Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction Optimization of Antioxidant Products from Hyrtios erectus and Its Antioxidant Activity
-
摘要: 为探索海绵动物抗氧化提取物的提取工艺及提取物的抗氧化活性,以H. erectus海绵乙醇提取物的DPPH自由基清除率为响应值,分别考察超声温度、超声时间和超声功率3个影响因素,通过Box-Behnken响应面设计确定最佳超声提取工艺。以该工艺提取物为实验材料,分析其对DPPH自由基、ABTS+•和•OH的清除效果,通过构建H2O2氧化损伤模型研究提取物对氧化损伤L02细胞的活力和对H2O2氧化应激胞内ROS含量的影响。结果表明:可操作的最佳工艺为超声温度57 ℃,超声时间60 min,超声功率490 W,在此条件下,提取物DPPH自由基清除率为61.98%±1.52%,与预测值62.16%吻合度较好,该提取物对DPPH自由基、ABTS+•和•OH具有良好的清除效果,提取物处理组细胞活力均显著高于模型组(P<0.05),且细胞内ROS荧光强度均极显著低于模型组(P<0.01)。总之,该工艺提取物具有较广泛的抗氧化活性,对H2O2氧化损伤的L02细胞具有保护作用,该研究可为抗氧化食品添加剂的研发提供理论支撑。Abstract: To explore the process of extraction and antioxidant activity of products from marine sponge, three influencing factors, ultrasonic temperature, ultrasonic time, and ultrasonic power were investigated respectively taking DPPH radicals scavenging rate of ethanol extracts from H. erectus as the response value, and the optimal ultrasonic-assisted extraction process was determined by Box-Behnken design. The extract obtained from H. erectus by the best ultrasonic-assisted process was detected for antioxidant activity, which included the scavenging effect on DPPH radicals, ABTS+• and •OH. The effects of the extract on viability of oxidative damage L02 cells and content of intracellular ROS were detected by constructing a cell model of H2O2 induced oxidative damage. The results showed that the optimized process conditions were as follows: Ultrasonic temperature was 57 ℃, ultrasonic time was 60 min, and ultrasonic power was 490 W. Under these conditions, the DPPH scavenging rate of the extract was 61.98%±1.52%, which agreed well with the predicted value of 62.16%. The extract showed good scavenging effects on DPPH radical, ABTS+• and •OH. The cell viability of treated groups was significantly higher than that of the model group (P<0.05), and the intensity of intracellular ROS fluorescence was significantly lower than that of the model group (P<0.01). In general, the product from H. erectus had a wide range of antioxidant activity, and it had a protective effect on H2O2 induced oxidative damage in L02 cells. This study provides theoretical support for the research and development of antioxidant food additives.
-
Keywords:
- response surface /
