Fractionation, Purification and Antioxidant, Antitumor Activity of Polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius Mycelia
-
摘要: 采用水提醇沉法制备桑黄菌丝体粗多糖,分别用终浓度为30%、45%和60%的硫酸铵溶液对桑黄菌丝体中粗多糖进行粗分离,并比较所得各多糖组分的抗氧化、抗肿瘤活性。对其中活性强的组分采用离子交换树脂柱色谱纯化,采用高效排阻色谱-折光示差检测器-多角度光散射仪对纯化多糖进行均一性分析和分子量测定。结果显示,45%硫酸铵分离多糖IPS45显示最强的抗肿瘤活性及较好的清除超氧阴离子活性,IPS45经DEAE-52纤维素离子交换柱纯化得到四个级分,经高效排阻色谱分析,其中蒸馏水洗脱级分(IPS45-W)为均一多糖,重均分子量为79.1 kDa;气相色谱分析其单糖组成为甘露糖:葡萄糖:半乳糖:未知单糖,摩尔比为1.57:8.38:1.09:1.00。IPS45-W可抑制HepG2细胞生长,当浓度为50 μg/mL时,对HepG2细胞的抑制率为56.74%,高于前期研究的乙醇沉淀分离所得桑黄菌丝体均一多糖同浓度下11%~35%的抑制率。该结果为不同组成的桑黄多糖的分离和应用提供依据。Abstract: The crude polysaccharide of Phellinus igniarius mycelia was prepared by the method of water extraction and ethanol precipitation. Then it was preliminarily fractionated by ammonium sulfate solution with the final concentration of 30%, 45% and 60%, respectively. The antioxidant and anti-tumor activities of the polysaccharides fractions were tested and compared with each other. The fraction which showed the strongest activity was further purified by ion exchange resin column chromatography. And the homogeneity and average molecular weight (MW) of purified polysaccharides were evaluated and determined by size-exclusion chromatography combined with multi-angel laser light scattering and refractive indexdetector (SEC-MALLS-RI). The results showed that 45% ammonium sulfate solution supernatant fraction (IPS45) had the strongest anti-tumor activity and better scavenging superoxide anion activity in fractions fractionated by different concentrations of ammonium sulfate. Four fractions were obtained from IPS45 by DEAE-52 cellulose ion exchange column purification. SEC-MALLS-RI analysis results showed that the ddH2O elution fraction (IPS45-W) was a homogeneous polysaccharide with a MW of 79.1 kDa. GC analysis indicated that IPS45-W was composed of mannose:glucose:galactose:unknown monosaccharide in a molar ratio of 1.57:8.38:1.09:1.00. The IPS45-W could inhibit the growth of HepG2 cells. Its inhibition rate was 56.74% at the concentration of 50 μg/mL. This inhibition rate of IPS45-W was higher than that of the homopolysaccharide (11%~35%) against HepG2 cells at same concentration, which from the Phellinus igniarius myceli polysaccharide fractionated by ethanol precipitation in previous studies. The results would provide the basis for the separation and application of different components of Phellinus igniariusmycelia polysaccharides.
-
