Research Progress on Processing Technology, Components, Microbial Diversity and Bioactivities of Pickled Tea
-
摘要: 酸茶以大叶种茶树叶为原料,经杀青、厌氧发酵、干燥等加工工艺制成,主要分布于我国云南、泰国、缅甸、老挝和日本。与普洱茶、黑茶等其他后发酵茶不同,乳酸菌是酸茶的优势微生物,赋予了其独特的风味品质特性,使酸茶作为一种新型乳酸菌茶叶制品正日益受到关注。近年来,国内外学者对酸茶的研究已经从营养化学成分向微生物多样性和生物学活性扩展。本文主要综述了不同地区酸茶制作工艺、微生物多样性和营养及化学成分,以及酸茶的抗氧化、抗菌和调节代谢综合症等生物学功效,并对酸茶益生菌资源、酸茶品质稳定性及标准化生产等问题进行了展望,以期为酸茶的深入研究开发提供参考。Abstract: Pickled tea is prepared from the leaves of Camellia sinensisa with a microbial fermentation process under an anaerobic condition after fixation followed by drying and mainly found in Yunnan of China, Thailand, Myanmar, Laos and Japan. Unlike other post-fermented teas such as Pu'erh tea and dark tea, lactic acid bacteria are the dominant microorganisms of pickled tea, bestowing pickled tea with unique flavor characteristics and functional activities. Pickled tea has gaining increasing attention as a novel tea product fermented with lactic acid bacteria. This paper mainly reviews the production process, microbial diversity and nutritional and chemical composition of pickled tea prepared in different regions, as well as the its bioactivity of including antioxidant, antibacterial and regulatory metabolic syndrome, in order to provide a scientific theoretical basis for the in-depth research, development, inheritance and protection of pickled tea. The problems of probiotic resource, its quality stability, and standard processing of pickled tea are prospected, providing reference for further research of this tea.
-
酸茶又称为腌茶,是我国云南少数民族德昂族和布朗族的传统茶叶制品,它是以大叶种茶叶为原料,经厌氧发酵制成,具有微酸味,故而得名酸茶;除德昂族和布朗族之外,酸茶在泰国、缅甸、老挝、日本的部分地区也有悠久的食用历史[1-2]。酸茶通常泡水饮用,也可作为一种零食来凉拌、直接嚼食或做成茶粥。乳酸菌发酵食品因含有被普遍认为是安全的乳酸菌,以及含有抗菌肽(如细菌素)、乙醇、有机酸、脂肪酸等活性成分,其健康功效日益受到关注[3]。研究证实,酸茶中主要优势微生物是乳酸菌,赋予了酸茶有别于其他发酵茶的品质特性及生理功能。本文对近年来国内外对酸茶的加工工艺、成分、微生物多样性及生物学功效的研究进展进行综述,以期为酸茶的深入研究及利用提供参考。
1. 酸茶的加工工艺
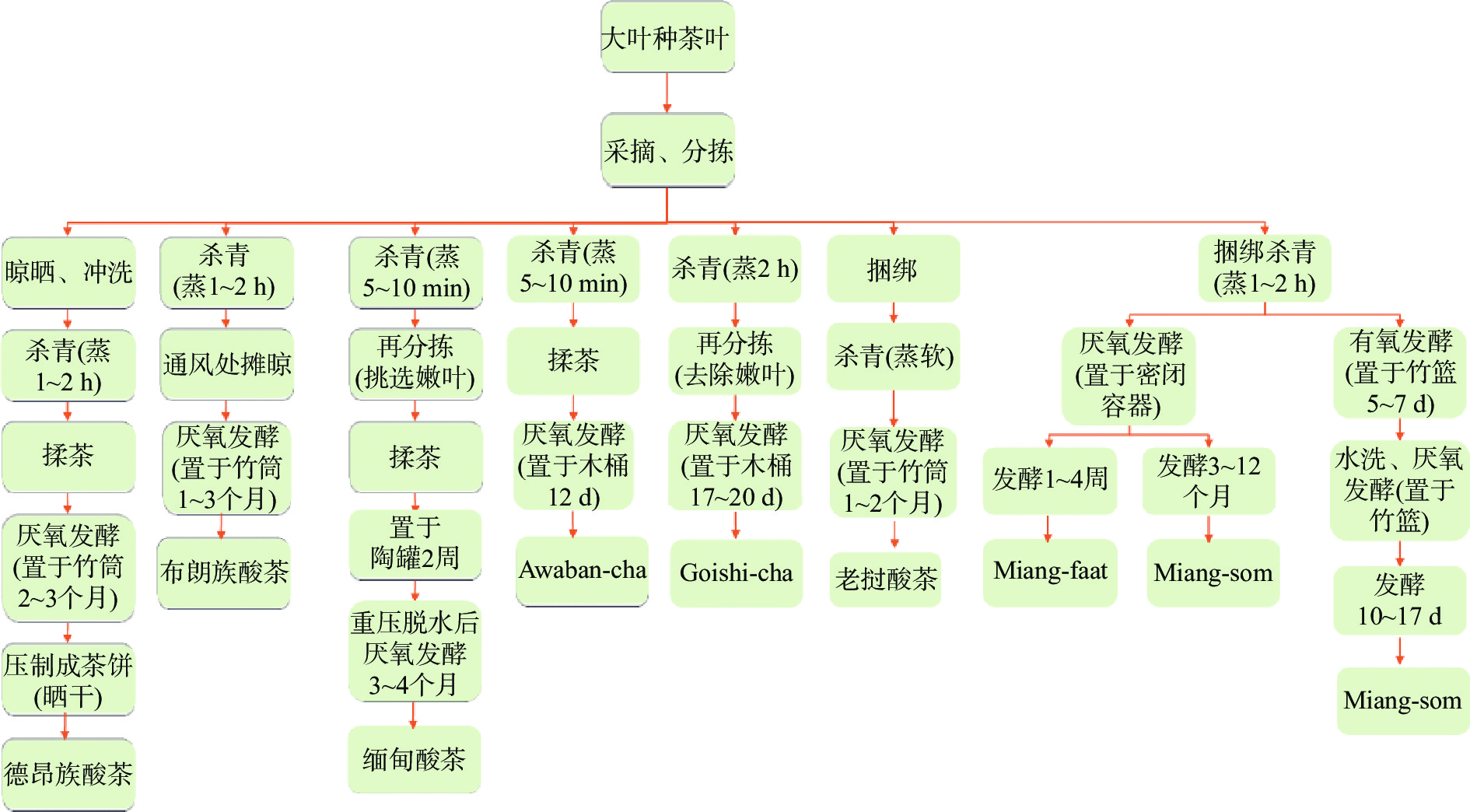
酸茶以大叶种茶树叶为原料,经杀青、揉茶、厌氧发酵、干燥等加工工艺制成,历经原料前处理、多菌种附着发酵及后处理的加工过程[4]。不同国家和地区的酸茶加工方法在杀青时间、发酵容器、发酵时间、后处理过程等存在差异,德昂族、布朗族、缅甸、日本和老挝酸茶均采用一步厌氧发酵工艺,而泰国酸茶分为一步厌氧发酵和有氧厌氧两步发酵工艺(见图1)。
我国酸茶包括德昂族酸茶和布朗族酸茶,其制作方式类似。德昂酸茶是先将分拣好的大叶种茶叶进行晾晒、杀青(蒸煮1~2 h)、揉制后用芭蕉叶包裹茶叶,埋入深坑内发酵2~3个月,将茶叶取出后在阳光下揉搓并晾晒,等茶叶稍干时又将其包裹埋入深坑压制成茶饼,取出后晒干即可泡饮;鲜食酸茶则要适当在埋入深坑时多发酵几天,取出后碾碎晒干,食用时用水泡发后凉拌,其味酸涩具有回味,可以增加食欲[5-6]。布朗酸茶是将茶叶晾晒再蒸煮杀青,先放在通风处摊晾,然后再装入新鲜竹筒压实、密封深埋厌氧发酵[7]。
