Identification of Adulterated Animal-derived Ingredients in Edible Animal Viscera Based on Capillary Gel Electrophoresis and DNA Barcoding Techniques
-
摘要: 建立并优化了使用基于DNA条形码技术对可食用内脏制品中包括猪、牛、羊、鸡、鸭、鹅、兔7种常见动物源成分进行掺假鉴别的方法。用生理盐水清洗和真空冷冻干燥预处理后的内脏样品,经DNA提取扩增后,扩增产物经毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统进行确认,克隆测序结果提交本地数据库Viscera进行比对,同时筛选出适合7种动物源内脏DNA扩增的通用引物COI-A,优化DNA模板量和退火温度,验证考察了19个可食用内脏掺假模型的最低掺假比例。7种动物的5类内脏的PCR扩增效率均为100%,最佳的DNA模板量和退火温度为2 μL和53 ℃,掺假成分的最低检出比例为5%。本方法灵敏度高,可靠性好,可作为常见可食用动物内脏掺假的有效检测方法。
-
关键词:
- 毛细管凝胶电泳 /
- DNA条形码 /
- 内脏 /
- 细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ⅰ /
- 掺假
Abstract: A DNA barcoding method with cytochrome C oxidase subunit I sequence (COI) was developed to identify 7 adulterated animal-derived components (including pig, cattle, sheep, chicken, duck, goose and rabbit) in edible viscera products. Samples were cleaned with physiological saline and pretreated by vacuum freeze drying before DNA extraction and amplification. PCR products were confirmed by capillary gel electrophoresis analysis system, and the cloned sequencing results were submitted to the local database (Viscera) for comparison. The universal primer set COI-A was used for the amplification, and the amount of DNA template and annealing temperature were optimized. Meanwhile, the minimum adulteration percentage of 19 edible viscera adulteration models was validated and examined. Results showed that the 5 viscera sources from 7 animal species can be completely amplified under the above conditions, the optimal DNA template volume and annealing temperature are 2 μL and 53 ℃ respectively, and the minimum detection percentage of adulterated components was 5%. The method is sensitive and reliable, which can be used for the identification of adulterated 7 animal-derived components in the edible viscera products. -
食用动物内脏一直是我国几千年饮食文化中重要的一部分,爆炒鸡心、熘肝尖、红烧鸭肠等等,很多可食用内脏是我国各种菜系中的经典之作,同时,近年来特别流行的火锅、烧烤及卤味文化,更是把各种动物内脏的吃法发挥到极致[1]。动物内脏不仅美味,而且营养丰富[2],能有效补充人体各种微量元素和维生素等营养元素的需求,防止由于这些营养元素的缺失而导致的各种疾病[3]。市面上常见的畜禽类内脏食材通常以整个部位进行销售,而猪牛羊畜类动物以及鸡鸭鹅等禽类动物内脏,由于其体型和种属相近的缘由,再加上不法商家会采用香精等对其原有的气味进行掩盖,经过粉碎、烟熏、腌制等深加工处理的可食用内脏,使其原有的感官性状发生改变,普通消费者很难用感官进行判断鉴别[4-6]。其次,不同来源内脏的价格差异,增加了用低价内脏来替代高价内脏的风险性。
近年来,越来越多基于分子水平的技术研究应用于食品掺假鉴别中,一般包括蛋白分析技术或者基于DNA分析[7-12]。由于基于蛋白的掺假技术存在无法区分相近物种或者深加工食品掺假等问题,基于DNA的技术具有较强的特异性和灵敏度,也可以对深加工食品进行鉴别,越来越多的掺假研究集中在基于DNA分析的技术方面[13-15]。
由于缺乏标准化和通用性等问题,大多数基于DNA分析的鉴别技术没有得到广泛的应用,局限性较明显,可靠性和专属性不强[16-17]。DNA条形码技术(DNA Barcoding)作为一种可靠快速的鉴定手段,越来越多的应用于各种领域的物种的鉴别,其是利用一段相对较短的DNA片段,该片段容易扩增且有足够的变异性[18-20]。很多研究采用线粒体细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ι(Cytochrome Coxidase Subunit I,COI)基因的650 bp左右大小的片段区域来研究可食用动物内脏的掺假,该片段符合DNA条形码技术对目标基因需具有足够的特异性和种间足够的多样性的要求,被用于多种动物源食品的掺假鉴别与应用中,也称全片段DNA条形码技术(Full-length DNA Barcoding)[21-22]。毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统是利用高压电场下,由于各DNA片段的大小、带电荷数、等电点等性质不同,在凝胶电泳上的迁移速度不一致,各组分依次移动至毛细管输出端附近的光检测器,检测和记录其吸光度,并将各组分以吸收峰的形式动态直观地记录下来,自动分析出各目的片段的碱基数[23-24]。毛细管凝胶电泳分析技术极大的简化了PCR产物的分析步骤,提高了检测效率,其检测分辨率低至3~5 bp,记录的吸光值使得PCR产物的分析更加直观并可以进行量化分析[25-26]。
