Analysis of Differential Metabolites between NFC and FC Bayberry Juice Based on UPLC-QTOF-MS
-
摘要: 为探究浓缩还原(From concentrate,FC)和非浓缩还原(Not from concentrate,NFC)杨梅汁成分的差异,本文借助超高效液相色谱-四极杆飞行时间质谱的代谢组学技术分析二者的代谢产物。通过正交偏最小二乘-判别分析实现了对NFC和FC杨梅汁的区分,根据变量投影重要度和差异倍数筛选出9个差异较大的代谢物,经对比发现,FC杨梅汁中对磺基苯甲酸、5-甲基四氢叶酸、矢车菊素、西瑞香素、花椒毒酚和异黄蝶呤等抗氧化活性成分的含量相对较低,而苦味物质(新橙皮苷、橙皮苷和槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷)含量相对较高。通过对差异代谢物的代谢途径分析,筛选出5条差异较大的代谢通路,其中苯丙氨酸代谢、黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成是NFC与FC杨梅汁中差异代谢物的关键代谢途径。本研究揭示了NFC与FC杨梅汁代谢产物的差异性,为NFC杨梅汁的加工与鉴别提供理论参考。
-
关键词:
- 非浓缩还原杨梅汁 /
- 超高效液相色谱-四级杆飞行时间质谱 /
- 代谢组学 /
- 代谢通路
Abstract: This study analyzed the differential composition between from concentrate (FC) and not from concentrate (NFC) bayberry juices by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS). NFC and FC bayberry juice were distinguished from each other by orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis, and 9 compounds that significantly differed in abundance between them were selected and identified according to the variable importance in the projection and the fold-change. By comparison, the content of antioxidant active components such as 4-sulfobenzoate, 5-methyltetrahydrofolic acid, cyanidin, daphnoretin, xanthotoxol and isoxanthopterin in FC bayberry juice were relatively low, whereas the bitter substances (neohesperidin, hesperidin and quercetin-3-O-neohesperidin) were relatively high. Metabolic pathways were analyzed on account of differential metabolites and five metabolic pathways with great differences were identified, among which phenylalanine metabolism, biosynthesis of flavonoids and flavonols were the key metabolic pathways of different metabolites in NFC and FC bayberry juice. This study revealed the difference of metabolites between NFC and FC bayberry juice, which provided theoretical reference for the processing and identification of NFC bayberry juice. -
杨梅(Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc
)是中国江南地区的珍贵水果之一,其营养功效丰富、品质风味独特,含有多种对人体有益的生物活性成分[1]。但其成熟于江南梅雨季节,采后极不耐储,通常被加工成杨梅干和杨梅汁等[2]。非浓缩还原果汁(NFC)是鲜榨果汁经巴氏杀菌后直接灌装而成的,既能保持果实原有风味,又能最大限度的保留果实中的各种功能性成分和营养物质,但价格偏高[3-4]。而浓缩还原果汁(FC)是由NFC果汁经浓缩、还原和杀菌等复杂过程制备而成且价格偏低,但该过程易导致品质风味物质劣变[5]。对于NFC与FC果汁成分的差异,研究学者针对化合物、同位素比例等做了一定的研究。Sun等[6]通过HS-SPME-GC-MS结合化学计量学对NFC与FC橙汁鉴别,筛选出25种差异化合物。有研究学者对NFC与FC橙汁中稳定同位素比率δD、δ18O进行分析,发现NFC橙汁的同位素含量明显高于FC橙汁[7]。但由于检测限、检测准确性等问题限制了上述技术在果汁行业的广泛应用。 代谢组学技术作为继基因组学、转录组学和蛋白组学后的新兴组学,因其灵敏度、分辨率高等优势,在食品的品质评估与溯源中得到广泛应用[8-9]。杨天铭等[10]基于UPLC-QTOF-MS技术在黄龙病脐橙与正常脐橙中鉴定出28个差异化合物。屠燕等[11]基于UPLC-QTOF-MS技术在不同产地丹参药材中鉴定出22个差异化学成分。刘晗璐等[12]基于代谢组学技术在NFC和FC橙汁中筛选并鉴定出16种差异化合物。Xu等[13]利用非靶向代谢组学技术对NFC橙汁和FC橙汁进行了鉴别,鉴定出13个潜在标记物,其中7个三肽标记物首次被报道。目前对于NFC/FC果汁的鉴别主要以橙汁为主,对于杨梅汁的研究主要集中在不同品种、贮藏期间的品质及风味变化,而对NFC/FC杨梅汁的差异性成分研究较少。因此本研究借助UPLC-QTOF-MS代谢组学技术结合多元统计分析等方法,根据代谢通路途径从植物代谢组学角度初步揭示NFC杨梅汁和FC杨梅汁差异代谢产物,旨在为NFC与FC杨梅汁成分差异分析提供理论和数据参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
实验原料为八成熟的仙居东魁杨梅(Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc
) 采集自中国浙江省台州市。由于杨梅果实的收获季节为5月至7月,本研究以每半月取一批次样品,并将采摘后挑选新鲜无伤害的置于−80 ℃冰箱保存,直至使用;甲醇、乙腈、甲酸 质谱级,购自Sigma-Aldrich。 MJ-JS2018A榨汁机 广东美的集团股份有限公司;DK-S12电热恒温水浴锅 上海森信实验仪器有限公司;ExionLC AD型超高效液相色谱 日本岛津公司;QTrap 6500型四极杆串联飞行时间质谱仪 美国AB Sciex公司;Heraeus Fresco17离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;MS 3 digital涡旋振荡器 德国IKA公司;ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3(1.8 μm 2.1 mm×100 mm)色谱柱 上海拜力生物科技有限公司;R3088真空旋转蒸发仪 美国Senco公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 杨梅汁的制备
参照刘晗璐等[12]的方法并略作修改。NFC杨梅汁的制备:将冷冻的杨梅果在室温下解冻后榨汁,使用4层纱布过滤除去果渣,将过滤的果汁置于耐高压聚乙烯塑料瓶中进行巴氏杀菌(80 ℃,10 min),冷却至室温置于−l80 ℃储存。
FC杨梅汁的制备:将NFC杨梅汁置于真空旋转蒸发仪中,60 ℃水浴下浓缩1 h左右直至糖度为60±1ºBrix,再使用纯净水复配至原始糖度值,置于耐高压聚乙烯塑料瓶中并进行巴氏杀菌(80 ℃,10 min),杀菌后迅速冷却至室温并置于−80 ℃储存。
1.2.2 样品前处理
将NFC和FC杨梅汁样品在4 ℃条件下以12000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液,使用提取液(甲醇:水=3:1)稀释5倍,涡旋30 s将其充分混合,经0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤,转移至1.5 mL进样小瓶中,等待上机检测。每个样品进行6次平行测定。
1.2.3 UPLC-QTOF-MS分析条件
参照Yang等[14]的方法并略作修改。色谱条件:色谱柱为ACQUITY UPLC BEH(150 mm×2.1 mm,1.7 μm;Waters Co),柱温箱温度为40 ℃,自动进样器温度为4 ℃,进样体积为2 μL,流动相A为含0.1%甲酸水溶液,流动相B为乙腈,洗脱梯度:0.0~0.5 min,98% A、2% B;0.5~10.0 min,98%~50% A、2%~50% B;10.0~13.0 min,5% A、95% B;13.0~15.0 min,98% A、2% B。
质谱条件:使用装备IonDrive Turbo V ESI离子源的SCIEX 6500 QTRAP+三重四极杆质谱仪,以多反应监测(MRM)模式进行质谱分析。电喷雾离子源(Electrospray ionization,ESI)进行海量数据采集,操作参数如下:离子喷雾电压:+5500/−4500 V,帘式气体:35 psi,温度:400 ℃,离子源气体1:60 psi,离子源气体2:60 psi,DP:±100 V。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据使用Excel进行整理,结果用平均数表示,通过SCIEX分析软件(1.6.3版)进行MRM数据的采集和处理。采用SIMCA 16.0软件,进行无监督的主成分分析和有监督的正交偏最小二乘判别分析,利用Origin 2021软件绘制代谢物的柱状图,同时利用差异代谢物的KEGG(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes)进行通路富集分析,获得代谢通路富集结果。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 NFC和FC杨梅汁的代谢产物总体分析
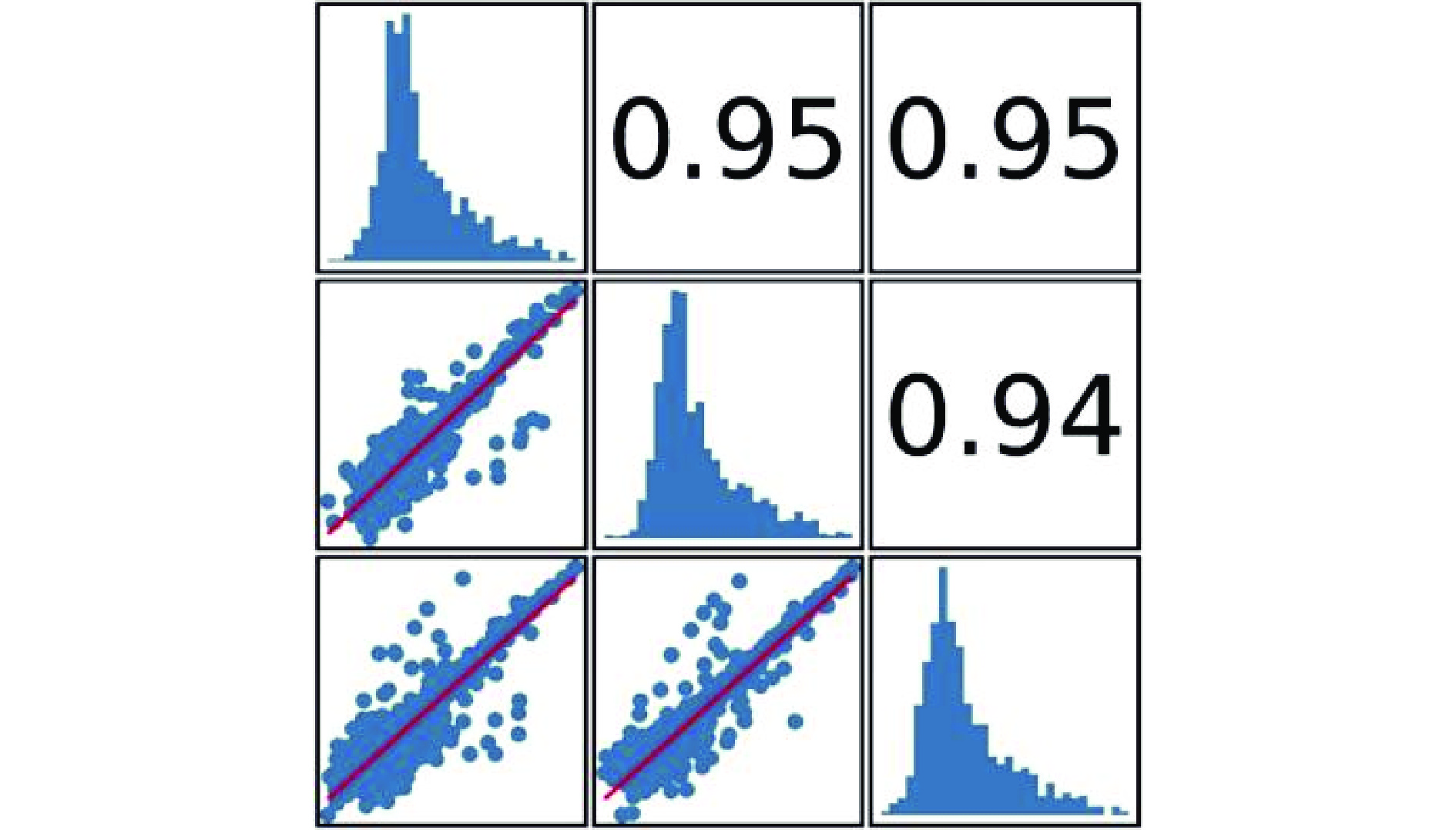
生物代谢组易受外界因素干扰,尤其是在物质提取、检测分析过程中存在误差,从而导致样品间产生差异,如果差异越小说明整个方法稳定性越好数据质量越高。为了考察数据的质量性,数据质量控制(Quality control,QC)是获得可重复性和准确性代谢组结果的必要步骤,因此对QC样本的相关性及内标的响应稳定性进行分析。QC样本相关性越接近于1(至少应≥0.7),说明整个方法稳定性越好数据质量越高;内标为外源引入的物质,QC样本内标浓度相同,所以内标的响应差异越小(RSD≤20%),说明系统越稳定,数据质量越高。从图1可以看出,在整个实验分析过程中QC样本相关性达0.95,RSD为5.66%,说明本次实验数据质量很高。基于迈维自建数据库MWDB及代谢物信息公共数据库,在NFC和FC杨梅汁中共鉴定出208个代谢产物,其中主要包括24个黄酮类物质、23个生物碱类物质、17个氨基酸及其衍生物、17个酚类物质等,虽然黄酮和生物碱类物质数量较多,但是氨基酸中脯氨酸的相对含量最高,氨基酸是果汁中重要的生物活性物质之一,对果汁的口感、气味和色泽具有重要影响[15]。所以根据这些代谢物的性质进一步说明杨梅汁具有独特的营养与风味。
2.2 NFC和FC杨梅汁的化学计量学分析
为了解NFC和FC杨梅汁中代谢物的积累情况,对两种杨梅汁进行主成分分析(PCA)。代谢组学分析中,PCA主要用于观察实验模型中的组间分离是否有异常点出现,以及反映组间和组内变异度的分析技术。主成分分析结果表明,R2X代表模型的拟合能力,累积为0.839大于0.5,Q2代表了模型的预测能力为0.451,结果表明PCA的模型拟合度较好。从得分图可以看出,样本全部处于95%置信区间内,NFC杨梅汁样品点和FC杨梅汁样品点分布离散,分别位于PC1的正负半轴,说明两者的代谢成分存在一定差异。PCA作为一种反映原始数据状态的无监督方法,环境等其他因素以及系统错误都会影响实验结果。从图2中可以看出前两个主成分分析的贡献率分别为15.3%和10.3%,总贡献率之和较低,无法反应整体分散程度。为排除因与实验无关的某些因素引起的代谢变化,应用有监督的正交偏最小二乘判别分析(Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA)进一步区分两组之间代谢物的差异数据,并依据该模型对数据进行分析,从而准确地鉴别出具有差异的代谢物[16]。
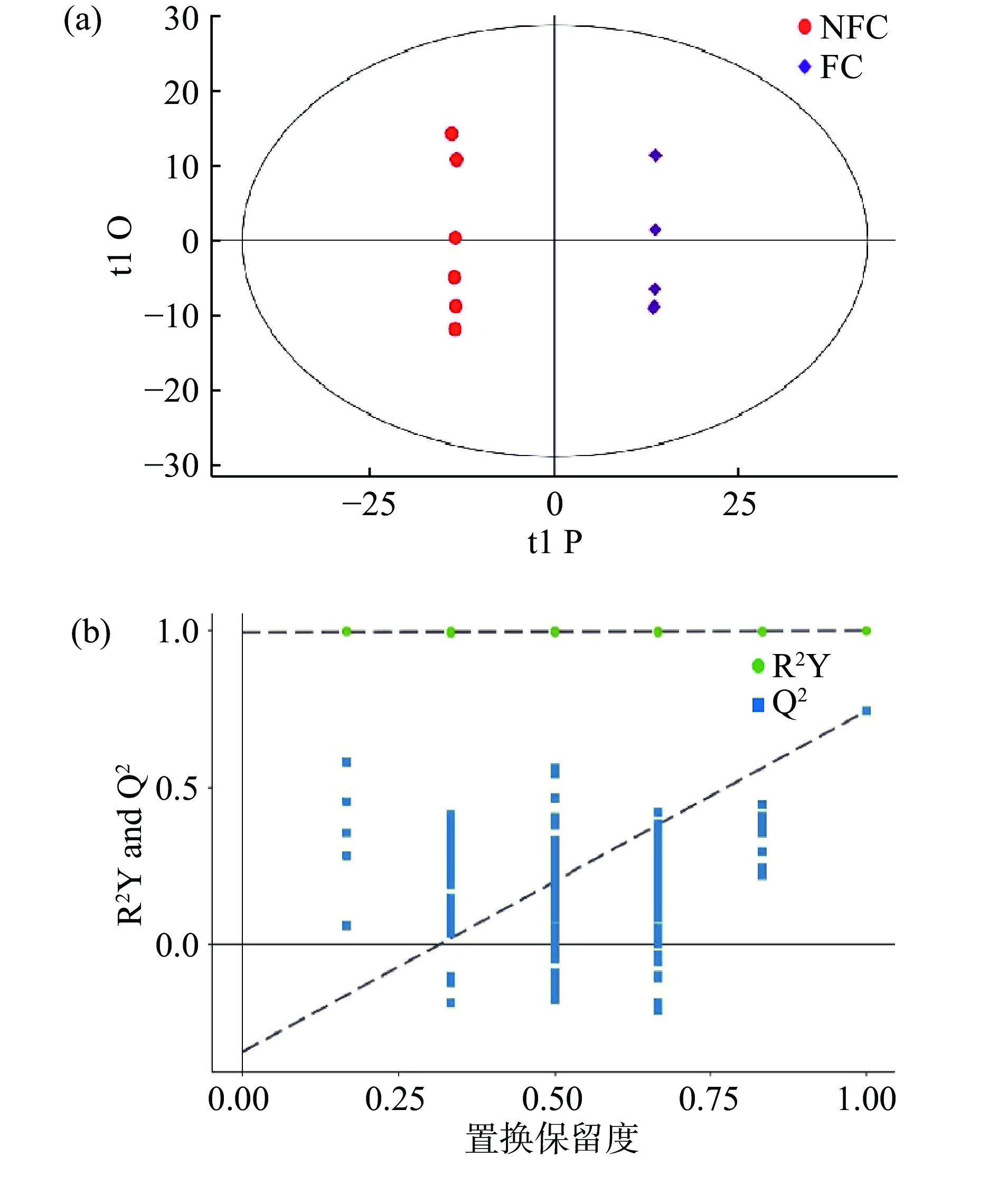
图3a为OPLS-DA得分图,从图中可以看出两组样本区分非常显著,说明两种果汁样品的代谢物组成差异较大。为了避免数据出现过拟合现象,从而确保模型的有效性,对模型进行置换检验以获取随机模型的R2和Q2,以此评估OPLS-DA得分图是否存在过拟合现象。图3b为OPLS-DA置换检验图,横坐标表示置换保留度,纵坐标表示R2Y或Q2值,绿色圆点表示R2Y值,蓝色方点表示Q2值,两条虚线分别表示R2Y和Q2的回归线。一般认为,当R2Y和Q2参数值越接近于1,说明模型解释或预测的能力越强,而该OPLS-DA模型的R2Y为1,Q2为0.744,说明建立的模型符合样本数据的真实情况。且从图中可以看出Q2值均小于R2Y值,Q2的回归线与纵坐标的截距小于零,一般认为截距为负值时,说明统计模型有效,没有出现过拟合[17],另外随着置换保留度的降低,随机模型Q2值逐渐减小,说明原模型具有良好的稳健性,不存在过拟合现象。
2.3 差异代谢物的筛选及分析
