Protective Effect of Phycocyanin on Cyclophosphamide-induced Immunocompromised Mice
-
摘要: 目的:研究藻蓝蛋白对环磷酰胺诱导小鼠肝肾组织损伤的保护作用,为评价肝肾治疗药物提供新的研究思路。方法:雌性BALB/c小鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、阳性对照组以及藻蓝蛋白低、中、高剂量组。采用腹腔注射环磷酰胺后建立小鼠肝肾损伤模型,然后空白组和模型组小鼠灌胃生理盐水,样品组给予不同剂量藻蓝蛋白溶液(50、100、200 mg/kg),阳性对照组灌胃盐酸左旋咪唑(40 mg/kg),灌胃时间5 d。采用试剂盒法分别测定各组小鼠血清中的白细胞介素-2(IL-2)、肿瘤因子-α(TNF-α)和免疫球蛋白(IgG)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、丙二醛(MDA)水平;肝组织的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、丙二醛(MDA)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、谷丙转氨酶(ALT);及肾组织的超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、丙二醛(MDA)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)、尿酸(UA)、尿素氮(BUN)水平并观察小鼠肝脏、肾脏组织形态学变化。结果:与模型组对比,藻蓝蛋白剂量组小鼠血清中的IL-2、TNF-α、MDA水平极显著下降(P<0.01);藻蓝蛋白高剂量组可明显降低血清中的IgG水平(P<0.05)并提高血清中的SOD水平(P<0.05);同时可降低由环磷酰胺引起的小鼠血清中MDA含量升高的情况(P<0.01),升高SOD活性(P<0.05);此外,藻蓝蛋白剂量组小鼠的肝组织GSH-Px水平极显著高于模型组(P<0.01),而MDA、ALT、AST水平均极显著低于模型组小鼠(P<0.01);相较于肝组织,藻蓝蛋白剂量组小鼠肾组织的MDA水平极显著低于模型组(P<0.01),仅低剂量藻蓝蛋白组小鼠肾组织的BUN水平极显著低于模型组(P<0.01),高剂量藻蓝蛋白组小鼠肾组织的UA水平极显著低于模型组(P<0.01)。结论:综合各项指标结果,藻蓝蛋白对环磷酰胺导致的小鼠肝肾损伤具有明显改善作用。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the protective effect of phycocyanin on hepatorenal co-damage in mice caused by cyclophosphamide, and to provide new research ideas for evaluating liver and kidney therapy drugs. Methods: Female BALB/c mice were randomly divided into blank group, model group, positive control group, high dose group, middle dose group and low dose group. The hepatic and kindy injury model of mice were established by intraperitoneal injection of cyclophosphamide (50, 100, 200 mg/kg), then the mice of blank group and model group were fed with normal saline, mice of positive control group were fed levimidazole hydrochloride (40 mg/kg) and the mice of dosage groups were fed different dosage of instant power of phycocyanin. Interleukin-2 (IL-2), tumournecrosis factor-α (TNF-α), immunoglobulin (IgG), superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA) of serum in mice, superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level of liver tissue and superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), uric acid (UA), urea nitrogenin (BUN) level of kindey tissue in each group mice were determined by reagent kit