- marine sponge /
- anti-oxidation /
- free radical /
- reactive oxygen species (ROS)
-
海绵属于多孔动物门,是最原始的多细胞动物,营固着生活,广泛分布在热带、温带和极地地区[1],目前已发现的海绵有9000多种[2]。海绵是仅次于珊瑚礁的第二大底栖生物群落,具有丰富的生物多样性[3],被认为是天然产物的重要来源[4]。据报道,从海洋无脊椎动物中分离出的15000多种海洋天然产物中30%以上来自海绵[5-6],显著高于其他海洋动物、陆生植物和微生物[7-8],为新药研制提供了大量高活性的先导化合物,目前海绵已成为海洋生物中研究最活跃的领域之一[9]。海绵天然产物主要包括生物碱[10-11]、聚酮类化合物、萜类化合物[12]、肽类、芳烃类、类萜类、大环内酯类、类固醇类和卤代化合物[13]等物质,以上物质表现出丰富的化学多样性[3],并且显示了较好的生物活性,如抗氧化活性[14]、抗菌活性[3]、抗癌活性[15]、抗病毒活性[16]、抗炎活性[17]和防污活性[18]等。
海绵天然产物抗氧化活性突出,研究发现H. erectus海绵提取物对DPPH自由基、超氧阴离子和羟基自由基具有较强的抗氧化活性[19],Dysidea arearia海绵中的Dysiarenon化合物通过抑制5-LOX/NF-κB/MAPK信号通路发挥抗氧化作用[20],海绵动物中酚类、胶原蛋白等物质是海绵中的主要抗氧化成分[21-22],海绵天然产物的抗氧化活性已成为海绵活性研究的一个重要方面[23]。超声辅助提取法因其效率高而被广泛应用于提取天然产物[24],本研究采用超声辅助法以抗氧化活性为响应值优化提取海绵天然产物,是针对抗氧化活性开展的工艺优化探讨,避免了传统优化工艺强调提取物得率而无法获取高活性物质的弊端。目前,海绵天然产物提取主要以乙醇或甲醇浸提为主[25],对海绵动物活性物质的提取工艺优化鲜有报道。
Hyrtios属海绵已被证明是次生代谢产物的丰富来源,H. erectus海绵作为Hyrtios属海绵中的重要成员,具有较高的研究价值[26],本实验以H. erectus海绵为原料,针对其抗氧化活性,采用Box-Behnken响应面设计优化提取工艺条件,并对最佳工艺提取产物的抗氧化活性进行分析验证,旨在探讨具有抗氧化特征的海绵天然产物的提取工艺,为后续研究源于海绵动物的抗氧化食品添加剂提供依据,也为特定活性天然产物的提取提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
海绵动物材料为H. erectus 采自海南省陵水黎族自治县新村潟湖及其新城镇附近海域;石油醚、二氯甲烷、乙酸乙酯、硫酸亚铁、过硫酸钾、H2O2、水杨酸钠、无水乙醇 分析纯,西陇科学股份有限公司;DPPH、ABTS+•、VC 分析纯,合肥巴斯夫生物科技有限公司;人肝细胞系L02细胞 中国科学院上海细胞库;RPMI1640培养基 美国GIBCO公司;杭牛血清 中国天津市TBD公司;CCK-8 上海东仁化学科技有限公司;细胞内ROS检测试剂盒 美国Sigma-Aldrich公司。
SpectraMax M2e多功能酶标仪 美国Molecular Devices;UV-5100紫外分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;RE311旋转蒸发仪、DKL410C烘箱 雅马拓科技贸易有限公司;JM-38D-40超声设备 深圳洁盟清洗设备有限公司;HHS-21-6水浴锅 上海博讯实业有限公司;D180二氧化碳培养箱 深圳市瑞沃德生命科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 海绵抗氧化产物提取工艺
海绵抗氧化产物提取参考Swantara等[27]的方法并稍作改动,将采集的海绵动物清洗后置于50 ℃烘箱内烘干至恒重,粉碎过20目筛,放置−20 ℃冰箱保存备用。取1.000 g海绵样品,以70%乙醇为提取溶剂,设置料液比为1:10[28],提取液以6000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液浓缩干燥得H. erectus粗提物。
1.2.2 单因素实验
以H. erectus提取物的DPPH自由基清除率为响应值,依次考察超声温度、超声时间和超声功率三个单因素对海绵动物乙醇提取物DPPH自由基清除率和得率的影响[29]。固定超声时间60 min和超声功率300 W不变,考察超声温度分别为30、40、50、60、70 ℃时对海绵动物乙醇提取物DPPH自由基清除率和得率的影响;固定超声温度50 ℃和超声功率300 W不变,考察超声时间分别为50、60、70、80、90、100 min时对海绵动物乙醇提取物DPPH自由基清除率和得率的影响;固定超声温度50 ℃和超声时间60 min不变,考察超声功率分别为200、300、400、500、600、700 W时对海绵动物乙醇提取物DPPH自由基清除率和得率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验设计与模型验证
根据单因素实验结果,以DPPH自由基清除率为响应值开展三因素三水平响应面试验,对所得结果进行多项式回归拟合及方差分析检验,得出各变量最佳参数,按照最佳参数进行验证实验以检验响应面分析的可靠性,因素水平见表1。