变量投影重要度(Variable Importance in the Projection,VIP)是OPLS-DA模型变量的权重值,可用于衡量各组分积累差异对各组样本分类判别的影响强度,通常认为数值大于1时,变量对组间分离具有显著贡献作用[18]。为了进一步确定二者产生差异的代谢物,本研究以差异倍数(Fold-Change)小于0.5或大于2,同时OPLS-DA模型第一主成分的VIP大于1为标准,一共筛选到40个差异代谢物(如表1),其中主要以黄酮类物质为主。
表 1 NFC和FC杨梅汁差异代谢物数量统计表Table 1. Statistical table of the number of different metabolites in NFC and FC bayberry juice序号 化合物名称 CAS 一级分类 保留时间
(min)VIP NFC FC Fold-Change Log-Fold
Change1 3-Methylxanthine
3-甲基黄嘌呤1076228 核苷酸及其衍生物 2.7102 1.6567 2.21394E-05 4.80232E-05 2.1691 1.1171 2 4-Sulfobenzoate
对磺基苯甲酸636782 有机酸 4.6827 1.9757 0.000551572 0.000226158 0.4100 −1.2862 3 5-Heneicosylresorcinol
5-二十一烷基间苯二酚70110597 酚类 12.0504 1.7222 1.38433E-05 4.2671E-05 3.0824 1.6241 4 5-Methyltetrahydrofolic acid
5-甲基四氢叶酸134350 叶酸及其衍生物 3.2800 2.2811 4.25081E-05 0.001182526 0.0359 −4.7980 5 5-Tricosyl-1,3-benzenediol
5-二十三烷基间苯二酚70110600 酚类 13.8461 1.3238 9.40658E-06 2.35345E-05 2.5019 1.3230 6 5'-S-Methyl-5'-thioadenosine
5'-脱氧-5'-甲硫腺苷2457809 核苷酸及其衍生物 3.9943 2.2488 0.022869482 0.062574256 2.7361 1.4521 7 Acanthoside B
刺五加甙B7374790 木脂素 6.5140 2.2535 0.020966336 0.052994448 2.5276 1.3378 8 Agomelatine
阿戈美拉汀138112762 其他类型 10.0029 1.4059 7.11534E-06 1.45277E-05 2.0417 1.0298 9 Spathulenol
桉油烯醇6750-60-3 孕烯醇酮脂类 10.8901 1.1233 7.36955E-05 0.000187933 2.5501 1.3506 10 alpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde
α-己基肉桂醛101-86-0 酚类 8.7053 2.0764 4.9007E-05 0.000104807 2.1386 1.0967 11 Colchicine
秋水仙碱64868 生物碱 5.0924 1.4547 2.11974E-05 4.46753E-05 2.1076 1.0756 12 Convolvine
旋花碱537304 生物碱 5.0687 1.6379 3.90251E-05 9.97865E-05 2.5570 1.3544 13 Cyanidin
矢车菊素528585 黄酮 5.8981 1.8438 0.019035589 0.00123141 0.0647 −3.9503 14 Daphnoretin
西瑞香素2034697 香豆素 11.4462 1.9410 0.000161841 4.41912E-05 0.2731 −1.8727 15 Deguelin
鱼藤素522178 黄酮 12.9237 1.7151 1.66812E-05 4.13666E-05 2.4798 1.3102 16 Ellagic acid
鞣花酸476664 酚类 6.1230 1.5896 0.000941028 0.002492296 2.6485 1.4052 17 Glucoliquiritin
葡萄糖基甘草苷93446185 黄酮 5.0662 1.9248 4.86499E-05 9.83577E-05 2.0217 1.0156 18 Guanine
鸟嘌呤73405 核苷酸及其衍生物 2.6279 1.1979 0.038949232 0.038949232 2.1531 1.1064 19 Hesperidin
橙皮苷520263 黄酮 6.6500 1.5464 0.000117743 1.95571E-05 6.0205 2.5899 20 Isovitexin
异牡荆黄素38953854 黄酮 5.8550 1.3641 0.000334646 8.11445E-05 4.1241 2.0441 21 Isoxanthopterin
异黄蝶呤529691 蝶呤类化合物 3.2561 2.2769 0.000158777 0.001439796 0.1103 −3.1808 22 Kaurenoic acid
贝壳杉烯酸6730832 二萜 5.9023 1.2883 0.066152256 0.030526902 2.1670 1.1157 23 Lithospermic acid
紫草酸28831654 苯丙素 7.1162 1.9551 2.98492E-05 8.34576E-06 3.5766 1.8386 24 Lucidin
芦西定478080 蒽醌 8.8947 1.7315 2.56859E-05 1.106E-05 2.3224 1.2156 25 Malvidin-3-O-galactoside
锦葵色素-3-O-半乳糖苷30113372 黄酮 7.7540 2.0037 1.60009E-05 3.94272E-06 4.0583 2.0209 26 Neohesperidin
新橙皮苷13241333 黄酮 6.7740 2.0316 0.00020561 2.79295E-05 7.3618 2.8801 27 Norlichexanthone
3,6,8-三羟基-1-甲基呫吨酮20716987 氧杂蒽酮 4.4813 1.9752 0.000357299 0.000165351 2.1609 1.1116 28 Octadecyl p-coumarate
对羟基桂皮酸十八酯72943885 苯丙素 12.0672 1.3026 7.70192E-05 2.68342E-05 2.8702 1.5211 29 Petasitenine
蜂斗菜烯碱60102376 生物碱 4.6827 1.4959 4.41133E-05 1.81308E-05 2.4331 1.2828 30 Phillyrin 连翘苷 487412 苯丙素 7.7610 1.4773 0.000204651 9.99422E-05 2.0477 1.0340 31 Porphobilinogen