缅甸酸茶“Lahpet”是将采集的大叶种茶树鲜叶蒸煮5~10 min灭酶,揉茶后置于陶罐中发酵2周,重压脱水后将叶子卷起来,迅速放入土罐中密封发酵3~4个月[8]。日本酸茶“Awaban-cha”是在七月份采集大叶种茶树鲜叶,分拣后经沸水杀青5~10 min,揉茶后放入木桶厌氧发酵,晾干后制成茶粉;而日本另外一种酸茶“Goishi-cha”是将鲜茶叶蒸2 h后再分拣,去除嫩叶,置于木桶中厌氧发酵17~20 d后形成外形紧结重实、色泽乌润、汤色暗褐、香味纯正且具有酸味的酸茶[9]。老挝酸茶是以大叶种茶树鲜叶为原料,用绳索绑成捆后蒸煮杀青,摊晾后装入新鲜竹筒内并用用芭蕉叶密封,埋于土坑中进行厌氧发酵[10]。泰国酸茶“Miang”可分为丝状真菌发酵法和非丝状真菌发酵法。两种发酵方法都是以大叶种茶树鲜叶为原料,用竹叶捆绑后放在木桶上蒸煮杀青2 h或以上去除内源酶,摊开晾干;丝状真菌发酵法是将杀青后茶叶放入竹篮中进行丝状真菌附着有氧发酵5~10 d,洗涤后用香蕉叶或塑料包裹后再放置于竹篮中厌氧发酵5~7 d,制成酸味的“Miang-som”;而非丝状真菌发酵法是直接将蒸煮杀青后的茶叶放入竹篮进行厌氧发酵,发酵1~4周制成涩味的“Miang-faat”,厌氧发酵3~12个月制成酸味的“Miang-som” [11-13]。
综上所述,酸茶加工主要采用的是家庭手工或手工作坊的自然发酵制备方式,缺乏相应的质量标准,导致产品品质不稳定。
2. 酸茶的活性成分
目前,关于酸茶的活性成分研究报道主要集中在多酚、生物碱、酚酸等方面。多酚类物质是酸茶中主要化学成分,酸茶发酵过程中微生物产生的酶可直接降解复杂多酚或影响细胞壁结构,释放出游离的可吸收酚类化合物[14],增加多酚的提取性,或通过茶中可利用的底物合成新的酚类物质,导致总多酚含量增加[15-17]。例如,Maung等[18-19]研究报道,与鲜茶相比,发酵7和14 d的缅甸酸茶“Laphet”中类黄酮和总多酚含量均增加,这一结果与德昂酸茶中总多酚含量变化一致[20]。此外,泰国酸茶“Miang”中浓缩单宁含量也明显增加,推测可能是由于微生物酶促氧化单体黄烷3-醇所致[21]。Unban等[22]研究指出制作工艺和发酵时间影响酸茶的多酚含量,与丝状真菌两步发酵法制备工艺相比,非丝状真菌一步发酵法制备的泰国酸茶“Miang”中总多酚有降低的趋势,而总黄酮和总单宁含量有增加的趋势,而发酵时间延长均使上述两种方法制备的酸茶中总多酚、总类黄酮、总单宁和总儿茶素含量降低。此外,酸茶发酵过程中咖啡因的含量降低[20],显著低于绿茶[9], 咖啡因含量降低的原因可能是因为乳酸菌发酵过程促使咖啡因与多元酚类结合成为复合物的结果[23]。
儿茶素是茶叶中主要的酚类物质,单体儿茶素表没食子儿茶素(epigallocatechin,EGC)、儿茶素(catechin ,C)、表儿茶素(epicatechin,EC)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(epigallocatechin gallate,EGCG)和表儿茶素没食子酸酯(epicatechin gallate,ECG)在不同地区的酸茶中均有报道,但没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(gallocatechin gallate,GCG)仅在德昂酸茶中检测发现[19, 24-26]。由于茶叶品种、采收季节、叶龄、气候以及种植管理方式的不同,不同地区酸茶中儿茶素的分布规律不尽相同 [13]。Nishioka等[25]对日本Naka和Kamikatsu地区的6个“Awaban-cha”酸茶样品中儿茶素进行了检测,结果显示不同地区、季节和原料制成的酸茶儿茶素含量及发酵前后的变化规律不同,但总体来说“Awaban-cha”中EGC和EGCG含量最多,发酵过程中乳酸菌产生的单宁酶可将EGCG降解为EGC和没食子酸,导致发酵后EGC含量增加。缅甸酸茶“Laphet”中以EGC和EC为主,EGC含量从原料茶中未检出到发酵后显著增加[19]。德昂酸茶与缅甸酸茶类似,含量最多的儿茶素是EGC和EC,发酵过程中EGC显著增加,C、EC、ECG和EGCG则明显减少[20, 26]。EC作为一类简单儿茶素,在pH较低的酸性环境中比其他儿茶素稳定性更强,因此EC在酸茶中可以维持较高含量[27]。不同地区的泰国酸茶中儿茶素含量存在一定差异,来自清迈San-kampang地区和南邦Muangpan 地区的酸(sour)和涩(astrigent)的泰国酸茶“Miang”中均有检测到EGCG和EGC,EGCG含量高于EGC,C未有检出,而清迈Mae-Tang 地区和帕府Meuang地区的酸茶“Miang”中含量最为丰富的是儿茶素C [21]。酸茶中酯型儿茶素降解产生的没食子酸进一步代谢产生邻苯三酚[27],邻苯三酚、EC和表阿夫儿茶精还可被还原为二苯丙烷衍生物[28]。
综上所述,酸茶发酵过程中总多酚含量增加,酸茶中主要多酚物质儿茶素组成发生变化,一般来说,酸茶发酵过程中酯型儿茶素含量降低,而非酯型儿茶素含量如EGC和EC含量显著增加,并代谢产生没食子酸、邻苯三酚、二苯丙烷衍生物等化学成分。
3. 酸茶中的微生物多样性
不同地区的酸茶中参与其发酵的微生物有一定差异,表1对不同酸茶中的微生物组成进行了总结。
表 1 酸茶微生物的发生情况Table 1. Microorganism composition in some pickled tea参与酸茶发酵的细菌主要有乳酸菌和芽孢杆菌,其中植物乳杆菌广泛存在于不同地区的酸茶。例如,德昂酸茶主要参与发酵的乳杆菌是植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)和嗜酸乳杆菌(Lactobacillus acidophilus)。泰国酸茶中主要参与发酵的乳杆菌有植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum)、Lactobacillus thailandensis sp. Nov、山茶乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus camelliae sp. Nov)、牛豆乳杆菌(Lactobacillus vaccinostercus)和戊糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus pentosus)。缅甸酸茶中参与发酵的乳杆菌则是以植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum)和丘状乳杆菌(L. collinoides)为主。日本酸茶中植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum)是参与发酵的主要乳杆菌。