桑黄是一类珍贵的药用真菌,其最早的药用记载源自两千多年前的《神农本草经》,《本草纲目》中也有桑黄疗效的记载[1]。随着现代药理学对桑黄研究的深入,20世纪90年代韩国将桑黄菌丝体列为抗肿瘤辅助药品[1]。多糖是桑黄发挥药理作用的最主要成分之一,其子实体及菌丝体多糖均具有显著的抗肿瘤、抗氧化作用[2]。如桑黄菌丝体多糖可抑制肿瘤[3-4]及抗环磷酰胺致突变作用[4],对超氧负离子和羟基自由基具有显著的清除作用[3,5],能明显增强小鼠免疫功能[6],对大鼠胶原诱导性关节炎具有治疗作用[7]。桑黄多糖具有的抗肿瘤、抗突变、抗氧化、免疫调节等活性,使其的应用价值越来越引起广泛重视。桑黄自然生长缓慢,液体发酵成为工业化制备桑黄菌丝体多糖的重要途径[5]。
多糖的提取分离是桑黄研究及应用的关键步骤,在此过程中要防止其结构变化和生物活性损失[2]。水提醇沉是多糖制备最常用的方法,热水浸提过程也伴随着蛋白质等水溶性杂质的溶出[2,8],伴随着多糖一起沉淀在粗多糖中[3,8]。多糖的分离纯化方法主要有色谱法、超滤法和非溶剂沉淀法[9]。与前两种方法需要相应配套设备不同,非溶剂沉淀法不需要特殊设备,处理量可以根据需要任意调节,适合工业化放大[9]。乙醇是最常用的非溶剂沉淀剂,已用于各种多糖的分级分离[8-10]。但乙醇作为有机溶剂容易造成蛋白变性,不适合应用于多糖-蛋白复合物的分级。与之相比,盐析法对蛋白结构及活性影响小[10],是蛋白质分离纯化中常采用的粗分离方法,如用于大豆蛋白[11]及卵清蛋白[12]的分离。除了用于分离蛋白,硫酸铵也可用作多糖分级的非溶剂沉淀剂。如Wu等[13]采用20%浓度硫酸铵分离黄芥末粘液果胶酶水解产物溶液中的多糖,并对比硫酸铵沉淀法与乙醇沉淀法制备多糖的得率及单糖组成,发现硫酸铵沉淀中的多糖组分含有更多葡萄糖,但得率较低。Wang等[14]采用三相分配法结合硫酸铵梯度沉淀法从新鲜秋葵荚中提取和分离生物活性多糖,发现所得多糖的重均分子量随着硫酸铵浓度增高而降低。硫酸铵由于对蛋白质具有保护作用[11],特别适合于多糖-蛋白复合物的初步纯化。如用不同浓度的硫酸铵溶液分离平菇粗多糖,在上清液和沉淀中得到的四个多糖组分显示出良好的抗肿瘤活性,其中两个组分为多糖-蛋白复合物[15]。Shi等[16]指出与乙醇沉淀相比,硫酸铵沉淀是分离具有不同理化性质的多糖组分的一种有效方法,并采用40%、60%和80%饱和度的硫酸铵溶液分离芦荟叶皮粗多糖,仅通过硫酸铵沉淀法一步分离就得到三个具有较高纯度的均一多糖。本课题组在前期研究中采用30%、60%和80%乙醇分步沉淀从桑黄菌丝体热水提取液中分离得到三个级分,采用DEAE-52纤维素离子交换色谱和凝胶柱色谱进一步纯化得到四个以葡聚糖为主的均一多糖[13]。桑黄粗多糖组成复杂,不同的分离分级方法有可能获得更高活性的桑黄多糖,另一方面也可探索分离条件对桑黄多糖组成结构及活性的影响。因此本研究采用硫酸铵对桑黄菌丝体粗多糖进行分级分离,比较不同浓度硫酸铵对分离多糖的体外抗氧化活性及抗肿瘤活性的影响,并与前期乙醇沉淀分离的桑黄多糖抗肿瘤活性进行对比,以期为不同组成的桑黄多糖的分离和应用提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
桑黄(Phellinus igniarius)菌种 菌株编号5.95,中国微生物菌种保藏管理委员会普通微生物保藏管理中心;小麦粉、麸皮粉 镇江农贸市场;桑枝 镇江医药公司;考马斯亮蓝G-250、牛血清蛋白、D-葡萄糖、D-甘露糖、D-半乳糖、D-(+)-木糖、α-L-(+)-鼠李糖 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;四甲基偶氮唑盐(MTT)、二甲亚砜(DMSO)、氯化硝基四氮唑(NBT) 南京生兴生物技术公司;吩嗪甲酯硫酸盐(PMS)、还原型辅酶(NADH) Sigma公司;重蒸酚 北京华越洋生物科技有限公司;DEAE-52 Cellulose Whatman公司;96孔细胞培养板 美国Corning公司;胎牛血清、DMSM培养基 Gibco公司;胰蛋白酶(2000 U) Invitrogen公司;HepG2肝癌细胞 购自上海细胞生物所,由江苏大学基础医学与医学技术学院保存;KH2PO4、MgSO4·7H2O、无水乙醇、H2SO4、NaCl 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
YC-211恒温培养摇床 上海福玛实验设备有限公司;UV-1601紫外可见分光光度计 北京瑞利分析仪器公司;Agilent 1100液相色谱系统(包含G1322A Degasser,G1311A Quat pump,G1362A RID) 安捷伦科技有限公司;DAWN HELEOS-Ⅱ多角度激光光散射系统 Wyatt公司;TSK-GEL 3000 PW(7.5×300 mm) 日本Tosoh;PL-L25-P200快速中压多糖纯化系统(配置恒流泵,梯度混合器,自动收集器,RI-102示差检测器) Shodex公司,由利穗科技有限公司组装;7890 A气相色谱仪 美国Aglient公司;MQX200全自动扫描酶标仪 美国BIO-TEK公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 摇瓶液体发酵
桑黄菌丝体多糖摇瓶发酵参照Li等[10]的方法。培养基配制:51.6 g小麦粉、13.8 g麸皮粉和10 g桑枝粉,加自来水配制至1000 mL沸水煮30 min,纱布过滤,取滤液,加入终浓度为0.98 g/L的KH2PO4和0.54 g/L的MgSO4·7H2O。在500 mL摇瓶中装新鲜培养基200 mL,121 ℃灭菌30 min后,按体积分数10%的量接种桑黄菌,于28 ℃、135 r/min恒温摇床培养振荡培养8 d。得到的桑黄菌丝体用自来水和蒸馏水清洗干净,冷冻干燥,置于干燥器内备用。
1.2.2 桑黄菌丝体多糖的提取和分离