method. Experimental results showed that compared with the model group, the serum levels of IL-2, TNF-α and MDA in mice in the phycocyanin dose group decreased significantly (P<0.01). The high-dose group of phycocyanin significantly reduced serum IgG levels (P<0.05) and increased serum SOD levels (P<0.05). At the same time, it could reduce the elevated content of MDA in mice caused by cyclophosphamide (P<0.01) and increase SOD activity (P<0.05). In addition, the GSH-Px levels of liver tissue in mice in the phycocyanin dose group were significantly higher than those in the model group (P<0.01), while the levels of MDA, ALT, and AST were significantly lower than those in the model group (P<0.01). Compared with liver tissue, the MDA level of mouse kidney tissue in the phycocyanin dose group was significantly lower than that in the model group (P<0.01), the BUN level of mouse kidney tissue in the low-dose phycocyanin group alone was significantly lower than that in the model group (P<0.01), and the UA level of mouse kidney tissue in the high-dose phycocyanin group was significantly lower than that in the model group (P<0.01). So the powder of phycocyanin had protective effect on cyclophosphamide-induced hepatic and kindy injury in mice.
-
Keywords:
- phycocyanin /
- cyclophosphamide /
- liver and kidney injury /
- protection
-
藻蓝蛋白(phycocyanin,PC)是从海藻细胞中分离和纯化出的一种具有生物活性的捕光色素[1],其结构上由α和β2个亚基组成。因无毒、水溶性好、色泽鲜艳而被广泛用作于食品添加剂和化妆品着色剂等领域[2],是国家批准允许使用的食用天然色素之一。研究表明,藻蓝蛋白作为源自微藻的天然食品添加剂具有多种生物学功能,且毒副作用小,已成为食品营养学领域非常有潜力的资源之一[3]。在现代的研究中,藻蓝蛋白具有显著地抗多种肿瘤细胞的作用,展现出在治疗人类癌症方面具有优异的应用价值[4-5],PC还具有抗氧化、治疗脑缺血损伤、抗炎性以及抗肿瘤等多种药理功能[6-7]。除在食药领域上的应用,PC也可被加工成荧光试剂、荧光探针和荧光示踪剂,用于医疗诊断、免疫学、生物工程等研究领域[8]。
环磷酰胺(cyclophosphamide,CTX)是临床应用最广泛的光谱烷化剂类抗肿瘤药物,对实体瘤等症状有疗效[9],其主要代谢产物丙烯醛的毒性会引起受治患者药物性肝、肾组织损伤[10],而表现为血清转氨酶升高及肝、肾组织防御性抗氧化系统的抗氧化功能降低[11-12];随着进一步发挥作用抑制肿瘤生长,但其对骨髓及免疫系统也造成了不可逆的损伤[13]。
肝肾损伤的病死率高,临床治疗难度大,可用的天然药物种类少,使用动物模型模仿研发有效治疗药物是药物研究中极为重要的实验方法[14],但现有的肝肾损伤动物模型构建过程操作复杂、花费高昂,滞后了对肝肾同时具有抗氧化保护作用的药物的筛选[15-16]。本研究以CTX建立免疫低下机体肝、肾脏损伤模型[17-18],从生理生化指标和肝脏、肾脏组织形态角度探究PC对机体免疫损伤的修复作用,以期从天然海洋药物资源中寻得理想的免疫调节药物,为PC的深度开发利用提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
