Optimization of Preparation Process and in Vitro Digestion Study of Anthocyanin/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites by Response Surface Methodology
-
摘要: 为了提高花青素的生物利用率,本研究采用共沉淀的方法制备花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物。利用响应面法(Response Surface Method,RSM)优化花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的合成,并对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物进行粒径分析、Zeta电位测定、扫描电子显微镜、傅里叶变换红外光谱分析以及体外模拟消化实验。结果表明花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的最佳制备条件为花青素与Fe3O4的质量比为1:46,反应时间为19.6 h,反应温度为47 ℃,此工艺条件下花青素的包封率为87.51%。该纳米复合物粒径分布集中在100~1200 nm,且分布均匀,Zeta电位为−48.15 mV。通过扫描电子显微镜观察到花青素与Fe3O4纳米粒子间形成了表面光滑的球状颗粒。花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物在1635、1083 cm−1处出现花青素C=O和C-H特征峰。体外消化实验得出花青素在胃液和肠液中的保留率为91.99%和46.23%,DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力在肠液中均提高(P<0.05)。因此,共沉淀法能够提高花青素的生物利用率,为花青素的高效使用提供了技术支持。
-
关键词:
- 花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物 /
- 响应面 /
- 体外消化 /
- 抗氧化活性 /
- 结构表征
Abstract: In order to improve the bioavailability of anthocyanins, a co-precipitation method was used to prepare anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nanocomposites in this study. The response surface method was used to optimize the synthesis of anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nanocomposites. The particle size analysis, Zeta potential measurement, scanning electron microscope, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and in vitro digestion simulation of anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nanocomposites were carried out. The results showed that the optimum conditions for the preparation of anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nnanocomposites were anthocyanin/Fe3O4 mass ratio of 1:46, reaction time 19.6 h, reaction temperature 47 ℃. The encapsulation rate of anthocyanin under these conditions was 87.51%. The particle size distribution of anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nanocomposites was concentrated in the range of 100~1200 nm with uniform distribution, and the Zeta potential was −48.15 mV. The formation of spherical particles with smooth surfaces between anthocyanin and Fe3O4 nanoparticles was observed by scanning electron microscopy. The anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nanocomplexes showed anthocyanin C=O and C-H characteristic peaks at 1635 cm−1 and 1083 cm−1. The in vitro digestion simulation showed that the retention of anthocyanin was 91.99% and 46.23% in gastric and intestinal fluids. The scavenging ability of DPPH and ABTS+ radicals was increased in the intestinal fluid (P<0.05). Therefore, co-precipitation method can improve the bioavailability of anthocyanins, and provide technical support for the efficient utilization of anthocyanins. -
花青素在大自然中的分布极其广泛。据研究报道统计27个科,73个属的500多种植物中含有花青素[1]。花青素存在于很多植物体内,例如甘蓝、紫薯、蓝莓、茶叶、黑米、桑葚等。天然存在的花青素种类多达250种,其中矢车菊色素(Cyanidin)、飞燕草色素(Delphinidin)、天竺葵色素(Pelargonidin)、芍药色素(Peonidin)、牵牛花色素(Petunidin)和锦葵色素(Malvidin)是最常见的6种花青素单体[2]。花青素在自然界中主要以花色苷的形式存在,含有丰富的糖苷键和酯键,易溶于水,可溶于甲醇,乙醇等醇类化合物,具有抗氧化[3],抗癌[4],清除自由基的功效[5]。
