Isolation of Zucchini Heteropolymeric Pectin and Preliminary Study on Its Hypoglycemic Activity
-
摘要: 为了促进西葫芦的深度开发,本研究对西葫芦杂聚果胶进行了分析和降血糖活性初探。采用酸碱联合处理提取分离西葫芦果胶,分别得到酸提果胶(ZPA)和残渣碱提果胶(ZPB)两个组分,分析了两个组分的得率、组成和结构性质。构建了熊蜂高脂饮食导致的糖尿病模型,初步探究西葫芦杂聚果胶ZPA和ZPB的降血糖活性。结果表明,ZPB的得率是ZPA的2.45倍,ZPA的平均分子量为70297 Da,多分散系数为1.149,ZPB的平均分子量为126170 Da,多分散系数为1.677,表明ZPB的分子分布范围较大,组成更为复杂。ZPA和ZPB的单糖组成均含有阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖醛酸、鼠李糖、甘露糖6种单糖,ZPB还含有葡萄糖、核糖2种单糖,可推测ZPA和ZPB均属于含有RG-I结构的杂聚果胶。经计算ZPA的RG-I结构较少但侧链长度较长,ZPB的RG-I结构多但侧链长度较短。利用熊蜂糖尿病模型发现ZPA和ZPB均能显著降低熊蜂血液葡萄糖和海藻糖水平,初步表明西葫芦杂聚果胶具有一定的降血糖活性。
-
关键词:
- 西葫芦 /
- 果胶 /
- 鼠李半乳糖醛酸聚糖-I /
- 降血糖活性
Abstract: To promote the deep processing of zucchini, heteropolymeric pectin fractions from zucchini was analyzed and their hypoglycemic activity was explored. Combining acid and base treatment, two pectin fractions were isolated, namely zucchini acid-extracted pectin (ZPA) and zucchini alkali-extracted pectin (ZPB). The yield, composition, and structural properties of two fractions were analyzed. Moreover, high-fat diet induced bumblebee diabetic model was established to explore the hypoglycemic activity of zucchini pectin. Results showed that the yield of ZPB was 2.45 times higher than that of ZPA. ZPA had an averaged molecular weight of 70297 Da and polydispersity index of 1.149, while ZPB had an averaged molecular weight of 126170 Da and polydispersity index of 1.677, indicating the more complex components of ZPB. Monosaccharides including arabinose, galactose, galacturonic acid, glucuronic acid, rhamnose, and mannose were found in both ZPA and ZPB, while glucose and ribose were only present in ZPA. It indicated that ZPA and ZPB were heteropolymeric pectins containing RG-I structure. ZPA had less but longer RG-I side chain, whereas ZPB had more and shorter RG-I side chain. Based on bumblebee diabetic model, ZPA and ZPB were found to significantly lower the blood glucose and trehalose level, indicating that zucchini pectin had potential hypoglycemic activity.-
