Constructing Rapid and Undamaged Detection Models for Main Physicochemical Indexes of Brewing Sorghum Based on Near Infrared Spectrum
-
摘要: 为满足对于酒用高粱直链淀粉、支链淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、单宁含量快速检测的需求,本文采用17种光谱数据预处理方法和4种波段挑选算法建立了这些指标的近红外光谱分析模型。结果表明,各指标最佳光谱预处理方法分别为一阶导数+多元散射校正+Z-score标准化、矢量归一化+均指中心化、标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化、多元散射校正、标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化,预测直链淀粉、支链淀粉、蛋白质、单宁含量最佳的波段挑选方法为蒙特卡洛-无信息变量消除,脂肪为竞争自适应重加权采样法。整粒高粱这5项指标最优模型的决定系数(R2)分别为0.9560、0.8765、0.9069、0.8658、0.8841,交叉验证均方根误差(RMSECV)值分别为1.3222、2.3477、0.3549、0.2164、0.1077,外部独立样品验证结果显示模型预测准确率高。本文所建立的近红外分析模型可为酿酒行业实现对高粱的快检提供技术参考。Abstract: To satisfy the demands of rapid determination of amylose, amylopectin, protein, fat, and tannin contents in brewing sorghums, in this paper, 17 spectral data preprocessing methods and 4 wavelength band selection algorithms were used to establish the near infrared spectral analysis models for these indexes. The results showed that the best spectral preprocessing methods for each index were 1st der (1st)+multiplicative scatter correction (MSC)+Z-score standardization (ZS), vector normalization (VN)+mean centering (MC), standard normal variate transformation (SNV)+ZS, MSC, SNV+ZS, respectively. The best wavelength band selection algorithm for predicting amylose, amylopectin, protein, and tannin contents was monte-carlo uninformative variable elimination, and that of fat was competitive adaptive reweighted sampling. The R2 in the optimal models for these 5 indexes of whole grain sorghums were 0.9560, 0.8765, 0.9069, 0.8658, 0.8841, and the RMSECV values were 1.3222, 2.3477, 0.3549, 0.2164, 0.1077, respectively. The validation results of external independent samples showed that the models had a high prediction accuracy. The NIR analysis model established in this study could provide a technical reference for the rapid detection of sorghums in the brewing industry.
-
随着酿酒行业的快速发展,对于酿酒原粮的需求在不断增长,对其品质分析效率需要得到进一步提高。高粱作为一种酿酒原料,其品质对于所酿造的白酒质量具有十分重要的作用[1-2],酱香型、浓香型等白酒的出酒率、质量等级、酒体风格与高粱的品质息息相关[3]。因此,需要开发一种高效、快捷、无损的高粱分析方法,以满足企业对高粱快速检测的需求[4]。
高粱直链淀粉、支链淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、单宁的含量会直接影响酿造白酒的产量和品质,是形成白酒中众多风味物质的主要物质基础,是评价酒用高粱酿酒特性的主要理化指标[5]。目前,这5项指标主要采用传统化学方法进行分析,但化学分析法操作不方便、步骤复杂、耗时长,不利于大批量样品的快速检测。而近红外光谱技术有无损、快速、操作简单等优点,其分析原理是基于样品中含氢基团X-H(X:C、N、O等)内部振动的倍频与合频吸收[6-8],近红外光有良好的透射性,能够携带部分原粮内部信息[9]。近年来近红外光谱技术被广泛应用于农业、医药、化工等各领域[10-12]。对于高粱的检测,张北举等[4]利用近红外光谱构建了用于分析高粱籽粒中直链淀粉和支链淀粉的快检模型,王勇生等[13]基于近红外光谱技术对高粱中粗脂肪、粗纤维、粗灰分进行了测定与分析,苏鹏飞等[14-15]利用近红外光谱对高粱淀粉和水分含量开展了快检技术的研究,Chadalavada[16]和Peiris [17]分别利用近红外光谱对高粱中蛋白质的含量进行了快速检测的研究。此外,利用近红外快检技术预测高粱中的总黄酮[18]、单宁[19]、花青素[20]的含量也有相关的研究报道。这些近红外光谱应用于高粱快检的研究多用于高粱单一指标的检测和评价,未有利用近红外光谱技术同时分析上述5个主要指标的相关研究报道。利用近红外光谱技术快速分析高粱等原粮的各指标,通常需要大量的样本进行建模后分析,而样本的近红外光谱除自身样品信息外,通常还携带外界条件下的无关信息,因此对建模光谱进行预处理及波段挑选是十分重要的[21-22]。通过提取光谱中的有用信息并消除无关信息和噪声[23],来提高光谱与理化指标间的相关性,从而获得高的信噪比,降低背景干扰,以此提高建模效率[24-25],实现对目标指标快速检测与分析的需求,以满足对酒用高粱品质快速检测的需求。
本文建立了一种能同时分析高粱直链淀粉、支链淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、单宁含量的近红外分析模型。考察了高粱籽粒整粒和粉碎梅花瓣两种形态对于光谱图和近红外预测模型的影响;采用了17种光谱预处理方法和4种波段挑选方法,通过选择最优组合,建立了预测高粱直链淀粉、支链淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、单宁含量的模型;最后对建立的模型进行了内部交叉验证及外部独立样品验证,以验证模型的预测能力。本研究实现了对酒用高粱主要指标的快速分析,为酿酒企业对高粱进行无损、高效、低成本的检测与品质评价提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
高粱 市面购买,共195个样品,包含金糯粱6号、泸州红1号、宜糯124号、郎糯1号等共计44个品种,进行光谱扫描前对样品充分混匀,以漫反射测量的方式获取样品近红外光谱信息;盐酸、氢氧化钾、氢氧化钠试剂为分析纯 国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
N500型傅里叶变换近红外光谱仪 北京中安信达科技有限公司;鼓风干燥箱 北京科伟永兴仪器有限公司;FW-200AD粉碎机 天津鑫博得仪器有限公司;Milli-Q Synergy超纯水系统 德国Merck公司;ME型分析天平 瑞士METTLER TOLEDO公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品理化指标的测定
