Effects of Reaction Conditions on the Formation of Furfural Compounds in Maillard Reaction System of Glucose-Glycine
-
摘要: 为了分析美拉德反应体系中糠醛类化合物的形成规律,本研究构建了葡萄糖-甘氨酸反应体系,探究了反应物配比、体系初始pH、加热时间和温度对5-羟甲基糠醛(5-Hydroxymethylfurfural,HMF)、2-糠醛(2-Furfural,F)和5-甲基糠醛(5-Methyl-2-furfural,MF)形成的影响,并分析了它们的形成动力学,预测了它们的表观活化能。结果显示:葡萄糖与甘氨酸的摩尔浓度比对糠醛类化合物的生成量有较大影响。HMF生成量随着摩尔浓度比的增大而持续增加,而F与MF的生成量在摩尔浓度比为1:1时达到最高值;酸性pH条件有利于HMF的形成,中性和碱性pH条件有利于F的形成,糠醛类化合物生成总量随着pH的增加而迅速减少;随着加热温度升高、加热时间延长,HMF、F和MF的生成量均逐渐增加;HMF和F的形成在温度较低时符合一级动力学模型(HMF:70~110 ℃;F:70 ℃),在温度较高时符合零级动力学模型(HMF:130 ℃;F:90~130 ℃);MF的形成符合零级动力学模型(90~130 ℃)。本研究可对食品热加工过程中HMF、F和MF的生成和控制提供理论指导。Abstract: The Maillard reaction system of glucose and glycine was applied to study the formations of furfural compounds. The effects of glucose/glycine molar concentration ratio, initial pH, heating temperature and time on the formations of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), 2-furfural (F) and 5-methyl-2-furfural (MF) were evaluated. The kinetic equations of HMF, F and MF were established and their apparent activation energies were also predicted. The results showed that: Glucose/glycine molar concentration ratio had great influence on the formations of furfural compounds. The formation of HMF continued to increase with the increase of ratio, and the formations of F and MF reached the maximum when the ratio was 1:1. The acidic pH conditions could promote the formation of HMF, while the neutral and alkaline pH conditions were conducive to the formation of F. The total amount of furfural compounds decreased rapidly with the increase of pH. The amounts of HMF, F, and MF in the glucose-glycine reaction system increased with the increase of heating temperature and time. The formations of HMF and F in glucose and glycine model followed first-order kinetics model at lower temperatures (HMF: 70~110 ℃; F: 70 ℃), while their formations were in accordance with zero-order kinetics model at higher temperatures (HMF: 130 ℃; F: 90~130 ℃). The formation of MF followed zero-order kinetics model at 90~130 ℃. The results would provide guidance on the production and control of HMF, F, and MF in the food thermal processing industry.
-
Keywords:
- furfural compounds /
- glucose /
- glycine /
- Maillard reaction /
- formation kinetics
-
糠醛类化合物是一类含有呋喃环的小分子化合物。食品中常见的糠醛类化合物主要有5-羟甲基糠醛(5-Hydroxymethylfurfural,HMF)、2-糠醛(2-Furfural,F)、2-呋喃甲基酮(2-Furyl-methyl ketone,FMC)和5-甲基糠醛(5-Methyl-2-furfural,MF)等。有研究表明,HMF具有致癌性、致突变性、器官毒性和遗传毒性等潜在危害[1-4];F具有较大的潜在遗传毒性和生殖毒性,被世界卫生组织国际癌症研究机构列为第三类致癌物质[5];MF和F曾被报道通过与细胞DNA反应具有诱变特性[6]。虽然糠醛类化合物具有潜在的毒性,但是限量范围内作为食品添加剂使用还是安全的。我国《食品添加剂使用标准》(GB 2760-2014)指出,F和MF允许作为食品用香料使用;美国环境保护署规定平均体重为70 kg的人,每日摄入F的最大值为0.2 mg[7];欧盟食品安全局给出每人每日摄入HMF最大参考值为1.6 mg;联邦风险评估研究所指出HMF的允许摄入量为4~30 mg/人/日[1]。因此,食品中糠醛类化合物的含量及影响因素的研究广受关注。