Keywords:
- zucchini /
- pectin /
- RG-I /
- hypoglycemic activity
-
果胶广泛存在于高等植物根、茎、叶、果的细胞壁中[1],是一种天然植物多糖,因其具有多种生物活性而在食品领域广泛应用[2]。目前市场上的商品果胶主要从柑橘皮渣中提取[3],其主要结构为同型半乳糖醛酸聚糖(Homogalacturonans,HG)[4]。天然果胶来源丰富且结构多样,除HG结构外,还存在鼠李半乳糖醛酸聚糖-I(Rhamnogalacturonan I,RG-I)、鼠李半乳糖醛酸聚糖-II(Rhamnogalacturonan II,RG-II)、木糖半乳糖醛酸聚糖(Xylogalacturonans,XGA)等结构[5]。
近期研究表明,RG-I结构果胶相较于商业HG结构果胶具有更优异的生物活性,如抗肿瘤、免疫调节、改善代谢性疾病、保护心脑血管等[6]。近年来,研究者从柑橘皮渣[7]、甜菜[8]、马铃薯[9]等植物中均分离出了RG-I构型果胶。欧洲学者从胡萝卜中分离的富含RG-I组分已申请加入欧盟新型食品(novel food)审查目录,新型果胶资源在国际上已逐步进入产业化应用阶段[10]。课题组前期从中国南瓜中分离制备了RG-I结构果胶,并检测了其与半乳凝集素-3(Galactin-3,Gal-3)的结合活性,发现南瓜RG-I果胶是天然的Gal-3抑制剂,拥有巨大的开发潜力[11]。西葫芦又称为美洲南瓜,南瓜属,是我国现存的四大南瓜品种之一[12],但目前鲜有对西葫芦果胶的研究[13]。有研究显示,在果胶提取中进行碱处理可以溶出更多RG-I果胶成分[14]。因此,本研究采用酸碱联合处理制备西葫芦果胶,分析其成分、分子量、均一度、单糖组成、红外图谱等,试图揭示西葫芦果胶的基本组成和结构特点。进一步利用糖尿病熊蜂模型初步探索了西葫芦果胶的降血糖活性,以期为西葫芦的精深加工和高值化利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
西葫芦 北京绿玉西葫芦,购买时间2022年3月,西葫芦长约25~30 cm,直径约8~10 cm;无水乙醇、盐酸、氢氧化钠、苯酚、间羟基联苯、四硼酸钠、硫酸 上海阿拉丁试剂公司;植物总酚测定试剂盒、BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒、葡萄糖微量检测试剂盒、海藻糖微量检测试剂盒 北京索莱宝公司;溴化钾、右旋糖酐Dextran系列标品、氯化钠、岩藻糖、鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、葡萄糖、木糖、甘露糖、核糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖醛酸、1-苯基-3-甲基-5-吡唑啉酮三氟乙酸 色谱纯,美国Sigma-Aldrich公司;其余试剂 均为分析纯。
KQ5200DE型数控超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;HJ-4A数显恒温多头磁力搅拌器 常州迈科诺仪器有限公司;高速多功能粉碎机 浙江省永康市敏业工贸有限公司;DHP-9082型电热恒温培养箱 上海一恒科技有限公司;XMTD-204数显恒温水浴锅 河北德科机械科技有限公司;Scout型电子天平 奥豪斯仪器;AS-M涡旋振荡器 索莱宝有限公司;RE.2000B旋转蒸发器 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;CR21G-Ⅲ高速冷冻离心机 日立HIT ACHI公司;冷冻干燥机 北京博医康实验仪器有限公司;SZPARK 10M微孔板检测系统 瑞士帝肯仪器生物公司;pH211C-1型酸度计 意大利哈纳公司;1515高效液相色谱仪 美国Waters公司;ΜV-2250紫外分光光度计 岛津SHIMADZΜ有限公司;傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 珀金埃尔默仪器公司;LC-DCY-12GK氮吹仪 上海力辰帮西仪器科技。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 西葫芦果胶的提取分离