花青素易受到外界温度,光照等的影响导致其生物利用率下降[6]。为了提高花青素的稳定性和生物利用度,有研究将花青素与生物相容性物质进行复合,如脂质体、葡聚糖、铁蛋白等,共同发挥复合物的功能化作用,通过物理化学屏障来抵御环境冲击、控制输送,达到保护花青素,增强其稳定性、生物利用度和健康效益的作用[7]。有研究发现自组装甲壳胺/硫酸软骨素纳米颗粒包埋黑米花青素有较好的热稳定性[8]。纳米载体能够通过提高花青素稳定性、保护其免受酶促降解而增强其体内的生物利用度、延长其在血浆中的停留时间,使花青素的生物活性最大化[9]。
纳米脂质体是一种粒径小于100 nm的脂质体结构。与游离化学药物相比,纳米脂质体有助于延长药物在循环中的生物利用度时间[10],提高药物疗效[11]和降低药物毒性[12]。Fe3O4纳米颗粒具有良好的化学稳定性、均匀的粒径和生物相容性,是制备磁性纳米吸附剂的常用材料[13]。史宇哲[14]利用水热法合成原花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物,结果表明制备的纳米复合物具有良好的吸附性能,能够提高原花青素的生物利用率,并且具备优良的抑菌性能。然而现有报道纳米复合物制备工艺繁琐,耗时长。相比较传统研究方法,本研究采用共沉淀的方法,具有制备工艺过程简单、操作方便和低成本等特点,同时利用响应面法更加精确纳米复合物的制备条件,且所需实验次数少,能减少实验试剂的使用,能够更高效地制备花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物。
本研究采用共沉淀的方法制备花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物。在单因素实验的基础上,利用响应面软件优化最佳提取条件。采用粒径和Zeta电位、扫描电子显微镜、傅里叶变换红外光谱用于研究复合物的形成及微观结构变化。并研究花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的体外消化活性,为提高花青素的生物利用率提供了新的思路和理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
Fe3O4纳米粒子(纯度99.5%) 上海罗恩试剂有限公司;黑米花青素(纯度25%) 陕西天叶有限公司;矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷(Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside,C3G)(纯度99.8%) 成都植标化纯生物技术有限公司;35%盐酸、99.5%甲醇和20%氨水 分析纯,成都市科隆化学品有限公司;胃蛋白酶(1:3000)、胰蛋白酶(1:250)和牛胆盐 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)均为分析纯 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
SB-5200DT超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;HNY-2008摇床、MULTISKAN GO酶标仪 上海塞默飞世尔科技有限公司;DHG-9053A鼓风干燥箱、HC-2518R高速冷冻离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;HH-1数显恒温水浴锅、DELTA 320精密pH计和Anton Paar Litesizer 500 Zeta电位及纳米粒度分析仪 常州奥华仪器有限公司;Thermo Fisher Nicolet Is10傅里叶红外光谱仪 江苏天瑞仪器股份有限公司;FEI Inspect F50扫描电子显微镜 上海泰思肯贸易有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的制备
花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的制备采用共沉淀的方法,同时参考蒋希芝[7]的方法做了修改。将100 mg花青素粉末溶于30 mL甲醇溶液,配制成花青素甲醇混合溶液,添加NH3·H2O调节其混合溶液pH为7.0~8.0去除酚基。将一定质量超声处理过的Fe3O4甲醇溶液添加到上述溶液中并混匀,将花青素和Fe3O4复合物置于一定温度的摇床中恒温振荡一定时间。取出后移液枪吸取上清液,剩余沉淀放入40 ℃温度烘箱中干燥4 h,得到黑色固体混合物。
1.2.2 花青素检测波长的选择
据研究报道,黑米花青素中含量最高的是矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷(Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside,C3G)[15],波长的检测参考刘长姣等[16]的研究稍作修改,称取2 mg的C3G于10 mL容量瓶中,用浓度为0.8%盐酸甲醇定容,得到浓度为0.2 mg/mL的储备液,吸取标准储备液0.2 mL于10 mL容量瓶中,再用0.8%盐酸甲醇溶液定容,利用酶标仪在400~800 nm波长范围内扫描。
1.2.3 花青素标准曲线的绘制
将1.2.2中配制好的储备液稀释成浓度分别为0、0.002、0.004、0.006、0.008、0.010 mg/mL的标准溶液,在最大吸收波长处检测吸光度,以浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标绘制标准曲线。
1.2.4 花青素包封率测定
包封率(Encapsulation Efficiency,EE)是指被包裹物质在脂质体悬液中占药物总量的百分量,是脂质体和纳米粒质量控制的一个重要指标[17]。将制备好的花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物溶于2 mL浓度为0.8%盐酸甲醇溶液中,利用高速冷冻离心机在4 ℃,10000 r/min条件下离心10 min,取上清液测定吸光度,通过花青素标准曲线测定游离花青素的浓度。计算公式为:
EE(%)=W1−W2W1×100 (1) 式中:W1为添加的花青素的总含量,mg;W2为2 mL纳米脂质体复合物中上清液花青素的含量,mg。
1.2.5 单因素实验
1.2.5.1 花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子质量比对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响
将花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子反应温度设置为50 ℃,反应时间为20 h,改变花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子的质量比为1:20、1:25、1:30、1:35、1:40、1:45和1:50,按照“1.2.1”制备花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物,以包封率为观察指标,按“1.2.4”测定包封率,选出最适合的质量比。
