导致了面团的面筋网络结构和淀粉的损伤,使得一部分结合水游离出来冻结,面团中冰晶形成的量增多,对面筋损伤增大,因而引起面团解冻后易于流变,品质下降[26]。而在-30 ℃下冻结,面团中的结合水不易被游离出来,能够较好地保持面条面团的面筋网络结构,保持面条冷冻面团的品质。
2.3.2 冷冻温度对面条质构特性的影响
表3为不同冷冻温度对面条质构品质的影响,主要从剪切力、硬度、粘附性、弹性、咀嚼性方面进行分析。由表3可知,随着冷冻温度的下降,除了面条的粘附性没有显著的改变,其它指标均有不同程度的改变。面条冷冻面团的剪切力随着冷冻温度的降低在−30 ℃达到最大值,在−30 ℃以后并无显著的变化。面条的TPA特性中硬度、弹性、咀嚼性都在−30 ℃的冷冻温度下达到最大值,而不同的冷冻温度对面条的粘附性无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
表 3 冷冻温度对面条质构品质的影响Table 3. Effect of freezing temperature on the texture of noodles冷冻温度
(℃)剪切力(N) 硬度(N) 粘附性 弹性 咀嚼性 −20 0.69±0.03b 64.32±3.32c 1.39±0.33a 0.75±0.06a 18.60±0.17b −30 0.87±0.06a 74.87±3.11a 1.16±0.05a 0.82±0.03a 19.73±0.06a −40 0.81±0.06ab 66.71±1.83b 1.12±0.04a 0.73±0.05a 18.03±0.81c 表 4 不同冷冻温度的冷冻面团面条蒸煮品质及感官品质Table 4. Cooking quality and sensory quality of frozen dough noodles at different freezing temperatures冷冻温度(℃) 蒸煮损失率(%) 吸水率(%) 感官得分(分) −20 2.90±0.64a 108.74±0.57a 65.80±1.23b −30 2.16±0.33b 102.85±1.37b 78.43±2.56a −40 2.59±0.88a 102.50±2.08b 78.56±2.17a 表 5 冷冻中心温度对面团可冻结水含量的影响Table 5. Influence of freezing center temperature on the freezing water content of dough冷冻中心温度(℃) ΔHm(Jg) WA(%) FW(%) −10 61.83±0.22b 37.76±1.64b 53.66±0.42b −14 60.90±0.24c 38.30±1.13a 53.63±0.39b −18 59.94±0.63d 34.43±0.84c 52.17±0.33c −22 67.58±0.24a 33.33±0.33d 60.76±0.54a −26 59.97±0.47d 34.08±0.55c 52.66±0.62c 表 6 冷冻中心温度对面条质构特性的影响Table 6. Effect of freezing center temperature on the texture characteristics of noodles冷冻中心
温度(℃)剪切力(N) 硬度(N) 粘附性 弹性 咀嚼性 −10 0.73±0.08b 71.73±0.72a 1.25±0.05b 0.81±2.39a 17.90±2.36a −14 0.77±0.02b 65.49±2.18c 1.83±0.12a 0.82±0.29a 17.73±0.74b −18 0.89±0.04a 67.04±1.73b 1.16±0.05c 0.82±0.51a 18.03±0.81a −22 0.86±0.09a 60.07±0.98d 1.37±0.02b 0.82±2.54a 17.70±3.02ab −26 0.85±0.05a 60.14±2.88d 1.41±0.13b 0.87±1.02a 18.80±0.57a 表 7 冷冻中心温度对面条蒸煮品质的影响Table 7. Effect of freezing center temperature on cooking quality of noodles冷冻中心温度(℃) 蒸煮损失率(%) 吸水率(%) 感官得分(分) −10 2.90±0.64a 101.74±0.57a 70.46±1.36c −14 2.58±0.19b 101.05±1.16a 75.71±2.08b −18 2.16±0.33c 100.85±1.37a 80.21±2.13a −22 2.99±0.59a 102.36±2.90a 78.34±1.47a −26 2.59±0.88b 102.00±2.08a 70.31±2.14c 通过上述分析可以得出,冷冻过程中形成的冰晶越少,对冷冻面团和面条的品质影响越小。硬度、弹性与面条结构、水分含量密切相关,而咀嚼性在数值上等于硬度、内聚性和弹性三者乘积,影响因素较多[27]。冷冻温度低则面团的冷冻速率快,面团中的水分能够迅速冻结成冰,形成体积较小的冰晶,对冷冻面团及面条的损害较小。
2.3.3 冷冻温度对面条蒸煮品质及感官品质的影响