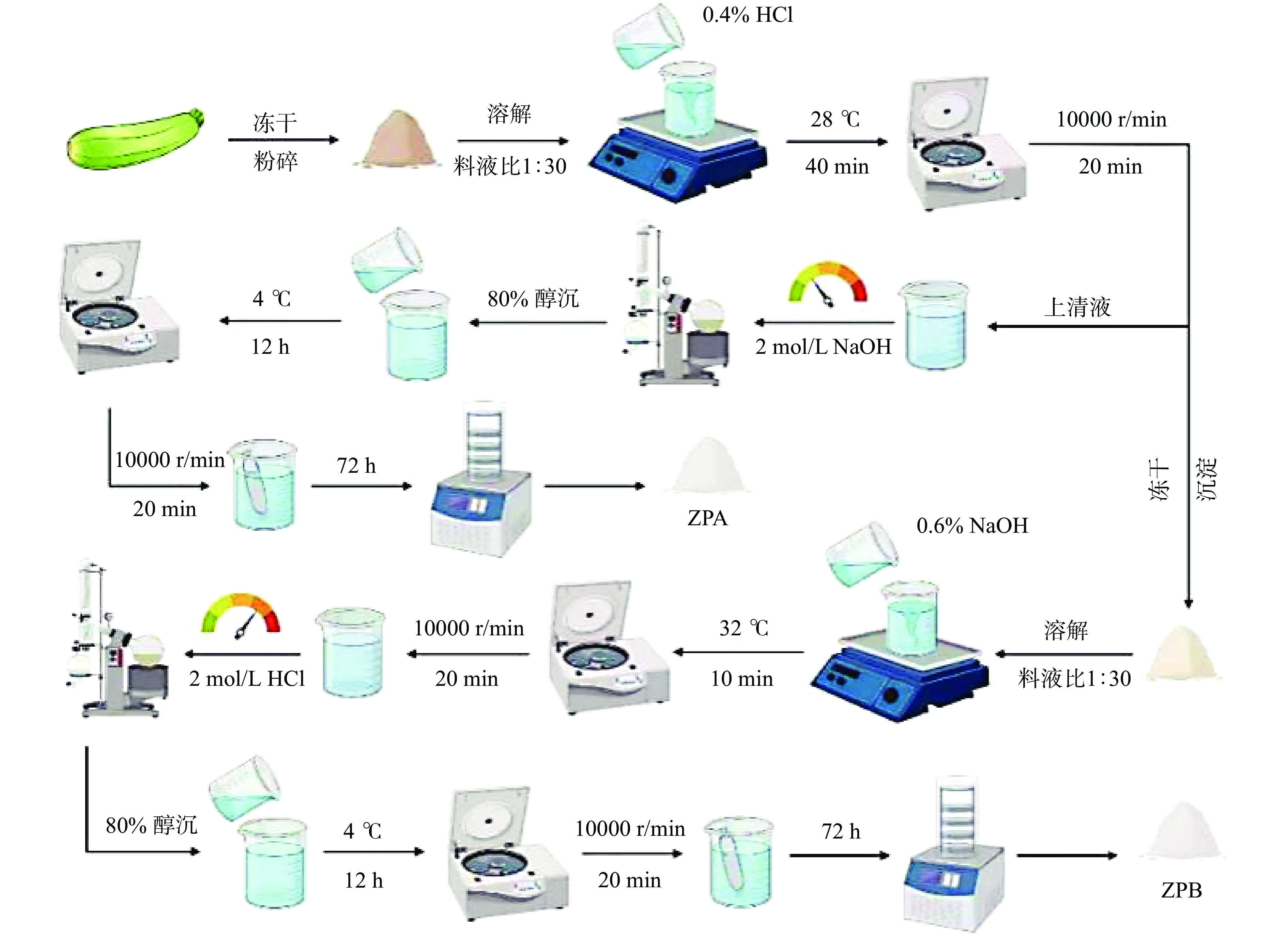
参照Zhang等[15]方法并修改,将西葫芦切片、冻干、粉碎后进行果胶的分离提取。0.4% HCl溶液以1:30的料液比溶解西葫芦粉末,28 ℃恒温搅拌40 min。10000 r/min常温离心20 min,取上清液,用NaOH调节pH至3~4。沉淀冻干粉碎,等待下一步处理。将调整pH后的上清液浓缩,加入无水乙醇至浓度为80%。4 ℃下沉淀12 h后以相同条件离心。取沉淀,用少量纯水溶解后进行72 h透析,冻干称重得到酸提果胶粗提物ZPA。取冻干后的残渣粉末,用0.6% NaOH以1:30的料液比重悬。32 ℃恒温搅拌10 min,相同条件离心后取上清液,用HCl调节溶液pH至6~7,浓缩后进行相同条件醇沉。再次离心,取沉淀进行相同条件透析,冻干称重得到酸提后碱提果胶粗提物ZPB(图1)。计算西葫芦果胶粗提物得率[16]。
1.2.2 成分测定
用硫酸-苯酚法[17]、间羟基联苯比色法[18],植物总酚测定试剂盒、BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒分别测定ZPA和ZPB中的总糖含量、糖醛酸含量、总酚含量和蛋白质含量。
1.2.3 结构性质测定
1.2.3.1 傅里叶变换红外光谱
将果胶样品干燥,取微量与KBr研磨压片。使用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪测定,扫描范围为4000~400 cm−1,分辨率4 cm−1,扫描32次[19]。
1.2.3.2 分子量
采用高效凝胶渗透色谱法[20](High Performance Gel Permeation Chromatography,HPGPC)测定ZPA和ZPB的分子量。以不同分子量的右旋糖酐(分子量1000、5000、12000、25000、50000、80000、150000、270000、410000、670000 Da)作为标准品。色谱条件如下:使用高效液相色谱仪配示差检测器,聚合物基质水溶性SEC(GFC)色谱柱OHZPAk SB-803 HQ、OhZPAk SB-804 HQ、OhZPAk SB-805 HQ(8×300 mm)三柱串联检测。流动相为0.05 mol/L NaCl溶液,流速0.6 mL/min,柱温40 ℃,进样量30 μL。根据色谱峰的保留时间和对应标准品相对分子质量得到三阶线性回归方程。
lgMp=−0.00058T3+0.06316T2−2.43087T+37.40914
式中:Mp表示相对分子质量;T表示保留时间(min)。
1.2.3.3 单糖组成
采用柱前1-苯基-3-甲基-5-吡唑啉酮(1-Phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone,PMP)衍生法,通过高效液相色谱法(High Performance Liquid Chromatography,HPLC)分析ZPA和ZPB的单糖组成[18]。取干净的色谱瓶,精确称量多糖样品5 mg(±0.05 mg),加入1 mL 2M 三氟乙酸(Trifluoroacetic acid,TFA)溶液,121 ℃加热2 h。通氮气,吹干。加入3 mL甲醇清洗,再吹干,重复甲醇清洗2~3次,加入5 mL无菌水溶解。将其与等体积0.6 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液充分混合后,加入100 mL 0.5 mol/L的PMP-甲醇溶液混匀,70 ℃反应100 min进行衍生化。盐酸中和后,用氯仿多次萃取除去未反应的PMP,制备好的样品溶液经0.22 μm滤膜过滤后进行HPLC分析。依次称取岩藻糖、鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖半乳糖、葡萄糖、木糖、甘露糖、核糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖醛酸单糖10 mg作为标准品,配置10、20、40、60、80、100、200、500 μg/mL的溶液,与样品溶液进行相同柱前衍生操作,完成后一并转入色谱瓶中待测。色谱条件如下:使用Thermo U3000液相色谱系统,色谱柱为ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18,流动相为乙腈:磷酸盐缓冲液(pH6.8)等度洗脱,流速为0.8 mL/min,柱温30 ℃,检测波长250 nm,进样量10 μL。