胆色素原487901 有机氮化合物 1.5874 1.7938 3.13247E-05 1.07281E-05 2.9199 1.5459 32 Practolol 心得宁 6673354 芳香类化合物 2.7359 1.7599 6.55189E-05 3.18083E-05 2.0598 1.0425 33 Quercetin 槲皮素 117395 黄酮 8.0700 2.0263 0.000592431 0.000201997 2.9329 1.5523 34 Quercetin 3-O-neohesperidoside
槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷32453364 黄酮 6.5859 2.0821 0.000220833 4.41036E-05 5.0072 2.3240 35 Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide
槲皮素3-O-葡萄糖酸苷22688795 黄酮 5.9246 1.4564 0.007305016 0.002638031 2.7691 1.4694 36 S-Lactoylglutathione
s-乳酰谷胱甘肽41656568 羧酸类及其衍生物 4.0922 1.7450 4.38305E-05 1.80098E-05 2.4337 1.2832 37 Sesamolin
芝麻林素526078 木脂素 7.5526 1.9163 8.92372E-05 3.21499E-05 2.7757 1.4728 38 Tricetin
三粒小麦黄酮520310 黄酮 8.0461 1.6950 0.007811074 0.003312599 2.3580 1.2376 39 Vitexin 2''-O-beta-L-rhamnoside
牡荆素-2-O-鼠李糖苷64820991 黄酮 12.1137 1.1012 2.31267E-05 6.31288E-06 3.6634 1.8732 40 Xanthotoxol
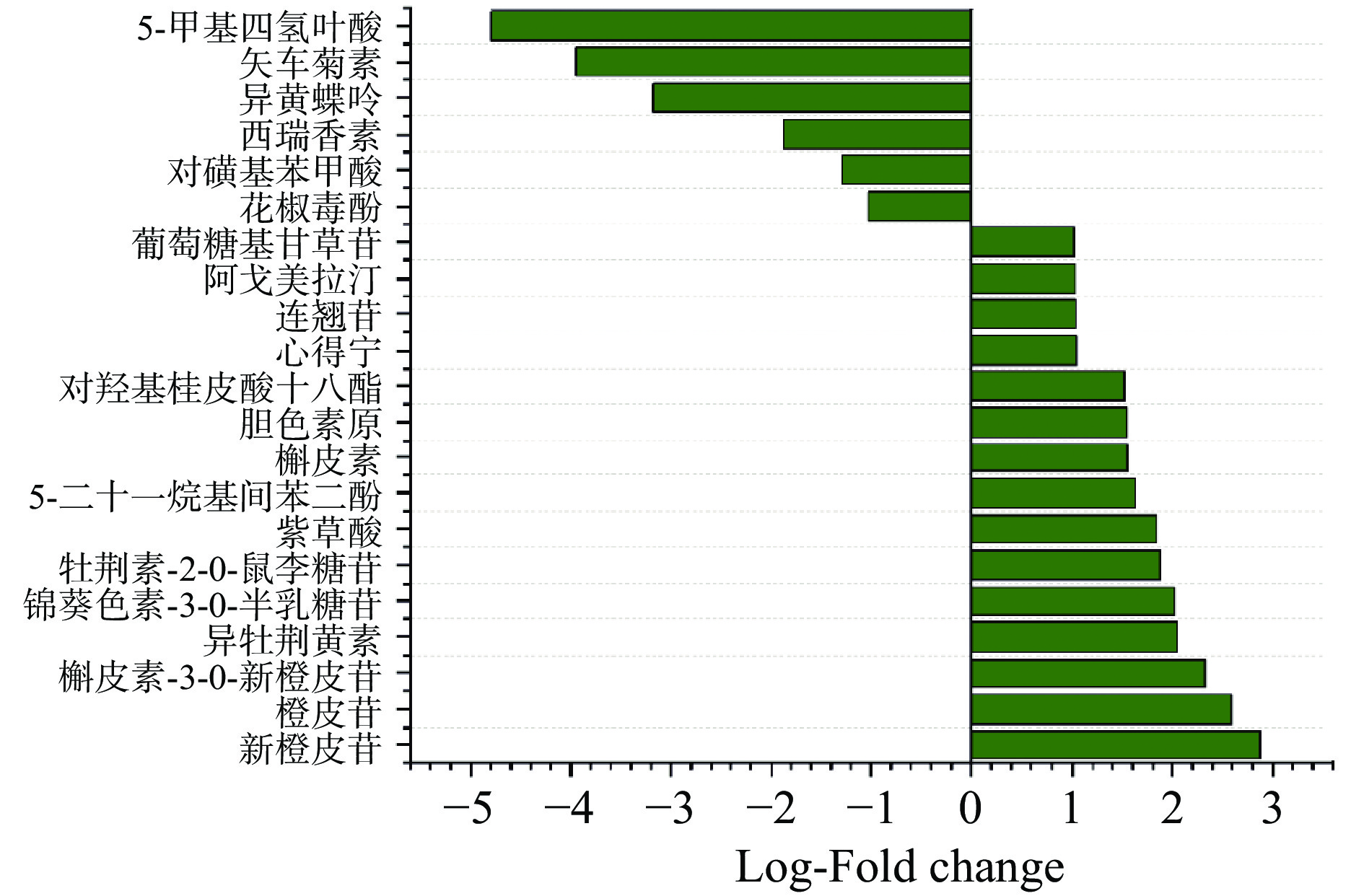
花椒毒酚2009247 香豆素 8.7429 1.7163 2.09788E-05 4.27557E-05 0.4907 −1.0272 为了更清楚的了解杨梅汁浓缩还原前后代谢物差异倍数的变化情况,制作了如图4所示的代谢物差异倍数柱状图,并将排名靠前(上调和下调)的20位代谢物进行展示,一般认为,当Fold-Change>2时,值越大差异越明显;当Fold-Change<0.5时,值越小差异越明显,所以结合Fold-Change大小筛选出9个差异最大的物质,分别是下调物质中的5-甲基四氢叶酸、矢车菊素、异黄蝶呤、西瑞香素、对磺基苯甲酸和花椒毒酚,上调物质中的新橙皮苷、橙皮苷、槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷。而它们所对应的Log-Fold change分别为−4.7980、−3.9503、−3.1808、−1.8727、−1.2862、−1.0272、2.8801、2.5899、2.3240。
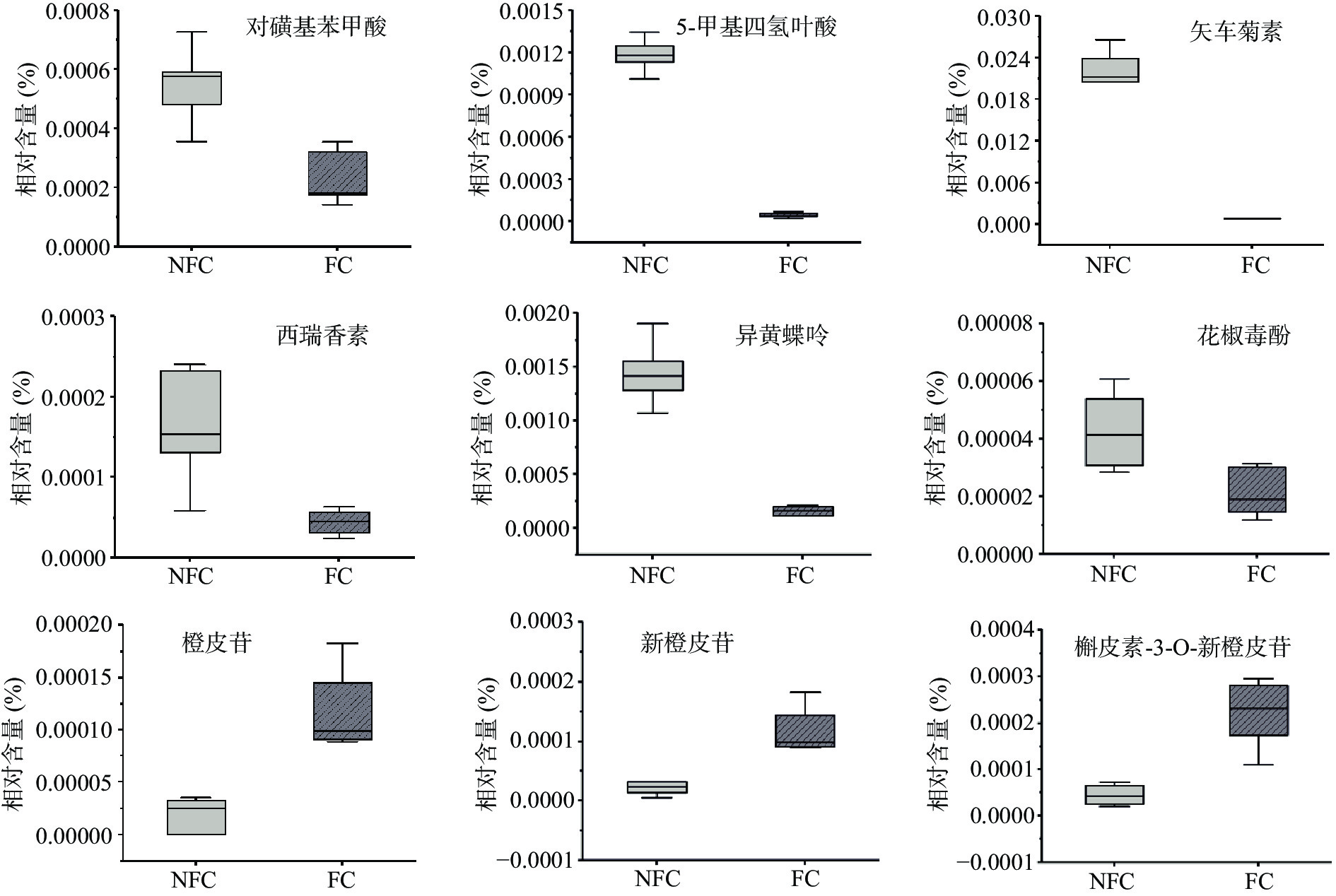
箱形图可以直观表达每种化合物在NFC和FC杨梅汁中的含量变化(图5)。从图中可以看出,与NFC杨梅汁相比,FC杨梅汁中的对磺基苯甲酸、5-甲基四氢叶酸、矢车菊素、西瑞香素、花椒毒酚和异黄蝶呤物质的含量相对较低,而新橙皮苷、橙皮苷和槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷物质的含量相对较高。西瑞香素、花椒毒酚属于香豆素类化合物,是生药中的一类重要的活性成分,具有抗菌、抗氧化等多种生物活性功能[19],但其不溶于冷水,易溶于热水,浓缩过程中随着温度的升高,水分不断蒸发,导致其含量有所损失。5-甲基四氢叶酸是合成叶酸活性化代谢的关键产物,在天然叶酸中活性最强,且在人体生命活动中起重要作用[20],但其稳定性较差,受温度、pH等因素影响, Islam[21]研究发现蒸煮和微波加热都使叶酸含量有所损失,与本研究结果类似,说明浓缩过程中的热处理会造成FC杨梅汁中的营养物质发生损失。矢车菊色素是花色苷中常见的一种化合物,而花色苷是黄酮物质中呈现红色的一族化合物,广泛存在于果蔬、花卉的根茎、花、果实中,能有效去除自由基,显示强烈的抗氧化性[22]。花色苷的稳定性受多种因素的影响,其中温度就是一个及其重要的因素,它对花色苷的降解具有显著影响作用,加热或高温都可加变色反应,尤其是在加热至沸腾时极易氧化褪色[23]。张燕等[24]的研究发现,当红莓的受热温度在45~75℃时,花色苷会发生降解,导致其含量及红值均发生显著下降。FC杨梅汁中这些物质含量减少,可能就是由于浓缩过程中水分的蒸发及加热处理。
新橙皮苷、橙皮苷和槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷属于黄酮物质,作为水果中主要的生物活性成分之一,具有较强的抗氧化活性,但受温度影响较大[25]。槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷是槲皮素和一种天然类黄酮的代谢产物,而槲皮素是大量存在的一种类黄酮化合物,常以苷类形式存在[26]。但橙皮苷、新橙皮苷、柠檬苦素等是柑橘类水果中常见的苦味代谢产物[27],其含量的高低对水果及果汁的感官品质具有较大影响[28]。橙皮苷是柑橘类水果白色内果皮中发现的主要的水溶性苦味成分[29],在加热过程中,随着时间的延长逐渐被析出,导致果汁的苦味增加。丁胜华等研究发现,高温处理导致橙皮中橙皮苷、没食子酸等类黄酮物质含量显著增加[30]。所以综上,浓缩过程的水分蒸发和加热可能就是导致NFC/FC杨梅汁代谢物产生差异的主要原因。
2.4 差异代谢物代谢通路富集分析
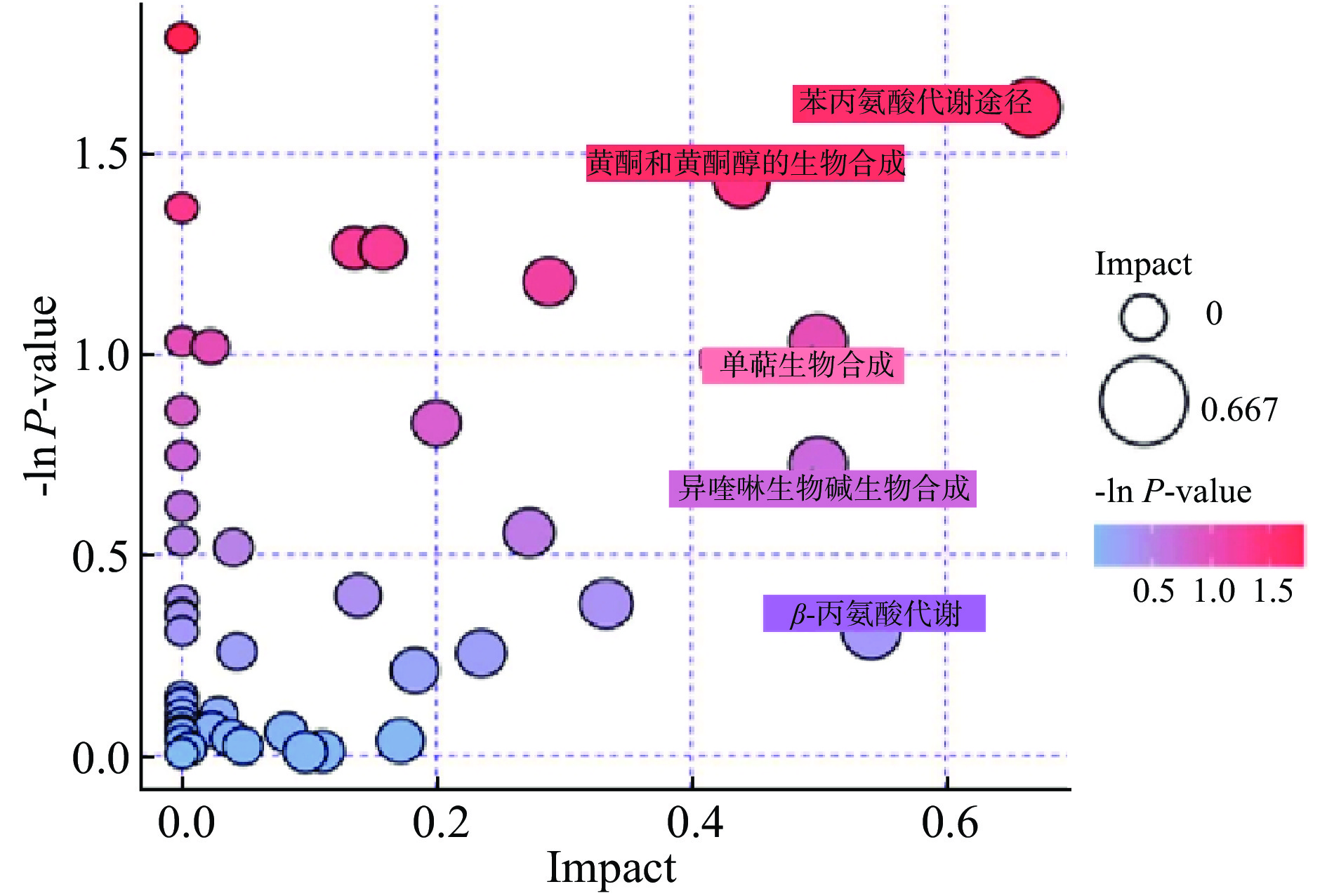
不同的代谢产物在生物体中相互作用,形成不同的代谢通路[31]。为深入了解差异代谢物涉及的代谢路径,通过KEGG数据库进一步对差异代谢物进行显著性富集分析,从而筛选出二者的差异代谢途径,并对其进行相关性分析[32]。根据鉴定出的代谢物共筛选出48条代谢通路,将其绘制成气泡图,如图6所示。图中每一个气泡代表一个代谢通路,而横坐标和气泡大小表示该通路在拓扑分析中的影响因子大小(Impact值),Impact值越大气泡越大,Impact值越小气泡越小;另外纵坐标和气泡颜色表示富集分析的P值(取负自然对数,即-ln(p)),红色越深代表-ln(p)的值越大,蓝色越深表示-ln(p)的值越小,而颜色越深表示富集程度越显著。