面条的蒸煮品质可以反映面团及面条的品质,一般而言,蒸煮损失率越低,吸水率越低,面团的面筋网络结构越完整,紧密程度越好,面条的品质越高。不同冻结温度下的冷冻面团面条的蒸煮损失率、吸水率与感官得分情况如表4所示。由表4可知,冷冻温度越低,面条的蒸煮损失率呈现下降趋势,并在−30 ℃达到最小值,冷冻温度低于−30 ℃时,面条的蒸煮损失率又有所上升,面汤变得浑浊。这可能是因为−20 ℃冻结条件下,面团的冷冻速率较慢,通过最大冰晶生成带的速度较慢,对面团结构的损害较大[28],而−30、−40 ℃的冷冻速率较快,对面团面筋网络结构破坏较小,因此在制面和煮面的过程中不易导致面团组分脱落,使得冷冻面团面条的蒸煮损失率较低。随着冷冻温度的降低,冷冻面团面条的吸水率也总体呈下降的趋势,但在−30和−40 ℃的冷冻温度下,样品的吸水率并无显著的变化(P>0.05),表明在较低的冷冻温度下,冷冻速率较快,所制得面条得水分分布更接近新鲜的面条。感官得分的变化也与蒸煮损失率与吸水率的变化相一致。冷冻温度越低,感官得分越高。虽然冷冻温度越低,冷冻速率越快,最终产品品质越好,但在本实验室的试验条件下,−30与−40 ℃的冻结条件并未出现显著性差异(P>0.05)。
2.4 不同冷冻中心温度对冷冻面团品质及面条品质的影响
2.4.1 冷冻中心温度对面团可冻结水含量的影响
由表5可以看出,冷冻面团的可冻结水含量因冷冻的中心温度不同而有显著性差异。随着冷冻中心温度的降低,面条冷冻面团的可冻结水含量显著降低(P<0.05),在−18 ℃的冷冻中心温度下,可冻结水含量达到最低,继续降低冷冻中心温度,面团的可冻结水含量并无显著的变化(P>0.05)。可能是因为面团冷冻过后需要进行冻藏一段时间,一般的商业冻藏温度为−18 ℃,冷冻中心温度高于或过低于−18 ℃,再将面团放入−18 ℃的环境下冻藏,这样会导致出现一个温度波动的过程,温度的波动导致重结晶现象的发生,使面团的可冻结水含量增加,重结晶现象发生,冰晶增多,体积增大。而面团的冷冻中心温度为−18 ℃则避免了温度的波动,可冻结水含量较少[29]。
2.4.2 冷冻中心温度对面条质构特性的影响
由表6可以看出,随着冷冻中心温度的下降,面条的剪切力随着冷冻中心温度的降低不断升高,在−18 ℃达到最大值,继而开始降低,但冷冻中心温度低于−18 ℃,面条的剪切力并无显著的差异(P>0.05)。随着冷冻中心温度的降低,面条的硬度、咀嚼性都有明显的上升,在−18 ℃达到最大值后,中心温度低于−18 ℃变化不显著(P>0.05),面条的粘附性随着中心温度的降低也不断减低,在−18 ℃粘附性最低,中心温度低于−18 ℃逐渐升高,但变化不显著(P>0.05)。这可能是因为面团冷冻后再在−18 ℃的环境中冻藏会有一个温度波动的过程,其它冷冻中心温度在冻藏时产生温度的波动,使面团内部发生重结晶现象,导致最终产品品质下降。冷冻中心温度对弹性影响并不显著(P>0.05)。因此,将面条面团中心温度降至−18 ℃后再进行冻藏,得到的最终产品冷冻面团面条的品质较优。
2.4.3 冷冻中心温度对面条蒸煮品质的影响
由表7可以看出,在−18 ℃的冷冻中心温度下,面条的蒸煮损失率显著低于其它的冷冻中心温度(P<0.05),冷冻面团面条的感官得分也随着冷冻中心温度的降低而呈升高后逐渐降低的趋势,并在−18 ℃的冷冻中心温度感官得分最高。这可能是因为在中心温度达到−18 ℃可以避免在冻藏过程中有较大的温度波动,导致面团冻藏过程中出现重结晶现象,破坏面团的网络结构,进而影响面条的口感。不同的冷冻中心温度对冷冻面团面条的吸水率影响并不显著(P>0.05)。因此,选择冷冻中心温度为−18 ℃,冷冻面团面条的蒸煮损失率较低,感官得分较高,能够较好地保持冷冻面团面条的品质。
3. 结论
面团的冷冻温度曲线与DSC扫描结果表明,冷冻温度越低,冷冻速率越快,通过冰结晶最大生成带的时间越短,从而形成体积更小、分布更加均匀的冰晶,对面团的机械性损伤较小,能够保持面团面筋结构的完整性。
不同冷冻温度对冷冻面团可冻结水含量与冷冻面团面条品质的影响的结果表明,冷冻温度对面团可冻结水含量影响显著(P<0.05),冷冻温度为−30 ℃时,可冻结水含量最少。随着冷冻温度的降低,冷冻面团面条的质构特性、蒸煮损失率、吸水率与感官得分均得到了明显的改善。其中面条的剪切力、硬度、弹性、咀嚼性都随着冷冻温度的降低呈先上升后下降的趋势,并在−30 ℃的冷冻温度下达到最大值,−30 ℃后并无显著的变化(P>0.05)。冷冻面团面条的蒸煮损失率与吸水率随着冷冻温度的下降呈先下降后上升的趋势,感官得分呈先上升后下降的趋势,均在-30 ℃的冷冻温度下达到最优,−30与−40 ℃之间的差异并不显著(P>0.05)。
冷冻至不同中心温度对面团可冻结水含量与面条品质影响的结果显示,冷冻至不同中心温度对面团可冻结水含量影响的差异并不大,在−18 ℃的中心温度下,可冻结水含量相对较少。随着冷冻中心温度的下降,面条的剪切力、硬度、咀嚼性都有明显的上升,在−18 ℃达到最大值。在−18 ℃的冷冻中心温度下,面条的蒸煮损失率显著低于其它的冷冻中心温度(P<0.05),感官得分也达到最高,但对冷冻面团面条的吸水率影响不显著(P>0.05)。
本研究为工业化生产提供了新的研究思路,为改良面条冷冻面团的生产工艺以及为今后研究关于面条冷冻面团改良剂方面的研究提供了一定的理论支持。
-
表 1 面条感官评分标准
Table 1 Sensory evaluation criteria for noodles
项目 满分 评分标准 色泽 10 面条的颜色、亮度。颜色为白色或奶黄色,亮度好:8.5~10分;亮度一般:6~8.4分;颜色暗、亮度差:1~5.9分 表观状态 10 面条表面光滑和膨胀程度。表面光滑细密:8.5~10分;表面较光滑、较细密:6.0~8.4分;表面粗糙且发生变形、膨胀:1~5.9分 适口性 20 咬断面条所需要的力的大小。咬力适中:17~20分;微硬或微软:12~16分;过硬或过软:1~11分 韧性 25 咀嚼时的咬劲及弹性大小。有咬劲且弹性好:21~25分;较有咬劲、较有弹性:15~20分;咬紧差、缺乏弹性:1~14分 粘性 25 咀嚼时的黏牙程度。不黏牙、爽口:21~25分;稍黏牙、较爽口:15~20分;样品发黏、爽口性差:10~14分 光滑性 5 品尝时口感的光滑程度。口感光滑:4.3~5分;较光滑:3~4.2分;不光滑:1~2.9分 食味 5 样品的味道。麦香味浓郁:4.3~5分;麦香味较浓郁、无异味:3~4.2分;有异味:1~2.9分 表 2 冷冻温度对面团可冻结水含量的影响