表 1 Box-Behnken设计的因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of Box-Behnken design因素 编码 水平 −1 0 1 超声温度(℃) A 40 50 60 超声时间(min) B 50 60 70 超声功率(W) C 400 500 600 1.2.4 粗提物得率的测定
粗提物得率以1.000 g海绵样品所提取的粗提物质量与海绵样品质量(1.000 g)的百分比表示,计算公式如下:
得率(%)=m1m0×100 (1) 式中,m1为粗提物质量(g),m0为海绵样品质量(g)。
1.2.5 自由基清除率测定
DPPH自由基清除率测定:测定方法参考文献[30-31],取3 mg粗提物溶于无水乙醇并定容3.0 mL,加入浓度为0.1 mmol·L−1的DPPH自由基乙醇溶液3.0 mL,振荡混匀,室温下避光反应30 min,于波长517 nm处测定吸光值。DPPH自由基清除率公式为:
清除率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 (2) 式中,A0为DPPH自由基+乙醇的吸光度,A1为样品+DPPH自由基+乙醇的吸光度,A2为样品+乙醇的吸光度。
ABTS+•清除率测定:测定方法参考文献[32],将等体积7.0 mmol·L−1 ABTS溶液与2.45 mmol·L−1过硫酸钾溶液混匀,避光反应16 h得到ABTS自由基贮备液。用95%乙醇对贮备液进行稀释,使其在波长734 nm处的吸光值为0.070±0.02,于30 ℃避光平衡30 min后得ABTS+•工作液。取0.5 mg提取物加入1 mL ABTS+•工作液(即0.5 mg·mL−1),于30 ℃避光反应4 min,测定波长为734 nm的吸光值。ABTS+•清除率公式为同式(2),式中,A0为ABTS+•+乙醇的吸光度,A1为样品+ABTS+•+乙醇的吸光度,A2为样品+乙醇的吸光度。
•OH清除率测定:参考文献[33],将2 mg样品加水至2 mL,再加入1.4 mL 6 mmol·L−1 H2O2,然后加入0.6 mL 20 mmol·L−1水杨酸钠和2 mL 1.5 mmol·L−1硫酸亚铁,37 ℃下恒温水浴1 h。以去离子水为参比溶液,在510 nm下测定吸光度。•OH清除率公式同式(2),式中,A0为空白对照液的吸光度,A1为样品测定管的吸光度,A2为样品本底管的吸光度。
上述3种自由基清除率均以0.5 mg·mL−1的VC为阳性对照[32]。
1.2.6 H2O2诱导L02细胞氧化损伤模型和L02细胞活力测定
参照杜毅超等[34]的方法并稍作改进,取对数期终浓度为1×105 cells·mL−1 L02细胞100 μL加入96孔板,5% CO2、37 ℃条件下培养12 h使细胞贴壁,弃培养基,加入100 μL无血清培养基继续培养4 h,弃培养基,然后加入100 μL终浓度为1.0 mmol·L−1的H2O2无血清培养基,继续培养4 h,即为氧化损伤模型组。样品组将100 μL无血清培养基替换为100 μL 含浓度为 0.125、0.25、0.5、1.0 mg·mL−1 提取物的无血清培养基,其他处理与氧化损伤模型相同,空白组除未加H2O2外,其他处理与氧化损伤模型组相同。样品组、模型组和空白组采用CCK-8检测细胞在450 nm波长处的OD值,计算细胞相对活性,计算公式如下:
细胞活性(%)=A1A0×100 (3) 式中,A0为空白组的吸光度,A1为样品的吸光度。
1.2.7 L02细胞内ROS测定
参照杜毅超等[34]的方法并稍作改进,按照1.2.5方法处理提取物组(提取物终浓度分别为0.125、0.25、0.5、1.0 mg·mL−1)、模型组和对照组,并将96孔板更换为24孔板,每孔加入的溶液扩大到5倍。严格按照细胞内ROS检测试剂盒说明书进行操作,记录各组细胞的荧光强度。
1.3 数据处理
每个实验重复3次取平均值,结果以平均值±标准差表示。采用Design Expert 8.0.6软件建立回归模型,开展方差分析(F检验)和模型回归分析。实验数据利用Microsoft Excel 2010软件进行统计和作图,采用SPSS 19.0软件进行显著水平分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素结果分析
2.1.1 超声提取温度的考察
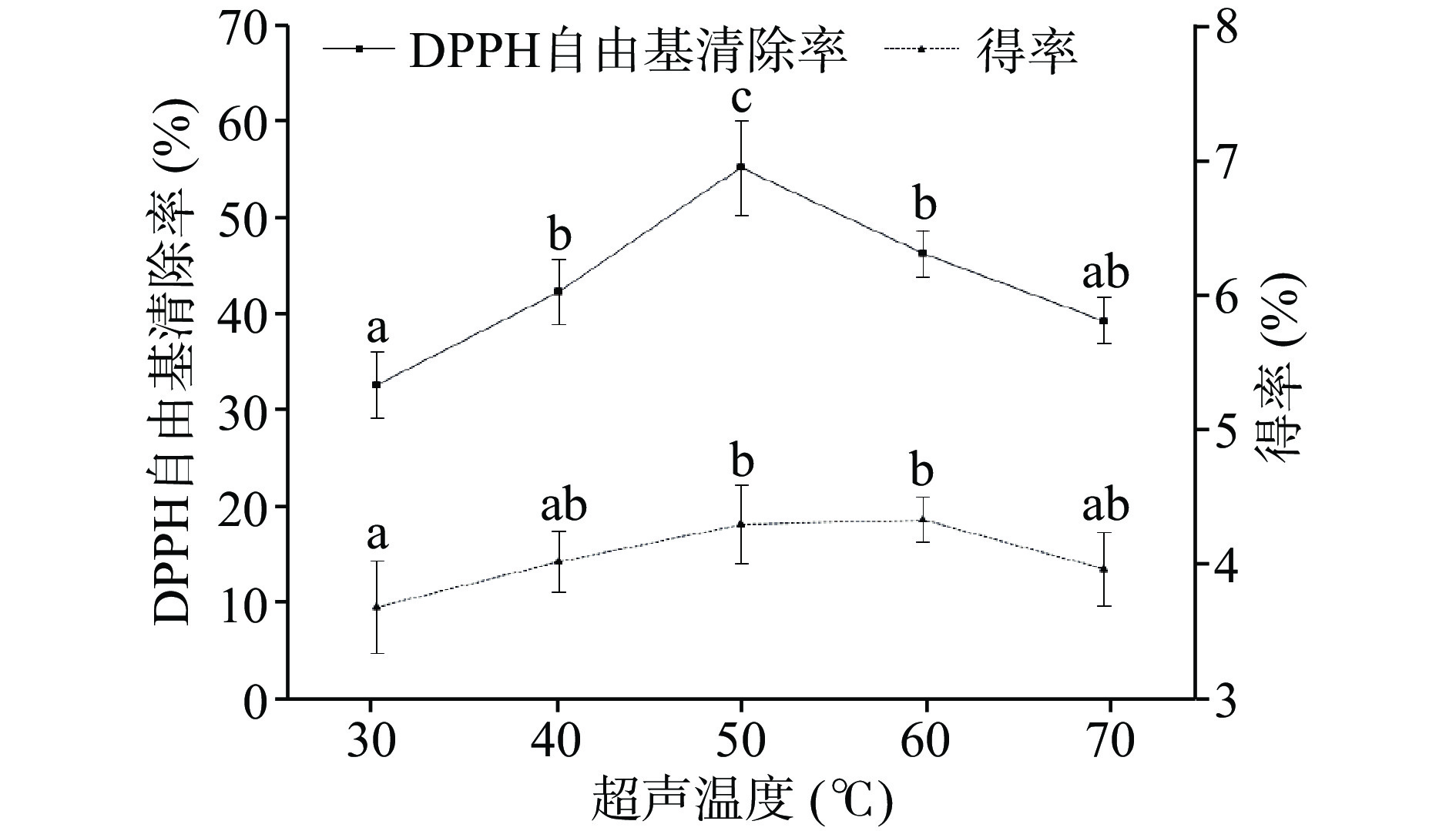
图1显示,随着超声温度的升高,提取物对DPPH自由基的清除率以及粗提物得率均呈现先升高再降低的趋势,其中超声温度在50 ℃时清除率达到峰值,峰值为55.14%±4.92%,分析认为超声提取的温度对提取物的抗氧化活性有影响,温度过高,可能破坏提取物的结构[32],反而清除率降低,因此,最佳超声温度选择50 ℃。
2.1.2 超声提取时间的考察
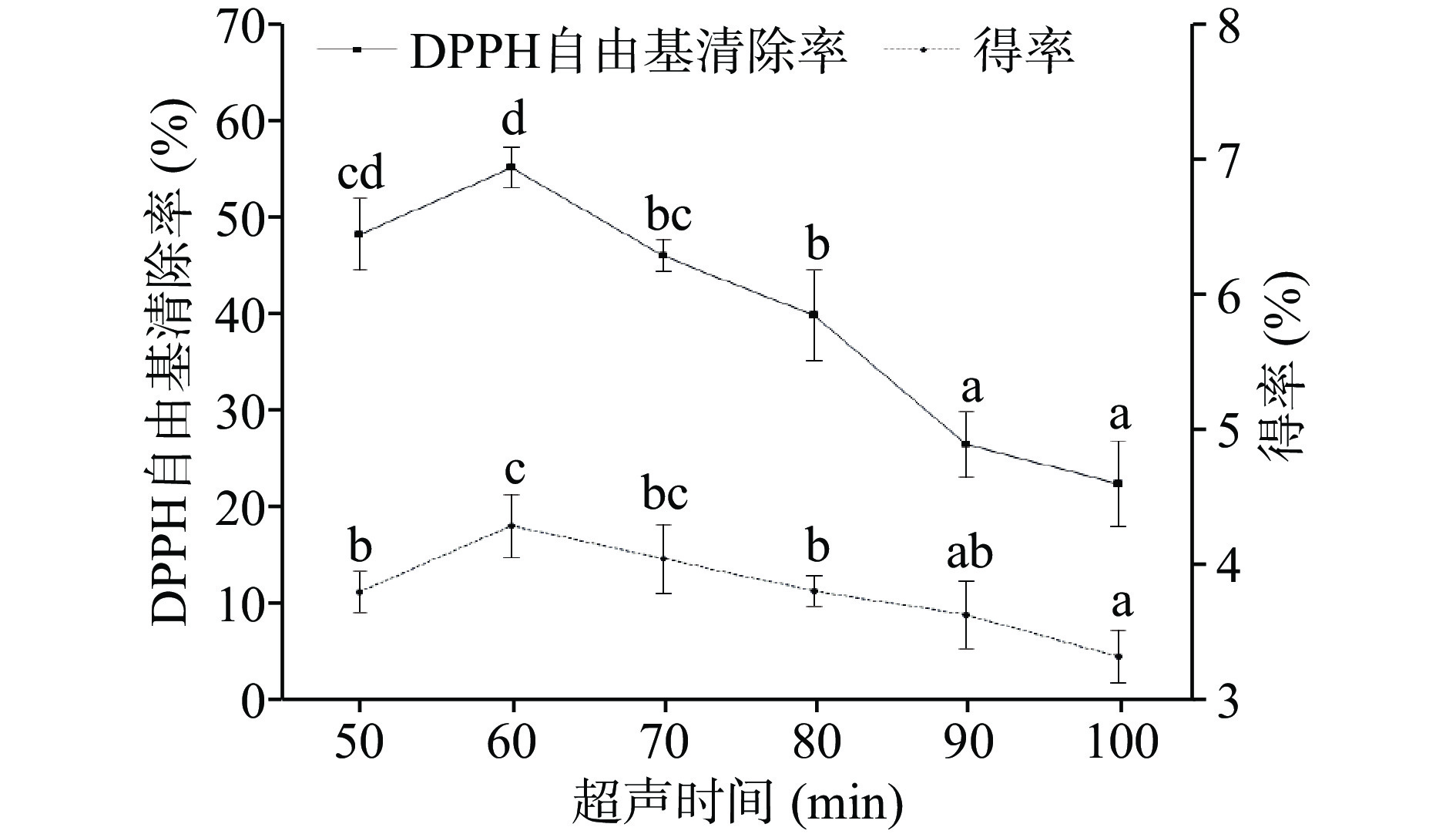