藻蓝蛋白(食品级A620/A280>0.7,色价(E^1%-1 cm,λ 620±5 nm)18) 由浙江宾美生物科技有限公司提供;BALB/c雌性小鼠 60只,杭州子源实验动物科技有限公司,体重约20 g,6~8周龄,实验动物生产许可证:SCXK(浙)2019-0004。SPF环境饲养(温度:25±0.5 ℃,相对湿度:60%~70%,光照12 h/黑暗12 h)。环磷酰胺(H22026738)、盐酸左旋咪唑(H37023800) 浙江中维药业有限公司;超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)试剂盒、丙二醛(MDA)试剂盒、谷胱甘肽氧化物酶(GSH-Px)试剂盒、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)试剂盒、谷草转氨酶(AST)试剂盒、尿酸(UA)试剂盒、尿素(BUN)试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所有限公司。
KQ-700DE数控超声波清洗器 昆明市超声仪器有限公司;TG16KR台式高速冷冻离心机 长沙东旺实验仪器有限公司;ESJ182-4电子天平 天津博达宏力称重设备有限公司;SpectraMax 190酶标仪 美国MD公司;UV-1150紫外可见分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 动物分组及处理
将BALB/c小鼠随机分为6组,每组10只,分别为空白对照组(CK组)、模型组(M组)、阳性对照组(LH组,给予盐酸左旋咪唑40 mg/kg)及藻蓝蛋白低、中、高剂量组(ZL、ZM、ZH组,50、100、200 mg/kg)。除空白组外,其余5组腹腔注射80 mg/kg的环磷酰胺[19-20],每天1次,连续5 d,构建环磷酰胺致肝肾损伤小鼠模型。造模完成后阳性对照组每天定时灌胃1次盐酸左旋咪唑溶液,藻蓝蛋白低、中、高剂量组相应灌胃不同剂量的藻蓝蛋白溶液,空白组和模型组给予等体积的生理盐水,连续给药21 d。每天观察小鼠进食情况、精神状态及给药后反应,每5 d测量1次体重。灌胃结束后处死小鼠。动物实验操作均按照国际实验动物伦理委员会行为准则要求进行。实验动物伦理审查批准号:2020-WJW-04。
1.2.2 生化指标的测定
脏器指数检测:无菌环境摘取胸腺、脾脏、肝脏、肾脏等相关器官称重,脏器指数按如下公式计算:
将小鼠称重后,眼眶后静脉丛采血滴入离心管中高速离心分离血清;按照ELISA试剂盒说明书测定血清中IL-2、TNF-α、IgG的含量以及测定SOD、MDA水平。
取肝肾,研磨并制备适宜浓度的肝肾匀浆液,取上清。采用考马斯亮蓝法检测肝肾组织中的蛋白含量,严格参照试剂盒方法,检测肝肾组织中的的SOD、MDA、GSH水平。同时检测肝功能损伤指标ALT、AST水平及肾功能损伤指标UA、BUN水平。
1.2.3 病理切片分析
取结构完整的小鼠肝、肾组织,完整浸泡于10%的甲醛溶液中,使用常规石蜡包埋并切片,进行H&E染色,最后观察小鼠肝、肾组织病理学变化。
1.3 数据处理
采用Origin 2018统计软件、GraphPad Prism 7.00绘图软件对实验数据进行处理,同时进行方差分析,差异显示在P<0.05和P<0.01时,结果具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 小鼠一般行为学观察
注射CTX期间及灌药结束观察周期内并未出现小鼠伤亡情况。CTX造模期间,给药组小鼠较空白组小鼠嗜睡、竖毛、应激反应强烈;出现大小便异常、行为滞缓等现象。剂量组小鼠灌胃藻蓝蛋白后的21 d里,小鼠活动正常,整体表现没有异常情况。
2.2 小鼠脏器指数分析
胸腺和脾脏作为机体内最重要的免疫器官,对机体的免疫功能影响最大[21],PC对CTX所致免疫低下小鼠的脏器指数的结果如表1所示。与空白组相比,模型组的小鼠体重存在极显著差异(P<0.01),结果具有统计学意义;模型组较空白组而言,器官指数虽明显降低,但不显著(P>0.05);较模型组来说,PC剂量组胸腺指数、脾脏指数极显著升高(P<0.01),说明藻蓝蛋白剂量能显著提高免疫损伤小鼠的相关免疫器官指数。从体重上看,模型组小鼠的肝脏和肾脏体重略小于空白对照组,PC的三个剂量组与空白对照组相比,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
表 1 PC对CTX致免疫低下小鼠免疫脏器指数的影响(n=6)Table 1. Effect of PC on immune organ index of CTX induced immunosuppressive mice (n=6)组别 解剖前体重(g) 胸腺指数(%) 脾脏指数(%) 肝脏指数(%) 肾脏指数(%) CK 20.0667±0.3559 0.0026±0.0002 0.0035±0.0001 0.0482±0.0009 0.0138±0.0004 M 17.8167±0.8495## 0.0025±0.0003 0.0035±0.0001 0.0473±0.0014 0.0135±0.0005 LH 20.4000±0.3847 0.0035±0.0007** 0.0044±0.0003** 0.0457±0.0013 0.0138±0.0003 ZL 20.4167±1.000 0.0038±0.0002** 0.0049±0.0004** 0.0449±0.0009 0.0139±0.0005 ZM 20.4000±1.0564 0.0037±0.0006** 0.0050±0.0003** 0.0458±0.0015 0.0136±0.0008 ZH 20.0500±0.7450 0.0039±0.0005** 0.0052±0.0005** 0.0455±0.0015 0.0135±0.0004 注:与空白组CK相比,##P<0.01;与模型组M相比,**P<0.01。 2.3 小鼠肝、肾组织病理学分析