1.2.5.2 花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子反应时间对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响
固定花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子反应温度为50 ℃,根据1.2.5.1得出的实验结果确定花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子的质量比为1:45,改变反应时间为8、12、16、20和24 h,按照“1.2.1”制备花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物,以包封率为观察指标,按“1.2.4”测定包封率,筛选出最适合的反应时间。
1.2.5.3 花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子反应温度对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响
根据1.2.5.1和1.2.5.2得出的实验结果确定花青素和Fe3O4纳米粒子质量比为1:45,反应时间为20 h,改变Fe3O4纳米粒子和花青素的反应温度为40、50、60和70 ℃,按照“1.2.1”制备花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物,以包封率为观察指标,按“1.2.4”测定包封率,筛选出最适合的反应温度。
1.2.6 响应面试验
在单因素实验的基础上,利用响应面试验来优化花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的制备工艺,以包封率(Y)为响应值,质量比(A),时间(B),温度(C)三个条件为自变量,采用Box-Behnken中心组合进行三因素三水平的响应面试验设计。响应面试验设计因素与水平如表1所示。
表 1 响应面试验因素水平设计Table 1. Factors and levels for response surface test因素 水平 −1 0 1 A质量比 1:40 1:45 1:50 B时间(h) 16 20 24 C温度(℃) 40 50 60 1.2.7 结构表征
1.2.7.1 粒径与Zeta电位测定
将Fe3O4纳米粒子和花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物充分溶解于2 mL去离子水中,设置超声分散时间为5 min,功率为200 W。利用Zeta电位和纳米粒径分析仪进行电荷量和粒径的测量。
1.2.7.2 微观形貌分析
在电压10 kV,工作距离11.2 mm条件下,将每个样品喷金处理,采用扫描电子显微镜对花青素粉末、Fe3O4纳米粒子和花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物进行微观形貌分析。
1.2.7.3 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
取适量的花青素粉末、Fe3O4纳米粒子和花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物分别与光谱级溴化钾1:100共同研磨,常压条件下加压成片状,在衰减全反射模式下,使用傅里叶红外光谱仪进行表征。
1.2.8 体外模拟消化实验
1.2.8.1 模拟消化样品的制备
参考李玉壬等[18]的方法稍做修改:准确称取100 mg花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物于50 mL离心管中,加入10 mL现配的人工模拟胃液(人工胃液配100 mL:100 mL蒸馏水、0.8 g NaCl、0.02 g KH2PO4、0.115 g Na2HPO4、0.35 g胃蛋白酶,用1 mol/mL HCl调节pH为2.5),于37 ℃,170 r/min振荡0、0.5、1.0 h进行人工模拟胃消化。胃消化后,先用0.9 mol/L NaHCO3将模拟胃消化液pH调为6.0±0.5,然后加入20 mL现配的模拟肠液(人工肠液配100 mL:100 mL蒸馏水、0.8 g NaCl、0.02 g KH2PO4、0.115 g Na2HPO4、1.8 g牛胆盐、0.1 g胰蛋白酶,用1 mol/mL氢氧化钠调节pH为8)于37 ℃,170 r/min振荡0、0.5、1.0 h。分别取不同时间点胃肠消化液离心(4500 r/min)10 min,取上清液测定花青素的含量及其抗氧化性。
1.2.8.2 花青素保留率测定
根据“1.2.3”花青素标准曲线的绘制,测定0、0.5、1.0 h胃消化和肠消化的样品溶液于520 nm波长下的吸光度,根据标准曲线方程,计算上清液中花青素含量M0,按照公式(2)计算花青素保留率(%)。
花青素保留率(%)=M1−M0M1×100 (2) 式中:M1为响应面条件下最优组合实际测得的包封花青素的总含量,mg;M0为模拟体外消化后上清液中花青素的含量,mg。
1.2.8.3 DPPH自由基清除能力的测定
参考金珊珊[19]方法作修改,分别取0、0.5、1.0 h模拟胃消化和肠消化阶段的待测液0.5 mL,加入2 mL 0.2 mmol/L DPPH乙醇溶液,混合均匀后黑暗中反应0.5 h,并在517 nm波长下测样品溶液吸光度值(A1),同时测定0.5 mL去离子水和2 mL DPPH乙醇溶液混合后的吸光度值A0以及0.5 mL样品溶液和2 mL无水乙醇混合后的吸光度值A2,按照下列公式计算DPPH自由基清除率(%):
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (3) 式中:A0为空白对照吸光值;A1为样品吸光值;A2为参比液吸光值。
1.2.8.4 ABTS+自由基清除能力的测定
参考朱文卿[20]方法作修改,7 mmol/L ABTS水溶液与2.45 mmol/L 过硫酸钾以1:1等体积混合,于黑暗条件下反应16 h得ABTS储备液,用无水乙醇在黑暗条件下稀释储备液,使其在734 nm波长下的吸光度为0.70±0.05,得ABTS反应液。分别取200 μL的0、0.5、1.0 h模拟胃消化和肠消化阶段的待测液与3 mL ABTS反应液混合,室温黑暗中反应1 h,在734 nm波长下测定吸光度值A1,同样条件下测定200 μL无水乙醇和3 mL ABTS反应液的吸光度A0,利用下面公式计算ABTS+自由基清除率(%):
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=A0−A1A0×100 (4) 式中:A0为空白对照吸光值;A1为样品的吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均设3次重复,数据用均数±标准差(