图2显示,超声时间对提取物的抗氧化活性和得率的影响均呈现迅速达到峰值,然后逐渐降低的特征,在超声提取时间为60 min时,提取物对DPPH自由基的清除率和得率均出现峰值,清除率峰值为55.02%±2.13%,得率峰值为4.28%±0.23%,分析认为由于超声波“空化效应”能促使活性物质的析出,当超声时间延长时,提取物的活性增强,得率增大,但是超声时间过长,超声波的机械振动可能影响活性成分的结构或者造成物质分解,导致提取物的活性和得率反而降低[35-37]。随着超声时间的变化,两个指标变化趋势相似,且峰值出现的时间相同,因此,最佳超声时间选择60 min。
2.1.3 超声提取功率的考察
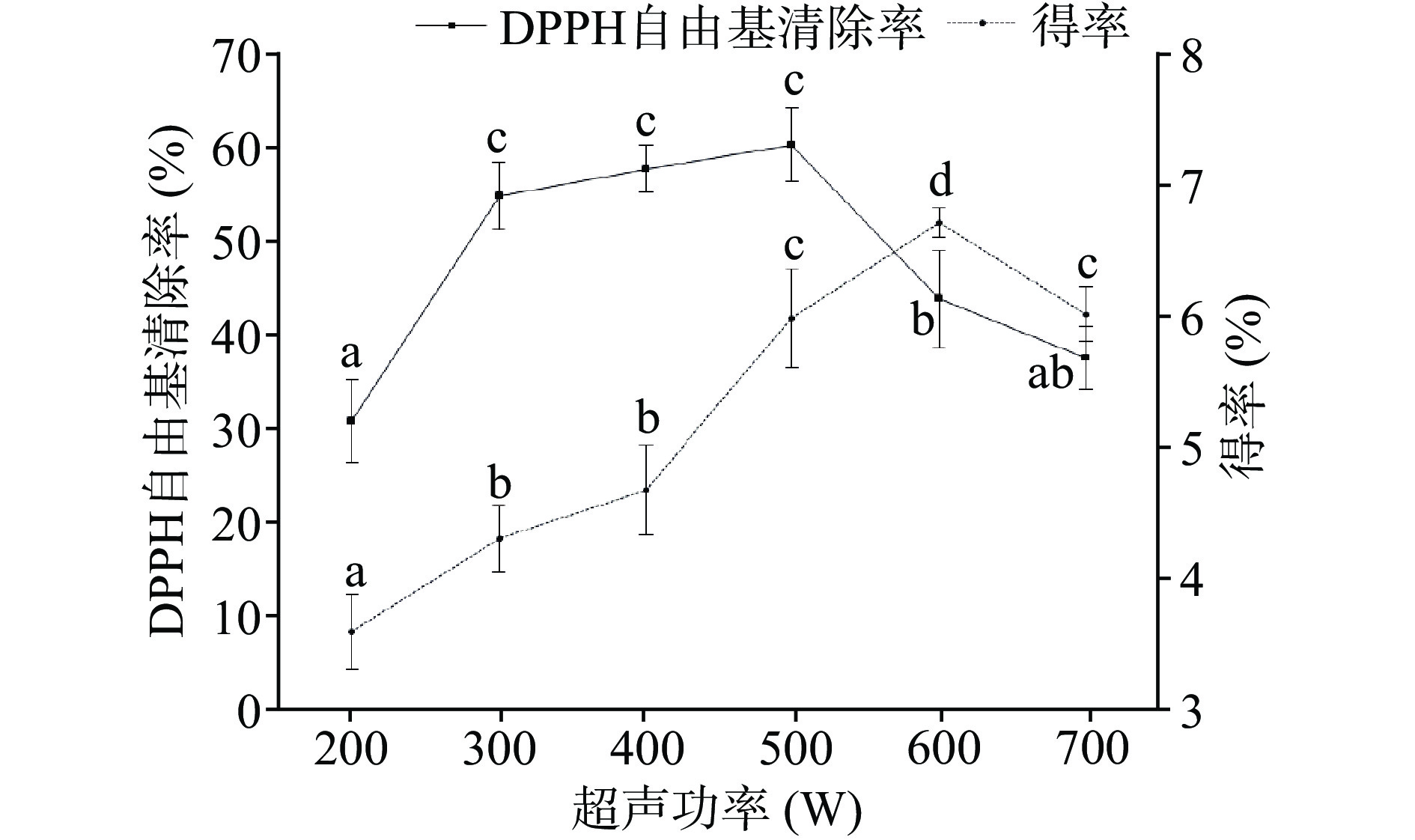
图3显示,随着超声功率的提高,提取物活性迅速增强,在300~500 W之间维持较高的水平,并在500 W时达到峰值60.35%±3.96%,然后呈现下降趋势。提取物得率先逐渐升高再降低,在600 W时达到峰值6.71%±0.11%。分析认为随着超声功率的增加,超声波的“空化效应”增强,破坏细胞壁的能力增强,有利于活性成分的析出,得率增加,但当超声功率继续提高时,机械振动可能会改变活性成分的结构,甚至促进物质分解,从而降低提取物的活性和得率[37-39]。此外,从清除率和得率的峰值对应的超声功率可看出提取物得率最高时,提取物活性却不是最强,如果以得率为响应值优化提取海绵天然产物,其抗氧化活性非最佳。因此,最佳超声功率选择500 W。
2.2 响应面结果分析
2.2.1 响应面法试验方案与结果
响应面试验的因素水平取值由单因素实验得出,各因子和水平情况见表1。依据Box-Behnken设计原理进行了17次试验(见表2)。
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计结果Table 2. Results of Box-Behnken experiments design试验号 A超声温度 B超声时间 C超声功率 Y DPPH自由基清除率(%) 1 0 1 −1 48.08±2.25 2 0 1 1 41.69±2.59 3 −1 −1 0 38.82±2.41 4 1 −1 0 46.31±1.70 5 0 0 0 62.03±1.11 6 1 1 0 41.65±1.25 7 −1 1 0 42.76±2.21 8 0 0 0 61.80±1.26 9 1 0 −1 45.36±1.59 10 0 −1 1 44.22±2.50 11 −1 0 −1 46.01±3.34 12 1 0 1 44.31±1.01 13 0 0 0 61.79±1.70 14 0 0 0 61.98±2.82 15 −1 0 1 37.47±1.33 16 0 −1 −1 47.49±2.13 17 0 0 0 62.09±3.15 2.2.2 回归方程与方差分析
采用Design Expert 8.0.6统计软件对表2试验结果进行多元回归分析获得多元二次回归模型:Y=61.94+1.57A−0.33B−2.41C−2.15AB+1.87AC−0.78BC−10.82A2−8.74B2−7.83C2。表3显示,该回归模型的P值小于0.0001,达到极显著的水平,说明错误实验概率非常小;模型的失拟项P值为0.1323,没有达到显著水平(P>0.05),说明模型与实验拟合程度较好,模型建立合理;模型的决定系数R2=0.9998,表明DPPH自由基清除率的实际值与预测值之间拟合度较好;模型的校正决定系数R2adj=0.9995,说明有99.95%的超声提取条件可以用该模型进行分析解释,即方程拟合回归效果好。变异系数CV值为0.4%,小于10%,进一步说明模型拟合度高,实验可行,可以用于优化海绵动物提取物的超声提取工艺。
表 3 回归模型方程的方差分析Table 3. Variance analysis of regression model equation方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 显著性 回归模型 1297.09 9 144.12 3800.45 <0.0001 ** A-超声温度 19.75 1 19.75 520.82 0.0001 ** B-超声时间 0.88 1 0.88 23.32 0.019 * C-超声功率 46.32 1 46.32 1221.46 <0.0001 ** AB 18.49 1 18.49 487.58 <0.0001 ** AC 14.03 1 14.03 369.84 <0.0001 ** BC 2.43 1 2.43 64.17 <0.0001 ** A2 492.73 1 492.73 12993.24 <0.0001 ** B2 321.28 1 321.28 8472.16 <0.0001 ** C2 258.32 1 258.32 6811.96 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.27 7 0.038 − − − 失拟项 0.19 3 0.064 3.43 0.1323 N 净误差 0.074 4 0.019 − − − 总离差 1297.36 16 − − − − R2=0.9998,R2adj=0.9995 注:*代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01,N代表差异无统计学意义,“−”表示无此项。 回归模型方差分析如表3所显示,回归模型中一次项A、C和二次项A2、B2、C2对清除率的影响均达到极显著水平(P<0.01),B项达到显著水平(P<0.05);交互项AB、AC、BC对清除率影响达到极显著水平(P<0.01);失拟项差异不显著(P>0.05)。根据表3中三因素的F值,得出A、B、C三因素对DPPH自由基清除率的影响主次顺序为C>A>B,即超声功率影响最大,超声温度次之,超声时间最小。