直链淀粉及支链淀粉分别参考GB/T 15683-2008《大米直链淀粉含量的测定》[26]与GB 7648-1987《水稻、玉米、谷子籽粒直链淀粉测定法》[27]进行测定,脂肪参照GB 5009.6-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪的测定》[28]中第一法进行测定,蛋白质参照GB/T 6432-2018《饲料中粗蛋白的测定》[29]中凯氏定氮法进行测定,单宁参照GB/T 15686-2008《高粱单宁含量的测定》[30]进行测定。
1.2.2 样品准备和光谱采集
对135个高粱整粒样品直接混匀后采集样品光谱信息,另外60个样品进行粉碎,粉碎后过40目筛,再混匀后采集样品光谱信息。
采用近红外光谱仪,以漫反射测量的方式获取样品光谱信息,样品放置在可旋转装置上,扫描范围4000~10000 cm−1,分辨率为8 cm−1,扫描32次获得平均光谱,每个样品重复扫描三次,最终取平均光谱作为样本光谱。
1.2.3 光谱预处理及波段挑选方法
光谱的预处理方法主要采用一阶导数(1st Der,1st)、二阶导数(2nd Der,2nd)、多元散射校正(Multiplicative Scatter Correction,MSC)、矢量归一化(Vector Normalization,VN)、标准正态变换(Standard Normal Variate transformation,SNV)、去趋势(Detrending,Det)、均值中心化(Mean Centering,MC)、标准化(Zscore Standardization,ZS)、减去一条直线(Subtract Straight Line, SSL)、消除常数偏移量(Eliminate Constant Offset,ECO)等方法中的一种或几种方法的组合。
波长变量筛选主要采取以下4种算法:反向区间偏最小二乘法(Backward interval PLS,BiPLS)、无信息变量消除法(Uninformative Variable Elimination,UVE)、蒙特卡洛-无信息变量消除(Monte-Carlo Uninformative Variable Elimination,MCUVE)、竞争自适应重加权采样法(Competitive Adaptive Reweighted Sampling,CARS)。
1.2.4 模型评价
对所建立的高粱理化指标预测模型采用交叉验证均方根误差(RMSECV)、预测均方根误差(RMSEP)、决定系数(R2)相关参数对模型质量进行评价,计算公式分别见式(1)、式(2)和式(3),采用内部交叉验证(Cross Validation)和外部独立样品验证方式进行模型预测能力的验证。
(1) (2) (3) 式中:n表示样本个数;YS表示样本的理化分析数值;YV表示交互验证样品近红外预测值;YC表示测试集样本的近红外预测值;YP表示所有样本的理化分析数值均值。
1.3 数据处理
所有的检测数据平行测定三次,取平均值。表格采用Excel 2019绘制,绘图采用Origin 2021软件。用NIRCal软件对光谱进行赋值、预处理、波段挑选以及建立模型,用Matlab软件对部分算法下的波点进行挑选。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 高粱形态对光谱的影响
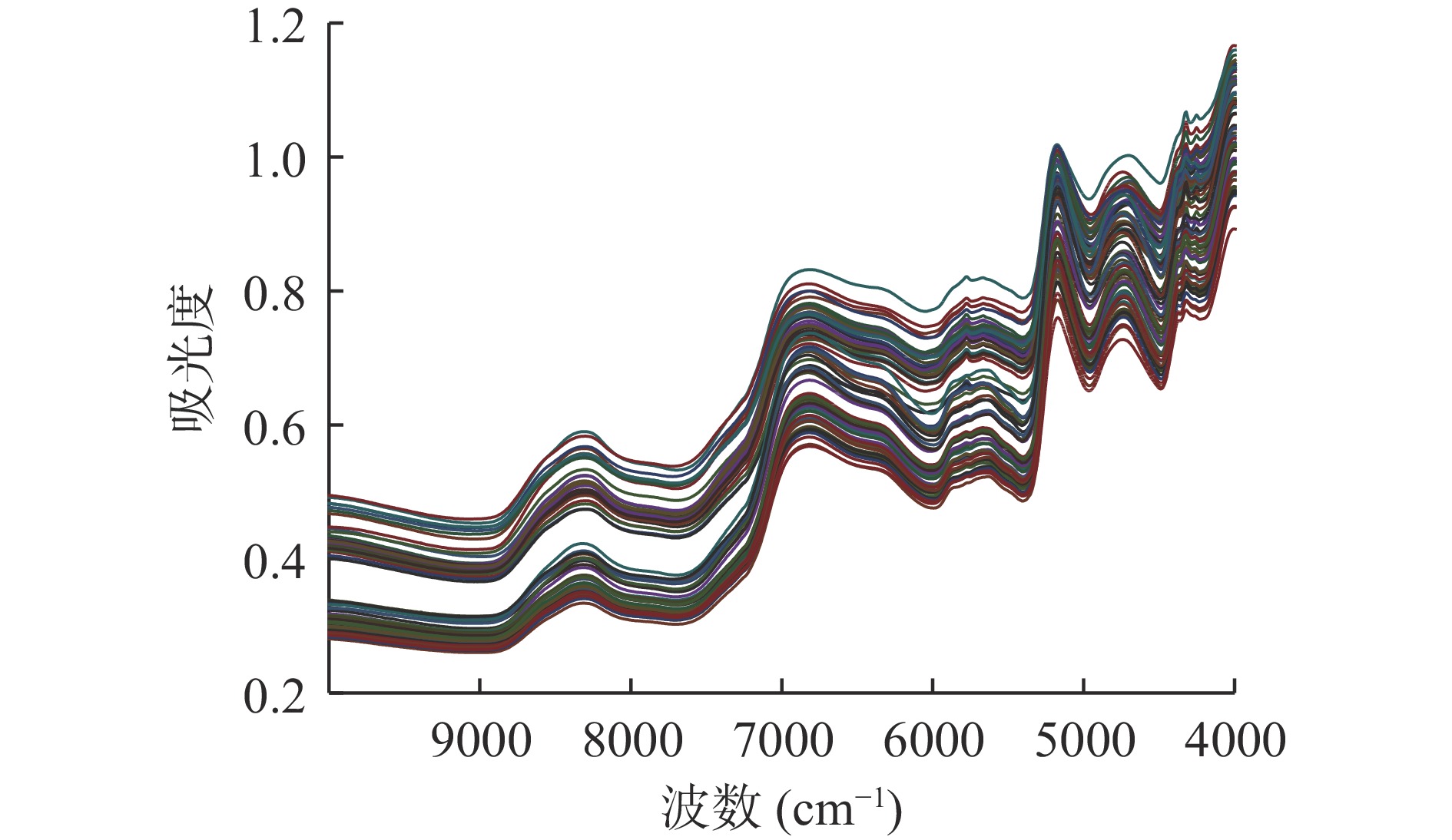
近红外光谱图能较好地反应高粱籽粒中碳水化合物的近红外信号组成,图1为高粱样品的近红外光谱图,图中4700 cm−1处为N-H伸缩振动,5184 cm−1处主要为淀粉中羟基O-H的拉伸与弯曲振动,6835 cm−1处主要为淀粉中O-H的反对称和对称拉伸,8316 cm−1处则与-CH3中的C-H键对称拉伸的二级倍频相关[31]。
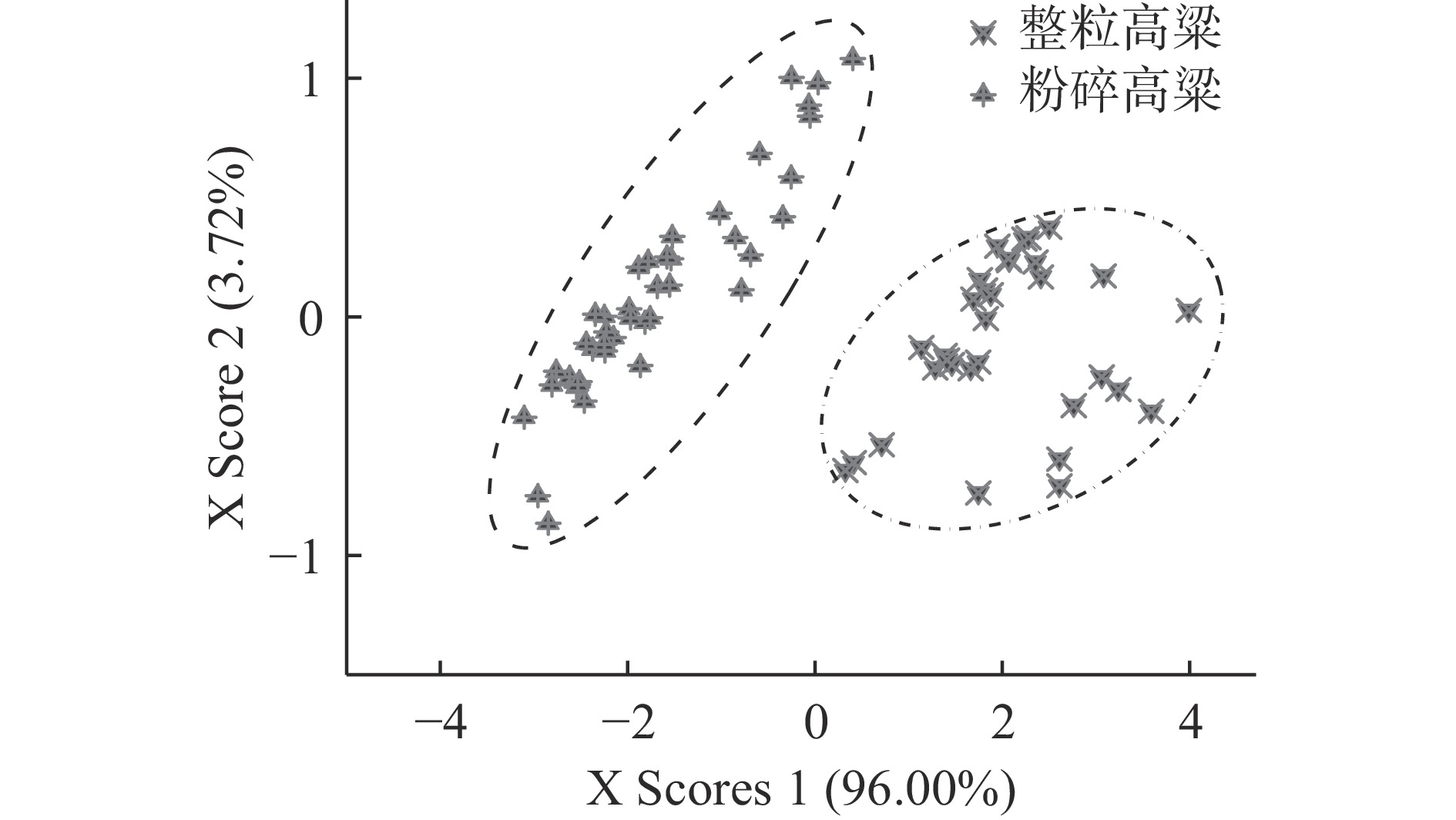
酿酒生产中,高粱主要以籽粒整粒和粉碎两种形式存在,在利用近红外光谱测定高粱样品时,其粒径大小以及样品的均匀程度,会对红外的吸收有较大影响[32]。因此,本节分别对高粱籽粒的整粒和粉碎样品分别进行了近红外光谱扫描,并对整粒和粉碎高粱的光谱图进行了主成分分析,结果如图2所示,近红外光谱能够区分高粱籽粒的形态。由于生产工艺的不同,有采用整粒高粱或粉碎成梅花瓣高粱进行酿酒生产,但高粱在验收和转运过程中通常以整粒的形式存在,因此接下来主要研究整粒高粱的红外光谱结合光谱预处理及波段挑选方法,对酒用高粱主要酿酒相关指标的含量分析建立预测模型。
2.2 光谱数据预处理
近红外光谱分析是从样品复杂的背景中提取对于建模有用的信息,样本光谱中除建模相关信息外,还包括较多的无关变量,因此对光谱数据进行预处理以及不同的预处理方法组合使用,是十分必要的[33]。本节对高粱的红外光谱进行建模,分别通过无预处理、附加预处理等17种单一或组合的光谱预处理方式,确定了各光谱预处理组合对于高粱指标建模的影响。其中附加预处理主要考察均值中心化及Z-score标准化两种方式。对筛选光谱预处理结果分析,通常所建立模型其R2越接近于1,RMSECV值越小,表明模型结构愈加合理[34]。高粱光谱预处理后,各指标RMSECV值较小的前10组合,结果如表1所示。直链淀粉在无任何预处理方法下,其RMSECV值为2.2603,附加预处理方法下均值中心化所得模型的RMSECV值更低,因此选定均值中心化作为高粱直链淀粉指标建模的附加预处理方法,在17种预处理方法及组合中,标准正态变量变换和去趋势组合时,所得RMSECV值最低为2.0760,因此选择其作为直链淀粉最终光谱预处理方法,标准正态变换与去趋势两种预处理方法主要对应消除光谱中的散射干扰和基线漂移问题[35],相比较于无任何附加预处理方法其RMSECV值明显降低;支链淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、单宁近红外光谱经过不同附加预处理方法计算后,最终所选方法下其RMSECV值分别为2.7791、0.4620、0.3148、0.2107,相较于无任何预处理时,RMSECV值均有所降低,表明光谱预处理可以更好地提升模型参数,因此对原粮近红外光谱进行预处理是极为重要的。
表 1 不同光谱预处理方法高粱理化指标的主要评价参数Table 1. Main evaluation parameters of physical and chemical indexes of sorghum with different spectrum pretreatments建模指标 序号 预处理方法 附加预处理方法 波长变量 推荐因子数 RMSECV 直链淀粉 1 无 无 780 19 2.2603 2 无 均值中心化 780 19 2.1086 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 19 2.0766 4 标准正态变量变换+去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 17 2.0760 5 去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 18 2.0918 6 减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 17 2.1389 7 多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 16 2.1504 8 一阶导+多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 15 2.2052 9 标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 17 2.2627 10 矢量归一化 Z-score标准化 780 18 2.3058 支链淀粉 1 无 无 780 14 3.3035 2 无 均值中心化 780 13 3.1574 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 13 3.1807 4 矢量归一化 均值中心化 780 16 2.7791 5 一阶导+多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 10 2.8253 6 一阶导+标准正态变量变换 均值中心化 780 10 2.8503 7 一阶导+矢量归一化 均值中心化 780 10 2.8767 8 多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 12 2.9310 9 减去一条直线 均值中心化 780 12 2.9604 10 一阶导+减去一条直线 均值中心化 780 10 2.9787 蛋白质 1 无 无 780 10 0.5933 2 无 均值中心化 780 13 0.5803 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 