桑黄菌丝体多糖的提取参照Li等[10]方法略做修改,具体为:干燥的桑黄菌丝体粉碎(过40目筛)按1:10 g/mL固液比加入无水乙醇浸提菌丝粉过夜、离心,重复操作2次,回收乙醇。菌丝体粉50 ℃烘箱干燥后按1:15 g/mL固液比加入蒸馏水,沸水提取2 h,5000 r/min于4 ℃离心15 min,取上清液。重复提取2次,合并上清液并旋蒸浓缩至1/4原体积,搅拌下缓慢加入4倍体积无水乙醇,静置于4 ℃冰箱中过夜。5000 r/min离心20 min分离沉淀,沉淀装入透析袋(10 kDa)中,流水透析48 h,蒸馏水透析48 h(4 h换一次水)。透析液浓缩、真空冷冻干燥,得到桑黄菌丝体粗多糖(记为CIP)。
桑黄菌丝体粗多糖的分级参照文献[15-16]的方法略有修改。称取一定量冻干的桑黄菌丝体粗多糖使其完全溶于蒸馏水中,配制成三份5 mg/mL的多糖溶液,8000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,25 ℃搅拌状态下(200 r/min)缓缓加入碾细的硫酸铵粉末,按照25 ℃时硫酸铵溶解度约40%、60%和80%量,分别使硫酸铵终浓度为30%、45%和60%(g/mL),25 ℃静置过夜,8000 r/min离心30 min,上清液分别标记为IPS30、IPS45和IPS60,沉淀标记为IPP30、IPP45和IPP60。各上清液和沉淀分别透析,流水72 h,蒸馏水48 h(4 h换水一次),1 mol/L的NaOH溶液调节至中性,浓缩、乙醇沉淀、冻干备用。
1.2.3 桑黄菌丝体多糖的纯化
桑黄菌丝体多糖的离子交换色谱纯化参照文献[10,17]进行,具体如下:称取一定量的IPS45完全溶于蒸馏水中,配制成20 mg/mL的多糖溶液,8000 r/min离心10 min,上清液加载到DEAE-52纤维素阴离子交换柱(4.0×100 cm)上,上样量5 mL,依次用蒸馏水、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mol/L的NaCl溶液梯度洗脱,流速2 mL/min,自动收集器收集,每管收集10 mL,折光示差检测器(RI)和苯酚硫酸法同步检测,同时测定其在280 nm处的吸光值,合并相同馏分,透析,减压浓缩,冷冻干燥。
1.2.4 桑黄多糖的检测分析
1.2.4.1 多糖含量和蛋白质含量的测定
采用苯酚硫酸法测定多糖的含量,以葡萄糖为标样[18]。配制一系列不同浓度的葡萄糖溶液,蒸馏水补至2.0 mL,分别加入1.0 mL 6%苯酚和5.0 mL浓硫酸反应,室温放置30 min后于490 nm测吸光值,蒸馏水为空白对照。横坐标(x)为多糖微克数,纵坐标为吸光度(Abs)值,得标准曲线:
蛋白质的测定方法采用考马斯亮蓝法,以牛血清蛋白(BSA)为标样[19]。配制一系列不同浓度的牛血清蛋白溶液,蒸馏水补至1.0 mL,分别加入4.0 mL考马斯亮蓝G-250,摇匀,室温放置5 min,595 nm下测吸光值,以蒸馏水为空白对照,横坐标(x)为蛋白微克数,纵坐标为吸光度(Abs)值,得标准曲线:
1.2.4.2 多糖的纯度鉴定及分子量测定
高效凝胶色谱(HPSEC)联合折光示差检测器(RI)和多角度光散射仪(MALLS)对桑黄菌丝体多糖进行纯度和分子量的检测[10,20]。色谱柱:TSK-GEL 3000PW(7.5×300 mm),流动相:0.1 mol/L的NaCl溶液,流速:0.5 mL/min,柱温:30 ℃。多糖溶液的示差折光指数增量(dn/dc)为0.125 mL/g。
取1 mg桑黄菌丝体多糖溶于流动相,配制成0.1 mol/L的溶液,过0.22 μm微孔过滤膜,上样20 μL。Astra软件用于数据的处理和分析。
1.2.4.3 单糖组成分析
单糖组成分析参照文献[21-22]方法:准确称取均一多糖10 mg于带塞试管中,加5 mL H2SO4溶液(2 mol/L),使多糖完全溶解,然后密封并置于沸水浴中反应8 h。反应完成后,取出冷却,逐渐加入BaCO3使反应液至中性,在4000 r/min下离心5 min,硫酸钡沉淀弃之,得上清液减压浓缩至干。然后加入吡啶(1.0 mL)和盐酸羟胺(10 mg),在90 ℃水浴中继续反应30 min,反应完成后,冷却至室温,再加入1.0 mL醋酸酐,90 ℃下反应30 min,反应完成后,即得到多糖的糖腈乙酸酯衍生物,通过GC检测即可得知各个多糖的单糖组成。按照上述操作方法制备各标准单糖的糖腈乙酸酯衍生物。
GC分析条件:气相色谱仪7980A,HP-5石英毛细管柱(30 m×320 μm×0.25 μm),FID检测器,柱流量1 mL/min。程序升温:柱初温120 ℃,第一阶段以5 ℃/min升温到200 ℃,第二阶段以2 ℃/min升温到215 ℃,第三阶段以20 ℃/min升温到270 ℃。进样口和检测器的温度都设定为250 ℃,进样量2 μL,分流比30:1。高纯氮做载气,流速30 mL/min,氢气流速35 mL/min,空气流速350 mL/min。
1.2.5 桑黄菌丝体多糖的抗氧化活性
1.2.5.1 超氧阴离子自由基清除能力测定
超氧阴离子自由基清除率参照文献[23]略作修改。多糖用Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH8.0,16 mmol/L)配制成样品溶液。1.50 mL样品溶液中依次加入300 µmol/L NBT 0.50 mL、468 µmol/L NADH 0.5 mL(16 mmol/L,pH8.0,Tris-HCl缓冲液配制),混匀,再加入60 µmol/L PMS溶液0.5 mL,25 ℃水浴5 min,在波长560 nm下测定吸光度,每种样品平行测定三次。以缓冲溶液为空白对照,清除率按下式计算:
式中:A1为样品测试值;A0为空白对照值。
1.2.5.2 羟基自由基清除能力的测定