通过Impact值和-ln(p)值综合分析得到与代谢物差异相关的代谢途径,从图6中可以看到,NFC与FC杨梅汁中的代谢物共参与48条代谢途径,其中富集程度较高的代谢通路共有5条,分别为苯丙氨酸代谢、黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成、单萜生物合成、异喹啉生物碱生物合成和β-丙氨酸代谢。其中苯丙氨酸代谢通路最为显著,P值为0.19867,-ln(p)为1.6161,富集在此通路上的L-苯丙氨酸在苯丙氨酸脱氨酶(Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase,PAL)的作用下生成苯丙素类代谢物(香豆素、萜类、木质素、花青素等)[33],而在苯丙氨酸羟化酶(Phenylalanine hydroxylase,PAH)的催化作用下则会生成L-酪氨酸。但L-苯丙氨酸稳定性受到温度的影响,受热时会发生部分降解[34],导致FC杨梅汁中香豆素(西瑞香素、花椒毒酚)、矢车菊素、L-酪氨酸含量减少。另外,黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成这条代谢途径,P值为0.23889,-ln(p)为1.6161,被检测到的代谢物为槲皮素和芦丁。槲皮素是杨梅中含量较丰富的黄酮醇化合物,其在二氢黄酮醇4-还原酶(Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase,DFR)作用下生成矢车菊素[35]。由于温度对黄酮类物质稳定性有较大影响[36],所以导致FC杨梅汁中由槲皮素转化生成的矢车菊素含量降低。所以综上说明苯丙氨酸代谢、黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成是NFC与FC杨梅汁的关键差异代谢途径。
3. 结论
本研究借助代谢组学技术,利用PCA和OPLS-DA分析了NFC和FC杨梅汁代谢产物的差异,并进一步识别潜在的标记化合物,为分析NFC与FC杨梅汁间差异成分提供了一种有效方法。根据VIP>1和Fold-Change>2或Fold-Change<0.5筛选出40个差异代谢物,基于差异倍数大小从40种代谢物中筛选出9个差异较大的代谢物。经分析发现,FC杨梅汁中对磺基苯甲酸、5-甲基四氢叶酸、矢车菊素、西瑞香素、花椒毒酚和异黄蝶呤等抗氧化活性成分的含量相对较低,而苦味代谢物(新橙皮苷、橙皮苷和槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷)的含量相对较高。通过对代谢通路分析,筛选出5条差异较大的代谢途径,分别为苯丙氨酸代谢、黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成、单萜生物合成、异喹啉生物碱生物合成和β-丙氨酸代谢。NFC与FC杨梅汁中筛选出的9个差异代谢物是以富集在通路上的L-苯丙氨酸和槲皮素在不同酶的作用转化生成,由于两种物质受温度的影响,使得转化生成的代谢物含量减少,而L-苯丙氨酸和槲皮素富集所在的通路为苯丙氨酸代谢、黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成。所以综上结果显示,9个代谢产物和苯丙氨酸代谢、黄酮和黄酮醇的生物合成是NFC与FC杨梅汁形成差异的主要代谢物和代谢途径。本研究说明代谢组学可用于阐明NFC和FC杨梅汁间的成分差异,为二者差异代谢物富集的代谢通路提供研究方向。
-
表 1 NFC和FC杨梅汁差异代谢物数量统计表
Table 1 Statistical table of the number of different metabolites in NFC and FC bayberry juice
序号 化合物名称 CAS 一级分类 保留时间
(min)VIP NFC FC Fold-Change Log-Fold
Change1 3-Methylxanthine
3-甲基黄嘌呤1076228 核苷酸及其衍生物 2.7102 1.6567 2.21394E-05 4.80232E-05 2.1691 1.1171 2 4-Sulfobenzoate
对磺基苯甲酸636782 有机酸 4.6827 1.9757 0.000551572 0.000226158 0.4100 −1.2862 3 5-Heneicosylresorcinol
5-二十一烷基间苯二酚70110597 酚类 12.0504 1.7222 1.38433E-05 4.2671E-05 3.0824 1.6241 4 5-Methyltetrahydrofolic acid
5-甲基四氢叶酸134350 叶酸及其衍生物 3.2800 2.2811 4.25081E-05 0.001182526 0.0359 −4.7980 5 5-Tricosyl-1,3-benzenediol
5-二十三烷基间苯二酚70110600 酚类 13.8461 1.3238 9.40658E-06 2.35345E-05 2.5019 1.3230 6 5'-S-Methyl-5'-thioadenosine
5'-脱氧-5'-甲硫腺苷2457809 核苷酸及其衍生物 3.9943 2.2488 0.022869482 0.062574256 2.7361 1.4521 7 Acanthoside B
刺五加甙B7374790 木脂素 6.5140 2.2535 0.020966336 0.052994448 2.5276 1.3378 8 Agomelatine
阿戈美拉汀138112762 其他类型 10.0029 1.4059 7.11534E-06 1.45277E-05 2.0417 1.0298 9 Spathulenol
桉油烯醇6750-60-3 孕烯醇酮脂类 10.8901 1.1233 7.36955E-05 0.000187933 2.5501 1.3506 10 alpha-Hexylcinnamaldehyde
α-己基肉桂醛101-86-0 酚类 8.7053 2.0764 4.9007E-05 0.000104807 2.1386 1.0967 11 Colchicine
秋水仙碱64868 生物碱 5.0924 1.4547 2.11974E-05 4.46753E-05 2.1076 1.0756 12 Convolvine
旋花碱537304 生物碱 5.0687 1.6379 3.90251E-05 9.97865E-05 2.5570 1.3544 13 Cyanidin
矢车菊素528585 黄酮 5.8981 1.8438 0.019035589 0.00123141 0.0647 −3.9503 14 Daphnoretin
西瑞香素2034697 香豆素 11.4462 1.9410 0.000161841 4.41912E-05 0.2731 −1.8727 15 Deguelin
鱼藤素522178 黄酮 12.9237 1.7151 1.66812E-05 4.13666E-05 2.4798 1.3102 16 Ellagic acid
鞣花酸476664 酚类 6.1230 1.5896 0.000941028 0.002492296 2.6485 1.4052 17 Glucoliquiritin
葡萄糖基甘草苷93446185 黄酮 5.0662 1.9248 4.86499E-05 9.83577E-05 2.0217 1.0156 18 Guanine
鸟嘌呤73405 核苷酸及其衍生物 2.6279 1.1979 0.038949232 0.038949232 2.1531 1.1064 19 Hesperidin
橙皮苷520263 黄酮 6.6500 1.5464 0.000117743 1.95571E-05 6.0205 2.5899 20 Isovitexin
异牡荆黄素38953854 黄酮 5.8550 1.3641 0.000334646 8.11445E-05 4.1241 2.0441 21 Isoxanthopterin
异黄蝶呤529691 蝶呤类化合物 3.2561 2.2769 0.000158777 0.001439796 0.1103 −3.1808 22 Kaurenoic acid