¯x±s )表示。采用SPSS 26.0软件进行差异显著性分析(P<0.05),利用Origin 9.1软件作图,利用Design-expert.V8.0.6软件进行响应面试验设计与分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。2. 结果与分析
2.1 检测波长的确定
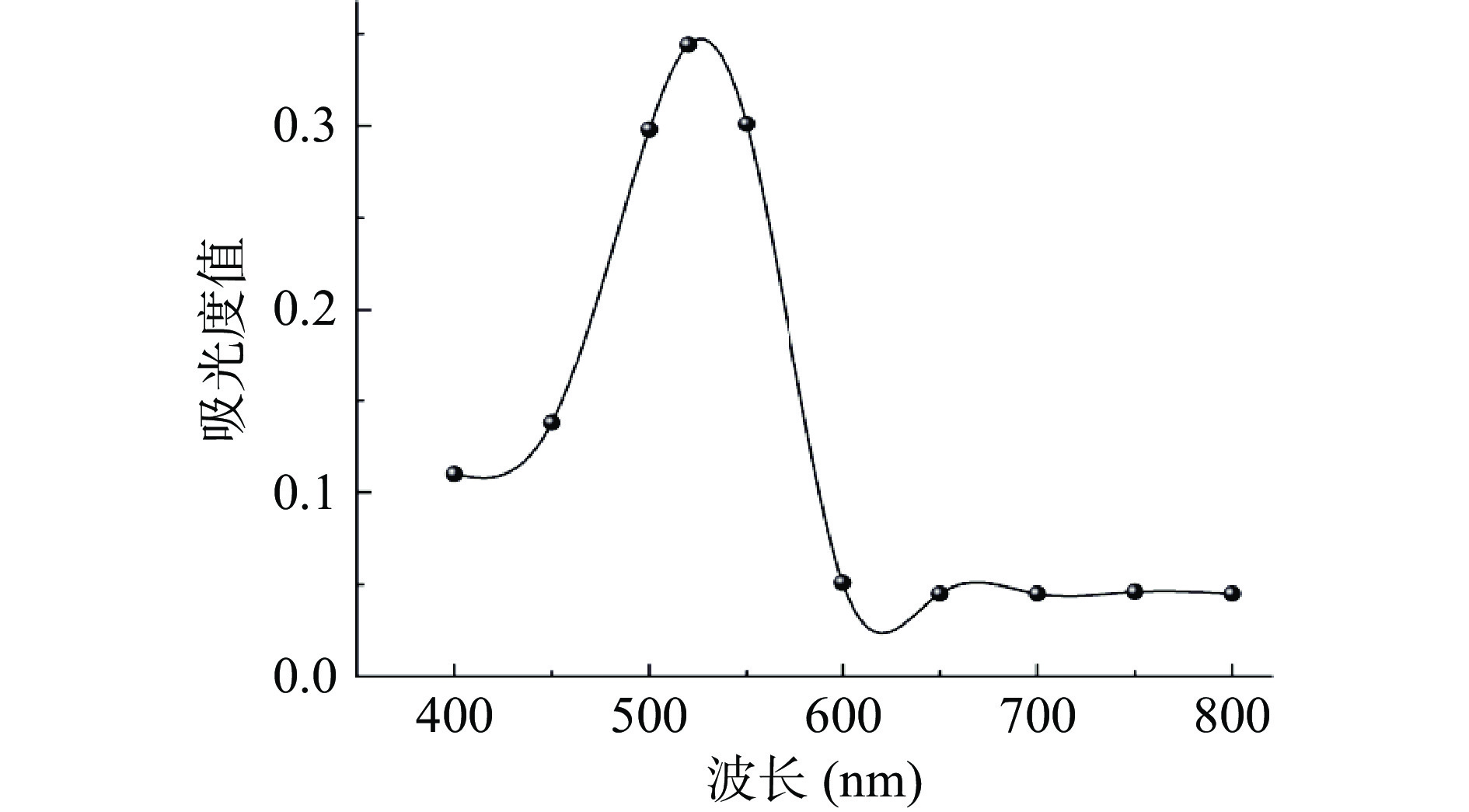
根据“1.2.2”中的方法,利用酶标仪在400~800 nm波长范围内对矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷溶液进行扫描,确定最大吸收波长为520 nm,如图1。标准曲线方程为:y=53.829x+0.0362,R2=0.9991。
2.2 单因素实验结果
2.2.1 花青素和Fe3O4质量比对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响
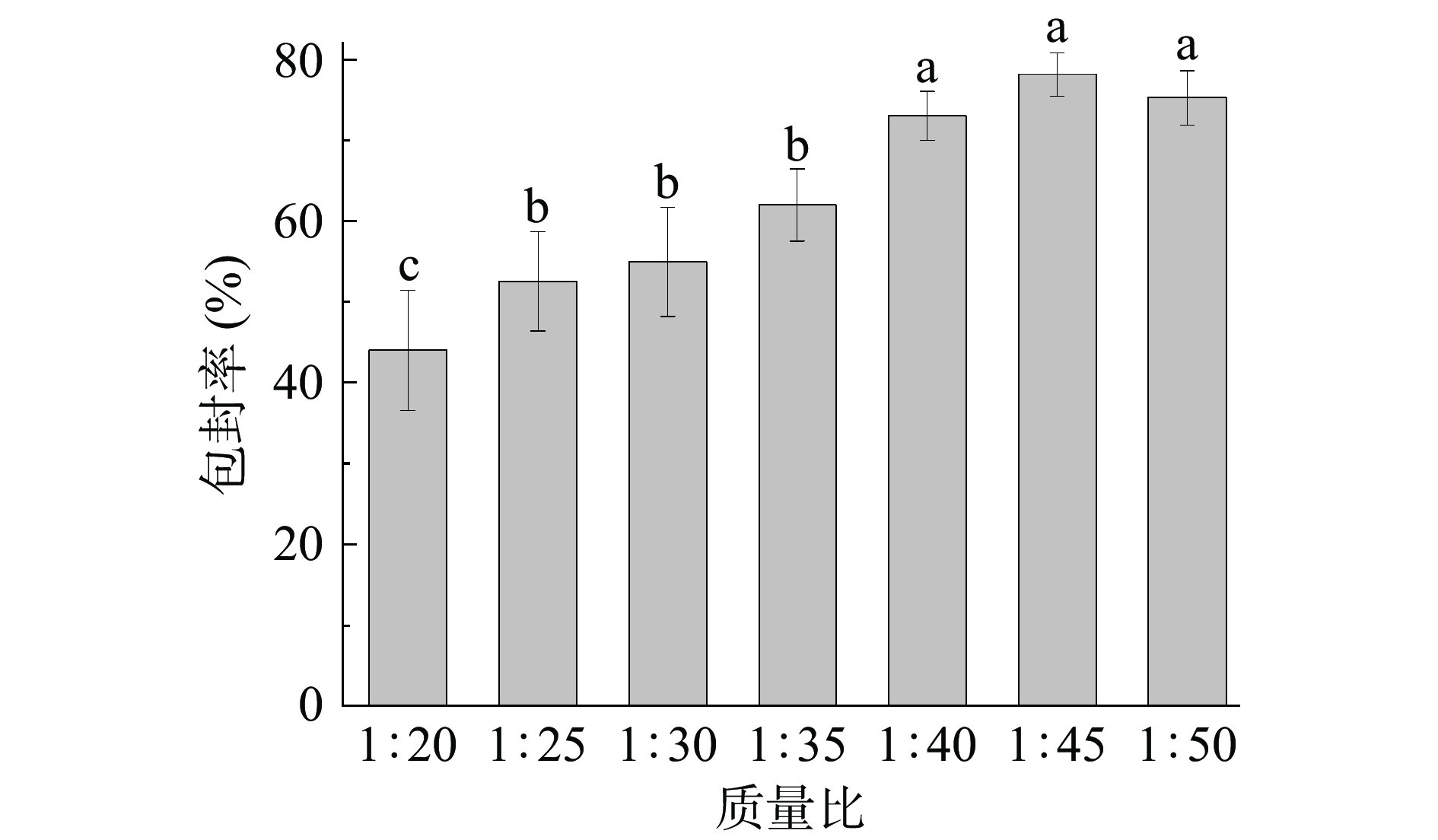
确定花青素与Fe3O4反应温度为50 ℃,反应时间为20 h条件下,研究花青素与Fe3O4质量比对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响。由图2可知,当m(花青素):m(Fe3O4)为1:20时,花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率最小;当花青素与Fe3O4质量比降至1:45时包封率达到最大,显著高于前四组(P<0.05),然后包封率下降。这可能是由于Fe3O4过量导致Fe3O4发生微量溶解[7],包封率下降。因此确定最佳的花青素与Fe3O4质量比为1:45。
2.2.2 花青素和Fe3O4反应时间对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响
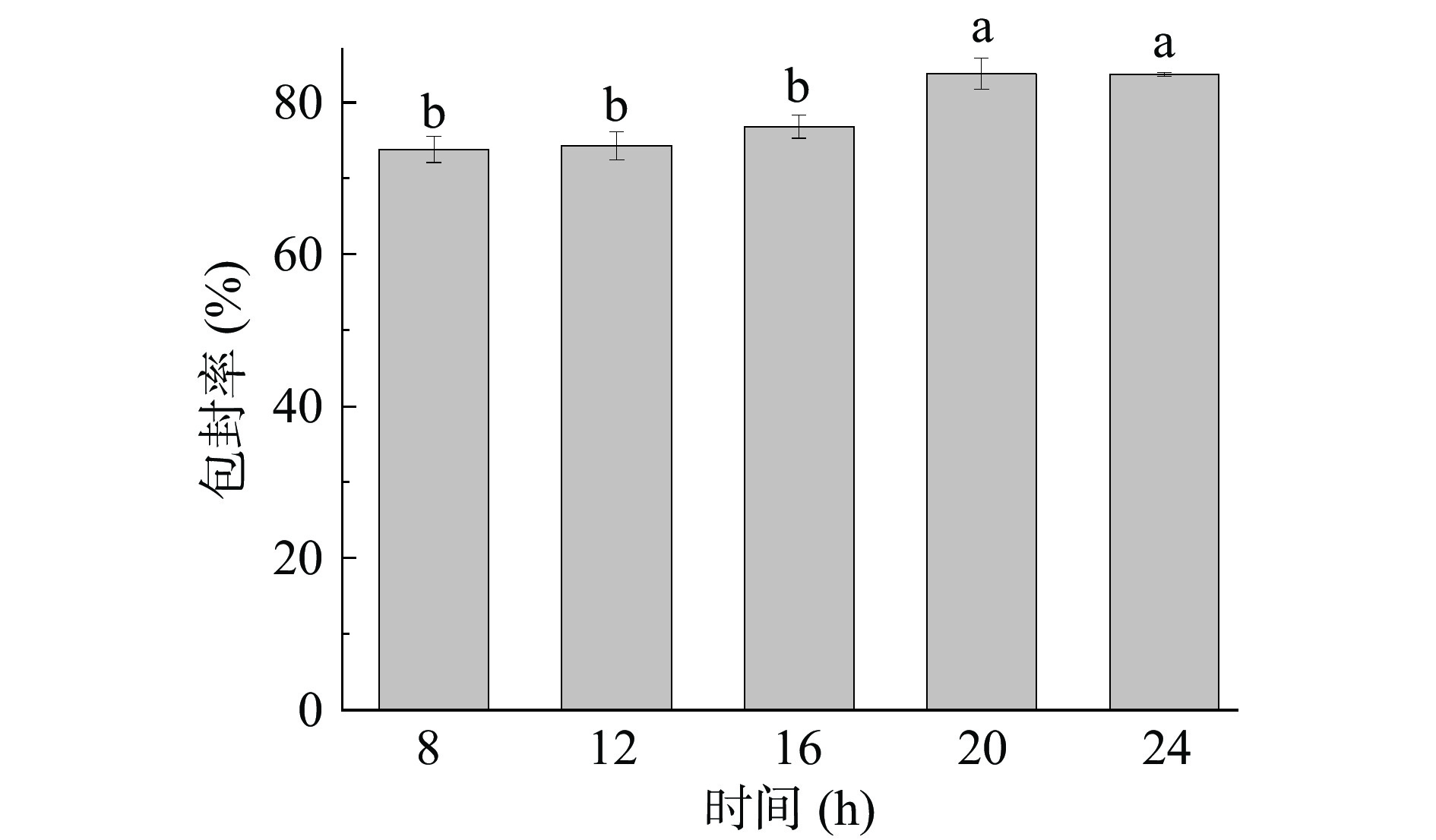
在花青素与Fe3O4质量比为1:45,反应温度为50 ℃条件下,实验研究不同反应时间对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响。由图3可见,8~20 h时包封率呈现逐渐上升的趋势,20 h时达到最大值,显著高于前三组(P<0.05),超过20 h包封率变化不显著(P>0.05),出现这种现象的原因可能是花青素带正电荷,Fe3O4纳米粒子带负电荷,随着时间的延长正负电荷紧密结合,交联性增强,Fe3O4纳米粒子对花青素的吸附性增强,但是随着时间进一步延长,花青素的氧化降解明显[21],导致包封率下降。由结果可见,确定花青素与Fe3O4的适宜反应时间为20 h。
2.2.3 花青素和Fe3O4反应温度对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响
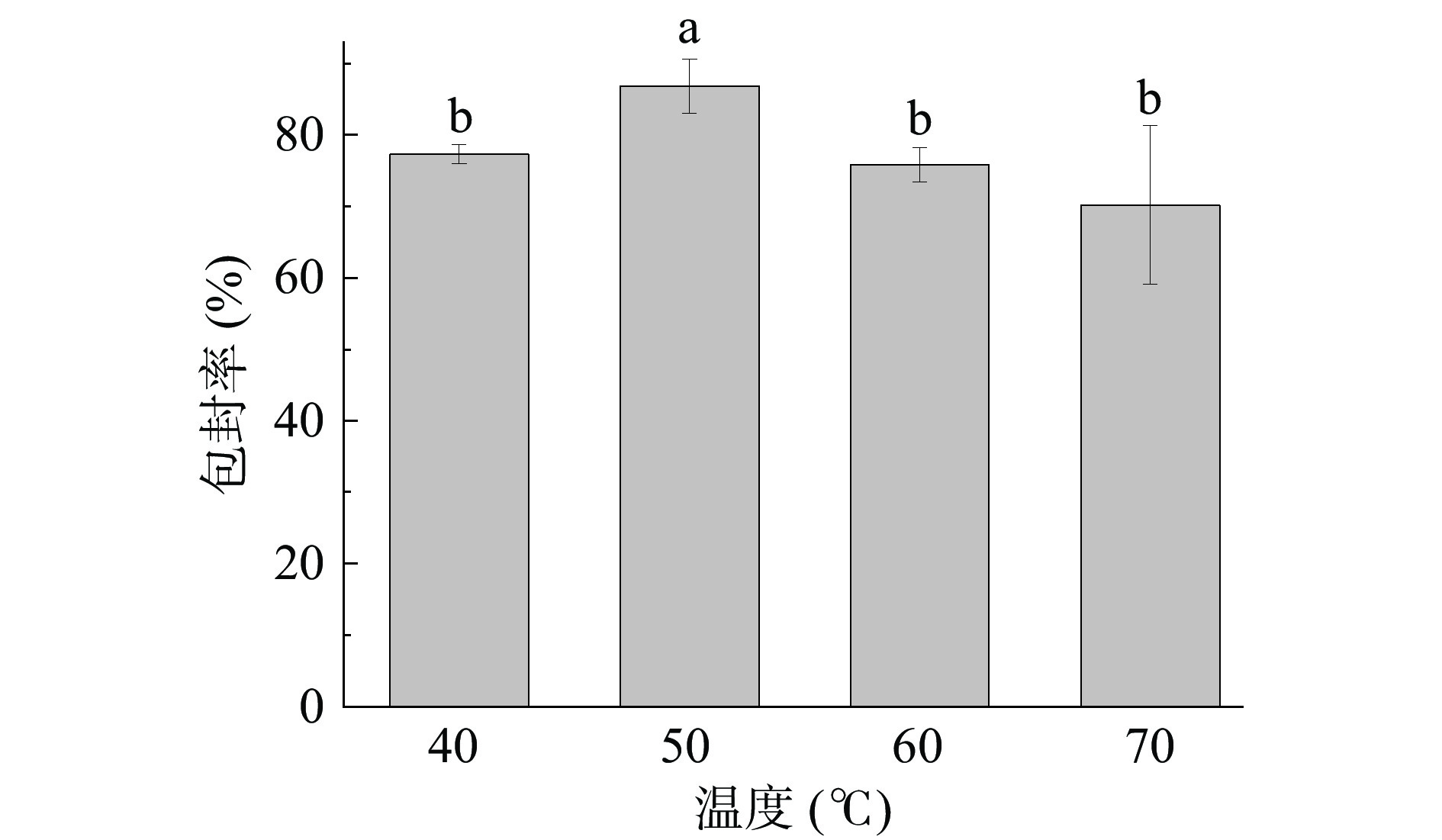
在花青素和Fe3O4质量比为1:45,反应时间为20 h条件下,改变花青素和Fe3O4的反应温度,探讨不同温度对花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物包封率的影响。由图4可见,反应温度从40 ℃增加到50 ℃时,包封率达到最大值,高于其他处理组(P<0.05),当温度超过50 ℃后包封率呈下降趋势,造成这种现象的原因可能是花青素对温度敏感,温度升高会使花青素中的查尔酮式结构增加,导致花青素的存在形式发生改变,Fe3O4纳米粒子对其吸附作用减弱,这与王立爽等[22]的研究相似:紫甘薯花青素稳定性随着温度的升高而下降,随着时间延长,花青素含量显著下降,导致包封率下降。由结果可见,确定花青素与Fe3O4的适宜反应温度为50 ℃。
2.3 响应面法优化花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的制备工艺
2.3.1 响应面优化试验结果及方差分析
在单因素实验的结果上,本实验主要以两者的质量比(A),反应时间(B),反应温度(C)为主要因素进行分析,以包封率(Y)作为响应值。响应面试验设计与结果见表2。利用Design-expert 8.0.6软件对实验结果进行二次回归拟合,得到A,B,C的二次回归方程如下:Y=86.87+4.02A+1.08B−5.17C−6.48AB+8.25AC+3.37BC−6.37A2−6.02B2−7.32C2。Box-Behnken响应面模型的方差分析结果见表3,由方差分析结果可知R2=0.9839,失拟度检验F值为6.37,“拟合不足”的P=0.0879,失拟项不显著,表明该模型无失拟因素存在,模型与实际值可以较好地拟合[23]。由拟合方程结果可知拟合模型F值为47.55,P<0.0001表明模型极显著,拟合良好。由表3还可以看出,模型中一次项A和C,二次项A2、B2、C2和交互项AB、AC和BC对花青素包封率影响极其显著(P<0.01);一次项B对花青素包封率的影响不显著,根据F值大小可以判断出各因素对花青素包封率的影响大小依次为C(温度)>A(质量比)>B(时间)。
表 2 响应面试验设计与结果Table 2. Response surface design experiment conditions and results试验号 A B C Y(%) 1 1 −1 0 81.89 2 1 0 −1 76.20 3 0 0 0 86.04 4 −1 −1 0 63.81 5 0 1 1 72.17 6 0 0 0 86.17 7 0 1 −1 75.95 8 −1 1 0 79.99 9 0 0 0 88.78 10 0 −1 −1 82.34 11 0 0 0 86.10 12 0 0 0 87.25 13 1 0 1 81.09 14 0 −1 1 63.63 15 −1 0 1 53.66 16 1 1 0 72.23 17 −1 0 −1 81.77 表 3 Box-Behnken响应面模型的方差分析Table 3. ANOVA for response surface model of Box-Behnken来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 1507.98 9 167.55 47.55 <0.0001 ** A 129.44 1 129.44 36.74 0.0005 ** B 9.40 1 9.40 2.67 0.1465 C 261.18 1 261.18 74.12 <0.0001 ** AB 166.93 1 166.93 47.38 0.0002 ** AC 272.25 1 272.25 77.27 <0.0001 ** BC 55.73 1 55.73 15.82 0.0053 ** A2 170.60 1 170.60 48.42 0.0002 ** B2 152.73 1 152.73 43.35 0.0003 ** C2 225.78 1 225.78 64.08 <0.0001 ** 残差 24.66 7 3.52 失拟项 19.10 3 6.37 4.58 0.0879 纯误差 5.56 4 1.39 总离差 1532.65 16 注:*P<0.05;**P<0.01。 2.3.2 响应面图和等高线图分析