单糖组成百分比参照文献[21]计算,RG-I比例和RG-I侧链糖基比例参照文献[22]计算。
1.2.4 西葫芦果胶的降血糖活性
1.2.4.1 熊蜂糖尿病模型的建立及实验设计
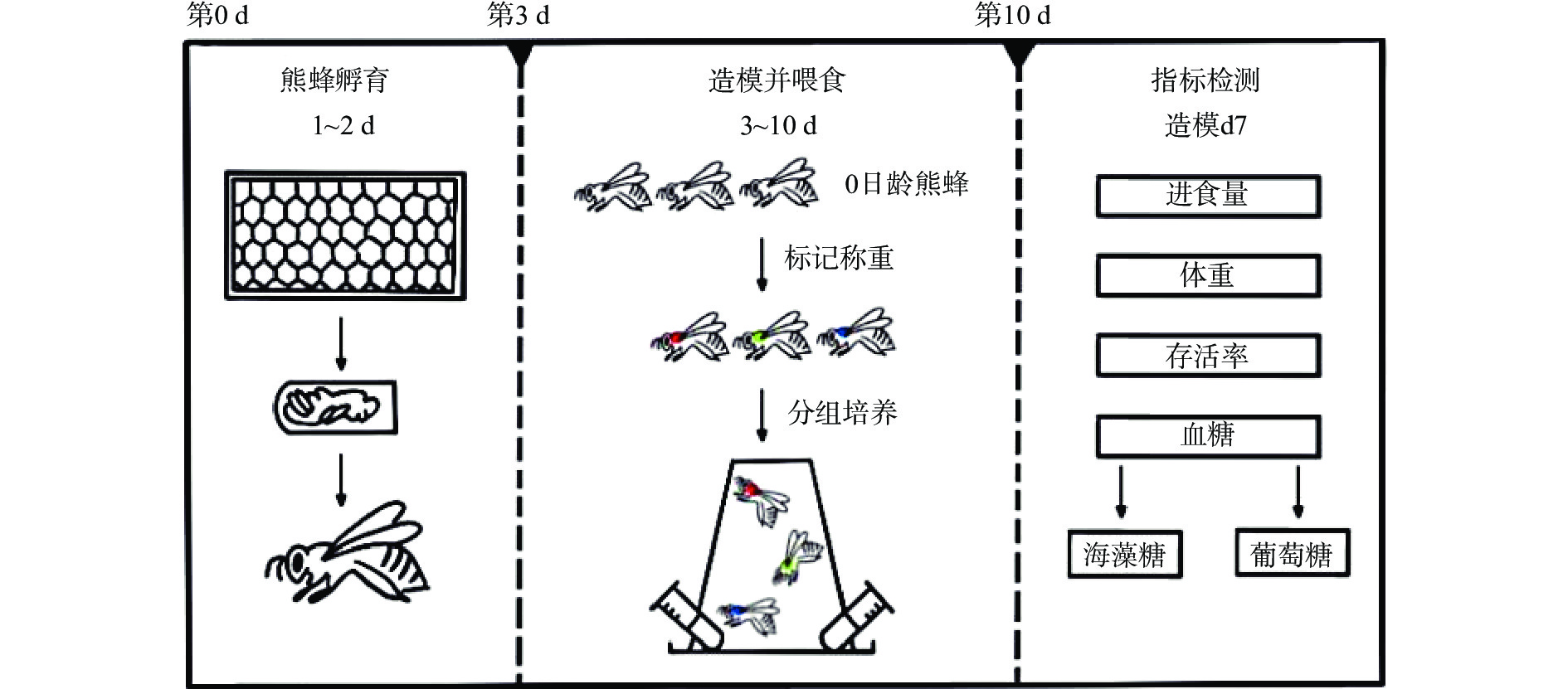
参照郎浩宇等[23]方法并修改,取健康、大小相近的0日龄熊蜂48只,分为四组,3只熊蜂为一杯,每组四杯。分别标记为正常饮食(Normal diet,ND)组、高脂饮食(High fat diet,HFD)组、ZPA组、ZPB组。ND组熊蜂喂食50%(质量体积比)的蔗糖水和花粉;HFD组熊蜂喂食掺有5%棕榈油的50%蔗糖水和掺油花粉;ZPA组喂食加入ZPA样品7.2 mg/mL的掺油蔗糖水和掺油花粉;ZPB组喂食加入ZPB样品7.2 mg/mL的掺油蔗糖水和掺油花粉。在熊蜂头背部相连坚硬处进行颜色标记,将熊蜂放置于29 ℃恒温培养箱中,保持湿度60%饲喂7日。在第0 d和第7 d测定单只熊蜂体重,根据颜色标记计算得到单只熊蜂体重增量(mg)。熊蜂实验示意图如图2所示。
1.2.4.2 血糖含量测定
取第7 d熊蜂,用20 μL的枪头在熊蜂头部下方连接处扎孔,反复采血至全部取出。采血过程全程在冰上进行以防止血液氧化。采血完成后需快速放入液氮冷冻,全部样品采集完成后放入−80 ℃冰箱进行冻存。血液样品解冻稀释后使用葡萄糖微量检测试剂盒、海藻糖微量检测试剂盒测定熊蜂血液中葡萄糖和海藻糖含量。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验设置三组平行,数据采用(平均值±标准差)表示。采用SPSS 24.0进行统计分析,多组之间比较采用单因素方差分析,不同小写字母表示处理间具有差异显著(P<0.05)。示意图绘制采用BioRender平台和PowerPoint软件。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 西葫芦果胶得率
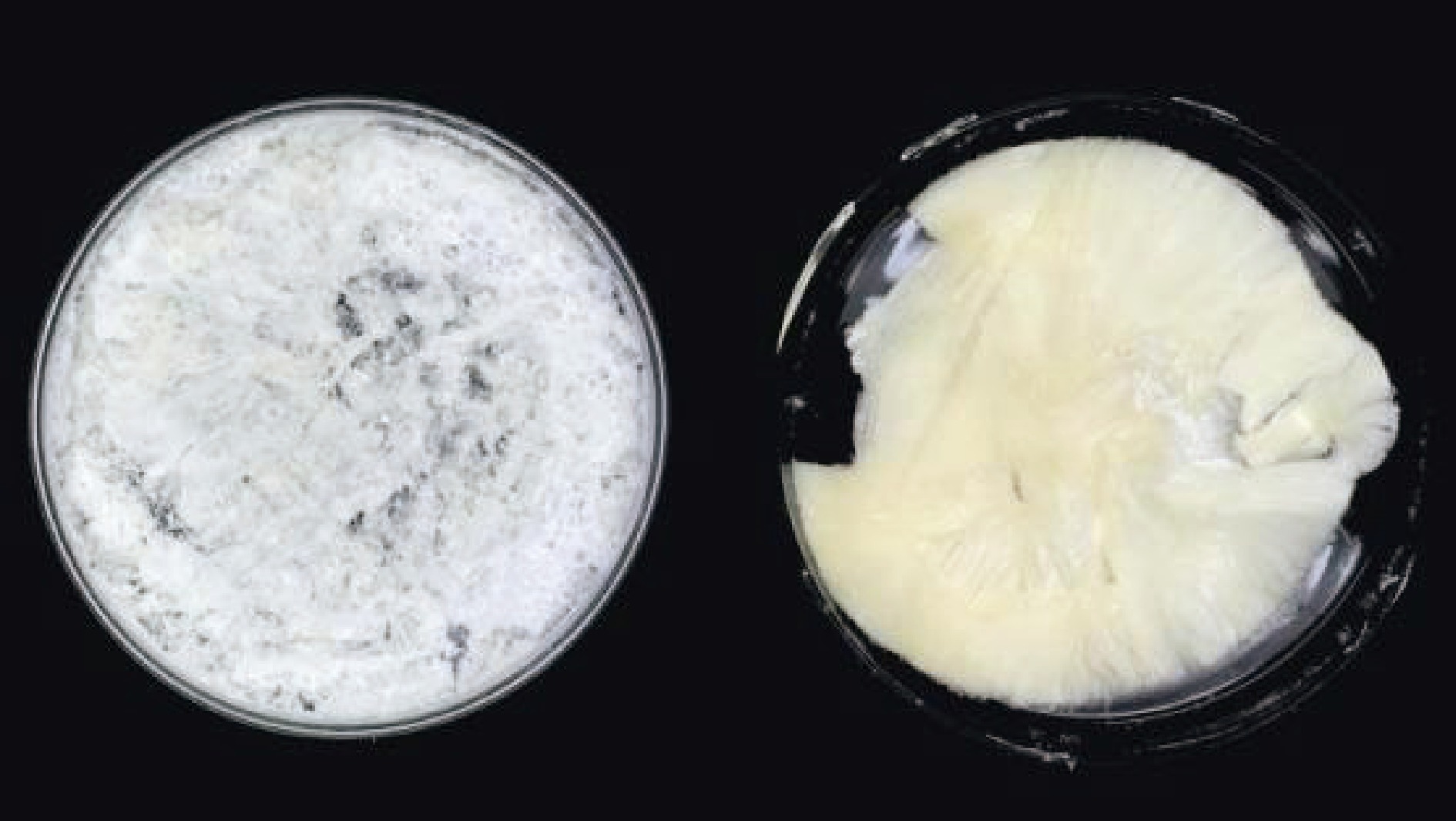
通过上述酸碱联合提取方法,得到如图3所示ZPA、ZPB两种西葫芦果胶粗提物样品。ZPA为柔软的白色絮状物,ZPB为略有韧性的白色片状物。ZPA提取量为3.46 g,得率为1.73%;ZPB提取量为8.48 g,粗提物得率为4.24%。酸碱联合提取果胶的得率是传统酸提法的2.45倍。这可能是因为碱液会破坏细胞壁,可促进果胶的释放[24]。卢久富[25]利用热水浸提法提取的西葫芦果胶得率为1.22%,与ZPA得率相似,远低于本方法ZPB的得率。推测因为碱液处理可以破坏果胶、半纤维素和纤维素之间的交联,使得细胞壁结果破坏,从而使更多的果胶溶出。本研究所采取的酸碱联合提取法可有效制备西葫芦果胶。
2.2 提取物主要成分分析
ZPA和ZPB的化学组成如表1所示。ZPB的总糖含量为40.03%±0.51%,高于ZPA(33.63%±0.59%)。ZPA的糖醛酸含量为9.37%±0.21%,ZPB的糖醛酸含量为9.19%±0.16%。由于没有进行进一步的纯化,ZPA和ZPB中都含有少量的酚类组分和一定比例的蛋白质,总体而言ZPB比ZPA的糖纯度稍高。
表 1 提取物主要成分含量(%)Table 1. Analysis of the basic ingredients (%)样品 总糖含量 糖醛酸含量 总酚含量 蛋白质含量 ZPA 33.63±0.59 9.37±0.21 1.16±0.03 17.74±0.50 ZPB 40.03±0.51 9.19±0.16 0.65±0.11 21.89±0.41 2.3 西葫芦果胶结构性质
2.3.1 傅里叶变换红外光谱
ZPA和ZPB的傅里叶变换红外光谱图如图4所示。两种果胶在400~4000 cm−1范围具有糖类的特征吸收峰[26]。3306 cm−1附近出现的宽峰是O-H和N-H伸缩振动的结果。2935 cm−1处的吸收峰由糖类C-H的伸缩振动吸收引起。在1648和1624 cm−1附近的吸收峰主要归属于酰胺基C=O的伸缩振动,证明其存在糖醛酸[27]。在1532 cm−1处的吸收峰主要是N-H的弯曲振动。在1420 cm−1附近出现的吸收峰主要是C-H的弯曲振动吸收所产生的。在1237 cm−1处的吸收峰主要是C-N的伸缩振动和N-H的变形振动。1048 cm−1左右的吸收峰主要是吡喃环中C-O伸缩振动。760和704 cm−1附近的吸收峰主要是由苯环C-H面外弯曲振动吸收产生的。ZPB的红外光谱存在一些与ZPA不一致的峰型。1324 cm−1处的吸收峰主要是C-H的弯曲振动。952和896 cm−1附近的吸收峰是羧基O-H键的面外弯曲振动。644 cm−1附近的吸收峰主要是N-H的面外弯曲振动[28]。综上,ZPA与ZPB的光谱峰形与峰位置相似,吸收峰位置的区别主要存在于红外光谱指纹区。二者多糖类型相似,结构存在不同。主要存在的官能团包括:O-H、C-H、N-H、C-O、C=O、苯环、C-N等。