糠醛类化合物广泛存在于咖啡、果汁、牛奶、蜂蜜、面包、干果、醋等多种热加工食品中,鲜少被发现存在于新鲜和未加工的食品中[8-12]。研究发现,糠醛类化合物易产生于食品热处理或长期储存过程中,主要是由碳水化合物在酸性条件下脱水形成,或在美拉德反应过程中产生[13-14]。美拉德反应是氨基化合物和羰基化合物之间发生的非酶褐变反应,在含有糖和蛋白质的食品中广泛存在。糠醛类化合物是与食品新鲜度和质量有关的识别参数,常被用来评价加工方法的质量和最终产品的感官特性[9]。糠醛类化合物的生成量受到体系pH、加热温度以及糖和氨基酸的种类和浓度的影响[15-23]。温度对美拉德反应具有很大的影响,温度越高其反应速率越快,HMF的生成量也随着反应温度的增加明显增多,甚至呈指数增长[24-26]。Zhang等[27]研究发现,随着烘烤温度和时间的增加,海绵蛋糕中HMF和F的生成量逐渐增加。本课题组[28]前期的研究也证实,较高的处理温度,可激发牛奶中产生更多的HMF和F,它们在各种牛奶中的含量对比为:超高温灭菌奶(135~150 ℃,2~4 s)>超高压巴氏杀菌奶(115~121 ℃,2~4 s)>高温短时巴氏杀菌奶(72~75 ℃,10~15 s)。
为了研究美拉德反应体系中糠醛类化合物的形成规律,探究反应条件对其生成量的影响,科研人员主要采用还原糖和氨基酸反应体系进行研究。目前,大部分研究主要关注HMF的生成。Zhang等[18]选用葡萄糖、蔗糖和半胱氨酸、谷氨酸、亮氨酸建立了6种糖-氨基酸模型,研究发现,随着糖和氨基酸(除半胱氨酸外)含量、温度和反应时间的增加,HMF的生成量增加;低pH可以促进HMF的形成;HMF的形成在葡萄糖-半胱氨酸/谷氨酸/亮氨酸和蔗糖-亮氨酸模型中符合一级动力学模型,在蔗糖-谷氨酸模型中符合零级动力学模型。曾世通等[29]研究了葡萄糖-丙氨酸美拉德反应体系中HMF的形成,发现HMF的生成量随着pH增加而减少,随着加热时间的延长而逐渐增加,在12 h时达到最大值。卢键媚等[22]基于果糖/蔗糖/葡萄糖-柠檬酸反应体系,研究发现pH降低和温度升高可促进HMF的形成,70~100 ℃时,HMF的形成符合零级动力学模型。王丹等[30]采用木糖、果糖、葡萄糖和赖氨酸分别构建了3种焦糖化和3种美拉德反应体系,在120 ℃油浴锅中分别加热10~120 min进行研究,发现随着加热时间延长,两种体系中HMF的含量均逐渐升高,但F仅在焦糖化体系中生成(尤其是木糖体系),在三种美拉德反应体系中均未被检出。
本研究以食品中广泛存在的葡萄糖和常用添加剂甘氨酸(结构最为简单的天然氨基酸)构成的美拉德反应体系为研究模型,采用高效液相色谱法测定糠醛类化合物(主要包括HMF、F和MF)的生成量,研究葡萄糖与甘氨酸的初始摩尔浓度比、体系初始pH、加热温度和加热时间等对美拉德反应体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响,并预测它们的形成动力学。本研究有望为控制热加工食品中糠醛类化合物的含量提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
HMF(纯度98%,色谱纯)、F(纯度99.5%,色谱纯)、FMC(纯度95.5%,色谱纯)、MF(纯度99.6%,色谱纯) 德国Dr.Ehrenstorfer公司;葡萄糖、甘氨酸、磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
AL104电子天平、PE28-Standard pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;SBH200D恒温金属浴 英国比比科技有限公司;Milli-Q超纯水仪 默克化工技术(上海)有限公司;1200高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 葡萄糖-甘氨酸反应体系的构建
将葡萄糖、甘氨酸配制成0.2 mol/L的溶液,准确移取4 mL溶液置于15 mL耐高温的玻璃管中,拧紧盖子密封,金属浴加热进行美拉德反应,反应后取出置于冰水浴中迅速冷却至室温(25 ℃)。
1.2.2 原料配比对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
以pH为7的磷酸盐缓冲溶液为溶剂,配制葡萄糖与甘氨酸的添加比例(摩尔浓度比)分别为1:4、1:3、1:2、1:1、2:1、3:1和4:1的溶液,加热温度为90 ℃,加热时间为3 h,进行美拉德反应并检测反应液中HMF、F和MF的含量,每组实验重复3次。
1.2.3 体系初始pH对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
分别精确称取一定质量的Na2HPO4和NaH2PO4,用去离子水配制成0.2 mol/L的溶液,将二者按一定比例混合,并用少量1 mol/L HCl或NaOH调整pH为 3、5、7、9和11,即得准确配制的不同pH的磷酸盐缓冲溶液。以其为溶剂,将葡萄糖和甘氨酸按照物质的量比1:1配制成0.2 mol/L的混合溶液,加热温度为110 ℃,加热时间为5 h,进行美拉德反应并检测反应液中HMF、F和MF的含量,每组实验重复3次。
1.2.4 加热时间对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
加热时间分别为1、2、3、4、5和6 h,加热温度为90 ℃,葡萄糖和甘氨酸的物质的量之比为1:1,进行美拉德反应并检测反应液中HMF、F和MF的含量,每组实验重复3次。
1.2.5 加热温度对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
加热温度分别为70、90、110和130 ℃,加热3 h,葡萄糖和甘氨酸的物质的量之比为1:1,进行美拉德反应并检测反应液中HMF、F和MF的含量,每组实验重复3次。
1.2.6 糠醛类化合物含量的测定
采用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)[28]测定样品中的HMF、F和MF的含量,具体液相色谱条件如下:
色谱柱:Waters Atlantis T3柱(3.0 mm×15 cm,3 μm);流动相A为超纯水,流动相B为乙腈;0~18.0 min,5%~65% B;18.0~20.0 min,65%~95% B;20.0~22.0 min,95% B;22.0~22.1 min,95%~5% B;22.1~30.0 min,5% B;流速:0.6 mL/min;色谱柱温度:30 ℃;进样量:5 μL;紫外-可见检测器检测波长:280 nm。