目前关于可食用动物内脏的掺假研究有限,未曾有对整个可食用动物内脏掺假风险进行系统性研究和评估,也没有一套完整的掺假鉴别技术来提供相关的技术支持,特别是可食用内脏复杂的基质以及掺假鉴别技术对样品前处理的特殊要求(比如防止漏检和误检),给可食用内脏鉴别带来一定的困难,再加上经济利益驱动,给一些不法商家提供了可乘之机,市售可食用内脏掺假行为层出不穷。本文以常见的7种动物源的5类可食用内脏为研究对象,首次将毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统与DNA条形码技术结合,建立基于COI序列的鉴别可食用动物内脏掺假的检测技术,以期能为市售可食用动物内脏的质量监督提供技术支持和保障。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
为了保证研究的动物内脏没有掺假,所用的5类可食用动物内脏(包括胃、肠、肝、肾、肺)于屠宰场屠宰整只猪、牛、羊、鸡、鸭、鹅、兔时取样,作为本研究方法学建立与优化的原料;共计25批次新鲜动物内脏及其制品 研究所用的实际样品来自杭州市农贸市场及超市,置于−20 ℃保存。
血液与组织DNA提取试剂盒、QIAxcel DNA High Resolution Kit (1200)、QX Alignment Marker 15/600 bp、QX DNA Size Marker 15~1500 bp 均购自德国Qiagen公司;即用PCR扩增试剂、扩增产物回收试剂盒 购自上海生工公司;T4连接试剂盒、DH5α感受态细胞 购自TaKaRa公司。
QIAxcel全自动毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统 购自德国Qiagen公司;Veriti 96孔梯度PCR仪 购自美国ABI公司;EYELA FDU-1100真空冷冻干燥器 购自日本东京理化公司;NanoDrop 1000微量核酸蛋白测定仪、冷冻高速离心机 均购自美国Thermo公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品预处理
将7种动物的5类可食用内脏以及25批次可食用动物制品分别用刀切成小块或小段后,取100 g样品泡于250 mL生理盐水中,超声处理30 min,过滤,去掉滤液,反复处理后直至除去血水,残渣用料理机进行粉碎处理,在−80 ℃下预冷4 h后的样品置真空冷冻干燥箱(温度≤−50 ℃,真空度≤1×10−4 Pa)处理24 h,冷冻干燥处理后的样品经粉碎过筛后,室温存放于干燥器中,备用。
1.2.2 DNA提取与纯化
由于动物内脏基质较复杂,需要一定的DNA纯化步骤才可以保证7种动物的5类内脏的DNA的扩增效率,本文在DNeasy血液与组织提取试剂盒的操作规程的基础上进行一定的改进,具体操作如下:0.5 g样品中加入2 mL ATL缓冲溶液和0.2 mL蛋白酶K,56 ℃裂解至溶液澄清。取裂解液0.25 mL,纯化过程按照试剂盒说明进行操作。最后将纯化的DNA用37 ℃预热的AE缓冲液洗脱DNA,−20 ℃储存备用。
1.2.3 COI基因的扩增
本文最终选用了Ivanova等[27]公开发表的一对引物(COI-A,详细序列见表1),为了方便DNA测序,在每对引物上连接M13,引物合成由杭州擎科生物技术有限公司提供支持。
表 1 基因引物序列Table 1. Primer sequence of genes引物 上游引物(F-Primer 5′-3′) 下游引物(R-Primer 5′-3′) COI-A[27] TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTTCTCAACCAACCACAARGAYATYGG CAGGAAACAGCTATGACTAGACTTCTGGGTGGCCRAARAAYCA COI-B[26] TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTICTCAACCAACCACAAAGACATIGG CAGGAAACAGCTATGACTAGACTTCTGGGTGGCCAAAGAATCA COI-C[26] TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTTCTCAACCAACCAIAAIGALATIGG CAGGAAACAGCTATGACTAGACTTCTGGGTGICCIAAIAAICA 本文采用了25 μL的PCR扩增体系,每个体系由以下试剂组成:12.5 μL即用PCR扩增试剂(上海生工公司),9.5 μL重蒸水,0.5 μL 10 μmol/L正向引物,0.5 μL 10 μmol/L反向引物,2 μL DNA模板。DNA条形码片段扩增程序:95 ℃预变性2 min;95 ℃变性1 min,46 ℃退火1 min,72 ℃延伸30 s(5个循环);95 ℃变性1 min,53 ℃退火1 min,72 ℃延伸30 s(35个循环);最后72 ℃延伸10 min。将扩增片段储存于−20 ℃,备用。
1.2.4 毛细管凝胶电泳确认
采用QIAxcel毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统对PCR扩增产物进行确认分析,对可食用动物内脏的COI基因的扩增效率进行初步确认。将Alignment Marker校准过并进行平衡的凝胶卡夹置于仪器内,样品分析盘内分别放入已加入10 μL DNA size marker以及动物内脏的扩增产物的小管,由于本文采用的扩增条件的扩增效率很高,本文最终将扩增产物用缓冲液稀释至100倍后再进行分析,毛细管凝胶电泳分析时间为5 min。PCR扩增产物经DNA High Resolution Kit (1200)凝胶电泳分离后进行确认分析。确认后的PCR产物送公司进行测序(杭州擎科生物技术有限公司),所得的测序结果经删除两端引物序列,获得最终的扩增序列。
1.2.5 PCR产物克隆测序
切胶回收纯化后的PCR产物与pGEM-T载体连接后,导入DH5α感受态细胞。36 ℃培养箱培养12 h,经过蓝-白筛选后,挑取10个不同的白色菌落接种到LB液体培养基培养过夜(36 ℃,150 r/min摇床),取菌液1 mL提取质粒DNA,送杭州擎科生物技术有限公司进行测序。