依据多元二次回归方程绘制的响应面图可以直接反应出各个因素之间相互作用的强弱,3D图中曲面的倾斜度越高,坡度越陡,说明两两因素交互作用越显著。等高线图也可以反映两个因素之间的交互作用的强弱,当等高线为椭圆时,表明两因素交互作用显著[24],等高线为圆形时交互作用不显著[25],由图5可以看出交互项AB、AC和BC对花青素包封率的影响极显著,这与表3方差分析的结果一致,证明该模型可靠性高。
2.3.3 验证实验
通过回归方程得到的最佳提取工艺条件为:花青素与Fe3O4的最佳质量比为1:45.75,时间为19.63 h,温度为46.72 ℃,此条件下花青素包封率为88.06%。为验证实验数据的可靠性,结合实验真实的具备条件,在花青素与Fe3O4质量比为1:46,反应时间为19.6 h,反应温度47 ℃条件下进行三次重复实验,得到的包封率为87.51%。与理论预测值相差0.6%,说明该模型优化的最佳提取工艺条件稳定可靠,具有实际应用价值。
2.4 结构表征结果
2.4.1 粒径与Zeta电位测定
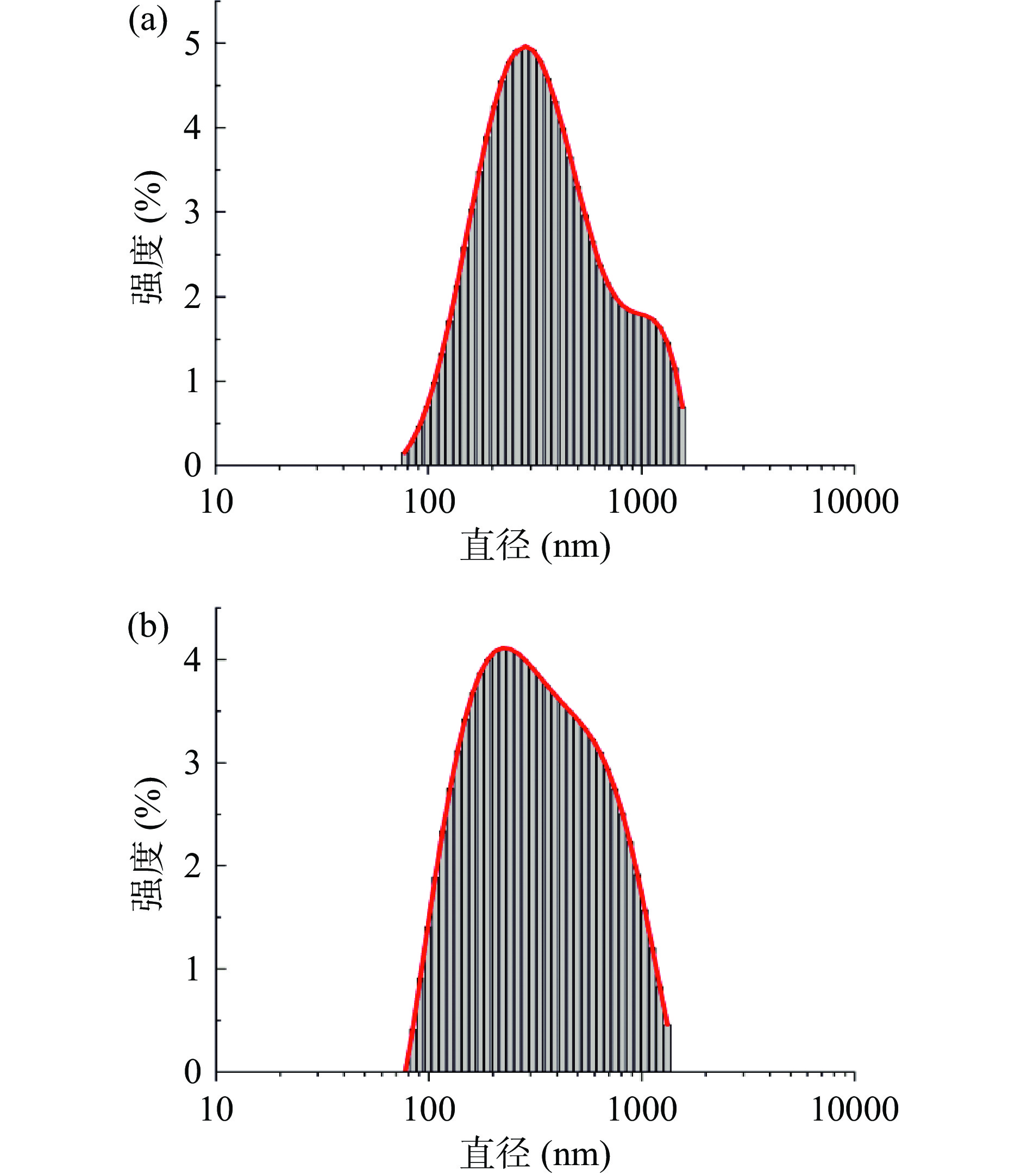
从表4可以看出花青素溶液带正电荷,Fe3O4溶液带负电荷,因此两者之间存在静电吸附作用,有利于二者的结合,且合成的花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物Zeta电位增大。Fe3O4和花青素/Fe3O4纳米粒子复合物的粒径分布如图6所示,Fe3O4的粒径分布范围在100~1000 nm,花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合材料粒径分布范围集中在100~1200 nm,合成的纳米复合物粒径大于Fe3O4纳米粒子,表明Fe3O4纳米粒子包覆花青素,导致粒径增大,形成花青素/Fe3O4磁性生物复合材料。
表 4 花青素、Fe3O4和花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的Zeta电位Table 4. Zeta potential of anthocyanin, Fe3O4 and anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nanocomposites材料 电位(mV) 平均电位(mV) 花青素 +10.41 +11.02 +11.63 +11.02 Fe3O4 −58.18 −58.78 −59.39 −58.78 花青素/Fe3O4 −47.55 −48.15 −48.75 −48.15 2.4.2 微观形貌分析
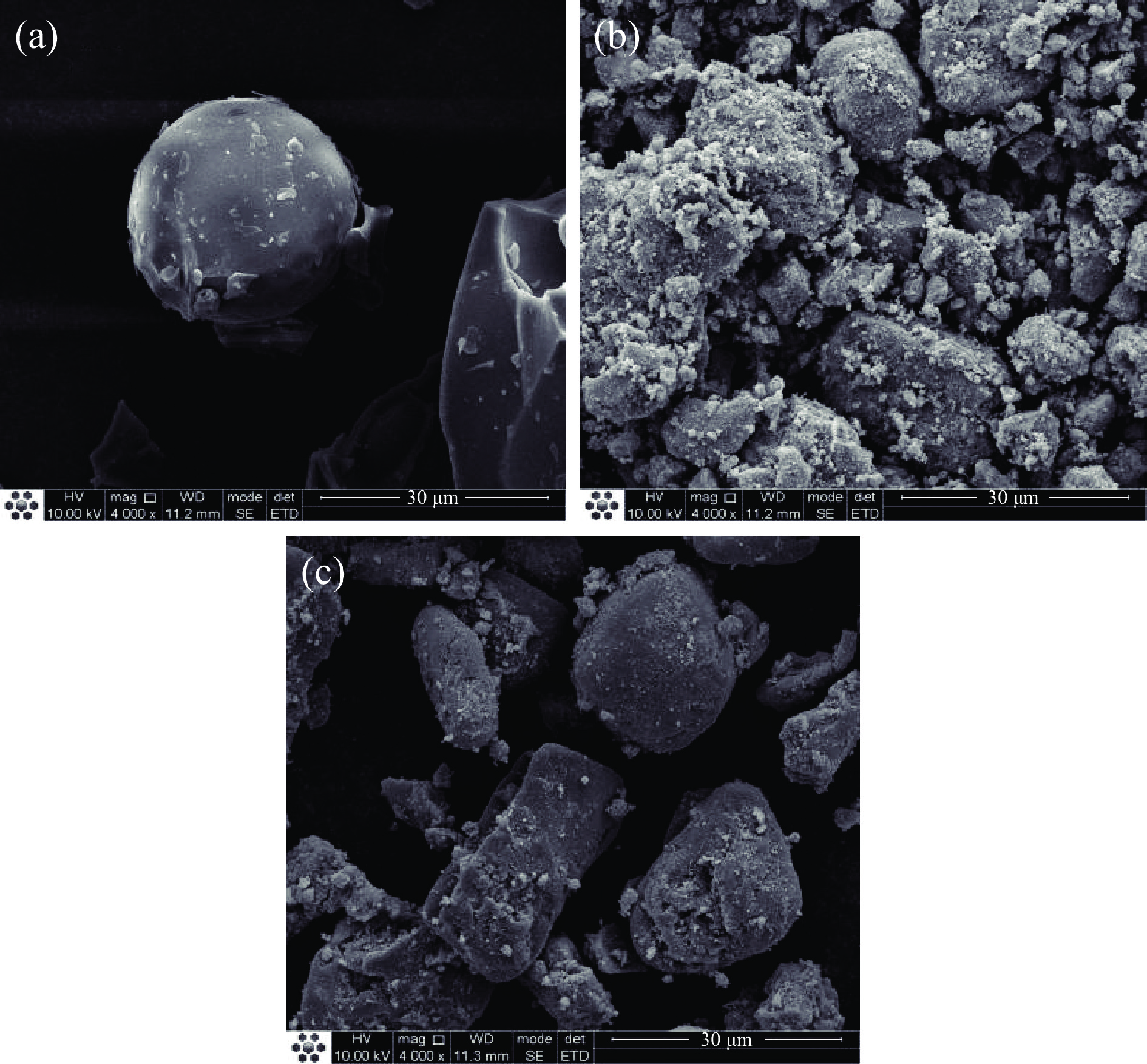
花青素粉末、Fe3O4纳米粒子、花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的扫描电镜图见图7。由图7可知,花青素粉末表面光滑无凸起。Fe3O4纳米粒子呈球状颗粒,表面粗糙。与Fe3O4纳米粒子相比,花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物表面光滑,说明花青素成功结合在Fe3O4纳米粒子表面。
2.4.3 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
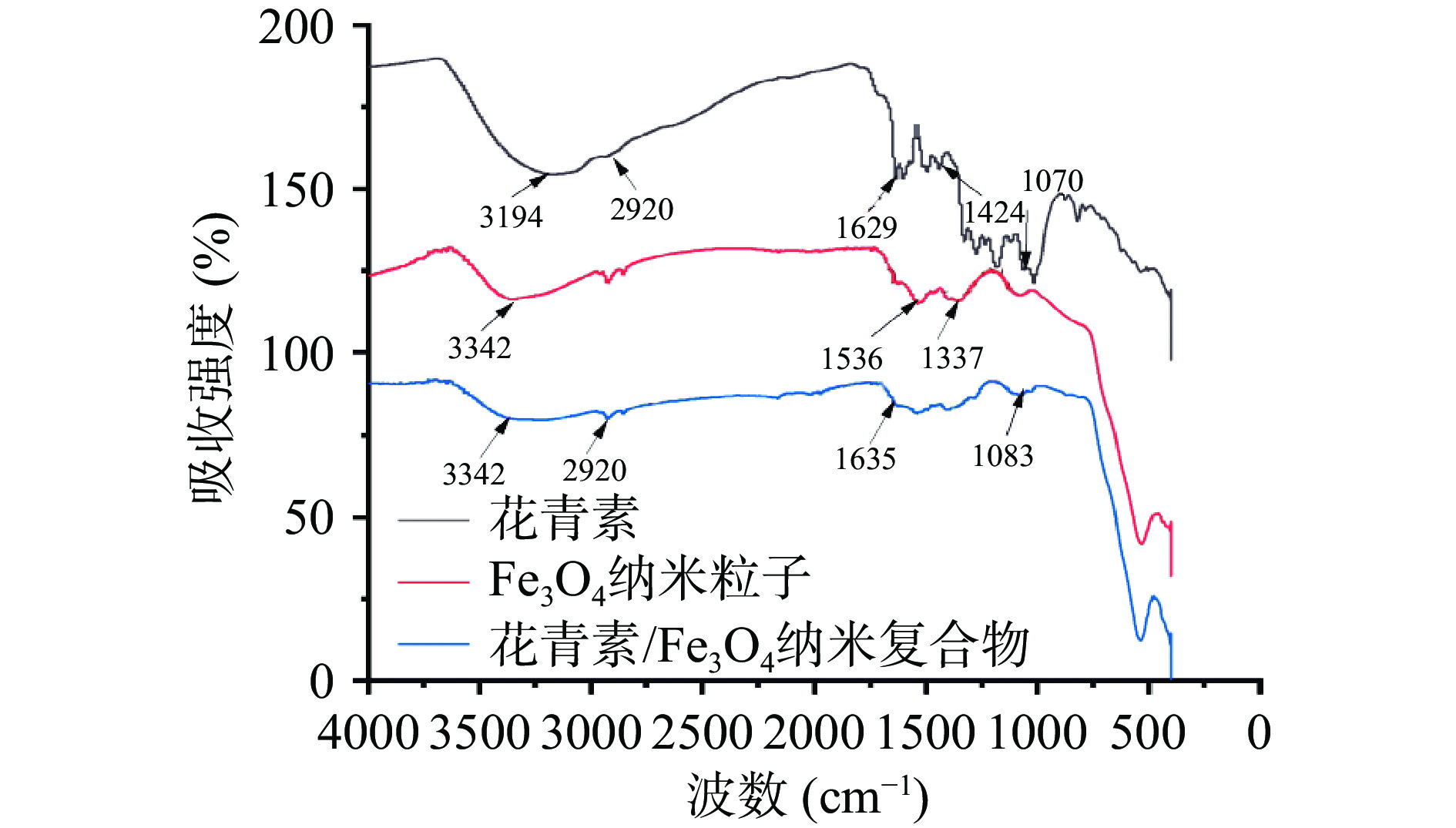
花青素粉末、Fe3O4纳米粒子、花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的傅里叶红外光谱见图8。由图8可知,花青素在3194和2920 cm−1处是氢键缔合的-OH伸缩振动吸收峰与C-H的伸缩振动吸收峰,在1629、1424和1070 cm−1分别为苯并吡喃芳香环振动的C=O、C=C芳香环拉伸振动和C-H芳香环变形振动吸收峰[26-27]。Fe3O4纳米粒子在3342、1536和1337 cm−1处出现吸收峰,分别代表O-H和C-N吸收峰[28]。花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物在1635、1083 cm−1出现特征峰,这是由花青素C=O和C-H拉伸引起,说明花青素与Fe3O4纳米粒子成功结合。
2.5 体外消化实验结果分析
2.5.1 模拟消化对花青素保留率的影响
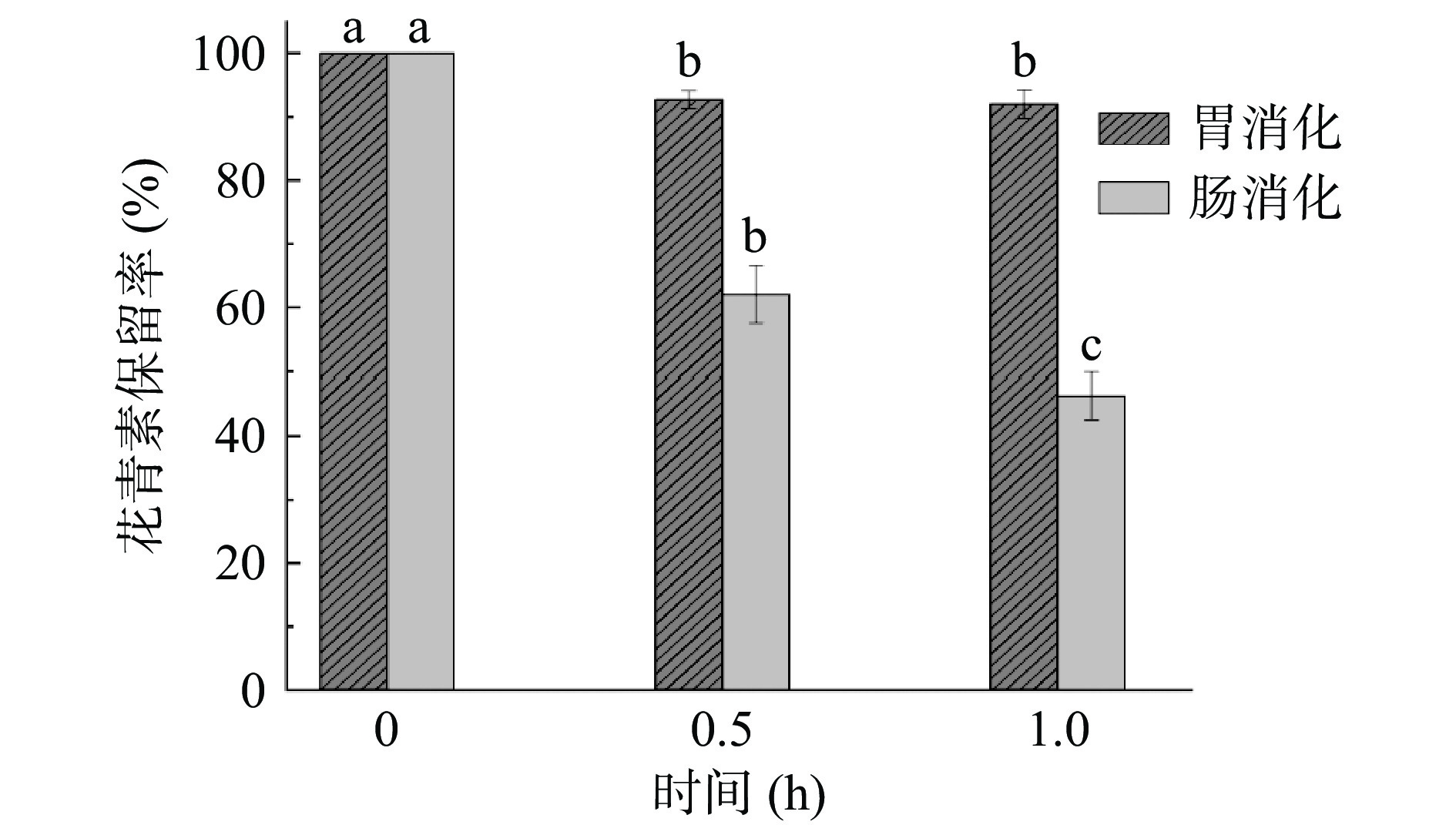
如图9所示,模拟胃肠消化后花青素保留率明显下降(P<0.05)。与0 h(未消化)相比,在模拟胃消化0.5 h时花青素保留率为92.73%,随着消化时间的延长,在1 h时,花青素保留率为91.99%,花青素含量趋于平稳,消化时间对花青素含量的变化没有显著影响(P>0.05)。与0 h相比,模拟肠消化1.0 h时,花青素含量显著降低了53.77%(P<0.05)。与胃消化相比,花青素在肠消化中损失量是胃消化的6.71倍,相比于肠部环境花青素在胃部环境中更加稳定。造成这种现象的原因可能是胃液的强酸性,花青素可稳定地以2-苯基苯并吡喃阳离子形式存在,且释放的花青素始终保持较高稳定性[29]。在肠部环境中花青素的降解速率快,这与姚惠芳等[30]的研究结果一致,造成这种差异的原因可能是当花青素进入到pH为8.0的肠道环境时,由于pH迅速上升,花青素以醌式结构、半缩酮、查儿酮等形式存在,稳定性下降。
2.5.2 DPPH自由基清除能力
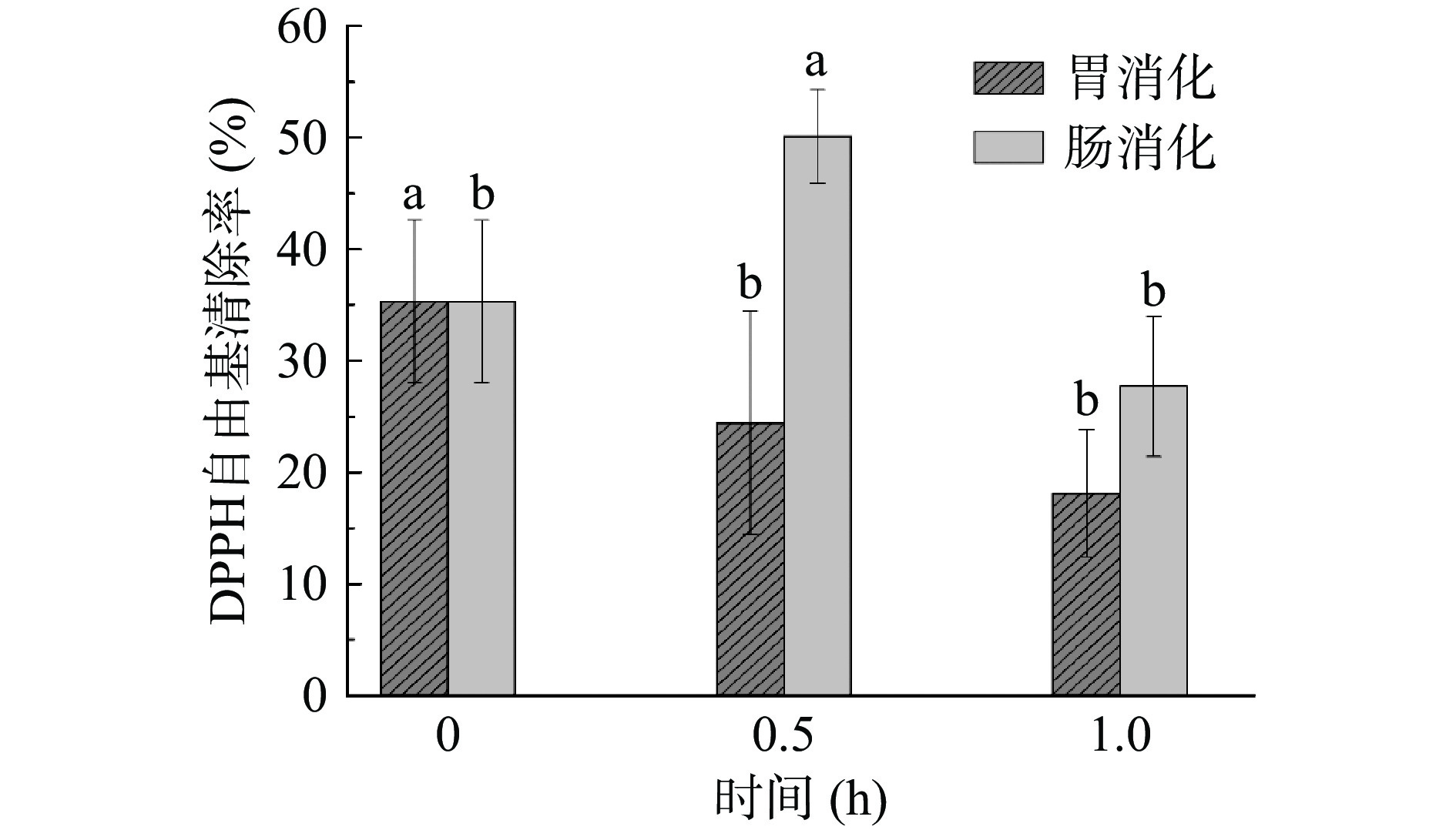
由图10可知,在胃消化过程中花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的DPPH自由基清除能力随消化时间的延长而减少,在0~0.5 h时间内DPPH自由基清除能力显著下降(P<0.05)。与0 h相比,胃消化1.0 h后DPPH自由基清除能力下降了17.21%。肠消化过程中DPPH自由基清除能力呈现先增加后减少的趋势,在消化时间达到0.5 h时DPPH自由基清除能力达到最大,变化显著(P<0.05)。肠消化过程中DPPH自由基清除率明显高于胃消化阶段,这是由于在肠消化液中消化酶的作用,使得花青素中的结合态酚分解释放出游离态酚[31-32],纳米复合物对DPPH自由基清除能力增加。
2.5.3 ABTS+自由基清除能力
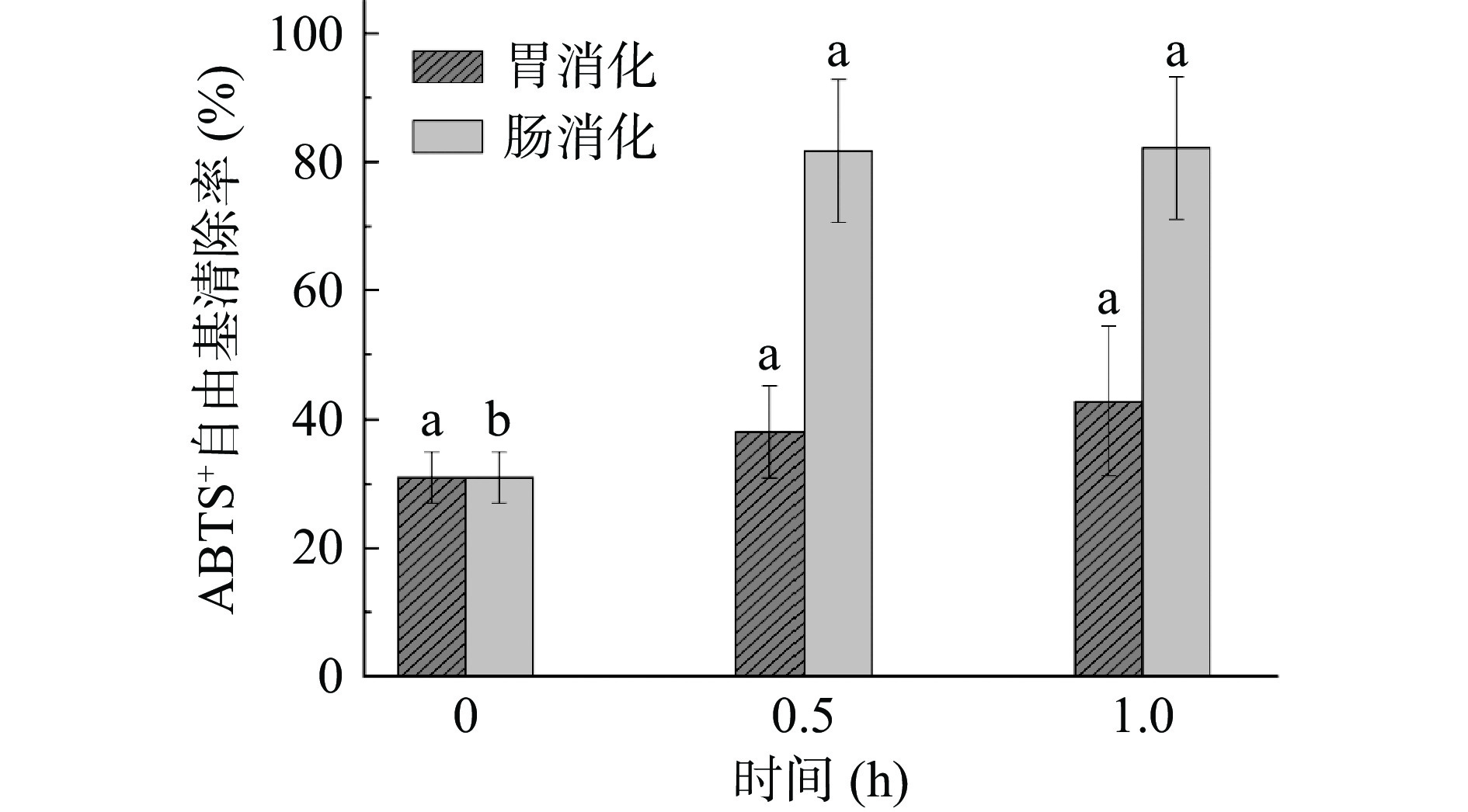