采用外标一点法计算了样品中的糠醛类化合物含量,详细的检测结果计算方法见参考文献[28]。
1.3 数据处理
采用零级动力学和一级动力学两种动力学模型对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的变化规律进行分析,公式如下:
零级动力学:Ct=C0+k0t (1) 一级动力学:Ct=C0exp(k1t) (2) 式中,Ct:检测指标在任意时间的浓度值(μmol/L);C0:检测指标的起始浓度值(μmol/L);t:美拉德反应时间(h);k0和k1:零级和一级动力学常数,单位分别为µmol/(L·h)和h−1。
Arrhenius公式:k=Aexp(−Ea/RT) (3) 式中,k为动力学常数;A为指前因子,也称为Arrhenius常数,单位与k相同;Ea为表观活化能,单位为kJ/mol,通常来说,Ea越小,反应越容易进行;R为摩尔气体常数,8.314 J/(mol·K);T为绝对温度,单位为K。
Arrhenius公式的对数形式为:lnk=lnA−Ea/RT (4) 将ln k对1/T作图,当其近似为一条直线时,由该直线的斜率和截距即可得到指前因子A和表观活化能Ea。
模型拟合度的评价指标:回归系数(R2)、精确因子(Af)、偏差因子(Bf)和均方根误差(RMSE)等参数通常用作模型的定量评价指标[31-32]。Af、Bf和R2的值越接近1,模型拟合得越好。
精确因子(Af):用于评价预测值与实测值之间的偏离度,其计算公式为:
Af=10∑|log(预测值实验值)|n (5) 偏差因子(Bf):用于判断实测值与预测值之间的大小关系,是过大预测(Bf >1)、过小预测(Bf <1)还是精确预测(Bf =1),其计算公式为:
Bf=10∑log(预测值实验值)n (6) 2. 结果与分析
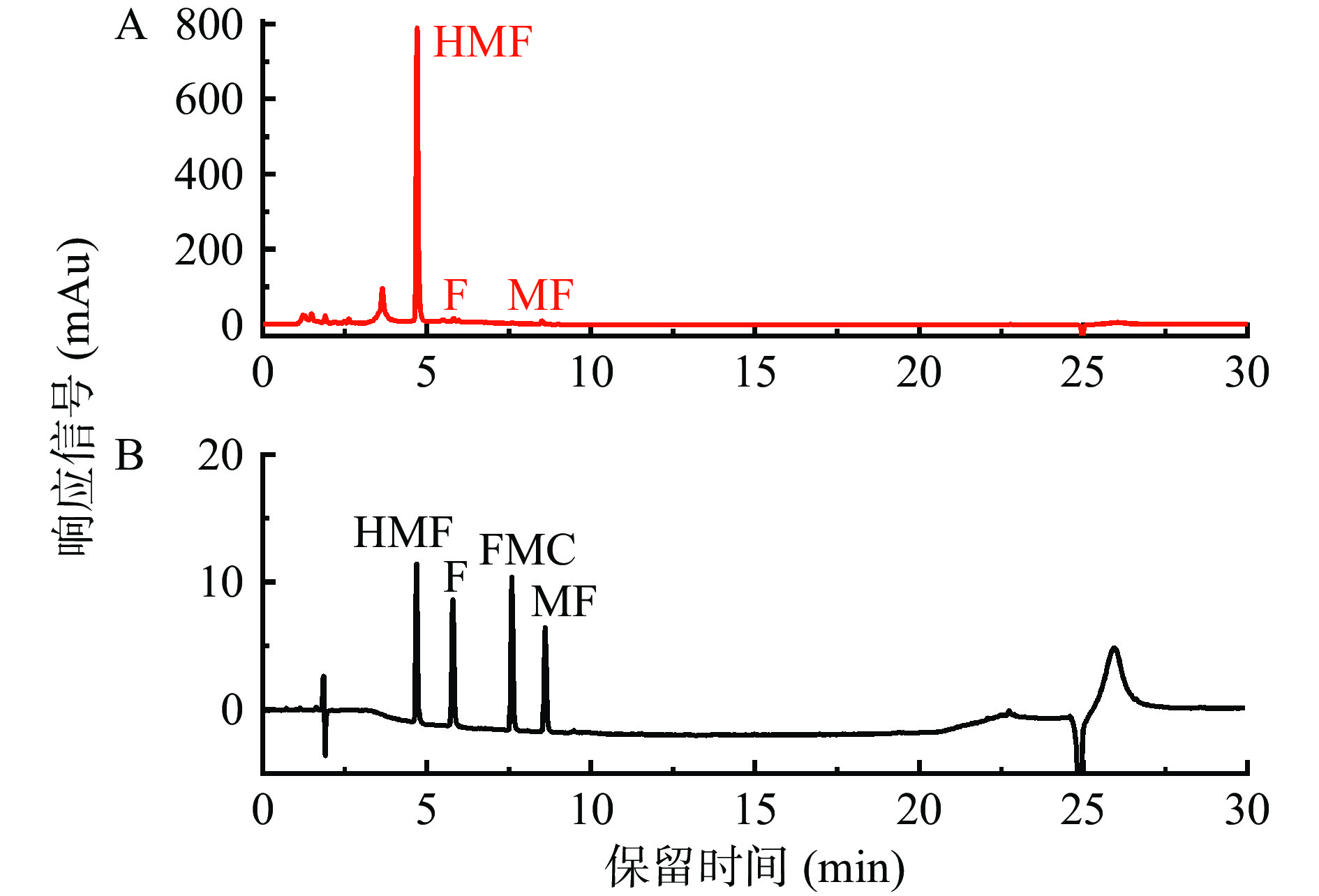
2.1 糠醛类化合物的高效液相色谱分析
标准品和美拉德反应样品中糠醛类化合物的HPLC分析如图1所示,其中,以pH3,加热温度为130 ℃,加热5 h条件下得到的美拉德反应样品为例。可以看出,四种糠醛类化合物HMF、F、FMC和MF能够很好地被分开,说明选定的HPLC测定条件能够很好地测定美拉德反应样品中的糠醛类化合物。本课题组采用该HPLC分析方法已成功对多种样品中糠醛类化合物进行了检测研究[28, 33-34]。
本研究葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系样品中很少能检测到FMC,因此,本研究主要针对HMF、F和MF进行测定。
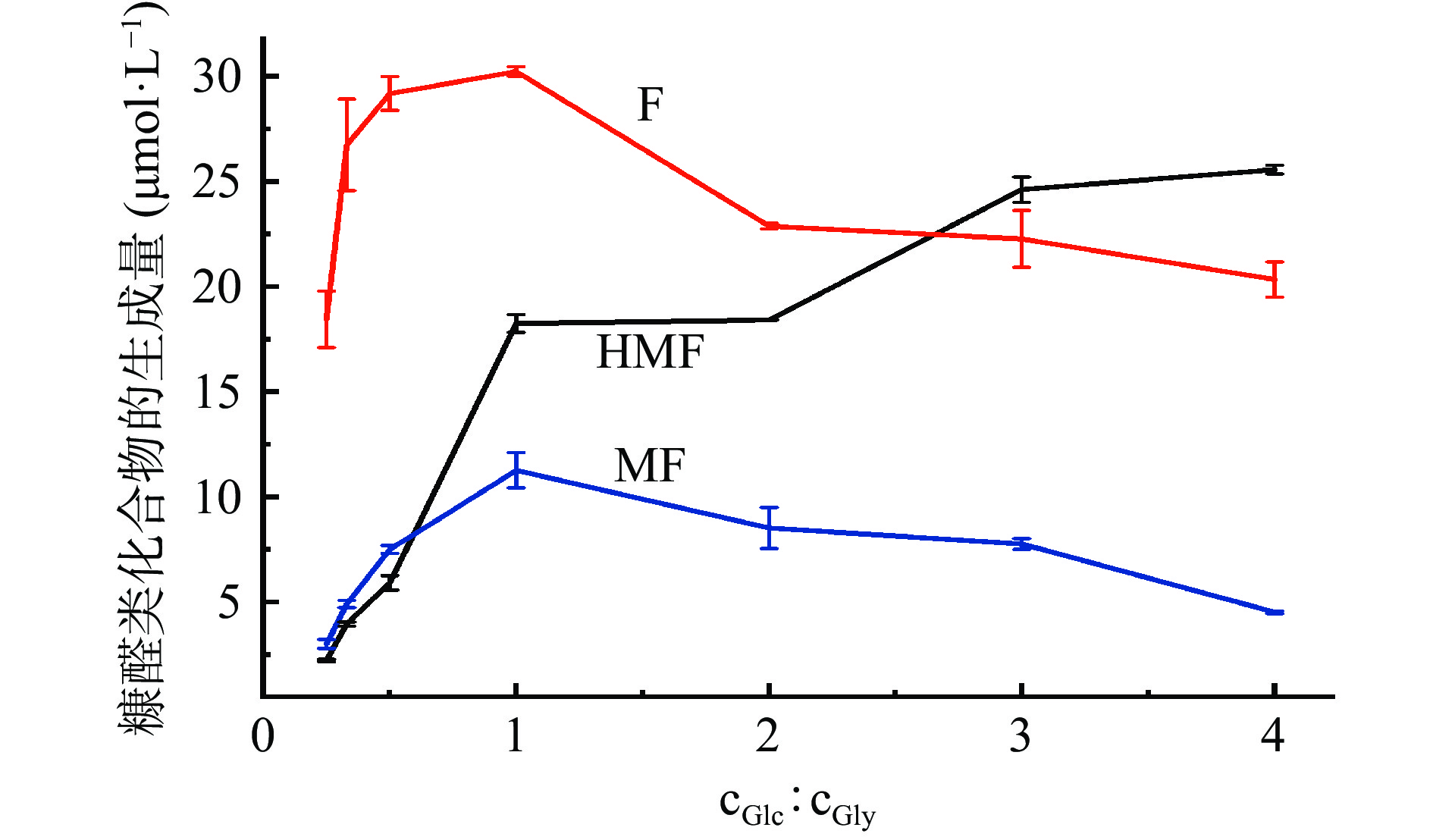
2.2 原料配比对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
反应体系pH为7,90 ℃加热3 h,葡萄糖和甘氨酸的添加比例对糠醛类化合物生成量的影响如图2所示,随着葡萄糖和甘氨酸的摩尔浓度比由1:4增加到1:1,HMF、F和MF的生成量均逐渐增大,其中HMF的增速最大,当葡萄糖和甘氨酸的添加比例由1:1增加到4:1时,F和MF的生成量则逐渐减小,而HMF的生成量继续增大,但增速趋缓,这说明葡萄糖含量的增加有利于HMF的生成。有报道指出单一糖溶液模拟体系在加热时,也可以经由焦糖化途径生成HMF[18, 35],本文的研究结果也恰好证明了这一点。当葡萄糖和甘氨酸的添加摩尔浓度比为1:1时,F和MF的生成量最大,HMF的生成量虽未达到最大值,但据文献报道,葡萄糖和甘氨酸通过美拉德反应生成HMF的分子个数之比为1:1[36-37],因此,后续关于反应条件对美拉德反应体系中糠醛类化合物形成的研究,选择葡萄糖和甘氨酸的添加摩尔浓度比为1:1。
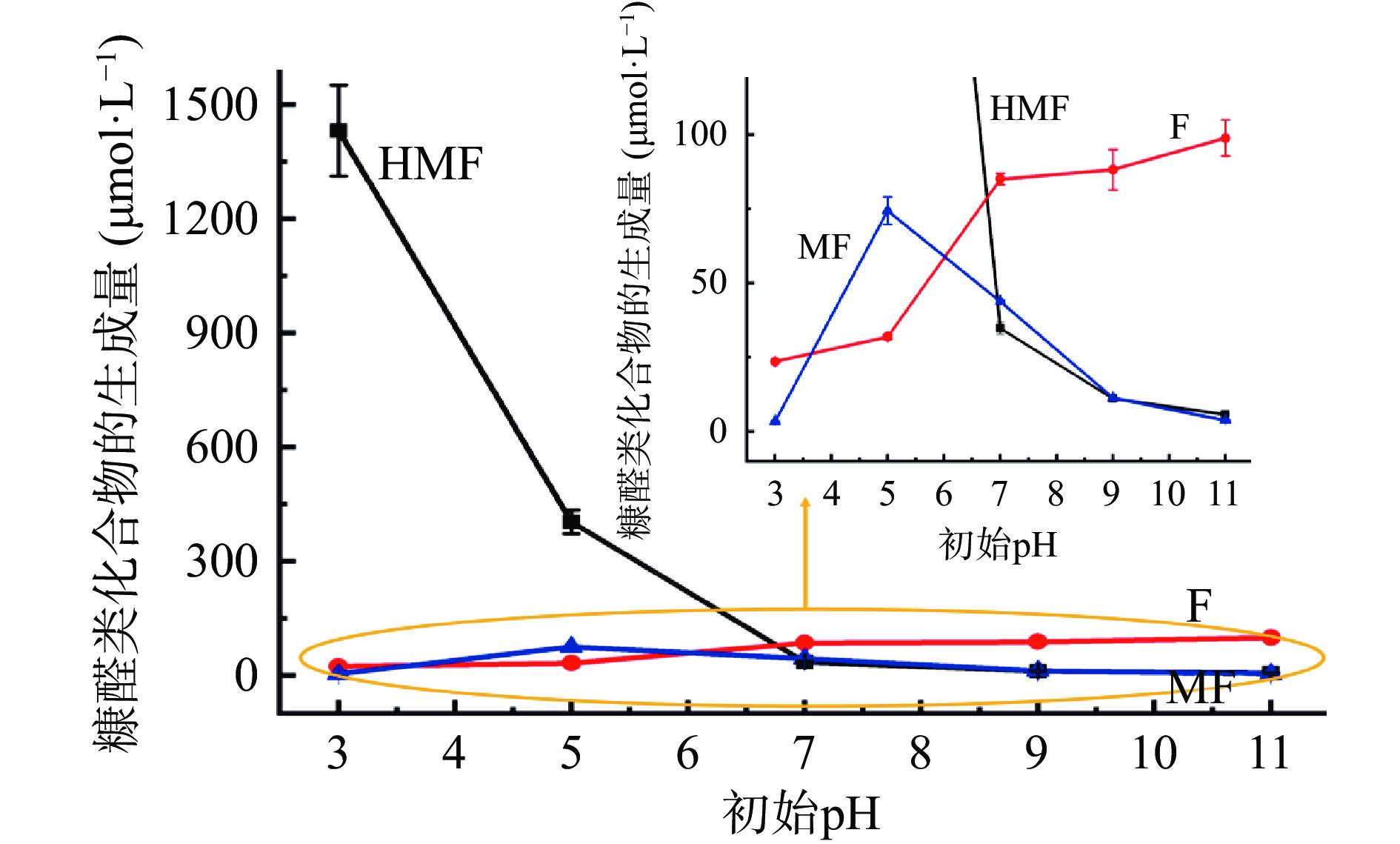
2.3 体系初始pH对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
由于在90 ℃,加热3 h条件下,当pH>7时,未检测到HMF、F和MF,无法实现对较宽pH范围(pH3~11)的研究。故选择在110 ℃,加热5 h条件下,研究体系不同初始pH对葡萄糖-甘氨酸美拉德反应体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响。由图3中可以看出,随着体系初始pH从3增加到7,反应体系中HMF的生成量急剧减小,从1431.64 μmol/L迅速减少到34.84 μmol/L;当体系初始pH从7增加到11时,反应体系中HMF的含量呈平缓减少趋势。说明酸性环境更有利于HMF的生成,这与文献报道的葡萄糖-丙氨酸、蔗糖-半胱氨酸、蔗糖-谷氨酸、蔗糖-亮氨酸等美拉德反应体系中HMF生成量随体系初始pH的变化趋势基本一致[18, 29]。其原因可能是:反应体系pH的降低促进了葡萄糖发生烯醇化反应生成3-脱氧葡萄糖醛酮,并进一步降解形成HMF[38-39]。
模拟体系中F的生成量随着体系初始pH从3增加到7而逐渐增大,当pH从7增加到11,F的生成量虽有增加,但增幅不大,说明在110 ℃时,中性和碱性环境有利于F的生成,而酸性环境不利于F的生成。MF的生成量在pH为5时达到最大值。
总体而言,当加热温度110 ℃,加热5 h时,初始pH<7时,HMF的生成量最多;初始pH≥7时,三种糠醛类化合物中F的生成量最多;HMF、F和MF的总生成量随着pH的增加而迅速减少,并有趋于平衡的趋势。因此,在实际生产过程中,可通过适当提高反应体系pH来抑制糠醛类化合物的形成。
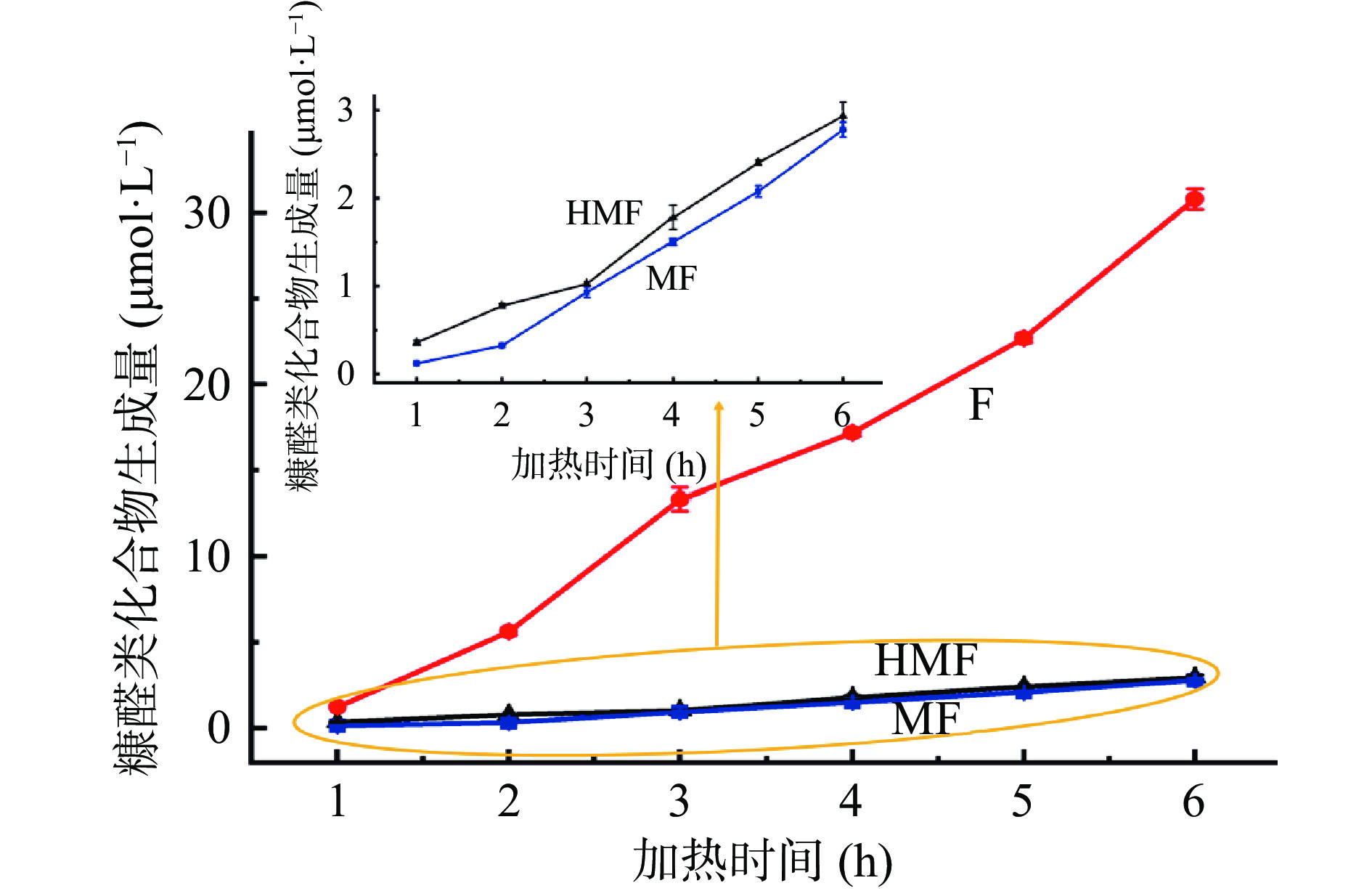
2.4 加热时间对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
在90 ℃,体系初始pH为7的条件下,不同加热时间对葡萄糖-甘氨酸美拉德反应模拟体系中糠醛类化合物的影响如图4所示。从图中可以看出,随着加热时间的延长,葡萄糖-甘氨酸美拉德反应模拟体系中HMF、F和MF的生成量均逐渐升高,这与已有文献报道葡萄糖-丙氨酸和葡萄糖/蔗糖-半胱氨酸/谷氨酸/亮氨酸美拉德反应体系中HMF的生成量随加热时间的变化趋势一致[18, 29]。在加热1~6 h的过程中,HMF的生成量由0.36 μmol/L增加至2.93 μmol/L;F的生成量由1.23 μmol/L增加至30.80 μmol/L;MF的生成量由0.12 μmol/L增加至2.78 μmol/L。HMF的生成量与加热时间之间呈现出指数增加的关系,所得拟合方程为ln C(t)=0.4139 t+ln 0.2903(R2=0.9501),符合一级反应动力学模型;F的生成量与加热时间之间成线性关系,得到的线性拟合方程为C(t)=5.7972 t–5.1545(R2=0.9882),符合零级反应动力学模型;MF的生成量与加热时间之间也成线性关系,拟合方程为C(t)=0.5466 t–0.6242(R2=0.9793),符合零级反应动力学模型。