2.2.3 交互作用分析
通过响应面软件生成因素交互作用的3D曲线图和等高线图,能直观地看出各因素两两交互作用对DPPH自由基清除率的影响。响应曲面的坡度及等高线的偏离程度可反映两两因素间的交互作用,响应面坡度越陡,表明二者间的交互作用越显著,对DPPH自由基清除率影响较大,反之越平缓则影响越小。图4显示,在超声功率一定的情况下,超声温度和超声时间的3D曲面图走势较明显,等高线偏离也较明显,两因素的交互作用对DPPH自由基清除率影响显著,与表3中AB项的P值小于0.0001相符,差异极显著(P<0.01);在超声时间一定的情况下,超声温度和超声功率的3D曲面图走势较明显,等高线偏离也较明显,但略小于AB的3D图走势和等高线的偏离,两因素的交互作用对DPPH自由基清除率影响显著,与表3中AC项的P值小于0.0001相符,差异极显著(P<0.01);在超声温度一定的情况下,超声时间和超声功率的3D曲面图走势较明显,等高线偏离明显,两因素的交互作用对DPPH自由基清除率影响显著,与表3中BC项的P值小于0.0001相符,差异极显著(P<0.01)。根据以上数据及图示,对各因素综合评价分析,各因素交互项的交互强弱顺序为:AB>AC>BC,并且AB、AC、BC交互作用均达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。
通过两因素交互作用的3D曲面图的分析可以发现,表3中的数据与图4的3D曲面图及等高线图相符,图表一致。
2.2.4 最佳提取工艺及验证实验
利用Design Expert统计软件对模型方程求解,预测的超声提取最优条件分别为56.62 ℃、59.80 min、485.55 W时,其响应值DPPH自由基清除率最大为62.16%。考虑工艺参数的实际可操作性,将超声温度、超声时间和超声功率分别修改为57 ℃、60 min、490 W。通过3次重复实验,实际测得提取物DPPH自由基清除率为61.98%±1.52%,与模型预测值62.16%吻合度较高,说明该模型有较高的可信性和有效性。
2.3 最佳提取工艺条件下的提取物抗氧化活性分析
2.3.1 抗氧化提取物对3种自由基的清除效果
如图5所示,在上述优化工艺条件下制备的提取物不仅对DPPH自由基具有良好的清除效果,清除率为61.98%±1.52%,对ABTS+•和•OH也表现出较好的清除效果,清除率分别为59.79%±2.73%、54.26%±6.54%,与Utkina等[40]报道的海绵提取物对ABTS+•最高抑制率60%吻合。尽管与VC对照相比还有差距,但作为粗提物对3种自由基的清除率均超过50%,反映出该提取工艺所提取的粗提物具有良好的抗氧化能力。
2.3.2 抗氧化提取物对H2O2氧化损伤L02细胞活力的影响
活性氧(ROS)是机体氧化代谢产生的性质活泼的含氧化合物,正常细胞通过特殊的机制维持氧化物与抗氧化物之间的平衡,细胞内ROS处于较低水平[41],当ROS过量时会引发氧化应激,破坏肝细胞的蛋白、脂质及DNA,进而破坏细胞结构,导致肝脏的结构及功能发生异常[34],本研究构建H2O2氧化损伤人正常肝细胞L02细胞模型,通过细胞活力反映提取物对L02细胞保护作用。图6显示,提取物组4个不同浓度对H2O2氧化损伤均有不同程度地减弱,细胞活力均显著(P<0.05)高于模型组,且0.25、0.5、1.0 mg·mL−1三个处理与模型组差异达到极显著水平(P<0.01),但各处理的细胞活力均低于空白对照,说明提取物对氧化损伤的肝细胞具有保护作用。
![]() 图 6 提取物对H2O2氧化损伤L02细胞活力的影响注:*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);+表示添加,−表示未添加;图7同。Figure 6. Effects of extracts on the viability of L02 cells damaged by H2O2 oxidation
图 6 提取物对H2O2氧化损伤L02细胞活力的影响注:*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);+表示添加,−表示未添加;图7同。Figure 6. Effects of extracts on the viability of L02 cells damaged by H2O2 oxidation2.3.3 抗氧化提取物对H2O2氧化应激L02细胞内ROS的影响