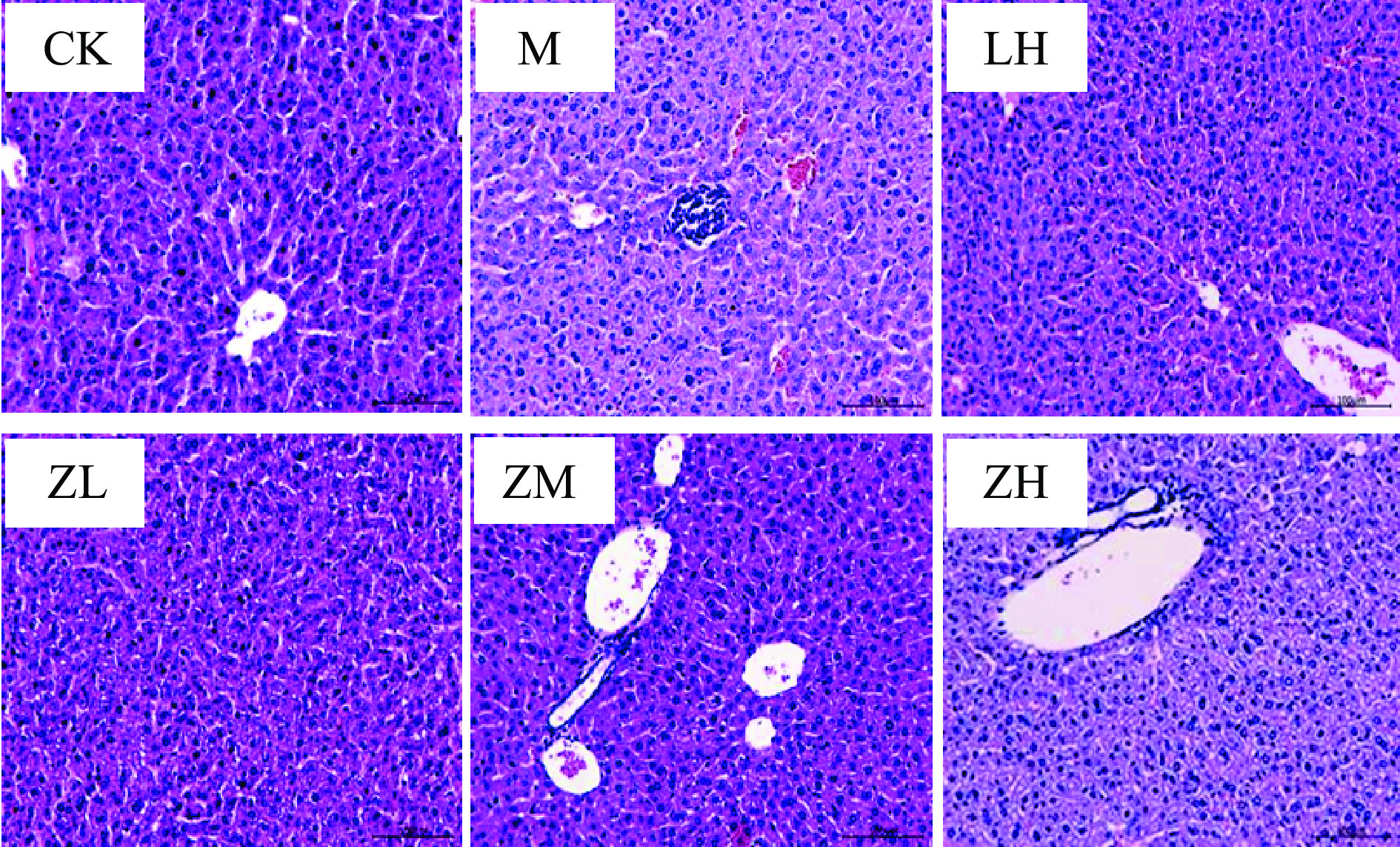
实验中各组小鼠的肝组织切片见图1,空白组小鼠肝组织形态正常,肝索结构清晰,细胞着色均匀,核膜界限清晰,能清楚看到肝小叶、汇管区等结构,未见明显损伤;模型组小鼠肝组织细胞索排列紊乱,不易辨认,肝血窦扩张,窦内出现较多红细胞和中性粒细胞,肝细胞包浆稀少,着色较浅,炎症细胞被浸润导致组织肿胀,细胞核缩小。而其他四组肝组织染色切片可清晰可见肝脏损伤明显减轻,肝小叶内偶见肿胀细胞,炎症细胞浸润数量明显降低,以盐酸左旋咪唑阳性对照组和PC中剂量组最为明显,高剂量PC组肝组织细胞空泡中血浆较少,肝脏损伤明显减轻。
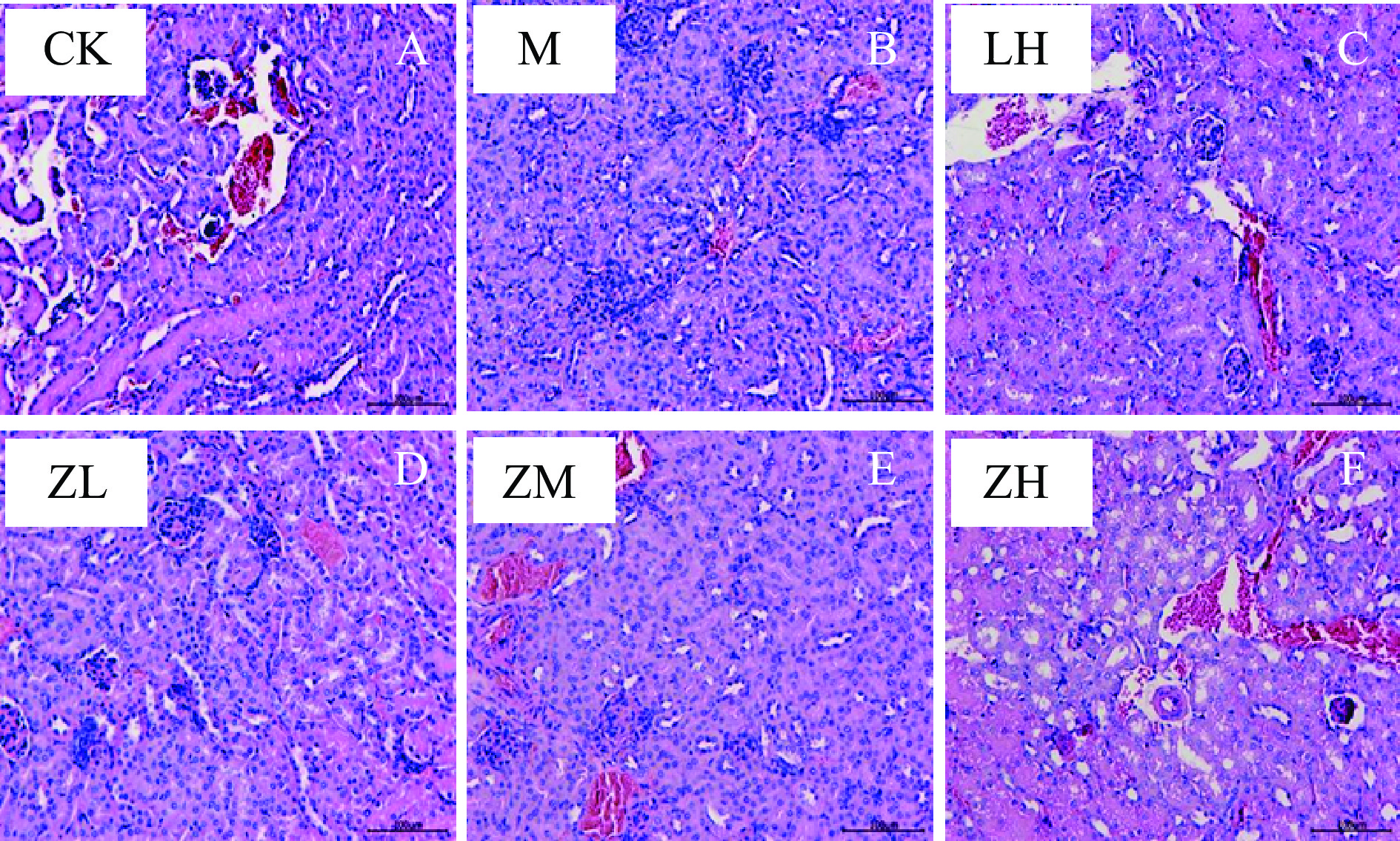
各组小鼠的肾组织切片如图2所示,空白对照组小鼠肾脏较模型组小鼠结构更为完整,肾小管包括近曲小管及远曲小管各部位上皮细胞无变性,排列有序,肾小囊明显,肾小体、肾小球、肾髓质等结构均正常,管腔形态大小正常,未见异状。PC各剂量组(图2D、图2E)肾组织无明显病变,但组织间有轻微出血现象;而盐酸左旋咪唑阳性对照组(图2C)及PC高剂量组(图2F)较空白对照来看,肾小球轻度萎缩,个别肾小管出现病理学现象,上皮细胞变性,肾小囊间隙更大,肾小管腔内有杂质出现。
2.4 PC对小鼠血清中SOD、MDA活力的影响
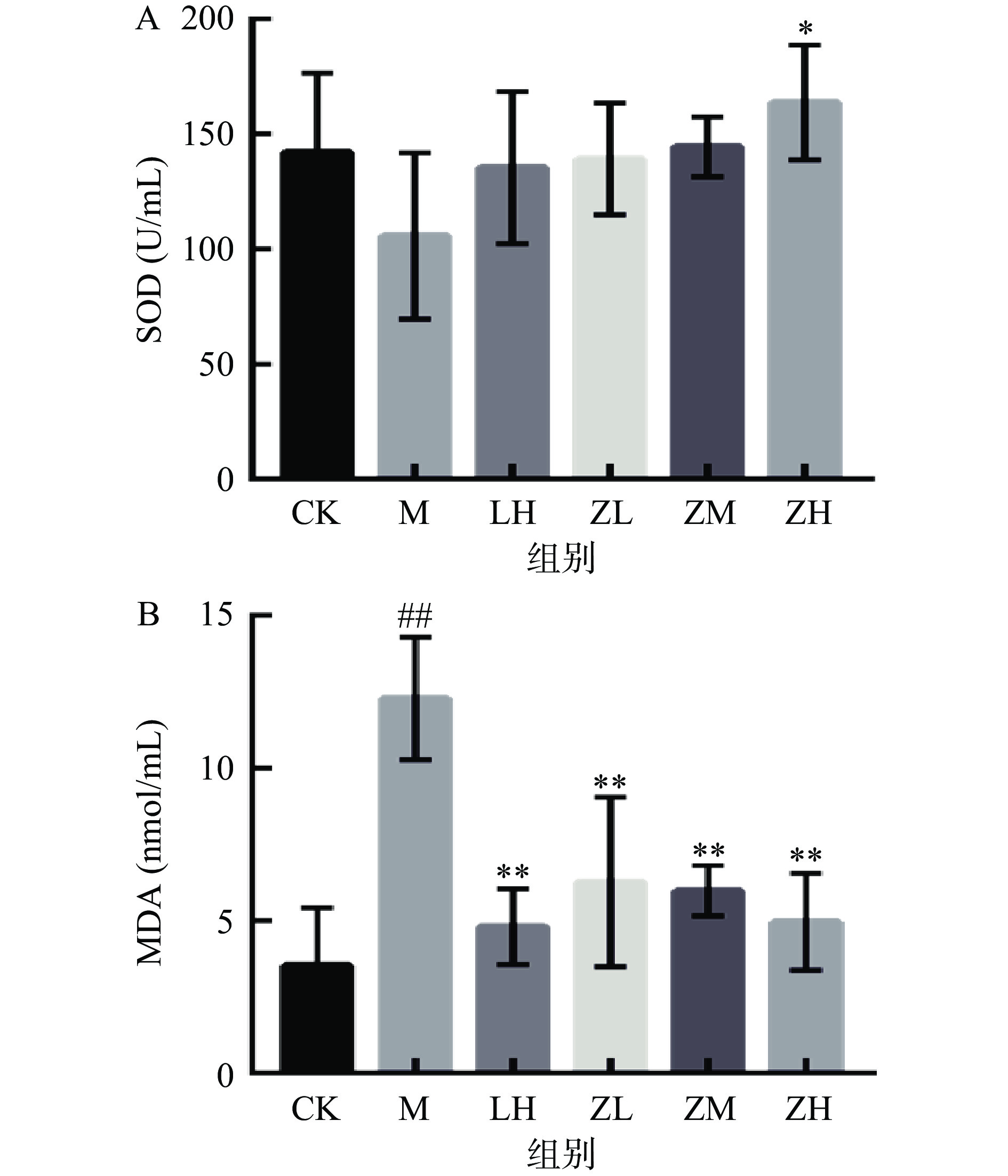
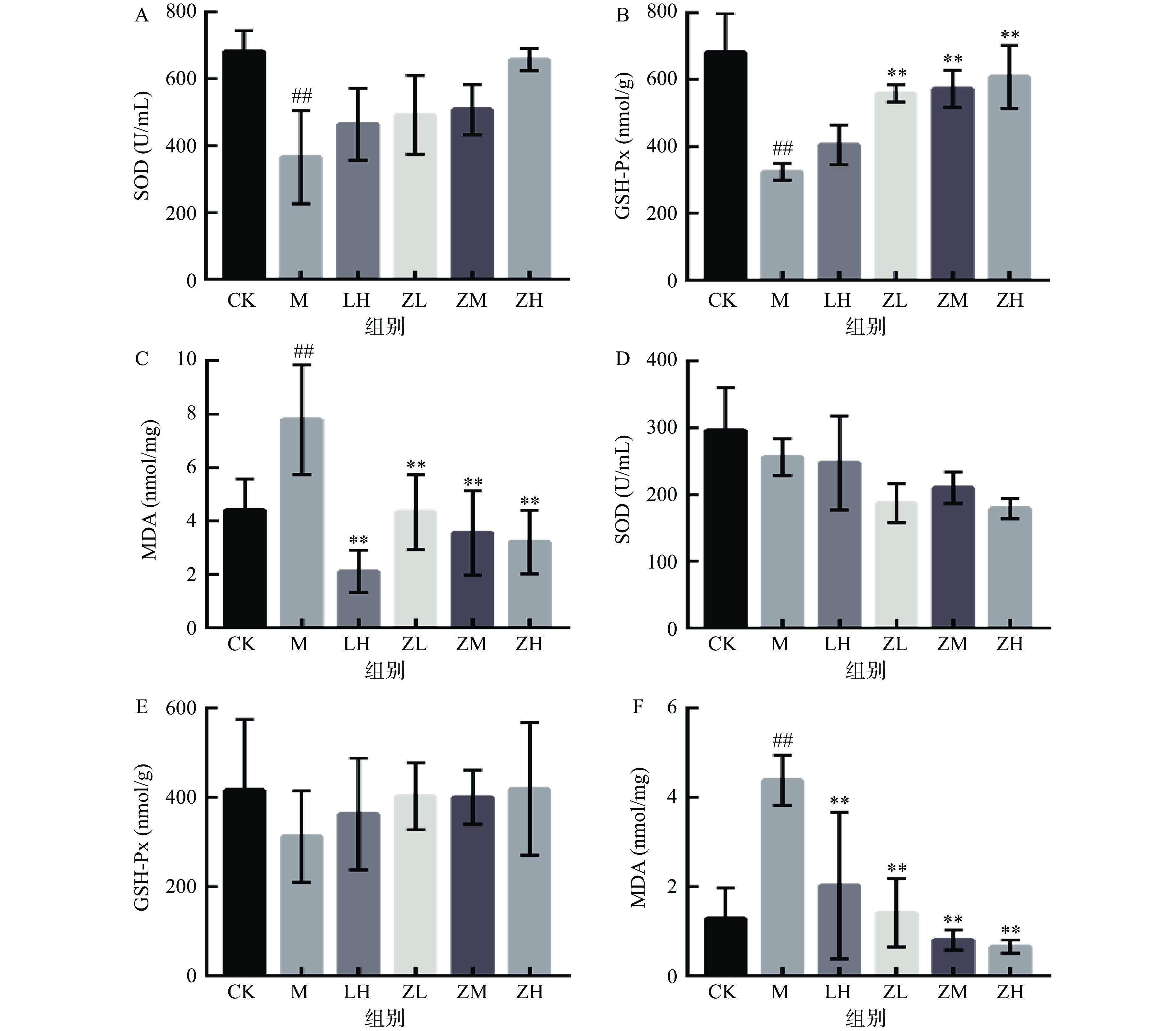
SOD是生物体中重要的抗氧化酶,当机体内SOD含量减少时,机体的抗氧化能力随之减弱,致使机体组织细胞受到自由基的攻击导致活性降低,MDA含量增高是也是氧自由基造成机体损伤的主要原因[22-23]。图3A结果显示,与空白对照组相比,注射CTX后的小鼠血清中的SOD活力降低,但结果并不显著(P>0.05)。相较于模型组,仅高剂量组小鼠的SOD水平显著升高(P<0.05);模型组小鼠血清中的MDA含量极显著高于空白组小鼠(P<0.01),初步可表明实验造模成功。而灌胃PC的各剂量组小鼠机体的SOD活性上升,MDA水平显著降低(P<0.01)。说明PC能提高机体的抗氧化水平,在一定程度上缓解CTX对小鼠造成的氧化应激损害。
2.5 PC对小鼠血清中细胞因子和免疫球蛋白的影响
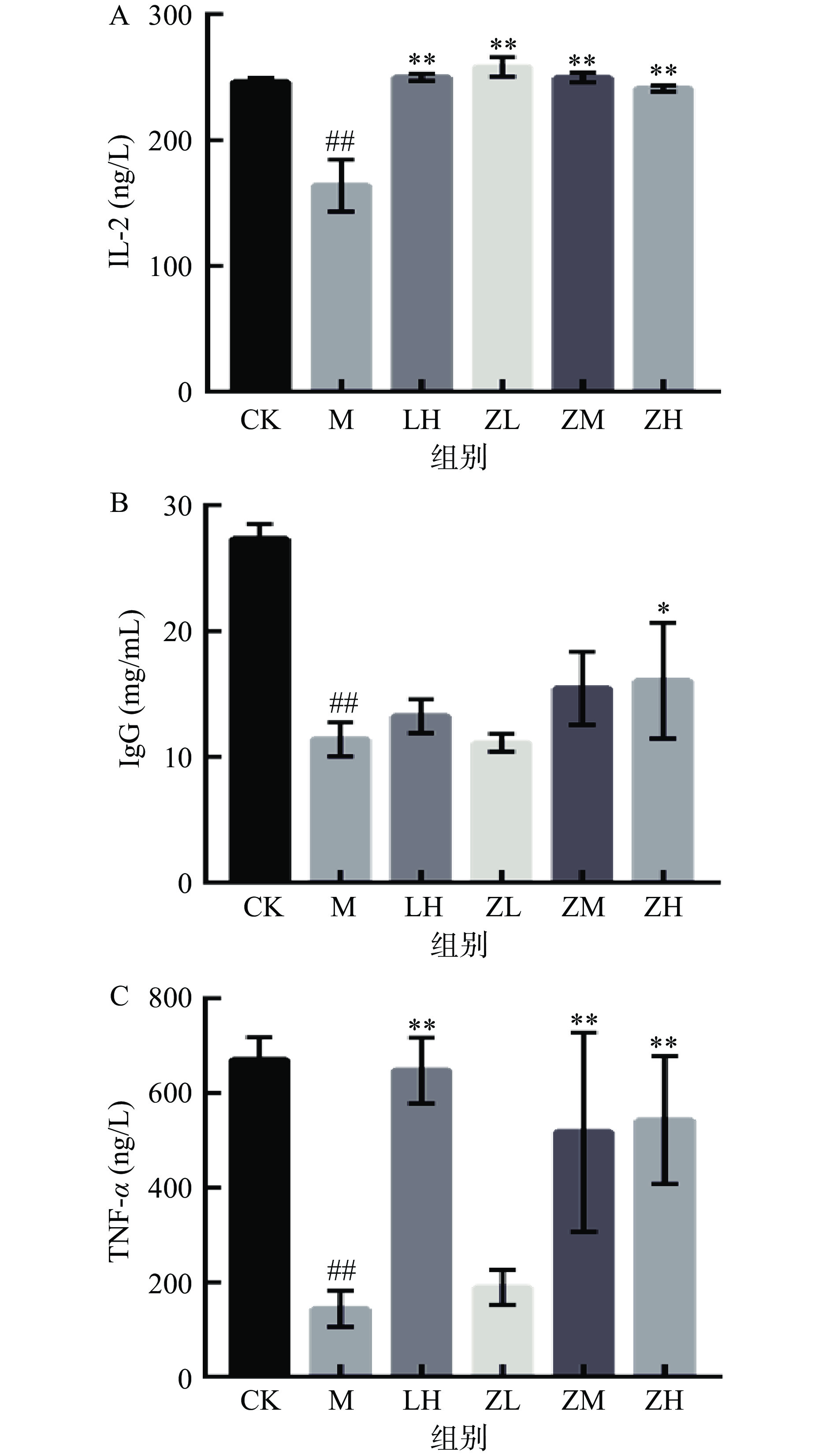
IL-2由Th1细胞分泌,是IL-1家族中典型的淋巴活性因子,在免疫应答、炎症反应等多种机体生长代谢方面的功能上有着举足轻重的作用[24-25]。PC对免疫低下小鼠血清中IL-2、IgG、TNF-α水平的影响结果见图4。与空白对相比,注射CTX模型组的血清白介素IL-2水平极显著降低机体(P<0.01),而PC灌胃各剂量组有明显提高血清中IL-2水平,表明PC有缓解因注射CTX造成免疫低下小鼠血清白介素IL-2水平的作用。
IgG作为机体中体液免疫过程中产生的主要抗体,具有抑菌免疫等多种生物活性[26]。如图4B所示,注射CTX会降低小鼠血清IgG水平(P<0.01),从而影响机体免疫调节机制。PC剂量组对于提高机体IgG水平与PC浓度呈正相关线性关系。
TNF-α在中枢神经系统中发挥稳态和病理生理作用,在病理情况下,系统疾病有关部分反应是由于TNF-α在炎症反应过程中的产生的[27-28]。TNF-α水平越高,体内越易诱导神经系统疾病的发生,如图4C所示,PC中、高剂量组可明显升高免疫低下小鼠血清中TNF-α水平,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.01)。
2.6 PC对小鼠肝、肾组织中生化指标的影响
测定器官组织的抗氧化活性可间接反映机体的抗氧化能力。如图5所示,与空白组相比,模型组肝肾SOD活力极显著降低(P<0.01),说明造模成功。在给予PC灌胃后,随着藻蓝蛋白剂量的增加,肝肾脏的SOD活力性明显增加,并且符合一定剂量依赖关系,表明PC能有效提高免疫低下型小鼠肝肾的SOD活力,发挥脏器的抗氧化能力。
GSH是编码对某些生命过程以及解毒和毒化机制至关重要的基因,具有提高机体免疫力,参与免疫调节的功能[29-30]。GSH-Px能清除因机体内细胞代谢活动而产生的羟自由基和过氧化物等代谢产物,与细胞损伤、衰亡等引发的多种疾病有直接关系[31]。由图5可知,模型组肝肾GSH-Px活性极显著低于空白组(P<0.01),说明造模成功。对于肝脏,在灌胃PC后,随着剂量的升高,各组的GSH-Px活性明显高于阳性对照组;对于肾脏来说,PC剂量组的GSH-Px活性虽高于模型组。
MDA含量可直接反应机体损伤程度,如图5所示,与空白对照组相比,模型组小鼠肝肾组织的MDA含量极显著升高(P<0.01),说明造模成功。在灌胃PC后,小鼠肝肾MDA含量不断降低,且两者之间存在一定的剂量依赖关系。由此可得出结论,PC能显著降低免疫低下型小鼠肝肾组织的MDA含量,恢复机体的抗氧化水平。
2.7 PC对小鼠肝、肾组织损伤敏感指标的影响
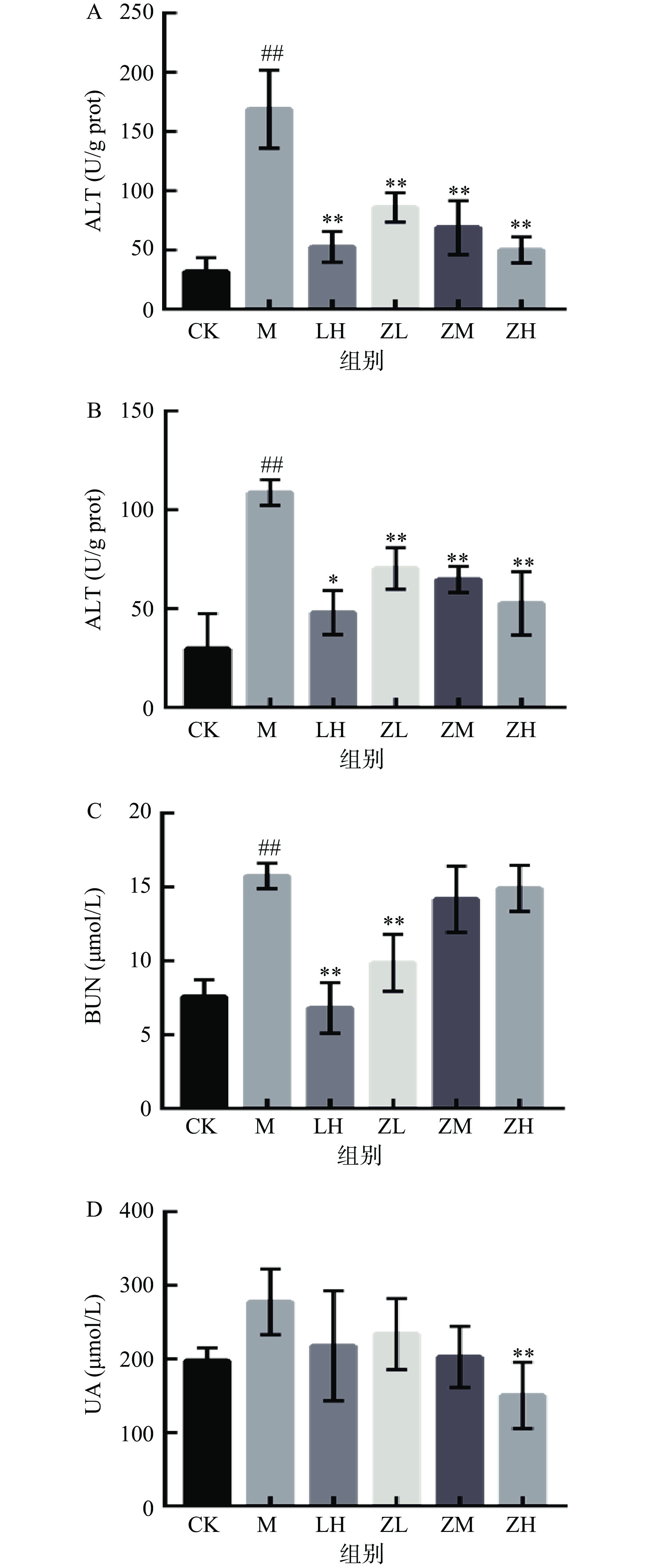
ALT和AST是临床应用最广泛的反映肝细胞损伤的生化指标,提示肝脏疾病信号[32]。如图6所示,与空白对照组比,模型组小鼠肝组织ALT、AST活力均极显著升高(P<0.01),说明小鼠CTX肝损伤模型造模成功。与模型组相比,PC剂量组肝脏中ALT、AST活性明显下降,尤其高剂量组下降的更为明显,总体呈现剂量依赖性降低(P<0.01)。结果表明,PC能降低病理小鼠肝功酶含量,对CTX致免疫低下型小鼠的肝脏具有良好的保护作用。
尿素氮(BUN)和尿酸(UA)是机体最常见的肾功能指标,是代谢的终产物,当肾脏受损时,肾组织中BUN和UA含量会升高,因此在一般药理学实验中,关注两者变化情况,能直观反映肾功能[33-34]。由图6看出,PC对免疫低下小鼠肾脏组织生化指标的异常影响显著。与空白组相比,模型组肾脏的BUN含量极显著升高(P<0.01),但UA含量无显著性差异(P>0.05)。与模型组相比,PC各剂量组肾脏BUN含量均有极显著下降(P<0.01)。灌胃PC后,各剂量组肾脏UA含量均呈下降趋势,但无显著性差异(P>0.05)。总体来看,PC对免疫低下小鼠的肾功能损伤有一定的恢复作用。
3. 讨论
利用环磷酰胺腹腔注射的方式构建了小鼠肝肾损伤模型,以盐酸左旋咪唑为阳性对照,以不同剂量藻蓝蛋白粉末灌胃治疗,考察了藻蓝蛋白对环磷酰胺诱导的小鼠肝肾损伤的保护作用。
小鼠肝肾组织的病理切片表明,环磷酰胺可诱导小鼠肝组织细胞索排列紊乱,肝血窦扩张,肿胀的症状,导致肾组织中肾小球轻度萎缩,管壁破裂的病理现状,而藻蓝蛋白中、高剂量组较模型组来看,情况皆有所改进,组间差距明显,即高浓度藻蓝蛋白具有缓解环磷酰胺损伤肝肾组织的保护作用;小鼠血清中的生理生化指标中,仅高剂量组小鼠的SOD水平显著高于模型组(P<0.05),但各剂量组间无显著性差异,且与阳性对照组无差异。但各剂量组MDA水平较于模型组来看均显著性降低,且达到极显著水平(P<0.01),模型组MDA含量极显著高于较空白组(P<0.01)。小鼠注射环磷酰胺后其血清中IL-2、TNF-α、IgG的含量均显著降低,但在摄入藻蓝蛋白溶液后,仅高剂量组雌性小鼠血清中IgG指标外,其他各组小鼠血清中IL-2、TNF-α的含量均极显著地高于模型组(P<0.01)。
ALT、AST是动物肝脏组织中重要的转氨酶,正常机体组织中含量为零或者很少,当机体肝组织损伤时,肝细胞浆内的ALT、AST会因为肝细胞膜通透性的增加而被释放入血使得血液中ALT和AST含量增加[35-36]。生理生化指标结果表明,剂量组小鼠较模型组小鼠肝脏组织中ALT、AST水平极显著升高(P<0.01),且组间差异显著,且活性与藻蓝蛋白溶液的摄入剂量间存在着剂量效应关系。BUN和UA是肾功能代谢的最终产物,正常组织中,BUN含量超过1.8 mmol/L,而UA含量较低[37]。实验结果表明,较模型组来看,仅低剂量组小鼠体内BUN水平极显著升高(P<0.01),中、高剂量组间无显著性差异;模型组小鼠与空白组小鼠的UA含量无显著性差异,仅高剂量组小鼠UA含量极显著升高(P<0.01)。在肝肾组织抗氧化防御系统中,SOD、GSH-Px是机体重要的抗氧化酶,具有清除自由基的作用。MDA是机体内脂质过氧化的代谢产物,是反映脂质过氧化的敏感指标,也可间接反映细胞的损伤程度[38]。藻蓝蛋白剂量组显示其明显可改善小鼠肝肾组织过氧化能力,同时显著性降低了小鼠肝肾组织中的MDA的含量(P<0.01),提示了藻蓝蛋白具有肝肾组织损伤的改善作用。另有Liu等[39]研究发现在CCl4诱导的小鼠肝损伤模型中,藻蓝蛋白也表现出强抗炎作用,可显著降低ALT、AST水平及TNF-α、细胞色素C的表达,增加白蛋白水平及SOD、增殖细胞核抗原的表达,促进肝细胞再生,改善急性肝衰竭小鼠的生存率;在顺铂诱导的小鼠肾毒性疾病模型中,藻蓝蛋白以剂量依赖性的方式阻止了氧化应激和肾损伤[40]。
4. 结论
在本研究中,增加藻蓝蛋白的剂量浓度,均有效提高环磷酰胺小鼠模型体重及脏器指数,缓解肝肾组织病理性损伤,增强小鼠血清中SOD及肝肾组织中SOD和GSH-Px活性,降低MDA含量,表明藻蓝蛋白可有效清除免疫抑制小鼠体内过多的自由基,减少其对机体的损害,能显著提高免疫抑制小鼠血清免疫因子IL-2、IgG和TNF-α的表达。200 mg/kg剂量浓度的藻蓝蛋白缓解免疫低下小鼠的肝肾组织损伤效果最好,增加藻蓝蛋白的浓度更有效提升其对机体的免疫调节能力,浓度过高会使机体产生毒副作用从而造成二次损伤。本文研究了藻蓝蛋白能够促进环磷酰胺诱导的免疫低下小鼠免疫功能的恢复,可在医药、保健食品领域上开展应用。
-
表 1 PC对CTX致免疫低下小鼠免疫脏器指数的影响(n=6)
Table 1 Effect of PC on immune organ index of CTX induced immunosuppressive mice (n=6)
组别 解剖前体重(g) 胸腺指数(%) 脾脏指数(%) 肝脏指数(%) 肾脏指数(%) CK 20.0667±0.3559 0.0026±0.0002 0.0035±0.0001 0.0482±0.0009 0.0138±0.0004 M 17.8167±0.8495## 0.0025±0.0003 0.0035±0.0001 0.0473±0.0014 0.0135±0.0005 LH 20.4000±0.3847 0.0035±0.0007** 0.0044±0.0003** 0.0457±0.0013 0.0138±0.0003 ZL 20.4167±1.000 0.0038±0.0002** 0.0049±0.0004** 0.0449±0.0009 0.0139±0.0005 ZM 20.4000±1.0564 0.0037±0.0006** 0.0050±0.0003** 0.0458±0.0015 0.0136±0.0008 ZH 20.0500±0.7450 0.0039±0.0005** 0.0052±0.0005** 0.0455±0.0015 0.0135±0.0004 注:与空白组CK相比,##P<0.01;与模型组M相比,**P<0.01。 -
[1] GORGICH M, PASSOSS M, MATA T, et al. Enhancing extraction and purification of phycocyanin from Arthrospira sp. with lower energy consumption[J]. Energy Reports, 2020, 6(Supplement 8): 312-318.
[2] 陶冉, 位正鹏, 崔蓉, 等. 藻类色素蛋白的资源开发和应用研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2010,31(4):377−380. [TAO R, WEI Z P, CUI R, et al. Resource development and application of algal pigment protein[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010,31(4):377−380. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2010.04.015 [3] HAMDAN N, JWAD B, JASIM S. Synergistic anticancer effects of phycocyanin and Citrullus colocynthis extract against WiDr, HCT-15 and HCT-116 colon cancer cell lines[J]. Gene Reports,2021,22:100972. doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100972
[4] 韩敏敏, 唐振洲, 米顺利, 等. 藻蓝蛋白抗肿瘤活性及作用机制研究进展[J]. 广西中医药大学学报,2021,24(4):81−85. [HAN M M, TANG Z Z, MI S L, et al. Research progress on antitumor activity and mechanism of action of phycocyanin[J]. Journal of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine,2021,24(4):81−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4441.2021.04.022 [5] 许丹丹, 徐雅琴, 隽行, 等. 富硒菊芋多糖的提取及其体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2021,37(30):121−127. [XU D D, XU Y Q, JUN X, et al. Extraction of selenium-rich Jerusalem artichoke polysaccharides and their antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2021,37(30):121−127. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0842 [6] FERNANDES E, FIGUEIRA F, LETTNIN A, et al. C-Phycocyanin: Cellular targets, mechanisms of action and multi drug resistance in cancer[J]. Pharmacological Reports,2018,70(1):75−80. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.07.018
[7] JIANG L Q, WANG Y J, YIN Q F, et al. Phycocyanin: A potential drug for cancer treatment[J]. Journal of Cancer,2017,8(17):3416−3429. doi: 10.7150/jca.21058
[8] HOI S, WINAYU B, HSUEH H, et al. Light factors and nitrogen availability to enhance biomass and C-phycocyanin productivity of Thermosynechococcus sp. CL-1[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal,2021,167:107899. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2020.107899
[9] 王小丹, 杜军, 刘克, 等. 黄伞脂溶性成分对环磷酰胺致小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中成药,2013,35(9):2013−2016. [WANG X D, DU J, LIU K, et al. Protective effect of fat-soluble components of yellow umbrella on cyclophosphamide-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2013,35(9):2013−2016. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2013.09.045 [10] 潘模英, 倪秀熊, 姚琪, 等. 紫杉醇和环磷酰胺致肝损伤程度的对比实验研究[J]. 黑龙江医药科学,2004,27(3):17−18. [PAN M Y, NI X X, YAO Q, et al. Comparative experimental study on the degree of liver damage caused by paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide[J]. Heilongjiang Medicine and Pharmacy,2004,27(3):17−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0104.2004.03.009 [11] 邵颖, 陈安徽, 张明, 等. 蛹虫草速溶粉对环磷酰胺致小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(9):290−294,305. [SHAO Y, CHEN X J, ZHANG M, et al. Protective effect of instant powder of Cordyceps militaris on liver damage caused by cyclophosphamide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(9):290−294,305. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.09.051 [12] 吴军, 赵凤鸣, 王明艳, 等. 四君子汤、六味地黄汤对环磷酰胺致小鼠免疫抑制的拮抗作用实验研究[J]. 四川中医,2007,25(10):12−14. [WU J, ZHAO F M, WANG M Y, et al. Experimental study on the antagonistic effect of Four Junzi Soup and Liuwei Dihuang Soup on immunosuppression in mice cyclophosphamide[J]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2007,25(10):12−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3649.2007.10.007 [13] WANG Y L, NI W, JIN X, et al. Vitexin-2-O-rhamnoside improves immunosuppression, oxidative stress, and phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt signal pathway in cyclophosphamide treated mice[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2022,925:174999. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174999
[14] 陈奇. 中药药理研究方法学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1993: 57 CHEN Q. Research methodology of traditional Chinese medicine pharmacology[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House (PMPH), 1993: 57.
[15] SANTIAGO-RABER M L, LAPORTE C, REIUINGER L, et al. Genetic basis of murine lupus[J]. Antoimmun Rev,2004,3:33. doi: 10.1016/S1568-9972(03)00062-4
[16] QU W M, MIYAZAKI T, TERADA M, et al. Genetic dissection of vasculitis in MRL/lpr lupus mice: A novel susceptibility locus invoIving the CD7+callele[J]. Eur J Immunol,2000,30:2027. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200007)30:7<2027::AID-IMMU2027>3.0.CO;2-S
[17] 张继东, 贾宁, 刘楷东, 等. 环磷酰胺的肝细胞损伤作用机制研究[J]. 中国药物与临床,2016,16(11):1664−1667. [ZHANG J D, JIA N, LIU K D, et al. Study on the mechanism of hepatocyte injury of cyclophosphamide[J]. Chinese Remedies & Clinics,2016,16(11):1664−1667. [18] 戚梦, 刘城移, 郭佩玲, 等. 蛹虫草MF27高抗氧化活性提取物筛选及保肝作用研究[J]. 菌物学报,2019,38(2):254−263. [QI M, LIU C Q, GUO P L, et al. Screening and hepatoprotective effect of high antioxidant activity extract of Cordyceps militaris MF27[J]. Mycosystema,2019,38(2):254−263. doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.180181 [19] 史鑫锐, 陈滢锴, 陈中婷, 等. 鸡血藤总黄酮对环磷酰胺所致小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学,2022,43(4):8−13. [SHI X R, CHEN Y K, CHEN Z T, et al. Protective effect of vine total flavonoids on liver damage in mice caused by cyclophosphamide[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science,2022,43(4):8−13. doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2022.04.002 [20] 何丹. 戊二醛聚合血红蛋白对环磷酰胺所致骨髓抑制及肝肾损伤小鼠的保护作用[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2021 HE D. Protective effect of glutaraldehyde polymerized hemoglobin on cyclophosphamide induced bone marrow suppression and liver and kidney injury in mice[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern University, 2021.
[21] 江益平, 马方励, 周联, 等. 香菇多糖对免疫抑制小鼠肠道派氏结T细胞的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报,2011,27(9):1236−1239. [JIANG Y P, MA F L, ZHOU L, et al. Effect of shiitake polysaccharides on intestinal Pin T cells in immunosuppressed mice[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin,2011,27(9):1236−1239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2011.09.013 [22] 杨善岚, 吴磊, 涂嘉欣, 等. 自由基致衰老的研究进展[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志,2022,26(5):589−594. [YANG S L, WU L, TU J X, et al. Research progress of free radical induced senescence[J]. Chinese Journal of Disease Control,2022,26(5):589−594. [23] LIU Z, XIA B, SARIC J, et al. Effects of vancomycin and ciprofloxacin on the NMRI mouse metabolism[J]. Journal of Proteome Research,2018,17(10):3565−3573. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00583
[24] 张林丽, 王艳, 刘莉. 细胞因子与炎症免疫疾病的研究进展[J]. 药学与临床研究,2020,28(3):202−205. [ZHANG L L, WANG Y, LIU L. Research progress of cytokines and inflammatory immune diseases[J]. Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research,2020,28(3):202−205. doi: 10.13664/j.cnki.pcr.2020.03.011 [25] YUTAKA K, RIE Y, MIKA W, et al. An international validation study of the IL-2 Luc assay for evaluating the potential immunotoxic effects of chemicals on T cells and a proposal for reference data for immunotoxic chemicals[J]. Toxicology in Vitro,2020,66:104832. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2020.104832
[26] 陈云, 李周勇, 史玉东, 等. 嗜热链球菌MN-BM-A01对小鼠免疫的调节作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(7):53−58. [CHEN Y, LI C Y, SHI Y D, et al. Regulatory effect of Streptococcus thermophilus MN-BM-A01 on mouse immunity[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2020,20(7):53−58. [27] 李兰, 钟达源, 杨开锋, 等. 益气养荣复经方对环磷酰胺诱导的卵巢早衰小鼠的治疗作用及保护机制[J]. 中医药信息,2021,38(11):47−52. [LI L, ZHONG D Q, YANG K F, et al. Therapeutic effect and protective mechanism of cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian premature aging mice induced by Yiqi Yangrong Meridian[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,38(11):47−52. doi: 10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.20211109 [28] FRIDA B G, CATHARINA H, CAROLINE B, et al. Inflammatory macrophage derived TNFα downregulates estrogen receptor α via FOXO3a inactivation in human breast cancer cells[J]. Experimental Cell Research,2020,390(1):111932. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111932
[29] 范亦菲, 郭琳, 靳文会, 等. 枸杞酸奶体外抗氧化活性和保肝功能研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2022,41(4):25−30. [FAN Y F, GUO L, JIN W H, et al. Antioxidant activity and liver protecting function of Lycium barbarum yoghurt in vitro[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2022,41(4):25−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2022.04.004 [30] SHI X W, HU H H, JI G J, et al. Effects of MTG and GSH on human sperm motility and DNA integrity during vitrification in the presence of trehalose[J]. Advances in Reproductive Sciences,2020,8(1):71−81. doi: 10.4236/arsci.2020.81007
[31] 孙慧, 付千, 戴晨曦, 等. 鞣花酸对马兜铃酸Ⅰ诱导小鼠急性肾损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(5):84−90. [SUN H, FU Q, DAI C X, et al. Protective effect of ellagic acid on acute renal injury induced by aristolochic acid Ⅰ in mice[J]. Food Science,2022,43(5):84−90. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210320-253 [32] 左爱仁, 吴莉, 舒青龙. 根皮素对硫代乙酰胺诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2021,40(10):50−55. [ZUO A R, WU L, SHU Q L. Protective effect of phloretin on acute liver injury induced by thioacetamide in mice[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2021,40(10):50−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2021.10.007 [33] 魏颖, 郭颖, 李明亮, 等. 紫苏籽肽抗疲劳功效及其作用机理[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(7):157−162. [WEI Y, GUO Y, LI M L, et al. Antifatigue effect and mechanism of perilla seed peptide[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2021,21(7):157−162. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.07.019 [34] LU H Y, YU N X, QI C Y, et al. Predictive value of serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, uric acid, and β2-microglobulin in the evaluation of acute kidney injury after orthotopic liver transplantation[J]. Chinese Medical Journal,2018,131(9):1059−1066. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.230726
[35] AUZA N G, WILLIAM G D, MICHAEL J M. Diagnosis and treatment of copper toxicosis in ruminant[J]. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association,1999,214:1624−1628.
[36] SU M, CHEN H, WEI C, et al. Potential protection of vitamin C against liver-lesioned mice[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2014,22:492−497. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.07.034
[37] 江海涛, 吴雨龙, 王仁雷, 等. 蛹虫草基质多糖对酒精所致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(13):223−227. [JIANG H T, WU Y L, WANG R L, et al. Protective effect of cordyceps militaris substrate polysaccharide on acute liver injury induced by alcohol in mice[J]. Food Science,2014,35(13):223−227. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201413043 [38] 尼罗帕尔·吐尔逊, 赵芳, 王欢. 血清调节性T细胞、CD34、CD117水平与多发性骨髓瘤患者早期肾损伤的相关性研究[J]. 中国医刊,2022,57(8):900−903. [TURSUN M L P R, ZHAO F, WANG H. Study on the relationship between the levels of serum regulatory T cells, CD34, CD117 and early renal injury in patients with multiple myeloma[J]. Chinese Medical Journal,2022,57(8):900−903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1070.2022.08.024 [39] LIU J, ZHANG Q Y, YU L M, et al. Phycocyanobilin accelerates liver regeneration and reduces mortality rate in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury mice[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology,2015,21(18):5465−5472. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465
[40] FERNANDEZ-ROJAS B, MEDINA-CAMPOS ON, HERNANDEZ-PANDO R, et al. C-phycocyanin prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through inhibition of oxidative stress[J]. Food & Function,2014,5(3):480−490.






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