13 0.5732 4 标准正态变量变换+去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 18 0.4620 5 标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 19 0.4709 6 多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 18 0.4903 7 最大最小归一化 Z-score标准化 780 13 0.4933 8 一阶导+标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 6 0.4947 9 一阶导+减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 8 0.4957 10 一阶导+多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 6 0.5115 脂肪 1 无 无 780 7 0.3377 2 无 均值中心化 780 7 0.3186 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 7 0.3313 4 标准正态变量变换 均值中心化 780 6 0.3148 5 矢量归一化 均值中心化 780 6 0.3148 6 多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 6 0.3175 7 减去一条直线 均值中心化 780 7 0.3186 8 导数 均值中心化 780 6 0.3214 9 最大最小归一化 均值中心化 780 6 0.3239 10 一阶导+多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 6 0.3240 单宁 1 无 无 780 9 0.2400 2 无 均值中心化 780 9 0.2384 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2368 4 减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 10 0.2107 5 一阶导+减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2196 6 标准正态变量变换+去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2212 7 标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2235 8 去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2245 9 多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2262 10 矢量归一化 Z-score标准化 780 7 0.2292 2.3 光谱的波段挑选及模型建立
为提高模型运算速度,降低模型复杂程度,并提高模型预测的准确性,需要对模型进行波段挑选[36]。对于模型建立的波段挑选方法,采用了反向区间偏最小二乘法(BiPLS)、无信息变量消除法(UVE)、蒙特卡洛-无信息变量消除(MCUVE)、竞争自适应重加权采样法(CARS)四种算法。在经过不同波段挑选方法的优化计算后,波长变量数显著减小,所得波数主要对应了酒用高粱各指标代表性化合物的主要官能基团的红外吸收峰[37],其既保留样品主要属性特征的同时,又提高了模型预测的效率。直链淀粉、支链淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、单宁5个指标在不同算法下对应模型参数如表2所示。
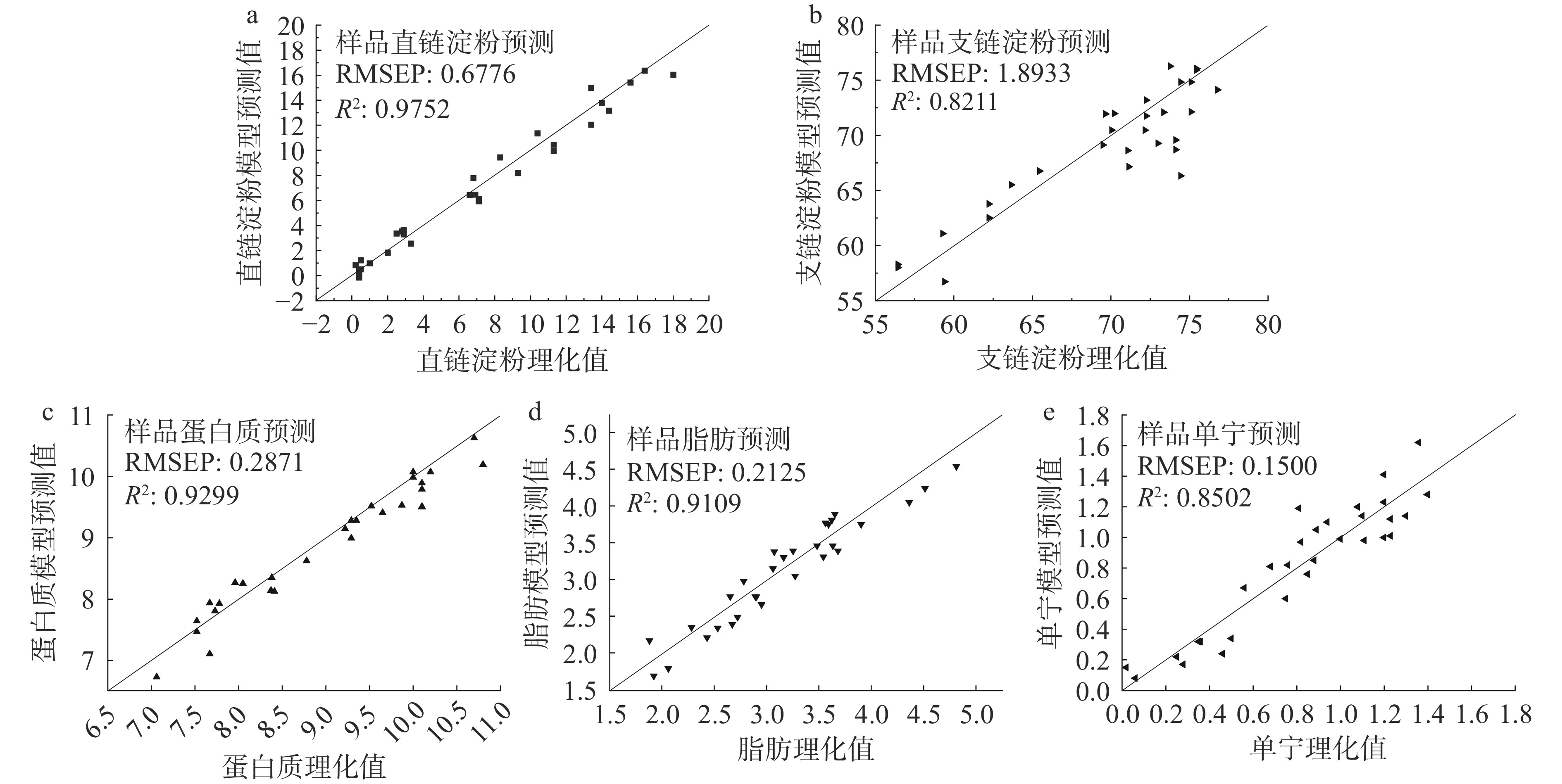
表 2 高粱理化指标近红外预测模型的主要参数Table 2. Main parameters of the NIR prediction model for physicochemical indexes of sorghums指标 序号 波段挑选方法 挑选波段(cm−1) 光谱处理方法 波长变量 因子数 RMSECV R2 直链淀粉 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4598、4606、… 去趋势+Z-score标准化 546 17 1.4690 0.9457 2 无信息变量消除 4058、4066、… 减去一条直线+Z-score标准化 156 13 1.6136 0.9345 3 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4027、4035、… 一阶导+多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 220 14 1.3222 0.9560 4 竞争自适应重加权采样 4042、4050、… 一阶导+多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 43 13 0.9561 0.9770 支链淀粉 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4004、4011、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 390 14 2.5854 0.8502 2 无信息变量消除 4035、4042、… 一阶导+标准正态变量变换+均值中心化 164 8 2.5727 0.8516 3 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4197、4413、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 90 13 2.3477 0.8765 4 竞争自适应重加权采样 4081、4197、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 24 12 2.0409 0.9067 蛋白质 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4004、4011、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 546 20 0.3631 0.9025 2 无信息变量消除 4104、4112、… 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+Z-score标准化 118 14 0.3894 0.8879 3 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4135、4359、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 230 15 0.3549 0.9069 4 竞争自适应重加权采样 4652、4937、… 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+Z-score标准化 30 14 0.2668 0.9474 脂肪 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4004、4011、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 624 7 0.2834 0.6963 2 反向区间PLS-区间分段数20 5200、5207、… 一阶导+矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 234 11 0.2340 0.7235 3 反向区间PLS-区间分段数30 5254、5261、… 一阶导+矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 234 11 0.2337 0.7269 4 无信息变量消除 4011、4019、… 导数+均值中心化 197 4 0.3069 0.6222 5 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4343、4613、… 多元散射校正+均值中心化 60 5 0.2936 0.7036 6 