酸茶中的真菌主要包括酵母菌和霉菌。例如,德昂酸茶和缅甸酸茶中参与发酵的真菌主要是酵母菌。德昂酸茶中是拉钱斯氏酵母(Lachancea fermentati);缅甸酸茶中参与发酵的真菌主要是曼氏毕赤酵母(Pichia manshurica)、博伊丁假丝酵母(Candida boidinii)和杰丁塞伯林德纳氏酵母(Cyberlindnera jadinii)。日本酸茶“Goishi-cha”中参与发酵的真菌则主要是烟曲霉(Aspergillus fumigatus)、黑曲霉(Aspergillus niger)、青霉菌属(Penicillium sp.)及短帚霉真菌(Scopulariopsis brevicaulis)[29-31]。
近年来,国内外学者对酸茶乳酸菌和真菌开展了分离鉴定研究。肖平等[32]采用传统培养分离法从实验室研制的酸茶中分离得到8株细菌和2株酵母菌,经过鉴定发现细菌均为植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)、酵母菌均为麦芽糖假丝酵母(Canadida maltosa)。万晶琼等[31]在德昂酸茶中分离得到19株细菌和4株真菌,细菌中5 株为芽孢杆菌种(Bacillus tequilensis),6 株为枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis),6株为芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus sp.),1株为不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter sp.),1株为解淀粉芽孢杆菌(Bacillus amyloliquefaciens);真菌中1株为微小根毛霉(Rhizomucor pusillus)、1株为Lachancea fermentati strain yHRM72、2株为酵母属真菌(Unclassified Saccharomycetales)。Cao等[33]从云南德宏的德昂族酸茶中分离得到的25株革兰氏阳性、过氧化氢酶阴性的菌株,采用16S rRNA基因序列分析方法,对德昂族酸茶分离的25株菌株进行鉴定,结果显示24株为植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum),其中1株为嗜酸乳杆菌(Lactobacillus acidophilus)。郭天杰等[34]从德昂酸茶中分离鉴定出芽孢杆菌 (Bacillus)、不动杆菌(Acinetobacte)、根毛霉 (Rhizomucor)、Lachancea和酵母(Saccharomycetales)等,经鉴定有乳杆菌(Lactobacillus)、乳球菌(Lactococcus)、肠球菌(Enterococcus)等微生物。Tanasupawa 等[30,35]发现泰国酸茶“Miang”中主要乳酸菌为Lactobacillus thailandensis sp. Nov、山茶乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus camelliae sp. Nov)、植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum)、Pediococcus siamensis sp. Nov、戊糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus pentosus)、牛豆乳杆菌(Lactobacillus vaccinostercus)和戊糖片球菌(Pediococcus)。Bo等[36]从“Lahpet”样品中分离得到8株乳酸菌和9株酵母菌,细菌中的优势菌株为植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus platarum)和丘状乳杆菌(L. collinoides),酵母中的优势菌株为曼氏毕赤酵母(Pichia manshurica)、博伊丁假丝酵母(Candida boidinii)和杰丁塞伯林德纳氏酵母(Cyberlindnera jadinii)。Okada等[37]研究发现,日本发酵茶“Goishi-cha”发酵的第一阶段主要包括烟曲霉(Aspergillus fumigatus)、黑曲霉(Aspergillus niger)、青霉菌属(Penicillium sp.)及短帚霉真菌(Scopulariopsis Brevicaulis)等真菌,再经过厌氧发酵后仅能分离到植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum)。而从 “Awaban-cha”中分离出的乳酸菌均为植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum)[38]。
由于茶叶中含有广谱抗菌化合物单宁酸和茶多酚,因此酸茶中还分布有耐单宁酸和茶多酚的芽孢杆菌。Rungsirivanich等[29]从泰国酸茶“Miang”中分离获得的16株芽孢杆菌,隶属于地衣芽孢杆菌(Bacillus licheniformis)、暹罗芽孢杆菌(Bacillus siamensis)和特基拉芽孢杆菌(Bacillus tequilensis),这些芽孢杆菌除了具有耐单宁酸和茶多酚的能力,还具有抗菌的作用,在 “Miang”的发酵过程中起到了一定的生物防治作用。