羟基自由基清除能力参照文献[24-25]略做修改。多糖用去离子水配制成样品溶液。邻二氮菲配制为0.75 mmol/L浓度的无水乙醇溶液,取1.0 mL邻二氮菲溶液分别加入2.0 mL磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.2 mol/L,pH7.40)和1.0 mL蒸馏水,于漩涡混合器充分混匀后,加入浓度为0.75 mmol/L硫酸亚铁溶液(FeSO4)1.0 mL,混匀,最后加入1.0 mL 0.01%双氧水(H2O2),37 ℃水浴反应60 min,于波长536 nm处测定吸光度,损伤管测得的吸光度值标记为A1。样品管以1.0 mL样品代替损伤管中1.0 mL蒸馏水,操作方法与上述相同,样品管测得的吸光值标记为A2。未损伤管用1.0 mL蒸馏水代替损伤管中的双氧水(H2O2),操作方法与上述相同,未损伤管测得吸光值标记为A3。每种样品平行测定三次。
式中:A1为损伤管测试值;A2为样品管测试值;A3为未损伤管测试值。
1.2.5.3 还原能力的测定
还原能力参照文献[25-26]的方法,稍作修改。多糖用去离子水配制成样品溶液。取1.0 mL样品溶液,加入2.5 mL铁氰化钾(1%)和2.5 mL磷酸盐缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH6.6),混匀,50 ℃水浴反应20 min。加入2.5 mL三氯乙酸(体积分数为10%)混匀。离心(3000 r/min,10 min),吸取上清液2.5 mL,加入0.5 mL FeCl3(0.1%)混合,于波长700 nm处测定吸光度。每种样品平行测定三次。
1.2.6 桑黄菌丝体多糖的体外细胞毒性
细胞活力测定参照文献[10,27]略做修改。分别将HepG2细胞悬液(5×104细胞/mL)接种于96孔板中,终体积为200 μL,在10% FBS的DMEM培养基培养(37 ℃,5% CO2)12 h。弃培养液,添加用培养基稀释的不同浓度的多糖溶液(不含多糖的培养基用作对照),每个浓度设置6个复孔,继续培养12 h。向每孔加20 μL MTT(5 mg/mL),再培养4 h,吸取出培养液,加入100 μL的DMSO,室温下振荡10 min,待孔内结晶物全部溶解,用酶标仪测570 nm处的吸光值(OD值),空白对照只加培养液,六次平行测定,细胞抑制率的公式如下:
1.3 数据处理
数据以3次独立样品测定结果的平均值±标准差表示;数据分析采用SPSS 19.0软件,显著性分析为The one-way analysis of variance(ANOVA,the Duncan test),多重比较采用LSD测验;P<0.05为差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 桑黄粗多糖及各组分的得率、多糖及蛋白质含量
桑黄菌丝体粉末经热水重复提取3次、提取液加入4倍乙醇沉淀,得到的沉淀透析、冻干、称重,以桑黄菌丝体粉重量为基准,计算粗多糖提取物得率为14.17%,其中多糖含量16.89%,蛋白含量3.59%。
采用不同浓度硫酸铵对粗多糖分级,得到的各上清液和各级沉淀经透析、干燥、称重,以粗多糖重量为基准,计算其得率,同时测定多糖及蛋白含量,如表1所示。通常,多糖的溶解度与其分子量呈负相关,硫酸铵浓度低时,溶解度小的多糖最先沉淀[9],而溶解度大的多糖仍保留在上清液中。其次多糖的溶解度还与其化学组成、连接方式及分支度有关[9]。由表1可见,经硫酸铵沉淀后,上清液中多糖含量明显高于沉淀中多糖的含量,推测桑黄多糖可能具有较大的溶解度或较高的分支度,增加了其在水中的溶解能力。随着硫酸铵浓度的增加,上清液中多糖含量逐渐增加,蛋白质含量则逐渐降低,但得率明显降低;而相应沉淀中多糖含量并未随着硫酸铵浓度的增加有明显升高,蛋白质含量高于上清液,并随着硫酸铵浓度增加略有提高。由此可见,桑黄多糖在水中的溶解性较好。因此,本研究首先关注于上清液中的多糖。
表 1 粗多糖各组分的得率、多糖和蛋白质的含量Table 1. Yields and contents of carbohydrate and protein of fractions from crude polysaccharides样品名称 IPS30 IPS45 IPS60 IPP30 IPP45 IPP60 得率(%) 16.72 7.86 6.5 − − − 多糖含量(%) 18.73 29.03 34.68 9.03 8.50 10.25 蛋白质含量(%) 3.03 2.47 2.00 5.02 5.17 5.41 注:“−”表示未检测。 2.2 桑黄粗多糖及各上清液组分的抗氧化活性及细胞毒性
将冻干的各上清液组分配置成一定浓度的溶液,进行抗氧化活性、抗肿瘤活性的检测。
2.2.1 体外抗氧化活性
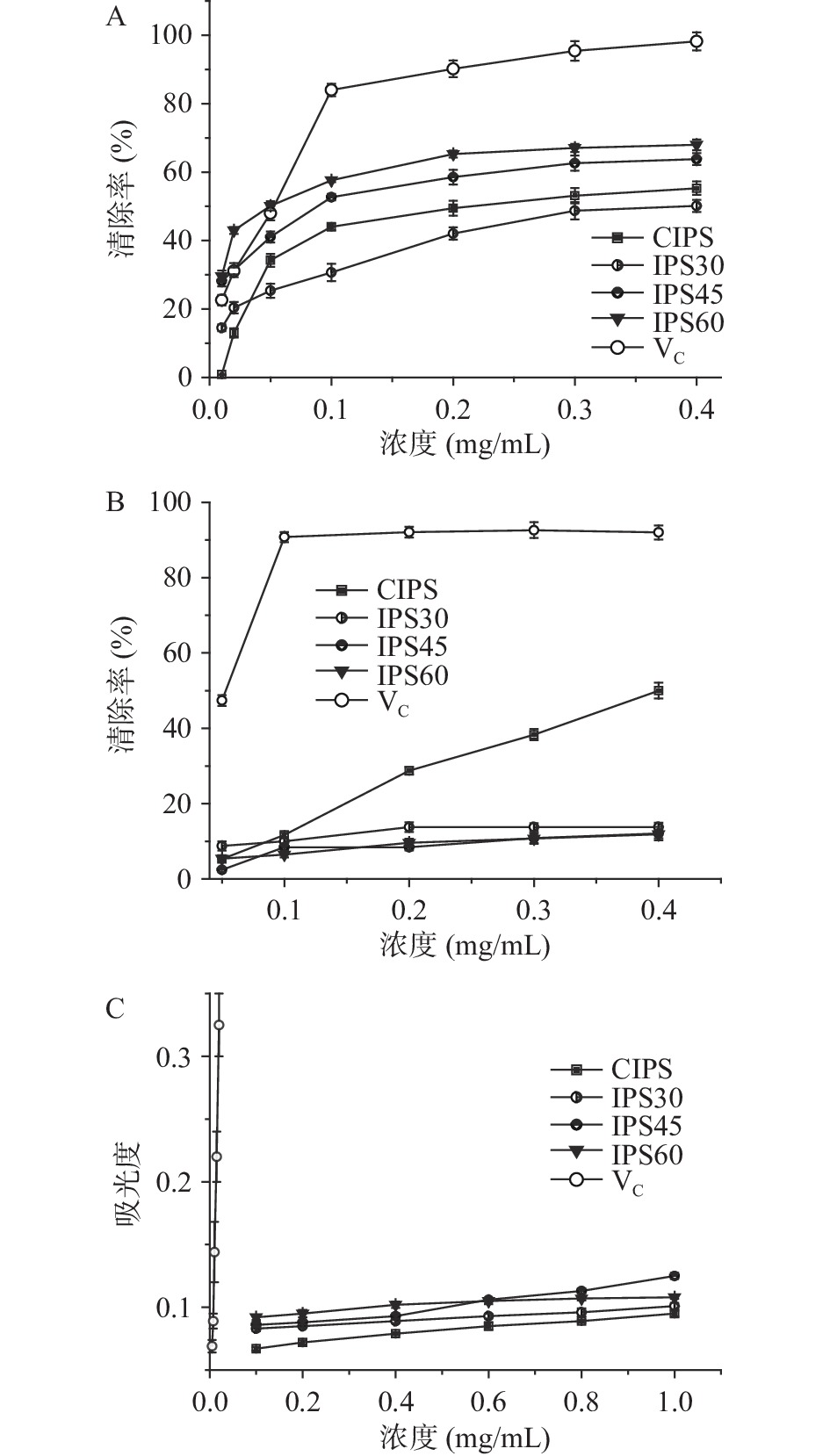
图1为粗多糖(CIPS)、IPS30、IPS45和IPS60对超氧阴离子自由基清除能力、羟基自由基清除能力及还原能力的测定结果。
超氧阴离子自由基具有很强的氧化性,大量的超氧阴离子存在于体内会造成体内细胞组织受损。图1A中在0.01~0.4 mg/mL的浓度范围内,粗多糖(CIPS)和各组分对超氧阴离子自由基的清除能力均随着浓度增加而逐渐增强,呈现显著的量效关系。当浓度达到0.4 mg/mL时,IPS60、IPS45、CIPS和IPS30对超氧阴离子的清除率依次为68%、63.8%、55.5%和50.1%,低于维生素C(VC)同样浓度下98.2%的清除率,但高于浓度为0.5 mg/mL的川芎多糖对超氧阴离子的清除率[23]。该结果表明桑黄粗多糖及各组分在低浓度条件下就具有良好的清除超氧阴离子的能力。本项目组前期采用乙醇分步沉淀得到桑黄粗多糖组分,当浓度为0.40 mg/mL时,30%、60%和80%乙醇沉淀组分对超氧阴离子的清除率分别为38.39%、52.98%和43.58%[24],均低于相同浓度下IPS60、IPS45对超氧阴离子的清除率。这可能由于乙醇沉淀粗多糖,取的是沉淀部分,分子量较大或分支度小的多糖容易被沉淀[9]。而本实验硫酸铵沉淀法,取的是上清液部分,得到的大多是小分子量、高分支度的多糖。