2.3.2 分子量
ZPA和ZPB的HPGPC色谱图如图5所示。ZPA在33.745 min处出现一较狭窄的对称峰,峰值为1.316;ZPB在33.437 min处出现一较宽的峰,峰值为0.586。ZPA和ZPB的分子量计算结果如表2所示。ZPB的分子量多分散性为1.677,大于ZPA(1.149),可与HPGPC色谱图峰型共同说明ZPA的分子量分布较为集中;ZPB的组分较为复杂,分子量分布较广。ZPA的平均分子量为70297 Da,数均分子量为61157 Da,ZPB的平均分子量为126170 Da,数均分子量为75229 Da。Zhang等[15]利用类似的酸碱联合法提取柑橘皮渣中的果胶并测定其分子量,碱提果胶的分子量同样高于酸提果胶。这可能是因为酸提取过程通常伴随着RG-I侧链中糖苷键以及半乳糖醛酸和鼠李糖残基之间酸不稳定键的水解,导致酸提果胶的分子量较小[29]。
表 2 分子量结果表Table 2. Molecular weight of ZPA and ZPB样品 保留时间(min) Mw(Da) Mn(Da) 多分散性 ZPA 34.745 70297 61157 1.149 ZPB 33.437 126170 75229 1.677 2.3.3 单糖组成
ZPA和ZPB的HPLC色谱图如图6所示。两种样品的单糖组成、含量和比例均存在一定差异。如表3所示,ZPA和ZPB中均含有鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、甘露糖、葡萄糖醛酸、半乳糖醛酸6种单糖。ZPB另含有一定量的葡萄糖和核糖。ZPA中甘露糖含量占比最高,为28.00%,鼠李糖含量占比最低,为2.07%。ZPB中半乳糖含量占比最高,为22.58%,核糖含量占比最低,为3.70%。
表 3 样品单糖组成百分比Table 3. Monosaccharide composition of samples样品 Rha Ara Gal Glc Man Rib Gal-UA Glc-UA ZPA 2.07 22.19 18.11 0 28.00 0 16.39 11.50 ZPB 6.33 10.92 22.58 15.08 16.73 3.70 17.81 6.85 由单糖组成结果可见,ZPA和ZPB均属于含有RG-I结构的杂聚果胶。鼠李糖和半乳糖醛酸是RG-I结构的主要组成部分[30],ZPB的RG-I比例(Rha/Gal-UA)为0.355,高于ZPA(0.126),说明其含有更多RG-I结构。阿拉伯糖和半乳糖是RG-I结构侧链的主要组成部分[31]。ZPA和ZPB均含有较高比例的阿拉伯糖和半乳糖,证明RG-I结构侧链保留较为完好。ZPA的RG-I侧链糖基比例((Gal+Ara)/Rha)为19.47,高于ZPB(5.29),这说明ZPA中RG-I侧链的长度要大于ZPB。总而言之,ZPA的RG-I结构较少但侧链长度较长,ZPB的RG-I结构多但侧链长度较短。同时,除了典型的RG-I结构特征外,ZPA和ZPB中还含有较多的甘露糖、葡萄糖、葡萄糖醛酸组分,表明ZPA和ZPB的组分或结构较为复杂,各个单糖是否来自于单一果胶组分还有待进一步分析验证。ZPA和ZPB的单糖组成存在差异的主要原因可能是碱溶液可以破坏果胶、半纤维素和纤维素之间的交联,溶出了更多结构多样的西葫芦果胶[10]。
2.4 西葫芦果胶降血糖活性
通过高脂饮食建立糖尿病熊蜂模型,如图7所示,高脂饮食(HFD)组的熊蜂体重增量显著高于未处理(ND)组(P<0.05),且雄蜂的主要血糖指标(葡萄糖和海藻糖浓度)也远远高于ND组,说明通过高脂处理进行的熊蜂糖尿病模型造模是有效的。在饮食中进行ZPA和ZPB干预后,样品处理组熊蜂的体重增量显著低于HFD组熊蜂(P<0.05),证明两种样品可以有效降低糖尿病模型熊蜂的体重,且样品ZPA的体重增量与ND组无显著性差异(P>0.05),说明ZPA在控制熊蜂体重方面具有更好的效果。同时,ZPA和ZPB样品处理组熊蜂的血糖指标均显著低于HFD组(P<0.05),证明两种样品可以有效降低糖尿病模型熊蜂的血糖,且二者对海藻糖浓度的降低效果明显优于对葡萄糖的降低效果。ZPA和ZPB在降低熊蜂血糖浓度的效果方面没有明显差异,说明两种结构和组成的果胶具有相似的降血糖活性。西葫芦果胶发挥降血糖活性可能与其调节机体代谢、改善肠道菌群紊乱有关,但具体的机制仍有待进一步验证。