Table 2 Influence of freezing temperature on the frozen water content of dough
表 3 冷冻温度对面条质构品质的影响
Table 3 Effect of freezing temperature on the texture of noodles
冷冻温度
(℃)剪切力(N) 硬度(N) 粘附性 弹性 咀嚼性 −20 0.69±0.03b 64.32±3.32c 1.39±0.33a 0.75±0.06a 18.60±0.17b −30 0.87±0.06a 74.87±3.11a 1.16±0.05a 0.82±0.03a 19.73±0.06a −40 0.81±0.06ab 66.71±1.83b 1.12±0.04a 0.73±0.05a 18.03±0.81c 表 4 不同冷冻温度的冷冻面团面条蒸煮品质及感官品质
Table 4 Cooking quality and sensory quality of frozen dough noodles at different freezing temperatures
冷冻温度(℃) 蒸煮损失率(%) 吸水率(%) 感官得分(分) −20 2.90±0.64a 108.74±0.57a 65.80±1.23b −30 2.16±0.33b 102.85±1.37b 78.43±2.56a −40 2.59±0.88a 102.50±2.08b 78.56±2.17a 表 5 冷冻中心温度对面团可冻结水含量的影响
Table 5 Influence of freezing center temperature on the freezing water content of dough
冷冻中心温度(℃) ΔHm(Jg) WA(%) FW(%) −10 61.83±0.22b 37.76±1.64b 53.66±0.42b −14 60.90±0.24c 38.30±1.13a 53.63±0.39b −18 59.94±0.63d 34.43±0.84c 52.17±0.33c −22 67.58±0.24a 33.33±0.33d 60.76±0.54a −26 59.97±0.47d 34.08±0.55c 52.66±0.62c 表 6 冷冻中心温度对面条质构特性的影响
Table 6 Effect of freezing center temperature on the texture characteristics of noodles
冷冻中心
温度(℃)剪切力(N) 硬度(N) 粘附性 弹性 咀嚼性 −10 0.73±0.08b 71.73±0.72a 1.25±0.05b 0.81±2.39a 17.90±2.36a −14 0.77±0.02b 65.49±2.18c 1.83±0.12a 0.82±0.29a 17.73±0.74b −18 0.89±0.04a 67.04±1.73b 1.16±0.05c 0.82±0.51a 18.03±0.81a −22 0.86±0.09a 60.07±0.98d 1.37±0.02b 0.82±2.54a 17.70±3.02ab −26 0.85±0.05a 60.14±2.88d 1.41±0.13b 0.87±1.02a 18.80±0.57a 表 7 冷冻中心温度对面条蒸煮品质的影响
Table 7 Effect of freezing center temperature on cooking quality of noodles
冷冻中心温度(℃) 蒸煮损失率(%) 吸水率(%) 感官得分(分) −10 2.90±0.64a 101.74±0.57a 70.46±1.36c −14 2.58±0.19b 101.05±1.16a 75.71±2.08b −18 2.16±0.33c 100.85±1.37a 80.21±2.13a −22 2.99±0.59a 102.36±2.90a 78.34±1.47a −26 2.59±0.88b 102.00±2.08a 70.31±2.14c -
[1] 张云焕, 赵文华, 马军涛, 等. 速冻面制食品品质改良剂的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2017,43(4):295−302. [ZHANG Y H, ZHAO W H, MA J T, et al. Research progress of quality improvers for frozen flour food[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2017,43(4):295−302. ZHANG Y H, ZHAO W H, MA J T, et al. Research progress of quality improvers for frozen flour food[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2017, 43(4): 295-302.
[2] 王秋玉. 冻融循环对预发酵冷冻生坯豆沙包品质劣变规律研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2022. WANG Q. Study on the effect of freeze-thaw cycle on the quality deterioration of pre-fermented frozen green beans[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2022.