采用DCFH-DA探针进一步分析抗氧化提取物对H2O2氧化应激L02细胞内ROS水平的影响,利用荧光染料DCFH-DA可以穿过细胞膜并在细胞内水解生成DCFH,DCFH被细胞内ROS氧化生成荧光物质DCF[42],再用多功能酶标仪在指定波长(激发波长488 nm、发射波长525 nm)处测定吸光度,根据DCF的荧光强度,定量检测细胞内活性氧水平。图7显示,模型组L02细胞内ROS荧光强度最强,反映出细胞内氧化和抗氧化失衡严重;未添加H2O2和抗氧化提取物的空白对照组,ROS荧光强度较低,细胞处于正常状态;与模型组比较,提取物的4个浓度处理L02细胞内ROS荧光强度均极显著低于模型组(P<0.01),且随着提取物浓度的升高,细胞内ROS荧光强度降低。此外,提取物浓度为1.0 mg·mL−1的处理细胞内ROS荧光强度低于CK组。
3. 结论
本实验通过响应面优化超声辅助提取海绵抗氧化成分,最佳提取工艺为超声温度57 ℃,超声时间60 min,超声功率490 W,在此条件下,提取物DPPH自由基清除率为61.98%±1.52%,与预测值62.16%吻合度较好。体外抗氧化实验表明,海绵提取物对DPPH自由基、ABTS+•和•OH具有良好的清除效果,并且,可显著提高氧化损伤模型L02细胞活力(P<0.05),极显著降低细胞内的ROS水平(P<0.01),对人肝氧化损伤具有显著的保护作用。总之,该工艺以抗氧化活性为响应值,针对天然产物特定功能开展的工艺优化探索,提高了目标提取物的精准性,而且工艺操作简单,安全可靠,可为抗氧化食品添加剂的开发提供理论支撑。
-
图 6 提取物对H2O2氧化损伤L02细胞活力的影响
注:*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);+表示添加,−表示未添加;图7同。
Figure 6. Effects of extracts on the viability of L02 cells damaged by H2O2 oxidation
表 1 Box-Behnken设计的因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of Box-Behnken design
因素 编码 水平 −1 0 1 超声温度(℃) A 40 50 60 超声时间(min) B 50 60 70 超声功率(W) C 400 500 600 表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计结果
Table 2 Results of Box-Behnken experiments design
试验号 A超声温度 B超声时间 C超声功率 Y DPPH自由基清除率(%) 1 0 1 −1 48.08±2.25 2 0 1 1 41.69±2.59 3 −1 −1 0 38.82±2.41 4 1 −1 0 46.31±1.70 5 0 0 0 62.03±1.11 6 1 1 0 41.65±1.25 7 −1 1 0 42.76±2.21 8 0 0 0 61.80±1.26 9 1 0 −1 45.36±1.59 10 0 −1 1 44.22±2.50 11 −1 0 −1 46.01±3.34 12 1 0 1 44.31±1.01 13 0 0 0 61.79±1.70 14 0 0 0 61.98±2.82 15 −1 0 1 37.47±1.33 16 0 −1 −1 47.49±2.13 17 0 0 0 62.09±3.15 表 3 回归模型方程的方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis of regression model equation
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 显著性 回归模型 1297.09 9 144.12 3800.45 <0.0001 ** A-超声温度 19.75 1 19.75 520.82 0.0001 ** B-超声时间 0.88 1 0.88 23.32 0.019 * C-超声功率 46.32 1 46.32 1221.46 <0.0001 ** AB 18.49 1 18.49 487.58 <0.0001 ** AC 14.03 1 14.03 369.84 <0.0001 ** BC 2.43 1 2.43 64.17 <0.0001 ** A2 492.73 1 492.73 12993.24 <0.0001 ** B2 321.28 1 321.28 8472.16 <0.0001 ** C2 258.32 1 258.32 6811.96 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.27 7 0.038 − − − 失拟项 0.19 3 0.064 3.43 0.1323 N 净误差 0.074 4 0.019 − − − 总离差 1297.36 16 − − − − R2=0.9998,R2adj=0.9995 注:*代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01,N代表差异无统计学意义,“−”表示无此项。 -
[1] UKOWIAK M. Utilizing sponge spicules in taxonomic, ecological and environmental reconstructions: A review[J]. Peer J,2020,8(2):e10601.