1.2.6 测序结果分析
将经删除两端引物和质粒序列后的测序结果提交本地数据库进行比对,进行DNA序列比对,便可以得到掺假样品中混有其他不同动物来源的内脏的序列,从而准确的分析出掺假样品中含有的动物源种类。同时利用美国国家生物信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI)数据库对样品的COI序列进行鉴定和相似度分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 掺假样品预处理方法的优化
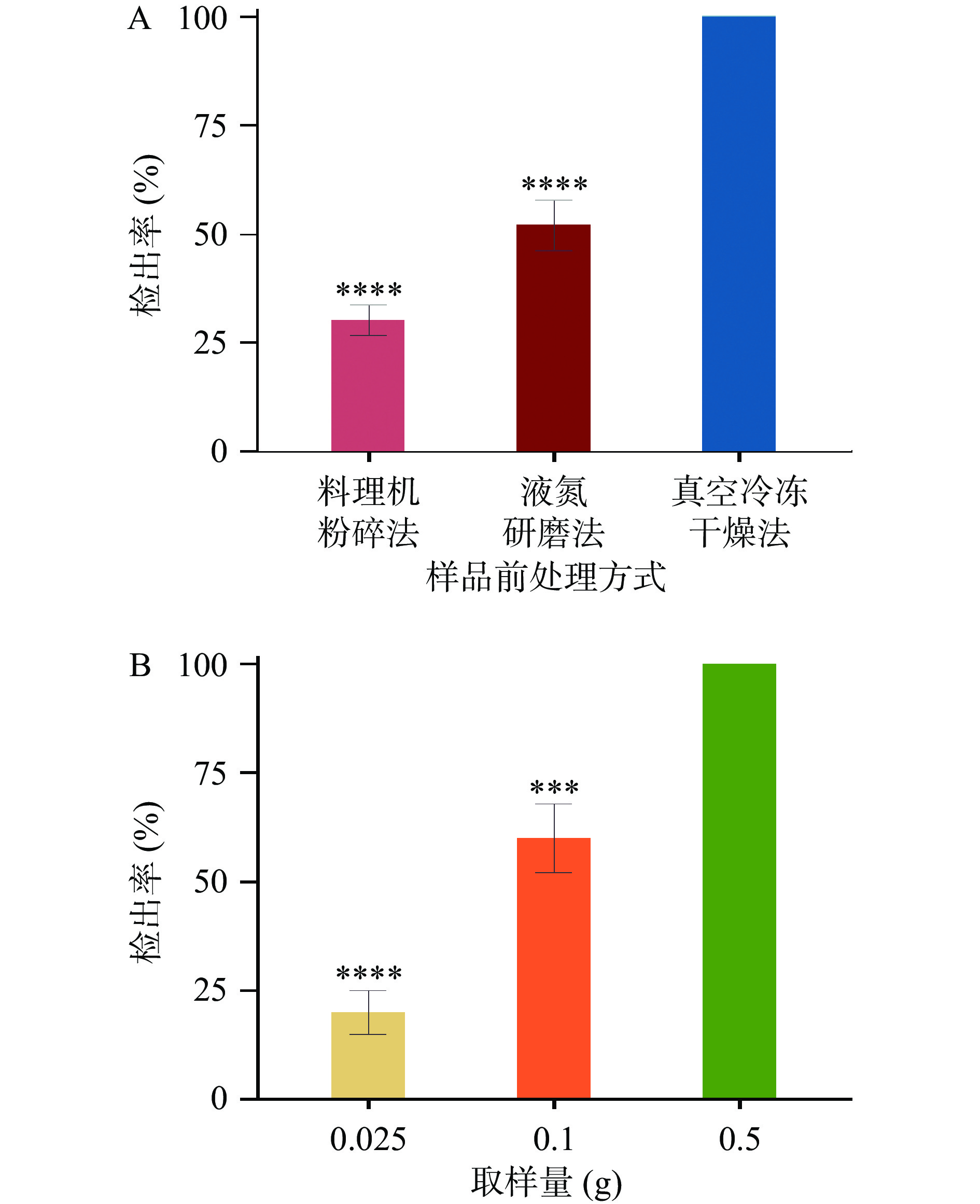
相对其他生物样本,动物内脏的基质较为复杂,一般在DNA提取纯化之前,需要采用一定的预清理方式,将含有的组织液和血液进行清除[28-30]。本文将切成小块的动物内脏用生理盐水浸泡并进行超声清洗处理。DNeasy血液与组织提取试剂盒的说明书的取样方式是采用一次性镊子直接从样品上取一定量的样品,由于本文是针对掺假样品的研究,取样的均一性和代表性直接影响最终实验结果。掺混样品预处理方式的选择会直接决定取样之前样品的均一性,是影响被取样品的代表性的最重要的因素。一般动物组织的分子生物学实验的预处理方式有2种,即料理机粉碎混匀和液氮研磨法。而现代高科技技术的不断进步,涌现出很多先进的样品前处理技术和设备,真空冷冻干燥技术也越来越多的应用于各个领域的前处理技术中。本文采用含10%鸡源性成分的鸭肠,来考察上述三种预处理方式的可靠性,具体操作如下:各取5组含10%鸡源性成分的鸭肠(每组20份样品),分别经三种预处理方式,前处理和分析参照1.2节,结果用鸡肠检出率来对样品均一性进行分析,由图1可知:采用真空冷冻干燥法进行预处理的样品检测结果,与其他两种预处理检测结果有显著性差异(P<0.001),鸡源性成分检出率达到100%,采用真空冷冻干燥处理后的掺假样品,由于将样品直接冷冻干燥,再用粉粹机处理成均一性较好的粉末混合样品,而其他两种方式处理的样品,有不同程度的漏检情况发生,所以本文最终选择真空冷冻干燥法对样品进行预处理。
一般生物样品的DNA提取与净化均可以完全按照DNA提取试剂盒的说明进行操作,比如样品的取样,用一次性镊子取10~25 mg即可。由于掺假样品对均一性的要求,取样量太少会影响样品的代表性,从而影响掺假检出情况,造成实验结果误判。本文采用含10%鸡源性成分的鸭肠考察动物内脏掺假样品中的最佳取样量,采用0.025、0.1、0.5 g三个取样量进行研究,结果发现,当取样量为0.5 g时,样品中检出鸡源性成分的比例为100%,而取样量为0.025 g和0.1 g时,均有不同程度的漏检情况,所以本文最终采用0.5 g的取样量对可食用内脏掺假样品进行DNA提取。
2.2 掺假样品DNA提取方式的优化
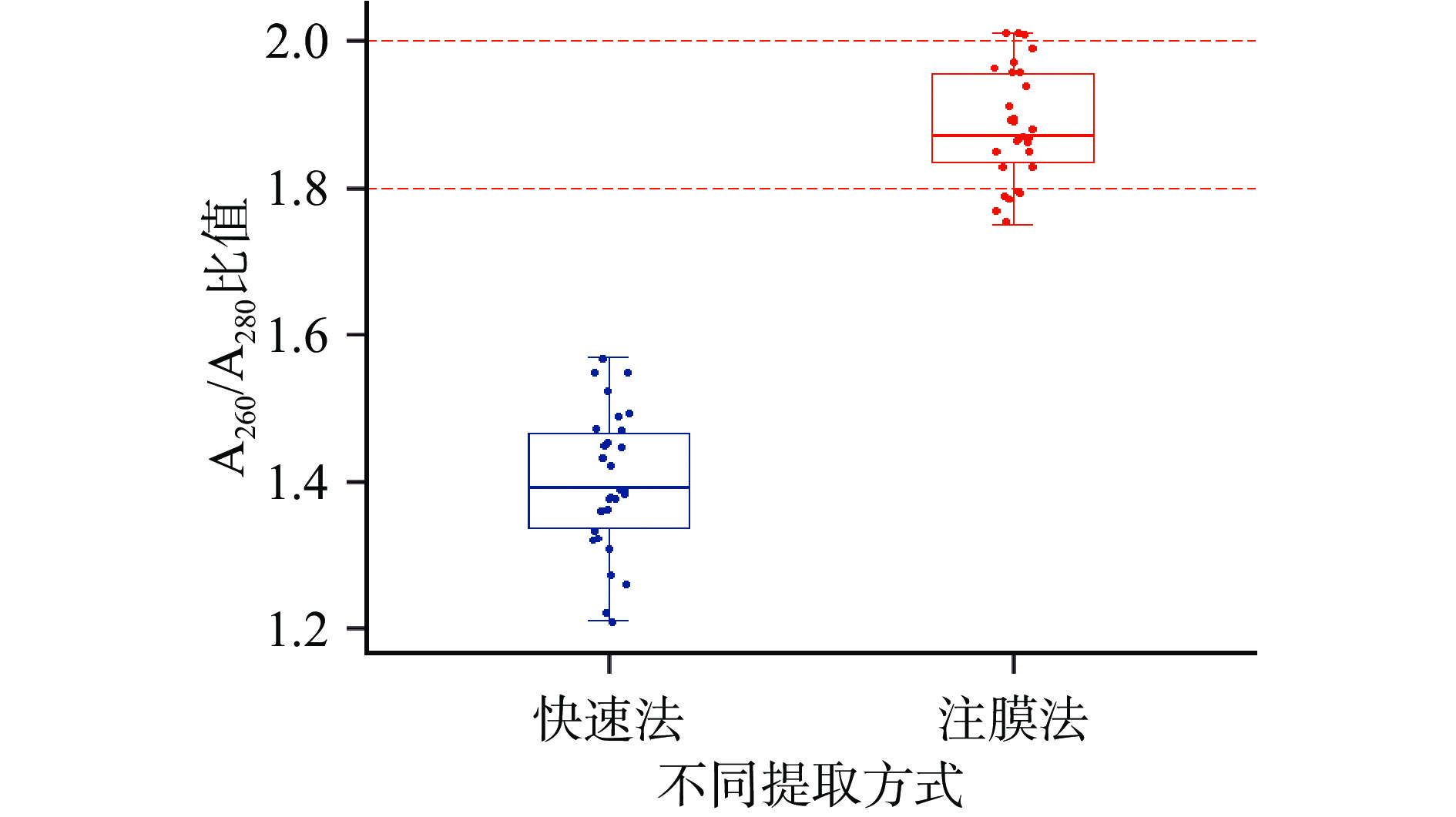
近年来实验室常用的商业化DNA提取试剂盒一般有两种类型,即快速提取法和柱模法提取试剂盒,快速提取试剂盒的优点是简单、快、效率高,缺点是没有去杂质步骤,可能会影响PCR扩增效率,而柱模法增加了深度纯化DNA的步骤,但是提取过程比较耗时[31-32]。本文采用两种提取试剂盒对7种动物的5类可食用内脏的DNA提取纯化效率进行考察,纯化效率用A260和A280的比值进行判断判断,如果比值在1.8~2.0之间,可以认为该DNA比较纯,质量较好[33],具体数据见图2。
从图2的统计图中可以看出,柱膜法提取的可食用内脏的DNA的A260/A280比值要比快速提取法高,纯度较高,质量较好,A260与A280的比值主要集中在1.8~2.0之间,而快速提取法提取DNA的A260与A280的比值在1.2~1.6之间,纯度较差,所以本文最终采用柱膜法对各种动物源的可食用内脏的DNA进行提取净化。
2.3 COI基因片段的扩增条件优化
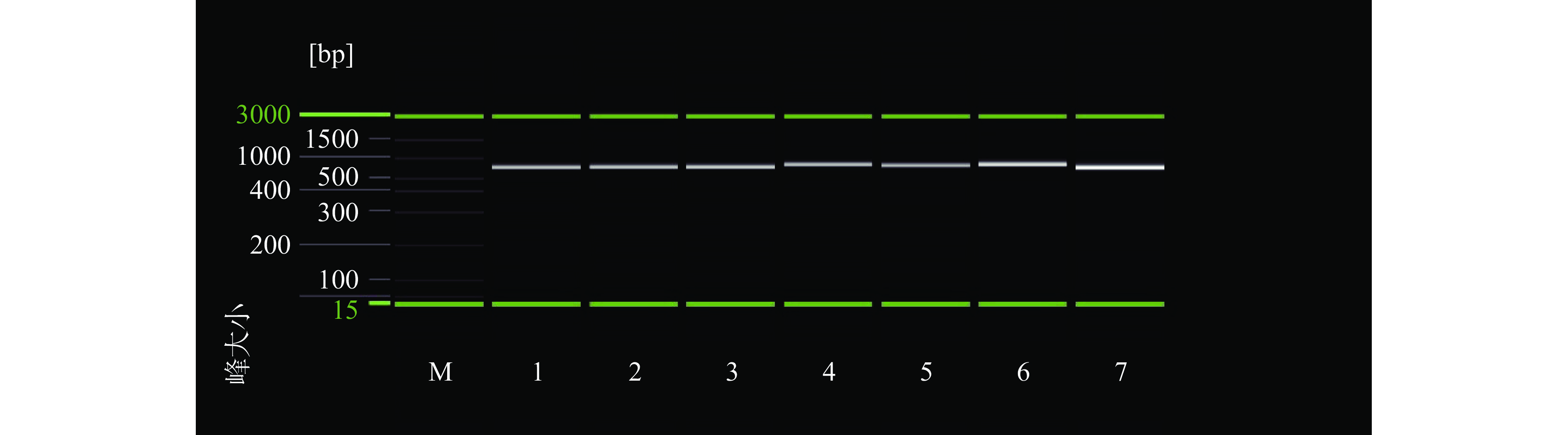
影响目标DNA片段扩增效率关键因素主要包括引物的选择、扩增体系中DNA模板浓度以及扩增程序中的退火温度[34-35]。DNA条形码技术的关键也是选择合适的引物,作为通用引物,在同一个扩增体系和条件下,能有效的扩增出研究的几种物种的目标DNA片段。本文选用了三对通用引物COI-A、COI-B和COI-C(具体引物序列详见表1),分别对7种动物源内脏进行扩增效率进行考察,三对引物扩增的目标片段均是线粒体COI基因上大小为658 bp的片段。7种动物的5类可食用内脏DNA经提取纯化并扩增后,扩增产物经QIAxcel毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统进行确认分析,结果发现,引物COI-B虽然能非常有效的扩增出7种动物的5类可食用内脏的基因片段,但是鹅的5类内脏的扩增效率低,相对于的条带的荧光值较低;引物COI-C几乎对所有7种动物的5类内脏的扩增效率都很低,从条带的荧光值可以判断扩增失败;而引物COI-A能全部高效的扩增出658 bp的目标片段,所以本文最终采用COI-A作为可食用内脏掺混研究的引物(具体见图3)。
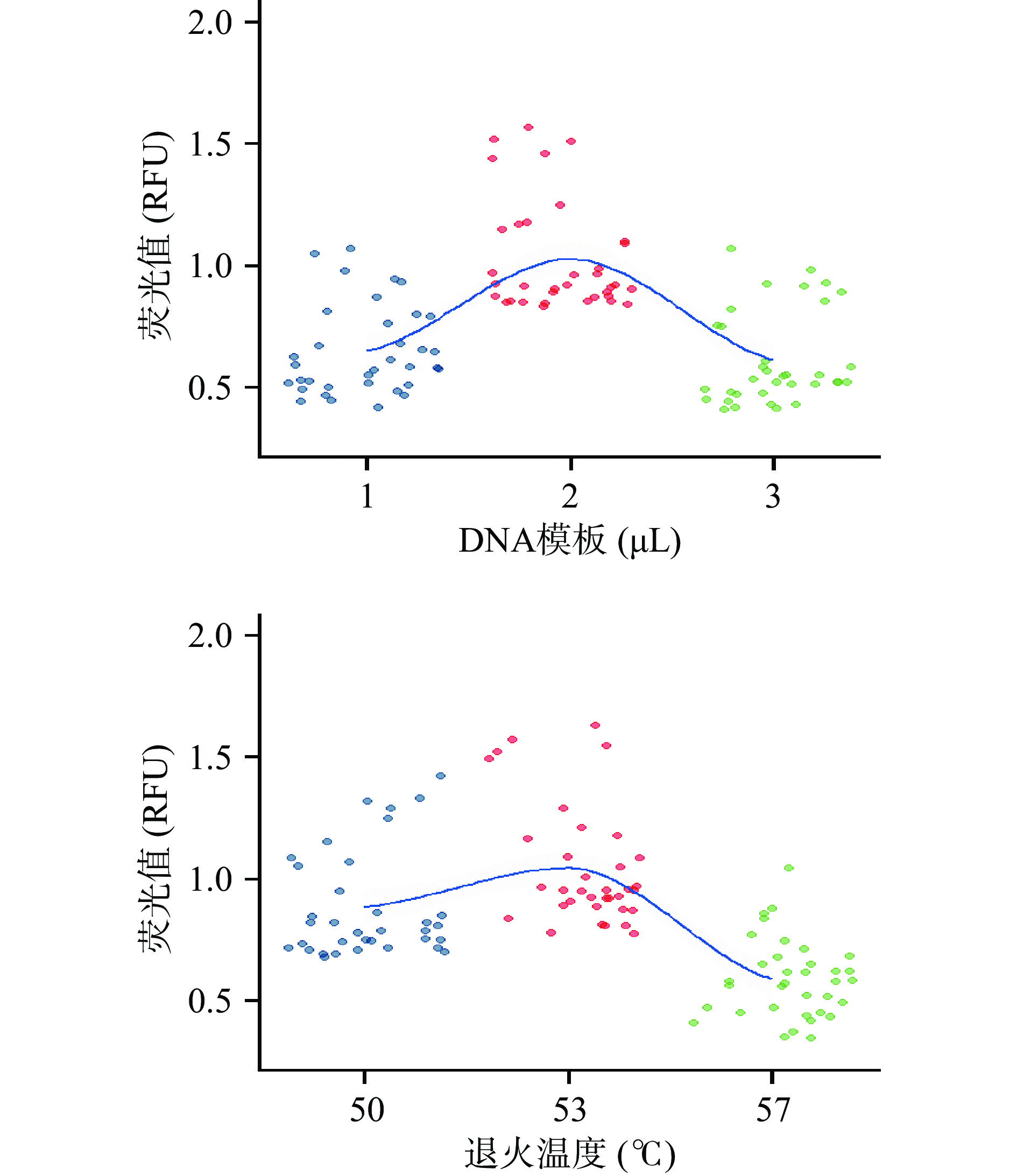
选择了合适的通用引物后,本文继续对扩增体系中的DNA模板量及PCR扩增程序中的退火温度进行优化。由于毛细管凝胶电泳上的毛细管输出端配置了光检测器,扩增产物条带在每个泳道上吸光度(荧光值)会被检测器记录,并转化为相应的条带信号,所以可以利用毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统记录的各个产物条带的荧光值,对扩增效率进行量化考察。在一定的扩增体系中,DNA模板的浓度过高或者过低,都会影响扩增效率,从而降低PCR扩增产物浓度,影响检测结果的灵敏度和有效性。本文考察了三个体积的DNA模板量,分别为1、2、3 μL,在同样的扩增条件下进行扩增后,扩增产物经毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统后读取相应的目标条带的荧光值(RFU),结果见图4。同时,在PCR扩增程序中,合适的退火温度是保证扩增效率以及产物特异性的关键因素,退火温度太低,会影响扩增产物的特异性,反之则会大幅度降低扩增效率。本文采用50、53以及57 ℃,3个退火温度分别对7种动物的5类内脏进行扩增效率的考察,扩增产物经毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统后读取相应的目标条带的荧光值(RFU),结果见图4。