3. 结论
RG-I是天然果胶的主要结构域之一,具有良好的生物活性。然而商品果胶主要由HG结构组成,缺乏RG-I活性成分。本研究利用酸碱联合提取法从西葫芦中制备得到两种果胶组分ZPA和ZPB,经鉴定均属于含有RG-I结构的杂聚果胶,ZPA的RG-I结构较少但侧链长度较长,ZPB的RG-I结构多但侧链长度较短。利用熊蜂糖尿病模型,发现ZPA和ZPB均能够显著降低糖尿病熊蜂的血糖水平,具有潜在的降血糖活性。然而ZPA和ZPB的果胶精细结构仍待进一步的分离纯化和解析,其降血糖的作用机制也有待进一步探讨。本研究对西葫芦果胶的基本组成、结构特征和活性进行了初步探讨,为西葫芦的深度加工和果胶组分的高值化利用奠定了基础。
-
表 1 提取物主要成分含量(%)
Table 1 Analysis of the basic ingredients (%)
样品 总糖含量 糖醛酸含量 总酚含量 蛋白质含量 ZPA 33.63±0.59 9.37±0.21 1.16±0.03 17.74±0.50 ZPB 40.03±0.51 9.19±0.16 0.65±0.11 21.89±0.41 表 2 分子量结果表
Table 2 Molecular weight of ZPA and ZPB
样品 保留时间(min) Mw(Da) Mn(Da) 多分散性 ZPA 34.745 70297 61157 1.149 ZPB 33.437 126170 75229 1.677 表 3 样品单糖组成百分比
Table 3 Monosaccharide composition of samples
样品 Rha Ara Gal Glc Man Rib Gal-UA Glc-UA ZPA 2.07 22.19 18.11 0 28.00 0 16.39 11.50 ZPB 6.33 10.92 22.58 15.08 16.73 3.70 17.81 6.85 -
[1] 田三德. 果胶生产现状及发展前景[J]. 中小企业科技,2003(6):12−13. [TIAN S D. Present situation and development of pectin production[J]. SME Technology,2003(6):12−13. [2] MISHRA R, DATT M, ZPAL K, et al. Preparation and characterization of amidated pectin based hydrogels for drug delivery system[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine,2008,19(6):2275−2280. doi: 10.1007/s10856-007-3310-4
[3] 苏东林, 戴少庆, 李高阳, 等. 柑橘果胶磷酸化制备工艺优化及其改性品质分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2015,15(8):127−135. [SU D L, DAI S Q, LI G Y, et al. Optimization of phosphorylation preparation process of citrus pectin and analysis of modified quality[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2015,15(8):127−135. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2015.08.019 [4] KOUBALA B, KANSCI G, MBOME L, et al. Effect of extraction conditions on some physicochemical characteristics of pectins from "Améliorée" and "Mango" mango peels[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2008,22(7):1345−1351. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.07.005