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4027、4050、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 210 6 0.2567 0.7704 7 竞争自适应重加权采样 4760、4775、… 一阶导+矢量归一化+均值中心化 43 4 0.2606 0.8405 8 竞争自适应重加权采样 4613、4629、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 36 7 0.2164 0.8658 单宁 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4598、4606、… 去趋势+Z-score标准化 468 11 0.1546 0.8136 2 反向区间PLS-区间分段数20 3996-5192、… 矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 546 18 0.1288 0.8569 3 反向区间PLS-区间分段数30 3996-5007、… 消除常数偏移量+Z-score标准化 546 13 0.1256 0.8608 4 无信息变量消除 4096、4212、… Z-score标准化 239 11 0.1449 0.8188 5 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4212、4220、… 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+Z-score标准化 150 11 0.1438 0.8103 6 竞争自适应重加权采样 4189、4235、… 消除常数偏移量+Z-score标准化 40 7 0.1078 0.8975 7 无 6061~10000 消除常数偏移量+Z-score标准化 492 13 0.1468 0.8212 8 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4259、4266、… 多元散射校正 140 12 0.1077 0.8841 注:模型验证方式为内部交叉验证,验证抽样方法为K折系统抽样。 在所选四种算法中,竞争自适应重加权采样波段挑选方法能极大地降低波长变量,提高模型参数并降低建模运算时间,但需注意防止波长变量过少导致样品信息减少,不能充分和及时反映光谱的变化[38],使得尽管模型参数较好,但模型预测效果较差,出现所谓的红外建模“欠拟合”现象。高粱蛋白质在模型波段挑选方法为蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除时,其近红外模型预测数值与理化数值如图3所示,采用光谱预处理方法为标准正态变量变换与Z-score标准化,波长变量数230,因子数15,以K折系统抽样的方式,进行内部交叉验证,其RMSECV值为0.3549,R2为0.9069(表2)。在高粱蛋白质指标四种模型中,在经过光谱预处理与波段挑选方法计算后,其中竞争自适应重加权采样波段挑选方法建立模型的参数最佳,其RMSECV值为0.2668,R2为0.9474,但考虑到其挑选的波长变量数仅30个波点,可能存在“欠拟合”的风险,因此未选用该模型;而以反向区间PLS方法、蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除两种方法所建立的模型,两模型的参数RMSECV和R2值表现相当,但反向区间PLS方法筛选的波长变量多达546个,且其因子数为20偏大,可能会引入过多的样品变量和噪音变量,因此未选择该模型,最终预测高粱蛋白质含量选择波段挑选方法为蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除。
预测直链淀粉与支链淀粉淀粉含量最优的方式为使用蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除作为波段挑选方法,直链淀粉采用一阶导、多元散射校正及Z-score标准化作为光谱预处理方法,最终模型因子数14,波长变量220,RMSECV值为1.3222,R2为0.9560。预测支链淀粉含量选择了矢量归一化和均指中心化为光谱预处理方法,最终模型因子数13,波长变量90,RMSECV值为2.3477,R2为0.8765。预测蛋白质含量的模型采用了蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除的波段挑选方法,光谱处理方法为标准正态变量变换与Z-score标准化,波长变量数230,因子数15,进行内部交叉验证,其RMSECV值为0.3549,R2为0.9069。预测脂肪含量的模型采用了竞争自适应重加权采样的波段挑选方法,光谱处理方法为标准正态变量变换与Z-score标准化,波长变量数36,因子数7,进行内部交叉验证,其RMSECV值为0.2164,R2为0.8658。预测蛋白质含量的模型采用了蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除的波段挑选方法,光谱处理方法为标准正态变量变换与Z-score标准化,波长变量数230,因子数15,进行内部交叉验证,其RMSECV值为0.3549,R2为0.9069。预测脂肪含量的模型采用了竞争自适应重加权采样的波段挑选方法,光谱处理方法为标准正态变量变换与Z-score标准化,波长变量数36,因子数7,进行内部交叉验证,其RMSECV值为0.2164,R2为0.8658。在建立预测单宁含量的模型时,波段挑选方法选择反向区间PLS时,对光谱区间进行更为细致的划分,模型的RMSECV和R2值提升明显。对单宁预测模型进一步优化时,在已有方法基础上,参考李霞[39]选取波段6061~10000 cm−1作为建模波段和成云玲[40]选择多元散射校正为波段预处理方法,最终预测单宁含量最佳方式是采用的波段挑选方法为蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除,光谱处理方法多为元散射校正,此时波长变量数较为合理,其因子数12,RMSECV值为0.1077,R2为0.8841。
综上所述,使用近红外光谱所建立的预测高粱主要酿酒理化指标含量模型,各指标RMSECV值较小,R2整体均大于0.8500,其中直链淀粉和蛋白质模型决定系数R2大于0.9000,表明所建立模型质量良好,可进行高粱后续各项理化指标的测定工作。
2.4 模型预测能力
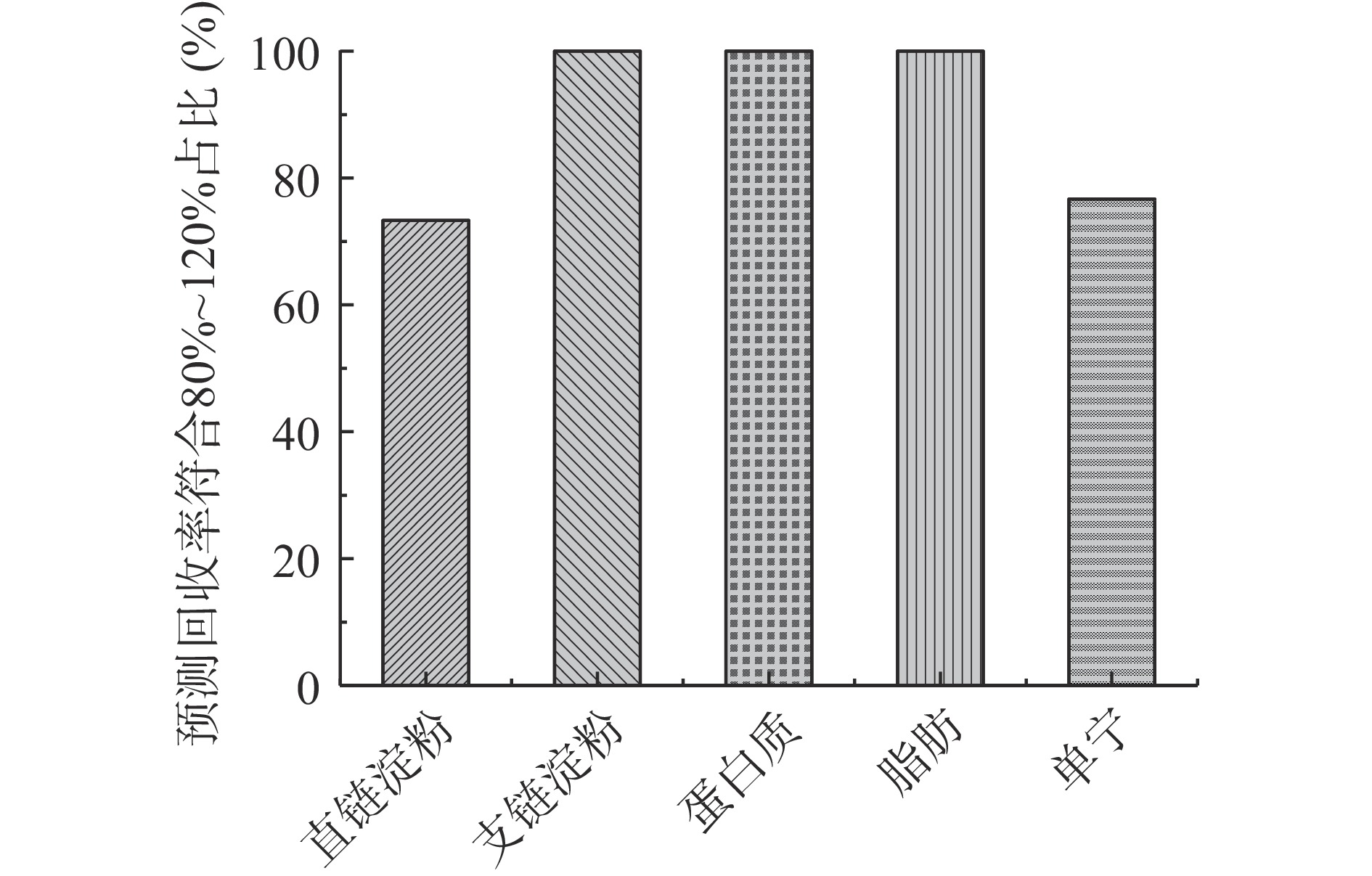
为更好的评价所建立模型对酒用高粱各理化指标的预测能力,选取了30个非建模的高粱样本进行模型的外部独立样品验证,利用预测均方根误差(RMSEP)、决定系数R2、预测回收率[19]作为评价的参数,各指标外部样品预测结果如图4、图5所示。30个外部独立验证样本直链淀粉含量的预测均方根误差RMSEP为0.6776,决定系数R2为0.9752,表明模型预测值与理化实际值一致性良好,独立验证样本中直链淀粉理化值存在较多的样本处于0.2%~0.5%区间,较低的基数导致其满足回收率在80%~120%之间的占比为73.33%。高粱支链淀粉外部独立验证样品理化数值处于53.36~76.78,RMSEP为1.8933,R2为0.8211,尽管其预测值和理化值一致性表现不如直链淀粉,但其理化数值基数大,预测回收率介于89.01%~108.64%,各样本都满足预测回收率在80%~120%之间。对30个样本蛋白质含量预测模型的均方根误差0.2871,决定系数R2为0.9299,30个样品预测回收率介于92.54%~103.83%之间。30个样品的脂肪含量预测模型的均方根误差0.2125,决定系数R2为0.9109,预测回收率介于87.37%~115.96%之间。高粱蛋白质和脂肪预测模型的预测值与理化值一致性良好,且外部独立样本预测回收率都在80~120%区间,其红外模型的预测值接近实验理化测定数值,可以满足实际生产过程对分析结果精度的要求。此外,单宁模型其独立样品验证所建模型的预测均方根误差为0.1500,决定系数R2为0.8502,预测回收率在80%~120%之间的占比为76.67%。
2.5 高粱籽粒形态对近红外模型的影响