如图11可知,在胃消化阶段,随着消化时间的延长,ABTS+自由基清除能力增加了11.80%。消化时间对ABTS+自由基清除能力没有显著影响(P>0.05)。在肠消化阶段ABTS+自由基清除能力显著增加51.18%(P<0.05)。在胃消化和肠消化过程中ABTS+自由基清除能力与花青素含量和DPPH自由基清除能力变化趋势不同。比较胃消化阶段和肠消化阶段ABTS+自由基清除能力结果可知肠消化后ABTS+自由基清除能力远大于胃消化阶段。造成这种现象的原因可能是多酚类化合物ABTS+自由基清除率呈现pH依赖性,随着pH的增高,清除能力变强,这与多酚化合物芳香环酚性羟基在弱碱性pH环境下去质子化有关[33],导致花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物对ABTS+自由基清除能力增加。
3. 结论
本研究利用共沉淀法合成花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物,在单因素实验基础上利用响应面法优化花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的合成,最佳提取条件为花青素与Fe3O4质量比为1:46,反应时间19.6 h,反应温度47 ℃。在此条件下,花青素包封率为87.51%,Fe3O4纳米粒子和花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的电位分别为−58.78 mV和−48.15 mV。扫描电子显微镜表明花青素与Fe3O4纳米粒子间形成了表面光滑的球状颗粒。傅里叶变换红外光谱结果发现花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物在1635 cm−1和1083 cm−1处出现花青素C=O和C-H特征峰。体外消化试验结果表明花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物在体外消化实验中的抗氧化性不同。在胃消化阶段0~1 h内花青素的保留率没有显著变化(P>0.05)。花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物DPPH自由基清除能力在胃消化阶段0~0.5 h内显著变化(P<0.05),肠消化阶段0.5 h时DPPH自由基清除能力达50.11%。在肠消化时间达1 h时花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物ABTS+自由基清除率为82.18%,约是DPPH自由基清除率的2.96倍。结果表明共沉淀法制备的花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物有助于提高花青素的生物利用率,并在体外消化实验不同消化阶段表现出不同抗氧化性。本实验为花青素纳米复合物研究和应用提供了实验依据。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Factors and levels for response surface test
因素 水平 −1 0 1 A质量比 1:40 1:45 1:50 B时间(h) 16 20 24 C温度(℃) 40 50 60 表 2 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 2 Response surface design experiment conditions and results
试验号 A B C Y(%) 1 1 −1 0 81.89 2 1 0 −1 76.20 3 0 0 0 86.04 4 −1 −1 0 63.81 5 0 1 1 72.17 6 0 0 0 86.17 7 0 1 −1 75.95 8 −1 1 0 79.99 9 0 0 0 88.78 10 0 −1 −1 82.34 11 0 0 0 86.10 12 0 0 0 87.25 13 1 0 1 81.09 14 0 −1 1 63.63 15 −1 0 1 53.66 16 1 1 0 72.23 17 −1 0 −1 81.77 表 3 Box-Behnken响应面模型的方差分析
Table 3 ANOVA for response surface model of Box-Behnken
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 1507.98 9 167.55 47.55 <0.0001 ** A 129.44 1 129.44 36.74 0.0005 ** B 9.40 1 9.40 2.67 0.1465 C 261.18 1 261.18 74.12 <0.0001 ** AB 166.93 1 166.93 47.38 0.0002 ** AC 272.25 1 272.25 77.27 <0.0001 ** BC 55.73 1 55.73 15.82 0.0053 ** A2 170.60 1 170.60 48.42 0.0002 ** B2 152.73 1 152.73 43.35 0.0003 ** C2 225.78 1 225.78 64.08 <0.0001 ** 残差 24.66 7 3.52 失拟项 19.10 3 6.37 4.58 0.0879 纯误差 5.56 4 1.39 总离差 1532.65 16 注:*P<0.05;**P<0.01。 表 4 花青素、Fe3O4和花青素/Fe3O4纳米复合物的Zeta电位
Table 4 Zeta potential of anthocyanin, Fe3O4 and anthocyanin/Fe3O4 nanocomposites
材料 电位(mV) 平均电位(mV) 花青素 +10.41 +11.02 +11.63 +11.02 Fe3O4 −58.18 −58.78 −59.39 −58.78 花青素/Fe3O4 −47.55 −48.15 −48.75 −48.15 -
[1] 马蓉. 紫色蔬菜中花色苷抗糖功能及抗炎功能的评价[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2020 MA R. Evaluation of anti-glycemic and anti-inflammatory function of anthocyanin in purple vegetables[D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2020.
[2] 张念, 彭怡霖, 陈细羽, 等. 超高效液相色谱法检测植物源性食品中花青素[J]. 分析科学学报,2022,38(1):17−23. [ZHANG N, PENG Y L, CHEN X Y, et al. Determination of anthocyanins in plant origin products by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Analytical Science,2022,38(1):17−23. doi: 10.13526/j.issn.1006-6144.2022.01.004 ZHANG N, PENG Y L, CHEN X Y, et al. Determination of anthocyanins in plant origin products by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Analytical Science, 2022, 38(1): 17-23. doi: 10.13526/j.issn.1006-6144.2022.01.004