羟自由基是一类化学性质非常活跃的自由基,易与碳水化合物、蛋白质、脂质和DNA发生反应,导致细胞损伤或死亡[25]。图1B显示在0.05~0.4 mg/mL的浓度范围内,粗多糖及各组分对羟基自由基的清除率。由图1B可见,CIPS对羟基自由基的清除率明显高于各组分而低于VC,且随着浓度增加而逐渐增强;在各级组分之间以IPS30对羟基自由基的清除能力略高于IPS45和IPS60,且随浓度增加各组分未呈现明显的量效关系。当浓度为0.4 mg/mL时,VC和CIPS对羟基自由基的清除率分别为92%和50%,IPS30、IPS45和IPS60的羟基自由基清除率分别为13.75%、12.05%和11.83%。该结果与相近浓度下乙醇沉淀所得桑黄菌丝体多糖的羟基自由基清除率相接近[5];高于0.5 mg/mL的川芎多糖对羟基自由基的清除率[23],低于川明参粗多糖同浓度下的清除率[25]。
图1C所示为质量浓度在0.1~1.0 mg/mL范围内,粗多糖、IPS30、IPS45和IPS60的还原能力。由图1C可见粗多糖和三个硫酸铵分离组分的还原力均较弱,可能与多糖为大分子物质,所具有的还原性末端相对较少有关。各组分IPS30、IPS45和IPS60吸光度值随浓度增加略有上升,其还原能力均强于粗多糖(P<0.05),但IPS30、IPS45和IPS60之间的还原能力无显著性差异(P>0.05)。当浓度为0.4 mg/mL时,IPS45、IPS60、IPS30和CIPS还原力分别为0.093、0.102、0.089和0.079,均远小于维生素C在0.02 mg/mL浓度时0.325的还原力。本项目组前期30%、60%和80%乙醇沉淀所得桑黄粗多糖各组分,在0.4 mg/mL浓度下的还原力为0.007、0.018和0.019[24],远低于本实验结果,这也可能与分子大小及分支度相关。随着浓度的增高,IPS45的还原能力提升速率有高于其它组分的趋势,当浓度上升到1.0 mg/mL时,IPS45的还原能力达0.125,高于IPS60的0.108。受样品量的限制,更高浓度的实验没能进行。
受样品量的影响,所有体外抗氧化实验样品浓度均不超过1.0 mg/mL,因此本实验仅反应了低浓度下硫酸铵分离的桑黄菌丝体多糖的抗氧化活性。这也说明硫酸铵分离的桑黄菌丝体多糖在0.4 mg/mL的浓度已经具有良好的清除超氧阴离子能力。
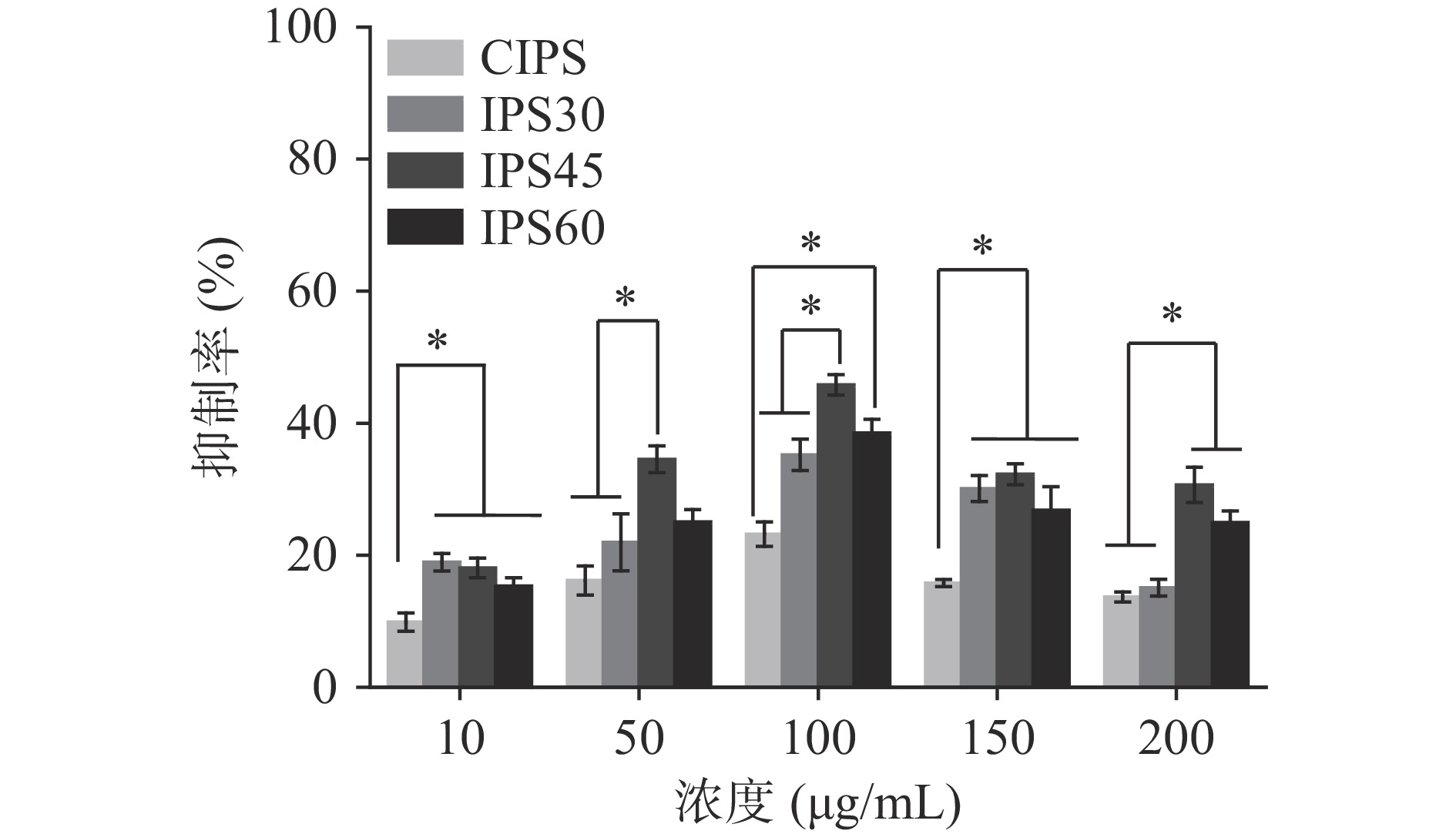
2.2.2 对肿瘤细胞生长的抑制作用
桑黄粗多糖及各组分对HepG2细胞生长抑制作用见图2。由图2可见CIPS及各组分对HepG2细胞生长均有一定的抑制作用,在浓度为10~100 μg/mL,生长抑制率随浓度增加而增高,浓度为100~200 μg/mL时,随着浓度增加,对HepG2细胞生长的抑制作用反而降低。在CIPS及各组分中,CIPS的抑制效果最弱,与IPS45和IPS60的抑制效果存在显著差异(P<0.05)。IPS45的抑制效果最强,但与IPS60并无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
综合考虑多糖各组分的得率、含量及抗氧化、抗肿瘤活性,取IPS45级分采用离子交换色谱进一步纯化。
2.3 IPS45的DEAE-52离子交换柱层析分离
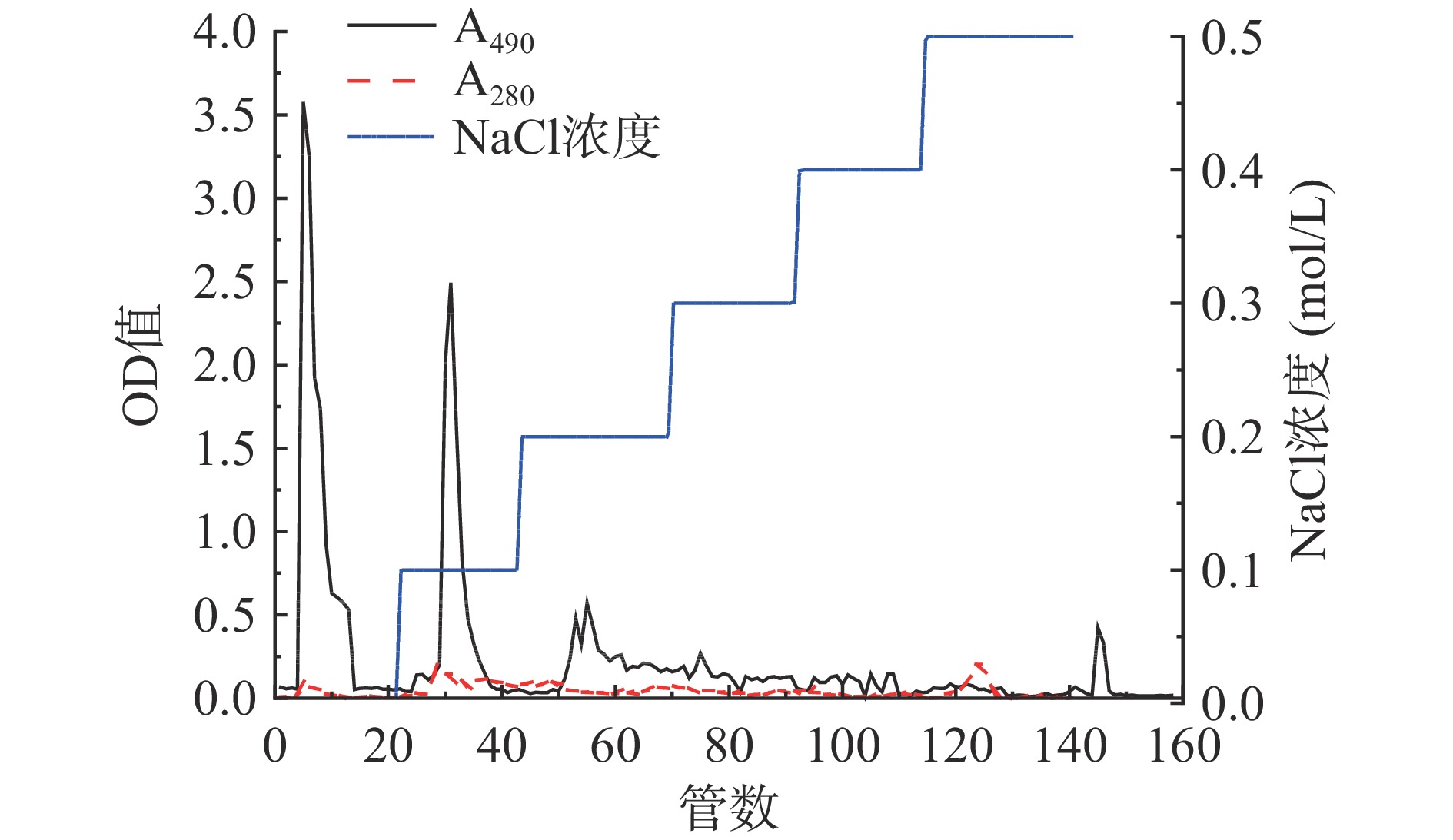
IPS45用DEAE-52离子交换柱分离,依次用0~0.5 mol/L的NaCl溶液梯度洗脱,苯酚硫酸法、280 nm处吸光度值同步检测,洗脱曲线见图3。由图3可见,在水和0.1 mol/L的NaCl洗脱部分各有一明显的A490吸收峰,表示洗脱液中多糖的含量很高,0.2 mol/L的NaCl溶液洗脱部分有一较矮的A490吸收峰;0.3~0.4 mol/L的NaCl洗脱液中,A490吸收很弱,说明洗脱液中多糖浓度很低;0.5 mol/L浓度以上的NaCl溶液洗脱组分中经苯酚硫酸法未检测出多糖,说明多糖已基本洗脱完全。根据图3显示的多糖吸收峰分别合并收集管,得到水洗脱组分标记为IPS45-W,0.1 mol/L的NaCl溶液洗脱组分为IPS45-1,0.2 mol/L的NaCl溶液洗脱组分为IPS45-2,0.3~0.5 mol/L的NaCl溶液洗脱管一起合并,标记为IPS45-3,各洗脱组分经透析、浓缩、冻干称重,得率分别为30%、7%、4%和1.6%。各级组分的多糖及蛋白含量见表2。IPS45中水洗脱部分占比最多,说明其多糖中糖醛酸含量较低。乙醇沉淀的桑黄多糖组分中也是相似,主要来自于水洗脱部分[10]。
表 2 IPS45经DEAE-52纯化后各级分的多糖与蛋白含量Table 2. The content of polysaccharides and proteins of IPS45 fractions purified by DEAE-52组分 得率(%) 多糖含量(%) 蛋白含量(%) IPS45-W 30.0 78.08 0.33 IPS45-1 7.0 47.89 0.65 IPS45-2 4.0 30.65 0.17 IPS45-3 1.6 27.94 0.57 2.4 多糖均一性及分子量的测定
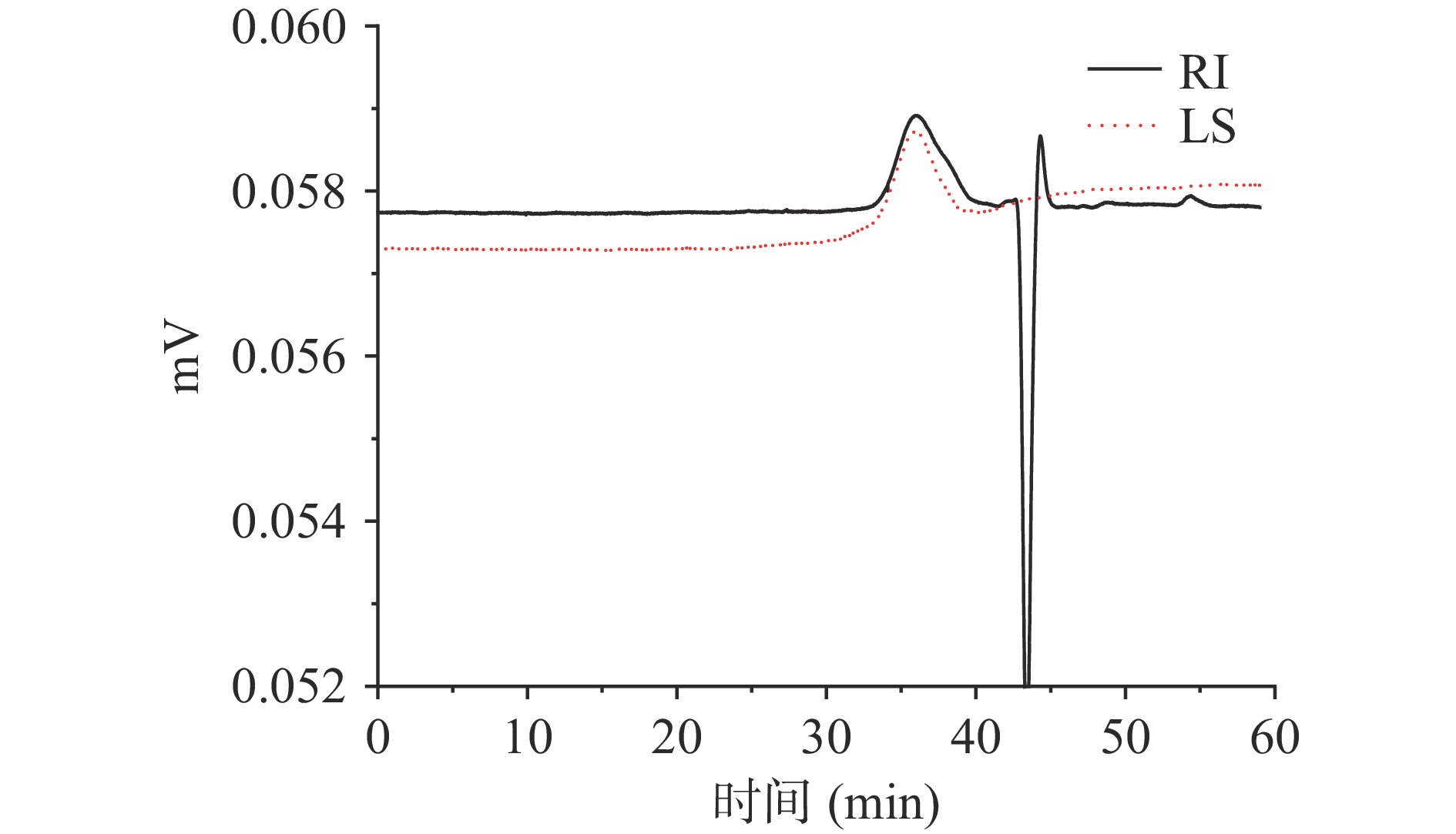
IPS45经DEAE-52离子交换柱分离得到的4个组分IPS45-W、IPS60-1、IPS60-2、IPS60-3分别采用高效凝胶渗透色谱、串联折光示差和十八角光散射(SEC-RI-MALLS)进行纯度和平均分子量测定。其中IPS45-W的折光示差图谱(SEC-RI)在35 min时有一对称均匀的出峰(见图4中RI),十八角光散射图谱(SEC-MALLS)中在相同时间也出现一个对称均匀的出峰(见图4中LS),由此可以推断IPS45-W组分可能为均一多糖,IPS45-W的重均分子量(MW)为79.1 kDa。而IPS45-1、IPS45-2和IPS45-3组分的SEC-RI图谱与SEC-MALLS图谱均出现多个不对称的峰,均不是均一多糖。
2.5 IPS45-W的单糖组成分析