综上所述,因加工工艺和地域的差异,不同地区的酸茶微生物种类的组成和比例具有明显差异,其中德昂、泰国和缅甸酸茶中主要微生物是植物乳杆菌、芽孢杆菌和酵母菌,日本酸茶“Awaban-cha”和“Goishi-cha”微生物结构不同,前者主要微生物是霉菌和植物乳杆菌,后者主要微生物是植物乳杆菌,表明揉茶工艺可能影响酸茶微生物组成。然而,目前研究主要集中于酸茶中微生物的种类,但其生化、酶学、加工特性等研究鲜有报道,需要在今后的研究深入阐明。
4. 酸茶中的风味物质
风味物质的组成对茶叶品质有重要影响,是决定茶产品品质和市场接受度的关键指标之一[39]。茶叶的风味是香气和滋味的综合作用,香气主要由挥发性成分决定,它对茶叶品质的贡献率高达25%~40%[40],而滋味主要包括茶多酚、氨基酸和可溶性多糖等呈味物质[41]。韩丽等[42] 研究发现,布朗酸茶中含量较高的香气物质分别为:氧化芳樟醇、芳樟醇、顺-3-己烯基丁酯、水杨酸甲酯、2-乙基苯酚、香叶醇、α-法尼烯和丙酸芳樟醇,占了酸茶总香气含量的 77.84%;且其中氧化芳樟醇Ⅰ 、Ⅱ、Ⅲ和Ⅳ含量占了酸茶香气成分总量的 49.70%。Kawakami等[43]采用气相色谱-质谱技术对日本酸茶“Goishi-cha”和“Awaban-cha”的香气成分进行分析,结果显示两种酸茶的香气基础均是(Z)-3-己烯醇、芳樟醇及其氧化物、水杨酸甲酯、苯甲醇、2-苯乙醇、乙酸和4-乙基苯酚,且随着发酵过程的进行,产生了新的物质如脂肪醇(包括3-戊醇、2-戊醇、2-甲基丙醇、丁醇和壬醇)和酸(如2-甲基丙酸、2-甲基丁酸、己酸和辛酸)。Michiko等[44]发现泰国酸茶“Miang”的香气浓缩物的主要成分是(Z)-3己烯醇、芳樟醇、氧化芳樟醇I、II、III、IV和水杨酸甲酯;醇类物质中脂肪醇含量最高为19.3%~21.4%,与蒸煮杀青而未发酵的茶叶相比,酸茶中仲醇(如2-丁醇、2-庚醇、4-庚-2-醇和1-辛-3-醇)和芳香醇(如苯甲醇和2-苯乙醇)的含量均显著增加;此外,在“Miang”还中检测到酚类化合物如4-甲基愈创木酚、4-乙基愈创木酚、4-丙基愈创木酚和异丁香酚,这些酚类可能是阿魏酸的降解产物,为“Miang”贡献了烟熏味。
综上所述,因酸茶发酵工艺的差异及地域文化的不同,所以各类酸茶的风味和成分也有一定的差异。酸茶中主要挥发性成分是氧化芳樟醇和水杨酸甲酯;发酵过程中,由于微生物的作用酸茶中的氨基酸和咖啡碱含量会减少,而醇类化合物含量增加,酸茶的香气也由原来的清香转变为浓烈的酸味、略带清凉的香型。
5. 酸茶的生物学功效
在乳酸菌等优势微生物的发酵作用下,酸茶中的儿茶素、黄酮、单宁等活性成分的含量和组成发生变化,并代谢产生了新的活性成分,同时酸茶中含有具有益生功能的乳酸菌、芽孢杆菌等菌株,使酸茶具有抗氧化、抗菌、调节代谢综合征等生物学功效[33,45]。
5.1 抗氧化活性
大量研究发现(表2),酸茶具有清除自由基、铁离子还原力和铜离子还原活性,已有报道酸茶中的多酚、单宁、黄酮、儿茶素、蛋白质、脂肪、新代谢物和乳酸菌具有抗氧化活性。
茶多酚能通过促进电子转移及氢原子传递,提高氧化还原电势,清除自由基及与金属离子活性中心发生螯合等机制发挥抗氧化作用[46]。Unban等[11]发现泰国酸茶“Miang”中的总多酚、总单宁、总黄酮类化合物和总儿茶素有良好的1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl Free Radical,DPPH)自由基清除能力;且除了酚类化合物,其他特定的化合物如生物转化蛋白质和脂肪,也可能有助于抗氧化性能。有研究表明,酸茶比鲜茶具有更强或者相当的抗氧化活性。Maung等[18]比较了缅甸酸茶“Laphet”和鲜茶的DPPH自由基清除活性,结果发现经发酵后的“Laphet”比鲜茶具有更强的抗氧化活性。Horie等[9]研究发现日本发酵茶“Goishi-cha”和 “Awaban-cha”的水提物具有较强的铜离子还原能力。Hiasa等[47]研究证实“Awaban-cha”含有一种特殊的抗氧化剂间苯二酚,该化合物是由乳酸菌厌氧发酵产生,间苯二酚的抗氧化活性与EGCG相当,间苯二酚还可以以浓度依赖型方式降低人脐静脉内皮细胞内的活性氧水平。
研究报道,酸茶中分离获得的乳酸菌也具有良好抗氧化活性。Cao等[33]研究发现从德昂酸茶中分离的植物乳杆菌ST和STDA10均具有较强的DPPH和2 ,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(2,2'-Azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate),ABTS)自由基清除率。Kridsada等[30]从泰国“Miang”样品中分离的戊糖乳杆菌和植物乳杆菌具有DPPH自由基清除能力,这些被选择的乳酸菌菌株也显示出用于商业益生元组合的特异性和对喷雾干燥过程的耐受性;其中,戊糖乳杆菌(L. pentosus A14-6)抗氧化活性最好,其细胞抗氧化特性支持其应用于各种食品或共生物保健品的开发。
5.2 抗菌活性
Cao等[33]采用琼脂孔扩散测定了从德昂酸茶中分离出的18种微生物抗菌活性,结果发现,所有菌株均表现出对鼠伤寒杆菌和大肠杆菌的抑制作用,18株菌株中有11株对鼠伤寒杆菌具有较强的抑菌活性;植物乳杆菌STDA5和ST对大肠杆菌表现出更强的抑制作用。Rungsirivanich等[29]采用琼脂孔扩散测定了从泰国酸茶“Miang”中分离出的微生物抗菌活性,其中暹罗芽孢杆菌(B. siamemsis)ML122-2、ML123-1和ML124-1对金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923)和Methicillin resistant S. aureus DMST 20625具有抑制作用,地衣芽孢杆菌(B. licheniformis) ML071-1、ML073-1、ML075-1和ML076-2对蜡样芽孢杆菌(B. cereus TISTR 687)和金色葡萄球菌(S. aureus ATCC 25923)具有抑制作用。