从图4可以看出,当DNA模板量为1 μL和3 μL时,7种动物源的5类内脏的凝胶条带的荧光值较模板量2 μL时小,而荧光值大小与扩增效率成正比;选择退火温度为53 ℃,7种动物源的5类内脏的凝胶条带的荧光值最高。所以本文最终选择DNA模板量为2 μL、退火温度为53 ℃的扩增条件作为7种动物源的5类内脏DNA条形码基因的最佳扩增条件。从毛细管凝胶电泳系统中可以看出,7种动物源的5类内脏在700 bp左右均有一条较明显的扩增条带(见图3)。然后将7种动物源的5类内脏的PCR扩增产物送至生物公司进行克隆测序,测序结果见表2。
表 2 7种动物源内脏的DNA条形码检测结果Table 2. DNA barcoding results for 7 samples found to contain one species序号(NO.) 内脏来源 基因相似度 物种匹配结果 1 猪 99% Sus scrofa(野猪) 2 牛 98% Bos primigenius(原始牛) 3 羊 99% Capra hircus(山羊) 4 鸭 98% Anas platyrhynchos(绿头鸭) 5 鸡 100% Gallus gallus(普通家鸡) 6 鹅 98% Anser(鹅属) 7 兔 100% Oryctolagus cuniculus(家兔) 2.4 可食用动物内脏掺假模型灵敏度和稳定性检测
本文根据常见的可食用动物内脏的掺假类型,根据经济价值的高低,对可能存在的掺假模式进行模拟,具体见表3。
表 3 可食用内脏掺假模型Table 3. Animal viscera adulteration model模型编号 高经济价值内脏 掺假内脏 灵敏度(%) 1 牛肝 猪肝 5 2 羊肝 猪肝 5 3 兔肝 猪肝 5 4 鹅肝 鸭肝 5 5 鹅肝 鸡肝 5 6 牛胃 猪胃 5 7 羊胃 猪胃 5 8 鹅胃 鸡胃 5 9 鹅胃 鸭胃 5 10 牛肠 猪肠 5 11 羊肠 猪肠 5 12 鹅肠 鸡肠 5 13 鹅肠 鸭肠 5 14 牛肾 猪肾 5 15 羊肾 猪肾 5 16 鹅肾 鸡肾 5 17 鹅肾 鸭肾 5 18 牛肺 猪肺 5 19 羊肺 猪肺 5 本文根据现有的可食用内脏的市场价格,根据其价格与供给量进行评估可食用内脏的经济价值,分成高经济价值可食用内脏和低经济价值可食用内脏,根据类型和感官性状等,建立了19个可食用内脏掺假模型,对可食用动物内脏中有可能掺假的其他动物源内脏进行掺假灵敏度的考察。结果发现,19个可食用内脏的掺假模型中的掺假成分检出灵敏度较合理,最低检出比例均能达到5%,能满足日常的检测要求。同时本文对19个掺假模型,分别采用5%、10%、15%三个掺假比例,进行稳定性考察。将上述扩增产物置−20 ℃进行保存,分别在第1、3、7 d进行检测,结果保持一致。
2.5 建立基于BLAST+的7种可食用动物内脏的DNA条形码本地数据库
基本局域连配检索工具(Basic local alignment search tool, BLAST)是由NCBI开发的序列查找和比对工具,BLAST及其相关数据库是快速进行数据查询匹配的有力工具[36]。目前BLAST本地化工具(BLAST+)及其数据库可以通过自行构建的方法脱机运行,即通过本地数据库进行查找,而无需连接到美国NCBI中央数据库[37]。本文根据测定的7种动物源的可食用动物内脏的COI基因序列,构建了常见的可食用内脏掺假的内脏DNA条形码本地数据库。将11种肉的微条形码片段核酸序列存为单一的FASTA格式文件viscera07,然后使用BLAST+工具包的makeblastdb命令(makeblastndb-in.\viscera07.fasta-dbtype nucl-parse_seqids-out Viscera),对上述序列文件进行数据格式化和索引化,形成可供BLAST检索的本地数据库Viscera。
取本文研究的可食用内脏的掺假模型、实际样品的测序结果,使用本地数据库的blastn命令将待检索序列结果对数据库进行检索,结果自动保存于result.txt文件。在结果目录下打开result.txt文件,根据比对得分(Score)情况进行结果分析。
2.6 可食用内脏制品检测
按照本文建立的方法,对25批次可食用内脏制品进行掺假鉴别,将克隆测序结果经建立的可食用动物内脏的DNA条形码本地数据库进行blast比对分析,结果见表4。
表 4 实际样品检测结果Table 4. Actual sample test results序号
(NO.)样品名称 DNA条形
码鉴定结果基因相似
度(%)判断
结果实时荧光定
性PCR法结果1 牛肝a 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 2 牛肝b 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 3 牛肝c 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 4 羊肝a 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 5 羊肝b 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 6 鹅肝a 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 7 鹅肝b 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 8 鹅肝c 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 9 鹅肝d 鸭源性成分 98 掺假 鸭源性成分 10 鹅肝e 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 11 牛百叶a 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 12 牛百叶b 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 13 牛百叶c 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 14 牛百叶d 猪源性成分 97 掺假 猪源性成分 15 牛百叶e 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 16 牛百叶f 猪源性成分 97 掺假 猪源性成分 17 牛肠a 