[5] YULIARTI O, OTHMANO R. Temperature dependence of acid and calcium-induced low-methoxyl pectin gel extracted from Cyclea barbata Miers[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,81:300−311. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.03.004
[6] CHENG H, ZHANG Z, LENG J, et al. The inhibitory effects and mechanisms of rhamnogalacturonan I pectin from potato on HT-29 colon cancer cell proliferation and cell cycle progression[J]. International Journal of Food Sciences & Nutrition,2013,64(1):36−43.
[7] ZHENG J, CHEN J, ZHANG H, et al. Gelling mechanism of RG-I enriched citrus pectin: Role of arabinose side-chains in cation- and acid-induced gelation[J]. Food Hydrocoll,2020,101:105536. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105536
[8] CÁRDENAS-FERNÁNDEZ M, HAMLEY-BENNETT C, LEAK D J, et al. Continuous enzymatic hydrolysis of sugar beet pectin and L-arabinose recovery within an integrated biorefinery[J]. Bioresour Technol,2018,269:195−202. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.069
[9] KHODAEI N, FERNANDEZ B, FLISS I, et al. Digestibility and prebiotic properties of potato rhamnogalacturonan polysaccharide and its galactose-rich oligosaccharides oligomers[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2016,136:1074−1084. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.106
[10] MOSLEMI M. Reviewing the recent advances in application of pectin for technical and health promotion purposes: From laboratory to market[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,254(5):117324.
[11] 赵婧. 南瓜酸性多糖的结构解析及其与功能蛋白的相互作用[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017 ZHAO J. Structure elucidation of pumpkin acidic polysaccharides and the interaction with functional proteins[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017.