[3] RU J Y, HAI B L, YANG Y, et al. Anticancer activities of proanthocyanidins from the plant Urceola huaitingii and their synergistic effects in combination with chemotherapeutics[J]. Fitoterapia,2016,112:175−182. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.05.015
[4] TOYAMA Y, TOSHIMA S, HIRANO T, et al. Polyphenol contents, antioxidant activitie, and anti-cancer cell proliferation properties at each stage of fruit development in intersectional hybrids between highbush blueberry and shashanbo (Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb.)[J]. Journal of Berry Research,2021,11(4):689−704. doi: 10.3233/JBR-210713
[5] 张勍, 汪晟坤, 连秀仪, 等. 夏黑葡萄花青素在D-半乳糖致衰老小鼠心肌细胞抗氧化和清除自由基中的作用[J]. 河南医学研究,2019,28(20):3649−3652. [ZHANG Q, WANG S K, LIAN X Y, et al. The antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects of Xiahei grape anthocyanin in myocardialcells of aging mice induced by D-galactose[J]. Henan Medical Research Henan Med Res,2019,28(20):3649−3652. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2019.20.001 ZHANG Q, WANG S K, LIAN X Y, et al. The antioxidant and free radical scavenging effects of Xiahei grape anthocyanin in myocardialcells of aging mice induced by D-galactose[J]. Henan Medical Research Henan Med Res, 2019, 28(20): 3649-3652. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2019.20.001
[6] 徐青, 王代波, 刘国华, 等. 花青素稳定性影响因素及改善方法研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(7):218−224. [XU Q, WANG D B, LIU G H, et al. Influencing factors and improving methods of anthocyanin stability[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(7):218−224. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.07.037 XU Q, WANG D B, LIU G H, et al. Influencing factors and improving methods of anthocyanin stability[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(7): 218-224. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.07.037
[7] 蒋希芝. 桑椹花青素的结构修饰和纳米复合物及其生物学特性研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2020 JIANG X Z. Structural modification and nanocomposites of mulberry anthocyanin and its biological characteristics[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[8] CHEN B H, STEPHEN I B. Nanoemulsion and nanoliposome based strategies for improving anthocyanin stability and bioavailability[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(5):1052. doi: 10.3390/nu11051052
[9] RAFIEE Z, BARZEGAR M, SAHARI M A, et al. Nanoliposomal carriers for improvement the bioavailability of high-valued phenolic compounds of pistachio green hull extract[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,220:115−122. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.207
[10] MA Y Y, XU J J, JIANG S S, et al. Effect of chitosan coating on the properties of nanoliposomes loaded with oyster protein hydrolysates: Stability during spray-drying and freeze-drying[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,385:132−603.
[11] WANG L, ZHOU B Q, LI Y H, et al. Lactoferrin modification of berberine nanoliposomes enhances the neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Neural Regeneration Research,2023,18(1):226−232. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.344841
[12] SUZANA G C, VICTOR H S A, ALINE M D S, et al. Advances and challenges in nanocarriers and nanomedicines for veterinary application[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,580:119−214.
[13] 汤宇峰, 李丽敏, 李嘉琪. 浅谈四氧化三铁纳米粒子的制备方法与利用现状[J]. 安徽化工,2022,48(1):14−16. [TANG Y F, LI L M, LI J Q. Research status and application prospect of oral in-situ gel[J]. Anhui Chemical Industry,2022,48(1):14−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-553X.2022.01.004 TANG Y F, LI L M, LI J Q. Research status and application prospect of oral in-situ gel[J]. Anhui Chemical Industry, 2022, 48(1): 14-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-553X.2022.01.004
[14] 史宇哲. 植物原花青素功能化的四氧化三铁制备及应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020 SHI Y Z. Preparation and application of functionalized iron tetroxide from proanthocyanidins[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2020.
[15] VIVIAN C I, LUIZ G L. Black rice (Oryza sativa L.): A review of its historical aspects, chemical composition, nutritional and functional properties, and applications and processing technologies[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,301:125−304.
[16] 刘长姣, 郑霞, 熊湘炜, 等. 分光光度法测定黑米花青素方法的建立[J]. 粮食与油脂,2019,32(1):73−77. [LIU C J, ZHENG X, XIONG X W, et al. Detection of anthocyanin in black rice by spectrophotometry[J]. Cereals& Oils,2019,32(1):73−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2019.01.020 LIU C J, ZHENG X, XIONG X W, et al. Detection of anthocyanin in black rice by spectrophotometry[J]. Cereals&Oils, 2019, 32(1): 73-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2019.01.020
[17] CHEN K L, NI X J, WANG L C, et al. Evaluation of the stability and the encapsulation efficiency of W/O/W; multiple emulsions by electrochemical determination[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology,2020,41(13):1949−1955. doi: 10.1080/01932691.2019.1645021
[18] 李玉壬, 王瑞, 王旭捷, 等. 茶多酚在模拟胃肠消化过程中含量及活性的变化规律[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(7):115−120, 22. [LI Y R, WANG R, WANG X J, et al. Changes in content and antioxidant activity of tea polyphenols during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology,2021,37(7):115−120, 22. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2021.7.0025 LI Y R, WANG R, WANG X J, et al. Changes in content and antioxidant activity of tea polyphenols during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal Digestion[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology, 2021, 37(7): 115-120, 22. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2021.7.0025
[19] 金珊珊. 燕麦β-葡聚糖的氧化及载姜黄素纳米复合物的研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2018 JIN S S. Study on the oxidation of β-glucan and curcumin-loaded oxidized β-glucan nanocomposite[D]. Fuzhou: Fuzhou University, 2018.
[20] 朱文卿. 牛蒡多糖-绿原酸复合物的制备、结构表征及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2022 ZHU W Q. Preparation, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of burdock polysaccharide-chlorogenic acid complex[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022.
[21] 刘凯. 蓝莓-绿茶复合饮料的制备研究[D]. 济南: 齐鲁工业大学, 2021 LIU K. Study on preparation of blueberry-green tea compound beverage[D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Technology, 2021.
[22] 王立爽, 蒋裕琪, 于凤桐, 等. 响应面法优化紫甘薯花青素微胶囊制备工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(19):191−196. [WANG L S, JIANG Y Q, YU F T, et al. Optimization of purple sweet potato anthocyanins microcapsules by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(19):191−196. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.19.035 WANG L S, JIANG Y Q, YU F T, et al. Optimization of purple sweet potato anthocyanins microcapsules by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(19): 191-196. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.19.035
[23] 李琳, 张国强, 石晓峰. Box-Behnken响应面法优化复方红黄口含片的醇提工艺[J]. 华西药学杂志,2020,35(4):416−423. [LI L, ZHANG G Q, SHI X F. Optimization of the alcohol extraction process of compound honghuang buccal tablets by Box-Behnken response surface method[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2020,35(4):416−423. doi: 10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2020.04.015 LI L, ZHANG G Q, SHI X F. Optimization of the alcohol extraction process of compound honghuang buccal tablets by Box-Behnken response surface method[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2020, 35(4): 416-423. doi: 10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2020.04.015
[24] 张怀予, 王军节, 陈园凡, 等. 水蒸气蒸馏法提取花椒精油及挥发性成分分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2014,40(7):166−172. [ZHANG H Y, WANG J J, CHEN Y F, et al. Optimization of steam distillation extraction of Zanthoxylum bungeanum essential oil by response surface methodology and essential volatile components analysis[J]. Food And Fermentation Industries,2014,40(7):166−172. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2014.07.017 ZHANG H Y, WANG J J, CHEN Y F, et al. Optimization of steam distillation extraction of Zanthoxylum bungeanum essential oil by response surface methodology and essential volatile components analysis[J]. Food And Fermentation Industries, 2014, 40(7): 166-172. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2014.07.017
[25] 杨海荣, 马绍英, 赵利敏, 等. 响应面分析法优化西兰花离体细胞系萝卜硫素提取工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(15):206−209, 214. [YANG H R, MA S Y, ZHAO L M, et al. Optimization of extraction technique of sulforaphane from broccoli callus via by response surface methodology (RSM)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(15):206−209, 214. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2012.15.033 YANG H R, MA S Y, ZHAO L M, et al. Optimization of extraction technique of sulforaphane from broccoli callus via by response surface methodology(RSM)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2012, 33(15): 206-209, 214. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2012.15.033
[26] 王蕾, 陈依, 杨雅其, 等. 蓝莓花青素脂质体的制备及其稳定性研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(5):85−94. [WANG L, CHEN Y, YANG Y Q, et al. Preparation and stability of blueberry anthocyanin liposomes[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(5):85−94. WANG L, CHEN Y, YANG Y Q, et al. Preparation and stability of blueberry anthocyanin liposomes[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 85-94.
[27] 姚乐, 王诗意, 周斐, 等. 壳聚糖/花青素复合薄膜的制备及鱼肉新鲜度监测[J]. 包装工程,2022,43(9):83−91. [YAO L, WANG S Y, ZHOU F, et al. Preparation of chitosan/anthocyanin composite film for monitoring of fish freshness[J]. Packaging Engineering,2022,43(9):83−91. doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2022.09.011 YAO L, WANG S Y, ZHOU F, et al. Preparation of chitosan/anthocyanin composite film for monitoring of fish freshness[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2022, 43(9): 83-91. doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2022.09.011
[28] BARRETO A C H, SANTIAGO V R, MAZZETTO S E, et al. Magnetic nanoparticles for a new drug delivery system to control quercetin releasing for cancer chemotherapy[J]. Journal of Nanoparticle Research,2011,13:6545−6553. doi: 10.1007/s11051-011-0559-9
[29] 陈程莉, 李丰泉, 刁倩, 等. 不同壁材对黑枸杞花青素微胶囊稳定性和缓释特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(16):78−85. [CHEN C L, LI F Q, DIAO Q, et al. Effects of different wall materials on the stability and sustained-release characteristics of anthocyanin microcapsules of Lycium ruthenicum Murr[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(16):78−85. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.023782 CHEN C L, LI F Q, DIAO Q, et al. Effects of different wall materials on the stability and sustained-release characteristics of anthocyanin microcapsules of Lycium ruthenicum Murr[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(16): 78-85. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.023782
[30] 姚惠芳, 董学艳, 景浩. 牛血清白蛋白与花青素纳米颗粒的特性及稳定性研究[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(1):1−6. [YAO H F, DONG X Y, JING H. Characteristics of bovine serum albumin-anthocyanin bioactive nanoparticles[J]. Food Science,2014,35(1):1−6. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201401001 YAO H F, DONG X Y, JING H. Characteristics of bovine serum albumin-anthocyanin bioactive nanoparticles[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(1): 1-6. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201401001
[31] 朱秀灵, 叶精勤, 盛伊健, 等. 体外模拟消化对苹果多酚及其抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(8):63−71. [ZHU X L, YE J Q, SHENG Y J, et al. Effects of in vitro simulated digestion on apple polyphenols and their antioxidant activities[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(8):63−71. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022747 ZHU X L, YE J Q, SHENG Y J, et al. Effects of in vitro simulated digestion on apple polyphenols and their antioxidant activities[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(8): 63-71. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022747
[32] JAYWARDENA N, AATAWANA M I, WAISUNDARA V Y. The total antioxidant capacity, total phenolics content and starch hydrolase inhibitory activity of fruit juices following pepsin (gastric) and pancreatin (duodenal) digestion[J]. Journal für Verbraucherschutz and Lebensmittelsicherheit,2015,10(4):349−357.
[33] TAGLIAZUCCHI D, VERZELLONI E, BERTOLINI D, et al. In vitro bio-accessibility and antioxidant activity of grape polyphenols[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,120(2):599−606. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.10.030
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 顾丹丹,董雪,张金秀,王晓茹,赵宗硕,王立安. 小麦羊肚菌菌粮制备工艺优化及营养成分、理化性质和抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2025(04): 237-245 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 马莉,季爱兵,曾胤,严亮. 蘑菇多糖生物活性及提取研究进展. 热带农业科学. 2024(06): 123-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