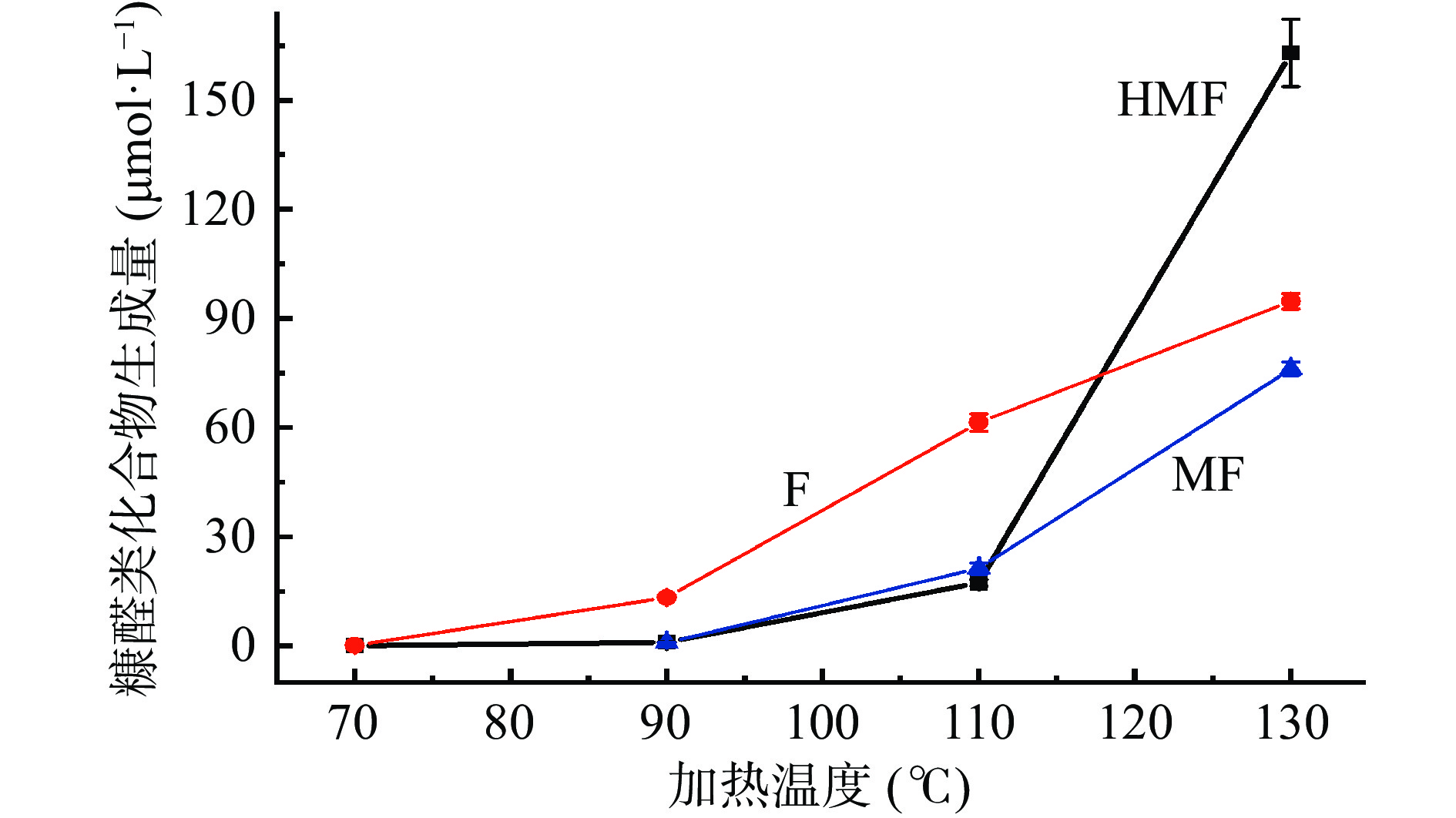
2.5 加热温度对葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响
在缓冲溶液初始pH为7,加热3 h的条件下,不同加热温度对葡萄糖-甘氨酸美拉德反应模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响如图5所示。整体而言,温度明显影响反应体系中糠醛类化合物HMF、F和MF的形成,温度越高,它们的生成量越大。其中,70 ℃时,未检测到MF,F(0.12 μmol/L)的生成量大于HMF(0.08 μmol/L);90 ℃和110 ℃,F的生成量分别为13.32 μmol/L和61.37 μmol/L,HMF的生成量分别为1.03 μmol/L和17.30 μmol/L,MF的生成量分别为0.93 μmol/L和21.33 μmol/L,可见,F的生成量明显大于HMF和MF;但是,当温度升高到130 ℃时,HMF的生成量明显增加至163.01 μmol/L,大大超过了F(94.77 μmol/L)和MF(76.19 μmol/L)。多项研究表明,高温下HMF的形成速度明显提高[24-27],Zhang等[18]关于六种糖-氨基酸美拉德反应模型中HMF生成动力学研究也证实,在所研究糖-氨基酸模型中,HMF的生成量均随温度的增加而升高。温度提高对糠醛类化合物形成的促进作用主要体现在两个方面:a.温度的提升可以促进葡萄糖的开环,而开链糖的浓度是决定反应速率的一个关键因素[40];b.高温可以促进葡萄糖烯醇化并进一步脱水形成HMF[41-42]。
结合2.3部分中初始pH对模拟体系中糠醛类化合物生成量的影响,可以看出,酸性和高温有利于HMF的生成。因此,在实际生产过程中,可通过适当提高反应体系pH和降低反应体系温度来抑制糠醛类化合物的形成。
2.6 葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系加热过程中糠醛类化合物的形成动力学分析
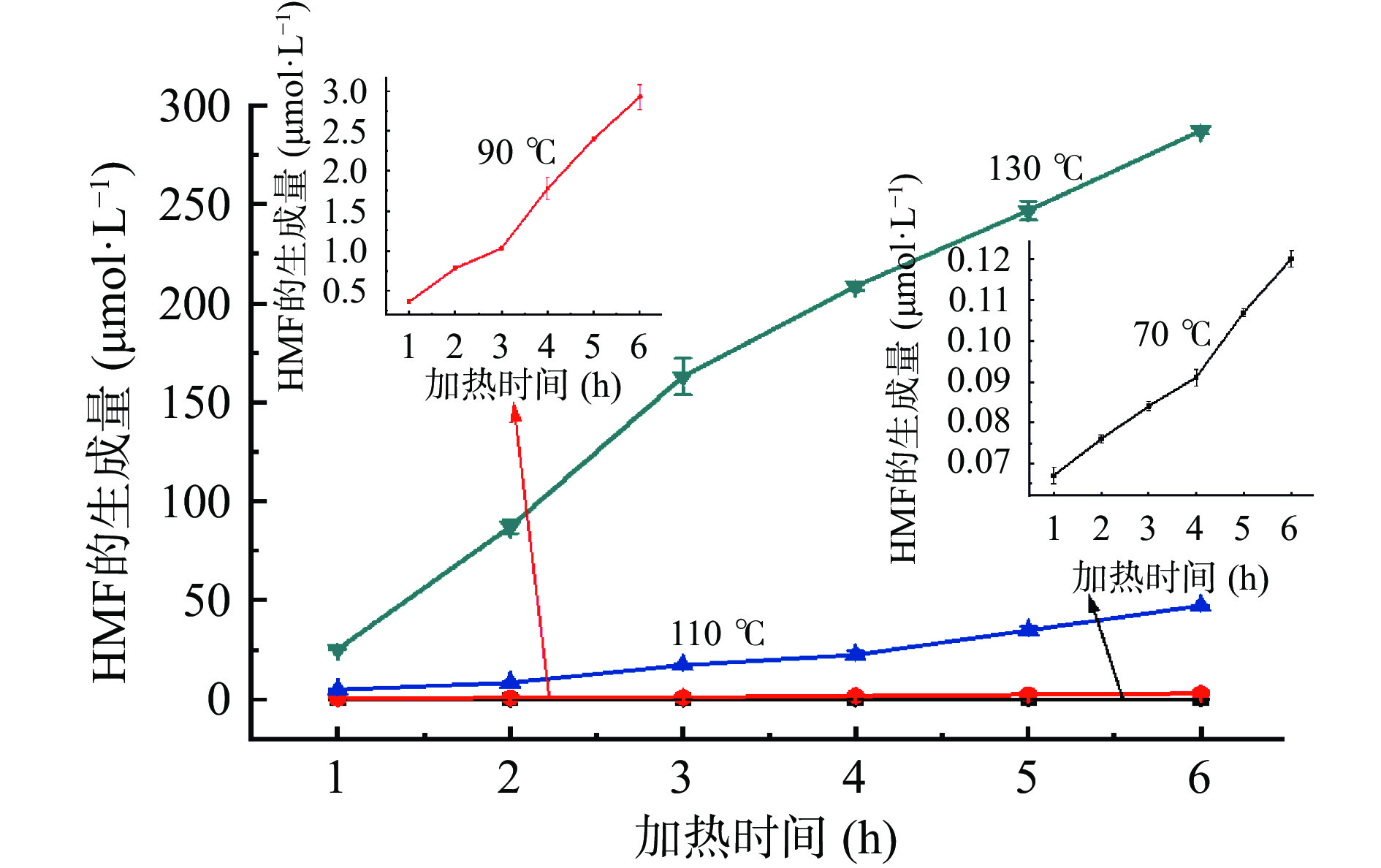
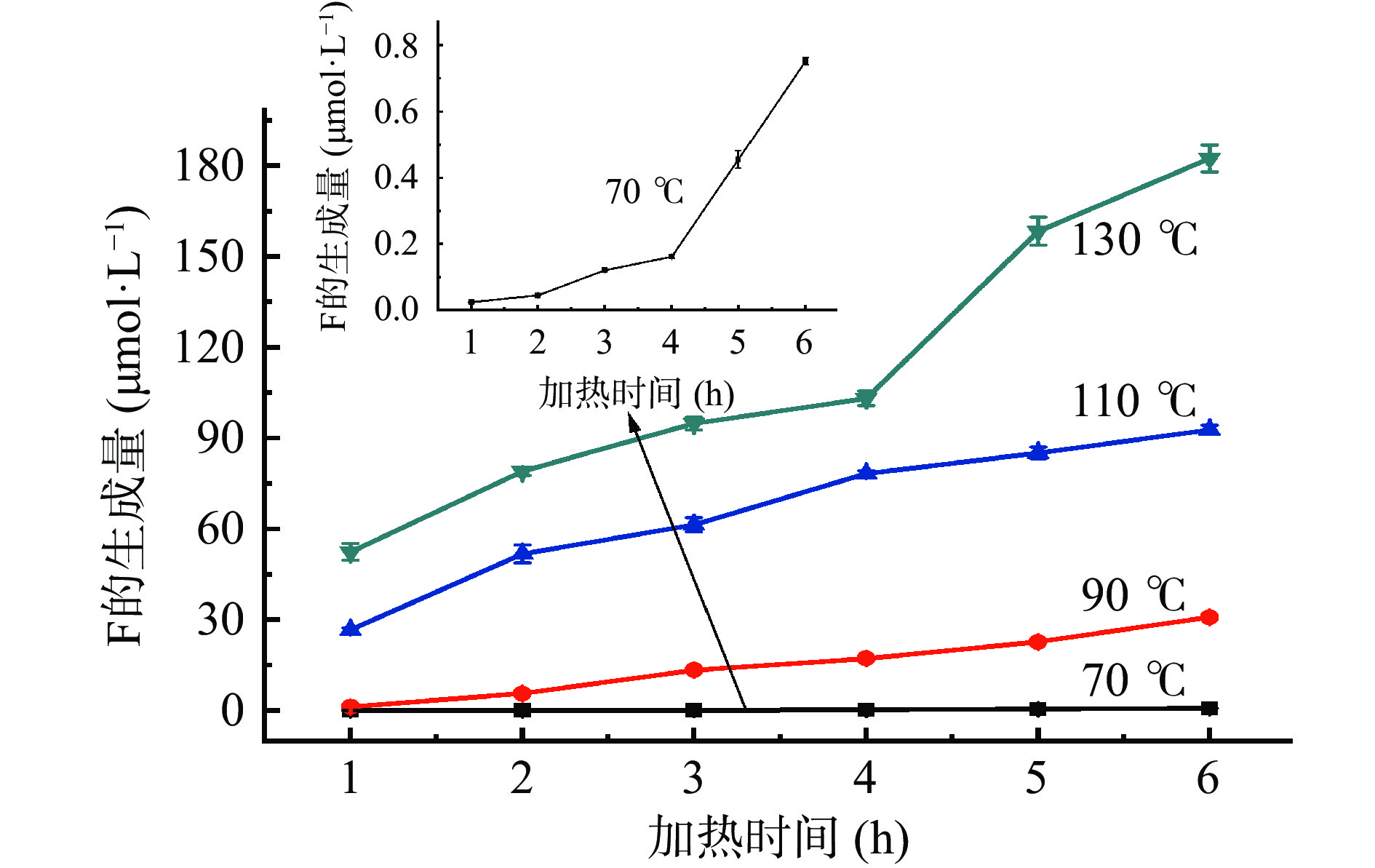
为了研究模拟体系中糠醛类化合物的形成动力学,考察了缓冲溶液pH为7时,葡萄糖和甘氨酸的摩尔浓度均为0.2 mol/L时,不同温度、不同加热时间时,葡萄糖-甘氨酸美拉德反应模拟体系中糠醛类化合物的生成量。随着加热时间的增加、加热温度的升高,糠醛类化合物(HMF、F和MF)生成量的变化如图6~图8所示。葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中糠醛类化合物的形成动力学分析见表1~表3。可以看出,糠醛类化合物HMF、F和FMC的生成量均随着反应时间的增加而增加,随着反应温度的升高而增加,温度越高,糠醛类化合物的增加量越显著;随着加热温度从70 ℃升高到130 ℃、加热时间从1 h增加到6 h,HMF和F的生成量由10−2量级增加到102量级(单位为μmol/L),MF的生成量从无法检出增加到139.67 μmol/L,可见加热温度和加热时间对糠醛类化合物生成量的影响非常大,尤其是反应温度的影响更为显著,原因在于较高的反应温度使烯醇缩合反应和相关的水解、脱水反应均比较容易进行[42-43]。因此,建立糠醛类化合物随温度和时间变化的动力学方程尤为重要。
表 2 模拟体系中F的形成动力学分析Table 2. Kinetic analysis of F formation in model system加热温度
(℃)拟合公式 速率常数k 模型评价 R2 Af Bf 70 ln C(t)=0.6988 t+ln 0.0121 0.6988 0.9839 1.1113 0.9796 90 C(t)=5.7972 t–5.1545 5.7972 0.9882 1.1822 0.9148 110 C(t)=12.7830 t+21.2226 12.7830 0.9402 1.0883 1.0153 130 C(t)=25.6020 t+22.0669 25.6020 0.9336 1.0855 0.9949 A 1.85×107 Ea 45.21 kJ/mol 注:A和Ea的数值由90、110和130 ℃的拟合公式计算得出。 加热温度和时间对模拟体系中HMF生成量的影响如图6所示,HMF的形成动力学分析如表1所示。经过分析可以发现,当加热温度为70~110 ℃时,随着加热时间从1 h增加到6 h,葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中HMF的生成量与加热时间呈指数增加的关系,符合一级动力学模型,计算得出,模拟体系中生成HMF的表观活化能Ea为38.10 kJ/mol。但在温度为130 ℃时,HMF生成量的指数拟合并不理想(R2=0.7852),更倾向于符合零级动力学模型(R2=0.9764)。文献报道[18],在90~110 ℃时,葡萄糖-半胱氨酸、葡萄糖-谷氨酸、葡萄糖-亮氨酸等美拉德模拟体系中HMF的形成均符合一级动力学模型。再结合本文的研究结果,可以看出,在大多数葡萄糖-氨基酸模拟体系中,HMF的形成在反应温度低于110 ℃时,符合一级动力学模型。
表 1 模拟体系中HMF的形成动力学分析Table 1. Kinetic analysis of HMF formation in model system加热温度