[12] 曾雄生. 中国南瓜史[J]. 中国农史,2016,35(3):3. [ZENG X S. History of Chinese pumpkin[J]. Chinese Agricultural History,2016,35(3):3. [13] 游新侠. 苹果渣中果胶提取、纯化及不同分子量果胶特性的研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2007 YOU X X. Study on the extraction and purification of pectin from apple pomace and the properties of pectin with different molecular weights[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2007.
[14] 安徽金枫果胶有限公司. 一种从西葫芦中提取果胶的方法: 中国, 201310176900.7[P]. 2013-08-28 Anhui Jinfeng Pectin Co., Ltd. A method of extracting pectin from zucchini: China, 201310176900.7[P]. 2013-08-28.
[15] ZHANG H, CHEN J, LI J, et al. Extraction and characterization of RG-I enriched pectic polysaccharides from mandarin citrus peel[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,79:579−586. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.12.002
[16] GUO X, HAN D, XI H, et al. Extraction of pectin from navel orange peel assisted by ultra-high pressure, microwave or traditional heating: A comparison[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,88(2):441−448. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.12.026
[17] ZHANG W, WU J, WENG L, et al. An improved phenol-sulfuric acid method for the determination of carbohydrates in the presence of persulfate[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,227:115332. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115332
[18] 朱明月, 仝文科, 杜红娜, 等. 天然植物人参中糖醛酸含量测定方法的建立[J]. 今日畜牧兽医,2021,37(1):5−7. [ZHU M Y, TONG W K, DU H N, et al. Establishment of a method for determination of uronic acid content in natural plant ginseng[J]. Livestock Veterinary Today,2021,37(1):5−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4092.2021.01.004 [19] 杨淑萍. 紫外分光光度法检测黄芪多糖含量[J]. 现代畜牧科技,2019(8):7−9. [YANG S P. Determination of astragalus polysaccharide content by ultraviolet spectrophotometry[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry Technology,2019(8):7−9. doi: 10.19369/j.cnki.2095-9737.2019.08.002 [20] 纪鹏, 魏彦明, 华永丽, 等. 当归及不同炮制品多糖傅里叶变换红外光谱识别[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2014(5):1270−1274. [JI P, WEI Y M, HUA Y L, et al. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy identification of angelica sinensis and different processed polysaccharides[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2014(5):1270−1274. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2014)05-1270-05 [21] 马定远, 陈君, 李萍, 等. 柱前衍生化高效液相色谱法分析多糖中的单糖组成[J]. 分析化学,2002,30(6):702−705. [MA D Y, CHEN J, LI P, et al. Analysis of monosaccharide composition in polysaccharides by precolumn derivatization high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2002,30(6):702−705. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3820.2002.06.016 [22] YANG J, MU T, MA M. Extraction, structure, and emulsifying properties of pectin from potato pulp[J]. Food Chemistry, 2018, 244: 197-205.
[23] 郎浩宇, 王小斐, 陈芳, 等. 新型模式平台——蜜蜂用于肠道菌群与营养健康研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(12):311−319. [LANG H Y, WANG X F, CHEN F, et al. A novel model platform-honeybees for the study of gut microbiota and nutritional health[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2020,20(12):311−319. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2020.12.037 [24] 吴琼, 郑成, 宁正祥, 等. 碱溶性银耳粗多糖的提取及其清除自由基作用的研究[J]. 食品科学,2007,28(6):153−155. [WU Q, ZHENG C, NING Z X, et al. Extraction of alkali-soluble tremella polysaccharide and its scavenging effect on free radicals[J]. Food Science,2007,28(6):153−155. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.06.033 [25] 卢久富. 西葫芦水溶性多糖抗氧化性的研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(16):9560−9561. [LU J F. Study on the antioxidant activity of water-soluble polysaccharides from zucchini[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science,2011,39(16):9560−9561. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.16.037 [26] 于叶霞, 李鹂, 王元忠. 基于光谱和色谱数据融合策略的青叶胆及近似种的鉴别研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(8):2440−2446. [YU Y X, LI P, WANG Y Z. Identification of C. chinensis and related species based on spectral and chromatographic data fusion strategy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2020,40(8):2440−2446. [27] 景永帅, 马云凤, 李明松, 等. 植物多糖结构解析方法研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(3):411−421. [JING Y S, MA Y F, LI M S, et al. Research progress on structural analysis methods of plant polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(3):411−421. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021010181 [28] WANG L, ZHAO Z, ZHAO H, et al. Pectin polysaccharide from Flos Magnoliae (Xin Yi, Magnolia biondii Pamp. flower buds): Hot-compressed water extraction, purification and partial structural characterization[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022(1):122.
[29] 梅家骏. 果胶的应用和生产简介[J]. 食品科学,1983(10):15−17. [MEI J J. Introduction to the application and production of pectin[J]. Food Science,1983(10):15−17. [30] CHEN J, CHENG H, ZHI Z, et al. Extraction temperature is a decisive factor for the properties of pectin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2020: 106160.
[31] NGOUEMAZONG E, CHRISTIAENS S, SHPIGELMAN A, et al. The emulsifying and emulsion stabilizing properties of pectin: A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2015,14(6):705−718. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12160
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 程娟娟,程江华,蔡永萍,万娅琼,徐雅芫. 大豆肽的功能活性及在食品加工产业中的应用. 中国调味品. 2024(06): 200-205 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