[2] PAUL V J, FREEMAN C J, AGARWAL V. Chemical ecology of marine sponges: New opportunities through “-Omics”[J]. Integrative and Comparative Biology,2019,59(4):765−776. doi: 10.1093/icb/icz014
[3] ANTENEH Y S, YANG Q, BROWN M H, et al. Antimicrobial activities of marine sponge-associated bacteria[J]. Microorganisms,2021,9(1):171. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010171
[4] El-DEMERDASH A, ATANASOV A G, HORBANCZUK O K, et al. Chemical diversity and biological activities of marine sponges of the genus Suberea: A systematic review[J]. Mar Drugs,2019,17(2):115. doi: 10.3390/md17020115
[5] DATTA D, TALAPATRA S N, SWARNAKAR S. Bioactive compounds from marine invertebrates for potential medicines-An overview[J]. Int Lett Nat Sci,2015,34:42−61.
[6] MARIEKE K DIRK M, RENE W. Towards commercial production of sponge medicines[J]. Mar Drugs,2009,7(4):787−802. doi: 10.3390/md7040787
[7] SIMMONS T L, ANDRIANASOLO E, MCPHAIL K, et al. Marine natural products as anticancer drugs[J]. Mol Cancer Ther,2005,4(2):333. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.333.4.2
[8] NEWMAN D J, CRAGG G M. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials[J]. J Nat Prod,2004,67(8):1216−1238. doi: 10.1021/np040031y
[9] CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVI S, et al. Marine natural products[J]. Nat Prod Rep,2019,36:122−173. doi: 10.1039/C8NP00092A
[10] ZHU J Y, LIU Y, LIU Z J, et al. Bioactive nitrogenous secondary metabolites from the marine sponge genus Haliclona[J]. Mar Drugs,2019,17(12):682. doi: 10.3390/md17120682
[11] NADAR V M, MANIVANNAN S, CHINNAIYAN R, et al. Review on marine sponge alkaloid, aaptamine: A potential anti-bacterial and anti-cancer drug[J]. Chem Biol Drug Des,2022,99:103−110. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13932
[12] ZHANG B, ZHANG T, XU J Z, et al. Marine sponge-associated fungi as potential novel bioactive natural product sources for drug discovery: A review[J]. Mini Rev Med Cheistry,2020,20:1966−2010. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666200826123248
[13] CHENG M M, TANG X L, SUN Y T, et al. Biological and chemical diversity of marine sponge-derived microorganisms over the last two decades from 1998 to 2017[J]. Molecules,2020,25(4):853. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040853
[14] SYAMSUDIN A, AWIK P D N, SRI N, et al. Cytotoxic and antioxidant activities of marine sponge diversity at pecaron bay pasir putih situbondo East Java, Indonesia[J]. J Phar Res,2013,6(7):685−689.
[15] ZHANG H W, ZHAO Z P, WANG H. Cytotoxic natural products from marine sponge-derived microorganisms[J]. Mar Drugs,2017,15(3):68. doi: 10.3390/md15030068
[16] CAMPOS P E, PICKON E, MORIOU C, et al. New antimalarial and antimicrobial tryptamine derivatives from the marine sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata[J]. Mar Drugs,2019,17(3):167. doi: 10.3390/md17030167
[17] KIM Y A, JI Y K, KIM N H, et al. Isoquinolinequinone derivatives from a marine sponge (Haliclona sp.) regulate inflammation in vitro system of intestine[J]. Mar Drugs,2021,19(2):90. doi: 10.3390/md19020090
[18] TINTILLIER F, MORIOU C, PETEK S, et al. Quorum sensing inhibitory and antifouling activities of new bromotyrosine metabolites from the polynesian sponge Pseudoceratinan sp.[J]. Mar Drugs,2020,18(5):272. doi: 10.3390/md18050272
[19] MUTHIYAN R, MAHANTA N, NAMBIKKAIRAJ B, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of a methanol extract from the marine sponge Hyrtios erectus[J]. Phcog Mag,2018,14:534−540. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_133_17
[20] HU T Y, ZHANG H, CHEN Y Y, et al. Dysiarenone from marine sponge Dysidea arenaria attenuates ROS and inflammation via inhibition of 5-LOX/NF-κB/MAPKs and upregulation of Nrf-2/OH-1 in RAW 264.7 macrophages[J]. J Inf Res,2021,14:587−597. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S283745
[21] GINER R M, RÍOS J L, MÁÑEZ S. Antioxidant activity of natural hydroquinones[J]. Antioxidants,2022,11(2):343. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020343
[22] SUNARWIDHI A L, ROSYANTARI A, PRASEDYA E S, et al. The correlation between total protein content and antioxidant activity of collagen isolated from a marine sponge Stylissa flabelliformis collected from North Lombok Indonesia coast[C]//IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing, 2021, 913(1): 012103.