由于高粱籽粒的形态、粒径大小对近红外光谱存在较大影响,为考察高粱籽粒形态对于所建近红外光谱模型的影响,分别取高粱籽粒整粒及粉碎样品的近红外光谱,选择各指标在不同算法下的最优模型,结果如表3所示。高粱籽粒粉碎样品所建立模型的RMSECV值比整粒高粱样品所建立模型值小,且R2值更大,表明籽粒粉碎高粱所建立模型更优于整粒高粱模型,其中尤以蛋白质和单宁含量对应近红外模型,籽粒粉碎样品显著优于整粒样品模型,这可能是由于粉碎后的高粱样品会更利于近红外光对样品的穿透,其吸收光谱能携带更多的样品信息,能更好地反映样品的特征信息。因此,根据实际生产环境的不同,可根据需要建立两套高粱各指标含量的分析模型。当需要对采购的大量高粱进行快速验收时,可采用整粒高粱所建立的近红外模型进行分析,以实现对样品无损、快速的检测和分析;在对样本理化值要求更为准确,特别是对高粱蛋白质、单宁含量准确性要求较高和在籽粒粉碎应用较多的生产单元中,可建立粉碎梅花瓣样高粱的近红外模型,以满足检测结果的精确性,并实现快速检测。
表 3 高粱籽粒整粒和粉碎样品的近红外模型影响Table 3. Comparison of NIR models of intact and crushed sorghum samples测定指标 高粱形态 波段挑选方法 光谱处理方法 波长变量 因子数 RMSECV R2 直链淀粉 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 一阶导+多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 220 14 1.3222 0.9560 粉碎 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 一阶导+矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 176 13 0.8739 0.9742 支链淀粉 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 矢量归一化+均值中心化 90 13 2.3477 0.8765 粉碎 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+均值中心化 125 15 2.2879 0.8780 蛋白质 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 230 15 0.3549 0.9069 粉碎 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 一阶导+标准正态变量变换+均值中心化 230 13 0.1171 0.9889 脂肪 整粒 竞争自适应重加权采样 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 36 7 0.2164 0.8658 粉碎 竞争自适应重加权采样 Z-score标准化 85 13 0.0932 0.8692 单宁 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 多元散射校正 140 12 0.1077 0.8841 粉碎 反向区间PLS-区间分段数30 多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 312 12 0.0776 0.9414 3. 结论
本文基于近红外光谱技术构建了高粱直链淀粉、支链淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、单宁含量的快速无损检测模型,通过17种光谱预处理方法消除光谱中无关变量,利用4种波段挑选算法实现模型复杂程度的降低,提高模型的预测运算速度,所建立模型具有较好的高粱指标预测能力,各指标最优模型的决定系数R2分别为0.9560、0.8765、0.9069、0.8658、0.8841,交叉验证均方根误差RMSECV值分别为1.3222、2.3477、0.3549、0.2164、0.1077,外部独立样品验证实验结果表明模型预测值与理化实测值一致性良好,高粱籽粒粉碎单独建模实验表明将高粱样品粉碎后能显著提高蛋白质和单宁含量近红外模型参数。本文建立了一种无损、快速、准确的分析酒用高粱主要指标的近红外快检模型,后续可扩展其他种类酿酒原粮的分析,为实际生产中酒用原粮品质的快速评价提供方法参考。
-
表 1 不同光谱预处理方法高粱理化指标的主要评价参数
Table 1 Main evaluation parameters of physical and chemical indexes of sorghum with different spectrum pretreatments
建模指标 序号 预处理方法 附加预处理方法 波长变量 推荐因子数 RMSECV 直链淀粉 1 无 无 780 19 2.2603 2 无 均值中心化 780 19 2.1086 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 19 2.0766 4 标准正态变量变换+去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 17 2.0760 5 去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 18 2.0918 6 减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 17 2.1389 7 多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 16 2.1504 8 一阶导+多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 15 2.2052 9 标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 17 2.2627 10 矢量归一化 Z-score标准化 780 18 2.3058 支链淀粉 1 无 无 780 14 3.3035 2 无 均值中心化 780 13 3.1574 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 13 3.1807 4 矢量归一化 均值中心化 780 16 2.7791 5 一阶导+多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 10 2.8253 6 一阶导+标准正态变量变换 均值中心化 780 10 2.8503 7 一阶导+矢量归一化 均值中心化 780 10 2.8767 8 多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 12 2.9310 9 减去一条直线 均值中心化 780 12 2.9604 10 一阶导+减去一条直线 均值中心化 780 10 2.9787 蛋白质 1 无 无 780 10 0.5933 2 无 均值中心化 780 13 0.5803 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 13 0.5732 4 标准正态变量变换+去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 18 0.4620 5 标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 19 0.4709 6 多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 18 0.4903 7 最大最小归一化 Z-score标准化 780 13 0.4933 8 一阶导+标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 6 0.4947 9 一阶导+减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 8 0.4957 10 一阶导+多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 6 0.5115 脂肪 1 无 无 780 7 0.3377 2 无 均值中心化 780 7 0.3186 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 7 0.3313 4 标准正态变量变换 均值中心化 780 6 0.3148 5 矢量归一化 均值中心化 780 6 0.3148 6 多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 6 0.3175 7 减去一条直线 均值中心化 780 7 0.3186 8 导数 均值中心化 780 6 0.3214 9 最大最小归一化 均值中心化 780 6 0.3239 10 一阶导+多元散射校正 均值中心化 780 6 0.3240 单宁 1 无 无 780 9 0.2400 2 无 均值中心化 780 9 0.2384 3 无 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2368 4 减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 10 0.2107 5 一阶导+减去一条直线 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2196 6 标准正态变量变换+去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2212 7 标准正态变量变换 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2235 8 去趋势 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2245 9 多元散射校正 Z-score标准化 780 9 0.2262 10 矢量归一化 Z-score标准化 780 7 0.2292 表 2 高粱理化指标近红外预测模型的主要参数