(℃)拟合公式 速率常数k 模型评价 R2 Af Bf 70 ln C(t)=0.1149 t+ln 0.0596 0.1149 0.9907 1.0053 1.0000 90 ln C(t)=0.4139 t+ln 0.2903 0.4139 0.9501 1.6303 0.7554 110 ln C(t)=0.4539 t+ln 3.5219 0.4539 0.9699 1.0390 1.0041 130 ln C(t)=0.4435 t+ln 27.9663 0.4435 0.7852 1.0710 1.0048 C(t)=52.4007 t–13.7264 52.4007 0.9764 1.1261 1.0567 A 8.61×104 Ea 38.10 kJ/mol 注:A和Ea的数值由70、90和110 ℃的拟合公式计算得出。 加热温度和时间对模拟体系中F生成量的影响如图7所示,F的形成动力学分析如表2所示。当加热温度为70 ℃时,随着加热时间从1 h增加到6 h,葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中F的生成量与加热时间之间呈指数增加的关系,符合一级动力学模型(R2=0.9839)。但是,当加热温度为90~130 ℃时,F的生成量与加热时间呈线性关系,符合零级动力学模型(R2=0.9336~0.9882),计算得出F生成量的表观活化能为45.21 kJ/mol。目前,尚未见有关于F的形成动力学的文献报道。
加热温度和时间对模拟体系中MF生成量的影响如图8所示,MF的形成动力学分析如表3所示。当加热温度为70 ℃时,葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中MF的含量未检出。当加热温度为90~130 ℃时,随着加热时间从1 h增加到6 h,葡萄糖-甘氨酸模拟体系中MF的生成量与加热时间呈线性关系,符合零级动力学模型,计算得出MF生成量的表观活化能为56.58 kJ/mol。目前,尚未见有关于MF的形成动力学的文献报道。
表 3 模拟体系中MF的形成动力学分析Table 3. Kinetic analysis of MF formation in model system加热温度
(℃)拟合公式 速率常数k 模型评价 R2 Af Bf 70 − − − − − 90 C(t)=0.5466 t–0.6242 0.5466 0.9793 1.1192 1.0988 110 C(t)=10.1591 t–8.7379 10.1591 0.9881 1.2387 0.8837 130 C(t)=22.7355 t+5.5775 22.7355 0.9906 1.0651 1.0179 A 5.25×108 Ea 56.58 kJ/mol 注:A和Ea的数值由90、110和130 ℃的拟合公式计算得出。 HMF、F和MF三种糠醛类化合物表观活化能的大小顺序为Ea, HMF<Ea, F<Ea, MF,说明在相同条件下,HMF更易生成。
3. 结论
本研究以葡萄糖-甘氨酸模型为研究对象,探究了葡萄糖与甘氨酸的摩尔浓度比、体系初始pH、加热时间和加热温度等因素对糠醛类化合物生成量的影响规律,并对HMF、F和MF的形成动力学进行了分析。结果表明,葡萄糖的添加量对糠醛类化合物生成量的影响大于甘氨酸的添加量,葡萄糖含量越高,HMF的生成量越多;酸性pH条件有利于HMF的形成,中性和碱性pH条件有利于F的形成;随着加热时间的延长、加热温度的增加,HMF、F和MF的生成量均逐渐增加,其中,温度的影响更为明显。这些结论表明,在实际生成过程中,可通过适当减少糖添加量、提高反应体系pH、降低反应体系温度、缩短反应时间等方式来抑制热加工食品中糠醛类化合物的形成。对HMF、F和MF形成动力学方程的模拟,可为预测不同反应时间、温度时糠醛类化合物的生成量提供参考。但是本研究对糠醛类化合物生成机理的研究不足,尤其是HMF、F、MF三者之间是否存在相互转化,转化机理如何等还有待进一步探讨。
-
表 2 模拟体系中F的形成动力学分析
Table 2 Kinetic analysis of F formation in model system
加热温度
(℃)拟合公式 速率常数k 模型评价 R2 Af Bf 70 ln C(t)=0.6988 t+ln 0.0121 0.6988 0.9839 1.1113 0.9796 90 C(t)=5.7972 t–5.1545 5.7972 0.9882 1.1822 0.9148 110 C(t)=12.7830 t+21.2226 12.7830 0.9402 1.0883 1.0153 130 C(t)=25.6020 t+22.0669 25.6020 0.9336 1.0855 0.9949 A 1.85×107 Ea 45.21 kJ/mol 注:A和Ea的数值由90、110和130 ℃的拟合公式计算得出。 表 1 模拟体系中HMF的形成动力学分析
Table 1 Kinetic analysis of HMF formation in model system
加热温度
(℃)拟合公式 速率常数k 模型评价 R2 Af Bf 70 ln C(t)=0.1149 t+ln 0.0596 0.1149 0.9907 1.0053 1.0000 90 ln C(t)=0.4139 t+ln 0.2903 0.4139 0.9501 1.6303 0.7554 110 ln C(t)=0.4539 t+ln 3.5219 0.4539 0.9699 1.0390 1.0041 130 ln C(t)=0.4435 t+ln 27.9663 0.4435 0.7852 1.0710 1.0048 C(t)=52.4007 t–13.7264 52.4007 0.9764 1.1261 1.0567 A 8.61×104 Ea 38.10 kJ/mol 注:A和Ea的数值由70、90和110 ℃的拟合公式计算得出。 表 3 模拟体系中MF的形成动力学分析
Table 3 Kinetic analysis of MF formation in model system
加热温度
(℃)拟合公式 速率常数k 模型评价 R2 Af Bf 70 − − − − − 90 C(t)=0.5466 t–0.6242 0.5466 0.9793 1.1192 1.0988 110 C(t)=10.1591 t–8.7379 10.1591 0.9881 1.2387 0.8837 130 C(t)=22.7355 t+5.5775 22.7355 0.9906 1.0651 1.0179 A 5.25×108 Ea 56.58 kJ/mol 注:A和Ea的数值由90、110和130 ℃的拟合公式计算得出。 -
[1] FARAG M R, ALAGAWANY M, BIN-JUMAH M, et al. The toxicological aspects of the heat-borne toxicant 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in animals: A review[J]. Molecules,2020,25(8):1941(1−13).