[3] 陈丽. 冷冻对非发酵面团水分状态和冰晶形态的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. CHEN L. Effect of freezing on moisture state and ice crystal morphology of non-fermented dough[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021.
[4] JACKEL S S. Frozen dough opportunities keep heating up[J]. Cereal Foods World, 1991.
[5] 白妮. 冷冻生胚油条的品质劣变机理及改良研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2022. BAI N. Study on the quality deterioration mechanism and improvement of frozen raw embryo fried dough sticks[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2022.
[6] MEZIANI S, IOANNOU I, JASNIEWSKI J, et al. Effects of freezing treatments on the fermentative activity and gluten network integrity of sweet dough[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2012,46(1):118−126. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.10.017
[7] YANG J, ZHANG B, ZHANG Y, et al. Effect of freezing rate and frozen storage on the rheological properties and protein structure of non-fermented doughs[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2021,293:110377. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2020.110377
[8] 郑子懿. 冷冻面条在储藏期间的品质变化研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2013. ZHEN Z Y. Study on the quality change of frozen noodles during storage[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2013.
[9] KONDAKCI T, ZHANG J W, ZHOU W. Impact of flour protein content and freezing conditions on the quality of frozen dough and corresponding steamed bread[J]. Food & Bioprocess Technology,2015,8(9):1877−1889.
[10] 中华人民共和国商业行业标准. LS/T 3202-1993面条用小麦粉[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1993. The People 's Republic of China commercial industry standards. LS/T 3202-1993 Wheat flour for noodles[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 1993.
[11] 杨静洁, 张波, 张影全, 等. 冷冻温度对非发酵面团蛋白质结构及面团特性的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(5):11−17. [YANG J J, ZHANG B, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Effect of freezing temperature on the protein structure and dough characteristics of non-fermented dough[J]. China Journal of Grain and Oil,2020,35(5):11−17. YANG J J, ZHANG B, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Effect of freezing temperature on the protein structure and dough characteristics of non-fermented dough[J]. China Journal of Grain and Oil, 2020, 35(5): 11-17.