Table 2 Main parameters of the NIR prediction model for physicochemical indexes of sorghums
指标 序号 波段挑选方法 挑选波段(cm−1) 光谱处理方法 波长变量 因子数 RMSECV R2 直链淀粉 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4598、4606、… 去趋势+Z-score标准化 546 17 1.4690 0.9457 2 无信息变量消除 4058、4066、… 减去一条直线+Z-score标准化 156 13 1.6136 0.9345 3 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4027、4035、… 一阶导+多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 220 14 1.3222 0.9560 4 竞争自适应重加权采样 4042、4050、… 一阶导+多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 43 13 0.9561 0.9770 支链淀粉 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4004、4011、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 390 14 2.5854 0.8502 2 无信息变量消除 4035、4042、… 一阶导+标准正态变量变换+均值中心化 164 8 2.5727 0.8516 3 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4197、4413、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 90 13 2.3477 0.8765 4 竞争自适应重加权采样 4081、4197、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 24 12 2.0409 0.9067 蛋白质 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4004、4011、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 546 20 0.3631 0.9025 2 无信息变量消除 4104、4112、… 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+Z-score标准化 118 14 0.3894 0.8879 3 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4135、4359、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 230 15 0.3549 0.9069 4 竞争自适应重加权采样 4652、4937、… 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+Z-score标准化 30 14 0.2668 0.9474 脂肪 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4004、4011、… 矢量归一化+均值中心化 624 7 0.2834 0.6963 2 反向区间PLS-区间分段数20 5200、5207、… 一阶导+矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 234 11 0.2340 0.7235 3 反向区间PLS-区间分段数30 5254、5261、… 一阶导+矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 234 11 0.2337 0.7269 4 无信息变量消除 4011、4019、… 导数+均值中心化 197 4 0.3069 0.6222 5 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4343、4613、… 多元散射校正+均值中心化 60 5 0.2936 0.7036 6 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4027、4050、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 210 6 0.2567 0.7704 7 竞争自适应重加权采样 4760、4775、… 一阶导+矢量归一化+均值中心化 43 4 0.2606 0.8405 8 竞争自适应重加权采样 4613、4629、… 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 36 7 0.2164 0.8658 单宁 1 反向区间PLS-区间分段数10 4598、4606、… 去趋势+Z-score标准化 468 11 0.1546 0.8136 2 反向区间PLS-区间分段数20 3996-5192、… 矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 546 18 0.1288 0.8569 3 反向区间PLS-区间分段数30 3996-5007、… 消除常数偏移量+Z-score标准化 546 13 0.1256 0.8608 4 无信息变量消除 4096、4212、… Z-score标准化 239 11 0.1449 0.8188 5 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4212、4220、… 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+Z-score标准化 150 11 0.1438 0.8103 6 竞争自适应重加权采样 4189、4235、… 消除常数偏移量+Z-score标准化 40 7 0.1078 0.8975 7 无 6061~10000 消除常数偏移量+Z-score标准化 492 13 0.1468 0.8212 8 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 4259、4266、… 多元散射校正 140 12 0.1077 0.8841 注:模型验证方式为内部交叉验证,验证抽样方法为K折系统抽样。 表 3 高粱籽粒整粒和粉碎样品的近红外模型影响
Table 3 Comparison of NIR models of intact and crushed sorghum samples