[2] BAUER-MARINOVIC M, TAUGNER F, FLORIAN S, et al. Toxicity studies with 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and its metabolite 5-sulphooxymethylfurfural in wild-type mice and transgenic mice expressing human sulphotransferases 1A1 and 1A2[J]. Archives of Toxicology,2012,86(5):701−711. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0807-5
[3] ABRAHAM K, GURTLER R, BERG K, et al. Toxicology and risk assessment of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in food[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2011,55(5):667−678.
[4] MONIEN B H, ENGST W, BARKNOWITZ G, et al. Mutagenicity of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in V79 cells expressing human SULT1A1: Identification and mass spectrometric quantification of DNA adducts formed[J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology,2012,25(7):1484−1492. doi: 10.1021/tx300150n
[5] 王金山, 牛凤云, 孙萍, 等. 糠醛毒性的研究[J]. 卫生毒理学杂志,1994,8(3):21−23. [WANG J, NIU F, SUN P, et al. Studies on the toxicity of furfural[J]. Journal of Toxicology,1994,8(3):21−23. WANG J, NIU F, SUN P, et al. Studies on the toxicity of furfural[J]. Journal of Toxicology, 1994, 8(3): 21−23.
[6] UDDIN S, HADI S M. Reactions of furfural and methylfurfural with DNA[J]. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology International,1995,35(1):185−195.
[7] PINEIRO-GARCIA A, GONZALEZ-ALATORRE G, VEGA-DIAZ S M, et al. Reduced graphene oxide coating with high performance for the solid phase micro-extraction of furfural in espresso coffee[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2020,14(1):314−321. doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00293-3
[8] GONG M, ZHOU Z, YU Y, et al. Investigation of the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural content of Chinese traditional fermented vinegars from different regions and its correlation with the saccharide and amino acid content[J]. LWT,2020,124:109175. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109175
[9] YILTIRAK S, KOCADAĞLI T, ÇELIK E E, et al. Effects of sprouting and fermentation on free asparagine and reducing sugars in wheat, einkorn, oat, rye, barley, and buckwheat and on acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation during heating[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(32):9419−9433. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03316
[10] GÜRSUL A I, VURAL G. Investigations on the formation of α-dicarbonyl compounds and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in fruit products during storage: New insights into the role of Maillard reaction[J]. Food Chemistry,2021:363.
[11] 孙莹, 苗榕芯. 浅谈饮料中5-羟甲基糠醛的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(13):206−209. [SUN Y, MIAO R X. Discussion on the progress of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural in beverages[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(13):206−209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.13.036 SUN Y, MIAO R X. Discussion on the progress of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural in beverages[J]. Food Research and development, 2018, 39(13): 206−209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.13.036
[12] 刘兴勇, 陈兴连, 林涛, 等. 烘焙程度对小粒咖啡5-羟甲基糠醛生成的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(1):324−331. [LIU X Y, CHEN X L, LIN T, et al. Effects of roasting degree on formation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural contents in coffea Arabica[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(1):324−331. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2022.01.035 LIU X Y, CHEN X L, LIN T, et al. Effects of roasting degree on formation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural contents in coffea Arabica[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(1): 324−331. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2022.01.035
[13] PELETEIRO S, LOPES A M D C, GARROTE G, et al. Manufacture of furfural in biphasic media made up of an ionic liquid and a co-solvent[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2015,77:163−166. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.08.048
[14] PESAVENTO M, MERLI D, BIESUZ R, et al. A MIP-based low-cost electrochemical sensor for 2-furaldehyde detection in beverages[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2021,1142(15):201−210.
[15] BOEKEL M A J S V. Effect of heating on Maillard reactions in milk[J]. Food Chemistry,1998,62(4):403−414. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00075-2
[16] KWAK E J, LIM S I. The effect of sugar, amino acid, metal ion, and NaCl on model Maillard reaction under pH control[J]. Amino Acids,2004,27(1):85−90.
[17] 孙方达, 孔保华, 韩齐, 等. 反应初始pH和加热时间对猪骨蛋白水解物美拉德产物特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(22):106−110. [SUN F D, KONG B H, HAN Q, et al. Influence of different initial pH and heating time on characteristic of the porcine bone protein hydrolysate Maillard products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(22):106−110. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.22.057 SUN F D, KONG B H, HAN Q, et al. Influence of different initial pH and heating time on characteristic of the porcine bone protein hydrolysate Maillard products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(22): 106−110. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.22.057
[18] ZHANG L, KONG Y, YANG X, et al. Kinetics of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation in the sugar-amino acid model of Maillard reaction[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2018,99(5):2340−2347.