[12] MEZIANI S, JASNIEWSKI J, GAIANI C, et al. Effects of freezing treatments on viscoelastic and structural behavior of frozen sweet dough[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2011,107(3-4):358−365. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.07.003
[13] CHOONGJIN, YOON, SANGEUN, et al. Effects of freezing rate and terminal freezing temperature on frozen croissant dough quality[J]. LWT-Food Science & Technology,2016,73:219−225.
[14] 徐云峰. 复配乳化剂提高酵母抗冻性及改善冷冻面团品质的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2010. XU Y F. Study on the improvement of yeast antifreeze and the quality of frozen dough by compound emulsifier[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2010.
[15] 文三彬. 煮制对面条中蛋白质及食用品质的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2015. WEN S B. Effects of cooking on protein and edible quality of noodles[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2015.
[16] 闫美姣, 李云龙, 李红梅, 等. 高杂粮含量面条制作的工艺优化[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,255(11):194−201. [YAN M J, LI Y L, LI H M. Process optimization of noodles with high grain content[J]. Modern Food Technology,2020,255(11):194−201. YAN M J, LI Y L, LI H M. Process optimization of noodles with high grain content[J]. Modern Food Technology, 2020, 255(11): 194-201.
[17] 程强. 冰晶形成和水分迁移影响冷冻酸面团中乳酸菌活力的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2021. CHENG Q. Study on the effect of ice crystal formation and water migration on the activity of lactic acid bacteria in frozen sourdough[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2021.
[18] 周泓伶. 磁场冻藏改善冷冻面团及其面包品质的机理探索[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2022. ZHOU H L. Exploring the mechanism of magnetic field freezing to improve the quality of frozen dough and bread[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2022.
[19] ZHOU H, JIN Y, HONG T, et al. Effect of static magnetic field on the quality of frozen bread dough[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,50(12):1−9.
[20] 秦跃奇. 冷冻和贮藏温度对馒头品质的影响及机理研究[D]. 新乡: 河南科技学院, 2022. QIN Y Q. Effect of freezing and storage temperature on the quality of steamed bread and its mechanism[D]. Xinxiang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2022.
[21] BALD J, BORJA A, MUXIKA I, et al. Assessing reference conditions and physico-chemical status according to the European Water Framework Directive: A case-study from the Basque Country (Northern Spain)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2005,50(12):1508−1522. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.06.019
[22] VAN DER SMAN R G M, VODA A, VAN DALEN G, et al. Ice crystal interspacing in frozen foods[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2013,116(2):622−626. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.12.045
[23] 王亚运. 冷冻玉米面条加工技术及冻藏期间品质变化的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2016. WANG Y Y. Study on processing technology of frozen corn noodles and quality changes during frozen storage[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2016.
[24] 贺亿杰. 魔芋葡甘聚糖对冷冻面筋蛋白特性及冷冻馒头品质的影响[D]. 新乡: 河南科技大学, 2019. HE Y J. Effects of konjac glucomannan on the properties of frozen gluten and the quality of frozen steamed bread[D]. Xinxiang: Henan University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[25] PETITOT M, BOYER L, MINIER C, et al. Fortification of pasta with split pea and faba bean flours: Pasta processing and quality evaluation[J]. Food Research International,2010,43(2):634−641. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2009.07.020
[26] 田萍萍. 小麦粉特性对速冻熟制面条在冻结及保藏期间品质的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2017. TIAN P P. Effect of wheat flour characteristics on the quality of frozen cooked noodles during freezing and preservation[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2017.
[27] BAIER-SCHENK A, HANDSCHIN S, SCH NAU M V, et al. In situ observation of the freezing process in wheat dough by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM): Formation of ice and changes in the gluten network[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2005,42(2):255−260. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2005.04.006
[28] LI Y, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Effect of ultrasound-assisted freezing on the textural characteristics of dough and the structural characterization of wheat gluten[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,56(7):3380−3390. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-03822-6
[29] 董轩. 冷冻熟制型兰州拉面制面工艺研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2019. DONG X. Research on the processing technology of frozen cooked Lanzhou noodles[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 龙会英,张德. 干热区紫花苜蓿的生产性能和营养价值评价. 草业科学. 2024(01): 117-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王子凌,张子豪,曾璐瑶,劳梦甜,王海滨,王琦,彭利娟,路洪艳,邹圣碧. 不同卤制加工阶段中食盐添加量对小龙虾尾品质及挥发性风味的影响. 食品科学. 2024(11): 52-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