测定指标 高粱形态 波段挑选方法 光谱处理方法 波长变量 因子数 RMSECV R2 直链淀粉 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 一阶导+多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 220 14 1.3222 0.9560 粉碎 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 一阶导+矢量归一化+Z-score标准化 176 13 0.8739 0.9742 支链淀粉 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 矢量归一化+均值中心化 90 13 2.3477 0.8765 粉碎 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 标准正态变量变换+去趋势+均值中心化 125 15 2.2879 0.8780 蛋白质 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 230 15 0.3549 0.9069 粉碎 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 一阶导+标准正态变量变换+均值中心化 230 13 0.1171 0.9889 脂肪 整粒 竞争自适应重加权采样 标准正态变量变换+Z-score标准化 36 7 0.2164 0.8658 粉碎 竞争自适应重加权采样 Z-score标准化 85 13 0.0932 0.8692 单宁 整粒 蒙特卡罗-无信息变量消除 多元散射校正 140 12 0.1077 0.8841 粉碎 反向区间PLS-区间分段数30 多元散射校正+Z-score标准化 312 12 0.0776 0.9414 -
[1] 钟敏, 张健. 原料糯高粱对酱香型白酒品质影响的研究现状[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(1):32−36. [ZHONG M, ZHANG J. Research status of effect of raw glutinous sorghum on quality of sauce-flavor Baijiu[J]. Chinese Brewing,2022,41(1):32−36. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.01.006 [2] 孙细珍, 熊亚青, 杜佳炜, 等. 不同品种高粱小曲白酒感官表征及重要风味物质对比分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(9):7. [SUN X X, XIONG Y Q, DU J W, et al. Comparative analysis of aroma compounds in Xiaoqu Baijiu fermented by different varieties of sorghum[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(9):7. [3] 程度, 曹建兰, 王珂佳, 等. 高粱对酱香型白酒品质影响的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(7):356−364. [CHENG D, CAO J L, WANG K J, et al. Progress in understanding the effect of sorghum on the quality of Maotai-flavor Baijiu[J]. Food Science,2022,43(7):356−364. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210116-182 [4] 张北举, 陈松树, 李魁印, 等. 基于近红外光谱的高粱籽粒直链淀粉, 支链淀粉含量检测模型的构建与应用[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(1):26−35. [ZHANG B J, CHEN S S, LI K Y, et al. Construction and application of detection model for amylose and amylopectin content in sorghum grains based on near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2022,55(1):26−35. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.01.003 [5] 时伟, 郑红梅, 柴丽娟, 等. 酒用高粱的营养成分及其酿造性能研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 48(21):11 SHI W, ZHENG H M, CHAI L J, et al. Research progress on the nutritional components and brewing performance of brewing sorghum[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(21):11.
[6] HOU Y, YUAN T J, XU J, et al. Study on identification of different producing areas of Gastrodia elata using multivariable selection and two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy of near infrared spectroscopy[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2019,44(4):740−749.
[7] CUI J, LI P, CAO L, et al. Achievement of broadband near-infrared phosphor Ca3Y2Ge3O12: Cr3+, Ce3+ via energy transfer for food analysis[J]. Journal of Luminescence,2021,237:118170. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2021.118170
[8] KHOSROSHAHI M E, PATEL Y, CHABOK R. Characterization of breast cancer antibody (anti-HER-II) conjugated on PEGylated gold nanourchin for active targeting[J]. Gold Bulletin,2022,55:149−159. doi: 10.1007/s13404-022-00316-w
[9] 王海英, 杨玉珍, 任国军, 等. 利用近红外技术对河套原酒入库指标的检测研究[J]. 酿酒科技,2017(1):37−41. [WANG H Y, YANG Y Z, REN G J, et al. Rapid detection of warehousing indexes of hetao base liquor by using near infrared technology[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology,2017(1):37−41. doi: 10.13746/j.njkj.2016276 [10] OMAR J, SLOWIKOWSKI B, BOIX A. Chemometric approach for discriminating tobacco trademarks by near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Forensic Science International,2019,294:15−20. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2018.10.016
[11] CHEN H, TAN C, LIN Z, et al. Quantifying several adulterants of Noto ginseng powder by near-infrared spectroscopy and multivariate calibration[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2018,211:280−286.