[19] ZHOU Y, LI Y, YU A. The effects of reactants ratios, reaction temperatures and times on Maillard reaction products of the L-ascorbic acid/L-glutamic acid system[J]. Food Science and Technology,2016,36(2):268−274. doi: 10.1590/1678-457X.02415
[20] 张凤梅, 汤高奇, 田玮, 等. 模式体系谷氨酸-葡萄糖美拉德反应程度研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(3):49−59. [ZHANG F M, TANG G Q, TIAN W, et al. Research on the process of glutamic acid and glucose Maillard reaction system[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(3):49−59. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2019.03.006 ZHANG F M, TANG G Q, TIAN W, et al. Research on the process of glutamic acid and glucose Maillard reaction system[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2019, 19(3): 49−59. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2019.03.006
[21] LI Y, JIA X, WANG Z, et al. Changes in harmful Maillard reaction products in low-temperature long-time pasteurization-treated milks reconstituted from whole-milk powders after different storage times[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2022,106:104280. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104280
[22] 卢键媚, 林晓蓉, 陈忠正, 等. 反应条件对糖-酸反应体系中3-脱氧葡萄糖醛酮及5-羟甲基糠醛形成的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(2):93−100. [LU J M, LIN X R, CHEN Z Z, et al. Effect of reaction conditions on the formation of 3-deoxyglucosone and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in sugar-acid reaction system[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(2):93−100. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021040327 LU J M, LIN X R, CHEN Z Z, et al. Effect of reaction conditions on the formation of 3-deoxyglucosone and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in sugar-acid reaction system[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(2): 93−100. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021040327
[23] 张泽宇, 曹雁平, 朱雨辰. 缓解食品中丙烯酰胺和5-羟甲基糠醛形成的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(2):324−333, 347. [ZHANG Z Y, CAO Y P, ZHU Y C. Mitigation strategies on acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in foods[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(2):324−333, 347. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.12.054 ZHANG Z Y, CAO Y P, ZHU Y C. Mitigation strategies on acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in foods[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(2): 324−333+347. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.12.054
[24] VHANGANI L N, WYK J V. Antioxidant activity of Maillard reaction products (MRPs) derived from fructose–lysine and ribose–lysine model systems[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,137(1−4):92−98. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.030
[25] ERIC K, RAYMOND L V, ABBAS S, et al. Temperature and cysteine addition effect on formation of sunflower hydrolysate Maillard reaction products and corresponding influence on sensory characteristics assessed by partial least square regression[J]. Food Research International,2014,57:242−258. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.030
[26] 朱秀清, 雷文华, 黄雨洋, 等. 5-羟甲基糠醛在食品中的变化及其安全性研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(15):4983−4991. [ZHU X Q, LEI W H, HUANG Y Y, et al. Research progress in changes of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in food and its satety[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(15):4983−4991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.15.spaqzljcjs202215029 ZHU X Q, LEI W H, HUANG Y Y, et al. Research progress in changes of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural in food and its satety[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2022, 13(15): 4983−4991. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.15.spaqzljcjs202215029
[27] ZHANG Y, SONG Y, HU X, et al. Effects of sugars in batter formula and baking conditions on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural formation in sponge cake models[J]. Food Research International,2012,49:439−445. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.07.012
[28] XING Q, MA Y, FU X, et al. Effects of heat treatment, homogenization pressure, and overprocessing on the content of furfural compounds in liquid milk[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,100:5276−5282. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10578
[29] 曾世通, 卢斌斌, 李鹏, 等. 丙氨酸与葡萄糖美拉德反应体系中HMF的形成分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2017,17(4):289−293. [ZENG S T, LU B B, LI P, et al. Analysis of the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation in Maillard reaction system of alanine and glucose[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2017,17(4):289−293. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2017.04.035 ZENG S T, LU B B, LI P, et al. Analysis of the 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation in Maillard reaction system of alanine and glucose[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2017, 17(4): 289−293. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2017.04.035
[30] 王丹, 况丹妮, 刘若阳, 等. 焦糖化与美拉德反应中DDMP、HMF及糠醛的生成研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(12):100−107. [WANG D, KUANG D, LIU R, et al. Formation of DDMP, HMF and furfural in caramelization and Maillard reaction[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(12):100−107. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021090221 WANG D, KUANG D, LIU R, et al. Formation of DDMP, HMF and furfural in caramelization and Maillard reaction[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(12): 100−107. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021090221
[31] ZHONG K, CHEN F, WANG Z, et al. Inactivation and kinetic model for the Escherichia coli treated by a co-axial pulsed electric field[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2005,221(6):752−758. doi: 10.1007/s00217-005-0015-0
[32] SANTILLANA FARAKOS S M, FRANK J F, SCHAFFNER D W. Modeling the influence of temperature, water activity and water mobility on the persistence of Salmonella in low-moisture foods[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2013,166(2):280−293. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.07.007
[33] XING Q, FU X, LIU Z, et al. Contents and evolution of potential furfural compounds in milk-based formula, ultra-high temperature milk and pasteurised yoghurt[J]. Internaitonal Dairy Journal,2021,120:105086. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2021.105086
[34] 邢倩倩. 高效液相色谱法测定干酪和炼乳中糠醛类化合物含量[J]. 乳业科学与技术,2021,44(1):28−32. [XING Q. Determination of furfural compounds in cheese and condensed milk by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Dairy Science and Technology,2021,44(1):28−32. doi: 10.15922/j.cnki.jdst.2021.01.006 XING Q. Determination of furfural compounds in cheese and condensed milk by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Dairy Science and Technology, 2021, 44(1): 28−32. doi: 10.15922/j.cnki.jdst.2021.01.006
[35] 张玉玉, 张兴, 章慧莺, 等. 3种单糖模拟体系中5-羟甲基糠醛的形成动力学分析[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(17):41−47. [ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG X, ZHANG H Y, et al. Kinetic studies on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation in three kinds of monosaccharide solution model systems during thermal processing[J]. Food Science,2014,35(17):41−47. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201417009 ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG X, ZHANG H Y, et al. Kinetic studies on 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation in three kinds of monosaccharide solution model systems during thermal processing[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(17): 41−47. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201417009
[36] JALBOUT A F, ROY A K, SHIPAR A H, et al. Density functional computational studies on the glucose and glycine Maillard reaction: Formation of the Amadori rearrangement products[J]. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry,2008,108(3):589−597. doi: 10.1002/qua.21438
[37] REN G R, ZHAO L J, SUN Q, et al. Explore the reaction mechanism of the Maillard reaction: A density functional theory study[J]. Journal of Molecular Modeling,2015,21:132. doi: 10.1007/s00894-015-2674-5
[38] CAPUANO E, FOGLIANO V. Acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF): A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food and mitigation strategies[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2011,44(4):793−810. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2010.11.002
[39] AKTAG I G, GOKMEN V. Multiresponse kinetic modelling of alpha-dicarbonyl compounds formation in fruit juices during storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,320:126620. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126620
[40] KAVOUSI P, MIRHOSSEINI H, GHAZALI H, et al. Formation and reduction of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural at frying temperature in model system as a function of amino acid and sugar composition[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,182:164−170. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.135
[41] GLATT H, SCHNEIDER H, MURKOVIC M, et al. Hydroxymethyl-substituted furans: Mutagenicity in Salmonella typhimurium strains engineered for expression of various human and rodent sulphotransferases[J]. Mutagenesis,2012,271:41−48.
[42] AIDA T M, TAJIMA K, WATANABE M, et al. Reactions of d-fructose in water at temperatures up to 400 °C and pressures up to MPa[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2007,42(1):110−119.
[43] ASGHARI F S, YOSHIDA H. Kinetics of the decomposition of fructose catalyzed by hydrochloric acid in subcritical water: Formation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, levulinic, and formic acids[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research,2007,46(23):7703−7710. doi: 10.1021/ie061673e
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 孟新涛,许铭强,张婷,古丽米热·祖努纳,牛逍瞳,郭金宝,刘国庆,马燕. 基于GC-IMS技术分析新疆不同品种核桃油挥发性成分的差异. 中国油脂. 2025(03): 102-109 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 古丽米热·祖努纳,孟新涛,叶朵朵,付慧鑫,乔雪,乔雅洁,张婷. 不同储藏温度下鲜羊肉品质及风味的变化. 现代食品科技. 2025(03): 203-221 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 乔雪,乔雅洁,付慧鑫,孟新涛,张婷. 低压静电场辅助解冻对牛肉品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(17): 48-56 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨秉坤,剧柠,丁雨红,郭蓉,龚绵红. 沙棘酸奶挥发性风味物质的GC-IMS表征. 食品工业科技. 2023(13): 308-315 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 张凡,张宇帆,苏心悦,徐文雅,安焕炯,马倩云,孙剑锋,王颉,王文秀. 基于顶空气相离子迁移谱的干腐病马铃薯挥发性成分分析. 食品科学. 2022(06): 317-323 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王福成,米思,李劲松,王雨行,王向红. 基于气相色谱-离子迁移谱技术分析不同包装条件对黄瓜风味的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(08): 296-304 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 马姗,于文龙,焦英帅,刘卫华,王向红. 不同减菌处理对凡纳对虾贮藏期间品质的影响. 食品科技. 2022(03): 116-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