Unban等[22]从泰国酸茶“Miang”中分离出的芽孢杆菌中,大部分芽孢杆菌和培养上清液会对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Typhimurium TISTR 292)产生抗菌活性。此外,Unban等[11]发现“Miang” 水提物对龋齿致病菌变形链球菌、胃肠道疾病霍乱弧菌、血清肠沙门菌和鼠伤寒沙门氏菌具有抗菌活性。Srikanjana等[48]从泰国酸茶“Miang”中分离出的发酵乳杆菌(Lactobacillus fermentum) FTL2311和FTL10BR对单增李斯特菌(Listeria monocytogenes DMST 17303)、伤寒沙门氏菌(Salmonella typhi DMST 5784)、志贺氏菌(Shigella sonnei DMST 561)和金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus DMST 6512)具有抗菌活性;并对其抗菌机理进行研究,结果表明发酵乳杆菌对致病菌细胞膜的破坏,从而导致致病菌细胞萎缩或开裂。
5.3 调节代谢综合征
代谢综合征是指机体同时存在多种代谢紊乱,如碳水化合物和脂肪等物质代谢发生紊乱而引起的糖尿病与心脑血管疾病等多种疾病的病理状态[49]。
酸茶中含有丰富的茶多酚,茶多酚具有降血脂作用。其主要机制包括:促进胃肠道蠕动,加速脂类物质消化代谢;抑制胰脂酶活性,阻碍吸收脂肪;抑制脂质过氧化以及脂类物质在血管内皮的沉积;提高肝酯酶活性;增强对激素敏感性脂肪酶的活性等[50]。此外,茶多酚和EGCG可以改善胰岛素抵抗、降低血清炎性因子水平,对高脂饮食诱发的小鼠肥胖、代谢综合征和脂肪肝均有良好的抑制效应[51]。Amiot等[52]针对饮食中摄入多酚类物质对代谢综合征的作用进行了分析,结果显示,茶多酚可显著降低体质量指数、腰围和改善脂类代谢,对代谢综合征具有一定的防治效果。Hiasa等[53]研究通过给小鼠口服麦芽糖、蔗糖或葡萄糖来升高小鼠的血糖,再通过给小鼠灌胃日本酸茶“Awaban-cha”水提取物,结果发现:与对照组(蒸馏水)相比,日本酸茶“Awaban-cha”对血糖曲线下面积(AUC)的抑制率达到了72%~83%,说明日本酸茶“Awaban-cha”可以通过降低血糖含量等机制来调节机体血糖平衡。Misako等[54]报道通过给大鼠灌胃3%的日本酸茶“Awaban-cha”提取物后,与对照组(不含任何茶提取物)相比,显著降低了大鼠的体重,体脂率与对照组相比也显著降低,这表明了酸茶中的活性物质具有抗肥胖的作用。杨卫星等[55]用德昂酸茶对高脂饮食小鼠进行干预,结果发现酸茶水提物能显著抑制高脂饮食小鼠白细胞数、中性粒细胞数、单核细胞数及淋巴细胞数,同时可以显著降低高脂饮食小鼠血清甘油三酯、谷丙转氨酶及肝脏谷草转氨酶活性;并且通过对肝脏组织形态学观察,发现酸茶水提物对小鼠高脂饮食所引起的肝脏损伤,如:脂肪堆积、变性和浸润细胞增加具有一定的保护和改善作用。卢薇等[56]研究发现,通过给大鼠灌胃德昂酸茶水浸提物,降低大鼠血清中谷草转氨酶、谷丙转氨酶活性,有效地降低了非酒精性脂肪肝,同时降低大鼠血清中总胆固醇和甘油三酯的含量,增加高密度脂蛋白总胆固醇的水平;升高大鼠血清和肝脏组织谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和超氧化物歧化酶的活性。
综上所述,酸茶能够通过清除自由基来减少过氧化环境的形成而发挥抗氧化作用,多酚及其代谢物是酸茶的抗氧化活性成分;酸茶中的乳酸菌、芽孢杆菌、酚类化合物以及发酵产生的有机酸等能显著抑制大肠杆菌等食源性致病菌增殖;尽管动物实验支持了酸茶提取物的降脂和降血糖作用,但其活性组分或成分及作用机制有待阐明,这将为酸茶作为功能性食品应用与代谢综合症人群的膳食干预提供依据。
6. 结论
酸茶由于其独特的风味和人文历史特点,成为了我国西南地区以及泰国、日本、缅甸等东南亚国家的传统特色民族食品。近年来研究发现酸茶具有优良的抗氧化活性、抗菌活性以及调节代谢综合征等生物学功效,且有研究显示酸茶具有与绿茶相当或更强的生物学活性,使酸茶在食品的保鲜及功能性食品研发中具有巨大发展潜力。本研究团队从酸茶中分离得到具有优良益生特性、抗氧化及免疫调节功能的植物乳杆菌菌株,且具有良好的多酚耐受性,这可能与酸茶中酸性和高多酚环境有关,表明酸茶蕴含的益生乳酸菌资源有待深入挖掘,且使酸茶有望成为添加益生菌的新型食品载体。本文总结发现,酸茶主要以家庭式或者手工作坊式自然发酵方式制备,微生物群落复杂,导致潜在有害微生物滋生、品质不稳定、产品安全性等问题,在今后的研究中,需要采用多组学手段深入、系统研究酸茶发酵过程中原料处理、加工工艺、微生物组成与品质的关系,开展有害微生物控制及安全性评价,研发酸茶发酵剂,为提高酸茶的品质及标准化生产提供理论依据。
-
表 1 酸茶微生物的发生情况
Table 1 Microorganism composition in some pickled tea
-
[1] 成功, 傅玮琳. 德昂族酸茶传统知识的保护与可持续发展[C]. 中国内蒙古呼和浩特: 第八届中国民族植物学学术研讨会暨第七届亚太民族植物学论坛, 2016: 104−105 CHENG G, FU W L. Protection and sustainable development of traditional knowledge of De'ang sour tea [C]. Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China: 8th China Ethnobotany Academic Symposium and 7th Asia Pacific Ethnobotany Forum, 2016: 104−105.