贝壳杉烯酸6730832 二萜 5.9023 1.2883 0.066152256 0.030526902 2.1670 1.1157 23 Lithospermic acid
紫草酸28831654 苯丙素 7.1162 1.9551 2.98492E-05 8.34576E-06 3.5766 1.8386 24 Lucidin
芦西定478080 蒽醌 8.8947 1.7315 2.56859E-05 1.106E-05 2.3224 1.2156 25 Malvidin-3-O-galactoside
锦葵色素-3-O-半乳糖苷30113372 黄酮 7.7540 2.0037 1.60009E-05 3.94272E-06 4.0583 2.0209 26 Neohesperidin
新橙皮苷13241333 黄酮 6.7740 2.0316 0.00020561 2.79295E-05 7.3618 2.8801 27 Norlichexanthone
3,6,8-三羟基-1-甲基呫吨酮20716987 氧杂蒽酮 4.4813 1.9752 0.000357299 0.000165351 2.1609 1.1116 28 Octadecyl p-coumarate
对羟基桂皮酸十八酯72943885 苯丙素 12.0672 1.3026 7.70192E-05 2.68342E-05 2.8702 1.5211 29 Petasitenine
蜂斗菜烯碱60102376 生物碱 4.6827 1.4959 4.41133E-05 1.81308E-05 2.4331 1.2828 30 Phillyrin 连翘苷 487412 苯丙素 7.7610 1.4773 0.000204651 9.99422E-05 2.0477 1.0340 31 Porphobilinogen
胆色素原487901 有机氮化合物 1.5874 1.7938 3.13247E-05 1.07281E-05 2.9199 1.5459 32 Practolol 心得宁 6673354 芳香类化合物 2.7359 1.7599 6.55189E-05 3.18083E-05 2.0598 1.0425 33 Quercetin 槲皮素 117395 黄酮 8.0700 2.0263 0.000592431 0.000201997 2.9329 1.5523 34 Quercetin 3-O-neohesperidoside
槲皮素-3-O-新橙皮苷32453364 黄酮 6.5859 2.0821 0.000220833 4.41036E-05 5.0072 2.3240 35 Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide
槲皮素3-O-葡萄糖酸苷22688795 黄酮 5.9246 1.4564 0.007305016 0.002638031 2.7691 1.4694 36 S-Lactoylglutathione
s-乳酰谷胱甘肽41656568 羧酸类及其衍生物 4.0922 1.7450 4.38305E-05 1.80098E-05 2.4337 1.2832 37 Sesamolin
芝麻林素526078 木脂素 7.5526 1.9163 8.92372E-05 3.21499E-05 2.7757 1.4728 38 Tricetin
三粒小麦黄酮520310 黄酮 8.0461 1.6950 0.007811074 0.003312599 2.3580 1.2376 39 Vitexin 2''-O-beta-L-rhamnoside
牡荆素-2-O-鼠李糖苷64820991 黄酮 12.1137 1.1012 2.31267E-05 6.31288E-06 3.6634 1.8732 40 Xanthotoxol
花椒毒酚2009247 香豆素 8.7429 1.7163 2.09788E-05 4.27557E-05 0.4907 −1.0272 -
[1] YU H, XIE T, HE L, et al. Characterization of aroma compounds in bayberry juice by sensory evaluation and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2020,14(1):505−513. doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00223-3
[2] FANG Z, BHANDARI B. Comparing the efficiency of protein and maltodextrin on spray drying of bayberry juice[J]. Food Research International,2012,48(2):478−483. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.05.025
[3] BARRECA D, GATTUSO G, BELLOCCO E, et al. Flavanones: Citrus phytochemical with health-promoting properties[J]. Biofactors,2017,43(4):495−506. doi: 10.1002/biof.1363
[4] 雷佳蕾. 非浓缩还原(NFC)苹果汁的同位素、多酚和DNA鉴伪方法的建立[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2020 LEI J L. Establishment of a method for identification of isotopes, polyphenols and DNA for non-concentrated reduction (NFC) apple juice[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2020.
[5] 康孟利, 崔燕, 尚海涛, 等. 非热杀菌在NFC果汁上的应用前景[J]. 北方园艺,2016(18):190−193. [KANG M L, CUI Y, SHANG H T, et al. Application prospect of non-thermal sterilization on NFC juice[J]. Northern Horticulture,2016(18):190−193. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.201618047 KANG M L, CUI Y, SHANG H T, et al. Application prospect of non-thermal sterilization on NFC juice[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2016, (18): 190-3. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.201618047