由五种标准单糖混标的乙酸酯化衍生物的气相色谱图5A可知,各单糖的出峰顺序依次为鼠李糖、木糖、甘露糖、葡萄糖和半乳糖[26-27],保留时间分别为14.421、15.059、19.431、19.674和20.213 min。将IPS45-W水解、酯化产物的气相色谱图(图5B)与标准单糖色谱图(图5A)比对,根据保留时间可知IPS45-W的糖链主要是由四种单糖构成的,除甘露糖、葡萄糖和半乳糖之外,在保留时间16.646 min多出一个无法与五种常见单糖标准品相对照的未知峰。根据各出峰面积平均百分含量得出IPS45-W中甘露糖:葡萄糖:半乳糖:未知单糖的摩尔比为1.57:8.38:1.09:1.00,以葡萄糖比例最高。
2.6 抗肿瘤活性研究
样品IPS45经过DEAE-52离子交换柱分离纯化后得到的IPS45-1、IPS45-2、IPS45-3、IPS45-W组分进行体外抗肿瘤活性试验,实验结果见图6。由图6可知,四个组分对HepG2细胞的抑制率均随着浓度增加有所增强,当浓度达到100 μg/mL时,抑制率达到最高,然后随着浓度增加略有降低。浓度为100 μg/mL时,IPS45-1、IPS45-2、IPS45-3、IPS45-W对HepG2细胞的抑制率分别为54.5%、48.4%、56.4%和60.2%,对HepG2细胞的抑制率均高于纯化前的组分IPS45相同浓度下的抑制率(45.8%),以均一多糖IPS45-W对HepG2细胞的抑制率为最高。差异性检验显示,其中IPS45-W的抑制率显著高于IPS45-2(P<0.05),而IPS45-1、IPS45-3、IPS45-W间则无显著差异(P>0.05)。当浓度为50 μg/mL时,IPS45-1、IPS45-2、IPS45-3、IPS45-W对HepG2细胞的抑制率分别为44.22%、44.95%、52.83%和56.74%,无明显差异。Pei等[28]对桑黄菌丝体均一多糖PL-N1进行抗肿瘤实验研究,在多糖浓度为50 μg/mL时,对HepG2的抑制率大约为12%,远低于本研究中相同浓度多糖对HepG2细胞的抑制率。
本课题组前期从Phellinus igniarius菌种(菌株编号5.95)摇瓶发酵所得菌丝体热水提取液中,采用30%、60%和80%乙醇分步沉淀沉淀得到的三个组分经DEAE-52离子交换色谱、Sephacryl S-400凝胶柱纯化后得到四个均一多糖,其中的三个均一多糖IPSW-1、IPSW-2和IPSW-4,均为由葡萄糖组成的同多糖;IPSW-4是以葡萄糖为主,由鼠李糖、木糖、甘露糖、葡萄糖和半乳糖组成的杂多糖(单糖摩尔比为1.29:1.21:1.0:43.86:1.86)[10]。浓度为70 μg/mL时,IPSW-1、IPSW-2、IPSW-3和IPSW-4对HepG2的抑制率达到最大,分别为39.0%、35.0%、25.0%和29.0%;在50 μg/mL浓度下,它们对HepG2的抑制率分别为35%、33%、21%和11%[16],均低于本研究所得均一多糖IPS45-W在50 μg/mL时56.74%的抑制率。多糖的抗肿瘤活性受其单糖组成、蛋白含量和分子量大小的影响[29-30],一般来说,多糖的分子量和水溶性越高,表明其抗肿瘤活性越高[31]。而本研究中,IPS45-W的分子量为79.1 kDa,远高于IPSW-1、IPSW-2、IPSW-3和IPSW-4(分别为34.1、17.7、15.1和21.7 kDa)的平均分子量;且IPS45-W是从45%硫酸铵上清液中分离的,其水溶性远高于从乙醇沉淀中分离的IPSW-1、IPSW-2、IPSW-3和IPSW-4。这可能是IPS45-W抗肿瘤活性强的原因之一。由本实验结果可以看出,对于同样的桑黄菌丝体热水提取液,不同分离方法得到的多糖组成不同,从乙醇沉淀中纯化得到的是以葡萄糖为主的同多糖;硫酸铵分离上清液中纯化得到的是多种单糖组成的杂多糖。
3. 结论
本实验初步研究了硫酸铵沉淀法对桑黄菌丝体粗多糖的分离效果及各组分的抗氧化、抗肿瘤活性的影响,并与前期乙醇沉淀法分离的桑黄菌丝体多糖各组分进行比较,为分离新的高活性桑黄均一多糖、深入研究桑黄多糖的分离方法与结构、活性的关系提供参考。
桑黄菌丝体粗多糖经不同浓度硫酸铵沉淀分离,从硫酸铵上清液中分离的多糖组分其水溶性远远高于乙醇沉淀中分离的桑黄多糖组分,相应的清除超氧阴离子活性和还原能力均高于乙醇沉淀的桑黄多糖组分。从45%硫酸铵沉淀粗多糖的上清液中经DEAE-52离子交换柱纯化得到一重均分子量79.1 kDa的均一多糖,为由甘露糖:葡萄糖:半乳糖:未知单糖组成的杂多糖,而从乙醇沉淀中纯化得到的是以葡聚糖为主的同多糖,且分子量均小于该杂多糖,该杂多糖在水中的高溶解性有可能与其高分支度相关。高分子量、高分支度和高溶解性,使该杂多糖对HepG2细胞生长抑制率远高于前期乙醇分步沉淀所得的桑黄菌丝体同多糖。乙醇和硫酸铵作为多糖分离中常用的两种非溶剂沉淀剂各有优势,可以考虑建立乙醇/硫酸铵分离体系用于多糖的分离,以获得更多的活性多糖。
-
表 1 粗多糖各组分的得率、多糖和蛋白质的含量
Table 1 Yields and contents of carbohydrate and protein of fractions from crude polysaccharides
样品名称 IPS30 IPS45 IPS60 IPP30 IPP45 IPP60 得率(%) 16.72 7.86 6.5 − − − 多糖含量(%) 18.73 29.03 34.68 9.03 8.50 10.25 蛋白质含量(%) 3.03 2.47 2.00 5.02 5.17 5.41 注:“−”表示未检测。 表 2 IPS45经DEAE-52纯化后各级分的多糖与蛋白含量
Table 2 The content of polysaccharides and proteins of IPS45 fractions purified by DEAE-52
组分 得率(%) 多糖含量(%) 蛋白含量(%) IPS45-W 30.0 78.08 0.33 IPS45-1 7.0 47.89 0.65 IPS45-2 4.0 30.65 0.17 IPS45-3 1.6 27.94 0.57 -