[2] 酸茶的味道, 微酸回甘的记忆[J]. 茶博览, 2013(2): 78−80. The taste of sour tea, a slightly sour and sweet memory[J]. Tea Expo, 2013 (2): 78-80.
[3] MATHUR H, BERESFORD T P, COTTER P D. Health benefits of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) fermentates[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(6):1679. doi: 10.3390/nu12061679
[4] 杨庆益, 何彩梅, 龚福明, 等. 酸茶的研究现状与进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(1):312−317. [YANG Q, HE C M, GONG F M, et al. Research on pickled tea: Present and future[J]. Food Science,2020,41(1):312−317. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181118-200 YANG Q, HE C M, GONG F M, et al. . Research on pickled tea: present and future [J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(1): 312-317. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181118-200
[5] 李昶罕, 秦莹. 德昂族酸茶的科技人类学考察[J]. 云南农业大学学报(社会科学),2015,9(1):116−122. [LI Y H, QIN Y. Investigation on the De'ang nationality acid tea from the perspective of the anthropology of science and technology[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Social Sciences),2015,9(1):116−122. LI Y H, QIN Y. Investigation on the De'ang nationality acid tea from the perspective of the anthropology of science and technology [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Social Sciences), 2015, 9(1): 116-122.
[6] 李淳信. 德昂族独特的酸茶技艺[J]. 今日民族,2008(7):43−44. [LI C X. Unique pickled tea technique of De'ang nationality[J]. Today's Nation,2008(7):43−44. LI C X. Unique pickled tea technique of De'ang nationality [J]. Today's Nation, 2008(7): 43-44.
[7] 陈红伟. 布朗族与茶[J]. 中国茶叶加工,2000(3):46−47. [CHEN H W. Braun and tea[J]. Chinese Tea Processing,2000(3):46−47. doi: 10.15905/j.cnki.33-1157/ts.2000.03.018 CHEN H W. Braun and tea [J]. Chinese Tea Processing, 2000, (3): 46-47. doi: 10.15905/j.cnki.33-1157/ts.2000.03.018
[8] HAN T, AYE K N. The legend of Laphet: A Myanmar fermented tea leaf[J]. Journal of Ethnic Foods,2015,2(4):173−178. doi: 10.1016/j.jef.2015.11.003
[9] HORIE M, NARA K, SUGINO S, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities among four kinds of Japanese traditional fermented tea[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2017,5(3):639−645.
[10] 权启爱, 陈叙达, 郑旭霞, 等. 金占芭花开璀璨舞姿交融茶更香——老挝茶产业考察记[J]. 中国茶叶,2018,40(12):55−61. [QUAN Q A, CHEN X D, ZHENG X X, et al. Jinzhanba blossoms and dances, and tea is more fragrant - Investigation of tea industry in Laos[J]. Chinese Tea,2018,40(12):55−61. QUAN Q A, CHEN X D, ZHENG X X, et al. Jinzhanba blossoms and dances, and tea is more fragrant -- Investigation of tea industry in Laos [J]. Chinese Tea, 2018, 40(12): 55-61.
[11] UNBAN K, KHATTHONGNGAM N, SHETTY K, et al. Nutritional biotransformation in traditional fermented tea (Miang) from north Thailand and its impact on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology -Mysore-,2019,56(5):2687−2699. doi: 10.1007/s13197-019-03758-x
[12] KETWAL S, CHUEAMCHAITRAKUN P, THEPPAKORN T, et al. Contents of total polyphenol, microorganisms and antioxidant capacities of pickled tea (Miang) commercially available in chiang rai [C]. Thailand, proceedings of the The 16th Food Innovation Asia Conference, 2014: 1-11.
[13] CHARTCHAIKHANONGNUCH, KRIDSADAUNBAN, APINUNKANPIENGJAI, et al. Recent research advances and ethno-botanical history of miang, a traditional fermented tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica) of northern Thailand[J]. Journal of Ethnic Foods,2017,4(3):135−144. doi: 10.1016/j.jef.2017.08.006
[14] ADEBO O A, MEZA I. Impact of fermentation on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of whole cereal grains: A mini review[J]. Molecules,2020,25(4):927. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040927
[15] SALAR R K, CERTIK M, BREZOVA V. Modulation of phenolic content and antioxidant activity of maize by solid state fermentation with Thamnidium elegans CCF 1456[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering,2012,17(1):109−116. doi: 10.1007/s12257-011-0455-2
[16] WANG Y, COMPAORE-SEREME D, SAWADOGO-LINGANI H, et al. Influence of dextran synthesized in situ on the rheological, technological and nutritional properties of whole grain pearl millet bread[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,285:221−230. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.126
[17] WANG Y, KONG D, GAO Y, et al. Chemical characterization and bioactivity of phenolics from Tieguanyin oolong tea[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2019,43(7):e12894.
[18] MAUNG P P. Determination of flavonoids and antioxidant activity in Laphet laboratory process and tea (Camellia sinensis) products between china and myanmar[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science & Technology,2013,5(3):533-537.
[19] MAUNG P P, QIAN H, CHAMBA M. Comparison of polyphenol content between laboratory processed Laphet and China and Myanmar tea (Camellia sinensis) products [J]. Pakistan Journal of Food Sciences, 2012, 22(4): 180-184.
[20] 魏琳, 卢凤美, 邵宛芳, 等. 酸茶发酵过程中感官品质及主要成分变化分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(14):69−74. [WEI L, LU F M, SHAO W F, et al. Analysis of changes in sensory quality and main components of sour tea during fermentation[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(14):69−74. WEI L, LU F M, SHAO W F, et al. Analysis of changes in sensory quality and main components of sour tea during fermentation [J] Food Research and Development, 2019, 40 (14): 69-74.