[6] SUN R, XING R, ZHANG J, et al. Authentication and quality evaluation of not from concentrate and from concentrate orange juice by HS-SPME-GC-MS coupled with chemometrics[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022:162.
[7] JACQUES B. Control of authenticity of fruit juices by isotopic analysis[J]. Journal of AOAC International,1973,56(3):739−742. doi: 10.1093/jaoac/56.3.739
[8] ZHANG J, WANG P, WEI X, et al. A metabolomics approach for authentication of Ophiocordyceps sinensis by liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Food Research International,2015,76:489−497. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.07.025
[9] YIN Q C, JI J B, ZHANG R H, et al. Identification and verification of key taste components in wampee using widely targeted metabolomics[J]. Food Chemistry-X,2022:13.
[10] 杨天铭, 刘渝辰, 梁露, 等. 基于UPLC-QTOF-MS技术探究黄龙病脐橙与正常脐橙的成分差异[J]. 南昌大学学报(理科版),2022,46(4):454−463. [YANG T M, LIU Y H, LIANG L, et al. Exploring the compositional differences between Huanglongbing navel oranges and normal navel oranges based on UPLC-QTOF-MS technology[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Science Edition),2022,46(4):454−463. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0464.2022.04.011 YANG T M, LIU Y H, LIANG L, et al. Exploring the compositional differences between Huanglongbing navel oranges and normal navel oranges based on UPLC-QTOF-MS technology[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Science Edition), 2022, 46(4): 454-463. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0464.2022.04.011
[11] 屠燕, 孙连娜, 董志颖, 等. 基于UPLC-QTOF-MS技术分析不同产地丹参药材化学成分的差异[J]. 中药材,2021,44(6):1337−1342. [TU Y, SUN L N, DONG Z Y, et al. Analysis of differences in chemical constituents of salvia miltiorrhiza from different origins based on UPLC-QTOF-MS technique[J]. Chinese Materia Medica,2021,44(6):1337−1342. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2021.06.009 TU Y, SUN L N, DONG Z Y, et al. Analysis of differences in chemical constituents of salvia miltiorrhiza from different origins based on UPLC-QTOF-MS technique[J]. Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 44(6): 1337-1342. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2021.06.009
[12] 刘晗璐, 张九凯, 韩建勋, 等. 基于UPLC-QTOF-MS代谢组学技术的NFC和FC橙汁差异成分比较[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(6):229−237. [LIU H L, ZHANG J K, HAN J X, et al. Comparison of differential components in NFC and FC orange juice based on UPLC-QTOF-MS metabolomics technology[J]. Food Science,2021,42(6):229−237. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191014-106 LIU H L, ZHANG J K, HAN J X, et al. Comparison of differential components in NFC and FC orange juice based on UPLC-QTOF-MS metabolomics technology [J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(6): 229-237. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191014-106
[13] XU L, XU Z, KELLY S, et al. Integrating untargeted metabolomics and targeted analysis for not from concentrate and from concentrate orange juices discrimination and authentication[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,329(prepublish):127−130.