[12] SIRSOMBOON P, POSOM J. On-line measurement of activation energy of ground bamboo using near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Renewable Energy,2019,133:480−488. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.10.051
[13] 王勇生, 李洁, 王博, 等. 基于近红外光谱扫描技术对高粱中粗脂肪、粗纤维、粗灰分含量的测定方法研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(3):181−185. [WANG Y S, LI J, WANG B, et al. Research on measurement of crude fat, crude fiber and ash contents in sorghum using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy method[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2020,35(3):181−185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.03.029 [14] 苏鹏飞, 张武岗. 基于NIR高粱淀粉含量快检技术的开发研究[J]. 酿酒科技,2022(2):107−110. [SU P F, ZHANG W G. Development of rapid detection technology for starch in sorghum based on NIR[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology,2022(2):107−110. [15] 苏鹏飞, 刘丽丽, 闫宗科, 等. 基于近红外高粱水分的快速分析研究[J]. 酿酒,2021,48(1):87−90. [SU P F, LIU L L, YAN Z K, et al. Study on NIR rapid analysis of water content in the sorghum[J]. Liquor Making,2021,48(1):87−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8110.2021.01.018 [16] PEIRIS K H S, BEAN S R, JAGADISH S V K. Extended multiplicative signal correction to improve prediction accuracy of protein content in weathered sorghum grain samples[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2020,97(5):1066−1074. doi: 10.1002/cche.10329
[17] CHADALAVADA K, ANBAZHAGAN K, NDOUR A, et al. NIR Instruments and prediction methods for rapid access to grain protein content in multiple cereals[J]. Sensors,2022,22(10):3710. doi: 10.3390/s22103710
[18] 刘敏轩, 王赟文, 韩建国. 高粱籽粒中多酚类物质的傅立叶变换近红外光谱分析[J]. 分析化学,2009,37(9):1275−1280. [LIU M X, WANG Y W, HAN J G. Determination of polyphenols in sorghum grains by near infrared reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2009,37(9):1275−1280. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2009.09.005 [19] 王文真, 孙采云. 应用近红外反射分析高粱籽粒蛋白质, 赖氨酸和单宁含量[J]. 河南农业科学,1993(3):7−9. [WANG W Z, SUN C Y. Analysis of sorghum grain protein, lysine and tannin content using near-infrared reflection[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,1993(3):7−9. [20] DYKES L, HOFFMANN JR L, PORTILLO-RODRIGUEZ O, et al. Prediction of total phenols, condensed tannins, and 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in sorghum grain using near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2014,60(1):138−142. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2014.02.002
[21] MABOOD F, JABEEN F, HUSSAIN J, et al. FT-NIRS coupled with chemometric methods as a rapid alternative tool for the detection & quantification of cow milk adulteration in camel milk samples[J]. Vibrational Spectroscopy,2017,92:245−250. doi: 10.1016/j.vibspec.2017.07.004
[22] YU H Y, NIU X Y, LIN H J, et al. A feasibility study on on-line determination of rice wine composition by Vis–NIR spectroscopy and least-squares support vector machines[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,113(1):291−296. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.06.083
[23] CHEN J, LI M, PAN T, et al. Rapid and non-destructive analysis for the identification of multi-grain rice seeds with near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2019,219:179−185. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2019.03.105
[24] SHI H, LEI Y, PRATES L L, et al. Evaluation of near-infrared (NIR) and Fourier transform mid-infrared (ATR-FT/MIR) spectroscopy techniques combined with chemometrics for the determination of crude protein and intestinal protein digestibility of wheat[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,272:507−513. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.075
[25] GORDON R, CHAPMAN J, POWER A, et al. Unfrazzled by fizziness: Identification of beers using attenuated total reflectance mid-infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2018,11(9):2360−2367. doi: 10.1007/s12161-018-1225-y
[26] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 15683-2008 大米直链淀粉含量的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008 General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 15683-2008 Rice-Determination of amylose content[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.
[27] 中华人民共和国农牧渔业部. GB 7648-1987 水稻、玉米、谷子籽粒直链淀粉测定法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1987 Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Fisheries of the People's Republic. GB 7648-1987 Determination of amylose of rice, maize and millet grain[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1987.
[28] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.6-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 State Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 5009.6-2016 National Standard for Food Safety Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[29] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 6432-2018 饲料中粗蛋白的测定 凯氏定氮法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018 State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 6432-2018 Determination of crude protein in feed Kjeldahl nitrogen determination method[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
[30] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 15686-2008 高粱 单宁含量的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008 General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB/T 15686-2008 Determination of tannin content in sorghum[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.
[31] SAMPAIO P S, SOARES A, CASTANHO A, et al. Optimization of rice amylose determination by NIR-spectroscopy using PLS chemometrics algorithms[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,242:196−204. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.058
[32] 杨丹, 刘新, 王川丕, 等. 绿茶样品粒度对近红外光谱图和模型的影响[J]. 食品科技,2012(11):278−281. [YANG D, LIU X, WANG C P, et al. Effect of green tea particle size on near infrared spectrogram and nitrogen content model[J]. Food Science and Technology,2012(11):278−281. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2012.11.017 [33] BIAN X, WANG K, TAN E, et al. A selective ensemble preprocessing strategy for near-infrared spectral quantitative analysis of complex samples[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems,2020,197:103916. doi: 10.1016/j.chemolab.2019.103916
[34] 雷敬卫, 李小庆, 白雁, 等. 近红外光谱法快速测定逍遥丸(浓缩丸)中水分含量[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(19):132−135. [LEI J W, LI X Q, BAI Y, et al. Rapid determination of moisture in Xiaoyao pills (condensed) by near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2013,19(19):132−135. [35] 余梅, 李尚科, 杨菲, 等. 基于近红外光谱技术与优化光谱预处理的陈皮产地鉴别研究[J]. 分析测试学报,2021,40(1):65−71. [YU M, LI S K, YANG F, et al. Identification on different origins of citri reticulatae pericarpium using near infrared spectroscopy combined with optimized spectral pretreatments[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2021,40(1):65−71. [36] LIU X W, CUI X Y, YU X M, et al. Understanding the thermal stability of human serum proteins with the related near-infrared spectral variables selected by Monte Carlo-uninformative variable elimination[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters,2017,28(7):1447−1452. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2017.03.021
[37] 熊雅婷, 李宗朋, 王健, 等. 近红外光谱波段优化在白酒酒醅成分分析中的应用[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2016,36(1):84−90. [XIONG Y T, LI Z P, WANG J, et al. The near infrared spectral bands optimal selection in the application of liquor fermented grains composition analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2016,36(1):84−90. [38] JUN L Y, CHEN H C, JIN L, et al. Near infrared determination of the content of caffeine in tea polyphenol[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2005,25(8):1243−1245.
[39] 李霞. 基于近红外光谱技术的赤霞珠干红葡萄酒品质指标检测方法研究[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2018 LI X. Rapid detection of quality index in cabernet sauvignon red wine based on near-infrared spectroscopy[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2018.
[40] 成云玲. 基于近红外高光谱成像技术的酿酒葡萄分类及单宁含量检测[D]. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2020 CHENG Y L. Detection of wine grape classification and tannins content based on near infrared hyperspectral imaging[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2020.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 路静,白术群,郑学玲,杨佳,杨凯. 低温胁迫萌芽对青稞γ-氨基丁酸合成的调控作用研究. 食品研究与开发. 2024(11): 72-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 路静,白术群,郑学玲. 萌芽谷物中γ-氨基丁酸代谢及应激积累机制的研究进展. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(17): 380-386 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 迟燕平,苗新宇,王景会,苏颖,牛红红,孙慕白,李达,华梅,代永刚. 产γ-氨基丁酸贝莱斯芽孢杆菌CLYB1的鉴定及基因组改组选育研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(19): 167-173 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 主港伟,韩世豪,许永杰,张晓顺,孟晓静,王斌,车霄. 植物乳杆菌(WSJ-06)缓解低剂量甲基汞诱导的斑马鱼焦虑样行为及机制. 现代消化及介入诊疗. 2022(10): 1245-1252 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)








 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