[21] ABDULLAHI A D, KODCHASEE P, UNBAN K, et al. Comparison of phenolic contents and scavenging activities of miang extracts derived from filamentous and non-filamentous fungi-based fermentation processes[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2021,10(7):1144. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071144
[22] UNBAN K, KOCHASEE P, SHETTY K, et al. Tannin-tolerant and extracellular tannase producing bacillus isolated from traditional fermented tea leaves and their probiotic functional properties[J]. Foods,2020,9(4):490. doi: 10.3390/foods9040490
[23] 许原, 吕峰, 刘崇禧. 乳酸菌发酵对武夷岩茶咖啡因含量的影响及活性评价[J]. 湖北农业科学,2014,53(18):4399−4401. [XU Y, LU F, LIU C X. Effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on caffeine content and activity evaluation of Wuyi rock tea[J]. Hubei Agricultural Science,2014,53(18):4399−4401. XU Y, LU F, LIU C X Effect of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on caffeine content and activity evaluation of Wuyi rock tea [J] Hubei Agricultural Science, 2014, 53 (18): 4399-4401.
[24] PHROMRUKACHAT S, TIENGBURANATUM N, NEECHUI J. Assessment of active ingredients in pickled tea [J]. Asian Journal of Food & Agro Industry, 2010.
[25] NISHIOKA H, MIZUNO T, IWAHASHI H, et al. Changes in lactic acid bacteria and components of Awa-bancha by anaerobic fermentation[J]. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,2020,84(9):1921−1935. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2020.1771677
[26] 潘洪彬, 曹振辉, 黄艾祥, 等. 德昂酸茶的主要理化成分及腌制后期乳酸菌的分离、鉴定[C]//石家庄: 乳酸菌健康及产业化: 第十一届乳酸菌与健康国际研讨会, 2016: 87−88 PAN H B, CAO Z H, HUANG A X, et al. The main physicochemical components of De'ang sour tea and the isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria during the later stage of pickling[C]//Shijiazhuang: Lactic Acid Bacteria Health and Industrialization: 11th International Symposium on Lactic Acid Bacteria and Health, 2016: 87−88.
[27] CHEN Z, ZHU Q Y, TSANG D, et al. Degradation of green tea catechins in tea drinks[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2001(1):49.
[28] SHII T, ASADA C, MATSUO Y, et al. Polyphenols in Lahpet-so and two new catechin metabolites produced by anaerobic microbial fermentation of green tea[J]. J Nat Med,2014,68(2):459−464. doi: 10.1007/s11418-014-0816-1
[29] RUNGSIRIVANICH P, THONGWAI N. Antibacterial activity and tannin tolerance of Bacillus spp. isolated from leaves of miang (Camellia sinensis (L. ) Kuntze var. assamica (J. W. Mast. ) Kitam. ) [C]. Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Environment, Energy and Biotechnology (ICEEB 2019), 2019: 26−33.
[30] KRIDSADA U, WIRUNYA C, SASITORN B, et al. Probiotic and antioxidant properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from indigenous fermented tea leaves (miang) of north Thailand and promising application in synbiotic formulation[J]. Fermentation,2021,7(3):195. doi: 10.3390/fermentation7030195
[31] 万晶琼. 酸茶发酵样品微生物与化学成分研究[D]. 昆明: 云南农业大学, 2016 WAN J Q. Study on microorganism and chemical composition of pickled tea fermentation samples[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Agricultural University, 2016.
[32] 肖平. 酸茶微生物菌系分离与鉴定及茶酒发酵技术研究[D]. 湖北: 华中农业大学, 2012 XIAO P. Isolation and identification of acid tea microbial strains and study on tea wine fermentation technology [D]. Hubei: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2012.
[33] CAO Z, PAN H, LI S, et al. In vitro evaluation of probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Yunnan De'ang pickled tea[J]. Probiotics & Antimicrobial Proteins,2019,11(1):103−112.
[34] 郭天杰, 王利妍, 段双梅, 等. 酸茶发酵样品微生物与化学成分研究[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(2):322−327. [GUO T J, WANG L Y, DUAN S M, et al. Study on microbial and chemical components of sour tea fermentation samples[J]. Food Industry,2019,40(2):322−327. GUO T J, WANG L Y, DUAN S M, et al. Study on microbial and chemical components of sour tea fermentation samples [J]. Food Industry, 2019, 40(2): 322-327.
[35] TANASUPAWAT S, PAKDEETO A, THAWAI C, et al. Identification of lactic acid bacteria from fermented tea leaves (miang) in Thailand and proposals of Lactobacillus thailandensis sp. Nov. , Lactobacillus camelliae sp. Nov., and Pediococcus siamensis sp. Nov[J]. Journal of General & Applied Microbiology,2007,53(1):7−15.
[36] BO B, KIM S A, HAN N S. Bacterial and fungal diversity in Laphet, traditional fermented tea leaves in Myanmar, analyzed by culturing, DNA amplicon-based sequencing, and PCR-DGGE methods[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2020,320:108508. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108508
[37] OKADA S, TAKAHASHI N, OHARA N, et al. Microorganisms in fermentation of Goishi-cha, Japanese fermented tea leaves microorganisms involving in the fermentation of Japanese fermented tea leaves part II[J]. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi,1996,43(9):1019−1027. doi: 10.3136/nskkk.43.1019
[38] MASANORI H, HIROAKI S, ATSUMI T, et al. Regional characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum group strains isolated from two kinds of Japanese post-fermented teas, Ishizuchi-kurocha and Awa-bancha[J]. Bioscience of Microbiota, Food and Health,2019,38(1):11−22. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.18-005
[39] 陈梅春, 陈峥, 史怀, 等. 陈年普洱茶特征风味成分分析[J]. 茶叶科学,2014,34(1):45−54. [CHEN M C, CHEN Z, SHI H, et al. Analysis of characteristic flavor components of aged Pu'er tea[J]. Tea Science,2014,34(1):45−54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2014.01.008 CHEN M C, CHEN Z, SHI H, et al. Analysis of characteristic flavor components of aged Pu'er tea [J]. Tea Science, 2014, 34 (1): 45-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2014.01.008
[40] 刘晓慧, 张丽霞, 王日为, 等. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用法分析黄茶香气成分[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(16):239−243. [LIU X H, ZHANG L X, WANG R W, et al. Analysis of aroma components of yellow tea by headspace solid phase microextraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2010,31(16):239−243. LIU X H, ZHANG L X, WANG R W, et al. Analysis of aroma components of yellow tea by headspace solid phase microextraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry [J]. Food Science, 2010, 31(16): 239-243.