[1] 吴声华, 戴玉成. 药用真菌桑黄的种类解析[J]. 菌物学报,2020,39(5):781−794. [WU S H, DAI Y C. Species clarification of the medicinal fungus Sanghuang[J]. Mycosystema,2020,39(5):781−794. [2] 王豪, 钱坤, 司静, 等. 桑黄类真菌多糖研究进展[J]. 菌物学报,2021,40(4):895−911. [WANG H, QIAN K, SI J, et al. Research advances on polysaccharides from sanghuang[J]. Mycosystema,2021,40(4):895−911. doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.200364 [3] 李彦颖, 张祺, 陈晓华, 等. 桑黄多糖的分离纯化、生物活性及其产品开发研究进展[J]. 食药用菌,2022,30(1):26−31. [LI Y Y, ZHANG Q, CHEN X H, et al. Research progress in purification, bio-activity and product development of polysaccharides from Sanghuang[J]. Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms,2022,30(1):26−31. [4] 李宜明, 沈业寿, 季俊虬, 等. 桑黄菌质多糖体外抑瘤及抗环磷酰胺致突变的作用[J]. 中国科学技术大学学报,2006,36(7):700−703. [LI Y M, SHEN Y S, JI J Q, et al. Inhibitory effect of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius on tumor growth in vitro and mytation induced by CP[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China,2006,36(7):700−703. [5] 周慧吉, 马海乐, 郭丹钊, 等. 不同体积分数乙醇沉淀桑黄胞内多糖的理化性质及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(19):34−38. [ZHOU H J, MA H L, GUO D Z, et al. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of intracellular polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius precipitated by different ethanol concentrations[J]. Food Science,2015,36(19):34−38. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201519006 [6] 李志涛, 朱会霞, 孙金旭, 等. 桑黄菌丝体多糖的提取及其免疫活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(20):35−39. [LI Z T, ZHU H X, SUN J X, et al. A study on the extraction and immune effect of polysaccharide from Phellinus igniarius mycelia[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(20):35−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.20.007 [7] 李金凤, 袁菁菁, 张艳, 等. 桑黄菌丝体多糖对胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠的治疗作用[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2014,38(5):526−530. [LI J F, YUAN J J, ZHANG Y, et al. Therapeutic effects of Phellinus igniarius mycelium polysaccharide on collagen-induced arthritis rats[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2014,38(5):526−530. [8] LEONG Y K, YANG F, CHANG J. Extraction of polysaccharides from edible mushrooms: Emerging technologies and recent advances[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,251:117006. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117006
[9] HU X H, GOFF H D. Fractionation of polysaccharides by gradient non-solvent precipitation: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,81:108−115.