[14] YANG X, LUO J, DUAN Y, et al. Simultaneous analysis of multiple pesticide residues in minor fruits by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/hybrid quadrupole time-of-fight mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,241:188−198. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.102
[15] WANG H Y, NI Y Y, HU X S, et al. Kinetics of amino acid loss in carrot juice concentrate during storage[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2007,40(5):785−792. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2006.03.020
[16] THEVENOT E A, ROUX A, XU Y, et al. Analysis of the human adult urinary metabolome variations with age, body mass index, and gender by implementing a comprehensive workflow for univariate and OPLS statistical analyses[J]. Journal of Proteome Research,2015,14(8):3322−3335. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00354
[17] 黄浩, 余鹏辉, 赵熙, 等. 不同季节保靖黄金茶1号工夫红茶挥发性成分的HS-SPME-GC-MS分析[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(12):188−196. [HUANG H, YU P H, ZHAO X, et al. HS-SPME-GC-MS analysis of volatile components in Baojing golden Tea No.1 Gongfu black tea in different seasons[J]. Food Science,2020,41(12):188−196. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190721-265 HUANG H, YU P H, ZHAO X, et al. HS-SPME-GC-MS analysis of volatile components in Baojing golden Tea No. 1 Gongfu black tea in different seasons[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(12): 188-196. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190721-265
[18] ZHANG G, WANG H, XIE W, et al. Comparison of triterpene compounds of four botanical parts from Poria cocos (Schw.) wolf using simultaneous qualitative and quantitative method and metabolomics approach[J]. Food Research International,2019,121:666−677. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.12.036
[19] ANNUNZIATA F, PINNA C, DALLAVALLE S, et al. An overview of coumarin as a versatile and readily accessible scaffold with broad-ranging biological activities[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(13):4618. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134618
[20] 连增林, 刘康, 顾锦华, 等. 叶酸与5-甲基四氢叶酸的生物学特征与应用[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2022,33(2):230−239. [LIAN Z L, LIU K, GU J H, et al. Biological characteristics and application of folic acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate[J]. China Food Additives,2022,33(2):230−239. LIAN Z L, LIU K, GU J H, et al. Biological characteristics and application of folic acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate[J]. China Food Additives, 2022, 33(2): 230-239.
[21] ISLAM M S. 小麦和鲜食玉米存贮及加工过程中的叶酸稳定性研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021 ISLAM M S. 小麦和鲜食玉米存贮及加工过程中的叶酸稳定性研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2021. [ISLAM M S. Study on folic acid stability during storage and processing of wheat and fresh corn[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021.
[22] 吴莉, 齐婧敏, 吕庆章. 六种花青素类化合物抗氧化活性的DFT研究[J]. 化学研究与应用,2014,26(7):997−1003. [WU L, QI J M, LÜ Q Z. DFT study on antioxidant activity of six anthocyanins[J]. Chemical Research and Applications,2014,26(7):997−1003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2014.07.007 WU L, QI J M, LV Q Z. DFT study on antioxidant activity of six anthocyanins[J]. Chemical Research and Applications, 2014, 26(7): 997-1003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2014.07.007
[23] CABRITA L, FOSSEN T, ANDERSEN O M. Colour and stability of the six common anthocyanidin 3-glucosides in aqueous solutions[J]. Food Chemistry,2000,68(1):101−107. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00170-3
[24] 张燕, 谢玫珍, 廖小军. 热和紫外辐照对红莓花色苷稳定性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2005(3):37−40. [ZHANG Y, XIE M Z, LIAO X J. Effects of heat and ultraviolet irradiation on the stability of cranberry anthocyanins[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2005(3):37−40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2005.03.010 ZHANG Y, XIE M Z, LIAO X J. Effects of heat and ultraviolet irradiation on the stability of cranberry anthocyanins [J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2005, (3): 37-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2005.03.010
[25] 周明, 徐明生, 陈金印, 等. ‘修水化红’甜橙皮热风干燥动力学及其品质特性分析[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(11):141−149. [ZHOU M, XU M S, CHEN J Y, et al. Analysis of hot air drying kinetics and quality characteristics of 'Xiushuihuahong' sweet orange peel[J]. Food Science,2020,41(11):141−149. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190710-132 ZHOU M, XU M S, CHEN J Y, et al. Analysis of hot air drying kinetics and quality characteristics of 'Xiushuihuahong' sweet orange peel [J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(11): 141-149. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190710-132
[26] 刘意隆. 杨梅黄酮醇鉴定、纯化及其抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的构效机制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020 LIU Y L. Identification, purification and structure-activity mechanism of myricetin flavonols and their inhibition of α-glucosidase[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020.
[27] 张娜威, 潘思轶, 范刚, 等. 柑橘果汁中的苦味物质及脱苦技术研究进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报,2021,40(1):40−48. [ZHANG N W, PAN S Y, FAN G, et al. Research progress on bitter substances in citrus juice and its debittering technology[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University,2021,40(1):40−48. doi: 10.13300/j.cnki.hnlkxb.2021.01.005 ZHANG N W, PAN S Y, FAN G, et al. Research progress on bitter substances in citrus juice and its debittering technology [J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021, 40(1): 40-48. doi: 10.13300/j.cnki.hnlkxb.2021.01.005
[28] LI S, WANG Z, DING F, et al. Content changes of bitter compounds in 'Guoqing No.1' satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) during fruit development of consecutive 3 seasons[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,145:963−969. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.040
[29] FISHER F J, A W T. A high-pressure liquid chromatographic method for the resolution and quantitation of naringin and naringenin rutinoside in grapefruit juice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1976,24(4):898−899. doi: 10.1021/jf60206a026
[30] 丁胜华, 王蓉蓉, 李高阳, 等. 干燥温度对橙皮干燥动力学、酚类物质及抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2016,16(11):137−144. [DING S H, WANG R R, LI G Y, et al. Effects of drying temperature on drying kinetics, phenolic substances and antioxidant properties of orange peel[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2016,16(11):137−144. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2016.11.019 DING S H, WANG R R, LI G Y, et al. Effects of drying temperature on drying kinetics, phenolic substances and antioxidant properties of orange peel [J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2016, 16(11): 137-144. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2016.11.019
[31] KANEHISA M, GOTO S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2000,28(1):27−30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27
[32] XIA J, SINELNIKOV I V, HAN B, et al. Metabo analyst 3.0-making metabolomics more meaningful[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2015,43(W1):W251−W257. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv380
[33] 王玉, 杨雪, 杨蕊菁, 等. 调控苯丙烷类生物合成的MYB类转录因子研究进展[J]. 安徽农业大学学报,2019,46(5):859−864. [WANG Y, YANG X, YANG R J, et al. Research progress of MYB transcription factors regulating phenylpropane biosynthesis[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2019,46(5):859−864. doi: 10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.20191122.018 WANG Y, YANG X, YANG R J, et al. Research progress of MYB transcription factors regulating phenylpropane biosynthesis [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2019, 46(5): 859-864. doi: 10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.20191122.018
[34] 赵建存, 宋英杰, 王振圣, 等. 苯丙氨酸/酪氨酸代谢途径及其相关产物与非酒精性脂肪肝的关系[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志,2022,29(3):404−409. [ZHAO J C, SONG Y J, WANG Z S, et al. Relationship between phenylalanine/tyrosine metabolic pathway and its related products and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Basic and Clinical Medicine,2022,29(3):404−409. ZHAO J C, SONG Y J, WANG Z S, et al. Relationship between phenylalanine/tyrosine metabolic pathway and its related products and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Basic and Clinical Medicine, 2022, 29(3): 404-409.
[35] 曹运琳, 邢梦云, 徐昌杰, 等. 植物黄酮醇生物合成及其调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报,2018,45(1):177−192. [CAO Y L, XING M Y, XU C J, et al. Research progress in plant flavonol biosynthesis and its regulation[J]. Journal of Horticulture,2018,45(1):177−192. doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0306 CAO Y L, XING M Y, XU C J, et al. Research progress in plant flavonol biosynthesis and its regulation[J]. Journal of Horticulture, 2018, 45(1): 177-192. doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0306
[36] 吴振, 李红, 王勇德, 等. 不同热处理温度对蓝莓果汁在冷藏过程中多酚和黄酮含量的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(17):209−215. [WU Z, LI H, WANG Y D, et al. Effects of different heat treatment temperatures on the contents of polyphenols and flavonoids in blueberry juice during cold storage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2019,45(17):209−215. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.020573 WU Z, LI H, WANG Y D, et al. Effects of different heat treatment temperatures on the contents of polyphenols and flavonoids in blueberry juice during cold storage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2019, 45(17): 209-215. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.020573





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