[41] 刘盼盼, 邓余良, 尹军峰, 等. 绿茶滋味量化及其与化学组分的相关性研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2014,14(12):173−181. [LIU P P, DENG Y L, YIN J F, et al. Study on the quantification of green tea taste and its correlation with chemical components[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2014,14(12):173−181. LIU P P, DENG Y L, YIN J F, et al. Study on the quantification of green tea taste and its correlation with chemical components [J]. Chinese Journal of Food, 2014, 14 (12): 173-181.
[42] 韩丽, 罗向前, 谢志英, 等. 布朗族酸茶理化及香气成分初步研究[J]. 西南农业学报,2011,24(2):504−508. [HAN L, LUO X Q, XIE Z Y, et al. Preliminary study on physicochemical and aroma components of brown Pickled tea[J]. Southwest Agricultural Journal,2011,24(2):504−508. HAN L, LUO X Q, XIE Z Y, et al. Preliminary study on physicochemical and aroma components of brown Pickled tea [J]. Southwest Agricultural Journal, 2011, 24 (2): 504-508.
[43] KAWAKAMI M, UCHIDA H, KOBAYASHI A, et al. The effects on Awa-cha flavor of Pickling and solar-drying[J]. Agricultural and biological chemistry,1989,53(1):271−275.
[44] MICHIKO, KAWAKAMI, GRIANGSAK, et al. Flavor constituents of pickled tea, miang, in Thailand[J]. Agricultural & Biological Chemistry,1987,51(6):1683−1687.
[45] REICHART P A. Oral cancer and precancer related to betel and miang chewing in Thailand: A review[J]. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine,2010,24(6):241−243.
[46] KARAOSMANOGLU H, KILMARTIN P A. Tea extracts as antioxidants for food preservation [J]. Handbook of Antioxidants for Food Preservation, 2015: 219-233.
[47] HIASA M, KUROKAWA M, OHTA K, et al. Identification and purification of resorcinol, an antioxidant specific to Awa-ban (pickled and anaerobically fermented) tea[J]. Food Research International,2013,54(1):72−80. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.05.036
[48] SRIKANJANA K, SIRIPORN O. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of acid and bile resistant strains of Lactobacillus fermentum isolated from miang[J]. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology,2009,40(4):757−766. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822009000400005
[49] 吴峰, 葛华, 赵安东, 等. 茶多酚防治糖脂尿酸代谢异常及代谢综合征研究进展[J]. 人民军医,2021,64(7):667−671. [WU F, GE H, ZHAO A D, et al. Research progress of tea polyphenols in preventing and treating abnormal metabolism of glycolipid and uric acid and metabolic syndrome[J]. People's Military Medical Journal,2021,64(7):667−671. WU F, GE H, ZHAO A D, et al. Research progress of tea polyphenols in preventing and treating abnormal metabolism of glycolipid and uric acid and metabolic syndrome [J]. People's Military Medical Journal, 2021, 64 (7): 667-671.
[50] 武芳芹. 茶多酚功能及其调节脂类物质代谢机理研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技,2015(21):286−287. [WU F Q. Research Pro-gress of tea polyphenols function and its mechanism of regulating lipid metabolism[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2015(21):286−287. WU F Q. Research Progress of tea polyphenols function and its mechanism of regulating lipid metabolism [J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, (21): 286-287.
[51] YU-KUO C, CONNIE C, R R K, et al. Effects of green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on newly developed high-fat/western-style diet-induced obesity and metabolic syndrome in mice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(21):11862−11871.
[52] AMIOT M J, RIVA C, VINET A. Effects of dietary polyphenols on metabolic syndrome features in humans: A systematic review[J]. Obesity Reviews,2016,17(7):573−586.
[53] HIASA M, KUROKAWA M, AKITA H, et al. Suppression of increased blood glucose levels in mice by Awa-ban tea following oral administration of mono- and disaccharides[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2014,8(1):188−192.
[54] MISAKO S, TAKAHIRO S, SHOHEI K, et al. Awa (Tokushima) lactate-fermented tea as well as green tea enhance the effect of diet restriction on obesity in rats[J]. Journal of Medical Investigation Jmi,2009,56(1,2):42. doi: 10.2152/jmi.56.42
[55] 杨卫星, 杨莉, 侯艳, 等. 酸茶对高脂饮食小鼠白细胞、血脂及肝功能的影响[J]. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2019,40(4):89−94. [YANG W X, YANG L, HOU Y, et al. Effects of pickled tea on leukocyte, blood lipid and liver function in mice fed with high fat diet[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agriculture and Life Sciences),2019,40(4):89−94. YANG W X, YANG L, HOU Y, et al. Effects of pickled tea on leukocyte, blood lipid and liver function in mice fed with high fat diet [J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2019, 40 (4): 89-94.
[56] 卢薇, 邵宛芳, 卢凤美, 等. 德昂族酸茶防治非酒精性脂肪肝作用的研究[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2020,35(1):114−121. [LU W, SHAO W F, LU F M, et al. The preventive effect of suancha from De’ang nationality on non-alcoholic fatty liver[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science),2020,35(1):114−121. doi: 10.12101/j.issn.1004-390X(n).201909029 LU W, SHAO W F, LU F M, et al. The preventive effect of suancha from De’ang nationality on non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2020, 35(1): 114-121. doi: 10.12101/j.issn.1004-390X(n).201909029
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 孙婷婷,魏彤竹,王晓丹,王伟杰,李雪. 辽宁省2021—2022年餐饮食品蜡样芽胞杆菌毒力基因和耐药特征检测. 中国热带医学. 2024(02): 223-227 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨景,王崇林,张蕾. 2017—2021年德州市食品风险监测蜡样芽孢杆菌检出情况. 中国当代医药. 2024(09): 141-143+148 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 贾伟娟,宋丽丽,张玲艳,王学理. 蜡样芽胞杆菌毒素的最新研究进展. 中国抗生素杂志. 2022(06): 534-542 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