[10] LI S C, YANG X M, MA H L, et al. Purification, characterization and antitumor activity of polysaccharides extracted from Phellinus igniarius mycelia[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,133:24−30. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.013
[11] 赵小莉, 付洋, 赵强, 等. 硫酸铵沉淀分离富硒大豆蛋白的初步研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(13):92−95. [ZHAO X L, FU Y, ZHAO Q, et al. Preliminary study on ammonium sulfate precipitation of selenium-enriched soybean protein isolate[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(13):92−95. [12] 王倩, 贺萍, 林如歌, 等. 鸭蛋卵清蛋白的结构、组成分析及其功能活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(8):67−73. [WANG Q, HE P, LIN R G, et al. Structure, composition analysis and functional activity of duck egg ovalbumin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(8):67−73. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.08.012 [13] WU Y, CUIS W, ESJIN N A M, et al. Fractionation and partial characterization of non-pectic polysaccharides from yellow mustard mucilage[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2009,23(6):1535−1541. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.10.010
[14] WANG C, YU Y B, CHEN T T, et al. Innovative preparation, physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of bioactive polysaccharides from fresh okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L. Moench)[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,320:126647. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126647
[15] ZHANG M, ZHU L, CUI S W, et al. Fractionation, partial characterization and bioactivity of water-soluble polysaccharides and polysaccharide-protein complexes from Pleurotus geesteranus[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2011,48(1):5−12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.09.003
[16] SHI X D, NIE S P, YIN J Y, et al. Polysaccharide from leaf skin of Aloe barbadensis Miller: Part I. Extraction, fractionation, physicochemical properties and structural characterization[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,73:176−183. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.06.039
[17] 何慕雪, 孟凡成, 王春明, 等. 1种水溶性霸王花多糖的分离纯化及结构鉴定[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(18):106−112. [HE M X, MENG F C, WANG C M, et al. Isolation, purification and structural characterization of a water-soluble polysaccharide from the flower of Hylocereus undatus (Haw.) Britton & Rose[J]. Food Science,2017,38(18):106−112. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201718017 [18] 王迎香, 唐子惟, 彭腾, 等. 苯酚-硫酸法测定酒蒸多花黄精多糖含量的优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(18):308−316. [WANG Y X, TANG Z W, PENG T, et al. Optimization of phenol sulfuric acid method for the polysaccharide content of wine-steamed Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(18):308−316. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021010069 [19] 孙永才, 孙京新, 王宝维, 等. 纳地青霉发酵鸭血食用品质的变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(10):154−158. [SUN Y C, SUN J X, WANG B W, et al. The changing of eating quality of duck blood fermented by Penicillium nalgiovense[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(10):154−158. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.10.029 [20] CHEN Z, WANG C, MA H, et al. Physicochemical and functional characteristics of polysaccharides from okra extracted by using ultrasound at different frequencies[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,361:130138. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130138
[21] 江和栋, 牛仙, 万仁口, 等. 灵芝孢子多糖的提取工艺优化及单糖组成、抗氧化活性分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(4):159−167. [JIANG H D, NIU X, WAN R K, et al. Optimization of extraction and analysis of monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activity of Ganoderma lucidum spore polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(4):159−167. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.04.019 [22] 卫强, 任定美, 李四聪, 等. 皖南山区红豆杉多糖提取、纯化方法及单糖组成分析[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(16):190−197. [WEI Q, REN D M, LI S C, et al. Extraction and purification of polysaccharides from stems and leaves of Taxus grown in mountain areas in southern Anhui Province and their monosaccharide composition[J]. Food Science,2017,38(16):190−197. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201716030 [23] 陈欢, 姜媛媛, 徐峰, 等. 不同干燥方式对川芎多糖理化性质及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 中成药,2021,43(1):173−177. [CHEN H, JIANG Y Y, XU F, et al. Effects of different drying methods on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of Ligusticum chuanxiong polysaccharides[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2021,43(1):173−177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.01.034 [24] 李世超. 桑黄菌丝体多糖的分离纯化、活性研究和结构分析[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2015. LI S C. Isolation, purification, bioactivity and structure analysis of polysaccharides from Phellinus igniarius mycelium[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2015.
[25] 高涛, 唐华丽, 罗振宇, 等. 川明参粗多糖初级结构解析及其体外抗氧化活性[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(8):275−282. [GAO T, TANG H L, LUO Z Y, et al. Primary structure analysis and antioxidant activity in vitro of crude polysaccharide from Chuanminshen violaceum[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(8):275−282. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.08.029 [26] 胡彦波, 翟丽媛, 刘扬, 等. 薇菜多糖的分离纯化及体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(1):59−66. [HU Y B, ZHAI L Y, LIU Y, et al. Isolation, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Osmunda japonica[J]. Food Science,2022,43(1):59−66. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210426-373 [27] 谢丽源, 张勇, 郭勇, 等. 桑黄菌丝体多糖的分离纯化及理化性质分析[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(5):143−147. [XIE L Y, ZHANG Y, GUO Y, et al. Isolation, purification and physico-chemical characteristics analysis of mycelial polysaccharides from Phellinus baumii[J]. Food Science,2011,32(5):143−147. [28] PEI J J, WANG Z B, MA H L, et al. Structural features and antitumor activity of a novel polysaccharide from alkaline extract of Phellinus linteus mycelia[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,115:472−477. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.017
[29] MINGYEOU L, JIECHUNG T. Antioxidant properties of polysaccharides from the willow bracket medicinal mushroom, Phellinus igniarius (L.) Quél. (Aphyllophoromycetideae) in submerged culture[J]. International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms,2009,11(4):383−394. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushr.v11.i4.50
[30] XIN M, LIANG H, LUO L. Antitumor polysaccharides from mushrooms: A review on the structural characteristics, antitumor mechanisms and immunomodulating activities[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2016,424:30−41. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2016.02.008
[31] LI X, JIAO L, ZHANG X, et al. Anti-tumor and immunomodulating activities of proteoglycans from mycelium of Phellinus nigricans and culture medium[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2008,8(6):909−915.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杨戬,刘伯扬,王丹慧,高永亮,赵三军,赵凯,李慧,仪虹伯. 基于中红外光谱的牛乳中A 2β-酪蛋白检测方法研究. 中国乳业. 2024(11): 144-148+156 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张立佳,莫楠,刘丽君,韩晓旭,赖世云,任一平,尹睿杰,李翠枝. 羊乳婴幼儿配方粉中牛乳成分鉴别与测定模型的建立. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(08): 195-203 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)










 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