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 18 牛肠b 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 19 鹅肠a 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 20 鹅肠b 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 21 鹅肠c 鸭源性成分 99 掺假 鸭源性成分 22 鹅肠d 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 23 牛肺 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 24 羊肺a 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 25 羊肺b 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 本文利用建立的检测和分析方法对25批次可食用内脏制品进行掺假鉴别研究,25批次可食用内脏制品包括6批次的牛百叶(牛胃)、5批次的鹅肝、4批次的鹅肠、3批次的牛肝、2批次的羊肝、2批次的牛肠、2批次的羊肺以及1批次的牛肺。所有的样品经预处理、DNA提取纯化扩增后,在毛细管凝胶色谱分析上700 bp左右的位置均有一条较清晰的条带。将扩增产物进行切胶纯化后,进行克隆测序,测序结果经建立的可食用动物内脏的DNA条形码本地数据库进行blast比对分析。比对结果发现,25批次的可食用内脏制品检出2批次的猪源性成分和2批次的鸭源性成分,掺假比例为16%:其中6批次的牛百叶制品中检出2批次的猪源性成分,不合格率为33%;4批次的鹅肠制品中检出1批次的鸭源性成分,不合格率为25%;5批次的鹅肝制品中检出1批次的鸭源性成分,不合格率为20%。为了验证本检测方法的可靠性,我们对上述4批次的掺假样品参照农业部标准NY/T 3309-2018《肉类源性成分鉴定 实时荧光定性PCR法》进行检测,结果与本方法一致(见表4)。从上述检测结果可以看出,市售可食用内脏制品中,牛百叶、鹅肠、鹅肝等三类内脏制品比较容易有掺假问题,需要重点关注。
3. 结论
本文建立了基于QIAxcel 毛细管凝胶电泳分析系统结合DNA条形码技术对7种可食用内脏进行掺假鉴定,优化了样品前处理、DNA提取和PCR扩增条件。扩增产物进行克隆测序所得的COI基于序列在建立的可食用动物内脏的DNA条形码本地数据库Viscera进行BLAST比对,进行掺假鉴别。本方法检出灵敏度较合适,适合正常的可食用内脏掺假鉴别,又不会出现误判。传统的基于DAN分析的鉴定技术一般使用特异性引物进行扩增,方法的通用性不强,掺假筛选能力一般;而DNA条形码技术采用通用型引物,可以一次性检测可食用动物内脏中的7种动物源成分,效率高,通用性强。但是本方法也存在一定的缺点,比如DNA条形码扩增产物的后续分析和确认需要较昂贵的设备和需要较专业的技术人员,且克隆测序的时间较长,所以今后在动物源成分的掺假鉴定技术研究方向,亟需开发一种耗时短、效率高、特异性强的DNA条形码扩增产物确认技术手段。
-
表 1 基因引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence of genes
引物 上游引物(F-Primer 5′-3′) 下游引物(R-Primer 5′-3′) COI-A[27] TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTTCTCAACCAACCACAARGAYATYGG CAGGAAACAGCTATGACTAGACTTCTGGGTGGCCRAARAAYCA COI-B[26] TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTICTCAACCAACCACAAAGACATIGG CAGGAAACAGCTATGACTAGACTTCTGGGTGGCCAAAGAATCA COI-C[26] TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGTTCTCAACCAACCAIAAIGALATIGG CAGGAAACAGCTATGACTAGACTTCTGGGTGICCIAAIAAICA 表 2 7种动物源内脏的DNA条形码检测结果
Table 2 DNA barcoding results for 7 samples found to contain one species
序号(NO.) 内脏来源 基因相似度 物种匹配结果 1 猪 99% Sus scrofa(野猪) 2 牛 98% Bos primigenius(原始牛) 3 羊 99% Capra hircus(山羊) 4 鸭 98% Anas platyrhynchos(绿头鸭) 5 鸡 100% Gallus gallus(普通家鸡) 6 鹅 98% Anser(鹅属) 7 兔 100% Oryctolagus cuniculus(家兔) 表 3 可食用内脏掺假模型
Table 3 Animal viscera adulteration model
模型编号 高经济价值内脏 掺假内脏 灵敏度(%) 1 牛肝 猪肝 5 2 羊肝 猪肝 5 3 兔肝 猪肝 5 4 鹅肝 鸭肝 5 5 鹅肝 鸡肝 5 6 牛胃 猪胃 5 7 羊胃 猪胃 5 8 鹅胃 鸡胃 5 9 鹅胃 鸭胃 5 10 牛肠 猪肠 5 11 羊肠 猪肠 5 12 鹅肠 鸡肠 5 13 鹅肠 鸭肠 5 14 牛肾 猪肾 5 15 羊肾 猪肾 5 16 鹅肾 鸡肾 5 17 鹅肾 鸭肾 5 18 牛肺 猪肺 5 19 羊肺 猪肺 5 表 4 实际样品检测结果
Table 4 Actual sample test results
序号
(NO.)样品名称 DNA条形
码鉴定结果基因相似
度(%)判断
结果实时荧光定
性PCR法结果1 牛肝a 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 2 牛肝b 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 3 牛肝c 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 4 羊肝a 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 5 羊肝b 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 6 鹅肝a 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 7 鹅肝b 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 8 鹅肝c 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 9 鹅肝d 鸭源性成分 98 掺假 鸭源性成分 10 鹅肝e 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 11 牛百叶a 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 12 牛百叶b 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 13 牛百叶c 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 14 牛百叶d 猪源性成分 97 掺假 猪源性成分 15 牛百叶e 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 16 牛百叶f 猪源性成分 97 掺假 猪源性成分 17 牛肠a 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 18 牛肠b 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 19 鹅肠a 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 20 鹅肠b 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 21 鹅肠c 鸭源性成分 99 掺假 鸭源性成分 22 鹅肠d 鹅源性成分 99 符合 鹅源性成分 23 牛肺 牛源性成分 98 符合 牛源性成分 24 羊肺a 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 25 羊肺b 羊源性成分 99 符合 羊源性成分 -
[1] 王学平. 畜禽产品加工的综合利用发展趋势[J]. 肉类研究,2008(11):11−14. [WANG X P. The comprehensive utilization of the livestock and poultry products processing[J]. Meat Research,2008(11):11−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8123.2008.11.006 WANG X P. The comprehensive utilization of the livestock and poultry products processing[J]. Meat Research, 2008, (11): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8123.2008.11.006
[2] 王晓雄. 吃动物内脏的好与坏[J]. 安全与健康,2017(12):51. [WANG X X. The benefits and disadvantages of eating animal viscera[J]. Safety & Health,2017(12):51. WANG X X. The benefits and disadvantages of eating animal viscera[J]. Safety & Health, 2017, (12): 51.
[3] 张文文, 梅娜娜, 钤莉妍, 等. 驴肝与猪肝、鸡肝和鹅肝之间的营养成分比较[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(16):4435−4439. [ZHANG W W, MEI N N, QIAN L Y, et al. Comparison of nutrients between donkey liver and pig liver, chicken liver and goose liver[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2018,9(16):4435−4439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.16.041 ZHANG W W, MEI N N, QIAN L Y, et al. Comparison of nutrients between donkey liver and pig liver, chicken liver and goose liver [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2018, 9(16): 4435-4439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.16.041
[4] 李珮斯, 苏永祺, 郭新东, 等. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定动物内脏中金属元素含量[J]. 安徽农业科学,2013,41(21):8915−8917. [LI P S, SU Y Q, GUO X D, et al. Content determination of metal elements in animal viscera by microwave digestion-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2013,41(21):8915−8917. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.21.037 LI P S, SU Y Q, GUO X D, et al. Content determination of metal elements in animal viscera by microwave digestion-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(21): 8915-8917. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.21.037
[5] 林竹光, 孙若男, 张莉莉, 等. 气相色谱-质谱法同时测定动物内脏中的14种酞酸酯类环境激素残留[J]. 色谱,2008(3):280−284. [LIN Z G, SUN R N, ZHANG L L, et al. Simultaneous determination of 14 phthalate ester residues in animal innards by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with electron impact ionization[J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography,2008(3):280−284. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.03.003 LIN Z G, SUN R N, ZHANG L L, et al. Simultaneous determination of 14 phthalate ester residues in animal innards by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with electron impact ionization [J]. Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2008, (3): 280-284. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8713.2008.03.003
[6] 魏法山, 巩阿娜, 谢文佳, 等. 我国畜禽内脏食用安全指标检测分析[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2017,8(9):3667−3673. [WEI F S, GONG A N, XIE W J, et al. Detection and analysis of edible safety of livestock and poultry viscera in China[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2017,8(9):3667−3673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2017.09.066 WEI F S, GONG A N, XIE W J, et al. Detection and analysis of edible safety of livestock and poultry viscera in China [J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2017, 8(9): 3667-3673. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2017.09.066
[7] ERBAN T, SHCHERBACHENKO E, TALACKO P, et al. A single honey proteome dataset for identifying adulteration by foreign amylases and mining various protein markers natural to honey[J]. Journal of Proteomics,2021,239:104157. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2021.104157
[8] KRITIKOU A S, AALIZADEH R, DAMALAS D E, et al. MALDI-TOF-MS integrated workflow for food authenticity investigations: An untargeted protein-based approach for rapid detection of PDO feta cheese adulteration[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,370:131057. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131057
[9] MONTOWSKA M, FORNAL E. Absolute quantification of targeted meat and allergenic protein additive peptide markers in meat products[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,274:857−864. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.131
[10] LECRENIER M C, MARIEN A, VEYS P, et al. Inter-laboratory study on the detection of bovine processed animal protein in feed by LC-MS/MS-based proteomics[J]. Food Control,2021,125:107944. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.107944
[11] FORNAL E, MONTOWSKA M. Species-specific peptide-based liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry monitoring of three poultry species in processed meat products[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,285:489−498.
[12] HAO X K, FU L L, SHAO L L, et al. Quantification of major milk proteins using ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometry and its application in milk authenticity analysis[J]. Food Control,2022,131:108455. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108455
[13] COTTENET G, BLANCPAIN C, CHUAH P F, et al. Evaluation and application of a next generation sequencing approach for meat species identification[J]. Food Control,2020,110:107003. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.107003
[14] GALAL-KHALLAF A. Multiplex PCR and 12S rRNA gene sequencing for detection of meat adulteration: A case study in the Egyptian markets[J]. Gene,2021,764:145062. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145062
[15] WANG N, XING R R, ZHOU M Y, et al. Application of DNA barcoding and metabarcoding for species identification in salmon products[J]. Food Additives & Contaminants,2021,38(5):754−768.
[16] CAOBY H, ZHENG K Z, JIANG J F, et al. A novel method to detect meat adulteration by recombinase polymerase amplification and SYBR green I[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,266:73−78. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.05.115
[17] KANG T S, TANAKA T. Comparison of quantitative methods based on SYBR Green real-time qPCR to estimate pork meat adulteration in processed beef products[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,269:549−558. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.141
[18] QUINTO C A, TINOCO R, HELLBERG R S. DNA barcoding reveals mislabeling of game meat species on the U. S. commercial market[J]. Food Control,2016,59:386−392. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.05.043
[19] ZIA Q, ALAWAMI M, MOKHTAR N F, et al. Current analytical methods for porcine identification in meat and meat products[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,324:126664. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126664
[20] XING R R, HU R R, HAN J X, et al. DNA barcoding and mini-barcoding in authenticating processed animal-derived food: A case study involving the Chinese market[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,309:125653. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125653
[21] AHMED N, SANGALE D, TIKNAIK A, et al. Authentication of origin of meat species processed under various Indian culinary procedures using DNA barcoding[J]. Food Control, 2018, 90: 259−265.
[22] KANE D E, HELLBERG R S. Identification of species in ground meat products sold on the U. S. commercial market using DNA-based methods[J]. Food Control,2016,59:158−163. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.05.020
[23] BARAKAT H, EI-GARHY H A S, MOUSTAFA M M A. Detection of pork adulteration in processed meat by species-specific PCR-QIAxcel procedure based on D-loop and cytb genes[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2014,98:9805−9816. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6084-x
[24] SEN F, UNCU A O, UNCU A T, et al. The trnL (UAA)-trnF (GAA) intergenic spacer is a robust marker of green pea (Pisum sativum L.) adulteration in economically valuable pistachio nuts (Pistacia vera L.)[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(7):3056−3061. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10336
[25] ELSAYED M S A E. A first insight into the application of high discriminatory MIRU-VNTR typing using QIAxcel technology for genotyping Mycobacterium bovis isolated from the Delta area in Egypt[J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution,2019,71:211−214. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2019.04.004
[26] HAJIBABAEI M, SINGER G A C, HEBERT P D N, et al. DNA barcoding: How it complements taxonomy, molecular phylogenetics and population genetics[J]. Trends in Genetics,2007,23(4):167−172. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2007.02.001
[27] IVANOVA N V, DEWAARD J R, HEBERT P D N. An inexpensive automation-friendly protocol for recovering high-quality DNA[J]. Molecular Ecology Notes,2006,6:998−1002. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01428.x
[28] RAO M S, CHAKRABORTY G, MURTHY K S. Market drivers and discovering technologies in meat species identification[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2019,12:2416−2429. doi: 10.1007/s12161-019-01591-8
[29] KUMAR A, RODRIGUES V, BASKARAN K, et al. DNA barcode based species-specific marker for Ocimum tenuiflorum and its applicability in quantification of adulteration in herbal formulations using qPCR[J]. Journal of Herbal Medicine,2020,23:100376. doi: 10.1016/j.hermed.2020.100376
[30] DAI Z Y, QIAO J, YANG S R, et al. Species authentication of common meat based on PCR analysis of the mitochondrial COI Gene[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2015,176:1770−1780. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1715-y
[31] LIU W W, TAO J, XUE M, et al. A multiplex PCR method mediated by universal primers for the identification of eight meat ingredients in food products[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2019,245:2385−2392. doi: 10.1007/s00217-019-03350-9
[32] DUNHAM-CHEATHAM S M, KLINGLER K B, ESTRADA M V, et al. Using a next-generation sequencing approach to DNA metabarcoding for identification of adulteration and potential sources of mercury in commercial cat and dog foods[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2021,778:146102. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146102
[33] COTTENET G, SONNARD V, BLANCPAIN C, et al. A DNA macro-array to simultaneously identify 32 meat species in food samples[J]. Food Control,2016,67:135−143. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.02.042
[34] SWETHA V P, SHEEJA T E, SASIKUMAR B. DNA barcoding as an authentication tool for food and agricultural commodities[J]. Current Trends in Biotechnology & Pharmacy,2016,10(4):384−402.
[35] HELLBERG R S, HERNANDEZ B C, HERNANDEZ E L. Identification of meat and poultry species in food products using DNA barcoding[J]. Food Controll,2017,80:23−28. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.04.025
[36] 励炯, 吴琼, 扈明洁, 等. 基于细胞色素C氧化酶亚基Ⅰ序列的DNA微条形码技术鉴别11种生鲜肉制品掺假的研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2021,47(1):52−59. [LI J, WU Q, HU M J, et al. Identification of adulteration in 11 fresh meat products by DNA mini-barcoding methods based on cytochrome C oxidase subunit Ⅰ (COⅠ) sequence[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences),2021,47(1):52−59. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9209.2020.04.291 LI J, WU Q, HU M J, et al. Identification of adulteration in 11 fresh meat products by DNA mini-barcoding methods based on cytochrome C oxidase subunit Ⅰ (COⅠ) sequence[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2021, 47(1): 52-59. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9209.2020.04.291
[37] 郜星晨, 姜伟. 三峡库区常见鱼类DNA条形码本地BLAST数据库的构建和应用[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2021,40(5):1952−1964. [HAO X C, JIANG W. The construction and application of BLAST database of DNA barcode for common fish in the three gorges reservoir[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2021,40(5):1952−1964. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.040.001952 HAO X C, JIANG W. The construction and application of BLAST database of DNA barcode for common fish in the three gorges reservoir [J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2021, 40(5): 1952-1964. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.040.001952
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 蔡梦婷,刘荔,黄若楠,孙学宁,曾名湧. 亲水胶体调控全牡蛎-大豆分离蛋白热诱导凝胶的形成机制. 食品工业科技. 2024(23): 129-139 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