[23] OOGARAH P N, RAMANJOOLOO A, ROVISHAM J, et al. Assessing antioxidant activity and phenolic content of marine sponges from mauritius waters[J]. International Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemical Research,2020,12:123−131.
[24] AFSHARI K, SAMAVATI V, SHAHIDI S A. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and in-vitro antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Hibiscus leaf[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,74:558−567. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.07.023
[25] 张红军. 三种西沙海绵化学成分和生物活性研究[D]. 上海: 第二军医大学, 2009 ZHANG H J. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of three marine sponges from Paracel Islands[D]. Shanghai: The Second Military Medical University, 2009.
[26] YOUSSEF D T A. Hyrtioerectines A-C, Cytotoxic Alkaloids from the red sea sponge Hyrtios erectus[J]. Journal of Natural Products,2005,68(9):1416−1419. doi: 10.1021/np050142c
[27] SWANTARA I M D, RITA W S, HERNINDY R A. Isolation and phytochemical test of anticancer isolate of sponge Hyrtios erecta[J]. Jhsm Unud J,2017,1:16−20. doi: 10.24843/JHSM.2017.v01.i01.p05
[28] AL-MASSARANI S M, EL-GAMAL A A, AL-SAID M S, et al. Studies on the red sea sponge Haliclona sp. for its chemical and cytotoxic properties[J]. Pharmacognosy Magazine,2016,12(46):114. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.177906
[29] 陈江艳, 王维滔, 董益阳, 等. 响应面优化蒲公英橡胶草菊糖提取工艺及其MALDI-TOF MS分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(1):205−212. [CHEN J Y, WANG W T, DONG Y Y, et al. Optimization of extraction of inulin from Taraxacum kok-saghyz Rodin by response surface methodology and its MALDI-TOF MS analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(1):205−212. [30] 钱燕芳, 石晨莹, 陈贵堂. 桑葚多糖超声提取、脱色工艺优化及其抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(16):201−210. [QIAN Yanfang, SHI Chenying, CHEN Guitang. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction and decolorization process of polysaccharides from Mori fructus and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(16):201−210. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021110007 [31] 叶兆伟, 叶润, 赫丁轩, 等. 息半夏多糖提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2022,33(1):90−98. [YE Z W, YE R, HAO D X, et al. Optimization of polysaccharide extraction from Xi Pinellia ternate by response surface methodology and its antioxidant activity[J]. China Food Additives,2022,33(1):90−98. doi: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2022.01.014 [32] 常国立, 房祥军, 陈明, 等. 杨梅核多酚提取优化及体外抗氧化和降血糖活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(1):212−218. [CHANG G L, FANG X J, CHEN M, et al. Extraction optimization and in vitro antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity of polyphenols from Myrica rubra kernel[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(1):212−218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.1.spkj202201032 [33] AATI H N, EL-GAMAL A, KAYSER O. Chemical composition and biological activity of the essential oil from the root of Jatropha pelargoniifolia Courb. native to Saudi Arabia[J]. Saudi Pharm J,2019,27(1):88−95. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.09.001
[34] 杜毅超, 张浩, 黄治伟, 等. 芹菜素对H2O2诱导人肝细胞L02氧化损伤模型的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2020,36(5):1077−1081. [DU Y C, ZHANG H, HUANG Z W, et al. Effect of apigenin on H2O2-induced oxidative injury in human hepatocytes L02[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2020,36(5):1077−1081. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.05.025 [35] LI C, YANG F, HUANG Y, et al. Comparison of hydrodynamic and ultrasonic cavitation effects on soy protein isolate functionality[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2020,265:109697. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.109697
[36] YE L, ZHU X, WEI X. Damage characteristics and surface description of near-wall materials subjected to ultrasonic cavitation[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2020,67:105175. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105175
[37] 罗维巍, 李双, 刁全平, 等. 响应面法优化超声提取酸浆宿萼中叶黄素的工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2022,33(1):62−68. [LUO W W, LI S, DIAO Q P, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction process for lutein from calyx of Physalis by response surface methodology and its antioxidant capacity study[J]. China Food Additives,2022,33(1):62−68. [38] 杨秋明, 宋江峰, 李大婧, 等. 响应面法优化超声波提取南瓜皮叶黄素的工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(1):149−155. [YANG Q M, SONG J F, LI D J, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction process for lutein from pumpkin peel by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(1):149−155. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.01.028 [39] GUO H, CHENG J, MAO Y, et al. Synergistic effect of ultrasound and switchable hydrophilicity solvent promotes microalgal cell disruption and lipid extraction for biodiesel production[J]. Bioresource Technology,2022,343:126087. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126087
[40] UTKINA N K. Antioxidant activity of zyzzyanones and makaluvamines from the marine sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa[J]. Natural Product Communications,2013,8(11):1551−1552.
[41] 崔素萍, 陈丹, 穆秋霞, 等. 细胞氧化应激的危害及抗氧化应激的研究进展[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2022,34(4):74−79, 133. [CUI S P, CHEN D, MU Q X, et al. Harm of cellular oxidative stress and research progress of anti-oxidative stress[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University,2022,34(4):74−79, 133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2022.04.011 [42] 蔡瑾, 闫然, 王梦亮, 等. 二氢槲皮素对大肠杆菌的抑菌作用机理[J/OL]. 食品科学: 1−14 [2022-09-26] DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220512-148. CAI J, YAN R, WANG M L, et al. The mechanism of antimicrobial action of dihydroquercetin against Escherichia coli[J]. Food Science, 1−14 [2022-09-26] DOI: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220512-148.





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:



